Abstract
A long-standing question in gene regulation is how remote enhancers communicate with their target promoters, and specifically how chromatin topology dynamically relates to gene activation. Here, we combine genome editing and multi-color live imaging to simultaneously visualize physical enhancer–promoter interaction and transcription at the single cell level in Drosophila embryos. Examining transcriptional activation of a reporter by the endogenous even-skipped enhancers 150 kb away, we identify three distinct topological conformation states and measure their transition kinetics. We show that sustained proximity of the enhancer to its target is required for activation. Transcription in turn affects the 3D topology, as it enhances the temporal stability of the proximal conformation and is associated with further spatial compaction. Furthermore, the facilitated long-range activation results in transcriptional competition at the locus, causing corresponding developmental defects. Our approach thus offers quantitative insight into the spatial and temporal determinants of long-range gene regulation and their implications for cellular fates.
Enhancers play a key role in the control of gene expression that is essential for development1–3. These 50–1500 base pair cis-regulatory elements stimulate transcription from core promoters in a time- and tissue-specific manner by recruiting context-dependent transcriptional activators and repressors4–6. Whole-genome methods have shown that the human genome is riddled with enhancers, with estimates ranging from 200,000 to over a million7. Importantly, a significant fraction of enhancers are located at large genomic distances from the promoters they regulate8–10. Even for a compact genome like Drosophila melanogaster, at least 30% of enhancer–promoter interactions occur over 20 kb, and in many cases over intervening genes11–13.
Despite extensive studies over more than three decades, many questions still remain as to how enhancers communicate with their target promoters over large genomic distances14. Static measurements, employing, e.g., fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and 3C-based genomic experiments, provided evidence supporting physical interactions between a distal enhancer and a target promoter15–19. Yet we still lack a dynamic characterization that could distinguish transient contact from the formation of stable topological structures and disentangle cause from consequence in the relationship between such topological structures and transcription. To address these fundamental questions we have developed a live imaging approach to track the spatial positions of an enhancer and its target promoter and to simultaneously monitor transcriptional activity in developing fly embryos. By employing this approach, we reveal, at the single-cell level, a dynamic interplay between enhancer-promoter (E-P) topology and transcriptional activity.
Live imaging of chromatin topology and transcription
To examine long-range transcriptional activation, we placed a reporter gene 142 kb from the well-studied Drosophila even-skipped (eve) locus, which contains a set of five enhancers that drive a seven-striped expression pattern in the cellular blastoderm (Supplementary Fig. 1). While this chosen distance is generally larger than that observed for known enhancer–promoter interactions in the early fly embryo, it is comparable to and even smaller than the distances over which many enhancers function in higher eukaryotes8–10,20. Notably, at such distance the chromatin fiber can display fast random movements, which creates an entropic hurdle for specific long-range chromatin interactions and thus a kinetic barrier for the establishment of a productive pre-initiation complex. We therefore included in our reporter cassette the 368bp insulator element homie (Supplementary Fig. 1a)21,22, which facilitates the formation of a stable loop by self-pairing with the endogenous homie element23 located at the 3′ end of the eve locus21,22. In fixed embryos containing our reporter cassette, we observe sporadic expression (~15%) of the reporter gene, solely within the limits of the endogenous eve stripes (Supplementary Fig. 1b), which strongly suggests that the reporter is specifically activated by the eve enhancers 142 kb away21.
In order to simultaneously visualize the location of the endogenous eve enhancers, the location of the promoter of the reporter, and its transcriptional activity in living embryos, we designed a three-color imaging system. First, we utilized two orthogonal stem-loop-based labeling cassettes24–26; MS2 stem loops were introduced via CRISPR genome editing to the endogenous eve gene, and PP7 stem loops were added to the reporter gene (Fig. 1a, Supplementary Fig. 2a-b, Supplementary Video 1). Maternally expressed fluorescent coat proteins bind the corresponding nascent stem-loops upon transcription, providing a dynamic readout of gene activity (Fig. 1a). Owing to the strong transcriptional activity of the eve gene, the corresponding fluorescent focus further serves as a marker for the nuclear position of the eve enhancers, which are located within 10kb of the eve promoter (Supplementary Fig. 1a). In addition, we took advantage of a recently developed DNA labeling system27,28 to mark the position of the reporter gene in a manner that is independent of its activity. Namely, Burkholderia parS DNA sequences were included in the reporter gene, nucleating the binding of ParB-GFP fusion proteins (Fig. 1a).
Figure 1. Three-color live imaging of enhancer-promoter movement and transcriptional activity.
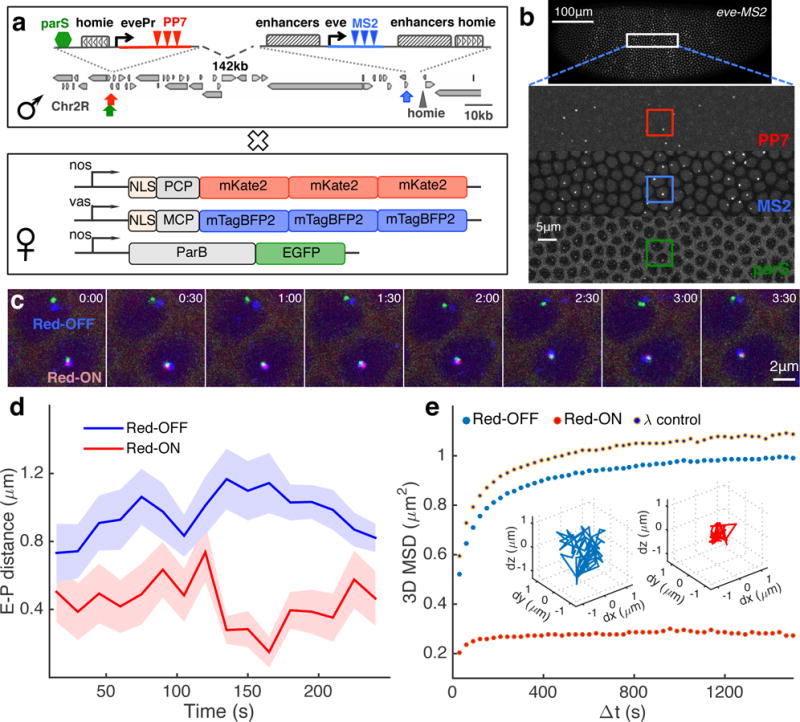
a, Male flies carrying the modified eve locus are crossed with females carrying maternally expressed blue, red and green fluorescent proteins that are fused to MS2 coat protein (MCP), PP7 coat protein (PCP) and ParB DNA binding protein, respectively. In the male flies, a reporter with an eve promoter (evePr) driving PP7 transcription is integrated at −142 kb upstream of an MS2-tagged endogenous eve locus in the Drosophila genome. An ectopic homie insulator sequence is also included in the reporter in order to force loop formation through homie-homie pairing. Furthermore, a parS sequence is integrated near the homie-evePr-PP7 reporter. b, Snapshot of a representative embryo generated from crosses shown in a. The embryo displays fluorescent foci for MS2, PP7 and parS in the corresponding channels. c, 8 snapshots of a time course following two nuclei for ~4 min. The lower nucleus displays PP7 activity (Red-ON), the upper has none (Red-OFF). d, Instantaneous physical enhancer–promoter (E-P) distance between endogenous eve enhancers (blue signal) and the PP7 reporter (green signal) as a function of time for the Red-OFF and Red-ON nuclei in c. Error bar corresponds to measurement error estimated from the co-localization control experiments (see Supplementary Fig. 3). e, Population-averaged MSD calculated from E-P distance trajectories obtained from all Red-ON (n=720) and Red-OFF (n=7,163) nuclei, as well as for a control construct where homie in the reporter is replaced by phage λ DNA (λ control, n=1,453). Inset shows two representative trajectories for a Red-OFF nucleus (blue) and a Red-ON (red) nucleus, respectively.
Using three-color time-lapse confocal microscopy, we captured stacks of optical sections of the surface of two-hour-old (nuclear cycle 14, nc14) embryos carrying the tagged eve locus and the parS-homie-evePr-PP7 reporter (Supplementary Video 2). In these stacks we can clearly identify individual fluorescent foci in 70–100 nuclei simultaneously (Fig. 1b). In the blue channel we observed the endogenous transcriptional activity of the eve gene in its characteristic seven-striped pattern. This pattern is quantitatively identical to that observed from the endogenous eve gene (Supplementary Fig. 2c-g, Supplementary Video 1). In the green channel we observed parB foci in all nuclei of the developing embryo, tracking the position and the movement of the reporter locus (Fig. 1b). Finally, in the red channel we observed the reporter’s transcriptional activity in a subset of nuclei within the (blue) eve stripes (Fig. 1b), consistent with our results from fixed embryos (Supplementary Fig. 1b).
