Abstract
Molecular crowding, a ubiquitous feature of the cellular environment, has significant implications in the kinetics and equilibrium of biopolymer interactions. In this study, a single charged polypeptide is exposed to competing forces that drive it into a transmembrane protein pore versus forces that pull it outside. Using single-molecule electrophysiology, we provide compelling experimental evidence that the kinetic details of the polypeptide-pore interactions are substantially affected by high concentrations of less-penetrating polyethylene glycols (PEGs). At a polymer concentration above a critical value, the presence of these neutral macromolecular crowders increases the rate constant of association, but decreases the rate constant of dissociation, resulting in a stronger polypeptide-pore interaction. Moreover, a larger-molecular weight PEG exhibits a lower rate constant of association, but a higher rate constant of dissociation than those values corresponding to a smaller-molecular weight PEG. These outcomes are in accord with a lower diffusion constant of the polypeptide and higher depletion - attraction forces between the polypeptide and transmembrane protein pore under crowding and confinement conditions.
Keywords: α-hemolysin, peptide-protein interactions, single-molecule kinetics, single-channel electrical recordings, free-energy landscape, polymer
Graphical Abstract
A cellular milieu is filled with numerous hydrophilic macromolecules that contribute to a high weight per volume concentration.1 Macromolecular crowding plays an essential role in many cellular processes, such as protein folding, stability, and dynamics. In addition, crowding has implications in other critical phenomena, including reaction kinetics and biochemical equilibria.2–4 The major mechanism by which crowding agents influence transport properties and reactivity features of biopolymers is the excluded volume effect.4, 5 Crowding is highly significant in interactions of polypeptides with protein pores, porins and channels.6 One such example is the N-terminus peptide at the tip of the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) protein, which is a monomeric β barrel.7 Introducing polymers to an in vitro experiment can be an example of excluded volume effect. Therefore, we question how crowding polymers affect the kinetics and equilibrium of the interactions between a polypeptide and a transmembrane protein pore. These interactions can be detected by monitoring the changes that occur in transmembrane ionic current as a result of the application of a voltage bias.6, 8-18 However, crowding agents, such as neutral, water-soluble, and flexible polymers, partition into a nanoscale protein pore in a size-dependent manner.19-24 Given this interesting property, recent studies have highlighted the importance of selective pore penetration by smaller polymers against larger, less-penetrating polymers.25 Aksoyoglu and colleagues26 have systematically documented that in a nonideal binary polymer mixture easily penetrating polymers are pushed into the pore lumen by relatively less-penetrating polymers.
In this study, we investigated the effect of large, less-penetrating polyethylene glycols (PEGs) on the interactions between a charged polypeptide and the interior of staphylococcal α-hemolysin (αHL) pore, a heptameric protein of known X-ray crystal structure.27 This protein comprises a roughly spherical vestibule located in the extramembranous side and a transmembrane, 14-stranded β barrel with an average internal diameter of ~20 Å (Fig. 1). As a test case, we used Syn B2, a 23-residue cationic signal-sequence polypeptide,28, 29 which features five positive elementary charges at physiological pH. This positive polypeptide interacts with the slightly anionic β-barrel of αHL,30, 31 producing large-amplitude current blockades.32 Here, these current blockades are employed to determine how PEGs of varying molecular size affect the Syn B2 - αHL interactions. This study demonstrates that the single-molecule kinetic details of these interactions are significantly affected by the presence of less-penetrating PEGs. Specifically, both the rate constant of association, kon, and dissociation, koff, of the Syn B2 - αHL interactions depend on the PEG molecular size and its concentration. Finally, we developed a semiquantitative method for determining the partition coefficient of the polypeptide into the pore interior and found a synergistic effect of the electrostatic and depletion – attraction forces on these interactions under crowding and confinement conditions.
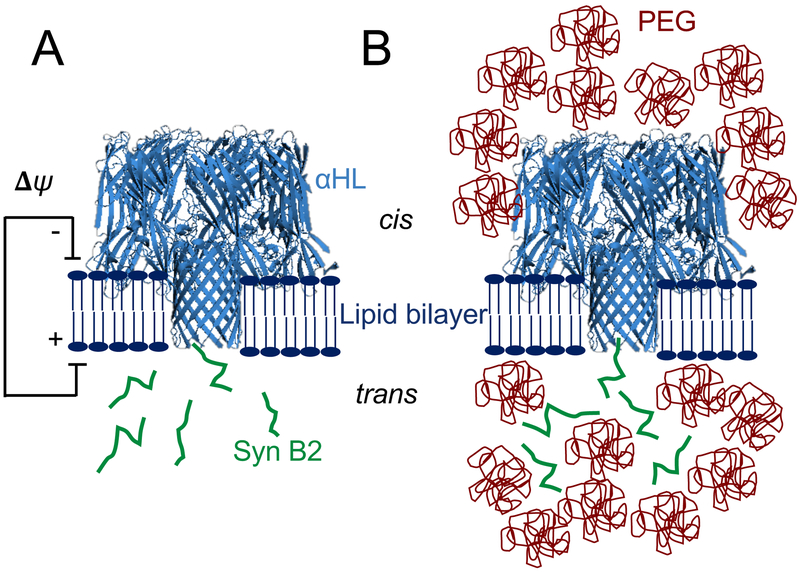
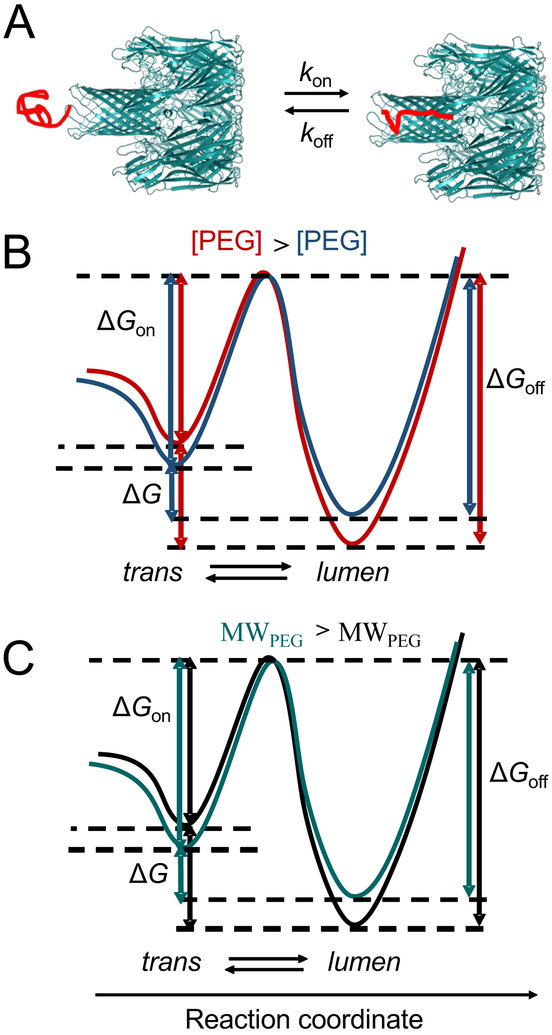
Figure 1: Interaction between a positively charged Syn B2 polypeptide with a single αHL protein pore.
