Abstract
Large birthweight, or macrosomia, is one of the commonest complications for pregnancies affected by diabetes. As macrosomia is associated with an increased risk of a number of adverse outcomes for both the mother and offspring, accurate antenatal prediction of fetal macrosomia could be beneficial in guiding appropriate models of care and interventions that may avoid or reduce these associated risks. However, current prediction strategies which include physical examination and ultrasound assessment, are imprecise. Biomarkers are proving useful in various specialties and may offer a new avenue for improved prediction of macrosomia. Prime biomarker candidates in pregnancies with diabetes include maternal glycaemic markers (glucose, 1,5-anhydroglucitol, glycosylated hemoglobin) and hormones proposed implicated in placental nutrient transfer (adiponectin and insulin-like growth factor-1). There is some support for an association of these biomarkers with birthweight and/or macrosomia, although current evidence in this emerging field is still limited. Thus, although biomarkers hold promise, further investigation is needed to elucidate the potential clinical utility of biomarkers for macrosomia prediction for pregnancies affected by diabetes.
Keywords: diabetes, pregnancy, macrosomia, birthweight, biomarkers
Introduction
With the increasing prevalence amongst women of childbearing age, diabetes mellitus is one of most common pre-existing medical conditions affecting pregnancy (1). Together, type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) affect around 1% of pregnancies (2). Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is also on the rise, particularly since the changes in diagnostic criteria (3), with a prevalence of around 13% (4). This is of concern as maternal diabetes increases the risks associated with pregnancy (5, 6).
While there are higher rates of many adverse pregnancy outcomes, abnormal fetal growth and birthweight is particularly important due to the substantial frequency of occurrence (7, 8). Indeed, reports estimate macrosomia occurs in up to 60% of pregnancies affected by pre-existing diabetes (9). While macrosomia is common and occurs even in otherwise uncomplicated diabetic pregnancies (10), fetal growth restriction (FGR) and small-for-gestational-age (SGA) tend to occur in diabetic pregnancies complicated by other conditions, such as underlying maternal vascular disease (11, 12). For this reason, macrosomia in pregnancies affected by diabetes will form the focus of this review.
Macrosomia is defined in various ways. One method of defining macrosomia is according to the absolute birthweight being equal to or above a certain threshold, usually 4,000 g (13). Another definition is according to a birthweight percentile that accounts for the gestational age at birth, with macrosomia commonly defined as being above the 90th centile (also called large-for-gestational-age, LGA)(13, 14). The term macrosomia used here will encompass both of these definitions. Where possible, the abbreviated definition used by a referenced study will be mentioned, with the full definition provided in the supplementary table (Supplementary Table 1).
Given the potentially serious consequences for the mother and child, there is significant interest in predicting fetal macrosomia (13). Accurate identification holds potential for guiding appropriate management and interventions, with the aim of improving outcomes (15). However, currently available methods of macrosomia prediction demonstrate only modest predictive ability, which limits their use in tailoring obstetric decisions (13, 15).
The latest area of interest for potentially improving macrosomia prediction has been in the field of biomarkers. A biomarker in this context refers to a biological molecule that can be objectively assessed as an indicator of a physiological or pathological process or state, and therefore may have potential value for predicting certain outcomes (16, 17). A number of biomarkers have been investigated to determine whether they have an association with birthweight and macrosomia. Relevant biomarkers have been purposefully selected for further discussion.
The aim of this review is to examine the available literature for a relationship between selected biomarkers and birthweight and/or macrosomia. Pregnancies without diabetes in addition to pregnancies affected by diabetes will be discussed for comparison. The review will provide a brief overview of the determinants of fetal growth, the need for macrosomia prediction, and current prediction strategies. It will then focus on the selected biomarkers and provide evaluation of their birthweight/macrosomia prediction potential.
Methods
Medline, Embase, and PubMed databases were searched in 2017. The following subject headings (and synonyms) were combined: pregnancy, diabetes mellitus, type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, birthweight, fetal weight, macrosomia, large-for-gestational-age, biomarker, predictor. Specific searches also included the terms blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, 1,5-anhydroglucitol, lipids, adiponectin, and insulin-like growth factor-1, as well as a search without diabetes terms. In addition, bibliographies of collected publications were manually searched.
Articles were selected if a biomarker from a maternal or fetal/neonatal biological sample was tested for an association with any measure of birthweight or macrosomia. This search identified a list of previously studied biomarkers (Table 1). Exclusion criteria included samples taken from pregnancies affected by FGR/SGA, multiple pregnancy, non-human studies, conference abstracts, and non-English articles.
Table 1.
Biomarkers investigated for an association with birthweight or macrosomia (excluding FGR/SGA).
| Biomarker (Alphabetical order) | Source | Significant association with birthweight/macrosomia (Most adjusted result used. Maternal diabetes status of sample population provided; all were pregnant unless otherwise stated) | Non-significant association with birthweight/macrosomia (Most adjusted result used. Maternal diabetes status of sample population provided; all were pregnant unless otherwise stated) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,5-Anhydroglucitol | •Maternal blood | (18) T1DM, T2DM, GDM (19) T1DM, T2DM, GDM (20) T1DM |
(21) GDM, No diabetes |
| 25-Hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) | •Maternal blood | (22) T2DM, GDM, No diabetes | |
| 32-33 Split proinsulin | •Umbilical cord blood | (23) T1DM, No diabetes | |
| Acid-Labile Subunit (ALS) | •Umbilical cord blood | (24) Diabetes status not stated | |
| Acylation Stimulating Protein (ASP) | •Umbilical cord blood | (25) No diabetes (pregnant), No diabetes (non-pregnant) |
|
| Adiponectin | •Maternal blood | (26) GDM, No diabetes (27) GDM, No diabetes (pregnant), No diabetes (non-pregnant) (28) GDM, No diabetes (29) GDM, No diabetes (30) GIGT, No diabetes (31) No diabetes (32) No diabetes (33) No diabetes (31) No diabetes (34) No diabetes (34) No diabetes (35) No diabetes |
(36) GDM, No diabetes (37) GDM, No diabetes (38) No diabetes (39) No diabetes |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (36) GDM, No diabetes (40) GDM, No diabetes (32) No diabetes (39) No diabetes (41) No diabetes (42) No diabetes (43) No diabetes (44) No diabetes (45) No diabetes |
(23) T1DM, No diabetes (46) T2DM, GDM, No diabetes (47) No diabetes (48) No diabetes (38) No diabetes |
|
| •Amniotic fluid | (49) Diabetes status not stated | ||
| Albumin | •Amniotic fluid | (50) GDM, No diabetes | |
| Alpha-Feto Protein (AFP) ratio (maternal serum AFP / amniotic fluid AFP) |
•Maternal blood •Amniotic fluid |
(51) Diabetes status not stated | |
| Alpha Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (α-hCG) | •Maternal blood | (52) IDDM, No diabetes | |
| Amino acids | •Umbilical cord blood | (53) IDDM, No diabetes | |
| Anti-insulin antibodies | •Maternal blood •Cord blood |
(54) IDDM, GDM, No diabetes | |
| Apelin | •Maternal blood •Cord blood |
(54) GDM, No diabetes | |
| Apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1) |
•Maternal blood | (30) GIGT, No diabetes (55) No diabetes |
|
| Apolipoprotein A5 (APOA5) S19W polymorphism | •Umbilical cord blood | (56) Diabetes status not-stated | |
| Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) | •Maternal blood | (30) GIGT, No diabetes (55) No diabetes |
|
| Aspartate aminotransferase | •Maternal blood | (57) No diabetes | |
| Beta Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin (β-hCG) | •Maternal blood | (58) Diabetes, No diabetes | (59) No diabetes |
| Beta-Hydroxybutyrate (β-OHB) | •Maternal blood | (60) Diabetes, No diabetes | |
| Bilirubin | •Maternal blood | (57) No diabetes | |
| Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) |
•Maternal blood •Umbilical cord blood |
(61) Diabetes status not stated | |
| Chemerin | •Umbilical cord blood | (62) GDM, No diabetes | |
| Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10 or ubiquinone) | •Amniotic fluid | (63) GDM, No diabetes | |
| Copeptin | •Umbilical cord blood | (64) Diabetes, No diabetes | |
| Cortisol | •Maternal saliva | (65) No diabetes (66) Diabetes status not stated |
|
| •Amniotic fluid | (67) No diabetes | ||
| C-peptide | •Umbilical cord blood | (53) IDDM, No diabetes (48) No diabetes (68) No diabetes |
|
| •Amniotic fluid | (69) Diabetes status not stated | ||
| C-Reactive Protein (CRP) |
•Maternal blood | (30) GIGT, No diabetes (34) No diabetes |
|
| Creatinine | •Maternal blood | (70) T1DM (57) No diabetes |
|
| Cytokines: Interleukin (IL) IL-β, IL-6, IL-8 |
•Maternal blood | (71) No diabetes | |
| Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) |
•Umbilical cord blood | (72) IDDM, GDM, No diabetes | |
| •Amniotic fluid | (73) Diabetes status not stated | ||
| E-selectin | •Maternal blood | (74) T1DM, T2DM | |
| Estriol | •Maternal blood | (38) No diabetes | |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (38) No diabetes | ||
| Estradiol | •Maternal blood | (57) No diabetes | |
| Free thyroxine (FT4) | •Maternal blood | (75) No diabetes | |
| Fructosamine | •Maternal blood | (76) IDDM (77) Diabetes (type not specified) (54) IDDM, GDM, No diabetes (78) Pre-existing diabetes, GDM, No diabetes (79) GDM, No diabetes |
(80) Pre-existing diabetes, GDM, No diabetes (81) T2DM, GDM (82) GDM, GIGT, No diabetes |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (78) Pre-existing diabetes, GDM, No diabetes | ||
| Fat mass- and obesity- associated (FTO) gene mRNA | •Placenta | (83) No diabetes | |
| Ghrelin | •Neonatal blood | (84) GDM, No diabetes (85) No diabetes |
|
| Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) - active | •Maternal blood | (86) No diabetes | |
| Glucose | •Maternal blood | (87) Pre-existing diabetes (88) IDDM (89) IDDM (90) T1DM (91) T1DM (92) T1DM (93) T1DM, No diabetes (94) GDM, GIGT, No diabetes (95) GDM, GIGT, No diabetes (96) GDM, No diabetes (97) GDM, No diabetes (98) GDM, No diabetes |
(109) IDDM (110) GDM (111) GDM (25) No diabetes (pregnant), No diabetes (non-pregnant) |
| (99) GDM, No diabetes (100) GDM, No diabetes (101) GDM (30) GIGT, No diabetes (102) No diabetes (103) No diabetes (104) No diabetes (105) No diabetes (106) No diabetes (107) No diabetes (108) No diabetes |
|||
| •Umbilical cord blood | (48) No diabetes | ||
| •Amniotic fluid | (112) No diabetes | ||
| •Maternal urine | (113) No diabetes | ||
| Glycated albumin | •Maternal blood | (114) GDM, No diabetes | |
| Glycine/valine ratio | •Amniotic fluid | ||
| Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) | •Maternal blood | (115) Pre-existing diabetes, GDM (116) Pre-existing diabetes, No diabetes (109) Pre-existing diabetes (117) IDDM, GDM, ‘Probably normal’, Normal (118) IDDM, No diabetes (119) IDDM (120) IDDM, GDM, No diabetes (121) T1DM, T2DM (122) T1DM, T2DM (81) T2DM, GDM (123) T1DM (124) T1DM (20) T1DM (125) T1DM (126) T1DM (127) T1DM (91) T1DM (128) T1DM (90) T1DM (92) T1DM (129) T1DM, No diabetes (130) No diabetes (131) No diabetes (103) No diabetes (132) No diabetes |
(87) Pre-existing diabetes (88) IDDM (18) T1DM, T2DM, GDM (19) T1DM, T2DM, GDM (133) T1DM (95) GDM, IGT, No diabetes (134) GDM, IGT, No diabetes (21) GDM, No diabetes (111) GDM (135) GDM (136) GIGT, No diabetes (137) No diabetes (pregnant), No diabetes (non-pregnant) (138) No diabetes (139) No diabetes |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (68) No diabetes | ||
| Glycosylated proteins | •Maternal blood | (140) T1DM, No diabetes (103) No diabetes |
(118) IDDM, No diabetes |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (140) T1DM, No diabetes | ||
| Growth factor receptor-bound protein 10 (GRB10) gene single nucleotide polymorphism rs12540874 A>G |
•Placenta | (141) No diabetes | |
| Growth Hormone Binding Protein |
•Maternal blood | (142) IDDM, NIDDM, No diabetes | |
| HDL-Cholesterol (HDL-C) |
•Maternal blood | (143) T1DM, T2DM, No diabetes (111) GDM (144) GDM |
|
| (145) GDM, No diabetes (100) GDM, No diabetes (146) No diabetes (55) No diabetes (146) No diabetes (147) No diabetes |
(21) GDM, No diabetes (30) GIGT, No diabetes (57) No diabetes |
||
| •Umbilical cord blood | (43) No diabetes | (148) T1DM, No diabetes (68) No diabetes |
|
| Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) | •Amniotic fluid | (149) No diabetes | |
| Homocysteine | •Maternal blood •Umbilical cord blood |
(150) Diabetes status not stated | |
| Insulin | •Maternal blood | (30) GIGT, No diabetes | |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (151) IDDM, No diabetes (23) T1DM, No diabetes (62) GDM, No diabetes (64) Diabetes, No diabetes (43) No diabetes (152) No diabetes (48) No diabetes (68) No diabetes |
||
| •Amniotic fluid | (153) IDDM, GDM, No diabetes (154) T1DM, T2DM, GDM, GIGT, No diabetes (155) T1DM |
(69) Diabetes status not stated | |
| Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) | •Maternal blood | (156) IDDM (142) IDDM, NIDDM, No diabetes (157) T1DM, T2DM, GDM, No diabetes (158) T1DM (159) GDM, No diabetes (160) Diabetes status not stated (161) No diabetes (162) No diabetes |
(163) IDDM, No diabetes (164) T1DM, No diabetes (126) T1DM (165) GDM, No diabetes (166) Diabetes status not stated (38) No diabetes (167) No diabetes (168) No diabetes |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (169) Pre-existing diabetes, GDM, No diabetes (170) IDDM, NIDDM, No diabetes (171) T1DM, T2DM, GDM (172) T1DM, GDM, No diabetes (173) T1DM, No diabetes (174) GDM, No diabetes (24) Diabetes status not stated (175) Diabetes status not stated (166) Diabetes status not stated (161) No diabetes (176) No diabetes |
(177) T1DM, No diabetes (164) T1DM, No diabetes (38) No diabetes (178) No diabetes (168) No diabetes |
|
