Abstract
Caries and periodontitis are the two most common human dental diseases and are caused by dysbiosis of oral flora. Although commensal microorganisms have been demonstrated to protect against pathogens and promote oral health, most previous studies have addressed pathogenesis rather than commensalism. Streptococcus sanguinis is a commensal bacterium that is abundant in the oral biofilm and whose presence is correlated with health. Here, we focus on the mechanism of biofilm formation in S. sanguinis and the interaction of S. sanguinis with caries- and periodontitis-associated pathogens. In addition, since S. sanguinis is well known as a cause of infective endocarditis, we discuss the relationship between S. sanguinis biofilm formation and its pathogenicity in endocarditis.
Keywords: : biofilm, oral microbiota, Streptococcus sanguinis
The mouth is the gateway of the human body and is in frequent contact with the external environment. Microbial communities in the mouth may be impacted by various environmental conditions [1]. When the homeostasis of oral microbiomes is disrupted, certain oral diseases may emerge. Two of the most prevalent diseases in the oral cavity are dental caries and periodontitis [2]. According to the 2016 global burden of disease study, periodontal disease was the 11th most prevalent human disease affecting 750,847 million people worldwide [2]. Published findings from the CDC estimate that half of Americans over 30 years of age have periodontal disease [3]. Caries of permanent teeth was the most prevalent disease, affecting 2.44 billion people and caries of deciduous teeth was the 17th most prevalent human disease worldwide [2]. In the USA alone, approximately 37% of children (2–8 years) have experienced dental caries in primary teeth and 58% of adolescents (12–19 years) have suffered dental caries in permanent teeth [4]. These oral diseases, if left untreated, lead to pain, dental abscesses, destruction of bone and other serious health problems. They have also been found to be strongly associated with an increase in mortality rate [5–7]. In addition, dental care in the USA represented about 5% of the country's spending on all healthcare, or US$111 billion, in 2012 [8]. The WHO reports dental caries as the fourth most expensive chronic disease to treat in most industrialized countries [9]. Given the extent of the problem, oral diseases are a major public health concern.
Using culture-independent approaches, primarily 16S rRNA gene-based cloning studies, it was estimated that the human oral cavity harbors approximately 700 prokaryote species, and more than half remain uncultivated once isolated from the complex oral environment [10]. The oral cavity is an ecologically unstable, saliva-bathed landscape providing numerous distinct habitats for bacteria to colonize, including the unique nonshedding surfaces of the teeth [11]. Some bacterial communities show a predilection for certain oral spaces and are commonly isolated from samples from particular sites. Colonization of the host within these niches is facilitated by the formation of biofilms, which may be defined as microbial communities embedded in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances of bacterial origin [12]. Mature oral biofilms (dental plaque) have overall compositions that differ between niches and individuals, but have been shown to have a relative degree of species composition stability among the principal species [13–16]. However, it has been shown that the bacterial population profile is significantly different between a healthy oral cavity and one with oral disease. The initiation of chronic bacterially mediated periodontal diseases has now been identified as a compositional shift of dental plaque flora from predominantly Gram-positive facultative anaerobes to predominantly obligate Gram-negative anaerobes [17–19].
Characteristics of Streptococcus sanguinis
Streptococcus sanguinis, previously known as S. sanguis, is typically associated with healthy plaque biofilm [13–16,20–22]. It is a Gram-positive, nonspore-forming, facultative anaerobe. Like other streptococci, cell division of S. sanguinis occurs along a single axis, resulting in chains or pairs of cocci. S. sanguinis has generally been reported as being nonmotile. This has recently been challenged, as Gurung et al. reported that S. sanguinis strain 2908 is capable of surface-associated twitching motility facilitated by retractable type-IV pili [23,24].
In 2007, Xu et al. published the genome sequence of S. sanguinis SK36, which was originally isolated from human dental plaque [25]. The genome is a circular DNA molecule comprised of 2,388,435 bp, encoding 2274 predicted proteins [25]. There are 61 predicted tRNA genes producing all 20 amino acids and 50 putative carbohydrate transporters, including phosphotransferase system enzymes specific for transport of glucose, fructose, mannose, cellobiose, glucosides, fructose, lactose, trehalose, mannose, galactitol and maltose [25]. S. sanguinis seems to be able to utilize a broad range of carbohydrate sources for survival.
S. sanguinis is a pioneering colonizer, aiding in the attachment of succeeding organisms, and a key player in oral biofilm development [26–28]. Caufield et al. recorded the time of colonization of S. sanguinis in 45 infants. In their research, 25% of the infants had acquired S. sanguinis within 8 months of age, and 75% had S. sanguinis by 11.4 months; the median age of colonization by S. sanguinis was 9.0 months [27]. S. sanguinis is a commensal bacterium that is widely distributed in the oral cavity. It exists on tooth surfaces, oral mucosa surfaces and in human saliva [20,29,30]. As a facultative anaerobic species, S. sanguinis is abundant in both supragingival and subgingival plaque [15,31]. At different tooth locations, the biomass of S. sanguinis may differ significantly despite similarities in plaque mass [32]. It is present in high proportions at the lower incisor/canine sites of teeth, but in low proportions at the upper molar sites [32]. S. sanguinis has also been shown to form biofilm on different dental implant surfaces [33–35]. It is worth noting that the incidence of peri-implant complications significantly increases in patients with periodontitis [36]. Several studies demonstrate that plaque formation on dental implants results in peri-implant mucositis [37,38]. However, it is still not clear whether S. sanguinis promotes or reduces this effect.
Factors that affect biofilm formation in S. sanguinis
The attachment of S. sanguinis to the tooth surface
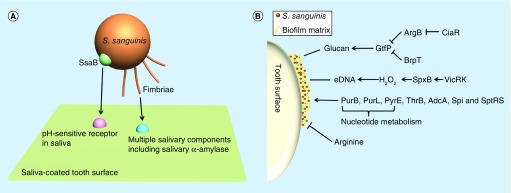
The first step in biofilm formation is the process of single cells attaching to a surface [39]. Fimbriae are involved in attachment to both animate and inanimate surfaces and in the formation of biofilms in many species of bacteria [40]. In 1985, Fachon-Kalweit et al. reported that fimbriae mediated the adhesion of S. sanguinis to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite (the main substance of the tooth surface) [41]. Okahashi et al. later identified three pilus proteins PilA, PilB and PilC in S. sanguinis SK36 [42]. A ΔpilABC mutant was defective in accumulation on saliva-coated surfaces and biofilm formation [42]. These investigators also showed that PilB and PilC bound to human whole saliva [42]. Moreover, PilC bound to multiple salivary components, one of which was found to be salivary α-amylase (Figure 1A) [42]. Tooth surfaces are coated with a large amount of salivary proteins [29]. Pilus binding to salivary components may help S. sanguinis attach to tooth surfaces and initiate biofilm formation in the oral cavity.
Figure 1. . Impact factors of biofilm formation in Streptococcus sanguinis.
(A) Pioneer S. sanguinis bacterium (orange) recognizing tooth surface salivary pellicle receptors (pink and blue) and forming initial bonds. Model shows recognition of multiple types of attachment receptors including long-range attachment, for example, fimbriae (orange) which can bind to multiple salivary components (blue) and SsaB (green) which may mediate attachment to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite via an uncharacterized pH-sensitive receptor (pink). (B) The response regulator CiaR of the CiaRH two-component system can inhibit the expression of ArgB which in turn leads to the upregulation of gtfP. Upregulation of gtfP can also be triggered by the deletion of BrpT. An increase in GtfP promotes the synthesis of glucan which enhances biofilm formation. The two-component system VicRK regulates the expression of pyruvate oxidase SpxB. Upregulation of SpxB will increase H2O2 and vice versa. Increased H2O2 induces cellular autolysis and subsequent eDNA release. Deletions in PurB, PurL, PyrE, ThrB, AdcA, Spi and SptRS, all show a decrease in biofilm formation. Exogenous L-arginine has been shown to decrease biofilm formation with mechanisms unknown.
SsaB was first described as a saliva-binding protein that mediates attachment to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite via an uncharacterized pH-sensitive receptor [43]. Although SsaB has been demonstrated to be a lipoprotein [44], it is still not clear what targets SsaB binds to or, indeed, whether it is an adhesin at all, given that the evidence suggesting this function was indirect [43]. SsaB is also a virulence factor for infective endocarditis [45–49].
The glycoprotein serine-rich protein A (SrpA) has been found to mediate the binding of S. sanguinis to human platelets [50,51]. Recent studies analyzed the crystal structure of SrpA and revealed that SrpA bound to human sialoglycans [52,53]. The sialoglycan binding region of SrpA in S. sanguinis is homologous to two other sialoglycan-binding adhesins, GspB and Hsa in Streptococcus gordonii [54,55]. GspB and Hsa, which are alleles, have been shown to bind to human salivary proteins [54]. A srpAmutant has been shown to bind poorly to microtiter plates in vitro [56]; however, there is still no evidence demonstrating that SrpA mediates attachment or biofilm formation of S. sanguinis in the oral cavity.
The maturation of S. sanguinis biofilm
In most biofilms, <10% of the dry mass is composed of microorganisms, while the biofilm matrix can account for the remainder [40]. The most important components of biofilm matrix are polysaccharides, proteins, nucleic acids and lipids, which mediate cell–cell and cell–surface adhesion to form cohesive, 3D polymeric networks [40].
In S. sanguinis, glucans are the main biofilm polymer formed in the presence of sucrose and are composed mostly of α-1,6-linked and α-1,3-linked glucose [57]. The linkage of glucans made in the presence of sera, starch hydrolysates and dextran are different from that of control glucan [57]. The biofilm formation ability of S. sanguinis differs dramatically depending on the growth medium used [58]. These studies indicate that different media components can affect glucan levels and structure, affecting biofilm formation. In addition, the oxygen concentration also affects biofilm formation even when cultured in the same medium [58], perhaps due to changes in metabolic pathways affecting glucan biosynthesis.
