Three 1-[(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(halobenzoyl)piperazines adopt very similar molecular conformations but, while the molecules of the 3-fluorobenzoyl are linked by hydrogen bonds into a three-dimensional structure, there are no hydrogen bonds in either of the 2,6-difluorobenzoyl and 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl analogues.
Keywords: piperazines, crystal structure, molecular conformation, hydrogen bonding, supramolecular assembly
Abstract
In each of the compounds 1-[(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(3-fluorobenzoyl)piperazine, C19H19FN2O3 (I), 1-[(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)piperazine, C19H18F2N2O3 (II), and 1-[(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,4-dichlorobenzoyl)piperazine, C19H19Cl2N2O3 (III), the piperazine rings adopt a chair conformation with the (1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl substituent occupying an equatorial site: the five-membered rings are all slightly folded across the O⋯O line leading to envelope conformations. The dihedral angle between the planar amidic fragment and the haloaryl ring is 62.97 (5)° in (I) but 77.72 (12)° and 75.50 (5)° in (II) and (III), respectively. Despite their similarity in constitution and conformation, the supramolecular interactions in (I)–(III) differ: in (I), a combination of C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bonds links the molecules into a three-dimensional framework structure, but there are no hydrogen bonds of any sort in either (II) or (III), although the structure of (III) contains a short Cl⋯Cl contact between inversion-related pairs of molecules.
Chemical context
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]piperazine is an important intermediate for the synthesis (Duncton et al., 2006 ▸; Hamid & Williams, 2007 ▸) of piribedil, 1-[(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(pyrimidin-2-yl)piperazine, which is used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, particularly in the reduction of tremor (Rondot & Ziegler, 1992 ▸; Millan et al., 2001 ▸). The synthetic routes to piribedil reported hitherto have utilized either palladium-catalysed (Duncton et al., 2006 ▸) or ruthenium-catalysed (Hamid & Williams, 2007 ▸) processes, requiring extensive purification procedures to ensure that the final product is free of heavy metals. With this in mind, we have now synthesized a series of N-aroyl analogues (I)–(III) (Figs. 1 ▸–3 ▸
▸) using a metal-free procedure involving a straightforward coupling reaction between 1-[(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]piperazine and a carboxylic acid, promoted by 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodimide as the dehydrating agent, and we report here the molecular and supramolecular structures of compounds (I)–(III).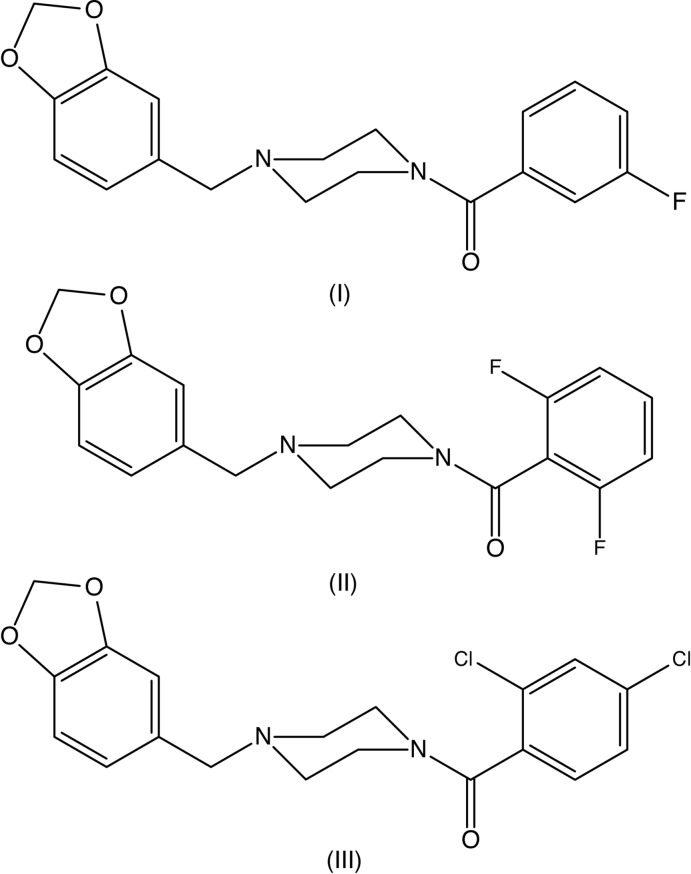
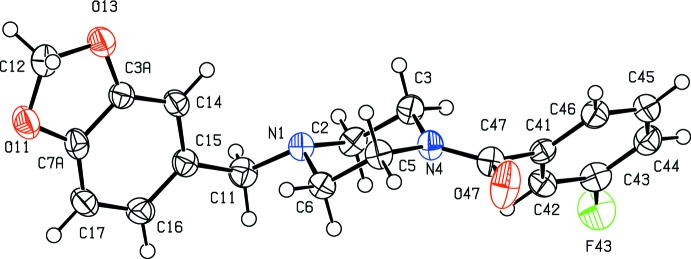
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of compound (I) showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
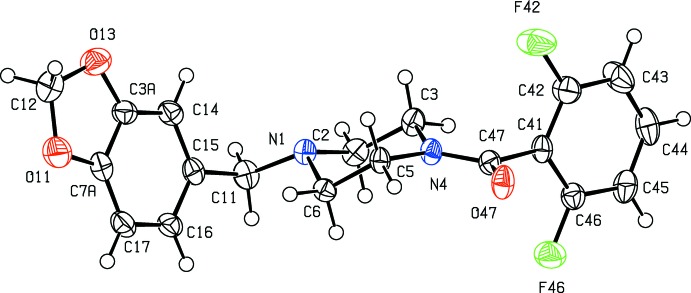
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of compound (II) showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
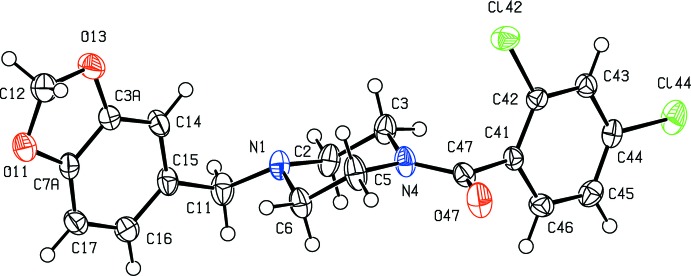
Figure 3.
The molecular structure of compound (III) showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Structural commentary
In each of (I)–(III), the five-membered ring is slightly non-planar: while the atoms O11, C7A, C3A and O13 are co-planar, as expected, the atom C12 is slightly displaced from this plane by 0.150 (2), 0.099 (6) and 0.210 (2) Å in (I)–(III), respectively, giving an envelope conformation in each case, with the ring folded across the line O11⋯O13. The piperazine rings all adopt chair conformations with the substituent at atom N1 in an equatorial site, while the atoms of the amide fragment (C3, N4, C5, C47, O47 and C41) are coplanar. The only significant conformational difference between the molecules in (I)–(III) lies in the dihedral angle between the amide unit and the adjacent aryl ring (C41–C46), 62.97 (5)° in (I) but 77.72 (12) and 75.50 (5)° in (II) and (III), respectively. The molecules of (I)–(III) exhibit no internal symmetry and hence they are all conformationally chiral, but the space groups (Table 2 ▸) confirm that equal numbers of the two conformational enantiomorphs are present in each crystal.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | (III) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | |||
| Chemical formula | C19H19FN2O3 | C19H18F2N2O3 | C19H18Cl2N2O3 |
| M r | 342.36 | 360.35 | 393.25 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n | Orthorhombic, P c a21 | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 173 | 173 | 173 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 12.2358 (16), 10.3185 (14), 14.2310 (19) | 14.2762 (9), 15.9821 (10), 7.3753 (5) | 12.2889 (14), 12.3034 (14), 13.3667 (15) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 111.199 (2), 90 | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 116.295 (1), 90 |
| V (Å3) | 1675.2 (4) | 1682.78 (19) | 1811.9 (4) |
| Z | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.38 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.48 × 0.29 × 0.28 | 0.91 × 0.35 × 0.17 | 0.49 × 0.48 × 0.38 |
| Data collection | |||
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD | Bruker APEXII CCD | Bruker APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2015 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2015 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.813, 0.972 | 0.587, 0.981 | 0.776, 0.867 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 8635, 3674, 2975 | 9016, 3743, 3449 | 9718, 4054, 3545 |
| R int | 0.021 | 0.057 | 0.017 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.651 | 0.650 | 0.648 |
| Refinement | |||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.040, 0.114, 1.10 | 0.054, 0.155, 1.16 | 0.031, 0.087, 1.04 |
| No. of reflections | 3674 | 3743 | 4054 |
| No. of parameters | 226 | 235 | 235 |
| No. of restraints | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.24, −0.18 | 0.17, −0.22 | 0.37, −0.38 |
| Absolute structure | – | Flack x determined using 1369 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) | – |
Supramolecular features
Despite their similar molecular constitutions and conformations, compounds (I)–(III) all exhibit different types of direction-specific intermolecular interactions. In the crystal structure of compound (I), a combination of one C—H⋯O hydrogen bond and two C—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸) links the molecules into a three-dimensional framework structure, whose formation can readily be analysed in terms of simple sub-structures (Ferguson et al., 1998a
▸,b
▸; Gregson et al., 2000 ▸). The C—H⋯O hydrogen bond links molecules related by the 21 screw axis along (0.25, y, 0.25) to form a C(5) (Etter, 1990 ▸; Etter et al., 1990 ▸; Bernstein et al., 1995 ▸) chain running parallel to the [010] direction. In addition, the C—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bond having atom C5 as the donor links molecules related by the 21 screw axis along (0.75, y, 0.25) into a second chain running parallel to [010] and, together, these two interactions generate a sheet lying parallel to (001) (Fig. 4 ▸). The second C—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bond, having atom C45 as the donor, links molecules related by the n-glide plane at y = 0.75 into a chain running parallel to the [10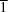 ] direction (Fig. 5 ▸), and chains of this type link the (001) sheets into a continuous three-dimensional structure. It is interesting to note that both C—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bonds utilize the same ring as the acceptor, with one donor approaching each face of this ring (Fig. 6 ▸), with the angle H5i⋯Cg1⋯H45ii = 152°, where Cg1 represents the centroid of the ring (C3A, C14, C15, C16, C17, C7A) and the symmetry codes are (i)
] direction (Fig. 5 ▸), and chains of this type link the (001) sheets into a continuous three-dimensional structure. It is interesting to note that both C—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bonds utilize the same ring as the acceptor, with one donor approaching each face of this ring (Fig. 6 ▸), with the angle H5i⋯Cg1⋯H45ii = 152°, where Cg1 represents the centroid of the ring (C3A, C14, C15, C16, C17, C7A) and the symmetry codes are (i)  − x, −
− x, −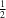 + y,
+ y, 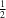 − z) and (ii) (
− z) and (ii) (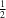 + x,
+ x,  − y, −
− y, −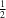 + z). Hence, the two molecules providing the donor atoms here are related by inversion across (1, 1/2, 0). In this structure, the atoms of type O11 in the molecules at (x, y, z) and (2 − x, 1 − y, −z) are separated by a distance of only 2.7888 (18) Å. At the same time, the atoms C12 and H12 at (x, y, z) are distant from O11 at (2 − x, 1 − y, −z) by 2.66 and 3.008 (2) Å, respectively, with an associated C—H⋯O angle of 101°; the H⋯O distance is too long and the C—H⋯O angle is too small for this contact to be regarded as a hydrogen bond, but the short O⋯O distance here is perhaps associated with this ‘failed’ hydrogen bond involving atom C12.