| Insulin-like Growth Factor-2 (IGF-2) | •Maternal blood | (142) IDDM, NIDDM, No diabetes (156) IDDM (158) T1DM (159) GDM, No diabetes |
(159) GDM, No diabetes (168) No diabetes (176) No diabetes |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (38) No diabetes (169) Pre-existing diabetes, GDM, No diabetes (168) No diabetes |
||
| Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-1 (IGFBP-1) | •Maternal blood | (142) IDDM, NIDDM, No diabetes | |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (179) T1DM, T2DM, GDM (178) No diabetes |
||
| Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-2 (IGFBP-2) | •Maternal blood | (142) IDDM, NIDDM, No diabetes | |
| Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 (IGFBP-3) | •Maternal blood | (38) No diabetes (142) IDDM, NIDDM, No diabetes |
|
| •Umbilical cord blood | (24) Diabetes status not stated | (38) No diabetes | |
| Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor (IGF1R) mRNA |
•Placenta | (180) GDM, No diabetes | |
| Interlukin-6 (IL-6) | •Umbilical cord blood | (48) No diabetes | |
| Irisin | •Umbilical cord blood | (181) GDM, No diabetes | |
| LDL-Cholesterol (LDL-C) |
•Maternal blood | (143) T1DM, T2DM, No diabetes (21) GDM, No diabetes (111) GDM (30) GIGT, No diabetes (55) No diabetes (57) No diabetes (146) No diabetes |
|
| •Umbilical cord blood | (148) T1DM, No diabetes | (43) No diabetes (68) No diabetes |
|
| Leptin | •Maternal blood | (182) T1DM, No diabetes (30) GIGT, No diabetes (183) GDM, No diabetes (184) No diabetes |
|
| •Umbilical cord blood | (182) T1DM, No diabetes (184) No diabetes (43) No diabetes (185) No diabetes (41) No diabetes (47) No diabetes (178) No diabetes |
(48) No diabetes | |
| Lipoxin A4 (LXA4) | •Maternal blood | (186) GDM, No diabetes | |
| Metabolites: taurine, creatinine, betaine, glycine, citrate, myo-inositol | •Neonatal urine | (187) Diabetes status not stated | |
| MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) | •Placenta | (188) No diabetes | |
| MicroRNAs (miR): miR-141-3p, miR-200c-3p | •Maternal blood | (189) Diabetes status not stated | |
| MicroRNA-376a (miR-376a) | •Maternal blood | (190) No diabetes | |
| Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) | •Maternal blood | (191) GDM, No diabetes | |
| Nesfatin-1 | •Maternal blood | (54) GDM, No diabetes | |
| •Cord blood | (54) GDM, No diabetes | ||
| Obestatin | •Umbilical cord blood | (62) GDM, No diabetes | |
| Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) |
•Umbilical cord blood | (46) T2DM, GDM, No diabetes | |
| Platelets | •Umbilical cord blood | (129) T1DM, No diabetes | |
| Placental Growth Factor (PlGF) | •Maternal blood | (192) Diabetes, No diabetes (193) Diabetes, No diabetes |
|
| •Amniotic fluid | (49) Diabetes status not stated | ||
| Placental Growth Hormone (PGH) | •Maternal blood | (142) Pre-existing IDDM, NIDDM, No diabetes (164) T1DM, No diabetes (158) T1DM (126) T1DM |
(194) No diabetes (194) No diabetes |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (164) T1DM, No diabetes | ||
| Placental imprinted genes: BLCAP, DLK1, H19, IGF2, MEG3, MEST, NNAT, NDN, PLAGL1 |
•Placenta | (195) Diabetes status not-stated | |
| Placental Lactogen | •Maternal blood | (57) No diabetes | |
| Placental Protein 13 (PP13) | •Maternal blood | (196) Diabetes status not stated | |
| Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-type 1 (PAI-1) | •Maternal blood | (34) No diabetes | |
| Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-2 (PAI-2) | •Maternal blood | (192) Diabetes not excluded | |
| Pregnancy-Associated Plasma Protein-A (PAPP-A) | •Maternal blood | (58) Diabetes, No diabetes (197) Diabetes, No diabetes (198) No diabetes (199) Diabetes status not stated |
(59) No diabetes |
| Progesterone | •Maternal blood | (38) No diabetes | |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (38) No diabetes | ||
| Prolactin | •Maternal blood | (38) No diabetes | |
| Regulated on Activation, Normal T cell Express and Secreted upon uptake (RANTES) | •Umbilical cord blood | (200) T2DM, GDM, No diabetes | |
| Retinol-Binding Protein 4 (RBP4) | •Umbilical cord blood | (201) GDM, No diabetes | |
| Resistin | •Maternal blood | (202) GDM, No diabetes (34) No diabetes |
|
| •Umbilical cord blood | (202) GDM, No diabetes | ||
| RNA: PHLDB2, CLDN1, C15orf29, LPHN3, LEP, GCH1, | •Placenta | (203) Diabetes status not stated | |
| Sex Hormone Binding Globulin (SHBG) | •Maternal blood | (38) No diabetes | |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (174) GDM, No diabetes | (38) No diabetes | |
| Soluble Fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1) |
•Maternal blood | (192) Diabetes, No diabetes | |
| Soluble Fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 /Placental Growth Factor ratio |
•Maternal blood | (193) No diabetes | |
| Soluble Leptin Receptor (sOB-R) | •Umbilical cord blood | (47) No diabetes | |
| Soluble TNF-α receptor-2 (TNFR2) | •Maternal blood •Umbilical cord blood |
(35) No diabetes | |
| Squalene | •Maternal blood | (204) GDM, No diabetes | |
| Stromal Cell-derived Factor-1a (SDF-1a) | •Amniotic fluid | (205) No diabetes | |
| Testosterone | •Maternal blood | (38) No diabetes | |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (38) No diabetes | ||
| Total cholesterol | •Maternal blood | (111) GDM (21) GDM, No diabetes (30) GIGT, No diabetes |
|
| (146) No diabetes (55) No diabetes |
|||
| •Umbilical cord blood | (206) GDM, No diabetes | (43) No diabetes (68) No diabetes |
|
| Total lipids | •Maternal blood | (111) GDM | |
| Triglycerides | •Maternal blood | (143) T1DM, T2DM, No diabetes (94) GDM, GIGT, No diabetes (207) GDM, GIGT, No diabetes (208) GDM, No diabetes (209) GDM (144) GDM (210) GDM, No diabetes (146) No diabetes (211) No diabetes (212) No diabetes (213) No diabetes (146) No diabetes (214) No diabetes (25) No diabetes (pregnant), No diabetes (non-pregnant) |
(148) T1DM, No diabetes (21) GDM, No diabetes (111) GDM (100) GDM, No diabetes (30) GIGT, No diabetes (215) No diabetes |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (211) No diabetes (215) No diabetes |
(43) No diabetes (55) No diabetes |
|
| Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) | •Maternal blood | (71) No diabetes | |
| Uric acid | •Maternal blood | (55) No diabetes | |
| Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (sVCAM-1) | •Maternal blood | (74) T1DM, T2DM | |
| Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) | •Maternal blood | (193) No diabetes (216) Diabetes status not stated |
|
| Very Low Density Lipoprotein (VLDL) | •Maternal blood | (57) No diabetes | |
| Visfatin | •Maternal blood | (48) No diabetes | |
| •Umbilical cord blood | (48) No diabetes | ||
| Vitamin C | •Maternal blood •Umbilical cord blood |
(217) No diabetes |
T1DM, Type 1 diabetes mellitus; T2DM, Type 2 diabetes mellitus; GDM, Gestational diabetes mellitus; IDDM, Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus; NIIDM, Non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus; GIGT, Gestational impaired glucose tolerance.
Discussion
Determinants of fetal growth
Normal fetal growth relies on the complex interplay of multiple factors, including genetic and environmental influences arising from the parents, fetus, and placenta (218). A key determinant of abnormal growth is altered substrate supply to the fetus (219). In normal pregnancy, maternal insulin resistance increases across gestation, becoming most pronounced in the third trimester when the majority of fetal growth takes place (220). This adaptive change promotes diversion of glucose across the placenta down its concentration gradient to the fetus (221). However, in pregnancies affected by diabetes, such transfer is exaggerated due to maternal hyperglycaemia (221). This excess glucose supply is believed to be central to diabetes-related fetal overgrowth. Indeed, the hyperglycaemia-hyperinsulinaemia hypothesis (also known as the Pedersen hypothesis), has been the prevailing explanation for macrosomia in diabetic pregnancies (220). It proposes that maternal hyperglycaemia leads to fetal hyperglycaemia, which stimulates maturation and hypertrophy of the fetal pancreas (222). This results in hypersecretion of insulin, and as insulin is a dominant fetal growth hormone, acceleration of fetal growth occurs (219). The modified Pedersen hypothesis also includes maternal amino acids and lipids in addition to glucose, contending that these insulin-responsive maternal fuels lead to an increase in “mixed nutrients” supplied to the fetus, which in turn elevates fetal insulin and drives excessive growth (220).
Rationale for macrosomia prediction
Antenatal prediction of fetal macrosomia prediction is desirable for many reasons. Firstly, macrosomia is a common obstetric complication, affecting a significant number of pregnancies. According to recent Australian figures, the rate of macrosomia (birthweight ≥ 4,000 g) amongst pregnancies with pre-existing type 1 and type 2 diabetes was 25 and 18% for male and female offspring, respectively (2). However, as previously mentioned, other populations have reported rates up to 60% (for pre-existing diabetes), which is approximately six times the rate for women without diabetes (9).
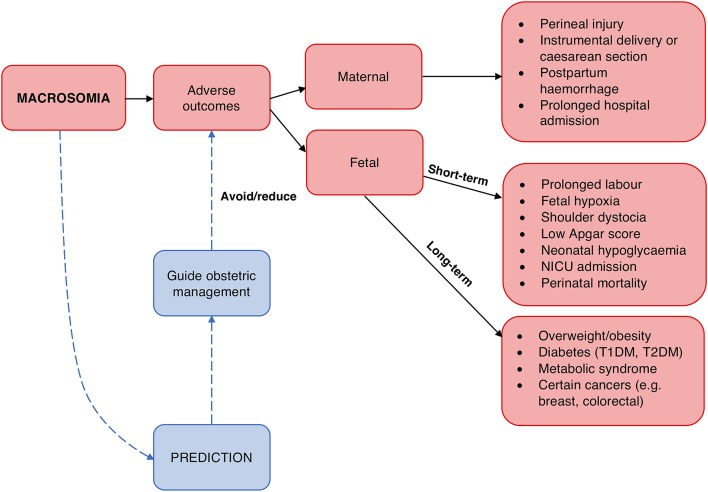
Secondly, macrosomia carries risks for the mother and fetus (Figure 1). Prominent risks include obstructed labor, cesarean section, instrumental delivery, perineal trauma, and birth injuries such as shoulder dystocia, an obstetric emergency involving difficulty delivering the fetal shoulders (14, 223, 224). Moreover, the risk of shoulder dystocia is greater in pregnancies affected by diabetes for any given birthweight, perhaps due to the altered fetal body proportions (14, 232). Longer-term risks include obesity and diabetes in the offspring (225, 226), possibly reflecting fetal programming as proposed by the “developmental origins of adult disease” or Barker hypothesis (233, 234).
Figure 1.
Rationale for macrosomia prediction. Macrosomia is associated with a number of adverse outcomes for both the mother and fetus (223–231). Prediction of macrosomia may reduce or avoid these via guiding appropriate obstetric management.
By identifying pregnancies at increased perinatal risk, macrosomia prediction allows for tailoring obstetric care. Appropriate management and interventions could be employed to avoid or reduce the associated risks. Induction of labor and elective cesarean section are possible options; although, definitive evidence for improved outcomes and cost-effectiveness from these strategies is lacking at present (15, 235). Thus, further development and evaluation of appropriate management options is needed, and improved prediction strategies could be instrumental in this.
Available methods for macrosomia prediction
Different methods for predicting macrosomia are currently available, as outlined in Table 2. Risk-factor based prediction aims to assess the likelihood of macrosomia based on identified unmodifiable and modifiable risk factors (13). Diabetes is the strongest risk factor for macrosomia (13, 235), and even maternal hyperglycaemia below diagnostic thresholds for diabetes increases the risk (102). Maternal body mass index (BMI) and gestational weight gain (GWG) are also well-established risk factors (252, 253), with pre-pregnancy obesity increasing the odds of macrosomia by threefold (254). Furthermore, clinical methods of fetal size estimation include physical examination techniques, with symphysis fundal height measurement and abdominal palpation being the primary manoeuvres (255). Maternal estimation of fetal weight by parous women has also been described (247). Finally, ultrasound estimation of fetal weight is routinely used, which employs formulae incorporating fetal biometric parameters (248).
Table 2.
Evaluation of available methods for macrosomia prediction.
| Method | Description | Performance | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk-factor assessment |
|
|
|
|
| Symphysis fundal height (SFH) measurement |
|
|
||
| Abdominal palpation |
|
|
|
|
| Maternal estimation |
|
|
|
|
| Ultrasound assessment |
|
|
|
PPV, positive predictive value; NPV, negative predictive value.
In comparing the performance of the available prediction methods, the broad conclusion is that no single method demonstrates clear superiority over the others (246, 256). Importantly, these current methods all have their limitations—a major limitation is their imprecision, displaying a sensitivity and specificity for macrosomia detection of around 55 and 90%, respectively (15, 246). The false positive and false negative rates are of concern, as inaccurate results can carry serious consequences including unnecessary intervention (14, 256, 257). Thus, these methods have limited clinical utility and caution is needed if used to guide management (15). From this it is evident there exists a need to improve macrosomia prediction beyond current capabilities, particularly in pregnancies affected by diabetes.
Biomarkers for macrosomia prediction
Biomarkers may hold potential for enhancing macrosomia prediction. Biomarkers represent a biological source of information, revealing unique insight into the in-utero environment that may be leading to accelerated fetal growth. Hence by reflecting the possible proximal determinants of excessive growth, biomarkers could provide predictive capacity for macrosomia.
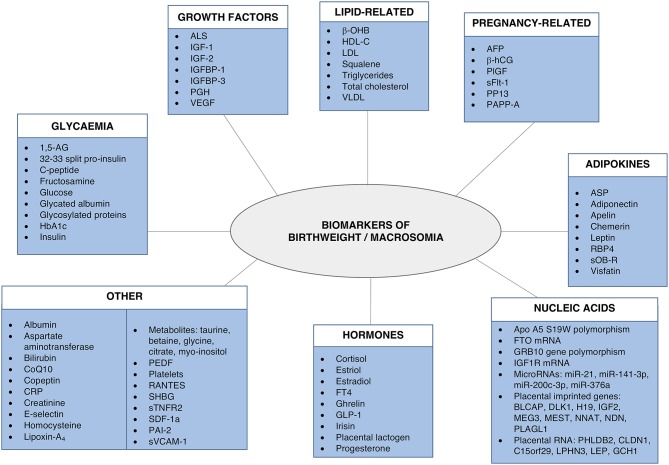
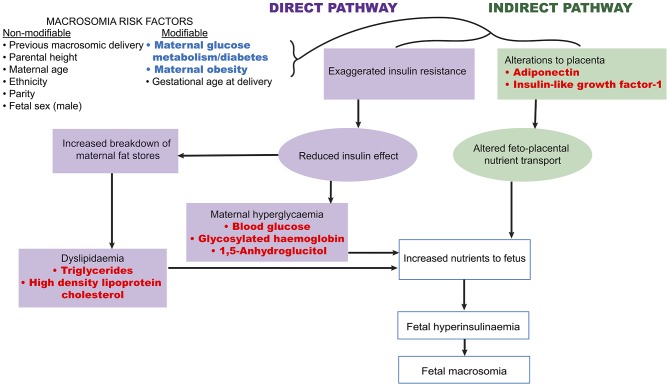
A number of fetal and maternal biomarkers have been previously assessed for an association with birthweight or macrosomia in pregnancies with and without diabetes (Table 1;Figure 2). An approach to selecting biomarkers for further evaluation was informed by the known risk factors for macrosomia. The risk factors for which a detectable biological correlate (biomarker) may be present and therefore may reflect “proximal macrosomia determinants” are maternal glucose metabolism/diabetes and maternal weight (pre-pregnancy obesity and GWG). Although the underlying mechanisms by which these risk factors mediate their influence on fetal growth have not yet been definitively determined, a theory linking these two with fetal macrosomia considers “direct” and “indirect” pathways (249, 258) (Figure 3).
Figure 2.
Biomarkers associated with birthweight and/or macrosomia. Biomarkers that have previously demonstrated a significant association with birthweight and/or macrosomia. Abbreviations provided in Table 1.
Figure 3.
Proposed link between macrosomia risk factors and the selected biomarkers. Maternal diabetes and obesity have proposed links to fetal macrosomia via direct and indirect effects on fetal growth (249, 258). Biomarkers (red) possibly related to these pathways may therefore capture information that has predictive capacity for macrosomia.