These three florescent foci thus provide us the means to measure the physical distance between the enhancers and the reporter, as well as to monitor the reporter’s transcriptional activity. To ascertain our ability to accurately measure these properties, several control experiments were performed. To estimate the precision of our distance measurements, we generated a synthetic construct (localization control) in which all three fluorescent proteins are co-localized within a genomic distance of 2.0 kb (Supplementary Fig. 3a). By analyzing embryos carrying this construct, we were able to calibrate chromatic aberrations from the microscope and to estimate measurement errors in spot localization (180±6 nm (mean±SE), i.e. ~75nm in x/y and ~150 nm in the axial direction, see Supplementary Fig. 3b-h). Our optical resolution measured from diffraction-limited multi-color fluorescent beads is 20 nm in x/y and 50 nm in the axial direction (Supplementary Fig. 3b-h). Thus, measurement error originating from optics only accounts for ~10% of the variance in our distance measurement.
We also tested whether our genomic labeling approach introduces perturbations in the system (see experiments and discussion in Supplementary Fig. 4) by 1) removing the maternal ParB supply, 2) placing the parS sequence at different locations relative to the lacZ reporter, and 3) employing the more traditional lacO/LacI system instead29,30. In no case was the presence of ParB proteins found to affect the activation kinetics of the PP7 reporter (Supplementary Fig. 4e). Furthermore, we did not observe any significant difference in chromatin dynamics or transcription kinetics when the parS tag was placed at different locations or replaced by the lacO tag (Supplementary Fig. 4b-g). These results are consistent with previous studies, in which the parS/ParB system was found to be non-disruptive to chromatin structure31.
An initial examination of the nuclei in which the PP7 reporter is inactive (Red-OFF) vs. those in which it is active (Red-ON) points to a close connection between transcription and the physical proximity of the enhancer-promoter (hereinafter E-P) pair (Supplementary Video 3). In Red-OFF nuclei, the reporter is well separated from the eve enhancers, while in Red-ON nuclei, all three fluorescent foci appear to be attached together (Fig. 1c). Specifically, when computing the instantaneous spatial distance between the eve enhancer and the reporter promoter (i.e. the blue to green foci distance, E-P distance), a significantly shorter distance is observed for the Red-ON compared to the Red-OFF nuclei (Fig. 1d and Supplementary Fig. 4a-c). Moreover, computing the change in the E-P distance across a time interval of variable size gives access to the 3D mean squared displacement (MSD) for the E-P distance trajectories in the two classes of nuclei (Fig. 1e and Supplementary Fig. 4d). The MSD curve reaches a plateau for both types, indicating spatial confinement of the E-P distance. Expectedly, the size of this confinement (i.e. the spatial limit explored by the E-P pair) in the active (Red-ON) nuclei is smaller than that in the inactive (Red-OFF) nuclei (0.52 vs. ~1.02 μm2, Fig. 1e).
Necessity of sustained physical proximity for transcription
To assess the temporal relationship between E-P proximity and the processes of transcriptional activation and inactivation, we identified all time traces in which we observed nascent transcription in the PP7 reporter gene switching from OFF to ON (n=286) and switching from ON to OFF (n=203), respectively. When we aligned ~20 min time windows of both sets of traces centered around the switching time point, we observed a strong association between physical proximity and activity.
The OFF-to-ON set (Fig. 2a, Supplementary Fig. 5a-b, Supplementary Video 4a-c) displays a sharp transition in transcriptional activity, with rates comparable to those previously reported for active nuclei exiting mitosis32. The distance between the eve enhancers and the reporter promoter (i.e., the blue to green foci distance) converged continuously until this sharp onset of transcription. At this point the E-P distance (root-mean-squared (RMS) distance) corresponds to ~340 nm. These findings suggest that E-P proximity is required in order to initiate the transgene’s transcriptional activity.
Figure 2. Sustained physical enhancer–promoter proximity is necessary for productive transcription.
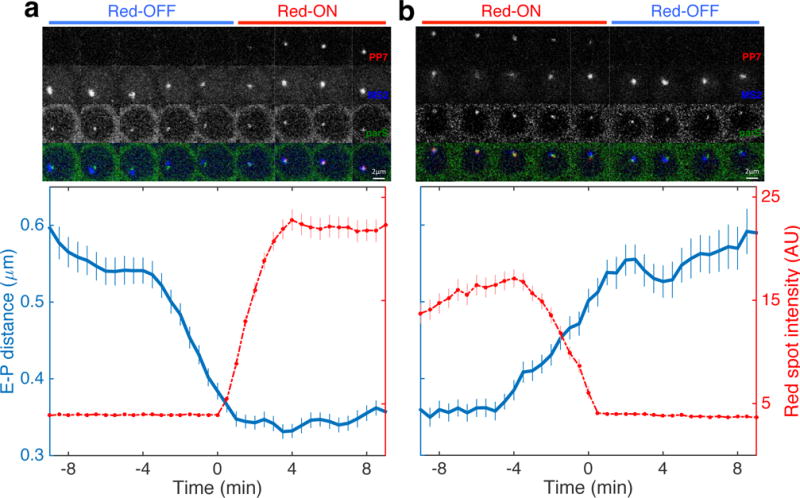
a, Average transcription activity (red) and E-P distance (RMS distance between blue and green foci) as a function of time for 286 nuclei transitioning from the Red-OFF to Red-ON state. Time series for individual nuclei are aligned such that PP7 activity starts at 0 min, i.e. first occurrence of red signal. Top panel shows a series of raw images of a representative nucleus that transitions from Red-OFF to Red-ON (see also Supplementary Video 4). b, Average transcription activity and E-P distance as a function of time for 203 nuclei transitioning from Red-ON to Red-OFF. Time series for individual nuclei are aligned such that PP7 activity ends at 0 min, i.e. disappearance of red signal. The top panel shows a series of raw images of a representative nucleus that transitions from Red-ON to Red-OFF (see also Supplementary Video 4). All error bars are standard errors of the mean.
Correspondingly, the sharp drop in transcriptional activity observed in the ON-to-OFF set of time traces is accompanied by an increase in the RMS E-P distance (Fig. 2b, Supplementary Fig. 5c-d, Supplementary Video 4d-f). While polymerases (RNA polymerase II, PolII) already engaged in transcription will continue to give rise to a detectable red focus even after the separation of the eve enhancers from the promoter (likely accounting for the largest part of the observed ~4 min delay32,33), it seems transcription initiation ceases as soon as the eve enhancers and the reporter promoter physically separate. Overall, these results fit with a model in which sustained E-P physical association is necessary for continuous initiation of transcription.
Characterization of three topological states
To establish a quantitative link between physical proximity and transcriptional activity, we constructed the distribution of time-averaged RMS E-P distances, across all data acquired. We examined time traces from 7,883 nuclei, across 84 individual embryos, taken over a 30 min period in nc14 and calculated the time-averaged RMS E-P distances over a sliding window along each trace (Fig. 3a and Supplementary Fig. 6a, see Methods). We found a bi-modal distribution that can be fitted by a mixture of two Gaussians, one harboring 87% of all RMS samples with a mean of 709±110 nm (mean±STD) and the other, smaller in proportion, with a mean of 353±82 nm.
Figure 3. Characterization of topological enhancer-promoter conformations, the kinetic transitions between them, and their relation to transcriptional activation.
