Abstract
TAR DNA-binding protein (TDP-43) is a ubiquitously expressed nuclear protein, which participates in a number of cellular processes and has been identified as the major pathological factor in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD). Here we constructed a conditional TDP-43 mouse with depletion of TDP-43 in the mouse forebrain and find that the mice exhibit a whole spectrum of age-dependent frontotemporal dementia-like behaviour abnormalities including perturbation of social behaviour, development of dementia-like behaviour, changes of activities of daily living, and memory loss at a later stage of life. These variations are accompanied with inflammation, neurodegeneration, and abnormal synaptic plasticity of the mouse CA1 neurons. Importantly, analysis of the cortical RNA transcripts of the conditional knockout mice at the pre−/post-symptomatic stages and the corresponding wild type mice reveals age-dependent alterations in the expression levels and RNA processing patterns of a set of genes closely associated with inflammation, social behaviour, synaptic plasticity, and neuron survival. This study not only supports the scenario that loss-of-function of TDP-43 in mice may recapitulate key behaviour features of the FTLD diseases, but also provides a list of TDP-43 target genes/transcript isoforms useful for future therapeutic research.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s40478-019-0674-x) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Circular RNAs/ frontotemporal lobar degeneration/ loss-of-function/ Mis-processing/TDP-43
Introduction
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) are both incurable and rapidly progressive neurodegenerative diseases of the central nerves system, and they have overlapping spectra of pathogenic features [75]. While patients with FTLD exhibit a range of progressive changes in language dysfunction, behavioural abnormality, personality change, memory deficit, or motor neuron dysfunction [71], muscle weakness and motor neuron degeneration are the predominant symptoms of ALS [76]. The cytoplasmic ubiquitinated inclusions (UBIs) consisting of relocated nuclear TDP-43 protein is a common pathological characteristic observed in 50% of FTLD (FTLD-TDP) and 95% of ALS (ALS-TDP) [4, 18, 47, 54].
TDP-43, or TAR DNA-binding protein-43 [55], encoded by the highly conserved Tardbp gene [82] is a RNA-binding protein involved in transcriptional repression, pre-mRNA splicing, and translation [1, 49, 62, 76, 83]. TDP-43 in the diseased cells of the patients’ brains of FTLD-TDP or spinal cords of ALS-TDP is characterized with abnormal ubiquitination, hyperphosphorylation, and enhanced cleavage to generate the 25 kDa and 35 kDa C-terminal fragments (TDP-25 and TDP-35) [4, 54]. Furthermore, TDP-43 is partially or completely cleared from the nuclei of neuronal and/ or glial cells containing cytosolic TDP-43 (+) UBIs [53].
Mouse models with transgenic overexpression of TDP-43, knock-out/ knock-down of Tardbp gene expression often serve as the biological system for exploring the physiological functions of TDP-43 and its pathogenic roles in neurodegeneration [75]. Most of the transgenic TDP-43 mouse lines overexpress human TDP-43, wild type or mutants, under the control of pan-neuronal promoter, and the resulting phenotypes appear to be primarily relevant to ALS [57, 63]. Studies have engineered the mice to overexpress wild-type TDP-43 or induced depletion of TDP-43 in the forebrain region, which sufficed to cause neurodegeneration of brain [33, 43, 78]. However, the pathological features of most of these various mouse models do not follow a pattern of adult-onset diseases. Furthermore, the analysis of their behavioural deficits has been predominantly based on motor function or Alzheimer disease-related tests [75]. On the other hand, FTLD patients with behavioural abnormalities (behavioural variant frontotemporal dementia, bvFTLD) present predominantly with persistent changes in behaviour and social functioning, which manifest in disinhibition, apathy, altered food preferences and executive deficits. Also, impairment of motor function and hippocampal-dependent learning/memory are rare in early stage bvFTLD [61].
Moreover, the relative contributions of loss-of-function and gain-of-cytotoxicity to the neurodegeneration in FTLD-TDP or ALS-TDP remain to be better defined [44, 45, 47, 76, 83]. The physiological functions of TDP-43 in different mammalian tissues also await further investigation. Our previous results have shown that TDP-43 is important for early mouse embryo development [88] and that loss-of-TDP-43 function in spinal motor neurons can generate many of the ALS-TDP phenotypes [89]. To explore the normal physiological function of TDP-43 and examine whether depletion of TDP-43 expression in brain could cause the neurodegeneration in FTLD-TDP, we have utilized the Tardbplx mouse line [88] and generated conditional knockout mice (TDP-43 cKO) with forebrain-specific depletion of TDP-43. We find that these mice exhibit a range of pathological phenotypes in striking similarity to FTLD. We further generate high-throughput RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) data from pre- and post-symptomatic TDP-43 cKO mice and the corresponding wild type mice, and show that some of these pathological phenotypes correlate well with specific changes of the gene expression profile in the forebrain upon depletion of TDP-43.
Results
Generation of mouse lines with αCaMKII promoter-directed depletion of forebrain TDP-43
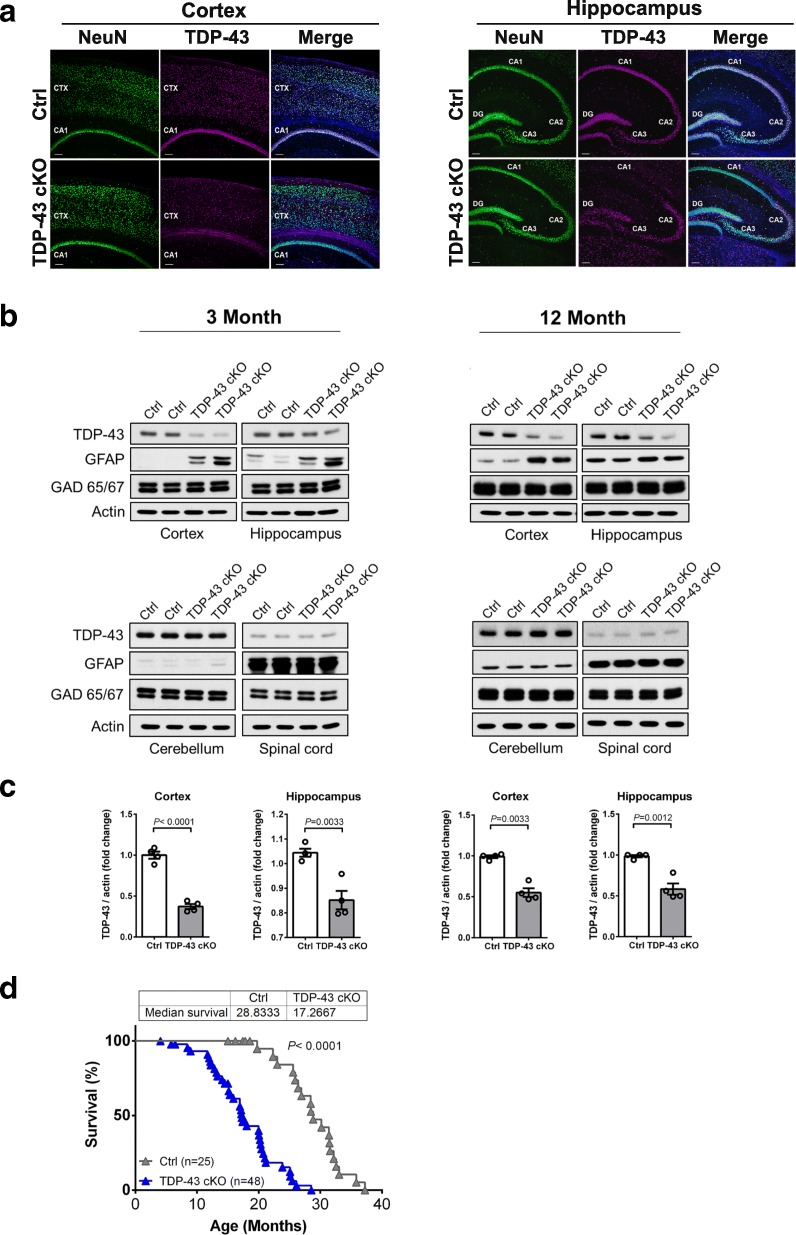
To understand the pathophysiological role of TDP-43 in adult brain, we generated conditional knock-out mice with forebrain-specific deletion of Tardbp gene by crossing Tardbp floxP mice with αCaMKII-Cre mice (T29–1 line) [88], the latter of which express αCaMKII-Cre only in neurons of the adult mouse brain [79]. Mice with Tardbpflox/flox, Cre+ alleles, referred to as TDP-43 cKO, were born at normal Mendelian ratios and appeared indistinguishable from their wild type littermate controls (Tardbpflox/flox, Cre-, referred to as Ctrl) at birth. As expected, immunohistochemistry analysis of the TDP-43 cKO mice at 2 months of age confirmed the deletion of Tardbp gene and consequent depletion of TDP-43 expression in the forebrain region, in particular in the CA1 pyramidal cell layer of the hippocampus (Fig. 1a and Additional file 1: Figure S2a). Western blot analysis of TDP-43 expression in the TDP-43 cKO mice at 3 and 12 months of age also supported that depletion of TDP-43 was restricted to the cortex and hippocampus (upper panels of Fig. 1b and c), but not in cerebellum and spinal cord (lower panels of Fig. 1b). 50% of TDP-43 cKO mice died around the age of 17 months, approximately 12 months shorter than the Ctrl mice (Fig. 1d). Collectively, the results in Fig. 1 demonstrate the successful establishment of a mouse model with postnatal depletion of TDP-43 in the forebrain and the shortened life span of TDP-43 cKO mice in comparison to their wild type littermate controls.
Fig. 1.
A mouse model (TDP-43 cKO) with αCaMKII promoter-directed depletion of TDP-43 in forebrain neurons. a Immunofluorescence staining analysis of brain sections from a cohort of 2-month-old Ctrl and TDP-43 cKO mice (TDP-43, magenta; NeuN, green; DAPI, blue). Cortex, CTX; cornu ammonis area, CA; dentate gyrus, DG. Scale bar represents 100 μm. b Western blotting analysis of the relative expression levels of TDP-43 and GFAP proteins in different tissues including cortex, hippocampus, cerebellum, and spinal cord of 3- and 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice and Ctrls. Note that ~ 50% reduction of TDP-43 protein level in the hippocampus and ~ 60% reduction of TDP-43 protein level in the cortex, but not in the cerebellum, and spinal cord in TDP-43 cKO mice. The Western blot patterns are exemplified in b, and the results of statistical analysis by unpaired student’s t test are shown in c P < 0.05 was considered significant. Data are represented as the average of 4 mice per group, with error bars reported as SEM. d Kaplan-Meyer survival curves of TDP-43 cKO mice and the Ctrls. Note the significantly shortened lifespan of TDP-43 cKO mice (P < 0.0001, log-rank Mantel-Cox test). The mean survival days are 28.8 months for the Ctrl mice and 17.2 months for the TDP-43 cKO mice
Perturbation of social behaviour and development of dementia-like behaviour in TDP-43 cKO mice at the early stage of behaviour variations
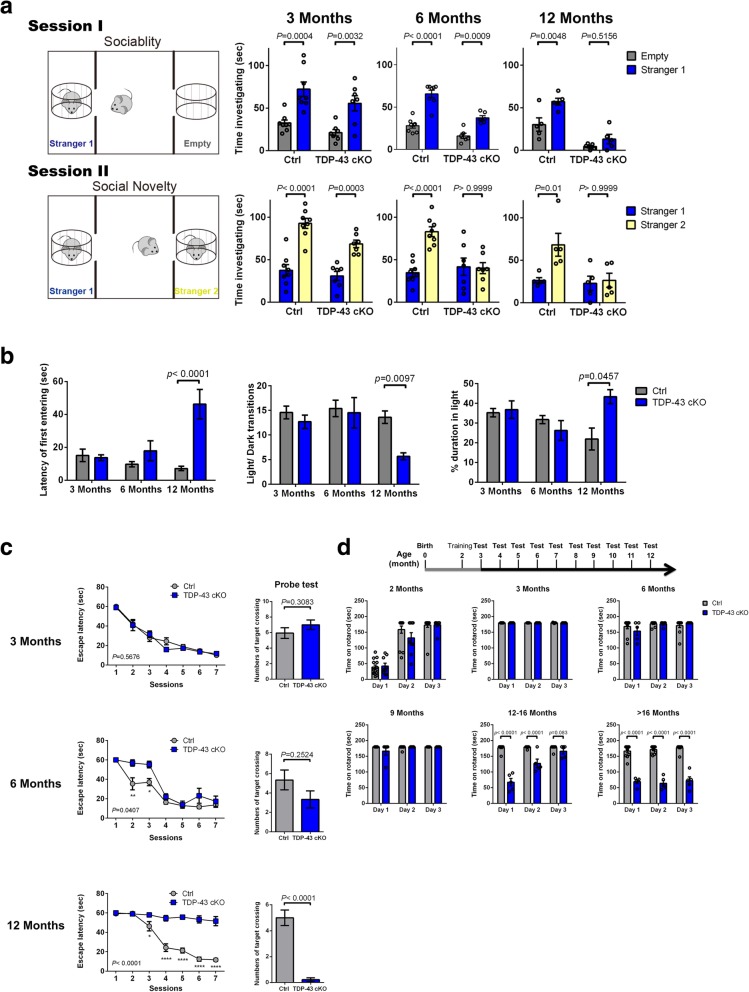
TDP-43 has been identified as the major pathological protein in 50% of FTLD patients [80] and FTLD is characterized by a preponderance of abnormalities in social behaviour rather than memory, especially in the early stages of the disease [61]. Hence, we tested the social interaction behaviour of TDP-43 cKO mice by the three-chamber sociability and social novelty test [38] at 3, 6, and 12 months of age. In the test for social preference (session I), unlike the Ctrls, 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice showed no preference for their conspecific (stranger 1) over the object by spending similar time investigating the empty cage and stranger 1 (upper panels, Fig. 2a). In the test for preference of social novelty and social recognition (session II), either 6- or 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice failed to demonstrate a preference for unfamiliar mouse (stranger 2) compared with the familiar one (stranger 1) (lower panels, Fig. 2a). TDP-43 cKO mice exhibited a progressive decline in their capability of social interaction as observed among the bvFTLD patients.
Fig. 2.
