Abstract
Postpartum mammary gland involution is a tissue remodeling event that occurs in all mammals in the absence of nursing or after weaning to return the gland to the pre-pregnant state. The tissue microenvironment created by involution has proven to be tumor promotional. Here we report that the GPI-linked protein semaphorin 7a (SEMA7A) is expressed on mammary epithelial cells during involution and use preclinical models to demonstrate that tumors induced during involution express high levels of SEMA7A. Overexpression of SEMA7A promoted the presence of myeloid-derived podoplanin (PDPN)-expressing cells in the tumor microenvironment and during involution. SEMA7A drove the expression of PDPN in macrophages, which led to integrin- and PDPN-dependent motility and adherence to lymphatic endothelial cells to promote lymphangiogenesis. In support of this mechanism, mammary tissue from SEMA7A-knockout mice exhibited decreased myeloid-derived PDPN-expressing cells, PDPN-expressing endothelial cells, and lymphatic vessel density. Furthermore, co-expression of SEMA7A, PDPN, and macrophage marker CD68 predicted for decreased distant metastasis-free survival in a cohort of over 600 cases of breast cancer as well as in ovarian, lung, and gastric cancers. Together our results indicate that SEMA7A may orchestrate macrophage-mediated lymphatic vessel remodeling, which in turn drives metastasis in breast cancer
Keywords: Breast cancer, macrophage, lymphatic, involution, semaphorin 7a
Introduction:
Semaphorin 7a (SEMA7A), or CDw108, is an 80-kDa glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored membrane glycoprotein originally identified as preferentially expressed on activated T lymphocytes, erythrocytes, and in some leukemia cell lines(1). In addition, SEMA7A mRNA expression is observed in some adult tissues such as placenta, testis, lung, brain, thymus and spleen(1). Roles for SEMA7A have been identified in neuronal guidance and immune modulation(2–4). The SEMA7A protein can exist as a membrane bound or shed form after cleavage of the GPI membrane anchor; once shed SEMA7A, can act in both cell autonomous and non-autonomous manners. As such, SEMA7A has been shown to promote motility of melanocytes, neuronal and immune cells through its signaling via β−1 integrin (2, 3, 5). More recently, SEMA7A has been described as tumor promotional. Specifically, SEMA7A drives tumor progression via promotion of tumor growth, invasiveness, adhesion to tumor associated extracellular matrices, epithelial to mesenchymal transition, and metastasis in models of melanoma, glioblastoma, and oral and breast carcinoma(6–9). Additionally, tumor-derived SEMA7A can alter the breast tumor microenvironment by increasing the presence of macrophages with pro-angiogenic phenotypes and by increasing tumor-associated lymphatics(7, 8). Overall, data to date suggest that SEMA7A expression is sufficient to alter both tumor cell biology and the tumor microenvironment.
SEMA7A also has defined roles in tissue remodeling during fibrosis(4); in the mammary gland, postpartum breast/mammary gland involution is a fibrosis-like remodeling event that is essential for returning the mammary tissue to a pre-pregnant-like state after pregnancy and/or lactation in mammals. In the absence of proper coordination of postpartum involution, multiple rounds of lactation could not occur in mammals. While the majority of studies investigating postpartum mammary gland involution have occurred in rodents, recent confirmation in human tissues suggest that mechanisms of involution appear to be conserved amongst species (10–12). Postpartum mammary involution is characterized by epithelial cell apoptosis, immune cell infiltration, extracellular matrix (ECM) and vascular remodeling, and alterations to immune cell infiltrates into the tissue microenvironment(11, 13–20). Macrophages play an essential part in the involution program as demonstrated by data showing that macrophage ablation blocks the execution of weaning-induced mammary epithelial cell death in mice(11). We have identified that programs of lymphangiogenesis are activated during involution and that peak macrophage infiltration (involution day 3) precedes peak lymph vessel density (LVD) (involution day 6) in mouse mammary tissues during involution(11, 21). Roles for macrophages in lymphangiogenesis have been described previously(22–30). In addition, SEMA7A stimulates monocyte, neutrophil, and macrophage chemotaxis(7, 31, 32) as well as tumor associated lymphangiogenesis(8). Here, we have sought to investigate whether macrophages and SEMA7A cooperate to promote mammary lymphangiogenesis during involution as well as lymphangiogenesis in mouse mammary tumor models.
Our results show that SEMA7A is expressed in the mammary epithelium during postpartum involution and suggest that SEMA7A may be involved in macrophage-mediated lymphangiogenesis, or lymphatic mimicry by macrophages, during normal development and in breast cancer. Using pre-clinical models, we show that subsets of monocytes and macrophages express the lymphatic marker podoplanin (PDPN) in a SEMA7A dependent manner, that SEMA7A promotes macrophage motility, adherence to, and incorporation into lymphatic-like structures in vitro, and that PDPN-expressing macrophages isolated from mouse mammary glands during involution are sufficient to drive lymphangiogenesis. We also show that SEMA7A is significantly associated with decreased survival in lymph node-positive breast cancer patients. Additionally, we show that a gene signature comprised of SEMA7A, the macrophage marker CD68, and PDPN is associated with poor prognosis in breast, ovarian, lung and gastric cancer—indicating that this triad may predict for aggressive tumors in multiple tumor types. Together our results suggest that SEMA7A-dependent macrophage-driven lymphangiogenesis may be an important driver of breast tumor metastasis via the lymph vasculature. Furthermore, we identify a novel, developmentally-regulated mechanism of inflammation-induced lymphangiogenesis that may inform studies beyond those of mammary development and breast cancer.
Materials and Methods
Cell culture.
Authenticated 66cl4-luciferase cells were acquired from H. Ford (University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Denver, CO, USA). Authenticated E0771 cells were acquired from CH3 BioSystems (Amherst, NY, USA). Cells were cultured as previously described. 66cl4-luciferase and E0771 cells were transfected with plasmids containing DDK-tagged SEMA7A or a DDK empty vector control using X-tremeGENE transfection reagent (Sigma Aldrich, cat. #XTG9-RO). Transfected cells were selected using G418. Human dermal lymphatic endothelial cells (HDLECs) were purchased from PromoCell and cultured on plates coated with 10μg/ml Matrigel. All other HDLEC culturing was performed according to manufacturer’s instructions. J774 and RAW264.7 macrophages were obtained from the laboratory of Raphael Nemenoff and cultured as previously described(11). All cells were kept at low passage, tested for mycoplasma following thawing from liquid nitrogen using the Lonza MycoAlert detection kit, and allowed to grow for up to ten passages before new cells were thawed.
Animal studies.
All animal procedures were approved by the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Sema7atm1Alk/J mice (Jackson Laboratories), C57Bl/6, and BALB/c (Charles River Laboratories) were housed and bred as previously described(10). Briefly, Sema7atm1Alk/J (a generous gift from Alex Kolodkin at John’s Hopkins University) and C57Bl/6 female mice (age 6–8 weeks) were bred with BALB/c males and BALB/c female mice were bred with C57Bl/6 male mice. Age-matched nulliparous animals were set aside as controls. Mammary gland involution was initiated in the bred females by force-weaning pups at 10–14 days post-parturition. For normal involution studies, tissues were obtained from nulliparous and involution (Inv 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, and 28) mice. Rat tissues analyzed were from a previously described study(11). For the 66cl4 tumor studies, 200,000 66cl4-DDK or 66cl4-DDK SEMA7A-overexpressing cells were injected into the number 4 left and right mammary glands of BALB/c dams 1 day after forced weaning (involution group) or into age-matched nulliparous control females. For the E0771 tumor studies, 250,000 E0771-DDK or E0771-DDK SEMA7A-overexpressing cells were injected into the number 4 left and right mammary glands of C57Bl/6 dams 1 day after forced weaning (involution group) or into age-matched nulliparous control females. Tumor study mice were sacrificed based on primary tumor cell growth or ulceration at 3–4 weeks post injection (66cl4) or 2–3 weeks post injection (E0771). In vivo studies were performed in triplicate with representative or pooled data shown.
Matrigel plug assay.
To generate macrophages for the Matrigel plug assay, BALB/c mice were bred (described above) and mammary tissues harvested and digested to single cells (described below); macrophages were isolated by F4/80 magnetic bead selection. Equal numbers of mammary macrophages harvested from nulliparous and involution groups were mixed with phenol red free Matrigel (Corning # 356231) and injected 1:1 with 66cl4 tumor cells into intact mammary fat pads of nulliparous BALB/c mice. Eight days later the mammary gland with Matrigel plug intact was harvested and fixed in 10% NBF. Sections were obtained and analyzed for F480+LYVE-1+ structures by immunofluorescence.
