Abstract
Alterations in the mechanical properties of erythrocytes occurring in inflammatory and hematologic disorders such as sickle cell disease (SCD) and malaria often lead to increased endothelial permeability, haemolysis, and microvascular obstruction. However, the associations among these pathological phenomena remain unknown. Here, we report a perfusable, endothelialized microvasculature-on-a-chip featuring an interpenetrating-polymer-network hydrogel that recapitulates the stiffness of blood-vessel intima, basement membrane self-deposition and self-healing endothelial barrier function for longer than 1 month. The microsystem enables the real-time visualization, with high spatiotemporal resolution, of microvascular obstruction and endothelial permeability under physiological flow conditions. We found how extracellular heme, a hemolytic byproduct, induces delayed but reversible endothelial permeability in a dose-dependent manner, and demonstrate that endothelial interactions with SCD or malaria-infected erythrocytes cause reversible microchannel occlusion and increased in situ endothelial permeability. The microvasculature-on-a-chip enables mechanistic insight into the endothelial barrier dysfunction associated with SCD, malaria and other inflammatory and haematological diseases.
The vascular endothelium defines the interface between blood and tissue, forming a semi-permeable barrier that controls the exchange of nutrients and soluble factors1, 2. In numerous hematologic and inflammatory diseases, such as sickle cell disease (SCD) and malaria, endothelial barrier dysfunction is associated with the pathophysiologic hallmarks of these disorders, specifically, the polymerization of sickle hemoglobin in red blood cells (RBCs) in SCD and RBC infection with plasmodium parasites in malaria leading to microvascular obstruction and hemolysis3, 4, 5, 6. While animal models have vastly improved our understanding of these diseases, the underlying mechanisms of endothelial barrier dysfunction in SCD and malaria remain unknown due to the complex interplay of in vivo factors that are difficult to manipulate and the different pathological phenotypes between animals and humans7, 8, 9, 10, 11. Therefore, complementary in vitro microvascular systems that feature human endothelial cells (ECs) are needed to provide a reductionist, quantitative insight into endothelial barrier dysfunction in SCD, malaria, and other hematologic disorders.
While perfusable microvascular networks can be engineered in solid polymeric materials, these materials possess moduli ranging from 50 kPa to several MPa12, 13, 14, which is much higher than the stiffness of tissues surrounding blood vessels, and can lead to endothelial dysfunction and compromise the engineered endothelial barrier function15, 16. In contrast, hydrogel materials can be fine-tuned to a more physiologically relevant stiffness (~ hundreds of Pa to 50 kPa), and thus have been widely utilized for engineering microvascular networks. Hydrogel-based perfusable microvascular networks can be engineered by “bottom-up” approaches via vasculogenesis and angiogenesis17, 18, 19, 20, which is valuable for studies such as cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. However, these microvascular networks exhibit unstability in vascular size, length and geometry, which results in uncontrollable flow patterns. While “top-down” approaches can fabricate hydrogel microchannels with precise size and geometry and enable well-defined and controlled flow patterns21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, most of these approaches involve fabricated microchannels with a size no smaller than 50 μm. Although some groups have engineered in vitro microvasculature models down to 20 μm, they are only limited to straight channels29. No “top-down” approach has been reported for engineering vasculature network with branches at microvasculature sizescale (< 30 μm) which is more suitable for the investigation of endothelial barrier function in hematological disorders of the microcirculation, such as SCD and malaria. Moreover, no published reports to date have described in vitro microvasculature models that maintain appropriate physiological barrier function long-term (weeks to months) to investigate not only endothelial dysfunction, but also the restoration of barrier integrity after an acute complication or insult is removed.
To that end, we employed an agarose-gelatin interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) hydrogel to develop an endothelialized microvascular-sized fluidic system using a “top-down” approach. Specifically, this hydrogel-based IPN microfluidic device mimics the in vivo diameter of postcapillary venules and the corresponding wall shear stress, and the stiffness of the blood vessel intima, which collectively enables the cultured endothelial monolayer to appropriately assemble a laminin- and collagen IV-rich basement membrane and maintain barrier function for over 1 month under continuous laminar flow conditions. Using this microvasculature-on-a-chip system, we elucidated how inflammatory mediators, hemolytic byproducts, and pathologically altered RBCs that lead to microchannel obstruction in hematologic diseases spatiotemporally alter barrier function, and affect the subsequent recovery of barrier function. This hydrogel-based endothelial network system demonstrates significant promise for investigating how molecular and cellular interactions directly mediate microvascular endothelial barrier dysfunction in a wide spectrum of other diseases.
Results
Engineering a hydrogel-based microvasculature-on-a-chip using an interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) with physiologically relevant stiffness
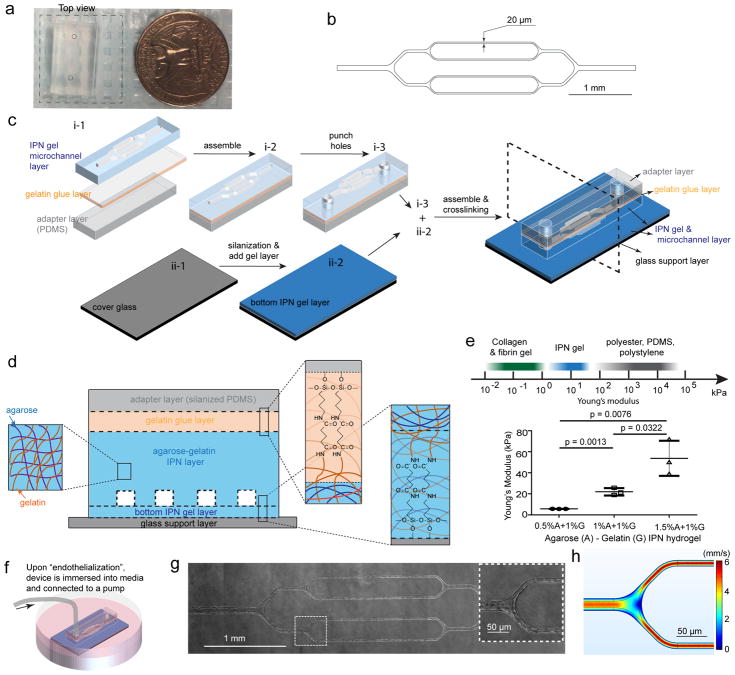
To fabricate perfusable microvascular-sized channels that allow for the study of microvessel occlusion, we applied conventional microfluidic techniques to an agarose-gelatin IPN (Figure 1a). A silicon master mold of branching microchannels was fabricated via standard photolithography; the smallest channels are 20 μm in width and height to approximate postcapillary venule size14 (Figure 1b). High fidelity transfer of the patterned microvasculature network from the master mold to an IPN hydrogel is achieved by casting the agarose-gelatin solution in the mold at 65°C, and removing the solidified IPN hydrogel from the mold at 4°C. This enables the high throughput production of multiple identical hydrogel-based microdevices from a single master mold. To ensure constant microchannel perfusion and prevent stiff inlet tubing from damaging the IPN hydrogel, a silanized polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) adaptor layer was glued to the hydrogel channel layer via a gelatin layer. The bottom hydrogel layer (~200 μm thick) was then covalently attached to a silanized glass cover slide (Figure 1c) to allow for high-resolution videomicroscopy. To prevent microchannel collapse resulting from a housing or clamping system27, 30, we covalently bonded each layer together via gelatin using carbodiimide crosslinker chemistry (Figure 1d)31. The stiffness of the tissues surrounding healthy arteries was reported to be ~ 35 kPa15, 16, 32, and the stiffness of the softest tissues in the body, was found to be ~ 1 kPa33. We therefore deduce that the tissues surrounding microvasculature has a stiffness between 1 to 35 kPa, and therefore we fine-tuned the Young’s modulus (E) of the IPN (Figure 1e) to E ~20 kPa by using 1% (w/v) agarose and 1% (w/v) gelatin. After endothelial cell (EC) seeding, the microdevice is immersed in culture medium (Figure 1f), allowing fluid to freely diffuse across the IPN hydrogel layers. The ECs reach confluence one to two days post-seeding and span the three-dimensional inner surface of the microchannels under laminar flow conditions (Figure 1g). Due to the microvascular sizescale of our microchannels in which the size of the ECs approximates that of the microchannels, the presence of ECs cultured in the channels leads to a “rounding out” of the luminal space (Suppl. Figure 1). To recapitulate the flow in 20μm diameter postcapillary venules34, 35, the average flow velocity in the smallest channels was set to ~2.8 mm/s (Figure 1h), which corresponds to a wall shear stress of ~8.8 dynes/cm2 (computational fluidic dynamic modeling in Suppl. Figure 2). Under these continuous, constant flow conditions, ECs align with the direction of flow in the microchannels (Suppl. Figure 3). The versatility of the system is evidenced by our ability to culture ECs obtained from different vascular beds: human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMVECs), and human lung microvascular endothelial cells (HLMVECs).
