Significance
MDMX is an important regulator of p53 during embryonic development and malignant transformation. Using a combination of mouse knockin model, cell culture, and biochemical analysis, we demonstrate that the MDMX acidic domain interacts with the p53 DNA-binding domain and inhibits p53 DNA binding in the test tube and in tissues. This interaction is important for regulating p53 transcriptional activity and tumor suppressor function under physiological conditions. Furthermore, the results suggest that the MDMX acidic domain has p53-independent function that inhibits the progression of Myc-mediated lymphomas. The study provides physiological evidence on the mechanism of p53 regulation by MDMX, and identifies the structural basis for novel MDMX activities that warrants future investigation.
Keywords: p53, MDMX, CK1α, DNA binding, Myc
Abstract
The MDM2 homolog MDMX oncoprotein is indispensable for inhibition of p53 during normal embryonic development and malignant transformation, yet how MDMX harnesses p53 functions is unclear. In addition to a canonical N-terminal p53-binding domain, recent work suggests the central acidic domain of MDMX regulates p53 interaction through intramolecular mimicry and engages in second-site interaction with the p53 core domain in vitro. To test the physiological relevance of these interactions, we generated an MDMX knockin mouse having substitutions in a conserved WW motif necessary for these functions (W201S/W202G). Notably, MDMXSG cells have normal p53 level but increased p53 DNA binding and target gene expression, and rapidly senesce. In vivo, MDMXSG inhibits early-phase disease in Eµ-Myc transgenic mice but accelerates the onset of lethal lymphoma and shortens overall survival. Therefore, MDMX is an important regulator of p53 DNA binding, which complements the role of MDM2 in regulating p53 level. Furthermore, the results suggest that the WW motif has dual functions that regulate p53 and inhibit Myc-driven lymphomas independent of p53.
The p53 tumor suppressor is a transcription factor that plays important roles in promoting homeostasis, DNA repair, cell-cycle arrest, and/or apoptosis in response to damage and stress (1). p53 binds to specific DNA sequences in its target genes as a tetramer. The core DNA-binding domain has poor thermostability, and rapidly undergoes spontaneous denaturation at physiological temperatures (2). Wild-type p53 can be activated by numerous cellular and environmental signals and induces the expression of target genes (3). MDM2 and MDMX are key regulatory proteins that control p53 levels and transcriptional activity by binding to p53 with high affinity (4). Genetic analyses have shown that both MDM2 and MDMX are essential for controlling p53 activity during embryogenesis (5–7). MDMX has less critical roles in inhibiting p53 in adult tissues than MDM2, where somatic knockout studies have shown significantly milder phenotypes (8–10).
p53 is present at low levels in unstressed tissues due to its rapid turnover. This is mainly achieved via binding and ubiquitylation of p53 by MDM2, which functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase to promote p53 proteasomal degradation (11, 12). Accordingly, MDM2 depletion or inhibition of MDM2–p53 binding leads to marked increases in p53 and the activation of its target genes. The ability of MDM2 to ubiquitinate p53 is regulated by ATM-mediated phosphorylation of MDM2 or by its interaction with the ARF tumor suppressor (13). Further, MDM2 also inhibits p53 binding to DNA. Specifically, the central acidic domain of MDM2 interacts with the p53 DNA-binding domain, promoting a mutant-like conformational change (Pab240-positive) that blocks DNA binding (14–16). However, given the prominent role of MDM2 in regulating p53 degradation, the physiological significance of inhibiting p53 DNA binding remains unclear.
MDMX lacks robust E3 ligase activity but plays an important role in regulating p53 transcriptional function. For example, MDMX expression and phosphorylation by the ATM/Chk2 pathway have significant roles in the p53 DNA damage response in adult mice (17, 18). Further, MDMX levels are controlled by MDM2-mediated ubiquitination in a stress-dependent fashion (19, 20), and rapid degradation of MDMX occurs after DNA damage through phosphorylation of several C-terminal sites (21, 22). Finally, ribosomal stress promotes MDMX degradation through L11–MDM2 interaction (23), and oncogenic stress promotes MDMX degradation via ARF, which binds to MDM2 to promote MDMX ubiquitination without the need for MDMX C-terminal phosphorylation (24).
MDMX knockout in mice leads to p53 activation without significant stabilization (25), and the mechanism by which MDMX inhibits p53 remains unclear. Recent studies suggest MDMX cooperates with CK1α to inhibit p53 DNA binding (26). The central region (residues 170 to 303, loosely termed the acidic domain) of MDMX contains 36 acidic residues and 9 basic residues, and is important for inhibiting p53 DNA binding. Specifically, after the N-terminal domain of MDMX binds to the N terminus of p53, the acidic domain of MDMX establishes a second-site interaction with the p53 core domain to inhibit DNA binding. Further, CK1α binds to the MDMX acidic domain and phosphorylates S289, and this promotes the acidic domain–core domain interaction. Accordingly, MDMX or CK1α knockdown stimulates p53 binding to DNA, suggesting MDMX is an important regulator of p53 DNA binding (26).
In vitro, the MDMX acidic domain also engages in intramolecular interactions with the N-terminal p53-binding domain and inhibits MDMX–p53 binding (27, 28). A conserved sequence in the acidic domain surrounding the hydrophobic residues W200/W201 (WW motif) interacts with the p53-binding pocket in the N-terminal domain. This intramolecular p53 mimetic sequence reduces p53 binding affinity, and has been proposed to have autoregulatory function (27, 29). In a simplified setting that measures the affinity between the N-terminal domains of p53 and MDMX, the presence of the WW motif inhibits the binding by ∼400-fold (30). Mutation of the WW element disrupts the intramolecular interaction with the N-terminal pocket and blocks the ability of the acidic domain to interact with the DNA-binding domain of p53 (26, 27). These biochemical data suggest that the WW element has important functions in regulating both MDMX and p53.
To assess the physiological relevance of the intramolecular interactions and p53 binding mediated by the MDMX acidic domain, we generated a knockin mouse model that expresses MDMX bearing mutation of the WW motif (WW to SG). The results showed that homozygous MDMXSG cells and tissues display augmented p53 DNA binding and transcriptional functions. Further, in the context of the Eμ-Myc transgenic mouse, a validated model of human B lymphoma (31), MDMXSG inhibits the early phase of disease but accelerates the onset of lethal lymphomas. The results suggest that in addition to regulating p53, the WW motif has important p53-independent roles in suppressing tumorigenesis.
Results
Generation of the MDMXSG Knockin Mutant Mouse.
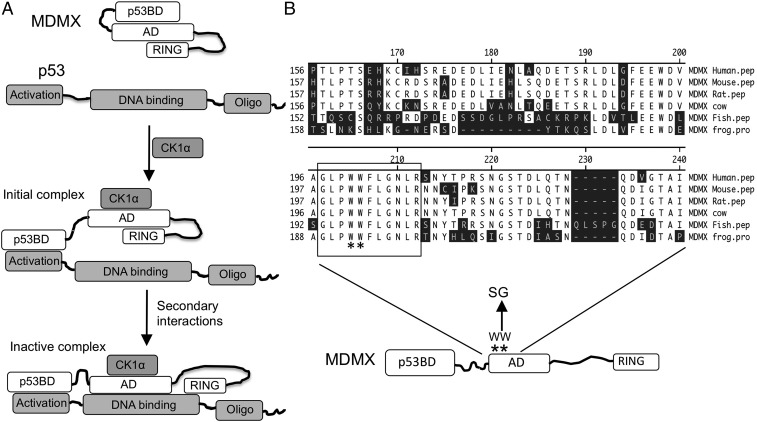
Previous in vitro binding studies suggested the central acidic domain of MDMX directs intramolecular interactions and also binds to the p53 DNA-binding domain. Further, CK1α stimulates the interaction between the MDMX acidic domain and the p53 core domain, inhibiting p53 DNA binding (Fig. 1A). The conserved region around residue 200 in MDMX serves as a mimetic of the p53 N terminus to interact with the p53-binding pocket (Fig. 1B). The W200S/W201G mutation disrupts the MDMX intramolecular interactions, MDMX–CK1α binding, and acidic domain–p53 core binding (26, 27). To assess the biological function of the WW motif in vivo, mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells were targeted by homologous recombination to introduce the W201S/W202G substitutions (equivalent to W200S/W201G of human MDMX) into MDM4 exon 8 (Fig. 2A). Two independent strains of MDMXSG mice were generated. Interbreeding of MDMXSG/+ mice generated MDMXSG/SG offspring at the expected ratio of ∼25%; thus, the SG mutation did not cause embryonic lethality or affect early development. Expression of the mutant allele was confirmed by sequencing of the MDMX mRNA in mouse tissue (Fig. S1). MDMXSG/SG homozygous mice were outwardly normal and showed no signs of developmental issues up to 1 y old.