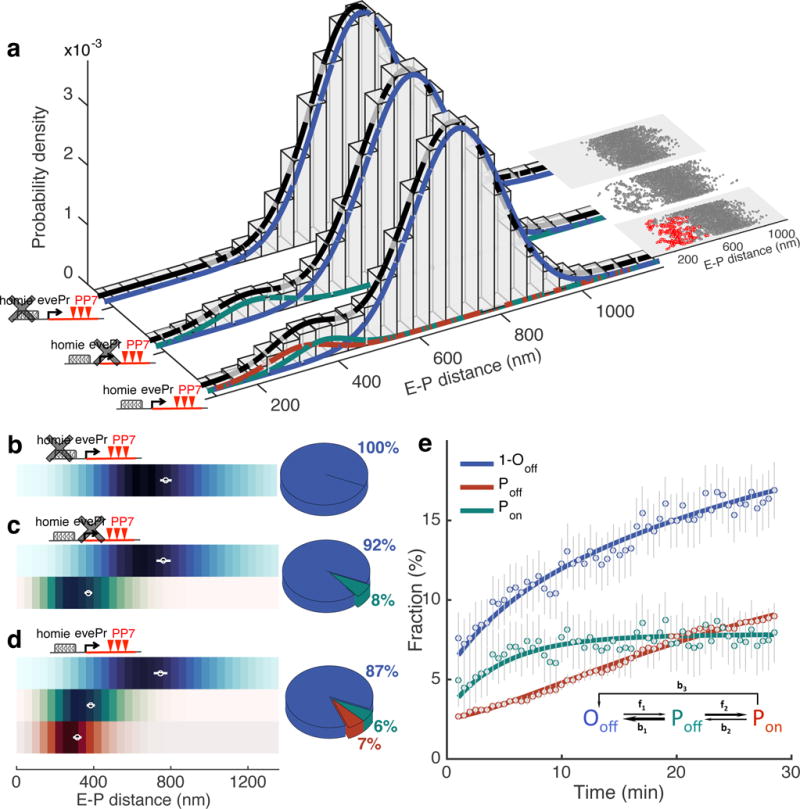
a, E-P distance distribution for three experimental constructs: parS-homie-evePr-PP7 (n=265,277 RMS E-P distances from 7,883 trajectories in 84 embryos), parS-homie-noPr-PP7 (n=81,629 RMS E-P distances from 2,566 trajectories in 29 embryos) and parS-λ-evePr-PP7 (n=49,587 RMS E-P distances from 1,453 trajectories in 15 embryos). A 5-min sliding window along each time trace is used to calculate RMS E-P distances. Gaussian mixture models for all RMS samples are shown with black curves for each construct. Gaussian mixture models for RMS samples in which PP7 is not active are shown with blue (larger mean) and green (smaller mean) curves. Red curve is Gaussian fitting for all RMS distance samples accompanied by continuous PP7 transcription. Insets show scatter plots of RMS distance from one representative embryo for each construct. Each data point is a time-averaged RMS distance. Red points indicate continuous PP7 transcription across the window. b-d, Distribution of instantaneous E-P distance for E-P topological states classified as Ooff (blue), Poff (green) or Pon (red) for parS-λ-evePr-PP7 (b), parS-homie-noPr-PP7 (c) and parS-homie-evePr-PP7 (d). Means±STD of RMS distance calculated from individual embryos shown as white circles with bars. Adjacent pie charts show the fraction of each E-P topological state. See also Supplementary Fig. 8. e, Fraction of each topological state for the parS-homie-evePr-PP7 construct as a function of developmental time, starting 25 min into nc14. Error bars are bootstrapped standard errors of state fractions. Solid lines are fits derived from kinetic parameters obtained from MCMC (Markov Chain Monte Carlo) inference. Inset shows the kinetic model capturing the transitions between the three topological states; arrow widths represent transition time scales (wider arrows correspond to faster rates, see Supplementary Fig. 9 for values).
To gain insight into the topological conformation underlying these two disparate populations, we employed a variant of our reporter construct in which the homie sequence is replaced by λ DNA of the same length (parS-λ-evePr-PP7). When we constructed the corresponding RMS E-P distance distribution from 1,453 nuclei in 15 embryos carrying this construct, we observed a unimodal Gaussian with a mean of 730±112 nm, similar to the large population obtained with the parS-homie-evePr-PP7 construct (Fig 3a and Supplementary Fig. 6c). This indicates that the Gaussian with the larger mean, common to both constructs, likely represents nuclei in an open, unpaired conformation. In contrast, the smaller population, with the short E-P distances, observed only with the homie-containing construct, likely stems from nuclei in a homie–homie paired conformation, which are evidently missing in the λ replacement construct. Furthermore, consistent with these postulated underlying conformations, the mean of the large Gaussian increases (i.e., shifts to larger distances) when we move the PP7 reporter to a genomic location more distal from the eve locus (from −142 kb to −589 kb, Supplementary Fig. 6d), while the mean of the smaller Gaussian remains unchanged. In addition, the size of the smaller Gaussian is clearly reduced in reporter constructs containing truncated versions of the homie element (Supplementary Fig. 7).
Using these distance distributions, we next examined reporter activities. The most noticeable observation stems from the reporter with the λ replacement, in which transcription is largely abolished. This confirms the necessity for sustained proximity for productive transcription in our system. Indeed, for the parS-homie-evePr-PP7 construct, the sub-distribution of the E-P distances obtained only from time traces displaying PP7 transcriptional activity is fully contained within the smaller Gaussian (red curve in Fig 3a, Supplementary Fig. 6a), i.e. all transcriptionally active reporters are physically close to the eve enhancers. However, among all E-P distances occupying the small Gaussian, in only 54% is the reporter active (Fig 3a). The presence of traces in which the promoter is close to the enhancers but nevertheless inactive (green curves, Fig 3a, Supplementary Fig. 6e) suggests that the proximity obtained by homie–homie pairing is not sufficient to ensure transcription. Notably, upon homie–homie pairing, the linear genomic distance between the reporter promoter and the eve enhancers is less than 10kb, which is similar to the enhancer-promoter distances in the endogenous eve locus. Thus, while architectural proteins can bridge the gap between long-range enhancer-promoter interactions (e.g., 142kb) and short-range interactions (e.g., 1-10kb), the facilitated proximity is not sufficient to assure transcription.
Transcription reinforces topological compaction
Our analysis reveals three possible topological states of E-P interaction: 1) open conformations that are transcriptionally inactive (Ooff state), 2) homie–homie paired conformations that are transcriptionally inactive (Poff state), and 3) homie-homie paired conformations that are transcriptionally active (Pon state). To assess the physical properties and the transition kinetics of these states, we assigned each time point of the 7,883 time traces to one of the three states. Specifically, we used a Bayes classifier to distinguish between the unpaired and the paired state, using time traces from the parS-λ-evePr-PP7 construct for the open state (O) and time traces with PP7 activity for the paired state (P) as training samples. Furthermore, we used the presence of the PP7 (red) signal to further divide the paired state (P) into an inactive Poff state and an active Pon state (Supplementary Fig. 8a-j; for detail see Methods).
When we compared the distance distribution of the inactive paired (Poff) and the active paired (Pon) states, we found that the mean (±STD) RMS E-P distance for the Poff state (385±15 nm) is significantly larger than for the Pon state (331±16 nm) (Fig. 3d and Supplementary Fig. 8k). The shorter RMS distance in the transcriptionally active state is indicative of an enhanced compaction of the locus when the reporter is active.
To further examine the relationship between compaction and transcription, we employed an additional variant of our reporter cassette, in which we deleted the promoter from our transgene (parS-homie-noPr-PP7). The RMS E-P distance distribution for this construct recovers the bi-modal distribution from the original construct representing the Ooff and Poff states (calculated from 2,566 nuclei in 29 embryos, Fig. 3a and Supplementary Fig. 6b). In particular, the mean RMS E-P distance of the Poff state measured for this promoter-less construct (374±14 nm, mean±STD) coincides with that measured for the full construct (Fig. 3c, Supplementary Fig. 8k), and is thus larger than that of the Pon population (Fig. 3d, Supplementary Fig. 8k). Together, these results argue for the association of transcription with a smaller physical confinement.
Transcription enhances stability of the paired conformation
Interestingly, we found that the parS-homie-noPr-PP7 construct, which is non-permissive for transcription, has a smaller fraction of the population in the homie paired conformation (P state) than does the parS-homie-evePr-PP7 construct, which is permissive for transcription (8% versus 13%, Fig. 3c-d). This suggests that transcription is not only associated with a more confined spatial conformation but may also be associated with a temporal stabilization of the paired conformation.
In order to test this, we use a set of first-order reactions to model the kinetic transitions between the three topological states described above (Fig. 3e, Supplementary Fig. 9a, see Methods). Using this model, we determined the transition rates by fitting the model-derived equations to the measured time courses of the fractional occupancies for each of the three states (Fig. 3e and Supplementary Fig. 9a-h). The transition from an open topology to the homie-homie pairing state (f1 = 0.017 min−1) takes on average 1h. This rate is ~8 times slower than the time it takes for the enhancer to explore the entire confined space in the vicinity of the promoter in the parS-λ-evePr-PP7 construct, as predicted by our MSD results, assuming a simple first-passage model34 (where the time t=(1.1μm2/6D)1/α, Fig. 1e and Supplementary Fig. 4d). It is possible that the homie orientation preference for pairing23 (as was also described for other architectural factors, such as CTCF35,36) constrains productive passages, thereby contributing to this slower rate. Notably, this rate of pairing is roughly an order of magnitude slower than the rapid transcriptional events that take place in the early fly embryo. This requirement of rapidity is possibly facilitated by closer E-P distances, characteristic of early developmental genes, than the 142kb that we explored here.
Examining the other transition rates obtained from our model confirms the stabilizing effect of transcription on locus topology: the dissociation of the homie–homie pairing complex in the absence of transcription (b1 = 0.144 min−1) is on average over ten times faster than the escape from the transcriptionally active state Pon (b2 = 0.014 min−1, b3 = 0.011 min−1, Supplementary Fig. 9e-g). These rates capture the escape from the transcriptionally active state Pon (b2 and b3) and recapitulate quantitatively the measured durations of transcriptional activity (length of Red-ON trajectories, Supplementary Fig. 9h). Intriguingly, the average duration of the transcriptionally active state is about 40 min (1/(b2+b3)), which coincides with the length of the developmental time window in which the eve stripe enhancers are active in nc14. This transcription-dependent stabilization might thus serve to reinforce the locus functionality for the appropriate developmental time scales.