Glucosyltranferases are responsible for the synthesis of adhesive glucans from sucrose [59]. The genome annotation shows that S. sanguinis SK36 contains two gtf genes, gtfA and gtfP [25], of which gtfP is the only gene shown to produce glucan, and it has also been reported to promote the adherence of S. sanguinis to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite and to increase biofilm formation (Figure 1B) [60–62]. The deletion of gtfP decreases the production of both water soluble glucan and water insoluble glucan [61] and as a result reduces biofilm formation [60–62]. The response regulator CiaR of the CiaRH two-component system and a transcriptional regulator BrpT have been reported to modulate the expression of the gtfP gene [61,62]. The deletion of ciaR reduces the transcription of gtfP through upregulating arginine biosynthesis genes, especially argB, leading to a defective biofilm formation [62]. The ΔbrpT mutant promotes the expression of gtfP and displays increased biofilm formation ability [61]. These studies suggest that gtfP is a key gene for glucan synthesis and biofilm formation in S. sanguinis. However, because glucan production is affected by media composition [57,58], other genes may participate in glucan biosynthesis and biofilm formation.
Extracellular DNA (eDNA) is another essential component for biofilm formation in many species, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa [63] and Staphylococcus aureus [64]. In S. sanguinis, H2O2 produced by SpxB is able to cause DNA release which induces cell aggregation [65]. This phenomenon can be attenuated by DNase I treatment, indicating that eDNA promotes cell–cell binding and may contribute to the maturation of biofilms [65]. A vicK knockout mutation inhibits H2O2 production and eDNA release, which decreases biofilm formation [66]. In this study, when biofilms were cultured in brain heart infusion (BHI) medium with 1% sucrose for 2 or 4 h, DNase I treatment significantly decreased biofilm formation [66], while another study reported that DNase I treatment had no effect when added after biofilms were allowed to form in biofilm medium for 24 h [62]. Although some studies showed that reduction of eDNA release and the decrease of biofilm formation appeared simultaneously in Δnox or ΔccpA mutants, the authors did not present direct evidence to show linkage between these two phenomena [67,68]. The different results may be due to the conditions used for biofilm formation, or from the duration of growth prior to addition of DNase I. It is possible that eDNA may play a more important role before the synthesis of a large amounts of glucans or in an environmental condition that lacks carbon sources required for glucan synthesis.
L-arginine can be secreted by salivary glands [69]. There are several studies showing that L-arginine decreases biofilm formation in Streptococcus mutans [70–72]. Zhu et al. reported that the biofilm formation of S. sanguinis was also reduced by exogenous L-arginine [62]. Furthermore, the deletion of genes involved in the arginine biosynthesis pathway promoted the expression of gtfP, increased the production of water insoluble glucan and enhanced biofilm formation in S. sanguinis [62]. However, the mechanisms by which exogenous L-arginine and arginine biosynthesis impact the expression of gtfP are not clear. Additionally, the question also remains whether or not exogenous arginine affects S. mutans and S. sanguinis biofilm formation by the same mechanism.
Several genes have been reported to impact biofilm formation by unknown mechanisms in S. sanguinis, including purB, purL, pyrE, thrB, adcA, spi, sptR and sptS [58,73,74]. It is interesting that genes (purB, purL and pyrE) related to nucleotide biosynthesis are involved in the biofilm formation network. It has been well studied that several nucleotides, such as cyclic di-GMP, cyclic di-AMP, cAMP and (p)ppGpp are widely used as small molecular signals for modulating biofilm formation in other bacteria [75–78]; however, this has not been demonstrated in S. sanguinis. More research should be done to explore whether any of these nucleotides regulate biofilm formation in S. sanguinis.
The relationship of S. sanguinis with dental caries
Description of dental caries
Dental caries is a chronic, transmissible disease that results in the demineralization of dental hard tissues [79,80]. It is caused by attachment of certain microbes to tooth surfaces through formation of the biofilm known as dental plaque, followed by metabolism of sugar into organic acids and, as a result, dissolution of enamel [17]. There are several genera of bacteria capable of inducing the acidic environment in oral biofilms, such as mutans streptococci [81], Lactobacillus spp. [82,83], Bifidobacterium spp. [84] and Actinomyces spp. [85]. Candida albicans also significantly contributes to caries pathogenesis [83,86–88]. Although not present in every case [89,90], S. mutans is one of the most common acid producers and is a significant impact factor in most cases of caries [20,21,85,91–93]. It is worth noting that there is always a complex biofilm present and caries is driven through the action of multiple species in many cases [14,20,93].
Evidence of inverse association of S. sanguinis with dental caries
By comparing colony numbers of caries and caries-free samples, Becker et al. determined that S. sanguinis was the only species identified that was significantly associated with dental health when comparing caries-active and caries-free children [93]. With the development of sequencing technologies, more and more 16S rRNA gene sequencing and metagenomic studies have been performed to discover bacterial species positively or negatively related to dental caries. Streptococcus sanguinis has been frequently if not consistently associated with oral health in these studies [13,14]. It has an inverse relationship with bacterial species that are caries associated and may have an antagonistic effect against cariogenic species [13–14,20–21]. Streptococcus mutans in particular is a well-studied example of a cariogenic species that competes with S. sanguinis.
Antagonism between S. sanguinis & S. mutans
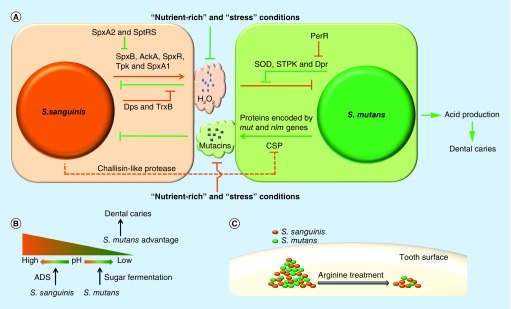
In one study, oral colonization of infants with S. sanguinis was correlated with a significant delay in colonization with mutans streptococci [27]. The phenomenon of antagonism between S. sanguinis and S. mutans was first described in 1976 [94]. Kreth et al. further illustrated that the outcome of the interaction in vitro was dependent on environmental conditions, such as cell density, nutritional availability and pH [95]. When S. sanguinis and S. mutans were inoculated onto half-strength BHI plates, the previously inoculated species could inhibit the growth of the later inoculated species, but simultaneous inoculation by both species resulted in coexistence [95]. Furthermore, the authors showed that H2O2 produced by S. sanguinis repressed the growth of S. mutans [95], a conclusion that has also been supported by clinical research and in silico analysis [96,97]. Conversely, mutacins I and IV secreted by S. mutans suppressed the survival of S. sanguinis (Figure 2A) [95]. Because of defects in mutacin and H2O2 production, the competition between S. sanguinis and S. mutans disappeared in ‘nutrient-rich’ (BHI plus 1% sucrose, buffered to pH 7) and ‘stress’ (BHI at pH 5.5) conditions [95]. The ‘nutrient-rich’ condition may provide more carbon sources for glucan and acid production in S. mutans and facilitate its growth. At the same time, the inhibition of S. sanguinis H2O2 production in the ‘nutrient-rich’ condition may be another reason for an overgrowth of S. mutans and may contribute to the association of a high sugar diet with dental caries [1]. However, the mechanisms of mutual inhibition are not completely understood.
Figure 2. . Mechanisms of antagonism between Streptococcus sanguinis and Streptococcus mutans.
(A) H2O2 generated by Streptococcus sanguinis inhibits the growth of Streptococcus mutans and itself. Enzymes for reactive oxygen species degradation are produced by both species to increase their H2O2 resistance. Mutacins are synthesized by S. mutans to suppress the growth of S. sanguinis. CSP of S. mutans is necessary for mutacins production and can be inactivated by S. sanguinis. (B) S. mutans can generate acids from fermentable sugars to induce dental caries. However, the pH homeostasis may be maintained by the arginine deiminase system of S. sanguinis to prevent against dental caries. (C) L-arginine treatment decreases the biomass of S. mutans more than that of S. sanguinis.
ADS: Arginine deiminase system; CSP: Competence-stimulating peptide; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; STPK: Serine/threonine protein kinase.
H2O2 is a type of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and can cause serious damage to cellular macromolecules, including proteins and DNA. In S. sanguinis, SpxB is a pyruvate oxidase that converts pyruvate to acetyl phosphate and H2O2 [98]. Oxygen is consumed in this reaction [98–101]. In addition, several other genes (ackA, spxR, tpk and spxA1) are also involved in the generation of H2O2 by mechanisms that are unknown but are likely related to SpxB activity [102,103], while spxA2, sptR and sptS suppress expression of the spxB gene and inhibit H2O2 production [74,104].
H2O2 produced by S. sanguinis is not only harmful to S. mutans but can also induce autolysis in S. sanguinis [65,105]. Because of the resulting release of eDNA, these genes may also impact biofilm formation. Dps and TrxB have been shown to contribute to H2O2 resistance in S. sanguinis [106]. Dps is a ferritin-like iron-binding protein that likely prevents the generation of toxic hydroxyl radicals produced by the interaction of Fe2+ with H2O2, thereby protecting cells from oxidative damage [107]. TrxB is a thioredoxin reductase that reduces oxidized thioredoxin [108]. Because thioredoxin participates in the formation of reduced disulfide bonds in oxidized proteins, TrxB attenuates the ROS damage [108]. The deletion of both dps and trxB severely decreased H2O2 resistance in S. sanguinis [106]. However, deletion of the gene encoding the superoxide dismutase SodA did not affect H2O2 resistance in S. sanguinis, while the same mutation decreased H2O2 resistance in S. gordonii [106]. In addition, a glutathione peroxidase BasA was predicted to be a gene responsible for the degradation of H2O2 in S. sanguinis [97].
In S. sanguinis, genes related to the generation of H2O2 (spxB, ackA, spxR, tpk and spxA1) are all essential for repressing the growth of S. mutans [102,103]. To protect against H2O2 damage, S. mutans also has a H2O2 resistance system [109,110]. As in S. sanguinis, Dpr (a Dps-like protein) plays an important role in the resistance of S. mutans to ROS [107]. A Δdpr mutant is hypersensitive to H2O2 and more readily killed by S. sanguinis and S. gordonii [109,110]. When co-cultured with S. gordonii, Dpr production is increased in S. mutans to protect against H2O2 damage [109]. The expression of dpr is negatively regulated by the peroxide regulator PerR [110]. As a result, deletion of perR promotes dpr expression and reduces susceptibility to H2O2 [110]. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and a eukaryotic-type serine/threonine protein kinase also contribute to the ability of S. mutans to deal with ROS damage and coexist with S. sanguinis [110]. Since H2O2 producers such as S. sanguinis are prevalent in the oral cavity, Dpr, PerR, SOD and serine/threonine protein kinase may be essential for S. mutans survival in the presence of early colonizing oral streptococci.