Fig. 1.
MDMX acidic domain regulates MDMX and p53 through intra- and intermolecular interactions. (A) A model of p53 inhibition by MDMX. The central acidic domain (AD) of MDMX engages in intramolecular interactions with the p53 binding domain (p53BD) and RING domains in the absence of p53. CK1α binding disrupts intramolecular interactions of AD with p53BD, increasing the apparent affinity of the MDMX N terminus for p53. Following formation of the initial MDMX–p53 complex, the AD also establishes interaction with the p53 core domain, stabilizing the complex and blocking p53 binding to DNA. (B) Partial sequence of the MDMX AD showing the conserved WW motif important for autoinhibition and the substitution mutations introduced into the mouse germline.
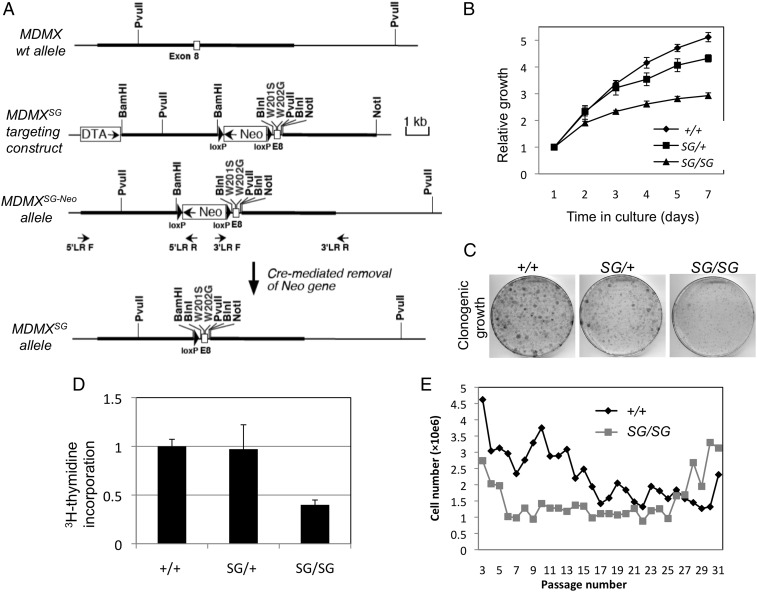
Fig. 2.
Generation of MDMXSG mutant mice and embryo fibroblasts. (A) Diagram of the knockin targeting construct for introducing the W201S/W202G substitutions into mouse MDMX. (B) Growth curve of primary MEFs. MEFs of the indicated genotypes (from littermates) were cultured under identical conditions, and cell numbers were determined at the indicated intervals. Three cell lines were tested for each genotype. (C) MEFs were plated at low density (500 cells per 10-cm plate) and cultured for 14 d. Colonies were stained with crystal violet. The result is representative of three cell lines for each genotype. (D) The rates of cell proliferation in the indicated MEFs (n = 3) were determined by pulse labeling with [3H]thymidine and measuring the incorporation into DNA. (E) Primary MEFs from wild-type and MDMXSG/SG littermate embryos were cultured following the 3T3 protocol. The cell density at each passage is plotted. The result is representative of three cell lines for each genotype. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
Spontaneous Senescence of MDMXSG/SG Fibroblasts.
Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) were generated from 13.5-d-old MDMXSG/SG and MDMXSG/+ embryos for both strains of MDMXSG mice. Three MDMXSG/SG embryos from each strain were used to generate independent MEF cell lines. Early-passage MDMXSG/SG MEFs proliferated at a slower rate in culture compared with MDMXSG/+ and WT (MDMX+/+) MEFs (representative data are shown in Fig. 2B). When plated at low density, the colony formation efficiency of MDMXSG/SG MEFs was significantly reduced compared with WT and MDMXSG/+ cells (Fig. 2C). The MDMXSG/SG MEFs showed no obvious signs of apoptosis but had reduced rates of DNA synthesis (Fig. 2D), consistent with a cell proliferation defect. MDMXSG/+ cells displayed small or no defects in cell growth, colony formation, and DNA synthesis (Fig. 2 B–D). When cultured following the 3T3 protocol, WT MEFs gradually entered crisis (p53-mediated senescence arrest) after ∼20 passages, whereas MDMXSG/SG MEFs stopped proliferating after only 5 or 6 passages. Both MEF genotypes produced immortalized lines after 25 passages (Fig. 2E).
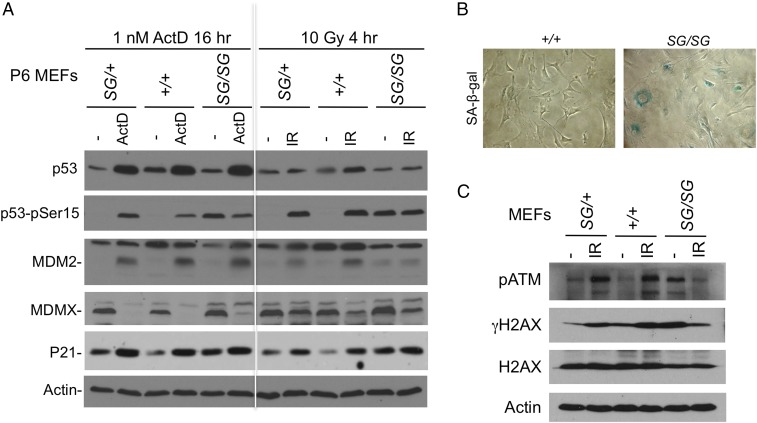
Analysis of p53 pathway markers showed normal basal p53 levels in MDMXSG/SG, MDMXSG/+, and MDMX+/+ MEFs and a similar response to ribosomal stress following treatment with 1 nM actinomycin D. However, both passage 2 (P2) and P6 MDMXSG/SG cells had reproducibly higher basal levels of p21Cip1 protein and mRNA than MDMX+/+ MEFs (Fig. 3A and Fig. S2). Further, after six passages, MDMXSG/SG MEFs showed significant basal phosphorylation of p53 on S15 and displayed impaired p53 accumulation after irradiation (IR) (Fig. 3A). Further analysis showed that the MDMXSG/SG cells had increased SA-β-gal staining (Fig. 3B) and γH2AX (Fig. 3C) compared with MDMX+/+ MEFs of the same passage. Thus, MDMXSG/SG MEFs showed a faster onset of senescence (32). These results were representative of multiple MEF cell lines from both MDMXSG mouse strains. Therefore, the further experiments below were performed using one MDMXSG mouse strain.
Fig. 3.