Figure 1. Engineering an interpenetrating network (IPN) hydrogel-based microvasculature-on-a-chip for investigating endothelial barrier function and cellular interactions in hematologic diseases.
a) Macroscopic top view of the microdevice. The dashed square indicates the transparent bottom layer. b) CAD design for the photolithography mask that defines the microfluidic channel geometry. c) Schematic of microdevice fabrication. d) Schematic of agarose-gelatin IPN layer and the bonding of each layers via gelatin using carbodiimide crosslinker chemistry. e) The IPN hydrogel can be tuned to mimic the physiological stiffness of the blood vessel intima, while synthetic polymeric materials are much stiffer. Data were plotted as the mean ± s.d. with n=3 independent experiments. P-values were calculated using unpaired, two-sided Student’s t-test. (* P<0.05, ** P<0.01). f) The microdevice seeded with endothelial cells was immersed into culture media, and maintained under constant physiologic laminar flow for up to 4 weeks. g) A representative stitched composite of brightfield microscopy images of a microvasculature-on-a-chip after 14 days of culture. Insert: higher magnification image of the dashed box. h) Computational fluid dynamics modeling of the microchannels confirming physiologic laminar flow conditions.
Permeability of the microvasculature-on-a-chip recapitulates the endothelial barrier function of the microcirculation over long (>1 month) timescales
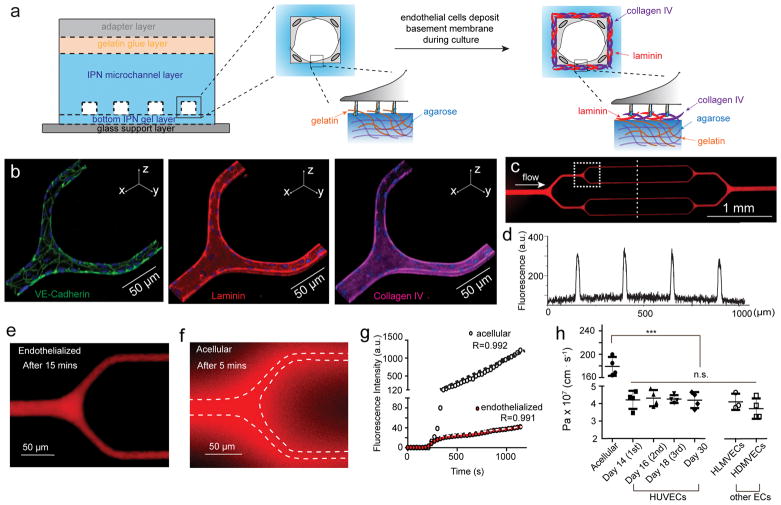
All tested EC types maintained a functional, semi-permeable barrier in our hydrogel microchannels 1 month post-seeding under continuous laminar flow conditions, without lumen collapse. The cultured endothelium in our engineered IPN microvasculature appropriately assembles its own basement membrane, depositing a continuous sheet of both laminin and collagen IV (Figure 2a–b and Suppl. Figure 4–5). Moreover, the physiologic conditions of our system enable the ECs to continuously and dynamically remodel their basement membrane, which occurs in vivo, as evidenced by the endothelial expression of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2), a collagen IV-cleaving enzyme (Suppl. Figure 6). In contrast, ECs cultured in PDMS-based microfluidic devices, which are significantly stiffer, do not assemble a basement membrane (Suppl. Figure 7). Importantly, the engineered microvasculature from all three EC types express continuous VE-cadherin under physiologic laminar flow, indicating the physiologic formation of adherens junctions, and thus establishing endothelial barrier integrity36 (Figure 2b, Movie 1 and Suppl. Figure 4–5). When perfused with Alexa Fluor 594-tagged bovine serum albumin (BSA-AF594), control acellular microdevices showed significant leakage within 3 minutes of perfusion (Figure 2f), while endothelialized microdevices maintained barrier integrity throughout the period of 15–20 minute measurement (Figure 2c–e). To further characterize this aspect of our system, the apparent permeability coefficient (Pa) of BSA-AF594 was quantified by measuring fluorescence intensity in the smallest channels over 15 minutes of perfusion (Suppl. Figure 8 and Movie 2–3). We found that our engineered microvasculature with HUVECs, HDMVECs, and HLMVECs all exhibited a permeability of ~ 4 × 10−7 cm/s (~40 times lower than acellular microdevices), similar to that of mammalian venules ((1.5 ± 0.5) × 10−7 cm/s)12, 37 in vivo and lower than that in most previously reported in vitro models12, 27, 30 (Figure 2g–h). The apparent permeability of the engineered microvasculature was confirmed by perfusion of an alternative molecular tracer, FITC-conjugated 70 kDa dextran (Suppl. Figure 9). In contrast, the permeability of the engineered microvasculature was significantly increased when agarose-gelatin IPNs of higher stiffnesses (~ 50 kPa) were utilized. On the other hand, endothelial cell culture in the softest devices (~5 kPa) was not feasible, likely due to the weaker mechanical stability as compared to those of the stiffer devices which cannot sustain the wall shear stress and intravascular pressure within the microchannels (Suppl. Figure 10). These data suggest a critical role of substrate stiffness in regulating the endothelial barrier function that is consistent with previous reports15, 16. Furthermore, unlike other currently existing systems, our engineered microvasculature maintained stable barrier function one month post-seeding (Figure 2h). Taken together, these data indicate that by mimicking key biological and biophysical features of the in vivo microvasculature, our hydrogel-based microdevices enable long-term preservation of endothelial barrier function in vitro. This system then allows pathologically altered RBCs, with or without associated inflammatory mediators, to be perfused into the engineered microvasculature under physiological flow conditions, and the spatiotemporal effects on barrier function to be quantitatively assessed via perfusion of a fluorescent molecular tracer (Suppl. Figure 11).
Figure 2. Engineered microvasculature exhibits appropriate endothelial barrier function.
a) Schematic showing while seeded endothelial cells initially adhered to gelatin, they appropriately assembly basement membrane during culture. b) Representative 3D confocal microscopy immunostaining images of the adherens junction protein VE-cadherin and the basement membrane proteins laminin and collagen-IV, self-deposited by HUVECs after 14 days of culture. c) A representative stitched composite of epi-fluorescence images after 15-minute perfusion of BSA-AF594. d) Fluorescence intensity of the BSA-AF594 along the linescan across the engineered microvasculature in panel b. e) Higher magnification view of the engineered microvasculature demonstrating that the system is impermeable to BSA under physiologic flow conditions. f) In acellular (non-endothelialized) microsystems, significant diffusion of BSA occured as early as 5 minutes after perfusion (dashed lines define the microchannel borders). g) Representative plots of BSA-AF594 fluorescence intensity over time in permeability assays for both acellular and endothelialized microdevices. h) Quantified apparent permeability (Pa) of the engineered microvasculature to BSA remained similar across different endothelial cell types, and is approximately 40× less than that in acellular microchannels. Data was plotted as the mean ± s.d. with n=4 independent biological replicates expect for HLMVECs (n=3). P-values were calculated using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (*** P < 0.001). The permeability of the engineered microvasculature was also stably maintained for over 4 weeks and permeability can be measured at multiple sequential time points.
