Abstract
Compounds with multitarget activity (promiscuity) are increasingly sought in drug discovery. However, promiscuous compounds are often viewed controversially in light of potential assay artifacts that may give rise to false-positive activity annotations. We have reasoned that the strongest evidence for true multitarget activity of small molecules would be provided by experimentally determined structures of ligand–target complexes. Therefore, we have carried out a systematic search of currently available X-ray structures for compounds forming complexes with different targets. Rather unexpectedly, 1418 such crystallographic ligands were identified, including 702 that formed complexes with targets from different protein families (multifamily ligands). About half of these multifamily ligands originated from the medicinal chemistry literature, making it possible to consider additional target annotations and search for analogues. From 168 distinct series of analogues containing one or more multifamily ligands, 133 unique analogue-series-based scaffolds were isolated that can serve as templates for the design of new compounds with multitarget activity. As a part of our study, all of the multifamily ligands we have identified and the analogue-series-based scaffolds are made freely available.
1. Introduction
Over the past decade, the interest in small molecules with multitarget activity has been steadily on the rise,1−3 especially in the context of polypharmacology.4−7 This concept refers to increasing evidence that the efficacy of drugs frequently depends on engagement of multiple therapeutic targets.4−7 Accordingly, the molecular foundation of polypharmacology, which also includes undesired side effects, is provided by specific interactions of compounds with multiple targets.8 However, while multitarget drug discovery is given prime consideration in therapeutic areas such as neurodegenerative diseases3 and oncology,9 compound promiscuity per se is often viewed controversially.8 This is the case because it is generally difficult to draw the line between true multitarget activity of small molecules8 and aggregation effects or potential reactivity under assay conditions,10−13 which may or may not14,15 lead to artifacts and false-positive assay signals.13,16,17 Hence, differentiating between multitarget activity and assay interference has become a major task in biological screening and medicinal chemistry.17 In addition to their drug discovery relevance, small molecules with true multitarget activity are also of high interest for basic research in order to explore why and how such chemical entities are capable of forming specific interactions with multiple targets, especially if these targets are only distantly related or unrelated and have different functions.
We have been interested in identifying compounds that are active against target proteins from different families. In light of potential caveats associated with promiscuity analysis (vide supra), we have reasoned that particularly strong evidence and support for multitarget activity would be provided by structural data confirming that compounds are indeed bound to active sites of different target proteins. Therefore, we have carried out a systematic search for X-ray structures of ligands bound to multiple target proteins from different families. This search was complemented by identifying and analyzing series of analogues involving such ligands, thereby bridging between structural biology and medicinal chemistry.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Crystallographic Ligands
From 102 625 entries in the RCSB Protein Data Bank (PDB),18 23 580 crystallographic ligands were extracted, which included 11 039 organic compounds with a molecular weight of at least 300 Da and unique structures. This subset of PDB ligands provided the basis for our analysis. The complete selection protocol is summarized in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
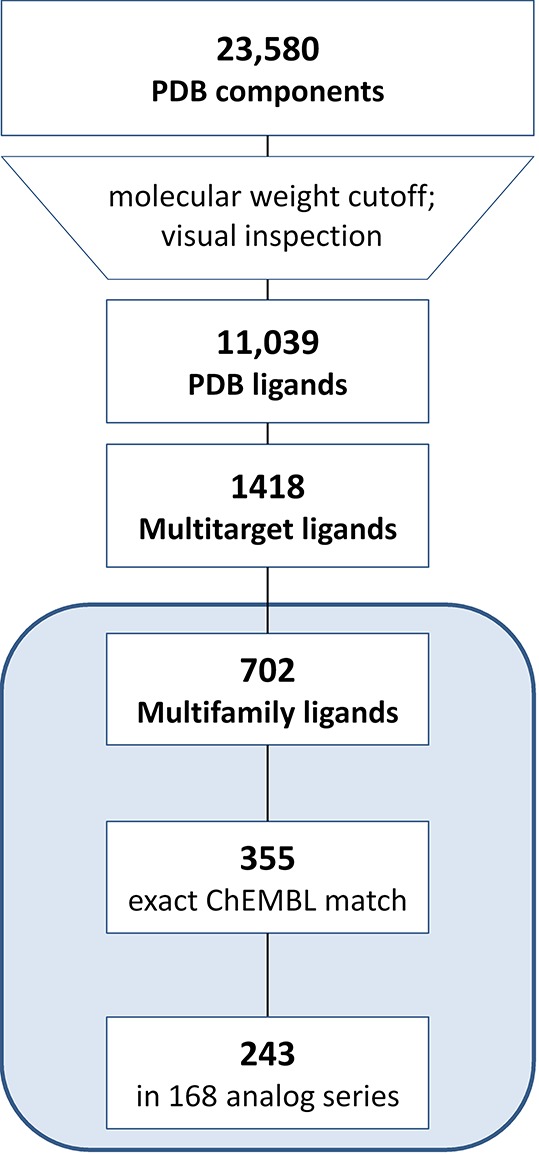
Compound selection. The protocol applied to select crystallographic ligands, multitarget and multifamily ligands, and analogues from medicinal chemistry is summarized.
