ABSTRACT
Biological nitrogen fixation is catalyzed by nitrogenase, a complex metalloenzyme found only in prokaryotes. N2 fixation is energetically highly expensive, and an energy-generating process such as photosynthesis can meet the energy demand of N2 fixation. However, synthesis and expression of nitrogenase are exquisitely sensitive to the presence of oxygen. Thus, engineering nitrogen fixation activity in photosynthetic organisms that produce oxygen is challenging. Cyanobacteria are oxygenic photosynthetic prokaryotes, and some of them also fix N2. Here, we demonstrate a feasible way to engineer nitrogenase activity in the nondiazotrophic cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 through the transfer of 35 nitrogen fixation (nif) genes from the diazotrophic cyanobacterium Cyanothece sp. ATCC 51142. In addition, we have identified the minimal nif cluster required for such activity in Synechocystis 6803. Moreover, nitrogenase activity was significantly improved by increasing the expression levels of nif genes. Importantly, the O2 tolerance of nitrogenase was enhanced by introduction of uptake hydrogenase genes, showing this to be a functional way to improve nitrogenase enzyme activity under micro-oxic conditions. To date, our efforts have resulted in engineered Synechocystis 6803 strains that, remarkably, have more than 30% of the N2 fixation activity of Cyanothece 51142, the highest such activity established in any nondiazotrophic oxygenic photosynthetic organism. This report establishes a baseline for the ultimate goal of engineering nitrogen fixation ability in crop plants.
KEYWORDS: cyanobacteria, N2 fixation, O2 tolerance, photosynthesis, synechocystis
IMPORTANCE
Application of chemically synthesized nitrogen fertilizers has revolutionized agriculture. However, the energetic costs of such production processes and the widespread application of fertilizers have raised serious environmental issues. A sustainable alternative is to endow to crop plants the ability to fix atmospheric N2 in situ. One long-term approach is to transfer all nif genes from a prokaryote to plant cells and to express nitrogenase in an energy-producing organelle, chloroplast, or mitochondrion. In this context, Synechocystis 6803, the nondiazotrophic cyanobacterium utilized in this study, provides a model chassis for rapid investigation of the necessary requirements to establish diazotrophy in an oxygenic phototroph.
INTRODUCTION
The ability to introduce into crop plants the machinery to fix their own nitrogen via direct transfer of nitrogen fixation (nif) genes is envisioned to be key for the next agricultural revolution (1–3). However, engineering diazotrophic plants, however attractive a proposition, is an extreme challenge, due to the complexities in the biosynthesis of active nitrogenase, the enzyme that catalyzes nitrogen fixation, and the difficulty of coupling plant metabolism to supply energy and reducing power for the nitrogen fixation process (4). An additional impediment in the scenario is that photosynthesis produces O2, which is highly toxic with respect to the synthesis and activity of nitrogenase (5).
Diazotrophy occurs only in limited species of bacteria and archaea (6). Nitrogen fixation is mainly catalyzed by an iron- and molybdenum-dependent nitrogenase enzyme complex, with two enzymatic components, an iron protein dinitrogenase reductase (NifH) and an iron-molybdenum protein dinitrogenase (NifDK) (7, 8). Three metal-dependent cofactors, the F cluster, P cluster, and M cluster, are necessary to form the holoenzyme for electron transfer to reduce atmospheric N2 to form ammonia, the biologically available form of N2 (9, 10). A significant number of additional nif genes are required for the biosynthesis of these metallocluster cofactors and for the maturation of nitrogenase to form a fully functional enzyme (11, 12).
Transferring nitrogen fixation to nondiazotrophs has been attempted for decades. To date, the heterotrophic bacterium Escherichia coli has been successfully engineered for nitrogen fixation activity through transfer of nif genes from various diazotrophic species (13–17). Attempts to engineer eukaryotic species for heterologous nitrogen fixation activity, including the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, have been unsuccessful. Limited success was reached only in expressing the NifH component as an active moiety in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (18). While all the Nif components have been successfully expressed in yeast cells, the formation of a fully functional nitrogenase complex has not yet been achieved (19–22).
Expression of nitrogenase components in plants has also been attempted in a few studies. Individual expression of 16 Nif proteins targeted to the plant mitochondria has been reported recently, but none of the structural components showed enzymatic activity (23). Another recent study showed that an active NifH component can be formed in tobacco chloroplasts (24), indicating that expression of active nitrogenase in chloroplasts might be a viable way to engineer crop plants to fix nitrogen in the future (25). Since it is widely accepted that a cyanobacterial ancestor was the progenitor of chloroplasts (26), engineering a cyanobacterium to fix nitrogen may pave the way to achieving the final goal of engineering nitrogen-fixing ability into crop plants. We have utilized the nondiazotrophic cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 (here Synechocystis 6803) as a chassis to engineer nitrogen fixation activity into an oxygenic photosynthetic organism.
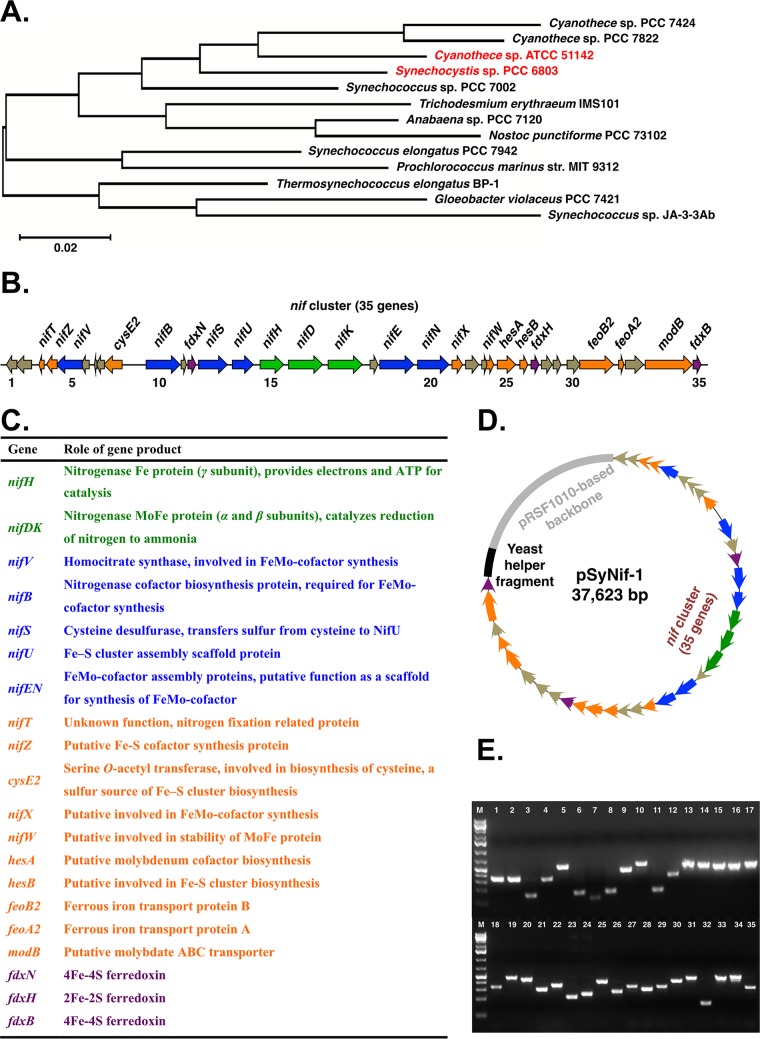
The unicellular diazotrophic cyanobacterium Cyanothece sp. ATCC 51142 (here Cyanothece 51142) uses temporal separation as its strategy to protect nitrogenase from O2 produced by photosynthesis (27, 28). Within Cyanothece, the two conflicting processes, photosynthesis and N2 fixation, occur sequentially during the diurnal periods, such that photosynthesis and O2 evolution are performed during the day whereas N2 is fixed at night (29). The energy requirements for nitrogenase are met in Cyanothece by the catabolism of glycogen. Glycogen is accumulated in the light as the storage form of fixed CO2 and is later degraded in the dark to provide energy for nitrogenase. The provision of energy coupled with high rates of respiration ensures a low-oxygen intracellular environment and sufficient supplies of energy for N2 fixation (30). The Cyanothece 51142 genome contains the most complete contiguous set of nitrogen fixation and related genes forming the nif cluster, which contains 35 genes (cce_0545 to cce_0579), encoding structural proteins, metal cofactor synthesis proteins, ferredoxins, and proteins with unknown but necessary functions (Fig. 1). All 35 genes exhibit similar oscillating diurnal patterns of transcription during light/dark cycles, showing a high level of transcription in the dark and notably reduced levels in light (27). Such synchronized transcriptional patterns also confirm that all of these genes are related to nitrogen fixation.