As mentioned above, S. mutans produces mutacins that inhibit the growth of S. sanguinis and some other early colonizing oral streptococci [111]. For more information about mutacins, the interested reader is directed to the following review on this topic [112]. Streptococcus sanguinis has been shown to reduce mutacin production by inactivating the S. mutans competence-stimulating peptide (CSP), a quorum sensing signal inducing mutacin gene expression [113]. The mechanism by which this occurs in S. sanguinis may be similar to that of S. gordonii, which produces a challisin-like protease that degrades S. mutans competence-stimulating peptide [113].
Streptococcus mutans and other acidogenic organisms can generate acids from fermentable sugars, which are responsible for the pathogenesis of dental caries (Figure 2B) [114–116]. Because S. sanguinis is more sensitive to acidic conditions than S. mutans [117], the acid microenvironment condition generated by aciduric bacteria may result in decreased abundance of S. sanguinis prior to or concomitant with the development of dental caries. In the oral commensal community, some oral bacteria produce alkali from the metabolism of arginine via the arginine deiminase system (ADS), which protects against caries caused by S. mutans and other aciduric bacteria [118,119]. S. sanguinis is the most prevalent species in the oral cavity that contains the ADS [120]. It may utilize the ADS to maintain pH homeostasis and gain an advantage in competing with S. mutans.
Previous studies reported that a higher concentration of L-arginine existed in the saliva of dental caries-free individuals than that of caries-active individuals [121,122], which suggested that humans may use L-arginine as a weapon to fight against the acid producers in oral biofilm. L-arginine treatment directly reduces the amount of insoluble extracellular polysaccharide production [71,72], which significantly altered the architecture of the biofilm in S. mutans [72]. Although biofilm formation by S. sanguinis is also repressed by exogenous L-arginine [62,123], the addition of arginine reduces the biomass of S. mutans more than that of S. sanguinis within dual-species biofilms (Figure 2C) [123]. In other words, the L-arginine treatment enriches for S. sanguinis but decreases the abundance of S. mutans. In addition, treatment with 15 mg/ml of L-arginine (a clinically effective concentration) decreased the proportion of S. mutans, increased the proportion of S. gordonii and maintained the Actinomyces naeslundii proportion within biofilms [70]. Moreover, a recent study showed that combinatory use of arginine with fluoride could increase S. sanguinis levels further and suppress S. mutans, and thus significantly retard the demineralizing capability of saliva-derived oral biofilm [124]. These studies indicate that L-arginine treatment may be a promising ecological approach to caries management.
In summary, both epidemiological and in vitro studies suggest that S. sanguinis may suppress the generation of dental caries. Nonetheless, we still lack direct evidence to support a definite conclusion concerning the role of S. sanguinis in dental caries. The oral microbiome is exposed to a variety of environmental conditions that may affect this relationship. As an example, the abundance of S. sanguinis is decreased by smoking [125], which may also attenuate its ability to compete against pathogens. It will be of interest to identify new environmental factors leading to dysbiosis. Moreover, a better understanding of these factors may provide new strategies to prevent or treat dental caries.
The association of Streptococcus sanguinis with periodontitis
Description of periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease that compromises the integrity of the tooth-supporting tissues, including gingiva, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone. Over time periodontitis leads to periodontal ligament destruction, loss of supporting alveolar bone and loosening of teeth [1]. In addition, periodontitis is associated with atherosclerosis, adverse pregnancy outcomes, rheumatoid arthritis, aspiration pneumonia and cancer [126–131]. Periodontitis is caused by persistent exposure of periodontal tissue to an ecologically unbalanced polymicrobial dental-plaque community [18,132–133]. In this community, periodontitis-associated microorganisms synergistically interact for enhanced colonization, nutrient procurement and persistence in an inflammatory environment [133,134]. Several bacterial species have been reported to participate in the periodontal disease pathogenesis, such as the ‘red-complex’ bacteria (Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythia and Treponema denticola) [16,135–139], Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans [138–140] and the orange complex bacteria (Fusobacterium nucleatum, PeptoStreptococcus micros, Prevotella intermedia, Prevotella nigrescens, Eubacterium nodatum and Streptococcus constellatus) [16,139,141,142]. The interested reader is directed to the following review on newly discovered pathogens associated with periodontitis [143]. More details about the pathogenesis of periodontitis can be found in several excellent reviews [18,141,144,145].
Evidence of the association of S. sanguinis with periodontitis
During the transition from periodontal health to periodontal disease, the components of microbiomes shift from mostly Gram-positive to mostly Gram-negative species [146]. Streptococcus sanguinis is one of the most important Gram-positive commensal bacteria in the oral cavity [147]. 16S rRNA sequencing data suggest that S. sanguinis has significantly increased abundance in healthy versus diseased subgingival microbiome samples and is a constituent of the core microbiome in periodontal health [15–16,22].
Gingival epithelial cells are stimulated by oral commensal bacteria to produce IL-8 and β-defensins, which may protect periodontal tissue against periodontitis-associated pathogens [148–155]. As a major component of the oral commensal microbiome, S. sanguinis may participate in this process. At the same time, the host response induced by S. sanguinis is much weaker than that induced by P. gingivalis or F. nucleatum. This may be one mechanism by which the host benefits from S. sanguinis competing with these pathogens in the oral cavity [156]. More details about host immune responses to oral microbial flora are shown in the following review [157].
Interaction of S. sanguinis with periodontitis-associated pathogens
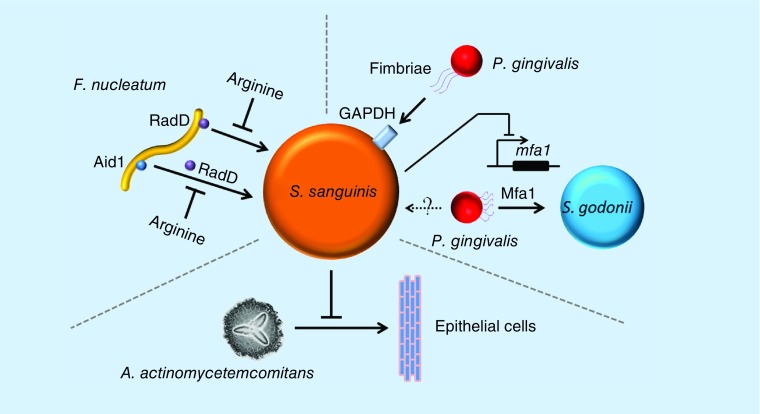
Although suggested to be a health-associated bacterium by 16S rRNA sequencing studies, S. sanguinis may be a potential binding target for the localization of pathogens within dental plaque [158,159]. Porphyromonas gingivalis is thought to be the major etiologic agent in chronic periodontitis [135,160]. The fimbriae of P. gingivalis are able to bind to several streptococcal species, including S. sanguinis, Streptococcus oralis, S. gordonii and Streptococcus parasanguinis (Figure 3) [158]. Western blot analysis demonstrates that purified recombinant fimbrillin of P. gingivalis binds to cell-surface glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases of these streptococci, indicating that P. gingivalis may utilize fimbriae to attach to these bacteria for biofilm formation [158]. Streptococcus sanguinis inhibits the transcription of the mfa1 gene. This gene encodes a structural subunit of P. gingivalis-short fimbriae that mediates coadhesion between P. gingivalis and S. gordonii [161,162]. It is not clear whether Mfa1 promotes the attachment of P. gingivalis to S. sanguinis.
Figure 3. . Interaction of Streptococcus sanguinis with periodontitis-associated pathogens.
Fusobacterium nucleatum can attach to Streptococcus sanguinis via RadD or Aid1. Aid1 attachment is mediated by RadD. Both interactions can be inhibited by the presence of arginine. Porphyromonas gingivalis can attach to S. sanguinis by fimbriae to surface glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases receptors. P. gingivalis can attach to Streptococcus gordonii using small fimbriae made from the adhesin Mfa1. Perhaps this mechanism is also utilized for attachment to S. sanguinis. However, it is known that S. sanguinis can suppress the expression of the mfa1 gene. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans colonization of epithelial cells in a flow chamber will be repressed by the colonization of S. sanguinis.
F. nucleatum is a periodontal pathogen associated with a wide array of human diseases involving chronic and aggressive periodontitis [163]. It has been reported to coaggregate with many oral microorganisms, such as S. sanguinis, S. mutans and P. gingivalis [159]. Moreover, it enhances the coaggregation between S. sanguinis and P. gingivalis [159]. Later studies discovered that an arginine-inhibitable adhesin RadD of F. nucleatum enhances the coaggregation with the Gram-positive ‘early oral colonizers’ including S. sanguinis, Streptococcus oralis, S. gordonii and Actinomyces naeslundii [164]. Deletion of radD decreases S. sanguinis–F. nucleatum dual-species biofilm formation, suggesting that the RadD adhesin plays an essential role in interspecies adherence and multispecies biofilm formation [164]. Another gene, aid1, has also been shown to enhance coaggregation [165]. Additionally, Aid1 function is dependent on RadD and is abolished in the presence of arginine [165]. An in vitro mixed-species oral microbiota system can be stimulated by F. nucleatum to produce H2O2, subsequently killing F. nucleatum [166]. However, H2O2 production and its killing effect are reduced when F. nucleatum is allowed to form coaggregates with S. sanguinis prior to addition to the mixed community [166]. Because a ΔradD mutant is defective in coaggregation, the H2O2 damage of the mutant is not attenuated by exposure to S. sanguinis [166]. These studies suggest that S. sanguinis may help F. nucleatum to survive in the oral cavity. Since the activities of both RadD and Aid1 are inhibited by L-arginine, this raises the interesting question of whether S. sanguinis increases L-arginine biosynthesis in response to F. nucleatum attachment.
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans is another well-studied pathogen associated with periodontal diseases such as localized aggressive periodontitis and, consequently, bone resorption [167,168]. Under flow conditions, the colonization of soft tissue surfaces by A. actinomycetemcomitans is reduced by several streptococci species, and especially by S. sanguinis, indicating the potential beneficial effects of S. sanguinis for preventing periodontitis caused by A. actinomycetemcomitans [169].