2.2. Multitarget and Multifamily Ligands
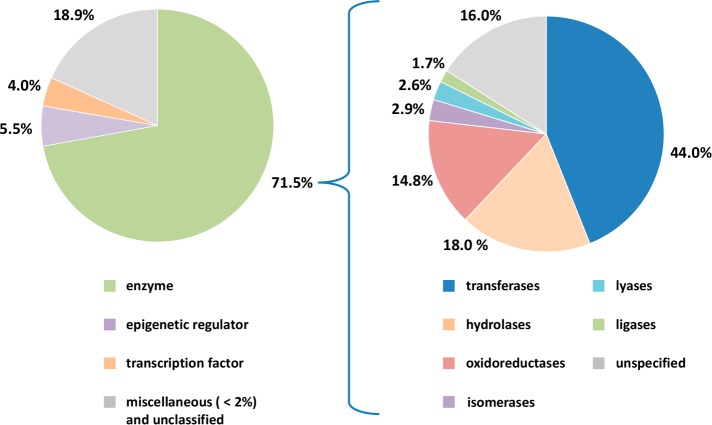
The selected PDB ligands were found to contain 1418 compounds from X-ray structures of complexes with at least two different target proteins (i.e., multitarget ligands; Figure 1). We then determined that these multitarget ligands contained a subset of 702 compounds whose crystallographic targets originated from different families (i.e., multifamily ligands; Figure 1). For this subset, the median value was three targets per ligand. Multifamily ligands were most interesting to us because their structurally confirmed targets were only distantly related (if not unrelated). Targets of multifamily ligands included 488 human proteins, which were distributed across different families as shown in Figure 2. The majority of targets were enzymes. Among these, transferases were prevalent. This observation can be explained by considering that the composition of the PDB is biased toward targets that are straightforward to crystallize (such as many cytoplasmic enzymes). Consequently, some major classes of pharmaceutical targets such as G-protein-coupled receptors and other membrane proteins continue to be under-represented in the PDB. It is possible to compensate this inherent target bias in part by mapping of multifamily ligands from the PDB to ChEMBL and searching for additional target annotations of these ligands and available structural analogues from medicinal chemistry, as further discussed below.
Figure 2.
Distribution of human targets of multifamily ligands. The pie chart on the left reports the distribution of human targets from complex X-ray structures with multifamily ligands. For enzymes, the distribution of catalytic functions is shown in the pie chart on the right.