The direct pathway relates to insulin effectiveness and action (221, 249). Maternal diabetes and/or obesity affects this pathway via exaggerating the physiological insulin resistance that develops during pregnancy, which in-turn contributes to maternal hyperglycaemia and dyslipidaemia (249). This then leads to increased nutrient delivery to the fetus, subsequently resulting in fetal hyperinsulinaemia and macrosomia as per the modified Pedersen hypothesis (249, 258). Thus, biomarkers of maternal glycaemic control that may provide indication of the glycaemia-related risk of the direct pathway include blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG). While maternal triglycerides and cholesterol may be markers of the dyslipidaemia-related effects on growth. On the other hand, the indirect pathway centers on placental function (249). Placental changes that have been linked to maternal diabetes and obesity, such as alterations in structure, utero-placental blood flow, and placental transporters, may lead to altered feto-placental nutrient transport (249, 259). This likewise increases nutrient delivery to the fetus and stimulates fetal hyperinsulinaeamia. As adiponectin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) are proposed to be involved in these placental alterations, they therefore represent potential biomarkers of this indirect pathway (249). Hence these biomarkers are prime candidates to be assessed for associations with fetal weight. Maternal rather than fetal (cord blood) biomarkers will be the focus due to being the source relevant for antenatal predictive testing. Pre-existing diabetes, GDM, and pregnancies without diabetes will be examined in turn (results summarized in Table 3).
Table 3.
Summary of evidence in support of an association between the selected biomarkers and birthweight/macrosomia.
| Biomarker (Maternal source unless otherwise stated) | T1DM | T2DM | GDM | No diabetes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood glucose |
|
|
|
|
| Glycosylated hemoglobin |
|
|
|
|
| 1,5-Anhydroglucitol |
|
|
|
|
| Lipids |
|
|
|
|
| Adiponectin |
|
|
|
|
| Insulin-like growth factor-1 |
|
|
|
|
Blood glucose
In women with pre-existing diabetes, various parameters of blood glucose have been assessed for associations with birthweight. The Diabetes in Early Pregnancy (DIEP) study focused on elucidating the contribution of fasting verses postprandial glucose to infant birthweight, comparing women with T1DM and controls across pregnancy (93). The findings indicated that postprandial glucose was more important for macrosomia (birthweight ≥ 90th percentile) risk, with the third trimester postprandial glucose levels the strongest predictor. Other studies also support the importance of postprandial blood glucose; with postprandial glucose levels in the third trimester predicting macrosomia (birthweight >90th percentile) (87), and mean postprandial glucose in the second trimester associated with birthweight (91). However, these studies have often analyzed the fasting and postprandial glucose measurements as the average across a whole trimester, hindering more specific timing effects of glycaemia on macrosomia risk to be determined. Addressing this by calculating the mean fasting and post-prandial glucose measurements over 3 week blocks in women with pre-existing diabetes, Persson et al. found the mean fasting glucose levels between 27 and 29 weeks' gestation were independently associated with macrosomia (birthweight >2 standard deviations), whereas postprandial levels were not (88). This fasting glucose measurement and pre-pregnancy weight together accounted for 12% of the variance in birthweight. In addition to the different time periods over which averages were calculated, variations in the measurement methods including the use of patient self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) via a glucometer compared to laboratory testing, could have contributed to the conflicting findings. Nonetheless, they substantiate the contribution of second and third trimester maternal glycaemia to fetal growth in pregnancies complicated by pre-existing diabetes (89, 260, 261).
Furthermore, as postprandial hyperglycaemia involves transitory glycaemic excursions, this supports the notion that glucose fluctuations in addition to chronic hyperglycaemia, are important in influencing excessive fetal growth (92, 123, 124). To comprehensively assess such temporal patterns in glucose control, continuous glucose monitoring systems (CGMS) are needed, particularly in women with T1DM, as fluctuations are often missed by SMBG (262, 263). Indeed, initial studies using CGMS have shown maternal glucose excursion profiles are related to macrosomia (90, 264–266). For example, a multi-center study involving women with T1DM and T2DM using CGMS, identified that glucose excursions at specific time periods throughout the day were associated with macrosomia (birthweight >90th percentile) in each trimester (264). For the second and third trimesters, the macrosomia-related glucose levels were higher and showed greater variability.
Meanwhile, studies in the setting of GDM have mostly used measures of maternal glucose obtained from the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). These measures, particularly the fasting values, have often been associated with macrosomia (95–99). Although, a Canadian study found glucose levels (fasting or post-glucose load) only independently accounted for 3–5% of the variance in birthweight (98).
Importantly, maternal glycaemia has been shown to be related to macrosomia risk amongst healthy women in the absence of overt diabetes (102, 103). The landmark study in the area is the Hyperglycaemia and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes (HAPO) study. This multinational investigation assessed outcomes associated with glucose parameters from the OGTT at 24–32 weeks' gestation in healthy pregnant women (102). The blinded data from ~23,000 participants demonstrated linear associations between increasing maternal glucose levels below diagnostic thresholds for diabetes with both birthweight above the 90th percentile and umbilical cord blood C-peptide above the 90th percentile (indicative of fetal hyperinsulinaemia). The findings support the Pedersen hypothesis and indicated even mild maternal hyperglycaemia without diabetes increases macrosomia risk, which has had subsequent implications for GDM diagnostic thresholds.
However, other studies with participants of varying diabetes status have not found blood glucose to be associated with birthweight (25, 109–111). Variations in glucose testing protocols and treatment regimens may provide some explanation for this. Thus, uncertainties remain regarding the utility of blood glucose for birthweight/macrosomia prediction (8).
Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c)
HbA1c is produced by non-enzymatic glycosylation of hemoglobin. It is a long-term marker of glycaemic control, reflecting the average glucose concentration over the previous 2–3 months (267, 268).
In women with pre-existing diabetes, macrosomia and birthweight have been significantly associated with HbA1c measured at different time points. In multiple studies, third trimester values have demonstrated positive associations with macrosomia (90, 92, 109, 123, 126, 127) and birthweight (91, 128). A notable study is a prospective nation-wide investigation of 289 women with T1DM in The Netherlands (123). Amongst this cohort with acceptable glycaemic control, the third trimester HbA1c measurement was the strongest predictor of macrosomia (birthweight >90th percentile), accounting for 4.7% of the variance of macrosomia. Furthermore, HbA1c measured in trimester 1 (119, 121), or trimester 2 and 3 (116, 124, 125, 129) have also been associated with birthweight or macrosomia. Across all of these studies, HbA1c has been reported to explain ~5–23% of variance in birthweight (119, 123).
Contrastingly, other research groups have not found a significant association between HbA1c and birthweight (19, 87, 88, 269). Contributing factors to these inconsistencies may include the sample collection time-points and the use of averages of HbA1c across varying periods. This could be influential as HbA1c normally declines during pregnancy and is a retrospective weighted average marker (267). It may also relate to the study protocol reducing glycaemic variability (87, 88) or to differences in analytical assays (270).
In addition, a prominent issue is the persistence of high macrosomia rates in women with pre-existing diabetes even when HbA1c values indicate “good” glycaemic control (87, 92, 123, 133). This “macrosomia despite normoglycaemia” may be linked to HbA1c-determined normoglycaemia not revealing glycaemic variability. As previously mentioned, postprandial hyperglycaemia and glycaemic fluctuations are considered important in accelerating growth (8, 271). This is consistent with some studies indicating tighter blood glucose control and thus reduced glycaemic excursions, can reduce macrosomia incidence (260, 272, 273).
There is weaker evidence for a significant association between HbA1c and birthweight in women with GDM (21, 95, 111, 134, 135). This may related to the reduced aberrations in HbA1c in GDM compared with T1DM and T2DM (274). Also, many studies have measured HbA1c at the same time as GDM diagnostic testing (around 28 weeks' gestation) for convenience. However, when HbA1c was measured at delivery in women with GDM, HbA1c >6.8% was associated with a fivefold increased risk of macrosomia (birthweight ≥4,000 g) compared with HbA1c<6.0% (81). Later HbA1c testing may therefore be more useful for predicting macrosomia.
Meanwhile, for women without diabetes, a correlation between HbA1c at various times with birthweight has been identified by some (103, 130, 131, 139), but not other researchers (137, 138). In the HAPO cohort, glucose measures had a significantly stronger association with birthweight than HbA1c (132). Furthermore, another study assessed ultrasound and HbA1c prediction of macrosomia (birthweight ≥4,000 g) within 1 week prior to delivery (138). It found HbA1c measurements were not useful and thus could not improve ultrasound prediction accuracy. However, HbA1c levels were low in this cohort without diabetes. Thus overall, HbA1c may be more useful in women with pre-existing diabetes and later in pregnancy.
1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG)
1,5-AG is the 1-deoxy form of glucose and is a short-term glycaemic marker (275). During normoglycaemia, serum 1,5-AG is in a steady-state, with >99% renal reabsorption (275). However in hyperglycaemic conditions, glucose competitively inhibits renal reabsorption of 1,5-AG, thereby increasing 1,5-AG excretion and reducing the serum 1,5-AG concentration (268). It reflects the glycaemic control over the preceding 24 h to 2 weeks, and importantly, it can capture glycaemic fluctuations (268, 275).
With these benefits in detecting glycaemic excursions, Nowak et al. compared 1,5-AG and HbA1c in pregnant women with T1DM and found 1,5-AG was the stronger predictor of macrosomia (birthweight >90th percentile) (20). The receiver operator characteristic (ROC) area under the curve (AUC) for third trimester 1,5-AG macrosomia prediction was 0.81. This improved to 0.84 with the addition of HbA1c, and could achieve sensitivity and specificity of 86 and 71%, respectively. As 80% of the cases of macrosomia occurred in women that met HbA1c targets, it suggested that glucose excursions that were not reflected in the HbA1c level but were captured by the 1,5-AG values may have contributed to fetal overgrowth. This assertion was supported by CGMS records which showed 1,5-AG was strongly correlated with CGMS indices including a measure of glucose variability, but HbA1c was not.
Building on this, a study involving women with T1DM, T2DM, and GDM found that there was a significant inverse association between 1,5-AG and birthweight z-score across the groups (19). Of note, HbA1c was not associated with birthweight, possibly due to the participants having overall low HbA1c measurements. The authors contend however, that as 1,5-AG was significantly associated with birthweight even amongst a population with good glycaemic control according to HbA1c, it could be used to identify the subset of pregnancies that are at risk of macrosomia, despite HbA1c within target ranges.
Wright et al. similarly found an inverse linear association between mean 1,5-AG and birthweight z-scores in a cohort of T1DM, T2DM, and GDM pregnancies (18). The association for mean HbA1c was not significant. The lack of blood glucose data (SMBG/CGMS) is a limitation, as conclusions regarding glycaemic control and fluctuations require consideration of these immediate measures of glycaemia.
In contrast, a study comparing women with GDM and pregnant women without diabetes did not find 1,5-AG to be a significant predictor of birthweight (21). Although, serum 1,5-AG concentration was significantly lower in the women with GDM compared to controls and there was a trend for an inverse association between 1,5-AG and birthweight in the GDM group.
There have been concerns that the reduction in renal glucose threshold during normal pregnancy may affect renal excretion of 1,5-AG and thus serum levels, thereby possibly limiting the utility of 1,5-AG in reflecting glycaemic changes while pregnant (275, 276). However, the few available evaluations of 1,5-AG as a marker of glycaemic control in pregnancies complicated by diabetes have shown that it performs well (20, 277).
Lipids
Lipid metabolism is altered during normal pregnancy. Increased fat storage occurs initially in the “anabolic phase” of pregnancy (278). The switch to the “catabolic phase” in the third trimester involves prominent lipolysis promoted by insulin resistance (279, 280). This is paralleled with an increase in the major lipid fractions, predominantly triglycerides (220, 278); which is seen to a greater extent in women with diabetes (278, 281). In accordance with the modified Pedersen hypothesis, maternal lipids may be an important fuel in fetal overgrowth (220).
Of all lipids, triglycerides have been most consistently related to birthweight in pregnancies with diabetes. A study comparing women with T1DM, T2DM, and controls found both third trimester triglycerides and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) were significantly associated with macrosomia (birthweight >90th percentile), independent of maternal glycaemic control (143). In GDM pregnancies, maternal triglycerides have also been identified as a predictor of macrosomia independent of maternal BMI and glycaemic control (144, 209). Moreover, the ratio of triglycerides to HDL-C has also been examined in women with well-controlled GDM and women without diabetes at 24–28 weeks' gestation (282). The ROC AUC for macrosomia (birthweight >90th percentile) prediction was 0.668, which increased to 0.806 when combined with HbA1c and pre-pregnancy BMI. However, the overall prevalence of macrosomia was low in this population. Together these results indicate lipid alterations may play a distinct role in macrosomia development amongst women with diabetes. Indeed, maternal lipids have been proposed as a potential key factor in “macrosomia despite normoglycaemia” (10, 283).
In women without diabetes, second or third trimester maternal triglycerides have been found to be positively associated with birthweight (25, 211), as well as an independent predictor of macrosomia (94, 146, 207, 212, 213). In a Japanese cohort, maternal fasting hypertrigylceridaemia significantly independently predicted macrosomia (birthweight >90th percentile), with an odds ratio of 11.6 (214). Notably, triglycerides were more strongly associated with fetal growth than maternal glycaemia; although, the small sample size (146 people) may have limited analysis. It is supported however by a similar finding in a cohort that included women with GDM (208). In this study, the triglyceride concentrations after an OGTT were independently associated with birthweight and also predicted glucose intolerance.
Furthermore, macrosomia risk, and birthweight has been inversely associated with second and third trimester maternal HDL-C concentrations in women with pre-existing diabetes (143) and GDM or healthy pregnancies (55, 100, 111, 146, 147). In Zhou et al.'s study which included GDM pregnancies, low HDL-C (<2.2 mmol/L) at 20 weeks' gestation predicted macrosomia (birthweight >4,000 g) with 65% sensitivity and 48% specificity (55).
In contrast, other lipid parameters have less supportive evidence. In women without diabetes, very-low density lipoprotein cholesterol (VLDL-C) has been negatively associated with birthweight (57). While low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) has mostly demonstrated non-significant results (21, 30, 55, 143).
Overall, these studies suggest differential importance of maternal lipid fractions for fetal growth. Again, some studies have not found an association between lipids and birthweight or macrosomia in diabetic or healthy pregnancies (21, 30). Measurement timing may be relevant to this due to the changes in lipid profile and hence possibly their role across pregnancy.
Adiponectin
Adiponectin is an adipokine—a bioactive peptide derived from adipose tissue (284). It has important roles in regulating insulin sensitivity and metabolism, and is inversely related to adipose mass and insulin resistance (284, 285). Given this, adiponectin is a possible mediator in the link between maternal adiposity, insulin resistance, and excessive fetal growth (284, 286). Maternal adiponectin may influence fetal growth via altering placental substrate transport as it does not traverse the placenta (286).
There is a notable lack of investigation of maternal adiponectin in women with pre-existing diabetes. Fetal adiponectin however, has received some attention. A comparison of neonates from mothers with T1DM with healthy controls found umbilical cord blood adiponectin collected at birth was not associated with birthweight (23). Similarly, cord blood adiponectin was not associated with birthweight in a study examining offspring of women with T2DM, GDM, and controls (46).
