Abstract
Objectives
A systematic review to assess the evidence supporting surgical repair of digital nerve injury versus no repair in adults in terms of clinical outcomes.
Design
A Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses-compliant systematic review with methodology based on the Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions.
Data sources
Databases included OvidMEDLINE, EMBASE, AMED, clinicaltrials.gov and the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, searched from inception until 10 November 2018.
Eligibility criteria
Adult digital nerve injury in which either direct repair or no repair was undertaken and an outcome measure was recorded.
Data extraction and synthesis
Study data extracted included demographics, injury type and extent, timing, treatment details, outcome data and time points, adverse outcomes, hand therapy and return to work. The National Institute of Health quality assessment tool for case series was used to assess risk of bias.
Results
Thirty studies were included. One compared surgical repair with non-repair. All studies were case series of between 15 and 110 nerve injuries, with heterogeneous patient, injury and treatment characteristics. Two studies detailed nerve repair without magnification. Static 2-point discrimination (s2PD) was the most commonly reported outcome measure. Return of protective sensation was achieved in most cases in the nerve repair and no nerve repair groups. Repair resulted in better s2PD than no repair, but <25% repaired nerves achieved normal levels. Adverse outcomes were similar between repair and no repair groups.
Conclusions
Only level IV evidence is available to support surgical repair of digital nerves in adults. Return of normal sensibility is uncommon and almost all unrepaired nerves regained protective sensation by 6 months and all patients declined further surgery. There was no difference in adverse outcomes. There is currently a lack of high-quality evidence to support surgical repair of digital nerve injuries in adults and further research is needed.
PROSPERO registration number
CRD42017065092.
Keywords: digital nerve, nerve injury, nerve repair
Strengths and limitations of this study.
This systematic review was conducted in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines, using methodology based on the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions.
Using a comprehensive search strategy, all available and relevant published literature on this topic was included for evaluation.
The quality of the included studies was low and were at high risk of bias.
Surgical techniques, including the use of magnification have evolved since some of the earlier studies.
Outcome data were incompletely and variably reported across the included studies.
Introduction
The incidence of digital nerve injuries in a typical European urban district is 6.2 per 100 000 inhabitants per year.1 They arise from a mixture of domestic and work-related accidents and occur in all age groups. They most commonly occur in the working age population and are 2–5 times more common in men compared with women.1–6 Standard practice following digital nerve injury is direct end-to-end surgical repair of the nerve using microsutures, with alternative techniques described if a nerve gap prevents direct repair.7–11
A conservative estimated cost to the UK National Health Service of digital nerve injury and repair is £10 million per year. This does not consider patient-related costs of time off work and loss of income.12 The perceived advantage of performing surgical repair is that direct coaptation of the nerve endings is more likely to result in a better outcome for the patient and a lower incidence of neuroma than not repairing it. The most commonly reported outcome measures following repair include static or moving 2-point discrimination (s2PD or m2PD), pressure threshold detection and pain or temperature sensitivity.13–16 Less commonly reported measures include return to work, patient satisfaction and incidence of complications. Patient reported outcome measures are sparsely used in studies of digital nerve repair. Potential common complications from either repair or non-repair include neuroma and cold intolerance.3 4
Objective
The aim of this systematic review is to rigorously evaluate the quality of the evidence for surgical repair of unilateral adult digital nerve injury compared with no surgical repair; and to determine whether the outcomes and complications following surgical repair of a digital nerve injury in adults are superior when compared with no surgical repair.
Methods
This review was produced and reported in accordance to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines with methodology based on the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions.17 A protocol was developed and locally peer-reviewed a priori and registered in concordance with best practice in systematic reviews.
Search strategy
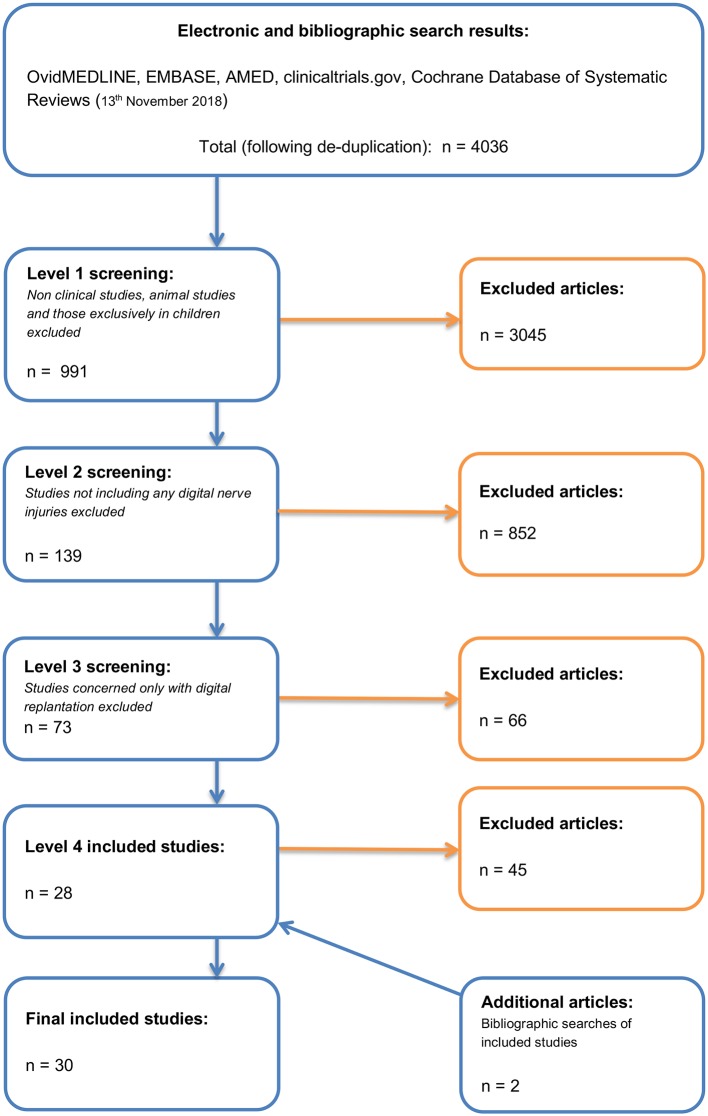
