Abstract
Background
Recently, validated risk models predicting adverse obstetric outcomes combined with risk-dependent care paths have been made available for early antenatal care in the southeastern part of the Netherlands. This study will evaluate implementation progress and impact of the new approach in obstetric care.
Objective
The objective of this paper is to describe the design of a study evaluating the impact of implementing risk-dependent care. Validated first-trimester prediction models are embedded in daily clinical practice and combined with risk-dependent obstetric care paths.
Methods
A multicenter prospective cohort study consisting of women who receive risk-dependent care is being performed from April 2017 to April 2018 (Expect Study II). Obstetric risk profiles will be calculated using a Web-based tool, the Expect prediction tool. The primary outcomes are the adherence of health care professionals and compliance of women. Secondary outcomes are patient satisfaction and cost-effectiveness. Outcome measures will be established using Web-based questionnaires. The secondary outcomes of the risk-dependent care cohort (Expect II) will be compared with the outcomes of a similar prospective cohort (Expect I). Women of this similar cohort received former care-as-usual and were prospectively included between July 1, 2013 and December 31, 2015 (Expect I).
Results
Currently, women are being recruited for the Expect Study II, and a total of 300 women are enrolled.
Conclusions
This study will provide information about the implementation and impact of a new approach in obstetric care using prediction models and risk-dependent obstetric care paths.
Trial Registration
Netherlands Trial Register NTR4143; http://www.trialregister.nl/trialreg/admin/rctview.asp?TC=4143 (Archived by WebCite at http://www.webcitation.org/6t8ijtpd9)
Keywords: cohort study, pregnancy, decision support techniques, prediction model, implementation, prevention, pre-eclampsia, gestational diabetes mellitus
Introduction
Perinatal mortality plays a pivotal role in the quality assessment of perinatal care [1]. In developed countries the main causes of perinatal mortality are small-for-gestational-age infancy (SGA), preterm birth (PTB), and asphyxia [2,3]. Pre-eclampsia (PE) is an important cause for both SGA and induced PTB [4]. Risks of asphyxia and birth injuries are increased among infants that are large-for-gestational-age (LGA) [5], which in turn is strongly associated with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) [6]. Thus, PE, GDM, PTB, SGA, and LGA are all directly or indirectly related to perinatal mortality.
A number of interventions have shown to be effective in the prevention of adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as calcium suppletion and low-dose aspirin treatment in case of PE [7-9], adequate management of GDM [5,10,11], and progesterone administration in women at risk of spontanous PTB [12]. Besides calcium supplementation, most of these interventions are not suitable for all pregnant women, because of either possible adverse effects, patient burden, or costs. Early prediction of obstetric risks may therefore help health care professionals in designing intervention strategies based on women’s individual risks.
Recently, we performed an external validation study of first trimester prediction models predicting the risk of PE, GDM, PTB, SGA and LGA (the Expect Study I) [13,14]. The Expect Study I identified clinically useful prediction models for PE and GDM. The Limburg Obstetric Consortium (LOC), midwives and gynecologists of the southeastern part of the Netherlands developed care pathways, for example, basic antenatal care for women at low risk and additional risk-dependent care for women with elevated risks of PE, GDM, PTB, SGA, or LGA. The LOC agreed to implement the risk models predicting PE and GDM, in order to identify women at increased risk of these outcomes, and to offer these women risk-dependent care.
The current protocol describes the design of a multicenter prospective cohort study (Expect Study II) evaluating the implementation progress of using these prediction models combined with tailored care paths for PE and GDM.
The primary aims of the Expect Study II are to measure adherence to the new risk-dependent care guidelines by health care professionals and compliance of pregnant women who received recommendations. The secondary aims are to evaluate its impact upon patient satisfaction and cost-effectiveness. Secondary aims will be studied by comparing these outcomes of the Expect II cohort with the Expect I cohort.