Engineered microvasculature responds in a physiological manner to barrier-disrupting inflammatory mediators and demonstrates a “self-healing” capability of the endothelial barrier integrity
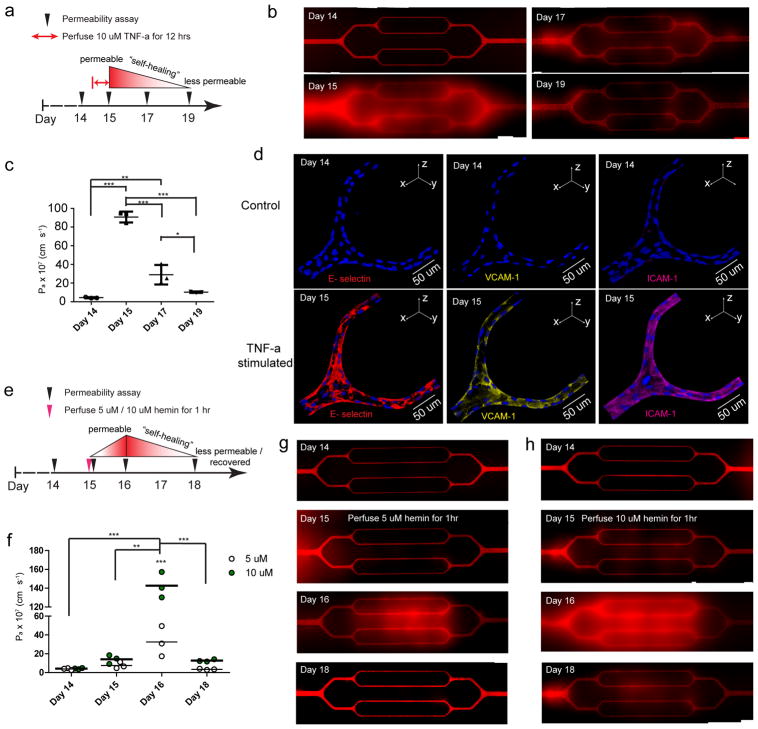
Since elevated levels of inflammatory cytokine TNF-α in both SCD and severe malaria contribute to endothelial barrier dysfunction38, 39, we sought to investigate how TNF-α affect the permeability in our engineered microvasculature. Overnight exposure to 10 ng/ml TNF-α (Figure 3a) induced HUVEC permeability throughout the microvasculature, and resulted in a ~ 20 fold increase in permeability (Figure 3b–c). Consistent with previous findings40, 41, TNF-α-stimulated endothelium shows upregulation of multiple adhesion molecules, including E-selectin, VCAM-1, and ICAM-1 (Figure 3d), but not P-selectin (Suppl. Figure 12). The long-term culture under physiologic flow conditions allowed by our system revealed that the barrier function of engineered microvasculature gradually “self-healed” after the removal of TNF-α: the permeability reduced to ~ 2.9 × 10−6 cm/s two days post-exposure, and to ~ 1.0 × 10−6 cm/s four days post-exposure. Our system thus responds to cytokine stimulus in a physiologically relevant manner, and reveals the endothelium’s ability to self-heal barrier function42.
Figure 3. The spatiotemporal dynamics of endothelial barrier dysfunction in response to perfusion of inflammatory cytokines and hemolytic byproducts and the “self-healing” of engineered endothelial barrier integrity upon removal of those agents can be visualized and tracked.
a) The experimental timeline and design with TNF-α. b) Stitched composite of epifluorescence images indicate that exposure to 10 ng/ml TNF-α for 12 hours significantly increased permeability in the engineered microvasculature, but over 4 days, the TNF-α-stimulated endothelium “self-healed” and gradually became less permeable, recovering its barrier function. c) Quantitative apparent permeability measurements of the BSA tracer indicates that perfusion and stimulation with 10 ng/ml TNF-α for 12 hours appropriately and expectedly increased permeability of the engineered microvasculature by 20-fold. Post-TNF-α stimulation, the endothelial barrier function of engineered microvasculature “self-healed” and recovered within 4 days. Data was plotted as the mean ± s.d. with n=3 independent biological replicates. P-values were calculated using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (* P<0.05, ** P<0.01; *** P<0.001). d) Immunostaining indicates that TNF-α stimulation appropriately upregulated the expression of adhesion molecules in the engineered microvasculature. e) The experimental timeline and design with free hemin. f) Quantitative apparent permeability measurements of the BSA tracer at different time points of both pre- and post- hemin exposure indicates that the magnitude of barrier function loss and the system’s “self-healing” recovery thereof were hemin dose-dependent. Data was plotted as the mean ± s.d. with n=3 independent biological replicates. P-values were calculated using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (** P<0.01; *** P<0.001). g–h) Stitched composite of epifluorescence images from permeability measurements at different time points of both pre- and post- exposure to 5 μM and 10 μM hemin.
To further characterize our engineered microvasculature, we assessed how free heme, a hemolytic byproduct, directly affects endothelial permeability (Figure 3e). Studies by our group and others suggest that the high levels of extracellular heme released into the circulation upon RBC destruction in both SCD and malaria cause endothelial barrier dysfunction43, 44, 45. However, because the effects of extracellular heme in vivo are confounded by factors such as increased concentrations of cytokines and/or the presence of activated cells (monocytes, lymphocytes, platelets, etc), the effect of free heme itself on the endothelial barrier is unclear38. Using the reductionist approach our system enables, we found that the 1-hour perfusion of hemin at SCD relevant concentrations of 5–10 μM43, 44, 45, increased HUVEC permeability. Interestingly, permeability peaked at 1 day post-hemin exposure. Importantly, we found the hemin-induced endothelial permeability occurred in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 3f–h). Exposure to 5 μM free hemin for 1 hour resulted in a ~8 fold increase in permeability, with a return to baseline permeability 4 days post-exposure. In contrast, exposure to 10 μM free hemin resulted in a ~30 fold increase in permeability, and it did not return to baseline within 4 days. This dose-dependent, delayed permeability effect by free hemin was further confirmed in the engineered microvasculature using HDMVECs (Suppl. Figure 13). Collectively, these experiments establish that the engineered microvasculature responds physiologically to inflammatory mediators and hemolysis byproducts. In addition, our data not only answer a current question in SCD by confirming that heme directly causes a loss of endothelial barrier function, but also provide insight into the temporal pattern of this effect and its resolution over time.
Sickle erythrocyte-endothelial cell interactions induce microchannel occlusion and a loss of endothelial barrier function
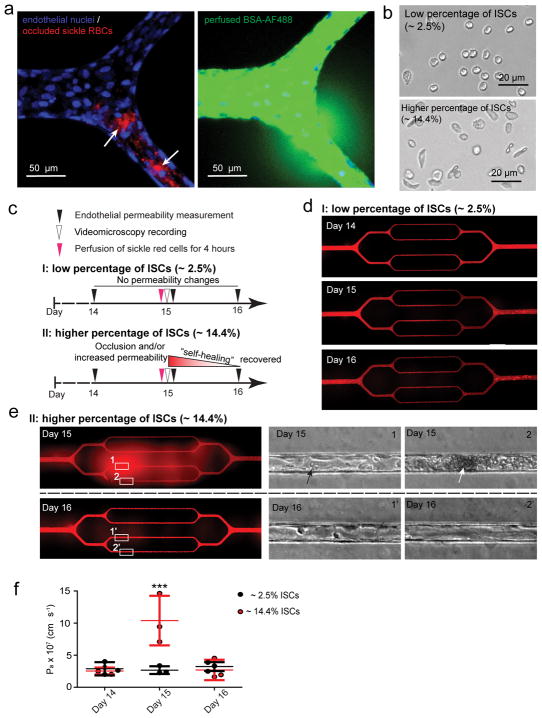
Chronic vasculopathy and vaso-occlusion crises are associated with SCD5, 6, 8, 9; however, the lack of mechanistic understanding of how these pathologies are linked prevents the development of effective therapeutics. While it is well established that the endothelium interacts with sickle RBCs, including the irreversibly sickled red blood cell (ISC) subpopulation9, it remains unclear whether sickle RBC-endothelium interactions are sufficient to increase vessel permeability and cause vaso-occlusion. Our system allows for the effective decoupling of the effects of RBCs from other cofounding in vivo factors—other cell populations, cytokines, and coagulation proteins. Initial experiments reveal that the 4-hour perfusion of RBCs isolated from a population of SCD patients induced microchannel occlusion and led to increased HUVEC permeability at the exact site of the obstruction (Figure 4a). To further investigate how sickle RBCs induce in vitro microvascular occlusion and endothelial permeability, we correlated the phenomenon with the morphology of sickle RBCs, and discerned two experimental scenarios (Figure 4b).