(A) Syn B2 is electrically pulled into the pore lumen of the αHL protein as a result of the application of a transmembrane potential. Syn B2 was added to the trans side of the lipid bilayer; (B) Syn B2 polypeptide partition into the pore lumen as a result of an electrostatic pulling force and a PEG-induced pushing force deriving from osmotic pressure.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Polymer partitioning into a nanopore depends on its molecular size and concentration.
Electrical recordings were acquired using a single αHL protein pore reconstituted into a planar lipid bilayer (Fig. 1).28 Here, all experiments were conducted in 300 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, and at an applied transmembrane potential of +80 mV. Under these conditions, the αHL protein pore showed a quiet open-state current with a unitary conductance of 0.29 ± 0.01 nS (n=7 distinct experiments; (Supporting Information, Fig. S1). However, the open-state current of αHL became unstable in the presence of high-concentration PEGs at a greater voltage than +80 mV (see below). We then systematically analyzed single-channel electrical recordings acquired in the presence of 2,000 Da PEG (PEG-2k), 4,000 Da PEG (PEG-4k), or 8,000 Da PEG (PEG-8k) added to both sides of the chamber. The average hydrodynamic radii of these polymers are greater than the internal diameter of the narrow transmembrane β-barrel region of the αHL protein (Fig. 1).19 Since PEG is a neutral polymer at a low-salt concentration,26, 33 we further assume that there is no electrostatic interaction between PEG and Syn B2. The presence of PEGs at a high concentration affected the stability of the open-state unitary current of αHL at an applied transmembrane potential of +100 mV regardless of the PEG molecular size (Supporting Information, Fig S2). Furthermore, the presence of PEGs produced frequent current noise fluctuations and a concentration-dependent alteration in the unitary conductance, as elaborated below.
The unitary conductance of the αHL protein pore in the presence of PEGs is a critical parameter, which indicates the polymers' ability to partition or not into the pore interior.19 Therefore, we then determined the normalized single-channel conductance, GN ([PEG]):
| (1) |
where G([PEG]) and G([0]) are the recorded single-channel conductance values of αHL at a certain PEG concentration, [PEG], and in the absence of PEG, respectively. In this article, [PEG] is reported in weight per volume (w/v) units. A normalized single-channel conductance lower than 1 would only occur when PEGs partition into the pore lumen, because they decrease the conductivity of the solution with respect to PEG-free bulk phase.19, 26, 34-38 On the contrary, a normalized unitary conductance greater than 1 would indicate that PEGs do not partition into the pore interior, because of the enhancement in the local salt concentration within the PEG-unoccupied volume.19, 26, 39
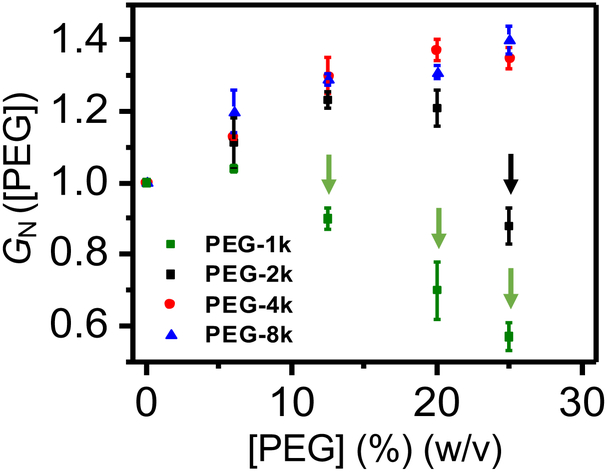
We determined that PEG-2k did not partition into the pore lumen in 300 mM KCl and at [PEG-2k] of up to 20% (w/v) (Fig. 2; Supporting Information, Table S1). This outcome contrasts to an earlier finding that PEG-2k is indeed an easily-penetrating polymer into αHL at 1 M NaCl.19, 34 Such a difference in polymer partitioning into αHL can be readily explained by the fact that a higher salt concentration increases the polymer partitioning due to electro-osmotic forces.14, 30, 40 GN ([PEG-2k]) followed a significant decrease to 0.88 ± 0.05 at a concentration of 25% (w/v), confirming that PEG-2k is indeed a penetrating polymer at these salt and polymer concentrations. Furthermore, PEG-1k did partition into the pore lumen for all inspected concentrations, except for 6% (w/v) PEG-1k, where GN is slightly higher than 1. Taken together, these findings show that our data are in good accord with previously published studies.19, 34 Furthermore, this outcome highlights the significance of salt concentration effect on partitioning of PEGs into nanopores.40
Figure 2: Normalized conductance of the αHL protein pore, GN ([PEG]).
Here, GN ([PEG]) = (G([PEG]))/(G([0])), where G([0]) was the measured unitary conductance in 300 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 7.4, and G([PEG]) was the measured unitary conductance in the presence of PEG-1k (green squares), PEG-2k (black squares), PEG-4k (red circles) or PEG-8k (blue triangles) added symmetrically to both sides of the chamber. The vertical arrows highlight cases in which the normalized conductance of the αHL protein pore in the presence of PEG, GN, is smaller than 1. For these cases, PEGs are easily-penetrating polymers. The applied transmembrane potential was +80 mV.
Our normalized conductance test also suggested that neither PEG-4k nor PEG-8k partitioned into the pore lumen at a polymer concentration in the range 0 - 25% (w/v). GN rose to ~1.4 at 25% (w/v) PEG-8k (Fig. 2). This value is slightly higher than normalized conductance values previously determined at higher salt concentrations. For example, Sergey Bezrukov and co-workers measured a GN value of ~1.1 at 15% (w/w) PEGs of greater molecular weight (≥ 3 kDa) and in 1 M NaCl.19 These distinctive experimental outcomes can also be explained by a smaller relative change in the electrolyte activity at a higher salt concentration with respect to that values determined at a lower salt concentration. Moreover, the presence of PEGs on both sides of the chamber increased the single-channel current noise fluctuations in the form of short-lived and low-amplitude current blockades. These blockades most likely resulted from very brief collisions of PEGs with the pore opening.21, 41 They exhibited an average dwell time of 0.033 ± 0.005 ms (mean ± s.d.; n = 9 distinct experiments) and a normalized current blockade (I/I0) within the range 0.5 - 0.6 (n = 9) (Supporting Information, Fig. S3). Here, I and I0 are the amplitudes of the current blockades and open-state unitary current, respectively. In the following sections of this article, since PEG is considered as a neutral polymer in a low-salt concentration solution, the effect of macromolecular crowding is reduced to the physical confinement of the free polypeptide.
The Syn B2 - αHL interactions under crowding conditions.