+ z). Hence, the two molecules providing the donor atoms here are related by inversion across (1, 1/2, 0). In this structure, the atoms of type O11 in the molecules at (x, y, z) and (2 − x, 1 − y, −z) are separated by a distance of only 2.7888 (18) Å. At the same time, the atoms C12 and H12 at (x, y, z) are distant from O11 at (2 − x, 1 − y, −z) by 2.66 and 3.008 (2) Å, respectively, with an associated C—H⋯O angle of 101°; the H⋯O distance is too long and the C—H⋯O angle is too small for this contact to be regarded as a hydrogen bond, but the short O⋯O distance here is perhaps associated with this ‘failed’ hydrogen bond involving atom C12.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
Cg1 represents the centroid of the C3A, C14, C15, C16, C17, C7A ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C42—H42⋯O47i | 0.95 | 2.34 | 3.273 (2) | 168 |
| C5—H5A⋯Cg1ii | 0.99 | 2.76 | 3.7310 (18) | 168 |
| C45—H45⋯Cg1iii | 0.95 | 2.90 | 3.7470 (18) | 149 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii) 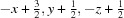 ; (iii)
; (iii) 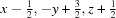 .
.
Figure 4.
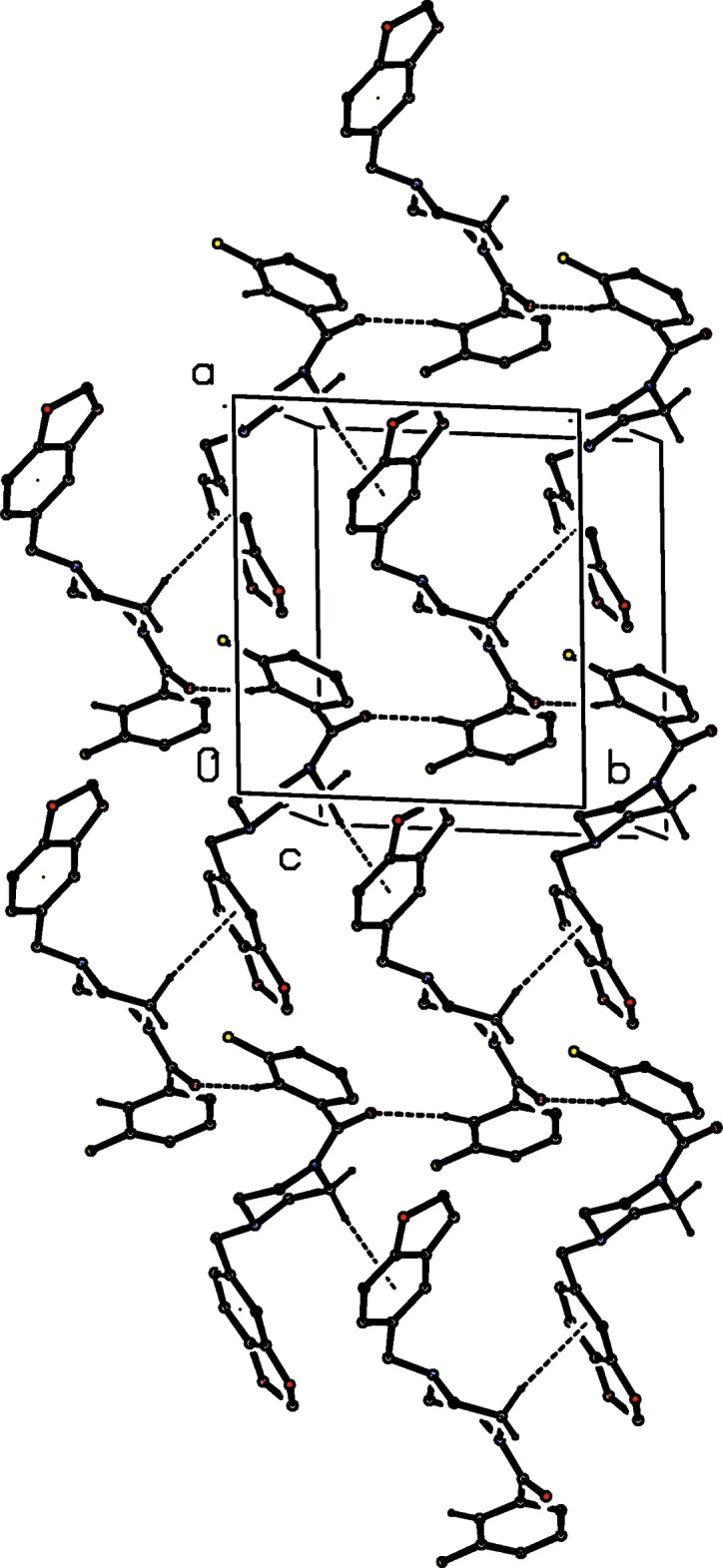
Part of the crystal structure of compound (I) showing the formation of a sheet lying parallel to (001) and built from C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bonds, which are drawn as dashed lines. For the sake of clarity, the H atoms bonded to the C atoms not involved in the motifs shown have been omitted.
Figure 5.
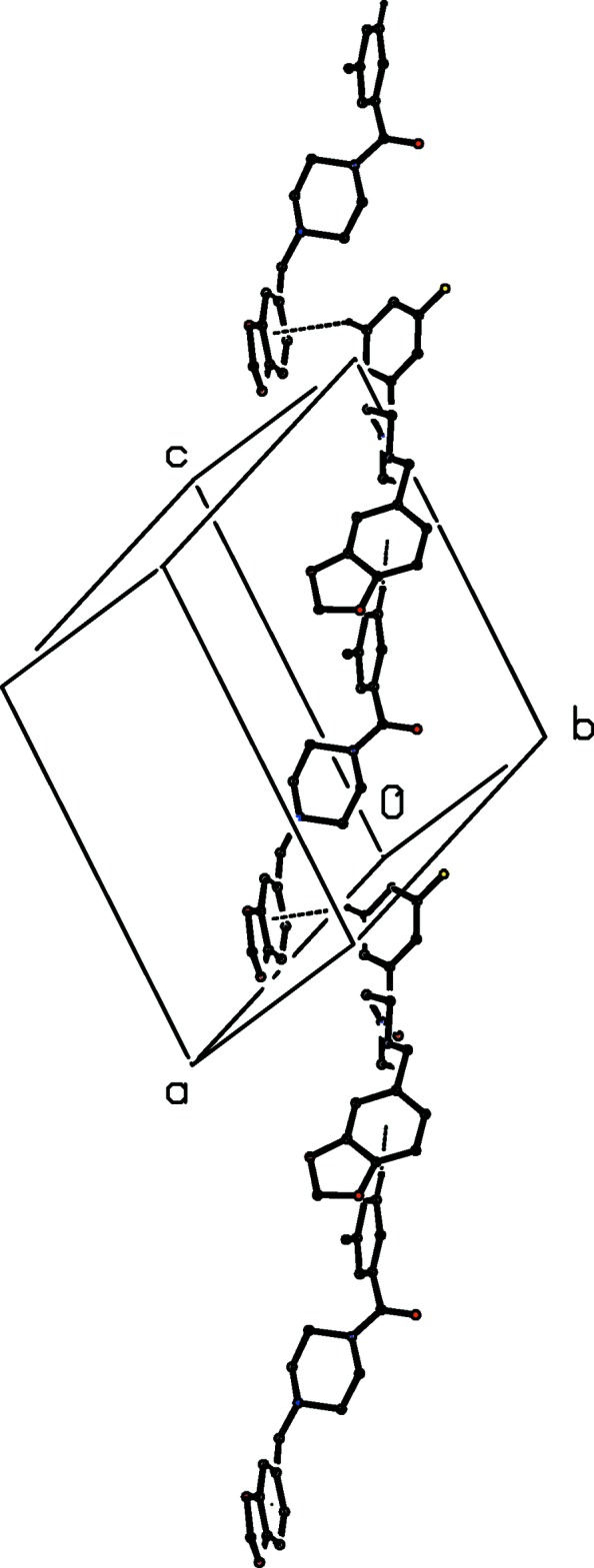
Part of the crystal structure of compound (I) showing the formation of a chain running parallel to [10 ] and built from C—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bonds, which are drawn as dashed lines. For the sake of clarity, the H atoms not involved in the motifs shown have been omitted.
] and built from C—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bonds, which are drawn as dashed lines. For the sake of clarity, the H atoms not involved in the motifs shown have been omitted.
