Abstract
Background
Hyperglycemia is prevalent in patients in the pediatric intensive care unit. The purpose of this study was to describe the benefits and risks of tight glucose control (TGC) in critically ill children.
Methods
A systemic review and meta-analysis of the literature was carried out on randomized controlled trials of TGC in critically ill children admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit. The databases searched were Medline, Embase, and CENTRAL databases until May 1, 2017. Paired reviewers independently screened citations, assessed risk of bias of included studies, and extracted data. A random-effects model was used to report all outcomes. The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation system was used to quantify absolute effects and quality of evidence. The primary outcome was hospital mortality. The secondary outcomes were hypoglycemia (any, severe), sepsis, new need for dialysis, and seizures.
Results
A total of 4030 patients were included from six studies. All six studies were rated as at low risk of bias. Our meta-analysis showed that TGC did not result in a decrease in risk of hospital mortality (odds ratio (OR), 0.95; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.62–1.45; I2 = 40%; moderate quality), sepsis (OR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.63–1.08), or seizures (OR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.59–1.63). TGC was associated with a decrease in new need for dialysis (OR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.45–0.86). However, TGC was associated with a significant increase in any hypoglycemia (OR, 4.39; 95% CI, 2.39–8.06) and severe hypoglycemia (OR, 4.11; 95% CI, 2.67–6.32).
Conclusions
Among critically ill children with hyperglycemia, TGC does not result in a decrease in hospital mortality, but appears to reduce a new need for dialysis. However, TGC is associated with higher incidence of hypoglycemia.
Systematic review registration
PROSPERO registration number CRD42017074039.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s13054-018-1976-2) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Hyperglycemia, Randomized controlled trial, Children, Tight glycemic control, Mortality
Background
Hyperglycemia is prevalent in patients in the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU), with more than 80% having a blood glucose concentration greater than 110 mg/dl, more than 60% a concentration greater than 150 mg/dl, and more than 30% a concentration exceeding 200 mg/dl [1–4]. The extent of hyperglycemia is associated with adverse outcomes, including organ failure, length of stay in the PICU, and death [1, 5–9]. Consequently, the practice of tight glucose control (TGC) with insulin treatment in critically ill children has emerged as a plausible strategy to improve outcomes. To achieve such ambitious goals in clinical practice, however, there are significant challenges in increased risk of hypoglycemia, additional personnel training, efficient utilization of medical resources, and radical revamping of glycemic management protocols [10]. Furthermore, insulin treatment for critically ill patients only works when the normal healthy fasting ranges for blood glucose concentrations are achieved, and these are lower in children than in adults [11].
Several investigations have examined the benefits and risks of using TGC in critically ill children. In 2009, Vlasselaers et al. [12] published a single-center, randomized controlled trial (RCT) of critically ill children showing that TGC of 80–110 mg/dl reduced hospital mortality by half, and reduced the infection rate and length of stay, but also presented extremely high rates of severe hypoglycemia. However, subsequent multicenter large RCTs of TGC have failed to replicate this mortality benefit [13, 14]. Furthermore, a recent trial, the Heart and Lung Failure—Pediatric Insulin Titration (HALF-PINT) trial, was stopped early because the data indicated a low likelihood of benefit and evidence for the possibility of harm [15].
A meta-analysis [16] has been published on this subject. However, results from two RCTs [15, 17] were not included in the study. Moreover, the meta-analysis failed to conducted subgroup analyses on critical variables or a formal evaluation of the quality of evidence (using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE)). Thus, a comprehensive overview of all RCTs involving critically ill children has never been performed, and the optimal glucose goal remains largely unknown.
Consequently, the considerable controversy of RCTs and the limitations of the prior meta-analysis prompted us to perform an updated systematic review and meta-analysis examining the risks and benefits of TGC as compared with usual care in critically ill children. Moreover, we conducted subgroup analyses on three variables that have been debated in the controversy over TGI: glucose goal (< 110 mg/dl or 110–140 mg/dl), patient setting (cardiac surgery or not cardiac surgery), and continuous glucose monitoring.
Methods
Protocol and guidance
The study protocol was prepared following PRISMA-P guidelines [18] and was registered at PROSPERO (CRD42017074039). The methods of the systematic review and meta-analysis followed PRISMA guidelines [19]. Reporting of statistical data in the study followed SAMPL guidelines [20].
Study selection
Inclusion criteria
We included RCTs that met each of the following criteria: the setting was a PICU, and the patient was child (age < 16 years); the intervention group received TGC (glucose goal < 140 mg/dl obtained using insulin treatment during part or all of the PICU stay); the comparison group received usual care (method of insulin administration and glucose goal could vary between trials); and the primary or secondary outcomes included hospital mortality, hypoglycemia (any, severe), new need for dialysis, sepsis, or seizures.
