Abstract
Purpose
Fibromyalgia (FM) can cause chronic widespread pain and seriously affect the quality of patient lives. Acupuncture therapy is widely used for pain management. However, the effect of acupuncture on FM is still uncertain. The aim of this review was to determine the effect and safety of acupuncture therapy on the pain intensity and quality of life in patients with FM.
Materials and methods
We searched PubMed, the Cochrane Library, Embase, the China National Knowledge Infrastructure, the Chinese Science and Technology Periodical Database, and the Chinese Biomedical Literature Database to collect randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of acupuncture for FM published before May 2018. A meta-analysis was performed according to the Cochrane systematic review method by using RevMan 5.3 software, and GRADE was used to evaluate the quality of the evidence.
Results
We identified 12 RCTs that compared acupuncture therapy to sham acupuncture or conventional medication. Meta-analysis showed that acupuncture was significantly better than sham acupuncture for relieving pain (MD =−1.04, 95% CI [−1.70, –0.38], P=0.002, I2=78%) and improving the quality of life (MD =−13.39, 95% CI [−21.69, –5.10], P=0.002, I2=82%), with low- to moderate-quality evidence in the short term. At follow-up in the long term, the effect of acupuncture was also superior to that of sham acupuncture. No serious adverse events were found during acupuncture.
Conclusion
Acupuncture therapy is an effective and safe treatment for patients with FM, and this treatment can be recommended for the management of FM.
Keywords: acupuncture, fibromyalgia, pain, quality of life, meta-analysis
Introduction
Fibromyalgia (FM) is characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain,1 is present in as much as 0.4% to 9.3% of the population,2 and is often accompanied by fatigue, sleep difficulties, cognitive dysfunction, depressed mood, or depressive episodes.3,4 FM can occur in all populations at every age, especially involving more middle-aged females than males.5 A recent study reported that the annual medical cost of FM was more than 12,993 million euros (32.5% corresponded to health care costs and 67.5% to indirect costs attributable to productivity losses) in Spain.6 Therefore, it is imperative to find effective therapies relieving pain and reducing social and economic burden.
The management of FM requires a multidimensional approach that includes patient education, behavioral therapy, exercise, and pain management.7 Unfortunately, no effective treatments for FM are presently available. The most common pharmacological therapies for the pain management of FM include amitriptyline, anticonvulsants, and serotonin noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors,8 or their combination.9 However, recent European guideline indicates that the effect size for most treatments is relatively modest and that all pharmacological therapies are only weak recommendations for FM.10 Moreover, the guideline suggests that initial management should focus on nonpharmacological therapies.10
There are different types of nonpharmacological interventions for FM. Acupuncture therapy is a significant component of nonpharmacological therapies. Modern medical researches indicate that the analgesic effects of acupuncture are known to activate peripheral and central pain control systems by releasing various endogenous opioids or nonopioid compounds, such as beta-endorphins, enkephalins, dynorphins, serotonin, norepinephrine, gamma-aminobutyric acid, or ATP.11–13 Excitingly, clinical studies of acupuncture therapy for FM showed promising results that acupuncture is effective in relieving symptoms of FM.14 However, the available systematic reviews published a few years ago indicated that there was no sufficient evidence to confirm the efficacy of acupuncture therapy for FM, mainly due to the small number of studies.15–17 Therefore, more randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were conducted to address this issue after demonstrating controversial results,18–20 which prompted us to conduct a meta-analysis of these primary studies to generate the pooled treatment effect of acupuncture on FM and offer suggestions for future studies and treatments.
Materials and methods
Protocol and registration
The protocol registration number is PROSPERO 2018 CRD42018094636 and is available at http://www.crd.york. ac.uk/PROSPERO/display_record.php?ID=CRD42018094636. This review was reported in compliance with the PRISMA statement.21
Search strategy
We searched for RCTs in the following electronic databases, without language restriction, from their inceptions until May 2018: PubMed, the Cochrane Library, Embase, the China National Knowledge Infrastructure, the Chinese Science and Technology Periodical Database, and the Chinese Biomedical Literature Database. The search words were fibro-myalgia (eg, fibromyalgia, fibrositis, fibromyositis, and FM) and acupuncture (eg, acupuncture, acupressure, acupoint, electroacupuncture, and electro-acupuncture [EA]). In addition, all the available reviews related to FM treatments were manually checked for any additional possibly relevant RCTs.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Types of studies: Only RCTs of acupuncture therapy for FM were included. Observational studies, cross-over studies, animal studies, conference abstracts, and letters were excluded, and the sample size of every study must be more than ten patients. The studies of unavailable data were excluded. There were no language restrictions.
Types of participants: Participants with FM must be diagnosed with a standard description of the diagnostic criteria (1990 American College of Rheumatology criteria).22 There are no limits to the age, gender, race, condition, duration, or intensity of the research subjects.
Types of interventions: Acupuncture therapy only included manual acupuncture and EA, regardless of different acupoints or needle materials. However, dry needling not based on traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) theory was excluded. Acupoint injections, laser acupuncture, moxibustion, cupping, herbal medicine, and any combination of the above were excluded. In addition, studies that compared different acupuncture therapies were also excluded.
Types of control groups: Sham acupuncture or conventional pharmacological therapies will be included. There were two types of sham acupuncture: a needling insertion into nonacupoints or ~1–2 cm from acupoints and nonpenetration by a blunt or retractable needle that contacts the skin without inserting the needle. Conventional pharmacological therapies do not contain herbal medicine.
Types of outcome measures: The primary outcome measures include a change in pain intensity and quality of life. The change in pain intensity was measured by using a VAS, a numerical rating scale (NRS), the Multidimensional Pain Inventory (MPI), or the McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ). Quality of life was evaluated using the fibromyalgia impact questionnaire (FIQ). The secondary outcome was an adverse event of acupuncture therapy to assess acupuncture safety.
Study selection and data extraction
According to the search strategy, one author (XCZ) performed the searches. Two investigators (XCZ and HC) reviewed the titles and abstracts of the references and screened eligible studies according to inclusion and exclusion criteria. Then, we downloaded the full text of the eligible studies to determine the final selection.
Two authors (XCZ and HC) independently extracted data from each study using a predesigned form. The information extracted included study design, patient characteristics, sample size, diagnostic criteria, interventions, treatment sessions, clinical outcome results, follow-up period, and adverse events. If there were any unclear or missed data, we attempted to contact authors for the details by phone or email. If we could not obtain access to the data by contacting the authors, then we would exclude the studies. Any disagreements were resolved by rechecking the primary papers and further consultation with the third author (WTX).
Assessment of risk of bias
Two independent investigators (XCZ and HC) evaluated the risk of bias (ROB) in each included trial according to the Cochrane risk of bias assessment tool. This tool contains seven items of ROB: random sequence generation (selection bias), allocation concealment (selection bias), blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias), blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias), incomplete outcome data (attrition bias), selective reporting (reporting bias), and other bias.23 For each item, ROB was graded as high, low, or unclear. Discrepancies were resolved by further discussion with the third author (WTX).
Quality of evidence
For each comparison in the meta-analysis, we assessed the quality of evidence by using the Grading of Recommendations assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) Guideline Development Tool (GRADEpro GDT, https://gradepro.org/).24 In this online system, the quality of RCTs was initially graded as high and then downgraded as moderate, low, or very low because of any limitations with respect to ROB, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision, or publication bias. Two authors (XCZ and HC) independently evaluated the quality of evidence according to the GRADE handbook,25 and consensus was adapted to resolve any disagreement.
Statistical analyses
The meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.3 software provided by the Cochrane Collaboration. Continuous outcomes were calculated with mean difference (MD) and 95% CI. Dichotomous outcomes were calculated with the risk ratio (RR) and 95% CI. The overall effect was evaluated by the Z test, and a P-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Considering the clinical heterogeneity of different acupuncture therapies, we performed subgroup analysis based on EA and manual acupuncture (MA). Statistical heterogeneity between studies was quantified by the I2 statistic. In accordance with the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (version 5.10), we defined I2 >50% as representing substantial heterogeneity, and the random effects model was used for meta-analysis.23
Statistical analyses
Sensitivity analyses were performed to explore potential sources of heterogeneity. Publication bias was estimated by funnel plot analysis if sufficient studies were included.
