Abstract
Hypokalemic periodic paralysis is a skeletal muscle disease characterized by episodic weakness associated with low serum potassium. We compared clinical and biophysical effects of R222W, the first hNaV1.4 domain I mutation linked to this disease. R222W patients exhibited a higher density of fibers with depolarized resting membrane potentials and produced action potentials that were attenuated compared to controls. Functional characterization of the R222W mutation in heterologous expression included the inactivation deficient IFM/QQQ background to isolate activation. R222W decreased sodium current and slowed activation without affecting probability. Consistent with the phenotype of muscle weakness, R222W shifted fast inactivation to hyperpolarized potentials, promoted more rapid entry, and slowed recovery. R222W increased the extent of slow inactivation and slowed its recovery. A two-compartment skeletal muscle fiber model revealed that defects in fast inactivation sufficiently explain action potential attenuation in patients. Molecular dynamics simulations showed that R222W disrupted electrostatic interactions within the gating pore, supporting the observation that R222W promotes omega current at hyperpolarized potentials. Sodium channel inactivation defects produced by R222W are the primary driver of skeletal muscle fiber action potential attenuation, while hyperpolarization-induced omega current produced by that mutation promotes muscle fiber depolarization.
Introduction
Familial hypokalemic periodic paralysis (HypoPP) is an autosomal dominant skeletal muscle disease characterized by episodes of flaccid muscle weakness in response to decreased serum potassium. Spontaneous episodes typically begin in the first two decades of life, triggered by hypokalemia induced by insulin secretion following carbohydrate-rich meals, glucocorticoids from stress or infection, or potassium reuptake in muscle at rest after strenuous work. Nearly all mutations causing familial HypoPP are found in voltage-gated ion channels of skeletal muscle, such as the hCaV1.1 calcium channel (encoded by CACNA1S) in type I HypoPP, or the homologous hNaV1.4 sodium channel (encoded by SCN4A) in type II HypoPP1,2. Mutations in inwardly-rectifying potassium channels have been identified in non-familial forms of periodic paralysis3. Voltage-gated ion channels share a common functional architecture, with a voltage sensor module (S1-S4 segments) and a pore module (S5-S6 segments). Neutralization of positively charged arginine residues in voltage-sensing S4 segments is a recurrent pattern for HypoPP mutations in calcium and sodium channels. These S4 alpha helices move outwardly with membrane depolarization and induce voltage-sensitive opening of the central conducting alpha pore.
In type II HypoPP, generalized sodium channel gating defects include reduced current density and enhanced fast or slow inactivation (reviewed in4). These findings do not explain why muscle fibers from patients exhibit a depolarization of membrane potential in low extracellular potassium5–7. Several studies have implicated an aberrant “omega current” through the voltage sensor module as a contributing factor towards this paradoxical depolarization (reviewed in1,4,8,9). Recent models predict that at resting potential, the outermost S4 arginine (R1) separates the extracellular space from cytoplasm by occluding a narrow constriction in the voltage sensor. This constriction, termed the gating charge transfer center or ‘gating pore’, is lined with a conserved aromatic S2 residue and conserved negative countercharges in S2 and S3. As the gating pore is sequentially occupied by arginines in the second and third positions in S4 (R2 and R3) with depolarization, transient interactions are made between these positively charged S4 residues and the residues of the gating charge transfer center8,10. Mutations that replace the bulky guanidyl side chain of an S4 arginine with a residue containing a smaller side chain abolish the separation between the cytoplasm and extracellular fluid and cause a proton- or cation-selective omega current that flows through the gating pore constriction. Mutations at R1 or R2 produce an omega current with membrane hyperpolarization11–13, while mutations at R3 produce this current with depolarization14,15. Thus, HypoPP S4 mutations may affect not only the voltage sensitivity and amplitude of the central alpha pore current, but also uncover an omega gating pore current that contributes to the clinical features of the channelopathy.
To date, S4 mutations associated with type II HypoPP have been identified in domains DI - DIII of hNaV1.416. The first DI-S4 mutation associated with HypoPP (R222W) was reported at R216,17. Affected family members presented with a clinical phenotype of respiratory insufficiency during severe weakness, with a fatal outcome of one member. Here, we report an additional family with the R222W mutation and characterize its effects in patient muscle fibers, in heterologous expression, and with computational simulations. Results from this combined approach to the investigation of R222W show that the mutation attenuates action potentials in patient muscle fibers by enhancing sodium channel inactivation and depolarizes muscle fibers by promoting an inwardly directed omega current. Our findings extend the investigation of HypoPP sodium channel mutations on skeletal muscle fiber excitability to include DI-S4 and are discussed with respect to the function of this channel region.
Results
Patients
The 52-year-old male proband had spontaneous morning paralytic attacks of 2-3 hours in duration, typically in the upper extremities. Complete tetraplegia occurred at age 18 and again at age 19. The weakness spells were associated with mild hypokalemia, 3-fold increased creatine kinase values, and myalgias that outlasted the weakness by several hours. Onset was at age 18, and frequency of attacks was once quarterly. The patient reported cold environment as a triggering factor. Additionally, a carbohydrate-rich meal on the ward at night triggered a weakness spell in the morning. Thyroid hormone levels were normal. An EMG of the tibialis anterior muscle showed a mild myopathic pattern but no pathologic spontaneous activity. The histology of the latissimus dorsi muscle revealed mild type 2 single fiber atrophy. Electron microscopy showed a proliferation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum but no tubular aggregates. Because of the predominant myalgias, muscle activities of forward and backward carnitine palmityl transferase were measured and were found normal, as were all routinely determined muscular enzyme activities. Molecular genetics identified a heterozygous hNaV1.4-R222W mutation (SCN4A-C664T) in the patient and three family members without history of weakness episodes (two females, one male).
In-vitro studies on native muscle fibers
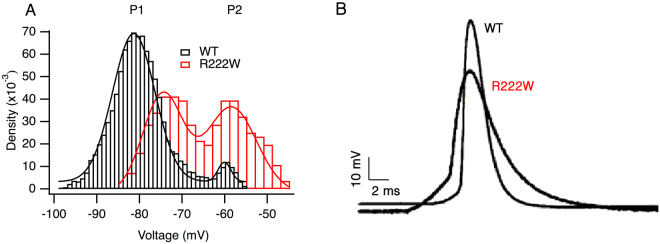
In bath solution containing 4 mM extracellular K+, excised control or patient R222W muscle fibers showed a bimodal distribution of resting membrane potentials (Fig. 1A). Gaussian fitting revealed peak values of P1 = −74.5 ± 0.4 mV in R222W (χ2 = 1.2 × 10−5), which were depolarized compared to control fibers (−80.9 ± 0.1 mV; χ2 = 4.0 × 10−6) and P2 values which were similar (−58.4 ± 0.4 mV for R222W and −60.2 ± 0.4 mV for controls). A larger fraction of patient fibers populated the P2 state compared to control fibers, suggesting an increased tendency to depolarize. Here, the respective densities for P1 and P2 were 0.56 and 0.52 in patient fibers, compared to 0.80 and 0.04 for control fibers. Decreasing the extracellular K+ to 1 mM severely depolarized patient muscle fiber potentials to a single peak at −50.0 mV ± 0.4 mV (data not shown). In contrast, control fibers in 1 mM K+ reveal a trimodal distribution15, with peaks at −89.7 ± 0.6, −72.7 ± 0.2, and −52.2 ± 0.5 mV, and with a larger fraction of muscle fibers at the more negative membrane potentials (respective densities of 0.14, 0.68, 0.25).
