The two ring systems are twisted by 51.40 (11)°. In the crystal, the molecules are linked via C—H⋯π interactions, forming a three-dimensional framework.
Keywords: crystal structure, Schiff base, Hirshfeld surface
Abstract
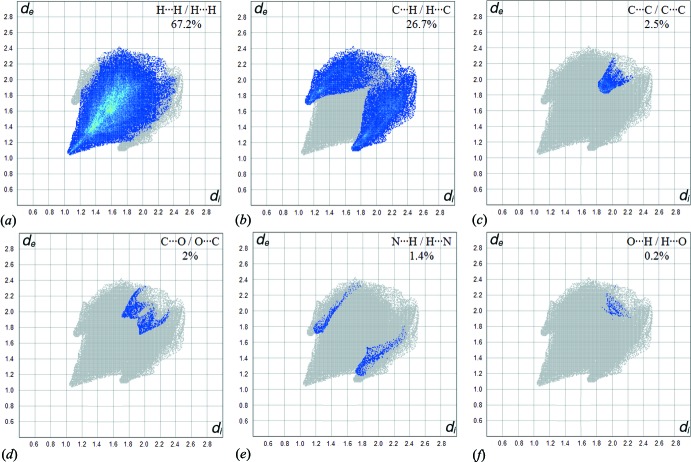
In the title Schiff base compound, C23H23NO, the two ring systems are twisted by 51.40 (11)° relative to each other. In the crystal, the molecules are connected by weak C—H⋯π interactions, generating a three-dimensional supramolecular structure. Hirshfeld surface analysis and two-dimensional fingerprint plots indicate that the most important contributions to the crystal packing are from H⋯H (67.2%), C⋯H/H⋯C (26.7%) and C⋯C (2.5%) interactions.
Chemical context
Schiff bases have found wide use as a ligands in coordination chemistry (Calligaris et al., 1972 ▸; Hökelek et al., 2004 ▸; Moroz et al., 2012 ▸) and are also important in various areas of chemistry and biochemistry because of their biological activity (El-masry et al., 2000 ▸). Many Schiff bases have some antibacterial, anticancer and antioxidant properties and have therefore been used as starting materials in the synthesis of important medicinal substances. In the present study, we designed a new type of Schiff base obtained by the reaction of 2-ethoxy-1-naphthaldehyde and 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1-naphtylamine to give (E)-N-[(2-ethoxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-amine. We report herein the synthesis, crystal structure and Hirshfeld structural analysis of the title compound.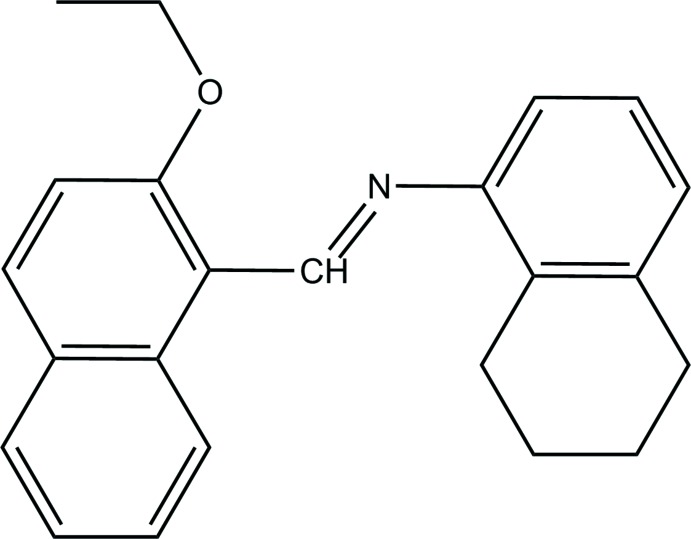
Structural commentary
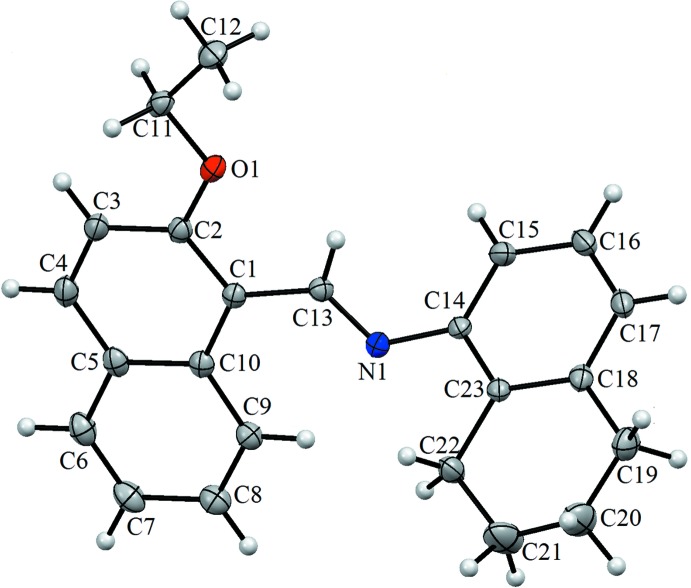
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, (I), contains one independent molecule (Fig. 1 ▸). the two ring systems are twisted by 51.40 (11)° relative to each other. The O1—C2 and O1—C11 bond lengths are 1.359 (4) and 1.423 (4) Å, respectively, while the C13=N1 and C14—N1 bond lengths are 1.262 (3) and 1.415 (5) Å, respectively.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 20% probability level.
