Abstract
Interaction with the world around us requires extracting meaningful signals to guide behavior. Each of the six mammalian senses (olfaction, vision, somatosensation, hearing, balance, and taste) has a unique primary map that extracts sense-specific information. Sensory systems in the periphery and their target neurons in the central nervous system develop independently and must develop specific connections for proper sensory processing. In addition, the regulation of sensory map formation is independent of and prior to central target neuronal development in several maps. This review provides an overview of the current level of understanding of primary map formation of the six mammalian senses. Cell cycle exit, combined with incompletely understood molecules and their regulation, provides chemoaffinity-mediated primary maps that are further refined by activity. The interplay between cell cycle exit, molecular guidance, and activity-mediated refinement is the basis of dominance stripes after redundant organ transplantations in the visual and balance system. A more advanced level of understanding of primary map formation could benefit ongoing restoration attempts of impaired senses by guiding proper functional connection formations of restored sensory organs with their central nervous system targets.
Keywords: primary sensory maps, retinotopic map, olfactory map, cochleotopic map, vestibular map, taste map
Introduction
Sensory organs are the windows of the brain to the environment, permitting behavioral interactions with conspecifics, prey, and predators. Finding an appropriate mate, being able to avoid being eaten, and finding food are essential features for survival and propagation. Sensory organs filter out the appropriate information for these tasks and relay it to the brain to elicit adequate motor responses 1– 3. Sensory map features depend on the specific sensory modality and the relevant information to be extracted. For example, somatotopic maps project a topographic array of sensors to reflect the sensor distribution, density, and activity of the skin to the brain 4– 6. Similarly, the retinotopic map projects distinct areas of the retina and the corresponding visual field as a two-dimensional (2D) map to the target brain area 7, 8, whereas the cochlea map projects a unidimensional map of distinct frequencies to specific areas of the cochlear nuclei 9 and auditory cortex 10, 11. Beyond primary sensory maps, central map formation underlies binocular vision and depth perception 12, 13. Likewise, the auditory space map is generated through binaural interactions 14– 16 whereas the mechanosensory lateral line 17 and the electrosensory space map 18 are generated through integration of distributed sensors across the body. In contrast to these emerging centrally synthesized maps and continuous primary maps, discrete olfactory maps project unique properties of the odorant stimuli perceived by distributed olfactory neurosensory cells convergently onto specific glomeruli 10, 19, 20. A variation of the latter theme is the incomplete segregation of movement detection in the vestibular system, where angular movements always cause concomitant linear acceleration. This causes partial convergence of afferents from organs dedicated to either linear or angular acceleration perception 21, 22. Even more difficult to understand are maps where a given stimulus and its intensity are differentially coded as the tastants for the yet-to-be-fully-defined taste map 23– 26.
During the last century, specific properties of a given sensory map and basic rules how to form them, such as the chemoaffinity theory 27 and activity-mediated synaptic plasticity theory 28, 29, have been worked out for some primary maps. Understanding the molecular cues that guide primary map development, the plasticity of primary map development mediated by activity to sharpen the map in neonates and adults 30– 33, and the translation of primary sensory afferent map formation into cortical and midbrain maps for multisensory integration 2, 6, 34, 35 will be the defining achievements of the 21st century. Toward this end, we provide here an overview of various primary sensory maps of mammals, characterized by continuous and discrete map properties 33. All primary maps require that a peripheral sense be wired to independently developing central target neurons by molecular cues in the target and matching cues expressed in the neurons as they navigate toward their target. Our aim is to turn primary sensory map formation into a neuronal pathfinding problem that combines with cell cycle exit to generate an embryonic primary map for each sense. Uncovering regulatory aspects of map formation across senses will facilitate sensory restoration badly needed for sensory repair of seniors in our rapidly aging societies.
Primary sensory maps compared
The six primary sensory maps of mammals have unique features and seemingly use distinct molecular cues, cell cycle exit, and activity combinations during development, regeneration, and plasticity. We will start with the best molecularly understood map formations followed by the less well understood map formations in the hindbrain, ending with the least understood map for taste that has recently seen dramatic revisions from past insights 24, 36.
Molecular odorant map
Adult map organization
Since the cloning of genes encoding a family of odorant receptor (OR) nearly 30 years ago 37, the understanding of olfactory map formation has leapfrogged to be perhaps the best molecularly understood sensory map. The basic principle is that a given olfactory sensory neuron (OSN), coding for a given OR, projects its axon to a molecularly specified olfactory glomerulus in the olfactory bulb (OB), where it converges with axons of other OSNs coding for the same OR 20, 38– 40. Thus, OSNs coding for the same OR converge to the same glomerulus ( Figure 1A). In the mouse, this results in a discrete expression of one of about 1100 ORs in a given OSN whose axon converges onto one or few of the roughly 3600 glomeruli. OR expression is not completely random but splits the olfactory epithelium into major divisions along the dorso-ventral axis, each with medio-lateral bands of randomly distributed OSNs that project to dorso-ventrally distinct sets of olfactory glomeruli 38, 39, 41. Specific odorant information is thus perceived by OSNs within certain zones that are, however, nearly randomly distributed within these zones. This is particularly obvious in mammals with a reduced complement of olfactory receptor genes that form glomeruli only in the ventral part of the OB 42. Odor information is encoded in the odorant-specific glomeruli and not in the topology of OSNs in the olfactory epithelium. This organizational principle allows OSNs to be continuously replaced 43 without any change in the important central information storage 1, 34. The brain learns and recognizes patterns of glomerular activity elicited by different odors 44.
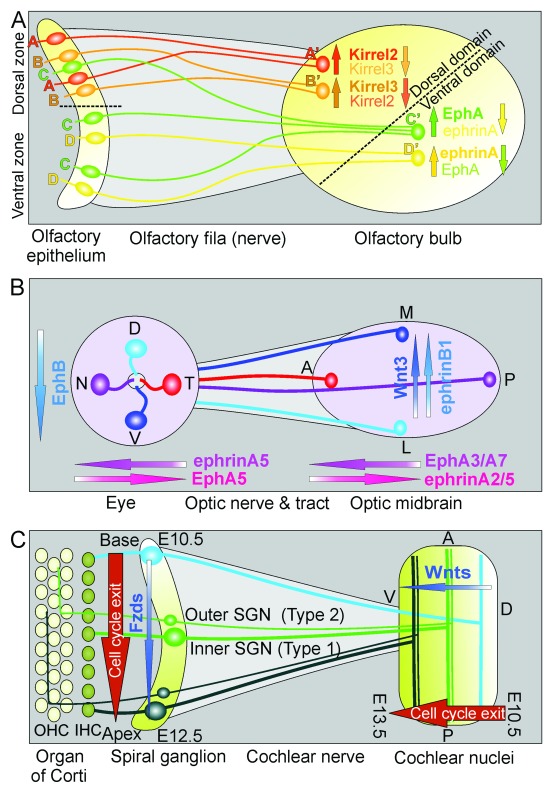
Figure 1. Development of three distinct mammalian sensory maps.
Molecular cues ( A, B) and spatio-temporal cues ( C) are shown for the nearly non-spatial olfactory map ( A), the two-dimensional (2D) retino-tectal map ( B), and the unidimensional auditory map ( C). ( A) The olfactory map defines different olfactory receptor molecules in the dorsal and ventral zone of the olfactory epithelium. Receptor cells displaying distinct olfactory receptors ( A– D) project their axons to the dorsal and ventral domain of the olfactory bulb where they converge and initiate olfactory glomeruli formation. Note that olfactory fibers sort before they reach the olfactory bulb and that some ventral zone receptors are expressed in the dorsal zone but afferents sort to the ventral domain. Different opposing gradients of receptors facilitate further the sorting of olfactory afferents. Within this limited topology, the distribution of specific olfactory receptor–expressing receptor cells is fairly random. ( B) The retino-tectal system maps a 2D surface (the retina ganglion cells) onto another 2D surface (the midbrain roof or tectum opticum) via highly ordered optic nerve/tract fiber pathways. Within the midbrain, the presorted fibers are further guided by molecular gradients matching retinal gradients of ligand/receptor distributions. ( C) The auditory map is unidimensional, projecting a species-specific frequency range from the mammalian hearing organ, the organ of Corti via orderly distributed spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs), and their fibers in the auditory (cochlear) nerve onto the ventral cochlear nucleus complex. Both SGNs and cochlear nucleus neurons show a matching temporal progression of cell cycle exit followed by matching differentiation that could be assisted by spatio-temporal expression changes of receptors and ligands (shown here are the putative Wnt/Fzd combinations) that further support the fiber sorting. Note that this map projects a single frequency of an inner hair cell of the organ of Corti via a set of SGNs onto longitudinal columns of cochlear nucleus neurons in a cell-to-band projection and thus is not a point-to-point map as the olfactory and visual map. Moreover, afferents innervating multiple outer hair cells (OHCs) generate a band-to-band projection centrally. A, anterior; D, dorsal; L, lateral; M, medial; N, nasal; P, posterior; T, temporal; V, ventral. Modified after 12, 41, 53– 58.