Exclusion criteria
Trials were excluded if the intervention was conducted primarily during the intraoperative period rather than during the PICU stay, or if we were unable to obtain adequate details of the study methodology or results from the article or study investigators.
Missing data
We contacted the investigators of all unpublished RCTs as well as any published RCTs in which data were missing to confirm eligibility and obtain additional study details.
Duplicate publications
If separate articles from the same RCT were published, the article with the most updated data was selected. In the case of duplicate publications, only one publication was included.
Information sources and search strategy
Medline, Embase, and the Cochrane Library at the CENTRAL Register of Controlled Trials were systematically searched. Gray literature was searched through appropriate databases (British Library Thesis Service, Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects, OpenGrey). We also consulted databases of clinical trial registries (ClinicalTrials.gov, World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, European Union Clinical Trials Register, ISRCTN Registry). The last electronic search was on May 1, 2017. We also hand searched the references to the retrieved articles and meta-analyses.
For the search strategy, we used a combination of keywords and MeSH terms for “child” AND “insulin”, using the sensitive search filters for therapeutic interventions (Additional file 1: Supplemental Digital Content).
Study selection
Two reviewers (YZ and LC) independently screened the titles and abstracts of retrieved reports for potential eligibility. They then screened the full text of potentially relevant trials. Disagreements were resolved by discussion and consensus or by consulting a third reviewer (TL).
Data collection process
Following removal of duplicate articles, two reviewers (YZ and LC) independently extracted data from the included RCTs using a standardized electronic form. Disagreements between the two reviewers were resolved by discussion and consensus or by consulting a third reviewer (TL). Another reviewer (FF) double-checked the extracted data.
Outcomes and prioritization
The primary outcome was hospital mortality because we considered a reduction in hospital mortality to be the most important potential benefit of TGC. Hospital mortality was defined as death occurring during the hospital stay or within 30 days following admission. In cases in which both in-hospital and 30-day outcomes were reported, the former was used for analysis.
The secondary outcomes were hypoglycemia (any, severe), sepsis, new need for dialysis, and seizures. We defined severe hypoglycemia as a blood glucose level below 40 mg/dl and any hypoglycemia as a blood glucose level below 60 mg/dl. We defined sepsis to encompass the terms septicemia, bacteremia, or a description of positive blood cultures; a general description of infection did not qualify.
Subgroup and sensitivity analyses
We performed subgroup analyses based on three variables prespecified clinically relevant to analysis outcomes: glucose goal in the tight control group, cardiac surgery, and continuous glucose monitoring. Subgroup analyses were performed only if there were at least two RCTs in each subgroup or a trial’s report permitted a comparison within the trial.
Differing opinions exist on the optimal level of TGC. The 2018 recommendations from the American Diabetes Association recommend targeting blood glucose levels of 140–180 mg/dl in critically ill patients [21–23]. We stratified studies by glucose goal in the TGC group into two categories: very tight control (upper limit of glucose goal < 110 mg/dl); and moderately tight control (upper limit of glucose goal 110–140 mg/dl).
Because of the concern that the pathophysiological effect of hyperglycemia may differ between patients with and without cardiac surgery, we stratified trials by PICU setting into two categories: cardiac surgery and not cardiac surgery. For trials involving mixed populations but not presenting separate data for patients with cardiac surgery, we included the pooled results in the cardiac surgery subgroup only if ≥ 50% of patients underwent cardiac surgery.
Continuous glucose monitoring has been shown to be safe and effective in children and adults, and may assist in the safer provision of tight glycemic control, with less hypoglycemia [24]. Thus, we stratified trials by whether they used continuous glucose monitoring to control blood glucose.
We conducted sensitivity analyses to examine the impact of using alternative effect measures (odds ratio vs relative risk), pooling methods (Peto vs Mantel–Haenszel (M–H) or inverse variance), statistical models (fixed vs random effects), and removing one study at a time.
Risk of bias and quality of evidence
Two reviewers (YZ and LC) independently assessed risk of bias (low risk of bias, high risk of bias, or unclear risk of bias) using the Cochrane risk of bias instrument, which deals with random sequence generation and allocation concealment (selection bias), blinding of study participants and personnel (performance bias), blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias), incomplete outcome data (attrition bias), selective reporting (reporting bias), and other bias. They resolved any disagreements by discussion and consensus or by consulting a third reviewer (TL). We judged trials with more than two high-risk components as having a moderate risk of bias, and trials with more than four high-risk components as having a high risk of bias. We used the GRADE approach to rate the quality of evidence and generate absolute estimates of effect for the outcomes [25].
