Abstract
Background
Changes in clinical variables associated with the administration of pimobendan to dogs with preclinical myxomatous mitral valve disease (MMVD) and cardiomegaly have not been described.
Objectives
To investigate the effect of pimobendan on clinical variables and the relationship between a change in heart size and the time to congestive heart failure (CHF) or cardiac‐related death (CRD) in dogs with MMVD and cardiomegaly. To determine whether pimobendan‐treated dogs differ from dogs receiving placebo at onset of CHF.
Animals
Three hundred and fifty‐four dogs with MMVD and cardiomegaly.
Materials and Methods
Prospective, blinded study with dogs randomized (ratio 1:1) to pimobendan (0.4–0.6 mg/kg/d) or placebo. Clinical, laboratory, and heart‐size variables in both groups were measured and compared at different time points (day 35 and onset of CHF) and over the study duration. Relationships between short‐term changes in echocardiographic variables and time to CHF or CRD were explored.
Results
At day 35, heart size had reduced in the pimobendan group: median change in (Δ) LVIDDN −0.06 (IQR: −0.15 to +0.02), P < 0.0001, and LA:Ao −0.08 (IQR: −0.23 to +0.03), P < 0.0001. Reduction in heart size was associated with increased time to CHF or CRD. Hazard ratio for a 0.1 increase in ΔLVIDDN was 1.26, P = 0.0003. Hazard ratio for a 0.1 increase in ΔLA:Ao was 1.14, P = 0.0002. At onset of CHF, groups were similar.
Conclusions and Clinical Importance
Pimobendan treatment reduces heart size. Reduced heart size is associated with improved outcome. At the onset of CHF, dogs treated with pimobendan were indistinguishable from those receiving placebo.
Keywords: Cardiology, Cardiovascular, Echocardiography, Endocardiosis, Heart Failure, Mitral regurgitation
Abbreviations
- 2D
2‐dimensional
- ALT
alanine aminotransferase
- AUC
area under the curve
- BCS
body condition score
- BPM
beats per minute
- CHF
congestive heart failure
- CI
confidence intervals
- CKCS
Cavalier King Charles Spaniels
- CRD
cardiac‐related death
- ECG
electrocardiogram
- EPIC
Evaluation of Pimobendan in dogs with Cardiomegaly Caused by Preclinical Mitral Valve Disease
- F
female
- FS%
fractional shortening
- FS
female spayed
- GPT
glutamic‐pyruvate transaminase
- HR
hazard ratio
- IQR
interquartile range
- K+
potassium
- LA/Ao
left atrial‐to‐aortic ratio
- LVIDd
left ventricular internal diameter in diastole
- LVIDDN
normalized left ventricular internal diameter in diastole
- LVIDs
left ventricular internal diameter in systole
- LVIDSN
normalized left ventricular internal diameter in systole
- MC
male castrated
- M
male
- MMVD
myxomatous mitral valve disease
- MR
mitral regurgitation
- Na+
sodium
- NA
not able to calculate
- PCV
packed cell volume
- PP
per protocol
- SAP
systolic arterial blood pressure
- TPC
total protein concentration
- UK
United Kingdom
- USA
United States of America
- VHS
vertebral heart sum
The “Evaluation of Pimobendan In dogs with Cardiomegaly caused by preclinical mitral valve disease” (EPIC) study1 was a multicenter, blinded, randomized, placebo‐controlled clinical trial evaluating the effect of pimobendan in delaying the onset of clinical signs in dogs with cardiac enlargement secondary to myxomatous mitral valve disease (MMVD). The main findings have been published and demonstrated a significant benefit of treatment in prolonging the time to the primary endpoint, which was a composite of the onset of congestive heart failure (CHF) or cardiac‐related death.1 Although the beneficial effects of the treatment were clear, none of the longitudinal effects of the drug on clinical, radiographic, and echocardiographic variables have yet been reported in dogs with preclinical MMVD.
Dogs with MMVD go through various stages of the disease.2 In the first stage of the disease (stage B1), dogs have insufficiency of their mitral valve, but there is no evidence of cardiac enlargement. In those dogs in which the disease progresses, heart size enlarges as a consequence of the left‐sided volume overload. Dogs with cardiac enlargement that have not yet developed signs of CHF are considered to be in stage B2. Signs of CHF develop in some dogs, typically after a period during which the heart undergoes progressively more rapid enlargement.3, 4, 5
Dogs with increased heart size and with the most rapid rate of change in heart size are at the greatest risk of development of CHF.4, 5 Increased heart size in dogs at all stages is predictive of an increased risk of cardiac‐related death.6, 7, 8
Previous studies of dogs with cardiomegaly secondary to heart disease have demonstrated a reduction in heart size associated with the administration of pimobendan.9, 10, 11, 12 In Doberman pinschers with preclinical dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), the degree to which the heart size reduced in response to the administration of pimobendan was predictive of a decreased likelihood of experiencing the primary endpoint of the study, which was a composite of CHF or cardiac‐related death.11
Longitudinal effects of pimobendan treatment have been described in dogs with stage C MMVD9 but have not been reported in dogs with stage B disease. Some dogs show subtle signs associated with their cardiac disease before overt signs of CHF develop. Such signs might include cough attributable to cardiomegaly,13 intolerance of exercise, increasing resting respiratory rate, and weight loss. No previous prospective study has described the change in clinical signs and other variables in a large cohort of dogs as they progress from stage B2 to stage C MMVD. Of the dogs enrolled in the EPIC study, 135 were confirmed to have developed CHF,1 and this population allows us to characterize the changes that occur as dogs progress from a preclinical stage of the disease, stage B2, into CHF.
The aims of this study were to investigate, in a population of dogs with stage B2 MMVD, the influence of treatment with pimobendan on clinical, radiographic, and echocardiographic variables in both the short and long term, and whether short‐term changes in echocardiographic variables might predict the time to the onset of CHF or cardiac‐related death. Additionally, we aimed to describe a large group of dogs as they progress from stage B2 to stage C MMVD and to determine whether dogs that develop CHF while receiving pimobendan differ from those that develop CHF while receiving placebo.
Materials and Methods
Trial Design
The EPIC trial was a prospective multicenter, blinded, randomized, placebo‐controlled study. Complete and detailed description of the study has been published.1
Dogs
Enrollment Criteria
Dogs were eligible for participation in the study provided that the owner had given informed consent.
To be eligible for inclusion, a dog had to be 6 years of age or older, have a body weight ≥4.1 and ≤15 kg, have a characteristic systolic heart murmur of moderate‐to‐high intensity (≥grade 3/6) with maximal intensity over the mitral area, have echocardiographic evidence of advanced MMVD defined as characteristic valvular lesions of the mitral valve apparatus, mitral regurgitation (MR) on the color Doppler echocardiogram, and have echocardiographic and radiographic evidence of cardiomegaly defined as a left atrial‐to‐aortic root ratio (LA/Ao) ≥1.6 measured in a short‐axis view,14 body weight normalized left ventricular internal diameter in diastole (LVIDDN)15 ≥1.7, and a vertebral heart sum (VHS) >10.5.16
Exclusion Criteria
Dogs were excluded from the study if they had any of the following: known clinically important systemic or other organ‐related disease that was expected to limit the dog's life expectancy or required chronic administration of cardiovascular medication precluded as part of the trial. Dogs with hypothyroidism could be included provided the investigator deemed them clinically stable on treatment. Dogs with current or previous evidence of cardiogenic pulmonary edema, pulmonary venous congestion or both, cardiac disease other than MMVD, clinically significant supraventricular, ventricular tachyarrhythmias or both (ie, requiring antiarrhythmic treatment), or evidence of pulmonary hypertension considered to be clinically relevant (RV:RA pressure gradient >65 mmHg) were excluded. Dogs with a history of chronic or recent administration (>14 days of duration or within 30 days of intended enrollment) of any precluded medication were excluded. Dogs that were pregnant or lactating were not eligible for enrollment. In the event that before study enrollment, if a dog had received short‐term treatment (<14 days) with a precluded agent, but was no longer receiving treatment and had not received it within 30 days of intended enrollment, then the dog was eligible for inclusion.
