Summary
Aims
Previous study suggests that mTOR signaling pathway may play an important role in epileptogenesis. The present work was designed to explore the contribution of raptor protein to the development of epilepsy and comorbidities.
Methods
Mice with conditional knockout of raptor protein were generated by cross‐bred Rptor flox/flox mice with nestin‐CRE mice. The expression of raptor protein was analyzed by Western blotting in brain tissue samples. Neuronal death and mossy fiber sprouting were detected by FJB staining and Timm staining, respectively. Spontaneous seizures were recorded by EEG–video system. Morris water maze, open field test, and excitability test were used to study the behaviors of Rptor CKO mice.
Results
As the consequence of deleting Rptor, downstream proteins of raptor in mTORC1 signaling were partly blocked. Rptor CKO mice exhibited decrease in body and brain weight under 7 weeks old and accordingly, cortical layer thickness. After kainic acid (KA)‐induced status epilepticus, overactivation of mTORC1 signaling was markedly reversed in Rptor CKO mice. Although low frequency of spontaneous seizure and seldom neuronal cell death were observed in both Rptor CKO and control littermates, KA seizure‐induced mossy fiber spouting were attenuated in Rptor CKO mice. Additionally, cognitive‐deficit and anxiety‐like behavior after KA‐induced seizures were partly reversed in Rptor CKO mice.
Conclusion
Loss of the Rptor gene in mice neural progenitor cells affects normal development in young age and may contribute to alleviate KA seizure‐induced behavioral abnormalities, suggesting that raptor protein plays an important role in seizure comorbidities.
Keywords: Behaviors, Epilepsy, Kainic acid, mTOR signaling pathway, Rptor CKO mice
Introduction
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) regulates protein synthesis, cell growth, cell proliferation, and autophagy in intracellular and extracellular signals. mTOR kinase forms two distinct complexes, mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1), and mTOR complex 2 (mTORC2) 1. mTORC1 is sensitive to rapamycin and consists of raptor, mLST8, PRAS40, and DEPTOR. It affects protein translation and synthesis by phosphorylating downstream p70 ribosomal S6 kinase, 4E‐BP1, and ribosomal S6 kinase 2, 3. PI3K and Akt, the upstream of mTORC1, phosphorylated mTORC1 at Ser2448 and responds to downstream p70 S6 kinase and ribosomal S6 kinase 4, 5, 6. mTORC2 includes rictor, mLST8 and SIN1, which is insensitive to rapamycin. mTORC2 contributes to the regulation of cytoskeleton and metabolism by phosphorylating downstream Akt 7, 8, 9.
Dysregulation of the mTOR signaling is observed in various diseases such as cancers, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases 10, 11, as well as a variety of neurological diseases 12, 13, 14, 15. In particular, in some types of epilepsy, such as in tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) and in animal models of acquired epilepsies, the mTOR has been involved in the pathology of epileptogenesis 16, 17, 18, 19. Our previous reports have shown that mTORC1 pathway is activated along with neuronal cell death, neurogenesis, mossy fiber sprouting, and spontaneous seizures in the animal model of acquired epilepsies 20, 21. Pretreatment with rapamycin, an mTOR inhibitor, can abolish those seizure‐induced mTOR activation and seizure‐induced comorbidities. In addition, posttreatment with rapamycin after status epilepticus blocks late mTOR activation and spontaneous seizures and correspondingly has antiepileptogenic effects 20.
However, we have observed a paradoxical increase of p‐S6 protein expression when rapamycin was administrated within 10 h in rats with or without seizure 21, 22. These paradoxical increases within short time raise our curiosity which is the key factor of mTOR signaling pathway in regulation of epileptogenesis. Raptor protein, a regulator‐associated protein of the mTOR, is activated when rapamycin was injected within a short time. We suggest that the raptor protein may affect the mTOR kinase and further phosphorylation of downstream ribosomal S6 kinase and play an important role in epileptogenesis. Thus, in this study, we generated a conditional Rptor gene knockout mice in the neural progenitor cells (Rptor CKO mice) to study the role of raptor. The mTOR signaling pathway expression in Rptor CKO mice in naïve status were first assessed. Then, the changes of mTOR signaling and mossy fiber spouting were detected after kainic acid (KA) induced status epileptics. Finally, cognitive function and anxiety‐like behaviors were analyzed in postepileptic period.