2.3. Exemplary Ligands and X-ray Structures
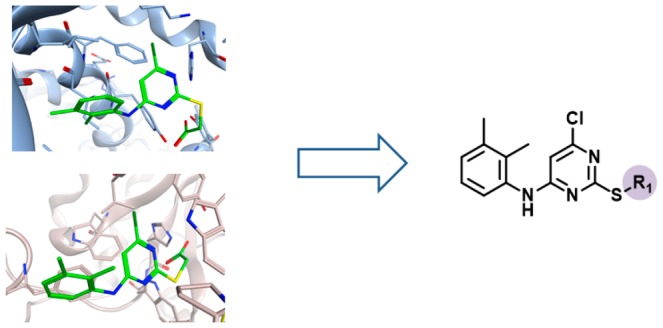
Figure 3 shows X-ray structures of ligands in complex with targets from different families. Comparison of X-ray structures of the same ligand in complex with different targets frequently revealed differences in binding modes. For instance, the phenothiazine derivative thioridazine shown in Figure 3a was found in five X-ray complexes with four targets from four different families. As an exemplary comparison, the binding mode of thioridazine observed in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 (MALT1),19 a cysteine protease, clearly differs from the one in aldehyde oxidase,20 an unrelated enzyme. While the tricyclic ring system of thioridazine is located in a hydrophobic pocket of MALT1, it is partially solvent-exposed in the X-ray complex with aldehyde oxidase. In addition, the positively charged N-methylpiperidinyl moiety forms charge-assisted hydrogen bonds with Glu397 of MALT1, whereas the tertiary amine of the ligand forms backbone interactions with the carbonyl oxygen of Arg1064 in the active site of aldehyde oxidase.
Figure 3.
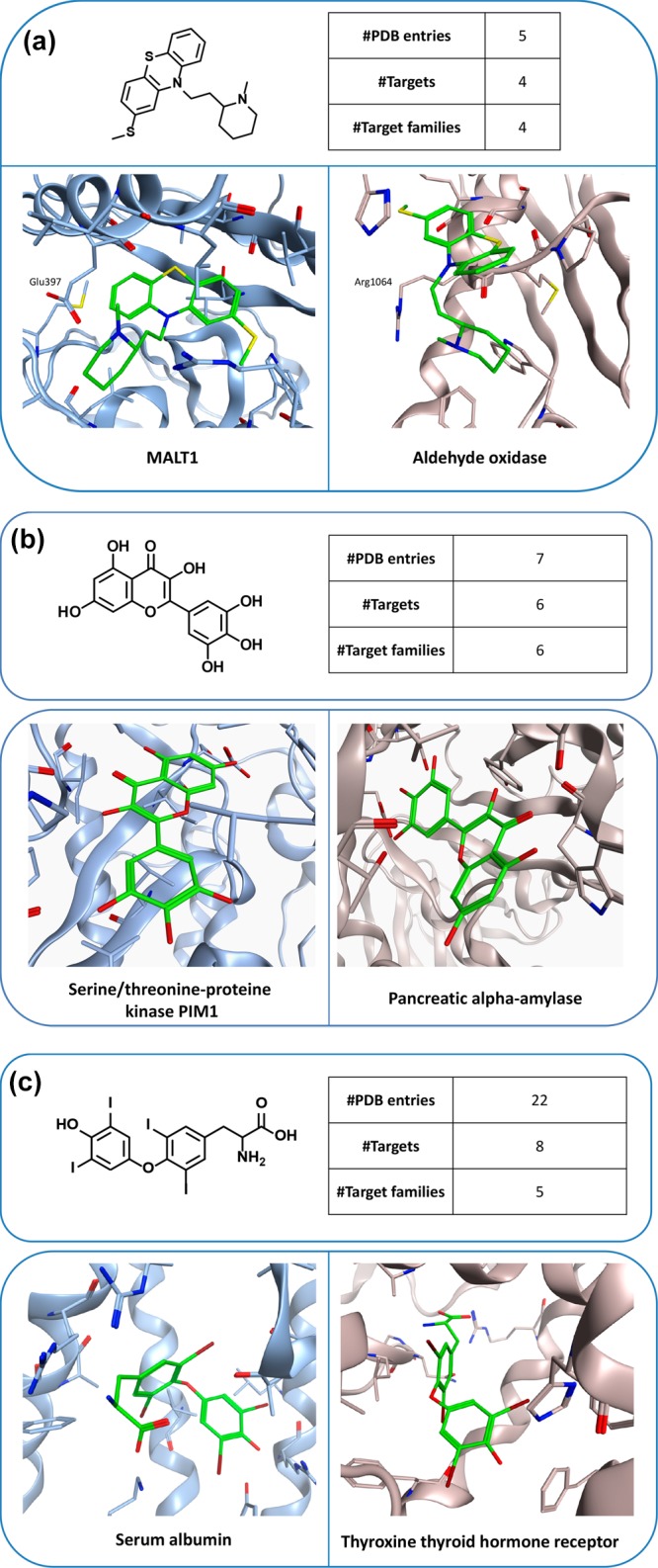
Multifamily ligands and X-ray structures. In (a–c), exemplary ligands and X-ray structures of their complexes with targets from different families are shown. For each ligand, the total number of complex X-ray structures, the number of PDB targets, and the number of families from which these targets originated are reported. In the X-ray structures, bound ligands are shown in stick representation with standard atom coloring.