Supramolecular features
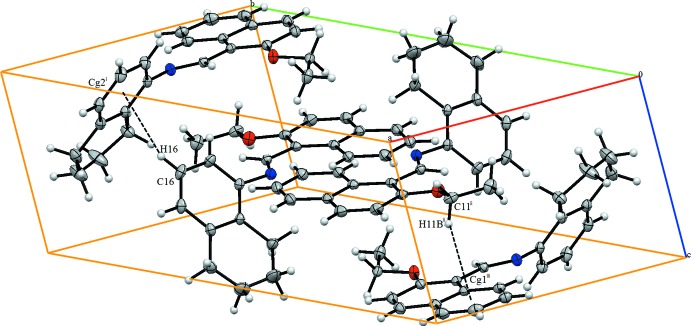
In the crystal, the molecules are connected by C—H⋯π interactions, generating a three-dimensional supramolecular structure (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C5–C10 and C14–C23 rings.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11—H11B⋯Cg1i | 0.97 | 2.91 | 3.799 | 153 |
| C16—H16⋯Cg2i | 0.93 | 2.96 | 3.728 | 141 |
Symmetry code: (i) 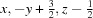 .
.
Figure 2.
A view of the crystal packing. Dashed lines denote C—H⋯π interactions. Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y +  , z −
, z − 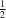 ; (ii) 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z; (iii) 1 − x, −
; (ii) 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z; (iii) 1 − x, −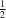 + y;
+ y;  − z.
− z.
Database survey
There are no direct precedents for the structure of (I) in the crystallographic literature (CSD version 5.39, update of August 2018; Groom et al., 2016 ▸). However, there are several precedents for (E)-N-benzylidene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-amine and (E)-N-[(2-ethoxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene]aniline including 2-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1,3-diphenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho[1,2-e][1,3]oxazine (Borah et al., 2014 ▸), 2-(2-nitrophenyl)-3-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one (Drawanz et al., 2017 ▸), N-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1,2-dihydro-3′H-spiro(benzo[f]chromene-3,1′-[2]benzofuran)-1-amine (Wu et al., 2013 ▸) and methyl (5aR,6aR,9R,10aR)-4-benzoyl-7-methyl4,5,5a,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10adecahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxylate dihydrate (Lee et al., 2015 ▸).
Hirshfeld surface analysis
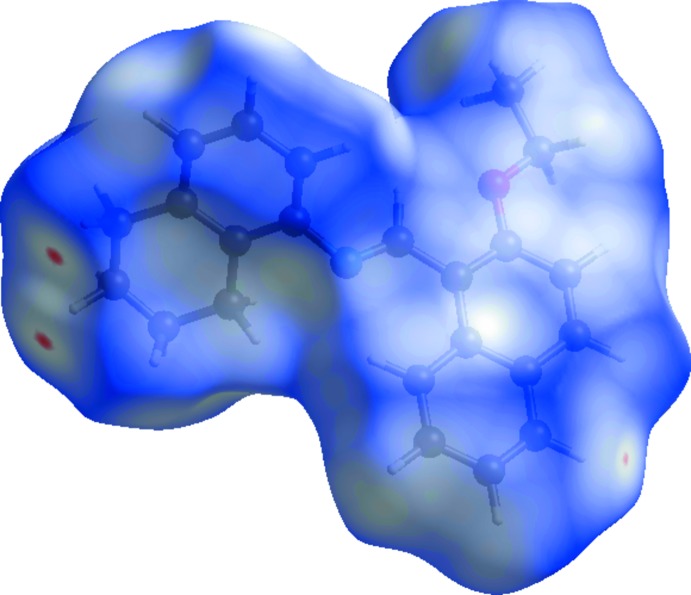
Hirshfield surface analysis was performed using CrystalExplorer (Turner et al., 2017 ▸). The Hirshfeld surfaces and their associated two-dimensional fingerprint plots were used to quantify the various intermolecular interactions. The Hirshfeld surface mapped over d norm is illustrated in Fig. 3 ▸ [colour scale of −0.067 (red) to 1.262 (blue) Å]. Red spots on this surface indicate the intermolecular contacts involved in strong hydrogen bonds and interatomic contacts (Gümüş et al., 2018 ▸; Kansiz et al., 2018 ▸; Sen et al., 2018 ▸).