The primary author (RLED) carried out a full systematic literature search of all records in the following databases: OvidMEDLINE (including OvidMEDLINE In-Process and Other Non-Indexed Citations), EMBASE, AMED, clinicaltrials.gov and the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. The search strategy (online supplementary appendix 1) was developed in conjunction with a medical information specialist. Both ‘free-text term’ and ‘MeSH term’ searches were completed, using variations of the keywords ‘digital nerve’, ‘injury’, ‘nerve injury’, ‘nerve repair’, ‘nerve surgery’ and were combined using Boolean operators.18 All languages were considered. The databases were searched from inception until 13 November 2018. All search results were merged and duplicate citations were discarded. Two authors screened titles and abstracts independently (RLED and JCRW) and studies unrelated to the research objective were discarded. The full texts of the relevant papers were retrieved and examined by each author independently for consideration for inclusion/exclusion based on predefined stratified criteria (figure 1—study attrition algorithm). The final list of the included studies was compared and discussed between all authors. The reference lists of the included papers and previous reviews were examined to ensure relevant studies had been considered. Any disparities regarding inclusion of articles were discussed between the authors and a joint decision was made based on the inclusion criteria. The published data from included studies were scrutinised for reporting of outcomes. If some relevant data were not available for extraction, then the authors of the study were contacted by email with a specific data request. If there was no reply, a reminder email was sent after 2 weeks. If we received no response, then we sent a further email and waited for 8 weeks for reply. If we still received no response, then the study was excluded and the authors notified.
Figure 1.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses study attrition algorithm.
bmjopen-2018-025443supp001.pdf (33.3KB, pdf)
Data extraction and analysis
Data collection and analysis was performed in accordance with the Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions, where applicable.17 Data were extracted onto a predefined electronic data extraction form by author (RLED), which was checked by the other authors separately. Data extracted from each paper included patient and injury demographics (gender, age, smoking status, injury type and extent including arterial injury), the timing and details of treatment (neurorrhaphy, other surgical techniques and no nerve repair) including suture gauge, use of magnification, experience level of surgeon, aftercare including hand therapy provision, outcome measures (any) and time of outcome measurement, plus any complications or negative outcomes. Descriptive statistics were performed for patient demographics and key outcomes where possible to allow for narrative synthesis. Formal meta-analysis was not performed due to a lack of comparative studies, variable outcome reporting and a consistently high risk of bias based on study design.
Risk of bias
The review authors (RLED and JCRW) assessed risk of bias for each study using National Institute of Health (NIH) tool for appraisal of case series. The tool was developed by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute and Research Triangle Institute International.19 This tool is designed specifically for methodological quality assessment in case series and as such was the most appropriate tool for use in this systematic review. Based on nine domains, each case series is assessed and given an overall rating: good, fair or poor (online supplementary appendix 2). We appraised the quality of evidence for each outcome based on the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach.20
bmjopen-2018-025443supp002.pdf (72.9KB, pdf)
Public and patient involvement
Patient and public involvement was not part of this systematic review but has been undertaken subsequently.
Results
Study selection
A total of 4036 records were screened using a study attrition algorithm (figure 1). Following step 3 of the algorithm, 73 full-text records were retrieved. One record in a Turkish language publication and two in Russian could not be obtained. Of the 73 records obtained, 15 were excluded since they detailed studies using only nerve graft or nerve wrap techniques rather than direct nerve repair. Three were excluded as being descriptive, non-clinical studies and one because there was insufficient detail to include. The corresponding author of this paper did not respond to a request for further information. A further 26 were excluded for other reasons (reporting of neuroma treatments, insufficient outcome measures recorded, not possible to distinguish mixed nerve repair results from digital nerve repairs). These left 28 studies from the original search which met the inclusion criteria and were suitable for data extraction and analysis. During review of the 73 records, the reference lists were scrutinised and those that appeared potentially relevant were obtained and screened. On this basis, one further study was included. One extra study was identified later, during manuscript write-up, which had been published since the original search. The total number of studies therefore included in this review was 30.
As per rigorous systematic review methodology, the terms of the original search were to scrutinise the databases from inception to the present day and therefore some historical articles were identified and included in our analysis. No papers were excluded based on publication date as this would have introduced selection bias and compromises methodology. Of course, certain aspects of surgical technique have evolved since the earlier articles were published and so we have ensured that the results are presented clearly to show results from different eras.