Amongst GDM pregnancies there have been variable results. Tsai and associates compared maternal adiponectin levels collected between 24 and 31 weeks' gestation in women with GDM and controls (26). Adiponectin was significantly lower in the GDM women, and a negative association between maternal adiponectin and birthweight was evident but only significant for the GDM group. Pre-pregnancy BMI ≥27 was also associated with lower adiponectin levels. Cseh et al. corroborated that maternal plasma adiponectin is significantly lower in women with GDM compared to non-diabetic pregnant women and age-matched non-diabetic non-pregnant women (27). Contrastingly though, a significant positive linear correlation was demonstrated between maternal plasma adiponectin and birthweight corrected for gestational age in both the GDM and non-diabetic groups. Meanwhile, others have not found an association between adiponectin and birthweight (36, 37). These conflicting findings may be related to differences between the populations, including BMI, ethnicity, and GDM management, as well as timing of the samples. The adiponectin fractions assessed may also be relevant, as one research group found that only the middle molecular weight isoforms were significantly negatively associated with birthweight in GDM (28).
Verhaeghe et al. also evaluated the value of metabolic biomarkers for birthweight prediction in GDM and control women (29). Maternal adiponectin combined with four other metabolic markers together added 2% to the ~10% explained birthweight variance from maternal body size parameters alone. However, only a single measurement was taken at 24–29 weeks' gestation and given insulin resistance is maximal in the third trimester, greater utility may be provided with later testing.
Findings from healthy pregnancies also provide insight. In two case-control studies involving women without diabetes, macrosomia groups had significantly lower maternal adiponectin concentrations compared with the controls (31, 32). In one of these, maternal adiponectin measured between 11 and 13 weeks' gestation improved macrosomia (birthweight >95th percentile) detection to 38.2% when added to maternal characteristics and obstetric history (compared with 34.6% without adiponectin) (31). Moreover, an independent inverse relationship was identified between maternal adiponectin and birthweight in a subset of the HAPO cohort (34). Although, other studies have not found a significant association with maternal adiponectin (38, 39).
Thus, despite inconsistencies there is indication adiponectin may be related to birthweight. Pre-existing diabetes is an area that particularly requires further investigation.
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1)
IGF-1 is a peptide hormone principally produced in the liver (287). Normal pregnancy involves changes in the maternal IGF axis, including variations to IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs) (287). Consequently, this results in increased free IGF-1, the biologically active form. With mitogenic and metabolic actions, maternal and fetal IGF-1 are believed to be important mediators in fetal growth (285, 287). For maternal IGF-1, this may be via its role in regulating transplacental nutrient transport (288, 289).
However, the literature on maternal IGF-1 in pre-existing diabetes is conflicting. In a prospective study involving serial maternal IGF-1 measurements in women with pre-existing diabetes, IGF-1 was significantly positively associated with macrosomia (156). Yet in a similar study involving only women with T1DM, there were no differences in maternal IGF-1 across pregnancy in diabetic women delivering a macrosomic neonate compared with appropriate birthweight neonate (126). A notable difference between the studies were the methods of macrosomia assessment. The first study created post-hoc groupings according to birthweight ratio whereas the second used the definition of birthweight >90th percentile. Likewise, another research group found macrosomia according to this latter definition was not significantly associated with maternal IGF-1 (142). Although, they did show maternal IGF-1 measured at 36 weeks' gestation was significantly associated with birthweight z-score (142). Thus, the assessment measure of birthweight/macrosomia may be relevant in identifying an association with a biomarker.
GDM pregnancies have also been investigated. In a study of GDM and control women, elevated IGF-1 in maternal blood in mid- and late- gestation and fetal cord blood at birth predicted macrosomia (birthweight >90th percentile) (159). This is consistent with a case-control study in which serum IGF-1 levels were significantly higher in the GDM women and their macrosomic neonates (birthweight >2 standard deviations) compared to matched controls with appropriate birthweight neonates (290). Other studies have also found IGF-1 related to birthweight (174, 291).
The relationship of IGF-1 to fetal growth across the different types of diabetes requires clarification. An investigation comparing women with T1DM, T2DM, GDM, and controls and found the third trimester median maternal IGF-1 values were not significantly different between the groups (157). Considering all the women with diabetes together, third trimester IGF-1 was positively associated with birthweight percentile, explaining 24% of the variation in birthweight. However, other reports suggest the changes across pregnancy in IGF-1 for pre-existing diabetes and GDM are different, with lower levels in pre-existing diabetes (163, 164, 177) and higher levels in GDM (258) compared with controls.
For pregnancies without diabetes, maternal IGF-1 (161, 162, 167) and fetal IGF-1 (38, 161, 166, 175, 176) have been associated with birthweight and macrosomia. These studies have been conducted in populations of various ethnicities. Non-significant associations have also been reported (165, 168, 178, 292). Such discrepancies may relate to factors such as the method of IGF-1 analysis, timing of measurements, or the sample size (287).
Altogether the evidence is conflicting. Adequate assessment has not been made of the predictive utility of IGF-1 for birthweight and macrosomia in women with diabetes.
Evaluation of macrosomia biomarkers
Biomarkers face many challenges in becoming adopted into routine clinical practice. One of the most important requirements is biomarker validation (16), which is particularly an issue in the field of macrosomia biomarkers. In this area, substantial variability exists amongst published results, with the heterogeneity of the studies a prominent contributor. Indeed, there is considerable variation in study designs, populations, measurement timing, outcome variables (including macrosomia definitions), and analytical methods. This limits the conclusions that can be made at this time and highlights the need for rigorous validation protocols to comprehensively evaluate macrosomia biomarker predictive performance. Future work in this field must also assess the cost-effectiveness of biomarker use. Biomarker adoption may become more feasible with improved accessibility of commercial biomarker kits and multiparametric biomarker testing for multiple pregnancy disorders together (e.g., with preeclampsia biomarkers as they also become validated).
Furthermore, as biomarkers may be useful as part of a combination approach, whereby biomarkers are incorporated into a prediction algorithm with other elements such as macrosomia risk factors, physical examination and ultrasound measurements, further investigation is also needed that compares biomarkers to and in combination with the other methods of macrosomia prediction. Of the limited such assessments available, biomarkers have improved predictive performance when combined with risk factors (29, 31, 282) but not ultrasound (138). A further step is to determine if improved macrosomia predictive accuracy can improve clinical outcomes.
Conclusion
Accurately predicting fetal macrosomia remains a desirable but challenging goal. While biomarkers hold promise for assisting in this plight, the current state of knowledge for macrosomia biomarkers is limited. The selected biomarkers in this review each have a theoretical link with macrosomia with some supportive evidence for an association with birthweight/macrosomia. However, due to the limitations of the literature, the true value of biomarkers is not yet clear. Further research is needed to address this, particularly in pregnancies affected by diabetes. A focus on this area is warranted as there is great potential and much to be gained by further exploration. Indeed, broader implications of this research includes providing greater insight into the pathophysiological processes of excessive growth; which is of special interest due to the links with later development of chronic disease (Barker hypothesis). Ultimately, improving outcomes for pregnant women and their babies is the driving force for this research.
Author contributions
SN was the primary author. EE, JS, and AS edited the manuscript. CH reviewed the manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2018.00407/full#supplementary-material
References
- 1.Coton SJ, Nazareth I, Petersen I. A cohort study of trends in the prevalence of pregestational diabetes in pregnancy recorded in UK general practice between 1995 and 2012. BMJ Open (2016) 6:e009494. 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009494 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Diabetes in Pregnancy: Its Impact on Australian Women and Their Babies. Diabetes series no. 14. (Cat. no. CVD 52) (2010).
- 3.Ferrara A. Increasing prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care (2007) 30(Suppl. 2):S141–6. 10.2337/dc07-s206 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Moses RG, Wong VCK, Lambert K, Morris GJ, San Gil F. The prevalence of hyperglycaemia in pregnancy in Australia. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. (2016) 56:341–5. 10.1111/ajo.12447 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wein P. Diabetes mellitus. In: Permezel M, Walker S, Kyprianou K, editors. Beischer & MacKay's Obstetrics, Gynaecology, and the Newborn. 4th ed. Chatswood, NSW: Elsevier Australia; (2015). p. 185–90. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chaudry R, Gilby P, Carroll P. Pre-existing (type 1 and type 2) diabetes in pregnancy. Obstet. Gynaecol. Reprod. Med. (2007) 17:339–44. 10.1016/j.ogrm.2007.09.001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Buchanan T. Pregnancy in preexisiting diabetes. In: Harris M, Cowie C, Stern M, Boyko E, Reiber G, Bennett P, editors. Diabetes in America. 2nd ed. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health; (1995). p. 719–33. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jovanovic L. What is so bad about a big baby? Diabetes Care (2001) 24:1317–8. 10.2337/diacare.24.8.1317 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kitzmiller JL, Block JM, Brown FM, Catalano PM, Conway DL, Coustan DR, et al. Managing preexisting diabetes for pregnancy: summary of evidence and consensus recommendations for care. Diabetes Care (2008) 31:1060–79. 10.2337/dc08-9020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Catalano PM, Hauguel-De Mouzon S. Review: is it time to revisit the pedersen hypothesis in the face of the obesity epidemic? Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2011) 204:479–87. 10.1016/j.ajog.2010.11.039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Moore TR, Hauguel-De Mouzon S, Catalano P. Diabetes in pregnancy. In: Creasy RK, Resnik R, Iams JD, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, editors. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; (2014). p. 988–1021. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dornhorst A. Diabetes in pregnancy. Women's Health Med. (2005) 2:8–12. 10.1383/wohm.2.2.8.63057 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Walsh JM, McAuliffe FM. Prediction and prevention of the macrosomic fetus. Eur J Obstet Gynecol. (2012) 162:125–30. 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2012.03.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Henriksen T. The macrosomic fetus: a challenge in current obstetrics. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. (2008) 87:134–45. 10.1080/00016340801899289 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Fetal Macrosomia. Obstet Gynecol. (2016) 128:e195–209. 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001767 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Biomarkers Definitions Working Group Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin Pharmacol Ther. (2001) 69:89–95. 10.1067/mcp.2001.113989 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Strimbu K, Tavel JA. What are biomarkers? Curr Opin HIV AIDS (2010) 5:463–6. 10.1097/COH.0b013e32833ed177 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kilpatrick ES, Keevilt BG, Richmond KL, Newland P, Addison GM. Plasma 1,5-anhydroglucitol concentrations are influenced by variations in the renal threshold for glucose. Diabetic Med. (1999) 16:496–9. 10.1046/j.1464-5491.1999.00093.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kerssen A, de Valk HW, Visser GHA. Sibling birthweight as a predictor of macrosomia in women with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia (2005) 48:1743–8. 10.1007/s00125-005-1851-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wright LA, Hirsch IB, Gooley TA, Brown Z. 1,5-Anhydroglucitol and neonatal complications in pregnancy complicated by diabetes. Endocrine Pract. (2015) 21:725–33. 10.4158/EP14437.OR [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Katon J, Reiber G, Williams MA, Yanez D, Miller E. Antenatal haemoglobin A1c and risk of large-for-gestational-age infants in a multi-ethnic cohort of women with gestational diabetes. Paediatr Perinatal Epidemiol. (2012) 26:208–17. 10.1111/j.1365-3016.2012.01266.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tseng YM, Hwang YS, Lu CL, Lin SJ, Tsai WH. Association of umbilical cord plasma acid-labile subunit of the insulin-like growth factor ternary complex with anthropometry in term newborns. Pediatr Neonatol. (2014) 55:139–44. 10.1016/j.pedneo.2013.09.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Teague AM, Fields DA, Aston CE, Short KR, Lyons TJ, Chernausek SD. Cord blood adipokines, neonatal anthropometrics and postnatal growth in offspring of Hispanic and Native American women with diabetes mellitus. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2015) 13:68. 10.1186/s12958-015-0061-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yarrington C, Zera C, Wilkins-Haug L, McElrath T. 751: Association of elevated birth weight with change in adiponectin across gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2014) 210:S369 10.1016/j.ajog.2013.10.784 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Peterson CM, Jovanovic L. Glucosylated proteins in normal and diabetic pregnancy. In: Weiss PA, Coustan DR, editors. Gestational Diabetes. New York, NY: Springer-Verlag; (1988). p. 107–14. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cseh K, Baranyi E, Melczer Z, Kaszás E, Palik E, Winkler G. Plasma adiponectin and pregnancy-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes Care (2004) 27:274–5. 10.2337/diacare.27.1.274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ballesteros M, Simón I, Vendrell J, Ceperuelo-Mallafré V, Miralles RM, Albaiges G, et al. Maternal and cord blood adiponectin multimeric forms in gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective analysis. Diabetes Care (2011) 34:2418–23. 10.2337/dc11-0788 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Verhaeghe J, van Bree R, Van Herck E. Maternal body size and birth weight: can insulin or adipokines do better? Metabolism (2006) 55:339–44. 10.1016/j.metabol.2005.09.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nanda S, Akolekar R, Sarquis R, Mosconi AP, Nicolaides KH. Maternal serum adiponectin at 11 to 13 weeks of gestation in the prediction of macrosomia. Prenat Diagn. (2011) 31:479–83. 10.1002/pd.2723 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Briana DD, Malamitsi-Puchner A. Adipocytokines in normal and complicated pregnancies. Reprod Sci. (2009) 16:921–37. 10.1177/1933719109336614 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang J, Shang L, Dong X, Wang X, Wu N, Wang S, et al. Relationship of adiponectin and resistin levels in umbilical serum, maternal serum and placenta with neonatal birth weight. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. (2010) 50:432–8. 10.1111/j.1479-828X.2010.01184.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lowe WL, Dyer AR, McIntyre HD, Lowe LP, McDade TW, Metzger BE. Inflammatory mediators and glucose in pregnancy: results from a subset of the Hyperglycemia and Adverse Pregnancy Outcome (HAPO) Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2010) 95:5427–34. 10.1210/jc.2010-1662 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.López-Bermejo A, Fernández-Real JM, Garrido E, Rovira R, Brichs R, Genaró P, et al. Maternal soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor type 2 (sTNFR2) and adiponectin are both related to blood pressure during gestation and infant's birthweight. Clin Endocrinol. (2004) 61:544–52. 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2004.02120.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lagiou P, Samoli E, Hsieh C-C, Lagiou A, Xu B, Yu G-P, et al. Maternal and cord blood hormones in relation to birth size. Eur J Epidemiol. (2014) 29:343–51. 10.1007/s10654-014-9914-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ategbo JM, Grissa O, Yessoufou A, Hichami A, Dramane KL, Moutairou K, et al. Modulation of adipokines and cytokines in gestational diabetes and macrosomia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2006) 91:4137–43. 10.1210/jc.2006-0980 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Horosz E, Bomba-Opon DA, Szymanska M, Wielgos M. Third trimester plasma adiponectin and leptin in gestational diabetes and normal pregnancies. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2011) 93:350–6. 10.1016/j.diabres.2011.05.