Welch et al. observed the spatial organization of complex natural microbiomes in oral samples by FISH [170]. Streptococci occupy a broad range of oral habitats [170]. At the periphery of the dental plaque samples, Streptococcus spp. appears at the distal tips of Corynebacterium spp. filaments, together with Haemophilus spp./Aggregatibacter spp. and Porphyromonas spp., and seems to mediate the association of Porphyromonas spp. with Haemophilus spp./Aggregatibacter spp. [170]. In addition, streptococci may create a microenvironment rich in CO2, lactate and acetate and low in oxygen, which facilitates the survival of Aggregatibacter spp., Capnocytophaga spp., Fusobacterium spp. and Leptotrichia spp. at the inner layer of dental plaque [170]. This study gives direct evidence of colocalization between Porphyromonas spp. and Streptococcus spp. However, it is possible that the Porphyromonas spp. here does not include P. gingivalis because the periphery of dental plaque is recognized as a presumably aerobic environment that would not be suitable for the growth of P. gingivalis [170]. On the other hand, streptococci were not only visible at the bottom, but also appeared at the periphery of dental plaque, suggesting that streptococcal species are a spatially available target for initial attachment of pathogens.
Given our limited knowledge, we cannot draw any firm conclusions about the role of S. sanguinis in the pathogenesis of periodontitis. Based on 16S rRNA sequencing data, S. sanguinis seems to be associated with periodontal health. However, it is not clear whether S. sanguinis actually promotes oral health or merely survives better at healthy sites, making it an indicator of oral health rather than a cause. Moreover, it is also a binding target for P. gingivalis and F. nucleatum. In current periodontitis models, pathogens exist in the biofilm formed on tooth surfaces inside of the periodontal pocket, and then attack oral epithelial cells nearby [18,144]. Because of the complex conditions in the oral cavity, such as salivary flow, immune system response and bleeding, it is difficult to establish an in vivo model that begins with a biofilm of S. sanguinis formed in periodontal pocket and then entails an input pathogen to induce periodontitis. To simplify the problem, the first question we need to clarify is whether the colonization of S. sanguinis on tooth surfaces impacts the attachment and biofilm formation of periodontitis-associated pathogens. The second question is how S. sanguinis responds to pathogen attachment.
Role of S. sanguinis biofilm formation in infective endocarditis
Apart from its role as a primary colonizer in the oral cavity, S. sanguinis is best known as a cause of infective endocarditis, an infection of the valves or endocardial lining of the heart [171]. Indeed, S. sanguinis was first known as ‘Streptococcus s.b.e.,’ for ‘subacute bacterial endocarditis’, and was recognized as a cause of endocarditis well before it was identified as an inhabitant of the oral cavity [172]. In a recent review, oral streptococci including S. sanguinis were recognized as one of the top three causes of endocarditis, alongside two other genera of Gram-positive cocci: staphylococci and enterococci [173].
Endocarditis begins when the causal agent enters the bloodstream to cause a bacteremia and is then carried by the blood to the heart. For oral streptococci, attention is often focused on invasive dental procedures as a cause of bacteremia, although oral streptococci have also been identified as the second-most frequent cause of endocarditis in intravenous drug users and ICU patients [173]. After reaching the heart, S. sanguinis must then adhere to the endocardium. Given the importance of biofilm formation for adhesion in the oral cavity, it would be reasonable to suspect that biofilm formation might be important for adhesion to endocardial surfaces as well. Indeed, endocarditis is often considered an example of a biofilm-mediated disease [174]. There are likely at least three reasons for this association. First, endocarditis occasionally accompanies infections of implanted cardiac devices, such as pacemakers or defibrillators [171]. In these cases, infections are typically caused by species that have been shown to produce biofilms in systemic infections, such as S. aureus or Staphylococcus epidermidis, and biofilms are often found [175]. However, these infections are typically not caused by S. sanguinis or other oral streptococci [176]. Second, even when infection is of the endocardium rather than an implanted device, some causative agents such as C. albicans likely produce biofilms [177]. Third, the typical lesion found in streptococcal (as well as staphylococcal and enterococcal) endocarditis, which is called a ‘vegetation’ [171,178], has some properties in common with a biofilm. Vegetation is a nodule that is composed primarily of platelets and fibrin. In animal models, and presumably in many human patients, sterile vegetations form in response to endocardial damage and precede infection, which explains why rheumatic heart disease, congenital heart conditions that create turbulent blood flow, and certain cardiac surgical procedures such as valve replacements put patients at high risk for subsequent endocarditis [171,179]. In a previous study employing an oral streptococcal isolate and a rabbit model of endocarditis in which cardiac catheterization was used to create minor endocardial damage prior to bacterial inoculation [178], infected vegetations were found to be comprised of bacterial microcolonies enclosed within a matrix of platelets and fibrin. This matrix is likely responsible for protecting embedded bacteria from phagocytic killing [178] and for the relatively long duration of antibiotic treatment that is required for cure [180]. These properties are typical of biofilm infections. Nevertheless, as indicated above, biofilm has been defined as an ‘aggregate of microorganisms in which cells that are frequently embedded within a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substance adhere to each other and/or to a surface’ [181]. Because the platelets and fibrin are not self produced by the infecting bacterium, a vegetation does not fit this definition of a biofilm.
Despite this lack of evidence, or perhaps because of it, other approaches have been used to address whether biofilm formation fitting the standard definition might be important for endocarditis causation, particularly in the earliest stages. Ge et al. [58] examined biofilm formation in a library of 800 signature-tagged mutants of S. sanguinis strain SK36 that had been used previously for an endocarditis virulence screen [182]. The later study identified eight mutants that were defective for biofilm formation in a standard crystal violet assay. Four of these mutants appeared to have reduced endocarditis virulence in the original screen, and the other four did not. Interestingly, five of the biofilm-defective mutants had insertions in genes related to purine or pyrimidine synthesis; the reduced-virulence mutants included two with insertions in the purB gene and the normal-virulence mutants included two with an insertion in the purL gene and one with an insertion in pyrE. The retention of virulence in one of the purL mutants and the pyrE mutant was confirmed, indicating that in vitro biofilm formation could be severely reduced without affecting endocarditis virulence in an animal model. Similar results have been obtained previously by another group working with the closely related oral species, S. gordonii [183]. Later studies employing isogenic mutants of Enterococcus faecalis [184] or analysis of biofilm formation in clinical strains isolated from patients with or without endocarditis also failed to uncover a correlation between biofilm-forming ability and endocarditis causation in E. faecalis [185], S. epidermidis [186] and S. aureus [187]. Finally, Ge et al. [58] showed previously that in vitro biofilm formation by S. sanguinis was far more efficient in the presence of sucrose because sucrose is converted into extracellular glucan [62]. The near absence of sucrose in the blood of normal people [188,189] would be expected to preclude glucan formation on infected heart valves.
The results presented above suggest that S. sanguinis endocarditis causation is not dependent upon biofilm formation. There are, to be sure, some caveats to this conclusion. Leuck et al. [190] reported that biofilm formation in a standard in vitro assay did not correlate with the ability of E. faecalis strains to form biofilms on porcine heart valve explants. It is possible that a similar situation exists with S. sanguinis. Biofilm formation in the cardiac environment could conceivably occur through mechanisms distinct from biofilm formation in the oral cavity or in vitro. Nevertheless, at present, there is no evidence for a role of biofilm formation in S. sanguinis-mediated endocarditis.
Conclusion & future perspective
There are several reasons why S. sanguinis is an ideal model organism for research on the interaction between commensal bacteria and pathogens in biofilms. First, S. sanguinis is highly abundant in a broad range of habitats in the oral cavity [15,20,29–31]. Second, the genome of S. sanguinis strain SK36 has been sequenced and this strain is highly amenable to genetic manipulation [25,191]. Third, many studies suggest that S. sanguinis is significantly related with oral health [13–16,89].
Current studies suggest that S. sanguinis competes with S. mutans, which may lessen or prevent dental caries. However, as a pioneering colonizer, S. sanguinis may also facilitate the attachment of succeeding pathogens. In addition, certain environmental conditions seem to affect the ability of S. sanguinis to maintain an ecologically balanced biofilm in the oral cavity. To more clearly define the role of S. sanguinis in oral health, the first requirement is to establish reasonable models of interaction between commensal bacteria and pathogens for these diseases. A suitable visualization technology is essential to distinguish different bacteria in dual- or multispecies biofilms. It has been reported that codon-optimized fluorescent proteins are available for continuous visualization of S. sanguinis and S. mutans in microaerobic conditions [62,192]. Luciferase enzymes will facilitate in vivo studies [193]. FISH can be used for multispecies biofilm observation [170]. Furthermore, there is significant variation in phenotypes within species of oral S. sanguinis [120,194]. Analysis of phenotypic and genotypic variations of S. sanguinis in different oral samples should be an effective method of exploration of the mechanisms by which S. sanguinis survives in different environmental conditions.
Both dental caries and periodontitis are caused by microbial dysbiosis in the oral cavity. It has been well established that the homeostasis of microbial communities is tightly related with health. However, much more research is aimed at examination of pathogenesis than commensalism. Our inattention to commensal microorganisms may cause many serious problems. For example, the abuse of broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy leads to dysbiosis in the oral cavity and constitutes the major risk factor for invasive candidiasis [195]. We have very limited knowledge concerning the mechanisms leading to microbial dysbiosis.
Future studies on beneficial commensal microorganisms should focus on two things – mechanisms by which commensal microbiota interact with pathogens and the factors leading to microbial dysbiosis. It is necessary to clarify the relationship between environment, beneficial commensal microorganisms, pathogens and diseases. A further understanding of commensal microbiomes will afford new strategies for not only management but prevention of oral diseases.
Executive summary.
Dental caries and periodontitis are two most prevalent diseases in the oral cavity. They are caused by the dysbiosis of oral microbiomes.
Streptococcus sanguinis is a pioneering colonizer and a key player in oral biofilm development.
The initial attachment of S. sanguinis is facilitated by its fimbriae and adhesins. The production of glucans and eDNA promotes the maturation of S. sanguinis biofilm.
Epidemiological studies suggested that S. sanguinis may suppress the generation of dental caries. In vitro studies showed the competition between S. sanguinis and S. mutans, a most common cariogenic species.