Study characteristics
Data were extracted from these 30, level IV studies to detail injury mechanisms, patient demographics, surgical intervention and timing of outcome measurements (table 1).
Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies
| Author | Year | Study type | Attrition rate | Number of digital nerve repairs analysed | Other structures injured | Injury mechanism | Intervention(s) and control | Timing of intervention (acute, delayed, mixed and unknown) | Average age of patient (years) | Children included (age<18) |
Male:female ratio (rounded up) |
| Bunnell et al21 | 1928 | Retrospective | Unknown | 45 | Yes | Various | Repair or graft | Delayed | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown |
| Shaffer and Cleveland32 | 1950 | Prospective | None at 3 months | 36 | Yes | Unknown | Repair | Delayed | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown |
| Nemethi20 | 1956 | Retrospective | Unknown | Not documented | Yes | Various | Repair | Acute | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown |
| Buncke50 | 1972 | Retrospective | Unknown | 20 | Unknown | Various | Repair | Unknown | 32 | Yes | 2:1 |
| Holst51 | 1975 | Retrospective | 27% | Not documented | Yes | Sharp | Repair | Delayed | Unknown | Yes | Unknown |
| Poppen et al44 | 1979 | Retrospective | 50% | 74 | Yes | Sharp | Repair | Delayed | 29 | Yes | 2:1 |
| Young et al47 | 1981 | Prospective | Unknown | 34 | Yes | Various | Epineural vs fascicular repair | Delayed | 29 | Yes | 2:1 |
| Khuc et al33 | 1982 | Retrospective | 32% | 110 | Yes | Various | Repair, neurolysis or graft | Mixed | 32 | Yes | 2:1 |
| Sullivan52 | 1985 | Retrospective | None | 42 | Yes | Various | Repair (three patients with no repair) | Mixed | Unknown | No | Unknown |
| Mailander et al43 | 1988 | Retrospective | 17% | 107 | Yes | Various | Repair | Acute | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown |
| Altissimi et al39 | 1991 | Retrospective | None | 54 | Yes | Various | Repair | Acute | 35 | Yes | 4:1 |
| Pereira et al30 | 1991 | Retrospective | None | 30 | Yes | Sharp | Repair or graft | Mixed | Unknown | Yes | 3:1 |
| Goldie et al29 | 1992 | Retrospective | Unknown | 30 | Yes | Unknown | Repair | Mixed | 40 | No | Unknown |
| Chaise et al25 | 1993 | Retrospective | Unknown | 110 | No | Sharp | Repair | Acute | 31 | Yes | Unknown |
| Chow and Ng49 | 1993 | Prospective | 35% | 72 | Yes | Unknown | Repair vs non-repair | Acute | Unknown | Unknown | 3:1 |
| Kallio 41 | 1993 | Retrospective | 20% | 151 | Yes | Various | Repair or graft | Delayed | 29 | Yes | 3:1 |
| Al-Ghazal et al38 | 1994 | Retrospective | 15% | 88 | Yes | Various | Repair | Acute | Unknown | Yes | 2:1 |
| Elias et al26 | 1994 | Retrospective | Unknown | 83 | Unknown | Various | Repair | Unknown | 30 | Yes | 5:1 |
| Vertruyen et al45 | 1994 | Retrospective | 42% | 65 | Yes | Various | Repair | Unknown | 23 | Unknown | 3:1 |
| Efstathopoulos et al31 | 1995 | Retrospective | 10% | 64 | Yes | Various | Repair | Acute | Unknown | Yes | 5:1 |
| Tadjalli et al27 | 1995 | Retrospective | 83% | 37 | Yes | Various | Repair | Unknown | 33 | Unknown | 2:1 |
| Wang et al46 | 1996 | Retrospective | Unknown | 76 | No | Various | Repair or graft | Unknown | Unknown | No | Unknown |
| Cheng et al40 | 2001 | Prospective | 18% | 65 | Yes | Unknown | Repair±early sensory re-education | Acute | 40 | Unknown | 3:1 |
| Segalman53 | 2001 | Retrospective | 80% | 19 | Yes | Various | Repair | Unknown | 64 | No | 1:1 |
| Portincasa54 | 2007 | Retrospective | Unknown | Not documented | Yes | Unknown | Repair or graft | Mixed | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown |
| Hohendorff et al3 | 2009 | Retrospective | 26% | 57 | Yes | Various | Repair of nerve±digital artery repair | Delayed | 39 | No | 3:1 |
| Lohmeyer et al4 | 2009 | Retrospective | 75% | 58 | Yes | Various | Repair or graft | Unknown | 41 | Yes | 3:1 |
| Thomas et al5 | 2015 | Retrospective | 5% | 25 | Yes | Sharp | Repair with loupe vs microscope | Acute | 45 | No | 3:1 |
| Fakin et al2 | 2016 | Retrospective | 46% | 93 | Yes | Various | Repair | Acute | 43 | No | 2:1 |
| Huber et al36 | 2017 | Retrospective | 77% | 15 | Yes | Various | Repair or conduit | Mixed | 39 | Unknown | 4:1 |
In total, 26 studies were retrospective case series and four were prospective. Seven included data on non-digital nerve injuries, but the results from the digital nerve repairs specifically could mostly be distinguished from the results in general. Eight studies included graft or conduit use as well as direct nerve repair, but again the nerve repair results could be distinguished from the other results. In 28 studies, other injuries were present, such as tendon injury or fracture, though the study attrition algorithm excluded studies where all cases were revascularisation and replantation injuries. Three studies did not document the number of digital nerve injuries included, the others ranged from 15 to 110 digital nerve injuries, in patients with an age range of 1–88 years, though age was not documented in six studies. There were significantly more male than female patients in 19 out of 20 studies that documented patient gender (up to 5:1 ratio).