Figure 3.
The Hirshfeld surface of the title compound mapped over d norm.
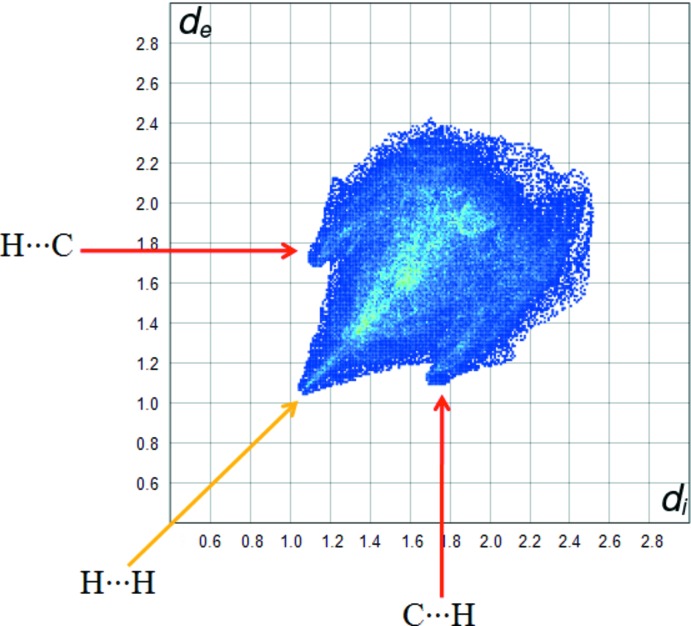
Fig. 4 ▸ shows the two-dimensional fingerprint of the sum of the contacts contributing to the Hirshfeld surface represented in normal mode. The graph shown in Fig. 5 ▸ a (H⋯H) shows the two-dimensional fingerprint of the (d i, d e) points associated with hydrogen atoms. It is characterized by an end point that points to the origin and corresponds to d i = d e = 1.08 Å, which indicates the presence of the H⋯H contacts in this study (67.2%). The graph shown in Fig. 5 ▸ b (C⋯H/H⋯C) shows the contacts between the carbon atoms inside the surface and the hydrogen atoms outside the surface and vice versa. The plot shows two symmetrical wings on the left and right sides (26.7%). Further, there are C⋯C (2.5%), C⋯O/O⋯C (2%), N⋯H/H⋯N (1.4%) and O⋯H/H⋯O (0.2%) contacts.
Figure 4.
A fingerprint plot for the title compound.
Figure 5.
Two-dimensional fingerprint plots for (a) H⋯H (67.2%), (b) C⋯H/H⋯C (26.7%), (c) C⋯C (2.5%), (d) C⋯O/O⋯C (2%), (e) N⋯H/H⋯N (1.4%) and (f) O⋯H/H⋯O (0.2%) contacts.
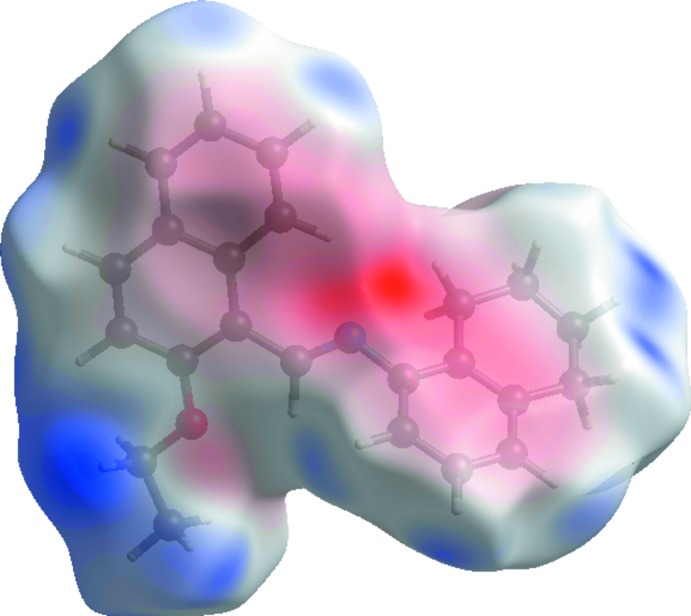
A view of the three-dimensional Hirshfeld surface of the title compound plotted over electrostatic potential energy in the range −0.048 to 0.033 a.u. using the STO-3G basis set at the Hartree–Fock level of theory is shown in Fig. 6 ▸; the donors and acceptors are shown as blue and red areas around the atoms related with positive (hydrogen-bond donors) and negative (hydrogen-bond acceptors) electrostatic potentials, respectively.