Figure 1.
R222W affects resting and action potentials in muscle fibers. The density of muscle fibers at various resting membrane potentials shows peaks at P1 (hyperpolarized) and P2 (depolarized) for control and R222W (A). P1 peaks are −80.9 ± 0.1 mV (control) and −74.5 ± 0.4 mV (R222W), with P2 peaks at −60.2 ± 0.4 mV (control) and −58.4 ± 0.4 mV (R222W). Action potentials in R222W (n = 10) fibers have a maximum amplitude of −8 ± 5 mV, significantly (P ≤ 0.05) less than that for control fibers (n = 6) at +11 ± 8 mV (B).
Action potentials of fibers harboring the R222W mutation showed undershoots of −8 mV ± 5 mV (n = 10) instead of overshoots as in control fibers (+11 ± 8 mV, n = 6, P ≤ 0.05) in accordance with a partially inactivated sodium channel population (Fig. 1B). The maximum rates of rise of R222W action potentials elicited from a holding potential of −80 mV were 0.2 ± 0.03 V/ms (n = 10) and therefore about 30% less than those from control fibers (0.3 ± 0.04 V/ms, n = 6, P ≤ 0.01, data not shown), also suggesting a reduced sodium channel availability.
Cut-open oocyte recordings: gating parameters
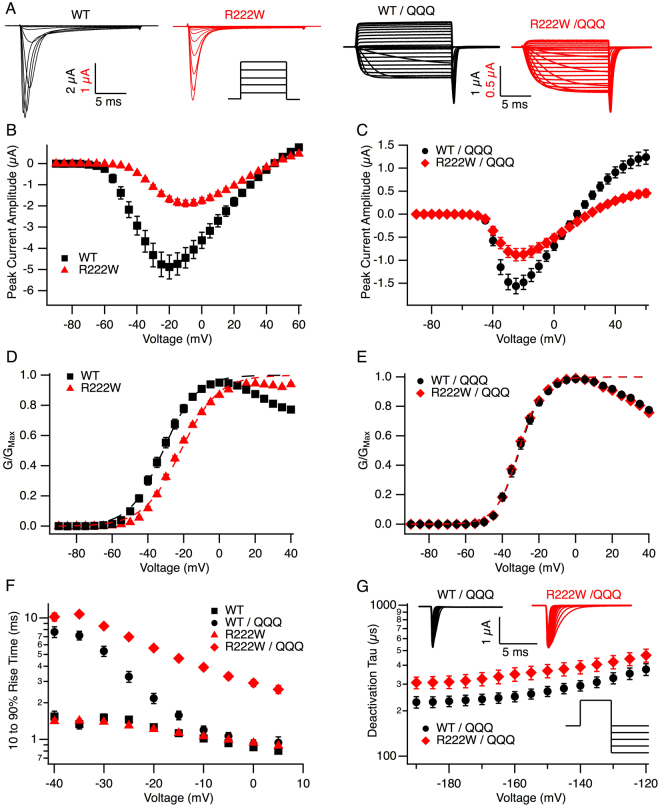
To determine whether hypoexcitability associated with the R222W mutation results from defects in sodium channel inactivation or depolarizing omega current, we characterized biophysical properties of mutant and wild type hNaV1.4 channels in heterologous expression, with results summarized in Table 1. R222W decreased peak current amplitude compared to wild type (P < 0.01; Fig. 2B) and significantly decreased the probability of activation, as indicated by a 10 mV depolarizing shift of G/V midpoint, and a significantly reduced slope (both P < 0.0001; Fig. 2D). In contrast, R222W did not affect activation kinetics calculated from 10–90% rise time (P = 0.3 at −10 mV; Fig. 2F).
Table 1.
Summary of electrophysiology results. Gating parameters obtained from WT or R222W channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes at 20 °C.
| Parameter | WT | R222W | Statistical Significance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SEM | N | Mean ± SEM | n | ||
| Peak Current Amplitude | |||||
| Native (µA) | −4.9 ± 0.6 | 126 | −1.9 ± 0.2 | 73 | U197 = 11515, P < 0.01 |
| IFM/QQQ (µA) | −1.6 ± 0.1 | 17 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 21 | t36 = 3.23, P = 0.003 |
| Activation Native | |||||
| Conductance midpoint (mV) | −32.3 ± 1.2 | 88 | −22.6 ± 0.7 | 81 | U167 = 1676, P < 0.0001 |
| Conductance slope | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 88 | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 81 | U167 = 774, P < 0.0001 |
| 10–90% Rise Time τ −10 mV (ms) | 1.0 ± 0.04 | 48 | 1.1 ± 0.03 | 73 | t119 = 0.92, P = 0.3 |
| Activation IFM/QQQ | |||||
| Conductance midpoint (mV) | −30.9 ± 0.9 | 48 | −31 ± 0.6 | 63 | U109 = 1453, P = 0.7 |
| Conductance slope | 5.8 ± 0.3 | 48 | 5.1 ± 0.2 | 63 | U109 = 1208, P = 0.07 |
| 10–90% rise time τ −10 mV (ms) | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 43 | 3.9 ± 0.2 | 45 | U86 = 29, P < 0.0001 |
| Deactivation IFM/QQQ | |||||
| τ at −160 mV (ms) | 0.3 ± 0.03 | 26 | 0.4 ± 0.04 | 29 | U53 = 239, P < 0.05 |
| Steady-State Fast Inactivation | |||||
| Midpoint (mV) | −59.4 ± 0.8 | 61 | −86.7 ± 0.9 | 53 | t112 = 23.7, P < 0.0001 |
| Slope | 5.1 ± 0.1 | 61 | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 53 | U112 = 718, P < 0.0001 |
| Open-state τ −20 mV (ms) | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 53 | 1.1 ± 0.03 | 50 | U101 = 920.5, P < 0.01 |
| Closed-state τ −65 mV (ms) | 22.7 ± 1.3 | 28 | 25.3 ± 2.3 | 40 | U66 = 526, P = 0.7 |
| Recovery τ −100 mV (ms) | 2.27 ± 0.02 | 17 | 41.4 ± 5.9 | 5 | U20 = 0.000, P < 0.0001 |
| Slow Inactivation | |||||
| Steady-state midpoint (mV) | −54.9 ± 2.9 | 32 | −96.1 ± 2.1 | 34 | U64 = 1043, P < 0.0001 |
| Steady-state slope | 0.8 ± 0.08 | 32 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 34 | U64 = 965, P < 0.0001 |
| Onset τ (s) | 28.2 ± 4.8 | 22 | 36.9 ± 8.6 | 17 | U37 = 175, P = 0.7 |
| Recovery τ (s) | 6.5 ± 0.9 | 25 | 37.1 ± 6.6 | 27 | U50 = 67, P < 0.0001 |
Figure 2.