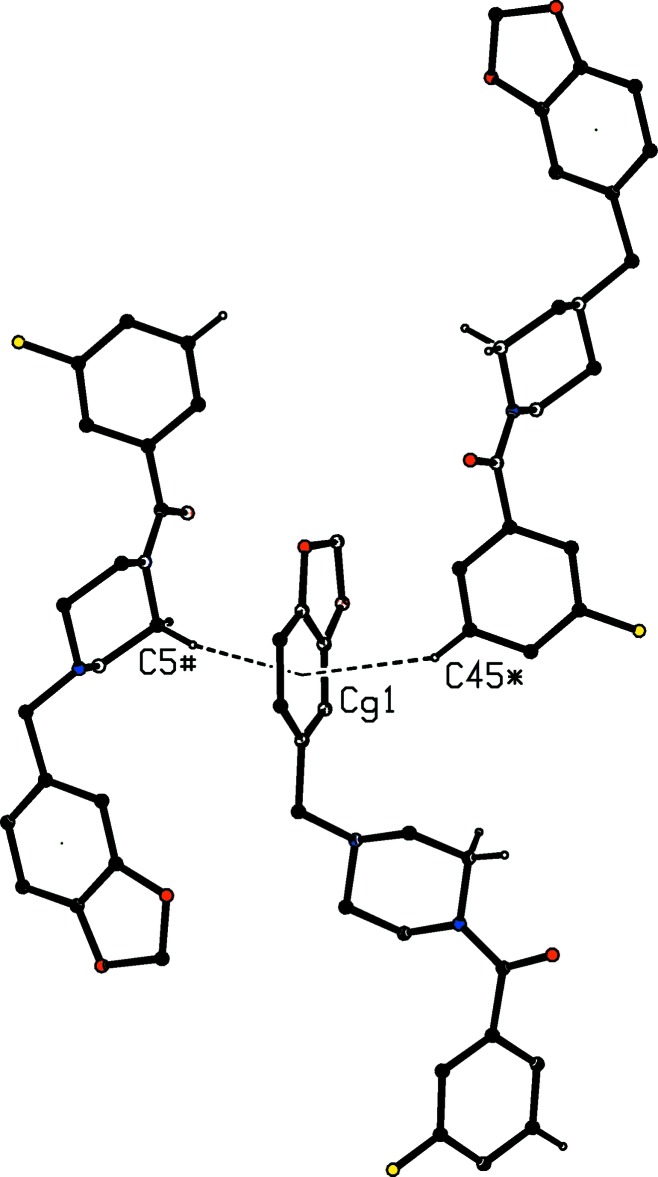
Figure 6.
Part of the crystal structure of compound (I) showing the two C—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bonds with a common aryl acceptor. The hydrogen bonds are drawn as dashed lines and, for the sake of clarity, the unit-cell outline and the H atoms bonded to the C atoms not involved in the motifs shown have been omitted. The atoms marked with an asterisk (*) or a hash (#) are at the symmetry positions ( + x,
+ x,  − y, −
− y, −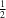 + z) and (
+ z) and ( − x, −
− x, −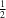 + y,
+ y, 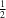 − z), respectively.
− z), respectively.
In contrast to the three-dimensional supramolecular assembly in (I) generated by three hydrogen bonds, the only direction-specific intermolecular interaction in (II) is a single C—H⋯O contact, in which the D–-H⋯A angle is only 123° so that this cannot be regarded as structurally significant (Wood et al., 2009 ▸). The only direction-specific intermolecular interactions in (III) are a C—Cl⋯(ring) contact involving the 1,3-dioxolane ring, but since this ring is not aromatic, this contact cannot be regarded as structurally significant; and a short Cl⋯Cl contact between inversion-related pairs of molecules. For the atoms of type Cl44 in the molecules at (x, y, z) and (−x, −y, 2 − z), the Cl⋯Cli distance is 3.3963 (7) Å with an associated C—Cl⋯Cli angle of 137.68 (5)° [symmetry code: (i) −x, −y, 2 − z]. For C—Cl⋯Cl angles of 90 and 180°, values of 1.78 and 1.58 Å have been suggested (Nyburg & Faerman, 1985 ▸) for the major and minor van der Waals radii: on this basis, a value of around 1.68 Å would seem appropriate to a C—Cl⋯Cl angle close to 135°, so that the observed Cl⋯Cl contact distance in (III) is not exceptional, and is probably therefore of no structural significance. Thus for both (II) and (III), the molecular packing depends solely on molecular shape and van der Waals forces.
Database survey
It is of interest briefly to compare the supramolecular assembly found here for compounds (I)–(III) with that observed in some related compounds. In 1-[(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(pyrimidin-2-yl)piperazine (piribedil), the molecules are linked into sheets by three independent C—H⋯π hydrogen bonds (Wu et al., 2013 ▸), and in 1-(2-iodobenzoyl)-4-(pyrimidin-2-yl)piperazine, the molecules are linked by a combination of C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π hydrogen bonds to form a three-dimensional structure which is augmented by π–π stacking interactions and N⋯I interactions (Mahesha et al., 2019 ▸). The amidic compound N-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(pyrimidin-2-yl)piperazine-1-carboxamide crystallizes with Z′ = 2 in space group P21/c, and the molecules are linked by two independent N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to form chains of 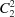 (8) type, although these are described as C(4) in the original report (Li, 2011 ▸). Finally, we note the structures of three salts derived by monoprotonation of the starting material 1-[(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]piperazine used in the synthesis of compounds (I)–(III): protonation occurs at the unsubstituted N atom of the piperazine unit in each of the picrate (Kavitha et al., 2014a
▸), 4-nitrobenzoate (Kavitha et al., 2014b
▸) and 4-chlorobenzoate (Kavitha et al., 2014c
▸) salts, although the schematic diagrams given for the two carboxylate salts depict protonation at the substituted N atom.
(8) type, although these are described as C(4) in the original report (Li, 2011 ▸). Finally, we note the structures of three salts derived by monoprotonation of the starting material 1-[(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]piperazine used in the synthesis of compounds (I)–(III): protonation occurs at the unsubstituted N atom of the piperazine unit in each of the picrate (Kavitha et al., 2014a
▸), 4-nitrobenzoate (Kavitha et al., 2014b
▸) and 4-chlorobenzoate (Kavitha et al., 2014c
▸) salts, although the schematic diagrams given for the two carboxylate salts depict protonation at the substituted N atom.
Synthesis and crystallization
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]piperazine was purchased from Sigma–Aldrich and used as received. For the synthesis of compounds (I)–(III), 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodimide (207 mg, 1.08 mmol), 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (121.6 mg, 0.9 mmol) and triethylamine (0.5 ml, 3.7 mmol) were added to solutions of the appropriately substituted benzoic acid [3-fluorobenzoic acid for (I), 2,6-difluorobenzoic acid for (II) or 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid for (III)] (0.9 mmol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (5 ml) and the resulting mixtures were then stirred at 273 K for 20 min. A solution of 1-[(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]piperazine (200 mg, 0.9 mmol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (5 ml) was then added to each mixture and stirring was continued overnight at ambient temperature. When the reactions were complete as confirmed using thin-layer chromatography, an excess of water was added to each of the mixtures, which were then exhaustively extracted using ethyl acetate. Each of the organic fractions was then washed successively with aqueous hydrochloric acid (1 mol dm−3), then with a saturated aqueous solution of sodium hydrogencarbonate, and finally with brine. The organic fractions were then dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure. Slow evaporation of these solutions, at ambient temperature and in the presence of air, gave crystals of compounds (I)–(III) suitable for single-crystal X-ray diffraction: m.p. (I) 383–386 K, (II) 373 K, (III) 394–396 K.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. All H atoms were located in difference maps, and they were subsequently treated as riding atoms in geometrically idealized positions with C—H distances 0.95 Å (aromatic) or 0.99 Å (CH2) and with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C). For compound (I), fifteen bad outlier reflections were omitted from the data set. For compound (II), the correct orientation of the structure with respect to the polar axis direction could not be established because of the lack of significant resonant scattering: thus calculation of the Flack x parameter (Flack, 1983 ▸) using using 1369 quotients of the type [(I +) − (I −)]/[(I +) + (I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) gave a value −0.3 (10), which must be regarded as indeterminate (Flack & Bernardinelli, 2000 ▸), despite the 93% coverage of Friedel pairs, while the value of the Hooft y parameter (Hooft et al., 2008 ▸), y = −0.2 (6), is likewise indeterminate.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II, III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019000458/zl2747sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019000458/zl2747Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019000458/zl2747IIsup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019000458/zl2747IIIsup4.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019000458/zl2747Isup5.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019000458/zl2747IIsup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019000458/zl2747IIIsup7.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
NM is grateful to the University of Mysore for research facilities.