The results from 16S rRNA sequencing indicated that S. sanguinis might be associated with periodontal health. However, in vitro studies exhibited that S. sanguinis may also facilitate the attachment of succeeding pathogens associated with periodontitis.
In contrast to the situation in the oral cavity, there is as yet no evidence that biofilm formation is important for S. sanguinis in the cardiac environment in relation to infective endocarditis.
Future studies should focus on mechanisms by which commensal microbiota interact with pathogens and the factors leading to microbial dysbiosis.
Acknowledgements
The authors state that they have tried to present a comprehensive review of the field, and they apologize to all colleagues whose work they may have overlooked.
Footnotes
Author contributions
All authors wrote, reviewed and discussed the manuscript.
Financial & competing interests disclosure
This work was supported by NIH grants R01DE023078 and R01DE018138 (PX). The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Open access
This work is licensed under the Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
References
Papers of special note have been highlighted as: • of interest; •• of considerable interest
- 1.Silk H. Diseases of the mouth. Prim. Care. 2014;41(1):75–90. doi: 10.1016/j.pop.2013.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1211–1259. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Eke PI, Dye B, Wei L, Thornton-Evans G, Genco R. Prevalence of periodontitis in adults in the United States: 2009 and 2010. J. Dent. Res. 2012;91(10):914–920. doi: 10.1177/0022034512457373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dye BA, Thornton-Evans G, Li X, Iafolla TJ. Dental caries and sealant prevalence in children and adolescents in the United States, 2011–2012. NCHS. Data Brief. 2015;(191):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kim JK, Baker LA, Davarian S, Crimmins E. Oral health problems and mortality. J. Dent. Sci. 2013 doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2012.12.011. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jansson L, Lavstedt S, Frithiof L. Relationship between oral health and mortality rate. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2002;29(11):1029–1034. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051x.2002.291108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Adolph M, Darnaud C, Thomas F, et al. Oral health in relation to all-cause mortality: the IPC cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:44604. doi: 10.1038/srep44604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wall T, Nasseh K, Vujicic M. US dental spending remains flat through 2012. Health Policy Resources Center Research Brief. American Dental Association. January. 2014 www.ada.org/∼/media/ADA/Science and Research/Files/HPRCBrief_0114_1.ashx [Google Scholar]
- 9.Petersen PE. World Health Organization global policy for improvement of oral health – World Health Assembly 2007. Int. Dent. J. 2008;58(3):115–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1875-595x.2008.tb00185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dewhirst FE, Chen T, Izard J, et al. The human oral microbiome. J. Bacteriol. 2010;192(19):5002–5017. doi: 10.1128/JB.00542-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Meyer DH, Fives-Taylor PM. Oral pathogens: from dental plaque to cardiac disease. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1998;1(1):88–95. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(98)80147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Flemming H-C, Wingender J, Szewzyk U, Steinberg P, Rice SA, Kjelleberg S. Biofilms: an emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016;14(9):563–575. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bik EM, Long CD, Armitage GC, et al. Bacterial diversity in the oral cavity of 10 healthy individuals. ISME J. 2010;4(8):962–974. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2010.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Belda-Ferre P, Alcaraz LD, Cabrera-Rubio R, et al. The oral metagenome in health and disease. ISME J. 2012;6(1):46–56. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2011.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Abusleme L, Dupuy AK, Dutzan N, et al. The subgingival microbiome in health and periodontitis and its relationship with community biomass and inflammation. ISME J. 2013;7(5):1016–1025. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2012.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Griffen AL, Beall CJ, Campbell JH, et al. Distinct and complex bacterial profiles in human periodontitis and health revealed by 16S pyrosequencing. ISME J. 2012;6(6):1176–1185. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2011.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pitts NB, Zero DT, Marsh PD, et al. Dental caries. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2017;3:17030. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; •• A comprehensive review of dental caries.
- 18.Darveau RP. Periodontitis: a polymicrobial disruption of host homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010;8(7):481–490. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; •• A comprehensive review of periodontitis.
- 19.Scully C, El-Kabir M, Samaranayake LP. Candida and oral candidosis: a review. Crit. Rev. Oral. Biol. Med. 1994;5(2):125–157. doi: 10.1177/10454411940050020101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gross EL, Beall CJ, Kutsch SR, Firestone ND, Leys EJ, Griffen AL. Beyond Streptococcus mutans: dental caries onset linked to multiple species by 16S rRNA community analysis. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(10):e47722. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Corby P, Lyons-Weiler J, Bretz W, et al. Microbial risk indicators of early childhood caries. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005;43(11):5753–5759. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.11.5753-5759.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Goncalves LF, Fermiano D, Feres M, et al. Levels of Selenomonas species in generalized aggressive periodontitis. J. Periodontal. Res. 2012;47(6):711–718. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2012.01485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gurung I, Spielman I, Davies MR, et al. Functional analysis of an unusual type IV pilus in the Gram-positive Streptococcus sanguinis . Mol. Microbiol. 2016;99(2):380–392. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gurung I, Berry J-L, Hall AM, Pelicic V. Cloning-independent markerless gene editing in Streptococcus sanguinis: novel insights in type IV pilus biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;45(6):e40. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xu P, Alves JM, Kitten T, et al. Genome of the opportunistic pathogen Streptococcus sanguinis . J. Bacteriol. 2007;189(8):3166–3175. doi: 10.1128/JB.01808-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; • Whole genome sequencing of Streptococcus sanguinis SK36.
- 26.Socransky S, Manganiello A, Propas D, Oram V, Houte JV. Bacteriological studies of developing supragingival dental plaque. J. Periodontal. Res. 1977;12(2):90–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1977.tb00112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Caufield PW, Dasanayake AP, Li Y, Pan Y, Hsu J, Hardin JM. Natural history of Streptococcus sanguinis in the oral cavity of infants: evidence for a discrete window of infectivity. Infect. Immun. 2000;68(7):4018–4023. doi: 10.1128/iai.68.7.4018-4023.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Aas JA, Paster BJ, Stokes LN, Olsen I, Dewhirst FE. Defining the normal bacterial flora of the oral cavity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005;43(11):5721–5732. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.11.5721-5732.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Seoudi N, Bergmeier LA, Drobniewski F, Paster B, Fortune F. The oral mucosal and salivary microbial community of Behçet's syndrome and recurrent aphthous stomatitis. J. Oral Microbiol. 2015;7(1):27150. doi: 10.3402/jom.v7.27150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Francavilla R, Ercolini D, Piccolo M, et al. Salivary microbiota and metabolome associated with celiac disease. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2014;80(11):3416–3425. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00362-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hintao J, Teanpaisan R, Chongsuvivatwong V, Ratarasan C, Dahlen G. The microbiological profiles of saliva, supragingival and subgingival plaque and dental caries in adults with and without Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Oral. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007;22(3):175–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302X.2007.00341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Haffajee A, Teles R, Patel M, Song X, Yaskell T, Socransky S. Factors affecting human supragingival biofilm composition. II. Tooth position. J. Periodontal. Res. 2009;44(4):520–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2008.01155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pita PPC, Rodrigues JA, Ota-Tsuzuki C, et al. Oral streptococci biofilm formation on different implant surface topographies. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015:159625. doi: 10.1155/2015/159625. 2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Winkler C, Schäfer L, Felthaus O, et al. The bacterial adhesion on and the cytotoxicity of various dental cements used for implant-supported fixed restorations. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2014;72(4):241–250. doi: 10.3109/00016357.2013.828320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lee J-H, Jeong W-S, Seo S-J, et al. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma functionalized dental implant for enhancement of bacterial resistance and osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 2017;33(3):257–270. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2016.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Smith MM, Knight ET, Al-Harthi L, Leichter JW. Chronic periodontitis and implant dentistry. Periodontal. 2000. 2017;74(1):63–73. doi: 10.1111/prd.12190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ericsson I, Berglundh T, Marinello C, Liljenberg B, Lindhe J. Long-standing plaque and gingivitis at implants and teeth in the dog. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1992;3(3):99–103. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.1992.030301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Pontoriero R, Tonelli M, Carnevale G, Mombelli A, Nyman S, Lang N. Experimentally induced peri-implant mucositis. A clinical study in humans. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1994;5(4):254–259. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.1994.050409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Stoodley P, Sauer K, Davies DG, Costerton JW. Biofilms as complex differentiated communities. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002;56(1):187–209. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Flemming H-C, Wingender J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010;8(9):623–633. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Fachon-Kalweit S, Elder BL, Fives-Taylor P. Antibodies that bind to fimbriae block adhesion of Streptococcus sanguis to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect. Immun. 1985;48(3):617–624. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.617-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Okahashi N, Nakata M, Terao Y, et al. Pili of oral Streptococcus sanguinis bind to salivary amylase and promote the biofilm formation. Microb. Pathog. 2011;50(3):148–154. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2011.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ganeshkumar N, Song M, Mcbride B. Cloning of a Streptococcus sanguis adhesin which mediates binding to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect. Immun. 1988;56(5):1150–1157. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1150-1157.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ganeshkumar N, Arora N, Kolenbrander P. Saliva-binding protein (SsaB) from Streptococcus sanguis 12 is a lipoprotein. J. Bacteriol. 1993;175(2):572–574. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.2.572-574.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Herzberg M. Platelet-streptococcal interactions in endocarditis. Crit. Rev. Oral. Biol. Med. 1996;7(3):222–236. doi: 10.1177/10454411960070030201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Das S, Kanamoto T, Ge X, et al. Contribution of lipoproteins and lipoprotein processing to endocarditis virulence in Streptococcus sanguinis . J. Bacteriol. 