Details of study sites, randomization and blinding, concomitant treatment, and data management have previously been described.1
Trial Medication
Pimobendan veruma was administered PO at a target dose of 0.4–0.6 mg/kg/d as per registered label instructions in most countries where the product was licensed. Placebo was administered in a similar manner. Placebo and verum tablets and packaging containers were visually identical.
Schedule of Events
Before inclusion, a case history was taken for each dog. The dog then underwent a physical examination, echocardiography, thoracic radiography, and routine hematology and blood biochemistry (performed at laboratories local to each investigator) with a minimum database consisting of packed cell volume (PCV), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), glutamic pyruvate transaminase (GPT), total protein concentration (TPC), creatinine, potassium (K+), and sodium (Na+) concentrations. Re‐examinations were scheduled at day 35 and approximately 4 months after inclusion. Thereafter, the dogs were scheduled for re‐examination every 4 months. Details of examinations that were undertaken on each visit are provided in Table 1.
Table 1.
Schedule of procedures undergone by animals remaining in the per‐protocol population of the study at different examinations
| Day 0 | Day 35 (±7 days) | 4 monthsa (±30 days) | 8 monthsb | Event | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Questionnaire | X | X | X | X | X |
| Physical examination | X | X | X | X | X |
| Thoracic radiograph | X | X | X | ||
| Echocardiography | X | X | X | ||
| Hematology and clinical chemistry | X | X | X |
4 months from day 0 and every 8 months thereafter.
8 months from day 0 and every 8 months thereafter.
Clinical Evaluation
At inclusion, dog characteristics such as breed, age, sex, and neutering status were noted. The body weight, body condition score (BCS), rectal temperature, and respiratory rate were measured at each visit.
Echocardiography
Echocardiography was performed on unsedated dogs. The following measurements were each taken over at least 3 cardiac cycles, and the mean was recorded as follows: the LA/Ao obtained from the right parasternal short‐axis 2D view as previously described,14 the left ventricular internal diameter at end‐diastole (LVIDd), and left ventricular internal diameter at end‐systole (LVIDs) measured on the M‐mode echocardiogram, obtained from the right parasternal short‐axis view.17 M‐mode values were used to derive the fractional shortening (FS%). Normalized dimensions15 were calculated according to the following formulae: normalized LVIDd (LVIDDN) = LVIDd(cm)/(BW (kg))0.294; normalized LVIDs (LVIDSN) = LVIDs(cm)/(BW(kg))0.315.
Thoracic Radiography
Thoracic radiography was performed at inclusion, 8 months after inclusion and every 8 months thereafter for as long as the dog remained in the per‐protocol (PP) population. It was also performed at the time a dog was considered to have developed signs of CHF. Right lateral and dorsoventral projections were used to evaluate the thorax. Cardiac size was assessed by the VHS method,9 and pulmonary edema and congestion were recorded, when considered to be present, by the attending cardiologist.
Primary Endpoint
The primary endpoint was a composite of the development of left‐sided CHF verified by an endpoint committee, euthanasia for a cardiac reason, or death presumed to be cardiac in origin. The primary outcome variable of the study was the time period from inclusion until the primary endpoint was reached.
Visit data for the day 35 visit were included in the analyses provided the dog was re‐examined between 28 and 42 days (day 35 ± 7 days) after initiation of treatment. Visit data for subsequent visits were included in between‐group comparisons for each visit providing the visit took place within 30 days of the scheduled date of re‐examination.
Quality of life variables were assessed at baseline by an ordinal scoring system (Table S1). After baseline assessment of quality of life variables, at each subsequent visit, owners were asked to score the following characteristics on a 5‐point scale (Table 2): appetite, demeanor, exercise tolerance, fainting, respiratory effort, cough, and nocturnal dyspnea/coughing.
Table 2.
Ordinal scoring system used for quality of life observations; appetite, demeanor, exercise tolerance, fainting, respiratory effort, cough, and nocturnal dyspnea/coughing
| Owner's Perception of Quality of Life | Ordinal Score Ascribed | Summary Category for Between‐Group Comparisons |
|---|---|---|
| Greatly improved | 1 |
Improved Score = +1 |
| Improved | 2 | |
| Unchanged | 3 |
Unchanged Score = 0 |
| Deteriorated | 4 |
Deteriorated Score = −1 |
| Severely deteriorated | 5 |
Owners were also asked to measure resting respiratory rate before every re‐examination, and the average resting respiratory rate during that period was noted. Instruction was provided to owners who were advised to count the respiratory rate over one minute within the week before each re‐examination. Ideally, this was performed on several days, and the average of the measurements obtained was recorded as a single value at the corresponding visit.
Statistical Methods
Any dog in the study population that was confirmed to have met all inclusion criteria (and none of the exclusion criteria) was included in the PP population until one of the following occurred: The dog reached the primary endpoint, the dog was censored from the primary endpoint analysis due to the occurrence of an event that precluded continuation in that population, or the end of the study was reached. All analyses described herein were conducted on dogs that remained in the PP population.
For continuous variables that were measured at both baseline and day 35, a “change from baseline” variable was created by subtracting the value obtained at baseline from the day 35 value.
For every dog for which any of the clinical or radiographic continuous variables (ie, body weight, rectal temperature, respiratory rate, owner‐measured resting respiratory rate, heart rate, and VHS) were measured on at least one additional visit after baseline assessment (2 occasions after baseline for owner‐measured respiratory rate), a curve was constructed by plotting each data point on a graph with the unit of measurement on the vertical axis and time on the horizontal axis. The area under the curve (AUC) averaged for the number of days between the first and last observation was calculated, thus giving an average value for that variable that incorporated all of the observations made and was independent of the duration of time the dog remained in the study.18 These summary values were then compared between treatment groups.
For comparison of quality of life characteristics between groups at specific visits, dogs in each group were classified on an ordinal scale to be improved (+1), unchanged (0), or deteriorated (−1) (Table 2).
For ordinal variables measured on the same scale at baseline and all subsequent visits (ie, BCS, heart murmur intensity, and heart disease class), dogs were classified as having increased (+1), remained unchanged (0), or decreased (−1).
Between‐group comparisons of the change in ordinal variables were undertaken at each scheduled visit up to the visit at which fewer than 50% of dogs remained in each group.
For all continuous and ordinal variables, between‐group comparisons were made by Mann‐Whitney tests. For within‐group paired comparisons of all ordinal and continuous variables, the Wilcoxon signed ranks test was used.
The results of multivariable Cox proportional hazards analysis analyzing the association between treatment and clinical variables measured at baseline and the time to the primary endpoint have been described in this population.1 In this longitudinal analysis, the effects of a change in echocardiographic variables on time to the primary endpoint were explored by multivariable Cox proportional hazards analysis. Separate multivariable models were constructed for each of 4 echocardiographic variables; LVIDDN, LVIDSN, LA/Ao, and FS%. In each model, the baseline value of the variable, the change from baseline at day 35, and the treatment effect were entered as explanatory variables. Time to the primary endpoint was the dependent variable. For each model, all dogs in the PP population for which paired observations were available to derive a value for the change from baseline at day 35 were entered into each analysis. Dogs leaving the PP population for reasons other than reaching the primary endpoint were right‐censored at the time of leaving the population. Variables entered into each multivariable model were assessed for collinearity with other variables in the same model and to ensure that the proportional hazards and linearity assumptions were met.