Ectopic E-P interaction results in developmental defects
In our experiments, the eve stripe enhancers, distributed within the ~16kb of the eve locus (Supplementary Fig. 1a), drive expression of both the introduced reporter gene and the endogenous eve gene, which could possibly lead to competitive dynamics. To test this hypothesis, we compared eve transcriptional activity (i.e., the intensity of the blue MS2 signal) in each individual nucleus in which the PP7 reporter gene is active to the activity in its neighboring nuclei in which the reporter is inactive (Fig. 4a, see Methods). Strikingly, for each eve stripe, we measured a 5%-20% reduction in endogenous eve transcription in nuclei in which the reporter gene is also transcribed compared to neighboring nuclei in which it is not transcribed. The average reduction per nucleus is highest for stripe 5, and lowest for stripes 3 and 7.
Figure 4. Long-distance-mediated promoter competition results in patterning phenotypes.
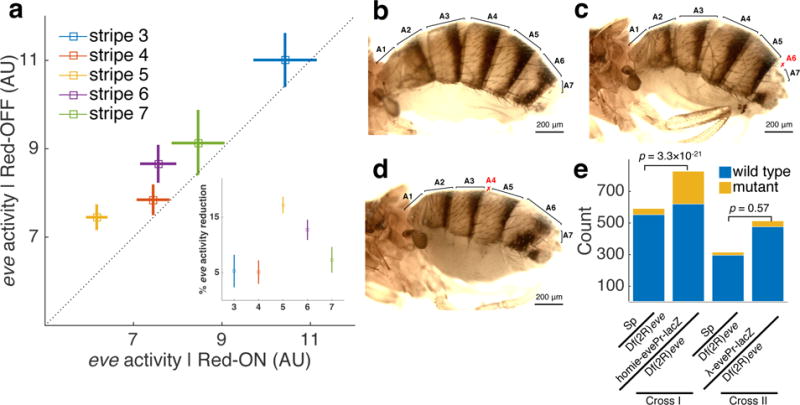
a, Endogenous eve-MS2 activity in nuclei that also display PP7 reporter activity (x-axis) is lower than in the neighboring nuclei where PP7 is not expressed (y-axis). Means±SEMs (n=45, 106, 143, 85 and 27 PP7 expressing nuclei for stripe 3-7, respectively). Inset: Reduction in eve-MS2 activity for each stripe. Error bars are bootstrapped standard errors of the percentage reduction. b-d, Adult wild-type (b) and mutant (c, d) flies from crosses between Sp/homie-evePr-lacZ males and CyO/Df(2R)eve− females. c and d show defects in abdominal segments A4 and A6, respectively, resulting from reduced eve activity in stripe 5 and stripe 6, respectively. Abdominal segments are labeled, with defective segments marked in red. e, Results of phenotype scoring. Mutant counts include both A4 and A6 phenotypes. Cross I: single Sp/homie-evePr-lacZ males were crossed with CyO/Df(2R)eve− females, and scoring results from 47 individual vials were summed. Cross II: single Sp/λ-evePr-lacZ males were crossed with CyO/Df(2R)eve− females, and results from 23 individual vials were summed. P-values are from one-tailed Fisher’s exact test.
eve is a primary pair-rule gene that is essential for segment patterning, allowing us to test whether the observed reduction in eve transcription has a phenotypic consequence. We crossed males carrying a tag-less homie-evePr-lacZ transgene at −142 kb to females heterozygous for a wild-type eve gene and an eve deficiency (Df(2R)eve) (Supplementary Fig. 10a). eve is weakly haploinsufficient, and 6% of +/Df(2R)eve flies display patterning defects in even-numbered parasegments (Supplementary Fig. 10b-e). Consistent with the reduction in the level of eve nascent transcripts, the presence of the homie-evePr-lacZ transgene exacerbates eve haploinsufficiency (Fig. 4b-d, Supplementary Fig. 10a). Altogether 27% of the homie-evePr-lacZ/Df(2R)eve flies have abdominal defects, which corresponds to a ~5-fold increase compared to the control crosses in which homie is replaced by phage λ DNA (Fig. 4e, Supplementary Fig. 10a). Taken together, these results suggest that interference between two promoters in the early embryo can have phenotypic consequences for patterning in the adult. These findings reinforce the view that manipulating topological chromatin structures can functionally alter developmental programs37,38.
Discussion
Simultaneous multi-color live imaging of gene activity and the positions of genomic foci reveals a dynamic interplay between chromatin topology and transcriptional activity. By analyzing this interplay, we identify a requirement for a distinct topological structure that brings promoter and distant enhancer together in the nucleus, formed through pairing of insulator elements, for the initiation and maintenance of transcription. The temporal concordance between cessation of transcription and physical dissociation of this paired conformation argues against a suggested ‘hit-and-run’ model and argues in favor of the requirement for persistent physical E-P proximity for sustained transcription.
Notably, the physical proximity attained by insulator pairing is not a guarantee for transcriptional activation. This observation will prompt further investigation as to the mechanisms underling the transition to an active state. These might involve a second, entropy-based search step resulting in direct physical contact between the enhancer and promoter, and/or entail transcription factor binding with the involvement of other components of the transcription machinery (e.g., mediator, PolII pause-release), or a change in local chromatin accessibility, each of which was previously associated with transitions from a transcriptionally ‘off’ to an ‘on’ state12,39–43.
Our measurements provide further insights into the open debate whether topology precedes transcription44,45. Specifically, our results argue for a complex interplay, as we observe a transcription-mediated reshaping of the kinetic landscape of 3D genome organization. While transcription requires physical proximity, it is in turn associated with further spatial compaction and temporal stabilization. It is possible that transcription can only occur within close proximity (even within the range of Poff distances), and that the observed spatial compaction could result from a biased sampling of the Poff distribution by transcription and not necessarily an active mechanism of compaction. The observed compaction is also consistent with recently proposed hypotheses that phase behaviors might contribute to the formation of Pol II ‘factories’ or transcription ‘hubs’ within topologically associated domains46–48.
Overall, we identify and characterize three states; one in which the distal enhancer and the promoter are not together (Ooff), a second in which they are “within range” (as afforded by insulator pairing) but the gene is transcriptionally inactive (Poff) and a third, which seems stabilized by transcriptional activation (Pon), and in which they are close together. These results are consistent with several recent observations obtained from fixed samples, including observations of proximity of an enhancer to a promoter prior to activation12, and of an increase in co-localization in expressing tissues49. Our observations suggesting that transcription is associated with a different 3D landscape are also in line with recent Hi-C experiments carried out in the early Drosophila embryo, in which the authors suggest an effect of transcription on local chromatin organization, such as co-localization of boundaries and local compaction44.
Interestingly, topological domain boundaries, as captured by recent early embryo Hi-C experiments, coincide with DNA regions that are rich in insulator protein binding44,50. Indeed, previous studies showed that insulator proteins demarcate regulatory units of the fly genome, often separating differentially expressed genes51. These proteins have been suggested not only to contribute to the formation of boundaries but also to facilitate physical interactions between boundaries to form “loop domains”44,50, likely through protein pairing52. Importantly such interactions between insulators were specifically also implicated in mediating long-range activation52,53. While such long-range interactions might not be ubiquitous in the very early embryo undergoing rapid nuclear divisions (0-2 h), in slightly older embryos (3-8 h) they were found to be prevalent (with a reporter median distance of 110 kb)12.
Our observation of a nearly inactive reporter at a distance of ~140 kb in the absence of the homie insulator suggests the necessity of these architectural elements in mediating long-range activation. Naturally, the exact properties of such elements could differ, affecting for instance the likelihood of pairing even upon an encounter (e.g. depending on orientation preferences) and the stability of the paired configuration. Such differences could then influence to some degree the kinetics of transcription (e.g. affecting the rate of escape from the paired transcribing state). In the constructs presented here we chose to include the homie element, due a documented role in the endogenous eve locus22. This allowed us to obtain pairing over long distances and thereby enabled our live examination of enhancer-promoter interactions, linking 3D topology and transcription. The overall landscape of the fly genome, as it emerges from mapping insulator binding, chromosome conformation capture experiments, and locus-specific studies, suggests that our genomic constructs (with activation over >100kb distance, and with physical proximity facilitated by insulator pairing) are capturing fundamental properties of long-range activation in flies, and likely also in other higher eukaryotes.
Finally, we show that a perturbation involving long-range activation by an endogenous enhancer can have clear phenotypic implications. This strengthens previous observations linking disease and aberrant transcription to 3D genome structure38,54, and highlights the necessity of methods to mechanistically study these links55. Extensions of our approach to study different genes, regulated by enhancers at different distances, whose interaction is mediated by different architectural proteins, and in various developmental stages and organisms, will thus likely uncover new mechanistic insights into enhancer–promoter interactions.