Methods
Study Design and Recruitment
In April 2017, the Expect prediction tool, was introduced. The Expect prediction tool was developed to enable individual risk assessment during early pregnancy regarding the risks of PE, GDM, PTB, SGA, and LGA. Validated models selected by the LOC to predict PE and GDM have been incorporated into this tool (unpublished study submitted by Meertens et al, January 2018). Risk assessment of spontaneous PTB, SGA and LGA is achieved using the revised LOC guidelines [15]. For nulliparous women, the prediction tool comprises 14 variables concerning anthropometric data, relevant medical history, and family history. For multiparous women the tool enquires 6 more variables, all concerning the women’s obstetric history.
The Expect prediction tool is a Web-based form which calculates the estimated risk profiles. This tool was made available for health care professionals via the Expect study website for implementation in daily obstetric care. Besides the estimated risks of adverse pregnancy outcomes, the tool provides recommendations for tailored antenatal care based on personalized risks (ie, risk-dependent care). In addition, patient information brochures relevant to the patient’s risk profile will be automatically generated. The health care professionals can use this tool during one of the pregnant woman’s antenatal visits before 16 weeks of pregnancy. Using a shared decision approach, the appropriate risk-dependent care path with corresponding preventive measures and check-ups will be selected.
In order to implement risk-dependent care successfully, midwives and gynecologists are encouraged to use the Expect prediction tool by representatives of the LOC. The Expect prediction tool is introduced by email to all obstetric health care professionals in the region. Furthermore, oral presentations will be given at every hospital and at local midwifery meetings. Additionally, the hospitals and midwifery practices are contacted regularly by phone and in person to evaluate the Expect prediction tool.
The midwives and gynecologists play a central role in enrolling pregnant women into the Expect Study II, by asking women whether they are interested in receiving further information about participating in the Expect Study II. Almost every pregnant woman is eligible for our study. The exclusion criteria are (1) maternal age <18 years, (2) documented multiple pregnancy, and (3) ≥16 weeks of gestation at intake. The eligibility criteria are identical to those of the Expect Study I cohort [13]. Eligible women agreeing to participate are asked to give informed consent and to complete 4 Web-based surveys at enrolment, 24 weeks and 34 weeks of gestation, and 6 weeks after due date.
A personal link to the first online survey will be sent immediately after enrolment. If the survey was not accessed or incomplete, 2 automatic reminders will be sent by email at 3-day intervals for surveys one to three and at 6-day intervals for the postpartum survey. In case of non-response, women will be contacted by phone (provided that a correct phone number is available). If women report PTB at the beginning of survey two or three, they will automatically be redirected to the postpartum survey.
The medical ethical committee of Maastricht University Medical Centre evaluated the study protocol and declared that the study did not fall within the scope of the Dutch Medical Research Involving Human Subjects Act (WMO; METC-17-4-057).
Tailored-Care Paths
The LOC consists of midwives (n=9), gynecologists (n=9), professionals in maternity care (n=2), researchers (n=3), and an independent chairman. They meet four to five times annually and represent the University medical school, midwifery academy, all hospitals, and roughly 80% (n=90) of the midwives of the province. The midwives and gynecologists of the LOC revised the content of obstetric care. We will briefly describe the most important changes regarding antenatal care compared to former care-as-usual which has been observed during Expect Study I. All women will receive basic antenatal care. In the new tailored care paths, recommendations about calcium and vitamin D supplementation are emphasized for all women and an additional ultrasound for fetal growth assessment at 32 weeks of pregnancy is introduced as part of basic antenatal care.
An overview of the care pathways is provided in Table 1. Additional risk-dependent care for women with a mildly elevated risk of PE comprises the recommendation of preventive aspirin treatment, 80-100 mg aspirin daily from 12 weeks up to 36 weeks of pregnancy. Obstetric care for women with a substantial risk of PE additionally comprises of extended blood tests, blood pressure measurements every 2 weeks from 14 weeks up to 40 weeks of gestation, and 2 additional ultrasounds for fetal growth measurements.