We then examined the effect of less-penetrating PEGs (PEG-4k and PEG-8k) on the Syn B2-αHL interactions. These polymers did not partition into the pore lumen for the 0 – 25% (w/v) range of the PEG concentrations. In the absence of PEGs, the addition of 20 μM Syn B2 to the trans side of the αHL pore (Fig. 1) led to single-channel current blockades with a frequency, dwell time, and normalized current blockade (I/I0) of 4.2 ± 0.5 s−1, 0.30 ± 0.04 ms, and 0.76 ± 0.03 (mean ± s.d.; n = 6), respectively (Supporting Information, Fig. S4, Table S2). However, in the presence of 25% (w/v) PEG-4k Syn B2-induced current blockades exhibited an average frequency, dwell time, and normalized current blockade of ~27 s−1, 0.80 ± 0.20 ms, and ~0.82 (n = 8), respectively. These values were determined using a low-pass Bessel frequency of 5 kHz. Brief PEG-induced current blockades in the low-microsecond time range were removed for an improved signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and further data analysis. A low-pass Bessel filtering process of the single-channel electrical trace at a frequency of 1 kHz, whose corresponding dead time is ~183 μs,21, 42 removed most short-lived and low-amplitude PEG-4k-induced current spikes without affecting the dwell time of the Syn B2-produced events (Supporting Information, Fig. S5). Using this approach, we noted that the event frequency and dwell time of Syn B2-induced current blockades were 29.3 ± 0.8 s−1 and 0.72 ± 0.10 ms (mean ± s.d.; n = 5), respectively, at a filter frequency of 1 kHz (Supporting Information, Fig. S6, Table S2). Therefore, the short-lived PEG-induced current blockades were ignored in further data analysis, as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS.
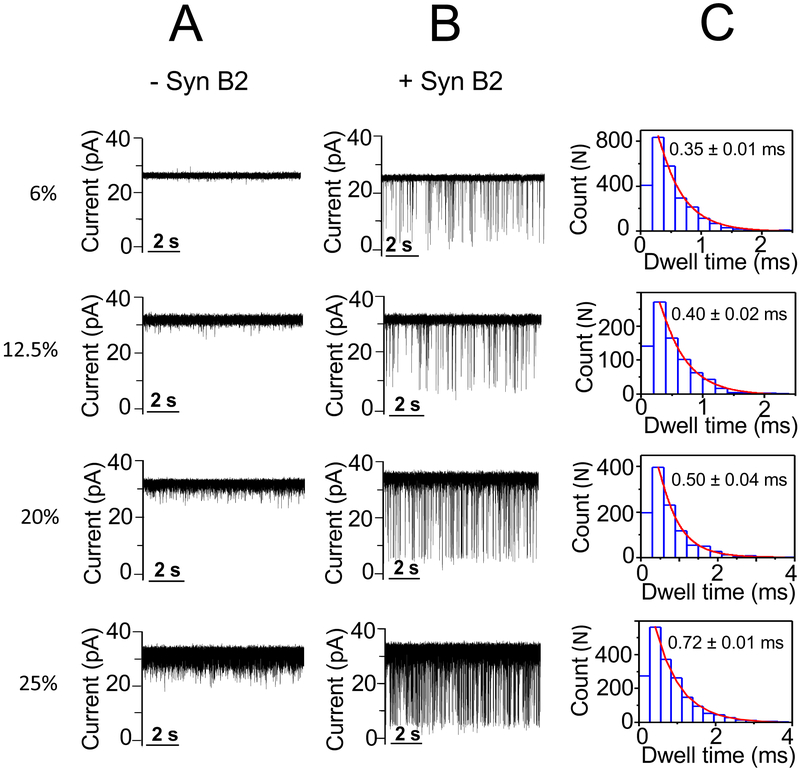
No statistically significant alterations in the event frequency and dwell time of the Syn B2-induced current blockades were produced by 6% (w/v) PEG-4k with respect to that value acquired in a PEG-free solution, as follows: 5.0 ± 0.7 s−1 and 0.35 ± 0.01 ms (mean ± s.d.; n = 3), respectively (Fig. 3; Supporting Information, Table S2, Fig. S6). In contrast, enhancement in both the event frequency and dwell time values were recorded at 20% (w/v) and 25% (w/v) PEG-4k. In accord with these results noted with PEG-4k, both the event frequency and dwell time values of the Syn B2-induced current blockades increased at elevated PEG-8k concentrations (Fig. 4; Supporting Information, Table S2, Fig. S6). These findings suggest that indeed the excluded-volume effect of the less-penetrating PEGs is the most likely mechanism for affecting the Syn B2-αHL interactions. Specifically, at semi-dilute concentration regime the presence of these crowding PEGs induces a depletion interaction43-46 that causes an effective attraction force between Syn B2 and αHL. This attraction force leads to a higher probability of Syn B2-αHL interactions and a longer Syn B2 capture into the pore lumen. Our results are in excellent agreement with prior studies of Kozer and coworkers.43 They have discovered relatively faster association rate constants of transient protein-protein interactions in polymer solutions at semi-dilute regime with respect to kinetic data acquired in a polymer-free solution.
Figure 3: Single-channel electrical recordings of the αHL protein pore in the presence of Syn B2 and in PEG-4k-containing solutions.
(A) The figure illustrates representative single-channel electrical traces in the absence of Syn B2, but in the presence of PEG-4k of varying concentration; (B) Representative single-channel electrical traces acquired when 20 μM Syn B2 was added to the trans side and in the presence of PEG-4k of varying concentration; (C) Representative dwell time histograms of the Syn B2-induced current blockades obtained at each examined PEG concentration. The fittings of the dwell-time histograms were executed using a single-exponential probability function. They were validated by a logarithm likelihood ratio (LLR) test.57, 58 Single-channel electrical traces were processed using a 1 kHz low-pass Bessel filter. The [PEG-4k] values are indicated on the left side. PEGs were symmetrically added to both sides of the chamber. The other experimental conditions were the same as those stated in the caption of Fig. 2.