Online Methods
Plasmid construction
The MS2 stem loop cassette is amplified from a previously described hbP2-MS2 plasmid32. An optimized 24×PP7 sequence is a gift from T. Fukaya26. homie is amplified from chr2R:9,988,750-9,989,118 (dm6). parS sequence from Burkholderia (J2315, chr3:3,440-3,821, GB: AM747722) is a gift from K. Bystricky and F. Paire. MCP and PCP are amplified from Addgene #5298556. 3xmTagBFP2 is amplified from Addgene #6244957. mKate2 is a gift from J. Ling, and a set of three was fused to make 3xmKate2. ParB-GFP is a gift from K. Bystricky and F. Paire. The 256xlacO cassette is cut from addgene #3314358. LacI::GFP is amplified from Addgene #4094359. All plasmids used for transgenic experiments were made through standard cloning procedures. Plasmid maps and cloning details are available upon request.
Transgenic fly generation
To tag endogenous eve with MS2 stem loops, a two-step transgenic strategy was used. First, an attP site was integrated into the 1st intron of eve using CRIPSR-mediated homology-directed repair. The homology arms were amplified from the genomic DNA of BDSC #51324, which was used as a genomic source for nos-Cas9. The two Cas9 cutting sites are at chr2R:9,979,604-9,979,605 and chr2R:9,980,605-9,980,606 (dm6), respectively. Second, an attB-MS2-lacZ-eve3′UTR plasmid was used to deliver MS2 into the attP site. A genomic source of phiC31 integrase (BDSC #34770) was used for the second injection. The final eve-MS2 transformant carries a ~9.5kb insertion (selection markers) between the MS2-lacZ-eve 3′UTR and the downstream eve enhancers.
The eve-MS2 flies were crossed with a 2xattP genomic landing site at chr2R:9,836,454 (dm6, −142kb to eve promoter22) to obtain recombinants that carry eve-MS2 and the −142kb landing site in cis. The reporter transgenes were then integrated into the landing site through recombination-mediated cassette exchange using BDSC #34770 as the integrase source.
For the fluorescence-tagged maternal proteins (MCP::3xmTagBFP2, PCP::3xmKate2 and MCP::mCherry), a genomic landing site at 38F160 was used. For maternal ParB::eGFP, LacI::GFP and PCP::eGFP, a landing site at 89B8 was used. All microinjections were performed as described previously61 or through BestGene injection service.
Fluorescence in-situ hybridization
smFISH followed a previously described protocol62. Atto labeled probe sets targeting eve CDS and the 5′ 1.7kb of lacZ were used. Raw images were processed following Little et al.63 to identify all cytoplasmic spots and transcription spots. A cytoplasmic unit (CU) that corresponds to the fluorescence intensity of a single cytoplasmic mRNA was calculated. Specifically, a sliding window of 220×220×23 pixel (16.5×16.5×7.4 μm3) was applied to the raw image stack and the total pixel values in the window were plot against the number of cytoplasmic spots found in the window. A linear fit in the range of 0-100 cytoplasmic spots was applied to extract CU for each probe set (Supplementary Fig. 2f, inset). In order to get the number of Pol II in each transcription spot, a cylinder mask (d=13 pixel, h=7 pixel) centered at the brightest pixel in each transcription spot was used to calculate total spot intensities, which were converted using the corresponding CU and probe configuration for the transcribed sequence. Because the eve-MS2 allele is targeted by only a part of the eve probe set, a conversion factor was calculated from the proportion of bound probes. The CU obtained from the full-length eve transcripts was then adjusted using this conversion factor in order to get pol II number on eve-MS2 from the eve channel (y-axis in Supplementary Fig. 2f).
Phenotypic scoring
The homie-evePr-lacZ/CyO flies or the λ-evePr-lacZ/CyO flies were crossed with an isogenic yw;Sp/CyO (BDSC #8379) to get Sp/homie-evePr-lacZ and Sp/λ-evePr-lacZ males. Single males were then crossed with CyO/Dp(2R)eve− virgins22 in order to score phenotypic defects in the next generation. Since phenotypic penetrance can be very sensitive to environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity, food, etc.) and genetic background, our crossing and scoring scheme included controls for all these potentially confounding factors.
Microscopy and imaging conditions
For imaging parS containing transgenes, virgins carrying three fluorescent protein fusions (yw; MCP::3xmTagBFP2/PCP::3xmKate2; ParB::eGFP/+) were crossed with males carrying the eve-MS2 allele and the reporter transgene. For the 0kb co-localization control, virgins carrying three fluorescent protein fusions (yw, MCP::3xmTagBFP2/MCP::mCherry; PCP::eGFP/+) were crossed with males carrying the hbP2-24×MS2PP7-kni transgene. For the lacO/LacI control, virgins with three fluorescent protein fusions (yw; MCP::3xmTagBFP2/PCP::3xmKate2; LacI::GFP/+) were used. The embryos from the above crosses were manually dechorionated and mounted as described32. For bead experiments, 200 nm three-color coated TetraSpec beads were used.
All images were acquired on a Leica SP5 confocal microscope with a Leica oil immersion 63× NA1.44 objective. Three laser lines at 405 nm (0.4 μW), 488 nm (1.1 μW) and 591 nm (0.5 μW) were used to excite the blue, green and red fluorophores, respectively. For bead experiments, we modulated laser powers in order to get a spectrum of emission signals. Three HyD detectors in photon counting mode were used to collect fluorescence emission spectra. Voxel size for all images was set at 107nmx107nmx334nm, and the total volume imaged was about 110×27×8 μm3. Frame interval for all time-lapse videos was 30 s, except for the ones shown in Fig. 1C (15 s). Images were taken at 1,024×256×25 voxels and focused on the posterior half of the embryo, encompassing eve stripes 3–7. Embryos that exit mitosis 13 were timed64. Imaging started at 20±2 min into nc14 and finished at gastrulation (62±2 min into nc14).
Image processing and data analysis (All image processing and data analysis was performed using MATLAB R2015a, MathWorks):
1. Nuclear segmentation and tracking
Nuclear segmentation was performed on the difference between the blue and red channels (NLS::MCP::3xmTagBFP2 is enriched in the nuclear compartment while ParB-eGFP is enriched in the cytoplasm): the maximum z-projection of the green channel was subtracted from the blue channel, and the resulting image was subsequently Gaussian blurred (σ=5), binarized (using a local Otsu’s threshold at 5×5 μm2) and opened with a disk of diameter d=5 pixels. A watershed transformation was performed on the distance matrix calculated from the binarized image to get the segmentation for each frame, and a nuclear mask was calculated from each segmented region.
Since each frame contains only 70–100 nuclei, we used an exhaustive search for nuclear tracking. Because both the whole embryo and the nuclei might move during imaging, we calculated a local vector that recapitulates the nuclear movement by minimizing cross-correlation between nuclear masks of two consecutive frames. After correcting for movement, we multiplied each nuclear mask at time t to all individual nuclear masks from t+1, and the matching nucleus was selected based on the total pixel value of the product images. All nuclear segmentation and tracking results were scrutinized manually.
2. Candidate spot identification
We build a candidate spot library for each video. First, raw image stacks from each of the three channels were sharpened using a 3D bandpass filter of size 11×11×7 pixels, which was derived from subtracting a uniform filter from a Gaussian kernel (σ=(1, 1, 0.6) pixel). We treated all local maxima in the filtered image as putative spots, and a cylinder mask with diameter of 13 pixels (1.4 μm) and a height of 7 pixel (2.3 μm) centered at each local maximum was constructed. The size of the mask was determined by the size of the mega-spot images (Supplementary Fig. 3e-h) and covered >97% of signals emitted from the chromatin foci. Therein we summed up all pixels inside the mask to get the intensity of each putative spot. Finally, for each nucleus at each time point, an intensity threshold was chosen to select candidate spots from the local maxima, in such a way that the maximum number of candidate spots in the nucleus was less than 20. In the subsequent steps, we filtered the candidate spot library using information on nuclear lineage, spot tracking and the relative location of spot pairs.
3. Spot tracking
The intensity-weighted centroid was calculated within the mask of each candidate spot, and the FracShift algorithm65 was applied to find the sub-pixel center for each spot. No sub-pixel bias was observed after 10 FracShift iterations. We did spot tracking in each nuclear lineage. For each lineage, candidate spots located in the corresponding nuclear region (from the nuclear segmentation results) were used for tracking. Spot tracking was performed in three steps: a pre-tracking step, a gap-filling step and a Bayes filtering step.
Step I: For the pre-tracking step, we tracked the two brightest candidate spots in each nucleus. The maximally allowable displacement of spots from the consecutive frames was determined from the MSD at Δt=30s (1 frame, see Part 9 below and Supplementary Fig. 4d) and the measurement error (eL, see Part 5 below and Supplementary Fig. 3a-d) for each dimension. Specifically, for each candidate spot at time t, a search zone of size 3× ( +eL) was set up around the spot center. After correcting for nuclear shift, a candidate spot in the searching zone at time t+1 was recorded, and other candidate spots were discarded. In the <1% of cases where there was more than one candidate spot in the search zone, the brightest one was chosen. Finally, all traces shorter than 2 min are treated as false positives and discarded. These false positive traces are usually clusters of completed mRNAs that are undergoing nuclear export. All tracking was performed on videos of 35 min length (22–58 min in n.c.14). The three channels (MS2, PP7 and parS) were tracked independently. Pre-tracking results from all channels were compiled according to nuclear lineages.