Figure 4. Sickle red cell-endothelial cell interactions in and of themselves induce microchannel occlusion and loss of endothelial barrier function in the engineered microvasculature.
a) Representative 3D confocal microscope images of endothelialized microchannels occluded by sickle RBCs (pre-stained with R18; pointed by arrows) and the resultant, co-localized increased endothelial permeability and leakage of BSA-AF488 in situ. b) Representative bright field images of blood smears reveal two experimental scenarios involving our SCD patients’ blood samples. c) The experimental timeline and design. d) Representative stitched composite of epi-fluorescence images indicate that perfusion of low percentages of ISCs for 4 hours caused no change in permeability in the engineered microvasculature. e) Representative stitched composite of epi-fluorescence images and brightfield microscopy images of the boxed regions indicate that perfusion of high percentages of ISCs for 4 hours caused temporary microchannel occlusion and was sufficient, in and of itself and in the absence of other blood cell populations or exogenous inflammatory mediators, to induce loss of endothelial barrier function and increased permeability in the engineered microvasculature. Within 1 day of continued culture and perfusion, the ISC microchannel occlusion cleared and the engineered microvasculature “self-healed”, gradually recovering its barrier function (black arrow: adherent sickle RBCs; white arrow: RBC aggregate that occludes the microchannel). f) Quantitative apparent permeability measurements of the BSA tracer at different time points of both pre- and post-perfusion of ISCs from sickle cell patients. The data was plotted as the mean ± s.d. with n=3 independent replicates. Samples with either low or high ratio of ISC were obtained from three different SCD patients. P-values were calculated with two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (*** P<0.001).
All SCD patients have a percentage of ISCs46 that maintain pathologically increased stiffness and sickled shape even under normoxic conditions and are known to be involved in the pathophysiology of the disease (Figure 4b). When the blood from SCD patients had a low percentage of ISCs (~2.5%) (morphological analysis using ImageJ as described in Online Methods), the 4 hour perfusion of RBCs did not affect endothelial permeability (Figure 4c–f, and Movie 4), which is similar as that perfused with RBCs from healthy individuals (Suppl. Figure 14). In contrast, when SCD patients had a significantly higher percentage of ISCs (~ 14.4%, Figure 4b), RBCs adhered to the engineered microvasculature, and in vitro vaso-occlusion occurred in some microchannels after 4 hours of perfusion, which obstructed the entire microchannel and completely ceased the flow of RBCs through those microchannels (Figure 4e, and Movie 5). Furthermore, the permeability increased ~2 fold at the exact sites of sickle RBC adhesion (Figures 4f). These interactions, however, did not lead to stable sickle RBC adhesion or sustained in vitro vaso-occlusion under flow conditions, as both were eliminated 1 day after RBC perfusion (Figure 4e). Importantly, endothelial permeability returned to the baseline pre-perfusion levels (Figure 4f). Since ISCs are stiffer than normal RBCs, we investigated whether the increased stiffness of RBCs, in and of itself, can induce endothelial permeability. Accordingly, normal healthy RBCs were exposed to 0.065% glutaraldehyde which leads to RBC stiffnesses similar to that of ISCs47, 48, and RBC suspensions containing 15% of these stiffened RBCs were perfused through the endothelialized channels. Interestingly, 4 hour perfusion increased the permeability of engineered endothelium, and complete in vitro occlusion and the cessation of the flow of RBCs in some microchannels were also observed (Suppl. Figure 15), which suggests that the elevated stiffness of ISCs contribute to the increased permeability in engineered endothelium. As ISCs are both stiffer than normal healthy RBCs and harbor pathologic adhesive properties that may induce downstream endothelial pro-inflammatory signaling, this experiment demonstrates how increased RBC stiffness alone may disrupt endothelial barrier function without the need for ligand-receptor adhesion and highlights our system’s capability to decouple biophysical from biological phenomena. Our data show that the interaction of a high ratio of artificially-stiffened RBCs or ISCs with the endothelium is sufficient to cause microvascular permeability and occlusion at RBC adhesion sites. Moreover, we demonstrate the capability of our engineered microvasculature to assess pathologic blood cell-endothelial interactions over longer timescales than existing in vitro systems, thereby enabling investigation of the resolution of cellular interactions in hematologic diseases and fulfilling an unmet clinical and scientific need.
Plasmodium falciparum-infected RBCs (iRBCs) act alone, and in concert with TNF-α, to disrupt endothelial barrier function
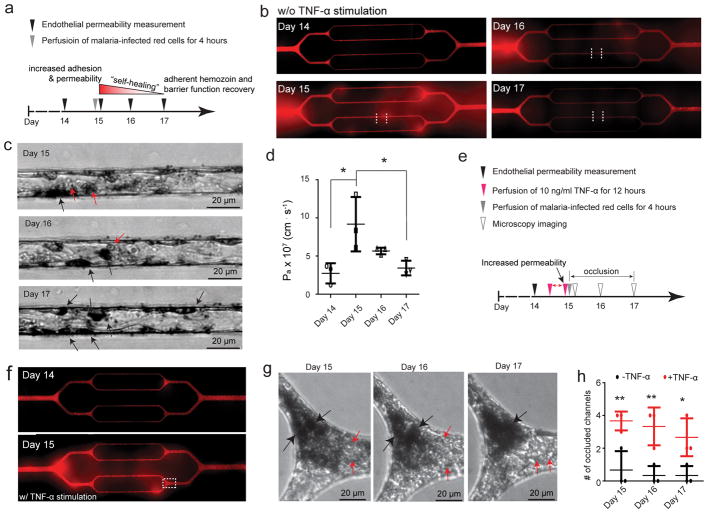
Cerebral malaria (CM) is a life-threatening complication of malaria characterized by the loss of endothelial barrier function10, 49, 50 whose underlying mechanism has long been debated7, 10. It is currently unknown what combination of factors—cytoadhesion of iRBCs, inflammatory cytokines, hemolysis, and/or direct interactions with immune cells—are required to induce loss of endothelial barrier function in CM. Our engineered microvasculature can decouple the complex factors implicated in the pathogenesis of CM to address this question (Figure 5a). We found that perfusion of iRBCs alone resulted in an ~2-fold increase in HUVEC permeability (Figure 5b–d) at the locations of iRBC cytoadhesion (Figure 5b–c, and Movie 6), whereas the occlusion was barely observed in the microchannels. Post-iRBC perfusion, the permeability recovered to baseline in 2 days (Figure 5d). During healing of endothelial barrier integrity, the endothelium engulfed the malarial pigment hemozoin, which indicates that the malarial byproducts, hemozoin, is not associated with increased endothelial permeability (Figure 5b–d).
Figure 5. Endothelial interactions with Plasmodium-infected RBCs (iRBCs) in and of themselves are sufficient to disrupt endothelial barrier function and act synergistically with TNF-α.
a) The experimental timeline and design for perfusion of iRBCs (clone 3D7). b) Representative stitched composites of epi-fluorescence images indicate 4-hour perfusion of iRBCs, in and of itself and in the absence of other blood cell populations or exogenous inflammatory mediators, increased the endothelial permeability, which “self-healed” and recovered barrier function upon cessation of iRBC perfusion. c) Brightfield microscopy images of the regions between the dashed white lines in panel b indicate that iRBCs adhered to the endothelium after perfusion, and engulfed malarial pigment hemozoin remained over time (red arrows: iRBCs; black arrows: hemozoin). d) Quantitative Pa measurements of BSA indicate perfusion of iRBCs alone increased endothelium permeability, while barrier function steadily recovered over several days upon cessation of iRBC perfusion. Data was plotted as the mean ± s.d. with n=3 independent biological replicates. P-values were calculated using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (* P<0.05). e) The experimental timeline and design with TNF-α stimulation. f) Representative stitched composite of epi-fluorescence images indicate the increased permeability after TNF-α stimulation. g) Brightfield microscopy images of box in f) indicate that perfusion of iRBCs into TNF-α-stimulated endothelium caused severe microchannel occlusion, and as the iRBC aggregate density attenuated over time, hemozoin aggregated and increased in density over two days of continued culture (black arrows: hemozoin aggregates; red arrows: individual RBCs). h) TNF-α stimulation significantly increased the number of occluded microchannels compared to perfusion of iRBCs alone in the engineered microvasculature. Data was plotted as the mean ± s.d. with n=3 independent biological replicates. P-values were calculated using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (* P<0.05; ** P<0.01).