Tumor cell clonogenic assay.
Lung and axillary lymph node metastases were analyzed by clonogenic assays as previously described(10). Briefly, axillary lymph nodes and lungs were harvested from 66cl4 tumor-containing mice (from above). Excised tissues were minced and digested with a final concentration of 500units/ml collagenase type II and IV and 20μg/ml DNase (Worthington Biochemical Corporation). Tissues were digested at 37°C for 90 minutes, washed, plated in complete media plus 6-thioguanine, and left to grow for 2 weeks when the plates were washed, stained with crystal violet, and colonies quantitated.
Immunohistochemistry.
Immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and quantitation for SEMA7A, CD68, PDPN, LYVE-1, and F4/80 was performed as previously described(8, 10, 11, 33).
Flow cytometry.
Cell populations from mammary glands and tumors were assessed using flow cytometry. Tissues and tumors were digested using 500units/ml collagenase type II and IV and 20μg/ml DNase and incubated at 37°C for 90 minutes prior to filtering through a 100μm filter. For the endothelial/epithelial panel, cells were stained with CD45 (BV510; Biolegend #103137), CD31 (Pacific Blue; Biolegend #102422), PDPN (APC; Biolegend #127410), CD49f (PerCP; Biolegend #313617), EpCAM (APC-Cy7; Biolegend #118218), and SEMA7A (FITC; Abcam #26012). For the macrophage panel, cells were stained with CD45 (BV510), CD11b (PerCP; Biolegend #101229), F4/80 (APC-Cy7; Biolegend #123117), CD64 (Pacific Blue; Biolegend #139309), MerTK (FITC; Biolegend #151503), and PDPN (APC). Cells were analyzed on a Beckman Coulter CyAn ADP© using Summit© software in the UCCC Flow Cytometry Core or the Tamburini Laboratory at the CU Anschutz Medical Campus. Data were analyzed using FlowJo analysis software.
Lymphangiogenesis.
In a 96-well plate, 4mg/ml matrigel pads, containing 5μg/ml recombinant SEMA7A (purified by the UCCC Tissue Culture Core) and/or 0.6μg/ml anti-β1-integrin (BD BioSciences, clone: 9EG7, #553715), pMAB (ThermoFischer #MA5–16270), and IgG (BD BioSciences, clone: R35–95, #553927) were allowed to solidify for 2 hours at 37°C prior to cell seeding. After 2 hours, 15,000 HDLECs and 15,000 macrophages [stained green with CellTracker (Invitrogen #C2925)] were seeded on the tops of the matrigel pads in 50% endothelial cell media and 50% experimental medias (containing identical compounds and concentrations as above). Macrophages used for experiments in matrigel plug assays were isolated from nulliparous and involution mammary glands using F4/80 magnetic bead separation. J774 and RAW264.7 macrophages used in other experiments were pretreated overnight with either 5μg/ml SEMA7A, 0.6ug/ml anti-β1-integrin, 0.6μg/ml pMAB, or 0.6μg/ml IgG. After cells were seeded on matrigel pads, images were taken 4 hours later using Zeiss Zen software, and the surface areas of tubule formations were calculated using ImageJ software. Experiments were replicated in triplicate with representative or pooled data shown.
Macrophage migration assay.
Macrophage migration was assessed using a transwell-filter migration assay. RAW264.7 macrophages were pretreated overnight with either 5μg/ml SEMA7A, 0.6μg/ml anti-β1-integrin, 0.6μg/ml pMAB, or 0.6μg/ml IgG. The following day, treated macrophages were seeded into a collagen-coated transwell filter in serum-free media placed into a well containing serum-free media+5μg/ml SEMA7A. After 4 hours, the media was removed and filters were fixed using 10% neutral-buffered formalin. Following fixation, filters were stained with crystal violet, images were taken using Zeiss Zen software, and stained surface area of migrating cells was calculated using ImageJ software. Experiments were replicated in triplicate with representative data shown.
Macrophage endothelial cell adhesion assay.
Ability of macrophages to adhere to endothelial cells was assessed using an endothelial cell adhesion assay. HDLECs were plated in a 24-well plate coated with 10μg/ml matrigel and allowed to form a monolayer overnight. At the same time, RAW264.7 macrophages were pretreated overnight with either 5μg/ml SEMA7A, 0.6μg/ml anti-β1-integrin, 0.6μg/ml pMAB, or 0.6μg/ml IgG. The following day, treated macrophages were harvested and stained using CellTracker and seeded on top of the HDLEC monolayer. After 4 hours, the media was removed, wells were washed 3x with 1X PBS, images were taken using Zeiss Zen software, and adherent cell area was calculated using ImageJ software. Experiments were replicated in triplicate with representative data shown.
Macrophage expression of podoplanin.
Macrophages were plated in 6-well plates with complete media +/− 5μg/ml SEMA7A and incubated at 37°C for 24, 48, or 72 hours. Cells were harvested and RNA was isolated using Zymo Quick RNA microprep kit (Zymo Research, cat. #R1050). cDNA was synthesized from 1,000ng RNA using the Bio-Rad cDNA Synthesis Kit and cDNA was amplified using primers for reference gene β-actin (Actb) (forward: TTGCTGACAGGATGCAGAAGGAGA, reverse: ACTCCTGCTTGCTGATCCACATCT) and Pdpn (forward:GGGACAGGATAGGGCAATAAG, reverse: GGAGAGATGGTTCAGTGGTTAG). qPCR was performed using Bio-Rad SYBR Green Supermix with the following conditions: 95°C for 3 minutes, 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 seconds, 60°C for 30 seconds, and 72°C for 30 seconds.
Human tissue acquisition.
Research using deidentified human breast tissue was conducted under a protocol deemed exempt from subject consent as approved by the Colorado Multiple Institution Review Board (COMIRB) and tissues were acquired by Virginia Borges as previously reported(46). Dr. Borges obtained written informed consent from the patients, the studies were conducted in accordance with recognized ethical guidelines (e.g., Declaration of Helsinki, CIOMS, Belmont Report, U.S. Common Rule), and the studies were approved by an institutional review board.
Human tissue data.
Analysis of SEMA7A expression in histologically normal tissues from breast biopsy or surgical specimens was performed by quantitative IHC, described below. All normal tissues examined were greater than 1mm from adjacent tumor and determined to be histologically normal.
Aperio Software Analysis for Quantification of IHC
Entire histological sections were imaged with Aperio ScanCope T3 scanner at 0.47 microns/pixel. The images were then down-sampled to a resolution of 1.5 microns per pixel to facilitate subsequent image manipulation. Areas for quantification were annotated using Aperio analysis tools and percent weak, medium, and strong was determined using the color-deconvolution tool. Percent positive was calculated as total medium + strong IHC positive signal divided by total stained area multiplied by 100. Lymphatic vessel density was quantitated as previously described(10).
Kaplan Meier Survival Statistics.
Survival statistics were performed using KmPlot analysis on cohorts of tissues. The Kaplan Meier plotter is capableof assessing the effect of 54,675 genes on survival using 10,461 cancer samples. These include 5,143 breast, 1,816 ovarian, 2,437 lung and 1,065 gastric cancer patients with a mean follow-up of 69 / 40 / 49 / 33 months.
Statistics.
Unpaired t-test and one-way ANOVA were performed in GraphPad Prism, assuming independent samples and normal distributions. Only P-values of less than 0.05 were considered significant.
Results:
Mammary macrophages and LEC marker expression.
Lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor (LYVE-1) is highly expressed on lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) and has been utilized as a marker for newly formed lymphatic vessels in mouse tissues(34, 35). Activated macrophages can express LYVE-1 in certain contexts(35, 36) and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) express LYVE-1(37, 38). To identify whether mammary macrophages express LYVE-1 and whether LYVE-1-expressing macrophages are associated with the lymphatic vasculature during involution, we performed dual immunofluorescence (IF) for LYVE-1 and F4/80—a marker of murine macrophages. We observe that LYVE-1+F4/80+ single cells are present in nulliparous tissues and that lymphatic-like structures express both LYVE-1+F4/80+ in mammary tissues at involution day 6 (Figure 1A), which is the peak of lymphatic vessel density (LVD) during involution(10). High resolution analysis and 3D re-construction of these structures revealed the presence of both F4/80 and LYVE-1expressing cells within the structure (Figure 1B). Quantification of these chimeric structures reveal significantly more of them in mouse mammary tissues during involution, with peak density at involution day 6, when compared to tissues from virgin or nulliparous mice (Figure 1C). We also provide immunohistochemical (IHC) evidence that single LYVE-1 positive cells are observed early during involution, prior to the increase in LVD, in both rat and mouse tissues (SFigure1A-D). Additionally, using a multicolor IHC stain for lymphatics (podoplanin, PDPN) and macrophages (CD68) in human breast tissues we observed structures composed of CD68+ and PDPN+ cells from women biopsied during involution (Figure 1D).
Figure 1: LYVE-1 expressing macrophages during involution.
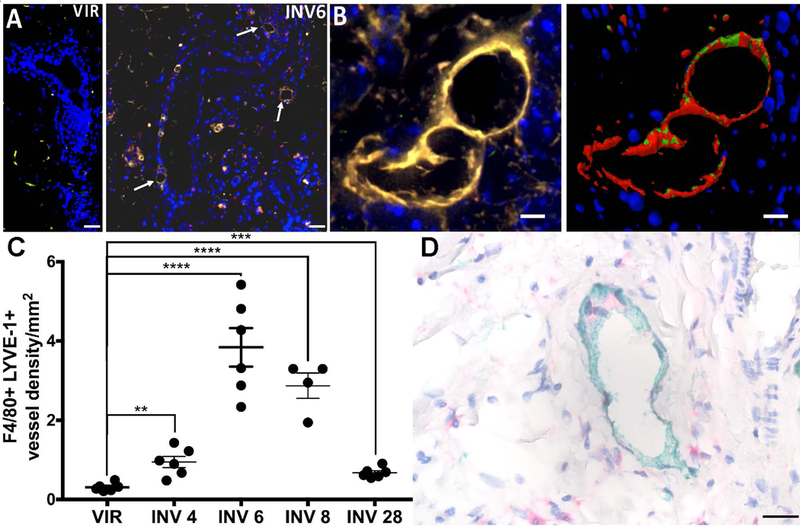
A) Vessel-like structures that stain positive for LYVE-1 (green) and F4/80 (red) are abundant during involution. B) Merged image and 3D reconstruction of a LYVE-1+F4/80+ vessel at involution day 6. C) Quantification of LYVE-1+F4/80+ vessel density in mouse mammary glands from virgin mice and mice at various stages of involution. D) Macrophage (CD68-pink) and lymphatic (PDPN-green) interaction in breast tissue biopsied from a women less than one year after pregnancy. Unpaired t-test: **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Arrows point to vessels that were quatntitated. Scale bars=50μm.
To further describe mammary macrophage-lymphatic characteristics during involution, we performed flow cytometry analysis on mouse mammary tissues harvested from nulliparous mice and mice at involution day 6. We used the general immune cell marker CD45, endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM-1, or CD31), epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), and PDPN. Consistent with our previous results, we observed increased LECs (CD45-EpCAM-CD31+PDPN+) at involution day 6 in comparison to nulliparous (Figure 2A). Also consistent with a previous report, we observed an increase in CD45+CD11b+ leukocytes during involution(17) (Figure 2B). We also observed a CD45+PDPN+ population of leukocytes during involution. (Figure 2C). To further characterize the CD45+ PDPN+ cells we examined F4/80, a widely used marker of murine macrophages; CD64, constitutively found on monocytes and macrophages; and MerTK, a macrophage apoptotic cell receptor found primarily on phagocytic macrophages (Figure 2D; gating strategy in SFigure2A). In the involution group, we detected a significant increase in CD45+CD11b+F4/80loCD64+ cells (Figure 2E), which we characterize as monocytes. We then identified macrophages through their co-expression of CD11b+F4/80hiCD64+MerTKhi to show that macrophages also increased in number during involution (Figure 2F). Importantly, the MerTKhi cells were also F4/80hi and we show that these cells exhibit increased expression of PDPN during involution (Figure 2G & H). Together, our results suggest that monocytes may be recruited into the mammary gland during involution and differentiated into PDPN-expressing macrophages. Consistent with this hypothesis, analysis of microarray data from whole mouse mammary glands harvested during the involution cycle reveals expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1, or CCL2)—which is involved in monocyte infiltration into tissues during inflammation—and its receptor (CCR2) during involution (SFigure2B&C)(14, 19). Finally, to determine whether mammary macrophages are primed for promotion of lymphangiogenesis, we isolated F4/80+ mammary macrophages from nulliparous and involution day 6 mouse mammary glands which were then co-cultured for 24h with human dermal lymphatic endothelial cells (HDLECs) in tube formation assays. Increased tubule area was observed when the LECs were cultured with involution-derived macrophages in comparison to the LECs cultured with nulliparous-derived macrophages (Figure 2I & J).
Figure 2: Podoplanin expression on macrophages drives lymphangiogenesis.
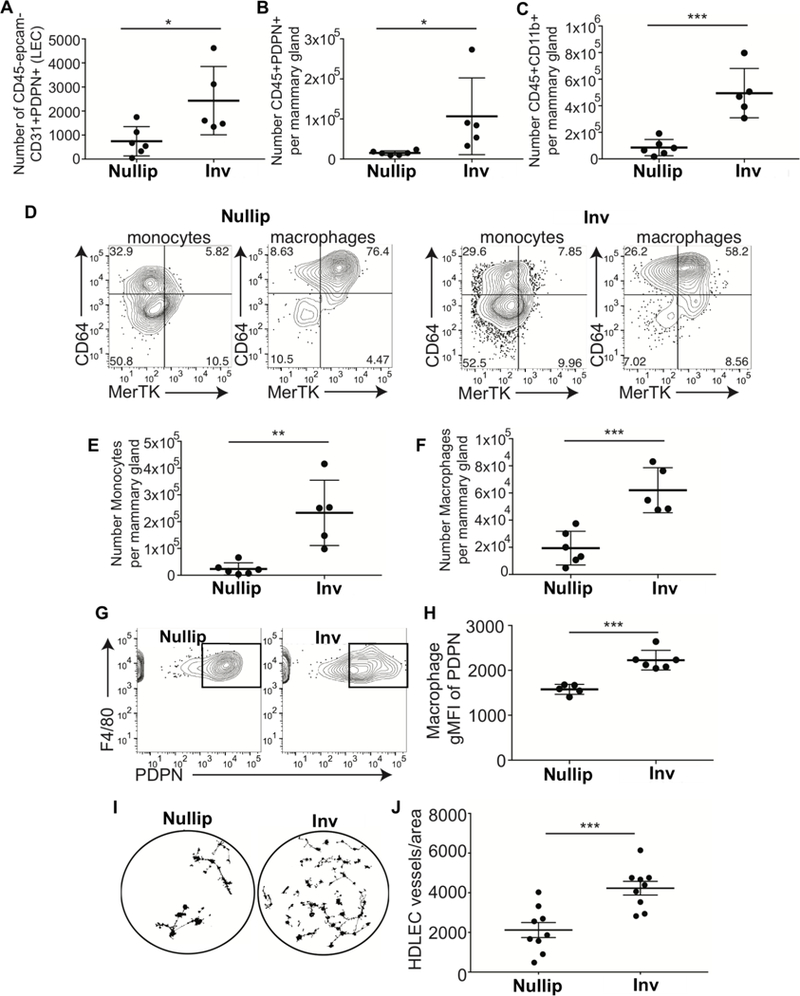
Flow cytometry analysis of cells isolated from nulliparous or involution day 6 mouse mammary tissues reveals A) increased lymphatic endothelial cells, B) PDPN+ leukocytes, C) PDPN+ myeloid cells, D-F) monocytes and macrophages, as well as G&H) PDPN-expressing F4/80+ macrophages. I&J) F4/80+ macrophages isolated from nulliparous and involution day 6 mouse mammary glands enhance in vitro lymphangiogenesis. Unpaired t-test: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
Semaphorin 7a promotes pro-lymphatic macrophages in the tumor microenvironment