Step II: After collecting the pre-tracking results, we analyzed for each channel 1) the distribution of spot axial positions, 2) the distribution of spot intensities, 3) the distribution of displacement vectors, and additionally for the blue (eve-MS2) channel, 4) the distribution of spot anterior-posterior positions. We then implemented a Dijkstra algorithm66 to find the minimal path that fills the gaps in the pre-tracking results. Specifically, using the distributions described above, we calculated a cost function (log likelihood) for each link that connects any two candidate spots from two consecutive frames, and constructed the set of links that minimized the sum of the costs across the gap. At the end of this gap-filling step, we obtain one tracked spot for each nucleus at each time point.
Step III: Finally, we filtered these tracked spots using a Bayes binary filter. First, a false positive data set (FP) is constructed by re-tracking the candidate spot library after removing spots that were previously tracked. The pre-tracking result from Step I was used as the true positive set (TP). For each spot obtained from Step II, we then used the information (info) of its location, intensity, the displacement from the previous frame and the displacement toward the next frame to obtain likelihood p(info|FP) and p(info|TP), respectively. Next, we calculated the priors p(FP) and p(TP) by fitting a two-component Gaussian mixture model for the vectors that connects the tracked blue and green spots in the same nucleus. Finally, we obtained the posterior probability p(TP|info) and used a cutoff that maximizes the Matthews correlation coefficient to filter false positive spots. The sensitivity of the filter ranged from 96.2% to 99.1%, and the false discovery rate was less than 1%.
4. Calibrating chromatic aberrations
Chromatic aberration was corrected in order to measure distance between spots of different colors. The calibration was data-driven and internally controlled. We assumed that the vector between a spot pair of two different colors in the same nucleus has a zero mean in each dimension. An MS2 spot (blue), for instance, has the same probability of appearing on top of the associating parS spot (green) as the probability of appearing below it, and the distribution is symmetric around zero. We performed additional control experiments to verify this assumption (see below).
We pooled raw instantaneous spot-pair distances from all nuclei at all time points in all available embryos and analyzed the raw distances as a function of the spot-pair positions in the image field of view (e.g., Supplementary Fig. 3b shows the blue-green distance in the x-direction as a function of the x-position in the image of view). We applied a multivariate normal regression model (Ai = piβ + ei, i=x,y,z) in order to get the correction matrix β, where Ai is the 3-D response vector for the chromatic aberration, pi is the spot position with a constant term and ei is a normally distributed error. For each spot pair, chromatic aberration was calculated using β, and the calibrated distances were used in further analysis. The correction matrix was calculated on a weekly basis, using all embryos imaged over the week (embryo number ranging from 12 to 25, usually of the same genotype).
In order to test the validity of the zero mean assumption described above, we did two control experiments. First, we imaged our co-localization control embryos in which blue, green and red fluorescent proteins co-localized within a genomic distance of 2 kb (Supplementary Fig. 3a). Second, we made videos of the 200 nm 3-color TetraSpec beads. These experiments were performed during the same week and under the same optical settings as for the parS-homie-evePr-PP7 embryos, and the images were analyzed using the same code pipeline. Next, we applied the same calibration method to obtain the correction matrix for the control embryos or beads. There was no significant difference between the fitting parameters obtained from the parS-homie-evePr-PP7 embryos and those from the control embryos or beads (Supplementary Fig. 3b). Specifically, applying the correction matrix derived from the control embryos on the experimental embryos introduced <0.6% difference in the calibrated distances.
5. Estimating localization errors
In order to estimate the precision in our distance measurement, we used the 3-color control embryos described above. Briefly, the standard deviation (STD) from the fitted line (Supplementary Fig. 3b, middle), which is the mean after chromatic correction, represents the localization error (eL). For example, for the distance between the MS2 (blue) and parS (green) spots, the STDs for the lateral and axial direction are 75 nm and 150 nm, respectively (Supplementary Fig. 3c). These errors were subtracted in the calculations of time or population-averaged RMS distances (see Part 6 below).
We then assessed whether these localization errors result from optics or from the dynamic properties of our live embryos. From the beads videos we measured lateral and axial errors of 20 nm and 50 nm, respectively (Supplementary Fig. 3c). The differences in the measurement errors between embryos and beads were not due to differences in photon counts (Supplementary Fig. 3d). We conclude that approximately 2/3 of our localization errors were derived from the properties of the live system. At least two factors might contribute to the increased errors we observed in the embryo. First, the nuclei were imaged during S or G2 phase, and individual transcription spots actually represent two sister chromatids. Second, each z-slice takes ~1 s, and the expected MSD is ~0.1 μm2 from the extrapolation of our MSD analysis. As a result, the movement of the spots between two consecutive z-stacks introduces ‘motion blurr’, which leads to increased localization error. Since the parS-homie-eve-PP7 embryos are expected to share the same biological and optical properties as the 3-color control embryos, we assume the same localization errors.
6. Calculating RMS (root-mean-squared) distances
We report time- or population-averaged RMS distances between the MS2 (blue) and the parS (green) spot pairs. For time-averaged RMS distances, instantaneous distances measured at different time points in the same nucleus were averaged. We analyzed the distribution of RMS distances calculated at different time scales, either for the complete time trace (Supplementary Fig. 6) or for a short time window (5 min, Fig. 3a) in order to characterize topological transitions occurring at the relevant time scales. We further classified all RMS distances into two groups (Red-ON and Red-OFF) according to the presence or absence of the red signal (PP7 transcription). For RMS distances obtained from the complete traces, Red-OFF RMS distances were calculated from traces that never show PP7 transcription, while Red-ON RMS distances were calculated from the part of the traces that displayed PP7 activity (Supplementary Fig. 6). For RMS distances obtained from short sliding time windows, Red-OFF RMS distances were calculated from traces that never showed PP7 transcription, and Red-ON RMS distances were calculated from traces that displayed PP7 activity at all time points across the window (Fig. 3a).
We also calculated population-averaged RMS distances (Fig. 2, Fig. 3b-d and Supplementary Fig. 8k) for a group of nuclei that shared the same temporal or spatial register. For example, we aligned all traces with Red-OFF to Red-ON transitions and calculated the RMS distances from nuclei aligned at the same time relative to the initiation of PP7 transcription (Fig. 2a). Similarly, we calculated RMS distances for all nuclei classified as being in the same topological state (Fig. 3b-d and Supplementary Fig. 8k).
Since the measurement errors (ei) described in the previous section and spot pair distances did not seem to be correlated, we reported an error-corrected RMScorr, obtained by subtracting the errors from the raw RMS distances: RMScorr2 = RMS2 − Σi=(dx,dy,dz) ei2 = Σi=(dx,dy,dz)<i+ei>2 − Σi=(dx,dy,dz)ei2, where i is the actual blue-green (MS2-parS) distance in each dimension and ei is the localization error in the corresponding dimension, which is the STD obtained from the 3-color control (Supplementary Fig. 3c).
7. Gaussian mixture fits
The PDFs (probability distribution functions) of RMS distances (except for the λ control in Fig. 3c) were modeled with two-component Gaussian mixtures with five parameters: two means (μ1 and μ2) and STDs (σ1 and σ2) for the two Gaussians and the proportion (p) of the components. Maximum likelihood estimates were performed using MATLAB’s mle function. The fitting results were robust to the choice of initial values, and convergence was always reached after 250 iterations. For the parS-homie-evePr-PP7 embryos, the Gaussian component with the smaller mean is composed of two populations.
8. Time trace alignment
Time series of PP7 activities were aligned with respect to 1) the initiation of PP7 transcription, i.e. the first time point at which nascent PP7 transcripts (red spots) could be detected, or 2) the termination of PP7 transcription, i.e. the last time point at which PP7 transcripts could be identified. 90% of nuclei with PP7 activities contained single PP7 activity traces. For the other 10% of nuclei in which there are two PP7 activity traces, we aligned the initiation of the first trace or the termination of the second. There were cases where eve-MS2 and PP7 transcription started at the same time, presumably because homie-homie pairing occurred before eve enhancers started to function. Therefore, for the initiation analysis, we only aligned PP7 activity traces where eve-MS2 transcription appeared at least 3 min before PP7 transcription was activated. Similarly, for the termination analysis, we only aligned PP7 activity traces where eve-MS2 transcription lasted for at least 3 min after PP7 transcription ceased.
9. MSD analysis
We analyzed the relative motion between two associated spots (e.g. MS2 and parS) by computing the time-averaged mean squared displacement (MSD), i.e. the mean squared change in distances, between a specific spot pair over all time points separated by time interval Δt (Supplementary Fig. 4d). We computed an embryo-averaged MSD and a population-averaged MSD by pooling all spot pairs in an embryo and all spot pairs in a population of embryos, respectively. The embryo-averaged and population-averaged 3D MSDs were fit to a model for 3D anomalous diffusion, i.e. MSD = 6D(Δt)α with an anomalous diffusion coefficient D and a scaling factor α that were extracted. Non-linear least-squares fits were performed for Δt < 4 min.