Data synthesis
Computations were performed with RevMan 5.3.3 software (freeware available from The Cochrane Collaboration). We used the M–H method as the primary analysis to estimate the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Two-tailed P < 0.05 was considered a criterion for statistical significance. We report the results of the random-effects model for all outcomes. We assessed heterogeneity with the Cochran Q test and the I2 test, with I2 values exceeding 25%, 50%, and 75% representing low, moderate, and high heterogeneity, respectively [26]. If an analysis included 10 or more RCTs, we planned to use a funnel plot to explore the possibility of published bias.
Results
Search results and characteristics of included studies
The literature search yielded 154 articles, of which 22 were reviewed in full text (Fig. 1). Of these articles, six RCTs [12–15, 17, 27] met the inclusion criteria. The six included trials randomized 4030 patients (1980 to tight glycemic control and 2050 to receiving control) (Table 1). Trials were conducted in a diverse array of countries, half of them at a single center. Study sizes ranged widely (88–1369 patients), with two trials enrolling fewer than 300 patients and four trials enrolling more than 700 patients. The study participants encompass a broad distribution of critically ill children (Vlasselaers et al. [12], mixed with 75% cardiac surgery; Macrae et al. [13], mixed with 60% cardiac surgery; Jeschke et al. [27], severe burns; Agus et al. [14], cardiac surgery; Agus et al. [15], noncardiac surgery; Alsweiler et al. [17], preterm). TGI, as well as mean achieved glucose levels, varied between trials in both the tight control and usual care groups (Additional file 1: Supplemental Digital Content Table S1).
Fig. 1.
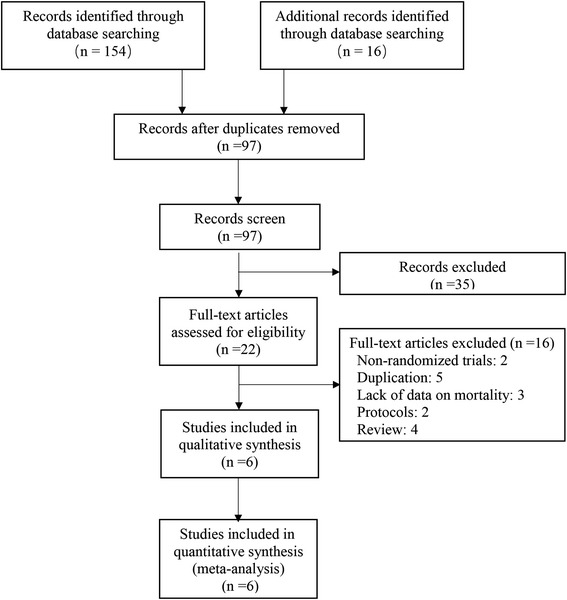
Study selection for inclusion in meta-analysis
Table 1.
Characteristics of studies comparing tight and usual glucose control
| Author | Year | Size (n) | Centers (n) | Country | Setting | Age, median (IQR) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tight control | Usual control | ||||||
| Vlasselaers et al. [12] | 2009 | 700 | 1 | Belgium | Mixed with 75% cardiac surgery | 1.4 (0.3–5.5) | 1.3 (0.3–4.6) |
| Jeschke et al. [27] | 2010 | 239 | 1 | USA | Burns | 7.7 (5.2)a | 10.8 (5.4)a |
| Agus et al. [14] | 2012 | 980 | 2 | USA | Cardiac surgery | 0.4 (0.2–0.8) | 0.4 (0.2–0.9) |
| Alsweiler et al. [17] | 2012 | 88 | 1 | New Zealand | Preterm | Preterm babies | |
| Macrae et al. [13] | 2014 | 1369 | 13 | UK | Mixed with 60% cardiac surgery | 0.5 (0.1–2.7) | |
| Agus et al. [15] | 2017 | 713 | 35 | USA | Mixed without cardiac surgery | 5.5 (1.4–12.5) | 6.7 (1.7–12.8) |
IQR interquartile range
aMean (standard deviation)
Risk of bias and quality of evidence
Treating clinicians were not blinded to treatment allocation in any of the trials. Most investigators were, however, blinded to treatment and outcomes. Study quality appraisal indicated that studies were of variable quality (Fig. 2) and that all six trials had a low risk of bias. Table 2 presents GRADE summary findings for all outcomes.
Fig. 2.

Risk of bias summary. Agus 2010 [14], Agus 2017 [15], Alsweiler 2012 [17], Jeschke 2010 [27], Macrae 2014 [13], Vlasselaers 2009 [12]
Table 2.