supplementary crystallographic information
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(3-fluorobenzoyl)piperazine (I). Crystal data
| C19H19FN2O3 | F(000) = 720 |
| Mr = 342.36 | Dx = 1.357 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 12.2358 (16) Å | Cell parameters from 3689 reflections |
| b = 10.3185 (14) Å | θ = 1.9–27.6° |
| c = 14.2310 (19) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 111.199 (2)° | T = 173 K |
| V = 1675.2 (4) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.48 × 0.29 × 0.28 mm |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(3-fluorobenzoyl)piperazine (I). Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3674 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine focus sealed tube | 2975 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.021 |
| Detector resolution: 0.3333 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.6°, θmin = 1.9° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −10→15 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2015) | k = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.813, Tmax = 0.972 | l = −18→9 |
| 8635 measured reflections |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(3-fluorobenzoyl)piperazine (I). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.114 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0476P)2 + 0.4713P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.10 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3674 reflections | Δρmax = 0.24 e Å−3 |
| 226 parameters | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(3-fluorobenzoyl)piperazine (I). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(3-fluorobenzoyl)piperazine (I). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.57212 (10) | 0.47476 (11) | 0.26954 (9) | 0.0303 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.51223 (13) | 0.44782 (14) | 0.33984 (11) | 0.0330 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.5622 | 0.3918 | 0.3952 | 0.040* | |
| H2B | 0.4379 | 0.4014 | 0.3043 | 0.040* | |
| C3 | 0.48694 (13) | 0.57400 (15) | 0.38272 (11) | 0.0356 (3) | |
| H3A | 0.4438 | 0.5560 | 0.4283 | 0.043* | |
| H3B | 0.5616 | 0.6173 | 0.4224 | 0.043* | |
| N4 | 0.41697 (11) | 0.65903 (12) | 0.30093 (9) | 0.0327 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.47088 (13) | 0.68273 (14) | 0.22552 (11) | 0.0327 (3) | |
| H5A | 0.5444 | 0.7325 | 0.2564 | 0.039* | |
| H5B | 0.4170 | 0.7344 | 0.1691 | 0.039* | |
| C6 | 0.49704 (13) | 0.55452 (14) | 0.18609 (11) | 0.0313 (3) | |
| H6A | 0.4228 | 0.5081 | 0.1502 | 0.038* | |
| H6B | 0.5368 | 0.5704 | 0.1377 | 0.038* | |
| C11 | 0.60711 (14) | 0.35498 (14) | 0.23287 (12) | 0.0368 (3) | |
| H11A | 0.5367 | 0.3124 | 0.1845 | 0.044* | |
| H11B | 0.6424 | 0.2951 | 0.2903 | 0.044* | |
| O11 | 0.95161 (10) | 0.44449 (12) | 0.06543 (9) | 0.0460 (3) | |
| C12 | 1.01387 (15) | 0.54464 (18) | 0.13322 (13) | 0.0450 (4) | |
| H12A | 1.0984 | 0.5232 | 0.1624 | 0.054* | |
| H12B | 1.0049 | 0.6279 | 0.0967 | 0.054* | |
| O13 | 0.96722 (10) | 0.55552 (12) | 0.21141 (9) | 0.0453 (3) | |
| C3A | 0.86787 (13) | 0.48056 (14) | 0.18111 (11) | 0.0317 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.78769 (13) | 0.46591 (14) | 0.22718 (11) | 0.0323 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.7950 | 0.5118 | 0.2870 | 0.039* | |
| C15 | 0.69410 (13) | 0.37999 (14) | 0.18201 (11) | 0.0327 (3) | |
| C16 | 0.68486 (14) | 0.31574 (15) | 0.09369 (12) | 0.0384 (4) | |
| H16 | 0.6203 | 0.2592 | 0.0636 | 0.046* | |
| C17 | 0.76762 (14) | 0.33156 (16) | 0.04750 (12) | 0.0399 (4) | |
| H17 | 0.7610 | 0.2869 | −0.0127 | 0.048* | |
| C7A | 0.85801 (14) | 0.41432 (14) | 0.09347 (11) | 0.0347 (3) | |
| C47 | 0.32103 (13) | 0.72461 (14) | 0.29797 (11) | 0.0328 (3) | |
| O47 | 0.27475 (12) | 0.80626 (13) | 0.23290 (10) | 0.0583 (4) | |
| C41 | 0.26784 (12) | 0.69823 (13) | 0.37650 (11) | 0.0291 (3) | |
| C42 | 0.22151 (13) | 0.57722 (14) | 0.38544 (11) | 0.0333 (3) | |
| H42 | 0.2306 | 0.5049 | 0.3476 | 0.040* | |
| C43 | 0.16209 (14) | 0.56607 (15) | 0.45098 (12) | 0.0367 (3) | |
| F43 | 0.11374 (10) | 0.44972 (10) | 0.45775 (9) | 0.0590 (3) | |
| C44 | 0.14867 (13) | 0.66616 (16) | 0.50952 (12) | 0.0377 (4) | |
| H44 | 0.1079 | 0.6542 | 0.5544 | 0.045* | |
| C45 | 0.19660 (13) | 0.78531 (16) | 0.50088 (12) | 0.0381 (4) | |
| H45 | 0.1896 | 0.8563 | 0.5409 | 0.046* | |
| C46 | 0.25459 (13) | 0.80141 (14) | 0.43428 (12) | 0.0345 (3) | |
| H46 | 0.2857 | 0.8839 | 0.4280 | 0.041* |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(3-fluorobenzoyl)piperazine (I). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0328 (6) | 0.0277 (6) | 0.0323 (6) | 0.0018 (5) | 0.0140 (5) | 0.0033 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0307 (7) | 0.0341 (8) | 0.0338 (8) | 0.0021 (6) | 0.0113 (6) | 0.0106 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0349 (8) | 0.0444 (9) | 0.0275 (7) | 0.0076 (6) | 0.0114 (6) | 0.0080 (6) |
| N4 | 0.0373 (7) | 0.0345 (7) | 0.0283 (6) | 0.0068 (5) | 0.0145 (5) | 0.0068 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0388 (8) | 0.0300 (7) | 0.0317 (7) | 0.0015 (6) | 0.0157 (6) | 0.0061 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0350 (8) | 0.0311 (7) | 0.0285 (7) | −0.0005 (6) | 0.0121 (6) | 0.0025 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0408 (8) | 0.0276 (7) | 0.0427 (9) | 0.0007 (6) | 0.0160 (7) | 0.0009 (6) |
| O11 | 0.0512 (7) | 0.0504 (7) | 0.0447 (7) | −0.0015 (5) | 0.0275 (6) | −0.0093 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0400 (9) | 0.0524 (10) | 0.0469 (10) | 0.0013 (7) | 0.0209 (8) | −0.0054 (8) |
| O13 | 0.0426 (6) | 0.0511 (7) | 0.0478 (7) | −0.0086 (5) | 0.0231 (6) | −0.0146 (5) |
| C3A | 0.0325 (7) | 0.0279 (7) | 0.0318 (7) | 0.0059 (6) | 0.0082 (6) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0367 (8) | 0.0306 (7) | 0.0290 (7) | 0.0048 (6) | 0.0113 (6) | −0.0022 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0351 (8) | 0.0273 (7) | 0.0344 (8) | 0.0064 (6) | 0.0108 (6) | 0.0013 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0358 (8) | 0.0344 (8) | 0.0391 (8) | 0.0030 (6) | 0.0066 (7) | −0.0068 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0465 (9) | 0.0388 (8) | 0.0324 (8) | 0.0077 (7) | 0.0117 (7) | −0.0073 (6) |
| C7A | 0.0401 (8) | 0.0330 (8) | 0.0330 (8) | 0.0109 (6) | 0.0160 (7) | 0.0023 (6) |
| C47 | 0.0369 (8) | 0.0260 (7) | 0.0370 (8) | 0.0018 (6) | 0.0150 (6) | 0.0059 (6) |
| O47 | 0.0624 (8) | 0.0576 (8) | 0.0686 (9) | 0.0303 (6) | 0.0401 (7) | 0.0385 (7) |
| C41 | 0.0263 (7) | 0.0280 (7) | 0.0303 (7) | 0.0019 (5) | 0.0071 (6) | 0.0036 (5) |
| C42 | 0.0400 (8) | 0.0268 (7) | 0.0329 (7) | −0.0001 (6) | 0.0128 (7) | 0.0002 (6) |
| C43 | 0.0383 (8) | 0.0311 (8) | 0.0398 (8) | −0.0047 (6) | 0.0130 (7) | 0.0068 (6) |
| F43 | 0.0759 (8) | 0.0378 (6) | 0.0757 (7) | −0.0142 (5) | 0.0424 (6) | 0.0061 (5) |
| C44 | 0.0342 (8) | 0.0466 (9) | 0.0337 (8) | 0.0027 (7) | 0.0141 (7) | 0.0058 (7) |
| C45 | 0.0368 (8) | 0.0382 (8) | 0.0387 (8) | 0.0020 (6) | 0.0127 (7) | −0.0064 (7) |
| C46 | 0.0332 (8) | 0.0270 (7) | 0.0431 (8) | −0.0020 (6) | 0.0135 (7) | −0.0006 (6) |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(3-fluorobenzoyl)piperazine (I). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—C6 | 1.4638 (18) | O13—C3A | 1.3722 (18) |
| N1—C11 | 1.4645 (18) | C3A—C14 | 1.371 (2) |
| N1—C2 | 1.4647 (18) | C3A—C7A | 1.389 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.517 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.406 (2) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C15—C16 | 1.389 (2) |
| C3—N4 | 1.4619 (18) | C16—C17 | 1.402 (2) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9900 | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3B | 0.9900 | C17—C7A | 1.363 (2) |
| N4—C47 | 1.3423 (19) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| N4—C5 | 1.4692 (17) | C47—O47 | 1.2283 (18) |
| C5—C6 | 1.5156 (19) | C47—C41 | 1.507 (2) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9900 | C41—C46 | 1.390 (2) |
| C5—H5B | 0.9900 | C41—C42 | 1.3960 (19) |
| C6—H6A | 0.9900 | C42—C43 | 1.379 (2) |
| C6—H6B | 0.9900 | C42—H42 | 0.9500 |
| C11—C15 | 1.510 (2) | C43—F43 | 1.3572 (17) |
| C11—H11A | 0.9900 | C43—C44 | 1.374 (2) |
| C11—H11B | 0.9900 | C44—C45 | 1.387 (2) |
| O11—C7A | 1.3777 (19) | C44—H44 | 0.9500 |
| O11—C12 | 1.431 (2) | C45—C46 | 1.384 (2) |
| C12—O13 | 1.4268 (19) | C45—H45 | 0.9500 |
| C12—H12A | 0.9900 | C46—H46 | 0.9500 |
| C12—H12B | 0.9900 | ||
| C6—N1—C11 | 111.35 (11) | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.4 |
| C6—N1—C2 | 109.80 (11) | C3A—O13—C12 | 105.63 (12) |