Results
Study selection
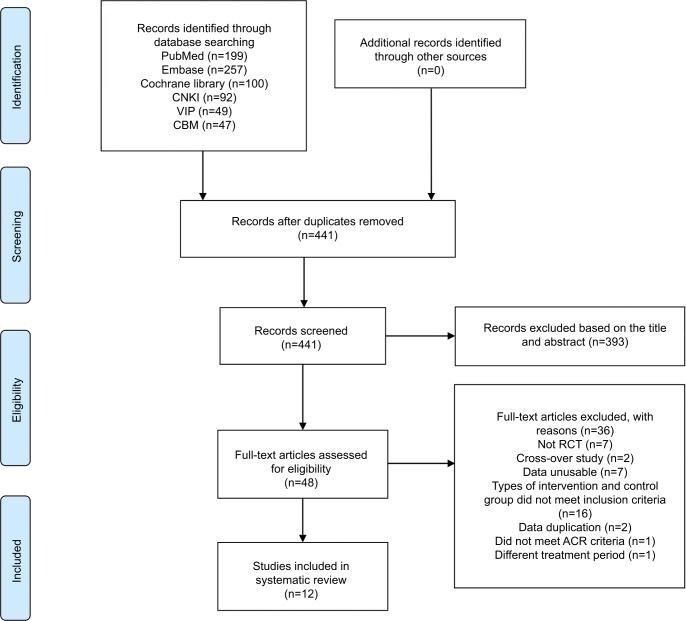
A total of 744 studies were identified from all the initial searches; 441 studies were retained after screening and removing duplications, and 393 studies were excluded according to the title and abstract. Then, 48 full-text studies were further assessed for eligibility. Of these, 36 studies were excluded because of not RCTs, inappropriate intervention, data duplication, or data unusable (Table S1). Finally, 12 RCTs14,18–20,26–33 were eligible and included in the systematic review. The flow chart of the study selection process is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Review flow diagram.
Abbreviations: ACR, American College of Rheumatology; CBM, Chinese Biomedical Literature Database; CNKI, China National Knowledge Infrastructure; RCT, randomized controlled trial; VIP, Chinese Science and Technology Periodical Database.
Description of the included studies
In 12 studies, all FM patients were diagnosed by the 1990 American College of Rheumatology criteria. The sample size ranged from 20 to 164 participants. Nine articles were published in English,14,18–20,27,29,30,32,33 two in Chinese,28,31 and one in Portuguese.26 Two studies used EA,14,30 and the other ten studies used MA.18–20,26–29,31–33 The main characteristics of the included studies are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies
| Study | Country | Diagnostic criteria | Sample size (AG/CG) | Interventions | Treatment period | Outcomes | Measurement time points (weeks) | Adverse events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karatay et al 201820 | Turkey | ACR 1990 criteria | 25/25/25 (all female) | AG: real MA CG1: sham acupuncture CG2: simulated acupuncture CG1 was selected as sham acupuncture group |
8 sessions for 4 weeks, each session lasting 30 minutes | VAS FIQ |
0, 4, 8, 16 | NO |
| Ugurlu et al 201719 | Turkey | ACR 1990 criteria | 25/25 (all female) | AG: real MA CG: sham acupuncture |
12 sessions for 8 weeks, each session lasting 30 minutes | VAS FIQ |
0, 4, 8 | NO |
| Vas et al 201618 | Spain | ACR 1990 criteria | 80/82 (all female) | AG: real MA CG: sham acupuncture |
9 sessions for 9 weeks, each session lasting 20 minutes | VAS FIQ |
0, 10, 24, 48 | Not serious, mild |
| Stival et al 201426 | Brazil | ACR 1990 criteria | 21/15 (female: 14/17) | AG: real MA CG: sham acupuncture |
1 session for 20 minutes | VAS | Before and immediately after treatment | NR |
| Harte et al 201327 | USA | ACR 1990 criteria | 22/28 (all female) | AG: real MA CG: sham acupuncture |
9 sessions for 4 weeks, each session lasting 30 minutes | VAS SF-MPQ |
0, 4 | NR |
| Gong et al 201028 | China | ACR 1990 criteria | 30/30 (female: 21/19) | AG: real MA CG: amitriptyline |
AG: 36 sessions for 3 months, each session lasting 30 minutes CG: every day for 3 months | VAS | 0, 12, 24 | NR |
| Harris et al 200929 | USA | ACR 1990 criteria | 10/10 (all female) | AG: real MA CG: sham acupuncture |
9 sessions for 4 weeks | SF-MPQ | 0, 4 | NR |
| Martin et al 200630 | USA | ACR 1990 criteria | 25/25 (female: 25/24) | AG: real EA CG: sham EA |
6 sessions for 2–3 weeks | MPI FIQ |
0, 3, 7, 31 | Not serious, mild |
| Guo et al 200531 | China | ACR 1990 criteria | 19/19 (female: 16/15) | AG: real MA CG: amitriptyline |
AG: 28 sessions for 30 days, each session lasting 30 minutes CG: every morning for 30 days | VAS | 0, 4 | NR |
| Harris et al 200532 | USA | ACR 1990 criteria | 29/30/28/27 (female: 29/27/24/26) | AG: traditional site with stimulation CG1: traditional site without stimulation CG2: nontraditional site with stimulation CG3: nontraditional site with no stimulation CG3 was selected as sham acupuncture group |
18 sessions for 9 weeks, each session lasting 20 minutes | NRS | 0, 3, 4, 8, 9, 10, 13, 15 | NR |
| Assefi et al 200533 | USA | ACR 1990 criteria | 25/25/24/25 (female: 22/24/24/24) | AG: real MA CG1: needling for unrelated condition CG2: sham needling CG3: simulated acupuncture CG2 was selected as sham acupuncture group |
24 sessions for 12 weeks, each session lasting 30 minutes | VAS | 0, 1, 4, 8, 12, 24, 36 | Not serious, mild |
| Deluze et al 199214 | Switzerland | ACR 1990 criteria | 36/34 (female: 33/21) | AG: real EA CG: sham EA |
6 sessions for 3 weeks | VAS | 0, 3 | Not serious, mild |
Abbreviations: ACR, American College of Rheumatology; AG, acupuncture group; CG, control group; EA, electro-acupuncture; FIQ, fibromyalgia impact questionnaire; MA, manual acupuncture; MPI, Multidimensional Pain inventory; NR, not reported; NRS, numeric rating scale; SF-MPQ, short form of McGill Pain Questionnaire.
Risk of bias within studies
Most of the studies were rated as low ROB, except for four studies.19,26,28,31 Eight studies used computer software or a random number table for random sequence generation.14,18,19,26,27,29,32,33 Two studies reported that participants were divided randomly according to the order of admission, and they did not perform allocation concealment.28,31 Eight studies performed allocation concealment by opaque sealed envelopes or central allocation.14,18,20,27,29,30,32,33 The acupuncturists in all studies were not blinded. Nine studies performed blinding of participants and outcome assessment.14,18,20,26,27,29,30,32,33 There were no missing data in five studies,19,26,28,29,31 and seven other studies reported dropout numbers and reasons.14,18,20,27,30,32,33 Six studies did not report any details about adverse events.26–29,31,32 The ROB summary is presented in Figure 2.
Figure 2.
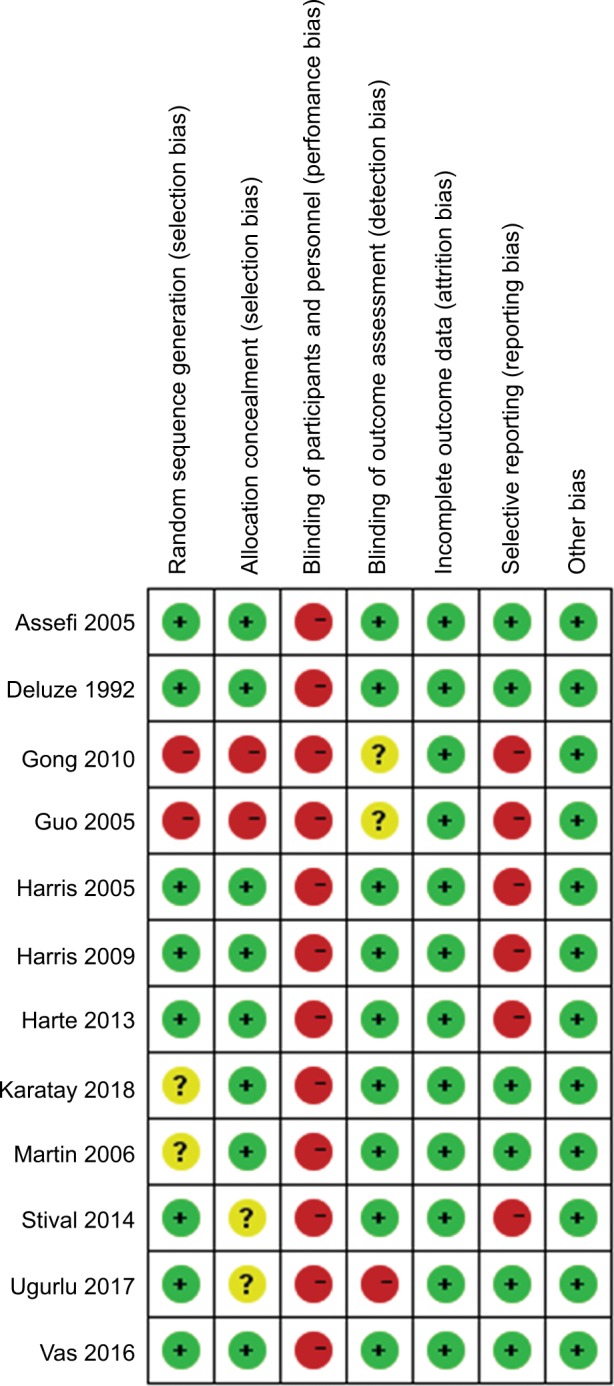
Risk of bias summary.