Figure 3b shows an example of an inverted ligand binding mode in two different active sites. The flavonoid myricetin was found in seven complex structures involving six targets from six different families. It displays opposite head-to-tail orientations when bound to human pancreas amylase21 and the ATP-binding site of PIM1 kinase.22
Binding modes can also be compared for multifamily ligands when interactions with different targets lead to desired or undesired functional effects. An example is shown in Figure 3c, where the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) is bound to the IIa subdomain of human serum albumin23 or the ligand binding domain of thyroxine thyroid hormone receptor beta (TR), its natural receptor.24 Binding to serum albumin causes hyperthyroxinemia.23 Notably, T4 reaches deep into the TR binding pocket, where it interacts with three arginine residues via charge-assisted hydrogen bonds. In addition, the iodine atoms of T4 are accommodated in small subsites mostly formed by the side chains of Phe459 and Phe455. By contrast, T4 binds to human serum albumin in a surface-directed manner and predominantly interacts with residues that are partially solvent-exposed.
2.4. Multifamily Ligands from Medicinal Chemistry
A subset of 355 of the 702 multifamily ligands were detected in the ChEMBL database,27 the major public repository of compounds and activity data from the medicinal chemistry literature. For these ligands, ChEMBL target annotations from high-confidence direct binding/inhibition assays were collected. Taking these additional annotations into account represented an expansion into medicinal chemistry target space and increased the median value from three PDB (vide supra) to 17 unique PDB/ChEMBL targets per multifamily ligand. Thus, crystallographic multifamily ligands were generally promiscuous on the basis of medicinal chemistry data. Although it cannot be excluded that some target annotations from assays might be false positives, the availability of multiple X-ray structures of these ligands in complex with different targets lends credence to their promiscuous nature, strongly suggesting their relevance for the study of multitarget activity and polypharmacology.
2.5. Analogues of Multifamily Ligands
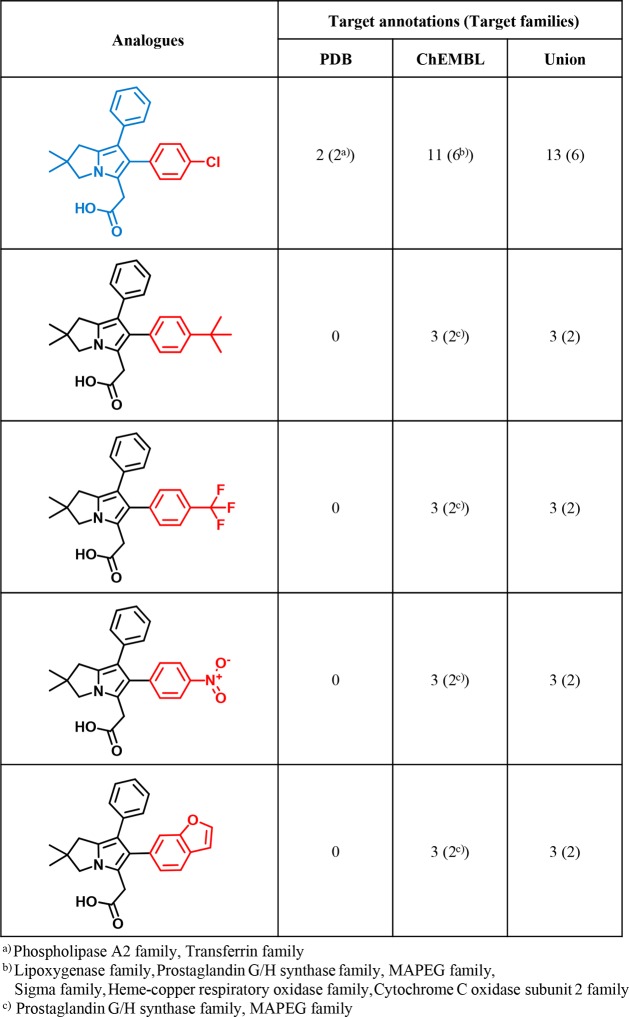
For the 355 multifamily ligands available in ChEMBL, a systematic search for analogue series (ASs) was carried out. For 243 of these ligands, analogues were detected, yielding 168 unique ASs. Each AS consisted of at least one X-ray ligand and varying numbers of noncrystallographic analogues from ChEMBL. An exemplary AS is depicted in Figure 4. This AS contains an X-ray ligand and several ChEMBL compounds with multitarget annotations, providing corroborating evidence for the promiscuity of the multifamily ligand from the PDB.