10. Classification of instantaneous topological states
Because of the fast chromatin motion (D=0.04 μm2s−0.24, Fig. 1e and Supplementary Fig. 4d) and the relatively small confinement of the enhancer-promoter locus (~1μm for the open state), distributions of the instantaneous E-P distance for the open state and the homie-homie paired state overlapped significantly, which hindered the characterization of the instantaneous topological state of the enhancer-promoter locus. We therefore took advantage of the continuity of live imaging and calculated the velocity of the relative E-P movement (displacement across one frame) at each time point (Supplementary Fig. 8a, b). Since the time scale of topological state transitions seems to be at least one order of magnitude slower than the time resolution of our live imaging (which is validated by our kinetic model), the velocities provide extra information for identifying the instantaneous topological state.
We therefore used a binary classifier to classify each enhancer-promoter locus at each time point regarding its topological state, either open (O) or paired (P). We applied one training sample for each of the two states. For the open state, we used time series traces obtained from the parS-λ-evePr-PP7 embryos, which presumably were composed solely of the open state. For the paired state, we used all traces where PP7 transcription occurred, considering that physical proximity is required for promoter activity so that time series traces accompanied by PP7 activity were exclusively in the paired state. For each training sample, we modeled the joint distribution of the distance vector and the velocity vectors as a multivariate Gaussian (Supplementary Fig. 8c-j). There is a negative correlation (-0.32, Pearson correlation coefficient) between velocities measured in two consecutive frames (Supplementary Fig. 8g-j), which is consistent with the strong sub-diffusive behavior we observed from the MSD analysis (α = 0.24, Supplementary Fig. 4d).
Using the distance and the velocity information (Data), we calculated the likelihood p(Data|O-state) and p(Data|P-state) from the two trained joint distributions, respectively. Furthermore, we calculate the priors p(P-state) and p(O-state), for each developmental time point, by pooling data from all embryos. Specifically, we used a time window (5 min) centered at the specific time point and calculated the RMS distance for each nucleus. The distribution of these RMS distances was modeled as a two-component Gaussian mixture, and the proportion of the Gaussian component with the smaller mean was used as prior p(P-state) for this developmental time point.
The posterior probability p(P-state|Data) was then calculated according to Bayes rule. Finally, we estimated the errors (specificity and sensitivity) of our classifier from the two training samples, and a posterior probability cutoff that maximizes the Matthews correlation coefficient was used for state calling.
11. Modeling topological state transitions and MCMC Inference of kinetic parameters
We used a set of first-order reactions to model the transitions between the three topological states (Supplementary Fig. 9a). Based on the finding that physical proximity is required for transcriptional activation, we built a model such that Pon occurs only after Poff is established. Assuming that the parameters f1 and b1 are the same for both the parS-homie-evePr-PP7 and the parS-homie-noPr-PP7 constructs, we also used the Ooff time series from the latter to constrain our parameter inference.
In order to infer the kinetic parameters, we used Metropolis-Hastings algorithm to perform MCMC. Specifically, given a parameter set:
where the three Fini are the initial conditions for the indicated states and genotype, we used time series to calculate likelihood:
where is solved numerically from the coupled ODEs (Supplementary Fig. 9a) with MATLAB ode45. Fj=1,2,3 corresponds to the measured time series of the fraction of the Ooff state for parS-homie-evePr-PP7, the fraction of the Pon state for parS-homie-evePr-PP7 and the fraction of the Ooff state for parS-homie-noPr-PP7, respectively, and i = 1,2,…,T are the developmental time points from 25 to 55 min in nuclear cycle 14.
Using prior and a log-normal proposal distribution:
we generated a Markov chain to sample posterior distributions of the kinetic parameters with acceptance probability:
All simulated chains converged after 5,000 iterations, and we used 90,000 stationary samples to represent the posterior distributions of the kinetic parameters (Supplementary Fig. 9c-g).
12. Transcriptional activity measurements
Transcriptional activity was measured as the sum of the pixel intensities in the spot mask (d = 1.4 μm, h = 2.3 μm). For aligned PP7 activity traces (Fig. 2 and Supplementary Fig. 5) where PP7 was not active (Red-OFF part), a mask around the parS spot (green) in the same nucleus was made. The mask was allowed to shift within the range defined by the mean parS-PP7 (green-red) distance. The maximal integrated intensity in the red channel was used as the PP7 activity.
13. Endogenous eve activity comparison
For each trace with PP7 activity, we integrated eve-MS2 activity in the same nucleus to get eve-MS2 activity while PP7 transcription is active (eve|Red-ON, Fig. 4a, x-axis). Only nuclei with PP7 activity lasting longer than 12 min were used. In order to obtain the control, which is the eve-MS2 activity while PP7 transcription is not active (eve|Red-OFF, Fig. 4a, y-axis), we calculated the mean of the integrated eve-MS2 activities in the neighboring nuclei where PP7 was not transcribed. Neighborhood is defined as nuclei within a 20μm anterior-posterior bin centered at the nucleus displaying PP7 activity. The time interval for eve-MS2 activity integration is the same as for the PP7 expressing nucleus. The time-averaged integrated intensity is shown in Fig. 4a.
Statistical analysis
Two-tailed Wilcoxon rank sum tests were performed to compare E-P distances in different topological states. One-tailed Fisher’s exact tests were performed to test for enhanced penetrance of the phenotypic defects associated with the homie transgenes. MCMC inference of the kinetics parameters is described in Image processing and data analysis. Representative images/videos were replicated in at least 3 independent experiments, as indicated in the relevant figure legends.
Data accessibility
Raw spot localization data is provided as Supplementary Dataset 1. Supplementary videos are provided as supplementary material 2 through 4.
Code availability
Custom codes (MATLAB) used for image processing and data analysis can be made available upon request. All details of algorithms are described in the Online Methods and references cited therein.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health (U01 EB021239, U01 DA047730, R01 GM097275, R01 GM117458) and the National Science Foundation (PHY-1734030). H.C. was supported by the Charles H. Revson Biomedical Science Fellowship. M.L. was supported by the Rothschild, EMBO and HFSP fellowships.
Footnotes
Author contributions
H.C. and T.G. conceived the main ideas regarding live cell image generation, processing and analysis. M.F. and J.B.J. developed the homie-eve system to create quantifiably distinct architectural and transcriptional states. H.C. designed the study to marry these technologies. H.C., M.F. and J.B.J. designed and generated the transgenic flies. H.C. and L.B. performed the imaging experiments. H.C., L.B., M.L. and T.G. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript.