Effects of interventions
Real acupuncture vs sham acupuncture
Pain changes after treatment
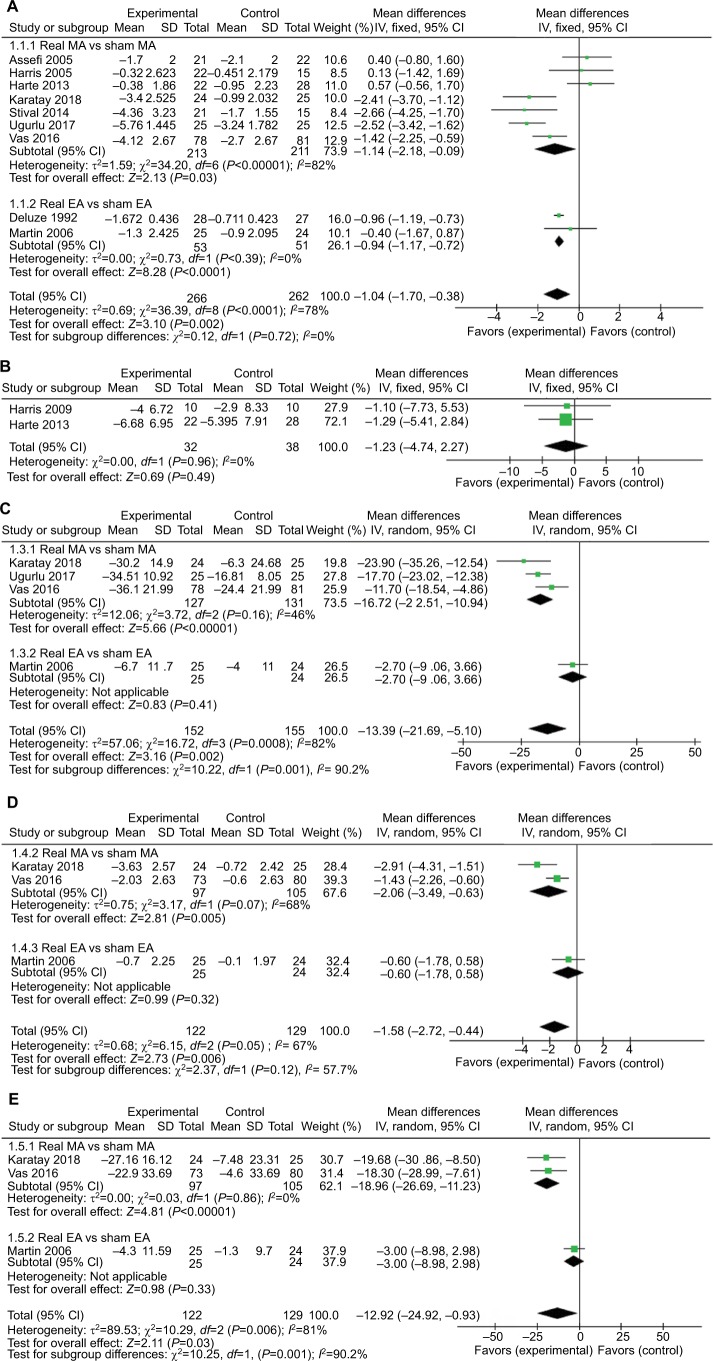
The data regarding pain changes were reported in all studies. Eight studies compared real MA with sham MA,18–20,26,27,29,32,33 and two studies compared real EA with sham EA.14,30 We performed a meta-analysis of pain changes (VAS, 0–10 cm scale). The overall meta-analysis of nine studies showed that real acupuncture was significantly better than sham acupuncture in reducing pain after treatment (MD =−1.04, 95% CI [−1.70, –0.38], P=0.002, I2=78%; Figure 3A). The quality of evidence was downgraded because of inconsistency and evaluated as moderate (Table 2). The subgroup analysis indicated that both real MA (MD =−1.14, 95% CI [−2.18, –0.09], P=0.03, I2=82%; Figure 3A) and real EA (MD =−0.94, 95% CI [−1.17, –0.72], P<0.00001, I2=0%; Figure 3A) were statistically significantly better than sham acupuncture in reducing pain after treatment. The quality of evidence was moderate for the comparison of real MA vs sham MA and low for the comparison of real EA vs sham EA (Table 2).
Figure 3.
Forest plot comparing real acupuncture vs sham acupuncture.
Notes: (A) Outcome: pain changes after treatment (VAS, 0–10 cm scale). (B) Outcome: pain changes after treatment (SF-MPQ). (C) Outcome: FIQ changes after treatment. (D) Outcome: long-term effect of pain changes (VAS, 0–10 cm scale). (E) Outcome: long-term effect of FIQ changes.
Abbreviations: EA, electro-acupuncture; FIQ, fibromyalgia impact questionnaire; MA, manual acupuncture; SF-MPQ, short form of McGill Pain Questionnaire.
Table 2.