Figure 4.
Analogue series. Shown is an exemplary AS including a multifamily ligand (blue core). For the crystallographic ligand, the number of PDB targets, the number of targets reported in ChEMBL, and the number of unique targets are given. For each ChEMBL analogue, the number of targets from ChEMBL is provided. In each case, the corresponding number of target families is given in parentheses. ChEMBL analogues have no PDB target annotations. Substituents that distinguish analogues are colored red.
2.6. Scaffolds and Design Templates
From ASs containing multifamily ligands, analogue series-based (ASB) scaffolds28,29 were derived. By design, ASB scaffolds take retrosynthetic criteria into account and capture chemical information on compound series, including the conserved substructure and substitution sites where analogues are distinguished.28,29 For 133 of the 168 ASs with multifamily ligands ASB scaffolds could be derived. Exemplary scaffolds are shown in Figure 5. Since ASs were associated with multiple targets, further extending the set of PDB targets of multifamily ligands, the corresponding ASB scaffolds also represent templates for the design of compounds with different multitarget activities. On the basis of each scaffold, different target combinations can be explored. The ASB scaffolds also make it possible to differentiate between template structures with different degrees of promiscuity. For example, scaffolds from highly promiscuous analogue series, as shown in Figure 5, might be deprioritized as template structures for the design of compounds with desired activity against a few targets, even if these targets are contained in the scaffold-associated target profiles. Instead, scaffolds from other less promiscuous series with desired targets might be considered. Furthermore, for ASB scaffolds with target combinations of interest, it is advisible to inspect the target annotations of individual analogues to rationalize the series-based target profile in more detail. Analogues can be easily obtained by substructure searching using ASB scaffolds.
Figure 5.
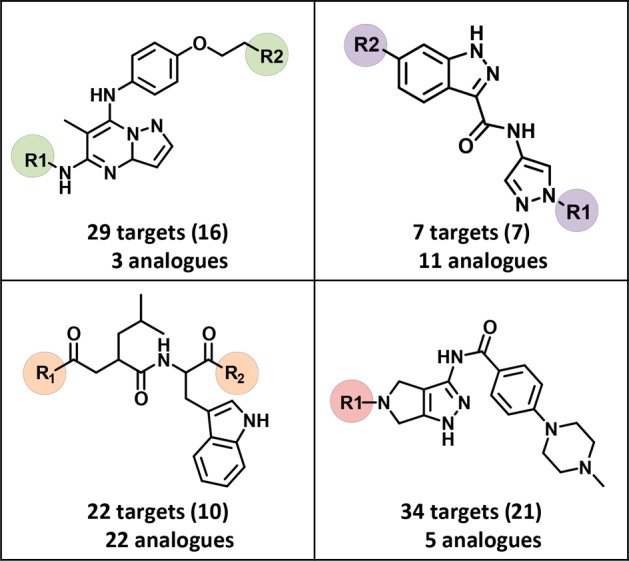
Exemplary scaffolds. Shown are examples of ASB scaffolds representing series of promiscuous structural analogues, including multifamily ligands. For each scaffold, the total number of unique targets against which the analogues were active and (in parentheses) the number of corresponding target families are reported. Substitution sites in ASB scaffolds are highlighted.