Development
The main and accessory (vomeronasal) olfactory epithelium develops from the olfactory placode that also gives rise to a set of gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH)-positive neurons migrating into the hypothalamus 45– 48. This allows the olfactory system to interconnect with the retina in some species 49. A sequence of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) genes, in combination with other transcription factors, guides the transformation of the olfactory placode cells into OSNs 50, 51. Dorso-ventral zones of ORs are expressed in selective OSNs and each OSN projects specific odorant molecule information to a given glomerulus 52. Matching gradients of OR expression define the pathfinding properties of OSNs to select a given band of glomeruli and a specific glomerulus within that band ( Figure 1 and Figure 2). Misexpression of a given OR in another set of OSNs results in misdirection to a different glomerulus. This supports the idea that both the selection of a given OR and the level of gene expression bestow on an OSN an identity that allows the OSN growth cone to navigate to a specific glomerulus. The G protein–coupled ORs define expression levels of adenylate cyclases such as Ac3 33. Knockouts of Ac3 lead to disorganized OR projections. This appears to be related to Ac3-mediated activation of downstream guidance cues via cAMP/CREB/PKA, such as neuropilin 1 ( Nrp1). Gradients of Nrp1 code for anterior-posterior patterning 53 in combination with matching expression of semaphorins 59– 61. However, detailed tests question the proposed model of Nrp1 guidance by showing more complicated outcomes inconsistent with the simple Nrp1 gradient model 54. Since G-coupled ORs are found on the growth cone of OSNs, those ORs could locally interact with the environment to guide confined responses via the cAMP/PKA intracellular signal cascades. Though clearly important, a gradation of G protein/cAMP alone is not the only cue, and Robo/Slit is used for larger-scale dorso-ventral patterning 40, 62. In addition, two different classes of OSNs have been identified and their axons sort out as they extend toward the OB, leading to a complete segregation of axons of dorsal but not ventral OSNs 40. This fiber sorting ( Figure 1A and Figure 2A) happens prior to and even in the absence of OBs, establishing a topographic order of OSN axons as they approach the OB 53. Further refinement of the olfactory mapping is achieved through differential expression and activity-regulated levels of ephrinA ligands and Eph-A5 receptors as well as the molecularly related Kirrel2/3 ( Figure 1A). In a given glomerulus, there is an opposing gradient of either the Kirrel2/3 pair dorsal or ephrinA/EphA5 ventral. This expression defines a dorsal and a ventral domain of glomeruli ( Figure 1A) matching to the dorso-ventral zones of OR expressing OSNs in the olfactory epithelium. Thus, although the dorso-ventral patterning of bands of OSNs to project to bands of olfactory glomeruli seems to be settled, the details of antero-posterior patterning remain less clear and seemingly are less precise 54.
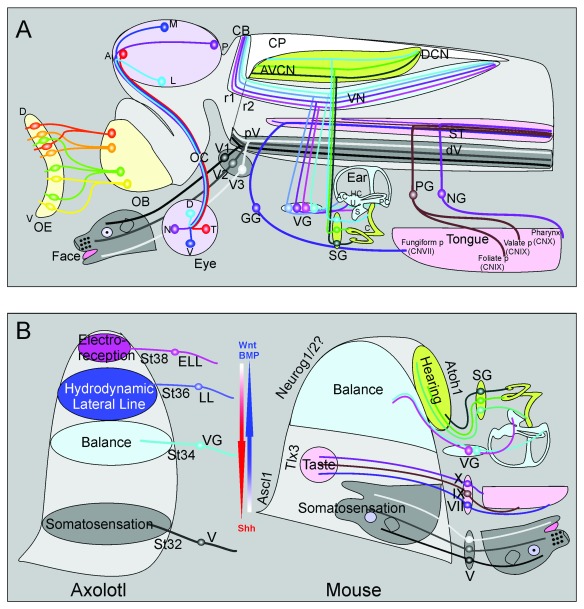
Figure 2. Distribution of sensory maps and the development of hindbrain sensory maps.
( A) Schematic presentation of the main features of the six cranial senses projected onto an embryonic mouse brain. (Pale yellow, left) Distributed olfactory sensory neurons of the olfactory epithelia coalesce their axons before reaching a specific olfactory glomerulus in the olfactory bulb (OB). (Pale lavender) Axons of retina ganglion neurons leave the eye orderly to project via the optic nerve to the optic chiasm (OC). Crossed contralateral axons form the orderly optic tract that distributes axons within the midbrain using matching gradients of several factors. (Gray) The trigeminal ganglion has three distinct branches and matching sensory neuron populations that reach different areas of the face. The central axons form in a temporal progression resulting in an inverted presentation of the face. (Pale pink) Taste buds of the tongue and pharynx are innervated by three cranial nerves that form a somewhat orotopic central projection to the solitary tract. (Light blue) The five vestibular sensory organs are innervated by somewhat orderly distributed sensory neurons that project via the vestibular nerve. Within the brain, vestibular afferents from different ear organs are partially segregated and partially overlapping in the various vestibular nuclei as well as the posterior lobes of the cerebellum. (Pale green) The organ of Corti of the cochlea is innervated by a temporally generated longitudinal array of spiral ganglion neurons that project in an orderly organization to dorso-ventral distinct regions of the cochlear nucleus complex, projecting a one-dimensional frequency array along the cochlea onto a matching frequency array of afferents in the cochlear nuclei. ( B) (Left) In the axolotl, there is a timing factor of afferent ingrowth such that the most ventral trigeminal projection reaches the hindbrain first (V at stage 32) whereas the most dorsal projection from the electroreceptive (lateral line) ampullary organs reaches the most dorsal part of the hindbrain last (ELL, stage 38). The inner ear vestibular ganglia (VG, stage 34) and mechanosensory lateral line ganglia (LL, stage 36) are reaching the alar plate between those extremes. (Right) In the mouse, the dorso-ventral patterning of the hindbrain is driven by countergradients of Wnt/BMP and Shh to regulate expression of transcription factors defining various nuclei. How these gradients define the positon of central nuclei and afferents is not completely clear. A temporal gradient of afferent development and projection development has thus far been demonstrated only for the spiral ganglion, taste and trigeminal system where the first neurons to form are the first to project to the most ventral part of their respective tract. Note that the auditory nuclei show an apparent inversion such that the most ventral projection from the basal spiral ganglion ends up in the more dorso-medial part of the cochlear nuclei because of the morphogenetic changes in cochlear nucleus neuron position. A, anterior; AC, anterior crista; Ascl1/Mash1, achaete-scute family basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor 1; Atoh7, atonal basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor 7; AVCN, antero-ventral cochlear nucleus; BMP, bone morphogenic protein; C, cochlea; CB, cerebellum; CN V, VII, IX, X, cranial nerve V, VII, IX, X; CP, choroid plexus of IV ventricle; D, dorsal; DCN, dorsal cochlear nucleus; dV, descending trigeminal tract; ELL, electroreceptive (ampullary organ) lateral line; GG, geniculate ganglion; HC, horizontal crista; L, lateral; LL, (mechanosensory) lateral line; M, medial; N, nasal; Neurog1/2, Neurogenin 1/2; NG, nodose ganglion; OB, olfactory bulb; OC, optic chiasm; OE, olfactory epithelium; P, posterior; PC, posterior crista; PG, petrosal ganglion; pV, principal trigeminal nucleus; r1, rhombomere 1; r2, rhombomere 2; S, saccule; SG, spiral ganglion; Shh, sonic hedgehog; ST, solitary tract; T, temporal; TIx3, T-cell leukemia homeobox 3; U, utricle; V, ventral; V1, ophthalmic branch of trigeminal nerve; V2, maxillary branch; V3, mandibular branch; VG, vestibular ganglion; VN, vestibular nucleus complex. Modified after 5, 12, 17, 33, 36, 54, 56, 63– 66.
Olfactory epithelium manipulation
Past work has established that ingrowing OSN axons of transplanted olfactory epithelia can generate glomeruli wherever they project to in the forebrain or midbrain 45 but are unable to form glomeruli in the hindbrain 67. These placode transplantation experiments suggest that perhaps OSNs play a role in sculpting their own target area in the forebrain and midbrain. OB formation depends on ingrowing OSN axons, and no OB forms in mammals without an olfactory epithelium 42, 68. This indicates a self-organizational principle of OSNs beyond fiber fasciculation 53 that requires additional molecular exploration to help restore smelling to anosmic people.
Retinotopic map
Adult organization
Retinal ganglion neurons (RGNs) in a given position are driven by local spontaneous or induced activities in their specific receptive field of visual stimuli. RGNs send this information through their terminals onto a matching position of the roof of the midbrain, known as the non-mammalian optic tectum or mammalian superior colliculus ( Figure 1B and Figure 2A). Sperry’s 27, 69 experiments on frogs showed that a severed optic nerve re-establishes a functional map. However, rotating the eye before RGNs re-establish midbrain connections results in mismapping of the visual field that cannot be corrected for by activity. Sperry therefore proposed a chemoaffinity map that guides neurites from specific areas of the visual field/retina to matching positions of the midbrain. This basic idea led to a mathematical model of molecular countergradients 70. Sperry’s experiments and Gierer’s model stimulated the discovery of an orthogonal diffusion gradient of ephrin ligands and receptors in the retina and matching expression in the midbrain 13, 33. These gradients ensure that a given ganglion cell projects to a matching area of the midbrain ( Figure 1B). The retinotopic map projects a continuous topographic set of visual field information encoded by RGNs from one surface (the retina) point-to-point onto another surface (the midbrain) for further processing of the 2D topological information. This helps, for example, direct attention to specific objects, in particular moving objects, as is obvious after visual cortex lesions, known as “blindsight” 71, 72.
Development
The retina develops as an evagination of the diencephalon that interacts with the lens placode for normal eye development 46, 73. Blocking retina evagination results in cellular transformation of the diencephalic wall with distinct retinal receptors and various retinal neuron layers 74. In contrast to the olfactory epithelium and its continuous renewal of OSNs, all retina neurons and sensory cells develop once in a concentric progression 75 through clonal expansion out of proliferative precursors using a series of transcription factors that define, in combination, specific retinal cell types 76. RGNs require the bHLH factor Atoh7 and other factors for their differentiation 77– 79 to form the roughly 30 recognizable RGN types 80. How Atoh7 and downstream transcription factors regulate the molecular guidance cues that allow a given RGN to exit the retina 80, sort along the optic nerve 81, and grow through the optic chiasm 82 to project, via the orderly optic tract 83, to a discrete region of the contralateral midbrain 80 remains incompletely understood 12. Graded expression of several molecules and receptors redundantly defines how the surface of the retina is mapped via targeted projection of RGNs onto the midbrain 12, 33. Ephrin-A/EphA has naso-temporal and ephrin-B/EphB dorso-ventral concentration-dependent attractive and repellent effects that define a narrow region in which terminal arbors of a given RGN can form. Eliminating multiple ligand/receptor pairs causes broad distribution of RGN axons; however, some very crude topology remains even after the main ligand/receptor pairing has been deleted 13. Multigene knockouts combined with removal of activity result in diffuse and broad innervation 8, 80. Additional molecular gradients are provided by a Wnt3 gradient that defines, redundant to the ephrin-B/EphB gradient, the medio-lateral slope in the midbrain for dorso-ventral RGN axonal sorting 33, 84. The midbrain Wnt3 gradient is translated into differential projections using Ryk gradients on RGN axons to modify, via repellent actions, the attraction mediated by Fzd receptor activity. Additional redundancy is provided by other secreted factors like En-2 85, 86. Activity of axons is not needed to define the overall projection 87, 88, but axonal arbors in the midbrain become less confined without activity. If both molecular map and activity are disrupted in combined mutants, the resulting maps of individual RGNs can cover large areas of the midbrain 89. This demonstrates that neuronal activity combines with molecular specificity to sharpen the retinotopic map 7 and provides the basis for ocular stripe formation in three-eyed frogs 90, 91.