Effect size and GRADE quality of evidence
| Certainty assessment | No. of patients | Effect | Certainty | Importance | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of studies | Study design | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other considerations | Real acupuncture | Sham acupuncture | Absolute (95% CI) | ||
| Pain changes after treatment (VAS, 0–10 cm scale) – real acupuncture vs sham acupuncture | |||||||||||
| 9 | Randomized trials | Not seriousa | Seriousb | Not seriousc | Not seriousd | Nonee | 266 | 262 | MD 1.04 lower (1.70 lower to 0.38 lower) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate | Critical |
| Pain changes after treatment (VAS, 0–10 cm scale) – real MA vs sham MA | |||||||||||
| 7 | Randomized trials | Not seriousa | Seriousb | Not seriousc | Not seriousd | Nonee | 213 | 211 | MD 1.14 lower (2.18 lower to 0.09 lower) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate | Critical |
| Pain changes after treatment (VAS, 0–10 cm scale) – real EA vs sham EA | |||||||||||
| 2 | Randomized trials | Not seriousa | Not seriousf | Not seriousc | Seriousg | Publication bias strongly suspectedh | 53 | 51 | MD 0.94 lower (1.17 lower to 0.72 lower) | ⊕⊕◯◯ Low | Critical |
| Pain changes after treatment (SF-MPQ scale) – real MA vs sham MA | |||||||||||
| 2 | Randomized trials | Not seriousa | Not seriousf | Not seriousc | Seriousg | Publication bias strongly suspectedh | 32 | 38 | MD 1.23 lower (4.74 lower to 2.27 higher) | ⊕⊕◯◯ Low | Critical |
| FIQ changes after treatment – real acupuncture vs sham acupuncture | |||||||||||
| 4 | Randomized trials | Not seriousa | Seriousb | Not seriousc | Seriousg | Nonee | 152 | 155 | MD 13.39 lower (21.69 lower to 5.1 lower) | ⊕⊕◯◯ Low | Critical |
| FIQ changes after treatment – real MA vs sham MA | |||||||||||
| 3 | Randomized trials | Not seriousa | Not seriousf | Not seriousc | Seriousg | Nonee | 127 | 131 | MD 16.72 lower (22.51 lower to 10.94 lower) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate | Critical |
| FIQ changes after treatment – real EA vs sham EA | |||||||||||
| 1 | Randomized trials | Not seriousi | Not seriousj | Not seriousc | Seriousg | Publication bias strongly suspectedh | 25 | 24 | MD 2.7 lower (9.06 lower to 3.66 higher) | ⊕⊕◯◯ Low | Critical |
| Long-term effect of pain changes (VAS, 0–10 cm scale) – real acupuncture vs sham acupuncture | |||||||||||
| 3 | Randomized trials | Not seriousa | Seriousb | Not Seriousc | Seriousg | Nonee | 122 | 129 | MD 1.58 lower (2.72 lower to 0.44 lower) | ⊕⊕◯◯ Low | Critical |
| Long-term effect of pain changes (VAS, 0–10 cm scale) – real MA vs sham MA | |||||||||||
| 2 | Randomized trials | Not seriousa | Seriousb | Not seriousc | Seriousg | Publication bias strongly suspectedh | 97 | 105 | MD 2.06 lower (3.49 lower to 0.63 lower) | ⊕◯◯◯ Very low | Critical |
| Long-term effect of pain changes (VAS, 0–10 cm scale) – real EA vs sham EA | |||||||||||
| 1 | Randomized trials | Not seriousi | Not seriousj | Not seriousc | Seriousg | Publication bias strongly suspectedh | 25 | 24 | MD 0.6 lower (1.78 lower to 0.58 higher) | ⊕⊕◯◯ Low | Critical |
| Long-term effect of FIQ changes – real acupuncture vs sham acupuncture | |||||||||||
| 3 | Randomized trials | Not seriousa | Seriousb | Not seriousc | Seriousg | Nonee | 122 | 129 | MD 12.92 lower (24.92 lower to 0.93 lower) | ⊕⊕◯◯ Low | Critical |
| Long-term effect of FIQ changes – real MA vs sham MA | |||||||||||
| 2 | Randomized trials | Not seriousa | Not seriousf | Not seriousc | Seriousg | Publication bias strongly suspectedh | 97 | 105 | MD 18.96 lower (26.69 lower to 11.23 lower) | ⊕⊕◯◯ Low | Critical |
| Long-term effect of FIQ changes – real EA vs sham EA | |||||||||||
| 1 | Randomized trials | Not seriousi | Not seriousj | Not seriousc | Seriousg | Publication bias strongly suspectedh | 25 | 24 | MD 3.0 lower (8.98 lower to 2.98 higher) | ⊕⊕◯◯ Low | Critical |
| Pain changes after treatment (VAS, 0–10 cm scale) – real acupuncture vs conventional medication | |||||||||||
| 2 | Randomized trials | Seriousk | Not seriousf | Not seriousc | Seriousg | Publication bias strongly suspectedh | 49 | 49 | MD 1.81 lower (2.43 lower to 1.18 lower) | ⊕◯◯◯ Very low | Critical |
Notes:
<25% of studies had high risk of bias.
I2 is >50%.
Direct comparison and outcomes.
Total sample size is >400.
No clear publication bias was detected.
I2 is <50%.
Total sample size is <400.
Only one study or two studies consider potential publication bias.
The study had low risk of bias.
Only one study and no inconsistency.
Two studies had high risk of bias.
Abbreviations: EA, electro-acupuncture; FIQ, fibromyalgia impact questionnaire; MA, manual acupuncture; MD, mean difference; SF-MPQ, short form of McGill Pain Questionnaire.
Only two studies measured pain intensity by using a short form of MPQ (SF-MPQ).27,29 The pooled results indicated that there were no statistically significant differences in pain reduction between real MA and sham MA (MD =−1.23, 95% CI [–4.74, 2.27], P=0.49, I2=0%; Figure 3B). The quality of evidence was evaluated as low (downgraded because of imprecision and publication bias, Table 2)
Quality of life: FIQ changes after treatment
Four studies evaluated quality of life by using the FIQ score.18–20,30 The pooled results indicated that real acupuncture was significantly better than sham acupuncture in improving quality of life after treatment (MD =−13.39, 95% CI [−21.69, –5.10], P=0.002, I2=82%; Figure 3C). The quality of evidence was evaluated as low (downgraded because of inconsistency and imprecision, Table 2). The subgroup analysis showed that the real MA of three studies was sig nificantly better than sham MA for improving quality of life after treatment (MD =−16.72, 95% CI [−22.51, –10.94], P<0.00001, I2=46%; Figure 3C), and the quality of evidence was evaluated as moderate (Table 2). However, there was no statistically significant difference between real EA and sham EA based on one study (MD =−2.7, 95% CI [–9.06, 3.66], P=0.41; Figure 3C), and the quality of evidence was evaluated as low (Table 2).
Long-term effect of acupuncture
There were three studies that followed-up long-term (more than three months after treatment) to assess the effect of acupuncture, and the data can be obtained.18,20,30 Because more than one follow-up result was measured among the studies (Table 1), we included the last follow-up result in our pooled analysis.
Two studies compared real MA with sham MA, and one study compared real EA with sham EA. The pooled results indicated that real acupuncture had a superior long-term effect on reducing pain and improving the quality of life compared with sham acupuncture (MD =−1.58, 95% CI [−2.72, –0.44], P=0.006, I2=67%, Figure 3D; MD =−12.92, 95% CI [−24.92, –0.93], P=0.03, I2=81%; Figure 3E). Because of inconsistency and imprecision, the quality of evidence was downgraded and evaluated as low (Table 2). The subgroup analysis showed that real MA was significantly better than sham MA for reducing pain and improving the quality of life in the long term (MD =−2.06, 95% CI [−3.49, –0.63], P=0.005, I2=68%, Figure 3D; MD =−18.96, 95% CI [−26.69, –11.23], P<0.00001, I2=0%, Figure 3E), and the quality of evidence was evaluated as very low and low, respectively (Table 2). However, there were no statistically significant differences between real EA and sham EA for reducing pain and improving the quality of life in the long term (MD =−0.6, 95% CI [–1.78, 0.58], P=0.32, Figure 3D; MD =−3.0, 95% CI [–8.98, 2.98], P=0.33; Figure 3E), and the quality of evidence was evaluated as low (Table 2).
Adverse events
Six studies reported no serious adverse events,14,18–20,30,33 of which four studies observed mild adverse events, such as bruising, soreness, nausea, discomfort of needle insertion, and aggravation of symptoms.14,18,30,33 These mild adverse events were more common in the real acupuncture group than in the sham acupuncture group. The other four studies did not provide any details about adverse events.26,27,29,32
Real acupuncture vs conventional medication
Pain changes after treatment
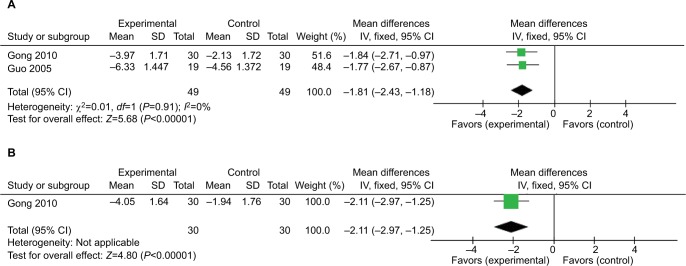
Two studies compared real acupuncture with conventional medication and reported the data on pain changes (VAS, 0–10 cm scale).28,31 The pooled results showed that real acupuncture was statistically significantly better than conventional medication in reducing pain after treatment (MD =−1.81, 95% CI [−2.43, –1.18], P<0.00001, I2=0%; Figure 4A). However, the quality of evidence was downgraded because of ROB, imprecision and publication bias and was evaluated as very low (Table 2).
Figure 4.
Forest plot comparing real acupuncture vs conventional medication.
Notes: (A) Outcome: pain changes after treatment (VAS, 0–10 cm scale). (B) Outcome: long-term effect of pain changes (VAS, 0–10 cm scale).
Long-term effect of acupuncture
Two studies28,31 included follow-up observations at 6 months after treatment, but only one study provided data on pain changes (VAS, 0–10 cm scale). The result indicated that real acupuncture yielded significantly more pain reduction than conventional medication at follow-up (MD =−2.11, 95% CI [−2.97, –1.25], P<0.00001; Figure 4B).
Adverse events
There were no details about any adverse events reported.