Table 1.
Overview of care pathways.
| Gestational age (weeks) | Basic antenatal care for all women | Additional risk-dependent care | ||||
|
|
|
Pre-eclampsia (mildly elevated risk) | Pre-eclampsia (high risk) | Gestational diabetes mellitus | Small or large gestational age infancy | Spontaneous preterm birth |
| 6-10 | Intake and risk assessment using the Expect prediction tool and general recommendations (eg, Calcium and vitamin D intake) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 10-12 | Confirmation gestational age (crown rump length ultrasound) and blood tests (eg, blood type, hemoglobin) | Low dose aspirin prophylaxis | Low dose aspirin prophylaxis and extended blood tests (eg, renal function) |
|
|
Cervical length measurement |
| 14 |
|
|
BPa measurement |
|
|
|
| 16 |
|
|
BP measurement | OGTTb (in case of history of GDMc) |
|
Cervical length measurement and progesterone prophylaxis |
| 18-20 | Check-up (eg, BP and symphysio-fundal height measurements) and ultrasound screening for congenital abnormalities |
|
|
|
|
Cervical length measurement |
| 22 |
|
|
BP measurement |
|
|
|
| 24-26 | Check-up |
|
BP measurement | OGTT |
|
Cervical length measurement |
| 27 | Additional blood tests (depending on Rhesus genotype) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 28 |
|
|
BP measurement and ultrasound fetal biometry | Ultrasound fetal biometry | Ultrasound fetal biometry | Cervical length measurement |
| 30 | anti-D immunoglobulin prophylaxis (depending on genotype) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 32 | Check-up, blood tests (eg, hemoglobin), and ultrasound fetal biometry |
|
|
|
|
Cervical length measurement |
| 34 |
|
|
BP measurement |
|
|
|
| 36 | Check up and ultrasound fetal biometry |
|
Ultrasound fetal biometry |
|
Ultrasound fetal biometry |
|
| 37 |
|
|
BP measurement |
|
|
|
| 38 |
|
|
BP measurement |
|
|
|
| 39 |
|
|
BP measurement |
|
|
|
| 40 | Check-up and shared decision regarding induction of labor |
|
|
|
|
|
| 41-42 | Check-up |
|
|
|
|
|
aBP: blood pressure.
bOGTT: oral glucose tolerance test according to the International Association of the Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Group's (IADPSG) criteria.
cGDM: gestational diabetes mellitus.
Women with a history of GDM are advised to have an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) at 16 and 26 weeks of pregnancy. Women with a mildly elevated risk are advised to have an OGTT at 24 weeks of pregnancy. Furthermore, in both cases, women will receive two additional ultrasounds for fetal growth measurements in addition to basic antenatal care.
Outcome Measures and Measurement
The primary outcomes are health care professionals’ adherence to key recommendations and compliance of the women involved in the study. Adherence is defined as the proportion of women that actually received the key recommendations they should have received from their health care professional according to the LOC guidelines. Adherence will be analyzed regarding recommendations of adequate vitamin D (yes or no) and calcium intake (yes or no) for all women, preventive aspirin treatment (yes or no) for women with elevated PE risks, and OGTT (yes or no) for women with elevated GDM risks.
Compliance is defined as the proportion of women whom comply with the LOC recommendations they have received (yes, no or partially). Compliance will be analyzed regarding: adequate vitamin D (10 microgram per day) and calcium (1,000 milligram per day) intake, preventive aspirin treatment, and OGTT.
The secondary outcomes are patient satisfaction and cost-effectiveness. These secondary outcomes of Expect Study II will be compared to the outcomes of Expect Study I.
Patient satisfaction will be measured by validated patient satisfaction questionnaires. The Patient Satisfaction Questionnaire Short Form will be incorporated in antepartum surveys two and three. In the postpartum survey, patient satisfaction will be assessed by the Pregnancy and Childbirth Questionnaire (PCQ) [16]. The PCQ is validated for Dutch women who recently gave birth and addresses three topics: women’s satisfaction with the health care professional during pregnancy, health education, and satisfaction with the health care professional during labor. Furthermore, Truijens et al showed the PCQ is sensitive to pick up effects regarding patient satisfaction due to simulation-based obstetric team training [17].