Progressively dismissing of social recognition and development of behaviour variants of the TDP-43 cKO mice. a For social interaction test (Session 1), the mean lengths of time (±SEM) the mouse spent in the chamber with the stranger (“Stranger 1”) and in the opposite chamber (“Empty”) are compared in the histograms. For social memory and novelty test (Session II), the mean durations of time (±SEM) in the chamber with the unfamiliar mouse from the sociability phase (“Stranger 1”) and in the opposite chamber with a new unfamiliar mouse (“Stranger 2”) are compared in the histograms. Statistical analysis was done by Two-way ANOVA (N = 8/group) with error bars reported as SEM, P < 0.05 was considered significant. b Light/ dark box test. The latencies of mouse entering the dark box for the first time, the light/dark transition periods, and durations of mouse in the light box were measured for mice of the ages of 3 months, 6 months, and 12 months, respectively, and statistical analysis was done by unpaired t test (N = 12/group) with error bars reported as SEM, P < 0.05 was considered significant. c Morris water maze tests. In the hidden platform test (left panels), the 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice had longer latencies to escape onto the hidden platform. Statistical analysis was done in curves by Two way ANOVA (N = 8/group) with error bars reported as SEM, P < 0.05 was considered significant. In the probe trial on the 8th session (right panels), the 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice traveled crossed the target, where the hidden platform was previously placed, significantly less times than the Ctrl mice. Statistical analysis was done in the histograms by unpaired t test with error bars reported as SEM. d Accelerated rotarod test. Ctrl and TDP-43 cKO mice were trained at the age of 2 months and then tested monthly on the accelerated rotarod (N = 11~14 in Ctrl group; N = 6~9 in TDP-43 cKO group). The histograms of latencies before falling showed that at 12 months of age, the TDP-43 cKO mice failed to memorize the rotarod running but re-learned right after the second day of training. At the end stage, e.g. older than 16 months, the TDP-43 cKO mice were unable to re-learn the rotarod running. Statistical analysis was done by unpaired t test with error bars reported as SEM, P < 0.05 was considered significant
The light/dark box test [20] was used to assess the anxiety-like behaviour [74] of the TDP-43 cKO mice. TDP-43 cKO mice at 12-month-old showed an increased latency in moving from the brightly lit area to the dark area, an increase in time spent in the light area, and markedly decreased crossings between light and dark area in comparison to the Ctrl mice (Fig. 2b). These data suggest that depletion of TDP-43 in mice lead to develop the dementia-like behaviour [43].
Sequential impairment of learning/ memory capability and locomotor function in TDP-43 cKO mice at later stage of behaviour variations
FTLD patients usually did not display cognitive deficits until later stage of the disease [52]. We used the Morris Water Maze to examine the hippocampus-dependent learning/memory, including acquisition of spatial memory and long-term spatial memory [81] of TDP-43 cKO mice. As shown in Fig. 2c, TDP-43 cKO mice show severe learning/memory impairment at the age of 12 months (left panels of Fig. 2c). In the probe trial, only the 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice exhibited a significant smaller numbers of target platform crossings in comparison to the age-matched Ctrls (right panels of Fig. 2c). Overall, the progressive dementia of the TDP-43 cKO mice strongly suggests that the functional requirement of TDP-43 in learning/ memory at later stage of life [43].
Defective motor coordination developed in the late stages of a proportion of patients with FTLD [11]. We thus examined the locomotor activity of TDP-43 cKO mice using the accelerated rotarod tests. While no difference in motor performance could be found between Ctrl and TDP-43 cKO mice before the age of 12 months, older TDP-43 cKO mice exhibited reduced motor performance on the 1st day of test (Fig. 2d). Interestingly, their performance would become better on the 2nd day of test, and there was no difference between the TDP-43 cKO and Ctrl mice on the 3rd day of test (Fig. 2d). This result suggested that the impairment of rotarod performance of the TDP-43 cKO mice was mainly due to their memory loss. They barely remembered how to perform on the rotarod, but could re-learn after 1st day of test. However, while the motor deficiency was also observed after 16 months of age, it could not be reversed on the 2nd or 3rd day of test (Fig. 2d). The massive degeneration of cortex might result in the reduced motor performance after 16 months of age which the TDP-43 cKO mice loss their memory and learning ability to perform rotartod. Neverless, the above data show that in addition to severe memory loss developed after 12 months of age, TDP-43 cKO mice also exhibit motor dysfunction after the age of 16 months. This pattern is in interesting parallel to the sequential impairment of these two neuronal functions during FTLD pathogenesis [75].
Progressively changes of nesting behaviour and eating habits in TDP-43 cKO mice
Beside cognitive dysfunction, patients with dementia including FTLD also exhibit decreased activities of daily living (ADL). We analyzed the changes of eating habits in TDP-43 cKO mice and found reduced food intake by the aged TDP-43 cKO mice (Additional file 1: Figure S1c) but not in younger ones (Additional file 1: Figure S1a and S1b). We also compared nest construction scores [21] between the Ctrl and TDP-43 cKO mice. There was a significant difference in the nesting behaviour between TDP-43 cKO and Ctrls at 12 months of age (Additional file 1: Figure S1d). Taken together, these results indicate that accompanying with the dementia phenotype, aged TDP-43 cKO mice also developed a progressive decrease of their ADL.
Brain atrophy, neuronal loss, and neuronal degeneration of the TDP-43 cKO mice
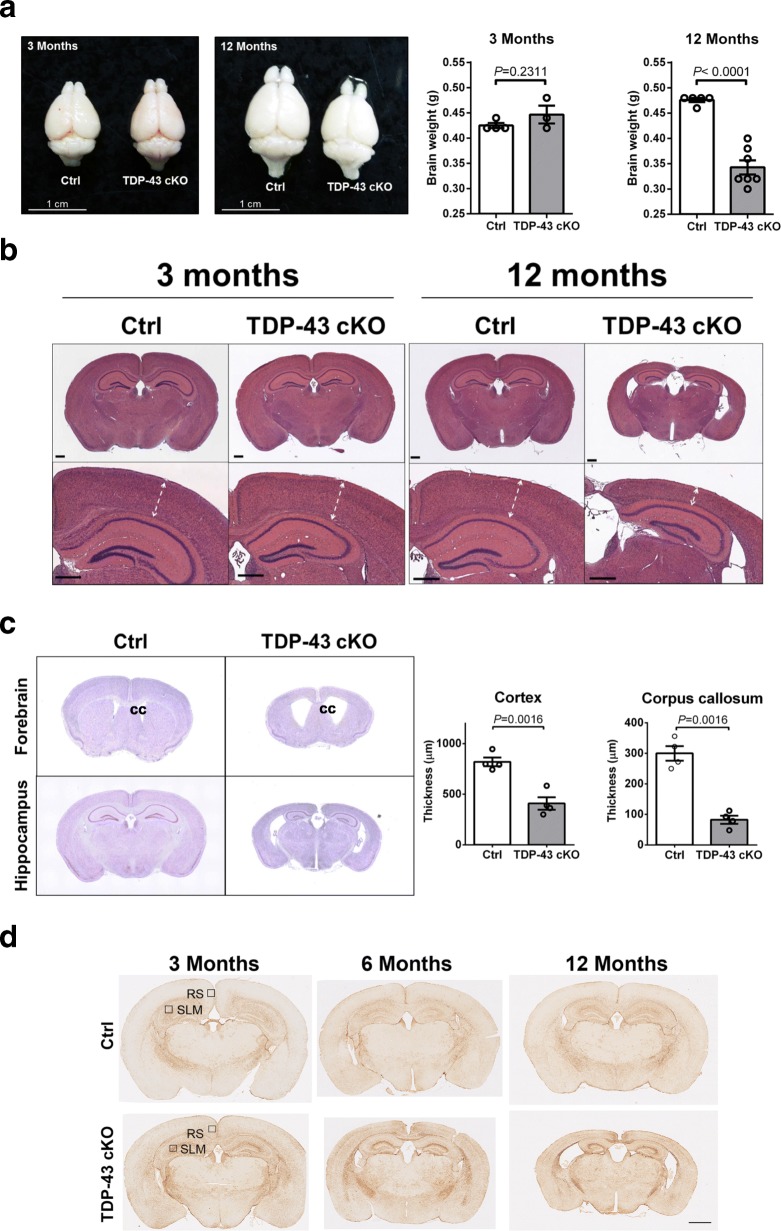
Necropsy examination showed that the 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice, but not 3-month-old ones, had a significant reduction of the overall brain size and its weight when compared to age-matched Ctrls, which appeared to be mainly due to a decrease in the size of the cortical areas (Fig. 3a). In parallel, hematoxylin and eosin staining showed aberrant cellular patterns and layering in the cortex of 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice (Fig. 3b and Additional file 1: Figure S2). Also, the thickness of cerebral cortex was reduced and the size of the ventricles was enlarged when compared to the Ctrls (Fig. 3b and c). These results are indicated that depletion of TDP-43 causes the brain atrophy in mice [43].
Fig. 3.
Brain atrophy and reactive astrocytosis in TDP-43 cKO mice. a Left, representative photo images of the brains of Ctrl and TDP-43 cKO mice at the ages of 3 months and 12 months. The total brain weights were also determined and compared in histograms on the right. N = 4–7 mice per group. Statistical analysis was done by unpaired t test with error bars reported as SEM, P < 0.05 was considered significant. b Representative histological images of the brain sections of 3- and 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice and their littermate Ctrls. More detailed characterizations are presented in Additional file 1: Figure S2. c Left panels, Nessie staining images of the forebrain and hippocampus sections from the Ctrl and TDP-43 cKO mice showing marked atrophy at corpus callosum (cc) and ventricle enlargement in the brain of 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice compared to Ctrls. The total cortex thickness and corpus callosum thickness were calculated by the length of cortex area and corpus callosum. N = 4 mice per group. Statistical analysis was done by unpaired t test with error bars reported as SEM, P < 0.05 was considered significant. d Immunohistochemistry staining with anti-GFAP revealing high numbers of GFAP-positive astrocytes in the retrosplenial cortex (RS) region of the cortex and stratum lacunosum-moleculare (SLM) region in the brain of TDP-43 cKO mice
Massive neuronal degeneration was observed in the cortex and hippocampus of 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice (Additional file 1: Figure S2 b-d). In particular, Golgi staining showed that the average length of the dendrites on dendritic stems of the layer V neurons of 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice was shorter than that of the control group (Fig. 4a). Morever, the numbers of neuron with the beading or shorter dendrites [48, 71, 72] were increased mainly in the layer V pyramidal neuron of TDP-43 cKO mice at the age of 12 months (Fig. 4b and c). Immunofluorescense staining showed that the number of neurofilament H marker (SMI-32)-positive neurons in layer III/ V of retrosplenial cortex (RS), but not those in the somatosensory cortex, decreased in TDP-43 cKO mice (Fig. 4d). Taken together, there appears to be significant and progressive neuronal degeneration in TDP-43 cKO mice in a selective vulnerability manner, with distinct neuronal populations in different cortical layers compromised by the depletion of TDP-43.
Fig. 4.
Dendritic alternations of neurons in the cortex of aged TDP-43 cKO mice. Golgi staining was used to visualize the neuronal dendrites in the cortex of 3- and 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice in comparison to the Ctrl mice. a Representative images of the Golgi-staining patterns in the left 2 panels show the obvious morphology changes and dendritic shortening of the cortical neuron of 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice in comparison to the Ctrl mice. Scale bar is 500 μm. Quantitative comparison of the dendritic lengths of cortical layer V neurons of TDP-43 cKO and Ctrl mice is shown in the right two diagrams. Note the significant reduction of the average dendritic length in 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO. Statistical analysis was done by unpaired t test with the error bars being SEM. P < 0.05 was considered significant. b Enlarged views of cortical layer V neurons. Representative images show the cortical dendrites with segmental beading dendrites (arrow heads) and degenerated spines (arrows), respectively. Scale bar is 20 μm. c Quantifications of the % of cortical layer V neurons with beading dendrites (left histogram) or shorter dendrites (right histogram). Statistically analyzed by unpaired t test with error bars reported as SEM, P < 0.05 was considered significant. Note the markedly increase of abnormal dendrites in TDP-43 cKO mice at the age of 12 months, but not 3 months. d Immunofluorescence staining with anti-neurofilament H (SMI-32) (green) showing a marked decrease of the neuron numbers in the cortical layer III/ V of the retrosplenial cortex (RS) of TDP-43 cKO mouse brain but not Ctrls. Enlarged views of RS region are shown in the upper left corner of each image
Chronic astrocytosis in the forebrain of TDP-43 cKO mice
We assessed the astrocyte response during the progressive cortical degeneration describe above. As shown, GFAP-positive astrocytes in the cortical layers and hippocampus of Ctrl mice of different ages were mainly found in the corpus callosum and rarely in the neuronal layers of the cortex (upper panels, Fig. 3d). Furthermore, their slim morphology suggested a resting state of the astrocytes (upper panels, Additional file 1: Figure S3a). In stark contrast, large numbers of tufted enlarged GFAP-positive astrocytes were found in the retrosplenial cortex (RS) and in the stratum lacunosum-moleculare (SLM) region of the hippocampus of TDP-43 cKO mice (lower panels, Fig. 3d and Additional file 1: Figure S3a) and they progressively increased during aging (Additional file 1: Figure S3a and b), coinciding with the progressive thinning of the cortex exemplified in Fig. 3b. However, no microglia activation was observed at all stages of the Ctrl and TDP-43 cKO mice analyzed (Additional file 1: Figure S3c). These results indicated that progressive astrogliosis, but not microgliosis was found in TDP-43 cKO mice which reflecting the neuropathological changes. Taken together, depletion of TDP-43 in the forebrain neurons resulted in a substantial and persisting activation of the astrocytes.
Impaired synaptic plasticity in TDP-43 cKO mice
TDP-43 has been shown to be a modulator of synaptic plasticity in transgenic mouse models of ALS and FTLD [30]. We investigated whether depletion of TDP-43 indeed affected the synaptic plasticity by examining the Schaeffecr collateral pathway of TDP-43 cKO mice for synaptic plasticity, long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD). As shown in Additional file 1: Figure S4, the magnitude of long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) in the hippocampal slices from 2-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice was unaffected (Additional file 1: Figure S4a and c). At the age of 12 months, LTP in the hippocampus of TDP-43 cKO mice were significantly lower than the Ctrl mice (Additional file 1: Figure S4b and c). Alltogether, these results show that depletion of TDP-43 in the forebrain neurons affects the synaptic functions.