R222W slows activation and deactivation. Traces of sodium currents in response to step depolarizations from −90 to +60 mV for 20 ms are shown in (A), along with a schematic of the protocol for activation. I/V relationships are plotted for WT (n = 126) and R222W (n = 73) in (B) and compared in (C) utilizing the IFM/QQQ background (n = 17 and n = 21, respectively). G/V relationships fit to a Boltzmann function with the asymptote held at one are shown in (D, native background) and (E, IFM/QQQ background). R222W produces a +10.4 mV shift compared to WT in the native (n = 81 and n = 88, respectively), but not IFM/QQQ background (n = 63 and n = 48, respectively). Times for 10–90% rise to peak activation are shown in (F) for WT and mutant channels with the native (n = 48 and n = 73, respectively) or IFM/QQQ background (n = 43 and n = 45, respectively). Activation is slowed by R222W in the absence of IFM-mediated inactivation. Deactivation time constants are shown in (G) for WT/QQQ (n = 26) and R222W/QQQ (n = 29). R222W/QQQ slows deactivation as determined from tail currents (shown in inset) elicited by depolarizing channels to the empirical reversal potential for 30 ms, followed by 20 ms hyperpolarizing commands from −190 to −120 mV. Values are shown in Table 1.
The inactivation deficient IFM/QQQ background18 was used to isolate activation and deactivation from indirect effects of fast inactivation on measured sodium currents. R222W/QQQ significantly decreased peak current amplitude (P < 0.01; Fig. 2C) but was without effect on activation probability compared to hNaV1.4/QQQ (P = 0.7 for midpoint, P = 0.07 for slope; Fig. 2E). However, activation and deactivation kinetics were each slowed by R222W compared to hNaV1.4 in the IFM/QQQ background (activation at −10 mV, P < 0.0001; Fig. 2F; deactivation at −160 mV, P < 0.05; Fig. 2G).
The observed decrease in probability of activation in R222W channels might be due to enhanced fast inactivation. R222W produced a 27 mV hyperpolarizing shift in the midpoint of the steady-state fast inactivation curve, and with a decreased slope (both P < 0.0001; Fig. 3A). Closed-state fast inactivation in R222W and wild type hNaV1.4 are compared at −65 mV in Fig. 3B. While R222W elicited greater completion than hNaV1.4 at this voltage (91 ± 0.8% versus 21 ± 1.6%, P < 0.0001), kinetics of closed-state entry into fast inactivation were similar (P = 0.7). R222W accelerated open-state entry into fast inactivation (Fig. 3C) and slowed recovery (−100 mV, P < 0.0001; Fig. 3D).
Figure 3.
R222W stabilizes the fast-inactivated state. Steady-state fast inactivation is shown in (A). Channels were conditioned for 300 ms from −140 mV to +20 mV, and channel availability tested with 20 ms, −20 mV test pulses (inset). R222W (n = 53) produces a −27 mV shift in the midpoint of the steady state fast inactivation curve compared to WT (n = 61). Time course of closed-state inactivation is shown in (B) for a variable-duration conditioning potential of −65 mV (protocol used shown in inset); R222W (n = 40) elicits more complete inactivation than WT (n = 28). Onset of fast inactivation from the open state is shown in (C). Compared to WT (n = 53), R222W (n = 50) accelerates open-state fast inactivation as determined from the decay of sodium currents in response to 20 ms step depolarizations from −40 mV to +20 mV. Recovery from fast inactivation is shown in (D). R222W (n = 5) slows recovery compared to WT (n = 17), measured by a double pulse protocol in which channels were inactivated for 100 ms and hyperpolarized (−100 mV shown) for increasing durations, followed by a 20 ms, −20 mV test pulse to test channel availability. Values are shown in Table 1.
Slow inactivation parameters were determined as putative, additional gating defects for the R222W mutation. Slow inactivation in hNaV1.4 reached 77 ± 2% completion (Fig. 4A), consistent with patch-clamp studies of this isoform expressed in oocytes19. R222W increased completion of slow inactivation to 96 ± 0.5% (P < 0.0001), produced a 41 mV hyperpolarizing shift of midpoint, and with increased slope (both P < 0.0001). Whereas onset of slow inactivation was similar in R222W and hNaV1.4 (Fig. 4B), R222W prolonged the recovery from slow inactivation (37 ± 7 s versus 6.5 ± 1 s, P < 0.0001; Fig. 4C). Taken together with the above results, our findings indicate that the R222W mutation stabilizes sodium channel inactivation and suggest that these effects are casual to the hypoexcitable phenotype.
Figure 4.
R222W enhances slow inactivation. In all experiments, channels were recovered from fast inactivation at −120 mV (20 ms) prior to a test pulse at −20 mV to assess channel availability. Steady-state slow inactivation is shown in (A) from experiments in which channels were conditioned to voltages shown for 90 s prior to test. R222W (n = 34) significantly increases the completion and probability of slow inactivation compared to WT (n = 32). In (B), onset of slow inactivation was determined from loss of channel availability following a variable duration (0 to 360 s) depolarization to 0 mV. R222W (n = 17) did not significantly affect onset of slow inactivation compared to WT (n = 22). For recovery (C), a 0 mV, 90 s command to promote slow inactivation was followed by variable duration (0 to 360 s) hyperpolarization at −120 mV and test. R222W (n = 27) slows recovery from slow inactivation compared to WT (n = 25). Values are shown in Table 1.
Cut-Open Oocyte Recordings: omega current
R222W, but not wild type hNaV1.4, produced an inwardly directed sodium current detected at voltages more negative than −40 mV (P < 0.01; Fig. 5). Omega current was not observed when Na+ was replaced by NMDG (N-methyl D-glucamine) as the relative cation in the external solution. Thus, the HypoPP mutation at DI-S4:R2 produced a cationic omega current in response to membrane hyperpolarization, as previously observed for type II HypoPP mutations at DII-S4:R213 or at DIII-S4:R220.
Figure 5.