MDMXSG/SG MEFs undergo spontaneous growth arrest and express hallmarks of chronic DNA damage. (A) Low-passage MEFs (P6) of the indicated genotypes were treated with 1 nM actinomycin D for 18 h or 10 Gy gamma irradiation for 4 h, and analyzed for expression of p53 pathway markers. The result is representative of three cell lines for each genotype. (B) MDMXSG/SG and WT control MEFs cultured for 10 passages were stained for SA-β-gal activity as a marker for senescence. The result is representative of three cell lines for each genotype. (C) MEFs cultured for 10 passages were analyzed for markers of the DNA damage response.
Increased p53 Activity in MDMXSG/SG Mice.
MDMXSG/SG mice showed no obvious phenotypes when observed for up to 1 y, except for a noticeable reduction in fertility in the homozygous mice. MDMXSG/SG mice had normal numbers of peripheral red and white blood cells compared with wild-type littermates in blood count analysis. The survival of MDMXSG/SG mice after irradiation did not differ from wild-type controls (Fig. S3A). However, MDMXSG/SG mice showed more hair graying and loss of pigmentation in the digits following treatment with IR (Fig. S3 C and D), suggesting the function or proliferation of some MDMXSG/SG cell types was reduced after IR. TUNEL staining revealed modest increases in apoptosis in the thymus after irradiation (Fig. 4 A and B). The MDMXSG/SG mice also showed increased tolerance to oxidative stress when challenged with the mitochondrial poison paraquat (Fig. S3B). Further attempts to determine MDMXSG effects on the expression of p53 target genes implicated in antioxidant response (Sesn1, Tp53inp1, Apex1, Sod2, Gpx1, and Aldh1a1) were uninformative due to large variations between animals.
Fig. 4.
Increased p53 activity in MDMXSG/SG mouse tissues. (A) The thymus of mice 4 h after irradiation was analyzed for apoptosis using TUNEL staining. (B) Quantitation of apoptotic cells in the thymus 4 h after 6 Gy irradiation (n = 3; P < 0.01). Error bars indicate standard deviation. (C) The tissues of mice 4 h after 6 Gy irradiation were analyzed for p53 pathway markers by Western blot. The result is representative of >3 mice for each genotype.
Analysis of p53 activity in the spleen and thymus of MDMXSG/SG mice revealed similar levels of p53 protein accumulation after IR (Fig. 4C). However, there were several hallmarks of increased p53 activity in these MDMXSG/SG tissues, including increased (i) basal levels of PUMA protein in the thymus; (ii) PARP cleavage and TUNEL+ cells in the thymus after IR; and (iii) p21Cip1 levels in the spleen after IR (Fig. 4 B and C).
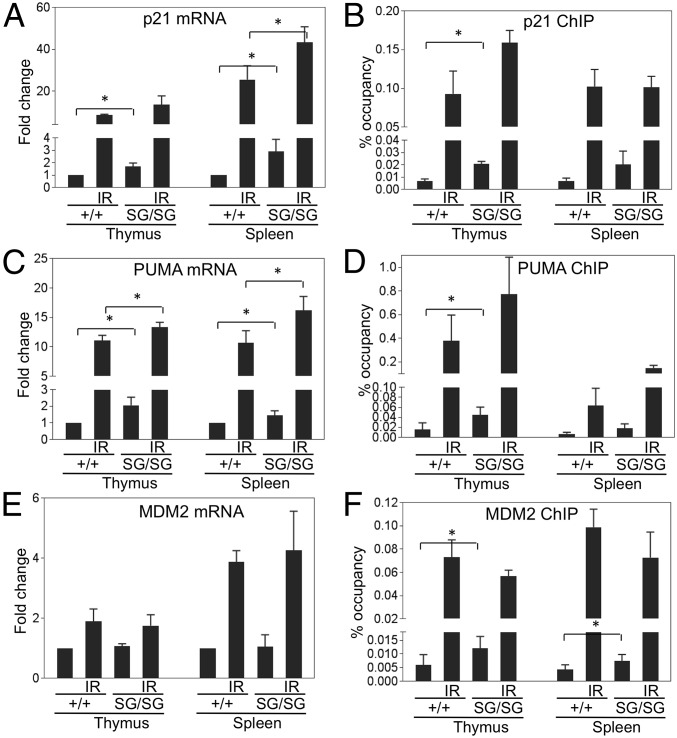
Analysis of p21Cip1 mRNA levels showed two- to threefold higher basal expression in the MDMXSG/SG spleen and thymus (Fig. 5A). Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) revealed increased p53 binding to the p21Cip1 promoter in freshly isolated MDMXSG splenocytes and thymocytes (Fig. 5B). Increased basal levels of PUMA mRNA and p53 bound to the PUMA promoter were also manifest in MDMXSG thymocytes (Fig. 5 C and D). There was also a reproducible increase of basal p53 binding to the MDM2 promoter in the thymus and spleen (Fig. 5F), although no significant changes in basal levels of MDM2 mRNA were detected (Fig. 5E), presumably due to p53-independent activation by other factors. Finally, although there were trends, MDMXSG/SG thymocytes and splenocytes did not show consistently higher p53 target gene mRNA levels and DNA binding after irradiation (Fig. 5), but this could be due to increased apoptosis in these tissues after irradiation that interfered with the analyses. Thus, MDMXSG/SG mouse tissues have increased basal p53 DNA binding and transcriptional activity.
Fig. 5.
Increased basal p53 DNA binding and transcriptional output in MDMXSG/SG mice. The thymocytes and splenocytes of mice 4 h after treatment with 6 Gy IR (n = 3) or untreated controls (n = 3) were analyzed for p53 target gene mRNA expression (A, C, and E) by RT-PCR and p53 binding (B, D, and F) to the corresponding promoters by ChIP. *P < 0.05. Sample pairs without a P value indicates no statistical difference.
MDMXSG Is Defective in Inhibiting DNA Binding of p53.
Previous in vitro studies suggested that human MDMXSG has two functional changes: (i) increased N-terminal affinity for p53 due to loss of intramolecular autoinhibition; and (ii) reduced binding to CK1α (27). Analysis of MDMXSG/SG thymocytes using immunoprecipitation showed that MDMXSG coprecipitated with a similar amount of p53 as WT MDMX (Fig. 6A). However, less CK1α coprecipitated with MDMXSG in splenocytes and thymocytes (Fig. 6B). Accordingly, there were reductions in S289 phosphorylation (S289 is a target site for CK1α) in MDMXSG/SG versus WT thymocytes (Fig. 6C). CK1α enhances MDMX–p53 binding in part by stimulating a second-site interaction between the acidic domain and core domain (26). The ability of MDMXSG to retain normal p53 binding may be due to increased N-terminal affinity for p53 that compensates for the weaker acidic domain–core domain binding.
Fig. 6.
Biochemical defects of MDMXSG. (A) MDMX–p53 binding in the thymus was determined by IP-Western blot before and after irradiation. The result is representative of three animals for each genotype. WCE, whole cell extract. (B) MDMX–CK1α binding in mouse tissues was determined by IP-Western blot. (C) Mouse tissues were analyzed for MDMX S289 phosphorylation by IP-Western blot using a phospho-specific pS289-MDMX antibody. (D) FLAG-tagged MDMX was coexpressed with p53 and CK1α in H1299 cells. The MDMX–p53 complex was purified using FLAG antibody beads. The DNA binding activity of the complex was determined by pull down using a biotinylated oligonucleotide with a p53 binding site. FLAG-p53 and FLAG-MDM2 were used as positive controls. (E) Detection of MDMX domain interaction with p53 using a fragment release assay. Beads loaded with GST-p53 were used to capture protease-cleavable MDMXc3 expressed in H1299 cells. The complex was cleaved with PreScission, and the partition of MDMX fragments on the beads and in the supernatant was determined by Western blot. SQ, region with ATM phosphorylation sites. (F) Result of the fragment release assay using MDMX, the MDMX–CK1α complex, and SG mutant. The ratios of each MDMX fragment on the beads and in the supernatant indicate the binding affinity to p53 after cleavage of MDMXc3. Specificity control: The MDMX AD fragment does not bind to GST-p53-1–82 without the core domain.