Genome-wide analysis of the neocortex transcriptomes of pre- and post-symptomatic TDP-43 cKO mice in comparison to ctrl mice
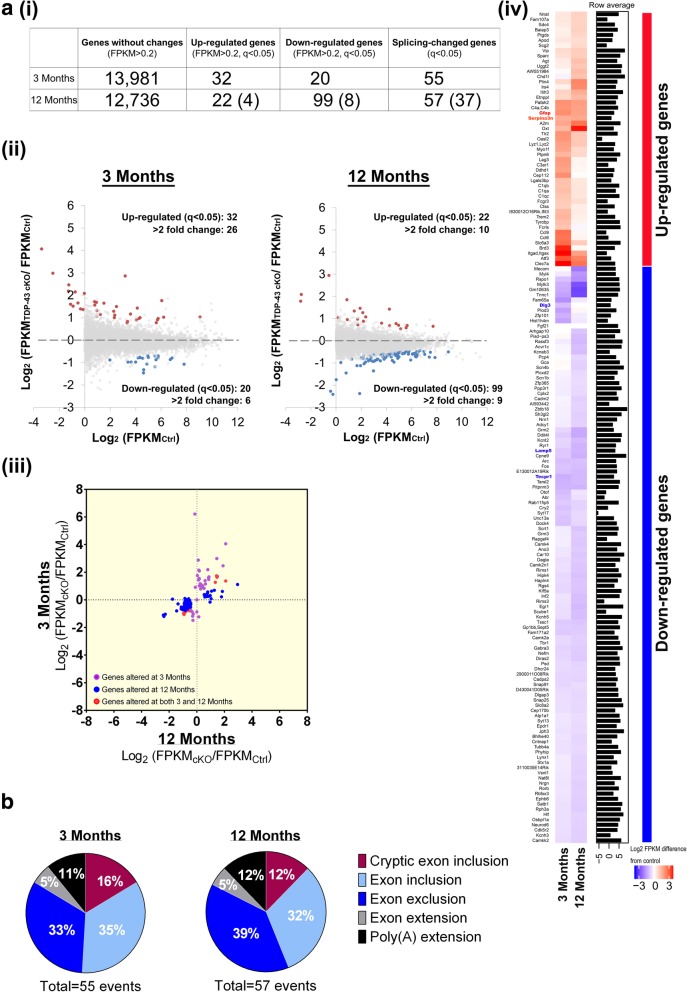
Transcripts exhibiting alternations of their expression levels or splicing patterns in TDP-43 depleted cells other than cortex have been identified before by RNA-seq analysis [5, 37, 58]. However, a transcriptome-wide analysis of the relationship between TDP-43 targeted RNAs and TDP-43 regulated behaviour/phenotypes was lacking. We used paired-end deep sequencing (see Materials and Methods) to examine the gene expression profiles in the neocortex (the region indicated in the left part of Additional file 1: Figure S2a) of TDP-43 cKO mice and their corresponding littermate controls at both the pre-symptomatic (3-month) and post-symptomatic (12-month) stages. The differential expression analysis (see Materials and Methods) revealed 52 and 121 up-/down-regulated genes at the ages of 3 months and 12 months, respectively (Fig. 5a-(i)). Interestingly, the number of the down-regulated genes was much greater in 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice than in 3-month-old cKO ones (Fig. 5a-(ii)), in correlation with the progression of the FTLD-like pathological phenotypes of the mutant mice (Fig. 2-4).
Fig. 5.
Analysis of the impact of mRNA transcriptomes in neocortex of 3- or 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice. a(i), The numbers of the unchanged, up-regulated, down-regulated, and splicing-changed genes, respectively, in the neocortex of 3- or 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice in comparison to the Ctrls. Only gene expression changed with FPKM> 0.2 were considered in the analysis. The numbers in the parentheses are the numbers of the differentially expressed genes in the neocortex of TDP-43 cKO mice at both the ages of 3 months and 12 months in comparison to the Ctrls. (ii), Scatter plot showing log2 fold change of neocortex gene expression of 3-month-old (left panel) and 12-month-old (right panel) TDP-43 cKO mice and control mice, respectively. The red, blue, and gray dots indicate up-regulated (q < 0.05), down-regulated (q < 0.05), and non-significantly changed genes, respectively, in the neocortex of TDP-43 cKO mice. Each dot represents the mean value of data from analysis of triplicate neocortex sample sets. (iii), Scatter plot showing the correlation of log2 fold change of genes altered in the neocortex of TDP-43 cKO mice at 12 months (x axis) and 3 months (y axis) of age. The purple and blue dots indicate neocortex genes the expression levels of which are altered only in 3-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice (40 genes) and only in 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice (109 genes), respectively. The 12 neocortex genes deregulated in TDP-43 cKO mice at both ages are indicated by the red dots (12 genes). (iv), Heat map representation of the expression patterns of the 161 (40 + 109 + 12) genes de-regulated in the neocortex of TDP-43 cKO mice. The expression levels of up-regulated and down-regulated genes are highlighted with different red and blue colors, respectively, in the 2 columns, with the individual gene names indicated on the side of the columns. b, Cortical RNAs of TDP-43 cKO and Ctrl mice at the age of 3 months or 12 months were analyzed by Cufflink/MISO as described. The percentages (%) of the processing alternations, i.e. alternative uses of poly-A sites (“poly (A) extension”), extensions of conserved exons (“Exon extension”), inclusions of conserved exons (“Exon inclusion”), exclusion of conserved exons (“Exon exclusion”) and inclusion of cryptic exons (“Cryptic exon inclusion”), are shown
Significantly, most of the transcripts with increased abundance in TDP-43 cKO mice associated with activation of astrocytes, whereas the majority of transcripts with decreased abundance were associated with calcium signaling and synaptic transmission—likely reflecting the astrocytosis and synaptic transmision deficit that progressively occurred with aging in TDP-43 cKO cortex (Table 1). Consistent with the correlation of these up/down regulated cortex genes with the age-dependent pathogenesis of TDP-43 cKO mice, most of the gene expression differences between the TDP-43 cKO cortex and Ctrl cotex became greater magnified as the mice aged (Fig. 5a-(i) and 5a-(iv)).
Table 1.
The genes with altered mRNA levels in the neocortex of 3-month and 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice in comparison to the Ctrls are listed
| Gene symbol | Name | RefSeq ID | Log2(TDP-43 cKO/ Ctrl) | Significant (q<0.05) | FTLD patient | White et al. [86] | Other references | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 Months | 12 months | 3 Months | 12 months | 5 Months frontal cortex | 20 Months frontal cortex | |||||||
| Common | MB- | Common | MB- | |||||||||
| Rabggtb | Rab geranylgeranyltransferase beta subunit | NM_011231 | 6.21 | -0.14 | ● | |||||||
| Clec7a | C-type lectin domain containing 7A | NM_020008 | 4.06 | 2.09 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Itgad | Integrin alpha-D | NM_001029872 | 2.99 | 1.45 | ● | |||||||
| Brd3 | bromodomain containing 3 | NM_023336 | 2.88 | 0.11 | ● | |||||||
| Atf3 | activating transcription factor 3 | NM_007498 | 2.47 | 1.90 | ● | |||||||
| Slc6a3 | solute carrier family 6 member 3 | NM_010020 | 2.19 | 0.80 | ● | |||||||
| Ccl9 | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 6 | NM_011338 | 2.15 | 0.15 | ● | |||||||
| Ccl6 | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 9 | NM_009139 | 2.09 | 0.18 | ● | |||||||
| Cep112 | centrosomal protein 112 | NM_029586 | 1.76 | 0.04 | ● | |||||||
| Pafah2 | platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase 2 | NM_001285872 | 1.69 | 1.50 | ● | |||||||
| Tlr2 | toll like receptor 2 | NP_036035 | 1.66 | 0.88 | ● | |||||||
| Oasl2 | 2'-5' oligoadenylate synthetase-like 2 | NM_011854 | 1.61 | 0.85 | ● | |||||||
| Lag3 | lymphocyte-activation gene 3 | NM_008479 | 1.55 | 0.17 | ● | ● | ||||||
| C3ar1 | complement C3a receptor 1 | NP_033909 | 1.52 | 0.18 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Lyz1,Lyz2 | lysozyme 1 | NM_017372 | 1.48 | 0.86 | ● | |||||||
| Ddhd1 | DDHD domain containing 1 | NM_176845 | 1.44 | 0.13 | ● | |||||||
| Myo1f | myosin IF | NM_053214 | 1.39 | 0.60 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Trem2 | triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 | NM_001272078 | 1.16 | 0.25 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Ptpn6 | protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 6 | NM_001077705 | 1.15 | 0.63 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Ifit3b | interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 3B | NM_001005858 | 1.11 | 0.31 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| C1qa | complement component 1, q subcomponent, alpha polypeptide | NM_007572 | 1.02 | 0.42 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Tyrobp | TYRO protein tyrosine kinase binding protein | NM_011662 | 1.01 | 0.19 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Lgals3bp | lectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 3 binding protein | NM_011150 | 0.99 | 0.38 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| C1qb | complement component 1, q subcomponent, beta polypeptide | NM_009777 | 0.96 | 0.41 | ● | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | |||||
| C1qc | complement component 1, q subcomponent, C chain | NM_007574 | 0.90 | 0.39 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Fcrls | Fc receptor-like S, scavenger receptor | NM_030707 | 0.91 | -0.11 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Fcgr3 | Fc receptor, IgG, low affinity III | NM_010188 | 0.83 | 0.53 | ● | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | |||||
| Ctss | cathepsin S | NM_001267695 | 0.79 | 0.28 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Ripor1 | Rho family interacting cell polarization regulator 1 | NM_001081241 | -1.48 | -0.28 | ● | |||||||
| Plod3 | procollagen-lysine, 2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 3 | NM_011962 | -1.23 | 0.14 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Hist1h4m | histone cluster 1, H4m | NM_175654 | -1.18 | -0.30 | ● | |||||||
| Zfp101 | zinc finger protein 101 | NM_009542 | -1.02 | -0.26 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Dlg3 | discs large MAGUK scaffold protein 3 | NM_007863 | -0.87 | 0.00 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | (LaClair et al. [43]) | |||||
| Otof | otoferlin | NM_001100395 | -0.86 | -0.34 | ● | ● (up) | ||||||
| Dock4 | dedicator of cytokinesis 4 | NM_172803 | -0.79 | -0.52 | ● | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | |||||
| Abr | active BCR-related gene | NM_001291186 | -0.79 | -0.41 | ● | (LaClair et al. [43]) | ||||||
| Syt17 | synaptotagmin XVII | NM_138649 | -0.70 | -0.48 | ● | |||||||
| Unc13a | unc-13 homolog A (C. elegans) | NP_001025044 | -0.77 | -0.48 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Rab11fip5 | RAB11 family interacting protein 5 (class I) | NM_001003955 | -0.69 | -0.58 | ● | |||||||
| Fgf21 | fibroblast growth factor 21 | NM_020013 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ● | |||||||
| Gfap | glial fibrillary acidic protein | NM_001131020 | 1.74 | 1.43 | ● | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||
| Serpina3n | serine (or cysteine) peptidase inhibitor, clade A, member 3N | NP_035588 | 1.27 | 1.34 | ● | ● | ||||||
| C4a,C4b | complement component 4a/b | NM_011413 | 1.64 | 1.46 | ● | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | |||||
| A2m | alpha-2-macroglobulin | NM_175628 | 1.37 | 2.09 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Tecpr1 | tectonin beta-propeller repeat containing 1 | NP_081686 | -1.06 | -0.93 | ● | ● | (LaClair et al. [43]) | |||||
| Tarsl2 | threonyl-tRNA synthetase-like 2 | NM_172310 | -1.00 | -0.90 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Pitpnm3 | PITPNM family member 3 | NM_001024927 | -0.97 | -0.96 | ● | ● | ● (up) | ● (up) | (LaClair et al. [43]) | |||
| Epop | elongin BC and polycomb repressive complex 2 associated protein | NM_175332 | -0.80 | -0.90 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Arc | activity regulated cytoskeletal-associated protein | NM_001276684 | -0.84 | -0.80 | ● | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||
| Cry2 | cryptochrome 2 (photolyase-like) | NM_009963 | -0.78 | -0.58 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Lamp5 | lysosomal-associated membrane protein family, member 5 | NM_029530 | -0.71 | -0.96 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Fam171a2 | family with sequence similarity 171, member A2 | NM_199200 | -0.70 | -0.65 | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| Oxt | oxytocin/neurophysin I prepropeptide | NM_011025 | 1.11 | 2.95 | ● | |||||||
| Plin4 | perilipin 4 | NM_020568 | 0.61 | 1.85 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Irs4 | insulin receptor substrate 4 | NP_034702 | 0.22 | 1.79 | ● | |||||||
| Itih3 | inter-alpha trypsin inhibitor, heavy chain 3 | NM_008407 | 0.69 | 1.27 | ● | |||||||
| Etnppl | ethanolamine phosphate phospholyase | NM_001163587 | 0.63 | 1.07 | ● | |||||||
| AW551984 | expressed sequence AW551984 | NM_001199556 | 0.08 | 1.04 | ● | |||||||
| Agt | angiotensinogen (serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A, member 8) | NM_007428 | 0.31 | 0.97 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Chd1l | chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 1-like | NM_026539 | -0.16 | 0.96 | ● | |||||||
| Uggt2 | UDP-glucose glycoprotein glucosyltransferase 2 | NM_001081252 | 0.26 | 0.87 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Vip | vasoactive intestinal polypeptide | NM_001313969 | 0.57 | 0.79 | ● | |||||||
| Sparc | secreted acidic cysteine rich glycoprotein | NM_001290817 | 0.48 | 0.77 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ● | ● (down) | ||||
| Baiap3 | BAI1-associated protein 3 | NM_001163270 | 0.24 | 0.72 | ● | |||||||
| Nnat | neuronatin | NM_001291128 | 0.37 | 0.70 | ● | |||||||
| Fam107a | family with sequence similarity 107, member A | NM_183187 | 0.38 | 0.69 | ● | |||||||
| Sdc4 | syndecan 4 | NM_011521 | 0.33 | 0.68 | ● | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | |||||
| Ptgds | prostaglandin D2 synthase (brain) | NM_008963 | 0.27 | 0.65 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Scg2 | secretogranin II | NM_001310680 | 0.21 | 0.58 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Apod | apolipoprotein D | NM_001301353 | 0.38 | 0.54 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | |||||
| Tnnc1 | troponin C1, slow skeletal and cardiac type | NP_033419 | -1.20 | -2.38 | ● | |||||||
| Gm10635 | predicted gene 10635 | NR_045336 | -1.10 | -2.42 | ● | |||||||
| Mylk3 | myosin light chain kinase 3 | NM_175441 | -1.04 | -2.28 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Mecom | MDS1 and EVI1 complex locus | NM_007963 | 0.05 | -1.76 | ● | |||||||
| Rspo1 | R-spondin 1 | NP_619624 | -0.80 | -1.46 | ● | |||||||
| Myl4 | myosin, light polypeptide 4 | NM_010858 | -0.29 | -1.36 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Ddit4l | DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4-like | NM_030143 | -0.65 | -1.13 | ● | |||||||
| Grm2 | glutamate receptor, metabotropic 2 | NM_001160353 | -0.52 | -1.12 | ● | |||||||
| Cpne9 | copine family member IX | NM_170673 | -0.70 | -1.04 | ● | |||||||
| Ryr1 | ryanodine receptor 1 | NP_033135 | -0.58 | -0.98 | ● | ● (up) | ||||||
| Rassf3 | Ras association domain family member 3 | NP_620406 | -0.26 | -0.91 | ● | |||||||
| Egr1 | early growth response 1 | NM_007913 | -0.42 | -0.90 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ● (down) | |||||
| Kcnt2 | potassium channel, subfamily T, member 2 | NM_001081027 | -0.54 | -0.89 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Rims3 | regulating synaptic membrane exocytosis 3 | NM_182929 | -0.38 | -0.84 | ● | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | |||||
| Pisd-ps3 | phosphatidylserine decarboxylase, pseudogene 3 | NR_003518 | 0.10 | -0.86 | ● | |||||||
| Kcnab3 | potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, beta member 3 | NM_010599 | -0.11 | -0.86 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Fos | FBJ osteosarcoma oncogene | NM_010234 | -0.77 | -0.84 | ● | |||||||