Eye manipulation
Molecular cue interactions with activity-mediated refinement result in “ocular dominance” column formation after additional eye transplantations 91. Differential eye activity is needed for the formation of these “ocular dominance” stripes 29, 90. “Ocular dominance” stripes also form after crushing an optic nerve results in misguided regeneration. Such stripes are maintained only if the contralateral nerve is either eliminated or also regenerates 92, 93. In line with the role of patterned activity in these processes is the absence of RGN axon segregation in the bilaterally projecting retino-midbrain systems found in fossorial vertebrates 94. How activity relates to neurotrophic release and thus long-term sustenance of regenerated RGNs remains debated 33, 80. Beyond three-eyed frogs and optic nerve crush-mediated “ocular dominance” stripe formation, some transplantation studies claim successful regrowth of RGN axons from the spinal cord to the midbrain 95 and RGN axons apparently can innervate the olfactory cortex 96, 97 or can restore visual guidance even after transplantations to unusual positions on a tadpole 98, 99, indicating alternative ways for visual information flow to the brain. How far such effects in amphibians can be translated to mammalian optic nerve regeneration 80 remains to be seen.
Somatosensory map
Adult organization
The cortical somatosensory map is the prototypical surface-to-surface map whereby dermatomes are mapped onto the cortex 100, and local variations 101 reflect various sensor densities and functional differences 102, 103. The somatosensory map thus is a 2D surface-to-surface projection comparable to the retinotopic map. However, in contrast to the simple retina surface projecting onto the tectal surface, closer examination reveals a complicated relationship between primary somatosensory afferent input and the formation of distorted, continuous surface map in the spinal cord and brainstem and the somatosensory map in layer IV of the somatosensory cortex 6, 104. Manipulating the periphery affects the central map, but the details of how phantom sensations are generated or how maps are altered after peripheral manipulations remain somewhat obscure 6, 105, 106.
Development
For simplicity, we concentrate here on the trigeminal somatosensory system and exclude the spinal cord somatosensory map formation. The trigeminal sensory system is composed of ganglion neurons with three distinct embryonic origins: the trigeminal ganglion derived from both trigeminal placode and neural crest 5 and the mesencephalic sensory neurons of the mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus (MesV) derived from the brain 107. Loss of Npr2 results in lack of bifurcation, blocking MesV branches from leaving the brain and thus depriving the brain of proprioceptor input 108. Topology of trigeminal ganglion neurons is defined by diffusible factors ( Wnt, Fgf8, and Bmp4) and localized expression of various transcription factors ( Tbx1, Onecut, and Hmx1) as well as differential expression of neurotrophins Ntf3 and Bdnf 5 that enable innervation of distinct regions of the facial skin. Projections into the hindbrain develop before peripheral processes reach the skin target ( Table 1), indicating that trigeminal central processes are guided independently of their peripheral targets. The trigeminal nucleus target neurons in the terminal nuclei depend on Mash1/Acsl1 that is directed in its expression within the hindbrain dorso-ventral patterning mediated by BMP/Wnt/Shh gradients, as in the spinal cord 109. Gradients of these factors may also play a role in afferent guidance 110– 112 but details remain to be worked out. Trigeminal ganglion afferents entering rhombomere 2 bifurcate to form a short ascending branch, ending at the rhombomere 1/2 boundary ( Figure 2A), and a long descending branch to the upper cervical levels of the spinal cord 5. The dorso-ventral pattern reflects the initial inverted mandibular-maxillary-ophthalmic projection ( Figure 2A,B), whereas the antero-posterior facial fields covered by each trigeminal branch are mapped lateral (posterior) to medial (anterior 5, 103). As fibers extend along the hindbrain, second-order trigeminal neurons differentiate and may provide instruction to form a secondary axis along the lateral-medial plane 5. These features are particularly obvious in mutant mice with a doubling of the whisker-related barrel field 102. How the whisker afferents generate the respective “barrelettes” in the brainstem 113 is not yet understood in molecular detail 5, 102, but it is clear that activity mediated by N-methyl- d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors sharpens the map 5, 103.
Table 1. Timing of mouse sensory neurogenesis and map projection.
| Sense | Sensory neuron
“birthdate” |
Sensory cell
“birthdate” |
Second-order
neuronal “birthdate” |
Afferents reach
central target |
Afferents reach
peripheral target |
References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olfaction | OSN, continuous | OSN, continuous | E11-postnatal | Continuous | NA | 116 |
| Vision | E10.5–E13
central- peripheral |
E11–15 | E15–P0 | E16–P0 | NA | 75 |
| Somato-
sensation |
E8.25–9 | NA, mostly free
nerve endings |
E10.5–15.5 | E9.5–10 | E12.5–15.5 | 5, 98 |
| Balance | E9.5–E13.5 | E10.5 postnatal | E9.5–15.5 | E10.5 | E10.5–E18.5 | 22, 117– 119 |
| Hearing | E10.5–12.5
base-apex |
E12.5–14.5
apex-base |
E10.5–14.5 | E12.5–14.5 | E14.5–19.5 | 57, 58, 117, 120, 121 |
| Taste | E8.5–10.5 | Continuous | E10.5–14.5 | E10.5 | E13.5–14.5 | 64, 122, 117 |
Cell cycle exit gradients are clearly documented only in the retina (central to peripheral progression) and hearing (base to apex for spiral ganglion neurons, apex to base for hair cells, and high frequency to low frequency in anterior cochlear nuclei). NA, not applicable; OSN, olfactory sensory neuron that is also the sensory cell.
Extirpation and transplantation of whiskers
Physical manipulation of the whiskers plays a role in the maturation of the “barrelettes” in the brainstem as well as cortical barrels 101. Transplantation of supernumerary whiskers causes formation of barrelettes in the trigeminal nucleus and barrel fields in the cortex, whereas blockade of activity prevents barrelette formation 103 without disrupting overall sensory projection patterns. How relative activity results in gene expression and altered cortical map configuration in the somatosensory system is currently being investigated 106.
Vestibular maps for linear and angular acceleration detection
Adult organization
Vestibular afferents to different end organs originate from overlapping populations of vestibular neurons within the vestibular ganglion 114, 115. Central projections from distinct end organs show that the two types of vestibular receptors—the canals for angular acceleration and the otoconia bearing linear acceleration organs—have both discrete and overlapping projections 21, 123, possibly reflecting that all angular acceleration prompts additional linear stimulation. Each of the segregated and common signals is related to rhombomere-specific nuclei with different outputs 17, 63. An added complexity, shared with the lateral line system of mechanosensors, is the opposing polarity of hair cells in linear but not angular acceleration sensors 124, 125.
Development
Beyond descriptive analysis of development of central projections 22, no molecular analysis exists that could explain the partial and incomplete segregation of vestibular sensory neurons projecting to different end organs and the partially segregated and partially overlapping central projection. Afferents innervating hair cells with different polarities project centrally to different rostro-caudal targets, such as the cerebellum and caudal hindbrain 126. Nrp2 plays a role in regulating bifurcation 127, but how a lack of bifurcation translates into a differential pattern of central and peripheral targets has not been revealed. Neural crest–derived Schwann cells provide some peripheral guidance 128 but seem to have no effect on central projections 129. Neither developing targets nor neurotrophic support from targets is needed to guide growing vestibular afferents to the correct ear organ 130, 131, but stop signals are needed to confine growing peripheral fibers to specific sensory organs 132. In the related system of lateral line mechanosensors, cell cycle exit of sensory neurons defines their central target, distinguishing between primary sensory cells connecting to the Mauthner cell and secondary sensory cells that lack such connections 124. How much of this development in fish plays a role in vestibular development in mammals remains speculative 125. More data on possible ErbB 128, 133 and Eph 134, 135 involvement in vestibular afferent ordering are warranted.
Ear manipulations
Transplantation of developing ears 136 has established that guidance cues are highly conserved between vertebrates 136, 137. The ability to form functional connections with the hindbrain does not depend on the entry point of vestibular ganglion processes into the hindbrain. Functional rerouting to the vestibular nucleus of afferents from transplanted ears that entered into the spinal cord has been demonstrated 138. Transplantation and rotation of a third ear to generate non-matching stimulation relative to the native ear’s sensory epithelia result in “vestibular dominance columns” 139. These “vestibular dominance columns” may reflect a compromise between molecular guidance cues and their activity-related refinement that was first identified in the visual system 33, 90. More information on molecular and activity-mediated vestibular projection ordering is needed to guide restoration of vestibular function through neuronal transplantation to prevent falls of the growing number of seniors with vestibular neurosensory loss 140.
Tonotopic map
Adult organization
The auditory system segregates sounds of high to low frequencies along the base-to-apex length of the cochlea and projects this unidimensional frequency information via topographically restricted spiral ganglion neurons to discrete isofrequency bands within the cochlear nucleus complex 9, generating a single inner hair cell–to–projection band topology ( Figure 1C and Figure 2A,B). Second-order neurons project an isofrequency map onto third-order neurons 141 that use time and intensity differences to extract sound direction by comparing the identical frequency of the two ears 16 to generate a sound space map 15. Although cortical neurons can be excited by specific frequencies, the granularity and response properties of cortical neurons differ from those of brainstem neurons 10. The idea that the cortical tonotopic map is continuous at the microscale was recently questioned by using more sophisticated techniques: adjacent cortical response properties vary by up to three octaves, indicating a discontinuous microscale frequency map 104.