Injury types were mixed in 20 studies, sharp in five studies and not documented in five studies. Time from injury to surgical repair varied from 0 to 30 months, though 17 studies had all, or nearly all, immediate repairs. Nerve repair sutures used included 6–0 or 7–0 silk in the earlier studies (Bunnell described his suture as ‘finest silk’) and nylon in later studies, ranging from 8-0 gauge to 10–0 gauge. Magnification was used in 20 studies, either loupes or microscope, not specified or not always used in eight studies and not used in two, which were both written prior to the introduction of the operating microscope.21 22
Outcome measures
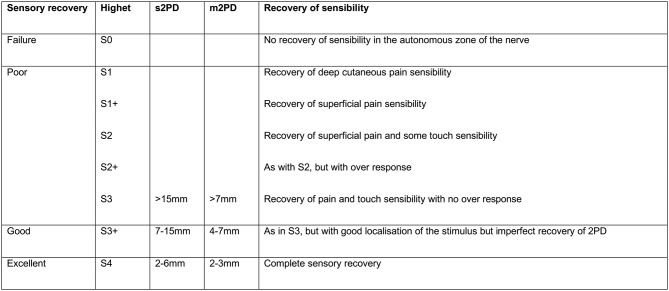
s2PD first described by Weber in 1835 was the most widely recorded outcome measure (26 studies). Ideally, this was recorded as an absolute value, with comparison to the corresponding portion of the contralateral, uninjured finger. Normal values in an uninjured finger-tip range from 2 to 6 mm. Classification schemes such as Medical Research Council scoring system from 1954, modified by MacKinnon and Dellon (often referred to as Modified Highet (figure 2), group a range of values into subjective headings.23–25 This scoring system was frequently used in the studies to report results following nerve repair. Using the Modified Highet classification, ‘Grade 4’ or ‘Excellent’ recovery may have an s2PD of 6 mm, which could be up to 4 mm wider than preinjury or the contralateral digit. Equally, a ‘Poor’ outcome according to Highet could have a large s2PD of >15 mm but with no pain or functional loss. The way in which s2PD was recorded varied between studies, making comparisons difficult. We have attempted to simplify comparisons by extracting only the Highet grade 4 results from each paper, where s2PD was 6 mm or less following nerve repair (table 2). The range of Highet grade 4 results achieved was between 8% and 60% following nerve repair, with an average across the studies of 24%.
Figure 2.
Modified Highet classification of nerve recovery.
Table 2.
Primary outcome of s2PD for digital nerve repair
| Primary author and year | Number of digital nerve repairs analysed | Timing of results measurement (m=months y=years) | Number of nerve repairs with s2PD 6 mm or less: Highet grade 4 | Children (age<18) included |
| Bunnell 192821 | 45 | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown |
| Shaffer and Cleveland et al 195032 | 36 | 3–12 m | Unknown | Unknown |
| Nemethi 195620 | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown |
| Buncke 197250 | 20 | Unknown | 12 (60%) | Yes |
| Holst 197551 | Unknown | 26 m | Unknown | Yes |
| Poppen et al 197944 | 74 | 5y | 12 (16%) | Yes |
| Young et al 198147 | 34 | Unknown | 11 (32%) | Yes |
| Khuc et al 198233 | 110 | 6m | 9 (8%) | Yes |
| Sullivan 198552 | 42 | 6.5-8y | 9 (21%) | No |
| Mailander et al 198843 | 107 | 6–60 m | 25 (23%) | Unknown |
s2PD, static 2-point discrimination.
Other objective recorded outcome measures recorded included m2PD as described by Dellon, pressure threshold testing, sharp/dull discrimination (protective sensation), temperature discrimination, stereognosis, sweating and nerve conduction.15 23
Documentation of patient recorded outcome measures was much less common. Three of the more recent studies recorded the Disability of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand score, one recorded return to work as well as a score of leisure, self-care and productivity and eight further studies recorded the patients’ opinion of their treatment. All eight had a different method for recording patient opinion. In six, this was in the form of a rating of outcome for example, ‘excellent, good, fair, poor’ or ‘grade 1–4’ or ‘very happy, reasonable, unhappy’ and in two, the patient was asked to subjectively express their return of sensation.
Predictive factors
Using s2PD as the prime outcome measure, the degree of nerve recovery following repair was influenced by other factors in several studies. These included uncontrollable variables such as the age of patient, the severity, mechanism or level of the original injury and controllable variables such as the experience level of the operating surgeon (table 3). The effects of these predictive factors were inconsistent across studies, with the notable exception of patient age and surgical experience level. Certain factors historically thought to influence outcome such as the smoking status of the patient, the presence of a concomitant digital artery injury and the time interval between injury and repair of the nerve were not consistently shown to have an impact.