GRADE evidence profile of outcomes, tight glucose control vs usual glucose control
| Outcome | Number of children (studies) | Effect | Qualitya | Importance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative effect, OR (95% CI) | Absolute risk (95% CI) | ||||
| Hospital mortality | 4021 (6 studies) | 0.95 (0.62–1.45) | 3 fewer per 1000 (from 20 fewer to 23 more) | ⊕ ⊕ ⊕⊝ moderateb | Critical |
| Severe hypoglycemia (glucose < 40 ml/dl) | 3835 (5 studies) | 4.11 (2.67–6.32) | 42 more per 1000 (from 23 more to 69 more)b | ⊕ ⊕ ⊕ ⊕ high | Critical |
| Any hypoglycemia (glucose < 60 mg/dl) | 3747 (4 studies) | 4.57 (2.24–9.33) | 157 more per 1000 (from 61 more to 299 more) | ⊕ ⊕ ⊕ ⊕ highb | Critical |
| Dialysis | 3049 (3 studies) | 0.63 (0.45–0.86) | 24 fewer per 1000 (from 9 fewer to 36 fewer) | ⊕ ⊕ ⊕ ⊕ highb | Important |
| Seizures | 3047 (3 studies) | 0.98 (0.59–1.63) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 8 fewer to 12 more) | ⊕ ⊕ ⊝⊝ lowb,c | Important |
| Sepsis | 4021 (6 studies) | 0.83 (0.63–1.08) | 20 fewer per 1000 (from 45 fewer to 9 more) | ⊕ ⊕ ⊕ ⊕ high | Important |
GRADE Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation, OR odds ratio, CI confidence interval
aHigh quality, further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect; moderate quality, further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate; low quality, further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate; very low quality, we are very uncertain about the estimate
bWide confidence
cHigh heterogeneity
Primary outcome: hospital mortality
Hospital mortality was reported in six trials. These trials reported 223 deaths (TGC, 110/1974 (5.6%); UGC, 113/2047 (5.5%)). Our meta-analysis showed no significant difference in mortality between tight control vs usual control (OR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.62–1.45; P = 0.82; I2 = 40%; Fig. 3). Tests for heterogeneity identified the trial by Vlasselaers et al. [12] as having outlying results, which appeared to be explained by the lowest glucose target in the six trials. Exclusion of the outlying trial resolved this heterogeneity (I2 = 0%, P = 0.40), but did not significantly change the findings (OR, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.84–1.52).
Fig. 3.

Association of tight glucose control vs usual glucose control with hospital mortality, any hypoglycemia and severe hypoglycemia. CI confidence interval, Agus 2010 [14], Agus 2017 [15], Alsweiler 2012 [17], Jeschke 2010 [27], Macrae 2014 [13], Vlasselaers 2009 [12]
Sensitivity analyses using an alternative statistical method, effect measure, analysis model, and after removing one study at a time showed similar results for hospital mortality.
Secondary outcomes: hypoglycemia, sepsis, new need for dialysis, seizures
Hypoglycemia was reported in five published trials. TGC was associated with an increased risk of severe hypoglycemia (OR, 4.11; 95% CI, 2.67–6.32; I2 = 0%; 42 more per 1000 patients; high quality) and any hypoglycemia (OR, 4.39; 95% CI, 2.39–8.06; I2 = 83%; 157 more per 1000 patients; high quality) (Table 2 and Fig. 3).
New need for dialysis was reported in three trials, and the overall incidence was 5.6% (TGC, 4.5%; usual glucose care, 6.8%). TGC was associated with decrease in dialysis (OR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.45–0.86; Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.

Association of tight glucose control vs usual glucose control with sepsis, new need for dialysis, seizures. CI confidence interval, Agus 2010 [14], Agus 2017 [15], Alsweiler 2012 [17], Jeschke 2010 [27], Macrae 2014 [13], Vlasselaers 2009 [12]
TGC did not result in a significant decrease in sepsis or seizures (Fig. 4).
Subgroup analyses
We performed three subgroup analyses by the target of TGC, by whether cardiac surgery or not, and by whether using continuous glucose monitoring for insulin adjustment. However, there were no differences between groups observed concerning those factors (Tables 3, 4 and 5).
Table 3.