In order to perform cost-effectiveness calculations, we will calculate two incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs). The first ICER expresses the health care costs per one neonatal composite outcome prevented. The neonatal composite outcome is defined as perinatal death within seven days after birth, asphyxia (Apgar score <7 after 5 minutes), admission to a neonatal intensive care unit within 28 days after birth, SGA (birthweight <2.3 weight percentile), and very preterm birth (birth before 32 completed weeks of pregnancy) [13]. The second ICER will express the health care cost per one maternal gained Quality Adjusted Life Year (QALY).
Data Collection
For the primary outcomes, we will use the data collected for the Expect Study II. For the secondary outcomes, when comparing the effects of risk-dependent care with former care-as-usual, the outcomes of the Expect Study II will be compared with the outcomes of the Expect Study I. For this reason, the survey intervals and the questions regarding the secondary outcomes are similar between the two studies.
In the Expect Study II, data will be collected using the Expect prediction tool, comprising women’s personal risk profile, and Web-based patient surveys. A structured overview of patient enrolment and data collection for the Expect Study II is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
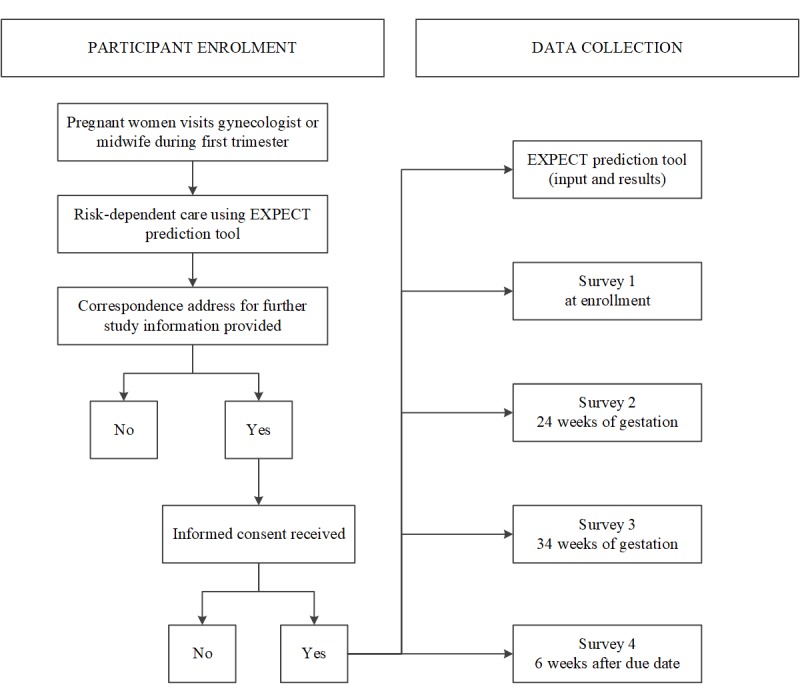
Flowchart of participant enrolment and data collection of the Expect Study II. Whether or not a woman participates to the Expect Study II does not affect the health care women receive during their pregnancy.
The first survey addresses the following topics: (1) recommendations and information given by health care professionals, (2) women’s intention to comply with these recommendations, (3) dietary intake of calcium and vitamin D and sunlight exposure, and (4) vitamin and mineral supplement usage.
The second and third surveys are comparable to each other and will address the following topics: (1) patient satisfaction, (2) women’s state anxiety, (3) maternal quality of life, (4) changes in vitamin and mineral supplement usage, and (5) health care resource use.