Table 3.
Predictive factors for sensory recovery following nerve repair
| Author and year | Positive predictive factors for sensory recovery | Factors with no impact on sensory recovery |
| Shaffer and Cleveland 195032 | Level of injury | Timing of repair |
| Poppen et al 197944 | Age<20 | Timing of repair, injury severity |
| Young et al 198147 | Age<20<40 | |
| Mailänder et al 198843 | Age<10…<60, injury severity Experience level of surgeon |
Injury mechanism |
| Altissimi et al 199139 | Age<10<40 | Digital artery injury, injury mechanism |
| Chaise et al 199325 | Age | |
| Kallio 199341 | Age<15<40 Timing of repair<3 months<12 months |
Level of injury, injury mechanism |
| Al-Ghazal et al 199438 | Age<12, smoking status (favouring non-smokers) Injury mechanism |
Injury severity |
| Elias et al 199426 | Age<40, injury mechanism, timing of repair Experience level of surgeon |
Injury severity, digital artery injury |
| Vertruyen et al 199445 | Age<30, injury severity | |
| Efstathopoulos et al 199531 | Age<10 <40 | |
| Tadjalli et al 199527 | Injury severity (score, combining injury mechanism, severity and other factors) | |
| Wang et al 199646 | Age<40, injury mechanism | |
| Cheng et al 200140 | Age, early sensory re-education | |
| Hohendorff et al 20093 | Smoking status, injury mechanism, Digital artery repair | |
| Lohmeyer et al 20094 | Age<20 |
Injury severity, smoking status Systemic disease for example, diabetes |
| Fakin et al 20162 | Experience level of surgeon |
Smoking status, age (study used adults only) Injury mechanism, digital artery injury Postoperative immobilisation |
Factors in italics variously described as ‘predictive’ and ‘not predictive’ across different papers.
Adverse outcomes
Eight studies documented the neuroma incidence after digital nerve repair (table 4) and one further study mentioned neuroma without giving the incidence. Neuroma was reported in 22 out of 475 patients across these eight studies, giving an incidence of 4.6%. The range was from 0% to 20%. In the two studies that each had a cohort of unrepaired nerves, the neuroma incidence in their combined cohort was in 2 in 39 patients (5%). Five studies documented cold intolerance in repaired nerves, with incidences of 2%, 8%, 39%, 44% and 53%.3 4 26–28 It is possible that this problem was under-reported across the other 25 studies, as cold intolerance is known to be very common even 2 years after hand injuries.29
Table 4.
Neuroma incidence following nerve repair
| Author and year | Number of repaired digital nerves in study | Neuroma incidence |
| Shaffer and Cleveland 195032 | 71 | 3 (4%) |
| Buncke 197250 | 20 | 4 (20%) |
| Khuc et al 198233 | 110 | 4 (4%) |
| Sullivan 198552 | 42 | 3 (7%) |
| Pereira et al 199130 | 30 | 5 (17%) |
| Chow and Ng 199349 | 72 | 0% |
| Tadjalli et al 199527 | 37 | 1 (3%) |
| Fakin et al 20162 | 93 | 2 (2%) |
| 8/30 studies reported a neuroma incidence | Total number of cases: 475 | Pooled incidence (22/475): 4.6% |
Hyperaesthesia or unpleasant sensory disturbance had a high incidence in two studies of repaired nerves, with 67% and 40% patients affected for up to 2 years.30 31 Three other nerve repair papers give an incidence of unpleasant sensory disturbance of 8%, 12% and 1%.3 32 Chronic regional pain syndrome was also mentioned following nerve repair.33
Infection was only mentioned in two papers, one with an incidence of 8% and the other 3.6%.28 34 This is likely due to the retrospective nature of most studies, where the patients were recalled for testing often long after their initial discharge from hospital care and the paper focused on mid- to long-term test results rather than self-limiting or treated complications. No study reported any cases of iatrogenic injury or other hospital error and none explored whether patients had symptoms relating to their surgical scar as opposed to the scar from their original injury.