| Scube1 | signal peptide, CUB domain, EGF-like 1 | NM_001271472 | -0.43 | -0.83 | ● | ● (up) | ||||||
| Kcnh5 | potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 5 | NM_172805 | -0.45 | -0.83 | ● | |||||||
| Inf2 | inverted formin, FH2 and WH2 domain containing | NM_198411 | -0.35 | -0.83 | ● | |||||||
| Acvr1c | activin A receptor, type IC | NM_001111030 | -0.13 | -0.82 | ● | |||||||
| Hipk4 | homeodomain interacting protein kinase 4 | NP_001028487 | -0.51 | -0.81 | ● | |||||||
| Scrt1 | scratch family zinc finger 1 | NM_130893 | -0.26 | -0.77 | ● | |||||||
| Hapln4 | hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 4 | NM_177900 | -0.47 | -0.75 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Kif5a | kinesin family member 5A | NM_001039000 | -0.52 | -0.76 | ● | |||||||
| Arhgap10 | Rho GTPase activating protein 10 | NP_001074833 | 0.00 | -0.75 | ● | |||||||
| Camk2n1 | calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitor 1 | NM_025451 | -0.40 | -0.74 | ● | ● | ● (down) | |||||
| Car10 | carbonic anhydrase 10 | NP_082572 | -0.33 | -0.73 | ● | |||||||
| Camk4 | calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV | NM_009793 | -0.24 | -0.73 | ● | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | |||||
| Rims1 | regulating synaptic membrane exocytosis 1 | NM_001012623 | -0.42 | -0.73 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | |||||
| Eipr1 | EARP complex and GARP complex interacting protein 1 | NM_201357 | -0.68 | -0.73 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Rgs4 | regulator of G-protein signaling 4 | NM_009062 | -0.52 | -0.73 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Rapgef4 | Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 4 | NM_001204165 | -0.23 | -0.70 | ● | ● (down) | ||||||
| Dagla | diacylglycerol lipase, alpha | NM_198114 | -0.43 | -0.69 | ● | |||||||
| Diras2 | DIRAS family, GTP-binding RAS-like 2 | NM_001024474 | -0.52 | -0.69 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Gp1bb | glycoprotein Ib, beta polypeptide | NM_001001999 | -0.65 | -0.68 | ● | |||||||
| Ano3 | anoctamin 3 | NM_001128103 | -0.33 | -0.67 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Grm3 | glutamate receptor, metabotropic 3 | NM_181850 | -0.26 | -0.67 | ● | |||||||
| Nefm | neurofilament, medium polypeptide | NM_008691 | -0.53 | -0.66 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Gabra3 | gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, subunit alpha 3 | NM_008067 | -0.57 | -0.65 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Rph3a | rabphilin 3A | NM_001302344 | -0.39 | -0.65 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Tbr1 | T-box brain gene 1 | NM_009322 | -0.51 | -0.63 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Satb1 | special AT-rich sequence binding protein 1 | NM_001163630 | -0.39 | -0.64 | ● | |||||||
| Sh3gl2 | SH3-domain GRB2-like 2 | NM_019535 | -0.22 | -0.63 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Ephb6 | Eph receptor B6 | NM_001146351 | -0.37 | -0.63 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | |||||
| Kcnh3 | potassium voltage-gated channel, subfamily H (eag-related), member 3 | NM_010601 | -0.43 | -0.62 | ● | |||||||
| Nrgn | neurogranin | NM_022029 | -0.35 | -0.62 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Cadm2 | cell adhesion molecule 2 | NM_001145977 | -0.17 | -0.61 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Camkk2 | calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2, beta | NM_001199676 | -0.44 | -0.61 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Rorb | RAR-related orphan receptor beta | NM_001043354 | -0.34 | -0.60 | ● | |||||||
| Scn4b | sodium channel, type IV, beta | NP_001013408 | 0.05 | -0.60 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Camk2a | calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alpha | NM_001286809 | -0.50 | -0.60 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Nrn1 | neuritin 1 | NM_153529 | -0.24 | -0.60 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Cdk5r2 | cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 2 (p39) | NM_009872 | -0.42 | -0.60 | ● | |||||||
| Rbfox3 | RNA binding protein, fox-1 homolog (C. elegans) 3 | NM_001024931 | -0.34 | -0.60 | ● | |||||||
| Gca | grancalcin | NP_663498 | 0.08 | -0.59 | ● | |||||||
| Osbpl1a | oxysterol binding protein-like 1A | NM_001252489 | -0.39 | -0.59 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Vsnl1 | visinin-like 1 | NM_012038 | -0.32 | -0.59 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ● | |||||
| Adcy1 | adenylate cyclase 1 | NM_009622 | -0.25 | -0.59 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | |||||
| Neurod6 | neurogenic differentiation 6 | NM_009717 | -0.41 | -0.59 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| AI593442 | expressed sequence AI593442 | NM_001286641 | -0.19 | -0.58 | ● | |||||||
| Stx1a | syntaxin 1A (brain) | NM_016801 | -0.28 | -0.57 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | |||||
| Nat8l | N-acetyltransferase 8-like | NP_001001985 | -0.34 | -0.57 | ● | |||||||
| 3110035E14Rik | RIKEN cDNA 3110035E14 gene | NM_178399 | -0.28 | -0.57 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Zbtb18 | zinc finger and BTB domain containing 18 | NM_001012330 | -0.22 | -0.57 | ● | |||||||
| Hlf | hepatic leukemia factor | NM_172563 | -0.39 | -0.56 | ● | |||||||
| Lynx1 | Ly6/neurotoxin 1 | NM_011838 | -0.28 | -0.56 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Cadps2 | Ca2+-dependent activator protein for secretion 2 | NM_001252105 | -0.53 | -0.56 | ● | |||||||
| Psd | pleckstrin and Sec7 domain containing | NM_133694 | -0.47 | -0.56 | ● | |||||||
| Dhcr24 | 24-dehydrocholesterol reductase | NM_053272 | -0.49 | -0.54 | ● | ● | ||||||
| 2900011O08Rik | RIKEN cDNA 2900011O08 gene | NM_144518 | -0.53 | -0.53 | ● | |||||||
| Dlgap3 | discs, large (Drosophila) homolog-associated protein 3 | NM_001302081 | -0.43 | -0.52 | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | ||||||
| Bhlhe40 | basic helix-loop-helix family, member e40 | NM_011498 | -0.35 | -0.53 | ● | |||||||
| Pcp4 | Purkinje cell protein 4 | NM_008791 | -0.04 | -0.52 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ● | |||||
| Cntnap1 | contactin associated protein-like 1 | NM_016782 | -0.38 | -0.52 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Cep170b | centrosomal protein 170B | NM_001024602 | -0.42 | -0.51 | ● | |||||||
| Plcxd2 | phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, X domain containing 2 | NM_001134480 | -0.16 | -0.50 | ● | |||||||
| Cplx2 | complexin 2 | NM_009946 | -0.26 | -0.50 | ● | |||||||
| Phyhip | phytanoyl-CoA hydroxylase interacting protein | NM_145981 | -0.38 | -0.50 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Snap25 | synaptosomal-associated protein 25 | NM_001291056 | -0.43 | -0.50 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Slc8a2 | solute carrier family 8 (sodium/calcium exchanger), member 2 | NM_001347561 | -0.42 | -0.50 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| D430041D05Rik | RIKEN cDNA D430041D05 gene | NM_001033347 | -0.47 | -0.49 | ● | |||||||
| Tubb4a | tubulin, beta 4A class IVA | NM_009451 | -0.38 | -0.49 | ● | |||||||
| Ppp3r1 | protein phosphatase 3, regulatory subunit B, alpha isoform (calcineurin B, type I) | NM_024459 | -0.25 | -0.48 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ● | |||||
| Epdr1 | ependymin related protein 1 (zebrafish) | NM_134065 | -0.35 | -0.48 | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| Scn1b | sodium channel, voltage-gated, type I, beta | NM_011322 | -0.20 | -0.47 | ● | |||||||
| Jph3 | junctophilin 3 | NM_020605 | -0.39 | -0.47 | ● | ● | ||||||
| Syt13 | synaptotagmin XIII | NM_030725 | -0.33 | -0.45 | ● | ● | (Polymenidou et al. [58]) | |||||
| Snap91 | synaptosomal-associated protein 91 | NM_001277982 | -0.53 | -0.45 | ● | (Chen-Plotkin et al. [17]) | ||||||
| Zfp365 | zinc finger protein 365 | NM_178679 | -0.24 | -0.44 | ● | |||||||
| Atp1a1 | ATPase, Na+/K+ transporting, alpha 1 polypeptide | NM_144900 | -0.33 | -0.44 | ● | |||||||
The down-regulated genes are indicated by the "-" sign in the columns of Log2 (TDP-43 cKO/Ctrl). The genes that have been reported to have altered mRNA levels in the FTLD patients and in the striatum or hippocampus upon TDP-43 depletion are indicated in the far right column
Up/down-regulated TDP-43 cKO mouse neocortex genes associated with inflammation, autophagy, and synaptic function
Significantly, 26 genes and 10 genes were up-regulated by > 2 fold in 3- and 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mouse neocortex, respectively (Fig. 5a-(ii) and Table 1), and most of them encoded the inflammatory proteins. Three out of these up-regulated genes, i.e. Gfap, Serpina3a, and C4a/C4b, were constitutively up-regulated at both the ages of 3 months and 12 months (Additional file 1: Figure S5a), as also quantified by qRT-PCR (Additional file 1: Figure S5b). Of the three genes, increase of Gfap and Serpina3n mRNAs in reactive astrocyte was reported in brain injury and in several neurodegeneration diseases [26, 93]. We also calculated and compared the intron sizes of TDP-43-regulated genes in the Ctrl and TDP-43 cKO mouse neocortex. It was found that the total lengths of the introns of down-regulated neocortex genes in TDP-43 cKO mice (the median values being 30,061 bp and 28,604 bp at the ages of 3 months and 12 months, respectively) were larger than those of control (the median value being 11,754 bp), whereas the trend was not observed for the up-regulated neocotex genes (the median values being 9968 bp and 13,098 bp at the ages of 3 months and 12 months, respectively) (Additional file 1: Figure S5c). To assess the empirical P values, we calculated the median values of the total intron lengths of 100 genes randomly selected from the annotated mouse protein-coding genes and the process was repeated for 10,000 times. Indeed, the down-regulated neocortex genes of the TDP-43 cKO mice at either the age of 3 months or 12 months possessed significantly longer total introns than expected, with the P values < 0.001. This result is consistent with the previous observation that down-regulated genes in striatum upon TDP-43 reduction tend to have long introns [58].
Increase of Gfap protein in the cortex and hippocampus of TDP-43 cKO mice at the ages of 3 months and 12 months was confirmed by Western blotting, respectively (Fig. 1b). Note that one additional band in GFAP immunoblotting in protein extracts of 3-month-old mice could be the isoform of GFAP protein. On the other hand, most of 20 down-regulated genes in the neocortex of 3-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice (Fig. 5a) encoded proteins involved in the functions of synapse, e.g. Dlg3, endosome, e.g. Lamp5, and autophagosome, e.g. Tecpr1 (Table 1). Furthermore, eight of these 20 down-regulated genes were constitutively repressed in the neocortex of TDP-43 cKO mice at the age of 12 month (Fig. 5a and Table 1).
We also analyzed the altered expression of several genes by Western blotting. Firstly, autophagy defect was reported in Tecprl gene knockout mice with increased expression of an autophagy substrate, p62 [14]. As shown in Additional file 1: Figure S5d, the level of p62 protein was increased in the cortex of TDP-43 cKO mice at all ages analyzed. Secondly, consistent with the RNA-seq data (Additional file 1: Fig. S5a) and RT-qPCR analysis (Additional file 1: Figure S5b), the levels of SAP102 protein, which was encoded by the Dlg3 gene mentioned above and involved in synaptic plasticity by regulating the recycling of NMDA receptor NMDAR [13], in the cortex and synaptosome of TDP-43 cKO mice were reduced in an age-dependent manner (Additional file 1: Figure S5e). Since NMDA receptor (NMDAR)-mediated responses regulated the levels and activities of CaMKII family members [48], we also examined the levels of different synaptic proteins including the CaM kinase proteins CaMK4, NMDAR submit NR2b, and phospho-Erk1/2. Indeed, the amounts of these proteins were all greatly reduced in the cortex and/or synaptosome of 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice in comparison to the Ctrl mice (Additional file 1: Figure S5e), while the amount of SAP102 was decreased in the cortex and synaptosome of early stage TDP-43 cKO mice. Thus, depletion of TDP-43 in the cortex indeed would down-regulate the expression of a specific set of genes and this could contribute in part to the impairment of synaptic functions (Additional file 1: Figure S4) and behaviour deficits (Fig. 2) in an age-dependent manner.
Mis-regulation of RNA processing
Abrrant RNA processing was increasingly recognized as a potential contributor to the development/ pathogenesis of neurological diseases [68]. Among the different RNA processing events, alternative splicing (AS) is one major mechanism for the enhancement of transcriptome diversity. A growing number of human diseases were correlated with RNA mis-splicing [3]. There are several different types of alternative splicing events including inclusion/exclusion of conserved (consitutively present in wild type RNAs) or non-conserved (cryptic)(absent in the wild type RNAs) exons as well as the alternative splicing site selection leading to extension of conserved exons. To investigate the regulatory role of AS in the forebrain neurons of TDP-43 cKO mice, we used the Cufflink [77] and MISO (Mixture of Isoforms) [40] programs to examine usage changes of alternatively spliced exons (ASEs) and poly(A) sites. In comparison to the Ctrl mice, 55 and 57 transcript processing events exhibited remarkably usage changes of ASEs or polyA sites in the neocortex of 3- and 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice, respectively, (Fig. 5b, Additional file 1: Figure S6 and S7). Most (> 85%) of these changed transcript events were ASEs (Fig. 5b and Table 2). Inclusion of cryptic exons was also observed (Additional file 1: Figure S6d and Table 2). Notably, some of these transcript events with siginificant usage changes were found only in 3-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice, e.g. Pdp1, or only in 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice, e.g. Ranbp17, while others were found at both ages (Table 2). For example, polyA site usage of the Kctd2 transcript was altered in cKO mice at both ages and the Polr1b transcript was altered only in 3-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice (Additional file 1: Figure S7 and Table 2).
Table 2.