FIG 1 .
Introduction of nif genes into Synechocystis 6803. (A) Maximum likelihood 16S rRNA gene phylogeny of cyanobacteria. (B and C) Schemes showing the genetic organization of the nif cluster (B) and the role of each gene product (C) in Cyanothece 51142. Shown are the genes for the three structural proteins (nifHDK; green), necessary cofactors (blue), accessory proteins (orange), ferredoxins (purple), and hypothetical proteins (brown). Gene names and annotations are from GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/) and Cyanobase (http://genome.microbedb.jp/cyanobase). (D) A schematic map of plasmid pSyNif-1 containing the entire nif cluster. The backbone (gray) is from broad host plasmid pRSF1010, which can replicate in Synechocystis 6803. The yeast helper fragment (black) contains CEN6 and ARS as an ori and ura3 as a selection marker. (E) Transcription of all 35 genes in engineered Synechocystis 6803. Each lane represents a gene in the nif cluster, as numbered in panel B. Total RNA was extracted from cells cultured in BG110 medium under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions, and cDNA was used as the template for PCR.
In the current study, we successfully transferred and expressed this large nif gene cluster in nondiazotrophic Synechocystis 6803 with resultant N2 fixation activity. Subsequent engineering of the cluster and its expression levels have led to nitrogenase activities as high as 30% of that in Cyanothece 51142.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Introduction of nif genes into Synechocystis 6803.
Synechocystis 6803 has a close phylogenetic relationship with Cyanothece 51142 (Fig. 1A) (31). The large nif cluster from Cyanothece 51142 (28.34-kb region of DNA) was transferred into wild-type Synechocystis 6803 on a single extrachromosomal plasmid. This large plasmid, pSyNif-1, containing the entire nif cluster with 35 genes (Fig. 1D), was constructed using the DNA assembler method (32). The chassis of this vector was based on pRSF1010 (33), and this self-replicating pSyNif-1 plasmid was transferred into Synechocystis 6803 by conjugation, generating the engineered strain TSyNif-1. Remarkably, over the past 4 years since its introduction into the heterologous host, pSyNif-1 has been stably maintained in its entirety in Synechocystis (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). Furthermore, all introduced Cyanothece genes were transcribed (Fig. 1E) as detected by reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR), indicating that native promoters in the nif cluster from Cyanothece 51142 can drive transcription of genes in Synechocystis 6803. An acetylene reduction assay method for nitrogen fixation detected nitrogenase activity under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions for strain TSyNif-1 (Fig. 2). Nitrogen fixation reached an activity level of 2% relative to that in Cyanothece 51142 grown under similar conditions. This is the first time that a nondiazotrophic phototroph has been engineered for biosynthesis of a fully functional nitrogenase enzyme and has been found to exhibit detectible and stable nitrogen fixation activity.
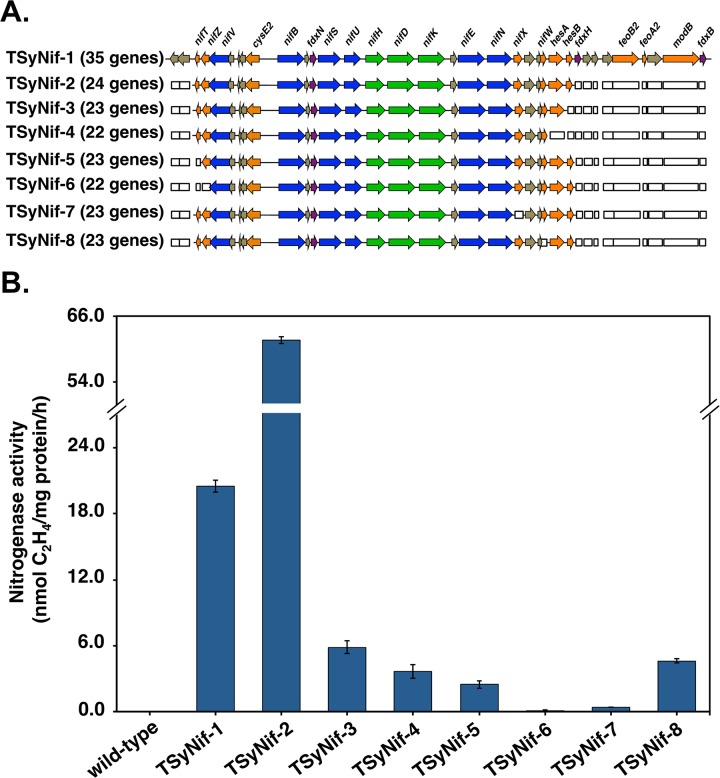
FIG 2 .
The minimal nif cluster required for nitrogen fixation activity in Synechocystis 6803. (A) Scheme showing the top-down method to determine the minimal nif cluster. The hollow rectangles represent the genes deleted from the cluster, and the colored rectangles represent the remaining genes. (B) Nitrogen fixation activity in engineered strains. Samples were collected from cultures under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions in BG110 medium. Nitrogen fixation activity was assayed by acetylene reduction, and error bars represent the standard deviations observed from at least three independent experiments.
Growth of engineered strains compared to the wild-type strain of Synechocystis 6803. Cells were cultured in BG11 medium under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions. Error bars represent the standard deviations of results from at least three independent experiments. Download FIG S1, PDF file, 0.05 MB (49.4KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
The minimal required gene cluster for nitrogen fixation activity.
Gene expression parameters for Synechocystis 6803 are not as well understood as those for E. coli. Thus, the refactoring of nif genes as performed in E. coli and Klebsiella (16, 34) to determine the minimal requirement of genes for nitrogen fixation in Synechocystis 6803 is impractical at this stage. Therefore, we approached the identification of a minimal nif cluster for nitrogen fixation using a “top-down” method, which determines the influence of a gene on nitrogenase activity by selectively removing individual genes from the nif cluster (Fig. 2). Extrapolating the genetic requirements for nitrogen fixation activity observed in studies in which nif genes were introduced in E. coli (14, 15), we determined that genes for all homologous proteins introduced into E. coli are present in the Cyanothece 51142 nif cluster between gene nifT and hesB (Fig. 1). Hence, our second plasmid, pSyNif-2, contains 24 genes in the nif cluster between nifT and hesB (Fig. 2). Eleven genes were removed that presumably encode three metal transporter proteins, two ferredoxins, and six proteins of unknown function, none of which have been analyzed previously, although they are associated with nitrogen fixation. Intriguingly, this second engineered TSyNif-2 strain with a reduced cluster of 24 genes has a 3-fold increase in nitrogen fixation activity compared to strain TSyNif-1 (Fig. 2). Although plasmids pSyNif-1 and pSyNif-2 have the same plasmid backbone (Fig. S2), the transcriptional levels of the structural genes nifH, nifD, and nifK are higher in the TSyNif-2 strain (Fig. 3). This improvement in nitrogenase activity could be the result of removal of one or more regulatory genes, which may encode a protein(s) that represses expression of genes in the nif cluster.