Development
Of all maps, the cochleotopic map is the simplest in terms of projecting just one dimension ( Figure 1C), the linear arrangement of spiral ganglion neurons onto a matching linear projection in the cochlear nuclei 55. Despite this apparent simplicity relative to olfactory and optic maps, surprisingly little is known about the molecular basis of this primary map formation 56. Spiral ganglion neurons exit the cell cycle in a base-to-apex progression 120, 57 and project to their central targets within 48 hours after exiting the cell cycle 121 in an orderly arrangement of afferent fibers within the cochlear nerve 56. A sequence of transcription factors defines the neuronal precursors and their development 142, 143. Evidence on two of these transcription factors— Neurod1 and Gata3—suggests their involvement in both peripheral and central process navigation by expressing yet-to-be-determined downstream factors in developing spiral ganglion neurons 56, 144, 145. How exactly these transcription factors regulate the essential interactions with Schwann cells to keep spiral ganglion neurons within the right position 129 or with various substrate information to navigate to distinct types of hair cells 146, 147 remains to be shown. For the first time in any primary sensory map, mouse mutants now exist with molecularly induced peripheral and central misguidance that cannot be corrected for by near-normal auditory activity 56. Consistent with developmental data in the somatosensory 5 and olfactory 53 system, neither peripheral nor central target cells are needed to develop an orderly projection 148 and partial loss of central targets has no obvious effect on the primary central segregation of spiral ganglion afferents 149. Primary afferents give rise to secondary branches to project a refined topographic map along the cochlear nuclei. Likely candidates for the molecular guidance of organized second-order fiber projection are Wnts released from the rhombic lip 150. Defects in mapping are prominent in mice mutant for Prickle1, a downstream effector of the Wnt/Fzd pathway 151. Furthermore, Neurod1 is known to regulate Fzd receptors 152. In analogy to the retino-midbrain projection 84, Wnts may generate a gradient (or gradients) within which spiral ganglion afferents orient using a combination of Fzd and Ryk, both regulated by Neurod1 152. Other factors with limited effects are Hox genes, Nrp2 and Eph/ephrins 134, 56, 153 and possibly neuropilins and semaphorins 132, 147.
Experimental manipulations
Auditory refinement has been investigated by sound manipulation and surgical or molecular deletion of some parts of the adult or developing cochlea. Surviving spiral ganglion neurons remap remaining central afferents after either neurotrophin-mediated deletion 154 or various lesions of the auditory periphery 155– 157. This plasticity of the auditory system 158, 159 is likely governed by the Hebbian principle 28. Further studies on the recently described primary tonotopy-disrupted viable mice 56 could shed light onto limitations of such plastic reorganization. Such information is required for replacements of spiral ganglion neurons to improve hearing in the elderly with sound-induced neuropathy 160 or to improve cochlear implants 140 or replace ears 137.
Primary taste maps challenge past taste concepts
Adult organization
Many medical textbooks claim that different tastants are perceived by different taste buds and projected to distinct rostro-caudal subdivisions of the solitary tract 24. Further, it was thought that distinct information was gathered by different taste buds (fungiform, foliate, circumvallate papilla, and pharyngeal taste buds) and these tastants were carried by a separate cranial nerve innervating the different taste buds ( Figure 2A,B). Recent findings have radically changed this belief. A taste bud consists of 50 to 100 taste receptor cells 36, and all taste buds perceive all five tastants (sweet, sour, bitter, salty, and umami), each binding to a molecularly distinct receptor 48, 161. The graded taste information 23 is projected via three cranial nerves (VII, IX, X; Figure 2) to a dorso-ventral and rostro-caudal overlapping afferent distribution in the solitary tract that retains a rough orotopic organization 26, 36, 162. Highly conserved second-order neurons 163 project taste information to be combined with tongue-related somatosensation and olfaction into an integrated experience related to food intake 1, 36.
Development
Taste neurons are generated by epibranchial placodes using unique sets of transcription factors 164. Peripheral processes of taste neurons are not needed for mammalian taste bud induction 64, 165 but rather for maintenance of taste buds 166, 167. How taste afferents navigate to reach the right peripheral target to interact with the developing taste buds is unclear but is apparently not dependent on the neurotrophin Bdnf 168, 169. Autonomy of central afferent navigation is achieved in mice mutants that owing to null mutation for Tlx3 have no solitary nucleus development, but taste afferents seem to innervate adjacent nuclei in the absence of their specific target neurons 170. The expression of the solitary nucleus specifying transcription factor Tlx3 is directed by BMP gradients 111. Owing to the early death of these mutants, it is unclear how long afferents can be maintained in the absence of their central target. Notably, taste ganglion neurons express neurotrophins to be self-supporting in the absence of a peripheral or central target 168. Because all taste buds perceive all tastants with various thresholds 23, it remains unclear what specific information the rough orotopic projection of afferents extracts and how the differential activity of each taste bud to various concentrations of tastants 23 can be used to sharpen the taste map. Clearly, the orotopic organization is lost in higher-order projections, making the need of the orotopic primary map even more fuzzy 26.
Experimental manipulations
Crafting of tongues to foreign areas such as orbit and liver has long established the independence of taste bud development 171, 172. More experimental data are needed on the molecular guidance of taste afferents, the functional significance of orotopic organization, inter-solitary nucleus connections 25, 173, and higher-order interactions 174. Importantly, no data exist showing how the orotopic projection develops in the absence of taste buds 165 and where afferents end long term in the absence of a central target 170. Such information will be crucial to establish proper taste after complex orofacial surgery related to cancer or complex head trauma 175, 167.
Overview of brainstem maps
Olfactory and retinotopic maps differ from brainstem maps as the former either involve the only mammalian sensory neuron/cell (the OSN) with its own axon that is continuously replaced or deal with a region of the brain transformed into the retina, generating the “optic nerve” out of an intracerebral tract. In addition, both of the above-described maps provide a point-to-point connection that either projects one surface (the retina) onto another surface (the midbrain 8) in two dimensions or ensures that a given odor binding to distributed OSNs converges on the same glomerulus (olfactory map 33). No such point-to-point map is obvious in the hindbrain ( Figure 1C and Figure 2A) where a given peripheral connection (such as a specific area of the facial skin or the cochlea) is innervated by a neuron residing in a given ganglion with a distinct molecular (Neurog1 versus Neurog2 177, 122) and developmental (epibranchial placode, otic placode, trigeminal placode, and neural crest 46, 73, 164) origin. Instead of a point-to-point connection, each of the hindbrain targeting sensory neurons forms an extended longitudinal track along the alar plate of the hindbrain ( Figure 1C and Figure 2A). As a first approximation, the hindbrain alar plate can be regarded as a highly transformed part of the spinal cord that has developed rhombomere-specific nuclei, which receive hindbrain-specific innervation 109, 63, 178, 179. Within each of the longitudinal hindbrain tracks, rhombomere-specific nuclei can be identified 5, 17, 178, 179– 182, and each has its own higher-order projection. How the well-known cortical maps such as for somatosensation 5, 6 are exactly derived from the organizational principle of primary afferents 102, 103 is only in the case of the auditory and somatosensory system partially clarified 5, 10, 11. An emerging principle of hindbrain and visual map formation, likely not shared with the olfactory map because of its continuous replacement, is the role of cell cycle exit.
Cell cycle exit influences topology
Developmental features that play no role in olfactory or only a modulatory role in the retinotopic map formation 75, such as timing of cell cycle exit and axonal projection, seem to play an underexplored part in overall brainstem map formation 65, 183. Neurons of the alar plate and cranial ganglia have distinct, partially overlapping cell cycle exits 184– 117. Migration within the alar plate, as in the spinal cord 179, suggests that more sophisticated pulse-chase experiments with modern EdU/BrdU double labeling are needed to resolve temporal maps. Indeed, a very recent article showed that the anterior parts of the cochlear nucleus complex show a coordinated cell cycle exit matching that of spiral ganglion neurons 58. The temporal progression of spiral ganglion cell cycle exit 57, 120 and progressive development of spiral ganglion neurons and their central projections 121 imply a birth-dating bias toward map formation ( Figure 1C and Figure 2B). In addition to “birth-dating” map of secondary neurons of the alar plate, the cell cycle exit varies among peripheral neurons ( Table 1), most obviously in the auditory system 57, 120. The epibranchial derived neurons innervating the taste buds of the tongue project early in development to the solitary tract ( Table 1), long recognized as the first tract to form in the mammalian hindbrain 63, 170. First-born and projecting neurons of a given ganglion form the most ventral projection in the alar plate and within a given alar plate nucleus 65, 183. In amphibians and fish, afferents of different senses developing at different times project in a ventral-to-dorsal progression ( Figure 2B) to the hindbrain 65, 183 and form distinct aspects of some lateral line sensory maps 124. Beyond the birth-date related primary afferent fiber organization, the formation of alar plate nuclei and side branches of primary afferents makes it difficult to extract primary map formation and to derive general organizational principles 5 in mammals without more refined analysis as recently conducted in the visual system 75 and auditory system 58. In addition to cell cycle exit of alar plate and sensory neurons, there is a rostro-caudal progression in maturation leading to a rhombomere-specific second-order neuron cell cycle exit, matching the arrival and formation of secondary branches of primary sensory afferents 17, 103. These data suggest that more refined analysis of temporal progression of molecular guidance cues is warranted for the brainstem and visual projection development.
Summary
Primary sensory maps mirror the unique properties of a given sensory modality. Maps can reflect (a) local receptor density and activity (somatosensory), (b) convergence of distributed receptors (olfactory), (c) continuous one-dimensional (tonotopic) or (d) 2D (retinotopic and somatotopic) maps, or (e) convergence and segregation of information gathered by distinct sensory organs (vestibulotopic and orotopic) maps. An emerging principle of several maps is the role of cell cycle exit that allows distinct inputs to interact specifically with matching cell cycle–exited second-order neurons. This is particularly obvious in the temporal progression of afferent projections from various sensory systems in amphibians and bony fish, the temporal and maturational progression of spiral ganglion, and cochlear nucleus cell cycle exit, and it plays a role in RGN type specifications. Afferent fiber sorting prior to the target is an obvious common feature in all sensory systems and may reflect both fiber–fiber molecular interactions and cell cycle exit. As a consequence of fiber sorting, a crude topology of processes arises before a target is innervated and even in the absence of a target as demonstrated in the olfactory and auditory systems. Once the specific map has been established by various non-activity-related means, a common feature is that activity sharpens the map. To the best of our knowledge, there is only one developing sensory system currently known where a single deletion in a viable mutant results in near-random distribution of peripheral and central processes that cannot be corrected by physiological activity. Such mutants can test the limits of activity-mediated refinement of distorted primary maps.