Genes with altered mRNA processing patterns in the neocortex of TDP-43 cKO mice
| Gene | Location | Strand | Significant | Δmisoψ | White et al. [86] | References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 Months | 12 Months | 3 Months | 12 Months | 5 Months | 20 Months | |||||
| Cryptic | Cdh22 | Ch2:165183239-165183371 | - | ● | ● | 0.61 | 0.54 | Jeong et al. [37] | ||
| Cryptic | Camk1g | Ch1:193368867-193368952 | - | ● | ● | 0.46 | 0.59 | Jeong et al. [37] | ||
| Cryptic | Slc45a1 | Ch4:150630400-150630454 | - | ● | ● | 0.32 | 0.13 | Jeong et al. [37] | ||
| Cryptic | Synj2bp | Ch12:81509828-81510051 | - | ● | ● | 0.39 | 0.30 | Jeong et al. [37] | ||
| Cryptic | Hgsnat | Ch8:25945949-25945996 | - | ● | ● | 0.22 | 0.19 | Jeong et al. [37] | ||
| Cryptic | Adnp2 | Ch18:80138153-80138304 | - | ● | ● | 0.45 | 0.49 | Jeong et al. [37] | ||
| Cryptic | Abca8b | Ch11:109975240-109975477 | - | ● | ● | 0.18 | 0.18 | |||
| Cryptic | Upf3a | Ch8:13789928-13789967 | + | ● | 0.17 | 0.07 | ||||
| Cryptic | Letm1 | Ch5:33779574-33779604 | - | ● | 0.13 | 0.04 | Jeong et al. [37] | |||
| Inclusion | Sort1 | Ch3:108355472-108355570 | + | ● | ● | 0.35 | 0.40 | ●(exclusion) | ●(exclusion) | Polymenidou et al. [58] |
| Inclusion | Islr2-02 | Ch9:58200272-58200461 | - | ● | ● | 0.36 | 0.37 | |||
| Inclusion | Islr2-01 | Ch9:58200272-58200443 | - | ● | ● | 0.30 | 0.29 | |||
| Inclusion | Bsg | Ch10:80136663-80136743 | - | ● | ● | 0.25 | 0.13 | |||
| Inclusion | Vps13d | Ch4:145099352-145099463 | - | ● | ● | 0.23 | 0.18 | ●(inclusion) | ||
| Inclusion | Smg5 | Ch3:88340649-88340763 | + | ● | ● | 0.20 | 0.10 | |||
| Inclusion | Smarca4 | Ch9:21677953-21678051 | + | ● | ● | 0.20 | 0.24 | |||
| Inclusion | Uggt2 | Ch14:119043908-119044028 | - | ● | ● | 0.19 | 0.08 | |||
| Inclusion | Elac2 | Ch11:65005454-65005505 | - | ● | ● | 0.15 | 0.12 | |||
| Inclusion | Kcnmb4 | Ch10:116443772-116443912 | - | ● | ● | 0.11 | 0.08 | |||
| Inclusion | Dnajc5 | Ch2:181548926-181549000 | + | ● | ● | 0.10 | 0.13 | Polymenidou et al. [58] | ||
| Inclusion | Sun1 | Ch5:139230773-139230838 | + | ● | ● | -0.14 | 0.32 | |||
| Inclusion | Pdp1-01 | Ch4:11965614-11965648 | - | ● | 0.40 | 0.24 | ||||
| Inclusion | Tmem2 | Ch19:21780171-21780252 | + | ● | 0.40 | 0.19 | ||||
| Inclusion | Zfp30 | Ch7:29788049-29788175 | + | ● | 0.32 | -0.04 | ||||
| Inclusion | Zkscan16 | Ch4:58943943-58944160 | + | ● | 0.29 | 0.18 | ||||
| Inclusion | Nfia-02 | Ch4:98081725-98081816 | + | ● | 0.12 | 0.02 | ||||
| Inclusion | Lrrk2 | Ch15:91785371-91785527 | + | ● | 0.06 | -0.01 | ||||
| Inclusion | Atxn1 | Ch13:45849519-45849588 | - | ● | 0.10 | 0.09 | Polymenidou et al. [58] | |||
| Inclusion | Ranbp17 | Ch11:33283908-33283990 | - | ● | -0.17 | 0.28 | ||||
| Inclusion | Srr | Ch11:74919437-74919662 | - | ● | 0.11 | 0.22 | ||||
| Inclusion | Atad2b | Ch12:4970406-4970468 | + | ● | -0.03 | 0.15 | ||||
| Inclusion | Kctd10 | Ch5:114376771-114376866 | - | ● | 0.05 | 0.06 | ||||
| Inclusion | Pdp1-02 | Ch4:11965614-11965648 | - | ● | #REF! | 0.05 | ||||
| Inclusion | Mettl22 | Ch16:8482127-8482167 | + | ● | 0.00 | 0.03 | ||||
| Exclusion | Cobl | Ch11:12306958-12307128 | - | ● | ● | -0.34 | -0.41 | ●(inclusion) | ||
| Exclusion | Scamp1 | Ch13:94210577-94210678 | - | ● | ● | -0.31 | -0.26 | |||
| Exclusion | Ddx50 | Ch10:62627521-62627682 | - | ● | ● | -0.27 | -0.37 | |||
| Exclusion | Kcnip2-02 | Ch19:45797091-45797186 | - | ● | ● | -0.23 | -0.29 | |||
| Exclusion | Dtwd1 | Ch2:126158410-126158553 | + | ● | ● | -0.27 | -0.19 | |||
| Exclusion | Nlgn3 | ChX:101307075-101307134 | + | ● | ● | -0.22 | -0.15 | |||
| Exclusion | Lzts1 | Ch8:69182213-69182331 | - | ● | ● | -0.12 | -0.15 | |||
| Exclusion | Nrxn1 | Ch17:90701988-90702011 | - | ● | ● | -0.09 | -0.16 | |||
| Exclusion | Shisa4 | Ch1:135373152-135373285 | - | ● | ● | -0.07 | -0.14 | ●(inclusion) | ||
| Exclusion | Rdh13 | Ch7:4444978-4445122 | - | ● | ● | 0.08 | -0.26 | |||
| Exclusion | Atp11b | Ch3:35843571-35843696 | + | ● | -0.44 | -0.28 | ●(inclusion) | |||
| Exclusion | Gpatch1 | Ch7:35281332-35281480 | - | ● | -0.36 | 0.00 | ||||
| Exclusion | Kcnip2-01 | Ch19:45796279-45796332 | - | ● | -0.21 | -0.18 | ||||
| Exclusion | Nfia-01 | Ch4:98041551-98041679 | + | ● | -0.15 | 0.00 | ||||
| Exclusion | Dzip3 | Ch16:48951543-48952160 | - | ● | -0.13 | 0.01 | ||||
| Exclusion | Cacna1b-01 | Ch2:24618255-24618362 | - | ● | -0.04 | 0.01 | ||||
| Exclusion | Tmcc2 | Ch1:132380657-132381172 | - | ● | -0.05 | 0.01 | ||||
| Exclusion | Pcm1-01 | Ch8:41313302-41313460 | + | ● | -0.08 | -0.01 | ||||
| Exclusion | Cdk19-02 | Ch10:40466638-40466769 | + | ● | -0.02 | -0.04 | ||||
| Exclusion | Max | Ch12:76939430-76939514 | - | ● | -0.08 | -0.05 | ||||
| Exclusion | Phactr2 | Ch10:13253342-13253879 | - | ● | -0.16 | -0.08 | ||||
| Exclusion | Cdk19-01 | Ch10:40454015-40454072 | + | ● | 0.02 | -0.05 | ||||
| Exclusion | Rimbp2 | Ch5:128846922-128846991 | - | ● | -0.01 | -0.09 | ||||
| Exclusion | Clasp1-01 | Ch1:118512175-118512222 | + | ● | 0.02 | -0.12 | ||||
| Exclusion | Clasp1-03 | Ch1:118541675-118541698 | + | ● | 0.07 | -0.12 | ||||
| Exclusion | Cntln-01 | Ch4:84984369-84984500 | + | ● | -0.02 | -0.20 | ||||
| Exclusion | Agfg1 | Ch1:82891460-82891507 | + | ● | -0.16 | -0.26 | ||||
| Exclusion | Repin1 | Ch6:48594862-48594976 | + | ● | -0.07 | -0.24 | ||||
| Exclusion | Ppp3ca | Ch3:136932011-136932040 | + | ● | -0.09 | -0.11 | ●(inclusion) | ●(inclusion) | ||
| Exclusion | Hspa13 | Ch16:75758632-75758727 | - | ● | 0.01 | -0.08 | ||||
| Extension | Wbscr22 | Ch5:135063781-135063921 | - | ● | ● | 0.17 | 0.19 | Jeong et al. [37] | ||
| Extension | Chga | Ch12:102558298-102558559 | + | ● | ● | 0.08 | 0.06 | Jeong et al. [37] | ||
| Extension | Bptf | Ch11:107054456-107055318 | - | ● | ● | -0.10 | -0.11 | |||
| PolyA extension | Rapgefl1 | Ch11:98851076-98857648 | - | ● | ● | 0.17 | 0.21 | Jeong et al. [37] | ||
| PolyA extension | Kctd2 | Ch11:115430313-115433591 | + | ● | ● | 0.14 | 0.11 | |||
| PolyA extension | Kcnj4 | Ch15:79505196-79505875 | - | ● | ● | 0.09 | 0.06 | |||
| PolyA extension | Ergic1 | Ch17:26655067-26658770 | + | ● | ● | 0.05 | 0.09 | |||
| PolyA extension | Syt17 | Ch7:118378587-118379874 | - | ● | ● | 0.06 | 0.16 | |||
| PolyA extension | Polr1b | Ch2: 129125214:129126791 | + | ● | 0.14 | 0.13 | ||||
| PolyA extension | Elk1 | ChX:20932683-20935548 | - | ● | 0.19 | 0.22 | ||||
| PolyA extension | Ppp3cc | Ch14:70214901-70215786 | - | ● | 0.08 | 0.09 | ||||
The ψ (PSI, percentage of spliced in) score was defined as the percentage of transcripts containing the alternative splicing events and/ or alternative poly(A) site usage. The mRNAs with increase of splcing events, i.e. conserved exon inclusion/ exclusion, cryptic exon inclusion, and exon extension, as well as change of poly(A) site usage are indicated by Δ ψ > 0, mRNA with decrease of the processing events are indicated by Δ ψ < 0. Unpaired t test was used to calculate the significance from data of 3 independent samples. Note that changes of the pre-mRNA processing events of several genes including Cob1 in the TDP-43 cKO mice are oppisite to those observed in the TDP-43(Q331K) knock-in mice (White et al. [86])
We then examined some of the differential RNA processing events by RT-qPCR and/or semi-quantitative RT-PCR (Additional file 1: Figure S8 and Figure S9). For instance, Sortilin 1 (Sort1), a member of a family of cellular vacuolar protein sorting 10 (VSP10)-domain receptors, was primarily expressed in neurons and a key player in regulating the neuronal viability and function [87]. It was proposed that TDP-43 regulates the splicing of Sort1 mRNA in mouse striatum and cell lines [58, 60]. We confirmed Sort1(wt) as the main mRNA isoform encoding sortilin in mouse cortex by RT-PCR and Western blotting (Additional file 1: Figure S9a and b). However, depletion of TDP-43 expression in the neocortex of TDP-43 cKO mice led to the accumulation at all stages of the higher molecular weight RNA isoform Sort1(e17b) encoding a non-functional progranulin receptor Sortilin 1(e17b) [60] (Additional file 1: Figure S8a, S9a and b). Quantification analysis of Sort1 mRNA levels by qRT-PCR in different mouse brain areas confirmed this observation in both 3- and 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice (Additional file 1: Figure S8a). Other events of conserved and cryptic exon inclusions induced by depletion of TDP-43 were also comfirmed by qRT-PCR, as exemplified for Dnajc5,CaMK1g,and Adnp2, respectively (Additional file 1: Figure S8). Notably, the expression levels of the wild type isoforms of Sort 1 and Dnajc5 in the cortex of TDP-43 cKO mice were unaltered (Additional file 1: Figure S9c), while those of CaMK1g and Adnp2 were unchanged in the cortex of 3-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice (upper panels, Additional file 1: Figure S9d) but moderately increased at the age of 12 months (lower panels, Additional file 1: Figure S9d).
Mis-regulation of circular RNA processing in TDP-43 cKO mice
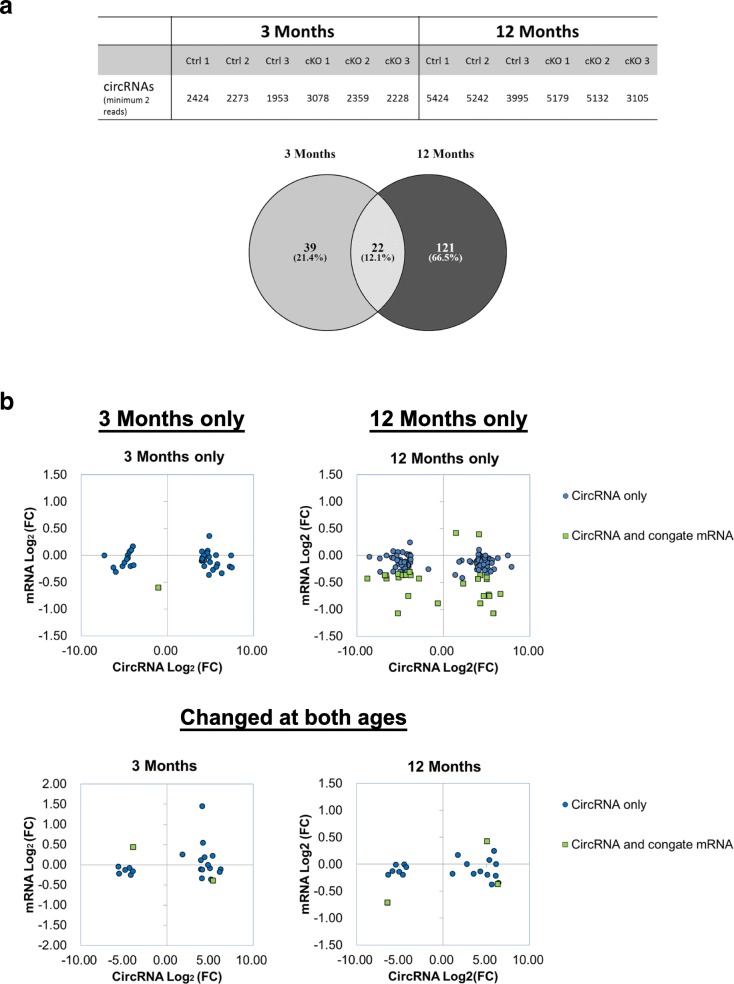
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are RNA molecules in which a covalent linkage termed a “backsplice” has formed between a downstream 3′ splice site and an upstream 5′ splice site in a linear pre-messenger RNA [73]. Previous studies have lead to the identification of thousands of circRNAs in diverse species [15, 31, 36, 67, 84] that are enriched in neuronal tissues and may play specific roles in neuronal processes [29, 65, 92]. Analysis of our RNA-seq data by the NCLscan pipeline [19] revealed that the expression levels of 182 circRNAs in the neocortex were significantly different between the TDP-43 cKO and Ctrl mice (Fig. 6 and Additional file 2: Table S1). Among them, the expression levels of 22 circRNAs were significantly altered in the neocortex of 3- as well as 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice when compared to the Ctrl mice. The levels of 39 circRNAs were changed only at the age of 3 months and 121 circRNAs were altered only at the age of 12 months (Fig. 6a and Additional file 2: Table S1). Notably, a considerable percentage of the circRNAs and their corresponding co-linear mRNA isoforms exhibited different changes of their expression levels in TDK-43 cKO in comparison to the Ctrl mice (Fig. 6b). This result reflects the previous observation that circRNAs and their co-linear counterparts could compete with each other for biogenesis during splicing [6, 16]. The biological significance of the alterations of expression levels of the circRNAs in the TDP-43 cKO mouse neocortex await to be examined.