2009;191(13):4166–4179. doi: 10.1128/JB.01739-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Turner LS, Das S, Kanamoto T, Munro CL, Kitten T. Development of genetic tools for in vivo virulence analysis of Streptococcus sanguinis . Microbiology. 2009;155(8):2573–2582. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.024513-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rhodes DV, Crump KE, Makhlynets O, et al. Genetic characterization and role in virulence of the ribonucleotide reductases of Streptococcus sanguinis . J. Biol. Chem. 2014;289(9):6273–6287. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.533620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Crump KE, Bainbridge B, Brusko S, et al. The relationship of the lipoprotein SsaB, manganese and superoxide dismutase in Streptococcus sanguinis virulence for endocarditis. Mol. Microbiol. 2014;92(6):1243–1259. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kerrigan SW, Douglas I, Wray A, et al. A role for glycoprotein Ib in Streptococcus sanguis-induced platelet aggregation. Blood. 2002;100(2):509–516. doi: 10.1182/blood.v100.2.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Plummer C, Wu H, Kerrigan SW, Meade G, Cox D, Ian Douglas C. A serine-rich glycoprotein of Streptococcus sanguis mediates adhesion to platelets via GPIb. Br. J. Haematol. 2005;129(1):101–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Loukachevitch LV, Bensing BA, Yu H, et al. Structures of the Streptococcus sanguinis SrpA binding region with human sialoglycans suggest features of the physiological ligand. Biochemistry. 2016;55(42):5927–5937. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bensing BA, Loukachevitch LV, Mcculloch KM, et al. Structural basis for sialoglycan binding by the Streptococcus sanguinis SrpA adhesin. J. Biol. Chem. 2016;291(14):7230–7240. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.701425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Takamatsu D, Bensing BA, Prakobphol A, Fisher SJ, Sullam PM. Binding of the streptococcal surface glycoproteins GspB and Hsa to human salivary proteins. Infect. Immun. 2006;74(3):1933–1940. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.3.1933-1940.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Takahashi Y, Konishi K, Cisar JO, Yoshikawa M. Identification and characterization of hsa, the gene encoding the sialic acid-binding adhesin of Streptococcus gordonii DL1. Infect. Immun. 2002;70(3):1209–1218. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.3.1209-1218.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Turner LS, Kanamoto T, Unoki T, Munro CL, Wu H, Kitten T. Comprehensive evaluation of Streptococcus sanguinis cell wall-anchored proteins in early infective endocarditis. Infect. Immun. 2009;77(11):4966–4975. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00760-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kopec LK, Vacca AM, Lindang-Evans SD, Bowen WH. Properties of Streptococcus sanguinis glucans formed under various conditions. Caries Res. 2001;35:67–74. doi: 10.1159/000047434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ge X, Kitten T, Chen Z, Lee SP, Munro CL, Xu P. Identification of Streptococcus sanguinis genes required for biofilm formation and examination of their role in endocarditis virulence. Infect. Immun. 2008;76(6):2551–2559. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00338-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Lemos JA, Abranches J, Burne RA. Responses of cariogenic streptococci to environmental stresses. Curr. Issues. Mol. Biol. 2005;7(1):95–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Yoshida Y, Konno H, Nagano K, et al. The influence of a glucosyltransferase, encoded by gtfP, on biofilm formation by Streptococcus sanguinis in a dual-species model. APMIS. 2014;122(10):951–960. doi: 10.1111/apm.12238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Liu J, Stone VN, Ge X, Tang M, Elrami F, Xu P. TetR family regulator brpT modulates biofilm formation in Streptococcus sanguinis . PLoS ONE. 2017;12(1):e0169301. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Zhu B, Ge X, Stone V, et al. ciaR impacts biofilm formation by regulating an arginine biosynthesis pathway in Streptococcus sanguinis SK36. Sci. Rep. 2017;7(1):17183. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17383-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; • Discovery of arginine biosynthesis pathway impacting biofilm formation.
- 63.Whitchurch CB, Tolker-Nielsen T, Ragas PC, Mattick JS. Extracellular DNA required for bacterial biofilm formation. Science. 2002;295(5559):1487. doi: 10.1126/science.295.5559.1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Dengler V, Foulston L, Defrancesco AS, Losick R. An electrostatic net model for the role of extracellular DNA in biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus . J. Bacteriol. 2015;197(24):3779–3787. doi: 10.1128/JB.00726-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kreth J, Vu H, Zhang Y, Herzberg MC. Characterization of hydrogen peroxide-induced DNA release by Streptococcus sanguinis and Streptococcus gordonii . J. Bacteriol. 2009;191(20):6281–6291. doi: 10.1128/JB.00906-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Moraes JJ, Stipp RN, Harth-Chu EN, Camargo TM, Höfling JF, Mattos-Graner RO. Two-component system VicRK regulates functions associated with establishment of Streptococcus sanguinis in biofilms. Infect. Immun. 2014;82(12):4941–4951. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01850-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ge X, Shi X, Shi L, et al. Involvement of NADH oxidase in biofilm formation in Streptococcus sanguinis . PLoS ONE. 2016;11(3):e0151142. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Zheng L, Chen Z, Itzek A, Ashby M, Kreth J. Catabolite control protein A controls hydrogen peroxide production and cell death in Streptococcus sanguinis . J. Bacteriol. 2011;193(2):516–526. doi: 10.1128/JB.01131-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Enwonwu C, Ilupeju F, Warren R. Arginine metabolism in the salivary glands of protein-deficient rats and its potential association with the oral microflora. Caries Res. 1994;28(2):99–105. doi: 10.1159/000261629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.He J, Hwang G, Liu Y, et al. l-arginine modifies the exopolysaccharide matrix and thwarts Streptococcus mutans outgrowth within mixed-species oral biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 2016;198(19):2651–2661. doi: 10.1128/JB.00021-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Huang X, Zhang K, Deng M, et al. Effect of arginine on the growth and biofilm formation of oral bacteria. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2017;82:256–262. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2017.06.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Sharma S, Lavender S, Woo J, et al. Nanoscale characterization of effect of L-arginine on Streptococcus mutans biofilm adhesion by atomic force microscopy. Microbiology. 2014;160(7):1466–1473. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.075267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Aynapudi J, El-Rami F, Ge X, et al. Involvement of signal peptidase I in Streptococcus sanguinis biofilm formation. Microbiology. 2017;163(9):1306–1318. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Camargo TM, Stipp RN, Alves LA, Harth-Chu EN, Hofling JF, Mattos-Graner RO. A novel two-component system of Streptococcus sanguinis affecting functions associated with viability in saliva and biofilm formation. Infect. Immun. 2018 doi: 10.1128/IAI.00942-17. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kalia D, Merey G, Nakayama S, et al. Nucleotide, c-di-GMP, c-di-AMP, cGMP, cAMP, (p) ppGpp signaling in bacteria and implications in pathogenesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013;42(1):305–341. doi: 10.1039/c2cs35206k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Gundlach J, Rath H, Herzberg C, Mäder U, Stülke J. Second messenger signaling in Bacillus subtilis: accumulation of cyclic di-AMP inhibits biofilm formation. Front. Microbiol. 2016;7:804. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Ono K, Oka R, Toyofuku M, et al. cAMP signaling affects irreversible attachment during biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Microbes Environ. 2014;29(1):104–106. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME13151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.De Paz LEC, Lemos JA, Wickström C, Sedgley CM. Role of (p)ppGpp in biofilm formation by Enterococcus faecalis . Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012;78(5):1627–1630. doi: 10.1128/AEM.07036-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Zero DT. Dental caries process. Dent. Clin. North. Am. 1999;43(4):635–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Featherstone JD. The continuum of dental caries – evidence for a dynamic disease process. J. Dent. Res. 2004;83(Spec No. C):C39–C42. doi: 10.1177/154405910408301s08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Van Houte J. Microbiological predictors of caries risk. Adv. Dent. Res. 1993;7(2):87–96. doi: 10.1177/08959374930070022001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Badet C, Thebaud NB. Ecology of lactobacilli in the oral cavity: a review of literature. Open. Microbiol. J. 2008;2:38–48. doi: 10.2174/1874285800802010038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Klinke T, Kneist S, De Soet JJ, et al. Acid production by oral strains of Candida albicans and lactobacilli. Caries Res. 2009;43(2):83–91. doi: 10.1159/000204911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Mantzourani M, Fenlon M, Beighton D. Association between Bifidobacteriaceae and the clinical severity of root caries lesions. Oral. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009;24(1):32–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302X.2008.00470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Van Houte J. Role of micro-organisms in caries etiology. J. Dent. Res. 1994;73(3):672–681. doi: 10.1177/00220345940730031301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Beighton D, Brailsford S, Samaranayake LP, et al. A multi-country comparison of caries-associated microflora in demographically diverse children. Community Dent. Health. 2004;21(1 Suppl.):96–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Moalic E, Gestalin A, Quinio D, Gest PE, Zerilli A, Le Flohic AM. The extent of oral fungal flora in 353 students and possible relationships with dental caries. Caries Res. 2001;35(2):149–155. doi: 10.1159/000047447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Raja M, Hannan A, Ali K. Association of oral candidal carriage with dental caries in children. Caries Res. 2010;44(3):272–276. doi: 10.1159/000314675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Gross EL, Leys EJ, Gasparovich SR, et al. Bacterial 16S sequence analysis of severe caries in young permanent teeth. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010;48(11):4121–4128. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01232-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Aas JA, Griffen AL, Dardis SR, et al. Bacteria of dental caries in primary and permanent teeth in children and young adults. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008;46(4):1407–1417. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01410-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Loesche WJ. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol. Rev. 1986;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Gao X, Jiang S, Koh D, Hsu CY. Salivary biomarkers for dental caries. Periodontol. 2000. 2016;70(1):128–141. doi: 10.1111/prd.12100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Becker MR, Paster BJ, Leys EJ, et al. Molecular analysis of bacterial species associated with childhood caries. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002;40(3):1001–1009. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.3.1001-1009.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Mikx F, Van Der Hoeven J, Plasschaert A, König K. Establishment and symbiosis of Actinomyces viscosus, Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans in germ-free Osborne-Mendel rats. Caries Res. 1976;10(2):123–132. doi: 10.1159/000260196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Kreth J, Merritt J, Shi W, Qi F. Competition and coexistence between Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguinis in the dental biofilm. J. Bacteriol. 2005;187(21):7193–7203. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.21.7193-7203.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; • H2O2 and mutacins were discovered as the weapons for the competition between S. sanguinis and Streptococcus mutans. The styles of the interaction were dependent on environmental conditions.