We have shown that implantation of mouse mammary tumor cells during involution results in tumors with increased lymph vessel density in the tumor microenvironment. Therefore, we hypothesized that involution-derived macrophages, which express more PDPN, may integrate into or recruit tumor-associated lymphatic vessels more robustly than nulliparous-derived macrophages, which do not express PDPN. To test our hypothesis, F4/80+ macrophages harvested from involution day 6 mouse mammary glands, or nulliparous controls, were mixed 1:1 with 66cl4 mouse mammary tumor cells, incorporated into a matrigel plug, and injected orthotopically into BALB/c mice. Plugs were harvested and dual IF revealed a significant increase in F4/80+LYVE+ staining associated with the matrigel plug that contained the involution-derived macrophages (Figure 3A). To determine whether SEMA7A contributes to tumor associated macrophage-mediated lymphangiogenesis, we engineered 66cl4 mouse mammary tumor cells to overexpress SEMA7A (SFigure 3A) and orthotopically injected them, along with empty vector controls, into nulliparous BALB/c mice. We also injected the empty vector control cell line into mice on involution day 1 to determine whether the involution microenvironment would be sufficient to support increased tumor-associated F4/80+PDPN+ cells. Consistent with our previously published results, SEMA7A and involution group tumors grew faster than the controls in nulliparous hosts (8, 10, 33) (Figure 3B). Interestingly, vector control cells injected at involution day 1 acquired SEMA7A-expression levels similar to those observed in the cells engineered to overexpress SEMA7A (Figure 3C). Flow cytometry analysis revealed that SEMA7A-overexpressing tumors and involution group tumors had increased CD45+F4/80+ and CD45+F4/80+PDPN+ cells (Figure 3D). We validated our flow analysis by showing increased F480+ cells in the tumor and LYVE-1+ vessels in the tumor microenvironment by IHC (Figure 3E & F). In an additional model, E0771 and E0771 SEMA7A cells were injected into C57BL/6 hosts. We utilized the E0771 cells for these additional studies to not only validate our results from the 66cl4 model, but to validate our results in a cell line that does not express detectable levels of SEMA7A by immunoblot, while the 66cl4 cells do (SFigure 3A). Consistent with this observation, baseline levels of both CD45+F480+PDPN+ cells and lymph vessel density (LYVE-1/mm2) are significantly reduced in the control E0771 cells compared to the 66cl4 controls (SFigure 3B&C). In the E0771 cell line, overexpression of SEMA7A was sufficient to drive increased tumor-associated CD45+F4/80+PDPN+ cells (Figure 3G), which also express MerTK (SFigure3D). Additionally, we observed increased LVD with OE of SEMA7A, which was lost in SEMA7A knockout (SEMA7A−/−) mice suggesting cooperation between host and tumor is necessary for the increased tumor associated LVD by SEMA7A (Figure 3H). Together, our results suggest that tumor-derived and host-derived SEMA7A can promote tumor-associated CD45+F4/80+PDPN+ cells and lymphatic vessels in the tumor microenvironment.
Figure 3: Semaphorin 7a promotes tumor-associated macrophages and lymphangiogenesis.
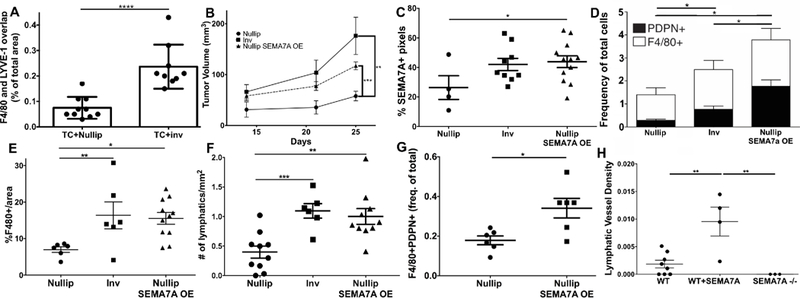
A) In an in vivo matrigel plug assay, 66cl4 tumor cells were mixed with macrophages isolated from nulliparous or recently weaned mice (at involution day 6). The resulting plugs were harvested and F4/80/LYVE-1 co-staining quantitated. B) Growth of 66cl4 cells engineered to overexpress SEMA7A compared to empty vector controls injected into nulliparous and involution day 1 mouse mammary tissues. C) SEMA7A expression by IHC in tumors from B. D) CD45+CD31-F4/80+PDPN+ cells in tumors from B. E) %F4/80+ cells and F) # LYVE-1+ vessel density in tumors from B. G) F4/80+PDPN+ cells in E0771 SEMA7A tumors in nulliparous mice. H) LYVE-1+ density in tumors from G with the addition of tumors from SEMA7A−/− hosts injected with E0771 cells. Unpaired t-test: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
SEMA7A and PDPN+ cell populations during postpartum mammary involution
To determine whether SEMA7A may play a role in recruiting and/or differentiating macrophages during involution, we first examined whether SEMA7A is expressed in the mouse mammary epithelium. We observed that SEMA7A expressing cells are rare in nulliparous mammary glands, but that ~8–15% of the epithelial (EpCAM+) cells at involution day 6 exhibit expression of SEMA7A (Figure 4A). To determine whether SEMA7A directly supports the presence of PDPN+ cell populations during mouse mammary gland involution, we examined cell populations isolated from involution day 6 mouse mammary tissues from transgenic mice that lack SEMA7A expression (Sema7atm1Alk/J)(2). We observed a significant reduction in LECs at involution day 6 in SEMA7A KO mice compared to wild-type C57BL/6 controls (Figure 4B). We also observed decreased PDPN+ leukocytes, monocytes, and macrophages (Figure 4C-F). These results suggest a role for SEMA7A in the influx and/or promotion of PDPN expression on monocytes and macrophages during involution. Interestingly, we also observed the presence of CD45+CD31+PDPN+ cells at involution day 6, which was not influenced by SEMA7A status (SFigure4A). Using IHC to identify lymphatics by LYVE-1 and macrophages by F4/80, we examined the relationship between lymphatics and macrophages in WT and KO mice at involution day 6 (Figure 4G). As expected, and consistent with our previous results, the lymphatics were tightly associated with the mammary epithelium and abundant in the WT mice (panel a). Additionally, the macrophages were frequently found near or associated with the lymphatics (panels b & c) and a lymphatic/macrophage network was evident in the lymph node. In contrast, lymphatic vessels were far less abundant in the KO and frequently found near the blood vessels, not the mammary epithelium (panel e). Furthermore, the lymphatic vessels that were present displayed altered morphology and there were fewer macrophages associated with them (panel f & g). Finally, the lymphatic/macrophage organization observed in the lymph node appears to be altered in the KO (panel h). Thus, we suggest a mechanism by which SEMA7A mediates macrophage-LEC and LEC-LEC connection to form lymphatic vessels during mammary gland involution and in the TME.
Figure 4: Semaphorin 7a promotes macrophage-mediated lymphatic mimicry.
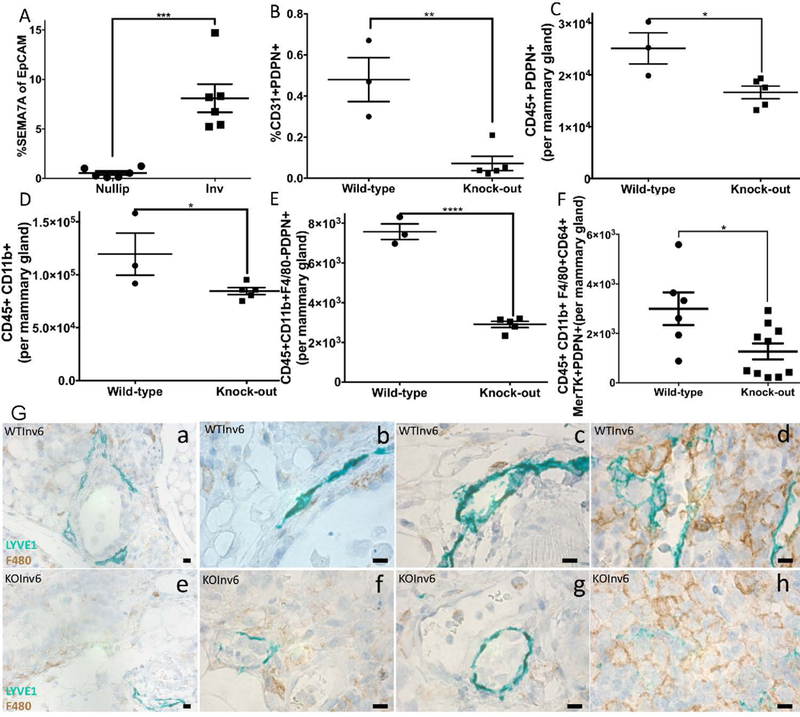
A) SEMA7A is expressed on EpCAM+ cells at involution day 6. In mammary glands from SEMA7A−/− mice we observe decreased B) LECs, C) PDPN+ immune cells, D) monocytes, and E&F) monocytes and macrophages expressing PDPN. G) LYVE-1 (green) and F4/80 (brown) IHC on involution day 6 mouse mammary glands from WT (top) and SEMA7A−/− (KO—bottom). Inset, a-c and e-g are mammary gland and d and h are lymph node. Unpaired t-test: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Scale bars=50μm.