Heterogeneity and sensitivity analyses
There was considerable heterogeneity (I2=78%) in the comparison of real acupuncture vs sham acupuncture on pain changes after treatment. We conducted sensitivity analyses by omitting potential heterogeneous studies to observe their influence on the pooled effect size. Two studies were omitted because their ROB was high.19,26 The third study was omitted because the mean data were measured from the published article and SD was taken from baseline.33 The fourth study was omitted because the data in the meta-analysis were transformed from NRS.32 All studies omitting either of the four mentioned studies were then recalculated to determine the pooled effect size. Sensitivity analyses indicated that the pooled effect was not changed when omitting either of the four mentioned studies. The result of sensitivity analyses on studies with low ROB was consistent with the result of all studies (Table S2). However, the heterogeneity was not resolved and may be caused by various acupoints, different measurement time points, and sham acupuncture methods. The sensitivity analyses of other outcomes were not conducted due to the low number of corresponding included studies.
Publication bias
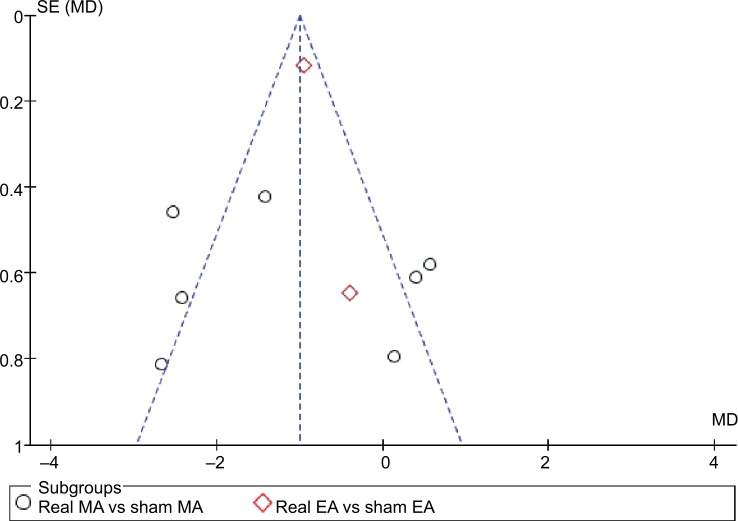
The funnel plot for pain changes after treatment demonstrated that visual inspection of the funnel plot was symmetric and no clear publication bias was detected (Figure 5).
Figure 5.
Funnel plot comparing real acupuncture vs sham acupuncture.
Note: Outcome: pain changes after treatment (VAS, 0–10 cm scale).
Abbreviations: EA, electro-acupuncture; MA, manual acupuncture; SE, standard error; MD, mean difference.
Discussion
Summary of the main findings
We included 12 RCTs that compared acupuncture therapy to sham acupuncture or conventional medication. With respect to reducing pain (VAS 0–10 cm scale), there was moderate-quality evidence showing that real acupuncture was more effective than sham acupuncture in the short term, and similar results were obtained with low-quality evidence in the long term. With respect to improving the quality of life, there was low-quality evidence showing that real acupuncture was more effective than sham acupuncture in both the short and long term. In the comparison of acupuncture vs conventional medication, we found very low-quality evidence showing that acupuncture was more effective in relieving pain in both the short and long term.
Subgroup analyses demonstrated that real MA was superior to sham MA in reducing pain (VAS, 0–10 cm scale) and improving the quality of life, with moderate-quality evidence in the short term and low- to very low-quality evidence in the long term. There were two studies that compared real EA with sham EA. The results indicated real EA was superior to sham EA in reducing pain in the short term with low-quality evidence, but no significant difference was observed in the long term with low-quality evidence. Only one study compared real EA with sham EA and reported the effect on improving the quality of life. The results demonstrated no significant difference between real EA and sham EA in both the short and long term with low-quality evidence.
According to the TCM theory, FM is categorized as Bi Syndrome; the invasion of pathogenic wind, cold, and dampness can affect imbalance in the flow of Qi and blood, and then cause pain, stiffness, and other symptoms in the body’s muscles, tendons, and joints.34 Therefore, the TCM mechanism of acupuncture for FM is to regulate the circulation of Qi and blood, combined with expelling cold and removing dampness. A modern medical study indicated that acupuncture can significantly increase blood flow in the skin and muscles of patients with FM,35 which is very important for reducing pain symptoms. As a primary mechanism of FM, the central sensitization of nervous system can decrease the pressure pain threshold, elicit hyperalgesia, and as a result, a noxious stimulus can cause more severe pain than in normal individuals.36,37 One recent animal study found that the upregulation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 and the phosphoactivation of extracellular signal regulated kinase were associated with mechanical hyperalgesia in FM model mice. EA at the bilateral Zusanli (ST36) acupoints can reverse the upregulation of these receptors and reduce mechanical hyperalgesia significantly.38 Another animal study showed that acid-sensing ion channel 3 and the ERK pathway participated in FM pain attenuated by EA.39 Additionally, acupuncture can regulate the central nervous system to release endogenous opioids and nonopioid compounds, such as endorphin, serotonin, enkephalins, dynorphin, norepinephrine, oxytocin, neuropeptide, and ATP. These substances are essential to decrease the hypersensitivity of pain and reduce pain symptoms.12,13,40,41 However, the specific mechanism of acupuncture therapy for FM is very complex and remains unknown. Therefore, more studies are needed in the future.
Comparison with previous systematic reviews
Previous meta-analyses have drawn various conclusions depending on the inclusion criteria and the number of included studies.15–17,42 One review42 published in 2010 included seven RCTs. The pooled analysis found strong evidence for the reduction of pain (standardized mean difference (SMD) =−0.25, 95% CI [−0.49, –0.02]) at posttreatment compared to control acupuncture, which contained sham and simulated acupuncture. However, sensitivity analysis indicated that this small analgesic effect of acupuncture was only present in studies with ROB. Therefore, this review concluded that acupuncture cannot be recommended for the management of FM. In 2013, one systematic review16 included 16 RCTs that compared acupuncture alone or combined with other interventions (cupping therapy, point injection, point catgut embedding, or moxibustion) to no treatment, sham, or conventional medication. The conclusion indicated that acupuncture alone or combined with cupping therapy was superior to conventional medications. However, acupuncture had no better effect than sham acupuncture on pain reduction. Another Cochrane review of acupuncture for FM was also published in 2013 and included nine RCTs.17 Pain severity measured with VAS, NRS, MPI, and MPQ was pooled in six studies, and the results indicated that acupuncture was no better than sham acupuncture in reducing pain (SMD =−0.14, 95% CI[–0.53, 0.25]). Therefore, the available systematic reviews demonstrated controversial conclusions about whether acupuncture was more effective than sham acupuncture in relieving pain.
Compared with previous systematic reviews, our review focused mainly on observing the efficacy of acupuncture alone, so we did not involve studies with mixed therapies. We included an additional five new RCTs published after 2013 in our review, three with low ROB and two with high ROB. Since the pain severity of patients was measured with VAS, NRS, MPI, or MPQ, this analysis may produce greater heterogeneity if the results of different measurement tools are directly pooled. Therefore, we extracted the results of the same tool as much as possible. Because most of the included studies used VAS as a measurement tool and FIQ contained VAS, we extracted the results of VAS to pool the analysis. Because one study data of the meta-analysis were transformed from NRS, we conducted sensitivity analyses by excluding this study and found that the pooled effect was not changed. We included nine RCTs, and the results indicated that real acupuncture was superior to sham acupuncture in reducing pain (VAS, 0–10 cm scale) in the short term with moderate-quality evidence (MD =−1.04, 95% CI [−1.70, –0.38]). This new conclusion of our review was completely different from that of previous research and can provide a better reference for clinical decisions because we analyzed direct VAS results.
Limitations and implications
This systematic review has several limitations. First, a low number of studies were included in our review, and most of the studies had a relatively small sample size. This limitation may lead to imprecise evidence. Second, there was considerable heterogeneity in our meta-analysis. We attempted to decrease the heterogeneity by subgroup and sensitivity analyses, but it was not completely resolved. We considered that this heterogeneity possibly derived from methodological bias and differences in acupoint selection, sham acupuncture method, and the frequency and duration of treatment. Third, only a few studies followed-up the patients after treatment and reported adverse events; thus, studies with more details about follow-up and adverse events would better evaluate the long-term effect and safety of acupuncture.
Given the above limitations, more rigorous larger-scale and well-designed RCTs are needed to provide higher-quality evidence and evaluate the efficacy of acupuncture for FM. First, future RCTs should correctly conduct random sequence generation, allocation concealment, and blinding to avoid ROB. Simultaneously, the details about follow-up, dropout, and adverse events must be reported thoroughly. Second, many different kinds of acupuncture are used to treat FM in clinical practice. Therefore, future studies comparing different acupuncture interventions are needed to find the most effective acupuncture treatment. Furthermore, the optimal duration and frequency of treatment are also important for FM. Third, all RCTs must be registered in advance and reported using standards for reporting interventions in clinical trials of acupuncture (STRICTA) guideline43 to improve the quality of future reports in this field.