Methods
Rptor CKO Mice and Drug Protocols
Rptor flox/flox mice maintained on a C57BL/6 background were obtained from Jackson Laboratories (Strain #013188, Bar Harbor, ME, USA). Nestin‐CRE mice were obtained from Model Animal Research Center of Nanjing University (J003771, Nanjing, China). Rptor flox/flox–nestin‐CRE knockout (Rptor CKO) mice with conditional inactivation of the Rptor gene in neural progenitor cells were generated by Rptor‐floxed allele and heterozygous nestin‐CRE. Rptor flox/flox mice and Rptor flox/wt–nestin‐CRE mice were used as controls. Genotyping was performed on tail lysates using primers as following: Rptor‐forward 5′‐ CTC AGT AGT GGT ATG TGC TCA G; Rptor‐reverse 5′‐ CTC AGT AGT GGT ATG TGC TCA G; Cre‐forward 5′‐ CCG GGC TGC CAC GAC CAA; CRE‐reverse 5′‐GGC GCG GCA ACA CCA TTT TT. Care and use of animals were conducted according to an animal protocol approved by the Zhejiang University Animal Studies Committee.
Male Rptor CKO mice and control littermates of 6 weeks of age were injected with KA (25 mg/kg, i.p) to induce acute status epilepticus. Seizure severity was scored by Racine scale 23, 24. Briefly, category 1 = immobility and facial twitch; category 2 = head nodding; category 3 = forelimb clonus; category 4 = rearing; and category 5 = rearing and falling. The onset of SE was defined as the beginning of category 4–5 seizures. If animals did not develop category 4–5 seizures 1 h after KA injection, an additional KA injection of 1/4 original doses was given, until the animals developed stage 4–5 seizures. If the animals did not develop stage 4 seizures after three additional application of KA, they were discarded.
Two cohorts of mice were used for Western blotting analysis 2 h after seizure onset or for FJB staining 1 week after seizure. Another cohort of mice was first used for EEG monitoring for 6 weeks and then subjected to behavior studies. They were finally used for Timm staining after finishing behavior studies.
Western Blot Analysis
Male Rptor CKO mice and control littermates were sacrificed for Western blot analysis of mTOR signaling pathway. Hippocampi were harvested at 2 h after onset of status seizure and sonicated in cold lysis buffer (50 mM Tris‐HCl pH7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM EDTA, 1% Triton X‐100) along with protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Sigma, USA). After centrifuged at 12,000 rpm at 4°C for 30 min, supernatant was used for Western blotting analysis as previously described 25. After incubated with primary antibody to phospho‐S6 (Ser240/244), S6, phospho‐Akt (Ser473), Akt, phosphor‐S6K (Thr389), raptor and GADPH (1:1000, Cell signaling technology, Danvers, MA, USA) at 4°C, the membranes were reacted with horseradish peroxidase‐labeled secondary antibody (1:1000, Beyotime, Nanjing, China). Signals were detected by chemiluminescent HRP substrate (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) and quantitatively analyzed with NIH ImageJ software (Bethesda, MD, USA).
Histology
For immunofluorescence experiments, 6‐week‐old Rptor CKO mice and control littermates were perfused with 0.1 M PBS followed by 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA). For Timm's staining, 2 months after KA (or saline) injection, alternative sodium sulfide was perfused before PFA as described previously 25, 26. The brains were removed and fixed in 4% PFA overnight, transferred into 30% sucrose solution, and kept at 4°C. Frozen coronary sections of 20 μm thick were cut using Microtome (Microm HM525, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Five sections selected from a one‐in‐six series were collected from each animal at the same level of hippocampus, starting at 2.8 mm posterior to bregma, and used for following staining.
Immunofluorescent Staining
Sections were blocked in 5% obtained serum with 0.1% Triton X‐100 in PBS for 1 h. Sections were then incubated with anti‐mouse CUX1 (1:200; Santa Cruz, CA, USA) overnight at 4°C, followed by an anti‐mouse IgG conjugated with Alexa Fluor‐546 (1:100) for 2 h at room temperature 27. An Olympus FV1000 confocal microscope with a 10×/0.3NA objective was used to acquire images. The layer II‐IV neuron (CUX1‐positive cells) thickness in neocortex was measured by Olympus Fluoview Ver.2.1a (Olympus, Shinjuku, Tokyo, Japan).
Timm Staining
Slices were incubated in the solution (composition: 50% arabic gum, 60 mL; citric acid buffer, 10 mL; 5.67% hydroquinone solution, 30 mL; 17% silver nitrate, 0.5 mL) in the dark for about 120 min. Mossy fiber sprouting in molecular layer of the dentate hilus and CA3 were visualized under a Nikon light microscopy (Tokyo, Japan). The degree of mossy fiber sprouting was assessed using semiquantitative analysis as the following 28: 1—sparse Timm granule in the supragranule zone; 2—more numerous granules in a continuous distribution; 3—prominent granules and patches; 4—dense lamina band in the supragranule layer; and 5—dense lamina band that extend to inner molecular layer.