| C11—N1—C2 | 111.48 (11) | C14—C3A—O13 | 128.14 (13) |
| N1—C2—C3 | 109.70 (12) | C14—C3A—C7A | 122.03 (14) |
| N1—C2—H2A | 109.7 | O13—C3A—C7A | 109.82 (13) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.7 | C3A—C14—C15 | 117.14 (13) |
| N1—C2—H2B | 109.7 | C3A—C14—H14 | 121.4 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 109.7 | C15—C14—H14 | 121.4 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.2 | C16—C15—C14 | 120.05 (14) |
| N4—C3—C2 | 109.93 (12) | C16—C15—C11 | 120.75 (14) |
| N4—C3—H3A | 109.7 | C14—C15—C11 | 119.16 (13) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 109.7 | C15—C16—C17 | 122.17 (15) |
| N4—C3—H3B | 109.7 | C15—C16—H16 | 118.9 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 109.7 | C17—C16—H16 | 118.9 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 108.2 | C7A—C17—C16 | 116.51 (14) |
| C47—N4—C3 | 125.54 (12) | C7A—C17—H17 | 121.7 |
| C47—N4—C5 | 120.78 (12) | C16—C17—H17 | 121.7 |
| C3—N4—C5 | 113.15 (11) | C17—C7A—O11 | 128.17 (14) |
| N4—C5—C6 | 109.62 (11) | C17—C7A—C3A | 122.10 (14) |
| N4—C5—H5A | 109.7 | O11—C7A—C3A | 109.73 (14) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 109.7 | O47—C47—N4 | 121.94 (13) |
| N4—C5—H5B | 109.7 | O47—C47—C41 | 118.54 (13) |
| C6—C5—H5B | 109.7 | N4—C47—C41 | 119.52 (12) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 108.2 | C46—C41—C42 | 119.54 (13) |
| N1—C6—C5 | 110.19 (12) | C46—C41—C47 | 118.31 (12) |
| N1—C6—H6A | 109.6 | C42—C41—C47 | 121.84 (13) |
| C5—C6—H6A | 109.6 | C43—C42—C41 | 117.84 (13) |
| N1—C6—H6B | 109.6 | C43—C42—H42 | 121.1 |
| C5—C6—H6B | 109.6 | C41—C42—H42 | 121.1 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 108.1 | F43—C43—C44 | 118.11 (14) |
| N1—C11—C15 | 111.97 (12) | F43—C43—C42 | 118.15 (14) |
| N1—C11—H11A | 109.2 | C44—C43—C42 | 123.73 (14) |
| C15—C11—H11A | 109.2 | C43—C44—C45 | 117.76 (14) |
| N1—C11—H11B | 109.2 | C43—C44—H44 | 121.1 |
| C15—C11—H11B | 109.2 | C45—C44—H44 | 121.1 |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 107.9 | C46—C45—C44 | 120.34 (14) |
| C7A—O11—C12 | 105.29 (11) | C46—C45—H45 | 119.8 |
| O13—C12—O11 | 108.48 (13) | C44—C45—H45 | 119.8 |
| O13—C12—H12A | 110.0 | C45—C46—C41 | 120.77 (14) |
| O11—C12—H12A | 110.0 | C45—C46—H46 | 119.6 |
| O13—C12—H12B | 110.0 | C41—C46—H46 | 119.6 |
| O11—C12—H12B | 110.0 | ||
| C6—N1—C2—C3 | −60.96 (15) | C16—C17—C7A—C3A | −0.4 (2) |
| C11—N1—C2—C3 | 175.17 (12) | C12—O11—C7A—C17 | 174.64 (16) |
| N1—C2—C3—N4 | 57.23 (15) | C12—O11—C7A—C3A | −6.53 (16) |
| C2—C3—N4—C47 | 133.38 (15) | C14—C3A—C7A—C17 | 0.5 (2) |
| C2—C3—N4—C5 | −55.00 (16) | O13—C3A—C7A—C17 | 179.30 (14) |
| C47—N4—C5—C6 | −133.39 (14) | C14—C3A—C7A—O11 | −178.38 (13) |
| C3—N4—C5—C6 | 54.54 (16) | O13—C3A—C7A—O11 | 0.39 (17) |
| C11—N1—C6—C5 | −175.10 (11) | C3—N4—C47—O47 | 171.03 (16) |
| C2—N1—C6—C5 | 60.95 (15) | C5—N4—C47—O47 | 0.0 (2) |
| N4—C5—C6—N1 | −56.63 (15) | C3—N4—C47—C41 | −8.9 (2) |
| C6—N1—C11—C15 | 71.31 (15) | C5—N4—C47—C41 | −179.92 (13) |
| C2—N1—C11—C15 | −165.70 (12) | O47—C47—C41—C46 | −56.5 (2) |
| C7A—O11—C12—O13 | 10.19 (17) | N4—C47—C41—C46 | 123.39 (16) |
| O11—C12—O13—C3A | −9.99 (17) | O47—C47—C41—C42 | 116.97 (17) |
| C12—O13—C3A—C14 | −175.37 (15) | N4—C47—C41—C42 | −63.11 (19) |
| C12—O13—C3A—C7A | 5.95 (17) | C46—C41—C42—C43 | 1.1 (2) |
| O13—C3A—C14—C15 | −178.36 (14) | C47—C41—C42—C43 | −172.33 (13) |
| C7A—C3A—C14—C15 | 0.2 (2) | C41—C42—C43—F43 | 178.02 (14) |
| C3A—C14—C15—C16 | −0.9 (2) | C41—C42—C43—C44 | −1.7 (2) |
| C3A—C14—C15—C11 | 176.73 (13) | F43—C43—C44—C45 | −178.92 (14) |
| N1—C11—C15—C16 | −138.33 (14) | C42—C43—C44—C45 | 0.8 (2) |
| N1—C11—C15—C14 | 44.02 (18) | C43—C44—C45—C46 | 0.7 (2) |
| C14—C15—C16—C17 | 1.1 (2) | C44—C45—C46—C41 | −1.3 (2) |
| C11—C15—C16—C17 | −176.55 (14) | C42—C41—C46—C45 | 0.4 (2) |
| C15—C16—C17—C7A | −0.4 (2) | C47—C41—C46—C45 | 174.01 (13) |
| C16—C17—C7A—O11 | 178.28 (14) |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(3-fluorobenzoyl)piperazine (I). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 represents the centroid of the C3A, C14, C15, C16, C17, C7A ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C42—H42···O47i | 0.95 | 2.34 | 3.273 (2) | 168 |
| C5—H5A···Cg1ii | 0.99 | 2.76 | 3.7310 (18) | 168 |
| C45—H45···Cg1iii | 0.95 | 2.90 | 3.7470 (18) | 149 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) −x+3/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) x−1/2, −y+3/2, z+1/2.
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)piperazine (II). Crystal data
| C19H18F2N2O3 | Dx = 1.422 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 360.35 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pca21 | Cell parameters from 3743 reflections |
| a = 14.2762 (9) Å | θ = 1.9–27.5° |
| b = 15.9821 (10) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| c = 7.3753 (5) Å | T = 173 K |
| V = 1682.78 (19) Å3 | Needle, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.91 × 0.35 × 0.17 mm |
| F(000) = 752 |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)piperazine (II). Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3743 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine focus sealed tube | 3449 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.057 |
| Detector resolution: 0.3333 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 1.9° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −14→18 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2015) | k = −16→20 |
| Tmin = 0.587, Tmax = 0.981 | l = −9→9 |
| 9016 measured reflections |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)piperazine (II). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.054 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.096P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.155 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.16 | Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3 |
| 3743 reflections | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
| 235 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 1369 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 1 restraint |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)piperazine (II). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)piperazine (II). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.36051 (17) | 0.62727 (15) | 0.3017 (3) | 0.0249 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.3856 (2) | 0.71107 (18) | 0.2369 (5) | 0.0302 (6) | |
| H2A | 0.3597 | 0.7197 | 0.1138 | 0.036* | |
| H2B | 0.4546 | 0.7163 | 0.2299 | 0.036* | |
| C3 | 0.3470 (2) | 0.77682 (17) | 0.3641 (4) | 0.0302 (6) | |
| H3A | 0.3686 | 0.8328 | 0.3249 | 0.036* | |
| H3B | 0.2777 | 0.7762 | 0.3590 | 0.036* | |
| N4 | 0.37766 (17) | 0.76146 (14) | 0.5509 (4) | 0.0265 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.3658 (2) | 0.67513 (15) | 0.6138 (4) | 0.0247 (5) | |
| H5A | 0.2984 | 0.6633 | 0.6317 | 0.030* | |
| H5B | 0.3979 | 0.6679 | 0.7317 | 0.030* | |
| C6 | 0.40582 (18) | 0.61456 (18) | 0.4776 (4) | 0.0243 (6) | |
| H6A | 0.4742 | 0.6236 | 0.4659 | 0.029* | |
| H6B | 0.3953 | 0.5564 | 0.5193 | 0.029* | |
| C11 | 0.3880 (2) | 0.5620 (2) | 0.1720 (4) | 0.0320 (7) | |
| H11A | 0.4569 | 0.5628 | 0.1566 | 0.038* | |
| H11B | 0.3592 | 0.5740 | 0.0526 | 0.038* | |
| O11 | 0.26117 (18) | 0.25056 (13) | 0.4272 (4) | 0.0445 (6) | |
| C12 | 0.1638 (3) | 0.2617 (2) | 0.3896 (6) | 0.0426 (8) | |
| H12A | 0.1431 | 0.2208 | 0.2971 | 0.051* | |
| H12B | 0.1266 | 0.2526 | 0.5011 | 0.051* | |
| O13 | 0.15012 (16) | 0.34454 (15) | 0.3247 (4) | 0.0436 (6) | |
| C3A | 0.2382 (2) | 0.37818 (18) | 0.3049 (5) | 0.0295 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.2621 (2) | 0.45542 (17) | 0.2400 (4) | 0.0299 (6) | |
| H14 | 0.2157 | 0.4937 | 0.1993 | 0.036* | |
| C15 | 0.35761 (19) | 0.47614 (18) | 0.2356 (4) | 0.0276 (6) | |
| C16 | 0.4231 (2) | 0.4189 (2) | 0.2983 (4) | 0.0309 (6) | |
| H16 | 0.4875 | 0.4339 | 0.2961 | 0.037* | |
| C17 | 0.3983 (2) | 0.34019 (19) | 0.3646 (5) | 0.0336 (7) | |
| H17 | 0.4438 | 0.3015 | 0.4067 | 0.040* | |
| C7A | 0.3045 (2) | 0.32183 (18) | 0.3656 (4) | 0.0317 (6) | |
| C47 | 0.4015 (2) | 0.82057 (17) | 0.6718 (4) | 0.0262 (6) | |
| O47 | 0.41835 (17) | 0.80559 (13) | 0.8317 (3) | 0.0366 (5) | |
| C41 | 0.4064 (2) | 0.91022 (16) | 0.6064 (5) | 0.0277 (6) | |
| C42 | 0.3281 (2) | 0.96071 (19) | 0.5945 (6) | 0.0384 (8) | |
| F42 | 0.24359 (14) | 0.92331 (12) | 0.6222 (4) | 0.0620 (8) | |
| C43 | 0.3316 (3) | 1.0447 (2) | 0.5555 (7) | 0.0476 (9) | |
| H43 | 0.2760 | 1.0772 | 0.5492 | 0.057* | |
| C44 | 0.4181 (3) | 1.0804 (2) | 0.5258 (5) | 0.0432 (9) | |
| H44 | 0.4221 | 1.1383 | 0.4980 | 0.052* | |