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Matuszek B, Burska A, Leszczynska–Gorzelak B, Donica H, Nowakowski A. Comparative analysis of adiponectin isoform distribution in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and after delivery. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. (2013) 92:951–9. 10.1111/aogs.12137 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chan T-F, Yuan S-SF, Chen H-S, Guu C-F, Wu L-C, Yeh Y-T, et al. Correlations between umbilical and maternal serum adiponectin levels and neonatal birthweights. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. (2004) 83:165–9. 10.1111/j.0001-6349.2004.0298.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Juul A. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor I and its binding proteins in health and disease. Growth Hormone IGF Res. (2003) 13:113–70. 10.1016/S1096-6374(03)00038-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sivan E, Mazaki-Tovi S, Pariente C, Efraty Y, Schiff E, Hemi R, et al. Adiponectin in human cord blood: relation to fetal birth weight and gender. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2003) 88:5656–60. 10.1210/jc.2003-031174 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kotani Y, Yokota I, Kitamura S, Matsuda J, Naito E, Kuroda Y. Plasma adiponectin levels in newborns are higher than those in adults and positively correlated with birth weight. Clin Endocrinol. (2004) 61:418–23. 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2004.02041.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tsai P-J, Yu C-H, Hsu S-P, Lee Y-H, Chiou C-H, Hsu Y-W, et al. Cord plasma concentrations of adiponectin and leptin in healthy term neonates: positive correlation with birthweight and neonatal adiposity. Clin Endocrinol. (2004) 61:88–93. 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2004.02057.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Inoue M, Itabashi K, Nakano Y, Tobe T. High-molecular-weight adiponectin and leptin levels in cord blood are associated with anthropometric measurements at birth. Horm Res Paediatr. (2008) 70:268–72. 10.1159/000157872 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mazaki-Tovi S, Kanety H, Pariente C, Hemi R, Schiff E, Sivan E. Cord blood adiponectin in large-for-gestational age newborns. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2005) 193:1238–42. 10.1016/j.ajog.2005.05.049 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lausten-Thomsen U, Christiansen M, Hedley PL, Holm JC, Schmiegelow K. Adipokines in umbilical cord blood from children born large for gestational age. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. (2016) 29:33–7. 10.1515/jpem-2014-0502 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tsai PJ, Yu CH, Hsu SP, Lee YH, Huang IT, Ho SC, et al. Maternal plasma adiponectin concentrations at 24 to 31 weeks of gestation: negative association with gestational diabetes mellitus. Nutrition (2005) 21:1095–99. 10.1016/j.nut.2005.03.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Valsamakis G, Papatheodorou DC, Margeli A, Bakoulas V, Kapantais E, Papassotiriou I, et al. First trimester maternal BMI is a positive predictor of cord blood c-peptide levels while maternal visfatin levels is a negative predictor of birth weight. Hormones (2014) 13:87–94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kalampokas E, Vrachnis N, Samoli E, Rizos D, Iliodromiti Z, Sifakis S, et al. Association of adiponectin and placental growth factor in amniotic fluid with second trimester fetal growth. In Vivo. (2012) 26:327–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Boisvert MR, Koski KG, Burns DH, Skinner CD. Early prediction of macrosomia based on an analysis of second trimester amniotic fluid by capillary electrophoresis. Biomarkers Med. (2012) 6:655–62. 10.2217/bmm.12.54 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sharony R, Dayan D, Kidron D, Manor M, Berkovitz A, Biron-Shental T, et al. Is the ratio of maternal serum to amniotic fluid AFP superior to serum levels as a predictor of pregnancy complications? Arch Gynecol Obst. (2016) 293:767–70. 10.1007/s00404-015-3905-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Camus-Bablon F, Cohen RM, Berk MA, Perisutti G, Hunter K, Frohman LA. Alterations in circulating human chorionic gonadotropin free alpha-subunit in insulin-dependent diabetic pregnancy: correlation with maternal characteristics. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (1990) 71:46–52. 10.1210/jcem-71-1-46 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Schwartz R, Gruppuso PA, Petzold K, Brambilla D, Hiilesmaa V, Teramo K. Hyperinsulinemia and macrosomia in the fetus of the diabetic mother. Diabetes Care (1994) 17:640–48. 10.2337/diacare.17.7.640 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Weiss PA, Kainer F, Purstner P, Zehetleitner G, Huttner U, Haas J. Anti-insulin antibodies and birth weight in pregnancies complicated by diabetes. Early Hum Dev. (1998) 53:145–54. 10.1016/S0378-3782(98)00047-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Aslan M, Celik O, Celik N, Turkcuoglu I, Yilmaz E, Karaer A, et al. Cord blood nesfatin-1 and apelin-36 levels in gestational diabetes mellitus. Endocrine (2012) 41:424. 10.1007/s12020-011-9577-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sommer C, Sletner L, Mørkrid K, Jenum AK, Inge Birkeland K. Effects of early pregnancy BMI, mid-gestational weight gain, glucose and lipid levels in pregnancy on offspring's birth weight and subcutaneous fat: a population-based cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth (2015) 15:1–9. 10.1186/s12884-015-0512-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Poon LCY, Karagiannis G, Stratieva V, Syngelaki A, Nicolaides KH. First-trimester prediction of macrosomia. Fetal Diagn Ther. (2011) 29:139–47. 10.1159/000318565 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Retnakaran R, Ye C, Hanley AJG, Connelly PW, Sermer M, Zinman B, et al. Effect of maternal weight, adipokines, glucose intolerance and lipids on infant birth weight among women without gestational diabetes mellitus. Can Med Assoc J. (2012) 184:1353–60. 10.1503/cmaj.111154 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Papastefanou I, Souka AP, Pilalis A, Eleftheriades M, Michalitsi V, Kassanos D. First trimester prediction of small- and large-for-gestation neonates by an integrated model incorporating ultrasound parameters, biochemical indices and maternal characteristics. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. (2012) 91:104–11. 10.1111/j.1600-0412.2011.01271.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Jovanovic L, Metzger BE, Knopp RH, conley MR, Park E, Lee YJ, et al. The diabetes in early pregnancy study: beta-hydroxybutyrate levels in type 1 diabetic pregnancy compared with normal pregnancy. NICHD-Diabetes in Early Pregnancy Study Group (DIEP). National Institute of Child Health and development. Diabetes Care (1998) 21:1978–84. 10.2337/diacare.21.11.1978 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Dent PB, Chiavetta J, Leeder S, Richards R, Rawls WE. Elevated levels of carcinoembryonic antigen in cord plasma. Cancer (1978) 42:224–28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Boutsikou T, Briana DD, Boutsikou M, Kafalidis G, Stamati L, Baka S, et al. Cord blood chemerin and obestatin levels in large for gestational age infants. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. (2013) 26:123–6. 10.3109/14767058.2012.728648 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Giannubilo SR, Tiano L, Ciavattini A, Landi B, Carnevali P, Principi F, et al. Amniotic coenzyme Q10: Is it related to pregnancy outcomes? Antioxid Redox Signal. (2014) 21:1582–6. 10.1089/ars.2014.5936 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Briana DD, Baka S, Boutsikou M, Boutsikou T, Xagorari M, Gourgiotis D, et al. Cord blood copeptin concentrations in fetal macrosomia. Metabolism (2016) 65:89–94. 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.09.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Bolten MI, Wurmser H, Buske-Kirschbaum A, Papoušek M, Pirke K-M, Hellhammer D. Cortisol levels in pregnancy as a psychobiological predictor for birth weight. Arch Women's Mental Health (2011) 14:33–41. 10.1007/s00737-010-0183-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Guardino CM, Schetter CD, Saxbe DE, Adam EK, Ramey SL, Shalowitz MU. Diurnal salivary cortisol patterns prior to pregnancy predict infant birth weight. Health Psychol. (2016) 35:625–33. 10.1037/hea0000313 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Baibazarova E, van de Beek C, Cohen-Kettenis PT, Buitelaar J, Shelton KH, van Goozen SHM. Influence of prenatal maternal stress, maternal plasma cortisol and cortisol in the amniotic fluid on birth outcomes and child temperament at 3 months. Psychoneuroendocrinology (2013) 38:907–15. 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.09.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hou R-L, Jin W-Y, Chen X-Y, Jin Y, Wang X-M, Shao J, et al. Cord blood C-peptide, insulin, HbA1c, and lipids levels in small- and large-for-gestational-age newborns. Med Sci Monitor. (2014) 20:2097–105. 10.12659/MSM.890929 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Stein RG, Meinusch M, Diessner J, Dietl J, Honig A, Zollner U. Amniotic fluid insulin and C-peptide as predictive markers for fetal macrosomia, birth injuries, and delivery complications? Med Sci Monitor. (2014) 20:54–8. 10.12659/MSM.889503 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Klemetti MM, Laivuori H, Tikkanen M, Nuutila M, Hiilesmaa V, Teramo K. Obstetric and perinatal outcome in type 1 diabetes patients with diabetic nephropathy during 1988–2011. Diabetologia (2015) 58:678–86. 10.1007/s00125-014-3488-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Farah N, Hogan AE, O'Connor N, Kennelly MM, O'Shea D, Turner MJ. Correlation between maternal inflammatory markers and fetomaternal adiposity. Cytokine (2012) 60:96–9. 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.05.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Loukovaara M, Leinonen P, Teramo K, Andersson S, Alfthan H, Stenman U-H. Diabetic pregnancy associated with increased epidermal growth factor in cord serum at term. Obstet Gynecol. (2004) 103:240–4. 10.1097/01.AOG.0000110545.64874.49 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Varner MW, Dildy GA, Hunter C, Dudley DJ, Clark SL, Mitchell MD. Amniotic fluid epidermal growth factor levels in normal and abnormal pregnancies. J Soc Gynecol Invest. (1996) 3:17–9. 10.1177/107155769600300104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Zawiejska A, Wender-Ozegowska E, Pietryga M, Brazert J. Maternal endothelial dysfunction and its association with abnormal fetal growth in diabetic pregnancy. Diabetic Med. (2011) 28:692–8. 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2011.03249.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Furnica RM, Gruson D, Lazarus JH, Maiter D, Bernard P, Daumerie C. First trimester isolated maternal hypothyroxinaemia: adverse maternal metabolic profile and impact on the obstetrical outcome. Clin Endocrinol. (2017) 86:576–83. 10.1111/cen.13301 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Page RC, Kirk BA, Fay T, Wilcox M, Hosking DJ, Jeffcoate WJ. Is macrosomia associated with poor glycaemic control in diabetic pregnancy? Diabetic Med. (1996) 13:170–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Csákány GM, Baranyi E, Simon J, Ołáh J, Mészáros J, Gáti I. Early prediction of fetal macrosomia in diabetes mellitus. J Perinatal Med. (1990) 18:297–303. 10.1515/jpme.1990.18.4.297 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Roberts AB, Baker JR, Court DJ, James AG, Henley P, Ronayne ID. Fructosamine in diabetic pregnancy. Lancet (1983) 2:998–1000. 10.1016/S0140-6736(83)90982-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Salemans T, van Dieijen-Visser M, Brombacher P, Peeters L. Value of maternal fructosamine in the screening of an unselected population for hyperglycemia-related complications in the newborn. Am J Perinatol. (1994) 11:4–8. 10.1055/s-2007-994523 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Cundy T, Gamble G, Manuel A, Townend K, Roberts A. Determinants of birth-weight in women with established and gestational diabetes. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. (1993) 33:249–54. 10.1111/j.1479-828X.1993.tb02078.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Kui L, Hui-xia Y. Value of fructosamine measurement in pregnant women with abnormal glucose tolerance. Chin Med J. (2006) 119:1861–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Karcaaltincaba D, Yalvac S, Kandemir O, Altun S. Glycosylated hemoglobin level in the second trimester predicts birth weight and amniotic fluid volume in non-diabetic pregnancies with abnormal screening test. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. (2010) 23:1193–9. 10.3109/14767050903511586 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Liu Z-W, Zhang J-T, Cai Q-Y, Zhang H-X, Wang Y-H, Yan H-T, et al. Birth weight is associated with placental fat mass- and obesity-associated gene expression and promoter methylation in a Chinese population. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. (2016) 29:106–11. 10.3109/14767058.2014.987749 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Kara M, Orbak Z, Döneray H, Ozkan B, Akcay F. The relationship between skinfold thickness and leptin, ghrelin, adiponectin, and resistin levels in infants of diabetic mothers. Fetal Pediatr Pathol. (2017) 36:1–7. 10.1080/15513815.2016.1217960 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ng PC, Lee CH, Lam CWK, Chan IHS, Wong E, Fok TF. Ghrelin in preterm and term newborns: relation to anthropometry, leptin and insulin. Clin Endocrinol. (2005) 63:217–22. 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2005.02328.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Valsamakis G, Papatheodorou DC, Naoum A, Margeli A, Papassotiriou I, Kapantais E, et al. Neonatal birth waist is positively predicted by second trimester maternal active ghrelin, a pro-appetite hormone, and negatively associated with third trimester maternal leptin, a pro-satiety hormone. Early Hum Dev. (2014) 90:487–92. 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2014.07.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Hardy DS. A multiethnic study of the predictors of macrosomia. Diabetes Educ. (1999) 25:925–33. 10.1177/014572179902500610 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Parfitt VJ, Clark JD, Turner GM, Hartog M. Maternal postprandial blood glucose levels influence infant birth weight in diabetic pregnancy. Diabetes Res. (1992) 19:133–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Raychaudhuri K, Maresh MJ. Glycemic control throughout pregnancy and fetal growth in insulin-dependent diabetes. Obstet Gynecol. (2000) 95:190–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Mello G, Parretti E, Mecacci F, La Torre P, Cioni R, Cianciulli D, et al. What degree of maternal metabolic control in women with type 1 diabetes is associated with normal body size and proportions in full-term infants? Diabetes Care (2000) 23:1494–8. 10.2337/diacare.23.10.1494 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Taslimi MM, Navabi K, Acosta R, Helmer A, El-Sayed YY. Concealed maternal blood glucose excursions correlate with birth weight centile. J Diabetes Sci Technol. (2008) 2:456–60. 10.1177/193229680800200315 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Persson B, Hanson U. Fetal size at birth in relation to quality of blood glucose control in pregnancies complicated by pregestational diabetes mellitus. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. (1996) 103:427–33. 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1996.tb09768.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Voormolen DN, DeVries JH, Evers IM, Mol BWJ, Franx A. The efficacy and effectiveness of continuous glucose monitoring during pregnancy: a systematic review. Obstet Gynecol Survey (2013) 68:753–63. 10.1097/OGX.0000000000000002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Combs CA, Gunderson E, Kitzmiller JL, Gavin LA, Main EK. Relationship of fetal macrosomia to maternal postprandial glucose control during pregnancy. Diabetes Care (1992) 15:1251–7. 10.2337/diacare.15.10.1251 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Kitajima M, Oka S, Yasuhi I, Fukuda M, Rii Y, Ishimaru T. Maternal serum triglyceride at 24–32 weeks' gestation and newborn weight in nondiabetic women with positive diabetic screens. Obstet Gynecol. (2001) 97:776–80. 10.1016/S0029-7844(01)01328-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Schrader HM, Jovanovic-Peterson L, Bevier WC, Peterson CM. Fasting plasma glucose and glycosylated plasma protein at 24 to 28 weeks of gestation predict macrosomia in the general obstetric population. Am J Perinatol. (1995) 12:247–51. 10.1055/s-2007-994465 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ouzilleau C, Roy MA, Leblanc L, Carpentier A, Maheux P. An observational study comparing 2-hour 75-g oral glucose tolerance with fasting plasma glucose in pregnant women: both poorly predictive of birth weight. Can Med Assoc J. (2003) 168:403–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Disse E, Graeppi-Dulac J, Joncour-Mills G, Dupuis O, Thivolet C. Heterogeneity of pregnancy outcomes and risk of LGA neonates in Caucasian females according to IADPSG criteria for gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes & Metab. (2013) 39:132–38. 10.1016/j.diabet.2012.09.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Nasrat H, Fageeh W, Abalkhail B, Yamani T, Ardawi MS. Determinants of pregnancy outcome in patients with gestational diabetes. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. (1996) 53:117–23. 10.1016/0020-7292(95)02635-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Lapolla A, Dalfrà MG, Bonomo M, Castiglioni MT, Di Cianni G, Masin M, et al. Can plasma glucose and HbA1c predict fetal growth in mothers with different glucose tolerance levels? Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2007) 77:465–70. 10.1016/j.diabres.2007.01.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Knopp RH, Bergelin RO, Wahl PW, Walden CE. Relationships of infant birth size to maternal lipoproteins, apoproteins, fuels, hormones, clinical chemistries, and body weight at 36 weeks gestation. Diabetes (1985) 34(Suppl. 2):71–7. 10.2337/diab.34.2.S71 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Farrar D, Fairley L, Santorelli G, Tuffnell D, Sheldon TA, Wright J, et al. Association between hyperglycaemia and adverse perinatal outcomes in south Asian and white British women: analysis of data from the Born in Bradford cohort. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2015) 3:795–804. 10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00255-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.The HAPO Study Cooperative Research Group. Hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcomes. N Engl J Med. (2008) 358:1991–2002. 10.1056/NEJMoa0707943 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Berk MA, Mimouni F, Miodovnik M, Hertzberg V, Valuck J. Macrosomia in infants of insulin-dependent diabetic mothers. Pediatrics (1989) 83:1029–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Corrado F, Benedetto AD, Cannata ML, Cannizzaro D, Giordano D, Indorato G, et al. A single abnormal value of the glucose tolerance test is related to increased adverse perinatal outcome. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. (2009) 22:597–601. 10.1080/14767050902801801 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Sylvestre G, Divon MY, Onyeije C, Fisher M. Diagnosis of macrosomia in the postdates population: combining sonographic estimates of fetal weight with glucose challenge testing. J Matern Fetal Med. (2000) 9:287–90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Dennedy MC, Avalos G, O'Reilly MW, O'Sullivan EP, Gaffney G, Dunne F. ATLANTIC-DIP: raised maternal body mass index (BMI) adversely affects maternal and fetal outcomes in glucose-tolerant women according to International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups (IADPSG) criteria. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 97:E608–E12. 10.1210/jc.2011-2674 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Sermer M, Naylor CD, Gare DJ, Kenshole AB, Ritchie JWK, Farine D, et al. Impact of increasing carbohydrate intolerance on maternal-fetal outcomes in 3637 women without gestational diabetes: the toronto tri-hospital gestational diabetes project. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (1995) 173:146–56. 10.1016/0002-9378(95)90183-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Stefos T, Sotiriadis A, Kaponis A, Dalkalitsis N, Lolis D. Amniotic fluid glucose at the time of genetic amniocentesis: Correlation with duration of pregnancy and birthweight. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. (2003) 106:144–7. 10.1016/S0301-2115(02)00230-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Krstevska B, Velkoska NV, Adamova G, Simeonova S, Dimitrovski C, Livrinova V, et al. Association between foetal growth and different maternal metabolic characteristics in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Contributions Maced Acad Sci Arts (2009) 30:103–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Saleh J, Al-Riyami HDS, Chaudhary TA, Cianflone K. Cord blood ASP is predicted by maternal lipids and correlates with fetal birth weight. Obesity (2008) 16:1193–8. 10.1038/oby.2008.45 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Dang K, Homko C, Reece EA. Factors associated with fetal macrosomia in offspring of gestational diabetic women. J Mater Med. (2000) 9:114–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Lawlor DA, Fraser A, Lindsay RS, Ness A, Dabelea D, Catalano P, et al. Association of existing diabetes, gestational diabetes and glycosuria in pregnancy with macrosomia and offspring body mass index, waist and fat mass in later childhood: findings from a prospective pregnancy cohort. Diabetologia (2010) 53:89–97. 10.1007/s00125-009-1560-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Li H-P, Wang F-H, Tao M-F, Huang Y-J, Jia W-P. Association between glycemic control and birthweight with glycated albumin in Chinese women with gestational diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig. (2016) 7:48–55. 10.1111/jdi.12383 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Bernstein IM, Silver R, Nair KS, Stirewalt WS. Amniotic fluid glycine-valine ratio and neonatal morbidity in fetal growth restriction. Obstet Gynecol. (1997) 90:933–7. 10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00533-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Widness JA, Schwartz HC, Thompson D. Glycohemoglobin (HbA(Ic)): A predictor of birth weight in infants of diabetic mothers. J Pediatr. (1978) 92:8–12. 10.1016/S0022-3476(78)80059-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Delaney SS, Coley RY, Brown Z. 1,5-Anhydroglucitol: a new predictor of neonatal birth weight in diabetic pregnancies. Eur J Obstet Gynecol. (2015) 189:55–8. 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2015.03.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Fadel HE, Elseweidy MM, Abraham EC. Glycosylated hemoglobin and protein levels in normal and diabetic pregnancies: relation to birth weight. Obstet Gynecol. (1986) 67:533–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Buckshee K, Kanitkar V, Karmarkar MG, Mittal S, Takkar D. Glycosylated hemoglobin level: an indicator of fetal birth weight and perinatal outcome. Indian J Pediatr. (1990) 57:448–50. 10.1007/BF02727940 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Nelson SM, Freeman DJ, Sattar N, Lindsay RS. Erythrocytosis in offspring of mothers with Type 1 diabetes-are factors other than insulin critical determinants? Diabetic Med. (2009) 26:887–92. 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2009.02797.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Glinianaia SV, Tennant PWG, Bilous RW, Rankin J, Bell R. HbA(1c) and birthweight in women with pre-conception type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a population-based cohort study. Diabetologia (2012) 55:3193–203. 10.1007/s00125-012-2721-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Gold AE, Reilly R, Little J, Walker JD. The effect of glycemic control in the pre-conception period and early pregnancy on birth weight in women with IDDM. Diabetes Care (1998) 21:535–8. 10.2337/diacare.21.4.535 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Anaka O, Houlihan C, Beim R, Ranzini AC. Does first-trimester hemoglobin A1C predict gestational diabetes and fetal outcome? Obstet Gynecol. (2014) 123:38S–9S. 10.1097/01.AOG.0000447315.90086.64 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Herranz L, Pallardo LF, Hillman N, Martin-Vaquero P, Villarroel A, Fernandez A. Maternal third trimester hyperglycaemic excursions predict large-for-gestational-age infants in type 1 diabetic pregnancy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2007) 75:42–6. 10.1016/j.diabres.2006.05.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Evers IM, de Valk HW, Mol BWJ, ter Braak EWMT, Visser GHA. Macrosomia despite good glycaemic control in Type I diabetic pregnancy; results of a nationwide study in The Netherlands. Diabetologia (2002) 45:1484–9. 10.1007/s00125-002-0958-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Vintzileos AM, Thompson JP. Glycohemoglobin determinations in normal pregnancy and in insulin-dependent diabetics. Obstet Gynecol. (1980) 56:435–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Damm P, Mersebach H, Råstam J, Kaaja R, Hod M, McCance DR, et al. Poor pregnancy outcome in women with type 1 diabetes is predicted by elevated HbA1c and spikes of high glucose values in the third trimester. J Mater Neonatal Med. (2014) 27:149–54. 10.3109/14767058.2013.806896 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Madsen H, Ditzel J. The influence of maternal weight, smoking, vascular complications and glucose regulation on the birth weight of infants of type 1 diabetic women. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. (1991) 39:175–9. 10.1016/0028-2243(91)90054-O [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Rey E, Attié C, Bonin A. The effects of first-trimester diabetes control on the incidence of macrosomia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (1999) 181:202–6. 10.1016/S0002-9378(99)70460-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Maresh MJA, Holmes VA, Patterson CC, Young IS, Pearson DWM, Walker JD, et al. Glycemic targets in the second and third trimester of pregnancy for women with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care (2015) 38:34–42. 10.2337/dc14-1755 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Versantvoort ARE, van Roosmalen J, Radder JK. Course of HbA1c in non-diabetic pregnancy related to birth weight. Neth J Med. (2013) 71:22–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Shobha P, Mathen S, Abraham J. Glycosylated hemoglobin values in nondiabetic pregnant women in the third trimester and adverse fetal outcomes: an observational study. J Family Med Primary Care. (2016) 5:646–51. 10.4103/2249-4863.197313 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Buse JB, Freeman JLR, Edelman SV, Jovanovic L, McGill JB. Serum 1,5-anhydroglucitol (GlycoMark): a short-term glycemic marker. Diabetes Technol Ther. (2003) 5:355–63. 10.1089/152091503765691839 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Kyne-Grzebalski D, Wood L, Marshall SM, Taylor R. Episodic hyperglycaemia in pregnant women with well-controlled Type 1 diabetes mellitus: a major potential factor underlying macrosomia. Diabetic Med. (1999) 16:702–6. 10.1046/j.1464-5491.1999.00131.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Swierzewska P, Kosinski M, Wójcik M, Dworacka M, Cypryk K. Family, anthropometric and biochemical factors affecting birth weight of infants born to GDM women. Ginekologia Polska. (2015) 86:499–503. 10.17772/gp/652 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Yu H, Qi X, Wang X. Application of glycated hemoglobin in the perinatal period. Int J Clin Exp Med. (2014) 7:4653–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Ghosh G, Pildes RS, Richton S, Ajayi O. Maternal and cord serum glycosylated protein in neonatal macrosomia and correlation with birth weight. Obstet Gynecol. (1990) 75:79–83. 10.1016/0020-7292(90)90678-E [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Weissmann-Brenner A, O'Reilly-Green C, Ferber A, Divon MY. Does the availability of maternal HbA1c results improve the accuracy of sonographic diagnosis of macrosomia? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. (2004) 23:466–71. 10.1002/uog.1031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Lowe LP, Metzger BE, Dyer AR, Lowe J, McCance DR, Lappin TRJ, et al. Hyperglycemia and Adverse Pregnancy Outcome (HAPO) Study: associations of maternal A1C and glucose with pregnancy outcomes. Diabetes Care (2012) 35:574–80. 10.2337/dc11-1687 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Drew NC. Obstetric short communications Glycosylated haemoglobin in normal pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol. (1985) 6:106 10.3109/01443618509079158 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Gonzalez-Renteria SM, Sosa-Macias M, Rodriguez-Moran M, Chairez-Hernandez I, Lares-Aseff IA, Guerrero-Romero F, et al. Association of the intronic polymorphism rs12540874 A>G of the GRB10 gene with high birth weight. Early Hum Dev. (2014) 90:545–8. 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2014.06.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Misra VK, Trudeau S, Perni U. Maternal serum lipids during pregnancy and infant birth weight: the influence of prepregnancy BMI. Obesity (2011) 19:1476–81. 10.1038/oby.2011.43 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Luo Z-C, Nuyt A-M, Delvin E, Audibert F, Girard I, Shatenstein B, et al. Maternal and fetal IGF-I and IGF-II levels, fetal growth, and gestational diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 97:1720–8. 10.1210/jc.2011-3296 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Simeonova-Krstevska S, Krstevska B, Velkoska-Nakova V, Hadji Lega M, Samardjiski I, Serafimoski V, et al. Effect of lipid parameters on foetal growth in gestational diabetes mellitus pregnancies. Prilozi (2014) 35:131–6. 10.2478/prilozi-2014-0017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Schaefer-Graf UM, Graf K, Kulbacka I, Kjos SL, Dudenhausen J, Vetter K, et al. Maternal lipids as strong determinants of fetal environment and growth in pregnancies with gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care (2008) 31:1858–63. 10.2337/dc08-0039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Nelson SM, Freeman DJ, Sattar N, Johnstone FD, Lindsay RS. IGF-1 and leptin associate with fetal HDL cholesterol at birth: examination in offspring of mothers with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes (2007) 56:2705–9. 10.2337/db07-0585 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Ahmad SM, Hazlina NH, Che Anuar CY, Faridah AR, Shukri Y. A study on factors affecting newborn weight and large for gestational age (LGA) newborns in non-diabetic mothers: the role of maternal serum triglycerides. Int Med J. (2006) 13:53–8. [Google Scholar]
- 147.Zhou J, Zhao X, Wang Z, Hu Y. Combination of lipids and uric acid in mid-second trimester can be used to predict adverse pregnancy outcomes. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. (2012) 25:2633–8. 10.3109/14767058.2012.704447 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Ohnishi Y, Yamashiro C, Yanagihara T, Hata T. Hepatocyte growth factor concentration in the early second-trimester amniotic fluid does not predict fetal growth at birth. Hum Reprod. (1999) 14:2625–8. 10.1093/humrep/14.10.2625 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Murphy MM, Scott JM, Arija V, Molloy AM, Fernandez-Ballart JD. Maternal homocysteine before conception and throughout pregnancy predicts fetal homocysteine and birth weight. Clin Chem. (2004) 50:1406–12. 10.1373/clinchem.2004.032904 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Schwartz R, Teramo KA. Effects of diabetic pregnancy on the fetus and newborn. Semin Perinatol. (2000) 24:120–35. 10.1053/sp.2000.6363 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Simental-Mendía LE, Casta-eda-Chacón A, Rodríguez-Morán M, Guerrero-Romero F. Birth-weight, insulin levels, and HOMA-IR in newborns at term. BMC Pediatr. (2012) 12:94. 10.1186/1471-2431-12-94 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Weerasiri T, Riley SF, Sheedy MT, Walstab JE, Wein P. Amniotic fluid insulin values in women with gestational diabetes as a predictor of emerging diabetes mellitus. Aust N Z J Obst Gynaecol. (1993) 33:358–61. 10.1111/j.1479-828X.1993.tb02108.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Fraser RB, Bruce C. Amniotic fluid insulin levels identify the fetus at risk of neonatal hypoglycaemia. Diabetic Med. (1999) 16:568–72. 10.1046/j.1464-5491.1999.00104.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Kainer F, Weiss PA, Hüttner U, Haas J. Ultrasound growth parameters in relation to levels of amniotic fluid insulin in women with diabetes type-I. Early Hum Dev. (1997) 49:113–21. 10.1016/S0378-3782(97)00026-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Fuglsang J, Lauszus F, Flyvbjerg A, Ovesen P. Human placental growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor I and -II, and insulin requirements during pregnancy in type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2003) 88:4355–61. 10.1210/jc.2003-030726 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.McIntyre HD, Serek R, Crane DI, Veveris-Lowe T, Parry A, Johnson S, et al. Placental growth hormone (GH), GH-binding protein, and insulin-like growth factor axis in normal, growth-retarded, and diabetic pregnancies: correlations with fetal growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2000) 85:1143–50. 10.1210/jc.85.3.1143 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Bhaumick B, Danilkewich A, Bala R. Insulin-like growth factors (IGF) I and II in diabetic pregnancy: suppression of normal pregnancy-induced rise of IGF-I. Diabetologia (1986) 29:792. 10.1007/BF00873218 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Asvold BO, Eskild A, Jenum PA, Vatten LJ. Maternal concentrations of insulin-like growth factor I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 during pregnancy and birth weight of offspring. Am Epidemiol. (2011) 174:129–35. 10.1093/aje/kwr067 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Grissa O, Yessoufou A, Mrisak I, Hichami A, Amoussou-Guenou D, Grissa A, et al. Growth factor concentrations and their placental mRNA expression are modulated in gestational diabetes mellitus: possible interactions with macrosomia. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. (2010) 10:7. 10.1186/1471-2393-10-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Roth S, Abernathy MP, Lee WH, Pratt L, Denne S, Golichowski A, et al. Insulin-like growth factors I and II peptide and messenger RNA levels in macrosomic infants of diabetic pregnancies. J Soc For Gynecol Invest. (1996) 3:78–84. 10.1177/107155769600300207 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Olausson H, Lof M, Brismar K, Forsum E, Sohlstrom A. Maternal serum concentrations of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF binding protein-1 before and during pregnancy in relation to maternal body weight and composition and infant birth weight. Br J Nutr. (2010) 104:842–8. 10.1017/S0007114510001224 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Osorio M, Torres J, Moya F, Pezzullo J, Salafia C, Baxter R, et al. Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF binding proteins-1,−2, and−3 in newborn serum: relationships to fetoplacental growth at term. Early Hum Dev. (1996) 46:15–26. 