The threshold of significance was defined as P < 0.05. All analyses were 2‐tailed. Statistical analyses were performed with a commercially available software program.b
Results
A flow diagram outlining the number of dogs in the PP population in each group at different time points and the number of dogs reaching the primary endpoint is illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
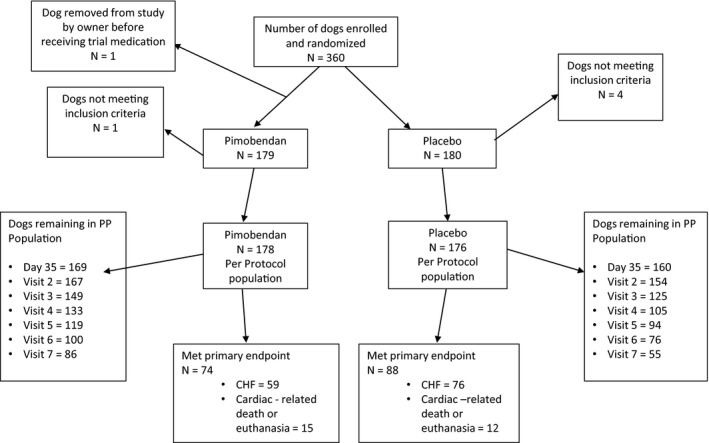
A flowchart illustrating the randomization of the 360 dogs in the study, the numbers of dogs reaching the different components of the primary endpoint in each treatment group, and the number of dogs in each treatment group remaining in the per‐protocol population at different scheduled visits. PP, per protocol; CHF, congestive heart failure.
Relevant baseline characteristics of the 2 treatment groups are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3.
Baseline characteristics of the 2 treatment groups in the per‐protocol population
| Variable | Treatment Groups | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pimobendan n = 178 | Placebo n = 176 | ||
| Dog characteristics | Age (years) | 9.0 (8.0–11.0) | 9.0 (7.0–11.0) |
| Sex (M/F/MC/FS) (%) | 36/6/75/61 (20/3/42/34) | 35/12/66/63 (20/7/38/36) | |
| Breed (CKCS/Dachshund/Miniature Schnauzer/Poodle/Yorkshire terrier/mixed breed/other) (%) | 77/12/5/4/0/26/54 (43/7/3/2/0/15/30) | 84/9/8/4/8/19/44 (47/5/5/2/5/11/25) | |
| Dose of test medication | Dose pimobendan (mg/d) | 0.49 (0.44–0.53) | NA |
| Quality of life and respiratory variables (see Table S1 for details) | Appetite (decreased/normal/increased) (%) | 4/165/9 (2/93/5) | 3/166/7 (2/94/4) |
| Demeanor (Alert/mildly lethargic/moderately lethargic) (%) | 175/3/0 (98/3/0) | 168/7/1 (95/4/1) | |
| Exercise tolerance (very good/good/decreased) (%) | 118/53/7 (66/30/4) | 99/70/7 (56/40/4) | |
| Fainting (none/rarely/occasional) (%) | 175/3/0 (98/2/0) | 170/4/2(97/2/1) | |
| Respiratory effort (normal/mildly increased/moderately increased) (%) | 172/5/1 (97/3/1) | 164/10/2 (93/6/1) | |
| Cough (none/occasional/frequent/persistent) (%) | 108/48/20/2 (61/27/11/1) | 123/35/17/1 (70/20/10/1) | |
| Nocturnal coughing (none/slight/moderate) (%) | 157/20/0 (89/11/0) | 163/10/2 (93/6/1) | |
| Physical examination variables | Body weight (kg) | 8.6 (6.9–10.6) | 9.0 (7.1–10.5) |
| Body condition score (underweight (1–3)/normal (4–6)/overweight (7–9)) (%) | 0/166/12 (0/93/7) | 5/148/23 (3/84/13) | |
| Rectal temperature (°C) | 38.7 (38.4–39.1) | 38.7 (38.4–39.0) | |
| Heart rate (BPM) | 124 (110–140) | 122 (112–140) | |
| Respiratory rate (breaths/min) | 28 (24–36) | 28 (24–36) | |
| Heart murmur intensity (moderate (grade 3–4)/severe (grade 5–6) (%) | 133/45 (75/25) | 133/43 (76/24) | |
| Diagnostic imaging variables | VHS | 11.3 (10.9–12.0) | 11.5 (11.0–11.9) |
| LVIDSN | 1.03 (0.93–1.14) | 1.02 (0.93–1.10) | |
| LVIDDN | 1.9 (1.8–2.1) | 1.9 (1.8–2.0) | |
| FS% (%) | 43 (39–48) | 44 (41–49) | |
| LA/Ao | 1.89 (1.73–2.10) | 1.86 (1.72–2.06) | |
| Laboratory variables | Na+ (mmol/L) | 148 (145–150) | 148 (146–149) |
| K+ (mmol/L) | 4.4 (4.1–4.8) | 4.4 (4.1–4.7) | |
| PCV (%) | 44.0 (41.0–48.0) | 44.0 (40.0–48.1) | |
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 70.7 (60.0–88.4) | 70.7 (61.0–82.2) | |
| TPC (g/L) | 65 (61–69) | 66 (62–70) | |
| GPT (ALT) (U/L) | 43 (29–68) | 42 (30–66) | |
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; BCS, body condition score; BPM, beats per minute; CKCS, Cavalier King Charles Spaniels; F, female; FS, female neutered; FS%, fractional shortening; GPT, glutamic‐pyruvate transaminase; K+, potassium concentration; LA/Ao, left atrial‐to‐aortic root ratio; LVIDd, left ventricular internal diameter in diastole; LVIDDN, normalized left ventricular internal diameter in diastole; LVIDs, left ventricular internal diameter in systole; LVIDSN, normalized left ventricular internal diameter in systole; M, male; MN, male neutered; Na+, sodium concentration; PCV, packed cell volume; TPC, total protein concentration; VHS, vertebral heart sum.
Continuous variables are reported as median (interquartile range). Categorical variables are reported as number (%).
Comparisons at Day 35
Between‐group comparisons of quality of life variables as perceived by owners at day 35 showed that the pimobendan and placebo groups were not significantly different in the extent to which any of the quality of life variables had changed (Table 4). Within‐group comparisons in the pimobendan group showed the following quality of life scores to have significantly improved: appetite, demeanor, exercise tolerance, and cough (Table 4). The scores for owner perceptions of demeanor and exercise tolerance were also significantly improved in the placebo group (Table 4).
Table 4.
Within‐group paired comparisons and between‐group unpaired comparisons of the change from baseline to day 35 of various quality of life and physical examination variables
| Categorical Variables | Treatment Group | N | Deteriorated | Unchanged | Improved | Within‐Group Comparison (Wilcoxon Signed Ranks) | Between‐Group Comparison (Mann‐Whitney) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appetite | Placebo | 160 | 6 | 140 | 14 | 0.12 | 0.33 |
| Pimobendan | 169 | 5 | 144 | 20 | 0.0012 | ||
| Demeanor | Placebo | 160 | 3 | 135 | 22 | <0.0001 | 0.34 |
| Pimobendan | 169 | 2 | 138 | 29 | <0.0001 | ||
| Exercise tolerance | Placebo | 160 | 4 | 132 | 24 | <0.0001 | 0.75 |
| Pimobendan | 169 | 3 | 144 | 22 | <0.0001 | ||
| Fainting | Placebo | 160 | 2 | 157 | 1 | 1.0000 | 0.65 |
| Pimobendan | 169 | 1 | 167 | 1 | 1.0000 | ||
| Respiratory effort | Placebo | 160 | 3 | 148 | 9 | 0.15 | 0.75 |
| Pimobendan | 169 | 1 | 162 | 6 | 0.13 | ||
| Cough | Placebo | 160 | 9 | 134 | 17 | 0.12 | 0.46 |
| Pimobendan | 169 | 6 | 143 | 20 | 0.0038 | ||
| Nocturnal dyspnea or cough | Placebo | 160 | 3 | 152 | 5 | 0.73 | 0.65 |
| Pimobendan | 169 | 2 | 161 | 6 | 0.29 | ||
| Body condition score | Placebo | 160 | 24 | 123 | 13 | 0.070 | 0.55 |
| Pimobendan | 169 | 24 | 127 | 18 | 0.36 | ||
| Heart failure stage | Placebo | 160 | – | 157 | 3 | 0.25 | 0.76 |
| Pimobendan | 169 | – | 165 | 4 | 0.13 |
| Decreased | Unchanged | Increased | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auscultation (change in murmur grade) | Placebo | 160 | 12 | 130 | 18 | 0.28 | 0.22 |
| Pimobendan | 169 | 21 | 131 | 17 | 0.52 |
All P‐values that appear in bold are < 0.05.