- 96.Giacaman RA, Torres S, Gómez Y, Muñoz-Sandoval C, Kreth J. Correlation of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguinis colonization and ex vivo hydrogen peroxide production in carious lesion-free and high caries adults. Arch. Oral Biol. 2015;60(1):154–159. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2014.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Valdebenito B, Tullume-Vergara PO, Gonzalez W, Kreth J. In silico analysis of the competition between Streptococcus sanguinis and Streptococcus mutans in the dental biofilm. Mol. Oral. Microbiol. 2017;33(2):168–180. doi: 10.1111/omi.12209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Carlsson J, Edlund MBK, Lundmark SK. Characteristics of a hydrogen peroxide-forming pyruvate oxidase from Streptococcus sanguis . Mol. Oral. Microbiol. 1987;2(1):15–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1987.tb00264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Carlsson J, Edlund MBK. Pyruvate oxidase in Streptococcus sanguis under various growth conditions. Mol. Oral. Microbiol. 1987;2(1):10–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1987.tb00263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Zheng L-Y, Itzek A, Chen Z-Y, Kreth J. Oxygen dependent pyruvate oxidase expression and production in Streptococcus sanguinis . Int. J. Oral Sci. 2011;3(2):82–89. doi: 10.4248/IJOS11030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Kreth J, Zhang Y, Herzberg MC. Streptococcal antagonism in oral biofilms: Streptococcus sanguinis and Streptococcus gordonii interference with Streptococcus mutans . J. Bacteriol. 2008;190(13):4632–4640. doi: 10.1128/JB.00276-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Chen L, Ge X, Dou Y, Wang X, Patel JR, Xu P. Identification of hydrogen peroxide production-related genes in Streptococcus sanguinis and their functional relationship with pyruvate oxidase. Microbiology. 2011;157(1):13–20. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.039669-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Chen L, Ge X, Wang X, Patel JR, Xu P. SpxA1 involved in hydrogen peroxide production, stress tolerance and endocarditis virulence in Streptococcus sanguinis . PLoS ONE. 2012;7(6):e40034. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Li T, Xu M, Zheng L. Is SpxA2 involved in hydrogen peroxide production and competence development in Streptococcus sanguinis? J. Med. Microbiol. 2017;66(7):981–989. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Li T, Zhai S, Xu M, et al. SpxB-mediated H2O2 induces programmed cell death in Streptococcus sanguinis . J. Basic Microbiol. 2016;56(7):741–752. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201500617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Xu Y, Itzek A, Kreth J. Comparison of genes required for H2O2 resistance in Streptococcus gordonii and Streptococcus sanguinis . Microbiology. 2014;160(12):2627–2638. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.082156-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Yamamoto Y, Poole LB, Hantgan RR, Kamio Y. An iron-binding protein, Dpr, from Streptococcus mutans prevents iron-dependent hydroxyl radical formation in vitro. J. Bacteriol. 2002;184(11):2931–2939. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.11.2931-2939.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Marco S, Rullo R, Albino A, Masullo M, De Vendittis E, Amato M. The thioredoxin system in the dental caries pathogen Streptococcus mutans and the food-industry bacterium Streptococcus thermophilus. Biochimie. 2013;95(11):2145–2156. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Yoshida A, Niki M, Yamamoto Y, Yasunaga A, Ansai T. Proteome analysis identifies the Dpr protein of Streptococcus mutans as an important factor in the presence of early streptococcal colonizers of tooth surfaces. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(3):e0121176. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Fujishima K, Kawada-Matsuo M, Oogai Y, Tokuda M, Torii M, Komatsuzawa H. dpr and sod in Streptococcus mutans are involved in coexistence with Streptococcus sanguinis, and PerR is associated with resistance to H2O2 . Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013;79(5):1436–1443. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03306-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Hossain MS, Biswas I. Mutacins from Streptococcus mutans UA159 are active against multiple streptococcal species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011;77(7):2428–2434. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02320-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Merritt J, Qi F. The mutacins of Streptococcus mutans: regulation and ecology. Mol. Oral. Microbiol. 2012;27(2):57–69. doi: 10.1111/j.2041-1014.2011.00634.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Wang B-Y, Kuramitsu HK. Interactions between oral bacteria: inhibition of Streptococcus mutans bacteriocin production by Streptococcus gordonii . Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005;71(1):354–362. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.1.354-362.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Banas JA. Virulence properties of Streptococcus mutans . Front. Biosci. 2004;9(10):1267–1277. doi: 10.2741/1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Klein MI, Hwang G, Santos PH, Campanella OH, Koo H. Streptococcus mutans-derived extracellular matrix in cariogenic oral biofilms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015;5:10. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Xiao J, Klein MI, Falsetta ML, et al. The exopolysaccharide matrix modulates the interaction between 3D architecture and virulence of a mixed-species oral biofilm. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(4):e1002623. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Takahashi N, Horiuchi M, Yamada T. Effects of acidification on growth and glycolysis of Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans . Mol. Oral. Microbiol. 1997;12(2):72–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1997.tb00620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Liu Y-L, Nascimento M, Burne RA. Progress toward understanding the contribution of alkali generation in dental biofilms to inhibition of dental caries. Int. J. Oral. Sci. 2012;4(3):135–140. doi: 10.1038/ijos.2012.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Burne RA, Marquis RE. Alkali production by oral bacteria and protection against dental caries. FEMS. Microbiol. Lett. 2000;193(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Huang X, Schulte RM, Burne RA, Nascimento MM. Characterization of the arginolytic microflora provides insights into pH homeostasis in human oral biofilms. Caries Res. 2015;49(2):165–176. doi: 10.1159/000365296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Vanwuyckhuyse B, Perinpanayagam H, Bevacqua D, et al. Association of free arginine and lysine concentrations in human parotid saliva with caries experience. J. Dent. Res. 1995;74(2):686–690. doi: 10.1177/00220345950740021001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Nascimento M, Gordan V, Garvan C, Browngardt C, Burne R. Correlations of oral bacterial arginine and urea catabolism with caries experience. Mol. Oral. Microbiol. 2009;24(2):89–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302X.2008.00477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Zheng X, Cheng X, Wang L, et al. Combinatorial effects of arginine and fluoride on oral bacteria. J. Dent. Res. 2015;94(2):344–353. doi: 10.1177/0022034514561259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Zheng X, He J, Wang L, et al. Ecological effect of arginine on oral microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2017;7(1):7206. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07042-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Shchipkova A, Nagaraja H, Kumar P. Subgingival microbial profiles of smokers with periodontitis. J. Dent. Res. 2010;89(11):1247–1253. doi: 10.1177/0022034510377203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Genco RJ, Van Dyke TE. Prevention: reducing the risk of CVD in patients with periodontitis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2010;7(9):479–480. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2010.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Lundberg K, Wegner N, Yucel-Lindberg T, Venables PJ. Periodontitis in RA-the citrullinated enolase connection. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010;6(12):727–730. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2010.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Kebschull M, Demmer RT, Papapanou PN. “Gum bug, leave my heart alone!” – epidemiologic and mechanistic evidence linking periodontal infections and atherosclerosis. J. Dent. Res. 2010;89(9):879–902. doi: 10.1177/0022034510375281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Whitmore SE, Lamont RJ. Oral bacteria and cancer. PLoS Pathog. 2014;10(3):e1003933. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Han YW, Wang X. Mobile microbiome: oral bacteria in extra-oral infections and inflammation. Dent. Res. 2013;92(6):485–491. doi: 10.1177/0022034513487559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Madianos PN, Bobetsis YA, Offenbacher S. Adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs) and periodontal disease: pathogenic mechanisms. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2013;40(Suppl. 14):S170–S180. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Rosier BT, De Jager M, Zaura E, Krom BP. Historical and contemporary hypotheses on the development of oral diseases: are we there yet? Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2014;4:92. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Hajishengallis G, Lamont RJ. Beyond the red complex and into more complexity: the polymicrobial synergy and dysbiosis (PSD) model of periodontal disease etiology. Mol. Oral. Microbiol. 2012;27(6):409–419. doi: 10.1111/j.2041-1014.2012.00663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Hajishengallis G, Lamont RJ. Breaking bad: manipulation of the host response by Porphyromonas gingivalis . Eur. J. Immunol. 2014;44(2):328–338. doi: 10.1002/eji.201344202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Olsen I, Yilmaz Ö. Modulation of inflammasome activity by Porphyromonas gingivalis in periodontitis and associated systemic diseases. J. Oral. Microbiol. 2016;8(1):30385. doi: 10.3402/jom.v8.30385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Holt SC, Ebersole JL. Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola, and Tannerella forsythia: the ‘red complex’, a prototype polybacterial pathogenic consortium in periodontitis. Periodontol. 2000. 2005;38(1):72–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2005.00113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Bodet C, Chandad F, Grenier D. Pathogenic potential of Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola and Tannerella forsythia, the red bacterial complex associated with periodontitis. Pathol. Biol. 2007;55(3–4):154–162. doi: 10.1016/j.patbio.2006.07.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Duran-Pinedo AE, Chen T, Teles R, et al. Community-wide transcriptome of the oral microbiome in subjects with and without periodontitis. ISME J. 2014;8(8):1659–1672. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2014.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Babaev E, Balmasova I, Mkrtumyan A, et al. Metagenomic analysis of gingival sulcus microbiota and pathogenesis of periodontitis associated with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017;163(6):718–721. doi: 10.1007/s10517-017-3888-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Åberg CH, Kelk P, Johansson A. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans: virulence of its leukotoxin and association with aggressive periodontitis. Virulence. 2015;6(3):188–195. doi: 10.4161/21505594.2014.982428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Socransky S, Haffajee A, Cugini M, Smith C, Kent R. Microbial complexes in subgingival plaque. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1998;25(2):134–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1998.tb02419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Könönen E, Müller HP. Microbiology of aggressive periodontitis. Periodontol. 2000. 2014;65(1):46–78. doi: 10.1111/prd.12016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Perez-Chaparro PJ, Goncalves C, Figueiredo LC, et al. Newly identified pathogens associated with periodontitis: a systematic review. J. Dent. Res. 2014;93(9):846–858. doi: 10.1177/0022034514542468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Hajishengallis G. Periodontitis: from microbial immune subversion to systemic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015;15(1):30–44. doi: 10.1038/nri3785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Hajishengallis G. The inflammophilic character of the periodontitis-associated microbiota. Mol. Oral. Microbiol. 2014;29(6):248–257. doi: 10.1111/omi.12065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Marsh PD. Microbial ecology of dental plaque and its significance in health and disease. Adv. Dent. Res. 1994;8(2):263–271. doi: 10.1177/08959374940080022001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Kreth J, Giacaman RA, Raghavan R, Merritt J. The road less traveled – defining molecular commensalism with Streptococcus sanguinis . Mol. Oral. Microbiol. 2017;32(3):181–196. doi: 10.1111/omi.12170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; •• A comprehensive review of S. sanguinis.