Figure 6.
A view of the three-dimensional Hirshfeld surface plotted over electrostatic potential energy.
Synthesis and crystallization
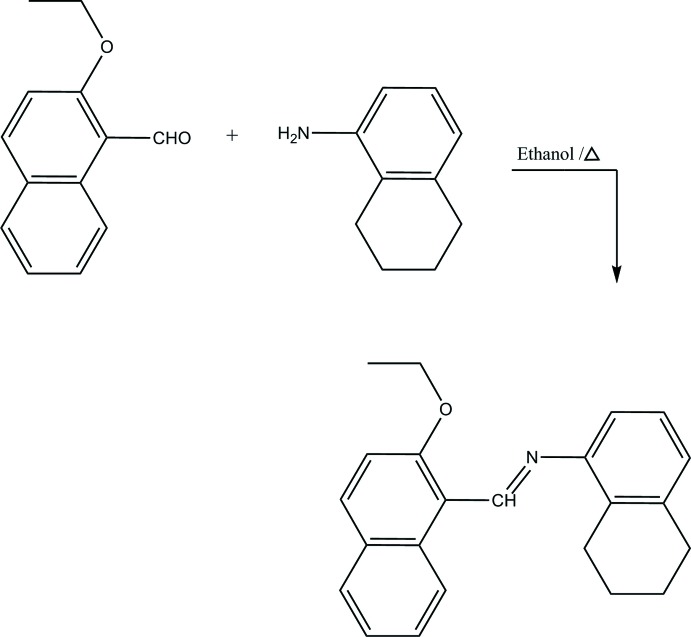
The title compound was prepared (Fig. 7 ▸) by refluxing a mixture of a solution containing 2-ethoxy-1-naphthaldehyde (20.0 mg, 0.1 mmol) in ethanol (20 mL) and a solution containing 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1-naphtylamine (14.72 mg, 0.1 mmol) in ethanol (20 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred for 5 h under reflux. Single crystals of the title compound suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow evaporation of an ethanol solution (yield: 60%; m.p. 416–418 K) .
Figure 7.
The synthesis of the title compound.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. Hydrogen atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model: C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C23H23NO |
| M r | 329.42 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 12.6628 (4), 20.3304 (9), 7.3838 (3) |
| β (°) | 104.895 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 1837.01 (13) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.07 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.61 × 0.47 × 0.25 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Stoe IPDS 2 |
| Absorption correction | Integration |
| T min, T max | 0.963, 0.982 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 22781, 3419, 2128 |
| R int | 0.106 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.606 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.081, 0.255, 1.04 |
| No. of reflections | 3419 |
| No. of parameters | 226 |
| No. of restraints | 19 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.44, −0.50 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018013117/xu5940sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018013117/xu5940Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018013117/xu5940Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1843572
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Ondokuz Mayıs University, Turkey, for the use of the Stoe IPDS 2 diffractometer (purchased under grant F.279 of the University Research Fund).