For the physical examination, diagnostic imaging, and laboratory variables (Table 5), in the pimobendan group, there were significant decreases in LVIDDN, LA/Ao, LVIDSN, plasma Na+ concentration, and creatinine. There was a significant increase in FS% in the pimobendan group. In the placebo group, the only significant change was a decrease in LA/Ao. Between‐group comparisons of the changes showed a significantly greater change in FS% in the pimobendan group, and greater reductions in LVIDDN, LA/Ao, and LVIDSN in the pimobendan group (Fig 2a–d).
Table 5.
Within‐group paired comparisons and between‐group unpaired comparisons of the change from baseline to day 35 of physical examination, echocardiographic, and laboratory variables
| Continuous Variables | Treatment Group | N | Absolute Change from Baseline Median (Interquartile Range) | Within‐Group Comparison (Wilcoxon Signed Ranks) | Between‐Group Comparison (Mann‐Whitney) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical examination variables | Body weight (kg) | Placebo | 159 | 0.00 (−0.20 to +0.20) | 0.90 | 0.86 |
| Pimobendan | 168 | 0.00 (−0.20 to +0.20) | 0.99 | |||
| Rectal temperature (°C) | Placebo | 160 | 0.00 (−0.30 to +0.30) | 0.47 | 0.98 | |
| Pimobendan | 164 | 0.00 (−0.30 to +0.30) | 0.80 | |||
| Respiratory rate (breaths/min) | Placebo | 152 | 0.0 (−4 to +6) | 0.24 | 0.51 | |
| Pimobendan | 154 | 0.0 (−4 to +4) | 0.60 | |||
| Heart rate (BPM) | Placebo | 160 | 0.0 (−10.0 to +12.0) | 0.37 | 0.26 | |
| Pimobendan | 169 | 0.0 (−12.0 to +10.0) | 0.32 | |||
| Echocardiographic variables | FS% (%) | Placebo | 160 | 0.00 (−3.75 to +3.20) | 0.55 | <0.0001 |
| Pimobendan | 169 | +2.00 (−1.00 to +5.00) | <0.0001 | |||
| LVIDDN | Placebo | 159 | +0.01 (−0.07 to +0.07) | 0.71 | <0.0001 | |
| Pimobendan | 168 | −0.06 (−0.15 to +0.02) | <0.0001 | |||
| LA/Ao | Placebo | 160 | −0.027 (−0.182 to +0.084) | 0.036 | 0.0076 | |
| Pimobendan | 169 | −0.080 (−0.229 to +0.028) | <0.0001 | |||
| LVIDSN | Placebo | 159 | +0.0144 (−0.0722 to +0.0715) | 0.33 | <0.0001 | |
| Pimobendan | 168 | −0.0614 (−0.1555 to −0.0033) | <0.0001 | |||
| Laboratory variables | Na+ (mmol/L) | Placebo | 159 | 0.000 (−2.000 to +2.000) | 0.82 | 0.21 |
| Pimobendan | 167 | 0.000 (−2.000 to +1.000) | 0.030 | |||
| K+ (mmol/L) | Placebo | 159 | 0.000 (−0.200 to +0.300) | 0.24 | 0.24 | |
| Pimobendan | 168 | 0.000 (−0.300 to +0.200) | 0.67 | |||
| PCV (%) | Placebo | 158 | 0.000 (−1.900 to +2.100) | 0.17 | 0.59 | |
| Pimobendan | 168 | +0.500 (−2.000 to +2.750) | 0.060 | |||
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | Placebo | 159 | 0.000 (−8.840 to +8.840) | 0.86 | 0.094 | |
| Pimobendan | 168 | 0.000 (−8.840 to +4.210) | 0.014 | |||
| TPC (g/L) | Placebo | 158 | 0.000 (−2.000 to +2.500) | 0.72 | 0.19 | |
| Pimobendan | 168 | +0.415 (−2.000 to +4.000) | 0.054 | |||
| GPT (ALT) (U/L) | Placebo | 159 | 0.000 (−6.000 to +8.000) | 0.52 | 0.38 | |
| Pimobendan | 168 | 0.000 (−9.000 to +6.000) | 0.48 |
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; BPM, beats per minute; FS%, fractional shortening; GPT, glutamic‐pyruvate transaminase; K+, potassium concentration; LA/Ao, left atrial‐to‐aortic root ratio; LVIDDN, normalized left ventricular internal diameter in diastole; LVIDSN, normalized left ventricular internal diameter in systole; Na+, sodium concentration; PCV, packed cell volume; TPC, total protein concentration; VHS, vertebral heart sum.
All P‐values that appear in bold are < 0.05.
Figure 2.
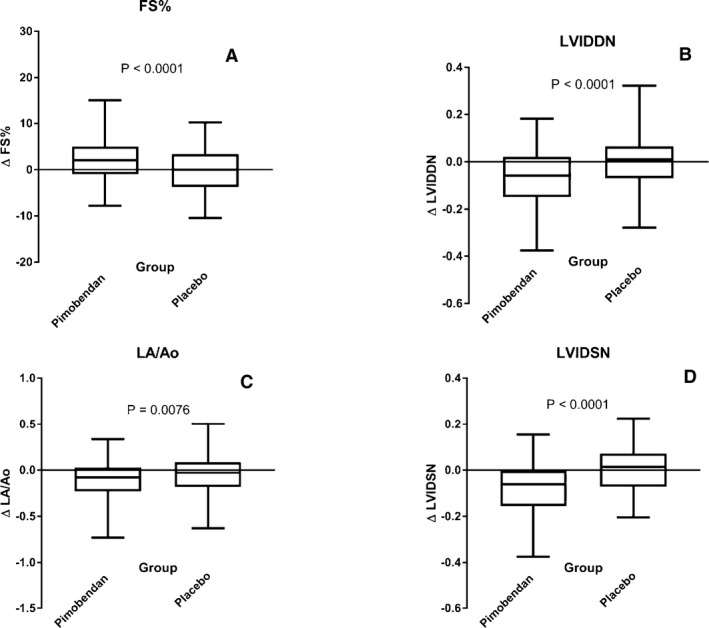
Four box and whiskers plots illustrating absolute values of the change in 4 different echocardiographic variables between baseline and day 35 in the 2 different treatment groups for (A) fractional shortening, (B) normalized left ventricular internal diameter in diastole, (C) left atrial‐to‐aortic ratio and (D) normalized left ventricular internal diameter in systole. The bold horizontal line indicates the median change, the boxes extend from the 25th to the 75th percentile. The whiskers extend from the 2.5th to the 97.5th percentile. P‐values are for between‐group comparisons by a Mann‐Whitney test. Δ, change in; FS%, fractional shortening; LA/Ao, left atrial‐to‐aortic root ratio; LVIDDN, normalized left ventricular internal diameter in diastole; LVIDSN, normalized left ventricular internal diameter in systole.
Prognostic Value of Change in LVIDDN, LA/Ao, LVIDSN, and FS% Between Baseline and Day 35 (Multivariable Cox Proportional Hazard Analysis)
Changes in echocardiographic variables between baseline and day 35 were significantly predictive of outcome in all multivariable models, except for change in FS% (Table 6). The hazard ratio (HR) for the treatment effect remained comparably constant and significant in all the models, except for the multivariable analysis including LVIDSN and change in LVIDSN, where the observed treatment effect was apparently reduced (and no longer significant). The 4 multivariable Cox proportional hazards models are summarized in Table 6. (A Forest plot for each model is illustrated in Fig S1a–d.) Proportional hazards and linearity assumptions were not violated, and no pair of variables entered into the same model showed unacceptable collinearity.
Table 6.