Fig. 6.
RNA-Seq analysis of circRNAs. a Upper panel, list of the numbers of cirRNAs in the neocortex of 3 each of TDP-43 cKO and Ctrl mice at the ages of 3 months and 12 months, respectively. Lower plot, venn diagram showing the numbers of cortex circRNAs the expression levels of which were different between the TDP-43 cKO and Ctrl mice at the ages of 3 months and 12 months, respectively. Note that the levels of 22 cricRNAs were changed at both ages. b Upper panels, scatter plot showing the correlation of log2 fold change (FC, TDP-43 cKO/Ctrl) of cortex circRNAs (x axis) and their cognate linear mRNAs (y axis) the levels of which were altered in TDP-43 cKO mice only at the age of 3 months or only at the age of 12 months in comparison to Ctrls. Lower panels, scatter plot showing the correlation of log2 FC of neocortex circRNAs (x axis) and their cognate linear RNAs (y axis) the levels of which were changed at both the ages of 3 months and 12 months in TDP-43 cKO mice in comparison to Ctrls. Blue circles indicate changes of the expression levels of only the circRNAs, while green squares indicate changes of the expression levels of both the circRNAs and their cognate mRNAs counterparts
Discussion
TDP-43 proteinopathy is assocaited with more than 95% of ALS (ALS-TDP) and more than 50% of FTLD (FTLD-TDP) [47]. A gain-of-toxicity mechanism for early pathogenesis of FTLD-TDP or ALS-TDP has been suggested in view of the aberrant RNA metabolism and/or purturbed autoregulation of TDP-43 caused by mutant TDP-43 in different mouse models [5, 24, 58, 59, 86, 89]. One the other hand, a common characteristic of TDP-43 pathology at the later stage of FTLD-TDP or ALS-TDP is the loss of nuclear TDP-43 with concomitant cytoplasmic TDP-43 accumulation in neurons and glia [54]. This nuclear clearing provides a disease mechanism that is at least partially driven by the loss of normal TDP-43 function in the nucleus, as supported by studies of different mouse models with knockout or knockdown of TDP-43 expression [89, 91]. The presence of the cytoplasmic TDP-43(+) inclusions would also cause gain of one or more cytotoxic properties [44].
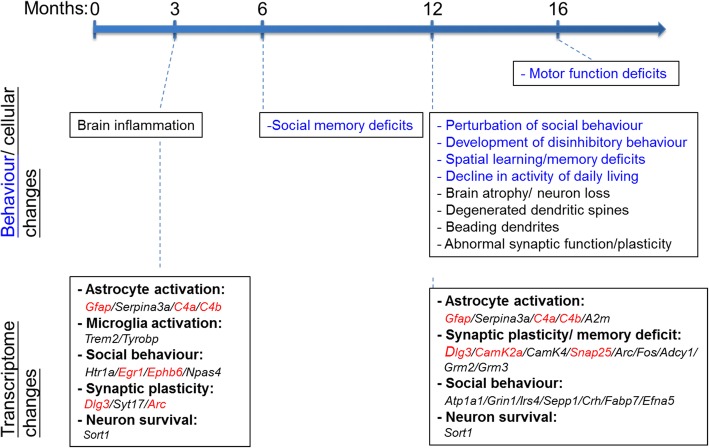
As summerized in Fig. 7, this study shows that CaMKII-directed conditional depletion of TDP-43 expression in the forebrain neurons has adverse effects on the mice, leading to shorter life span and a range of age-dependent phenotypes on the behavioural, cellular, as well as molecular levels that mimic FTLD, especially bvFTLD [61, 75]. Specifically, depletion of TDP-43 in αCaMKII-expressing neurons in the mouse forebrain (Fig. 1) results in progressive perturbation of social behaviour (Fig. 2a), development of dementia-like behaviour (Fig. 2b), and impairment of learning/memory (Fig. 2c). The behaviour deficits are accompanied with brain atrophy and neurodegeneration in the cortical hippocampal region and massive astrocytosis (Fig. 3-4). These findings together with analysis of the transcriptomes/gene expression profiles of mouse neocortex at the pre-symptomatic and post-symptomatic strages (Fig. 5, Fig. 6 and Additional file 1: Figures S5-S10) demonstrate the function of TDP-43 in cognition, and synaptic function in the adult brain. Notably, the large neurons in cortical layer V of TDP-43 cKO mice are more voulunerable to TDP-43 depletion (Fig. 4). This data is consisitent with the finding by Yang et al. [91], in which 10% reduction of TDP-43 protein level in the forebrain region of a TDP-43 knockdown mouse model could causes ~ 25% loss of large neurons in cortical layer V. Thus, there appears to be a selective vulnerability of the forebrain neurons, with distinct neuronal populations in different cortical layers compromised by the depletion of TDP-43. Notably, depletion of TDP-43 did not affect the sensory neurons of above mouse model [91]. Overall, this study demonstrates that loss-of-function of TDP-43 in the forebrain neurons would lead to a range of pathological changes of the mice on the phenotypic, molecular, and cellular levels that mimic those in FTLD-TDP.
Fig. 7.
Age-dependence of FTLD-like pathogenesis of TDP-43 cKO mice. The ages (months) of the detection of different behaviour (blue), cellular, and molecular pathologies in TDP-43 cKO mice upon conditional depletion of TDP-43 in their forebrain neurons are indicated along the time line on the top. Also listed in the 2 lower boxes are mis-regulated genes associated with specific pathogenic event, e.g. Gfap/ Serpina3a/ C4a/ C4b/ A2m and astrocyte activation, etc., are identified by RNA-Seq analysis of the TDP-43 cKO mouse neocortex on 3 and 12 months (genes altered in FTLD patients are indicated by red color), respectively. For more details, see text
Since one-fifth of the genes the expression of which are altered in TDP-43 cKO mice are also affected in FTLD patients [17] (Table 1), mis-regulation of TDP-43 RNA targets through the loss of TDP-43 function could at least in part contribute to the impairment of synaptic functions and disease pathogenesis of FTLD-TDP.
Comparison of our RNA-seq data (Table 1) to the Mouse Genome Informatics database (MGI) [8] has revealed that the mRNA levels of genes associated with anxiety-related behaviour and/ or social behaviours are significantly altered in the neocortex of TDP-43 cKO mice (Additional file 3: Table S2). Notably, Slc6a3, a gene encoding a sodium-dependent dopamine transporter and associated with anxiety disorder in autism spectrum disorder [56], is upregulated (by 4 fold) in the neocortex of TDP-43 cKO mice but only at the age of 3 months (Additional file 3: Table S2) [7, 9, 23, 28, 32, 39, 41, 50, 51, 66, 69, 90]. On the other hand, 16 of the rest 17 anxiety- and/or social behaviour–related genes listed in Additional file 3: Table S2 are up- or down-regulated in the neocortex TDP-43 cKO mice mainly at the age of 12 months when the behaviour abnormality shows up (Fig. 2). Egr1 was also demostrated in a TDP-43Q331K knockin mice at the age of 20 months (Table 1) [86].
Similarly, the cognition deficencies of the TDP-43 cKO mice are also associated with altered expression levels of specific genes, particularly those involved in synaptic transmission, as revealed by the transcriptome anaysis (Table 1 and Additional file 1: Figure S10) and electro-physiology measurement (Additional file 1: Figure S4). Besides those illustrated in Additional file 1: Figure S5, the expression level of dlg3, which encodes a major excitatory postsynaptic density protein SAP102 important in NMDARs recycling [95], is significantly down-regulated in 3-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice as compared with Ctrl mice (Table 1). In addition, several other synaptic function-associated genes, e.g. dlgap3, snap25, are down-regulated in the cortex of 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice (Table 1). Among the proteins encoded by these genes, Dlgap3 (PSD95-associated protein 3) is an excitatory postsynaptic protein implicated in the pathogenesis of obsessive-compulsive behaviours [85], and Snap-25 is a component of the SNARE protein complex and a promising cerebrospinal fluid biomarker for synapse degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease [10]. With respect to the abnormal LTP and LTD (Additional file 1: Figure S4), the protein levels of CaMKII and p-Erk (Additional file 1: Figure S5c and d) are decreased in the cortex of TDP-43 cKO mice. Altogether, it appears that combined deficiencies of the expression of a set of forebrain genes contributed to the age-dependent cognition impairment of TDP-43 cKO mice. However, down-regulation of synaptic genes could also be the results from the degeneration of the according brain region with neuron loss in TDP-43 cKO mice.
Patients with dementia (e.g., FTLD) often exhibit activation of inflammatory reponse [27]. In TDP-43 cKO mice, the progressive increase of astrocytosis in SLM region of hippocampus and RS region of the cortex (Additional file 1: Figure S3) is associated with upregulation of a range of inflammatory genes, including Gfap, C4a/C4b, Serpina3n, and A2m, at both 3- and 12 months of age (Fig. 7 and Table 1). Particularly, Serpina3n, is a marker of persistent reactive gliosis response induced in inflammation [93] and in ALS [25]. Several other genes induced in microglia activation, e.g., Cst7 and Clec7a, are also upregulated in TDP-43 cKO mice (Fig. 5d and Table 1). Taken together, the transcriptome analysis indicates that chronic neuroinflammation in TDP-43 cKO mice and by implication in FTLD-TDP patients’ results in part from mis-regulation of these genes.
Depletion of TDP-43 in the mouse forebrain also results in aberrant splicing of ~ 50 RNA transcripts in the cortex of 3- and/ or 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice (Fig. 5 and Table 2). Importantly, among these transcripts, Sort1, Adnp2, and Cdh22, the mutations or functional variants of which are associated with aging or neurodegenerative disorders [35, 42]. Furthermore, aberrant splcing of several genes including Dnajc5, Sort1, Pdp1, and Kcnip2, which also occus in TDP-43 knockdown cells of the striatum [58], does not affect the levels of their wild type mRNA isoforms (Additional file 1: Figure S9c). Consistently, the amounts of Dnajc5 protein in the cortex of TDP-43 cKO and Ctrl mice are similar (data not shown). On the other hand, the truncated sortilin protein accumulates in the cortex of TDP-43 cKO mice at different ages (Additional file 1: Figure S9b). Interestingly, decreasing the Sort1 e17b inclusion was reported by TDP-43Q331K knock-in mice with a mild FTD phenotype [86](Table 1). Since sortilin is a major neuronal APOE receptor [12], the truncated Sort1 (e17b) could act as a decoy receptor [60] competing with the wild type sortilin in the cortex of TDP-43 cKO mice thus affecting the neuronal viability and causing neurodegenertion.
Finally, cryptic exons are present in transcripts from a set of genes, including Camk1g, Hgsnat, Synj2bp, Adnp2, and Abca8b, in the neocortex of 3- and/or 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice (Table 2). Intriguingly, inclusion of the cryptic exon in CaMK1g would result in the loss-of-function of CaMK1γ that has been implicated in aging and ALS [22]. Besides CaMK1g and other gene transcripts reported previously [37, 46], we identified some novel cryptic exon inclusion events in several transcripts upon TDP-43 depletion (Table 2). Notably, cryptic exon inclusions often introduce premature termination codons (PTCs) and thereby result in nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) [34] of the inserted RNA transcripts. It has also been reported that TDP-43 could autoregulate itself through NMD [58]. Thus, we speculate that the accumulation of a portion of the cryptic exon-containing transcripts in the cortex of TDP-43 cKO mice might result from loss of TDP-43 function in NMD of these transcripts.
Conclusions
In summary, we have generated a conditional mouse model (TDP-43 cKO) with depletion of TDP-43 in the neurons of cortex and hippocampus. The TDP-43 cKO mice exhibit a spectrum of age-dependent social behaviour change, dementia-like behaviour, impairment of the cognition functions, and decline of ADL. The development of neurodegenerative pathology in TDP-43 cKO mice is closely associated with their behaviour and cognition changes, both of which are well correlated with the age-dependent alterations of the cortex transcriptomes. Notably, the transcriptomopathies of the TDP-43 cKO mouse cortex consist of changes of mRNA levels as well as pre-mRNA splicing patterns of many genes. Related to the latter changes, alternative splicing is known to play an essential role in brain function and mutations in factors involved in splicing regulation cause a range of neurological diseases [68]. Transcriptome analyse of autopsied brains from patients with ALS/FTLD reported have identified thousands of alternative splicing changes in part regulated by hnRNP [59] including TDP-43.
Overall, this study not only supports that loss-of-function of TDP-43 could be a major cause for FTLD-TDP pathogenesis, but also suggests a list of potential TDP-43 target genes that may be useful for future therapeutic development of FTLD-TDP.
Materials and methods
Generation of TDP-43 conditional knockout mouse
The Tardbp allele was knocked out specifically in the postmitotic pyramidal neurons in the forebrain by crossing mice carrying the Tardbp conditional allele (Tardbplx) with mice carrying a Cre-recombinase transgene driven by the CaMKIIα-promoter. The viability and weight of the mice were monitored regularly. Genotyping of the mice was performed by PCR of genomic DNAs from the tail biopsies.
RNA-seq analysis
For RNA-seq, the rRNA-depleted cortical RNAs from three biological replicates of sex-matched TDP-43 cKO as well as littermate Ctrl mice were converted to cDNAs and sequenced them in a strand-specific manner at National Center of Genomic Medicine (NCGM).. The RNAs were extracted from intact mouse cortical tissues and their concentrations determined using NanoDrop 8000 (Thermo Scientific). The RNA integrity was determined by Fragment Analyzer (Advanced Analytical Technologies). cDNAs from 5 μg of total RNA was used as an input material for library preparation using TruSeq RNA Sample Preparation Kit v2 (Illumina). Insert sizes of the libraries were confirmed using Fragment Analyzer (Advanced Analytical Technologies). The libraries were multiplexed and then sequenced on Illumina HiSeq2000 (Illumina) to generate 50 M of pair end 100 base pair reads per library. Data were processed using the TopHat, Cufflinks [77] and MISO [40].
RNA-seq normalization
The number of mapped fragments per kilobase of exon, per million mapped reads (FPKM) for each annotated protein-coding gene was determined to establish a metric of normalized gene expression. Approximately 80~85% of annotated protein-coding genes in mouse satisfied at least 1 FPKM in either condition. To judge the significance of differences between TDP-43 cKO and Ctrl mice, false discovery rates (q < 0.05) were used as the criteria for different replicates. The q value is an adjusted P value taking in to account the false discovery rate (FDR). We calculated the q value because the expression levels of thousands of genes from a small sample set (3 individual mice) were measured. The expression levels of transcripts in the neocortex of TDP-43 cKO mice relative to Ctrl mice were represented by log2 transformed values.