Assessment of risk of bias
All of the included studies were case series; they attract a Centre for Evidence Based Medicine level IV classification, and therefore an inherently high risk of bias.35 Based on the NIH Quality Assessment Tool for Case Series, nine studies were deemed to have a ‘Good’ quality rating, 15 ‘Fair’ and six ‘Poor’ (online supplementary appendix 2).19 The most common reasons for a ‘Fair’ or ‘Poor’ rating were the non-consecutive nature of cases, high attrition rates, lack of clearly defined objectives other than a simple reporting of a series and opaque results lacking in detail. According to the GRADE criteria, no recommendations for either repair or no repair can be made based on the currently available evidence for any of our primary or secondary outcomes.20
Discussion
Summary of evidence
This systematic review assessed the quality of the evidence supporting surgical repair of digital nerve injuries in adults and aimed to determine differences in outcomes between surgical repair and no repair. Thirty published series of results were identified from different centres around the world since 1928, predominantly retrospective case series. Criticism could be made against including historical studies from the 1920s and 1950s, where surgical techniques, in particular the use of magnification has since evolved; however, the stated use of magnification is not ubiquitous even among the much later studies, for example from 2017.36
To selectively exclude studies which do not expressly state magnification was used (10 studies) would make assumptions that magnification has a significant impact on outcome, introducing selection bias. This would be counter to established systematic review methodology and would reduce the validity of this review. Furthermore, it was not actually possible to extract the most important data (Highet grade 4 s2PD) from these papers for comparison and therefore their inclusion does not affect the conclusions of the review with regard to outcomes. The same argument can be used for the inclusion of studies where the timing of repair, though mostly acute, was somewhat variable, in particular since timing of repair was not found to affect outcome in this review. Other studies, however, that did not meet the criteria for inclusion in this review have suggested that early repair is beneficial.37
s2PD was the primary outcome measure selected. S2PD results were often grouped according to the Modified Highet Classification Grade 0 (no sensory recovery) to Grade 4 (excellent sensory recovery). There was a wide range of s2PD results after surgical repair: one study of 20 patients reported 60% achieving s2PD similar to expected preinjury levels (Grade 4) and one study of 110 patients reported only 8% achieving this level. Grouping together the 19 studies that showed this information, the overall Grade 4 s2PD result after nerve repair was only 24%. Ten of these studies included children (age <18) and a further six may have done. Younger age is associated with better outcomes and therefore it is possible that the ‘excellent’ results seen in some studies was influenced by patient age.4 26 27 32 38–47 It is therefore clear that despite surgical repair, very few patients actually achieve ‘normal’ preinjury levels of sensation and in fact the data may be skewed in favour of a better outcome due to younger patients being included in studies.
The 30 papers were scrutinised for the incidence of nerve-related complications such as neuroma and cold intolerance. Formation of a clinically problematic neuroma is often quoted by surgeons to justify digital nerve repair yet the incidence of neuroma and cold intolerance was inconsistently reported. The neuroma incidence varied from 0% to 20% with a pooled incidence of 4.6% in the repaired group and 5% in the unrepaired group. For cold intolerance, this varied from 2% to 53%. Therefore, there is no evidence to suggest that these complications are reduced by surgical repair of digital nerve injuries.
The age of the patient was a significant predictive factor for s2PD outcome following nerve repair in 14 studies.4 26 27 32 38–47 Although this systematic review evaluated adult digital nerve injury, it was apparent from the literature that children got much better results than adults.48 Indeed, younger adults got better outcomes than older adults, with the results gradually worsening with an older cohort. The experience level of the surgeon was also shown to improve outcomes.3 27 43 Other possible predictive factors were significant in some studies and not significant in others. These factors included injury mechanism, injury extent, the timing of surgical repair, smoking status and digital artery injury.
Four studies compared different techniques of repair or rehabilitation. One compared the results between loupe and microscope magnification,6 one between patients treated with and without early tactile stimulation,40 one between epineural and fascicular nerve repairs,47 and one between patients with or without repair of the digital artery.4 From these studies, only early tactile stimulation was shown to have a beneficial effect on outcome.40
The study that compared nerve repair with no repair was a prospective case series with 72 repaired nerves and 36 unrepaired nerves.49 From the original sample of 132 patients, 47 were lost to follow-up. The study showed a significant difference in the s2PD achieved between repair and non-repair patients. Highet grade 4 sensory recovery was achieved in 25% of the repaired group and in none of the unrepaired group. However, none of the unrepaired group of patients chose to undergo further surgery to improve their outcome and 94% had achieved restoration of protective sensibility. This study also showed that in the unrepaired group, sensory recovery plateaued at 6 months post surgery whereas in the repaired group it continued to improve up to 24 months post repair.
Limitations
This systematic review aimed to assess the quality of the evidence for surgical repair of unilateral adult digital nerve injury compared with no surgical repair and to explore differences in outcomes. We were limited by the methodological quality of the included studies, which were exclusively case series (level 4 evidence). This inevitably introduces high risk of bias and the data reported should be interpreted with this in mind. There was heterogeneous and incomplete outcome data reporting across the included studies, which also limits the strength of conclusions. Finally, despite rigorous systematic review methodology and comprehensive literature retrieval measures, it is possible that studies may have been missed from this review.
Conclusion
There is weak evidence to support digital nerve repair in adults with isolated digital nerve injury, in terms of return of normal sensibility and prevention of neuroma. Return of normal sensibility is uncommon and almost all unrepaired nerves regained protective sensation by 6 months and all patients declined further surgery. There was no difference in adverse outcomes. Some of the published literature is old and heterogeneous, with variability in surgical technique and outcome reporting and is limited to observational case series. There is also insufficient evidence not to support the current practice of carrying out surgical repair; however, further research is required to improve the justification for the treatment of this injury.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Grateful thanks to Katy Oak and Catriona Organ at Cornwall Health Library, who performed the literature search in conjunction with the authors. Also to Deborah Mogg, for obtaining the full text manuscripts.
Footnotes
Twitter: @JCRWormald
Contributors: RLED carried out the literature search in association with Cornwall Health Library. RLED and JCRW screened the search results, AJ searched for additional studies, RLED performed data extraction and manuscript write-up, JCRW compiled the references and JCRW and AJ made improvements and corrected the manuscript.