To test whether MDMXSG is deficient in inhibiting p53 DNA binding, we coexpressed FLAG-tagged MDMXSG or MDMX with p53 and CK1α and tested if the purified MDMX–p53 complex could bind to biotinylated DNA containing a canonical p53 binding site. As previously reported, MDM2 alone efficiently inhibited p53 DNA binding, whereas MDMX required the coexpression of CK1α to inhibit p53. Notably, the cooperation of CK1α with MDMXSG was less efficient than WT MDMX, correlated with the failure of CK1α to bind to MDMXSG (Fig. 6D).
CK1α cooperates with MDMX to inhibit p53 DNA binding by promoting a secondary interaction between the MDMX acidic domain and p53 core domain (26). To test if the SG mutation disrupts this binding, a protease-cleavable MDMXc3 construct was used to analyze binding of the acidic domain to immobilized GST-p53 in a fragment release assay (Fig. 6E). In this assay, MDMXc3 bound to GST-p53 beads was cleaved into fragments; the ratio of the MDMX fragment dissociating into the supernatant or remaining bound to the beads provided a measure of its p53 binding. CK1α coexpression significantly stimulated binding of the central domain of WT MDMX to p53 (compare the ratio of lane 1/lane 2 vs. lane 3/lane 4, Fig. 6F). In contrast, the MDMXSG central fragment binding to p53 was only weakly stimulated by CK1α (compare the ratio of lane 5/lane 6 vs. lane 7/lane 8, Fig. 6F). Specificity of the MDMX acidic domain–p53 core domain interaction was confirmed using immobilized GST-p53-1–82 to capture MDMXc3 (lanes 9 to 12, Fig. 6F). Thus, the MDMXSG central region does not cooperate with CK1α in binding to the p53 core domain, which may account for its defect in inhibiting p53 DNA binding.
MDMXSG Shortens Survival of Mice with Myc-Driven Lymphoma.
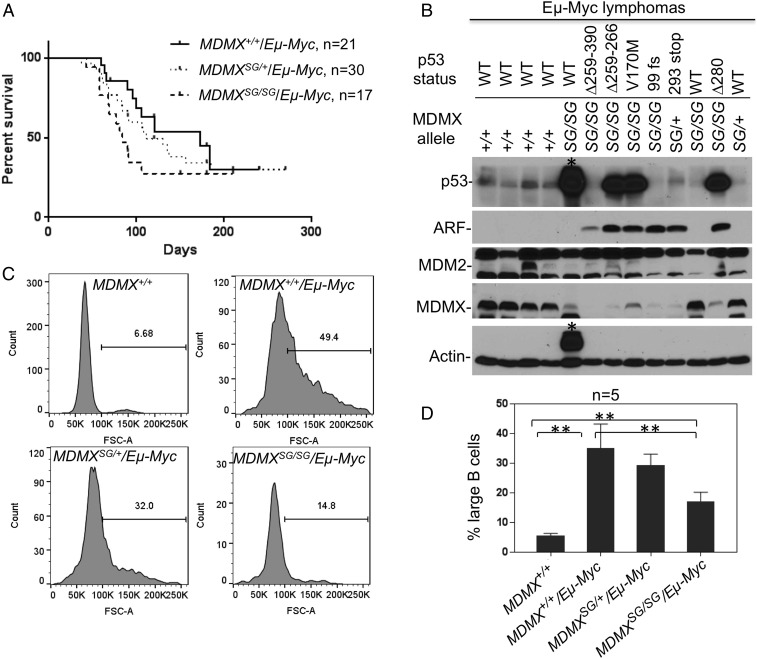
Increasing p53 activity extends the survival of tumor-prone mice in several models. To test the impact of MDMXSG on tumor development, MDMXSG/SG mice were crossed with Eµ-Myc transgenic mice, which develop lethal B-cell lymphoma at 4 to 6 mo (31), where tumor development is held in check via activation of the ARF-p53 pathway (33, 34). Unexpectedly, the Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/SG double-mutant mice had shorter survival than Eµ-Myc littermates, and succumbed to pre–B-cell lymphomas that are typical in these mice (P = 0.02; Fig. 7A). Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/+ littermates also had shorter survival than Eµ-Myc mice, but this did not reach statistical significance (P = 0.09; Fig. 7A).
Fig. 7.
MDMXSG inhibits Eµ-Myc lymphoma onset but shortens survival. (A) MDMXSG/SG mice were crossed with the Eµ-Myc transgenic mice to generate the three cohorts Eµ-Myc;MDMX+/+ (median survival 184 days), Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/+ (median survival 121 days), and Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/SG (median survival 84 days). Littermates were followed for lymphoma development. (B) Lymphoma tissues (enlarged spleens) of the indicated genotypes were analyzed for expression of p53 pathway markers. The status of p53 in each tumor sample was determined by RT-PCR amplification of p53 mRNA and sequencing of the entire p53 ORF. A tumor with a heavy background band that obscured the p53 blot is marked with an asterisk. (C) The peripheral blood B lymphocytes (CD19+) of 30-d-old littermates were analyzed by forward scatter. The fraction of large cells was determined. A histogram of one mouse for each genotype is shown. (D) Average fraction of large peripheral B lymphocytes in groups of five mice for each genotype (**P < 0.01). Error bars indicate standard deviation.
Inactivation of the ARF-p53 pathway is a hallmark during Eµ-Myc lymphoma development, and occurs through several means, including p53 mutation, biallelic deletion of ARF, and MDM2 overexpression (34). Analysis of lymphomas from Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/SG mice revealed that 8/10 (80%) contained mutation in the p53 ORF, including point mutations, internal deletions, insertions, and truncations (Fig. 7B and Fig. S4). These changes correlated with high levels of p53 or loss of p53 protein. p53 mutation was tightly correlated with high levels of ARF expression, which is induced by p53 loss of function (Fig. 7B and Fig. S4) (34). In contrast, p53 mutation was observed in 0/11 (0%) Eµ-Myc;MDMX+/+ tumors and 3/14 (21%) Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/+ tumors. Interestingly, all lymphomas having high levels of ARF had reduced levels of MDMX (Fig. 7B and Fig. S4). RT-PCR analysis suggested that high ARF protein coincided with high ARF mRNA, whereas loss of MDMX protein did not correlate with reduced MDMX mRNA levels, suggesting MDMX was degraded more rapidly in these tumors. These findings are consistent with our findings that ARF promotes MDMX ubiquitination and degradation via MDM2 (35). Thus, MDMXSG significantly increased the selection pressure for p53 mutations consistent with increased p53 activity, but unexpectedly failed to inhibit Myc-driven tumor progression.
MDMXSG Inhibits the Early Phase of Eµ-Myc Lymphoma Development.
The frequent p53 mutation in Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/SG tumors suggests that high p53 activity was a rate-limiting factor at certain stages of development. There are three distinct phases of disease in Eµ-Myc transgenics, where weanling-age mice have increased circulating large (proliferating) B cells that then disappear at older ages, only to reemerge later as aggressive lethal lymphomas (36). To assess early disease from peripheral blood, B cells of 30-d-old mice in the three cohorts were analyzed by flow cytometry for forward scatter. As expected (36), both Myc;MDMX+/+ and Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/+ mice had significant increases in proliferating B cells compared with wild-type littermates (∼30 vs. 5%; Fig. 7 C and D). In contrast, Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/SG mice had fewer proliferating B cells than Myc;MDMX+/+ and Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/+ littermates (∼15 vs. 30%; Fig. 7 C and D). Expression of p21 and PUMA was significantly higher in the peripheral lymphocytes of 30-d-old Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/SG mice compared with Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/+ (Fig. S5). Thus, despite failing to improve overall survival, MDMXSG appeared to partially attenuate early lymphoma development, which is consistent with increased basal p53 activity and strong selection for p53 mutation.