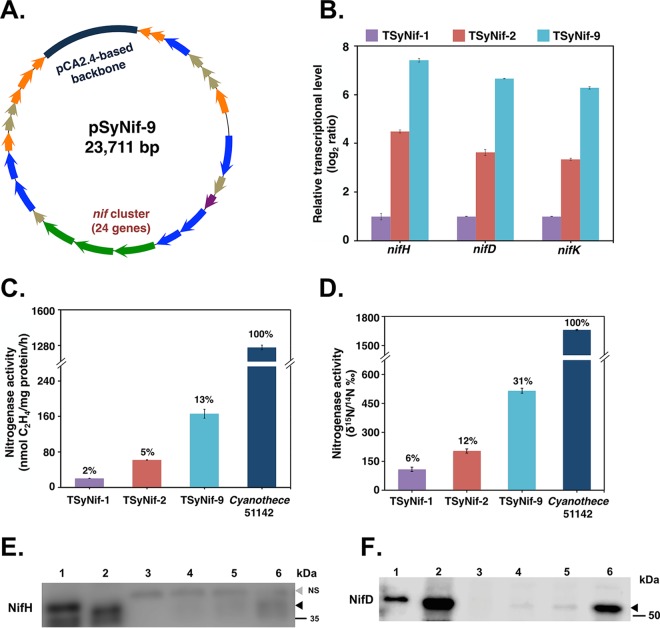
FIG 3 .
Enhancement of transcription levels of nif genes leads to higher nitrogen fixation activity. (A) A schematic map of plasmid pSyNif-9 containing the nif cluster with 24 genes from nifT to hesB. The backbone (dark blue) is from endogenous plasmid pCA2.4 of Synechocystis 6803. (B) Comparison of transcription levels of the nif structural genes in engineered strains through quantitative PCR (q-PCR). (C and D) Comparison of nitrogen fixation activities in engineered strains, as measured by C2H2 reduction assay (C) as well as 15N assimilation assay (D). (E) Western blot showing the presence of NifH protein in engineered Synechocystis 6803 strains. Lanes 1 to 6 represent 2.0 µg purified NifH-His protein from E. coli and 15 µg whole-cell extracts of Cyanothece 51142, the Synechocystis 6803 wild-type strain, TSyNif-1, TSyNif-2, and TSyNif-9, respectively. The black triangle indicates the band for NifH protein, while the gray one indicates the nonspecific band. (F) Western blot showing the presence of NifD protein in engineered Synechocystis 6803 strains. Lanes 1 to 6 represent 0.5 µg purified NifD-His protein from E. coli and 15 µg whole-cell extracts of Cyanothece 51142, the Synechocystis 6803 wild-type strain, TSyNif-1, TSyNif-2, and TSyNif-9, respectively. Cyanobacterial samples were collected from cultures under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions in BG110 medium. Error bars represent the standard deviations of results from at least three independent experiments.
Schematic map of plasmids used for expression of nif genes in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Replicating plasmids (A) pSyNif-1 (pSL2379) and (B) pSyNif-2 (pSL2397) were constructed using the DNA assembler method and introduced into the wild-type strain of Synechocystis 6803 by conjugation. The components of the plasmids are labeled as follows: backbone containing the bacterial replication machinery (gray), yeast helper fragment containing CEN6 and ARS H4 as an ori and containing ura3 as a selection marker (black), and the nif gene cluster from Cyanothece ATCC 51142. The colors of the nif genes are the same as in Fig. 1. Download FIG S2, PDF file, 0.3 MB (342.9KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
However, further removal of genes from both directions resulted in a decrease of nitrogen fixation activity by more than 10-fold for strains TSyNif-3 to TSyNif-6, from which genes hesB, hesAB, nifT, and nifTZ were removed, respectively (Fig. 2). Thus, this “top-down” approach determined that an essential minimal cluster from nifT to hesB is required for nitrogen fixation activity in Synechocystis 6803. Additionally, we investigated the removal of two more genes in the cluster, nifX and nifW, generating the two strains TSyNif-7 and TSyNif-8. Deletion of these two genes did not affect expression of surrounding genes (Fig. S3). However, nitrogen fixation activity levels dropped 100-fold and 10-fold, respectively, in these engineered strains (Fig. 2). We conclude that both nifX and nifW are important genes for nitrogen fixation. Notably, nifX exhibited a positive influence on N2 fixation in cyanobacteria, while it functions as a negative regulator for N2 fixation in the heterotrophic diazotroph Klebsiella oxytoca (35).
Transcription of nif genes in engineered Synechocystis 6803. (A) Transcripts of nif genes in Synechocystis 6803 strain TSyNif-2. Gene expression was detected by RT-PCR. Lanes 1 to 24 show genes from nifT to hesB in the cluster (Fig. 1B). (B to G) Expression of nifHDK and surrounding genes was examined in each engineered strain shown in Fig. 2 by RT-PCR. (B) TSyNif-3 (23 genes without hesB compared to TSyNIf-2). (C) TSyNif-4 (22 genes without hesAB compared to TSyNif-2). (D) TSyNif-5 (23 genes without nifT compared to TSyNif-2). (E) TSyNif-6 (22 genes without nifTZ compared to TSyNif-2). (F) TSyNif-7 (23 genes without nifX compared to TSyNif-2). (G) TSyNif-8 (23 genes without nifW compared to TSyNif-2). Cultures for RNA extraction were grown under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions in BG110 medium. Download FIG S3, PDF file, 4.3 MB (4.4MB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Improvement of nitrogen fixation activity.
To increase the RNA expression levels of the nitrogenase-related genes, we took advantage of three small endogenous plasmids in Synechocystis 6803: pCA2.4, pCB2.4, and pCC5.2. The heterologous genes harbored in these endogenous plasmids maintained higher transcriptional levels than those in a pRSF1010-based plasmid, because of the higher copy numbers of these three plasmids within Synechocystis (36, 37). First, we replaced the RSF1010 backbone of plasmid pSyNif-2 by the entire DNA segment of each of these endogenous episomes and then transferred the plasmids to Synechocystis 6803, generating three strains, TSyNif-9, TSyNif-10, and TSyNif-11, with the chassis of pCA2.4, pCB2.4, and pCC5.2, respectively (Fig. 3A; see also Fig. S4). As expected, genes nifH, nifD, and nifK in strain TSyNif-9 showed transcription levels that were severalfold higher than in TSyNif-2 (Fig. 3B). In addition, nitrogen fixation activity was increased by another 2- to 3-fold, reaching 13% for the acetylene reduction activity in TSyNif-9 relative to that observed in Cyanothece 51142 (Fig. 3C). Next, nitrogenase activity was directly assayed in the engineered strains using a 15N assimilation assay method. Remarkably, the highest activity obtained was from strain TSyNif-9, reaching 31% of 15N assimilation relative to Cyanothece 51142 (Fig. 3D). The activity data presented here is comparable to published data from studies on nitrogen fixation activity in engineered E. coli strains (Table 1). Additionally, both the NifH and NifD nitrogenase structural proteins were detected in whole-cell extracts via Western blotting by using antisera against the NifH and NifD proteins of Rhodospirillum rubrum, respectively (Fig. 3E and F). Although the protein level in Cyanothece 51142 is significantly higher than in the engineered Synechocystis 6803 strains, the NifD protein level in strain TSyNif-9 reached 10% of total cellular proteins (Fig. S4). It was also evident that the nitrogenase activities in the engineered strains were proportional to the level of nitrogenase structural proteins, which implied that optimizing the expression of nitrogenase proteins is critical for the activity. Most importantly, from an evolutionary standpoint, these results highlight the potential for engineering plant chloroplasts to fix nitrogen at a high level of activity, since oxygenic cyanobacteria are the progenitors of chloroplasts.