Semaphorin 7a promotes macrophage PDPN expression, motility, and adhesion to lymphatics
To determine whether SEMA7A directly promotes PDPN expression in macrophages, we treated cultured murine macrophages with recombinant SEMA7A and observed increased expression of Pdpn mRNA after 72 hours (Figure 5A). Conversely, we show that SEMA7A is not a driver of CD68 in cultured HDLECs (SFigure 4B). To determine whether SEMA7A can also promote motility of macrophages and incorporation into the lymphatic endothelium, we examined macrophage motility by transwell filter assay and adhesion to HDLEC monolayers with and without purified SEMA7A. We observed increased motility and adherence in the SEMA7A-treated conditions (Figure 5B&C). Next, we tested whether SEMA7A could promote 3D in vitro lymphangiogenesis with 1:1 LEC-macrophage co-cultures. Similar to our results with involution macrophages (Figure 2I), we observed that the lymphatic structures formed in vitro are larger and that macrophages associate/incorporate with the lymphatic structures more frequently with SEMA7A (Figure 5D & E; SFigure 4C). We did not see the same extensive vessel networks with the same number of LECs +SEMA7A as we did with the co-culture, suggesting that macrophages are doing more than just increasing the cell number in the assay (SFigure 4D). Since SEMA7A promotes motility of other cell types via β−1 integrin, and PDPN can also promote cell motiliy, we tested whether SEMA7A promotes macrophage motility in an integrin- and/or PDPN-dependent manner. We utilized function blocking antibodies against β−1 integrin and PDPN, 9EG7 or pMAB, respectively, in our transwell migration assay, adhesion assay, and 3D-lymphangiogenesis assay. Macrophage motility was most significantly blocked by 9EG7, and, only a slight decrease in motility was observed with pMAB (Figure 5F). In contrast, we also observed the most significantly disrupted adhesion with pMAB (Figure 5G) and overall incorporation into 3D structures was significantly disrupted in the presence of 9EG7 and/or pMAB (Figure 5H). Together, our results suggest that SEMA7A may stimulate mammary macrophage expression of PDPN, migration, and adhesion to the lymphatic endothelium to aid in neo-lymphatic formation during postpartum mammary gland involution and tumorigenesis.
Figure 5: Semaphorin 7a drives PDPN expression, macrophage motility, and adherence to endothelial cell monolayers.
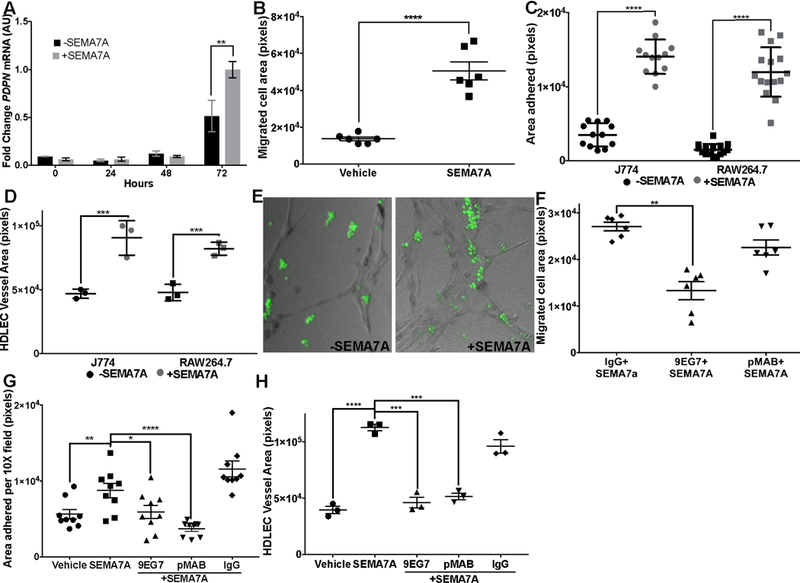
SEMA7A promotes macrophage A) expression of PDPN, B) migration and C) adherence to endothelial cell monolayers in 2D, and D&E) inclusion in vessel like structures in 3D. Induction of F) motility and G) adherence to LEC monolyaers in 2D is inhibited by blocking β−1 integrin (motility and adherence) and PDPN (adherence). H) Macrophage incorporation into 3D LEC vessel-like structures is inhibited by function blocking antibodies against β−1 integrin (9EG7) and PDPN (pMAB). Unpaired t-test: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
Involution lymphatics promote breast cancer metastasis
We have proposed that lymphatics observed in the mammary tissue during postpartum involution could facilitate early tumor cell dissemination in postpartum women. To test whether mouse mammary tumor cell lines transit via the lymphatics during active involution, we injected 66cl4 tumor cells into intact mammary glands at involution day 1, or into nulliparous controls, and examined both the primary tumor site (the mammary tissue) for lymphatic vessels, and distant (axillary) lymph nodes at involution days 4 and 6 for micrometastasis. We first confirmed increased LYVE-1+ vessels at days 4 and 6 of involution at the primary site (Figure 6A & B). Strikingly, the number of micrometastases in the axillary lymph nodes, harvested at days 4 and 6 of involution, is significantly increased at this early time point (Figure 6C). Together, these results suggest that involution lymphatics can support tumor cell transit via the lymphatic vasculature to result in early dissemination of postpartum tumors. Consistent with this result, we have previously published that normal breast tissue from women <1 year postpartum exhibits increased LVD and that breast cancer patients diagnosed <2 years of recent childbirth have increased lymph node involvement(10). We have also shown that macrophage infiltration, measured by CD68 expression, is increased in breast tissue during postpartum involution(11). Here we extend our observations to reveal that normal epithelium in breast tissue from women <5 years out from most recent pregnancy exhibits increased expression, on average, of SEMA7A compared to tissue from women who have never been pregnant (Figure 6D). We have also provided histological evidence that PDPN and CD68 co-occur in a patient that was diagnosed within 1 year postpartum, who was also positive for lymphatic vessel invasion (LVI) and LN involvement. We observe clusters of SEMA7A+ tumor cell emboli within lymphatics in the same patient, providing indirect evidence that macrophages, lymphatics, and SEMA7A may contribute to dissemination of tumor cells in postpartum women (Figure 6E).
Figure 6: Lymphatic trafficking of tumor cells is driven by involution and Semaphorin 7a.
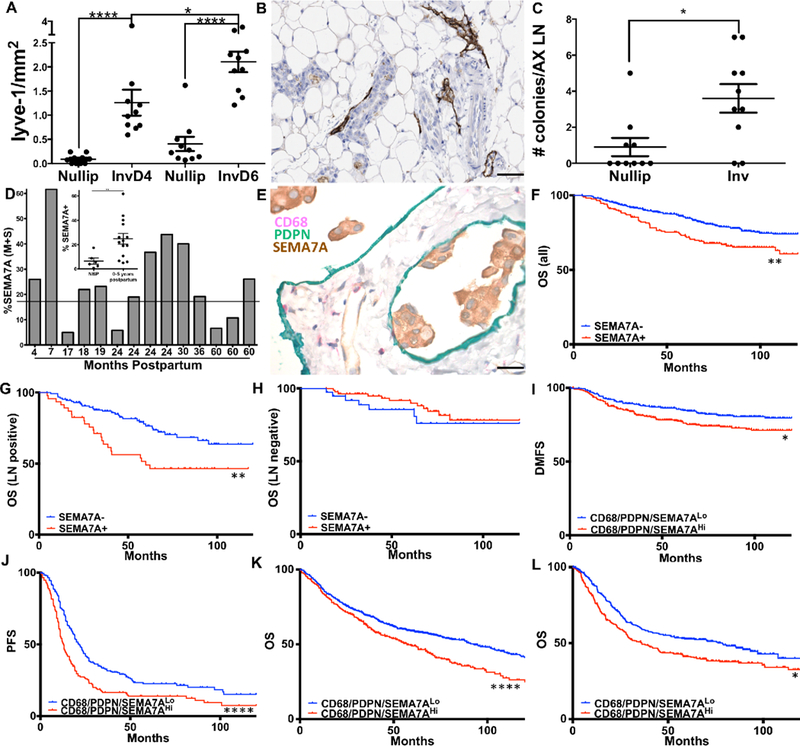
A) LVD in mouse mammary tissues injected with tumor cells at involution day 1 compared to those injected into nulliparous hosts. B) Representative image of lymphatics at involution day 6. C) Clonogenic assay reveals presence of micrometastasis/axillary lymph node during active involution. D) Quantitative IHC for SEMA7A expression in normal mammary tissue from never-been-pregnant women or women within 5 years of most recent childbirth. E) CD68, PDPN, and SEMA7A in a patient diagnosed within 1 year postpartum, who was also posititve for LVI and LN involvement. Overall survival analysis using KmPlot for F) all (n=626), G) LN negative (n=122), and H) LN positive (n=177) patients. I) Distant-metastatsis-free survival for patients co-expressing SEMA7A, PDPN, and CD68. J) Progression-free survival in ovarian cancer, K&L) overall survival in lung and gastric cancer. Unpaired t-test: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Scale bars=50μm.