EEG Recoding
Rptor CKO mice and control littermates were monitored for spontaneous seizures by weekly video–EEG recording sessions for 6 weeks after kainate administration. For surgical implantation of epidural and hippocampal depth electrodes, mice were anesthetized with 4% chloral hydrate in a stereotaxic frame 3d before kainate administration. Bilateral anterior and posterior epidural cortical screw electrodes, reference, and ground electrodes were inserted in the skull, soldered on electronic pins, and secured with dental cement (Patterson, Saint Paul, MN, USA). Mice were acclimated in cylindrical 10‐inch‐diameter acrylic cages for at least 1 day before monitoring with a digital video–EEG acquisition system (XLTEK). Multiple‐channel EEG was acquired using standard alternating current amplifiers with 1–70 Hz bandpass filters. Mice were monitored continuously for the first week and then an epoch of 48 h for each week thereafter. The average interictal grade of different groups was scored based on a four‐grade scale as previous reported 20: 1 = normal background activity (±6–8 Hz sinusoidal theta rhythm), no epileptiform spikes; 2 = mostly normal background activity, few epileptiform spikes; 3 = mostly abnormal background activity, many spikes; and 4 = burst‐suppression pattern.
Behavior Studies
After finishing EEG monitoring, mice were subjected to behavior studies which lasted for about 2 weeks.
Open Field Test
Open field test apparatus (40 cm × 40 cm × 40 cm) are made of white polyvinylchloride. Before the test, the mouse had 10 second to adapt the arena. Each mouse was placed in the center (36% area of open field) and allowed to freely explore the field for 5 min. The activities and behaviors were recorded with a video camera. The tracks of the mice were registered and analyzed with the software Smart V2.5 (Xinrong, Shanghai, China). The center entries, the time spent in the center, and the total distance were scored. The open field arena was thoroughly cleaned after the test of every mouse.
Test for Behavioral Hyperexcitability
Excitability and sensory responsiveness of mice were determined by approach‐response test and touch‐response test as described 29, 30. Each mouse was tested for five times totally. Before test, mouse was gently transferred to a testing arena and habituated for 15 min. (1) Approach‐response test: a pen vertically is moved slowly toward the face of the animal. Responses were scored as followed: 1, no reaction; 2, the mouse sniffs at the object; 3, the mouse moves away from the object; 4, the mouse freezes; 5, the mouse jerks away from the object; 6, the mice jumps with or without vocalizations. (2) Touch‐response test: The animal is gently prodded in the rump with the blunt end of a pen. Responses were scored as 1, no reaction; 2, the mouse turns toward the object; 3, the mouse moves away from the object; 4, the mouse freezes; 5, the mouse jerks around toward the touch; 6, the mouse turns away from the touch; and 7, the mouse jumps with or without vocalizations.
Morris Water Maze Test
Mice were tested for learning and memory using a Morris water maze. Mice were trained for four consecutive days before testing (four trails per day at interval of 1 h). The mouse was first placed on the platform for 10 seconds, then randomly placed in one of four different quadrants of the water tank. Recordings were stopped 10 seconds after the mouse reached the platform. The mouse was led to the platform if it did not get to the platform within 60 seconds and stayed there for 10 seconds. On the fifth day, mouse was placed in the quadrant diagonally opposite from the previous platform location and the time of reaching the platform (escape latency), swimming distance, swimming speed, and the number of the target quadrants were analyzed with the software Smart V2.5.
Statistics
Results were presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Differences among groups were compared by t‐test or one‐way ANOVA, accordingly with experimental design, using SPSS software (Version 19.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). P < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
The Activity of mTORC1 Pathway is Partly Blocked in Rptor CKO Mice
Rptor CKO mice were successfully generated as identified by genomic PCR (Figure 1A). Both Rptor CKO mice and littermate controls exhibited similar appearance and autonomous behaviors (Figure 1B). Although further behavior studies revealed a slight decrease in cognitive function in Rptor CKO mice, no significant changes were found between Rptor CKO mice and littermate controls in anxiety‐like behaviors, excitability, and cognition (Figure S1). To verify the inactivation of the Rptor gene, protein extracts from brain were analyzed by Western blotting. Almost 50% loss of raptor protein was found in 6‐week‐old mice as well as decreased downstream phospho‐S6 protein (Figure 1C,D). In contrast to the changes in the mTORC1 signaling, there was no significant alteration in phosphorylation of Akt, which is the upstream protein of raptor (Figure 1C,D).
Figure 1.