SG Mutation Abrogates the Growth Inhibition Activity of MDMX.
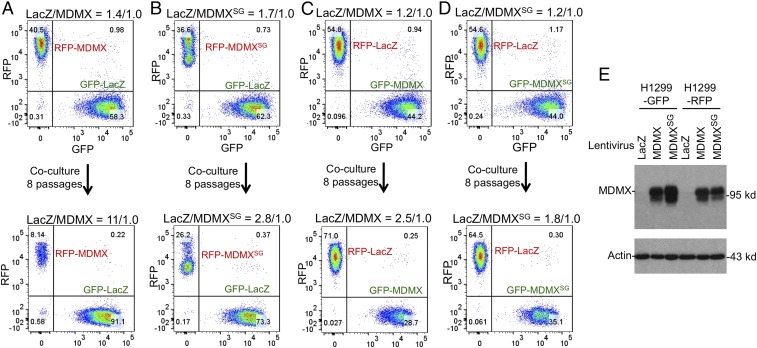
The short lifespan of Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/SG mice despite having higher p53 activity and attenuated early disease suggests that the SG mutation may disrupt p53-independent functions of MDMX that suppress tumor progression. Previous work showed that MDMX limits the proliferation of p53-null MEFs and delays spontaneous tumor development in p53-null mice (37). To test if the SG mutation affects the ability of MDMX to inhibit proliferation independent of p53, MDMX and MDMXSG were ectopically expressed in p53-null H1299 cells labeled with RFP or GFP (Fig. 8E). The MDMX-expressing cells were cocultured with control cells expressing LacZ in a competition assay. WT MDMX expression impaired cell proliferation (Fig. 8A), whereas MDMXSG had much a weaker effect on proliferation (Fig. 8B). Switching the fluorescent marker altered the magnitude of the growth inhibition phenotype but led to the same conclusion (Fig. 8 C and D). Conversely, knockdown of MDMX in DLD1 cells that express mutant p53S241F using two doxycycline-inducible shRNAs accelerated their proliferation (Fig. S6). Thus, MDMX has p53-independent growth-inhibitory activity that also requires the WW motif, and loss of this function may contribute to the accelerated tumorigenesis in Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/SG mice.
Fig. 8.
p53-independent growth inhibition by MDMX is inactivated by the SG mutation. (A) H1299 cells (p53-null) infected with lentivirus expressing GFP or RFP were used for secondary infection with lentivirus expressing LacZ or MDMX. The RFP-labeled MDMX-expressing cells and GFP-labeled LacZ control were mixed and cocultured for eight passages. The RFP/GFP ratio was determined before and after coculture by FACS. (B) Same as A except MDMXSG was expressed. (C and D) Same as A and B, except RFP/GFP labels were switched. (E) Western blot confirming similar expression levels of MDMX and MDMXSG in the fluorescence-labeled cells.
Discussion
MDMX has a well-established role as a negative regulator of p53 during embryonic development. However, the mechanism by which MDMX harnesses p53 in vivo is still unclear. The MDMX knockout models suggested that MDMX inhibits p53 transcriptional function by binding and blocking its transactivation domain. However, other studies have suggested that MDMX also regulates p53 degradation via forming heterodimers with MDM2, which was proposed to increase p53 ubiquitination (38–40). The results presented here suggest that MDMX regulates p53 by inhibiting its DNA binding function.
Of the known domains of MDMX, the roles of the N-terminal p53-binding domain and the C-terminal RING domain have been investigated in mice. One of the initial MDMX knockout models expressed a truncated MDMX lacking its N terminus, suggesting that loss of the p53-binding domain caused embryonic lethality (7). Further, the MDMX RING domain is also needed for mouse embryogenesis, possibly through heterodimerization with MDM2 RING (40, 41). Here we interrogated the roles of the recently identified WW motif in the central acidic domain of MDMX, which appears partially disordered. Notably, intrinsically unstructured regions often have important regulatory functions in directing interactions with protein partners (42).
In vitro studies have shown the MDMX acidic domain interacts with CK1α, the p53 core DNA-binding domain, and the N- and C-terminal domains of MDMX itself (26, 27). The conserved WW motif in the acidic domain is important for these interactions. The results here establish the physiological relevance of these interactions, where the WW motif is shown to interact with CK1α and inhibit p53 DNA binding. Specifically, mutation of the WW element augments p53 DNA binding and transcriptional activity in vivo without increasing p53 level. The N terminus of MDMX has been proposed to inhibit p53 by blocking the functions of the p53 transactivation domain. The in vivo analysis here showed that at physiological levels the N-terminal function of MDMX alone is not sufficient, as MDMXSG had nominal binding to p53 but failed to effectively inhibit p53 transcriptional functions. The results suggest that in addition to its limited role in p53 degradation, an important MDMX function is to regulate p53 DNA binding. This function may allow MDMX to play a complementary role to MDM2-mediated p53 degradation, regulating p53 activity under conditions where MDM2-mediated degradation is insufficient to fully control p53.
An unexpected finding of our study is that homozygous mutation of the WW motif accelerated the development of lymphoma in Eµ-Myc mice despite increasing p53 activity and suppressing early disease. This contrasts with previous studies where increasing p53 activity extends the survival of tumor-prone mice (through breeding into MDM2+/−, MDMX+/−, or MDM2 hypomorphic allele backgrounds) (17, 43, 44). Accordingly, reducing p53 activity generally accelerates tumor development (under conditions of p53+/−, MDMX phosphorylation-site mutation, or MDM2 or MDMX overexpression) (18, 45, 46). Further, increasing p53 activity in tumor models also increases the frequency of p53 mutation (MDM2+/−), whereas reducing p53 activity reduces the frequency of p53 mutation (MDM2 and MDMX transgenic overexpression) (43, 45, 46). These observations fit the established role of p53 as a classic tumor suppressor, that high p53 activity attenuates tumor progression and increases selection pressure for p53 mutation. The MDMXSG/SG mice partially conformed to this paradigm, in which higher basal p53 activity suppressed early-stage disease and increased p53 mutation frequency in end-stage tumors. However, the MDMXSG/SG mice succumbed to lethal lymphoma faster than those with WT MDMX. There are two potential mechanisms for this observation: (i) The presence of mutant p53 in up to 80% of Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/SG lymphomas may accelerate progression through gain of function (47); or (ii) the SG mutation may have disrupted a p53-independent tumor-suppressive activity of MDMX.
We consider mechanism (i) unlikely, since a previous study showed that p53 activation in the same Eµ-Myc lymphoma model through reducing MDM2 dosage (MDM2+/−) significantly extends survival despite also increasing p53 mutation frequency (43). The overall evidence favors mechanism (ii), namely that the SG mutation disrupted a p53-independent function of MDMX. Corroborating the in vivo results, our in vitro analysis of MDMX overexpression/depletion in tumor cell lines also suggests the WW element has growth-inhibitory functions independent of p53. These findings are in accord with previous studies showing that MDMX (i) interacts with the MRE11–Rad50–Nbs1 DNA repair complex (48); (ii) maintains genomic stability and reduces the proliferation rate of p53-null MEFs; and (iii) loss accelerates tumor development in p53–double-null mice (37). The biochemical basis of this function is currently unknown. A defect of MDMXSG is the loss of CK1α binding. CK1α is involved in the regulation of multiple pathways, including β-catenin/Wnt signaling and proliferation. Further work is needed to determine whether MDMX binding regulates CK1α function and its downstream targets.
In summary, our results identified an important structural element of MDMX in both regulating p53 and mediating p53-independent functions. The results underscore the complexity of MDMX structure and function. The early onset of lethal lymphomas in Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/SG mice showed that loss of the p53-independent activity accelerates tumor progression and completely cancels the survival benefit of p53 activation. In this context, the p53-independent function of the WW motif has significant tumor-suppressive effects. The results underscore the need to investigate MDMX functions in human tumors without wild-type p53, and suggest that MDMX targeting strategies for cancer treatment should preferably achieve p53 activation without disrupting its p53-independent antitumor activity.