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C23H23NO | F(000) = 704 |
| Mr = 329.42 | Dx = 1.191 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 12.6628 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 16587 reflections |
| b = 20.3304 (9) Å | θ = 1.7–27.9° |
| c = 7.3838 (3) Å | µ = 0.07 mm−1 |
| β = 104.895 (3)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1837.01 (13) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.61 × 0.47 × 0.25 mm |
Data collection
| Stoe IPDS 2 diffractometer | 3419 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: sealed X-ray tube, 12 x 0.4 mm long-fine focus | 2128 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 6.67 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.106 |
| rotation method scans | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 1.7° |
| Absorption correction: integration | h = −15→15 |
| Tmin = 0.963, Tmax = 0.982 | k = −24→24 |
| 22781 measured reflections | l = −8→8 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 19 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.081 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.255 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1536P)2 + 0.1088P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3419 reflections | Δρmax = 0.44 e Å−3 |
| 226 parameters | Δρmin = −0.50 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.3883 (2) | 0.69673 (14) | 0.5168 (4) | 0.0625 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.3335 (2) | 0.75663 (16) | 0.4960 (4) | 0.0705 (8) | |
| C3 | 0.2195 (3) | 0.7603 (2) | 0.4580 (5) | 0.0854 (10) | |
| H3 | 0.184711 | 0.800998 | 0.441177 | 0.102* | |
| C4 | 0.1603 (3) | 0.7044 (2) | 0.4460 (5) | 0.0881 (11) | |
| H4 | 0.084543 | 0.707238 | 0.418648 | 0.106* | |
| C5 | 0.2102 (3) | 0.64177 (19) | 0.4739 (4) | 0.0768 (9) | |
| C6 | 0.1485 (3) | 0.5844 (2) | 0.4686 (5) | 0.0945 (11) | |
| H6 | 0.073038 | 0.587938 | 0.447096 | 0.113* | |
| C7 | 0.1946 (4) | 0.5244 (2) | 0.4937 (5) | 0.1018 (12) | |
| H7 | 0.151649 | 0.487132 | 0.490683 | 0.122* | |
| C8 | 0.3094 (3) | 0.51870 (19) | 0.5248 (5) | 0.0917 (10) | |
| H8 | 0.342052 | 0.477395 | 0.540440 | 0.110* | |
| C9 | 0.3719 (3) | 0.57345 (16) | 0.5317 (4) | 0.0758 (8) | |
| H9 | 0.447121 | 0.568790 | 0.552983 | 0.091* | |
| C10 | 0.3259 (2) | 0.63747 (15) | 0.5075 (4) | 0.0666 (8) | |
| C11 | 0.3496 (3) | 0.87489 (16) | 0.5162 (5) | 0.0818 (10) | |
| H11A | 0.307563 | 0.876744 | 0.608818 | 0.098* | |
| H11B | 0.301597 | 0.884936 | 0.394231 | 0.098* | |
| C12 | 0.4418 (4) | 0.92253 (19) | 0.5636 (7) | 0.1034 (12) | |
| H12A | 0.413575 | 0.966242 | 0.566169 | 0.155* | |
| H12B | 0.488685 | 0.911972 | 0.684440 | 0.155* | |
| H12C | 0.482748 | 0.920123 | 0.470930 | 0.155* | |
| C13 | 0.5070 (2) | 0.69926 (14) | 0.5483 (4) | 0.0637 (7) | |
| H13 | 0.537591 | 0.740457 | 0.541243 | 0.076* | |
| C14 | 0.6849 (2) | 0.66195 (13) | 0.6046 (4) | 0.0620 (7) | |
| C15 | 0.7241 (3) | 0.69702 (15) | 0.4745 (5) | 0.0827 (10) | |
| H15 | 0.675637 | 0.716373 | 0.372129 | 0.099* | |
| C16 | 0.8353 (3) | 0.70314 (18) | 0.4975 (6) | 0.0942 (12) | |
| H16 | 0.861669 | 0.726596 | 0.410256 | 0.113* | |
| C17 | 0.9070 (3) | 0.67484 (17) | 0.6482 (6) | 0.0859 (10) | |
| H17 | 0.981742 | 0.679759 | 0.663076 | 0.103* | |
| C18 | 0.8696 (2) | 0.63895 (14) | 0.7789 (5) | 0.0725 (8) | |
| C19 | 0.9511 (3) | 0.6076 (2) | 0.9406 (7) | 0.1064 (12) | |
| H19A | 0.998028 | 0.578883 | 0.890880 | 0.128* | |
| H19B | 0.996683 | 0.641912 | 1.011812 | 0.128* | |
| C20 | 0.9048 (4) | 0.5702 (3) | 1.0659 (9) | 0.1519 (18) | |
| H20A | 0.944397 | 0.528870 | 1.087031 | 0.182* | |
| H20B | 0.922970 | 0.593431 | 1.184568 | 0.182* | |
| C21 | 0.7955 (4) | 0.5545 (4) | 1.0294 (9) | 0.169 (2) | |
| H21A | 0.775939 | 0.555005 | 1.148089 | 0.203* | |
| H21B | 0.787436 | 0.509438 | 0.984530 | 0.203* | |