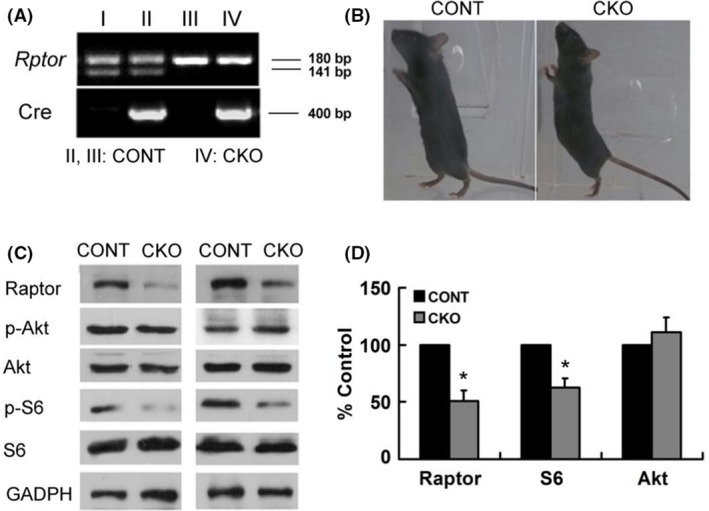
Rptor CKO mice had decreased mTORC1 signaling with normal appearance. (A) Genotyping of mice indicated that Rptor CKO mice of homozygous Rptor flox/flox allele and nestin‐CRE. (B) Normal appearance of Rptor CKO mice (CKO) and their control littermates (CONT). (C) Representative blots of Raptor, P‐Akt, Akt, P‐S6, S6, and GADPH protein expression in Rptor CKO mice and control littermates. (D) Quantitative summary demonstrated that significant decreases in the levels of raptor and P‐S6, but not P‐Akt. (n = 6 animals per group). *P < 0.05, by t‐test. Both male and female mice were used.
Rptor Deletion in Neuron Affects Body and Brain Development
To explore whether conditional knockout of Rptor had any effect on development, we monitored the body weights and brain weights in Rptor CKO mice and littermate controls. The average body weight of male Rptor CKO mice was lower than that of control littermates at the age younger than 7 weeks old (Figure 2A), whereas no obvious difference in body weight was noticed in female Rptor CKO and controls (Figure 2B). In addition, the brain weight of Rptor CKO mice was decreased compared to controls at 2 weeks of age (Figure 2C). Similar results were observed when compared the brain‐to‐body weight ratios between Rptor CKO mice and controlled littermates (Figure 2D). To further elucidate the factors responsible for the brain decrease, we analyzed the cortical layer thickness using markers restricted to Layer II‐IV (CUX1) neurons in 6‐week‐old mice. Rptor CKO mice showed less thickness of upper layer neurons (400.3 ± 12.3 μm vs. 346.0 ± 11.3 μm, P < 0.01, Figure 2E,F).
Figure 2.
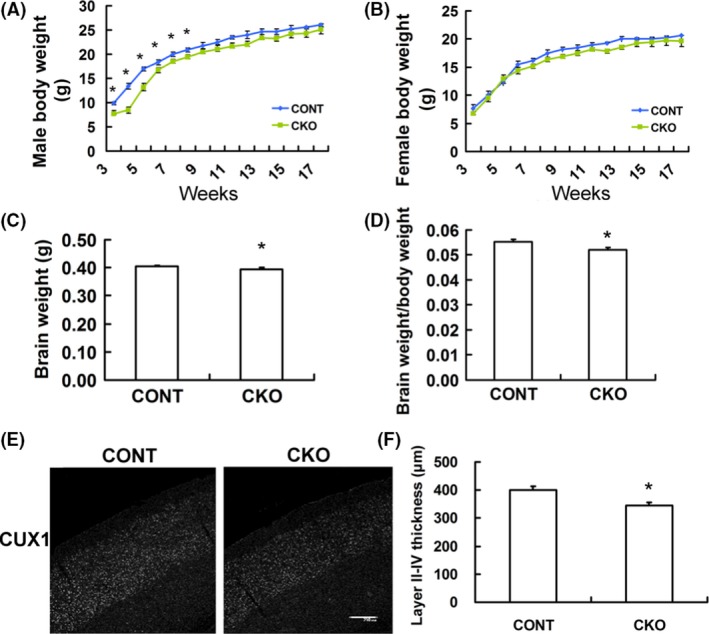
Decreased body weight, brain weight, and cortical thickness in Rptor CKO mice. (A, B) Body weight in male and female in Rptor CKO mice and control littermates (n = 15–20 mice per group). (C) Decreased brain weight in Rptor CKO mice when compared with littermate controls (n = 12 animals per group, 2 weeks old). (D) Brain/body weight ratio in Rptor CKO was lower when compared with littermate controls. (E) Cortical layer II‐IV thickness was identified by staining with the upper layer marker Cux1. (F) Quantitative summary demonstrated the significant decrease in cortical layer II‐IV thickness in Rptor CKO mice (n = 8 mice per group, 6 weeks old). Scale bar, 200 μm. *P < 0.05, by t‐test. Both male and female mice were used.