Materials and Methods
Generation of MDMXSG Knockin Mice.
A 0.5-kb fragment containing mouse MDMX exon 8 was generated having the coding sequence 5′-TGGTGG-3′ (W201/W202) changed to 5′-AGCGGC-3′ (S201/G202). The fragment was cloned into the pKII loxp vector. A 4.1-kb 5′ arm and 4.0-kb 3′ arm were amplified from a mouse BAC genomic clone using the following primers: MDM4-5AF 5′-GGGAGGATCCTGTCTCTGCTAGTGGCTGGTGAACTCA-3′ and MDM4-5AR 5′-GGGAGGATCCGCAAGCAAGAACACTATGAACAGA AGATCACTTC-3′; and MDM4-3AF 5′-GGGAGCGGCCGCACATTGAACCCTCTGCAAAGGCTGTGT-3′ and MDM4-3AR 5′-GGGAGCGGCCGCAGTCCTGTTGAGCCTGGAATTCACTATGT-3′. The 5′ and 3′ arms were attached to the exon 8 fragment preceded by a floxed Neo marker. The targeting vector was sequenced to confirm the joint ends, linearized, and electroporated into 129S6/C57BL/6 ES cells. Targeted ES cells were identified by PCR using the following primers: Neo5Mer2 5′-CATGCTCCAGACTGCCTTG-3′ and MDM4-3LRR1 5′-TCATCCGTAGTGTCTGAAACAATGGCAGTACCT-3′ (5-kb product); and MDM4-5LRF 5′-GTTCTTGATGGTCTGACTGTTGGATGCTGT-3′ and pkII5LRNeoR 5′-CGCCTTCTATCGCCTTCTTGACGAGTTCTTCTGA-3′ (4.5-kb product). The presence of the SG mutant allele was detected using the following primers: Mdm4mtF1 5′-TGGGAGGTTTGAGCCATACCATTAAGGT-3′ and Mdm4mtR1 5′-CAGTTGTTTCTCAAATTCCCTAGAAAGCCGCT-3′ (the underlined sequence anneals to the SG coding sequence, producing a 273-bp product). The floxed Neo selection marker was removed by breeding with CMV-Cre transgenic mice (C57BL/6, 006054; The Jackson Laboratory). For detecting the removal of the Neo cassette, the following primers were used: 5ArmF1 5′-TCTGCCTCCCGAGTACTTGGAT-3′ and Exon8R1 5′-AGCTCCTATTCTCAGTAAGGAGGA-3′ that flank the LoxP-Neo-LoxP cassette. The wild-type allele generated a 163-bp product, and the SG allele (after removing the Neo cassette) generated a 193-bp product containing a 30-bp LoxP sequence. After removing the Neo marker, the SG mice were further backcrossed for five generations with C57BL/6 mice. Expression of mutant MDMXSG mRNA was verified by RT-PCR and DNA sequencing using the following primers: 5′-TGCAGAGACTCCAGAGCAGA-3′ and 5′-TCATCATCCTTTCCCACCTC-3′. Two independent lines of MDMXSG mice were generated; one line was used for generating MEFs only, and the second line was subjected to full analysis.
Mouse Experiments.
Animals in the spontaneous tumor cohorts or IR-treated cohorts were euthanized if tumor burden was apparent or when the mice appeared moribund. Animals were maintained and used in accordance with federal guidelines and those established by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the University of South Florida. For Eμ-Myc studies, MDMXSG females were bred with Eµ-Myc transgenic males (in the C57BL/6 background) to obtain Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/+ offspring, which were then crossed with MDMXSG/+ mice to obtain Eµ-Myc;MDMXSG/SG mice. For the survival study, mice were palpated regularly for early signs of lymph-node enlargement and monitored for tumor progression and signs of morbidity. Moribund mice were humanely euthanized. Mouse tumors and organs were fixed in formalin for histopathology and snap-frozen for protein and RNA extraction. Irradiated tissue sections were analyzed with TUNEL staining using the In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit (ab206386; Abcam).
Plasmids and Cell Lines.
The MDMXc3 sequences containing LEVLFQGPDYKDDDDK (PreScission site + FLAG epitope), LEVLFQGPEEQKLISEEDL (PreScission site + Myc epitope), and LEVLFQGPYPYDVPDYA (PreScission site + HA epitope) were inserted after human MDMX residues 140, 350, and 429, respectively. Lung cancer cell line H1299 (p53-null) and MEFs were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium with 10% FBS. GST-PreScission protease fusion was purified from Escherichia coli using a glutathione agarose column. The LV-GFP and LV-RFP plasmids were gifts from Elaine Fuchs, Rockefeller University, New York (plasmids 25999 and 26001; Addgene). SMARTvector lentiviruses expressing doxycycline-inducible GFP/MDMX shRNA and RFP/control shRNA were purchased from Dharmacon.
Western Blot.
Cells were lysed in lysis buffer (50 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 8.0, 5 mM EDTA, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5% Nonidet P-40, 1× protease inhibitor mixture) and centrifuged for 10 min at 14,000 × g, and the insoluble debris was discarded. Cell lysate (10 to 50 µg of protein) was fractionated by SDS/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred to Immobilon-P filters (Millipore). The filters were blocked for 1 h with PBS containing 5% nonfat dry milk and 0.1% Tween 20 and incubated with primary and secondary antibodies, and the filters were developed using SuperSignal reagent (Thermo Scientific). MDM2 was detected using monoclonal antibody 4B2 or 2A10. Human MDMX was detected with monoclonal antibody 8C6, and mouse MDMX was detected using monoclonal antibody 7A8 (23). Mouse MDMX S289 phosphorylation was detected by immunoprecipitation using MDMX monoclonal antibody 10C2 generated in our laboratory, followed by Western blot using an antibody against phosphorylated human MDMX peptide spanning S289 (27, 28). S289 and the surrounding sequence share significant homology between human and mouse MDMX (human: EDSKSLSDD; mouse: EDSRSLSDD; S289 is underlined). Actin and CK1α antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. FLAG tag and β-actin antibody were from Sigma-Aldrich. Mouse p53 was detected using Pab421. DO-1 for human p53 and p21 antibody were from BD Pharmingen. Anti-p19ARF antibody was from Abcam. Anti-pATM, anti–p53-pSer15, and anti-cleaved PARP antibodies were from Cell Signaling. γH2AX and H2AX antibodies were from Millipore.
Proteolytic Fragment Release Assay.
H1299 cells were transiently transfected with MDMXc3 and CK1α plasmids using a standard calcium phosphate precipitation protocol. Cells were lysed using IP buffer (150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 8.0, 0.5% Nonidet P-40, 0.5 mM DTT, 10% glycerol). Cell lysate (1 mL) from ∼2 × 106 cells (a 10-cm plate) was incubated with 20 µL packed glutathione agarose beads loaded with ∼5 µg GST-p53 for 2 h at 4 °C. The beads were washed twice with PreScission buffer (150 mM NaCl, 10 mM Hepes, pH 7.5, 0.05% Nonidet P-40, 0.5 mM DTT, 10% glycerol) and suspended in 100 µL PreScission buffer. PreScission protease was added to 0.2 µg/µL final concentration, and the beads were incubated at 23 °C with shaking for 20 to 60 min. The protease digestion mixture was centrifuged at 2,000 × g for 10 s, and the beads (bound material) and supernatant (released material) were separated. The beads were washed once with PreScission buffer to remove residual supernatant. The beads and supernatant were boiled in Laemmli sample buffer and analyzed by SDS/PAGE and Western blot using 8C6 (N-terminal fragment) and FLAG (acidic domain fragment) antibodies to determine the bound/released ratio of MDMX fragments.