We have previously shown that SEMA7A expression is associated with a significant decrease in overall survival (OS) for breast cancer patients using the METABRIC dataset. A prediction of the results presented herein is that SEMA7A drives metastasis via the lymphatic system and thus, would be associated with decreased OS in patients who are lymph node (LN) positive. In confirmation of our previous results, analysis of the KmPlot dataset revealed a significant decrease in OS from breast cancer with expression of SEMA7A (n=664, HR=1.7, 95% CI: 1.22–2.36, p=0.0014), which was greater when the analysis was restricted to LN-positive patients (n=177, HR=2.19, CI:1.28–3.75, p=0.0032) and lost when only LN-negative patients were examined (n=122, HR=0.65, 95% CI: 0.26–1.66, p=0.37, n=122) (Figure 6 F-H). Interestingly, our data also predicted that SEMA7A expression would associate with increased metastasis, yet SEMA7A alone did not associate with decreased distant metastasis free survival (DMFS) in the KmPlot analysis (SFigure 4). To determine whether co-expression of SEMA7A, PDPN, and CD68 increased the probability of distant metastasis we examined DMFS in KmPlot; we observe that high levels of SEMA7A, PDPN, and CD68 together, but not any one alone (SFigure 5), result in a significant reduction in 10-year distant metastasis free survival rates (HR = 1.74 (1.21 − 2.49);P = 0.0025)(Figure 6I). The results of our analysis suggest SEMA7A is a potent driver of LN-positive disease and that co-expression of SEMA7A, PDPN, and CD68 predicts for metastasis in breast cancer patients. Additionally, we looked for co-occurrence of SEMA7A, PDPN, and CD68 in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) (Table 1) and observed significant co-occurrence between PDPN, CD68, and SEMA7A in breast cancer (Table 1). Finally, our gene triad appears to be associated with poor prognosis in additional epithelial-derived tumor types, where lymphangiogenesis at the primary site has been shown to be important for distant metastasis, including ovarian, lung, and gastric(39–41) (Figure 6 J-L). Cumulatively, our results suggest that SEMA7A, lymphatics, and macrophages cooperate to promote metastasis in breast cancer patients as well as in other cancer types where lymphangiogenesis occurs.
Table 1:
Analysis of TCGA-RNASeq data for co-occurrence of PDPN, CD68, and SEMA7A
| TCGA-RNASeq Co-occurance | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| PDPN | CD68 | SEMA7A | |
| PDPN | OR: >3, p<0.001 | OR: >3, p<0.001 | |
| CD68 | OR: >3, p=0.006 | ||
Discussion:
Previously, our lab identified SEMA7A as low/not expressed in normal breast tissue via mRNA analysis of human breast tissues in publicly available datasets. We also observed that SEMA7A was increased in human breast tumor samples and associated with decreased overall survival in breast cancer patients. We attributed the role of SEMA7A in decreasing patient survival to our observed decreases in tumor growth, invasion, and lymphangiogenesis that were revealed by our pre-clinical studies where we silenced SEMA7A in human breast tumor xenografts. Here, we identify a role for SEMA7A in modulation of normal mammary tissue lymphangiogenesis and the TME, using immunecompetent murine models whereby SEMA7A expression promotes macrophages to a lymphatic promoting phenotype. In addition, we observe that macrophages, SEMA7A, and lymphatic markers co-occur in patient samples where co-expression also significantly predicts for poor prognosis, suggesting these mechanisms are at play in breast cancer patients.
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are known to promote tumor lymphangiogenesis through both paracrine and cell autonomous modes(25–30). Specifically, TAMs can express pro-lymphangiogenic factors that can signal to the pre-existing lymphatic vessels and/or tumors and have been shown to mobilize what have been called “monocyte-derived lymphatic endothelial cell progenitors (MLECP)” which are LYVE-1 positive and integrate into lymphatic vessels prior to sprouting(29). While lymphatic marker expression on TAMS and activated macrophages has been reported (25–30, 35, 42), it has not been investigated in the normal adult mammary gland. Since alternatively-activated macrophages make up the majority of the macrophages in the adult mammary gland during postpartum involution (11, 17), we suspected that these “involution macrophages” may be like the MLECPs observed in tumors and/or capable of “lymphatic mimicry”. Our results indicate that involution macrophages are driven, in part, by mammary epithelial-cell expression of SEMA7A, that involution macrophages express lymphatic marker PDPN in a SEMA7A-dependent manner, and that involution macrophages associate with lymphatic vessels during involution. Whether these cells are actually endothelial cell progenitors is not addressed by our current studies and will be addressed by future studies that involve lineage tracing.
We do reveal that the PDPN-expressing macrophages likely participate in lymphangiogenesis by moving toward lymphatic structures and by adhering to lymphatic endothelial cells. We also show that in vitro lymphatic network formation is dependent on both PDPN-CLEC-2 interaction and a known receptor for SEMA7A, namely β−1 integrin. Inhibition of β−1 integrin, using an antibody that inhibits ligand binding, primarily blocked transwell migration of macrophages in response to SEMA7A, suggesting that the SEMA7A-β−1 integrin interaction functions to stimulate macrophage migration during involution. Conversely, the dominant effect of our PDPN inhibition strategy, which utilized an antibody that blocks the interaction of PDPN with its receptor CLEC-2, was on adhesion of SEMA7A treated macrophages to endothelial cell monolayers suggesting that this ligand receptor interaction is required for macrophage adherence to lymphatics. Cumulatively, our results suggest a mechanism by which SEMA7A promotes mammary macrophage migration through activation of β−1 integrin and adhesion through promoting the association between PDPN and CLEC-2. This mechanism is consistent with results from the literature where β−1 integrin is known to be expressed on monocyte-derived cells and to promote monocyte recruitment and activation. We predict that once the monocytes have been recruited from the bone marrow to the mammary gland they become differentiated into activated macrophages. Then, under continued exposure to the SEMA7A produced by the mammary epthelium, they express PDPN and adhere to existing lymphatic vessels to result in lymphatic expansion, which is facilitated through PDPN-CLEC-2 interaction. This observation is also supported by the literature whereby PDPN-CLEC-2 interaction has been shown to be important for platelet adhesion to lymphatic endothelium(43). Additionally, both PDPN-CLEC-2 and SEMA7A-β−1 integrin downstream signaling pathwyas lead to activation of pro-proliferative and pro-survival pathways, including Src and PI3K, thus, these interactions could result in proliferation and survival of the mammary macrophages and/or the lymphatic endothelial cells. Published data also suggest that PDPN mediates differentiation of keratinocytes by down regulation of β−1 integrin (44), suggesting there might be cross-talk between the two pathways. Additional studies are necessary to determine the stability of the interaction between PDPN-expressing macrophages and LECs, and the downstream pathways that are activated and/or deactivated, in order to conclude whether the effects of the interaction are transient or long lasting. Our results showing peak LVD during mid-involution, followed by regression, suggest that this mechanism may only prove true during transient lymphatic remodeling, which favors lymphatic mimicry rather than transdifferentiation. Finally, our studies provide the framework for a role for SEMA7A in monocyte influx into the mammary gland, which is suggestive of non-tissue-resident macrophages. Future studies will determine whether involution macrophages are derived from resident-tissue macrophages or from mobilization and differentiation of peripheral monocytes.