Association of tight glucose control vs usual care with outcomes among critically ill adults, stratified by tight control glucose goal
| Subgroup of trialsa | Number of trials | Event number/total number (%) | OR (95% CI) | I2 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tight control | Usual control | ||||
| Mortality | |||||
| Very tight control | 2 | 12/392 (3.1) | 19/369 (5.1) | 1.11 (0.12–10.60) | 73 |
| Moderately tight control | 4 | 98/1582 (6.2) | 94/1651 (5.7) | 1.10 (0.81–1.49) | 0 |
| Overall | 6 | 110/1974 (2.9) | 113/2047 (5.5) | 0.95 (0.62–1.45) | 40 |
| Any hypoglycemia (< 60 mg/dl) | |||||
| Very tight control | 2 | 112/392 (28.6) | 17/396 (4.3) | 9.35 (1.49–58.83) | 88 |
| Moderately tight control | 3 | 259/1533 (16.9) | 99/1514 (6.5) | 3.00 (2.07–4.34) | 54 |
| Overall | 5 | 371/1925 (19.3) | 116/1910 (6.1) | 4.39 (2.39–8.06) | 83 |
| Severe hypoglycemia (< 40 mg/dl) | |||||
| Very tight control | 2 | 24/392 (6.1) | 5/396 (8.7) | 5.23 (1.95–14.00) | 0 |
| Moderately tight control | 3 | 85/1533 (5.5) | 22/1514 (1.5) | 3.88 (2.41–6.26) | 0 |
| Overall | 5 | 109/1925 (18.4) | 27/1910 (5.8) | 4.11 (2.67–6.32) | 0 |
| Sepsis | |||||
| Very tight control | 2 | 121/392 (30.9) | 143/396 (36.1) | 1.01 (0.43–2.41) | 73 |
| Moderately tight control | 4 | 95/1582 (6.0) | 132/1651 (8.0) | 0.81 (0.59–1.12) | 18 |
| Overall | 6 | 216/1947 (11.1) | 275/2047 (13.4) | 0.83 (0.63–1.08) | 32 |
| Dialysis | |||||
| Very tight control | 1 | 2/349 (0.6) | 6/351 (1.7) | 0.33 (0.07–1.65) | NA |
| Moderately tight control | 2 | 67/1184 (5.7) | 97/1165 (8.3) | 0.64 (0.46–0.89) | 0 |
| Overall | 3 | 69/1533 (4.5) | 103/1516 (6.8) | 0.63 (0.45–0.86) | 0 |
| Seizures | |||||
| Very tight control | 0 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Moderately tight control | 3 | 31/1533 (2.0) | 31/1514 (2.0) | 0.98 (0.59–1.63) | 51 |
| Overall | 3 | 31/1533 (2.0) | 31/1514 (2.0) | 0.98 (0.59–1.63) | 51 |
OR odds ratio, CI confidence interval, NA not applicable
aVery tight control, glucose goal < 110 mg/dl; moderately tight control, glucose goal 110–140 mg/dl
Table 4.
Association of tight glucose control vs usual care with outcomes among critically ill adults, stratified by with cardiac surgery or without cardiac surgery
| Subgroup of trials | Number of trials | Event number/total number (%) | OR (95% CI) | I2 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tight control | Usual control | ||||
| Mortality | |||||
| Noncardiac surgery | 3 | 57/441 (12.9) | 45/394 (9.2) | 1.29 (0.52–3.23) | 29 |
| Cardiac surgery | 3 | 53/1533 (3.5) | 64/1516 (4.2) | 0.79 (0.50–1.26) | 26 |
| Overall | 6 | 110/1974 (5.6) | 113/2047 (5.0) | 0.95 (0.62–1.45) | 40 |
| Any hypoglycemia (< 60 mg/dl) | |||||
| Noncardiac surgery | 2 | 104/342 (30.4) | 45/394 (11.4) | 2.97 (2.01–4.41) | 0 |
| Cardiac surgery | 3 | 267/1533 (17.4) | 71/1516 (4.7) | 5.72 (1.95–16.73) | 91 |
| Overall | 5 | 371/1925 (19.3) | 116/1910 (6.1) | 4.39 (2.39–8.06) | 83 |
| Severe hypoglycemia (< 40 mg/dl) | |||||
| Noncardiac surgery | 2 | 25/392 (6.4) | 9/394 (2.3) | 2.95 (1.35–6.42) | 0 |
| Cardiac surgery | 3 | 84/1533 (5.5) | 18/1516 (1.2) | 4.76 (2.84–7.97) | 91 |
| Overall | 5 | 109/1925 (18.4) | 27/1910 (5.8) | 4.11 (2.67–6.32) | 0 |
| Sepsis | |||||
| Noncardiac surgery | 3 | 52/441 (11.8) | 79/531 (14.9) | 0.82 (0.55–1.22) | 67 |
| Cardiac surgery | 3 | 164/1633 (10.0) | 196/1516 (19.2) | 0.79 (0.62–1.00) | 0 |
| Overall | 6 | 216/1947 (11.0) | 275/2047 (13.4) | 0.83 (0.63–1.08) | 32 |
| Dialysis | |||||
| Noncardiac surgery | 3 | 69/1533 (4.5) | 103/1516 (6.8) | 0.63 (0.45–0.86) | 0 |
| Cardiac surgery | 0 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Overall | 3 | 69/1533 (4.5) | 103/1516 (6.8) | 0.63 (0.45–0.86) | 0 |
| Seizures | |||||
| Noncardiac surgery | 1 | 5/349 (1.4) | 10/349 (2.9) | 0.49 (0.17–1.46) | NA |
| Cardiac surgery | 2 | 26/1533 (1.7) | 21/1165 (1.8) | 1.22 (0.68–2.18) | 50 |
| Overall | 3 | 31/1533 (2.0) | 31/1514 (2.0) | 0.98 (0.59–1.63) | 51 |
OR odds ratio, CI confidence interval, NA not applicable
Table 5.