Conclusion
In summary, real acupuncture was more effective than sham acupuncture in relieving pain (VAS, 0–10 cm scale) and improving the quality of life in both the short and long term. Both EA and MA were better than sham acupuncture in relieving pain in the short term. Furthermore, acupuncture was more effective in relieving pain in both the short and long term compared with conventional medication. No serious adverse events were found during acupuncture. In brief, acupuncture therapy is an effective and safe treatment for patients with FM, and it can be recommended for the management of FM. However, more large-sample RCTs are needed to investigate the therapeutic effect of EA for FM in the long term.
Supplementary materials
Table S1.
Reasons for excluded studies
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Mist et al, 20181 | Acupuncture vs education |
| Ma et al, 20182 | Article in Chinese; not an RCT |
| AM et al, 20173 | Dry needling vs cross tape |
| Iannuccelli et al, 20174 | Not an RCT |
| Zucker et al, 20175 | Secondary analysis of original article Harris et al, 200537 |
| Li et al, 20166 | Article in Chinese; acupuncture + moxibustion vs Western medicine |
| Disa et al, 20167 | Acupuncture vs electro-acupuncture vs moxibustion |
| Yu et al, 20168 | Article in Chinese; acupuncture + herbal medicine vs Western medicine |
| Weber et al, 20159 | No acupuncture therapy |
| de Tommaso et al, 201410 | Cross-over study; only ten patients |
| Casanueva et al, 201411 | Dry needling vs medical treatment |
| Collazo et al, 201412 | Article in Spanish; acupuncture vs moxibustion vs scalp acupuncture |
| Shao et al, 201313 | Article in Chinese; data unusable |
| Collazo et al, 201314 | Article in Spanish; acupuncture vs scalp acupuncture |
| Hadianfard et al, 201215 | Different treatment period. Acupuncture group received therapy for 2 weeks and control group received fluoxetine orally for 8 weeks |
| Iannuccelli et al, 201216 | Not an RCT |
| Collazo et al, 201217 | Article in Spanish; acupuncture vs traditional Chinese dietary therapy |
| Itoh et al, 201018 | Five acupuncture treatments vs ten acupuncture treatments |
| Jiang et al, 201019 | Article in Chinese; acupuncture + cupping + Western medicine vs acupuncture + cupping vs Western medicine |
| Collazo et al, 201020 | Article in Spanish; not an RCT |
| Li et al, 200921 | Article in Chinese; lower Dan-Tian acupuncture vs conventional acupuncture |
| Zhao et al, 200922 | Article in Chinese; moxibustion + Western medicine vs Western medicine |
| Targino et al, 200823 | Acupuncture + tricyclic antidepressants + exercise vs tricyclic antidepressants + exercise |
| Harris et al, 200824 | Data unusable; only ten patients |
| Sun, 200825 | Article in Chinese; not an RCT |
| Li, 200726 | Article in Chinese; not an RCT |
| Li et al, 200627 | Article in Chinese; acupuncture + cupping + Western medicine vs vs Western medicine |
| Yao et al, 200628 | Article in Chinese; not an RCT; data unusable |
| Harris et al, 200629 | Secondary analysis of original article Harris et al, 200537 |
| Guo et al, 200530 | Data unusable |
| Wang et al, 200431 | Article in Chinese; not an RCT |
| Wang et al, 200232 | Article in Chinese; data unusable |
| Liu et al, 200233 | Article in Chinese; did not meet ACR criteria |
| Zhang et al, 200134 | Article in Chinese; data unusable |
| Sandberg et al,199935 | Cross-over study; only ten patients |
| Sprott et al, 199836 | Data unusable |
Abbreviations: ACR, American College of Rheumatology; RCT, randomized controlled trial.
Table S2.
Sensitivity analyses on pain changes after treatment
| Real acupuncture vs sham acupuncture | Effect size | Heterogeneity |
|---|---|---|
| All studies | MD =−1.04, 95% CI (−1.70, −0.38) | I2=78% |
| All studies except Ugurlu et al, 201738 | MD =−0.83, 95% CI (−1.47, −0.19) | I2=72% |
| All studies except Stival et al, 201439 | MD =−0.90, 95% CI (−1.57, −0.22) | I2=78% |
| All studies except Assefi et al, 201440 | MD =−1.21, 95% CI (−1.89, −0.53) | I2=77% |
| All studies except Harris et al, 200537 | MD =−1.15, 95% CI (−1.84, −0.46) | I2=80% |
| The studies with low risk of bias | MD =−0.65, 95% CI (−1.30, −0.01) | I2=71% |
References
- 1.Mist SD, Jones KD. Randomized controlled trial of acupuncture for women with fibromyalgia: group acupuncture with traditional Chi-nese medicine diagnosis-based point selection. Pain Med. 2018;19(9):1862–1871. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnx322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ma S, Zhao L, Cai C, Ma X, Peng S, Dai J. Clinical observation on treating 136 cases of fibromyalgia syndrome by acupuncture at Backshu point. Mod Chin Clin Med. 2018;25(02):11–13. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Castro-Sanchez AM, Garcia-Lopez H, Mataran-Penarrocha GA, et al. Effects of dry needling on spinal mobility and trigger points in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Pain Phys. 2017;2:37–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Iannuccelli C, Guzzo MP, Atzeni F, et al. Pain modulation in patients with fibromyalgia undergoing acupuncture treatment is associated with fluctuations in serum neuropeptide Y levels. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017;35(Suppl 105):81–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zucker NA, Tsodikov A, Mist SD, Cina S, Napadow V, Harris RE. Evoked pressure pain sensitivity is associated with differential analgesic response to verum and sham acupuncture in fibromyalgia. Pain Med. 2017;18(8):1582–1592. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnx001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Li D, Yang L, Li J. Fibromyalgia syndrome treated with acupuncture at the acupoints of the affected meridians and heavy moxibustion at painful points: a randomized controlled trial. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2016;36(2):147–151. Chinese. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dias PA, Guimaraes AB, Albuquerque AO, de Oliveira KL, Cavalcante ML, Guimaraes SB. Short-term complementary and alternative medicine on quality of life in women with fibromyalgia. J Integr Med. 2016;14(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/S2095-4964(16)60235-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yu J, Li L, Qin H, Chen Y, Jin S. Clinical observation of Zheng Qing Feng Tong Ning combined with acupuncture for fibromyalgia syndrome. Hubei J TCM. 2016;38(6):37–38. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Weber A, Werneck L, Paiva E, Gans P. Effects of music in combination with vibration in acupuncture points on the treatment of fibromyalgia. J Altern Complement Med. 2015;21(2):77–82. doi: 10.1089/acm.2014.0199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.de Tommaso M, Delussi M, Ricci K, D’Angelo G. Abdominal acupuncture changes cortical responses to nociceptive stimuli in fibromyalgia patients. Cns Neurosci Ther. 2014;20(6):565–567. doi: 10.1111/cns.12280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Casanueva B, Rivas P, Rodero B, Quintial C, Llorca J, Gonzalez-Gay MA. Short-term improvement following dry needle stimulation of tender points in fibromyalgia. Rheumatol Int. 2014;34(6):861–866. doi: 10.1007/s00296-013-2759-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Collazo E, Muñoz RMD, Aragonés MÁ, Gómez F. Randomized prospective study to assess the effectiveness of several therapeutic procedures of traditional Chinese medicine in alleviation of pain and improvement in the standard of living in patients with fibromyalgia. Rev Int Acupuntura. 2014;8(4):121–128. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shao M, Jiang M. Treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome with acupuncture of soothing liver and relieving depression. Hubei J TCM. 2013;35(12):62. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Collazo CE, Muñoz RMD. Scalp acupuncture and acupunture for treatment of patients with fibromyalgia. Prospective randomized study. Rev Int Acupuntura. 2013;7(1):6–11. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hadianfard MJ, Hosseinzadeh PM. A randomized clinical trial of fibromyalgia treatment with acupuncture compared with fluoxetine. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2012;14(10):631–640. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Iannuccelli C, Mannocci F, Guzzo MP, et al. Complementary treatment in fibromyalgia: combination of somatic and abdominal acupuncture. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012;30(6 Suppl 74):112–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Collazo CE. Acupuncture and traditional Chinese dietary therapy in the treatment of patients with fibromyalgia. A randomized prospective study. Rev Int Acupuntura. 2012;6(3):94–101. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Itoh K, Kitakoji H. Effects of acupuncture to treat fibromyalgia: a preliminary randomised controlled trial. Chin Med. 2010;5:11. doi: 10.1186/1749-8546-5-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jiang ZY, Li CD, Qiu L, et al. Combination of acupuncture, cupping and medicine for treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome: a multi-central randomized controlled trial. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2010;30(4):265–269. Chinese. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Collazo CE. Effectiveness of acupuncture therapy for pain relief in patients with fibromyalgia. Rev Int Acupuntura. 2010;4(1):52–58. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li B, Wang Y. Therapeutic effect of acupuncture at lower Dan-Tian on neuropsychiatric symptoms of fibromyalgia syndrome. Acta Chin Med Pharmacol. 2009;37(6):89–90. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhao RH, Zhu YB. Observation on therapeutic effect of herb-partitioned moxibustion on fibromyalgia syndrome. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2009;29(3):200–202. Chinese. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Targino RA, Imamura M, Kaziyama HH, et al. A randomized controlled trial of acupuncture added to usual treatment for fibromyalgia. J Rehabil Med. 2008;40(7):582–588. doi: 10.2340/16501977-0216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Harris RE, Sundgren PC, Pang Y, et al. Dynamic levels of glutamate within the insula are associated with improvements in multiple pain domains in fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(3):903–907. doi: 10.1002/art.23223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sun Y. 28 cases of fibromyalgia syndrome treated by acupuncture and moxibustion. World Chin Med. 2008;3(3):170–171. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Li Y. Sixty-six cases of fibromyalgia syndrome treated with affected meridian points. World J Acupunct Moxibustion. 2007;17(4):54–55. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fu Li, CD XY, Jiang ZY, et al. Clinical study on combination of acupuncture, cupping and medicine for treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2006;26(1):8–10. Chinese. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yao Q, Zhang X, Wang X. Treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome with Tiao Du Tong Mai acupuncture. J Clin Acupunct Moxibustion. 2006;22(2):24–25. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Harris RE, Gracely RH, McLean SA, et al. Comparison of clinical and evoked pain measures in fibromyalgia. J Pain. 2006;7(7):521–527. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2006.01.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Guo XJ, Jia J. Comparison of therapeutic effects on fibromyalgia syndrome between dermal-neurological electric stimulation and electric acupuncture. Adv Clin Rehabil. 2005;9(46):171–173. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang W, Liu Z, Wu Y. Clinical observation on 42 cases of fibromyalgia syndrome treated by acupuncture and moxibustion. J Tradit Chin Med. 2004;19(1):26–27. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wang S, Wang X, Zhang D, Xia P, Yang H. Clinical observation on therapeutic effect of acupuncture treatment based on syndrome differentiation of meridians on fibromyalgia. Zhongguo Zhen jiu. 2002;22(12):807–809. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Liu Q, Li F. Clinical analysis of 30 cases of fibromyalgia treated by acupuncture. Anthol Med. 2002;21(2):183–184. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhang Y. Clinical observation on acupuncture treatment of primary fibromyalgia syndrome. Zhongguo Zhen jiu. 2001;21(1):19–20. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sandberg M, Lundeberg T, Gerdle B. Manual acupuncture in fibromyalgia: a long-term pilot study. J Musculoskelet Pain. 1999;7(3):39–58. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sprott H. Efficiency of acupuncture in patients with fibromyalgia. Clin Bull Myofascial Ther. 1998;3(1):37–43. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Harris RE, Tian X, Williams DA, et al. Treatment of fibromyalgia with formula acupuncture: investigation of needle placement, needle stimulation, and treatment frequency. J Altern Complement Med. 2005;11(4):663–671. doi: 10.1089/acm.2005.11.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ugurlu FG, Sezer N, Aktekin L, Fidan F, Tok F, Akkus S. The effects of acupuncture versus sham acupuncture in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Acta Reumatol Port. 2017;42(1):32–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Stival RS, Cavalheiro PR, Stasiak CE, Galdino DT, Hoekstra BE, Schafranski MD. Acupuncture in fibromyalgia: a randomized, controlled study addressing the immediate pain response. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2014;54(6):431–436. doi: 10.1016/j.rbr.2014.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Assefi NP, Sherman KJ, Jacobsen C, Goldberg J, Smith WR, Buchwald D. A randomized clinical trial of acupuncture compared with sham acupuncture in fibromyalgia. Ann Intern Med. 2005;143(1):10–19. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-143-1-200507050-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81674067). The funding body had no role in the design of the study, in collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, and in writing the manuscript.
Footnotes
Author contributions
Study concept and design: GN, XZ. Acquisition of data: XZ, HC, WX. Analysis and interpretation of data: GN, XZ, HC, WX, YS, YG. Article drafting and critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: GN, XZ, HC, WX, YS, YG. Administrative, technical, or administrative support: GN, XZ, HC. Study supervision: GN, XZ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors contributed toward data analysis, drafting and revising the paper and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles MA, et al. 2016 Revisions to the 2010/2011 fibromyalgia diagnostic criteria. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016;46(3):319–329. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2016.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Queiroz LP. Worldwide epidemiology of fibromyalgia. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2013;17(8):356. doi: 10.1007/s11916-013-0356-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fitzcharles MA, Ste-Marie PA, Goldenberg DL, et al. 2012 Canadian Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of fibromyalgia syndrome: executive summary. Pain Res Manag. 2013;18(3):119–126. doi: 10.1155/2013/918216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Clauw DJ. Fibromyalgia: a clinical review. JAMA. 2014;311(15):1547–1555. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.3266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Häuser W, Ablin J, Fitzcharles M-A, et al. Fibromyalgia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;78:15022. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2015.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cabo-Meseguer A, Cerda-Olmedo G, Trillo-Mata JL. Fibromyalgia: prevalence, epidemiologic profiles and economic costs. Med Clin. 2017;149(10):441–448. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2017.06.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Theoharides TC, Tsilioni I, Arbetman L, et al. Fibromyalgia syndrome in need of effective treatments. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015;355(2):255–263. doi: 10.1124/jpet.115.227298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ablin J, Fitzcharles MA, Buskila D, Shir Y, Sommer C, Häuser W. Treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome: recommendations of recent evidence-based interdisciplinary guidelines with special emphasis on complementary and alternative therapies. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013(3):1–7. doi: 10.1155/2013/485272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Thorpe J, Shum B, Moore RA, Wiffen PJ, Gilron I. Combination pharmacotherapy for the treatment of fibromyalgia in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;2:CD010585. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010585.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Macfarlane GJ, Kronisch C, Dean LE, et al. EULAR revised recommendations for the management of fibromyalgia. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(2):318–328. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Coutaux A. Non-pharmacological treatments for pain relief: TENS and acupuncture. Joint Bone Spine. 2017;84(6):657–661. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2017.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ondrejkovicova A, Petrovics G, Svitkova K, Bajtekova B, Bangha O. Why acupuncture in pain treatment? Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2016;37(3):163–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tang Y, Yin HY, Rubini P, Illes P. Acupuncture-induced analgesia: a neurobiological basis in purinergic signaling. Neuroscientist. 2016;22(6):563–578. doi: 10.1177/1073858416654453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Deluze C, Bosia L, Zirbs A, Chantraine A, Vischer TL. Electroacupuncture in fibromyalgia: results of a controlled trial. BMJ. 1992;305(6864):1249–1252. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6864.1249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yang B, Yi G, Hong W, et al. Efficacy of acupuncture on fibromyalgia syndrome: a meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med. 2014;34(4):381–391. doi: 10.1016/s0254-6272(15)30037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cao H, Li X, Han M, Liu J. Acupoint stimulation for fibromyalgia: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:362831. doi: 10.1155/2013/362831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Deare JC, Zheng Z, Xue CC. Acupuncture for treating fibromyalgia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;31(5):CD007070. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007070.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Vas J, Santos-Rey K, Navarro-Pablo R, et al. Acupuncture for fibromyalgia in primary care: a randomised controlled trial. Acupunct Med. 2016;34(4):257–266. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2015-010950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ugˇurlu FG, Sezer N, Aktekin L, Fidan F, Tok F, Akkus¸ S. The effects of acupuncture versus sham acupuncture in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Acta Reumatol Port. 2017;42(1):32–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Karatay S, Okur SC, Uzkeser H, Yildirim K, Akcay F. Effects of acupuncture treatment on fibromyalgia symptoms, serotonin, and substance P levels: a randomized sham and placebo-controlled clinical trial. Pain Med. 2018;19(3):615–628. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnx263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P, PRISMA Group Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 2010;8(5):336–341. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 Criteria for the Classification of Fibromyalgia. Report of the Multicenter Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33(2):160–172. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. [Accessed June 15, 2018]. [updated March 2011] The Cochrane Collaboration; 2011. Available from http://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org/
- 24.Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ. 2008;336(7650):924–926. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A, editors. GRADE Handbook for Grading Quality of Evidence and Strength of Recommendations. [Accessed June 15, 2018]. [Updated October 2013[ The GRADE Working Group, 2013. Available from https://gdt.gradepro.org/app/handbook/handbook.html.