TABLE 1 .
Nitrogen fixation activity in diazotrophs and engineered strains
| Strain | Nitrogenase activity (nmol C2H4/mg protein/h) |
% activity (based on C2H2 reduction assay) |
% activity (based on 15N assimilation assay) |
Source or reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diazotrophs | ||||
| Cyanothece 51142 | 1,262 | 100 | 100 | This study |
| Azotobacter vinelandii | 3,300 | 100 | 100 | 52 |
| Paenibacillus sp. strain WLY78 | 3,050 | 100 | 100 | 14 |
| Pseudomonas stutzeri A1501 | 1,050 | 100 | NDe | 53 |
| Klebsiella oxytoca M5a1 | 3,708 | 100 | ND | 54 |
| Engineered strains | ||||
| TSyNif-1 | 20 | 2 | 6 | This study |
| TSyNif-9 | 166 | 13 | 31 | This study |
| Engineered E. colia | 180 | 5 | 35 | 15 |
| Engineered E. colib | 300 | 10 | 30 | 14 |
| Engineered E. colic | 105 | 10 | ND | 53 |
| Engineered E. colid | 740 | 20 | ND | 16 |
Nitrogen fixation genes from A. vinelandii and K. oxytoca.
Nitrogen fixation genes from Paenibacillus.
Nitrogen fixation genes from Pseudomonas.
Nitrogen fixation genes from K. oxytoca.
ND, not determined.
Improvement of nitrogen fixation activity by increasing plasmid copy number. (A and B) Schematic maps of plasmid pSyNif-10 and plasmid pSyNif-11 containing the nif cluster with 24 genes from nifT to hesB. The backbone (dark blue) is from endogenous plasmid pCB2.4 and plasmid pCC5.2 of Synechocystis 6803, respectively. (C) Comparison of nitrogen fixation activities in engineered strains measured by 15N assimilation assay. (D) Western blot showing the presence of the NifD protein in engineered Synechocystis 6803 cells. Lanes 1 to 3 represent 1.0 µg, 0.5 µg, and 0.25 µg purified NifD-His protein from E. coli, respectively; lanes 4 to 9 represent 15 µg whole-cell extracts of TSyNif-9, TSyNif-10, TSyNif-11, TSyNif-1, TSyNif-2, and the Synechocystis 6803 wild-type strain, respectively. Samples were collected from cultures grown under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions in BG110 medium. Error bars represent the standard deviations of results from at least three independent experiments. Download FIG S4, PDF file, 0.5 MB (559.2KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Nitrogen fixation activity in Synechocystis 6803.
Despite the additional metabolic load of expressing large cohorts of 35 or 24 genes related to nitrogen fixation being introduced in Synechocystis 6803, remarkably, the expression and activities of these heterologous proteins did not affect the growth of the engineered strains under diurnal light/dark conditions (Fig. S1). We used strain TSyNif-2 to assess the influence of oxygen and exogenous nitrate on nitrogenase activity under four conditions, BG11, BG110 (BG11 without nitrate), BG11 with 10 µM DCMU [3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1 dimethylurea] (no O2 evolution), and BG110 with 10 µM DCMU (Fig. S5). Interestingly, the transcript levels of the nifH, nifD, and nifK genes in the TSyNif-2 strain were downregulated by nitrate, which is similar to the results seen with Cyanothece 51142. Specifically, the depletion of nitrate improved the nitrogenase activity over 30-fold in BG110 with DCMU (Fig. S5). Nitrogen fixation activity was obtained only in an anaerobic environment when DCMU was added to the testing culture, although the headspace of all cultures was flushed with pure argon. These data indicate that oxygen generated by photosynthesis directly blocks nitrogenase activity in TSyNif-2, highlighting that one of the biggest challenges for engineering nitrogen fixation in oxygenic phototrophs is the sensitivity of nitrogenase to oxygen.
Characteristics of engineered Synechocystis 6803 strain TSyNif-2. (A) Comparison of nitrogenase activities in the TSyNif-2 strain under four different conditions. (B) Transcript levels of nifH, nifD, and nifK genes in TSyNif-2 strains were assayed by q-PCR. RNA was extracted from the cells grown under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions. Error bars represent the standard deviations of results from three independent replicates. Download FIG S5, PDF file, 0.1 MB (83.5KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Improvement of O2 tolerance by introduction of hydrogenase uptake.
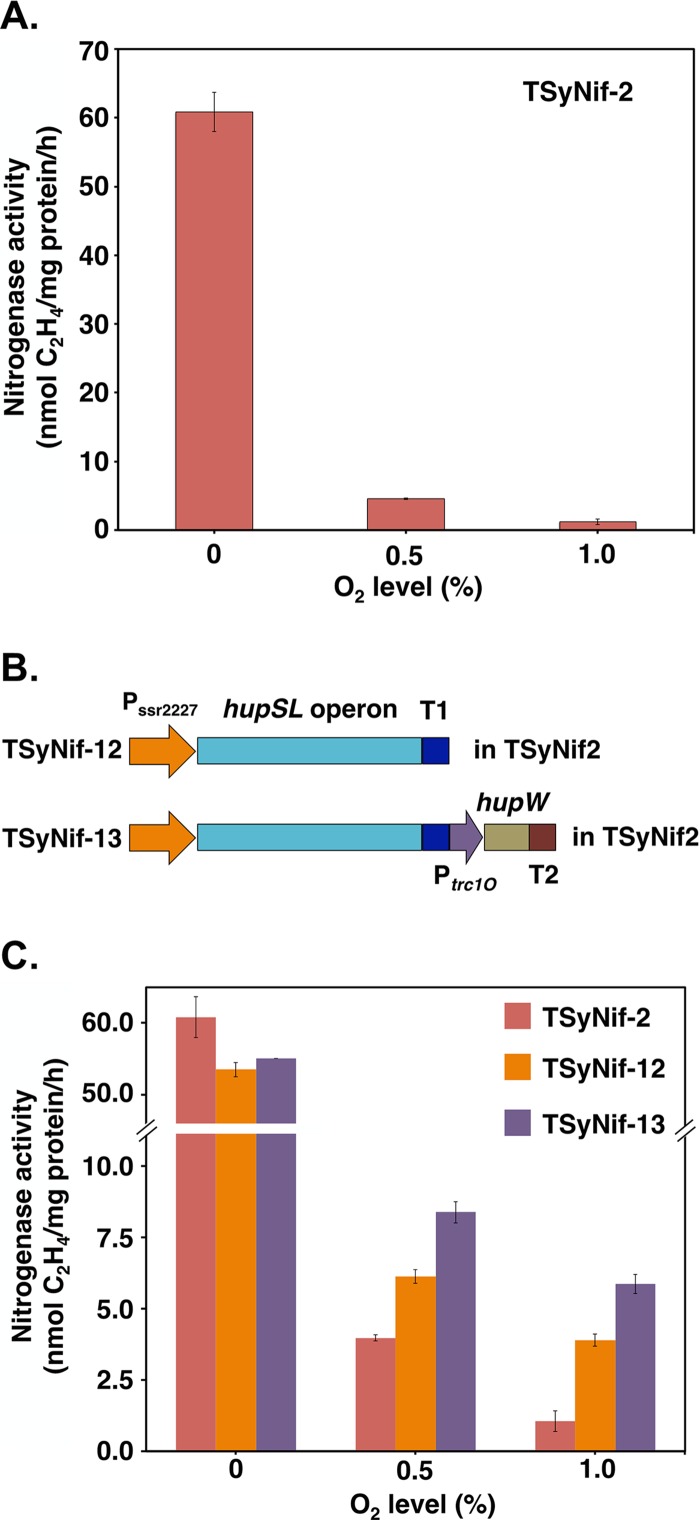
In order to test the oxygen sensitivity of nitrogen fixation activity in TSyNif-2, a measured amount of oxygen was added to the headspace of cultures grown in BG110 media to generate micro-oxic conditions of 0.5% and 1.0% of O2 in the sealed testing bottles. The activity dropped more than 10-fold and 60-fold (Fig. 4A), respectively, demonstrating that, as expected, nitrogen fixation activity in engineered Synechocystis 6803 is highly sensitive to O2. To enhance O2 tolerance under the same conditions, genes coding for the uptake hydrogenase enzyme from Cyanothece 51142 were introduced into the chromosome of the TSyNif-2 strain. The uptake hydrogenase is conserved in diazotrophic cyanobacteria (38) and has been shown to be necessary for nitrogen fixation under aerobic conditions in Cyanothece (39). The uptake hydrogenase may utilize the H2 produced by the nitrogenase, but it may have three other beneficial functions for the organism: supplying the organism with ATP via the oxyhydrogen (Knallgas) reaction; removing oxygen from nitrogenase, thereby protecting it from inactivation; and providing electrons (reducing power) to nitrogenase and other enzymes (39). The structural genes for this hydrogenase, hupS and hupL, present together in a single operon in Cyanothece 51142, were transformed into TSyNif-2, generating strain TSyNif-12 (Fig. 4B). In addition to the structural genes hupSL, a protease encoded by hupW is also present in Cyanothece 51142. HupW is required for the maturation of HupL protein through the processing of its C terminus (40). Thus, the hupSLW genes organized in two operons were transformed into TSynif-2 to generate the TSyNif-13 strain (Fig. 4B). The expression of hup genes in TSyNif-12 and TSyNif-13 was assessed by RT-PCR (Fig. S6). The introduction of the uptake hydrogenase did not affect nitrogen fixation activity under anaerobic conditions (Fig. 4C). Interestingly, under micro-oxic conditions, nitrogen fixation activity markedly improved with the expression of uptake hydrogenase, especially for strain TSyNif-13, with 2-fold and 6-fold increases in TSyNif-2 for O2 levels of 0.5% and 1.0%, respectively. The results described above suggest that expression of uptake hydrogenase proves to be highly effective in enhancing O2 tolerance of nitrogen fixation activity in the engineered Synechocystis strain.