Association of tight glucose control vs usual care with outcomes among critically ill adults, stratified by whether using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM)
| Subgroup of trials | Number of trials | Event number/total number (%) | OR (95% CI) | I2 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tight control | Usual control | ||||
| Mortality | |||||
| Using CGM | 3 | 97/1553 (12.9) | 86/1514 (9.2) | 1.13 (0.83–1.53) | 0 |
| Not using CGM | 3 | 13/441 (3.5) | 27/533 (4.2) | 0.70 (0.18–2.69) | 49 |
| Overall | 6 | 110/1974 (5.6) | 113/2047 (5.0) | 0.95 (0.62–1.45) | 40 |
| Any hypoglycemia (< 60 mg/dl) | |||||
| Using CGM | 3 | 259/1533 (30.4) | 99/1514 (11.4) | 3.00 (2.07–4.36) | 54 |
| Not using CGM | 2 | 24/392 (6.1) | 5/396 (4.7) | 5.23 (1.95–4.00) | 0 |
| Overall | 5 | 371/1925 (19.3) | 116/1910 (6.1) | 4.39 (2.39–8.06) | 83 |
| Severe hypoglycemia (< 40 mg/dl) | |||||
| Using CGM | 2 | 85/1533 (30.4) | 22/1514 (11.4) | 3.88 (2.41–6.26) | 0 |
| Not using CGM | 3 | 112/392 (28.6) | 17/396 (4.7) | 9.35 (1.49–58.83) | 88 |
| Overall | 5 | 109/1925 (18.4) | 27/1910 (5.8) | 4.11 (2.67–6.32) | 0 |
| Sepsis | |||||
| Using CGM | 3 | 91/1553 (12.9) | 101/1514 (9.2) | 0.88 (0.66–1.18) | 0 |
| Not using CGM | 3 | 125/441 (3.5) | 174/533 (4.2) | 0.76 (0.18–2.69) | 69 |
| Overall | 6 | 216/1947 (11.0) | 275/2047 (13.4) | 0.83 (0.63–1.08) | 32 |
| Dialysis | |||||
| Using CGM | 2 | 67/1184 (4.5) | 97/1165 (6.8) | 0.64 (0.46–0.89) | 0 |
| Not using CGM | 1 | 2/349 (4.5) | 6/351 (6.8) | 0.33 (0.07–1.65) | NA |
| Overall | 3 | 69/1533 (4.5) | 103/1516 (6.8) | 0.63 (0.45–0.86) | 0 |
| Seizures | |||||
| Using CGM | 3 | 31/1533 (2.0) | 31/1514 (2.0) | 0.98 (0.59–1.63) | 51 |
| Not using CGM | 0 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Overall | 3 | 31/1533 (2.0) | 31/1514 (2.0) | 0.98 (0.59–1.63) | 51 |
OR odds ratio, CI confidence interval, NA not applicable
Discussion
Findings and interpretations
In this meta-analysis of six RCTs of TGC vs usual care in critically ill children, we found no significant difference in risk of hospital death, sepsis, or seizures, although TGC was associated with a significant reduction in dialysis. On the other hand, we found clear evidence for the main harm of TGC: hypoglycemia increased roughly 4-fold. However, the rate of hypoglycemia varied greatly across RCTs. We performed three prespecified subgroup analyses, stratified by cardiac surgery, by continuous glucose monitoring, and by glucose goal in tight control group, to explore potential areas of bias, but subanalyses did not differ from the overall analysis. In short, our meta-analysis does not support the benefits of TGC reported in the initial trial by Vlasselaers et al. [12], yet it suggests a high risk of hypoglycemia.
Compared with other studies
A previous meta-analysis of four RCTs examined the benefits and risks of TGC in critically ill children [16]. Similar to our findings, the meta-analysis found no significant differences in mortality but an increased risk of hypoglycemia between TGC and usual care in critically ill children. They reported, however, that TGC appeared to reduce acquired sepsis in critically ill children (OR 0.76; 95% CI 0.59–0.99). This discrepancy with our findings could be explained by the small sample size of their study. Further, we have also provided absolute as well as relative risks and a formal rating of the quality of the evidence.