To study how humoral and cellular interactions synergistically affect endothelial barrier function in CM, we stimulated the engineered microvasculature with 10 ng/ml TNF-α overnight, followed by 4 hour perfusion of iRBCs (Figure 5e–f). TNF-α stimulation resulted in enhanced microchannel occlusion, and near complete obstruction of the microvasculature system by perfused iRBCs. Two days post-iRBC perfusion, microchannels remained completely occluded by the initial adherent iRBC aggregates and a growing hemozoin aggregate was present (Figure 5g–h). It is likely that this in vitro occlusion was sustained by the reduction of media flow due to the presence of large aggregates thereby allowed ongoing interactions between iRBCs and EC. Taken together, our data suggest that iRBC presence alone has the capacity to induce endothelial barrier dysfunction. Stimulation by inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α further exacerbates microvascular occlusion, leading to severe CM. Thus, our findings support the critical role played by iRBCs and inflammatory cytokines in vascular dysfunction/leakage, a feature commonly observed in CM7, 10.
Discussion
Here, we have taken a “top-down” approach and leveraged IPNs to develop a microvasculature-on-a-chip endowed with features that have not been reported by currently existing in vitro models (Suppl. Table 1): i) it is the first system, to our knowledge, that features a three-dimensional endothelial network at the microvascular size scale (20 μm) with well-controlled flow patterns, ii) it allows for long-term culture of endothelium under well-controlled flow conditions that mimic microvascular shear stress, iii) the engineered endothelium self-deposits appropriate basement membrane proteins and displays physiological endothelial barrier function for several weeks, iv) it enables quantitative assessment of endothelial permeability and real-time observation of in vitro vaso-occlusion with high spatial resolution, and v) it recapitulates in vivo recovery of endothelial barrier function, thereby enabling the study of this process in vitro. These features enable a more physiological microvascular environment in our device compared to other in vitro models, which is crucial for studying the endothelial barrier dysfunction in SCD and malaria. For example, the vaso-occlusion in SCD and microvascular obstruction in malaria more readily occurs in blood vessels of the microcirculation sizescale (< 30 μm) due largely to the restricted lumen spaces. Our model mimics the lumen diameter of postcapillary venules and the corresponding wall shear stress, and thus enables the study of the vaso-occlusion that occurs in vivo condition. Moreover, the endothelial barrier dysfunction and integrity restoration in inflammatory diseases is a chronic process. While existing in vitro systems are primarily conducive to studying acute events (sickle cell vaso-occlusion, microvascular occlusion with malaria, thrombosis), our system enables long term studies and culture, and therefore is conducive for studying the recovery of those acute events which obviously occur in vivo. This cannot be accomplished with existing in vitro technologies. Furthermore, we can also study how repeated insults affect endothelial function over time to determine how chronic endothelial dysfunction develops, which is the hallmark of many inflammatory and vascular diseases such as heart disease and sickle cell vasculopathy.
These attributes of the system properties are due to the integrated hydrogel material, the fabrication process, and optimized culture conditions. Since extracellular matrix stiffness regulates EC proliferation51 and VEGF signaling52, and increased matrix stiffness is associated with endothelial barrier dysfunction in diseases such as atherosclerosis15, 16, creating a system with appropriate stiffness can augment the physiologic relevance of the engineered microvasculature and facilitate physiologic endothelial barrier function15. The agarose-gelatin IPN hydrogel allows us to tune the stiffness to approximate that of the blood vessel intima, a feat not achievable by the solid polymeric materials used in existing vasculature models. In addition, unlike synthetic hydrogels, agarose hydrogels minimally swell or shrink53, thus allowing high fidelity transfer of network patterns during “top-down” fabrication. In addition, gelatin molecules in the IPN system not only provide adhesive domains for initial cell adhesion, spreading and migration, but also function as bonding molecules to allow assembly of the multiple layers via carbodiimide crosslinker chemistry. This assembly scheme is paramount to the system as it ensures physiological laminar flow for the entirety of the cell culture time period, thereby facilitating establishment and maintenance of physiological barrier function.
Previous studies suggest the pathology of SCD and malaria is closely associated with endothelial barrier dysfunction. However, how this endothelial barrier dysfunction initiates and progresses in the contexts of these diseases is largely unknown. Our model enables the decoupling of complex factors in the pathologic progression of endothelial dysfunction and vasculopathy to determine the effect of pathologic molecular and cellular interactions on endothelial barrier function in these diseases, which is unachievable using animal models and current in vitro systems. Our data indicate that the hemolytic byproduct hemin, irreversibly sickled RBCs and malaria-infected RBCs are all independent contributors of endothelial barrier dysfunction. Indeed, our system reveals the endothelium’s previously uncharacterized, unique dose-dependent and temporal response to the hemolytic byproduct hemin43, 44, 45, and demonstrated that interactions between the endothelium and pathologic RBCs, specifically sickle RBCs and malaria-infected RBCs, in and of themselves, under physiologic flow conditions directly leads to increased endothelial permeability at the site of interaction. By demonstrating that interactions between the endothelium and plasmodium-infected RBCs are sufficient to induce endothelial barrier dysfunction in malaria and do not require recruitment of other cells, such as lymphocytes, our studies provide insight into a longstanding debate within the field7. If unresolved, these chronic interactions between pathologic RBCs and hemolysis with the endothelium may lead to chronic endothelial barrier dysfunction and vasculopathy in patients with sickle cell disease and malaria, further bolstering the clinical relevance of our studies. Future work involving longer perfusion times that lead to more significant endothelial barrier dysfunction in our model as well as longer experiments (>2 months) may provide further insights into chronic sickle cell disease vasculopathy over time, of which no in vitro systems are currently capable of. Furthermore, the long-term nature of the experiments enabled by our system allows for assessing the biological events that occur during resolution of acute complications such as sickle cell vaso-occlusion or malarial microvascular obstruction, a capability that has not been reported in other in vitro systems. Our studies also suggest that our device could be used as a system to further study how molecular and cellular interactions directly affect the underlying pro-inflammatory signaling pathways of endothelial barrier dysfunction in these diseases, and to screen for drugs and therapeutic strategies in preventing endothelial barrier dysfunction.
Outlook
Here we demonstrate the engineering of endothelialized, IPN hydrogel-based microvascular-on-a-chip systems that recapitulate the size scale, flow conditions, and physiology of the microcirculation for a variety of different endothelial cell subtypes and exhibit appropriate barrier function that can be monitored with high spatiotemporal resolution but also over long time scales. Using this engineered microvasculature, we provide new insight into the direct effects of the hallmark pathologic molecular and cellular interactions in SCD and malaria on the endothelial barrier function. This endothelial permeability system can be readily applied to study microvascular endothelial barrier function in other relevant diseases, and holds promise as a research-enabling and drug discovery system.