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation and Quantitative PCR.
The ChIP assay was performed using standard procedures. Proteins were cross-linked to genomic DNA with 1% formaldehyde for 10 min at 23 °C. The cross-linking was stopped by 0.125 M glycine for 5 min at 23 °C. The cells were washed three times with ice-cold PBS and lysed in 0.45 mL RIPA buffer with proteinase inhibitor mixtures on ice for 10 min. The cell pellet was sonicated for eight cycles using a Bioruptor XL (Diagenode) (8 min per cycle, 30 s on and 30 s off) and then spun down at 14,000 × g for 10 min to remove debris. The lysates were precleared by incubating with a salmon sperm DNA/protein A agarose slurry for 30 min at 4 °C with rotation. The cleared lysates were diluted 1:6 in ChIP dilution buffer (0.01% SDS, 1.1% Triton X-100, 1.2 mM EDTA, 16.7 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 8.0, 167 mM NaCl). The samples were incubated with 1 μg antibody for 18 h at 4 °C with rotation. A protein A agarose slurry (50 µL) was added and incubated for 2 h at 4 °C. The beads were washed once each with low-salt buffer (0.1% SDS, 1% Triton X-100, 2 mM EDTA, 20 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl), high-salt buffer (0.1% SDS, 1% Triton X-100, 2 mM EDTA, 20 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 8.0, 500 mM NaCl), LiCl buffer (250 mM LiCl, 1% Nonidet P-40, 1% sodium deoxycholate, 1 mM EDTA, 10 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 8.0), and TE buffer (10 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 8.0, 1 mM EDTA). The beads were eluted twice with a total of 200 μL of elution buffer (1% SDS, 100 mM NaHCO3) at 25 °C for 15 min with shaking (1,000 rpm). NaCl was added to 200 mM and the samples were de-cross-linked at 65 °C for 18 h. Proteinase K (0.1 mg/mL), EDTA (10 mM), and Tris⋅HCl (pH 6.8; 40 mM) were added and incubated at 42 °C for 1 h. DNA was extracted using the GenElute PCR Clean-Up Kit (Sigma). The samples were subjected to SYBR Green real-time PCR analysis using the following primers: MDM2 promoter (5′-TCGGAGGAGCTAAGTCCTGA-3′ and 5′-CGGCAATAGCTCTCAAATGC-3′); p21Cip1 promoter (5′-TAGCTTTCTGGCCTTCAGGA-3′ and 5′-GGGGTCTCTGTCTCCATTCA-3′); and Puma promoter (5′-CACCCTAGGTCTGGGCTGT-3′ and 5′-AAGTCGGGGCTTGCAGTC-3′).
RNA Isolation and Quantitative PCR.
Total RNA was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen). cDNAs were prepared by reverse transcription of total RNA using the SuperScript III First-Strand Synthesis System (Invitrogen). The products were used for real-time PCR using the following primers: MDM2 (5′-CTCTGGACTCGGAAGATTACAGCC-3′ and 5′-CCTGTCTGATAGACTGTGACCCG-3′), p21Cip1 (5′-AATCCTGGTGATGTCCGACCTGTT-3′ and 5′-CGTCTCCGTGACGAAGTCAAAGTT-3′), Puma (5′-GCCCAGCAGCACTTAGAGTC-3′ and 5′-ACTCCTCCTCCTCCACACG-3′), and GAPDH (5′-TCACCACCATGGAGAAGGC-3′ and 5′-GCTAAGCAGTTGGTGGTGCA-3′).
Flow Cytometry.
Peripheral blood was collected from 30-d-old mice. Red blood cells were lysed with ACK buffer (0.15 M NH4Cl, 1 mM NaHCO3, 0.1 mM EDTA, pH 7.4). Cells (1 × 106) were stained with CD19-BUV737 (BD Pharmingen) for 20 min on ice and washed with PBS containing 0.5% BSA. Flow cytometry was performed to determine the forward scatter of CD19-positive cells. The data were analyzed using FlowJo software (TreeStar).
For growth competition analysis, H1299 cells were infected with LV-GFP or LV-RFP lentivirus. The H1299-GFP and H1299-RFP cells were then infected with lentivirus expressing MDMX or LacZ and selected with Zeocin. The pooled MDMX colonies (RFP- or GFP-labeled) and LacZ colonies (GFP- or RFP-labeled) were mixed at a ∼1:1 ratio, cultured for eight passages (1:20 split per passage), and subjected to FACS analysis using an LSR II flow cytometer (BD Biosciences). The data were analyzed using FlowJo software.
For growth competition analysis of MDMX knockdown, DLD1 cells were infected with SMARTvector lentiviruses (Dharmacon) expressing GFP/MDMX shRNA and RFP/control shRNA. After selection with puromycin, the RFP- and GFP-labeled cells were mixed and cultured for eight passages in the presence or absence of 0.1 µg/mL doxycycline and subjected to FACS analysis. To induce RFP and GFP expression, a cell mixture cultured for eight passages without doxycycline was also treated with 0.1 µg/mL doxycycline for 24 h before FACS analysis.
Purification of MDM2/MDMX-Associated p53 and DNA Affinity Immunoblotting.
H1299 cells were transiently transfected with FLAG-tagged MDM2, MDMX, and p53. Cells from a 10-cm plate were lysed in 1 mL of lysis buffer (50 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 8.0, 5 mM EDTA, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5% Nonidet P-40, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride) and centrifuged for 10 min at 14,000 × g, and the insoluble debris was discarded. The lysate was incubated with 40 μL M2-agarose bead slurry (Sigma) for 18 h at 4 °C. The beads were washed with lysis buffer, and the FLAG-tagged proteins with their binding partners were eluted with 150 μL of lysis buffer containing 50 μg/mL FLAG epitope peptide for 2 h at 4 °C. An aliquot of the eluted proteins was analyzed for expression levels by Western blot. Lysate containing equal levels of p53 was added to a 200-μL DNA-binding reaction mixture and incubated at 4 °C for 30 min. The DNA-binding reaction mixture contained 25 nM (0.01 nmol) double-stranded biotinylated oligonucleotide DNA representing the p53 binding site at the p21Cip1 promoter (biotin-5′-TCGAGAGGCATGTCTAGGCATGTCTC-3′ annealed with 5′-GAGACATGCCTAGACATGCCTCTCGA-3′), 2 µg poly(dI·dC), 5 mM DTT, 150 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris⋅HCl (pH 7.2), 1 mM EDTA, 0.1% Triton X-100, and 4% glycerol. Mutant control oligonucleotide contained biotin-5′-TCGAGAGGTCGCTCTAGGTCGCTCTC-3′ annealed with 5′-GAGAGCGACCTAGAGCGACCTCTCGA-3′. The DNA–protein complexes were captured with 0.1 mg of magnetic streptavidin beads (Promega) at 4 °C for 30 min. The beads were collected using a magnet and washed three times with DNA binding buffer. The bound proteins were eluted by boiling in sample buffer (4% SDS, 20% glycerol, 200 mM DTT, 120 mM Tris, pH 6.8, 0.002% bromophenol blue). The protein complexes were resolved by SDS/PAGE, and p53 was detected by Western blot using DO-1 antibody.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank the Moffitt Tissue Core and Flow Cytometry Core for assistance with the experiments. This work is supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (CA141244, CA186917, CA076379) and Florida Department of Health (4BB14) and NCI Cancer Center Support Grant P30-CA076292.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1719090115/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Wade M, Li YC, Wahl GM. MDM2, MDMX and p53 in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:83–96. doi: 10.1038/nrc3430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bullock AN, et al. Thermodynamic stability of wild-type and mutant p53 core domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:14338–14342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.26.14338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vousden KH, Lane DP. p53 in health and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:275–283. doi: 10.1038/nrm2147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Marine JC, Jochemsen AG. Mdmx as an essential regulator of p53 activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;331:750–760. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.03.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jones SN, Roe AE, Donehower LA, Bradley A. Rescue of embryonic lethality in Mdm2-deficient mice by absence of p53. Nature. 1995;378:206–208. doi: 10.1038/378206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Montes de Oca Luna R, Wagner DS, Lozano G. Rescue of early embryonic lethality in mdm2-deficient mice by deletion of p53. Nature. 1995;378:203–206. doi: 10.1038/378203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Parant J, et al. Rescue of embryonic lethality in Mdm4-null mice by loss of Trp53 suggests a nonoverlapping pathway with MDM2 to regulate p53. Nat Genet. 2001;29:92–95. doi: 10.1038/ng714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Grier JD, Xiong S, Elizondo-Fraire AC, Parant JM, Lozano G. Tissue-specific differences of p53 inhibition by Mdm2 and Mdm4. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:192–198. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.1.192-198.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Maetens M, et al. Distinct roles of Mdm2 and Mdm4 in red cell production. Blood. 2007;109:2630–2633. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-03-013656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xiong S, Van Pelt CS, Elizondo-Fraire AC, Liu G, Lozano G. Synergistic roles of Mdm2 and Mdm4 for p53 inhibition in central nervous system development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:3226–3231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508500103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A, Oren M. Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature. 