| C45 | 0.4992 (2) | 1.03346 (19) | 0.5357 (5) | 0.0375 (8) | |
| H45 | 0.5587 | 1.0584 | 0.5158 | 0.045* | |
| C46 | 0.4913 (2) | 0.94955 (18) | 0.5754 (5) | 0.0303 (6) | |
| F46 | 0.56966 (12) | 0.90206 (13) | 0.5843 (4) | 0.0464 (6) |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)piperazine (II). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0308 (11) | 0.0227 (11) | 0.0214 (11) | −0.0015 (9) | −0.0005 (9) | 0.0023 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0356 (14) | 0.0296 (15) | 0.0254 (14) | −0.0041 (12) | −0.0029 (12) | 0.0090 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0399 (14) | 0.0214 (12) | 0.0293 (16) | −0.0025 (11) | −0.0088 (12) | 0.0068 (12) |
| N4 | 0.0347 (11) | 0.0173 (10) | 0.0274 (13) | −0.0015 (9) | −0.0039 (10) | 0.0052 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0328 (12) | 0.0169 (11) | 0.0243 (13) | −0.0024 (10) | −0.0002 (11) | 0.0029 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0267 (12) | 0.0220 (13) | 0.0241 (14) | 0.0012 (10) | 0.0000 (11) | 0.0044 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0400 (15) | 0.0328 (15) | 0.0232 (14) | 0.0002 (13) | 0.0051 (12) | −0.0003 (12) |
| O11 | 0.0469 (14) | 0.0305 (11) | 0.0563 (17) | 0.0005 (10) | −0.0008 (12) | 0.0081 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0465 (19) | 0.0387 (17) | 0.043 (2) | −0.0081 (14) | −0.0024 (15) | −0.0013 (15) |
| O13 | 0.0332 (11) | 0.0427 (13) | 0.0547 (16) | −0.0046 (10) | −0.0009 (11) | 0.0050 (12) |
| C3A | 0.0282 (13) | 0.0343 (14) | 0.0260 (14) | 0.0040 (12) | −0.0012 (11) | −0.0043 (12) |
| C14 | 0.0338 (13) | 0.0308 (13) | 0.0252 (14) | 0.0072 (12) | −0.0048 (12) | −0.0008 (13) |
| C15 | 0.0371 (14) | 0.0266 (13) | 0.0191 (12) | 0.0031 (11) | 0.0018 (11) | −0.0044 (11) |
| C16 | 0.0283 (12) | 0.0336 (16) | 0.0307 (15) | 0.0059 (11) | 0.0018 (12) | −0.0063 (13) |
| C17 | 0.0374 (14) | 0.0270 (14) | 0.0365 (17) | 0.0093 (12) | −0.0025 (13) | −0.0011 (13) |
| C7A | 0.0420 (15) | 0.0242 (13) | 0.0289 (16) | 0.0036 (12) | 0.0004 (13) | −0.0027 (12) |
| C47 | 0.0293 (11) | 0.0188 (12) | 0.0304 (15) | −0.0014 (10) | −0.0014 (11) | 0.0043 (11) |
| O47 | 0.0560 (13) | 0.0233 (10) | 0.0305 (13) | −0.0055 (9) | −0.0064 (10) | 0.0021 (9) |
| C41 | 0.0365 (14) | 0.0183 (12) | 0.0284 (15) | −0.0031 (11) | −0.0002 (12) | 0.0023 (11) |
| C42 | 0.0344 (14) | 0.0295 (16) | 0.051 (2) | −0.0016 (12) | 0.0038 (14) | 0.0095 (15) |
| F42 | 0.0323 (9) | 0.0451 (11) | 0.109 (2) | −0.0006 (10) | 0.0056 (12) | 0.0293 (14) |
| C43 | 0.0502 (19) | 0.0283 (16) | 0.064 (3) | 0.0091 (14) | 0.0094 (18) | 0.0128 (16) |
| C44 | 0.068 (2) | 0.0187 (14) | 0.043 (2) | −0.0038 (14) | 0.0079 (17) | 0.0061 (13) |
| C45 | 0.0461 (17) | 0.0282 (14) | 0.038 (2) | −0.0127 (14) | 0.0074 (13) | 0.0019 (14) |
| C46 | 0.0331 (14) | 0.0265 (13) | 0.0313 (17) | −0.0021 (11) | 0.0026 (12) | 0.0003 (13) |
| F46 | 0.0330 (9) | 0.0404 (11) | 0.0658 (16) | 0.0006 (8) | 0.0054 (10) | 0.0060 (11) |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)piperazine (II). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—C6 | 1.464 (4) | O13—C3A | 1.375 (4) |
| N1—C2 | 1.466 (3) | C3A—C14 | 1.367 (4) |
| N1—C11 | 1.469 (4) | C3A—C7A | 1.381 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.513 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.404 (4) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C15—C16 | 1.388 (4) |
| C3—N4 | 1.466 (4) | C16—C17 | 1.395 (5) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9900 | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3B | 0.9900 | C17—C7A | 1.370 (4) |
| N4—C47 | 1.343 (4) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| N4—C5 | 1.465 (3) | C47—O47 | 1.227 (4) |
| C5—C6 | 1.507 (4) | C47—C41 | 1.513 (4) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9900 | C41—C42 | 1.382 (4) |
| C5—H5B | 0.9900 | C41—C46 | 1.384 (4) |
| C6—H6A | 0.9900 | C42—F42 | 1.362 (3) |
| C6—H6B | 0.9900 | C42—C43 | 1.373 (4) |
| C11—C15 | 1.514 (4) | C43—C44 | 1.379 (5) |
| C11—H11A | 0.9900 | C43—H43 | 0.9500 |
| C11—H11B | 0.9900 | C44—C45 | 1.381 (5) |
| O11—C7A | 1.374 (4) | C44—H44 | 0.9500 |
| O11—C12 | 1.429 (4) | C45—C46 | 1.377 (4) |
| C12—O13 | 1.422 (4) | C45—H45 | 0.9500 |
| C12—H12A | 0.9900 | C46—F46 | 1.354 (3) |
| C12—H12B | 0.9900 | ||
| C6—N1—C2 | 107.9 (2) | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.4 |
| C6—N1—C11 | 111.2 (2) | C3A—O13—C12 | 105.9 (2) |
| C2—N1—C11 | 111.8 (2) | C14—C3A—O13 | 128.2 (3) |
| N1—C2—C3 | 110.1 (3) | C14—C3A—C7A | 122.1 (3) |
| N1—C2—H2A | 109.6 | O13—C3A—C7A | 109.7 (3) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.6 | C3A—C14—C15 | 117.6 (3) |
| N1—C2—H2B | 109.6 | C3A—C14—H14 | 121.2 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 109.6 | C15—C14—H14 | 121.2 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.2 | C16—C15—C14 | 119.4 (3) |
| N4—C3—C2 | 111.0 (2) | C16—C15—C11 | 120.5 (3) |
| N4—C3—H3A | 109.4 | C14—C15—C11 | 120.0 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 109.4 | C15—C16—C17 | 122.6 (3) |
| N4—C3—H3B | 109.4 | C15—C16—H16 | 118.7 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 109.4 | C17—C16—H16 | 118.7 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 108.0 | C7A—C17—C16 | 116.3 (3) |
| C47—N4—C5 | 118.8 (3) | C7A—C17—H17 | 121.8 |
| C47—N4—C3 | 125.6 (2) | C16—C17—H17 | 121.8 |
| C5—N4—C3 | 114.9 (2) | C17—C7A—O11 | 128.3 (3) |
| N4—C5—C6 | 110.5 (2) | C17—C7A—C3A | 121.9 (3) |
| N4—C5—H5A | 109.6 | O11—C7A—C3A | 109.8 (3) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 109.6 | O47—C47—N4 | 123.4 (3) |
| N4—C5—H5B | 109.6 | O47—C47—C41 | 118.8 (3) |
| C6—C5—H5B | 109.6 | N4—C47—C41 | 117.8 (3) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 108.1 | C42—C41—C46 | 115.6 (2) |
| N1—C6—C5 | 109.5 (2) | C42—C41—C47 | 122.4 (2) |
| N1—C6—H6A | 109.8 | C46—C41—C47 | 121.6 (3) |
| C5—C6—H6A | 109.8 | F42—C42—C43 | 119.5 (3) |
| N1—C6—H6B | 109.8 | F42—C42—C41 | 116.8 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6B | 109.8 | C43—C42—C41 | 123.7 (3) |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 108.2 | C42—C43—C44 | 118.0 (3) |
| N1—C11—C15 | 111.4 (2) | C42—C43—H43 | 121.0 |
| N1—C11—H11A | 109.3 | C44—C43—H43 | 121.0 |
| C15—C11—H11A | 109.3 | C43—C44—C45 | 121.2 (3) |
| N1—C11—H11B | 109.3 | C43—C44—H44 | 119.4 |
| C15—C11—H11B | 109.3 | C45—C44—H44 | 119.4 |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 108.0 | C46—C45—C44 | 118.1 (3) |
| C7A—O11—C12 | 105.7 (2) | C46—C45—H45 | 120.9 |
| O13—C12—O11 | 108.4 (3) | C44—C45—H45 | 120.9 |
| O13—C12—H12A | 110.0 | F46—C46—C45 | 119.2 (3) |
| O11—C12—H12A | 110.0 | F46—C46—C41 | 117.4 (2) |
| O13—C12—H12B | 110.0 | C45—C46—C41 | 123.3 (3) |
| O11—C12—H12B | 110.0 | ||
| C6—N1—C2—C3 | −63.5 (3) | C12—O11—C7A—C3A | 4.4 (4) |
| C11—N1—C2—C3 | 173.9 (2) | C14—C3A—C7A—C17 | 0.1 (5) |
| N1—C2—C3—N4 | 54.5 (3) | O13—C3A—C7A—C17 | −178.7 (3) |
| C2—C3—N4—C47 | 142.2 (3) | C14—C3A—C7A—O11 | 178.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—N4—C5 | −48.1 (3) | O13—C3A—C7A—O11 | −0.4 (4) |
| C47—N4—C5—C6 | −140.1 (3) | C5—N4—C47—O47 | 3.6 (4) |
| C3—N4—C5—C6 | 49.5 (3) | C3—N4—C47—O47 | 173.0 (3) |
| C2—N1—C6—C5 | 65.0 (3) | C5—N4—C47—C41 | −175.7 (2) |
| C11—N1—C6—C5 | −172.1 (2) | C3—N4—C47—C41 | −6.3 (4) |
| N4—C5—C6—N1 | −57.3 (3) | O47—C47—C41—C42 | −95.9 (4) |
| C6—N1—C11—C15 | 62.1 (3) | N4—C47—C41—C42 | 83.4 (4) |
| C2—N1—C11—C15 | −177.2 (2) | O47—C47—C41—C46 | 76.3 (4) |
| C7A—O11—C12—O13 | −6.7 (4) | N4—C47—C41—C46 | −104.4 (4) |
| O11—C12—O13—C3A | 6.5 (4) | C46—C41—C42—F42 | 179.2 (3) |
| C12—O13—C3A—C14 | 177.4 (3) | C47—C41—C42—F42 | −8.2 (5) |
| C12—O13—C3A—C7A | −3.9 (4) | C46—C41—C42—C43 | −0.2 (6) |
| O13—C3A—C14—C15 | 179.0 (3) | C47—C41—C42—C43 | 172.4 (4) |
| C7A—C3A—C14—C15 | 0.4 (5) | F42—C42—C43—C44 | −179.1 (4) |
| C3A—C14—C15—C16 | −0.8 (4) | C41—C42—C43—C44 | 0.3 (7) |
| C3A—C14—C15—C11 | −177.6 (3) | C42—C43—C44—C45 | −0.3 (7) |
| N1—C11—C15—C16 | −107.8 (3) | C43—C44—C45—C46 | 0.3 (6) |
| N1—C11—C15—C14 | 69.0 (4) | C44—C45—C46—F46 | 179.4 (3) |
| C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.8 (5) | C44—C45—C46—C41 | −0.3 (5) |
| C11—C15—C16—C17 | 177.6 (3) | C42—C41—C46—F46 | −179.5 (3) |
| C15—C16—C17—C7A | −0.3 (5) | C47—C41—C46—F46 | 7.8 (5) |
| C16—C17—C7A—O11 | −178.2 (3) | C42—C41—C46—C45 | 0.3 (5) |
| C16—C17—C7A—C3A | −0.2 (5) | C47—C41—C46—C45 | −172.4 (3) |
| C12—O11—C7A—C17 | −177.4 (4) |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)piperazine (II). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C45—H45···O47i | 0.95 | 2.58 | 3.204 (4) | 123 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, −y+2, z−1/2.