- 26.Stival RS, Cavalheiro PR, Stasiak CE, Galdino DT, Hoekstra BE, Schafranski MD. Acupuncture in fibromyalgia: a randomized, controlled study addressing the immediate pain response. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2014;54(6):431–436. doi: 10.1016/j.rbr.2014.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Harte SE, Clauw DJ, Napadow V, Harris RE. Pressure pain sensitivity and insular combined glutamate and glutamine (Glx) are associated with subsequent clinical response to Sham but not traditional acupuncture in patients who have chronic pain. Med Acupunct. 2013;25(2):154–160. doi: 10.1089/acu.2013.0965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wei-Zhi G, Yu-Qi W. Observations on the therapeutic effect of acupuncture on fibromyalgia syndrome. Shanghai J Acupunct Moxibust. 2010;29(11):725–727. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Harris RE, Zubieta JK, Scott DJ, Napadow V, Gracely RH, Clauw DJ. Traditional Chinese acupuncture and placebo (sham) acupuncture are differentiated by their effects on mu-opioid receptors (MORs) Neuroimage. 2009;47(3):1077–1085. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.05.083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Martin DP, Sletten CD, Williams BA, Berger IH. Improvement in fibromyalgia symptoms with acupuncture: results of a randomized controlled trial. Mayo Clin Proc. 2006;81(6):749–757. doi: 10.4065/81.6.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Guo Y, Sun YZ. Clinical study on treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome with penetration needling at the back. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2005;25(2):98–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Harris RE, Tian X, Williams DA, et al. Treatment of fibromyalgia with formula acupuncture: investigation of needle placement, needle stimulation, and treatment frequency. J Altern Complement Med. 2005;11(4):663–671. doi: 10.1089/acm.2005.11.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Assefi NP, Sherman KJ, Jacobsen C, Goldberg J, Smith WR, Buchwald D. A randomized clinical trial of acupuncture compared with sham acupuncture in fibromyalgia. Ann Intern Med. 2005;143(1):10–19. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-143-1-200507050-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yang G, Liang S, Wei H. Treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome with traditional Chinese medicine. Int J Clin Acupunct. 2015;24(2):97–104. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kim SY, Min S, Lee H, et al. Changes of local blood flow in response to acupuncture stimulation: a systematic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016(6):1–11. doi: 10.1155/2016/9874207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wu MY, Huang MC, Chiang JH, Sun MF, Lee YC, Yen HR. Acupuncture decreased the risk of coronary heart disease in patients with fibromyal-gia in Taiwan: a nationwide matched cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1239-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ji RR, Nackley A, Huh Y, Terrando N, Maixner W. Neuroinflammation and central sensitization in chronic and widespread pain. Anesthesiology. 2018;129(2):343–366. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000002130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lin JG, Hsieh CL, Lin YW. Analgesic effect of electroacupuncture in a mouse fibromyalgia model: roles of TRPV1, TRPV4, and pERK. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0128037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yen LT, Hsieh CL, Hsu HC, Lin YW. Targeting ASIC3 for relieving mice fibromyalgia pain: roles of electroacupuncture, opioid, and adenosine. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):46663. doi: 10.1038/srep46663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Cidral-Filho FJ, da Silva MD, Moré AO, Córdova MM, Werner MF, Santos AR. Manual acupuncture inhibits mechanical hypersensitivity induced by spinal nerve ligation in rats. Neuroscience. 2011;193:370–376. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zhang R, Lao L, Ren K, Berman BM. Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on persistent pain. Anesthesiology. 2014;120(2):482–503. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Langhorst J, Klose P, Musial F, Irnich D, Häuser W. Efficacy of acupuncture in fibromyalgia syndrome: a systematic review with a meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Rheumatology. 2010;49(4):778–788. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kep439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.MacPherson H, Altman DG, Hammerschlag R, et al. Revised standards for reporting interventions in clinical trials of acupuncture (STRICTA): extending the CONSORT statement. PLoS Med. 2010;7(6):e1000261. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1.
Reasons for excluded studies
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Mist et al, 20181 | Acupuncture vs education |
| Ma et al, 20182 | Article in Chinese; not an RCT |
| AM et al, 20173 | Dry needling vs cross tape |
| Iannuccelli et al, 20174 | Not an RCT |
| Zucker et al, 20175 | Secondary analysis of original article Harris et al, 200537 |
| Li et al, 20166 | Article in Chinese; acupuncture + moxibustion vs Western medicine |
| Disa et al, 20167 | Acupuncture vs electro-acupuncture vs moxibustion |
| Yu et al, 20168 | Article in Chinese; acupuncture + herbal medicine vs Western medicine |
| Weber et al, 20159 | No acupuncture therapy |
| de Tommaso et al, 201410 | Cross-over study; only ten patients |
| Casanueva et al, 201411 | Dry needling vs medical treatment |
| Collazo et al, 201412 | Article in Spanish; acupuncture vs moxibustion vs scalp acupuncture |
| Shao et al, 201313 | Article in Chinese; data unusable |
| Collazo et al, 201314 | Article in Spanish; acupuncture vs scalp acupuncture |
| Hadianfard et al, 201215 | Different treatment period. Acupuncture group received therapy for 2 weeks and control group received fluoxetine orally for 8 weeks |
| Iannuccelli et al, 201216 | Not an RCT |
| Collazo et al, 201217 | Article in Spanish; acupuncture vs traditional Chinese dietary therapy |
| Itoh et al, 201018 | Five acupuncture treatments vs ten acupuncture treatments |
| Jiang et al, 201019 | Article in Chinese; acupuncture + cupping + Western medicine vs acupuncture + cupping vs Western medicine |
| Collazo et al, 201020 | Article in Spanish; not an RCT |
| Li et al, 200921 | Article in Chinese; lower Dan-Tian acupuncture vs conventional acupuncture |
| Zhao et al, 200922 | Article in Chinese; moxibustion + Western medicine vs Western medicine |
| Targino et al, 200823 | Acupuncture + tricyclic antidepressants + exercise vs tricyclic antidepressants + exercise |
| Harris et al, 200824 | Data unusable; only ten patients |
| Sun, 200825 | Article in Chinese; not an RCT |
| Li, 200726 | Article in Chinese; not an RCT |
| Li et al, 200627 | Article in Chinese; acupuncture + cupping + Western medicine vs vs Western medicine |
| Yao et al, 200628 | Article in Chinese; not an RCT; data unusable |
| Harris et al, 200629 | Secondary analysis of original article Harris et al, 200537 |
| Guo et al, 200530 | Data unusable |
| Wang et al, 200431 | Article in Chinese; not an RCT |
| Wang et al, 200232 | Article in Chinese; data unusable |
| Liu et al, 200233 | Article in Chinese; did not meet ACR criteria |
| Zhang et al, 200134 | Article in Chinese; data unusable |
| Sandberg et al,199935 | Cross-over study; only ten patients |
| Sprott et al, 199836 | Data unusable |
Abbreviations: ACR, American College of Rheumatology; RCT, randomized controlled trial.
Table S2.
Sensitivity analyses on pain changes after treatment
| Real acupuncture vs sham acupuncture | Effect size | Heterogeneity |
|---|---|---|
| All studies | MD =−1.04, 95% CI (−1.70, −0.38) | I2=78% |
| All studies except Ugurlu et al, 201738 | MD =−0.83, 95% CI (−1.47, −0.19) | I2=72% |
| All studies except Stival et al, 201439 | MD =−0.90, 95% CI (−1.57, −0.22) | I2=78% |
| All studies except Assefi et al, 201440 | MD =−1.21, 95% CI (−1.89, −0.53) | I2=77% |
| All studies except Harris et al, 200537 | MD =−1.15, 95% CI (−1.84, −0.46) | I2=80% |
| The studies with low risk of bias | MD =−0.65, 95% CI (−1.30, −0.01) | I2=71% |