FIG 4 .
Expression of uptake hydrogenase improves O2 tolerance of nitrogenase. (A) Effect of O2 on nitrogen fixation activity of the TSyNif-2 strain. (B) Schematic showing the insertion of uptake hydrogenase genes hupSL and hupW from Cyanothece 51142 into the chromosome of the TSyNif-2 strain. (C) Comparison of nitrogen fixation activities under different micro-oxic conditions. Samples were collected from cultures under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions in BG110 medium. Nitrogen fixation activity was assayed by acetylene reduction, and error bars represent the standard deviations of results from at least three independent experiments.
Transcriptional analysis of uptake hydrogenase genes. (A and B) RT-PCR analysis of hupSL and hupW genes in the (A) TSyNif-12 and (B) TSyNif-13 strains. Lanes 1 to 3 in both panels represent samples collected from BG11 medium, and lanes 4 to 6 represent samples collected from BG110 medium. RNA was extracted from the cells grown under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions. M, molecular mass standards. Download FIG S6, PDF file, 1.3 MB (1.4MB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
In this study, introduction of the nif gene cluster from Cyanothece 51142 enabled nitrogen fixation activity in Synechocystis 6803. The minimal cluster for 24 genes (Fig. 2) for nitrogenase activity will provide a useful framework for future studies to further enhance such activity by refactoring genes as previously done in Klebsiella oxytoca (34). Although uptake hydrogenase is a complex enzyme, introduction of its structural genes and a protease works as a mechanism providing protection from the toxicity of O2. The O2 toxicity to nitrogenase is likely the most difficult aspect to overcome to achieve nitrogen fixation activity under aerobic conditions.
A fully functional nitrogenase holoenzyme requires 8 electrons and 16 ATPs to reduce one molecule of N2 to ammonia. Thus, metabolism within cells needs to be adjusted to supply enough reducing power and energy for nitrogen fixation. Biosynthesis of fully functional nitrogenase is a complex process. This complexity increases the difficulty of finding the minimal genes and the best ratios of proteins expressed from the nif cluster in Synechocystis 6803. Genes with the same designations in different species occasionally have alternative functions (see Table S1 in the supplemental material). An example is the nifX gene, which functions as a negative regulator in Klebsiella oxytoca (35). Gene nifX is of importance in Cyanothece, since deletion of nifX affects nitrogenase activity.
Impact of various nif gene inactivations on nitrogenase activity in different engineered strains. Relative levels of activities with respect to that determined for the respective engineered strain with wild-type nif cluster are indicated. Download TABLE S1, PDF file, 0.05 MB (53KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Although multiple challenges and many barriers exist with respect to enabling plants to efficiently fix atmospheric nitrogen, we have engineered an oxygenic photosynthetic cell to fix N2 by reconfiguring the genetic processes for nitrogen fixation from Cyanothece 51142 to function in Synechocystis 6803. Our studies to date have established the highest rate of engineered nitrogen fixation activity in any nondiazotrophic oxygenic organism.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Microorganisms, culture conditions, and media.
All cyanobacterial strains, including Cyanothece 51142, Synechocystis 6803, and engineered strains (see Table S2 in the supplemental material), were cultured in 100-ml flasks of fresh BG11 medium (41) with appropriate antibiotics (20 µg/ml kanamycin, 15 µg/ml chloramphenicol, or 20 µg/ml spectinomycin). As a preculture, cells were grown at 30°C, with 150 rpm shaking, and under conditions of 50 µmol photons ⋅ m−2 ⋅ s−1 constant light. For the nitrogen fixation activity assay, unless otherwise stated, precultured cells were collected and washed with fresh BG110 medium (BG11 medium without nitrate) and resuspended in 500 ml fresh BG110 medium. Cells were grown at 30°C with air bubbling under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions with 50 µmol photons ⋅ m−2 ⋅ s−1 of light. Yeast and E. coli strains (listed in Table S2) used for construction of recombinant plasmids were grown with 200 rpm shaking in yeast extract-peptone-dextrose plus adenine (YPAD) medium (42) and LB medium at 30°C and 37°C, respectively.
Strains and plasmids used in this study. Download TABLE S2, PDF file, 0.1 MB (80.7KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Construction of recombinant plasmids and engineered strains.
Plasmids and strains used in this study are listed in Table S2, and all primers used in this study are listed in Table S3. Two methods were used to construct the plasmids: DNA assembler (32) and Gibson assembly (43). For building the large pSyNif-1 and pSyNif-2 plasmids containing the nif genes, genomic DNA from Cyanothece 51142 was used as the template for PCR, and all DNA fragments were combined using the DNA assembler method to form the plasmids in yeast. For the other recombinant plasmids listed in Table S2, Gibson assembly was the method used to construct them with DNA fragments amplified by PCR. Genomic DNAs from Cyanothece 51142 and the large pSyNif-2 plasmid were used as the templates for PCR to construct the plasmids for backbone replacement, the plasmids containing the uptake hydrogenase genes, or the plasmids used to remove specific nif genes. The sequences of all of the plasmids constructed in this study were verified (Genewiz, NJ).
Primers used in this study. Download TABLE S3, PDF file, 0.1 MB (79.2KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Plasmids pSyNif-1 and pSyNif-2 were introduced into the Synechocystis 6803 wild-type strain through the method of triparental conjugation (44) to form strains TSyNif-1 and TSyNif-2, respectively. The other recombinant plasmids were transformed into Synechocystis 6803 by natural transformation (45), and double homologous recombination integrated the fragments into the chromosome (for the uptake hydrogenase genes) or the plasmid (for the plasmid backbone replacement and for the specific removal of nif genes).
Reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) and quantitative PCR (q-PCR).
RT-PCR analysis was performed using RNA samples isolated from culture grown in BG110 medium at time point D1 (1 h into the dark period) under light/dark conditions. After extraction and quantification of RNA (46), 100 ng of DNase-treated RNA samples and Superscript II reverse transcriptase and random primers (Invitrogen) were used for reverse transcription according to the manufacturer’s instructions. cDNA generated after reverse transcription was used as the template for PCR to validate the transcription of genes.
q-PCR was performed on RNA samples extracted from culture grown in BG110 medium under light/dark conditions as previously described (27). Briefly, QRT-PCR Sybr green dUTP mix (ABgene) was used for the assay on an ABI 7500 system (Applied Biosystems). Each reaction was performed in three replicates, and the average threshold cycle (CT) value was used to calculate the relative transcriptional levels for the amounts of RNA. All primers used for RT-PCR and q-PCR are listed in Table S3.
Measurement of nitrogen fixation activity.
Nitrogen fixation activity was measured by an acetylene reduction assay (47) modified from a previously published method (48). Unless otherwise stated, the activity assay was performed as follows. A 25-ml volume of cyanobacterial culture was grown in BG110 medium with air bubbling under light/dark conditions as mentioned above and was transferred to a 125-ml air-tight glass vial. DCMU (10 μM) was added to the culture, vials were flushed with pure argon, and cultures were incubated under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions. Cells in the sealed vials were cultured overnight, and, at the D1 time point, 5 ml acetylene was added into the sealed vials, followed by 3 h of incubation in light at 30°C. Two hundred microliters of gas was sampled from the headspace and injected into an Agilent 6890 N gas chromatograph equipped with a Porapak N column and a flame ionization detector, using argon as the carrier gas. The temperatures of the detector, injector, and oven were 200°C, 150°C, and 100°C, respectively.
Total protein levels were determined on a plate reader (Bio-Tek Instruments, Winooski, VT) using a bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay kit (Pierce, Rockford, IL) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Total chlorophyll a was subjected to methanol extraction and quantification on an Olis DW2000 spectrophotometer (OnLine Instrument Systems, Inc., GA).
In vivo 15N2 incorporation assay.
All strains were grown under light/dark conditions as mentioned above, and 50-ml cultures were transferred into a 125-ml airtight glass vial. DCMU (10 μM) was added to the culture, vials were flushed with pure N2, and cultures were incubated under light/dark conditions. Cells in the sealed vials were cultured overnight, and, at the D1 time point, 8 ml of headspace gas was removed followed by injection of 8 ml of 15N2 gas (Cambridge Isotope Laboratories, Inc.) (98%+). After 8 h of incubation at 30°C in light (50 µmol photons ⋅ m−2 ⋅ s−1), the cultures were collected and dried in a laboratory oven at 50°C to 60°C for 24 h. The dried pellets were ground, weighed, and sealed into tin capsules. Isotope ratios were measured by elemental analyzer-isotope ratio mass spectrometry (EA-IRMS; Thermo Fisher Scientific), and values are indicated as δ15N (‰), where the number represents a linear transform of the 15N/14N isotope ratios, representing the per-mille difference between the isotope ratios in a sample and in atmospheric N2 (49). Data presented are mean values determined on the basis of results from at least two biological replicate cultures.
Western blot analysis.
The nifH (cce_0559) gene and nifD (cce_0560) gene were subjected to individual PCR amplifications from the genomic DNA of Cyanothece 51142, using the primers shown in Table S3. The PCR fragment was ligated into expression vector pET28a cleaved by NdeI and BamHI. The resulting plasmids (pET28a-nifH and pET28a-nifD) were used to produce NifH and NifD proteins, each with an N-terminal His6 tag. For overproduction of these proteins, E. coli BL21 (DE3) was transformed with plasmids pET28a-nifH and pET28a-nifD, respectively, and cultivated in LB medium at 37°C to an optical density at 600 nm (A600) of 0.3. Protein expression was induced by the addition of 0.2 mM isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside, and the culture was incubated for another 18 h at 20°C. After the cells were harvested, NifH and NifD were individually purified by nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) affinity chromatography. Briefly, harvested E. coli cells were resuspended in 20 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.0) containing 100 mM NaCl and in 2 mM β-mercaptoethanol supplemented with a protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma-Aldrich). Lysozyme was added to reach a concentration of 1 mg/ml, and the cells were lysed by freezing-thawing, followed by sonication. After cells were centrifuged at 13,000 rpm, the Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) was added to the supernatant (final concentration, 50 mM), and it was loaded onto a Ni-NTA agarose column (0.2 ml). After bound proteins were washed with the starting buffer containing 1 M NaCl, they were eluted with 0.3 ml of the starting buffer containing 250 mM imidazole. The purified protein was stored at −20°C and used as the positive control for Western blot assay.
Cyanobacterial cells cultured in N-free medium under conditions of light/dark cycles were collected at time point D4 (4 h after the dark phase) and resuspended in 0.5 ml TG buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl [pH 8.0], 10% glycerol) containing a protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma-Aldrich). A 0.5-ml volume of sterilized, acid-washed glass beads was added to the cells, and the mixture was disrupted using a bead beater (BioSpec Products). The resultant mixture was centrifuged for 10 min at 7,500 × g, and the supernatant was transferred into a new tube. The amount of protein was determined using bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay reagent (Thermo Scientific).
A 15-µg (total) protein extract from each sample was solubilized with 8× sample buffer (10 ml of 0.5 M Tris [pH 6.8], 15 ml of 70% glycerol, 8 ml of 20% sodium dodecyl sulfate, 4 ml of β-mercaptoethanol, 4 ml of 0.1% bromophenol blue) at 70°C for 10 min and separated on a sodium dodecyl sulfate (0.1% [wt/vol])-polyacrylamide (12.5% [wt/vol]) gel by electrophoresis. After electrophoresis, proteins were transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane (Millipore), blocked using 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) for 2 h at room temperature, and then separately incubated with the primary rabbit antibodies raised against NifH and NifD protein of Rhodospirillum rubrum (50, 51) diluted in 1.5% BSA (1:2,000) overnight at 4°C. The horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibody goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L)-HRP conjugate (Bio-Rad) was diluted at 1:5,000 in 1.5% BSA. Immunodetection was performed using Western blotting Luminol reagent (Millipore).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Huimin Zhao and his research group (University of Illinois) for introducing us to the use of the DNA Assembler method; Lingxia Zhao, Xiujun Duan, and Alicia Lohman for expert technical assistance; and members of the research groups of H.B.P., Costas Maranas, Tae Seok Moon, and Fuzhong Zhang for critical scientific discussions. D.L., M.L., J.Y., H.B.P., and M.B.-P. designed the experiments; D.L., M.L., J.Y., and M.B.-P. performed the experiments; D.L., M.L., H.B.P., and M.B.-P. wrote the paper.
This study was supported by the National Science Foundation (MCB-1331194).
Footnotes
Citation Liu D, Liberton M, Yu J, Pakrasi HB, Bhattacharyya-Pakrasi M. 2018. Engineering nitrogen fixation activity in an oxygenic phototroph. mBio 9:e01029-18. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01029-18.