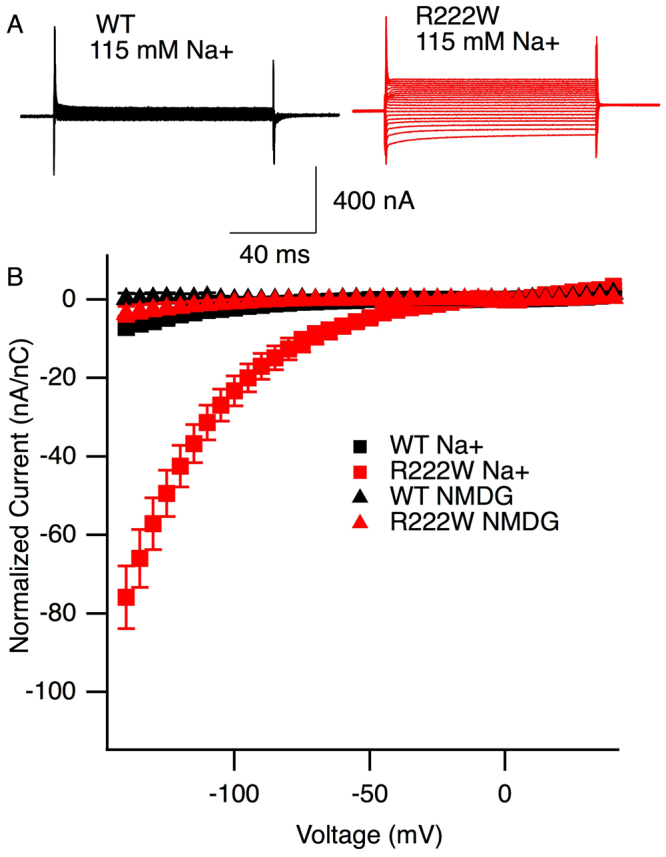
R222W promotes a cationic leak current. Current traces from TTX-blocked channels in response to step commands to voltages ranging from −140 mV to +40 mV are shown in (A) for WT and R222W, with 115 mM Na+ in the external bath solution. Ohmic current from −30 mV to +20 mV was subtracted from raw current values and normalized against anodic gating current recorded in response to +40 mV step depolarization. Plot of the normalized leak current as a function of gating charge at +40 mV is shown in (B, n = 8 to 12). With 115 mM Na+ external, R222W channels show an inwardly directed current at hyperpolarized voltages, not observed for WT channels. Ohmic responses are observed for R222W or WT when NMDG is used as the external cation.
Action potential modeling
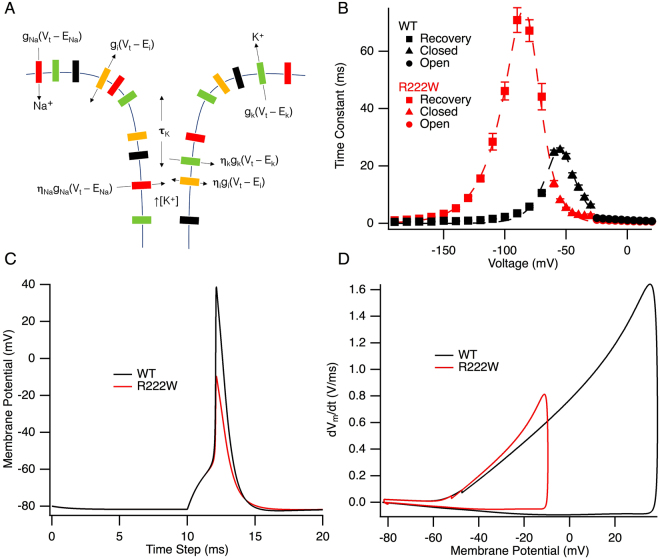
Summary time constants for the full range of voltages for entry into or recovery from the fast-inactivated state for hNaV1.4 or R222W are shown in Fig. 6B. Rate equations (Supplementary Table S2) were obtained from Gaussian fits to these curves and applied to the model as αh and βh parameters defining transition into, and exit from, the inactivated state. These empirically derived αh and βh constants were the only difference in parameters utilized to simulate WT and R222W action potentials. The simulated action potentials in R222W fibers showed an undershoot (peak height of −10 mV) compared to an overshoot in control fibers (peak height of +39 mV; Fig. 6C), a finding consistent with the observed effect of the mutation on action potentials recorded from patient muscle fibers. The phase diagram shows a slower peak rate of rise for R222W (0.8 V/ms) compared to WT (1.6 V/ms; Fig. 6D), also consistent with results from patient muscle fiber recordings.
Figure 6.
R222W action potential height is attenuated in simulation. A schematic of the main parameters used in the action potential model is shown in (A). The sarcolemma and t-tubule were both modeled, as well as potassium accumulation in the t-tubule. Barrier models of inactivation kinetics are shown in (B) for WT and R222W. Time constants were obtained at voltages from −190 mV to −70 mV (recovery), −60 mV to −30 mV (closed-state fast inactivation) and −25 mV to 20 mV (open-state fast inactivation). The fractional barrier distance is 0.50 for WT and 0.35 for R222W. The midpoint of the barrier is −55.1 mV for WT and −80.6 mV for R222W. These kinetic parameters were used to simulate wild type and R222W (attenuated) action potentials shown in (C), with peak height of the R222W action potential at −9.6 mV and that for WT at +38.7 mV. A phase diagram of the rate of voltage change is shown in (D). The peak rate of rise (0.8 V/ms) is 50% slower for R222W action potentials compared to WT (1.6 V/ms).
Molecular dynamics
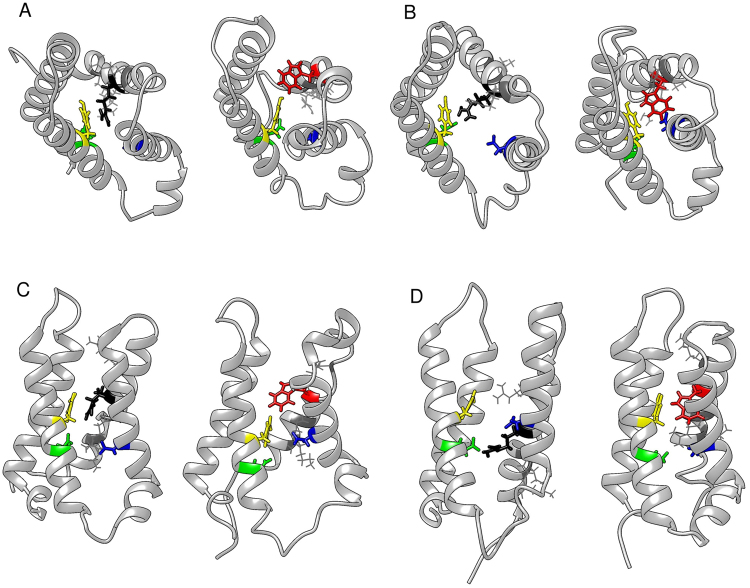
We utilized molecular dynamics simulations to examine the effect of tryptophan substitution at R222 on transient gating charge transfer center interactions during hyperpolarization, as a possible mechanism for R222W-elicited omega current. Here, the focus of investigation was the interaction of the residue at DI-S4:R2/W2 with the aromatic tyrosine in DI-S2 (Y168), and negative countercharges in DI-S2 (E171) and DI-S3 (D197). These conserved residues in the gating charge transfer center have been shown to interact with S4 residues and may occlude the gating pore10,21,22.