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,4-dichlorobenzoyl)piperazine (III). Crystal data
| C19H18Cl2N2O3 | F(000) = 816 |
| Mr = 393.25 | Dx = 1.442 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 12.2889 (14) Å | Cell parameters from 4054 reflections |
| b = 12.3034 (14) Å | θ = 2.4–27.4° |
| c = 13.3667 (15) Å | µ = 0.38 mm−1 |
| β = 116.295 (1)° | T = 173 K |
| V = 1811.9 (4) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.49 × 0.48 × 0.38 mm |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,4-dichlorobenzoyl)piperazine (III). Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 4054 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine focus sealed tube | 3545 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.017 |
| Detector resolution: 0.3333 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.4°, θmin = 2.4° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −15→11 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2015) | k = −15→15 |
| Tmin = 0.776, Tmax = 0.867 | l = −17→17 |
| 9718 measured reflections |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,4-dichlorobenzoyl)piperazine (III). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.031 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.087 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.043P)2 + 0.6034P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 4054 reflections | Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3 |
| 235 parameters | Δρmin = −0.37 e Å−3 |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,4-dichlorobenzoyl)piperazine (III). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,4-dichlorobenzoyl)piperazine (III). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.52986 (10) | 0.18706 (10) | 0.64831 (10) | 0.0293 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.48214 (12) | 0.13857 (13) | 0.72047 (12) | 0.0335 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.5451 | 0.1407 | 0.7989 | 0.040* | |
| H2B | 0.4609 | 0.0616 | 0.6993 | 0.040* | |
| C3 | 0.37079 (12) | 0.19934 (13) | 0.71033 (11) | 0.0321 (3) | |
| H3A | 0.3360 | 0.1622 | 0.7553 | 0.038* | |
| H3B | 0.3939 | 0.2740 | 0.7398 | 0.038* | |
| N4 | 0.27950 (10) | 0.20437 (11) | 0.59349 (9) | 0.0310 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.32597 (13) | 0.24338 (15) | 0.51615 (12) | 0.0376 (3) | |
| H5A | 0.3457 | 0.3217 | 0.5292 | 0.045* | |
| H5B | 0.2629 | 0.2343 | 0.4384 | 0.045* | |
| C6 | 0.43884 (13) | 0.18029 (13) | 0.53272 (12) | 0.0342 (3) | |
| H6A | 0.4173 | 0.1032 | 0.5122 | 0.041* | |
| H6B | 0.4723 | 0.2103 | 0.4834 | 0.041* | |
| C11 | 0.64509 (13) | 0.13691 (12) | 0.66549 (15) | 0.0371 (3) | |
| H11A | 0.6295 | 0.0625 | 0.6341 | 0.045* | |
| H11B | 0.6988 | 0.1313 | 0.7465 | 0.045* | |
| O11 | 0.87114 (9) | 0.40074 (9) | 0.46855 (9) | 0.0362 (2) | |
| C12 | 0.83867 (16) | 0.50226 (13) | 0.49898 (14) | 0.0407 (4) | |
| H12A | 0.7743 | 0.5375 | 0.4326 | 0.049* | |
| H12B | 0.9100 | 0.5511 | 0.5296 | 0.049* | |
| O13 | 0.79616 (10) | 0.48304 (9) | 0.58078 (10) | 0.0391 (3) | |
| C3A | 0.77539 (12) | 0.37264 (11) | 0.57687 (12) | 0.0280 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.71953 (12) | 0.31497 (12) | 0.62874 (12) | 0.0312 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.6897 | 0.3498 | 0.6751 | 0.037* | |
| C15 | 0.70819 (12) | 0.20229 (12) | 0.61057 (12) | 0.0299 (3) | |
| C16 | 0.75523 (12) | 0.15362 (12) | 0.54436 (12) | 0.0316 (3) | |
| H16 | 0.7471 | 0.0773 | 0.5330 | 0.038* | |
| C17 | 0.81427 (12) | 0.21356 (12) | 0.49382 (11) | 0.0311 (3) | |
| H17 | 0.8479 | 0.1795 | 0.4501 | 0.037* | |
| C7A | 0.82108 (11) | 0.32314 (12) | 0.51047 (11) | 0.0269 (3) | |
| C47 | 0.15968 (12) | 0.18798 (11) | 0.55740 (11) | 0.0273 (3) | |
| O47 | 0.08510 (9) | 0.19648 (11) | 0.45924 (8) | 0.0426 (3) | |
| C41 | 0.11656 (11) | 0.15520 (11) | 0.64264 (10) | 0.0240 (3) | |
| C42 | 0.09914 (11) | 0.22960 (10) | 0.71238 (10) | 0.0236 (3) | |
| Cl42 | 0.13921 (3) | 0.36508 (3) | 0.71225 (3) | 0.03486 (11) | |
| C43 | 0.04921 (11) | 0.19988 (11) | 0.78313 (11) | 0.0261 (3) | |
| H43 | 0.0384 | 0.2518 | 0.8306 | 0.031* | |
| C44 | 0.01549 (11) | 0.09273 (12) | 0.78272 (11) | 0.0276 (3) | |
| Cl44 | −0.04771 (4) | 0.05479 (4) | 0.87079 (3) | 0.04291 (12) | |
| C45 | 0.02990 (12) | 0.01613 (11) | 0.71408 (12) | 0.0310 (3) | |
| H45 | 0.0052 | −0.0570 | 0.7143 | 0.037* | |
| C46 | 0.08095 (12) | 0.04794 (11) | 0.64495 (12) | 0.0291 (3) | |
| H46 | 0.0920 | −0.0044 | 0.5980 | 0.035* |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,4-dichlorobenzoyl)piperazine (III). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0239 (5) | 0.0337 (6) | 0.0344 (6) | 0.0016 (5) | 0.0165 (5) | 0.0087 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0262 (6) | 0.0420 (8) | 0.0328 (7) | −0.0015 (6) | 0.0135 (6) | 0.0125 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0253 (6) | 0.0480 (9) | 0.0241 (6) | −0.0042 (6) | 0.0119 (5) | 0.0031 (6) |
| N4 | 0.0243 (5) | 0.0478 (7) | 0.0239 (5) | 0.0012 (5) | 0.0135 (5) | 0.0061 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0304 (7) | 0.0575 (10) | 0.0312 (7) | 0.0080 (7) | 0.0194 (6) | 0.0154 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0313 (7) | 0.0454 (9) | 0.0332 (7) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0208 (6) | 0.0042 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0294 (7) | 0.0333 (8) | 0.0526 (9) | 0.0061 (6) | 0.0217 (7) | 0.0129 (7) |
| O11 | 0.0389 (6) | 0.0424 (6) | 0.0378 (6) | −0.0031 (5) | 0.0265 (5) | 0.0000 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0499 (9) | 0.0396 (8) | 0.0452 (9) | −0.0087 (7) | 0.0326 (8) | −0.0021 (7) |
| O13 | 0.0537 (6) | 0.0300 (5) | 0.0509 (6) | −0.0066 (5) | 0.0388 (6) | −0.0041 (5) |
| C3A | 0.0256 (6) | 0.0292 (7) | 0.0320 (7) | 0.0002 (5) | 0.0153 (6) | −0.0009 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0307 (7) | 0.0328 (7) | 0.0389 (8) | 0.0036 (6) | 0.0235 (6) | 0.0016 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0214 (6) | 0.0319 (7) | 0.0377 (7) | 0.0051 (5) | 0.0143 (6) | 0.0062 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0250 (6) | 0.0287 (7) | 0.0378 (8) | 0.0046 (5) | 0.0110 (6) | −0.0008 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0255 (6) | 0.0386 (8) | 0.0291 (7) | 0.0053 (6) | 0.0120 (5) | −0.0041 (6) |
| C7A | 0.0193 (6) | 0.0379 (7) | 0.0241 (6) | −0.0003 (5) | 0.0103 (5) | 0.0004 (5) |
| C47 | 0.0259 (6) | 0.0336 (7) | 0.0251 (6) | 0.0026 (5) | 0.0137 (5) | −0.0010 (5) |
| O47 | 0.0286 (5) | 0.0743 (8) | 0.0238 (5) | 0.0021 (5) | 0.0106 (4) | 0.0031 (5) |
| C41 | 0.0186 (5) | 0.0306 (7) | 0.0226 (6) | 0.0011 (5) | 0.0090 (5) | −0.0002 (5) |
| C42 | 0.0232 (6) | 0.0246 (6) | 0.0233 (6) | −0.0024 (5) | 0.0105 (5) | 0.0000 (5) |
| Cl42 | 0.0493 (2) | 0.02548 (18) | 0.03616 (19) | −0.00753 (14) | 0.02471 (17) | −0.00147 (13) |
| C43 | 0.0246 (6) | 0.0315 (7) | 0.0237 (6) | −0.0015 (5) | 0.0121 (5) | −0.0013 (5) |
| C44 | 0.0211 (6) | 0.0351 (7) | 0.0261 (6) | −0.0021 (5) | 0.0101 (5) | 0.0063 (5) |
| Cl44 | 0.0431 (2) | 0.0533 (2) | 0.0397 (2) | −0.01166 (17) | 0.02503 (17) | 0.00825 (17) |
| C45 | 0.0276 (7) | 0.0253 (7) | 0.0361 (7) | −0.0013 (5) | 0.0105 (6) | 0.0046 (6) |
| C46 | 0.0274 (6) | 0.0271 (7) | 0.0311 (7) | 0.0039 (5) | 0.0115 (5) | −0.0025 (5) |
1-[(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl]-4-(2,4-dichlorobenzoyl)piperazine (III). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—C6 | 1.4540 (19) | O13—C3A | 1.3787 (17) |
| N1—C2 | 1.4600 (17) | C3A—C14 | 1.3701 (19) |
| N1—C11 | 1.4665 (17) | C3A—C7A | 1.3839 (19) |
| C2—C3 | 1.512 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.404 (2) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C15—C16 | 1.389 (2) |
| C3—N4 | 1.4660 (17) | C16—C17 | 1.400 (2) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9900 | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3B | 0.9900 | C17—C7A | 1.363 (2) |
| N4—C47 | 1.3462 (17) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| N4—C5 | 1.4658 (17) | C47—O47 | 1.2276 (17) |
| C5—C6 | 1.518 (2) | C47—C41 | 1.5088 (17) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9900 | C41—C42 | 1.3890 (18) |