REFERENCES
- 1.Stokstad E. 2016. The nitrogen fix. Science 353:1225–1227. doi: 10.1126/science.353.6305.1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Good A. 2018. Toward nitrogen-fixing plants. Science 359:869–870. doi: 10.1126/science.aas8737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vicente EJ, Dean DR. 2017. Keeping the nitrogen-fixation dream alive. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:3009–3011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1701560114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Burén S, Rubio LM. 2018. State of the art in eukaryotic nitrogenase engineering. FEMS Microbiol Lett 365:fnx274. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnx274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Curatti L, Rubio LM. 2014. Challenges to develop nitrogen-fixing cereals by direct nif-gene transfer. Plant Sci 225:130–137. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dos Santos PC, Fang Z, Mason SW, Setubal JC, Dixon R. 2012. Distribution of nitrogen fixation and nitrogenase-like sequences amongst microbial genomes. BMC Genomics 13:162. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hu Y, Ribbe MW. 2015. Nitrogenase and homologs. J Biol Inorg Chem 20:435–445. doi: 10.1007/s00775-014-1225-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mus F, Alleman AB, Pence N, Seefeldt LC, Peters JW. 2018. Exploring the alternatives of biological nitrogen fixation. Metallomics 10:523–538. doi: 10.1039/c8mt00038g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hu Y, Ribbe MW. 2013. Nitrogenase assembly. Biochim Biophys Acta 1827:1112–1122. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sickerman NS, Ribbe MW, Hu Y. 2017. Nitrogenase cofactor assembly: an elemental inventory. Acc Chem Res 50:2834–2841. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sickerman NS, Rettberg LA, Lee CC, Hu Y, Ribbe MW. 2017. Cluster assembly in nitrogenase. Essays Biochem 61:271–279. doi: 10.1042/EBC20160071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sickerman NS, Hu Y, Ribbe MW. 2017. Nitrogenase assembly: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol 595:261–302. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2017.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dixon RA, Postgate JR. 1972. Genetic transfer of nitrogen fixation from Klebsiella pneumoniae to Escherichia coli. Nature 237:102–103. doi: 10.1038/237102a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang L, Zhang L, Liu Z, Zhao D, Liu X, Zhang B, Xie J, Hong Y, Li P, Chen S, Dixon R, Li J. 2013. A minimal nitrogen fixation gene cluster from Paenibacillus sp. WLY78 enables expression of active nitrogenase in Escherichia coli. PLoS Genet 9:e1003865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yang J, Xie X, Wang X, Dixon R, Wang YP. 2014. Reconstruction and minimal gene requirements for the alternative iron-only nitrogenase in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:E3718–E3725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411185111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Smanski MJ, Bhatia S, Zhao D, Park Y, Woodruff LBA, Giannoukos G, Ciulla D, Busby M, Calderon J, Nicol R, Gordon DB, Densmore D, Voigt CA. 2014. Functional optimization of gene clusters by combinatorial design and assembly. Nat Biotechnol 32:1241–1249. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yang J, Xie X, Yang M, Dixon R, Wang YP. 2017. Modular electron-transport chains from eukaryotic organelles function to support nitrogenase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E2460–E2465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1620058114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cheng Q, Day A, Dowson-Day M, Shen GF, Dixon R. 2005. The Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase Fe protein gene (nifH) functionally substitutes for the chlL gene in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 329:966–975. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.02.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zamir A, Maina CV, Fink GR, Szalay AA. 1981. Stable chromosomal integration of the entire nitrogen fixation gene cluster from Klebsiella pneumoniae in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 78:3496–3500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.López-Torrejón G, Jiménez-Vicente E, Buesa JM, Hernandez JA, Verma HK, Rubio LM. 2016. Expression of a functional oxygen-labile nitrogenase component in the mitochondrial matrix of aerobically grown yeast. Nat Commun 7:11426. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pérez-González A, Kniewel R, Veldhuizen M, Verma HK, Navarro-Rodríguez M, Rubio LM, Caro E. 2017. Adaptation of the GoldenBraid modular cloning system and creation of a toolkit for the expression of heterologous proteins in yeast mitochondria. BMC Biotechnol 17:80. doi: 10.1186/s12896-017-0393-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Burén S, Young EM, Sweeny EA, Lopez-Torrejón G, Veldhuizen M, Voigt CA, Rubio LM. 2017. Formation of nitrogenase NifDK tetramers in the mitochondria of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Synth Biol 6:1043–1055. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.6b00371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Allen RS, Tilbrook K, Warden AC, Campbell PC, Rolland V, Singh SP, Wood CC. 2017. Expression of 16 nitrogenase proteins within the plant mitochondrial matrix. Front Plant Sci 8:287. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ivleva NB, Groat J, Staub JM, Stephens M. 2016. Expression of active subunit of nitrogenase via integration into plant organelle genome. PLoS One 11:e0160951. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Oldroyd GE, Dixon R. 2014. Biotechnological solutions to the nitrogen problem. Curr Opin Biotechnol 26:19–24. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2013.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Falcón LI, Magallón S, Castillo A. 2010. Dating the cyanobacterial ancestor of the chloroplast. ISME J 4:777–783. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2010.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Stöckel J, Welsh EA, Liberton M, Kunnvakkam R, Aurora R, Pakrasi HB. 2008. Global transcriptomic analysis of Cyanothece 51142 reveals robust diurnal oscillation of central metabolic processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:6156–6161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711068105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Červený J, Sinetova MA, Valledor L, Sherman LA, Nedbal L. 2013. Ultradian metabolic rhythm in the diazotrophic cyanobacterium Cyanothece sp. ATCC 51142. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:13210–13215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301171110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bandyopadhyay A, Elvitigala T, Welsh E, Stöckel J, Liberton M, Min H, Sherman LA, Pakrasi HB. 2011. Novel metabolic attributes of the genus Cyanothece, comprising a group of unicellular nitrogen-fixing cyanothece. MBio 2:e00214. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00214-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bandyopadhyay A, Elvitigala T, Liberton M, Pakrasi HB. 2013. Variations in the rhythms of respiration and nitrogen fixation in members of the unicellular diazotrophic cyanobacterial genus Cyanothece. Plant Physiol 161:1334–1346. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.208231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Shih PM, Wu D, Latifi A, Axen SD, Fewer DP, Talla E, Calteau A, Cai F, Tandeau de Marsac N, Rippka R, Herdman M, Sivonen K, Coursin T, Laurent T, Goodwin L, Nolan M, Davenport KW, Han CS, Rubin EM, Eisen JA, Woyke T, Gugger M, Kerfeld CA. 2013. Improving the coverage of the cyanobacterial phylum using diversity-driven genome sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:1053–1058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217107110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Shao Z, Zhao H, Zhao H. 2009. DNA assembler, an in vivo genetic method for rapid construction of biochemical pathways. Nucleic Acids Res 37:e16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Taton A, Unglaub F, Wright NE, Zeng WY, Paz-Yepes J, Brahamsha B, Palenik B, Peterson TC, Haerizadeh F, Golden SS, Golden JW. 2014. Broad-host-range vector system for synthetic biology and biotechnology in cyanobacteria. Nucleic Acids Res 42:e136. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Temme K, Zhao D, Voigt CA. 2012. Refactoring the nitrogen fixation gene cluster from Klebsiella oxytoca. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:7085–7090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1120788109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gosink MM, Franklin NM, Roberts GP. 1990. The product of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifX gene is a negative regulator of the nitrogen fixation (nif) regulon. J Bacteriol 172:1441–1447. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1441-1447.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ng AH, Berla BM, Pakrasi HB. 2015. Fine-tuning of photoautotrophic protein production by combining promoters and neutral sites in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:6857–6863. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01349-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Liu D, Pakrasi HB. 2018. Exploring native genetic elements as plug-in tools for synthetic biology in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Microb Cell Fact 17:48. doi: 10.1186/s12934-018-0897-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tamagnini P, Leitão E, Oliveira P, Ferreira D, Pinto F, Harris DJ, Heidorn T, Lindblad P. 2007. Cyanobacterial hydrogenases: diversity, regulation and applications. FEMS Microbiol Rev 31:692–720. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhang X, Sherman DM, Sherman LA. 2014. The uptake hydrogenase in the unicellular diazotrophic cyanobacterium Cyanothece sp. strain PCC 7822 protects nitrogenase from oxygen toxicity. J Bacteriol 196:840–849. doi: 10.1128/JB.01248-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wünschiers R, Batur M, Lindblad P. 2003. Presence and expression of hydrogenase specific C-terminal endopeptidases in cyanobacteria. BMC Microbiol 3:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-3-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Stanier RY, Deruelles J, Rippka R, Herdman M, Waterbury JB. 1979. Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. Microbiology 111:1–61. doi: 10.1099/00221287-111-1-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bergkessel M, Guthrie C. 2013. Chemical transformation of yeast. Methods Enzymol 529:311–320. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-418687-3.00026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gibson DG, Young L, Chuang RY, Venter JC, Hutchison CA III, Smith HO. 2009. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat Methods 6:343–345. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Golden SS, Brusslan J, Haselkorn R. 1987. Genetic engineering of the cyanobacterial chromosome. Methods Enzymol 153:215–231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Williams JGK. 1988. Construction of specific mutations in photosystem II photosynthetic reaction center by genetic engineering methods in Synechocystis 6803. Methods Enzymol 167:766–778. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kruse O, Rupprecht J, Mussgnug JH, Dismukes GC, Hankamer B. 2005. Photosynthesis: a blueprint for solar energy capture and biohydrogen production technologies. Photochem Photobiol Sci 4:957–970. doi: 10.1039/b506923h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Oda Y, Samanta SK, Rey FE, Wu L, Liu X, Yan T, Zhou J, Harwood CS. 2005. Functional genomic analysis of three nitrogenase isozymes in the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris. J Bacteriol 187:7784–7794. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.22.7784-7794.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bandyopadhyay A, Stöckel J, Min H, Sherman LA, Pakrasi HB. 2010. High rates of photobiological H2 production by a cyanobacterium under aerobic conditions. Nat Commun 1:139. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Montoya JP, Voss M, Kahler P, Capone DG. 1996. A simple, high-precision, high-sensitivity tracer assay for N2 fixation. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:986–993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Colón-López MS, Sherman DM, Sherman LA. 1997. Transcriptional and translational regulation of nitrogenase in light-dark- and continuous-light-grown cultures of the unicellular cyanobacterium Cyanothece sp. strain ATCC 51142. J Bacteriol 179:4319–4327. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.13.4319-4327.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Grunwald SK, Lies DP, Roberts GP, Ludden PW. 1995. Posttranslational regulation of nitrogenase in Rhodospirillum rubrum strains overexpressing the regulatory enzymes dinitrogenase reductase ADP-ribosyltransferase and dinitrogenase reductase activating glycohydrolase. J Bacteriol 177:628–635. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.3.628-635.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Curatti L, Brown CS, Ludden PW, Rubio LM. 2005. Genes required for rapid expression of nitrogenase activity in Azotobacter vinelandii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:6291–6296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501216102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Han Y, Lu N, Chen Q, Zhan Y, Liu W, Lu W, Zhu B, Lin M, Yang Z, Yan Y. 2015. Interspecies transfer and regulation of Pseudomonas stutzeri A1501 nitrogen fixation island in Escherichia coli. J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1339–1348. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1502.02027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kavanagh EP, Hill S. 1993. Oxygen inhibition of nitrogenase activity in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Gen Microbiol 139:1307–1314. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-6-1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Growth of engineered strains compared to the wild-type strain of Synechocystis 6803. Cells were cultured in BG11 medium under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions. Error bars represent the standard deviations of results from at least three independent experiments. Download FIG S1, PDF file, 0.05 MB (49.4KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Schematic map of plasmids used for expression of nif genes in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Replicating plasmids (A) pSyNif-1 (pSL2379) and (B) pSyNif-2 (pSL2397) were constructed using the DNA assembler method and introduced into the wild-type strain of Synechocystis 6803 by conjugation. The components of the plasmids are labeled as follows: backbone containing the bacterial replication machinery (gray), yeast helper fragment containing CEN6 and ARS H4 as an ori and containing ura3 as a selection marker (black), and the nif gene cluster from Cyanothece ATCC 51142. The colors of the nif genes are the same as in Fig. 1. Download FIG S2, PDF file, 0.3 MB (342.9KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Transcription of nif genes in engineered Synechocystis 6803. (A) Transcripts of nif genes in Synechocystis 6803 strain TSyNif-2. Gene expression was detected by RT-PCR. Lanes 1 to 24 show genes from nifT to hesB in the cluster (Fig. 1B). (B to G) Expression of nifHDK and surrounding genes was examined in each engineered strain shown in Fig. 2 by RT-PCR. (B) TSyNif-3 (23 genes without hesB compared to TSyNIf-2). (C) TSyNif-4 (22 genes without hesAB compared to TSyNif-2). (D) TSyNif-5 (23 genes without nifT compared to TSyNif-2). (E) TSyNif-6 (22 genes without nifTZ compared to TSyNif-2). (F) TSyNif-7 (23 genes without nifX compared to TSyNif-2). (G) TSyNif-8 (23 genes without nifW compared to TSyNif-2). Cultures for RNA extraction were grown under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions in BG110 medium. Download FIG S3, PDF file, 4.3 MB (4.4MB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Improvement of nitrogen fixation activity by increasing plasmid copy number. (A and B) Schematic maps of plasmid pSyNif-10 and plasmid pSyNif-11 containing the nif cluster with 24 genes from nifT to hesB. The backbone (dark blue) is from endogenous plasmid pCB2.4 and plasmid pCC5.2 of Synechocystis 6803, respectively. (C) Comparison of nitrogen fixation activities in engineered strains measured by 15N assimilation assay. (D) Western blot showing the presence of the NifD protein in engineered Synechocystis 6803 cells. Lanes 1 to 3 represent 1.0 µg, 0.5 µg, and 0.25 µg purified NifD-His protein from E. coli, respectively; lanes 4 to 9 represent 15 µg whole-cell extracts of TSyNif-9, TSyNif-10, TSyNif-11, TSyNif-1, TSyNif-2, and the Synechocystis 6803 wild-type strain, respectively. Samples were collected from cultures grown under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions in BG110 medium. Error bars represent the standard deviations of results from at least three independent experiments. Download FIG S4, PDF file, 0.5 MB (559.2KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Characteristics of engineered Synechocystis 6803 strain TSyNif-2. (A) Comparison of nitrogenase activities in the TSyNif-2 strain under four different conditions. (B) Transcript levels of nifH, nifD, and nifK genes in TSyNif-2 strains were assayed by q-PCR. RNA was extracted from the cells grown under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions. Error bars represent the standard deviations of results from three independent replicates. Download FIG S5, PDF file, 0.1 MB (83.5KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Transcriptional analysis of uptake hydrogenase genes. (A and B) RT-PCR analysis of hupSL and hupW genes in the (A) TSyNif-12 and (B) TSyNif-13 strains. Lanes 1 to 3 in both panels represent samples collected from BG11 medium, and lanes 4 to 6 represent samples collected from BG110 medium. RNA was extracted from the cells grown under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions. M, molecular mass standards. Download FIG S6, PDF file, 1.3 MB (1.4MB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Impact of various nif gene inactivations on nitrogenase activity in different engineered strains. Relative levels of activities with respect to that determined for the respective engineered strain with wild-type nif cluster are indicated. Download TABLE S1, PDF file, 0.05 MB (53KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Strains and plasmids used in this study. Download TABLE S2, PDF file, 0.1 MB (80.7KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Primers used in this study. Download TABLE S3, PDF file, 0.1 MB (79.2KB, pdf) .
Copyright © 2018 Liu et al.
This content is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.