2.7. Conclusions
We have systematically searched for crystallographic ligands bound to multiple targets from different families. Such X-ray data were thought to provide firm evidence for true multitarget activity of compounds. An unexpectedly large number of qualifying ligands (702) were identified that covered targets from a variety of families. Approximately half of these ligands originated from the medicinal chemistry literature, which yielded additional target annotations. Moreover, a total of 168 distinct series of analogues that contained X-ray ligands were identified. From these, 133 analogue-series-based scaffolds were extracted that captured chemical and target information on individual series. Crystallographic multifamily ligands represent a large, high-confidence knowledge base for multitarget activity. Scaffolds derived from ASs containing such ligands can be considered as templates for compound design. Therefore, multifamily ligands, scaffolds, and associated target information are made freely available as a part of this study. We also note that a variety of computational methods are available to predict targets of test compounds. The uncertainties associated with target predictions go much beyond experimental uncertainties associated with compound data. However, searching for compounds with true multitarget activities is difficult on the basis of experimental activity data, taking assay-dependent activity readouts and potential artifacts into account. For these reasons, X-ray structures of ligand–target complexes provided the initial focal point of our analysis and were complemented by taking medicinal chemistry data into account. By contrast, possible computational predictions were deliberately avoided, given the motivation and scope of our analysis.
3. Materials and Methods
All calculations were carried out using in-house Perl and Python scripts with the aid of the OpenEye chemistry toolkit,30 KNIME protocols,31 and RStudio.32 X-ray structures were graphically analyzed using the Molecular Operating Environment.33
3.1. Ligands from X-ray Structures
X-ray structures and associated compound data were extracted from the Ligand Expo section34 of the PDB.18 Salts and other buffer components were removed, and ligands with a molecular weight of at least 300 Da yielding unique aromatic nonstereo SMILES35 representations were retained. Application of the molecular weight cutoff ensured that small organic components and fragments were excluded from further consideration. All of the selected complex X-ray structures were visually inspected.
3.2. Compounds and Activity Data
From ChEMBL (release 23)27 a total of 853 533 unique compounds were extracted for which activity data from direct binding/inhibition assays (target relationship type “D”) were available.
3.3. Target Family Distribution
For crystallographic targets of human origin, family assignments were obtained by combining the classification schemes of UniProt36 and ChEMBL. In addition, known targets of all of the selected ChEMBL compounds were determined on the basis of unique UniProt identifiers.
3.4. Analogue Series and Scaffolds
From combined PDB and CHEMBL compounds, ASs were systematically extracted using a recently developed algorithm37 utilizing the matched molecular pair (MMP) formalism.38 An MMP is defined as a pair of compounds that are distinguished only by a structural change at a single site,38 often termed a chemical transformation.39 To generate MMPs, compounds were systematically fragmented39 according to retrosynthetic rules,40 yielding RECAP-MMPs.41 From ASs, recently introduced ASB scaffolds28,29 were extracted, which capture the conserved substructure of a series and all substitution sites.