Funding: JCRW is an NIHR Academic Clinical Fellow. This research is supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) infrastructure at NDORMS. The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health and Social Care. No funding was directly received for the development of this manuscript.
Competing interests: None declared.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: No additional data are available.
Patient consent for publication: Not required.
References
- 1. Cheng AS. Use of early tactile stimulation in rehabilitation of digital nerve injuries. Am J Occup Ther 2000;54:159–65. 10.5014/ajot.54.2.159 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Fakin RM, Calcagni M, Klein HJ, et al. . Long-term clinical outcome after epineural coaptation of digital nerves. J Hand Surg Eur Vol 2016;41:148–54. 10.1177/1753193415578986 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Hohendorff B, Staub L, Fritsche E, et al. . [Sensory nerve function after unilateral digital vascular-nerve injury: nerve repair with and without arterial repair]. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir 2009;41:306–11. 10.1055/s-0029-1238296 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Lohmeyer JA, Sommer B, Siemers F, et al. . Nerve injuries of the upper extremity-expected outcome and clinical examination. Plast Surg Nurs 2009;29:88–93. 10.1097/01.PSN.0000356867.18220.73 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Thomas PR, Saunders RJ, Means KR. Comparison of digital nerve sensory recovery after repair using loupe or operating microscope magnification. J Hand Surg Eur Vol 2015;40:608–13. 10.1177/1753193414556006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Dvali L, Mackinnon S. Nerve repair, grafting, and nerve transfers. Clin Plast Surg 2003;30:203–21. 10.1016/S0094-1298(02)00096-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Lundborg G. A 25-year perspective of peripheral nerve surgery: evolving neuroscientific concepts and clinical significance. J Hand Surg Am 2000;25:391–414. 10.1053/jhsu.2000.4165 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Paprottka FJ, Wolf P, Harder Y, et al. . Sensory recovery outcome after digital nerve repair in relation to different reconstructive techniques: meta-analysis and systematic review. Plast Surg Int 2013;2013:1–17. 10.1155/2013/704589 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Rinker B, Zoldos J, Weber RV, et al. . Use of Processed Nerve Allografts to Repair Nerve Injuries Greater Than 25 mm in the Hand. Ann Plast Surg 2017;78:S292–S295. 10.1097/SAP.0000000000001037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Suzuki Y, Ishikawa N, Tanihara M, et al. . Nontubulation Repair of Peripheral Nerve Gap Using Heparin/Alginate Gel Combined with b-FGF. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2016;4:e600 10.1097/GOX.0000000000000581 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Squitieri L, Bozic KJ, Pusic AL. The Role of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures in Value-Based Payment Reform. Value Health 2017;20:834–6. 10.1016/j.jval.2017.02.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Aberg M, Ljungberg C, Edin E, et al. . Considerations in evaluating new treatment alternatives following peripheral nerve injuries: a prospective clinical study of methods used to investigate sensory, motor and functional recovery. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2007;60:103–13. 10.1016/j.bjps.2006.04.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Dellon AL. The moving two-point discrimination test: clinical evaluation of the quickly adapting fiber/receptor system. J Hand Surg Am 1978;3:474–81. 10.1016/S0363-5023(78)80143-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Semmes J, Weinstein S, Ghent L, et al. . Reliability of the tests of sensation. Somatosensory Changes after Penetrating Brain Wounds in Man. Oxford, England: Harvard Univer. Press, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- 15. Thomson A. Experiments on the Sensibility of the Skin: Account of Some New Experiments on the Sensibility of the Skin, by Dr. Weber, Professor of Anatomy at Leipzig. The Boston Medical and Surgical Journal 1833;9:133–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: John Wiley, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 17. Montori VM, Wilczynski NL, Morgan D, et al. . Optimal search strategies for retrieving systematic reviews from Medline: analytical survey. BMJ 2005;330:68 10.1136/bmj.38336.804167.47 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. National Institute of Health (NIH) National Heart, Lung and BIood Institute and Research Triangle Institute International. NIH tool for appraisal of case series. 2018. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools (accessed 13 Nov 2018).