Combinations of classic embryologic manipulations, such as transplantations, rotations, or partial deletions, have been extremely helpful to formulate basic principles such as the chemoaffinity theory. Whereas the topographical information coded in such diffusible gradients may be uniform across all sensory maps, the molecular nature of specific guidance cues used certainly is not. However, it is noteworthy that several maps have a dorso-ventral axis that could reflect known countergradients of diffusible molecules needed to define different dorso-ventral nuclei, such as Bmp4, Wnt3, and Shh. Going forward, combining heterochronic and heterotopic transplantations with molecular perturbation of map formation and with the evaluation of the role of activity to sharpen such distorted maps will reveal how best to use such information to enhance sensory organ replacements for functional recovery to cure anosmia, blindness, vestibular, and auditory dysfunction. Whole face or tongue transplants could also benefit from an understanding of such detailed map formation. Clearly, cortical maps will plastically respond to peripheral manipulations, but meaningful integration of various sensory information requires that each primary map be appropriately organized to allow a multisensory cortical or subcortical integration of relevant information extracted out of primary maps.
Abbreviations
2D, two-dimensional; bHLH, basic helix-loop-helix; MesV, mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus; Nrp, natriuretic peptide receptor; OB, olfactory bulb; OR, odorant receptor; OSN, olfactory sensory neuron; RGN, retinal ganglion neuron
Acknowledgments
BF wishes to thank several colleagues for discussions of several ideas presented here. We would like to thank reviewers for very constructive and helpful suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Editorial Note on the Review Process
F1000 Faculty Reviews are commissioned from members of the prestigious F1000 Faculty and are edited as a service to readers. In order to make these reviews as comprehensive and accessible as possible, the referees provide input before publication and only the final, revised version is published. The referees who approved the final version are listed with their names and affiliations but without their reports on earlier versions (any comments will already have been addressed in the published version).
The referees who approved this article are:
Andrew D. Huberman, Department of Neurobiology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, USA
Jason W Triplett, Center for Neuroscience Research, Children's National Medical Center, Washington, DC, USA
Funding Statement
The authors were supported by the Czech Science Foundation (17-04719S to GP), the European Regional Development Fund (BIOCEVCZ.1.05/1.1.00/02.0109), the institutional support of the Czech Academy of Sciences (RVO: 86652036), and the National Institutes of Health (R01 AG060504 to BF and R03 DC015333 to KE).
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
[version 1; peer review: 2 approved]
References
- 1. Shepherd GM: Smell images and the flavour system in the human brain. Nature. 2006;444(7117):316–21. 10.1038/nature05405 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. D'Elia KP, Dasen JS: Topographic Maps: Motor Axons Wait Their Turn. Curr Biol. 2018;28(2):R86–R88. 10.1016/j.cub.2017.11.047 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Hebb DO: In The Organization of Behavior (Psychology Press),2005;102–120. [Google Scholar]
- 4. Laumonnerie C, Bechara A, Vilain N, et al. : Facial whisker pattern is not sufficient to instruct a whisker-related topographic map in the mouse somatosensory brainstem. Development. 2015;142(21):3704–12. 10.1242/dev.128736 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Erzurumlu RS, Murakami Y, Rijli FM: Mapping the face in the somatosensory brainstem. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11(4):252–63. 10.1038/nrn2804 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Brecht M: The Body Model Theory of Somatosensory Cortex. Neuron. 2017;94(5):985–92. 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.05.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Triplett JW: Molecular guidance of retinotopic map development in the midbrain. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2014;24(1):7–12. 10.1016/j.conb.2013.07.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Dhande OS, Huberman AD: Retinal ganglion cell maps in the brain: implications for visual processing. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2014;24(1):133–42. 10.1016/j.conb.2013.08.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Muniak MA, Connelly CJ, Suthakar K, et al. : Central Projections of Spiral Ganglion Neurons. In The Primary Auditory Neurons of the Mammalian Cochlea (Springer),2016;157–190. 10.1007/978-1-4939-3031-9_6 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Schreiner CE, Polley DB: Auditory map plasticity: Diversity in causes and consequences. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2014;24(1):143–56. 10.1016/j.conb.2013.11.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Schreiner CE, Winer JA: Auditory cortex mapmaking: principles, projections, and plasticity. Neuron. 2007;56(2):356–65. 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.10.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Seabrook TA, Burbridge TJ, Crair MC, et al. : Architecture, Function, and Assembly of the Mouse Visual System. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2017;40:499–538. 10.1146/annurev-neuro-071714-033842 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Huberman AD, Feller MB, Chapman B: Mechanisms underlying development of visual maps and receptive fields. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2008;31:479–509. 10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125533 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Jeffress LA: A place theory of sound localization. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1948;41(1):35–9. 10.1037/h0061495 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Carr CE, Peña JL: Cracking an improbable sensory map. J Exp Biol. 2016;219(Pt 24):3829–31. 10.1242/jeb.129635 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. McAlpine D, Grothe B: Sound localization and delay lines--do mammals fit the model? Trends Neurosci. 2003;26(7):347–50. 10.1016/S0166-2236(03)00140-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Chagnaud BP, Engelmann J, Fritzsch B, et al. : Sensing External and Self-Motion with Hair Cells: A Comparison of the Lateral Line and Vestibular Systems from a Developmental and Evolutionary Perspective. Brain Behav Evol. 2017;90(2):98–116. 10.1159/000456646 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Krahe R, Maler L: Neural maps in the electrosensory system of weakly electric fish. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2014;24(1):13–21. 10.1016/j.conb.2013.08.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Dang P, Fisher SA, Stefanik DJ, et al. : Coordination of olfactory receptor choice with guidance receptor expression and function in olfactory sensory neurons. PLoS Genet. 2018;14(1):e1007164. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007164 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 20. Mori K, Sakano H: How is the olfactory map formed and interpreted in the mammalian brain? Annu Rev Neurosci. 2011;34:467–99. 10.1146/annurev-neuro-112210-112917 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Straka H, Fritzsch B, Glover JC: Connecting ears to eye muscles: evolution of a 'simple' reflex arc. Brain Behav Evol. 2014;83(2):162–75. 10.1159/000357833 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Maklad A, Fritzsch B: Development of vestibular afferent projections into the hindbrain and their central targets. Brain Res Bull. 2003;60(5–6):497–510. 10.1016/S0361-9230(03)00054-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Wu A, Dvoryanchikov G, Pereira E, et al. : Breadth of tuning in taste afferent neurons varies with stimulus strength. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8171. 10.1038/ncomms9171 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 24. Smith DV, Margolskee RF: Making sense of taste. Sci Am. 2001;284(3):32–9. 10.1038/scientificamerican0906-84sp [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Chamma H, Jebai F, Sater FA, et al. : Taste mapping: A new approach for the taste regions. Asian Journal of Science and Technology. 2018;9(9):8710–8713. Reference Source [Google Scholar]
- 26. Lundy RF, Norgren R: Gustatory System. In The Rat Nervous System (Fourth Edition) Elsevier,2015;733–760. 10.1016/B978-0-12-374245-2.00026-7 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Sperry RW: Chemoaffinity in the orderly growth of nerve fiber patterns and connections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963;50(4):703–10. 10.1073/pnas.50.4.703 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Hebb DO: The Organization of Behavior. Wiley, New York,1949. Reference Source [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Ruthazer ES, Akerman CJ, Cline HT: Control of axon branch dynamics by correlated activity in vivo. Science. 2003;301(5629):66–70. 10.1126/science.1082545 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Babola TA, Li S, Gribizis A, et al. : Homeostatic Control of Spontaneous Activity in the Developing Auditory System. Neuron. 2018;99(3):511–524.e5. 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.07.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 31. Yu CR, Power J, Barnea G, et al. : Spontaneous neural activity is required for the establishment and maintenance of the olfactory sensory map. Neuron. 2004;42(4):553–66. 10.1016/S0896-6273(04)00224-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Leighton AH, Lohmann C: The Wiring of Developing Sensory Circuits-From Patterned Spontaneous Activity to Synaptic Plasticity Mechanisms. Front Neural Circuits. 2016;10:71. 10.3389/fncir.2016.00071 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Luo L, Flanagan JG: Development of continuous and discrete neural maps. Neuron. 2007;56(2):284–300. 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.10.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Dahmani L, Patel RM, Yang Y, et al. : An intrinsic association between olfactory identification and spatial memory in humans. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1): 4162. 10.1038/s41467-018-06569-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 35. Yu L, Cuppini C, Xu J, et al. : Cross-Modal Competition: The Default Computation for Multisensory Processing. J Neurosci. 2019;39(8):1374–85. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1806-18.2018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 36. Schier LA, Spector AC: The Functional and Neurobiological Properties of Bad Taste. Physiol Rev. 2019;99(1):605–63. 10.1152/physrev.00044.2017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 37. Buck L, Axel R: A novel multigene family may encode odorant receptors: A molecular basis for odor recognition. Cell. 1991;65(1):175–87. 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90418-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Nishizumi H, Sakano H: Developmental regulation of neural map formation in the mouse olfactory system. Dev Neurobiol. 2015;75(6):594–607. 10.1002/dneu.22268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Mombaerts P, Wang F, Dulac C, et al. : Visualizing an olfactory sensory map. Cell. 1996;87(4):675–86. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81387-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Bozza T, Vassalli A, Fuss S, et al. : Mapping of class I and class II odorant receptors to glomerular domains by two distinct types of olfactory sensory neurons in the mouse. Neuron. 2009;61(2):220–33. 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.11.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Flanagan JG: Neural map specification by gradients. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2006;16(1):59–66. 10.1016/j.conb.2006.01.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Kishida T, Thewissen J, Usip S, et al. : Organization and distribution of glomeruli in the bowhead whale olfactory bulb. PeerJ. 