Multivariable Cox proportional hazards models exploring the effect of treatment, change in an echocardiographic variable, and the value of the same variable recorded at baseline on time to the primary endpoint constructed for 4 echocardiographic variables; LVIDDN, LA/Ao, LVIDSN, and FS%
| Hazard Ratio | 95% Confidence Intervals of Hazard Ratio | P‐Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Change in LVIDDN model (n = 327) | |||
| Treatment (pimobendan) | 0.64 | 0.46–0.90 | 0.010 |
| LVIDDN (per 0.1 unit) | 1.30 | 1.20–1.41 | <0.0001 |
| Δ LVIDDN (per 0.1 unit change) | 1.26 | 1.11–1.43 | 0.0003 |
| Change in LA/Ao model (n = 329) | |||
| Treatment (pimobendan) | 0.63 | 0.46–0.88 | 0.0060 |
| LA/Ao (per 0.1 unit) | 1.21 | 1.15–1.28 | <0.0001 |
| Δ LA/Ao (per 0.1 unit change) | 1.14 | 1.06–1.22 | 0.0002 |
| Change in LVIDSN model (n = 327) | |||
| Treatment (pimobendan) | 0.71 | 0.51–1.00 | 0.051 |
| LVIDSN (per 0.1 unit) | 1.07 | 0.97–1.18 | 0.16 |
| Δ LVIDSN (per 0.1 unit change) | 1.22 | 1.05–1.41 | 0.0084 |
| Change in FS% model (n = 329) | |||
| Treatment (pimobendan) | 0.64 | 0.46–0.90 | 0.011 |
| FS % (per 10 units) | 1.47 | 1.16–1.85 | 0.0014 |
| Δ FS% (per 10 units change) | 1.05 | 0.77–1.44 | 0.75 |
Δ, Change in; FS%, fractional shortening; LA/Ao, left atrial‐to‐aortic root ratio; LVIDDN, normalized left ventricular internal diameter in diastole; LVIDSN, normalized left ventricular internal diameter in systole.
All P‐values that appear in bold are < 0.05.
Effect of Treatment Over Time
The AUCs adjusted for number of days in the study for: body weight, rectal temperature, respiratory rate, owner‐measured resting respiratory rate, heart rate, and VHS for each study group are summarized and compared between groups in Table 7. The median AUCs adjusted for number of days in the study for respiratory rate, heart rate, and VHS were significantly lower in the group receiving pimobendan.
Table 7.
Comparison between groups of the areas under the curve averaged over the number of days in the study for each dog for those continuous variables that were recorded regularly throughout the monitoring period and on at least 2 occasions
| Continuous Variables | Treatment Group | N | Median AUC Adjusted for Days in Study (IQR) | Between‐Group Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (kg) | Placebo | 173 | 8.5 (6.9–10.4) | 0.54 |
| Pimobendan | 176 | 8.8 (6.9–10.5) | ||
| Rectal temperature (°C) | Placebo | 173 | 38.6 (38.4–38.8) | 0.53 |
| Pimobendan | 176 | 38.6 (38.4–38.8) | ||
| Respiratory rate (breaths/min) | Placebo | 170 | 32 (26–40) | 0.49 |
| Pimobendan | 173 | 31 (26–38) | ||
| Owner‐measured resting respiratory rate (breaths/min) | Placebo | 156 | 24 (20–28) | 0.0051 |
| Pimobendan | 163 | 22 (19–26) | ||
| Heart rate (BPM) | Placebo | 173 | 130 (119–140) | 0.038 |
| Pimobendan | 176 | 124 (115–137) | ||
| Vertebral heart score (VHS) | Placebo | 157 | 11.9 (11.4–12.4) | 0.0009 |
| Pimobendan | 163 | 11.5 (11.0–12.2) |
BPM, beats per minute; VHS, vertebral heart sum.
All P‐values that appear in bold are < 0.05.
There were no consistent differences observed between treatment groups in quality of life scores, change in heart murmur intensity, change in heart disease stage, and change in BCS when they were compared at each visit up to the scheduled visit at 24 months, although heart failure score was worse at 20 months, and respiratory effort score was worse at 24 months in the placebo group (Table S2).
Comparison of Groups at the Onset of CHF
At the onset of CHF, there were no significant differences between treatment groups for any of the physical examination, diagnostic imaging, or laboratory variables recorded (Table 8). For all dogs that went on to develop CHF, there was, with the exception of serum Na+, K+, and PCV, a significant change from baseline to the onset of CHF in both the pimobendan and placebo group in all of the continuous clinical, diagnostic imaging, and laboratory variables recorded. The magnitude of the change from baseline of these variables for dogs from both groups combined is summarized in Table 9. Likewise, there was a significant worsening of quality of life variables, BCS, and heart murmur intensity in their score as all dogs progressed from baseline to CHF (Table 10). Only the difference in change in exercise tolerance was significantly different between groups, with a greater number of dogs in the pimobendan group experiencing deterioration in exercise tolerance at the onset of CHF (Table 10).
Table 8.
Values of physical examination, diagnostic imaging, and laboratory variables for those dogs that developed congestive heart failure, measured at the time of onset of heart failure summarized for the 2 treatment groups
| Continuous Variables | Treatment Group | N | Median Value at CHF and IQR | Between‐Group Comparison | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical examination variables | Body weight (kg) | Placebo | 73 | 8.7 (6.9–10.6) | 0.96 |
| Pimobendan | 58 | 9.2 (7.1–10.0) | |||
| Rectal temperature (°C) | Placebo | 66 | 38.6 (38.3–38.8) | 0.11 | |
| Pimobendan | 56 | 38.4 (38.0–38.8) | |||
| Respiratory rate (breaths/min) | Placebo | 69 | 44 (40–58) | 0.25 | |
| Pimobendan | 52 | 50 (36–66) | |||
| Owner‐measured resting respiratory rate (breaths/min) | Placebo | 58 | 36 (30–50) | 0.50 | |
| Pimobendan | 50 | 39 (34–50) | |||
| Heart rate (BPM) | Placebo | 71 | 150 (140–162) | 0.60 | |
| Pimobendan | 58 | 150 (140–164) | |||
| Diagnostic imaging variables | FS% (%) | Placebo | 67 | 46.6 (42.5–50.1) | 0.63 |
| Pimobendan | 55 | 46 (42.0–53.8) | |||
| LVIDDN | Placebo | 67 | 2.26 (2.14–2.51) | 0.94 | |
| Pimobendan | 55 | 2.27 (2.14–2.47) | |||
| LA/Ao | Placebo | 67 | 2.41 (2.15–2.80) | 1.00 | |
| Pimobendan | 55 | 2.47 (2.17–2.71) | |||
| LVIDSN | Placebo | 67 | 1.16 (1.03–1.33) | 0.62 | |
| Pimobendan | 55 | 1.13 (0.98–1.36) | |||
| VHS | Placebo | 72 | 13.0 (12.2–13.5) | 0.45 | |
| Pimobendan | 59 | 12.8 (12.1–13.5) | |||
| Laboratory variables | Na+ (mmol/L) | Placebo | 68 | 147.0 (145.4–150.0) | 0.66 |
| Pimobendan | 55 | 147.0 (146.0–149.0) | |||
| K+ (mmol/L) | Placebo | 68 | 4.50 (4.25–4.80) | 0.40 | |
| Pimobendan | 52 | 4.50 (4.00–4.80) | |||
| PCV (%) | Placebo | 66 | 41.5 (37.4–48.0) | 0.12 | |
| Pimobendan | 50 | 44.0 (40.0–47.0) | |||
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | Placebo | 68 | 78.8 (61.9–90.0) | 0.90 | |
| Pimobendan | 52 | 79.6 (64.9–87.2) | |||
| TPC (g/L) | Placebo | 66 | 64.0 (58.0–70.0) | 0.77 | |
| Pimobendan | 52 | 66.0 (60.5–68.0) | |||
| GPT (ALT) (U/L) | Placebo | 62 | 52.5 (35.0–77.0) | 0.68 | |
| Pimobendan | 51 | 54.0 (34.0–95.0) |
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; BPM, beats per minute; FS%, fractional shortening; GPT, glutamic‐pyruvate transaminase; K+, potassium concentration; LA/Ao, left atrial‐to‐aortic root ratio; LVIDDN, normalized left ventricular internal diameter in diastole; LVIDSN, normalized left ventricular internal diameter in systole; Na+, sodium concentration; PCV, packed cell volume; TPC, total protein concentration; VHS, vertebral heart sum.