We quantified a new finding, a decreased risk of dialysis with TGC. The previous meta-analysis studying the effect of TGC in critically ill children did not report the outcome of dialysis, whereas the meta-analysis of adults did not show this renoprotective effect [16, 28]. How to explain the conflicting results between our study and the other meta-analyses? One of the reasons may be the inclusion of different types of patients. The evidence for a renoprotective effect of TGC appears most pronounced in cardiac surgery patients [29]. In our study, dialysis was reported in three trials [12–14], and more than half of children in those trials underwent cardiac surgery.
Strengths and limitations
Strengths of this review include a comprehensive search for evidence; duplicate assessment of eligibility, risk of bias, and data abstraction; and assessments of risk of bias. We included a rigorous assessment of the quality of evidence and of the credibility of subgroup analyses. Moreover, we have presented absolute and relative risks, which are crucial for making decisions regarding use of TGC in critically ill children.
Our study also has limitations. First, although there were many similarities to the methodology of the included RCTs, there was also some variability, including nutritional supplementation, target of tight glycemic control, definition of hypoglycemia, blood glucose monitoring, quality of glucose control, and duration and route used for the insulin therapy protocols. These diversities may have influenced the pathophysiology and implications of hyperglycemia. We present the findings stratified by some widely debated variables—glucose goal in the tight control group, blood glucose monitoring, and whether cardiac surgery. However, we were unable to assess the effect of other important variables for lack of adequate data.
Second, since we have pooled results from individual RCTs, our analysis is limited by any flaws in the methodology of these underlying trials. For example, all trials not using a standard care group led to variable control groups.
Third, all included studies were conducted in developed countries. Thus, our findings are applicable only to developed countries. Further research in other countries would add to the generalizability.
Fourth, the small numbers of studies and those in individual subgroup analyses limited power in our conclusions. Moreover, the limited number of included trials afforded modest ability to detect the presence of publication bias [18]. However, publication bias is unlikely as most of included RCTs had negative results.
Conclusions
In summary, we believe the six trials included in our meta-analysis allow us to conclude about the benefits and risks of TGC critically ill children. We found that TGC was not associated with a significant reduction in hospital mortality, seizures, or sepsis, but appears to be associated with a reduction in new need for dialysis. However, TGC was associated with a markedly increased risk of hypoglycemia. These findings were consistent with recent guidelines [22, 23]. Thus, adoption of TGC in critically ill children cannot be recommended for routine use unless further high-quality and well-powered evidence shows benefit.
Key messages
Tight glycemic control does not appear to improve mortality in critically ill children.
Tight glycemic control reduces a new need for dialysis in critically ill children.
Tight glycemic control greatly increases the risk of hypoglycemia in critically ill children.
Additional file
is Supplemental Digital Content: Table S1. (DOCX 17 kb)
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This work is supported by projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (contract/grant number: 81100925, 81472361).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CI
Confidence interval
- OR
Odds ratio
- PICU
Pediatric intensive care unit
- RCT
Randomized controlled trial
- TGC
Tight glucose control
Authors’ contributions
YZ and LC carried out study conception, systematic search, manual search, data retrieval, assessment of risk of bias, analysis, draft of manuscript and revision according to other authors’ suggestions, and submission. TL and FF carried out analysis and critically revising the manuscript. AF carried out drafting and critically revising the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s13054-018-1976-2) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Contributor Information
Lvlin Chen, Email: chenlvlin1057@outlook.com.
Tiangui Li, Email: ltg101@163.com.
Fang Fang, Email: fangfang1057@outlook.com.
Yu Zhang, Email: tnt1057@gmail.com.
Andrew Faramand, Email: 48295109@qq.com.
