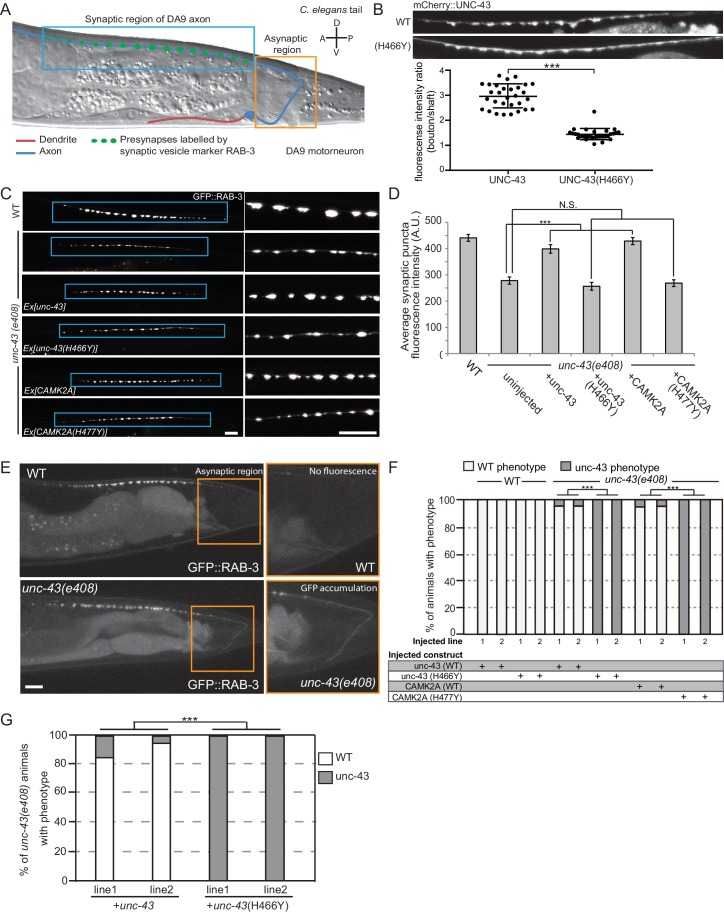
Figure 4. CAMK2AH477Y mutant fails to rescue synaptic defects in unc-43 C. elegans neurons.
(A) Schematic drawing of C. elegans motor neuron, DA9 in the tail region. DA9 extends a dendrite (red) anteriorly and an axon (blue) that extends posteriorly crosses the midline of the animal and anteriorly in the dorsal nerve cord (DNC). It forms approximately 20 en passant synapses within a discrete stretch along the DNC (blue box). DA9 presynaptic vesicles were marked with RAB-3 (GFP::RAB-3). The asynaptic region (yellow box) is devoid of any synaptic vesicle accumulation. (B) The localization of mCherry::UNC-43 and mCherry::UNC-43(H466Y) in DA9 synapses. Note that UNC-43 accumulates at synaptic boutons while UNC-43(H466Y) is diffusely localized. Fluorescent intensity of mCherry::UNC-43 was measured at synaptic boutons and along the axonal shaft. Graph plots the ratio of fluorescence intensity at synaptic boutons compared to the axonal shaft of 30 synapses from three animals. Graph shows the mean and error bars show SEM, ***p-value 6.32e−19, Student’s T-test. (C) Representative confocal images demonstrating presynaptic puncta size changes between WT and unc-43(e408) mutants. unc-43 mutants have smaller presynaptic puncta along the DNC. This defect is rescued by expression of either UNC-43 or CAMK2A in DA9 whilst the mutated UNC-43H466Y and CAMK2AH477Y fail to rescue. (D) Quantification of average puncta intensity from WT and unc-43(e408) animals. Error bars represent SEM with number of synaptic puncta quantified n > 80, N.S. is not significant, ***p-value<0.001 (uninjected vs unc-43 p-value 5.0e8, uninjected vs unc-43H466Y p-value 4.17, uninjected vs CAMK2A p-value 4.25e−12, uninjected vs CAMK2AH477Y p-value 9.40), One-Way ANOVA with Bonferroni posthoc test. (E) Representative confocal images showing mislocalization of GFP::RAB-3 into the asynaptic region (yellow box) in unc-43 DA9 neuron. (F) Rescue of the unc-43(e408) phenotype by DA9 cell-specific expression of UNC-43 or CAMK2A. UNC-43H466Y and CAMK2AH477Y fail to rescue the unc-43 phenotype. Graph shows the percentage of animals with the WT and unc-43 mutant phenotypes. ***p<0.001 (unc-43 vs unc-43H466Y p-value 2.13e−51, CAMK2A vs CAMK2AH477Y p-value 3.77e−50), Fisher Exact test with n = 100 animals scored for each line. (G) Behavioral rescue by expressing wild-type UNC-43 or UNC-43H466Y in unc-43(e408) mutants. The behavior was scored as either wild-type or unc-43. Two independent worm lines were analyzed for each condition. *** p-value 5.29e−41, Fisher Exact test with n = 100 animals scored for each line.