In order to document the nature and volume of health care resource used, women will be asked to record all visits to midwives, hospitals, and other care institutions. Furthermore, questions related to medication use, hospital admission, diagnostic and medical procedures, and the delivery will be asked. To minimize patient recall problems, information regarding the usage of health care resources will be requested at three intervals (surveys two, three and four) during the study period.
Survey four, the postpartum survey, addresses obstetric outcomes, compliance of health care recommendations, and the topics mentioned in survey two and three. Furthermore, this survey also contains questions regarding the health care consumption related to the neonate.
Sample size
According to the results of the validation study (Expect I) we expect approximately 30% of women to have an elevated estimated risk of PE, the obstetric complication with the lowest incidence (unpublished study submitted by Meertens et al, January 2018). Furthermore, an adherence of 70% and a compliance of approximately 40% is expected for the recommended aspirin treatment. This will result in approximately 21% and 12% respectively of the general population having an elevated risk of PE. In order to estimate these percentages with a precision of approximately 4% the required sample size is estimated at 400 participants [18].
Statistical Analysis
Missing values will be handled by imputation. Stochastic regression imputation with predictive mean matching as the imputation model will be used to prevent biased results based on complete case analysis only [19].
Adherence will be calculated by the proportion of women who reported to have received the LOC recommendations regarding adequate vitamin D and calcium intake, preventive aspirin treatment, and OGTT. Answers of participants will be linked to their estimated risk profile based on the Expect prediction tool.
Compliance will be analyzed by calculating the proportion of women who complied with the recommendations received from their health care professional regarding aspirin treatment, OGTT, vitamin D, and calcium intake. Vitamin D is analyzed based on supplement intake and sunlight exposure. Calcium intake is determined by calculating the daily intake from diet and supplement use. Dietary intake will be estimated using answers from a selection of questions from the Dutch National Food Frequency Questionnaire tool [20]. These questions address food products that cumulatively cover >80% of the variance in calcium intake [21]. Total intake of both nutrients will be compared with the recommended intake by the LOC (1000 milligram calcium per day and 10 microgram of vitamin D per day) in order to determine compliance to these recommendations.
The secondary outcomes, patient satisfaction and cost-effectiveness, will be analyzed by comparing Expect Study II with the outcomes of former care-as-usual (Expect Study I). Patient satisfaction scores will be analyzed using multiple linear regression.
For the economic evaluation, we will use a health care perspective according to the Dutch guidelines for cost calculations [22]. A time horizon of approximately eleven months, from onset of pregnancy up to six weeks post-partum, will be applied. Maternal quality of life will be evaluated using the Euroqol EQ-5D-3L and EuroQol Visual Analogue Scale (EQ VAS) questions which are incorporated in the surveys. The EQ-5D-3L and EQ VAS are standardized questionnaires used worldwide to assess quality of life. Maternal QALYs will be calculated using the corresponding utility scores based on the Dutch population [23,24]. All costs will be expressed as 2017 Euros and if necessary cost prices will be transformed to 2017 Euros using the Dutch Consumer Price Index [25]. Bootstrap- and standard sensitivity analyses will be performed to quantify the uncertainty regarding the cost-effectiveness outcomes.
Results
Currently, women are being recruited for the Expect Study II and a total of 300 women are enrolled. We expect to achieve our goal of 400 participants during April 2018 and postpartum data collection will be finished by March 2019. As a result, first study results are expected in 2019.
Discussion
This paper describes the protocol of an impact study regarding the implementation of externally validated prediction models combined with risk-based care pathways in obstetric care. Prediction models are becoming increasingly popular in medicine [26]. Although the number of prediction models being published has increased tremendously in recent years, the number of external validation studies remains small [26]. Furthermore, performances of models predicting adverse pregnancy outcomes and the efficacy of preventive interventions for these outcomes are generally documented separately [8,27,28]. Impact studies, describing the effect of using prediction models in daily practice combined with preventive interventions relevant to the estimated risk are nearly non-existent [26]. To the best of our knowledge no impact studies using prediction models in general obstetric practice have been published.