1997;387:296–299. doi: 10.1038/387296a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kubbutat MH, Jones SN, Vousden KH. Regulation of p53 stability by Mdm2. Nature. 1997;387:299–303. doi: 10.1038/387299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen J. The roles of MDM2 and MDMX phosphorylation in stress signaling to p53. Genes Cancer. 2012;3:274–282. doi: 10.1177/1947601912454733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cross B, et al. Inhibition of p53 DNA binding function by the MDM2 protein acidic domain. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:16018–16029. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.228981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sasaki M, Nie L, Maki CG. MDM2 binding induces a conformational change in p53 that is opposed by heat-shock protein 90 and precedes p53 proteasomal degradation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:14626–14634. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610514200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Shimizu H, et al. The conformationally flexible S9-S10 linker region in the core domain of p53 contains a novel MDM2 binding site whose mutation increases ubiquitination of p53 in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:28446–28458. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M202296200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Terzian T, et al. Haploinsufficiency of Mdm2 and Mdm4 in tumorigenesis and development. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27:5479–5485. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00555-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wang YV, Leblanc M, Wade M, Jochemsen AG, Wahl GM. Increased radioresistance and accelerated B cell lymphomas in mice with Mdmx mutations that prevent modifications by DNA-damage-activated kinases. Cancer Cell. 2009;16:33–43. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.05.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kawai H, et al. DNA damage-induced MDMX degradation is mediated by MDM2. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:45946–45953. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308295200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pan Y, Chen J. MDM2 promotes ubiquitination and degradation of MDMX. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:5113–5121. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.15.5113-5121.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chen L, Gilkes DM, Pan Y, Lane WS, Chen J. ATM and Chk2-dependent phosphorylation of MDMX contribute to p53 activation after DNA damage. EMBO J. 2005;24:3411–3422. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pereg Y, et al. Phosphorylation of Hdmx mediates its Hdm2- and ATM-dependent degradation in response to DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:5056–5061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408595102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gilkes DM, Chen L, Chen J. MDMX regulation of p53 response to ribosomal stress. EMBO J. 2006;25:5614–5625. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li X, et al. Abnormal MDMX degradation in tumor cells due to ARF deficiency. Oncogene. 2012;31:3721–3732. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Francoz S, et al. Mdm4 and Mdm2 cooperate to inhibit p53 activity in proliferating and quiescent cells in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:3232–3237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508476103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wei X, et al. Secondary interaction between MDMX and p53 core domain inhibits p53 DNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:E2558–E2563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603838113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chen L, et al. Autoinhibition of MDMX by intramolecular p53 mimicry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:4624–4629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1420833112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wu S, Chen L, Becker A, Schonbrunn E, Chen J. Casein kinase 1α regulates an MDMX intramolecular interaction to stimulate p53 binding. Mol Cell Biol. 2012;32:4821–4832. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00851-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bista M, Petrovich M, Fersht AR. MDMX contains an autoinhibitory sequence element. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:17814–17819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1317398110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Borcherds W, et al. Optimal affinity enhancement by a conserved flexible linker controls p53 mimicry in MdmX. Biophys J. 2017;112:2038–2042. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.04.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Adams JM, et al. The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985;318:533–538. doi: 10.1038/318533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rodier F, et al. DNA-SCARS: Distinct nuclear structures that sustain damage-induced senescence growth arrest and inflammatory cytokine secretion. J Cell Sci. 2011;124:68–81. doi: 10.1242/jcs.071340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schmitt CA, McCurrach ME, de Stanchina E, Wallace-Brodeur RR, Lowe SW. INK4a/ARF mutations accelerate lymphomagenesis and promote chemoresistance by disabling p53. Genes Dev. 1999;13:2670–2677. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.20.2670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Eischen CM, Weber JD, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ, Cleveland JL. Disruption of the ARF-Mdm2-p53 tumor suppressor pathway in Myc-induced lymphomagenesis. Genes Dev. 1999;13:2658–2669. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.20.2658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Li X, et al. Abnormal MDMX degradation in tumor cells due to ARF deficiency. Oncogene. 2012;31:3721–3732. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sidman CL, Shaffer DJ, Jacobsen K, Vargas SR, Osmond DG. Cell populations during tumorigenesis in Eu-myc transgenic mice. Leukemia. 1993;7:887–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Matijasevic Z, Steinman HA, Hoover K, Jones SN. MdmX promotes bipolar mitosis to suppress transformation and tumorigenesis in p53-deficient cells and mice. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:1265–1273. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01108-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kawai H, Lopez-Pajares V, Kim MM, Wiederschain D, Yuan ZM. RING domain-mediated interaction is a requirement for MDM2’s E3 ligase activity. Cancer Res. 2007;67:6026–6030. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wang X, Wang J, Jiang X. MdmX protein is essential for Mdm2 protein-mediated p53 polyubiquitination. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:23725–23734. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.213868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Huang L, et al. The p53 inhibitors MDM2/MDMX complex is required for control of p53 activity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:12001–12006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102309108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pant V, Xiong S, Iwakuma T, Quintás-Cardama A, Lozano G. Heterodimerization of Mdm2 and Mdm4 is critical for regulating p53 activity during embryogenesis but dispensable for p53 and Mdm2 stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:11995–12000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102241108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Dunker AK, Silman I, Uversky VN, Sussman JL. Function and structure of inherently disordered proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008;18:756–764. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Alt JR, Greiner TC, Cleveland JL, Eischen CM. Mdm2 haplo-insufficiency profoundly inhibits Myc-induced lymphomagenesis. EMBO J. 2003;22:1442–1450. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mendrysa SM, et al. Tumor suppression and normal aging in mice with constitutively high p53 activity. Genes Dev. 2006;20:16–21. doi: 10.1101/gad.1378506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wang P, et al. Elevated Mdm2 expression induces chromosomal instability and confers a survival and growth advantage to B cells. Oncogene. 2008;27:1590–1598. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Xiong S, et al. Spontaneous tumorigenesis in mice overexpressing the p53-negative regulator Mdm4. Cancer Res. 2010;70:7148–7154. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Muller PA, Vousden KH. Mutant p53 in cancer: New functions and therapeutic opportunities. Cancer Cell. 2014;25:304–317. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.01.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Carrillo AM, Bouska A, Arrate MP, Eischen CM. Mdmx promotes genomic instability independent of p53 and Mdm2. Oncogene. 2015;34:846–856. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.