Table 9.
Change from baseline to the onset of heart failure for values of physical examination, diagnostic imaging, and laboratory variables for those dogs that developed congestive heart failure summarized for the population as a whole
| Continuous Variables | N | Absolute Change from Baseline Median (Interquartile Range) | Comparison to Baseline | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical examination variables | Body weight (kg) | 131 | −0.30 (−0.7 to 0.1) | <0.001 |
| Rectal temperature (°C) | 122 | −0.3 (−0.7 to 0.1) | <0.001 | |
| Respiratory rate (breaths/min) | 118 | 16 (4–29) | <0.001 | |
| Heart rate (BPM) | 129 | 22 (8–38) | <0.001 | |
| Diagnostic imaging variables | FS% (%) | 122 | 2.6 (−2.6 to 7.7) | 0.003 |
| LVIDDN | 122 | 0.35 (0.14–0.49) | <0.001 | |
| LA/Ao | 122 | 0.47 (0.24–0.75) | <0.001 | |
| LVIDSN | 122 | 0.13 (−0.04 to 0.27) | <0.001 | |
| VHS | 131 | 1.3 (0.80–1.9) | <0.001 | |
| Laboratory variables | Na+ (mmol/L) | 120 | 0.00 (−3.0 to 2.0) | 0.24 |
| K+ (mmol/L) | 119 | 0.10 (−0.20 to 0.40) | 0.067 | |
| PCV (%) | 115 | −1.0 (−3.9 to 3.0) | 0.095 | |
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 119 | 0.0 (−8.8 to 17.7) | 0.018 | |
| TPC (g/L) | 116 | −2.0 (−5.5 to 3.0) | 0.027 | |
| GPT (ALT) (U/L) | 112 | 10.0 (−6.0 to 43.0) | <0.001 |
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; BPM, beats per minute; FS%, fractional shortening; GPT, glutamic‐pyruvate transaminase; K+, potassium concentration; LA/Ao, left atrial‐to‐aortic root ratio; LVIDDN, normalized left ventricular internal diameter in diastole; LVIDSN, normalized left ventricular internal diameter in systole; Na+, sodium concentration; PCV, packed cell volume; TPC, total protein concentration; VHS, vertebral heart sum.
All P‐values that appear in bold are < 0.05.
Table 10.
A summary of the number of dogs in each group that experienced a change in various clinical variables at the time of the onset of congestive heart failure
| Categorical Variables | Treatment Group | N | Deteriorated | Unchanged | Improved | Within‐Group Paired Longitudinal Comparisons (Wilcoxon signed ranks) | Between‐Group Comparison (Mann‐Whitney) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appetite | Placebo | 69 | 25 | 44 | 0 | <0.0001 | 0.26 |
| Pimobendan | 57 | 27 | 29 | 1 | |||
| Demeanor | Placebo | 69 | 41 | 28 | 0 | <0.0001 | 0.45 |
| Pimobendan | 57 | 38 | 18 | 1 | |||
| Exercise tolerance | Placebo | 69 | 41 | 28 | 0 | <0.0001 | 0.020 |
| Pimobendan | 57 | 45 | 12 | 0 | |||
| Fainting | Placebo | 69 | 14 | 55 | 0 | <0.0001 | 0.52 |
| Pimobendan | 57 | 9 | 48 | 0 | |||
| Respiratory effort | Placebo | 69 | 55 | 14 | 0 | <0.0001 | 0.074 |
| Pimobendan | 57 | 52 | 5 | 0 | |||
| Cough | Placebo | 69 | 60 | 6 | 3 | <0.0001 | 0.82 |
| Pimobendan | 57 | 50 | 6 | 1 | |||
| Nocturnal dyspnea or cough | Placebo | 67 | 46 | 21 | 0 | <0.0001 | 0.76 |
| Pimobendan | 56 | 37 | 19 | 0 |
| Decreased | Unchanged | Increased | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body condition score | Placebo | 72 | 26 | 37 | 9 | 0.0002 | 0.84 |
| Pimobendan | 58 | 21 | 28 | 9 | |||
| Heart murmur intensity | Placebo | 72 | 8 | 30 | 34 | <0.0001 | 0.17 |
| Pimobendan | 58 | 2 | 23 | 33 |
P‐values for paired comparisons with the same characteristics recorded from the same dogs at baseline are given in the penultimate column.
All P‐values that appear in bold are < 0.05.
Discussion
Our study has demonstrated a number of changes in dogs with preclinical MMVD administered pimobendan, which are different to those that occur in dogs that receive a placebo. Within the first month of treatment, dogs in the pimobendan group demonstrated significant reductions in 3 measures of heart size. The degree to which heart size reduced was predictive of outcome with a greater reduction in heart size associated with a prolongation of the time to the primary endpoint of the study. Heart size was on average lower for the duration of the study for dogs in the pimobendan group compared to those in the placebo group. Quality of life was perceived by owners to be improved after 1 month of treatment for both the placebo and pimobendan groups. At the onset of CHF, dogs receiving pimobendan were indistinguishable from those receiving placebo, and both groups had larger hearts and worse quality of life compared to baseline.
There is a reduction in heart size in dogs with MMVD9, 10, 12 and DCM11 administered pimobendan. Earlier studies have only evaluated the effect of initiation of pimobendan on dogs’ heart size after the onset of heart failure in dogs with MMVD. This is therefore the first study to show an effect of pimobendan in reducing the heart size of dogs with MMVD and cardiac enlargement before the onset of clinical signs. The reduction in heart size was evident by 3 different indices: LVIDDN, LVIDSN, and LA/Ao. Similar changes in left ventricular diameter have been shown in Dobermans with preclinical DCM.11 There was also an increase in the FS% of dogs receiving pimobendan. A small but significant reduction in left atrial size (LA/Ao) was also seen in the placebo group. One possible explanation for this would be “regression to the mean.” Regression to the mean can occur when a clinical measurement must exceed a threshold in order for a patient to be recruited to a study.19 Patients with “true” values for the measurement just below the threshold but an erroneously high measurement at the time of screening will enter the study, whereas those with true values just above the threshold with an erroneously low measurement will not. On a second measurement, despite the “true” value not having changed, if the measurement made is more reflective of the true measurement, it will appear to have fallen or “regressed to the mean.” In this case, as LA/Ao was one of the more stringent entry criteria, regression to the mean in some recruited patients makes it appear as though the value has fallen in the placebo group. Importantly the reduction in left atrial size was significantly greater in the pimobendan group compared to the placebo group (median −0.08 compared to −0.027), indicating that there was a true treatment effect as well as any change attributable to variation in measurement.