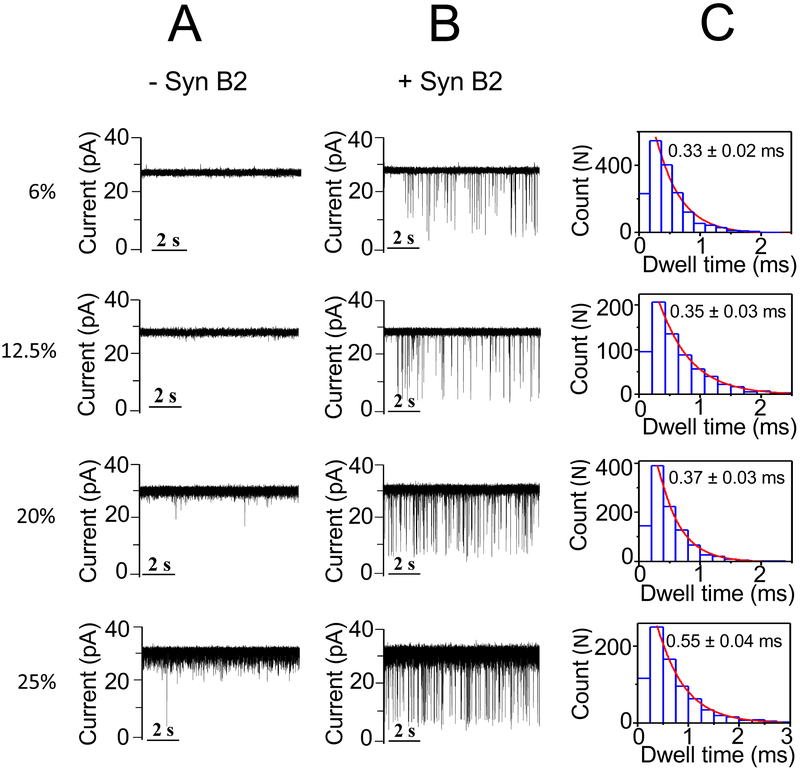
Figure 4: Single-channel electrical recordings of the αHL protein pore in the presence of Syn B2 and in PEG-8k-containing solutions.
(A) The figure illustrates representative single-channel electrical traces in the absence of Syn B2, but in the presence of PEG-8k of varying concentration; (B) Representative single-channel electrical traces acquired when 20 μM Syn B2 was added to the trans side and in the presence of PEG-8k of varying concentration; (C) Representative dwell time histograms of the Syn B2-induced current blockades obtained at each examined PEG concentration. The fittings of the dwell-time histograms were executed using a single-exponential probability function. They were validated by a logarithm likelihood ratio (LLR) test.57, 58 Single-channel electrical traces were processed using a 1 kHz low-pass Bessel filter. The [PEG-8k] values are indicated on the left side. PEGs were symmetrically added to both sides of the chamber. The other experimental conditions were the same as those stated in the caption of Fig. 2.
In the above results section, we determined that an increase in the event frequency of the Syn B2-induced current blockades is directly related to a greater depletion – attraction force at an elevated concentration of these less-penetrating PEGs. Here, we compared data acquired with PEG-4k and PEG-8k at concentrations within a range of 0 - 25% (w/v) (Supporting Information, Table S2). Interestingly, at increased PEG concentrations of 12.5, 20, and 25% (w/v), these event frequencies and dwell times are smaller for PEG-8k than those values recorded with PEG-4k (Fig. 3, Fig. 4, Supporting Information, Table S2, Fig. S6). For example, the event frequency and dwell time of the Syn B2-induced current blockades in the presence of 20% (w/v) PEG-4k were 12.5 ± 0.6 s−1 and 0.50 ± 0.04 ms (mean ± s.d.; n = 4), respectively. Under the same conditions, these values recorded in the presence of 20% (w/v) PEG-8k were 9.1 ± 1.4 s−1 and 0.37 ± 0.03 ms (mean ± s.d.; n = 4), respectively. This outcome can be explained in terms of differences in osmotic pressures exerted by PEGs of varying molecular size. Specifically, at a given PEG concentration (in w/v), the osmotic pressure produced by a lower-molecular weight PEG (e.g., more-penetrating PEG) is greater than that value produced by a larger-molecular weight PEG (e.g., less-penetrating PEG).23, 26, 47 For instance, at 25% (w/v) PEG concentration, the osmotic pressures produced by PEG-2k, PEG-4k, and PEG-8k are 314, 260, and 229 mOsmol/l, respectively.47 The physiological osmotic pressure is about 300 mOsmol/l.48 Therefore, these interaction parameters are not only affected by high concentrations of less-penetrating PEGs, but also by the polymers’ size.
Furthermore, these Syn B2-induced current transitions were examined in the presence of more-penetrating PEG-2k, whose molecular weight is relatively smaller than that of Syn B2 (e.g., Mw (Syn B2) = 2.9 kDa; Supporting Information, Fig. S7). A [PEG-2k] range of 0 - 20% (w/v) was inspected because 25% (w/v) PEG-2k penetrated the pore lumen, as judged by the recorded value of normalized conductance, GN (Fig. 2, Supporting Information, Table S1). In this case, the event frequency and dwell time values were 8.9 ± 1.4 s−1 and 0.40 ± 0.03 ms at 12.5% (w/v) PEG-2k (mean ± s.d.; n = 5), respectively (Supporting Information, Table S2). On the other hand, we noted that these values were 18.9 ± 2.3 s−1 and 0.56 ± 0.03 at 20% (w/v) PEG-2k (mean ± s.d.; n = 3), respectively. Data acquired for more-penetrating PEG-2k are in accord with an increase in the event frequency and dwell time at either a higher PEG concentration of the same molecular weight polymer or a lower-molecular weight polymer of the same PEG concentration. It should be noted that the effects of the PEG molecular size on the event frequency and dwell time are qualitatively distinctive when the molarity of PEGs is considered. For example, at a concentration of ~30 mM PEG, the frequency and dwell time produced by PEG-8k are greater than those values acquired with PEG-4k and PEG-2k (Supporting Information, Fig. S8). In other words, at a given number density of PEG molecules, the larger-molecular weight PEGs have a greater impact on the Syn B2-induced current blockades than that determined by the smaller-molecular weight PEGs. This outcome agrees well with an enhanced osmotic pressure of larger molecular-size PEGs at a constant PEG molarity.49
Syn B2 was added to the trans side (Fig. 1), but it might exit through either the trans or cis opening of the αHL protein pore. It has been previously shown that the dwell time of the polypeptide-αHL interactions exhibits a biphasic behavior with a maximum value reached at a critical transmembrane potential, Vc.28, 50 At a voltage bias lower than Vc, most current blockades are accompanied by polypeptide exit events toward the side of polypeptide addition (e.g., in this case the trans side). In contrast, at a voltage bias greater than Vc, most current blockades are followed by polypeptide exit events toward the opposite side. The frequencies of the trans and cis exit events depend on how different is the applied transmembrane potential with respect to Vc.50 In good accord with these prior studies, we found that the dwell time of Syn B2-induced current blockades in a PEG-free solution exhibited a biphasic pattern with a maximum value of ~0.9 ms, corresponding to a Vc of +180 mV (Supporting Information, Fig. S9). The high Vc value suggests a significant energetic barrier of the positively charged Syn B2 polypeptide29, 32 to traverse the slightly anion-selective β-barrel of the αHL protein.30, 31 Therefore, at a transmembrane potential of +80 mV, which is much lower than Vc, the polypeptide exits the pore lumen with a preferred direction through the trans opening. However, the addition of PEGs at a high concentration to both sides of the chamber caused an instability of the open-state unitary current of the αHL pore at a voltage bias of +100 mV (Supporting Information, Fig. S2). This instability of the open-state unitary current precluded the acquisition of the voltage dependence of event dwell time in the presence of PEGs at semi-dilute regime. It should be observed that PEG induced an increased event frequency and dwell time at a transmembrane potential of +80 mV with respect to that value determined in a PEG-free solution (Supporting Information, Table S2). The most significant PEG-induced modifications were noticed in the presence of 25% (w/v) PEG-4k. In this case, the event frequency and dwell time of Syn B2-induced current blockades, which were acquired at +80 mV, are closely similar to those determined in a PEG-free solution at +140 mV (Supporting Information, Table S2, Fig. S9). Again, this finding reveals strong attraction interactions between Syn B2 and αHL in the presence of less-penetrating PEGs at semi-dilute concentration regime.