After the R222W and wild type models were equilibrated with the residue of interest above the gating pore, a hyperpolarizing force was applied to the membrane. The native arginine moved towards Y168 to occlude the gating pore whereas the substituted tryptophan at R2 rotated towards the hydrophobic lipid environment as it moved into the gating pore (Fig. 7A,C). When the residue of interest was equilibrated within the gating pore and a hyperpolarizing potential was applied, R222 interacted with E171 across the gating pore, while the substituted tryptophan did not (Fig. 7B,D).
Figure 7.
W222 distrupts interactions within the gating charge transfer center. As R222 (black) or W222 (red) enters the gating pore (A top view, C side view), the native arginine appears to interact with Y168 (yellow) while the subsituted tryptophan side chain moves away from Y168. Interaction and distance measurements are recorded in Supplementary Table S3. As R222 or W222 moves down through the gating pore (B top view, D side view), R222 interacts with E171 (green) across the gating pore, whereas W222 does not cross the gating pore to interact with E171. The gating charge transfer center asparate (D197, blue) does not interact with R222 or W222 in simulation.
We tested whether the large hydrophobic side chain of the substituted tryptophan interacted unfavorably with residues of interest in the gating pore (Y168, E171 and D197). For the wild type model, Van der Waals and electrostatic interaction energies were favorable between R222 and Y168 (Supplementary Table S3). However, in the R222W model, Van der Waals energy between the substituted tryptophan and Y168 were not as favorable and the residues experienced electrostatic repulsion. Electrostatic interaction with E171 was also disrupted by R222W.
Discussion
Of the two families reported with the R222W mutation, the previously reported family has a severe clinical phenotype that includes respiratory insufficiency during attacks17, while the presently reported family has a mild clinical phenotype characterized by episodes of weakness in the extremities. Additionally, both families contain affected and unaffected mutation carriers, suggesting incomplete penetrance of the mutation, an effect described previously for DII-S4:R2 HypoPP mutations R672S23 and R672H24.
The observed diversity in phenotype for individuals with identical DI-S4 SCN4A mutations reported here and previously17 suggests that multiple factors likely play a role in the extent of muscle fiber paralysis. If we assume that R222W muscle fibers contain 50% mutated channels, an assumption that is consistent with an autosomal dominant disease25, our electrophysiological measurements show that at the observed −75 mV resting potential of patient muscle fibers, 51% of sodium channels are available for activation. Given that the index patient exhibited episodic weakness but did not experience paralysis with fibers at this resting potential, we can conclude that this amount of channel inhibition does not abolish action potential initiation and elicit paralysis. However, depolarization by only −10 mV would bring channel availability to 37%, reducing the probability of action potential firing26. Additional mutational or epigenetic variation (possibly affecting Kir2.1 channels or Na/K ATPase activity) may contribute to putative differences in muscle fiber depolarization in affected versus unaffected family members and may be requisite to promote the full paralytic phenotype as reported for one individual with the R222W mutation17.
The DI-S4: R222W mutation enhances both fast and slow inactivation, and attenuates action potentials in patient muscle fibers. Other SCN4A HypoPP mutations including DII-S4: R672G/H/S6,23 or DIII-S4: R1135C/H15 also enhance inactivation, and action potentials from patient muscle fibers harboring R672G6 or R1135H15 are attenuated. While our findings suggest that effects of R222W on fast and slow inactivation are more pronounced than those observed for DII-S4 or DIII-S4 mutations, it should be noted that our results were obtained with the Xenopus oocyte expression system, unlike previous studies on HypoPP sodium channel gating. In a recent report in which R222W was expressed in human embryonic kidney 293 cells, tryptophan substitution at DIS4: R222 did not affect the probability of inactivation, and slowed entry into fast inactivation27. Results from studies utilizing different expression systems and recording configurations renders comparison of the magnitude of effects of HypoPP mutations across domains intractable at present. Nevertheless, in the present study we compared the effect of R222W on simulated skeletal muscle fiber action potentials to those obtained from patient action potential recordings. The comparison between fibers housing WT or 50% R222W mutant channels in simulation was based exclusively on our empirically-derived gating parameters for fast inactivation. Notably, our simulations accurately reiterated the attenuation of muscle fiber action potentials in the index HypoPP patient and suggest that stabilization of the fast-inactivated state is causal to the effect of R222W on these action potentials.
The effect of R222W on action potentials was more severe in simulation than in muscle fiber recordings. However, our finding that peak sodium current amplitude was reduced in mutant channels suggests that functional expression of R222W might be impaired in vivo, reducing the impact of a loss of function mutation. Our simulations assuming 50% mutated channels would therefore predict a more severe phenotype than that seen in patient recordings. Previous studies have shown that reduced mutant sodium channel expression disrupts the ratio of wild type to mutated channels and contributes to the overall disease phenotype25,28. Nevertheless, while the relative reduction in peak sodium current amplitude observed for R222W compared to hNaV1.4 is similar in studies using mammalian expression27 or Xenopus oocytes (this study), it is uncertain whether this effect is also overt in patient muscle fibers and thus contributes to membrane hypoexcitability.
R222W does not affect the probability of sodium channel activation. The finding of a recent report showing that the R222W mutation expressed in mammalian cells does not shift the midpoint of G/V relations27 is in agreement with our findings comparing the effects of wild type and R222W channels in the IFM/QQQ background, expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Specifically, R222W produces a right shift of the G/V curve in the native background as an indirect consequence of enhanced closed-state fast inactivation, since activation probability is equivalent for R222W and wild type channels in the IFM/QQQ background. However, we also found that R222W/QQQ slows both activation and deactivation, suggesting that steric hindrance of the bulky tryptophan side chain as it moves through the gating pore alters S4 movement in response to either depolarization or hyperpolarization. Slowed activation elicited with tryptophan substitution at DIS4:R2 may contribute to the observed slow rate of rise of action potentials in R222W patient muscle fibers.
It has been proposed that a proton- or cation-selective omega current is a general feature of S4 mutations in type I or type II HypoPP1,2,4,8,9. Our measurements of leak current show that R222W promotes inward sodium current with an amplitude and over a range of hyperpolarized voltages similar to that recently reported for this mutation27. Hyperpolarization-elicited gating pore currents are also observed in analogous NaV1.4 HypoPP S4 mutations at R2 in domains II and III11,13,20. This predominant inward omega current overpowers the small outward potassium current produced by inwardly rectifying potassium channels and causes a depolarizing shift in membrane potential from P1 to P27,29. Recordings from muscle fibers from the index patient of the present study showed a greater density of fibers in the depolarized (P2) state compared to controls, and this density shift of fiber potential towards P2 was markedly increased with lowered extracellular potassium. From our electrophysiological recordings, it would be expected that inward omega (sodium) current promoted by R222W is observed at the normal resting potential and is more pronounced with hyperpolarization in the setting of hypokalemia.