The change in echocardiographic variables at day 35 (±7 days) was associated with outcome. Those dogs that had greater reductions in LA/Ao, LVIDDN, and LVIDSN tended to have longer periods before reaching the primary endpoint of the study. This effect was independent of the effect of pimobendan administration as shown by the multivariable analyses, in which the change in the echocardiographic variable was significantly associated with outcome even when the effect of pimobendan was included in the model. For instance, a 0.1‐unit increase in LA/Ao increased the risk of reaching the primary endpoint by 14% (HR = 1.14). A reduction in the LA/Ao by 0.1 units decreased the risk to 100/1.14%,that is, 87.7% representing a 12.3% reduction in risk. When the change in systolic diameter was included in the multivariable model, it appeared to diminish the effect of pimobendan administration to the greatest extent, making it appear nonsignificant (HR 0.71 [95% CI 0.51–1.00] P = 0.051). The same phenomenon was observed in the PROTECT study11 where in a multivariable analysis, the inclusion of the change in systolic diameter led to a widening of the 95% CI of the estimate of the treatment effect resulting in a nonsignificant P‐value for the treatment effect. This might indicate that the change in systolic diameter is an “intervening variable”20 and therefore on the causal pathway by which pimobendan mediates its favorable effect on outcome. The administration of pimobendan brings about a reduction in systolic diameter. If the reduction in systolic diameter is one of the major ways in which pimobendan mediates its favorable effect (ie, it intervenes on the “causal pathway”) once the reduction in systolic diameter is taken into account in a multivariable analysis, the association between treatment and the outcome is no longer apparent. These findings add further weight to the existing literature which suggests that, at least in part, the benefit of pimobendan treatment in canine heart disease is mediated through the reduction in heart size that it brings about. This speculation about a potential mechanism of action in dogs with MR is supported by experimental findings in dogs with induced MR which suggest that reduced heart size and enhanced contractile function are associated with a reduction in mitral regurgitant orifice area and therefore reduced MR.21, 22
The observed reduction in heart size appeared to be maintained over the duration of the study with the average heart size, as indicated by the AUC for the VHS, of dogs in the pimobendan group being smaller compared to dogs in the placebo group.
Change in quality of life variables did not differ significantly between groups at day 35. Although there were 2 quality of life variables, appetite and cough, that appeared to improve significantly in the pimobendan group and not the placebo group, between‐group comparisons did not reveal significant differences between groups. Both groups appeared to show a highly significant (P < 0.0001) improvement in demeanor and exercise tolerance at day 35, yet the difference between groups was not significant. These observed changes suggest a possible “placebo effect” with owners perceiving improvement in their dogs because they believed they were receiving medication. This observation emphasizes the importance of including a placebo group in clinical trials in which subjective judgments are made about responses to treatment. Almost all the dogs recruited to the study were perceived by their owners to be normal at the time of entry to the study; for instance, 96% of owners rated their dog's exercise tolerance as good or very good on entry to the study. It would therefore be less likely that a difference in improvement between groups could be shown given that the dogs were not considered to be showing clinical signs as a consequence of their disease. The absence of differences between groups may also be a reflection of the relatively crude means of rating quality of life scores that were used, by comparison to validated tools such as the FETCH score.23
Two clinical variables that were seen to be lower in the pimobendan group when compared to the placebo group over the duration of the study by the AUC method were the heart rate on physical examination and the owner‐measured resting respiratory rate. The median AUC of resting respiratory rate was 2 breaths per minute lower in the pimobendan group, and the median AUC of heart rate was 6 beats per minute lower. Given that higher heart rate and higher resting respiratory rate tend to be associated with more advanced MMVD6 and the onset of CHF,24 the lower rates in dogs treated with pimobendan might be an indication of improved stability of these dogs even though they were considered to be preclinical at the time of recruitment to the trial.
The magnitude of the differences observed in heart rate, resting respiratory rate, and VHS between groups as a consequence of treatment was considerably smaller than the observed variability within the population. For instance, the IQR for heart rate in the population as a whole at baseline was 30 beats per minute, whereas the difference observed between the medians for the AUCs observed in the 2 treatment groups was only 6 beats per minute. Thus, the changes were not sufficiently profound to allow the treatment groups to be discriminated, or to act as reliable indicators of a response to treatment in individual dogs. Similarly, although the difference observed between groups in the change in echocardiographic variables at day 35 was statistically highly significant, the magnitude of the absolute changes was relatively small (the median change was <7% of median baseline values). The within‐group variability of the measured changes was relatively large, and the magnitude of the changes in the 2 groups overlapped considerably (Fig 2). This means that individual dogs on pimobendan could not be reliably discriminated from those on placebo on the basis of the changes observed.
Not all dogs recruited to the EPIC study went on to develop CHF; however, the relatively large number of dogs (135 in total) that did develop CHF provides us with an opportunity to describe the changes that occur in a number of clinical, radiographic, and echocardiographic variables as dogs develop heart failure. In particular, we have paired observations in dogs obtained at baseline and at the time of onset of CHF. It is notable that the 2 treatment groups did not differ significantly in any of the measured characteristics at the onset of CHF; among other characteristics, heart size, heart rate, and respiratory rate were very similar in both groups at that time. The similar heart size seen in both groups suggests that by the onset of CHF, the heart size in dogs receiving pimobendan had increased up to a level comparable to that observed in the placebo group, despite being, on average, lower for the duration of the study as determined by the AUC comparison of VHS. If there is a critical heart size for a dog, which when reached is likely to be associated with the development of signs of CHF, it is possible that reducing heart size at the onset of treatment is one of the ways in which pimobendan delays the onset of CHF. We know from the main results of the EPIC study that dogs receiving pimobendan take longer to develop CHF, which may argue again in favor of the reduction in heart size being one of the primary ways in which this effect is mediated.
Our analysis also showed that a number of clinical and quality of life variables change in dogs as they develop CHF. In the population of dogs that developed CHF, body weight and rectal temperature decreased. Some of the biochemical variables also changed with creatinine and ALT increasing (although the median change for creatinine was zero) and total protein decreasing. No change in electrolyte concentrations or PCV was observed.
As might be expected, the quality of life variables measured universally showed evidence of deterioration at the onset of CHF with only the change in exercise tolerance differing between groups (with more pimobendan dogs showing evidence of deterioration). There was also a reduction in BCS and an increase in murmur intensity in both groups.
Limitations
The analyses described in this study are exploratory analyses of longitudinal data acquired from dogs in a randomized clinical trial. They do not relate directly to the primary hypothesis of the original study and should therefore be regarded as hypothesis generating. Statistical analyses are not corrected for multiple comparisons, and therefore, P‐values close to the threshold of significance should be interpreted with caution. For many of the more important conclusions of the study, for example, the reduction in heart size after 35 days, the P‐values associated with the comparisons are <0.0001 and therefore very unlikely to represent a type I statistical error.
Comparing groups in longitudinal studies is challenging, particularly when the rate at which individuals leave those groups is unequal, not at random and potentially related to what is being measured.25 For example, dogs with bigger hearts are more likely to be missing from the PP population because they have met the primary endpoint of the study. This unequal time spent in the study and unequal numbers of observations in the 2 groups can be partially compensated for by methods such as the AUC method we employ.18 This method is only likely to be appropriate for use with continuous variables where the values can be meaningfully averaged. When variables such as the quality of life variables we recorded are compared, such a method is probably not appropriate. Comparing groups at individual visits is problematic because lower numbers of animals will be left in the group that meets the primary endpoint of the study more quickly (in this study the placebo group). This means that after a given point in the study, those animals that remain are likely to be in some way exceptional rather than being representative of the population as a whole. For this reason, we did not compare quality of life variables between groups after 24 months when fewer than 50% of the dogs remained in each group.
Comparing quality of life between groups is also challenging because those dogs with a poor quality of life are likely to have left the study through either having met the primary endpoint or having been censored from the PP population for another reason. These types of events tended to occur sooner in the group receiving placebo, as was reflected by the results of the time to first event analysis we have already described1 and is indicated by the lower number of dogs remaining in the PP population in the placebo group. Thus, the populations being compared are those remaining in the study that continue to have a good quality of life, and differences between groups are not observed as is seen in Table S2. As acknowledged above, the method we used for assessing quality of life was a relatively insensitive, subjective, and unvalidated tool and may also have contributed to the absence of observed differences between groups. Having acknowledged these weaknesses in the method of measurement, it was still possible by this method for us to show a clear deterioration in quality of life associated with the onset of CHF.
Conclusions
In dogs with preclinical MMVD, pimobendan treatment results in a smaller heart size both in the short and long term. The degree to which heart size reduces in the short term is predictive of outcome with a greater reduction in heart size associated with a prolongation of the time to CHF or cardiac‐related death. In particular, the therapeutic benefit of pimobendan appears to be associated with the reduction in LV end‐systolic dimension. There were no consistent differences observed between treatment groups in quality of life variables, either in the short or long term as might be expected in a study of dogs with preclinical disease where deterioration in quality of life often signified reaching the primary endpoint or resulted in censoring. At the onset of CHF, dogs treated with pimobendan were indistinguishable from those receiving placebo showing clear evidence of a deterioration in quality of life and significant changes in a number of clinical, diagnostic imaging, and laboratory variables.