| C22 | 0.7136 (3) | 0.5943 (2) | 0.8964 (5) | 0.0927 (11) | |
| H22A | 0.680842 | 0.624872 | 0.966960 | 0.111* | |
| H22B | 0.656127 | 0.565356 | 0.828032 | 0.111* | |
| C23 | 0.7575 (2) | 0.63267 (13) | 0.7572 (4) | 0.0628 (7) | |
| N1 | 0.5720 (2) | 0.65120 (12) | 0.5839 (4) | 0.0702 (7) | |
| O1 | 0.39688 (19) | 0.81145 (11) | 0.5147 (4) | 0.0871 (7) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0606 (16) | 0.0751 (19) | 0.0516 (14) | 0.0063 (14) | 0.0141 (12) | −0.0002 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0663 (18) | 0.083 (2) | 0.0631 (16) | 0.0111 (15) | 0.0186 (13) | 0.0067 (14) |
| C3 | 0.075 (2) | 0.099 (3) | 0.087 (2) | 0.0223 (19) | 0.0294 (17) | 0.0176 (18) |
| C4 | 0.0625 (19) | 0.124 (3) | 0.079 (2) | 0.012 (2) | 0.0196 (15) | 0.0103 (19) |
| C5 | 0.0659 (18) | 0.109 (3) | 0.0561 (16) | −0.0054 (18) | 0.0159 (13) | 0.0011 (15) |
| C6 | 0.074 (2) | 0.125 (3) | 0.083 (2) | −0.018 (2) | 0.0178 (17) | −0.009 (2) |
| C7 | 0.103 (3) | 0.110 (3) | 0.093 (3) | −0.039 (3) | 0.027 (2) | −0.014 (2) |
| C8 | 0.098 (3) | 0.090 (2) | 0.087 (2) | −0.013 (2) | 0.0226 (18) | −0.0086 (18) |
| C9 | 0.0753 (19) | 0.079 (2) | 0.0730 (18) | −0.0078 (16) | 0.0182 (14) | −0.0048 (15) |
| C10 | 0.0665 (18) | 0.083 (2) | 0.0504 (14) | 0.0030 (14) | 0.0149 (12) | −0.0019 (13) |
| C11 | 0.102 (2) | 0.080 (2) | 0.0724 (18) | 0.0309 (19) | 0.0378 (17) | 0.0109 (16) |
| C12 | 0.117 (3) | 0.075 (2) | 0.129 (3) | 0.010 (2) | 0.050 (3) | −0.003 (2) |
| C13 | 0.0644 (16) | 0.0644 (17) | 0.0626 (16) | 0.0029 (14) | 0.0169 (13) | 0.0032 (12) |
| C14 | 0.0608 (16) | 0.0511 (14) | 0.0773 (17) | 0.0031 (12) | 0.0236 (13) | 0.0022 (13) |
| C15 | 0.093 (2) | 0.072 (2) | 0.091 (2) | 0.0124 (17) | 0.0383 (18) | 0.0218 (16) |
| C16 | 0.100 (3) | 0.082 (2) | 0.123 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.068 (2) | 0.014 (2) |
| C17 | 0.0700 (19) | 0.075 (2) | 0.124 (3) | −0.0022 (17) | 0.046 (2) | −0.005 (2) |
| C18 | 0.0618 (17) | 0.0638 (17) | 0.093 (2) | −0.0009 (14) | 0.0229 (15) | −0.0081 (15) |
| C19 | 0.066 (2) | 0.119 (3) | 0.123 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.0051 (19) | 0.007 (2) |
| C20 | 0.104 (3) | 0.190 (4) | 0.142 (4) | 0.011 (3) | −0.003 (3) | 0.065 (3) |
| C21 | 0.121 (3) | 0.221 (4) | 0.144 (3) | −0.013 (3) | −0.002 (3) | 0.097 (3) |
| C22 | 0.074 (2) | 0.115 (3) | 0.090 (2) | −0.0050 (19) | 0.0225 (17) | 0.031 (2) |
| C23 | 0.0603 (16) | 0.0541 (15) | 0.0766 (18) | −0.0005 (12) | 0.0225 (13) | 0.0002 (13) |
| N1 | 0.0605 (14) | 0.0681 (15) | 0.0816 (16) | 0.0047 (12) | 0.0173 (11) | 0.0063 (12) |
| O1 | 0.0777 (14) | 0.0726 (14) | 0.1156 (19) | 0.0173 (11) | 0.0335 (13) | 0.0041 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C2 | 1.390 (4) | C13—N1 | 1.262 (3) |
| C1—C10 | 1.432 (4) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C13 | 1.462 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.387 (4) |
| C2—O1 | 1.359 (4) | C14—C23 | 1.392 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.400 (4) | C14—N1 | 1.415 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.352 (5) | C15—C16 | 1.380 (5) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.413 (5) | C16—C17 | 1.368 (5) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.398 (5) | C17—C18 | 1.387 (5) |
| C5—C10 | 1.425 (4) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.345 (6) | C18—C23 | 1.393 (4) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C18—C19 | 1.504 (5) |
| C7—C8 | 1.417 (6) | C19—C20 | 1.434 (7) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C19—H19A | 0.9700 |
| C8—C9 | 1.359 (5) | C19—H19B | 0.9700 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C20—C21 | 1.378 (6) |
| C9—C10 | 1.418 (4) | C20—H20A | 0.9700 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | C20—H20B | 0.9700 |