Although the emergence of omega current upon substitution of an S4 arginine with tryptophan, an amino acid with a bulky side chain, is surprising, we note that R to W mutations associated with type II HypoPP (DII-S4:R3 in hNaV1.414) or with arrhythmic dilated cardiomyopathy (DI-S4:R3 in hNaV1.530) also promote cationic omega current that contributes to the pathogenesis of disease. Our molecular dynamics simulations showing that hNaV1.4-R222W S4 translocation during hyperpolarization results in an unfavorable interaction of the aromatic residue within the gating charge transfer center are similar to molecular dynamics results for hNaV1.5-R225W30.
In addition, our simulations reveal a strong electrostatic interaction of S4-R222 with S2-E171 during hyperpolarization that may play a role in occlusion of the gating pore. The R222-E171 interaction is predicted in simulation for NaV1.421 and disruption of the analogous interaction with substitution of a bulky side chain at R2 (R1239H in CaV1.1 in type I HypoPP22) generates a gating pore permeation pathway in simulation. In our molecular dynamics simulations, electrostatic interactions in the gating charge transfer center involving NaV1.4-R222 are absent with tryptophan substitution, which may provide the permeation pathway for sodium during hyperpolarization. Thus, our findings from recordings of leak current and molecular dynamics simulations are consistent with the interpretation that R222W promotes an omega current responsible for the depolarizing effect observed in skeletal muscle fibers of the index patient.
Sodium channel fast inactivation is dictated by activation of the DIV voltage sensor31. Not surprisingly, hNaV1.4 channelopathy mutations in this domain have significant effects on inactivation. Paramyotonia congenita mutations at DIV-S4:R1 (R1448C/H/P/L/S32) destabilize the fast-inactivated state exhibited as slowed entry and accelerated recovery, while congenital myasthenic syndrome mutations at DIV-S4:R3 (R1454W33) or DIV-S4:R4 (R1457H34) stabilize the fast-inactivated state with a hyperpolarized midpoint and slowed recovery, in addition to promoting slow inactivation. Interestingly, mixed paramyotonia/periodic paralysis phenotypes with mutation at DIV-S4:R2 (R1451L35) are accounted for by slowed entry and accelerated recovery from fast inactivation, and a hyperpolarized midpoint of fast and slow inactivation.
For hypokalemic periodic paralysis mutations in the S4 segments of domains II or III, general effects include stabilization of fast and slow inactivation, and slowed recovery, also observed in the present study with DI-S4:R222W. Thus, while the role of DIV-S4 in promoting inactivation is well established, S4 movement in other domains also contributes to sodium channel inactivation. Chanda et al.36 showed that DIV-S4 movement is coupled to S4 translocation in domains DI to DIII, with the highest cooperativity occurring between DI-S4 and DIV-S4. While the mechanism of S4 cooperativity remains uncertain, our finding that R222W significantly enhances fast inactivation raises the possibility that R222 is a determinant in coupling of DI-S4/DIV-S4 translocations that dictate sodium channel inactivation.
Materials and Methods
Patients and in-vitro studies on native muscle fibers
Whole EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid) blood was taken from patients, with informed consent, for SCN4A mutation screening. Complete gene sequencing was performed using PCR amplification and Sanger sequencing as described previously6,37. Patient studies were approved by the institutional review board in Ulm (Ethics Commission of Ulm University) and conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Muscle specimens were removed with informed consent from the quadriceps muscles of the index patient of family HypoPP5 (R222W) and three adult individuals with no neuromuscular disease under regional anesthesia. Muscle specimens were about 28 mm in length and 5 mm in diameter. They were further prepared into small bundles and allowed to stabilize over 2 h in a solution also used for resting membrane and action potential measurements. This solution contained 108 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 1.5 mM CaCl2, 0.7 mM MgSO4, 26.2 mM NaHCO3, 1.7 mM NaH2PO4, 9.6 mM Na-gluconate, 5.5 mM glucose, 7.6 mM sucrose, 290 mosmol/L, maintained at 37 °C, with pH adjusted to 7.4 by bubbling with 95% O2 and 5% CO2. In some experiments, extracellular K+ was decreased to 1 mM.
Membrane potentials were measured using a voltage amplifier (Turbo TEC-05, NPI Electronic Instruments, Tamm, Germany) and glass microelectrodes filled with 3 M KCl and input resistances of 5 to 10 MΩ. Histograms of the potentials were smoothed by density estimation (weighted averaging of rounded points). Parameters were obtained from a Gaussian fit for each peak according to f(x) = y0 + (A/w*sqrt(π/2))*exp(−2*((x-xn)/w)^2) where y0 is the minimum asymptote, A is density, xn is midpoint voltage, and w is a width (mV) coefficient value for the peak in question. Membrane potentials exhibited a two or three-peak density distribution of polarized and depolarized fibers. Action potential recordings were performed with a second microelectrode. This electrode delivered a constant current to hold various resting potentials for at least 1 min to promote recovery of voltage-gated sodium channels. Then, action potentials were elicited by short depolarizing pulses.
Oocyte voltage clamp experiments
Attempts to express the R222W mutation in mammalian cells were not successful. Therefore, we used Xenopus oocytes to characterize gating parameters and investigate putative omega currents in the HypoPP mutant. The gene for the alpha subunit of hNaV1.4 (SCN4A) was housed in pSP64T, and the beta 1 subunit gene (SCN1B) in pGH19. The mutation coding for R222W was constructed by incorporating the following mutant oligonucleotide primers:
Forward: CATCTCAGCCCTGAGGACCTTCTGGGTGCTGC
Reverse: GCAGCACCCAGAAGGTCCTCAGGGCTGAGATG
into SCN4A with PCR amplification (Quik Change II XL, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). We also utilized the SCN4A construct coding for the DIII-DIV linker mutation IFM1303QQQ that eliminates sodium channel fast inactivation18. Plasmid constructs were linearized with EcoRI (alpha subunit) or HindIII (beta subunit). SP6 or T3 RNA polymerases (Ambion mMESSAGE mMACHINE, Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) were used for in vitro transcription of alpha or beta subunit mRNA respectively. These were co-injected into Xenopus oocytes at a mass ratio of 1:3 alpha/beta subunit mRNA. Oocytes were cultured in a medium containing 96 mM NaCl, 2 mM KCl, 1.8 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, 5 mM HEPES (4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazine ethane sulfonic acid), 1 mM Na pyruvate, with 3% horse serum and 100 mg/L gentamicin sulfate, at 17.5 °C with gentle agitation for 3 to 7 days prior to recordings. All procedures for surgeries and care of Xenopus frogs were conducted according to protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Idaho State University, following ALAC guidelines.