ONLINE METHODS
Fabrication of IPN hydrogel-based microdevices
The silicon wafer master mold was fabricated using a standard photolithography, in which the geometric pattern of the smallest channels was designed as 20 μm in width and height. 1% (w/v) agarose (sigma) and 1% (w/v) gelatin from porcine skin (sigma) were dissolved in MES (sigma) buffer (pH=5.3) by heating. The solution was then poured onto the master mold, and solidified at 4°C. The solidified agarose-gelatin IPN gel was peeled off the master mold, so that the geometric pattern was transferred to the IPN hydrogel. The PDMS adaptor layer was silanized with trimethoxypropylsilane (sigma) 54, and then exposed to 0.05% glutaraldehyde aqueous solution for 30 minutes. After rinsing with DI water, 8% (w/v) gelatin solution was added to the silanized PDMS surface to form a thin layer. Once the gelatin solution solidified, the agarose-gelatin channel layer was placed onto the gelatin layer with the channel side facing up. Two holes were then punched through IPN channel, gelatin glue and PDMS adaptor layers as inlet and outlet, respectively. To fabricate the bottom hydrogel layer, the cover slide was silanized and treated with glutaraldehyde using the same protocol as that used for the PDMS adaptor layer. Agarose and gelatin solution was then added onto the treated cover slide to form a thin layer (~ 200 μm) of IPN hydrogel at 4°C. The hydrogel channel layer was then placed onto the bottom layer with the channel side facing to the bottom hydrogel layer. Finally, the assembled device was immersed into EDC (sigma)-NHS (sigma) MES solution at 4°C for overnight. The crosslinked and covalently bounded devices were then washed with 1× PBS for 6 times and kept in 1× PBS before seeding with endothelial cells.
Elastic modulus measurement using AFM nanoindentation
The Young’s Modulus of cross-linked gelatin-agarose gels was measured using an MFP-3D AFM from Asylum Research (Santa Barbara, CA). Measurements were collected in contact mode using a silicon nitride probe with Cr/Au reflex coating and a 0.09 N m−1 nominal spring constant (Asylum, BL-TR800PB). Exact spring constants were determined on glass using force curves and a thermal spectrum calibration via the MFP-3D software. Force curves were collected in a 20×20 array with trigger point = 0.3 V and analyzed via the MFP-3D analysis tools using the Hertz model (Poisson ratio = 0.5) with cone as the tip geometry. Three force maps were collected in separate areas on each sample and then averaged for the sample value. Three samples were measured per condition with sample values averaged for condition value. Condition error represents the standard deviation between sample averages.
Engineering microvasculature-on-a-chip using IPN hydrogel-based microdevices
HUVECs (Passage 3–6, Lonza) and HLMVECs (Passage 3–6, Lonza) were maintained in EGM and EGM-2-MV medium, respectively. HDMVECs (Passage 3–6, Thermofisher Scientific) was maintained in HDMVECs culture medium (Thermofisher Scientific). Before endothelial cell seeding, microdevices were immersed into the cell culture medium for overnight. To endothelialize the microdevices, the endothelial cells were detached from culture flask, and re-suspended in the culture medium containing 8% dextran (MW = ~70,000, sigma) at a concentration of ~ 5 × 106 cells/ml. The cell suspension was then injected into the microchannels. After the endothelial cells attached and spread in the microchannels, the microdevices were connected to a syringe (BD) full of cell culture medium using #30 thin wall PTFE tubing (Cole-Parmer Instrument), which was driven by a pump (Harvard Apparatus), and cultured under an appropriate constant laminar flow. To immunostain VE-cadherin, collagen IV and laminin, the endothelial cells were first fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and permeabilized with 0.05% triton X. The fixed engineered microvasculature was then blocked by perfusion of 1% BSA solution, followed by perfusion of the primary antibody, mouse anti-human VE-cadherin (1:100, F8, Santa Cruz Biotech), mouse anti-human collagen IV (1:100, abcam), or rabbit anti-human laminin (1:100, abcam). After washed with 1% BSA, the fixed microvasculature was perfused with secondary antibody, goat anti-mouse-Alexa Fluor 488 (1:100, Invitrogen), or goat anti-rabbit-Alexa Fluor 647 (1:100, Invitrogen), with hoescht 33342 (1:1000, sigma). After perfusion with 1× PBS, the stained microvasculature was imaged using confocal microscopy (Zeiss LSM 700).
Computational fluid dynamics modeling in the microchannels
Based on cross-sectional confocal images of our engineered endothelium, the corners of the microchannels were correspondingly rounded using a curvature with the radius of 10 μm using SolidWorks. The computational fluid dynamics modeling was performed using Comsol software. As the outlet is exposed to the atmosphere, the outlet boundary condition was set as a pressure outlet at 1 atm. The fluid viscosity was set as 7.8 × 10−4 Pa·S, the reported viscosity of cell culture medium 55. We also considered the channels as impermeable to fluid in the computational model, as the flux of fluid across the membrane is negligible compared to the volume of fluid perfused through the channel 55.
Quantitative assessment of endothelial permeability
The permeability assay was carried out, and the apparent permeability coefficient (Pa) of BSA-AF594 or BSA-AF 488 (Invitrogen) of the engineered microvasculature was quantitatively analyzed using an equation adapted from a previously published protocol (Eq 1.)56, 57, 58. To ensure the concentration used in the permeability assay is suitable for the equation, a calibration was carried out using PDMS-based microfluidic devices containing a same geometric pattern as IPN hydrogel based microdevices. The employed concentration of the BSA tracer (50 μg/ml) is determined within the concentration range (0–100 μg/ml), in which fluorescence intensity of the BSA tracer has a linear relationship with the BSA concentration (Suppl. Figure 16). During permeability assay, the cell culture medium containing 50 μg/ml BSA-AF593 (Invitrogen) was perfused into the engineered microvasculature or acellular microdevices for 15–20 minutes. The imaging field was set to include all four smallest channels (Suppl. Figure 8), and the epi-fluorescence images were taken every 30 seconds during a period of 15–20 minutes. To quantitatively analyze the apparent permeability of the engineered microvasculature, a window of 120 μm wide and 160 μm long was drawn across the microchannel, and the fluorescence intensity within this preset window was measured using ImageJ, which was plotted against time (Figure 1l, Suppl. Figure 8 and Movie 2–3). The Pa of BSA-AF594 of the engineered microvasculature was then calculated according to Equation (1).
| (1) |
where Pa is the apparent permeability coefficent, I0 is the initial intensity, I2 is the intensity at t2, I1 is the intensity at t1, and a is the width of the channel.
Investigate the responses of engineered microvasculature to the barrier-disrupting inflammatory mediators, TNF-α and free hemin
To ensure the engineered microvasculature exhibits an appropriate endothelial barrier function, the permeability assay was carried out before TNF-α stimulation. Then, culture medium containing 10 ng/ml TNF-α was perfused into the engineered microvasculature for 12 hours. To characterize the upregulated expression of adhesive molecules on the surface of TNF-α stimulated HUVECs, the microvasculature was immunostained using the similar protocol as described above (without permearizing the cells). The primary antibodies included mouse monoclonal anti-human E-selectin (1:100, CD62E, ThermoFisher Scientific), mouse monoclonal anti-human ICAM-1 (1:100, 15.2, ThermoFisher Scientific), mouse monoclonal anti-human VCAM-1 (1:100, BBIG-V1, R&D Systems), and mouse monoclonal anti-human P-selectin (1:100, AK4, Santa Cruz Biotech), and the secondary antibody, goat anti-mouse AF488 was used. To study how the endothelial barrier function recovered over time, permeability assays were performed right after, 2 days and 4 days after 12-hour TNF-α stimulation.
To study how free hemin affect endothelial barrier function, culture medium containing 5 or 10 μM (Sigma) free hemin was perfused into the engineered microvasculature for 1 hour. The HUVEC permeability assessment was carried out 1 day before, right after, 1 day after and 3 days after hemin exposure.