10.1016/0378-3782(96)01737-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Boyne MS, Thame M, Bennett FI, Osmond C, Miell JP, Forrester TE. The relationship among circulating insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF-binding proteins-1 and−2, and birth anthropometry: a prospective study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2003) 88:1687–91. 10.1210/jc.2002-020633 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Whittaker PG, Stewart MO, Taylor A, Howell RJS, Lind T. Insulin-like growth factor 1 and its binding protein 1 during normal and diabetic pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol. (1990) 76:223–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Zhang X, Decker A, Platt RW, Kramer MS. How big is too big? The perinatal consequences of fetal macrosomia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2008) 198:517.e1–6. 10.1016/j.ajog.2007.12.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Pathmaperuma A, Tennekoon K, Senanayake L, Karunanayake E. Maternal and cord blood levels of insulin-like growth factors-I and-II and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1: correlation with birth weight and maternal anthropometric indices. Ceylon Med J. (2009) 52:48–52. 10.4038/cmj.v52i2.1019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Faupel-Badger JM, Wang Y, Karumanchi SA, Stanczyk F, Pollak M, McElrath T, et al. Associations of pregnancy characteristics with maternal and cord steroid hormones, angiogenic factors, and insulin-like growth factor axis. Cancer Causes Control. (2011) 22:1587. 10.1007/s10552-011-9835-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Chellakooty M, Vangsgaard K, Larsen T, Scheike T, Falck-Larsen J, Legarth J, et al. A longitudinal study of intrauterine growth and the placental growth hormone (GH)-insulin-like growth factor I axis in maternal circulation: association between placental GH and fetal growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2004) 89:384–91. 10.1210/jc.2003-030282 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Liu Y-J, Tsushima T, Minei S, Sanaka M, Nagashima T, Yanagisawa K, et al. Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF-binding proteins (IGFBP-1,-2 and-3) in diabetic pregnancy: relationship to macrosomia. Endoc J. (1996) 43:221–31. 10.1507/endocrj.43.221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.El-Masry SA, El-Ganzoury MM, El-Farrash RA, Anwar M, Abd Ellatife RZ. Size at birth and insulin-like growth factor-I and its binding protein-1 among infants of diabetic mothers. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. (2013) 26:5–9. 10.3109/14767058.2012.718000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Åman J, Hansson U, Östlund I, Wall K, Persson B. Increased fat mass and cardiac septal hypertrophy in newborn infants of mothers with well-controlled diabetes during pregnancy. Neonatology (2011) 100:147–54. 10.1159/000323741 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Lindsay RS, Hamilton BA, Calder AA, Johnstone FD, Walker JD. The relation of insulin, leptin and IGF-1 to birthweight in offspring of women with type 1 diabetes. Clin Endocrinol. (2004) 61:353–9. 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2004.02104.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.El-Ganzoury MM, El-Masry SA, El-Farrash RA, Anwar M, Abd Ellatife RZ. Infants of diabetic mothers: echocardiographic measurements and cord blood IGF-I and IGFBP-1. Pediatr Diabetes. (2012) 13:189–96. 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2011.00811.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Lindsay RS, Westgate J, Beattie J, Pattison N, Gamble G, Mildenhall L, et al. Inverse changes in fetal insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 and IGF binding protein-1 in association with higher birth weight in maternal diabetes. Clin Endocrinol. (2007) 66:322–8. 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2006.02719.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Klauwer D, Blum WF, Hanitsch S, Rascher W, Lee PDK, Kiess W. IGF-I, IGF-II, free IGF-I and IGFBP-1,−2 and−3 levels in venous cord blood: relationship to birthweight, length and gestational age in healthy newborns. Acta Paediatr Int J Paediatr. (1997) 86:826–33. 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1997.tb08605.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Chiesa C, Osborn JF, Haass C, Natale F, Spinelli M, Scapillati E, et al. Ghrelin, leptin, IGF-1, IGFBP-3, and insulin concentrations at birth: is there a relationship with fetal growth and neonatal anthropometry? Clin Chem. (2008) 54:550–8. 10.1373/clinchem.2007.095299 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Higgins MF, Russell NE, Crossey PA, Nyhan KC, Brazil DP, McAuliffe FM. Maternal and fetal placental growth hormone and IGF axis in type 1 diabetic pregnancy. PLoS ONE (2012) 7:e29164. 10.1371/journal.pone.0029164 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Verhaeghe J, Pintiaux A, Van Herck E, Hennen G, Foidart J-M, Igout A. Placental GH, IGF-I, IGF-binding protein-1, and leptin during a glucose challenge test in pregnant women: relation with maternal body weight, glucose tolerance, and birth weight. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2002) 87:2875–82. 10.1210/jcem.87.6.8569 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Desgagne V, Hivert M-F, St-Pierre J, Guay S-P, Baillargeon J-P, Perron P, et al. Epigenetic dysregulation of the IGF system in placenta of newborns exposed to maternal impaired glucose tolerance. Epigenomics (2014) 6:193–207. 10.2217/epi.14.3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Joung KE, Park KH, Filippaios A, Dincer F, Christou H, Mantzoros CS. Cord blood irisin levels are positively correlated with birth weight in newborn infants. Metabolism (2015) 64:1507–14. 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.07.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Manderson JG, Patterson CC, Hadden DR, Traub AI, Leslie H, McCance DR. Leptin concentrations in maternal serum and cord blood in diabetic and nondiabetic pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2003) 188:1326–32. 10.1067/mob.2003.276 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Shroff MR, Holzman C, Tian Y, Evans RW, Sikorskii A. Mid-pregnancy maternal leptin levels, birthweight for gestational age and preterm delivery. Clin Endocrinol. (2013) 78:607–13. 10.1111/cen.12029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Walsh JM, Byrne J, Mahony RM, Foley ME, McAuliffe FM. Leptin, fetal growth and insulin resistance in non-diabetic pregnancies. Early Hum Dev. (2014) 90:271–4. 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2014.03.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Donnelly JM, Lindsay KL, Walsh JM, Horan M, Molloy EJ, McAuliffe FM. Fetal metabolic influences of neonatal anthropometry and adiposity. BMC Pediatr. (2015) 15:175. 10.1186/s12887-015-0499-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Lipa M, Bomba-Opon D, Lipa J, Bartnik P, Bartoszewicz Z, Wielgoś M. Lipoxin A4 (LXA4) as a potential first trimester biochemical marker of intrauterine growth disorders. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. (2016) 30:2495–249. 10.1080/14767058.2016.1254182 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Marincola FC, Dessì A, Pattumelli MG, Corbu S, Ossicini C, Ciccarelli S, et al. 1H NMR-based urine metabolic profile of IUGR, LGA, and AGA newborns in the first week of life. Clin Chim Acta. (2015) 451:28–34. 10.1016/j.cca.2015.08.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Jiang H, Wu W, Zhang M, Li J, Peng Y, Miao Tt, et al. Aberrant upregulation of miR-21 in placental tissues of macrosomia. J Perinatol. (2014) 34:658–63. 10.1038/jp.2014.58 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Ge Q, Zhu Y, Li H, Tian F, Xie X, Bai Y. Differential expression of circulating miRNAs in maternal plasma in pregnancies with fetal macrosomia. Int J Mol Med. (2015) 35:81–91. 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1989 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Hu L, Han J, Zheng F, Ma H, Chen J, Jiang Y, et al. Early second-trimester serum microRNAs as potential biomarker for nondiabetic macrosomia. Biomed Res Int. (2014) 2014:1–6. 10.1155/2014/603985 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Crovetto F, Lattuada D, Rossi G, Mangano S, Somigliana E, Bolis G, et al. A role for mitochondria in gestational diabetes mellitus? Gynecol Endocrinol. (2013) 29:259–62. 10.3109/09513590.2012.736556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Coolman M, Timmermans S, de Groot CJ, Russcher H, Lindemans J, Hofman A, et al. Angiogenic and fibrinolytic factors in blood during the first half of pregnancy and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Obst Gynecol. (2012) 119:1190–200. 10.1097/AOG.0b013e318256187f [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Sundrani D, Khot V, Pisal H, Mehendale S, Wagh G, Joshi A, et al. Gestation dependant changes in angiogenic factors and their associations with fetal growth measures in normotensive pregnancy. PLoS ONE (2013) 8:e0054153. 10.1371/journal.pone.0054153 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Chellakooty M, Skibsted L, Skouby SO, Andersson A-M, Petersen JH, Main KM, et al. Longitudinal study of serum placental GH in 455 normal pregnancies: correlation to gestational age, fetal gender, and weight. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2002) 87:2734–9. 10.1210/jcem.87.6.8544 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Kappil MA, Green BB, Armstrong DA, Sharp AJ, Lambertini L, Marsit CJ, et al. Placental expression profile of imprinted genes impacts birth weight. Epigenetics (2015) 10:842–9. 10.1080/15592294.2015.1073881 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Cowans NJ, Spencer K, Meiri H. First-trimester maternal placental protein 13 levels in pregnancies resulting in adverse outcomes. Prenatal Diagn. (2008) 28:121–5. 10.1002/pd.1921 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Giudice I, Benintende G, Di Nicolò AM, Mangiameli D, Carrara G, Randazzo C, et al. Correlation of neonatal weight with maternal serum levels of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A during the first trimester of pregnancy: a retrospective study. J Perinatal Med. (2015) 43:227–32. 10.1515/jpm-2013-0249 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Cignini P, Savasta LM, Gulino FA, Vitale SG, Mangiafico L, Mesoraca A, et al. Predictive value of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) and free beta-hCG on fetal growth restriction: results of a prospective study. Arch Gynecol Obstet. (2016) 293:1227–33. 10.1007/s00404-015-3947-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Godbole K, Kulkarni A, Kanade A, Kulkarni S, Godbole G, Wakankar A. Maternal serum aneuploidy screen and adverse pregnancy outcomes. J Obstet Gynaecol. (2016) 66(Suppl.1):141–8. 10.1007/s13224-015-0826-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Mestan K, Ouyang F, Matoba N, Pearson C, Ortiz K, Wang X. Maternal obesity, diabetes mellitus and cord blood biomarkers in large-for-gestational age infants. J Pediatr Biochem. (2010) 1:217–24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Chan T-F, Chen H-S, Chen Y-C, Lee C-H, Chou F-H, Chen IJ, et al. Increased serum retinol-binding protein 4 concentrations in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Reprod Sci. (2007) 14:169–74. 10.1177/1933719106298407 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Vitoratos N, Dimitrakaki A, Vlahos NF, Gregoriou O, Panoulis K, Christopoulos P, et al. Maternal and umbilical resistin levels do not correlate with infant birth weight either in normal pregnancies and or in pregnancies complicated with gestational diabetes. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. (2010) 23:1019–23. 10.3109/14767050903551459 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Sabri A, Lai D, D'Silva A, Seeho S, Kaur J, Ng C, et al. Differential placental gene expression in term pregnancies affected by fetal growth restriction and macrosomia. Fetal Diagn Ther. (2014) 36:173–80. 10.1159/000360535 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Miettinen HE, Rönö K, Koivusalo S, Stach-Lempinen B, Pöyhönen-Alho M, Eriksson JG, et al. Elevated serum squalene and cholesterol synthesis markers in pregnant obese women with gestational diabetes mellitus. J Lipid Res. (2014) 55:2644–54. 10.1194/jlr.P049510 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Tseng J-J, Chen Y-F, Hsieh Y-T, Chou M-M. Elevated amniotic fluid Stromal Cell-derived Factor-1α (SDF-1α) concentration in mid-gestation as a predictor of adverse birth outcomes. J Chin Med Assoc. (2009) 72:638–42. 10.1016/S1726-4901(09)70446-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Grissa O, Ategbo JM, Yessoufou A, Tabka Z, Miled A, Jerbi M, et al. Antioxidant status and circulating lipids are altered in human gestational diabetes and macrosomia. Transl Res. (2007) 150:164–71. 10.1016/j.trsl.2007.03.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Emet T, Ustuner IAAk, Guven SG, BalA+-k G, Ural UM, Tekin YB, et al. Plasma lipids and lipoproteins during pregnancy and related pregnancy outcomes. Arch Gynecol Obstet. (2013) 288:49–55. 10.1007/s00404-013-2750-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Jin W-Y, Lin S-L, Hou R-L, Chen X-Y, Han T, Jin Y, et al. Associations between maternal lipid profile and pregnancy complications and perinatal outcomes: a population-based study from China. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. (2016) 16:1–9. 10.1186/s12884-016-0852-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Clausen T, Burski TK, Øyen N, Godang K, Bollerslev J, Henriksen T. Maternal anthropometric and metabolic factors in the first half of pregnancy and risk of neonatal macrosomia in term pregnancies. A prospective study. Eur J Endocrinol. (2005) 153:887–94. 10.1530/eje.1.02034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Wang D, Xu S, Chen H, Zhong L, Wang Z. The associations between triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratios and the risks of gestational diabetes mellitus and large-for-gestational-age infant. Clin Endocrinol. (2015) 83:490–7. 10.1111/cen.12742 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Schaefer-Graf UM, Meitzner K, Ortega-Senovilla H, Graf K, Vetter K, Abou-Dakn M, et al. Differences in the implications of maternal lipids on fetal metabolism and growth between gestational diabetes mellitus and control pregnancies. Diabetic Med. (2011) 28:1053–9. 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2011.03346.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Hou RL, Zhou HH, Chen XY, Wang XM, Shao J, Zhao ZY. Effect of maternal lipid profile, C-peptide, insulin, and HBA1c levels during late pregnancy on large-for-gestational age newborns. World J Pediatr. (2014) 10:175–81. 10.1007/s12519-014-0488-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Mossayebi E, Arab Z, Rahmaniyan M, Almassinokiani F, Kabir A. Prediction of neonates' macrosomia with maternal lipid profile of healthy mothers. Pediatr Neonatol. (2013) 55:28–34. 10.1016/j.pedneo.2013.05.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Di Cianni G, Miccoli R, Volpe L, Lencioni C, Ghio A, Giovannitti MG, et al. Maternal triglyceride levels and newborn weight in pregnant women with normal glucose tolerance. Diabetic Med. (2004) 22:21–5. 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2004.01336.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Knopp RH, Magee MS, Walden CE, Bonet B, Benedetti TJ. Prediction of infant birth weight by GDM screening tests. Importance of plasma triglyceride. Diabetes Care. (1992) 15:1605–13. 10.2337/diacare.15.11.1605 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Kumarathasan P, Vincent R, Bielecki A, Blais E, Blank K, Das D, et al. Infant birth weight and third trimester maternal plasma markers of vascular integrity: the MIREC study. Biomarkers (2016) 21:257–66. 10.3109/1354750X.2015.1134663 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Hegazy AM, Younis NT, Nada OH, Ali EM. Maternal–cord blood vitamin C status and its relation to fetal growth and placental apoptosis. Egypt Pediatr Assoc Gazette (2014) 62:80–7. 10.1016/j.epag.2014.06.002 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Jaipaul JV, Newburn-Cook CV, O'Brien B, Demianczuk N. Modifiable risk factors for term large for gestational age births. Health Care Women Int. (2009) 30:802–23. 10.1080/07399330903066160 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Johnston LB, Clark AJL, Savage MO. Genetic factors contributing to birth weight. Arch Dis Childh Fetal Neonatal Edn. (2002) 86:F2–3. 10.1136/fn.86.1.F2-a [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Langer O. Fetal macrosomia: etiologic factors. Clin Obstet Gynecol. (2000) 43:283–97. 10.1097/00003081-200006000-00006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Metzger BE. Diabetes mellitus and pregnancy. In: Jameson JL, De Groot LJ, de Kretser DM, Giudice LC, Grossman AB, Melmed S, Potts JT, Weir GC, editors. Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric [Internet]. 7th Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; (2016). p. 788–804. [Google Scholar]
- 221.Knopp RH. Hormone-mediated changes in nutrient metabolism in pregnancy: a physiological basis for normal fetal development. Ann NY Acad Sci. (1997) 817:251–71. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1997.tb48212.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Pedersen J. The Pregnant Diabetic and her Newborn: Problems and Management. Copenhagen: Munksgaard; (1977). [Google Scholar]