3.5. Data Deposition
All of the multifamily ligands have been made available, together with their crystallographic targets, PDB identifiers, and total numbers of targets, including annotations from ChEMBL (if available). In addition, all of the ASB scaffolds derived from ASs containing multifamily ligands are provided. The collection of ligands and scaffolds is freely available in a deposition on the Zenodo open access platform.43
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to OpenEye Scientific Software, Inc., for the free academic license of the OpenEye Toolkits. D.S. was supported by Sonderforschungsbereich 704 of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Author Contributions
The study was carried out and the manuscript written with contributions of all authors. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
References
- Zimmermann G. R.; Lehar J.; Keith C. T. Multi-Target Therapeutics: When the Whole is greater than the Sum of the Parts. Drug Discovery Today 2007, 12, 34–42. 10.1016/j.drudis.2006.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J. J.; Pan W.; Hu Y. J.; Wang Y. T. Multi-Target Drugs: The Trend of Drug Research and Development. PLoS One 2012, 7, e40262. 10.1371/journal.pone.0040262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geldenhuys W. J.; Van der Schyf C. J. Designing Drugs with Multi-Target Activity: The Next Step in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Expert Opin. Drug Discovery 2013, 8, 115–129. 10.1517/17460441.2013.744746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anighoro A.; Bajorath J.; Rastelli G. Polypharmacology: Challenges and Opportunities in Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7874–7887. 10.1021/jm5006463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi M. L. Polypharmacology in a Single Drug: Multitarget Drugs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 1639–1645. 10.2174/0929867311320130004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi M. L.; Cavalli A. Multitarget Drug Discovery and Polypharmacology. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1190–1192. 10.1002/cmdc.201600161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosini M. Polypharmacology: The Rise of Multitarget Drugs over Combination Therapies. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 485–487. 10.4155/fmc.14.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y.; Bajorath J. Compound Promiscuity - What Can We Learn From Current Data. Drug Discovery Today 2013, 18, 644–650. 10.1016/j.drudis.2013.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight Z. A.; Lin H.; Shokat K. M. Targeting the Cancer Kinome through Polypharmacology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 130–137. 10.1038/nrc2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGovern S. L.; Caselli E.; Grigorieff N.; Shoichet B. K. A Common Mechanism Underlying Promiscuous Inhibitors from Virtual and High-Throughput Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 1712–1722. 10.1021/jm010533y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoichet B. K. Screening in a Spirit Haunted World. Drug Discovery Today 2006, 11, 607–615. 10.1016/j.drudis.2006.05.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baell J. B.; Holloway G. A. New Substructure Filters for Removal of Pan Assay Interference Compounds (PAINS) from Screening Libraries and for Their Exclusion in Bioassays. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2719–2740. 10.1021/jm901137j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baell J. B.; Walters M. A. Chemistry: Chemical Con Artists Foil Drug Discovery. Nature 2014, 513, 481–483. 10.1038/513481a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capuzzi S. J.; Muratov E. N.; Tropsha A. Phantom PAINS: Problems with the Utility of Alerts for Pan-Assay INterference CompoundS. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 417–427. 10.1021/acs.jcim.6b00465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasial S.; Hu Y.; Bajorath J. How Frequently Are Pan Assay Interference Compounds Active? Large-Scale Analysis of Screening Data Reveals Diverse Activity Profiles, Low Global Hit Frequency, and Many Consistently Inactive Compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 3879–3886. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilberg E.; Jasial S.; Stumpfe D.; Dimova D.; Bajorath J. Highly Promiscuous Small Molecules from Biological Screening Assays Include Many Pan-Assay Interference Compounds but Also Candidates for Polypharmacology. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 10285–10290. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich C.; Bertozzi C.; Georg G. I.; Kiessling L.; Lindsley C.; Liotta D.; Merz K. M. Jr.; Schepartz A.; Wang S. The Ecstasy and Agony of Assay Interference Compounds. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 387–390. 10.1021/acs.jcim.7b00105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman H. M.; Westbrook J.; Feng Z.; Gilliland G.; Bhat T. N.; Weissig H.; Shindyalov I. N.; Bourne P. E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. 10.1093/nar/28.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlauderer F.; Lammens K.; Nagel D.; Vincendeau M.; Eitelhuber A. C.; Verhelst S. H.; Kling D.; Chrusciel A.; Ruland J.; Krappmann D.; Hopfner K. P. Structural Analysis of Phenothiazine Derivatives as Allosteric Inhibitors of the MALT1 Paracaspase. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10384–10387. 10.1002/anie.201304290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coelho C.; Foti A.; Hartmann T.; Santos-Silva T.; Leimkühler S.; Romao M. J. Structural Insights into Xenobiotic and Inhibitor Binding to Human Aldehyde Oxidase. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 779–783. 10.1038/nchembio.1895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. K.; Li C.; Withers S. G.; Brayer G. D. Order and Disorder: Differential Structural Impacts of Myricetin and Ethyl Caffeate on Human Amylase, an Antidiabetic Target. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10177–10186. 10.1021/jm301273u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder S.; Zemskova M.; Zhang C.; Tabrizizad M.; Bremer R.; Neidigh J. W.; Lilly M. B. Characterization of a Potent and Selective Small-Molecule Inhibitor of the PIM1 Kinase. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 163–172. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petitpas I.; Petersen C. E.; Ha C. E.; Bhattacharya A. A.; Zunszain P. A.; Ghuman J.; Bhagavan N. V.; Curry S. Structural Basis of Albumin-Thyroxine Interactions and Familial Dysalbuminemic Hyperthyroxinemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003, 100, 6440–6445. 10.1073/pnas.1137188100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler B.; Webb P.; Apriletti J. W.; Huber B. R.; Togashi M.; Cunha Lima S. T.; Juric S.; Nilsson S.; Wagner R.; Fletterick R. J.; Baxter J. D. Thyroxine-Thyroid Hormone Receptor Interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 55801–55808. 10.1074/jbc.M410124200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaulton A.; Bellis L. J.; Bento A. P.; Chambers J.; Davies M.; Hersey A.; Light Y.; McGlinchey S.; Michalovich D.; Al-Lazikani B.; Overington J. P. ChEMBL: A Large-Scale Bioactivity Database for Drug Discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1100–D1107. 10.1093/nar/gkr777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimova D.; Stumpfe D.; Hu Y.; Bajorath J. ASB Scaffolds: Computational Design and Exploration of a New Type of Molecular Scaffolds for Medicinal Chemistry. Future Science OA 2016, 2, FSO149. 10.4155/fsoa-2016-0058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimova D.; Stumpfe D.; Bajorath J. Computational Design of New Molecular Scaffolds for Medicinal Chemistry, Part II: Generalization of Analog Series-Based Scaffolds. Future Sci. OA 2017, FSO267. 10.4155/fsoa-2017-0102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OEChem, version 1.7.7; OpenEye Scientific Software: Santa Fe, NM, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Berthold M. R.; Cebron N.; Dill F.; Gabriel T. R.; Kötter T.; Meinl T.; Ohl P.; Sieb C.; Thiel K.; Wiswedel B.. KNIME: The Konstanz Information Miner. In Studies in Classification, Data Analysis, and Knowledge Organization; Preisach C., Burkhart H., Schmidt-Thieme L., Decker R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, 2008; pp 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Molecular Operating Environment (MOE), version 2014.09; Chemical Computing Group: Montreal, QC, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Feng Z.; Chen L.; Maddula H.; Akcan O.; Oughtred R.; Berman H. M.; Westbrook J. Ligand Depot: A Data Warehouse for Ligands Bound to Macromolecules. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 2153–2155. 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; http://ligand-expo.rcsb.org/ (accessed Sept 28, 2017).
- Weininger D. SMILES, A Chemical Language and Information System. 1. Introduction to Methodology and Encoding Rules. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 1988, 28, 31–36. 10.1021/ci00057a005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D158–D169. 10.1093/nar/gkw1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpfe D.; Dimova D.; Bajorath J. Computational Method for the Systematic Identification of Analog Series and Key Compounds Representing Series and Their Biological Activity Profiles. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7667–7676. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain J.; Rea C. Computationally Efficient Algorithm to Identify Matched Molecular Pairs (MMPs) in Large Data Sets. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 339–348. 10.1021/ci900450m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffen E.; Leach A. G.; Robb G. R.; Warner D. J. Matched Molecular Pairs as a Medicinal Chemistry Tool. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 7739–7750. 10.1021/jm200452d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewell X. Q.; Judd D. B.; Watson S. P.; Hann M. M. RECAP - Retrosynthetic Combinatorial Analysis Procedure: A Powerful New Technique for Identifying Privileged Molecular Fragments with Useful Application in Combinatorial Chemistry. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1998, 38, 511–522. 10.1021/ci970429i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De la Vega de León A.; Bajorath J. Matched Molecular Pairs Derived by Retrosynthetic Fragmentation. MedChemComm 2014, 5, 64–67. 10.1039/C3MD00259D. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- https://zenodo.org/record/1116185 (accessed Nov 24, 2017).