Our studies also identify, for the first time, that SEMA7A is expressed on the normal mammary epithelium in women within 5 years of recent pregnancy and during the tissue remodeling phase of postpartum mammary involution in rodents. These observations are consistent with our results showing that lymphatic vessel density increases during normal involiuton in rodents and in normal breast tissue in women after lactation and remains elevated for up to six years later(10). Other studies have similarly suggested that inflammation and angiogenesis associated gene expression changes are observed in tissue from parous women, compared to nulliparous, and some of these changes persist in the breast tissue up to ten years after pregnancy(45). Furthermore, our own studies indicate that tumor cell expression of SEMA7A can be driven by exposure to the involution microenvironment (Figure 4A). These results suggest that tumors in women whose breast tissue has recently undergone involution may be “imprinted” upon by mechanisms that are activated during involution. Consistent with this hypothesis we have shown that human and murine tumor cells implanted during postpartum involution in rodents obtain (and retain, after involution is complete) multiple pro-tumorigenic attributes such as increased growth, invasion, expression of pro-inflammatory molecules, induction of lymphangiogenesis, and ability to seed metastatic sites (8, 10, 33). These models of postpartum breast cancer have provided us with mechanistic insight into why postpartum breast cancers, diagnosed within 5 years of recent pregnancy, are ~3 times more likely to develop metastasis when compared to never been pregnant patients with similar clinical characteristics, such as age and stage(46). Based on our data presented herein showing that SEMA7A is increased during involution, we are investigating whether SEMA7A is a primary driver of postpartum breast cancer aggressiveness in our University of Colorado Young Women’s cohort (46). Interestingly, a recent in silico analysis revealed two involution gene signatures that were significantly upregulated in inflammatory breast cancer (IBC)(47). IBC is a highly aggressive type of breast cancer that is characterized by tumor emboli in dermal lymphatics, which is reminiscent of what we have observed in mammary lymphatics of our postpartum patients(10)(Figure 6E). Importantly, when we mined the publicly available data, we identified that expression of SEMA7A was observed in one of the two signatures that are associated with IBC. Given the multiple similarities between IBC and involution—including macrophages, lymphatics, and the pro-inflammatory enzyme COX-2 (8, 10, 11, 33, 48)—it is possible that SEMA7A plays a significant role in the unique biology of both inflammatory and postpartum breast cancers.
Our analysis of additional cancer types also suggests that SEMA7A may play a general role in tumor metastasis and should therefore be investigated as a novel target for cancer therapeutics. Furthermore, our data showing that SEMA7A is a significant driver of decreased overall survival for LN+ patients suggest that SEMA7A primarily drives distant metastasis via the lymphatic vasculature, which is supported by our pre-clinical data that SEMA7A drives lymphangiogenesis. Two recent papers in Science identify a blood-lymphatic hybrid route for metastatic spread in pre-clinical models of melanoma and breast cancer(49, 50). Since SEMA7A has been shown to affect both angio- and lymphangiogenesis, it is possible that SEMA7A facilitates this hybrid route of metastasis and should be targeted to prevent metastasis. Given that SEMA7A expression is low in most adult tissues, targeting SEMA7A could have minimal toxicities. Furthermore, it is possible that SEMA7A could be a biomarker for patients who are at high risk for metastasis, and therefore should receive more aggressive therapy; since SEMA7A can be shed into the tumor microenvironment, it is also possible that SEMA7A could be detected in the blood. In summary, SEMA7A may be a promising target and biomarker for metastatic cancer.
Supplementary Material
Statement of Signficance:
SEMA7A, which is expressed on mammary cells during glandular involution, alters macrophage biology and lymphangiogenesis to drive breast cancer metastasis.
Acknowlegements:
Financial Support: Cancer League of Colorado AWD#173586-TL (T.Lyons, B.Tamburini, A. Elder), Colorado Clinical Translational Sciences Institute KL2TR001080 (T.Lyons, S. Black, A. Elder), Amercian Cancer Society RSG-16–171-010CSM (T.Lyons, A.Elder, L.Crump, V. Wessells ), National Cancer Institute R01 CA211696–01A1 (T.Lyons, A.Elder, L.Crump, V. Wessells),R21CA185226–01 (T.Lyons, S.Black, V. Wessells), AACR-BCRF 09–06-26 (V.Borges, P.Schedin, V.Wessells), NIH1R01CA169175–01 (V.Borges, P.Schedin, T.Lyons, A.Elder, and V.Wessells), and Grohne Family Foundation Grant (V.Borges, P.Schedin, T.Lyons). Imaging experiments performed in the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus Advance Light Microscopy Core, L.Crump, and T.Lyons were supported in part by NIH/NCATS Colorado CTSI Grant TR001082 and RR025780. Tissue Bio banking occurred in the Shared Resource of Colorado’s NIH/NCI Cancer Center Support Grant P30CA046934. Contents are the authors’ sole responsibility and do not necessarily represent official NIH views.The authors would also like to thank the following persons for all of their help in the production of this manuscript: Holly Martinson, Justin Pruitt, Charlene Tilton, Cera Neito, Kim Jordan, Michelle Borakove, Jeffrey Finlon, Gavin Ryan, Peter Hensen, , and the UC Cohort Patients.
Financial Support:
Cancer League of Colorado AWD#173586-TL, Colorado Clinical Translational Sciences Institute KL2TR001080, Amercian Cancer Society RSG-16–171-010CSM, National Cancer Institute R01 CA211696–01A1 and R21CA185226–01, AACR-BCRF 09–06-26, NIH1R01CA169175–01, and Grohne Family Foundation Grant, NIH/NCATS Colorado CTSI Grant TR001082 and RR025780, NCI Cancer Center Support Grant P30CA046934.
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest:
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References:
- 1.Yamada A, Kubo K, Takeshita T, Harashima N, Kawano K, Mine T et al. : Molecular cloning of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored molecule CDw108. Journal of immunology 1999, 162(7):4094–4100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pasterkamp RJ, Peschon JJ, Spriggs MK, Kolodkin AL: Semaphorin 7A promotes axon outgrowth through integrins and MAPKs. Nature 2003, 424(6947):398–405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Suzuki K, Okuno T, Yamamoto M, Pasterkamp RJ, Takegahara N, Takamatsu H et al. : Semaphorin 7A initiates T-cell-mediated inflammatory responses through alpha1beta1 integrin. Nature 2007, 446(7136):680–684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Reilkoff RA, Peng H, Murray LA, Peng X, Russell T, Montgomery R et al. : Semaphorin 7a+ regulatory T cells are associated with progressive idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and are implicated in transforming growth factor-beta1-induced pulmonary fibrosis. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 2013, 187(2):180–188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Scott GA, McClelland LA, Fricke AF: Semaphorin 7a promotes spreading and dendricity in human melanocytes through beta1-integrins. The Journal of investigative dermatology 2008, 128(1):151–161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ma B, Herzog EL, Lee CG, Peng X, Lee CM, Chen X et al. : Role of chitinase 3-like-1 and semaphorin 7a in pulmonary melanoma metastasis. Cancer research 2015, 75(3):487–496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Garcia-Areas R, Libreros S, Amat S, Keating P, Carrio R, Robinson P et al. : Semaphorin7A promotes tumor growth and exerts a pro-angiogenic effect in macrophages of mammary tumor-bearing mice. Frontiers in physiology 2014, 5:17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Black SA, Nelson AC, Gurule NJ, Futscher BW, Lyons TR: Semaphorin 7a exerts pleiotropic effects to promote breast tumor progression. Oncogene 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Allegra M, Zaragkoulias A, Vorgia E, Ioannou M, Litos G, Beug H et al. : Semaphorin-7a reverses the ERF-induced inhibition of EMT in Ras-dependent mouse mammary epithelial cells. Molecular biology of the cell 2012, 23(19):3873–3881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lyons TR, Borges VF, Betts CB, Guo Q, Kapoor P, Martinson HA et al. : Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent lymphangiogenesis promotes nodal metastasis of postpartum breast cancer. The Journal of clinical investigation 2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.O’Brien J, Lyons T, Monks J, Lucia MS, Wilson RS, Hines L et al. : Alternatively activated macrophages and collagen remodeling characterize the postpartum involuting mammary gland across species. The American journal of pathology 2010, 176(3):1241–1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jindal S, Gao D, Bell P, Albrektsen G, Edgerton SM, Ambrosone CB et al. : Postpartum breast involution reveals regression of secretory lobules mediated by tissue-remodeling. Breast cancer research : BCR 2014, 16(2):R31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Atabai K, Sheppard D, Werb Z: Roles of the innate immune system in mammary gland remodeling during involution. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2007, 12(1):37–45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Clarkson RW, Wayland MT, Lee J, Freeman T, Watson CJ: Gene expression profiling of mammary gland development reveals putative roles for death receptors and immune mediators in post-lactational regression. Breast cancer research : BCR 2004, 6(2):R92–109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li M, Liu X, Robinson G, Bar-Peled U, Wagner KU, Young WS et al. : Mammary-derived signals activate programmed cell death during the first stage of mammary gland involution. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1997, 94(7):3425–3430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lund LR, Romer J, Thomasset N, Solberg H, Pyke C, Bissell MJ et al. : Two distinct phases of apoptosis in mammary gland involution: proteinase-independent and -dependent pathways. Development 1996, 122(1):181–193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Martinson HA, Jindal S, Durand-Rougely C, Borges VF, Schedin P: Wound healing-like immune program facilitates postpartum mammary gland involution and tumor progression. International journal of cancer Journal international du cancer 2015, 136(8):1803–1813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ramirez RA, Lee A, Schedin P, Russell JS, Masso-Welch PA: Alterations in mast cell frequency and relationship to angiogenesis in the rat mammary gland during windows of physiologic tissue remodeling. Dev Dyn 2012, 241(5):890–900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Stein T, Morris JS, Davies CR, Weber-Hall SJ, Duffy MA, Heath VJ et al. : Involution of the mouse mammary gland is associated with an immune cascade and an acute-phase response, involving LBP, CD14 and STAT3. Breast cancer research : BCR 2004, 6(2):R75–91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Strange R, Li F, Saurer S, Burkhardt A, Friis RR: Apoptotic cell death and tissue remodelling during mouse mammary gland involution. Development 1992, 115(1):49–58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Borges VF, Elder AM, Lyons TR: Deciphering Pro-Lymphangiogenic Programs during Mammary Involution and Postpartum Breast Cancer. Front Oncol 2016, 6:227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Becker F, Kurmaeva E, Gavins FNE, Stevenson EV, Navratil AR, Jin L et al. : A Critical Role for Monocytes/Macrophages During Intestinal Inflammation-associated Lymphangiogenesis. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases 2016, 22(6):1326–1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cursiefen C, Chen L, Borges LP, Jackson D, Cao J, Radziejewski C et al. : VEGF-A stimulates lymphangiogenesis and hemangiogenesis in inflammatory neovascularization via macrophage recruitment. The Journal of clinical investigation 2004, 113(7):1040–1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Harvey NL, Gordon EJ: Deciphering the roles of macrophages in developmental and inflammation stimulated lymphangiogenesis. Vascular Cell 2012, 4(15). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jeon BH, Jang C, Han J, Kataru RP, Piao L, Jung K et al. : Profound but dysfunctional lymphangiogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor ligands from CD11b+ macrophages in advanced ovarian cancer. Cancer research 2008, 68(4):1100–1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kerjaschki D: The crucial role of macrophages in lymphangiogenesis. The Journal of clinical investigation 2005, 115(9):2316–2319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kim KE, Koh YJ, Jeon BH, Jang C, Han J, Kataru RP et al. : Role of CD11b+ macrophages in intraperitoneal lipopolysaccharide-induced aberrant lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic function in the diaphragm. The American journal of pathology 2009, 175(4):1733–1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Maruyama K, Ii M, Cursiefen C, Jackson DG, Keino H, Tomita M et al. : Inflammation-induced lymphangiogenesis in the cornea arises from CD11b-positive macrophages. The Journal of clinical investigation 2005, 115(9):2363–2372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ran S, Montgomery KE: Macrophage-Mediated Lymphangiogenesis: The Emerging Role of Macrophages as Lymphatic Endothelial Progenitors. Cancers (Basel) 2012, 4(3):618–657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zumsteg A, Baeriswyl V, Imaizumi N, Schwendener R, Ruegg C, Christofori G: Myeloid cells contribute to tumor lymphangiogenesis. PloS one 2009, 4(9):e7067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Morote-Garcia JC, Napiwotzky D, Kohler D, Rosenberger P: Endothelial Semaphorin 7A promotes neutrophil migration during hypoxia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2012, 109(35):14146–14151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Holmes S, Downs AM, Fosberry A, Hayes PD, Michalovich D, Murdoch P et al. : Sema7A is a potent monocyte stimulator. Scand J Immunol 2002, 56(3):270–275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lyons TR, O’Brien J, Borges VF, Conklin MW, Keely PJ, Eliceiri KW et al. : Postpartum mammary gland involution drives progression of ductal carcinoma in situ through collagen and COX-2. Nature medicine 2011, 17(9):1109–1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Podgrabinska S, Braun P, Velasco P, Kloos B, Pepper MS, Skobe M: Molecular characterization of lymphatic endothelial cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2002, 99(25):16069–16074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Xu H, Chen M, Reid DM, Forrester JV: LYVE-1-positive macrophages are present in normal murine eyes. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2007, 48(5):2162–2171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jiang S, Bailey AS, Goldman DC, Swain JR, Wong MH, Streeter PR et al. : Hematopoietic stem cells contribute to lymphatic endothelium. PloS one 2008, 3(11):e3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mantovani A, Locati M: Tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm of macrophage plasticity, diversity, and polarization: lessons and open questions. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 2013, 33(7):1478–1483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Stout RD, Watkins SK, Suttles J: Functional plasticity of macrophages: in situ reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages. J Leukoc Biol 2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nakamura Y, Yasuoka H, Tsujimoto M, Kurozumi K, Nakahara M, Nakao K et al. : Importance of lymph vessels in gastric cancer: a prognostic indicator in general and a predictor for lymph node metastasis in early stage cancer. J Clin Pathol 2006, 59(1):77–82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sundar SS, Zhang H, Brown P, Manek S, Han C, Kaur K et al. : Role of lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian cancer. British journal of cancer 2006, 94(11):1650–1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rouzaut A, Irigoyen M, Montuenga LM: Lymphangiogenesis and lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2007, 2(5):384–386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Dollt C, Becker K, Michel J, Melchers S, Weis CA, Schledzewski K et al. : The shedded ectodomain of Lyve-1 expressed on M2-like tumor-associated macrophages inhibits melanoma cell proliferation. Oncotarget 2017, 8(61):103682–103692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bertozzi CC, Schmaier AA, Mericko P, Hess PR, Zou Z, Chen M et al. : Platelets regulate lymphatic vascular development through CLEC-2-SLP-76 signaling. Blood 2010, 116(4):661–670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Honma∗ MF Masaru, Takahashi Hidetoshi, Iizuka Hajime: Podoplanin alters Journal of dermatological science 2013, 69:e1–e46. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Asztalos S, Gann PH, Hayes MK, Nonn L, Beam CA, Dai Y et al. : Gene expression patterns in the human breast after pregnancy. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2010, 3(3):301–311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Callihan EB, Gao D, Jindal S, Lyons TR, Manthey E, Edgerton S et al. : Postpartum diagnosis demonstrates a high risk for metastasis and merits an expanded definition of pregnancy-associated breast cancer. Breast cancer research and treatment 2013, 138(2):549–559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bambhroliya A, Van Wyhe RD, Kumar S, Debeb BG, Reddy JP, Van Laere S et al. : Gene set analysis of post-lactational mammary gland involution gene signatures in inflammatory and triple-negative breast cancer. PloS one 2018, 13(4):e0192689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lim B, Woodward WA, Wang X, Reuben JM, Ueno NT: Inflammatory breast cancer biology: the tumour microenvironment is key. Nature reviews Cancer 2018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Pereira ER, Kedrin D, Seano G, Gautier O, Meijer EFJ, Jones D et al. : Lymph node metastases can invade local blood vessels, exit the node, and colonize distant organs in mice. Science 2018, 359(6382):1403–1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Brown M, Assen FP, Leithner A, Abe J, Schachner H, Asfour G et al. : Lymph node blood vessels provide exit routes for metastatic tumor cell dissemination in mice. Science 2018, 359(6382):1408–1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