- 19. Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, et al. . GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008;336:924–6. 10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Nemethi CE. Repair of nerve injuries in the hand. West J Med 1956;84:35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Bunnell S. Repair of nerves and tendons of the hand. J Bone Joint Surg 1928;10:1–26. [Google Scholar]
- 22. Dellon AL, Curtis RM, Edgerton MT. Evaluating recovery of sensation in the hand following nerve injury. Johns Hopkins Med J 1972;130:235–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Dellon AL, Mackinnon SE. Surgery of the peripheral nerve. New York: Thieme Med Publishers, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- 24. Zachary LS, Dellon ES, Nicholas EM, et al. . The structural basis of Felice Fontana’s spiral bands and their relationship to nerve injury. J Reconstr Microsurg 1993;9:131–8. 10.1055/s-2007-1006661 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Chaise F, Friol JP, Gaisne E. [Results of emergency repair of wounds of palmar collateral nerves of the fingers]. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 1993;79:393–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Elias BE, Tropet Y, Brientini JM, et al. . Results of primary repair of digital nerve injuries. Ann Chir Main 1994;13:107–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Tadjalli HE, McIntyre FH, Dolynchuk KN, et al. . Digital nerve repair: relationship between severity of injury and sensibility recovery. Ann Plast Surg 1995;35:36–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. CAMPBELL DA, KAY SP. What is cold intolerance? J Hand Surg Am 1998;23:3–5. 10.1016/S0266-7681(98)80207-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Goldie BS, Coates CJ, Birch R. The long term result of digital nerve repair in no-man’s land. J Hand Surg Eur 1992;17B:75–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Pereira JH, Bowden RE, Gattuso JM, et al. . Comparison of results of repair of digital nerves by denatured muscle grafts and end-to-end sutures. J Hand Surg Br 1991;16:519–23. 10.1016/0266-7681(91)90107-Y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Efstathopoulos D, Gerostathopoulos N, Misitzis D, et al. . Clinical assessment of primary digital nerve repair. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 1995;264:45–7. 10.3109/17453679509157166 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Shaffer JM, Cleveland F. Delayed suture of sensory nerves of the hand. Ann Surg 1950;131:556–63. 10.1097/00000658-195004000-00008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Khuc T, Leclercq D, Carlier A. Microsurgical repair of 110 digital nerves. Acta Chir Belg 1982;82:271–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Thorsén F, Rosberg HE, Steen Carlsson K, et al. . Digital nerve injuries: epidemiology, results, costs, and impact on daily life. J Plast Surg Hand Surg 2012;46:184–90. 10.3109/2000656X.2012.676554 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Phillips B, Ball C, Sackett D, et al. . Levels of Evidence and Grades of Recommendation. Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine (CEBM). Oxford University. Oxford Press 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 36. Huber JL, Maier C, Mainka T, et al. . Recovery of mechanical detection thresholds after direct digital nerve repair versus conduit implantation. J Hand Surg Eur Vol 2017;42:720–30. 10.1177/1753193417699777 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Glickman LT, Mackinnon SE. Sensory recovery following digital replantation. Microsurgery 1990;11:236–42. 10.1002/micr.1920110311 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. al-Ghazal SK, McKiernan M, Khan K, et al. . Results of clinical assessment after primary digital nerve repair. J Hand Surg Br 1994;19:255–7. 10.1016/0266-7681(94)90180-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Altissimi M, Mancini GB, Azzara A. Results of primary repair of digital nerves. J Hand Surg Am 1991;16:546–7. 10.1016/0266-7681(91)90111-Z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Cheng AS, Hung L, Wong JM, et al. . A prospective study of early tactile stimulation after digital nerve repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2001;384:169–75. 10.1097/00003086-200103000-00020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Kallio PK. The results of secondary repair of 254 digital nerves. J Hand Surg Br 1993;18:327–30. 10.1016/0266-7681(93)90054-J [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Lohmeyer JA, Hülsemann W, Mann M, et al. . [Return of sensitivity after digital nerve reconstruction in children: how does age affect outcome?]. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir 2013;45:265–70. 10.1055/s-0033-1355425 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Mailänder P, Berger A, Schaller E, et al. . Results of primary nerve repair in the upper extremity. Microsurgery 1989;10:147–50. 10.1002/micr.1920100218 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Poppen NK, McCarroll HR, Doyle JR, et al. . Recovery of sensibility after suture of digital nerves. J Hand Surg Am 1979;4:212–26. 10.1016/S0363-5023(79)80156-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Vertruyen MF, Burgeon MA, Dachy BS, et al. . Sensory recovery after microsurgical repair of digital nerves. Acta Chir Belg 1994;94:325–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Wang WZ, Crain GM, Baylis W, et al. . Outcome of digital nerve injuries in adults. J Hand Surg Am 1996;21:138–43. 10.1016/S0363-5023(96)80167-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Young L, Wray RC, Weeks PM. A randomized prospective comparison of fascicular and epineural digital nerve repairs. Plast Reconstr Surg 1981;68:89–92. 10.1097/00006534-198107000-00018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Rosberg H-E, Hazer DB, Dahlin LB. Outcome of repaired digital nerve injuries in children – influence of age in a retrospective long-term follow-up. J Hand Surg Am 2015;40:e56 10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.06.094 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Chow SP, Ng C. Can a divided digital nerve on one side of the finger be left unrepaired? J Hand Surg Br 1993;18:629–30. 10.1016/0266-7681(93)90020-G [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Buncke Jr HJ. Digital nerve repairs. Surg Clin North Am 1972;52:1267–85. 10.1016/0266-7681(93)90020-G [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Holst HI. Primary peripheral nerve repair in the hand and upper extremity. J Trauma 1975;15:909–11. 10.1016/0266-7681(93)90020-G [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Sullivan DJ. Results of digital neurorrhaphy in adults. J Hand Surg: British Eur 1985;10:4 10.1016/0266-7681(93)90020-G [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Segalman KA, Cook PA, Wang BH, et al. . Digital neurorrhaphy after the age of 60 years. J Reconstr Microsurg 2001;17:85–8 10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.06.094 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Portincasa A, Gozzo G, Parisi D, et al. . Microsurgical treatment of injury to peripheral nerves in upper and lower limbs: a critical review of the last 8 years. Microsurgery 2007;27:455–62 10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.06.094 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
bmjopen-2018-025443supp001.pdf (33.3KB, pdf)
bmjopen-2018-025443supp002.pdf (72.9KB, pdf)