Competing financial interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- 1.Benoist C, Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981;290:304–10. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Levine M. Transcriptional enhancers in animal development and evolution. Curr Biol. 2010;20:R754–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.06.070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Long HK, Prescott SL, Wysocka J. Ever-Changing Landscapes: Transcriptional Enhancers in Development and Evolution. Cell. 2016;167:1170–1187. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.09.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Buecker C, Wysocka J. Enhancers as information integration hubs in development: lessons from genomics. Trends Genet. 2012;28:276–84. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2012.02.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kim TK, Shiekhattar R. Architectural and Functional Commonalities between Enhancers and Promoters. Cell. 2015;162:948–59. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Vernimmen D, Bickmore WA. The Hierarchy of Transcriptional Activation: From Enhancer to Promoter. Trends Genet. 2015;31:696–708. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2015.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Consortium, E.P. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature. 2012;489:57–74. doi: 10.1038/nature11247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tolhuis B, Palstra RJ, Splinter E, Grosveld F, de Laat W. Looping and interaction between hypersensitive sites in the active beta-globin locus. Mol Cell. 2002;10:1453–65. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00781-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Uslu VV, et al. Long-range enhancers regulating Myc expression are required for normal facial morphogenesis. Nat Genet. 2014;46:753–8. doi: 10.1038/ng.2971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhang Y, et al. Chromatin connectivity maps reveal dynamic promoter-enhancer long-range associations. Nature. 2013;504:306–10. doi: 10.1038/nature12716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Arnold CD, et al. Genome-wide quantitative enhancer activity maps identified by STARR-seq. Science. 2013;339:1074–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1232542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ghavi-Helm Y, et al. Enhancer loops appear stable during development and are associated with paused polymerase. Nature. 2014;512:96–100. doi: 10.1038/nature13417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kvon EZ, et al. Genome-scale functional characterization of Drosophila developmental enhancers in vivo. Nature. 2014;512:91–5. doi: 10.1038/nature13395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Levine M, Cattoglio C, Tjian R. Looping back to leap forward: transcription enters a new era. Cell. 2014;157:13–25. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kagey MH, et al. Mediator and cohesin connect gene expression and chromatin architecture. Nature. 2010;467:430–5. doi: 10.1038/nature09380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mifsud B, et al. Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C. Nat Genet. 2015;47:598–606. doi: 10.1038/ng.3286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Andrey G, et al. A switch between topological domains underlies HoxD genes collinearity in mouse limbs. Science. 2013;340:1234167. doi: 10.1126/science.1234167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Spitz F. Gene regulation at a distance: From remote enhancers to 3D regulatory ensembles. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016;57:57–67. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.06.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Carter D, Chakalova L, Osborne CS, Dai YF, Fraser P. Long-range chromatin regulatory interactions in vivo. Nat Genet. 2002;32:623–6. doi: 10.1038/ng1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sanyal A, Lajoie BR, Jain G, Dekker J. The long-range interaction landscape of gene promoters. Nature. 2012;489:109–13. doi: 10.1038/nature11279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fujioka M, Wu X, Jaynes JB. A chromatin insulator mediates transgene homing and very long-range enhancer-promoter communication. Development. 2009;136:3077–87. doi: 10.1242/dev.036467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Fujioka M, Sun G, Jaynes JB. The Drosophila eve insulator Homie promotes eve expression and protects the adjacent gene from repression by polycomb spreading. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1003883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fujioka M, Mistry H, Schedl P, Jaynes JB. Determinants of Chromosome Architecture: Insulator Pairing in cis and in trans. PLoS Genet. 2016;12:e1005889. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Larson DR, Zenklusen D, Wu B, Chao JA, Singer RH. Real-time observation of transcription initiation and elongation on an endogenous yeast gene. Science. 2011;332:475–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1202142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hocine S, Raymond P, Zenklusen D, Chao JA, Singer RH. Single-molecule analysis of gene expression using two-color RNA labeling in live yeast. Nat Methods. 2013;10:119–21. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Fukaya T, Lim B, Levine M. Enhancer Control of Transcriptional Bursting. Cell. 2016;166:358–68. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dubarry N, Pasta F, Lane D. ParABS systems of the four replicons of Burkholderia cenocepacia: new chromosome centromeres confer partition specificity. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:1489–96. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.4.1489-1496.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Saad H, et al. DNA dynamics during early double-strand break processing revealed by non-intrusive imaging of living cells. PLoS Genet. 2014;10:e1004187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gasser SM. Visualizing chromatin dynamics in interphase nuclei. Science. 2002;296:1412–6. doi: 10.1126/science.1067703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sinclair P, Bian Q, Plutz M, Heard E, Belmont AS. Dynamic plasticity of large-scale chromatin structure revealed by self-assembly of engineered chromosome regions. J Cell Biol. 2010;190:761–76. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200912167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bystricky K. Chromosome dynamics and folding in eukaryotes: Insights from live cell microscopy. FEBS Lett. 2015;589:3014–22. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Garcia HG, Tikhonov M, Lin A, Gregor T. Quantitative imaging of transcription in living Drosophila embryos links polymerase activity to patterning. Curr Biol. 2013;23:2140–5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.08.054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Fukaya T, Lim B, Levine M. Rapid Rates of Pol II Elongation in the Drosophila Embryo. Curr Biol. 2017;27:1387–1391. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.03.069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lucas JS, Zhang Y, Dudko OK, Murre C. 3D trajectories adopted by coding and regulatory DNA elements: first-passage times for genomic interactions. Cell. 2014;158:339–52. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Guo Y, et al. CRISPR Inversion of CTCF Sites Alters Genome Topology and Enhancer/Promoter Function. Cell. 2015;162:900–10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rao SS, et al. A 3D map of the human genome at kilobase resolution reveals principles of chromatin looping. Cell. 2014;159:1665–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.11.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Deng W, et al. Reactivation of developmentally silenced globin genes by forced chromatin looping. Cell. 2014;158:849–60. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Franke M, et al. Formation of new chromatin domains determines pathogenicity of genomic duplications. Nature. 2016;538:265–269. doi: 10.1038/nature19800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dixon JR, et al. Chromatin architecture reorganization during stem cell differentiation. Nature. 2015;518:331–6. doi: 10.1038/nature14222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Krijger PH, et al. Cell-of-Origin-Specific 3D Genome Structure Acquired during Somatic Cell Reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;18:597–610. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.01.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Raser JM, O’Shea EK. Control of stochasticity in eukaryotic gene expression. Science. 2004;304:1811–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1098641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Voss TC, Hager GL. Dynamic regulation of transcriptional states by chromatin and transcription factors. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15:69–81. doi: 10.1038/nrg3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sanchez A, Garcia HG, Jones D, Phillips R, Kondev J. Effect of promoter architecture on the cell-to-cell variability in gene expression. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011;7:e1001100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hug CB, Grimaldi AG, Kruse K, Vaquerizas JM. Chromatin Architecture Emerges during Zygotic Genome Activation Independent of Transcription. Cell. 2017;169:216–228.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.03.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rubin AJ, et al. Lineage-specific dynamic and pre-established enhancer-promoter contacts cooperate in terminal differentiation. Nat Genet. 2017 doi: 10.1038/ng.3935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hnisz D, Shrinivas K, Young RA, Chakraborty AK, Sharp PA. A Phase Separation Model for Transcriptional Control. Cell. 2017;169:13–23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sexton T, Umlauf D, Kurukuti S, Fraser P. The role of transcription factories in large-scale structure and dynamics of interphase chromatin. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2007;18:691–7. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2007.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Cho WK, et al. RNA Polymerase II cluster dynamics predict mRNA output in living cells. Elife. 2016;5 doi: 10.7554/eLife.13617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Williamson I, Lettice LA, Hill RE, Bickmore WA. Shh and ZRS enhancer colocalisation is specific to the zone of polarising activity. Development. 2016;143:2994–3001. doi: 10.1242/dev.139188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Stadler MR, Haines JE, Eisen MB. Convergence of topological domain boundaries, insulators, and polytene interbands revealed by high-resolution mapping of chromatin contacts in the early Drosophila melanogaster embryo. Elife. 2017;6 doi: 10.7554/eLife.29550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Negre N, et al. A comprehensive map of insulator elements for the Drosophila genome. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1000814. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kyrchanova O, Georgiev P. Chromatin insulators and long-distance interactions in Drosophila. FEBS Lett. 2014;588:8–14. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.10.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chetverina D, et al. Boundaries of loop domains (insulators): Determinants of chromosome form and function in multicellular eukaryotes. Bioessays. 2017;39 doi: 10.1002/bies.201600233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lupianez DG, et al. Disruptions of topological chromatin domains cause pathogenic rewiring of gene-enhancer interactions. Cell. 2015;161:1012–25. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.04.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bartman CR, Hsu SC, Hsiung CC, Raj A, Blobel GA. Enhancer Regulation of Transcriptional Bursting Parameters Revealed by Forced Chromatin Looping. Mol Cell. 2016;62:237–47. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.03.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wu B, Chen J, Singer RH. Background free imaging of single mRNAs in live cells using split fluorescent proteins. Sci Rep. 2014;4:3615. doi: 10.1038/srep03615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Sladitschek HL, Neveu PA. MXS-Chaining: A Highly Efficient Cloning Platform for Imaging and Flow Cytometry Approaches in Mammalian Systems. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Vodala S, Abruzzi KC, Rosbash M. The nuclear exosome and adenylation regulate posttranscriptional tethering of yeast GAL genes to the nuclear periphery. Mol Cell. 2008;31:104–13. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.05.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dubarry M, Loiodice I, Chen CL, Thermes C, Taddei A. Tight protein-DNA interactions favor gene silencing. Genes Dev. 2011;25:1365–70. doi: 10.1101/gad.611011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Bateman JR, Lee AM, Wu CT. Site-specific transformation of Drosophila via phiC31 integrase-mediated cassette exchange. Genetics. 2006;173:769–77. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.056945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Small S. In vivo analysis of lacZ fusion genes in transgenic Drosophila melanogaster. Methods Enzymol. 2000;326:146–59. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(00)26052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Little SC, Tkacik G, Kneeland TB, Wieschaus EF, Gregor T. The formation of the Bicoid morphogen gradient requires protein movement from anteriorly localized mRNA. PLoS Biol. 2011;9:e1000596. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Little SC, Tikhonov M, Gregor T. Precise developmental gene expression arises from globally stochastic transcriptional activity. Cell. 2013;154:789–800. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.07.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Dubuis JO, Samanta R, Gregor T. Accurate measurements of dynamics and reproducibility in small genetic networks. Mol Syst Biol. 2013;9:639. doi: 10.1038/msb.2012.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Gao Y, Kilfoil ML. Accurate detection and complete tracking of large populations of features in three dimensions. Opt Express. 2009;17:4685–704. doi: 10.1364/oe.17.004685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Dijkstra EW. A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. Numer Math. 1959;1:269–271. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Raw spot localization data is provided as Supplementary Dataset 1. Supplementary videos are provided as supplementary material 2 through 4.