The strengths of our design are the multicenter prospective data collection and the similarity of both cohorts. Recruitment in multiple centers, hospitals and midwife clinics, improves the probability of collecting a representative sample of the obstetric population. This is essential in the Netherlands, since most pregnant women receive antenatal care by midwives at outpatient clinics [29]. Furthermore, optimal measurement of the outcomes is achieved by prospective data collection [30]. Finally, because the two cohorts are kept as similar as possible, we are able to accurately compare the former care-as-usual with the new risk-dependent care.
Some limitations of the design must also be noted. First, since the comparison of secondary outcomes of Expect II with those of Expect I is essentially a before-and-after comparison, time trends in the outcomes can theoretically influence results. In the interpretation of the results, we will take such trends into account, fro exmaple, by looking at trends in the studied outcomes from other regions in the Netherlands.
A second possible limitation of our study is that several outcomes will solely be based on participant questionnaires. Potential recall bias, however, is limited due to the prospective design and the usage of 4 questionnaires at limited intervals. Additionally, questionnaires have been shown to be a valid method of data collection regarding perinatal outcomes and medication exposure during pregnancy [31,32]. In the questionnaires we urge respondents to answer honestly and emphasize that all answers will be treated confidentially and will not influence the care provided by their obstetric health care professional. Furthermore, the additional procedures recommended in the risk-dependent care path are all subject to a shared decision-making process between woman and health care professional. As a result, we expect there is currently no taboo regarding the compliance with given recommendations.
We hypothesize that risk-dependent care results in early detection or prevention of obstetric adverse events and can thus reduce prevalence of neonatal adverse events. However, due to low prevalence rates of approximately 5%, large cohorts (approximately two times 6,800 participants) are necessary in order to achieve sufficient power to detect a reduction of at least 20% [18]. Therefore, the influence of risk-dependent care on the incidence of the neonatal composite outcome will be analyzed using registry data of the region. Moreover, to achieve the desired effects of risk-dependent care, it first needs to be implemented successfully. Thus, implementation should first lead to behavioral changes for both health care professionals and pregnant women.
Abbreviations
- BP
blood pressure
- EQ VAS
EuroQol Visual Analogue Scale
- GDM
gestational diabetes mellitus
- IADPSG
International Association of the Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Group
- ICER
incremental cost-effectiveness ratio
- LGA
large-for-gestational-age
- LOC
Limburg Obstetric Consortium
- OGTT
oral glucose tolerance tes
- PCQ
Pregnancy and Childbirth Questionnaire
- PE
pre-eclampsia
- PTB
preterm birth
- QALY
Quality Adjusted Life Year
- SGA
small-for-gestational-age infancy
Peer-reviewer report.
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
References
- 1.Zeitlin J, Wildman K, Bréart G, Alexander S, Barros H, Blondel B, Buitendijk S, Gissler M, Macfarlane A. Selecting an indicator set for monitoring and evaluating perinatal health in Europe: criteria, methods and results from the PERISTAT project. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2003 Nov 28;111 Suppl 1:S5–S14. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2003.09.002.S0301211503004457 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Goldenberg RL, Culhane JF, Iams JD, Romero R. Epidemiology and causes of preterm birth. Lancet. 2008 Jan 05;371(9606):75–84. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60074-4.S0140-6736(08)60074-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ensing S, Abu-Hanna A, Schaaf JM, Mol BWJ, Ravelli ACJ. Trends in birth asphyxia, obstetric interventions and perinatal mortality among term singletons: a nationwide cohort study. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015 Apr;28(6):632–7. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2014.929111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Koullali B, Oudijk MA, Nijman TAJ, Mol BWJ, Pajkrt E. Risk assessment and management to prevent preterm birth. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016 Apr;21(2):80–8. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2016.01.005.S1744-165X(16)00015-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Horvath K, Koch K, Jeitler K, Matyas E, Bender R, Bastian H, Lange S, Siebenhofer A. Effects of treatment in women with gestational diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2010 Apr 01;340:c1395. doi: 10.1136/bmj.c1395. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/20360215 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Henriksen T. The macrosomic fetus: a challenge in current obstetrics. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2008;87(2):134–45. doi: 10.1080/00016340801899289.790034638 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Meertens LJE, Scheepers HCJ, Willemse JPMM, Spaanderman MEA, Smits LJM. Should women be advised to use calcium supplements during pregnancy? A decision analysis. Matern Child Nutr. 2018 Jan;14(1) doi: 10.1111/mcn.12479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Roberge S, Nicolaides K, Demers S, Hyett J, Chaillet N, Bujold E. The role of aspirin dose on the prevention of preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Feb;216(2):110–120.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2016.09.076.S0002-9378(16)30783-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rolnik DL, Wright D, Poon LC, O'Gorman N, Syngelaki A, de Paco Matallana C, Akolekar R, Cicero S, Janga D, Singh M, Molina FS, Persico N, Jani JC, Plasencia W, Papaioannou G, Tenenbaum-Gavish K, Meiri H, Gizurarson S, Maclagan K, Nicolaides KH. Aspirin versus Placebo in Pregnancies at High Risk for Preterm Preeclampsia. N Engl J Med. 2017 Dec 17;377(7):613–622. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1704559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.HAPO Study Cooperative Research Group. Metzger Boyd E, Lowe Lynn P, Dyer Alan R, Trimble Elisabeth R, Chaovarindr Udom, Coustan Donald R, Hadden David R, McCance David R, Hod Moshe, McIntyre Harold D, Oats Jeremy J N, Persson Bengt, Rogers Michael S, Sacks David A. Hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2008 May 08;358(19):1991–2002. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0707943.358/19/1991 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Poolsup N, Suksomboon N, Amin M. Effect of treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e92485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092485. http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092485 .PONE-D-14-01165 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dodd JM, Jones L, Flenady V, Cincotta R, Crowther CA. Prenatal administration of progesterone for preventing preterm birth in women considered to be at risk of preterm birth. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 31;(7):CD004947. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004947.pub3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Meertens LJE, Scheepers HC, de Vries RG, Dirksen CD, Korstjens I, Mulder AL, Nieuwenhuijze MJ, Nijhuis JG, Spaanderman ME, Smits LJ. External Validation Study of First Trimester Obstetric Prediction Models (Expect Study I): Research Protocol and Population Characteristics. JMIR Res Protoc. 2017 Oct 26;6(10):e203. doi: 10.2196/resprot.7837. http://www.researchprotocols.org/2017/10/e203/ v6i10e203 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Meertens LJ, van Montfort P, Scheepers HC, van Kuijk SM, Aardenburg R, Langenveld J, van Dooren IM, Zwaan IM, Spaanderman ME, Smits LJ. Prediction models for the risk of spontaneous preterm birth based on maternal characteristics: a systematic review and independent external validation. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2018 Apr 17; doi: 10.1111/aogs.13358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lemmens S, Spaanderman ME, Röselaers Y. Limburg Obstetric Quality System - Zorgpaden (aanbevelingen) Maastricht: LOQS; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Truijens SE, Pommer AM, van Runnard HPJ, Verhoeven CJ, Oei SG, Pop VJ. Development of the Pregnancy and Childbirth Questionnaire (PCQ): evaluating quality of care as perceived by women who recently gave birth. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2014 Mar;174:35–40. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2013.11.019.S0301-2115(13)00595-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Truijens SE, Banga FR, Fransen AF, Pop VJ, van Runnard Heimel PJ, Oei SG. The Effect of Multiprofessional Simulation-Based Obstetric Team Training on Patient-Reported Quality of Care: A Pilot Study. Simul Healthc. 2015 Aug;10(4):210–6. doi: 10.1097/SIH.0000000000000099.01266021-201508000-00003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dean AG, Sullivan KM, Soe MM. OpenEpi. 2013. [2018-01-25]. Open Source Epidemiologic Statistics for Public Health, Version 3 http://www.openepi.com/Menu/OE_Menu.htm .