- 148.Dixon DR, Bainbridge BW, Darveau RP. Modulation of the innate immune response within the periodontium. Periodontol. 2000. 2004;35(1):53–74. doi: 10.1111/j.0906-6713.2004.003556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Tonetti MS, Imboden MA, Gerber L, Lang NP, Laissue J, Mueller C. Localized expression of mRNA for phagocyte-specific chemotactic cytokines in human periodontal infections. Infect. Immun. 1994;62(9):4005–4014. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.9.4005-4014.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Lu Q, Samaranayake LP, Darveau RP, Jin L. Expression of human β-defensin-3 in gingival epithelia. J. Periodontal Res. 2005;40(6):474–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2005.00827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Darveau RP, Belton CM, Reife RA, Lamont RJ. Local chemokine paralysis, a novel pathogenic mechanism for Porphyromonas gingivalis . Infect. Immun. 1998;66(4):1660–1665. doi: 10.1128/iai.66.4.1660-1665.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Hasegawa Y, Mans JJ, Mao S, et al. Gingival epithelial cell transcriptional responses to commensal and opportunistic oral microbial species. Infect. Immun. 2007;75(5):2540–2547. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01957-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Huang GT-J, Zhang H-B, Dang HN, Haake SK. Differential regulation of cytokine genes in gingival epithelial cells challenged by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Porphyromonas gingivalis . Microb. Pathog. 2004;37(6):303–312. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2004.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Chung W, Dommisch H, Yin L, Dale B. Expression of defensins in gingiva and their role in periodontal health and disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007;13(30):3073–3083. doi: 10.2174/138161207782110435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Krisanaprakornkit S, Kimball JR, Weinberg A, Darveau RP, Bainbridge BW, Dale BA. Inducible expression of human β-defensin 2 by Fusobacterium nucleatum in oral epithelial cells: multiple signaling pathways and role of commensal bacteria in innate immunity and the epithelial barrier. Infect. Immun. 2000;68(5):2907–2915. doi: 10.1128/iai.68.5.2907-2915.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Peyret-Lacombe A, Brunel G, Watts M, Charveron M, Duplan H. TLR2 sensing of F. nucleatum and S. sanguinis distinctly triggered gingival innate response. Cytokine. 2009;46(2):201–210. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2009.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Sultan AS, Kong EF. The oral microbiome: a lesson in coexistence. PLoS Pathog. 2018;14(1):e1006719. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Maeda K, Nagata H, Nonaka A, Kataoka K, Tanaka M, Shizukuishi S. Oral streptococcal glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mediates interaction with Porphyromonas gingivalis fimbriae. Microbes Infect. 2004;6(13):1163–1170. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2004.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Bradshaw DJ, Marsh PD, Watson GK, Allison C. Role of Fusobacterium nucleatum and coaggregation in anaerobe survival in planktonic and biofilm oral microbial communities during aeration. Infect. Immun. 1998;66(10):4729–4732. doi: 10.1128/iai.66.10.4729-4732.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.How KY, Song KP, Chan KG. Porphyromonas gingivalis: an overview of periodontopathic pathogen below the gum line. Front. Microbiol. 2016 doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00053. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Park Y, James CE, Yoshimura F, Lamont RJ. Expression of the short fimbriae of Porphyromonas gingivalis is regulated in oral bacterial consortia. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006;262(1):65–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Park Y, Simionato MR, Sekiya K, et al. Short fimbriae of Porphyromonas gingivalis and their role in coadhesion with Streptococcus gordonii . Infect. Immun. 2005;73(7):3983–3989. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.7.3983-3989.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Han YW. Fusobacterium nucleatum: a commensal-turned pathogen. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015;23:141–147. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2014.11.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Kaplan CW, Lux R, Haake SK, Shi W. The Fusobacterium nucleatum outer membrane protein RadD is an arginine-inhibitable adhesin required for inter-species adherence and the structured architecture of multispecies biofilm. Mol. Microbiol. 2009;71(1):35–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06503.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Kaplan A, Kaplan CW, He X, Mchardy I, Shi W, Lux R. Characterization of aid1, a novel gene involved in Fusobacterium nucleatum interspecies interactions. Microb. Ecol. 2014;68(2):379–387. doi: 10.1007/s00248-014-0400-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.He X, Hu W, Kaplan CW, Guo L, Shi W, Lux R. Adherence to streptococci facilitates Fusobacterium nucleatum integration into an oral microbial community. Microb. Ecol. 2012;63(3):532–542. doi: 10.1007/s00248-011-9989-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Gholizadeh P, Pormohammad A, Eslami H, Gogani BS, Fakhrzadeh V, Kafil HS. Oral pathogenesis of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans . Microb. Pathog. 2017;113:303–311. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Herbert BA, Novince CM, Kirkwood KL. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, a potent immunoregulator of the periodontal host defense system and alveolar bone homeostasis. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2016;31(3):207–227. doi: 10.1111/omi.12119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Sliepen I, Van Essche M, Loozen G, Van Eldere J, Quirynen M, Teughels W. Interference with Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans: colonization of epithelial cells under hydrodynamic conditions. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2009;24(5):390–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302X.2009.00531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Mark Welch JL, Rossetti BJ, Rieken CW, Dewhirst FE, Borisy GG. Biogeography of a human oral microbiome at the micron scale. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2016;113(6):E791–E800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1522149113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; • An in vivo study of oral microbiome by FISH.
- 171.Cahill TJ, Prendergast BD. Infective endocarditis. Lancet. 2016;387(10021):882–893. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.White JC, Niven CF., Jr Streptococcus S.B.E.: A Streptococcus associated with subacute bacterial endocarditis. J. Bacteriol. 1946;51(6):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.51.6.717-722.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Vogkou CT, Vlachogiannis NI, Palaiodimos L, Kousoulis AA. The causative agents in infective endocarditis: a systematic review comprising 33,214 cases. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016;35(8):1227–1245. doi: 10.1007/s10096-016-2660-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Moser C, Pedersen HT, Lerche CJ, et al. Biofilms and host response – helpful or harmful. APMIS. 2017;125(4):320–338. doi: 10.1111/apm.12674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Marrie TJ, Nelligan J, Costerton JW. A scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of an infected endocardial pacemaker lead. Circulation. 1982;66(6):1339–1341. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.66.6.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Eberhard J, Stumpp N, Ismail F, et al. The oral cavity is not a primary source for implantable pacemaker or cardioverter defibrillator infections. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2013;8:73. doi: 10.1186/1749-8090-8-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Yuan SM. Fungal Endocarditis. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016;31(3):252–255. doi: 10.5935/1678-9741.20160026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Durack DT. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. IV. Structure and evolution of very early lesions. J. Pathol. 1975;115(2):81–89. doi: 10.1002/path.1711150204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Strom BL, Abrutyn E, Berlin JA, et al. Dental and cardiac risk factors for infective endocarditis – a population-based, case–control study. Ann. Intern. Med. 1998;129(10):761–769. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-129-10-199811150-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Baddour LM, Wilson WR, Bayer AS, et al. Infective endocarditis in adults: diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;132:1435–1486. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Vert M, Doi Y, Hellwich KH, et al. Terminology for biorelated polymers and applications (IUPAC Recommendations 2012) Pure Appl. Chem. 2012;84(2):377–408. [Google Scholar]
- 182.Paik S, Senty L, Das S, Noe JC, Munro CL, Kitten T. Identification of virulence determinants for endocarditis in Streptococcus sanguinis by signature-tagged mutagenesis. Infect. Immun. 2005;73(9):6064–6074. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.9.6064-6074.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Bizzini A, Beggah-Moller S, Moreillon P, Entenza JM. Lack of in vitro biofilm formation does not attenuate the virulence of Streptococcus gordonii in experimental endocarditis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2006;48(3):419–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2006.00168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Frank KL, Guiton PS, Barnes AMT, et al. AhrC and Eep are biofilm infection-associated virulence factors in Enterococcus faecalis . Infect. Immun. 2013;81(5):1696–1708. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01210-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Johansson D, Rasmussen M. Virulence factors in isolates of Enterococcus faecalis from infective endocarditis and from the normal flora. Microb. Pathog. 2013;55:28–31. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2012.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Perdreau-Remington F, Sande MA, Peters G, Chambers HF. The abilities of a Staphylococcus epidermidis wild-type strain and its slime-negative mutant to induce endocarditis in rabbits are comparable. Infect. Immun. 1998;66(6):2778–2781. doi: 10.1128/iai.66.6.2778-2781.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Guembe M, Alonso B, Lucio J, et al. Biofilm production is not associated with poor clinical outcome in 485 patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017 doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2017.10.018. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Shishido T, Yamaguchi T, Odaka T, Seimiya M, Saisho H, Nomura F. Significance of a novel sucrose permeability test using serum in the diagnosis of early gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005;11(44):6905–6909. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i44.6905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Sutherland LR, Verhoef M, Wallace JL, Van Rosendaal G, Crutcher R, Meddings JB. A simple, non-invasive marker of gastric damage: sucrose permeability. Lancet. 1994;343(8904):998–1000. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Leuck A-M, Johnson JR, Dunny GM. A widely used in vitro biofilm assay has questionable clinical significance for enterococcal endocarditis. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(9):e107282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Chen L, Ge X, Xu P. Identifying essential Streptococcus sanguinis genes using genome-wide deletion mutation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015;1279:15–23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2398-4_2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Vickerman MM, Mansfield JM, Zhu M, Walters KS, Banas JA. Codon-optimized fluorescent mTFP and mCherry for microscopic visualization and genetic counterselection of streptococci and enterococci. J. Microbiol. Methods. 2015;116:15–22. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2015.06.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Merritt J, Senpuku H, Kreth J. Let there be bioluminescence: development of a biophotonic imaging platform for in situ analyses of oral biofilms in animal models. Environ. Microbiol. 2016;18(1):174–190. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Pan YP, Li Y, Caufield PW. Phenotypic and genotypic diversity of Streptococcus sanguis in infants. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2001;16(4):235–242. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-302x.2001.160407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Kullberg BJ, Arendrup MC. Invasive candidiasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015;373(15):1445–1456. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1315399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]