Overactivation of mTORC1 Signaling Induced by KA Seizure was Reversed in Rptor CKO Mice
We have demonstrated that the mTOR signaling pathway is overactivated after KA‐induced seizure in previous study 20. To explore the change of mTOR signaling pathway after KA‐induced seizure in Rptor CKO mice, we detected p‐S6K, p‐S6, p‐Akt protein expression by Western blotting 2 h after KA‐induced seizure onset. KA treatment induced status epilepticus in almost each mouse. Similar to rats, the mice started forelimb clonus 20 min after KA injection and gradually progressed to rearing (stage 4) 40 min after KA injection, about 80% of mice finally developed rearing and falling (stage 5) within 1 h. The status epilepticus lasted for 1–3 h with the average duration about 2.4 h. A significant increase in the expression of p‐S6K, p‐S6 protein, and p‐Akt was exhibited in control mice 2 h after seizure onset. Although Rptor CKO mice also showed increase in the expression of p‐S6K and p‐S6 protein after KA‐induced seizure, it was significantly decreased as compared to that of control mice (Figure 3A,B). No obvious changes were noticed in p‐Akt expression (Figure 3C).
Figure 3.
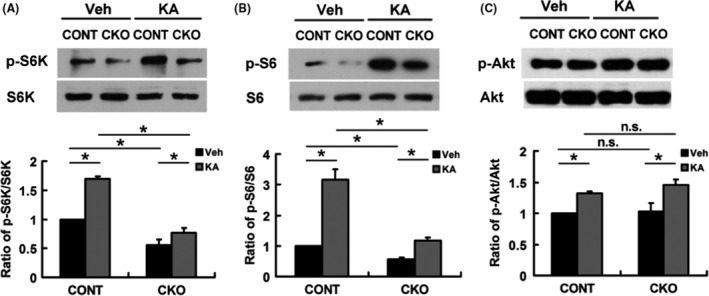
Overactivation of mTORC1 signaling is partly reversed in Rptor CKO mice. Seizure were induced by KA (25 mg/kg, i.p.) when controls were injected saline (Veh). Hippocampal protein was extracted 2 h after onset of seizure, and Western blotting analysis was performed. (A) Representative blots and statistical analysis of P‐S6K/S6K ratio. The ratio of P‐S6K/S6K ratio in both KA‐treated groups increased as compared to the Veh, while it decreased in CKO+KA group as compared to CONT+KA group. (B) Representative blots and statistical analysis of P‐S6/S6. The ratio of P‐S6/S6 in both KA‐treated groups increased as compared to the Veh groups, while it decreased in CKO+KA group as compared to CONT+KA group. (C) Representative blots and statistical analysis of P‐Akt/Akt. The ratio of P‐Akt/Akt of both KA‐treated groups increased as compared to the Veh groups, while no difference was noticed between CKO+KA group and CONT+KA group (n = 6 male mice per group). *P < 0.05, by one‐way ANOVA. NS= not significant.
Decreased Mossy Fiber Spouting in Rptor CKO Mice
We monitored spontaneous seizure in Rptor CKO mice and control mice for 6 weeks after KA‐induced seizure. Before KA injection, both control mice and CKO mice exhibited normal EEG. After monitoring for 6 weeks, we found that KA treatment did not induce robust spontaneous seizures in both control and Rptor CKO mice (Figure 4A,B). However, spikes were frequently presented in control mice whereas were seldom in Rptor CKO mice and the score of the EEG interictal background was significantly increased (Figure 4A,B). One of the ictal EEG was shown in Figure 4C; behaviorally, the animal kept still for several seconds and then started rearing and falling for 20–60 seconds. We then detected whether KA‐induced seizure had any effect on neuronal cell death and mossy fiber sprouting in Rptor CKO mice, which were implicated in the process of chronic epileptogenesis. Robust mossy fiber spouting in CA3 and dentate hilus (DG) was observed with Timm staining in control mice 6 weeks after KA‐induced seizure, while it was significantly attenuated in Rptor CKO mice (Figure 4D). Quantitative analysis showed that the score of mossy fiber spouting was significantly decreased in the Rptor CKO mice (Figure 4E). However, no obvious cell death was noticed in both groups (Figure 4F).
Figure 4.