Analysis of alternative splicng
The ψ (PSI, percentage of spliced in) score was defined as the percentage of transcripts containing the alternative splicing events and/ or alternative poly(A) site usage. The mRNAs with increase of splcing events, i.e. conserved exon inclusion/ exclusion, cryptic exon inclusion, and exon extension, as well as change of poly(A) site usage are indicated by Δ ψ > 0. mRNAs with decrease of the processing events are indicated by Δ ψ < 0. Multiple t test was used to calculate the significance from data of 3 independent samples and the Holm-Sidak method was used to correct for multiple t test.
Clustering analysis of protein-coding and noncoding transcripts
For the clustering, transcripts with an estimated expression of a minimum of 0.2 FPKM in both TDP-43 cKO and Ctrl mice were selected for analysis. The list of protein-coding transcripts was compiled based on the RefSeq/Enterz/Vega definitions.
Identification and analysis of circRNAs
circRNAs were identified by NCLscan (version 1.6; https://github.com/TreesLab/NCLscan/TreesLab/NCLscan) [20], which was reported to outperform other publicly-available tools in terms of precision and to be robust to background noise [19, 94], on the basis of the mouse reference genome (GRCm38) and the GENCODE annotation (version M10). The differential expression analysis was performed by DEseq2 [2] and edgeR [64], in which the circRNA supporting reads were normalized by Relative Log Expression (RLE) and Trimmed Mean of M-values (TMM), respectively. The P values were evaluated by the Wald test (DEseq2) and the Fisher’s exact test (edgeR), and then adjusted by the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure. In this study, the significantly differential expression of circRNAs between different stages should satisfy DEseq adjusted P < 0.05 and edgeR adjusted P < 0.05 simultaneously.
Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNAs were extracted from the cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum of 3-and 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice and their Ctrl littermates (N = 6 for each genotype) using TRIzol reagents (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Synthesis of cDNA followed the manufacturer’s protocol (Invitrogen). qRT-PCR was performed using Roche qPCR FastMix (Roche). Primers were designed using a primer design software (LightCycler Probe Design Software 2.0 from Roche). The expression levels were normalized to gapdh, and data are represented as fold change relative to the Ctrl mRNA levels. Significant differences were determined using un-paired t tests.
Nesting behaviour
Single-housed mice were transferred into a new cage with nest-building material, a 5 × 5 cm square of white compressed cotton pads (Nestlets TM; Ancare, Bellmore, NY) in a random corner. After 6, 24, and 48 h, nest building was scored on a scale of 0–5, as previously described [21]. All data are shown means ± SEM and analyzed using un-paired t tests.
Social interaction test
This test has been successfully employed to study social affiliation and interest in social novelty or social discrimination (social memory). The test was performed as described previously [70]. Briefly, in the first 10-min session, a test mouse was placed in the center of the three-chamber unit, where two empty wire cages were located in the left and right chambers to habituate the test mouse. The mouse was allowed to freely explore each chamber. In the second 10-min session, an age- and gender-matched C57BL/6J mouse (S1) that had never been exposed to the test mouse, was placed in one of the two wire cages. The wire cage on the other side remained empty (E). Then, the test mouse was placed in the center, and allowed to freely explore the chamber for 10 min. The test mouse was removed and in the last 10-min session, a second age- and gender-matched C57BL/6J stranger mouse (S2) that had never been exposed to the test mouse, was placed in one wire cage, which previously served as an empty cage. Thus, the test mouse would now have the choice between a mouse that was already familiar (S1) and a new stranger mouse (S2). The test mouse was placed in the center, and allowed to freely explore the chamber for 10 min. The movement of the mouse was recorded by a camera. The recorded video file was further analyzed by off-line video tracking software (EthoVision XT 7.0). Time spent in each chamber, and time spent within a 5 cm radius proximal to each wire cage were measured. All data shown are means ± SEM and analyzed using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc analysis.
Light/ dark box test
The light–dark box was custom made (45 × 20 × 20 cm) and divided into two parts: 1/3 was painted black, covered by the lid, and separated from the white compartment by the wall containing an opening (13 × 5 cm) at the floor level. The light side was illuminated by two 40 W light bulbs 50 cm above the floor. Each mouse was released in the center of the light compartment (facing away from the opening) and allowed to explore the area for 10 min. Video tracking equipment and software (EthoVision XT 8, Noldus) were used for following the animal’s position and movement. In addition, rearings and attempts (stretched attend postures at the opening) to enter either the light or the dark compartment were recorded manually.
Rotarod rod test
Mice were trained at the age of 2 months and then subjected to rotarod test monthly. The latencies before falling from the rod was recorded for 3 consecutive days.
Immunohistochemistry and histochemmistry staining
Mice were anesthetized and perfused with 4% paraformaldehyde. The hemispheres were embedded in paraffin, sliced into 10-μm sections, and mounted on slices. For immunostaining, the sections were washed with 0.1 M PBS buffer, quenched by 1% H2O2, blocked in serum with 0.05% Triton X-100 for 30 min, and incubated in rabbit anti-TDP-43 (Genetex, 1:1000), mouse anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (1:1000), mouse anti-SMI-32 (1:1000) and mouse anti-NeuN (Milipore, 1:200) at 4 °C overnight. After rinsing in PBS, the sections were incubated with biotinnlated goat antibody (Vector) for 60 min, followed by incubation with the avidin–biotin complex (Vector) for 45 min. The reaction products were developed by 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (Sigma, St Louis, MO).
To identify the cellular localization of TDP-43, slices were combined with hematoxylin. The hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain was used to visualize the overall morphology of the mouse brain. Nissl staining was applied to characterize the hippocampus size, cortical layer thickness, and neuron number. All data are presented as the mean with standard error, and statistical significance was tested by paired t-test.
Electrophysiology
Standard protocol was followed as described previously, with some modifications. In short, the mice were decapitated and their brains rapidly removed and placed in ice-cold artificial CSF (ACSF). 450 μm thick sections of isolated mouse hippocampus were transferred into an interface-type holding chamber in oxygenated ACSF (95% O2 and 5% CO2) at room temperature to allow recovery for at least 90 min before the recording. The field excitatory postsynaptic potential (fEPSP) at Schaffer collateral branches in CA1 region of the hippocampal slices was recorded. Three trains of stimuli at 100 Hz separated by 60 s were applied for LTP induction, and low frequency stimulation (1 Hz for 15 min) were applied for LTD induction. The slopes of the fEPSP were measured and the synaptic responses were normalized to the average of the baseline. All data are presented as the mean with mean standard deviation. Statistical significance was tested by paired t-test.
Statistical analyses
GraphPad Prism software was used for most statistical analysis. The statistical significance between means of control and TDP-43 cKO mouse groups was calculated by the two-tailed Student’s t-test. For comparisons involving more than two groups, one-way or two way ANOVA were used. Data are presented as measures for group means, and P < 0.05 was considered significant. Numbers of animals per group used in each experiment are indicated in figure legends.
Additional files
Figure S1. Altered activity of daily living (ADL) of TDP-43 cKO mice. Figure S2. Immunohistochemistry staining of brain slices. Figure S3. Persisting reactive astrocytosis in TDP-43 cKO mouse forebrain. Figure S4. Electrophysiology measurements. Figure S5. Mis-regulated genes in TDP-43 cKO mice. Figure S6. Alternations of the processing events of cortical RNAs in TDP-43 cKO mice. Figure S7. The alternative uses of poly(A) sites in the cortical RNAs of TDP-43 cKO mice. Figure S8. qRT-PCR validation of RNA splicing events altered in 3- and 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice. Figure S9. Validation of altered splicing events in TDP-43 cKO mice. Figure S10. Calcium signaling and synaptic long term potentiation pathway analysis using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA). (PDF 2990 kb)
Table S1. List of the chromosome numbers, donor positions, acceptors positions and gene names of the transcripts from which the individual circularRNAs change in the neocortex of 3- and 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice, but not Ctrl mice are listed. (PDF 141 kb)
Table S2. Changes of the mRNA levels of social behaviour-related genes in the neocortex of TDP-43 cKO mice relative to Ctrl mice. (PDF 72 kb)
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Yuh-Shan Jou and Wen-Chang Lin (IBMS, Academia Sinica) for their generous gifts of experimental advices. We thank the National Center for Genome Medicine for the technical/bioinformatics/statistics support and the expertise of Hsing Tsung Wu in bioinformatic analysis is greatly appreciated. The expertise of Sue-Ping Lee and Shu-Mei Huang in the Microscopy Core at IMB and all members of Bioinformatics Core at IMB are greatly appreciated. We sincerely convey our gratitude to IMB and Academia Sinica. This work was supported by the Frontier of Science Award from the National Science Council and a Senior Investigator Award from the Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan (R.O.C.).
Authors’ contributions
L.S.W and W.C.C. designed, performed, and interpreted this study with contributions from M.C.W. performed the experiments in Fig. 3c, and d, Additional file 1: Figures S2, S4, and S5. L.S.W and Y.C.W. analyzed sequencing experiments in Fig. 4, Additional file 1: Figures S7, and S8. C.Y.C, Y.H.T and T.J.C. analyzed sequencing experiments in Fig. 5. L.S.W and C.K.S. wrote the paper, and all authors edited it. C.K.S. obtained funding for this study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Trees-Juen Chuang, Email: trees@gate.sinica.edu.tw.
C.-K. James Shen, Phone: 011-886-2-27824188, Email: ckshen@gate.sinica.edu.tw.
References
- 1.Alami NH, Smith RB, Carrasco MA, Williams LA, Winborn CS, Han SSW, Kiskinis E, Winborn B, Freibaum BD, Kanagaraj A, et al. Axonal transport of TDP-43 mRNA granules is impaired by ALS-causing mutations. Neuron. 2014;81:536–543. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Anders S, Huber W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010;11:R106. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-10-r106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Anthony K, Gallo JM. Aberrant RNA processing events in neurological disorders. Brain Res. 2010;1338:67–77. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, Ikeda K, Nonaka T, Mori H, Mann D, Tsuchiya K, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y, et al. TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;351:602–611. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Arnold ES, Ling SC, Huelga SC, Lagier-Tourenne C, Polymenidou M, Ditsworth D, Kordasiewicz HB, McAlonis-Downes M, Platoshyn O, Parone PA, et al. ALS-linked TDP-43 mutations produce aberrant RNA splicing and adult-onset motor neuron disease without aggregation or loss of nuclear TDP-43. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:E736–E745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222809110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR, Ivanov A, Bartok O, Hanan M, Evantal N, Memczak S, Rajewsky N, Kadener S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell. 2014;56:55–66. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bianco SD, Peng JB, Takanaga H, Suzuki Y, Crescenzi A, Kos CH, Zhuang L, Freeman MR, Gouveia CH, Wu J, et al. Marked disturbance of calcium homeostasis in mice with targeted disruption of the Trpv6 calcium channel gene. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22:274–285. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.061110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Blake JA, Eppig JT, Kadin JA, Richardson JE, Smith CL, Bult CJ, the Mouse Genome Database G Mouse genome database (MGD)-2017: community knowledge resource for the laboratory mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:D723–D729. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Blundell J, Kaeser PS, Sudhof TC, Powell CM. RIM1alpha and interacting proteins involved in presynaptic plasticity mediate prepulse inhibition and additional behaviors linked to schizophrenia. J Neurosci. 2010;30:5326–5333. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0328-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brinkmalm A, Brinkmalm G, Honer WG, Frolich L, Hausner L, Minthon L, Hansson O, Wallin A, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, et al. SNAP-25 is a promising novel cerebrospinal fluid biomarker for synapse degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurodegener. 2014;9:53. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-9-53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Burrell JR, Kiernan MC, Vucic S, Hodges JR. Motor neuron dysfunction in frontotemporal dementia. Brain. 2011;134:2582–2594. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Carlo AS, Gustafsen C, Mastrobuoni G, Nielsen MS, Burgert T, Hartl D, Rohe M, Nykjaer A, Herz J, Heeren J, et al. The pro-neurotrophin receptor sortilin is a major neuronal apolipoprotein E receptor for catabolism of amyloid-beta peptide in the brain. J Neurosci. 2013;33:358–370. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2425-12.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen BS, Gray JA, Sanz-Clemente A, Wei Z, Thomas EV, Nicoll RA, Roche KW. SAP102 mediates synaptic clearance of NMDA receptors. Cell Rep. 2012;2:1120–1128. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.09.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen D, Fan W, Lu Y, Ding X, Chen S, Zhong Q. A mammalian autophagosome maturation mechanism mediated by TECPR1 and the Atg12-Atg5 conjugate. Mol Cell. 2012;45:629–641. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.12.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen I, Chen CY, Chuang TJ. Biogenesis, identification, and function of exonic circular RNAs. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2015;6:563–579. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chen LL, Yang L. Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2015;12:381–388. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1020271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chen-Plotkin AS, Geser F, Plotkin JB, Clark CM, Kwong LK, Yuan W, Grossman M, Van Deerlin VM, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM. Variations in the progranulin gene affect global gene expression in frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:1349–1362. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chen-Plotkin AS, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. TAR DNA-binding protein 43 in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010;6:211–220. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2010.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chuang TJ, Wu CS, Chen CY, Hung LY, Chiang TW, Yang MY. NCLscan: accurate identification of non-co-linear transcripts (fusion, trans-splicing and circular RNA) with a good balance between sensitivity and precision. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:e29. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Crawley J, Goodwin FK. Preliminary report of a simple animal behavior model for the anxiolytic effects of benzodiazepines. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1980;13:167–170. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(80)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Deacon RM. Assessing nest building in mice. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:1117–1119. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Deng M, Wei L, Zuo X, Tian Y, Xie F, Hu P, Zhu C, Yu F, Meng Y, Wang H, et al. Genome-wide association analyses in Han Chinese identify two new susceptibility loci for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Genet. 2013;45:697–700. doi: 10.1038/ng.2627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ferguson JN, Aldag JM, Insel TR, Young LJ. Oxytocin in the medial amygdala is essential for social recognition in the mouse. J Neurosci. 2001;21:8278–8285. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-20-08278.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fratta P, Sivakumar P, Humphrey J, Lo K, Ricketts T, Oliveira H, Brito-Armas JM, Kalmar B, Ule A, Yu Y et al (2018) Mice with endogenous TDP-43 mutations exhibit gain of splicing function and characteristics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. EMBO J 37. 10.15252/embj.201798684 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 25.Fukada Y, Yasui K, Kitayama M, Doi K, Nakano T, Watanabe Y, Nakashima K. Gene expression analysis of the murine model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: studies of the Leu126delTT mutation in SOD1. Brain Res. 2007;1160:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.05.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ghidoni R, Paterlini A, Albertini V, Binetti G, Benussi L. Losing protein in the brain: the case of progranulin. Brain Res. 2012;1476:172–182. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Glass CK, Saijo K, Winner B, Marchetto MC, Gage FH. Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell. 2010;140:918–934. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Glynn D, Gibson HE, Harte MK, Reim K, Jones S, Reynolds GP, Morton AJ. Clorgyline-mediated reversal of neurological deficits in a Complexin 2 knockout mouse. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19:3402–3412. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gruner H, Cortes-Lopez M, Cooper DA, Bauer M, Miura P. CircRNA accumulation in the aging mouse brain. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38907. doi: 10.1038/srep38907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gulino R, Forte S, Parenti R, Gulisano M. TDP-43 as a modulator of synaptic plasticity in a mouse model of spinal Motoneuron degeneration. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2015;14:55–60. doi: 10.2174/1871527314666150116115414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Guo JU, Agarwal V, Guo H, Bartel DP. Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014;15:409. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0409-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hagihara H, Horikawa T, Nakamura HK, Umemori J, Shoji H, Kamitani Y, Miyakawa T. Circadian gene circuitry predicts hyperactive behavior in a mood disorder mouse model. Cell Rep. 2016;14:2784–2796. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.02.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Igaz LM, Kwong LK, Lee EB, Chen-Plotkin A, Swanson E, Unger T, Malunda J, Xu Y, Winton MJ, Trojanowski JQ, et al. Dysregulation of the ALS-associated gene TDP-43 leads to neuronal death and degeneration in mice. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:726–738. doi: 10.1172/JCI44867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jangi M, Sharp PA. Building robust transcriptomes with master splicing factors. Cell. 2014;159:487–498. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jansen P, Giehl K, Nyengaard JR, Teng K, Lioubinski O, Sjoegaard SS, Breiderhoff T, Gotthardt M, Lin F, Eilers A, et al. Roles for the pro-neurotrophin receptor sortilin in neuronal development, aging and brain injury. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1449–1457. doi: 10.1038/nn2000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK, Burd CE, Liu J, Marzluff WF, Sharpless NE. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA. 2013;19:141–157. doi: 10.1261/rna.035667.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jeong YH, Ling JP, Lin SZ, Donde AN, Braunstein KE, Majounie E, Traynor BJ, LaClair KD, Lloyd TE, Wong PC. Tdp-43 cryptic exons are highly variable between cell types. Mol Neurodegener. 2017;12:13. doi: 10.1186/s13024-016-0144-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kaidanovich-Beilin O, Lipina T, Vukobradovic I, Roder J, Woodgett JR (2011) Assessment of social interaction behaviors. J Vis Exp. 10.3791/2473 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 39.Kataoka M, Yamamori S, Suzuki E, Watanabe S, Sato T, Miyaoka H, Azuma S, Ikegami S, Kuwahara R, Suzuki-Migishima R, et al. A single amino acid mutation in SNAP-25 induces anxiety-related behavior in mouse. PLoS One. 2011;6:e25158. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Katz Y, Wang ET, Airoldi EM, Burge CB. Analysis and design of RNA sequencing experiments for identifying isoform regulation. Nat Methods. 2010;7:1009–1015. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ko SW, Ao HS, Mendel AG, Qiu CS, Wei F, Milbrandt J, Zhuo M. Transcription factor Egr-1 is required for long-term fear memory and anxiety. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2005;57:421–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kushnir M, Dresner E, Mandel S, Gozes I. Silencing of the ADNP-family member, ADNP2, results in changes in cellular viability under oxidative stress. J Neurochem. 2008;105:537–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.LaClair KD, Donde A, Ling JP, Jeong YH, Chhabra R, Martin LJ, Wong PC. Depletion of TDP-43 decreases fibril and plaque beta-amyloid and exacerbates neurodegeneration in an Alzheimer's mouse model. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;132:859–873. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1637-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lagier-Tourenne C, Cleveland DW. Rethinking ALS: the FUS about TDP-43. Cell. 2009;136:1001–1004. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lee EB, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Gains or losses: molecular mechanisms of TDP43-mediated neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;13:38–50. doi: 10.1038/nrn3121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ling JP, Pletnikova O, Troncoso JC, Wong PC. TDP-43 repression of nonconserved cryptic exons is compromised in ALS-FTD. Science. 2015;349:650–655. doi: 10.1126/science.aab0983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ling SC, Polymenidou M, Cleveland DW. Converging mechanisms in ALS and FTD: disrupted RNA and protein homeostasis. Neuron. 2013;79:416–438. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.07.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Luscher C, Malenka RC (2012) NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation and long-term depression (LTP/LTD). Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4. 10.1101/cshperspect.a005710 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 49.Majumder P, Chu JF, Chatterjee B, Swamy KB, Shen CJ. Co-regulation of mRNA translation by TDP-43 and fragile X syndrome protein FMRP. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;132:721–738. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1603-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Masana MI, Sumaya IC, Becker-Andre M, Dubocovich ML. Behavioral characterization and modulation of circadian rhythms by light and melatonin in C3H/HeN mice homozygous for the RORbeta knockout. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;292:R2357–R2367. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00687.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Miyakawa T, Leiter LM, Gerber DJ, Gainetdinov RR, Sotnikova TD, Zeng H, Caron MG, Tonegawa S. Conditional calcineurin knockout mice exhibit multiple abnormal behaviors related to schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:8987–8992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1432926100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Neary D, Snowden JS, Gustafson L, Passant U, Stuss D, Black S, Freedman M, Kertesz A, Robert PH, Albert M, et al. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a consensus on clinical diagnostic criteria. Neurology. 1998;51:1546–1554. doi: 10.1212/WNL.51.6.1546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Neumann M, Igaz LM, Kwong LK, Nakashima-Yasuda H, Kolb SJ, Dreyfuss G, Kretzschmar HA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM. Absence of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins and survival motor neuron protein in TDP-43 positive inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;113:543–548. doi: 10.1007/s00401-007-0221-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT, Bruce J, Schuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM, et al. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science. 2006;314:130–133. doi: 10.1126/science.1134108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ou SH, Wu F, Harrich D, Garcia-Martinez LF, Gaynor RB. Cloning and characterization of a novel cellular protein, TDP-43, that binds to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 TAR DNA sequence motifs. J Virol. 1995;69:3584–3596. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.6.3584-3596.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Perona MT, Waters S, Hall FS, Sora I, Lesch KP, Murphy DL, Caron M, Uhl GR. Animal models of depression in dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine transporter knockout mice: prominent effects of dopamine transporter deletions. Behav Pharmacol. 2008;19:566–574. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e32830cd80f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Philips T, Rothstein JD (2015) Rodent models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Curr Protoc Pharmacol 69: 5 67 61-21 Doi 10.1002/0471141755.ph0567s69 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 58.Polymenidou M, Lagier-Tourenne C, Hutt KR, Huelga SC, Moran J, Liang TY, Ling SC, Sun E, Wancewicz E, Mazur C, et al. Long pre-mRNA depletion and RNA missplicing contribute to neuronal vulnerability from loss of TDP-43. Nat Neurosci. 2011;14:459–468. doi: 10.1038/nn.2779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Prudencio M, Belzil VV, Batra R, Ross CA, Gendron TF, Pregent LJ, Murray ME, Overstreet KK, Piazza-Johnston AE, Desaro P, et al. Distinct brain transcriptome profiles in C9orf72-associated and sporadic ALS. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18:1175–1182. doi: 10.1038/nn.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Prudencio M, Jansen-West KR, Lee WC, Gendron TF, Zhang YJ, Xu YF, Gass J, Stuani C, Stetler C, Rademakers R, et al. Misregulation of human sortilin splicing leads to the generation of a nonfunctional progranulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:21510–21515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1211577110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Rascovsky K, Hodges JR, Knopman D, Mendez MF, Kramer JH, Neuhaus J, van Swieten JC, Seelaar H, Dopper EG, Onyike CU, et al. Sensitivity of revised diagnostic criteria for the behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia. Brain. 2011;134:2456–2477. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Ratti A, Buratti E. Physiological functions and pathobiology of TDP-43 and FUS/TLS proteins. J Neurochem. 2016;138(Suppl 1):95–111. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Roberson ED. Mouse models of frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol. 2012;72:837–849. doi: 10.1002/ana.23722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:139–140. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Rybak-Wolf A, Stottmeister C, Glazar P, Jens M, Pino N, Giusti S, Hanan M, Behm M, Bartok O, Ashwal-Fluss R, et al. Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant, conserved, and dynamically expressed. Mol Cell. 2015;58:870–885. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.03.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Sadakata T, Shinoda Y, Oka M, Sekine Y, Furuichi T. Autistic-like behavioral phenotypes in a mouse model with copy number variation of the CAPS2/CADPS2 gene. FEBS Lett. 2013;587:54–59. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.10.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Salzman J, Gawad C, Wang PL, Lacayo N, Brown PO. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS One. 2012;7:e30733. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Scotti MM, Swanson MS. RNA mis-splicing in disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17:19–32. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2015.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Shum FW, Ko SW, Lee YS, Kaang BK, Zhuo M. Genetic alteration of anxiety and stress-like behavior in mice lacking CaMKIV. Mol Pain. 2005;1:22. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-1-22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Silverman JL, Yang M, Lord C, Crawley JN. Behavioural phenotyping assays for mouse models of autism. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11:490–502. doi: 10.1038/nrn2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Sotrel A, Williams RS, Kaufmann WE, Myers RH. Evidence for neuronal degeneration and dendritic plasticity in cortical pyramidal neurons of Huntington's disease: a quantitative Golgi study. Neurology. 1993;43:2088–2096. doi: 10.1212/WNL.43.10.2088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Swann JW, Al-Noori S, Jiang M, Lee CL. Spine loss and other dendritic abnormalities in epilepsy. Hippocampus. 2000;10:617–625. doi: 10.1002/1098-1063(2000)10:5<617::AID-HIPO13>3.0.CO;2-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Szabo L, Salzman J. Detecting circular RNAs: bioinformatic and experimental challenges. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17:679–692. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2016.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Takao K, Miyakawa T (2006) Light/dark transition test for mice. J Vis Exp 104. 10.3791/104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 75.Tan RH, Ke YD, Ittner LM, Halliday GM. ALS/FTLD: experimental models and reality. Acta Neuropathol. 2017;133:177–196. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1666-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Taylor JP, Brown RH, Jr, Cleveland DW. Decoding ALS: from genes to mechanism. Nature. 2016;539:197–206. doi: 10.1038/nature20413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL, Pachter L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and cufflinks. Nat Protoc. 2012;7:562–578. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Tsai KJ, Yang CH, Fang YH, Cho KH, Chien WL, Wang WT, Wu TW, Lin CP, Fu WM, Shen CK. Elevated expression of TDP-43 in the forebrain of mice is sufficient to cause neurological and pathological phenotypes mimicking FTLD-U. J Exp Med. 2010;207:1661–1673. doi: 10.1084/jem.20092164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Tsien JZ, Chen DF, Gerber D, Tom C, Mercer EH, Anderson DJ, Mayford M, Kandel ER, Tonegawa S. Subregion- and cell type-restricted gene knockout in mouse brain. Cell. 1996;87:1317–1326. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81826-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Van Mossevelde S, Engelborghs S, van der Zee J, Van Broeckhoven C. Genotype-phenotype links in frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Nat Rev Neurol. 2018;14:363–378. doi: 10.1038/s41582-018-0009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Vorhees CV, Williams MT. Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:848–858. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Wang HY, Wang IF, Bose J, Shen CK. Structural diversity and functional implications of the eukaryotic TDP gene family. Genomics. 2004;83:130–139. doi: 10.1016/S0888-7543(03)00214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Wang IF, Wu LS, Shen CK. TDP-43: an emerging new player in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Mol Med. 2008;14:479–485. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2008.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Wang PL, Bao Y, Yee MC, Barrett SP, Hogan GJ, Olsen MN, Dinneny JR, Brown PO, Salzman J. Circular RNA is expressed across the eukaryotic tree of life. PLoS One. 2014;9:e90859. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Welch JM, Lu J, Rodriguiz RM, Trotta NC, Peca J, Ding JD, Feliciano C, Chen M, Adams JP, Luo J, et al. Cortico-striatal synaptic defects and OCD-like behaviours in Sapap3-mutant mice. Nature. 2007;448:894–900. doi: 10.1038/nature06104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.White MA, Kim E, Duffy A, Adalbert R, Phillips BU, Peters OM, Stephenson J, Yang S, Massenzio F, Lin Z, et al. TDP-43 gains function due to perturbed autoregulation in a Tardbp knock-in mouse model of ALS-FTD. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21:552–563. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0113-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Willnow TE, Petersen CM, Nykjaer A. VPS10P-domain receptors - regulators of neuronal viability and function. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9:899–909. doi: 10.1038/nrn2516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Wu LS, Cheng WC, Hou SC, Yan YT, Jiang ST, Shen CK. TDP-43, a neuro-pathosignature factor, is essential for early mouse embryogenesis. Genesis. 2010;48:56–62. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Wu LS, Cheng WC, Shen CK. Targeted depletion of TDP-43 expression in the spinal cord motor neurons leads to the development of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-like phenotypes in mice. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:27335–27344. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.359000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Xu X, Coats JK, Yang CF, Wang A, Ahmed OM, Alvarado M, Izumi T, Shah NM. Modular genetic control of sexually dimorphic behaviors. Cell. 2012;148:596–607. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.12.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Yang C, Wang H, Qiao T, Yang B, Aliaga L, Qiu L, Tan W, Salameh J, McKenna-Yasek DM, Smith T et al (2014) Partial loss of TDP-43 function causes phenotypes of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111: E1121–E1129 10.1073/pnas.1322641111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 92.You X, Vlatkovic I, Babic A, Will T, Epstein I, Tushev G, Akbalik G, Wang M, Glock C, Quedenau C, et al. Neural circular RNAs are derived from synaptic genes and regulated by development and plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18:603–610. doi: 10.1038/nn.3975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Zamanian JL, Xu L, Foo LC, Nouri N, Zhou L, Giffard RG, Barres BA. Genomic analysis of reactive astrogliosis. J Neurosci. 2012;32:6391–6410. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6221-11.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Zeng X, Lin W, Guo M, Zou Q. A comprehensive overview and evaluation of circular RNA detection tools. PLoS Comput Biol. 2017;13:e1005420. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Zheng CY, Seabold GK, Horak M, Petralia RS. MAGUKs, synaptic development, and synaptic plasticity. Neuroscientist. 2011;17:493–512. doi: 10.1177/1073858410386384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. Altered activity of daily living (ADL) of TDP-43 cKO mice. Figure S2. Immunohistochemistry staining of brain slices. Figure S3. Persisting reactive astrocytosis in TDP-43 cKO mouse forebrain. Figure S4. Electrophysiology measurements. Figure S5. Mis-regulated genes in TDP-43 cKO mice. Figure S6. Alternations of the processing events of cortical RNAs in TDP-43 cKO mice. Figure S7. The alternative uses of poly(A) sites in the cortical RNAs of TDP-43 cKO mice. Figure S8. qRT-PCR validation of RNA splicing events altered in 3- and 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice. Figure S9. Validation of altered splicing events in TDP-43 cKO mice. Figure S10. Calcium signaling and synaptic long term potentiation pathway analysis using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA). (PDF 2990 kb)
Table S1. List of the chromosome numbers, donor positions, acceptors positions and gene names of the transcripts from which the individual circularRNAs change in the neocortex of 3- and 12-month-old TDP-43 cKO mice, but not Ctrl mice are listed. (PDF 141 kb)
Table S2. Changes of the mRNA levels of social behaviour-related genes in the neocortex of TDP-43 cKO mice relative to Ctrl mice. (PDF 72 kb)