2015;3:e897. 10.7717/peerj.897 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Yu CR, Wu Y: Regeneration and rewiring of rodent olfactory sensory neurons. Exp Neurol. 2017;287(Pt 3):395–408. 10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.06.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 44. Shipley M, Ennis M, Puche A: Olfactory System. (Academic Press, Amsterdam)2004;923–964. 10.1016/B978-012547638-6/50030-4 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Stout RP, Graziadei PP: Influence of the olfactory placode on the development of the brain in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Axonal growth and connections of the transplanted olfactory placode. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2175–86. 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90134-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Steventon B, Mayor R, Streit A: Neural crest and placode interaction during the development of the cranial sensory system. Dev Biol. 2014;389(1):28–38. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.01.021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Maier EC, Saxena A, Alsina B, et al. : Sensational placodes: neurogenesis in the otic and olfactory systems. Dev Biol. 2014;389(1):50–67. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.01.023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Mombaerts P: Genes and ligands for odorant, vomeronasal and taste receptors. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5(4):263–78. 10.1038/nrn1365 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Crapon de Caprona MD, Fritzsch B: The development of the retinopetal nucleus olfacto-retinalis of two cichlid fish as revealed by horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res. 1983;313(2):281–301. 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90227-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Kawauchi S, Kim J, Santos R, et al. : Foxg1 promotes olfactory neurogenesis by antagonizing Gdf11. Development. 2009;136(9):1453–64. 10.1242/dev.034967 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Panaliappan TK, Wittmann W, Jidigam VK, et al. : Sox2 is required for olfactory pit formation and olfactory neurogenesis through BMP restriction and Hes5 upregulation. Development. 2018;145(2): pii: dev153791. 10.1242/dev.153791 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 52. Tan L, Xie XS: A Near-Complete Spatial Map of Olfactory Receptors in the Mouse Main Olfactory Epithelium. Chem Senses. 2018;43(6):427–32. 10.1093/chemse/bjy030 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 53. Imai T, Yamazaki T, Kobayakawa R, et al. : Pre-target axon sorting establishes the neural map topography. Science. 2009;325(5940):585–90. 10.1126/science.1173596 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 54. Zapiec B, Bressel OC, Khan M, et al. : Neuropilin-1 and the Positions of Glomeruli in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. eNeuro. 2016;3(5): pii: ENEURO.0123-16.2016. 10.1523/ENEURO.0123-16.2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Rubel EW, Fritzsch B: Auditory system development: primary auditory neurons and their targets. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2002;25:51–101. 10.1146/annurev.neuro.25.112701.142849 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Macova I, Pysanenko K, Chumak T, et al. : Neurod1 Is Essential for the Primary Tonotopic Organization and Related Auditory Information Processing in the Midbrain. J Neurosci. 2019;39(6):984–1004. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2557-18.2018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Matei V, Pauley S, Kaing S, et al. : Smaller inner ear sensory epithelia in Neurog 1 null mice are related to earlier hair cell cycle exit. Dev Dyn. 2005;234(3):633–50. 10.1002/dvdy.20551 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Shepard AR, Scheffel JL, Yu WM: Relationships between neuronal birthdates and tonotopic positions in the mouse cochlear nucleus. J Comp Neurol. 2019;527(5):999–1011. 10.1002/cne.24575 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Sweeney LB, Couto A, Chou YH, et al. : Temporal target restriction of olfactory receptor neurons by Semaphorin-1a/PlexinA-mediated axon-axon interactions. Neuron. 2007;53(2):185–200. 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.12.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Wang Y, Bao X, Wu S, et al. : Semaphorin 3A as an inhibitive factor for migration of olfactory ensheathing cells through cofilin activation is involved in formation of olfactory nerve layer. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018;92:27–39. 10.1016/j.mcn.2018.06.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 61. Cloutier JF, Sahay A, Chang EC, et al. : Differential requirements for semaphorin 3F and Slit-1 in axonal targeting, fasciculation, and segregation of olfactory sensory neuron projections. J Neurosci. 2004;24(41):9087–96. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2786-04.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 62. Albeanu DF, Provost AC, Agarwal P, et al. : Olfactory marker protein regulates refinement of the glomerular map. bioRxiv. 2018; 309401. 10.1101/309401 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Glover JC, Elliott KL, Erives A, et al. : Wilhelm His' lasting insights into hindbrain and cranial ganglia development and evolution. Dev Biol. 2018;444(Suppl 1):S14–S24. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.02.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Fritzsch B, Sarai PA, Barbacid M, et al. : Mice with a targeted disruption of the neurotrophin receptor trkB lose their gustatory ganglion cells early but do develop taste buds. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1997;15(4–5):563–76. 10.1016/S0736-5748(96)00111-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Fritzsch B, Gregory D, Rosa-Molinar E: The development of the hindbrain afferent projections in the axolotl: evidence for timing as a specific mechanism of afferent fiber sorting. Zoology (Jena). 2005;108(4):297–306. 10.1016/j.zool.2005.08.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Fritzsch B, Elliott KL: Gene, cell, and organ multiplication drives inner ear evolution. Dev Biol. 2017;431(1):3–15. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.08.034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Morrison EE, Graziadei PP: Transplants of olfactory mucosa in the rat brain I. A light microscopic study of transplant organization. Brain Res. 1983;279(1–2):241–5. 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90184-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Kersigo J, D'Angelo A, Gray BD, et al. : The role of sensory organs and the forebrain for the development of the craniofacial shape as revealed by Foxg1-cre-mediated microRNA loss. Genesis. 2011;49(4):326–41. 10.1002/dvg.20714 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Sperry R: How a developing brain gets itself properly wired for adaptive function. In: The biopsychology of development (Academic Press New York).1971;27–44. Reference Source [Google Scholar]
- 70. Gierer A: Directional cues for growing axons forming the retinotectal projection. Development. 1987;101:479–489. Reference Source [Google Scholar]
- 71. Bridge H, Bell AH, Ainsworth M, et al. : Intact extrastriate visual network without primary visual cortex in a Rhesus macaque with naturally occurring Blindsight. bioRxiv. 2018; 447482. 10.1101/447482 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Cowey A, Stoerig P: Blindsight in monkeys. Nature. 1995;373(6511):247–9. 10.1038/373247a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Maharana SK, Schlosser G: A gene regulatory network underlying the formation of pre-placodal ectoderm in Xenopus laevis. BMC Biol. 2018;16(1):79. 10.1186/s12915-018-0540-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 74. Manns M, Fritzsch B: The eye in the brain: retinoic acid effects morphogenesis of the eye and pathway selection of axons but not the differentiation of the retina in Xenopus laevis. Neurosci Lett. 1991;127(2):150–4. 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90782-O [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Osterhout JA, El-Danaf RN, Nguyen PL, et al. : Birthdate and outgrowth timing predict cellular mechanisms of axon target matching in the developing visual pathway. Cell Rep. 2014;8(4):1006–17. 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.06.063 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Roberts JM, Vetter ML: From Retina to Stem Cell and Back Again: Memories of a Chromatin Journey. Cell Rep. 2018;22(10):2519–20. 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.02.078 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 77. Wu S, Chang KC, Goldberg JL: Retinal Cell Fate Specification. Trends Neurosci. 2018;41(4):165–7. 10.1016/j.tins.2018.02.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 78. Wang S, Sengel C, Emerson MM, et al. : A gene regulatory network controls the binary fate decision of rod and bipolar cells in the vertebrate retina. Dev Cell. 2014;30(5):513–27. 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.07.018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Lamb TD: Evolution of phototransduction, vertebrate photoreceptors and retina. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013;36:52–119. 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2013.06.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Varadarajan SG, Huberman AD: Assembly and repair of eye-to-brain connections. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018;53:198–209. 10.1016/j.conb.2018.10.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 81. Sitko AA, Kuwajima T, Mason CA: Eye-specific segregation and differential fasciculation of developing retinal ganglion cell axons in the mouse visual pathway. J Comp Neurol. 2018;526(7):1077–96. 10.1002/cne.24392 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 82. Kuwajima T, Soares CA, Sitko AA, et al. : SoxC Transcription Factors Promote Contralateral Retinal Ganglion Cell Differentiation and Axon Guidance in the Mouse Visual System. Neuron. 2017;93(5):1110–1125.e5. 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.01.029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 83. Zhang C, Kolodkin AL, Wong RO, et al. : Establishing Wiring Specificity in Visual System Circuits: From the Retina to the Brain. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2017;40(1):395–424. 10.1146/annurev-neuro-072116-031607 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Schmitt AM, Shi J, Wolf AM, et al. : Wnt-Ryk signalling mediates medial-lateral retinotectal topographic mapping. Nature. 2006;439(7072):31–7. 10.1038/nature04334 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 85. Brunet I, Weinl C, Piper M, et al. : The transcription factor Engrailed-2 guides retinal axons. Nature. 2005;438(7064):94–8. 10.1038/nature04110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 86. Wizenmann A, Brunet I, Lam J, et al. : Extracellular Engrailed participates in the topographic guidance of retinal axons in vivo. Neuron. 2009;64(3):355–66. 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.09.018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Harris WA: Neural activity and development. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:689–710. 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.003353 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Harris WA: The effects of eliminating impulse activity on the development of the retinotectal projection in salamanders. J Comp Neurol. 1980;194(2):303–17. 10.1002/cne.901940203 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Pfeiffenberger C, Cutforth T, Woods G, et al. : Ephrin-As and neural activity are required for eye-specific patterning during retinogeniculate mapping. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8(8):1022–7. 10.1038/nn1508 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Constantine-Paton M, Cline HT, Debski E: Patterned activity, synaptic convergence, and the NMDA receptor in developing visual pathways. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:129–54. 