| C11—O1 | 1.423 (4) | C21—C22 | 1.474 (6) |
| C11—C12 | 1.488 (5) | C21—H21A | 0.9700 |
| C11—H11A | 0.9700 | C21—H21B | 0.9700 |
| C11—H11B | 0.9700 | C22—C23 | 1.506 (4) |
| C12—H12A | 0.9600 | C22—H22A | 0.9700 |
| C12—H12B | 0.9600 | C22—H22B | 0.9700 |
| C12—H12C | 0.9600 | ||
| C2—C1—C10 | 118.6 (3) | C15—C14—C23 | 120.1 (3) |
| C2—C1—C13 | 116.7 (3) | C15—C14—N1 | 122.4 (3) |
| C10—C1—C13 | 124.7 (2) | C23—C14—N1 | 117.4 (2) |
| O1—C2—C1 | 116.2 (3) | C16—C15—C14 | 119.8 (3) |
| O1—C2—C3 | 121.8 (3) | C16—C15—H15 | 120.1 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 121.9 (3) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.1 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.6 (3) | C17—C16—C15 | 120.3 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.2 | C17—C16—H16 | 119.8 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.2 | C15—C16—H16 | 119.8 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.9 (3) | C16—C17—C18 | 120.9 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.0 | C16—C17—H17 | 119.6 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.0 | C18—C17—H17 | 119.6 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.4 (3) | C17—C18—C23 | 119.2 (3) |
| C6—C5—C10 | 119.8 (3) | C17—C18—C19 | 119.2 (3) |
| C4—C5—C10 | 118.8 (3) | C23—C18—C19 | 121.5 (3) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 122.2 (4) | C20—C19—C18 | 115.2 (3) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 118.9 | C20—C19—H19A | 108.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 118.9 | C18—C19—H19A | 108.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.2 (4) | C20—C19—H19B | 108.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.4 | C18—C19—H19B | 108.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.4 | H19A—C19—H19B | 107.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 120.1 (4) | C21—C20—C19 | 123.6 (4) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.9 | C21—C20—H20A | 106.4 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.9 | C19—C20—H20A | 106.4 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 122.1 (3) | C21—C20—H20B | 106.4 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.0 | C19—C20—H20B | 106.4 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.0 | H20A—C20—H20B | 106.5 |
| C9—C10—C5 | 116.6 (3) | C20—C21—C22 | 120.2 (5) |
| C9—C10—C1 | 124.3 (3) | C20—C21—H21A | 107.3 |
| C5—C10—C1 | 119.1 (3) | C22—C21—H21A | 107.3 |
| O1—C11—C12 | 106.6 (3) | C20—C21—H21B | 107.3 |
| O1—C11—H11A | 110.4 | C22—C21—H21B | 107.3 |
| C12—C11—H11A | 110.4 | H21A—C21—H21B | 106.9 |
| O1—C11—H11B | 110.4 | C21—C22—C23 | 114.8 (3) |
| C12—C11—H11B | 110.4 | C21—C22—H22A | 108.6 |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 108.6 | C23—C22—H22A | 108.6 |
| C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 | C21—C22—H22B | 108.6 |
| C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 | C23—C22—H22B | 108.6 |
| H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 | H22A—C22—H22B | 107.6 |
| C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C14—C23—C18 | 119.7 (3) |
| H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C14—C23—C22 | 119.4 (3) |
| H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C18—C23—C22 | 120.9 (3) |
| N1—C13—C1 | 126.6 (3) | C13—N1—C14 | 119.4 (2) |
| N1—C13—H13 | 116.7 | C2—O1—C11 | 120.4 (3) |
| C1—C13—H13 | 116.7 | ||
| C10—C1—C2—O1 | 177.0 (2) | N1—C14—C15—C16 | −176.8 (3) |
| C13—C1—C2—O1 | −2.6 (4) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −0.1 (5) |
| C10—C1—C2—C3 | −2.9 (4) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.8 (6) |