Supporting information
Figure S1. Four Forest plots illustrating the hazard ratios and their 95% confidence intervals obtained from the four multivariable Cox proportional hazards analysis models.
Table S1. Ordinal scoring system for clinical variables recorded at baseline.Table S2. P‐values for the between‐group comparison of ordinal quality of life and clinical variables at each of the visits up to and including the visit at 24 months.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Martin Vanselow for performing statistical analyses, Olaf Joens, Robert Jones, Auddie Sharp, Kurt Petersen, Lolita Nilsson, Fabrice Thoulon, and Jacques Gossellin for monitoring and administrative support during the study, and Kevin Christiansen, Laura Happon, Lisa Cellio, Mel Davis, Giorgia Santarelli, Michele Borgarelli, Mari Waterman, Sonya Wesselowski, Michael Aherne, Karen Johnson, Jess Douthat, Linda Slater, Kathy Glaze, Jill VanWhy, Amy Savarino, Matthew Miller, Crystal Hariu, Ryan Fries, Justin Carlson, Randolph Winter, Jordan Vitt, Kay Naden, Véronique Birault, Kristen Antoon, Suzanne Cunningham, Sarah Miller, Peter Holler, Julia Simak, Mary Perricone, April Jackson, Michele Dolson, Regan Rising, Curt Rehling, Geri Lake‐Bakaar, Julie Martin, Herbert W. Maisenbacher, Ashley Jones, Melanie Powell, Brandy Winter, Mary Bohannon, Heidi Chambers, Alice Defarges, Shauna Blois, Anthony Abrams‐Ogg, Nevena Borozan, Kristin A. Jacob, Heather Wink, Dina Berriochoa, Steven Ettinger, and Megan Buckner for assistance in recruitment and management of cases.
Conflict of Interest Declaration
This project was funded by Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health GmbH. A representative of Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health GmbH read the final draft before submission. Christoph Schummer and Philip Watson are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health GmbH. All other authors have received funding from Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health GmbH within the last 5 years for some or all of the following activities: research, travel, speaking fees, consultancy fees, and preparation of educational materials.
Off‐label Antimicrobial Declaration
Authors declare no off‐label use of antimicrobials.
Footnotes
Vetmedin 2.5 mg chewable tablets
SAS Version 8.2; SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA
References
- 1. Boswood A, Haggstrom J, Gordon SG, et al. Effect of pimobendan in dogs with preclinical myxomatous mitral valve disease and cardiomegaly: the EPIC study‐a randomized clinical trial. J Vet Intern Med 2016;30:1765–1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Atkins C, Bonagura J, Ettinger S, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of canine chronic valvular heart disease. J Vet Intern Med 2009;23:1142–1150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Hezzell MJ, Boswood A, Moonarmart W, et al. Selected echocardiographic variables change more rapidly in dogs that die from myxomatous mitral valve disease. J Vet Cardiol 2012;14:269–279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Lord P, Hansson K, Kvart C, et al. Rate of change of heart size before congestive heart failure in dogs with mitral regurgitation. J Small Anim Pract 2010;51:210–218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Reynolds CA, Brown DC, Rush JE, et al. Prediction of first onset of congestive heart failure in dogs with degenerative mitral valve disease: the PREDICT cohort study. J Vet Cardiol 2012;14:193–202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Borgarelli M, Savarino P, Crosara S, et al. Survival characteristics and prognostic variables of dogs with mitral regurgitation attributable to myxomatous valve disease. J Vet Intern Med 2008;22:120–128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Haggstrom J, Boswood A, O'Grady M, et al. Effect of pimobendan or benazepril hydrochloride on survival times in dogs with congestive heart failure caused by naturally occurring myxomatous mitral valve disease: the QUEST study. J Vet Intern Med 2008;22:1124–1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Moonarmart W, Boswood A, Luis Fuentes V, et al. N‐terminal pro B‐type natriuretic peptide and left ventricular diameter independently predict mortality in dogs with mitral valve disease. J Small Anim Pract 2010;51:84–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Haggstrom J, Boswood A, O'Grady M, et al. Longitudinal analysis of quality of life, clinical, radiographic, echocardiographic, and laboratory variables in dogs with myxomatous mitral valve disease receiving pimobendan or benazepril: the QUEST study. J Vet Intern Med 2013;27:1441–1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Lombard CW, Jons O, Bussadori CM. Clinical efficacy of pimobendan versus benazepril for the treatment of acquired atrioventricular valvular disease in dogs. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 2006;42:249–261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Summerfield NJ, Boswood A, O'Grady MR, et al. Efficacy of pimobendan in the prevention of congestive heart failure or sudden death in Doberman Pinschers with preclinical dilated cardiomyopathy (the PROTECT Study). J Vet Intern Med 2012;26:1337–1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Woolley R, Smith P, Munro E, et al. Effects of treatment type on vertebral heart size in dogs with myxomatous mitral valve disease. Int J Appl Res Vet Med 2007;5:43–48. [Google Scholar]
- 13. Ferasin L, Crews L, Biller DS, et al. Risk factors for coughing in dogs with naturally acquired myxomatous mitral valve disease. J Vet Intern Med 2013;27:286–292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Hansson K, Haggstrom J, Kvart C, et al. Left atrial to aortic root indices using two‐dimensional and M‐mode echocardiography in cavalier King Charles spaniels with and without left atrial enlargement. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 2002;43:568–575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Cornell CC, Kittleson MD, Della Torre P, et al. Allometric scaling of M‐mode cardiac measurements in normal adult dogs. J Vet Intern Med 2004;18:311–321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Hansson K, Haggstrom J, Kvart C, et al. Interobserver variability of vertebral heart size measurements in dogs with normal and enlarged hearts. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 2005;46:122–130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Thomas WP, Gaber CE, Jacobs GJ, et al. Recommendations for standards in transthoracic two‐dimensional echocardiography in the dog and cat. J Vet Intern Med 1993;7:247–252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Matthews JN, Altman DG, Campbell MJ, et al. Analysis of serial measurements in medical research. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 1990;300:230–235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Bland JM, Altman DG. Some examples of regression towards the mean. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 1994;309:780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Katz MH. Setting up a multivariable analysis In: Multivariable Analysis, 3rd ed Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2011:93–117. [Google Scholar]
- 21. Borgenhagen DM, Serur JR, Gorlin R, et al. Effects of left‐ventricular load and contractility on mitral regurgitant orifice size and flow in dog. Circulation 1977;56:106–113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Yoran C, Yellin EL, Becker RM, et al. Dynamic aspects of acute mitral regurgitation – effects of ventricular volume, pressure and contractility on the effective regurgitant orifice area. Circulation 1979;60:170–176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Freeman LM, Rush JE, Farabaugh AE, et al. Development and evaluation of a questionnaire for assessing health‐related quality of life in dogs with cardiac disease. J Am Vet Med Assoc 2005;226:1864–1868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Schober KE, Hart TM, Stern JA, et al. Effects of treatment on respiratory rate, serum natriuretic peptide concentration, and Doppler echocardiographic indices of left ventricular filling pressure in dogs with congestive heart failure secondary to degenerative mitral valve disease and dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Vet Med Assoc 2011;239:468–479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Lane P. Handling drop‐out in longitudinal clinical trials: a comparison of the LOCF and MMRM approaches. Pharm Stat 2008;7:93–106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. Four Forest plots illustrating the hazard ratios and their 95% confidence intervals obtained from the four multivariable Cox proportional hazards analysis models.
Table S1. Ordinal scoring system for clinical variables recorded at baseline.Table S2. P‐values for the between‐group comparison of ordinal quality of life and clinical variables at each of the visits up to and including the visit at 24 months.