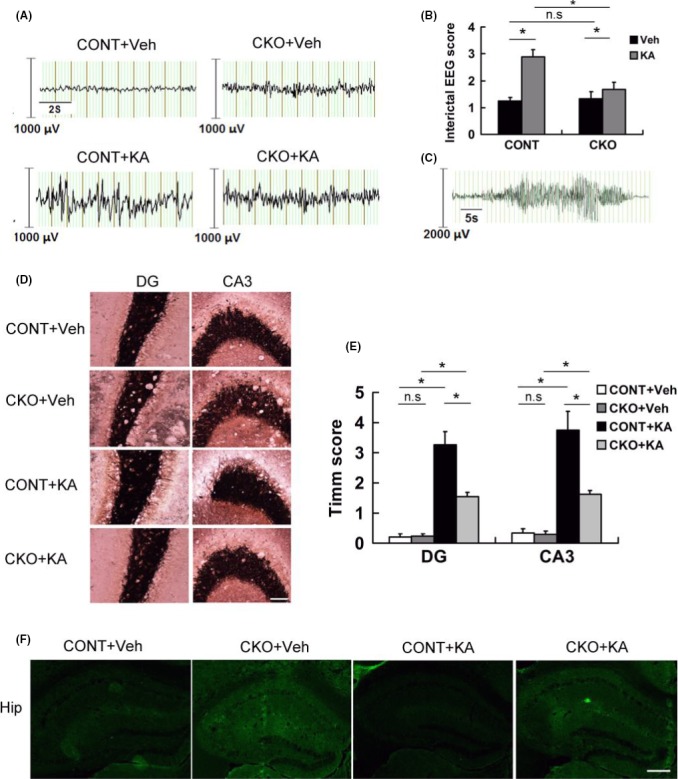
Epilepsy‐associated manifestation was attenuated in Rptor CKO mice. Control and Rptor CKO mice were treated with KA to induce status epilepticus and recorded with EEG. Mice were perfused and stained for mossy fiber sprouting 8 weeks after EEG recording. (A) Representative EEG background and interictal epileptiform spikes in different groups. (B) Score of EEG background spikes in different groups (n = 12 male mice per group). (C) Representative EEG depicting ictal activity from a spontaneous seizure. (D) Representative images of Timm staining in the dentate gyrus (DG) and CA3 zones (n = 6 male mice per group. Scale bar, 200 μm. (E) Quantitative summary of Timm staining. Robust mossy fiber sprouting was seen in KA‐treated control (CONT+KA) in the DG and CA3 zone, while it attenuated in Rptor CKO mice (CKO+KA) compared to their controls (CONT+KA or CKO+Veh). (F) Representative images of FJB staining 1 week after KA‐induced status epilepticus. No obvious cell death was noticed in all groups (n = 6 male mice per group). Scale bar, 10 μm. *P < 0.05 by one‐way ANOVA.
Decreased Anxiety‐Like Behavior and Cognitive Deficit in Rptor CKO Mice
During the monitoring of EEG, we found that Rptor CKO mice were not so irritable and overexciting as control mice after seizure. Thus, we conducted open field test, excitability test, and Morris water maze test to analyze the behaviors of Rptor CKO mice and their controls.
Open field test was used to investigate the anxiety‐like behavior in mice. After KA‐induced seizure, control mice exhibited anxiety‐like behaviors, which was evident by decreased center entries and center duration, whereas it was reversed in Rptor CKO mice (Figure 5A,B). Similarly, in the test of excitability, the increased score of approach‐response test (Figure 5C) and touch‐response test (Figure 5D) in KA‐treated control mice were reversed in Rptor CKO mice.
Figure 5.
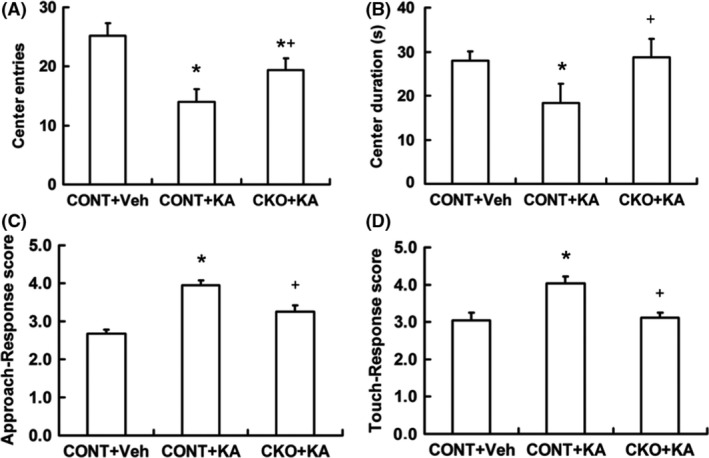
Rptor CKO mice show decreased anxiety‐like behaviors. Open field test and excitability test were performed 6 weeks after KA‐induced seizure. Both the center entries (A) and the center duration (B) in Rptor CKO mice (CKO+KA) were increased in open field test compared to controls (CONT+KA) after seizure. (C) The score of approach‐response test was decreased in Rptor CKO mice. (D) The score of touch‐response test was decreased in Rptor CKO mice (n = 12 male mice per group). *P < 0.05 compared to CONT+Veh, + P < 0.05 compared to CONT+KA by one‐way ANOVA.