10.1146/annurev.ne.13.030190.001021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Constantine-Paton M, Law MI: Eye-specific termination bands in tecta of three-eyed frogs. Science. 1978;202(4368):639–41. 10.1126/science.309179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Wilm C, Fritzsch B: Ipsilateral retinofugal projections in a percomorph bony fish: their experimental induction, specificity and maintenance; pp. 286–292. Brain Behav Evol. 1990;36(5):286–292. 10.1159/000115314 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Wilm C, Fritzsch B: Ipsilateral retinal projections into the tectum during regeneration of the optic nerve in the cichlid fish Haplochromis burtoni: a Dil study in fixed tissue. J Neurobiol. 1992;23(6):692–707. 10.1002/neu.480230608 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Fritzsch B, Himstedt W, Crapon de Caprona MD: Visual projections in larval Ichthyophis kohtaoensis (Amphibia: gymnophiona). Brain Res. 1985;355(2):201–10. 10.1016/0165-3806(85)90042-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Giorgi PP, Van der Loos H: Axons from eyes grafted in Xenopus can grow into the spinal cord and reach the optic tectum. Nature. 1978;275(5682):746–8. 10.1038/275746a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Scalia F: Synapse formation in the olfactory cortex by regenerating optic axons: ultrastructural evidence for polyspecific chemoaffinity. J Comp Neurol. 1987;263(4):497–513. 10.1002/cne.902630404 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Scalia F, Grant AC, Reyes M, et al. : Functional properties of regenerated optic axons terminating in the primary olfactory cortex. Brain Res. 1995;685(1–2):187–97. 10.1016/0006-8993(95)00426-Q [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Blackiston DJ, Anderson GM, Rahman N, et al. : A novel method for inducing nerve growth via modulation of host resting potential: gap junction-mediated and serotonergic signaling mechanisms. Neurotherapeutics. 2015;12(1):170–84. 10.1007/s13311-014-0317-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Blackiston DJ, Vien K, Levin M: Serotonergic stimulation induces nerve growth and promotes visual learning via posterior eye grafts in a vertebrate model of induced sensory plasticity. NPJ Regen Med. 2017;2:8. 10.1038/s41536-017-0012-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 100. Penfield WR, Rasmussen TB: The cerebral cortex of man: a clinical study of localization of function.1950. 10.1001/jama.1950.02920160086033 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Woolsey TA, Van der Loos H: The structural organization of layer IV in the somatosensory region (SI) of mouse cerebral cortex. The description of a cortical field composed of discrete cytoarchitectonic units. Brain Res. 1970;17(2):205–42. 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90079-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Renier N, Dominici C, Erzurumlu RS, et al. : A mutant with bilateral whisker to barrel inputs unveils somatosensory mapping rules in the cerebral cortex. eLife. 2017;6: pii: e23494. 10.7554/eLife.23494 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 103. Iwasato T, Erzurumlu RS: Development of tactile sensory circuits in the CNS. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018;53:66–75. 10.1016/j.conb.2018.06.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 104. Rothschild G, Mizrahi A: Global order and local disorder in brain maps. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2015;38:247–68. 10.1146/annurev-neuro-071013-014038 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Kole K, Scheenen W, Tiesinga P, et al. : Cellular diversity of the somatosensory cortical map plasticity. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018;84:100–15. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.11.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 106. Kole K, Komuro Y, Provaznik J, et al. : Transcriptional mapping of the primary somatosensory cortex upon sensory deprivation. GigaScience. 2017;6(10):1–6. 10.1093/gigascience/gix081 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 107. Fritzsch B, Northcutt RG: Cranial and spinal nerve organization in amphioxus and lampreys: evidence for an ancestral craniate pattern. Acta Anat (Basel). 1993;148(2–3):96–109. 10.1159/000147529 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Ter-Avetisyan G, Dumoulin A, Herrel A, et al. : Loss of Axon Bifurcation in Mesencephalic Trigeminal Neurons Impairs the Maximal Biting Force in Npr2-Deficient Mice. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:153. 10.3389/fncel.2018.00153 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 109. Hernandez-Miranda LR, Müller T, Birchmeier C: The dorsal spinal cord and hindbrain: From developmental mechanisms to functional circuits. Dev Biol. 2017;432(1):34–42. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.10.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 110. Brafman D, Willert K: Wnt/β-catenin signaling during early vertebrate neural development. Dev Neurobiol. 2017;77(11):1239–59. 10.1002/dneu.22517 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 111. Hornbruch A, Ma G, Ballermann MA, et al. : A BMP-mediated transcriptional cascade involving Cash1 and Tlx-3 specifies first-order relay sensory neurons in the developing hindbrain. Mech Dev. 2005;122(7–8):900–13. 10.1016/j.mod.2005.04.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112. Andrews MG, Del Castillo LM, Ochoa-Bolton E, et al. : BMPs direct sensory interneuron identity in the developing spinal cord using signal-specific not morphogenic activities. eLife. 2017;6: pii: e30647. 10.7554/eLife.30647 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 113. Ma PM, Woolsey TA: Cytoarchitectonic correlates of the vibrissae in the medullary trigeminal complex of the mouse. Brain Res. 1984;306(1–2):374–9. 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90390-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114. Maklad A, Fritzsch B: Incomplete segregation of endorgan-specific vestibular ganglion cells in mice and rats. J Vestib Res. 1999;9(6):387–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115. Vidal PP, Cullen K, Curthoys IS, et al. : The Vestibular System. In The Rat Nervous System Fourth Edition. Elsevier,2015;805–864. 10.1016/B978-0-12-374245-2.00028-0 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 116. Hinds JW: Autoradiographic study of histogenesis in the mouse olfactory bulb. I. Time of origin of neurons and neuroglia. J Comp Neurol. 1968;134(3):287–304. 10.1002/cne.901340304 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117. Pierce ET: Time of Origin of Neurons in the Brain Stem of the Mouse. In: Progress in brain research Elsevier:1973;40:53–65. 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60679-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118. Fritzsch B: Development of inner ear afferent connections: forming primary neurons and connecting them to the developing sensory epithelia. Brain Res Bull. 2003;60(5–6):423–33. 10.1016/S0361-9230(03)00048-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119. Ma Q, Chen Z, del Barco Barrantes I, et al. : neurogenin1 is essential for the determination of neuronal precursors for proximal cranial sensory ganglia. Neuron. 1998;20(3):469–82. 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80988-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120. Ruben RJ: Development of the inner ear of the mouse: a radioautographic study of terminal mitoses. Acta Otolaryngol. 1967;Suppl 220:1–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121. Fritzsch B, Pan N, Jahan I, et al. : Inner ear development: building a spiral ganglion and an organ of Corti out of unspecified ectoderm. Cell Tissue Res. 2015;361(1):7–24. 10.1007/s00441-014-2031-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122. Fode C, Gradwohl G, Morin X, et al. : The bHLH protein NEUROGENIN 2 is a determination factor for epibranchial placode-derived sensory neurons. Neuron. 1998;20(3):483–94. 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80989-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123. Maklad A, Fritzsch B: The developmental segregation of posterior crista and saccular vestibular fibers in mice: a carbocyanine tracer study using confocal microscopy. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2002;135(1–2):1–17. 10.1016/S0165-3806(01)00327-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124. Pujol-Martí J, Zecca A, Baudoin JP, et al. : Neuronal birth order identifies a dimorphic sensorineural map. J Neurosci. 2012;32(9):2976–87. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5157-11.2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125. Fritzsch B, López-Schier H: Evolution of Polarized Hair Cells in Aquatic Vertebrates and Their Connection to Directionally Sensitive Neurons. In Flow Sensing in Air and Water Springer,2014;271–294. 10.1007/978-3-642-41446-6_11 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 126. Maklad A, Kamel S, Wong E, et al. : Development and organization of polarity-specific segregation of primary vestibular afferent fibers in mice. Cell Tissue Res. 2010;340(2):303–21. 10.1007/s00441-010-0944-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127. Ter-Avetisyan G, Rathjen FG, Schmidt H: Bifurcation of axons from cranial sensory neurons is disabled in the absence of Npr2-induced cGMP signaling. J Neurosci. 2014;34(3):737–47. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4183-13.2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128. Golding JP, Trainor P, Krumlauf R, et al. : Defects in pathfinding by cranial neural crest cells in mice lacking the neuregulin receptor ErbB4. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2(2):103–9. 10.1038/35000058 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 129. Mao Y, Reiprich S, Wegner M, et al. : Targeted deletion of Sox10 by Wnt1-cre defects neuronal migration and projection in the mouse inner ear. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e94580. 10.1371/journal.pone.0094580 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130. Fritzsch B, Matei VA, Nichols DH, et al. : Atoh1 null mice show directed afferent fiber growth to undifferentiated ear sensory epithelia followed by incomplete fiber retention. Dev Dyn. 2005;233(2):570–83. 10.1002/dvdy.20370 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131. Fritzsch B, Kersigo J, Yang T, et al. : Neurotrophic Factor Function During Ear Development: Expression Changes Define Critical Phases for Neuronal Viability. In The Primary Auditory Neurons of the Mammalian Cochlea Springer,2016;49–84. 10.1007/978-1-4939-3031-9_3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 132. Gu C, Rodriguez ER, Reimert DV, et al. : Neuropilin-1 conveys semaphorin and VEGF signaling during neural and cardiovascular development. Dev Cell. 2003;5(1):45–57. 10.1016/S1534-5807(03)00169-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 133. Morris JK, Maklad A, Hansen LA, et al. : A disorganized innervation of the inner ear persists in the absence of ErbB2. Brain Res. 2006;1091(1):186–99. 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.02.090 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134. Cramer KS, Miko IJ: Eph-ephrin signaling in nervous system development [version 1; peer review: 2 approved]. F1000Res. 2016;5(F1000 Faculty Rev): 413. 10.12688/f1000research.7417.1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135. Cowan CA, Yokoyama N, Bianchi LM, et al. : EphB2 guides axons at the midline and is necessary for normal vestibular function. Neuron. 2000;26(2):417–30. 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81174-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136. Constantine-Paton M: Trajectories of axons in ectopic VIIIth nerves. Dev Biol. 1983;97(1):239–44. 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90081-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137. Elliott KL, Fritzsch B: Ear transplantations reveal conservation of inner ear afferent pathfinding cues. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1): 13819. 10.1038/s41598-018-31952-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138. Gordy C, Straka H, Houston DW, et al. : Transplantation of Ears Provides Insights into Inner Ear Afferent Pathfinding Properties. Dev Neurobiol. 