Investigate the effects of sickle erythrocyte-endothelial cell interactions on endothelial barrier function in the engineered microvasculature
Sickle cell blood samples were collected from sickle cell patients who were taking hydroxyurea treatment. RBCs were isolated via centrifugation, and washed with 1× PBS for three times to remove most of the plasma proteins. The brightfield images of RBC smears were taken. The circularity of individual RBCs in the smear images was analyzed using ImageJ, and the RBCs with circularity lower than 0.5 were determined as irreversibly sickled red cells (ISCs). In some experiments, isolated RBCs were first stained with Octadecyl Rhodamine B Chloride (R18), followed by 3× wash using 1× PBS. Isolated RBCs were resuspended into cell culture medium to reach a hematocrit of ~40%. In experiments using glutaraldehyde-stiffened RBCs, RBCs from healthy donors were isolated by centrifugation, and washed with 1× PBS for three times. RBCs were then exposed to 0.065% (w/v) glutaraldehyde for 30 mins, followed by washing with 1× PBS for 6 times to remove the glutaraldehyde residue. These glutaraldehyde-stiffened RBCs were then mixed with normal RBCs in a ratio of 3:5, which were resuspended into cell culture medium to reach a hematocrit of ~40%. The cell culture medium for resuspending RBCs contains 1 unit/ml hirudin (Sigma), which de-activates residue thrombin in the medium and avoids the formation of tiny fibrin aggregates. The resuspended RBCs were perfused into the engineered microvasculature for 4 hours, in the end of which perfusion of sickle RBCs was recorded with videomicroscopy (Movie 4–5). The permeability assay was also carried out right after, 1 day and 2 days after 4-hour perfusion of sickled RBCs. In the experiments using R18-stained RBCs, the engineered microvasculature was stained first with hoescht 33342 before perfusion of R18-stained RBCs. After perfusion of R18-stained RBCs for 4 hours, BSA-AF488 was perfused into the engineered microvasculature, and then the microchannel occlusion and BSA leakage from the occluded microchannels were imaged using confocal microscope.
Culture of human malaria parasites
Plasmodium falciparum clone 3D7 and W2 were cultured under standard conditions using human O+ blood in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% pooled human AB serum. Cultures were maintained in a 37°C incubator under 5% CO2 atmosphere. Parasite density or parasitemia was determined by Giemsa staining of thin blood smear, and parasitemia of at least 3% was used for our experiments.
Investigate the effects of endothelial interactions with Plasmodium-infected RBCs (iRBCs) and TNF-α on endothelial barrier function in the engineered microvasculature
iRBCs were isolated via centrifugation and resuspended into cell culture medium to reach a hematocrit of 40%. The resuspended iRBCs were perfused into the non-TNF-α stimulated or TNF-α stimulated engineered microvasculature for 4 hours, in the end of which perfusion of iRBCs was recorded using videomicroscopy (Movie 6). The permeability assay was carried out right after, 1 day and 2 days after perfusion of iRBCs.
Statistical analysis
GraphPad Prism version 5.0 (GraphPad Software) was used for all calculations. Statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t-tests, one-way or two-way ANOVAs with Bonferroni’s post-test determined by sample distribution and variance. Differences with P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Figures were prepared using GraphPad Prism (GraphPad). All data points are derived from three or more biological or technical replicates as indicated for each experiment.
Study approval
Informed consents were obtained for all subjects. All protocols were approved by institutional review boards of Emory University.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was performed in part at the Georgia Tech Institute for Electronics and Nanotechnology, a member of the National Nanotechnology Coordinated Infrastructure, which is supported by the National Science Foundation (Grant ECCS-1542174). We acknowledge the clinical research personnel at Emory/Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta who helped with obtaining samples and the patients for donating their blood. We acknowledge Dr. David Archer and Dr. Lou Ann Brown for their valuable discussions. We acknowledge the rest of the Lam lab for technical support and suggestions. Financial support for this work was provided by National Science Foundation CAREER Award 1150235 (to W.A.L.); National Institutes of Health Grants U01HL117721 (to S.F.O, C.H.J., and W.A.L.), U54HL112309 (to W.A.L.), R01HL121264 (to W.A.L.)
Footnotes
Author contributions
YQ and WAL designed the device. YQ, WAL, SFO, CHJ and TJL conceived and designed the project. YQ, BA, YS, CH, RT, PNM, RM and JC performed the experimental work. YQ, WAL, SFO, CHJ, and TJL analyzed the data. YQ, WAL, SFO, CHJ, TJL, PNM and JC wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results.
Competing financial interests
The authors declare no competing financial and non-financial interests.
References
- 1.Deanfield JE, Halcox JP, Rabelink TJ. Endothelial function and dysfunction - Testing and clinical relevance. Circulation. 2007;115(10):1285–1295. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.652859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mehta D, Malik AB. Signaling mechanisms regulating endothelial permeability. Physiol Rev. 2006;86(1):279–367. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00012.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Buffet PA, Safeukui I, Deplaine G, Brousse V, Prendki V, Thellier M, et al. The pathogenesis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in humans: insights from splenic physiology. Blood. 2011;117(2):381–392. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-04-202911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Faille D, El-Assaad F, Alessi MC, Fusai T, Combes V, Grau GE. Platelet-endothelial cell interactions in cerebral malaria: the end of a cordial understanding. Thromb Haemost. 2009;102(6):1093–1102. doi: 10.1160/TH09-05-0337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ghosh S, Tan F, Ofori-Acquah SF. Spatiotemporal dysfunction of the vascular permeability barrier in transgenic mice with sickle cell disease. Anemia. 2012;2012:582018. doi: 10.1155/2012/582018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hebbel RP, Osarogiagbon R, Kaul D. The endothelial biology of sickle cell disease: Inflammation and a chronic vasculopathy. Microcirculation. 2004;11(2):129–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Frevert U, Nacer A. Fatal cerebral malaria: a venous efflux problem. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014;4:155. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ghosh S, Ihunnah CA, Hazra R, Walker AL, Hansen JM, Archer DR, et al. Nonhematopoietic Nrf2 dominantly impedes adult progression of sickle cell anemia in mice. JCI Insight. 2016;1(4) doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.81090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Manwani D, Frenette PS. Vaso-occlusion in sickle cell disease: pathophysiology and novel targeted therapies. Blood. 2013;122(24):3892–3898. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-05-498311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Storm J, Craig AG. Pathogenesis of cerebral malaria--inflammation and cytoadherence. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014;4:100. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vercellotti GM, Belcher JD. Not simply misshapen red cells: multimolecular and cellular events in sickle vaso-occlusion. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(4):1462–1465. doi: 10.1172/JCI75238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhang BY, Montgomery M, Chamberlain MD, Ogawa S, Korolj A, Pahnke A, et al. Biodegradable scaffold with built-in vasculature for organ-on-a-chip engineering and direct surgical anastomosis. Nat Mater. 2016;15(6):669. doi: 10.1038/nmat4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Johnston ID, McCluskey DK, Tan CKL, Tracey MC. Mechanical characterization of bulk Sylgard 184 for microfluidics and microengineering. J Micromech Microeng. 2014;24(3) [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tsai M, Kita A, Leach J, Rounsevell R, Huang JN, Moake J, et al. In vitro modeling of the microvascular occlusion and thrombosis that occur in hematologic diseases using microfluidic technology. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(1):408–418. doi: 10.1172/JCI58753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Huynh J, Nishimura N, Rana K, Peloquin JM, Califano JP, Montague CR, et al. Age-related intimal stiffening enhances endothelial permeability and leukocyte transmigration. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3(112):112ra122. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kohn JC, Lampi MC, Reinhart-King CA. Age-related vascular stiffening: causes and consequences. Frontiers in genetics. 2015;6:112. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Carrion B, Huang CP, Ghajar CM, Kachgal S, Kniazeva E, Jeon NL, et al. Recreating the Perivascular Niche Ex Vivo Using a Microfluidic Approach. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2010;107(6):1020–1028. doi: 10.1002/bit.22891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chen MB, Lamar JM, Li R, Hynes RO, Kamm RD. Elucidation of the Roles of Tumor Integrin beta1 in the Extravasation Stage of the Metastasis Cascade. Cancer research. 2016;76(9):2513–2524. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wang XL, Phan DTT, Sobrino A, George SC, Hughes CCW, Lee AP. Engineering anastomosis between living capillary networks and endothelial cell-lined microfluidic channels. Lab Chip. 2016;16(2):282–290. doi: 10.1039/c5lc01050k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Whisler JA, Chen MB, Kamm RD. Control of Perfusable Microvascular Network Morphology Using a Multiculture Microfluidic System. Tissue Eng Part C-Me. 2014;20(7):543–552. doi: 10.1089/ten.tec.2013.0370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Price GM, Wong KHK, Truslow JG, Leung AD, Acharya C, Tien J. Effect of mechanical factors on the function of engineered human blood microvessels in microfluidic collagen gels. Biomaterials. 2010;31(24):6182–6189. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.04.041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wong KHK, Truslow JG, Tien J. The role of cyclic AMP in normalizing the function of engineered human blood microvessels in microfluidic collagen gels. Biomaterials. 2010;31(17):4706–4714. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.02.041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Nichol JW, Koshy ST, Bae H, Hwang CM, Yamanlar S, Khademhosseini A. Cell-laden microengineered gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2010;31(21):5536–5544. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.03.064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nguyen DHT, Stapleton SC, Yang MT, Cha SS, Choi CK, Galie PA, et al. Biomimetic model to reconstitute angiogenic sprouting morphogenesis in vitro. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(17):6712–6717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1221526110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Heintz KA, Bregenzer ME, Mantle JL, Lee KH, West JL, Slater JH. Fabrication of 3D Biomimetic Microfluidic Networks in Hydrogels. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(17):2153–2160. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201600351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Brandenberg N, Lutolf MP. In Situ Patterning of Microfluidic Networks in 3D Cell-Laden Hydrogels. Adv Mater. 2016;28(34):7450–7456. doi: 10.1002/adma.201601099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zheng Y, Chen J, Craven M, Choi NW, Totorica S, Diaz-Santana A, et al. In vitro microvessels for the study of angiogenesis and thrombosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(24):9342–9347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201240109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Miller JS, Stevens KR, Yang MT, Baker BM, Nguyen DHT, Cohen DM, et al. Rapid casting of patterned vascular networks for perfusable engineered three-dimensional tissues. Nat Mater. 2012;11(9):768–774. doi: 10.1038/nmat3357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Linville RM, Boland NF, Covarrubias G, Price GM, Tien J. Physical and Chemical Signals That Promote Vascularization of Capillary-Scale Channels. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2016;9(1):73–84. doi: 10.1007/s12195-016-0429-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chrobak KM, Potter DR, Tien J. Formation of perfused, functional microvascular tubes in vitro. Microvasc Res. 2006;71(3):185–196. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2006.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kuijpers AJ, Engbers GHM, Krijgsveld J, Zaat SAJ, Dankert J, Feijen J. Cross-linking and characterisation of gelatin matrices for biomedical applications. J Biomat Sci-Polym E. 2000;11(3):225–243. doi: 10.1163/156856200743670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yu Q, Zhou J, Fung YC. Neutral axis location in bending and Young’s modulus of different layers of arterial wall. The American journal of physiology. 1993;265(1 Pt 2):H52–60. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.265.1.H52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Handorf AM, Zhou YX, Halanski MA, Li WJ. Tissue Stiffness Dictates Development, Homeostasis, and Disease Progression. Organogenesis. 2015;11(1):1–15. doi: 10.1080/15476278.2015.1019687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jain RK. Delivery of molecular and cellular medicine to solid tumors. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;46(1–3):149–168. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(00)00131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Warkentin TE, Moore JC, Anand SS, Lonn EM, Morgan DG. Gastrointestinal bleeding, angiodysplasia, cardiovascular disease, and acquired von Willebrand syndrome. Transfus Med Rev. 2003;17(4):272–286. doi: 10.1016/s0887-7963(03)00037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Giannotta M, Trani M, Dejana E. VE-cadherin and endothelial adherens junctions: active guardians of vascular integrity. Dev Cell. 2013;26(5):441–454. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.08.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yuan W, Lv Y, Zeng M, Fu BM. Non-invasive measurement of solute permeability in cerebral microvessels of the rat. Microvasc Res. 2009;77(2):166–173. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2008.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhang DC, Xu CL, Manwani D, Frenette PS. Neutrophils, platelets, and inflammatory pathways at the nexus of sickle cell disease pathophysiology. Blood. 2016;127(7):801–809. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-09-618538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gimenez F, Barraud de Lagerie S, Fernandez C, Pino P, Mazier D. Tumor necrosis factor alpha in the pathogenesis of cerebral malaria. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003;60(8):1623–1635. doi: 10.1007/s00018-003-2347-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chang J, Patton JT, Sarkar A, Ernst B, Magnani JL, Frenette PS. GMI-1070, a novel pan-selectin antagonist, reverses acute vascular occlusions in sickle cell mice. Blood. 2010;116(10):1779–1786. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-12-260513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yao L, Setiadi H, Xia L, Laszik Z, Taylor FB, McEver RP. Divergent inducible expression of P-selectin and E-selectin in mice and primates. Blood. 1999;94(11):3820–3828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Martinelli R, Kamei M, Sage PT, Massol R, Varghese L, Sciuto T, et al. Release of cellular tension signals self-restorative ventral lamellipodia to heal barrier micro-wounds. The Journal of cell biology. 2013;201(3):449–465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201209077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Schaer DJ, Buehler PW, Alayash AI, Belcher JD, Vercellotti GM. Hemolysis and free hemoglobin revisited: exploring hemoglobin and hemin scavengers as a novel class of therapeutic proteins. Blood. 2013;121(8):1276–1284. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-11-451229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Belcher JD, Chen C, Nguyen J, Milbauer L, Abdulla F, Alayash AI, et al. Heme triggers TLR4 signaling leading to endothelial cell activation and vaso-occlusion in murine sickle cell disease. Blood. 2014;123(3):377–390. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-04-495887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ghosh S, Adisa OA, Chappa P, Tan F, Jackson KA, Archer DR, et al. Extracellular hemin crisis triggers acute chest syndrome in sickle mice. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(11):4809–4820. doi: 10.1172/JCI64578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Asakura T, Asakura K, Obata K, Mattiello J, Ballas SK. Blood samples collected under venous oxygen pressure from patients with sickle cell disease contain a significant number of a new type of reversibly sickled cells: constancy of the percentage of sickled cells in individual patients during steady state. Am J Hematol. 2005;80(4):249–256. doi: 10.1002/ajh.20468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Byun H, Hillman TR, Higgins JM, Diez-Silva M, Peng ZL, Dao M, et al. Optical measurement of biomechanical properties of individual erythrocytes from a sickle cell patient. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(11):4130–4138. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.07.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lu X, Tang ZY, Zeng Z, Chen X, Yao WJ, Yan ZY, et al. The measurement of shear modulus and membrane surface viscosity of RBC membrane with Ektacytometry: A new technique. Math Biosci. 2007;209(1):190–204. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2006.09.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bernabeu M, Danziger SA, Avril M, Vaz M, Babar PH, Brazier AJ, et al. Severe adult malaria is associated with specific PfEMP1 adhesion types and high parasite biomass. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113(23):E3270–E3279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1524294113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Turner L, Lavstsen T, Berger SS, Wang CW, Petersen JEV, Avril M, et al. Severe malaria is associated with parasite binding to endothelial protein C receptor. Nature. 2013;498(7455):502. doi: 10.1038/nature12216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yeh YT, Hur SS, Chang J, Wang KC, Chiu JJ, Li YS, et al. Matrix Stiffness Regulates Endothelial Cell Proliferation through Septin 9. Plos One. 2012;7(10) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sack KD, Teran M, Nugent MA. Extracellular Matrix Stiffness Controls VEGF Signaling and Processing in Endothelial Cells. Journal of cellular physiology. 2016;231(9):2026–2039. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hayashi A, Kanzaki T. Swelling of agarose gel and its related changes. Food Hydrocolloid. 1987;1(4):317–325. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Qiu Y, Brown AC, Myers DR, Sakurai Y, Mannino RG, Tran R, et al. Platelet mechanosensing of substrate stiffness during clot formation mediates adhesion, spreading, and activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(40):14430–14435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1322917111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wang C, Lu H, Schwartz MA. A novel in vitro flow system for changing flow direction on endothelial cells. J Biomech. 2012;45(7):1212–1218. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2012.01.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Price GM, Tien J. Methods for Forming Human Microvascular Tubes In Vitro and Measuring Their Macromolecular Permeability. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;671:281–293. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-551-0_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Yuan F, Leunig M, Berk DA, Jain RK. Microvascular permeability of albumin, vascular surface area, and vascular volume measured in human adenocarcinoma LS174T using dorsal chamber in SCID mice. Microvasc Res. 1993;45(3):269–289. doi: 10.1006/mvre.1993.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Yuan Y, Chilian WM, Granger HJ, Zawieja DC. Permeability to albumin in isolated coronary venules. Am J Physiol. 1993;265(2 Pt 2):H543–552. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.265.2.H543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.