Central alpha pore currents were recorded with the cut-open oocyte configuration using a CA-1B amplifier (Dagan Corporation, Minneapolis, MN) and acquired with PatchMaster 2.37 software (HEKA, Bellmore, NY). External bath solution contained 2 mM CaOH2, 10 mM HEPES, 115 mM NaOH. The internal solution contained 115 mM N-methyl D-glucamine (NMDG), 10 mM HEPES, 2 mM EGTA (ethylene glycol bis(2-amino-ether) tetra-acetic acid). Oocytes were permeabilized by adding 0.5% saponin in internal solution to the bottom chamber. Glass microelectrodes with resistances of 0.6 to 0.9 MΩ were used for recording membrane potential against ground for voltage clamp. Leak currents were recorded in the same cut-open oocyte configuration. For these experiments, the external solution contained 2.5 mM BaOH to reduce background leak13 with Na+ or NMDG as the relevant cation. Channels were blocked with 2 µM TTX (tetrodotoxin; Alamone Laboratories, Jerusalem, Israel) after equilibration of oocyte interior for 40 min. All experiments were performed at 20 °C using a HCC-100A amplifier and Peltier device (Dagan). Data were acquired at 10 or 20 µs per point from voltage clamp protocols with leak subtraction using a p/4 protocol (omitted for leak current recordings) and with a holding potential of −120 mV. Sodium currents were analyzed with curve-fitting routines with PulseFit 8.67 and Igor Pro 6.37.
Activation conductance was determined from I/V relations according to equation (1)
| 1 |
where GNa is sodium conductance, INa is the peak sodium current amplitude, and (VM – ENa) is the driving force (test potential VM, empirical sodium reversal potential ENa). Normalized current amplitudes from steady-state G/V or inactivation curves were plotted against the conditioning voltage and fitted using a Boltzmann function using equation (2):
| 2 |
where G/GMAX is the normalized activation conductance, I/IMAX is the normalized channel availability, z is the apparent valence, e0 is the elementary charge, VM is the test potential, V0.5 is the midpoint, k is the Boltzmann constant and T is temperature in K.
Kinetics were calculated by fitting data according to equation (3):
| 3 |
where I(t) is sodium current as a function of time, A is the asymptote, τ is the time constant for deactivation (tD) or inactivation (tH), and offset is the plateau asymptote.
Action Potential Modeling
A two-compartment model of a skeletal muscle fiber was constructed in MATLAB using the Hodgkin-Huxley system of equations38 and methods similar to Cannon et al.39. Briefly, we modeled alteration of sarcolemmal and t-tubule membrane potential as a result of sodium, potassium and nonselective leak currents. Simulated muscle fibers were held at −80 mV until current was applied to stimulate an action potential. Sodium conductance was defined as m3h and potassium conductance was defined as n4. Voltage-dependent rate constants for sodium channel inactivation (h) were calculated from experimentally determined kinetics of fast inactivation entry and recovery. To test the specific effects of inactivation defects, the h parameter was the only difference between simulations of fibers containing native or R222W proteins. Gating parameters for sodium channel activation (m) and potassium channel activation (n) were from Cannon et al.39 and Filatov et al.40. However, the kβm parameter (Supplementary Table S1) was adjusted until slope and midpoint of the sodium channel activation G/V curve mimicked those obtained from experiments employing the IFM/QQQ background mutation. Simulated action potentials in a muscle fiber harboring the R222W mutation were created by defining sodium current from equation (4):
| 4 |
assuming equivalent sodium current contribution from wild type and mutant channels25,41. Equations and gating parameters used are summarized in supplementary information.
Molecular Modeling
An alignment of the top 100 most similar sequences to SCN4A was conducted using PSI-BLAST and the Clustal Omega server. Wild type and R222W homology models of hNaV1.4 DI were created using MODELLER with the crystal structure of a eukaryotic voltage-gated sodium channel used as the template (PDB 5X0M42). The residue of interest (R222 or W222) was positioned above the gating pore (Fig. 7A top view, C side view) or within the gating pore (Fig. 7B top view, D side view) using methods similar to Wood et al.43. The voltage sensor module (S1–S4) was embedded in a POPC (palmityl-o-phosphatidyl-choline) membrane, solvated with TIP3 (transferable intermolecular potential with 3 points), and ionized with 0.15 M NaCl using VMD (visual molecular dynamics) following methods similar to Groome et al.15. A CHARMM36 force field was used for the protein and the membrane. NAMD 2.9 (not another molecular dynamics) was used to run molecular dynamics simulations. The system was minimized for 1000 steps and lipid tails allowed to relax for 2 ns, followed by equilibration with the protein restrained for 6 ns. The entire system was allowed to relax until the RMSD (root mean square deviation) of the alpha carbons reached its asymptote. Hyperpolarization was simulated by applying a constant electric field perpendicular to the membrane to move R222 or W222 into, or through the gating pore. Trajectory analyses were completed using PLUMED, VMD RMSD calculator and NAMD Energy plug-ins.
Statistical analyses
Two-tailed Student’s t-tests were used to determine significant differences between data sets with equal variances, and two-tailed Mann-Whitney U tests were used when comparing data sets of unequal variances. An f-test of equality of variances was used to determine which test to use. Data are displayed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) unless otherwise noted, and criterion for statistical significance was set at P < 0.05. For goodness-of-fit tests used to evaluate the fit of models, the chi-squared value was reported.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the non-profit Else-Kröner-Fresenius Foundation, The German DGM Muscle Disease Society, Taro Pharmaceuticals, and the German BMBF Ministry for the IonNeurOnet project jointly to KJR and FLH, by NIH 1R15NS093579-01A1 to JRG and by an Institutional Development Award (IDeA) from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the NIH under Grant P20GM103408 to ISU. FLH is endowed Senior Research Professor of Neuroscience of the non-profit Hertie Foundation. The Idaho National Laboratory HPC was used for all molecular dynamics simulations through the Idaho University Consortium.
Author Contributions
L.B.E. and J.R.G. wrote the main text of the manuscript and prepared Figures. K.J.R. and F.L.H. contributed to writing the main text, and provided experimental data for Fig. 1. P.A. and V.W. provided experimental data for Figs 2–4, and 7, respectively. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Frank Lehmann-Horn is deceased.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1038/s41598-018-28594-5.