Partition coefficient of Syn B2 into a nanopore under crowding conditions.
We then explored the partition coefficient (Π) of the Syn B2 polypeptide into the αHL protein pore in a PEG-free solution and in the presence of the PEGs of varying molecular size. Π was calculated using the following equation:21
| (1) |
where NA and Vbarrel are Avogadro’s number and nanopore volume, respectively. For the β-barrel of the αHL protein pore, Vbarrel is ~10,000 Å3.21, 27 Toccupied indicates the total time in which the polypeptide spends inside the pore lumen during the entire time of recording, Ttotal. Csol is the polypeptide concentration in solution. At a low occupancy,21
| (2) |
where [C]*=1/(NA Vbarrel). Therefore, [C]* is ~0.17 M. Here, Kd is the equilibrium dissociation constant:
| (3) |
where kon and koff are the kinetic rate constants of association and dissociation of the Syn B2-αHL interactions, respectively. Therefore, the partition coefficient was calculated using the following expression:
| (4) |
Here, τon and τoff denote the inter-event duration and dwell time of the Syn B2-produced current blockades, respectively. In this case, event frequency is the reciprocal of τon.
In a PEG-free solution, the partition coefficient of Syn B2 into the αHL pore at a transmembrane potential of +80 mV was 10.5 ± 1.9 (mean ± s.d.; n = 7) (Supporting Information, Fig. S10A, Table S3). This result agrees well with a prior determination of the partition coefficient of an alanine-rich peptide of a closely similar length and charge.50 Π is ~10 at a voltage bias of +100 mV and in 1 M KCl. A significant effect of the electrostatic pulling force on Π was noted. Thus, its calculated values at applied transmembrane potentials of +100 and +160 mV were 26.3 ± 3.5 and 272 ± 40 (mean ± s.d.; n = 3), respectively. Moreover, we found a substantial effect of less-penetrating PEGs on Π when [PEG] was at semi-dilute regime. For example, the partition coefficient calculated at +80 mV in a solution incubated with 25% (w/v) PEG-4k was almost identical to that value observed at +150 mV in a PEG-free solution (Supporting Information, Fig. S10B, Table S4). Furthermore, Π was 88 ± 12 (mean ± s.d.; n = 6), 52 ± 5 (mean ± s.d.; n = 4), and 28 ± 5 (mean ± s.d.; n = 7) in the presence of 20% (w/v) PEG-2k, PEG-4k, and PEG-8k, respectively. Therefore, a smaller-molecular weight PEG produces a significant increase in the partition coefficient. The vice-versa is true for a higher-molecular size PEG. Interestingly, Π determined for 6% (w/v) PEG-8k and 12.5% (w/v) PEG-8k was comparable with that value acquired in a PEG-free solution.
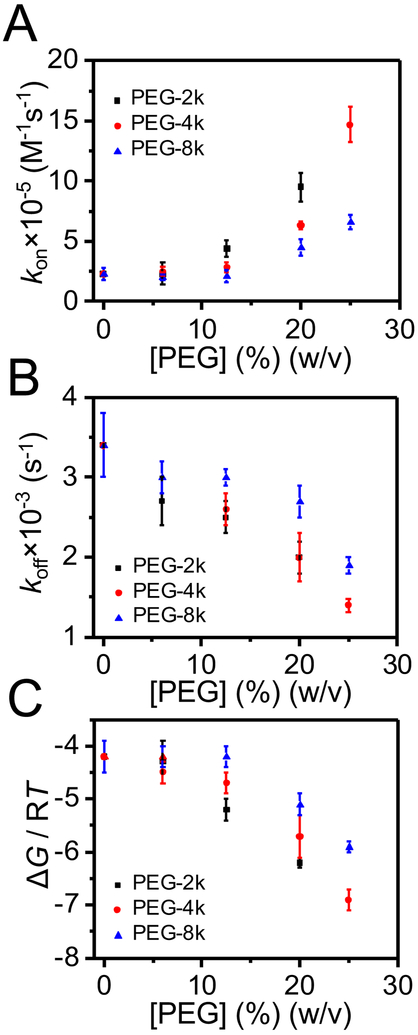
The kinetic rate constant, koff, is the sum of kofftrans and koffcis, which denote the rate constants of dissociation through the trans and cis openings of the pore, respectively.32 Because most Syn B2 exit events occur across the trans opening of the pore, kofftrans >> koffcis. Fig. 5A illustrates the dependence of the kinetic rate constant of association, kon, on the concentration of PEGs of varying molecular size. Interestingly, the kon value is unaltered in the lower PEG concentration regime (e.g., 0 - 12.5% (w/v)) of less-penetrating PEG-4k and PEG-8k (Supporting Information, Table S5). The association rate constant is given by:51
| (5) |
Here, kD and kreact denote the kinetic rate constants under diffusion and reaction (or transition-state) control, respectively. At dilute regime of [PEG], viscosity of the solution reduces the translational diffusion coefficient, lowering the kD. In contrast, the PEG-induced osmotic force increases the capture rate of Syn B2 by the αHL protein pore, enhancing the kreact.43 Therefore, we judge that in the regime of low concentrations of less-penetrating PEG-4k and PEG-8k, there are compensatory effects of viscosity and osmotic forces. Conversely, at highly increased PEG concentrations (at semi-dilute regime), greater than 12.5% (w/v), the depletion – attraction forces between Syn B2 and αHL exert a dominant role, amplifying the reaction rate constant. On the other hand, the koff value is unchanged for 0 - 6% (w/v) PEG-2k, 0 - 12.5% (w/v) PEG-4k, or 0 - 20% (w/v) PEG-8k (Fig. 5B). We then determined the values of the binding free energy, ΔG, using the values of kon and koff (Supporting Information, Table S5) as well as eq. (3) and standard thermodynamic relationship between the equilibrium dissociation constant, Kd, and ΔG (e.g., ΔG = RT lnKd). These values are presented in Fig. 5C.
Figure 5: Single-molecule kinetics of the Syn B2-αHL interactions.
(A) The dependence of the kinetic rate constant of association, kon, on the concentration of less-penetrating PEGs; (B) The dependence of the kinetic rate constant of dissociation, koff, on the concentration of less-penetrating PEGs; (C) Free energy, ΔG, of the Syn B2-αHL complex formation in the presence of PEG-2k (black squares), PEG-4k (red circles) and PEG-8k (blue triangles). PEGs were symmetrically added to both sides of the chamber. The other experimental conditions were the same as those stated in the caption of Fig. 2.