2018;78(11):1064–80. 10.1002/dneu.22629 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139. Elliott KL, Houston DW, Fritzsch B: Sensory afferent segregation in three-eared frogs resemble the dominance columns observed in three-eyed frogs. Sci Rep. 2015;5: 8338. 10.1038/srep08338 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140. Fattal D, Hansen M, Fritzsch B: Aging-Related Balance Impairment and Hearing Loss. The Wiley Handbook on the Aging Mind and Brain2018;315–336. 10.1002/9781118772034.ch16 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 141. Malmierca MS: Auditory System. The Rat Nervous System (Fourth Edition) Elsevier,2015;865–946. 10.1016/B978-0-12-374245-2.00029-2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 142. Goodrich LV: Early Development of the Spiral Ganglion. The Primary Auditory Neurons of the Mammalian Cochlea Springer,2016;11–48. 10.1007/978-1-4939-3031-9_2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 143. Fritzsch B, Eberl DF, Beisel KW: The role of bHLH genes in ear development and evolution: revisiting a 10-year-old hypothesis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010;67(18):3089–99. 10.1007/s00018-010-0403-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144. Jahan I, Kersigo J, Pan N, et al. : Neurod1 regulates survival and formation of connections in mouse ear and brain. Cell Tissue Res. 2010;341(1):95–110. 10.1007/s00441-010-0984-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145. Appler JM, Lu CC, Druckenbrod NR, et al. : Gata3 is a critical regulator of cochlear wiring. J Neurosci. 2013;33(8):3679–91. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4703-12.2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 146. Coate TM, Spita NA, Zhang KD, et al. : Neuropilin-2/Semaphorin-3F-mediated repulsion promotes inner hair cell innervation by spiral ganglion neurons. eLife. 2015;4. 10.7554/eLife.07830 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147. Zhang KD, Coate TM: Recent advances in the development and function of type II spiral ganglion neurons in the mammalian inner ear. Semin Cell Dev Biol.Elsevier,2017;65:80–87. 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.09.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148. Elliott KL, Kersigo J, Pan N, et al. : Spiral Ganglion Neuron Projection Development to the Hindbrain in Mice Lacking Peripheral and/or Central Target Differentiation. Front Neural Circuits. 2017;11:25. 10.3389/fncir.2017.00025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149. Maricich SM, Xia A, Mathes EL, et al. : Atoh1-lineal neurons are required for hearing and for the survival of neurons in the spiral ganglion and brainstem accessory auditory nuclei. J Neurosci. 2009;29(36):11123–33. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2232-09.2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150. Parr BA, Shea MJ, Vassileva G, et al. : Mouse Wnt genes exhibit discrete domains of expression in the early embryonic CNS and limb buds. Development. 1993;119(1):247–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151. Yang T, Kersigo J, Wu S, et al. : Prickle1 regulates neurite outgrowth of apical spiral ganglion neurons but not hair cell polarity in the murine cochlea. PLoS One. 2017;12(8):e0183773. 10.1371/journal.pone.0183773 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152. Pataskar A, Jung J, Smialowski P, et al. : NeuroD1 reprograms chromatin and transcription factor landscapes to induce the neuronal program. EMBO J. 2016;35(1):24–45. 10.15252/embj.201591206 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 153. Karmakar K, Narita Y, Fadok J, et al. : Hox2 Genes Are Required for Tonotopic Map Precision and Sound Discrimination in the Mouse Auditory Brainstem. Cell Rep. 2017;18(1):185–97. 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 154. Fritzsch B, Fariñas I, Reichardt LF: Lack of neurotrophin 3 causes losses of both classes of spiral ganglion neurons in the cochlea in a region-specific fashion. J Neurosci. 1997;17(16):6213–25. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-16-06213.1997 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155. Komiya H, Eggermont JJ: Spontaneous firing activity of cortical neurons in adult cats with reorganized tonotopic map following pure-tone trauma. Acta Otolaryngol. 2000;120(6):750–6. 10.1080/000164800750000298 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156. Eggermont JJ: Acquired hearing loss and brain plasticity. Hear Res. 2017;343:176–90. 10.1016/j.heares.2016.05.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 157. Harrison RV: Biologic Development of the Auditory System From Periphery to Cortex. Comprehensive Handbook of Pediatric Audiology2016;23 Reference Source [Google Scholar]
- 158. de Villers-Sidani E, Merzenich MM: Lifelong plasticity in the rat auditory cortex: basic mechanisms and role of sensory experience. Prog Brain Res.Elsevier,2011;191:119–131. 10.1016/B978-0-444-53752-2.00009-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159. Syka J: Plastic changes in the central auditory system after hearing loss, restoration of function, and during learning. Physiol Rev. 2002;82(3):601–36. 10.1152/physrev.00002.2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160. Liberman MC: Noise-induced and age-related hearing loss: new perspectives and potential therapies [version 1; peer review: 4 approved]. F1000Res. 2017;6:927. 10.12688/f1000research.11310.1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161. Ren W, Aihara E, Lei W, et al. : Transcriptome analyses of taste organoids reveal multiple pathways involved in taste cell generation. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):4004. 10.1038/s41598-017-04099-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 162. May OL, Hill DL: Gustatory terminal field organization and developmental plasticity in the nucleus of the solitary tract revealed through triple-fluorescence labeling. J Comp Neurol. 2006;497(4):658–69. 10.1002/cne.21023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163. Vendrell-Llopis N, Yaksi E: Evolutionary conserved brainstem circuits encode category, concentration and mixtures of taste. Sci Rep. 2015;5: 17825. 10.1038/srep17825 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164. O'Neill P, Mak SS, Fritzsch B, et al. : The amniote paratympanic organ develops from a previously undiscovered sensory placode. Nat Commun. 2012;3: 1041. 10.1038/ncomms2036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 165. Okubo T, Pevny LH, Hogan BL: Sox2 is required for development of taste bud sensory cells. Genes Dev. 2006;20(19):2654–9. 10.1101/gad.1457106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166. Barlow LA: Progress and renewal in gustation: new insights into taste bud development. Development. 2015;142(21):3620–9. 10.1242/dev.120394 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167. Thirumangalathu S, Harlow DE, Driskell AL, et al. : Fate mapping of mammalian embryonic taste bud progenitors. Development. 2009;136(9):1519–28. 10.1242/dev.029090 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168. Hellard D, Brosenitsch T, Fritzsch B, et al. : Cranial sensory neuron development in the absence of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in BDNF/Bax double null mice. Dev Biol. 2004;275(1):34–43. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.07.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169. Fritzsch B, Pauley S, Matei V, et al. : Mutant mice reveal the molecular and cellular basis for specific sensory connections to inner ear epithelia and primary nuclei of the brain. Hear Res. 2005;206(1–2):52–63. 10.1016/j.heares.2004.11.025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170. Qian Y, Fritzsch B, Shirasawa S, et al. : Formation of brainstem (nor)adrenergic centers and first-order relay visceral sensory neurons is dependent on homeodomain protein Rnx/Tlx3. Genes Dev. 2001;15(19):2533–45. 10.1101/gad.921501 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171. Poritsky R, Singer M: Intraperitoneal transplants of taste buds in the newt. Anat Rec. 1977;188(2):219–27. 10.1002/ar.1091880207 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172. Poritsky RL, Singer M: The fate of taste buds in tongue transplants to the orbit in the urodele, Triturus. J Exp Zool. 1963;153(3):211–8. 10.1002/jez.1401530303 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 173. Travers S, Breza J, Harley J, et al. : Neurons with diverse phenotypes project from the caudal to the rostral nucleus of the solitary tract. J Comp Neurol. 2018;526(14):2319–38. 10.1002/cne.24501 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 174. Herzog LE, Pascual LM, Scott SC, et al. : Interaction of taste and place coding in the hippocampus. bioRxiv. 2018; 431353. 10.1101/431353 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175. Birchall M: Tongue transplantation. Lancet. 2004;363(9422):1663. 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16287-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176. Kulahci Y, Klimczak A, Madajka M, et al. : Long-term survival of composite hemiface/mandible/tongue allografts correlates with multilineage chimerism development in the lymphoid and myeloid compartments of recipients. Transplantation. 2010;90(8):843–52. 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181f28bb0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177. Ma Q, Anderson DJ, Fritzsch B: Neurogenin 1 null mutant ears develop fewer, morphologically normal hair cells in smaller sensory epithelia devoid of innervation. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2000;1(2):129–43. 10.1007/s101620010017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178. Fritzsch B, Elliott KL, Glover JC: Gaskell revisited: new insights into spinal autonomics necessitate a revised motor neuron nomenclature. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;370(2):195–209. 10.1007/s00441-017-2676-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179. Lai HC, Seal RP, Johnson JE: Making sense out of spinal cord somatosensory development. Development. 2016;143(19):3434–48. 10.1242/dev.139592 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180. Frank D, Sela-Donenfeld D: Hindbrain induction and patterning during early vertebrate development. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(5):941–60. 10.1007/s00018-018-2974-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 181. Parker HJ, Bronner ME, Krumlauf R: The vertebrate Hox gene regulatory network for hindbrain segmentation: Evolution and diversification: Coupling of a Hox gene regulatory network to hindbrain segmentation is an ancient trait originating at the base of vertebrates. Bioessays. 2016;38(6):526–38. 10.1002/bies.201600010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182. Di Bonito M, Studer M, Puelles L: Nuclear derivatives and axonal projections originating from rhombomere 4 in the mouse hindbrain. Brain Struct Funct. 2017;222(8):3509–42. 10.1007/s00429-017-1416-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; F1000 Recommendation
- 183. Zecca A, Dyballa S, Voltes A, et al. : The Order and Place of Neuronal Differentiation Establish the Topography of Sensory Projections and the Entry Points within the Hindbrain. J Neurosci. 2015;35(19):7475–86. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3743-14.2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184. Altman J, Bayer SA: Development of the cranial nerve ganglia and related nuclei in the rat. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1982;74:1–90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185. Altman J, Bayer SA: Development of the brain stem in the rat. III. Thymidine-radiographic study of the time of origin of neurons of the vestibular and auditory nuclei of the upper medulla. J Comp Neurol. 1980;194(4):877–904. 10.1002/cne.901940410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186. McCabe KL, Sechrist JW, Bronner-Fraser M: Birth of ophthalmic trigeminal neurons initiates early in the placodal ectoderm. J Comp Neurol. 2009;514(2):161–73. 10.1002/cne.22004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]