- 223.Jolly MC, Sebire NJ, Harris JP, Regan L, Robinson S. Risk factors for macrosomia and its clinical consequences: a study of 350,311 pregnancies. Eur J Obstet Gynecol. (2003) 111:9–14. 10.1016/S0301-2115(03)00154-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Stotland NE, Caughey AB, Breed EM, Escobar GJ. Risk factors and obstetric complications associated with macrosomia. Int J Gynecol Obstet. (2004) 87:220–6. 10.1016/j.ijgo.2004.08.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Sparano S, Ahrens W, Henauw S, Marild S, Molnar D, Moreno L, et al. Being macrosomic at birth is an independent predictor of overweight in children: results from the IDEFICS study. Mater Child Health J. (2013) 17:1373–81. 10.1007/s10995-012-1136-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Harder T, Rodekamp E, Schellong K, Dudenhausen JW, Plagemann A. Birth weight and subsequent risk of type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol. (2007) 165:849–57. 10.1093/aje/kwk071 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Harder T, Roepke K, Diller N, Stechling Y, Dudenhausen JW, Plagemann A. Birth weight, early weight gain, and subsequent risk of type 1 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol. (2009) 169:1428–36. 10.1093/aje/kwp065 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Boney CM, Verma A, Tucker R, Vohr BR. Metabolic syndrome in childhood: association with birth weight, maternal obesity, and gestational diabetes mellitus. Pediatrics (2005) 115:e290-e6. 10.1542/peds.2004-1808 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Michels KB, Trichopoulos D. Birthweight as a risk factor for breast cancer. Lancet (1996) 348:1542–6. 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)03102-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Wang P, He X, Wang B, Wang Y. Birth weight and risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Colorectal Dis. (2014) 29:1017–8. 10.1007/s00384-014-1889-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Savvidou MD, Akolekar R, Samaha RBB, Masconi AP, Nicolaides KH. Maternal serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels at 11(+0)−13(+6) weeks in pregnant women with diabetes mellitus and in those with macrosomic neonates. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. (2011) 118:951–5. 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2011.02982.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Sacks DA. Etiology, detection, and management of fetal macrosomia in pregnancies complicated by diabetes mellitus. Clin Obstet Gynecol. (2007) 50:980–9. 10.1097/GRF.0b013e31815a6242 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.De Boo HA, Harding JE. The developmental origins of adult disease (Barker) hypothesis. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. (2006) 46:4–14. 10.1111/j.1479-828X.2006.00506.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Barker DJ. Maternal nutrition, fetal nutrition, and disease in later life. Nutrition (1997) 13:807–13. 10.1016/S0899-9007(97)00193-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Zamorski MA, Biggs WS. Management of suspected fetal macrosomia. Am Family Phys. (2001) 63:302–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Rice F, Thapar A. Estimating the relative contributions of maternal genetic, paternal genetic and intrauterine factors to offspring birth weight and head circumference. Early Hum Dev. (2010) 86:425–32. 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2010.05.021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Catalano PM, Drago NM, Amini SB. Factors affecting fetal growth and body composition. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (1995) 172:1459–63. 10.1016/0002-9378(95)90478-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Donnelley EL, Raynes-Greenow CH, Turner RM, Carberry AE, Jeffery HE. Antenatal predictors and body composition of large-for-gestational-age newborns: perinatal health outcomes. J Perinatol. (2014) 34:698. 10.1038/jp.2014.90 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Nahum GG, Stanislaw H, Huffaker BJ. Accurate prediction of term birth weight from prospectively measurable maternal characteristics. J Reprod Med. (1999) 44:705–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Haram K, Pirhonen J, Bergsjø P. Suspected big baby: a difficult clinical problem in obstetrics. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. (2002) 81:185–94. 10.1034/j.1600-0412.2002.810301.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Sparks TN, Cheng YW, McLaughlin B, Esakoff TF, Caughey AB. Fundal height: a useful screening tool for fetal growth? J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. (2011) 24:708–12. 10.3109/14767058.2010.516285 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Engstrom JL, Work BA, Jr. Prenatal prediction of small- and large- for-gestational age neonates. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. (1992) 21:486–95. 10.1111/j.1552-6909.1992.tb01769.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Persson B, Stangenberg M, Lunell NO, Brodin U, Holmberg NG, Vaclavinkova V. Prediction of size of infants at birth by measurement of symphysis fundus height. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. (1986) 93:206–11. 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1986.tb07894.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Drassinower D, Timofeev J, Chun-Chih H, Benson JE, Driggers RW, Landy HJ. Accuracy of clinically estimated fetal weight in pregnancies complicated by diabetes mellitus and obesity. Am J Perinatol. (2014) 31:31–7. 10.1055/s-0033-1334450 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Hoopmann M, Abele H, Wagner N, Wallwiener D, Kagan KO. Performance of 36 different weight estimation formulae in fetuses with macrosomia. Fetal Diagn Ther. (2010) 27:204–13. 10.1159/000299475 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Nahum GG. Predicting fetal weight: are Leopold's maneuvers still worth teaching to medical students and house staff? J Reprod Med. (2002) 47:271–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.Chauhan SP, Sullivan CA, Lutton TC, Magann EF, Morrison JC. Parous patients' estimate of birth weight in postterm pregnancy. J Perinatol. (1995) 15:192–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Hui L. Australian charts for assessing fetal growth: a review. ASUM Ultrasound Bull. (2008) 11:12–8. [Google Scholar]
- 249.O'brien CM, Poprzeczny A, Dodd JM. Implications of maternal obesity on fetal growth and the role of ultrasound. Exp Rev Endocrinol Metab. (2017) 12:45–58. 10.1080/17446651.2017.1271707 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Farrell T, Fraser R, Chan K. Ultrasonic fetal weight estimation in women with pregnancy complicated by diabetes. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. (2004) 83:1065–6. 10.1111/j.0001-6349.2004.00469.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Lewis RM, Demmelmair H, Gaillard R, Godfrey KM, Hauguel-de Mouzon S, Huppertz B, et al. The placental exposome: placental determinants of fetal adiposity and postnatal body composition. Ann Nutr Metab. (2013) 63:208–15. 10.1159/000355222 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Siega-Riz AM, Viswanathan M, Moos M-K, Deierlein A, Mumford S, Knaack J, et al. Review: A systematic review of outcomes of maternal weight gain according to the Institute of Medicine recommendations: birthweight, fetal growth, and postpartum weight retention. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2009) 201:339.e1–14. 10.1016/j.ajog.2009.07.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Ramsay JE, Greer IA. Obesity in pregnancy. Fetal Mater Med Rev. (2004) 15:109–32. 10.1017/S096553950400126319880362 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Yu Z, Han S, Zhu J, Sun X, Ji C, Guo X. Pre-pregnancy body mass index in relation to infant birth weight and offspring overweight/obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 8:e61627. (2013). 10.1371/journal.pone.0061627 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Chatfield J. ACOG issues guidelines on fetal macrosomia. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Am Fam Physician. (2001) 64:169–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 256.O'Reilly-Green C, Divon M. Sonographic and clinical methods in the diagnosis of macrosomia. Clin Obstet Gynecol. (2000) 43:309–20. 10.1097/00003081-200006000-00008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 257.Melamed N, Yogev Y, Meizner I, Mashiach R, Ben-Haroush A. Sonographic prediction of fetal macrosomia: the consequences of false diagnosis. J Ultrasound Med. (2010) 29:225–30. 10.7863/jum.2010.29.2.225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Hiden U, Froehlich J, Desoye G. Diabetes and the placenta. In: Kay H, Nelson MD, Wang Y, editors. The Placenta: From Development to Disease. 1st ed. West Sussex: Wiley-Blackwell; (2011). p. 228–36. 43. [Google Scholar]
- 259.Jovanovic-Peterson L, Peterson CM, Reed GF, Metzger BE, Mills JL, Knopp RH, et al. Maternal postprandial glucose levels and infant birth weight: the diabetes in early pregnancy study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (1991) 164:103–11. 10.1016/0002-9378(91)90637-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 260.The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Pregnancy outcomes in the diabetes control and complications trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (1996) 174:1343–53. 10.1016/S0002-9378(96)70683-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 261.Johnstone FD, Mao JH, Steel JM, Prescott RJ, Hume R. Factors affecting fetal weight distribution in women with type I diabetes. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. (2000) 107:1001–6. 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2000.tb10403.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 262.Kerssen A, de Valk HW, Visser GHA. Do HbA1c levels and the self-monitoring of blood glucose levels adequately reflect glycaemic control during pregnancy in women with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia (2006) 49:25–8. 10.1007/s00125-005-0057-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 263.Law GR, Ellison GTH, Secher AL, Damm P, Mathiesen ER, Temple R, et al. Analysis of continuous glucose monitoring in pregnant women with diabetes: distinct temporal patterns of glucose associated with large-for-gestational-age infants. Diabetes Care (2015) 38:1319–25. 10.2337/dc15-0070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 264.Kerssen A, de Valk HW, Visser GHA. Increased second trimester maternal glucose levels are related to extremely large-for-gestational-age infants in women with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care (2007) 30:1069–74. 10.2337/dc06-1985 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 265.Murphy HR, Rayman G, Lewis K, Kelly S, Johal B, Duffield K, et al. Effectiveness of continuous glucose monitoring in pregnant women with diabetes: randomised clinical trial. Br Med J. (2008) 337:907–10. 10.1136/bmj.a1680 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 266.Shen S, Lu J, Zhang L, He J, Li W, Chen N, et al. Single fasting plasma glucose versus 75-g oral glucose-tolerance test in prediction of adverse perinatal outcomes: a cohort study. EBioMedicine (2017) 16:284–91. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.01.025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 267.Lee J-E. Alternative biomarkers for assessing glycemic control in diabetes: fructosamine, glycated albumin, and 1,5-anhydroglucitol. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. (2015) 20:74–8. 10.6065/apem.2015.20.2.74 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 268.Ringholm L, Juul A, Pedersen-Bjergaard U, Thorsteinsson B, Damm P, Mathiesen ER. Lower levels of placental growth hormone in early pregnancy in women with type 1 diabetes and large for gestational age infants. Growth Horm IGF Res. (2015) 25:312–5. 10.1016/j.ghir.2015.11.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 269.Weykamp C, John WG, Mosca A. A review of the challenge in measuring hemoglobin A1c. J Diabetes Sci Technol. (2009) 3:439–45. 10.1177/193229680900300306 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 270.Lepercq J, Taupin P, Dubois-Laforgue D, Duranteau L, Lahlou N, Boitard C, et al. Heterogeneity of fetal growth in type 1 diabetic pregnancy. Diabetes Metab. (2001) 27:339–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 271.Middleton P, Crowther CA, Simmonds L. Different intensities of glycaemic control for pregnant women with pre-existing diabetes. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev. (2016) 67:CD008540 10.1002/14651858.CD008540.pub4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 272.Lin CC, River J, River P, Blix PM, Moawad AH. Good diabetic control early in pregnancy and favorable fetal outcome. Obstet Gynecol. (1986) 67:51–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 273.Schaefer-Graf UM, Kjos SL, Kilavuz O, Plagemann A, Brauer M, Dudenhausen JW, et al. Determinants of fetal growth at different periods of pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes mellitus or impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care (2003) 26:193–8. 10.2337/diacare.26.1.193 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 274.Cahill AG, Tuuli MG, Colvin R, Cade WT, Macones GA. Markers of glycemic control and neonatal morbidity in high-risk insulin-resistant pregnancies. Am J Perinatol. (2016) 33:151–6. 10.1055/s-0035-1562929 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 275.Nowak N, Skupien J, Cyganek K, Matejko B, Malecki MT. 1,5-Anhydroglucitol as a marker of maternal glycaemic control and predictor of neonatal birthweight in pregnancies complicated by type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia (2013) 56:709–13. 10.1007/s00125-013-2830-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 276.Dworacka M, Wender-Ozegowska E, Winiarska H, Borowska M, Zawiejska A, Pietryga M, et al. Plasma anhydro-d-glucitol (1,5-AG) as an indicator of hyperglycaemic excursions in pregnant women with diabetes. Diabetic Med. (2006) 23:171–5. 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2005.01752.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 277.Knopp RH, Montes A, Childs M, Li JR, Mabuchi H. Metabolic adjustments in normal and diabetic pregnancy. Clin Obstet Gynecol. (1981) 24:21–49. 10.1097/00003081-198103000-00006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 278.Herrera E. Metabolic adaptations in pregnancy and their implications for the availability of substrates to the fetus. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2000) 54:S47–51. 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600984 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 279.Larque E, Pagan A, Prieto MT, Blanco JE, Gil-Sanchez A, Zornoza-Moreno M, et al. Placental fatty acid transfer: a key factor in fetal growth. Ann Nutr Metab. (2014) 64:247–53. 10.1159/000365028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 280.Herrera E, Ortega-Senovilla H. Disturbances in lipid metabolism in diabetic pregnancy - Are these the cause of the problem? Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2010) 24:515–25. 10.1016/j.beem.2010.05.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 281.Gobl CS, Handisurya A, Klein K, Bozkurt L, Luger A, Bancher-Todesca D, et al. Changes in serum lipid levels during pregnancy in type 1 and type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care (2010) 33:2071–3. 10.2337/dc10-0484 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 282.Olmos PR, Rigotti A, Busso D, Berkowitz L, Santos JL, Borzone GR, et al. Maternal hypertriglyceridemia: a link between maternal overweight-obesity and macrosomia in gestational diabetes. Obesity (2014) 22:2156–63. 10.1002/oby.20816 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 283.Geraghty AA, Alberdi G, O'Sullivan EJ, O'Brien EC, Crosbie B, Twomey PJ, et al. Maternal blood lipid profile during pregnancy and associations with child ddiposity: findings from the ROLO study. PLoS ONE (2016) 11:1–13. 10.1371/journal.pone.0161206 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 284.Higgins M, Mc Auliffe F. A review of maternal and fetal growth factors in diabetic pregnancy. Curr Diabetes Rev. (2010) 6:116–25. 10.2174/157339910790909431 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 285.Aye ILMH, Powell TL, Jansson T. Review: Adiponectin – The missing link between maternal adiposity, placental transport and fetal growth? Placenta (2013) 34:S40–5. 10.1016/j.placenta.2012.11.024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 286.Lindsay RS, Walker JD, Havel PJ, Hamilton BA, Calder AA, Johnstone FD. Adiponectin is present in cord blood but is unrelated to birth weight. Diabetes Care (2003) 26:2244–9. 10.2337/diacare.26.8.2244 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 287.Bloomfield FH, Spiroski AM, Harding JE. Fetal growth factors and fetal nutrition. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. (2013) 18:118–23. 10.1016/j.siny.2013.03.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 288.Forbes K, Westwood M. The IGF axis and placental function. A mini review. Horm Res. (2008) 69:129–37. 10.1159/000112585 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 289.Lauszus FF, Klebe JG, Flyvbjerg A. Macrosomia associated with maternal serum insulin-like growth factor-I and -II in diabetic pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. (2001) 97:734–41. 10.1159/000181285 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 290.Simmons D. Interrelation between umbilical cord serum sex hormones, sex hormone-binding globulin, insulin-like growth factor I, and insulin in neonates from normal pregnancies and pregnancies complicated by diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (1995) 80:2217–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 291.Hall K, Hansson U, Lundin G, Luthman M, Persson B, Povoa G, et al. Serum levels of somatomedins and somatomedin-binding protein in pregnant women with type I or gestational diabetes and their infants. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (1986) 63:1300–6. 10.1210/jcem-63-6-1300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 292.Tennekoon KH, Poopalapillai J, Karunanayake AG, Jayasinghe HD, Kumarasiri JM, De SWAP, et al. Association of cord blood leptin, soluble leptin receptor, insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 on birth indices in healthy full-term newborns. Horm Res Paediatr. (2014) 81:232–8. 10.1159/000356919 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.