Morris water maze was used to study the cognitive functions of mice. KA‐induced seizure resulted in the increase of escape latency (Figure 6A) and swimming length (Figure 6B) in control mice, but it was partly and significantly reversed in Rptor CKO mice. No difference of swimming velocity was noticed in all the three groups (Figure 6C). Accordingly, the number of crossings of the target quadrant after removal of the platform was decreased in controls after KA‐induced seizure, while no significant change was noticed in Rptor CKO mice (Figure 6D). All these data indicate that less damage in cognitive deficit in Rptor CKO mice after KA‐induced seizure.
Figure 6.
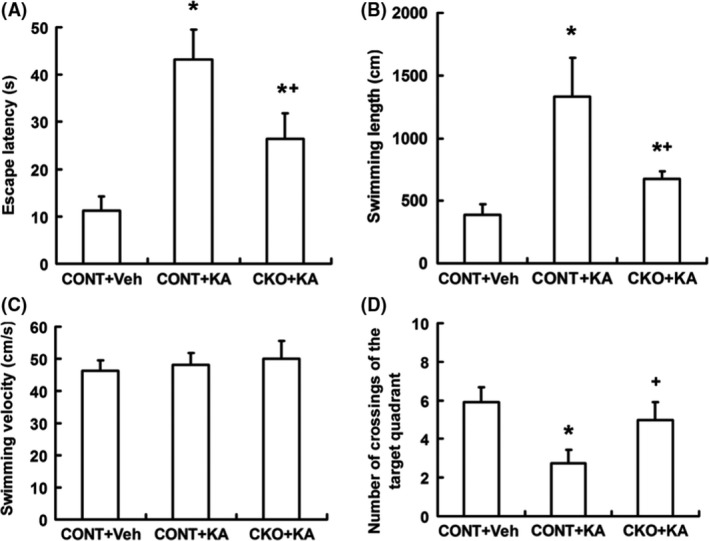
Rptor CKO mice have decreased cognitive deficit after KA‐induced status epilepticus. Morris water maze test were performed at 6 weeks after KA‐induced seizure. (A) The escape latency of three groups. Both KA‐treated groups exhibited increased latency compared to veh‐treated groups, while it was markedly reversed in CKO+KA mice compared to CONT+KA mice. (B) Swimming length of three groups. CONT+KA mice showed prolonged swimming length. (C) Swimming velocity of three groups. No differences were noticed. (D) The number of crossings of the target quadrant after removal of the platform was significantly decreased in CONT+KA, but in CKO+KA (n = 12 male mice per group). *P < 0.05 compared to CONT+Veh, + P < 0.05 compared to CONT+KA by one‐way ANOVA.
Discussion
In this study, we observed the role of raptor in naïve and KA‐induced status epilepticus mice by conditional knockout Rptor gene in neural progenitor cells. We found that (1) Rptor CKO mice had decreased expression of raptor and S6 protein, normal appearance, decreased male body weight, brain weight, and neocortical thickness; (2) Rptor CKO mice exhibited less overactivation of mTOR signaling pathway, spike occurrence in EEG recording, and mossy fiber sprouting after KA‐induced seizure; and (3) Rptor CKO mice revealed decreased anxiety‐like behavior and less damage in cognitive deficit.
The Rptor CKO mice had similar appearance with their controls. Knockout of the Rptor gene in neuron results in raptor protein decrease as well as downstream p‐S6 protein; however, the upstream p‐Akt protein and mTORC2‐related protein were not affected. As the mTOR signaling pathway is well balanced and controlled with complex upstream regulation and downstream feedback, the effects of knockout of the Rptor gene in neuron may be blurred. Thus, although decreased body weight and brain weight were observed in the early age of Rptor CKO mice, no obvious cognitive deficits were recorded. Given that mTORC1 signaling influences cell growth, proliferation, and metabolism, deleting of the Rptor gene in neural progenitor cells may account for the decreased thickness of Layer II‐IV neurons.
In KA model of rats, rats have been observed chronic epilepsy in a few weeks after KA‐induced seizure 20, 31; however, in the present study, only one of 12 in Rptor CKO mice and two of 12 in control mice exhibited spontaneous seizure after KA‐induced seizure (Table 1). Meanwhile, no obvious neuron death were found in both groups. Rptor CKO mice and their controls had the background of C57BL/6 series. It has reported that C57BL/6 series mice have a tolerance to hypoxia, which may protect the neurons from the harm of oxygen deficit‐induced cell death and subsequently, protect the mice from spontaneous seizure occurrence 32. However, report also shows that C57BL/6 mice subjected to hypoxia‐induced neonatal seizure developed earlier, more frequent, and longer duration seizures when treated with KA in late life, although spontaneous seizures were not monitored 33. Thus, status epilepticus induced by intraperitoneal injection of KA may not be a good model to trigger epileptogenesis in C57BL/6 mice. However, mossy fiber sprouting was found in most control mice but not in Rptor CKO mice after KA‐induced seizure; these data further prove that raptor is the key protein in mTOR signaling pathway‐regulated cell proliferation and protein synthesis.