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Jurkat-Rott K, Groome JR, Lehmann-Horn F. Pathophysiological role of omega pore current in channelopathies. Front. Neuropharmacol. 2012;3:1–15. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2012.00112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cannon SC. Channelopathies of skeletal muscle excitability. Compr. Physiol. 2015;5:761–90. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c140062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cheng C-J, Kuo E, Huang C-L. Extracellular potassium homeostasis: insights from hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Semin. Nephrol. 2013;33:237–247. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2013.04.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Groome, J. R., Moreau, A. & Delemotte, L. Gating pore currents in sodium channels. In: Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology: Sodium channels and related disorders (ed. Chahine, M.) (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg) (2017). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 5.Rudel R, Lehmann-Horn F, Ricker K, Kuther G. Hypokalemic periodic paralysis: in vitro investigation of muscle fiber membrane parameters. Muscle Nerve. 1984;7:110–120. doi: 10.1002/mus.880070205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jurkat-Rott K, et al. Voltage sensor mutations cause hypokalemic periodic paralysis type 2 by enhanced inactivation and reduced current. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2000;97:9549–9554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.17.9549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jurkat-Rott K, et al. K+ -dependent paradoxical membrane depolarization and Na+ overload, major and reversible contributors to weakness by ion channel leaks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:4036–4041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811277106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Moreau A, Gosselin-Badaroudine P, Chahine M. Biophysics, pathophysiology, and pharmacology of ion channel gating pores. Front. Pharmacol. 2014;5:1–19. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cannon SC. Voltage-sensor mutations in channelopathies of skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 2010;588:1887–1895. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.186874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tao X, Lee A, Limapichat W, Dougherty D, MacKinnon R. A gating charge transfer center in voltage sensors. Science. 2010;328:67–73. doi: 10.1126/science.1185954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sokolov S, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. Gating pore currents in an inherited channelopathy. Nature. 2007;446:76–78. doi: 10.1038/nature05598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Struyk AF, Cannon SC. A Na+ channel mutation linked to hypokalemic periodic paralysis exposes a proton-selective gating pore. J. Gen. Physiol. 2007;130:11–20. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200709755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Struyk AF, Markin VS, Francis D, Cannon SC. Gating pore currents in DIIS4 mutations of NaV1.4 associated with periodic paralysis: saturation of ion flux and implications of disease pathogenesis. J. Gen. Physiol. 2008;132:447–54. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200809967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sokolov S, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. Depolarization-activated gating pore current conducted by mutant sodium channels in potassium-sensitive normokalemic periodic paralysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2008;105:19980–19985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810562105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Groome JR, et al. NaV1.4 mutations cause hypokalemic periodic paralysis by disrupting IIIS4 movement during recovery. Brain. 2014;137:998–1008. doi: 10.1093/brain/awu015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Matthews E, et al. Voltage sensor loss accounts for most cases of hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Neurology. 2009;72:1544–1547. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000342387.65477.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Park YH, Kim JB. An atypical phenotype of hypokalemic periodic paralysis caused by a mutation in the sodium channel gene SCN4A. Korean J. Pediatr. 2010;53:909–912. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2010.53.10.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.West JW, et al. A cluster of hydrophobic amino acid residues required for fast Na+ -channel inactivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1992;89:10910–10914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Richmond JE, Featherstone DE, Ruben PC. Human Na+ channel fast and slow inactivation in paramyotonia congenita mutants expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J. Physiol. 1997;499:589–600. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp021952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Francis DG, Rybalchenko V, Struyk A, Cannon SC. Leaky sodium channels from voltage sensor mutations in periodic paralysis, but not myotonia. Neurology. 2011;76:1–7. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318219fb57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gosselin-Badaroudine P, Delemotte L, Moreau A, Klein ML, Chahine M. Gating pore currents and the resting state of NaV1.4 voltage sensor domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2012;109:19250–19255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217990109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Monteleone S, et al. Mechanisms responsible for w-pore currents in CaV calcium channel voltage-sensing domains. Biophys. J. 2017;113:1485–1495. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.08.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bendahhou S, Cummins TR, Griggs RC, Fu YH, Ptácek LJ. Sodium channel inactivation defects are associated with acetazolamide-exacerbated hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Ann. Neurol. 2001;50:417–420. doi: 10.1002/ana.1144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ke Q, et al. The mutation R672H in SCN4A gene exists in Chinese patients with hypokalaemic periodic paralysis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006;86:724–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mitrovic N, George AL, Rudel R, Lehmann-Horn F, Lerche H. Mutant channels contribute <50% to Na+ current in paramyotonia congenita muscle. Brain. 1999;122:1085–1092. doi: 10.1093/brain/122.6.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cannon SC. An expanding view for the molecular basis of familial periodic paralysis. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2002;12:533–543. doi: 10.1016/S0960-8966(02)00007-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mannikko R, et al. Spider toxin inhibits gating pore currents underlying periodic paralysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA. 2018;115:4495–4500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1720185115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bednarz M, et al. A novel Ile1455Thr variant in the skeletal muscle sodium channel alpha subunit is associated with a severe adult onset proximal myopathy with electrical myotonia and a mild paramyotonia phenotype. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2017;27:175–182. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2016.09.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Struyk A, Cannon SC. Paradoxical depolarization of Ba2+- treated muscle exposed to low extracellular K+: insights into resting potential abnormalities in hypokalemic paralysis. Muscle Nerve. 2008;37:326–337. doi: 10.1002/mus.20928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Moreau A, Gosselin-Badaroudine P, Delemotte L, Klein ML, Chahine M. Gating pore currents are defects in common with two NaV1.5 mutations in patients with mixed arrhythmias and dilated cardiomyopathy. J. Gen. Physiol. 2015;145:93–106. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201411304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Capes DL, Goldschen-Ohm MP, Arcisio-Miranda M, Bezanilla F, Chanda B. Domain IV voltage-sensor movement is both sufficient and necessary for fast inactivation in sodium channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2013;142:101–112. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201310998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chahine M, et al. Sodium channel mutations in paramyotonia congenita uncouple activation from inactivation. Neuron. 1994;12:281–294. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Habbout K, et al. A recessive NaV1.4 mutation underlies congenital myasthenic syndrome with periodic paralysis. Neurology. 2016;86:161–169. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Arnold WD, et al. Defective fast inactivation recovery of NaV1.4 in congenital myasthenic syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 2015;77:840–850. doi: 10.1002/ana.24389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Poulin H, et al. Substitutions of the S4DIV R2 residue (R1451) in NaV1.4 lead to complex forms of paramyotonia and periodic paralyses. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:1–14. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17765-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chanda B, Asamoah OK, Bezanilla F. Coupling interactions between voltage sensors of the sodium channel as revealed by site-specific measurements. J. Gen. Physiol. 2004;123:217–230. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200308971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jurkat-Rott K, et al. A calcium channel mutation causing hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1994;3:1415–1419. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.8.1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 1952;117:500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cannon SC, Brown RH, Corey DP. Theoretical reconstruction of myotonia and paralysis caused by incomplete inactivation of sodium channels. Biophys. J. 1993;65:270–286. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81045-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Filatov GN, Pinter MJ, Rich MM. Resting potential-dependent regulation of the voltage sensitivity of sodium channel gating in rat skeletal muscle in vivo. J. Gen. Physiol. 2005;126:161–172. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200509337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Featherstone, D. E., Fujimoto, E. & Ruben, P. C. A defect in skeletal muscle sodium channel deactivation exacerbates hyperexcitability in human paramyotonia congenita. J. Physiol.506, 627–638 (1998). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 42.Shen H, et al. Structure of a eukaryotic voltage-gated sodium channel at near-atomic resolution. Science. 2017;355:924–936. doi: 10.1126/science.aak9803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wood ML, et al. Water wires in atomistic models of the Hv1 proton channel. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2012;1818:286–293. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.07.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.