CONCLUSIONS
We represented the free-energy landscape of the capture-release transitions of the Syn B2 polypeptide from an αHL protein pore. These single-molecule transitions primarily occurred between the “trans” and “lumen” substates (Fig. 6A). It should be noted that a voltage bias tilts the free-energy landscape, reducing the energetic barrier of the polypeptide to enter the pore.50 At semi-dilute regime, an increase in the concentration of less-penetrating PEGs produces a depletion interaction45, 46 that leads to an attractive force43, 44 between Syn B2 and αHL. In this case, the PEG chains entangle and capture Syn B2 into the polymer mesh. At increased PEG concentrations, there is an entropic repulsion among polymers. Syn B2 and αHL feature depletion layers, whose thickness depends on the PEG molecular size. This entropic repulsion among the mass centers of PEGs converts into an attraction force between Syn B2 and αHL when they get sufficiently close to each other, so that their depletion layers overlap. This attraction force represents the molecular basis for a higher probability of the Syn B2-αHL interactions and a longer Syn B2 capture into the pore lumen. In other words, an increased concentration of the less-penetrating PEGs produces an elevated kon, but a reduced koff. These changes correspond to a decrease in the activation free energy of the capture events, ΔGon, but an increase in the activation free energy of the release events, ΔGoff (Fig. 6B). Given these conditions, an increase in the concentration of less-penetrating PEGs results in an increase in the binding free energy, ΔG. On the other hand, for a given PEG concentration, an increase in the molecular weight of PEGs produces a slower capture transition (e.g., a reduced kon), but a faster release transition (e.g., an amplified koff) (Fig. 6C). This results in a decrease in the binding free energy. The opposite is true for a decrease in the molecular size of less-penetrating PEGs. This is because for a given PEG concentration, the osmotic pressure determined by a lower-molecular weight PEG (e.g., more-penetrating PEG) is greater than that value determined by a higher-molecular weight PEG (e.g., less-penetrating PEG).23, 26, 47
Figure 6: Free energy profile of the Syn B2-αHL interactions.
(A) Cartoon showing the two substates of the Syn B2 polypeptides, in the trans conformation (“trans”) and under nanopore confinement (“lumen”); (B) Qualitative representation of the free energy profile at an increased concentration of less-penetrating PEGs; (C) Qualitative representation of the free energy profile at an increased PEG molecular size.
All experiments in this work were conducted in 300 mM KCl, because we wanted to bring the salt concentration near to physiological condition. Yet, the αHL protein pore exhibits irregular, short-lived current fluctuations in 150 mM KCl.52 Here, we found that high-concentration PEGs also reduce the stability of open-state conductance even in 300 mM KCl. These instabilities in the open-state conductance are amplified by an elevated positive voltage bias and might likely be detrimental for further data analysis of experiments in the presence of Syn B2 and less-penetrating PEGs. Therefore, we used a slightly increased salt concentration with respect to physiological condition. In this case, the intrinsic voltage-induced gating fluctuations of the αHL protein pore were absent at a physiological potential.42 On the other hand, a 1 M KCl salt concentration would substantially enhance the SNR. Under these conditions, it is likely that other details might be unraveled, which are not otherwise apparent at a reduced SNR that corresponds to 300 mM KCl. We speculate that a 1 M KCl salt concentration will not qualitatively change our model. This postulation relies upon comparisons and contrasts between the outcomes of this work and those obtained in previously published studies at various salt concentrations.19, 23, 40 Specifically, the data points illustrated in Fig. 2, which pertain to normalized conductance in the presence of less-penetrating PEGs, will be shifted to lower values at increased salt concentrations. Quantitatively, a higher salt concentration would favor an increase in the partition coefficient due to electroosmotic flow.30, 31 Finally, there is no theoretical reason to believe that the impacts of the PEG molecular size and concentration on the Syn B2-αHL interactions would qualitatively be altered under these conditions. This is reasoned by the fact that our kinetic and equilibrium data agree well with the changes in PEG-induced osmotic pressure.
In summary, we show that the presence of less-penetrating PEGs at increased concentrations greater than a critical value produces significant alterations in the kinetics and equilibrium of the interactions of a positively charged polypeptide with a protein nanopore. Macromolecular crowding lowers the energy barrier for polypeptide partitioning, amplifying the association rate constant. In contrast, modest changes in the dissociation rate constant are brought about by macromolecular crowding, which is in accord with prior studies on other protein-protein interactions.51 Correspondingly, this results in a stronger polypeptide-pore interaction that depends on both the PEG concentration and polymer’s molecular size. Enhanced polypeptide-pore interactions pertain to an increased osmotic pressure and depletion – attraction forces that usually occur in transient protein-protein complex formations under crowding conditions.43 We think that the outcomes of this study are applicable to other polypeptide-pore systems. The kinetic rate constants and partitioning data specifically depend on the physicochemical features of inspected polypeptides.28 In future, this approach might be applied to other studies that involve weak-affinity reactants, enhancing their binding durations40, 53, 54 for satisfactory signal resolution and data analysis in single-molecule detection.55
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Poly(ethylene glycols) (PEGs) of average molecular weight 2,000 Da (PEG-2k), 4,000 Da (PEG-4k) and 8,000 Da (PEG-8k) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). α-hemolysin (αHL) was also obtained from Sigma-Aldrich. The cationic 23-residue polypeptide Syn B2,28, 29 whose sequence is the following: MLSRQQSQRQSRQQSQRQSRYLL (Mw = 2.9 kDa), was purchased from Peptide 2.0 Inc. (Chantilly, VA). The identity and purity of Syn B2 were confirmed by the C18 reversed-phase HPLC and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry prior to use (Peptide 2.0 Inc.). Single-channel electrical recordings were performed as previously described.56 Both the cis and trans compartments of the chamber were filled with the buffer solution containing 300 mM KCl, 10mM Tris, pH 7.4. In the experiments that included PEGs, different concentrations of PEG solutions, which ranged from 6% to 25% (w/v) in the above-mentioned buffer solution, were symmetrically added to both sides of the chamber. A lipid bilayer of 1,2-diphytanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (Avanti Polar Lipids, Alabaster, AL) was formed across the 100 μm-wide aperture on a 25 μm-thick Teflon partition (Goodfellow Corporation, Malvern, PA). The aperture was pretreated with 5% (v/v) hexadecane (Sigma-Aldrich) dissolved in pentane (Fisher HPLC grade, Fair Lawn, NJ). A protein sample of αHL was added to the cis side to a final concentration of 0.03 ng/μl. The cis side was grounded and a positive current (upward deflection) represents positive charge moving from the trans to cis side. Upon insertion of a single channel, the polypeptide was added to the trans side of the membrane at a final concentration of 20 μM. Single-channel electrical traces were recorded using a patch-clamp amplifier (Axopatch 200B, Axon instrument, Foster City, CA) in the wholecell mode with a CV-203BU headstage. A PC desktop was equipped with a DigiData 1440 A/D converter (Axon) for data acquisition. The signal was low-pass Bessel filtered at a frequency of 10 kHz using an 8-pole low-pass Bessel filter (Model 900, Frequency Devices, Ottawa, IL) and digitized at a rate of 50 kHz. To remove the current blockades created by PEG, all the electrical traces were filtered at a frequency of 1 kHz. Data acquisition was processed using pClamp 10 (Axon). Clampfit 10.6 (Axon) and Origin 8.6 (Microcal Software, Northampton, MA) were used for data analysis and representation, respectively. Dwell-time histograms were fitted with a single-exponential probability function, as they were validated by a logarithm likelihood ratio (LLR) test.57, 58 The association rate constant, kon, was calculated using the equation: kon = 1/(τonCsol), where τon and Csol are the inter-event duration and final peptide concentration in solution, respectively. The dissociation rate constant, koff, was derived using the equation: koff = 1/τoff, where τoff denotes the residence time of the Syn B2 polypeptide within the pore lumen. Free energy of this interaction, ΔG, was calculated using the equation: ΔG = RT ln Kd = RT ln koff /kon, where R and T are the general gas constant and absolute temperature, respectively. Here, Kd indicates the equilibrium dissociation constant.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors would like to thank A. Thakur for his assistance during the very early stages of this project. This research project was supported by US National Institutes of Health grants GM088403 (to L.M.) and GM129429 (to L.M.), and the National Science Foundation grant REU DMR-1460784 (to L.A.M.).