- 19.van de rHEIJDEN GJ, Donders AR, Stijnen T, Moons KG. Imputation of missing values is superior to complete case analysis and the missing-indicator method in multivariable diagnostic research: a clinical example. J Clin Epidemiol. 2006 Oct;59(10):1102–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.01.015.S0895-4356(06)00198-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Molag ML, de Vries JH, Duif N, Ocké MC, Dagnelie PC, Goldbohm RA, van't Veer P. Selecting informative food items for compiling food-frequency questionnaires: comparison of procedures. Br J Nutr. 2010 Aug;104(3):446–56. doi: 10.1017/S0007114510000401.S0007114510000401 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.van Rossum CTM, Fransen HP, Verkaik-Kloosterman J, Buurma-Rethans EJM, Ocké MC. RIVM. 2011. [2018-01-25]. Dutch National Food Consumption Survey 2007-2010 http://www.rivm.nl/bibliotheek/rapporten/350050006.pdf .
- 22.Hakkaart-van Roijen L, van der Linden N, Bouwmans C, Kanters T, Tan S. Kostenhandleiding: Methodologie van kostenonderzoek en referentieprijzen voor economische evaluaties in de gezondheidszorg. Institute for Medical Technology Assessment, Erasmus University Rotterdam. 2015 [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lamers LM, Stalmeier PF, McDonnell J, Krabbe PF, van Busschbach JJ. [Measuring the quality of life in economic evaluations: the Dutch EQ-5D tariff] Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2005 Jul 09;149(28):1574–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.EuroQol Group EuroQol--a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy. 1990 Dec;16(3):199–208. doi: 10.1016/0168-8510(90)90421-9.0168-8510(90)90421-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.CBS . Dutch consumer price index. Centraal bureau voor de Statistiek: Consumentenprijsindex; 2018. [2018-01-25]. http://statline.cbs.nl/Statweb/ [Google Scholar]
- 26.Moons KGM, Kengne AP, Grobbee DE, Royston P, Vergouwe Y, Altman DG, Woodward M. Risk prediction models: II. External validation, model updating, and impact assessment. Heart. 2012 May;98(9):691–8. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2011-301247.heartjnl-2011-301247 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kleinrouweler CE, Cheong-See FM, Collins GS, Kwee A, Thangaratinam S, Khan KS, Mol BW, Pajkrt E, Moons KG, Schuit E. Prognostic models in obstetrics: available, but far from applicable. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Jan;214(1):79–90.e36. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2015.06.013.S0002-9378(15)00596-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Falavigna M, Schmidt MI, Trujillo J, Alves LF, Wendland ER, Torloni MR, Colagiuri S, Duncan BB. Effectiveness of gestational diabetes treatment: a systematic review with quality of evidence assessment. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012 Dec;98(3):396–405. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2012.09.002.S0168-8227(12)00306-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Visser GHA. Obstetric care in the Netherlands: relic or example? J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2012 Oct;34(10):971–975. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(16)35410-X.S1701-2163(16)35410-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Moons KG, Royston P, Vergouwe Y, Grobbee DE, Altman DG. Prognosis and prognostic research: what, why, and how? BMJ. 2009 Feb 23;338:b375. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.van Gelder MMHJ, Vorstenbosch S, Derks L, Te Winkel B, van Puijenbroek EP, Roeleveld N. Web-based questionnaires to assess perinatal outcome proved to be valid. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017 Oct;90:136–143. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.07.004.S0895-4356(16)30652-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sundermann AC, Hartmann KE, Jones SH, Torstenson ES, Velez EDR. Validation of maternal recall of early pregnancy medication exposure using prospective diary data. Ann Epidemiol. 2017 Feb;27(2):135–139.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2016.11.015. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/28012836 .S1047-2797(16)30531-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Peer-reviewer report.