| C5—H5B | 0.9900 | C41—C46 | 1.3950 (19) |
| C6—H6A | 0.9900 | C42—C43 | 1.3852 (17) |
| C6—H6B | 0.9900 | C42—Cl42 | 1.7383 (13) |
| C11—C15 | 1.5138 (19) | C43—C44 | 1.381 (2) |
| C11—H11A | 0.9900 | C43—H43 | 0.9500 |
| C11—H11B | 0.9900 | C44—C45 | 1.380 (2) |
| O11—C7A | 1.3817 (17) | C44—Cl44 | 1.7370 (13) |
| O11—C12 | 1.4242 (19) | C45—C46 | 1.384 (2) |
| C12—O13 | 1.4249 (17) | C45—H45 | 0.9500 |
| C12—H12A | 0.9900 | C46—H46 | 0.9500 |
| C12—H12B | 0.9900 | ||
| C6—N1—C2 | 109.49 (11) | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.4 |
| C6—N1—C11 | 112.16 (12) | C3A—O13—C12 | 105.01 (11) |
| C2—N1—C11 | 111.54 (11) | C14—C3A—O13 | 128.09 (13) |
| N1—C2—C3 | 110.56 (11) | C14—C3A—C7A | 122.22 (13) |
| N1—C2—H2A | 109.5 | O13—C3A—C7A | 109.69 (12) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.5 | C3A—C14—C15 | 117.23 (13) |
| N1—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C3A—C14—H14 | 121.4 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C15—C14—H14 | 121.4 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.1 | C16—C15—C14 | 119.91 (13) |
| N4—C3—C2 | 110.58 (12) | C16—C15—C11 | 121.81 (13) |
| N4—C3—H3A | 109.5 | C14—C15—C11 | 118.28 (13) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 109.5 | C15—C16—C17 | 122.09 (14) |
| N4—C3—H3B | 109.5 | C15—C16—H16 | 119.0 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 109.5 | C17—C16—H16 | 119.0 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 108.1 | C7A—C17—C16 | 116.72 (13) |
| C47—N4—C5 | 120.16 (11) | C7A—C17—H17 | 121.6 |
| C47—N4—C3 | 125.09 (11) | C16—C17—H17 | 121.6 |
| C5—N4—C3 | 114.32 (11) | C17—C7A—O11 | 128.57 (12) |
| N4—C5—C6 | 110.25 (12) | C17—C7A—C3A | 121.80 (13) |
| N4—C5—H5A | 109.6 | O11—C7A—C3A | 109.63 (12) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 109.6 | O47—C47—N4 | 123.39 (13) |
| N4—C5—H5B | 109.6 | O47—C47—C41 | 118.97 (12) |
| C6—C5—H5B | 109.6 | N4—C47—C41 | 117.62 (11) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 108.1 | C42—C41—C46 | 117.74 (12) |
| N1—C6—C5 | 110.42 (12) | C42—C41—C47 | 122.74 (12) |
| N1—C6—H6A | 109.6 | C46—C41—C47 | 119.22 (12) |
| C5—C6—H6A | 109.6 | C43—C42—C41 | 122.06 (12) |
| N1—C6—H6B | 109.6 | C43—C42—Cl42 | 117.72 (10) |
| C5—C6—H6B | 109.6 | C41—C42—Cl42 | 120.22 (10) |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 108.1 | C44—C43—C42 | 118.17 (12) |
| N1—C11—C15 | 111.53 (11) | C44—C43—H43 | 120.9 |
| N1—C11—H11A | 109.3 | C42—C43—H43 | 120.9 |
| C15—C11—H11A | 109.3 | C45—C44—C43 | 121.85 (12) |
| N1—C11—H11B | 109.3 | C45—C44—Cl44 | 119.64 (11) |
| C15—C11—H11B | 109.3 | C43—C44—Cl44 | 118.50 (11) |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 108.0 | C44—C45—C46 | 118.71 (13) |
| C7A—O11—C12 | 105.00 (10) | C44—C45—H45 | 120.6 |
| O11—C12—O13 | 108.54 (12) | C46—C45—H45 | 120.6 |
| O11—C12—H12A | 110.0 | C45—C46—C41 | 121.47 (13) |
| O13—C12—H12A | 110.0 | C45—C46—H46 | 119.3 |
| O11—C12—H12B | 110.0 | C41—C46—H46 | 119.3 |
| O13—C12—H12B | 110.0 | ||
| C6—N1—C2—C3 | −61.31 (16) | C12—O11—C7A—C17 | 172.09 (14) |
| C11—N1—C2—C3 | 173.95 (13) | C12—O11—C7A—C3A | −8.17 (15) |
| N1—C2—C3—N4 | 55.00 (16) | C14—C3A—C7A—C17 | −0.7 (2) |
| C2—C3—N4—C47 | 136.85 (14) | O13—C3A—C7A—C17 | 178.96 (13) |
| C2—C3—N4—C5 | −50.77 (17) | C14—C3A—C7A—O11 | 179.50 (12) |
| C47—N4—C5—C6 | −136.22 (14) | O13—C3A—C7A—O11 | −0.81 (15) |
| C3—N4—C5—C6 | 50.99 (18) | C5—N4—C47—O47 | 5.4 (2) |
| C2—N1—C6—C5 | 61.64 (16) | C3—N4—C47—O47 | 177.41 (14) |
| C11—N1—C6—C5 | −173.97 (12) | C5—N4—C47—C41 | −175.89 (13) |
| N4—C5—C6—N1 | −55.75 (17) | C3—N4—C47—C41 | −3.9 (2) |
| C6—N1—C11—C15 | 69.26 (16) | O47—C47—C41—C42 | −100.59 (16) |
| C2—N1—C11—C15 | −167.51 (13) | N4—C47—C41—C42 | 80.68 (17) |
| C7A—O11—C12—O13 | 14.03 (16) | O47—C47—C41—C46 | 72.85 (18) |
| O11—C12—O13—C3A | −14.51 (16) | N4—C47—C41—C46 | −105.88 (15) |
| C12—O13—C3A—C14 | −170.92 (15) | C46—C41—C42—C43 | 0.52 (19) |
| C12—O13—C3A—C7A | 9.41 (16) | C47—C41—C42—C43 | 174.06 (12) |
| O13—C3A—C14—C15 | 179.33 (14) | C46—C41—C42—Cl42 | −178.99 (10) |
| C7A—C3A—C14—C15 | −1.0 (2) | C47—C41—C42—Cl42 | −5.46 (17) |
| C3A—C14—C15—C16 | 1.5 (2) | C41—C42—C43—C44 | −0.42 (19) |
| C3A—C14—C15—C11 | −179.07 (12) | Cl42—C42—C43—C44 | 179.11 (10) |
| N1—C11—C15—C16 | −132.47 (14) | C42—C43—C44—C45 | −0.3 (2) |
| N1—C11—C15—C14 | 48.08 (19) | C42—C43—C44—Cl44 | −179.77 (10) |
| C14—C15—C16—C17 | −0.2 (2) | C43—C44—C45—C46 | 0.8 (2) |
| C11—C15—C16—C17 | −179.64 (13) | Cl44—C44—C45—C46 | −179.70 (10) |
| C15—C16—C17—C7A | −1.5 (2) | C44—C45—C46—C41 | −0.7 (2) |
| C16—C17—C7A—O11 | −178.31 (12) | C42—C41—C46—C45 | 0.03 (19) |
| C16—C17—C7A—C3A | 2.0 (2) | C47—C41—C46—C45 | −173.74 (12) |
Funding Statement
This work was funded by University Grants Commission grants BSR Faculty Fellowship and Rajeev Gandhi Fellowship.
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2004). APEX2. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2013). SAINT, Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2015). SADABS, Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Duncton, M. A. J., Roffey, J. R. A., Hamlyn, R. J. & Adams, D. R. (2006). Tetrahedron Lett. 47, 2549–2552.
- Etter, M. C. (1990). Acc. Chem. Res. 23, 120–126.
- Etter, M. C., MacDonald, J. C. & Bernstein, J. (1990). Acta Cryst. B46, 256–262. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, G., Glidewell, C., Gregson, R. M. & Meehan, P. R. (1998a). Acta Cryst. B54, 129–138.
- Ferguson, G., Glidewell, C., Gregson, R. M. & Meehan, P. R. (1998b). Acta Cryst. B54, 139–150.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Flack, H. D. & Bernardinelli, G. (2000). J. Appl. Cryst. 33, 1143–1148.
- Gregson, R. M., Glidewell, C., Ferguson, G. & Lough, A. J. (2000). Acta Cryst. B56, 39–57. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hamid, M. H. S. A. & Williams, J. M. J. (2007). Tetrahedron Lett. 48, 8263–8265.
- Hooft, R. W. W., Straver, L. H. & Spek, A. L. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 96–103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kavitha, C. N., Kaur, M., Anderson, B. J., Jasinski, J. P. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2014a). Acta Cryst. E70, o208–o209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kavitha, C. N., Kaur, M., Anderson, B. J., Jasinski, J. P. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2014b). Acta Cryst. E70, o270–o271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kavitha, C. N., Kaur, M., Anderson, B. J., Jasinski, J. P. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2014c). Acta Cryst. E70, o283–o284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-F. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o2575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Mahesha, N., Yathirajan, H. S., Furuya, T., Akitsu, T. & Glidewell, C. (2019). Acta Cryst. E75, 129–133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Millan, M. J., Cussac, D., Milligan, G., Carr, C., Audinot, V., Gobert, A., Lejeune, F., Rivet, J.-M., Brocco, M., Duqueyroix, D., Nicolas, J.-P., Boutin, J. A. & Newman-Tancredi, A. (2001). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 297, 876–887. [PubMed]
- Nyburg, S. C. & Faerman, C. H. (1985). Acta Cryst. B41, 274–279.
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rondot, P. & Ziegler, M. (1992). J. Neurol. 239, S28–S34. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wood, P. A., Allen, F. H. & Pidcock, E. (2009). CrystEngComm, 11, 1563–1571.
- Wu, C., Li, J., Wei, H., Hang, Y. & Jiang, Y. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o1140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II, III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019000458/zl2747sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019000458/zl2747Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019000458/zl2747IIsup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019000458/zl2747IIIsup4.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019000458/zl2747Isup5.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019000458/zl2747IIsup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019000458/zl2747IIIsup7.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report