Footnotes
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. (i) αHL exhibits a quiet single-channel electrical current in a PEG-free solution; (ii) αHL closes at increased transmembrane potentials in the presence of less-penetrating PEGs; (iii) Dependence of the normalized unitary conductance on the PEG molecular weight and PEG concentration; (iv) 1 kHz low-pass Bessel filter eliminates the very brief current blockades produced by PEGs; (v) Less-penetrating PEGs affect the Syn B2-αHL interactions; (vi) The Syn B2-αHL interactions depend on the applied transmembrane potential; (vii) Dependence of the partition coefficient of the Syn B2 polypeptide into the αHL protein pore on the PEG concentration and PEG molecular size; (viii) Single-molecule kinetics of the Syn B2-αHL interactions in PEG-containing solutions. These materials are available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org
REFERENCES
- 1.Rivas G; Minton AP, Macromolecular Crowding In Vitro, In Vivo, and In Between. Trends Biochem. Sci 2016, 41, 970–981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rivas G; Minton AP, Toward an Understanding of Biochemical Equilibria within Living Cells. Biophys. Rev 2018, 10, 241–253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.van Oijen AM; Dixon NE, Probing Molecular Choreography through Single-Molecule Biochemistry. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 2015, 22, 948–952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Minton AP, Quantitative Assessment of the Relative Contributions of Steric Repulsion and Chemical Interactions to Macromolecular Crowding. Biopolymers 2013, 99, 239–244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chen Y; Luo K, Dynamics of Polymer Translocation Through a Nanopore Induced by Different Sizes of Crowding Agents. J. Chem. Phys 2013, 138, 204903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hoogerheide DP; Gurnev PA; Rostovtseva TK; Bezrukov SM, Real-Time Nanopore-Based Recognition of Protein Translocation Success. Biophys. J 2018, 114, 772–776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shuvo SR; Ferens FG; Court DA, The N-terminus of VDAC: Structure, Mutational Analysis, and a Potential Role in Regulating Barrel Shape. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 1350–1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.T.C S; Long YT; Stefureac RI; Bediako-Amoa I; Kraatz HB; Lee JS, Structure of Peptides Investigated by Nanopore Analysis. Nano Lett. 2005, 4, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Goodrich CP; Kirmizialtin S; Huyghues-Despointes BM; Zhu AP; Scholtz JM; Makarov DE; Movileanu L, Single-Molecule Electrophoresis of Beta-Hairpin Peptides by Electrical Recordings and Langevin Dynamics Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 3332–3335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Movileanu L, Squeezing a Single Polypeptide through a Nanopore. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 925–931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Movileanu L, Interrogating Single Proteins through Nanopores: Challenges and Opportunities. Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 333–341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mereuta L; Roy M; Asandei A; Lee JK; Park Y; Andricioaei I; Luchian T, Slowing Down Single-Molecule Trafficking Through a Protein Nanopore Reveals Intermediates for Peptide Translocation. Sci. Rep 2014, 4, 3885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Asandei A; Schiopu I; Chinappi M; Seo CH; Park Y; Luchian T, Electroosmotic Trap Against the Electrophoretic Force Near a Protein Nanopore Reveals Peptide Dynamics During Capture and Translocation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 13166–13179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Huang G; Willems K; Soskine M; Wloka C; Maglia G, Electro-Osmotic Capture and Ionic Discrimination of Peptide and Protein Biomarkers with FraC Nanopores. Nat. Commun 2017, 8, 935–945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Waduge P; Hu R; Bandarkar P; Yamazaki H; Cressiot B; Zhao Q; Whitford PC; Wanunu M, Nanopore-Based Measurements of Protein Size, Fluctuations, and Conformational Changes. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 5706–5716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chavis AE; Brady KT; Hatmaker GA; Angevine CE; Kothalawala N; Dass A; Robertson JWF; Reiner JE, Single Molecule Nanopore Spectrometry for Peptide Detection. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1319–1328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Piguet F; Ouldali H; Pastoriza-Gallego M; Manivet P; Pelta J; Oukhaled A, Identification of Single Amino Acid Differences in Uniformly Charged Homopolymeric Peptides with Aerolysin Nanopore. Nat. Commun 2018, 9, 966–978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Varongchayakul N; Song J; Meller A; Grinstaff MW, Single-Molecule Protein Sensing in a Nanopore: a Tutorial. Chem. Soc. Rev 2018, 47, 8512–8524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bezrukov SM; Vodyanoy I; Brutyan RA; Kasianowicz JJ, Dynamics and Free Energy of Polymers Partitioning into a Nanoscale Pore. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 8517–8522. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Movileanu L; Bayley H, Partitioning of a Polymer into a Nanoscopic Protein Pore Obeys a Simple Scaling Law. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 2001, 98, 10137–10141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Movileanu L; Cheley S; Bayley H, Partitioning of Individual Flexible Polymers into a Nanoscopic Protein Pore. Biophys. J 2003, 85, 897–910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Slonkina E; Kolomeisky AB, Polymer Translocation Through a Long Nanopore. J. Chem. Phys 2003, 118, 7112–7118. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Krasilnikov OV; Bezrukov SM, Polymer Partitioning from Nonideal Solutions into Protein Voids. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 2650–2657. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gurnev PA; Stanley CB; Aksoyoglu MA; Hong K; Parsegian VA; Bezrukov SM, Poly(ethylene Glycol)s in Semidilute Regime: Radius of Gyration in the Bulk and Partitioning into a Nanopore. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 2477–2483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Podgornik R; Hopkins J; Parsegian VA; Muthukumar M, Polymers Pushing Polymers: Polymer Mixtures in Thermodynamic Equilibrium with a Pore. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 8921–8928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Aksoyoglu MA; Podgornik R; Bezrukov SM; Gurnev PA; Muthukumar M; Parsegian VA, Size-Dependent Forced PEG Partitioning into Channels: VDAC, OmpC, and Alpha-Hemolysin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 2016, 113, 9003–9008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Song LZ; Hobaugh MR; Shustak C; Cheley S; Bayley H; Gouaux JE, Structure of Staphylococcal Alpha-Hemolysin, a Heptameric Transmembrane Pore. Science 1996, 274, 1859–1866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wolfe AJ; Mohammad MM; Cheley S; Bayley H; Movileanu L, Catalyzing the Translocation of Polypeptides Through Attractive Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2007, 129, 14034–14041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mohammad MM; Movileanu L, Excursion of a Single Polypeptide into a Protein Pore: Simple Physics, but Complicated Biology. Eur. Biophys. J 2008, 37, 913–925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gu LQ; Cheley S; Bayley H, Electroosmotic Enhancement of the Binding of a Neutral Molecule to a Transmembrane Pore. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 2003, 100, 15498–15503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Menestrina G, Ionic Channels Formed by Staphylococcus-Aureus Alpha-Toxin - Voltage-Dependent Inhibition by Divalent and Trivalent Cations. J. Membr. Biol 1986, 90, 177–190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bikwemu R; Wolfe AJ; Xing X; Movileanu L, Facilitated Translocation of Polypeptides Through a Single Nanopore. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 454117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Stojilkovic KS; Berezhkovskii AM; Zitserman VY; Bezrukov SM, Conductivity and Microviscosity of Electrolyte Solutions Containing Polyethylene Glycols. J. Chem. Phys 2003, 119, 6973–6978. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bezrukov SM; Kasianowicz JJ, The Charge State of an Ion Channel Controls Neutral Polymer Entry Into its Pore. Eur. Biophys. J. Biophys.Lett 1997, 26, 471–476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Movileanu L; Cheley S; Howorka S; Braha O; Bayley H, Location of a Constriction in the Lumen of a Transmembrane Pore by Targeted Covalent Attachment of Polymer Molecules. J. Gen. Physiol 2001, 117, 239–251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Reiner JE; Kasianowicz JJ; Nablo BJ; Robertson JW, Theory for Polymer Analysis using Nanopore-Based Single-Molecule Mass Spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 2010, 107, 12080–12085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Niedzwiecki DJ; Mohammad MM; Movileanu L, Inspection of the Engineered FhuA deltaC/delta4L Protein Nanopore by Polymer Exclusion. Biophys. J 2012, 103, 2115–2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mohammad MM; Iyer R; Howard KR; McPike MP; Borer PN; Movileanu L, Engineering a Rigid Protein Tunnel for Biomolecular Detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2012, 134, 9521–9531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bezrukov SM; Vodyanoy I, Probing Alamethicin Channels with Water-Soluble Polymers - Effect on Conductance of Channel States. Biophys. J 1993, 64, 16–25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rodrigues CG; Machado DC; Chevtchenko SF; Krasilnikov OV, Mechanism of KCl Enhancement in Detection of Nonionic Polymers by Nanopore Sensors. Biophys. J 2008, 95, 5186–5192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Krasilnikov OV; Rodrigues CG; Bezrukov SM, Single Polymer Molecules in a Protein Nanopore in the Limit of a Strong Polymer-Pore Attraction. Phys. Rev. Lett 2006, 97, 018301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sackmann B; Neher E, Single-Channel Recording. Second Edition ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kozer N; Kuttner YY; Haran G; Schreiber G, Protein-Protein Association in Polymer Solutions: from Dilute to Semidilute to Concentrated. Biophys. J 2007, 92, 2139–2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Phillip Y; Sherman E; Haran G; Schreiber G, Common Crowding Agents Have only a Small Effect on Protein-Protein Interactions. Biophys. J 2009, 97, 875–885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sapir L; Harries D, Origin of Enthalpic Depletion Forces. J. Phys. Chem. Lett 2014, 5, 1061–1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sapir L; Harries D, Macromolecular Stabilization by Excluded Cosolutes: Mean Field Theory of Crowded Solutions. J. Chem. Theor. Comput 2015, 11, 3478–3490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Reid C; Rand RP, Fits to Osmotic Pressure Data. Biophys. J 1997, 73, 1692–1694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rasouli M, Basic Concepts and Practical Equations on Osmolality: Biochemical Approach. Clin. Biochem 2016, 49, 936–941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Money NP, Osmotic Pressure of Aqueous Polyethylene Glycols : Relationship Between Molecular Weight and Vapor Pressure Deficit. Plant Physiol. 1989, 91, 766–769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Movileanu L; Schmittschmitt JP; Scholtz JM; Bayley H, Interactions of the Peptides with a Protein Pore. Biophys. J 2005, 89, 1030–1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Zhou HX; Rivas G; Minton AP, Macromolecular Crowding and Confinement: Biochemical, Biophysical, and Potential Physiological Consequences. Annu. Rev. Biophys 2008, 37, 375–397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Mohammad MM; Movileanu L, Impact of Distant Charge Reversals within a Robust Beta-Barrel Protein Pore. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, I114, 8750–8759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Robertson JW; Rodrigues CG; Stanford VM; Rubinson KA; Krasilnikov OV; Kasianowicz JJ, Single-Molecule Mass Spectrometry in Solution using a Solitary Nanopore. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 2007, 104, 8207–8211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Baaken G; Halimeh I; Bacri L; Pelta J; Oukhaled A; Behrends JC, High-Resolution Size-Discrimination of Single Nonionic Synthetic Polymers with a Highly Charged Biological Nanopore. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6443–6449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Thakur AK; Movileanu L, Real-Time Measurement of Protein-Protein Interactions at Single-Molecule Resolution using a Biological Nanopore. Nat. Biotechnol 2019, 37, 96–101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Thakur AK; Larimi MG; Gooden K; Movileanu L, Aberrantly Large Single-Channel Conductance of Polyhistidine Arm-Containing Protein Nanopores. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 4895–4905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.McManus OB; Magleby KL, Kinetic States and Modes of Single Large-Conductance Calcium-Activated Potassium Channels in Cultured Rat Skeletal-Muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 1988, 402, 79–120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Couoh-Cardel S; Hsueh YC; Wilkens S; Movileanu L, Yeast V-ATPase Proteolipid Ring Acts as a Large-Conductance Transmembrane Protein Pore. Sci. Rep 2016, 6, 24774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.