| C13—C1—C2—C3 | 177.5 (3) | C16—C17—C18—C23 | −1.0 (5) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −178.1 (3) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 178.9 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.8 (5) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −178.6 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.1 (5) | C23—C18—C19—C20 | 1.3 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 177.4 (3) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 9.9 (10) |
| C3—C4—C5—C10 | −2.8 (5) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | −22.6 (12) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 179.6 (3) | C20—C21—C22—C23 | 22.4 (9) |
| C10—C5—C6—C7 | −0.3 (5) | C15—C14—C23—C18 | 0.2 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.6 (6) | N1—C14—C23—C18 | 176.8 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 0.9 (6) | C15—C14—C23—C22 | −179.5 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.4 (5) | N1—C14—C23—C22 | −2.9 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C5 | −0.5 (4) | C17—C18—C23—C14 | 0.5 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C1 | 178.9 (3) | C19—C18—C23—C14 | −179.4 (3) |
| C6—C5—C10—C9 | 0.8 (4) | C17—C18—C23—C22 | −179.8 (3) |
| C4—C5—C10—C9 | −179.0 (3) | C19—C18—C23—C22 | 0.3 (5) |
| C6—C5—C10—C1 | −178.6 (3) | C21—C22—C23—C14 | 168.1 (4) |
| C4—C5—C10—C1 | 1.6 (4) | C21—C22—C23—C18 | −11.6 (6) |
| C2—C1—C10—C9 | −178.2 (3) | C1—C13—N1—C14 | 177.9 (3) |
| C13—C1—C10—C9 | 1.4 (4) | C15—C14—N1—C13 | −49.8 (4) |
| C2—C1—C10—C5 | 1.2 (4) | C23—C14—N1—C13 | 133.7 (3) |
| C13—C1—C10—C5 | −179.3 (3) | C1—C2—O1—C11 | −173.1 (3) |
| C2—C1—C13—N1 | 174.5 (3) | C3—C2—O1—C11 | 6.8 (4) |
| C10—C1—C13—N1 | −5.1 (5) | C12—C11—O1—C2 | 172.7 (3) |
| C23—C14—C15—C16 | −0.4 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C5–C10 and C14–C23 rings.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C11—H11B···Cg1i | 0.97 | 2.91 | 3.799 | 153 |
| C16—H16···Cg2i | 0.93 | 2.96 | 3.728 | 141 |
Symmetry code: (i) x, −y+3/2, z−1/2.
References
- Borah, R., Dutta, A. K., Sarma, P., Dutta, C. & Sarma, B. (2014). RSC Adv. 4, 10912–10917.
- Calligaris, M., Nardin, G. M. J. & Randaccio, C. (1972). Coord. Chem. Rev. 7, 385–403.
- Drawanz, B. B., Zimmer, G. C., Rodrigues, L. V., Nörnberg, A. B., Hörner, M., Frizzo, C. P. & Cunico, W. (2017). Synthesis, 49, 5167–5175.
- El-masry, A. H., Fahmy, H. H. & Ali Abdelwahed, S. (2000). Molecules, 5, 1429–1438.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gümüş, M. K., Kansız, S., Aydemir, E., Gorobets, N. Y. & Dege, N. (2018). J. Mol. Struct. 1168, 280–290.
- Hökelek, T., Bilge, S., Demiriz, Ş., Özgüç, B. & Kılıç, Z. (2004). Acta Cryst. C60, o803–o805. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kansiz, S., Almarhoon, Z. M. & Dege, N. (2018). Acta Cryst. E74, 217–220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lee, K., Poudel, Y. B., Glinkerman, C. M. & Boger, D. L. (2015). Tetrahedron, 71, 5897–5905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Moroz, Y. S., Demeshko, S., Haukka, M., Mokhir, A., Mitra, U., Stocker, M., Müller, P., Meyer, F. & Fritsky, I. O. (2012). Inorg. Chem. 51, 7445–7447. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sen, P., Kansiz, S., Dege, N., Iskenderov, T. S. & Yildiz, S. Z. (2018). Acta Cryst. E74, 994–997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Stoe & Cie (2002). X-AREA and X-RED32. Stoe & Cie GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany.
- Turner, M. J., MacKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). Crystal Explorer17.5. University of Western Australia, Perth.
- Wu, H., He, Y.-P. & Gong, L.-Z. (2013). Org. Lett. 15, 460–463. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018013117/xu5940sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018013117/xu5940Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018013117/xu5940Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1843572
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report