References
- 1.Preissig CM, Rigby MR. Pediatric critical illness hyperglycemia: risk factors associated with development and severity of hyperglycemia in critically ill children. J Pediatr. 2009;155(5):734–739. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Allen HF, Rake A, Roy M, Brenner D, McKiernan CA. Prospective detection of hyperglycemia in critically ill children using continuous glucose monitoring. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2008;9(2):153–158. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e3181668b33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bowlby D, Rapaport R, Hojsak J. Hyperglycemia in critically ill children. J Pediatr. 2006;148(6):847. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2005.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Srinivasan V, Spinella PC, Drott HR, Roth CL, Helfaer MA, Nadkarni V. Association of timing, duration, and intensity of hyperglycemia with intensive care unit mortality in critically ill children. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2004;5(4):329–336. doi: 10.1097/01.PCC.0000128607.68261.7C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gordillo R, Ahluwalia T, Woroniecki R. Hyperglycemia and acute kidney injury in critically ill children. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2016;9:201–204. doi: 10.2147/IJNRD.S115096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Marsillio LE, Ginsburg SL, Rosenbaum CH, Coffin SE, Naim MY, Priestley MA, Srinivasan V. Hyperglycemia at the time of acquiring central catheter-associated bloodstream infections is associated with mortality in critically ill children. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2015;16(7):621–628. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000000445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kyle UG, Coss Bu JA, Kennedy CE, Jefferson LS. Organ dysfunction is associated with hyperglycemia in critically ill children. Intensive Care Med. 2010;36(2):312–320. doi: 10.1007/s00134-009-1703-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Otto-Buczkowska E, Dworzecki T, Mazur U. Alterations of blood glucose homeostasis in critically ill children—hyperglycemia. Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2007;13(1):43–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Faustino EV, Apkon M. Persistent hyperglycemia in critically ill children. J Pediatr. 2005;146(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2004.08.076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kovalaske MA, Gandhi GY. Glycemic control in the medical intensive care unit. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2009;3(6):1330–1341. doi: 10.1177/193229680900300613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Brown TC, Connelly JF, Dunlop ME, McDougall PN, Tibballs J. Fasting plasma glucose in children. Aust Paediatr J. 1980;16(1):28–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1980.tb02480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vlasselaers D, Milants I, Desmet L, Wouters PJ, Vanhorebeek I, van den Heuvel I, Mesotten D, Casaer MP, Meyfroidt G, Ingels C, et al. Intensive insulin therapy for patients in paediatric intensive care: a prospective, randomised controlled study. Lancet (London, England) 2009;373(9663):547–556. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Macrae D, Grieve R, Allen E, Sadique Z, Morris K, Pappachan J, Parslow R, Tasker RC, Elbourne D. A randomized trial of hyperglycemic control in pediatric intensive care. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(2):107–118. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1302564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Agus MS, Steil GM, Wypij D, Costello JM, Laussen PC, Langer M, Alexander JL, Scoppettuolo LA, Pigula FA, Charpie JR, et al. Tight glycemic control versus standard care after pediatric cardiac surgery. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(13):1208–1219. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1206044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Agus MS, Wypij D, Hirshberg EL, Srinivasan V, Faustino EV, Luckett PM, Alexander JL, Asaro LA, Curley MA, Steil GM, et al. Tight glycemic control in critically ill children. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(8):729–741. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1612348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Srinivasan V, Agus MS. Tight glucose control in critically ill children—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Diabetes. 2014;15(2):75–83. doi: 10.1111/pedi.12134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Alsweiler JM, Harding JE, Bloomfield FH. Tight glycemic control with insulin in hyperglycemic preterm babies: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2012;129(4):639–647. doi: 10.1542/peds.2011-2470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Stewart LA, Group P-P Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 2015;349:g7647. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g7647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):W65–W94. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lang TA, Altman DG. Basic statistical reporting for articles published in biomedical journals: the “Statistical Analyses and Methods in the Published Literature” or the SAMPL Guidelines. Int J Nurs Stud. 2015;52(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2014.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R, Kumar A, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Nunnally ME, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016. Crit Care Med. 2017;45(3):486–552. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.American Diabetes Association 14. Diabetes Care in the Hospital: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(Suppl 1):S144–S151. doi: 10.2337/dc18-S014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.American Diabetes Association 12. Children and Adolescents: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(Suppl 1):S126–S136. doi: 10.2337/dc18-S012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yeh HC, Brown TT, Maruthur N, Ranasinghe P, Berger Z, Suh YD, Wilson LM, Haberl EB, Brick J, Bass EB, et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of methods of insulin delivery and glucose monitoring for diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157(5):336–347. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-157-5-201209040-00508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Schunemann HJ, Group GW GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2008;336(7650):924–926. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–1558. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jeschke MG, Kulp GA, Kraft R, Finnerty CC, Mlcak R, Lee JO, Herndon DN. Intensive insulin therapy in severely burned pediatric patients: a prospective randomized trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;182(3):351–359. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201002-0190OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wiener RS, Wiener DC, Larson RJ. Benefits and risks of tight glucose control in critically ill adults: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2008;300(8):933–944. doi: 10.1001/jama.300.8.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gunst J, Schetz M. Clinical benefits of tight glycaemic control: effect on the kidney. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2009;23(4):431–439. doi: 10.1016/j.bpa.2009.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
is Supplemental Digital Content: Table S1. (DOCX 17 kb)
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.