Table 1.
Frequency of spontaneous seizures of Rptor CKO mice and controls in 48 h
| Groups/Weeks (per 48 h) | 1w | 2w | 3w | 4w | 5w | 6w |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CONT+KA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.2 |
| CKO+KA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Anxiety‐like behavior, a comorbidity of seizure, has been reported in patient with TSC 34, 35 and in several mouse models with epilepsy 33, 36. However, the molecular and cellular mechanism of this anxiety‐like behavior is not clear. In this study, we found that Rptor CKO mice reversed the anxiety‐like behavior induced by KA‐induced status epilepticus. As knockout of Rptor gene in neural progenitor cells inhibits the mTOR signaling, this finding raises the possibility that overactivated mTOR signaling may be a reasonable mechanism in anxiety‐like behavior. Anxiety‐like behavior may also result from KA‐induced spikes proved by EEG, although very less spontaneous seizures is found in control and Rptor CKO mice. Further experiments are needed to elucidate the mechanism of decrease in anxiety‐like behavior in Rptor CKO mice.
The relationship of the mTOR signaling and synaptic formation has been investigated extensively 37, 38. Synaptic plasticity is the alteration of the strength of connections which changes with the synaptic activity. Long‐term potentiation and long‐term depression of synaptic transmission, the two main formations of long‐term synaptic activity, are widely recognized as the molecular mechanism of learning and memory 39, 40. Protein synthesis is important for synaptic plasticity. In the present study, we found that knockout of Rptor gene in neuron protected the mice from the damage of cognitive deficits after KA‐induced status epilepticus. As LTP and seizures both involve highly synchronized, excessive electrical activity, it is perhaps not surprising that knockout of the Rptor gene and thus the block of the mTORC1 signaling could protect the mice from the damage in cognitive function.
In conclusion, our data show that knockout of the Rptor gene in mice neural progenitor cells mildly affects the development in young age; however, it protects the mice from the KA seizure‐induced damages including the seizure‐like spike, cognitive‐deficit and anxiety‐like behavior. Together with our previous study, our present data show that mTORC1 plays a key role in the regulation of epileptogenesis and associated comorbidities.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Standard
All animal experiments were performed in accordance with guidelines approved by Zhejiang University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Supporting information
Figure S1 Behaviors studies showed no different in Rptor CKO mice and controls in naïve condition.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81371429 to L. Z.), Department of Science and Technology of Zhejiang Province, Project of Experiment Animal Platform (2013C37026 to L.Z.), Hangzhou Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Scholars (2014 to L. Z.), and Hangzhou Science and Technology Major Project for Innovation (20152013A02 to L. Z.).
Contributor Information
Xi‐Mei Wu, Email: xiwu@zju.edu.cn.
Ling‐Hui Zeng, Email: zenglh@zucc.edu.cn.
References
- 1. Wullschleger S, Loewith R, Hall MN. Tor signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 2006;124:471–484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Kim DH, Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, et al. Mtor interacts with raptor to form a nutrient‐sensitive complex that signals to the cell growth machinery. Cell 2002;110:163–175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Fingar DC, Richardson CJ, Tee AR, Cheatham L, Tsou C, Blenis J. Mtor controls cell cycle progression through its cell growth effectors s6k1 and 4e‐bp1/eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4e. Mol Cell Biol 2004;24:200–216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Dennis PB, Jaeschke A, Saitoh M, Fowler B, Kozma SC, Thomas G. Mammalian tor: A homeostatic atp sensor. Science 2001;294:1102–1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Nave BT, Ouwens M, Withers DJ, Alessi DR, Shepherd PR. Mammalian target of rapamycin is a direct target for protein kinase b: Identification of a convergence point for opposing effects of insulin and amino‐acid deficiency on protein translation. Biochem J 1999;344(Pt 2):427–431. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Peterson RT, Beal PA, Comb MJ, Schreiber SL. Fkbp12‐rapamycin‐associated protein (frap) autophosphorylates at serine 2481 under translationally repressive conditions. J Biol Chem 2000;275:7416–7423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Kim DH, et al. Rictor, a novel binding partner of mtor, defines a rapamycin‐insensitive and raptor‐independent pathway that regulates the cytoskeleton. Curr Biol 2004;14:1296–1302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Laplante M, Sabatini D. Mtor signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 2012;149:274–293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM. Phosphorylation and regulation of akt/pkb by the rictor‐mtor complex. Science 2005;307:1098–1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Zoncu R, Efeyan A, Sabatini DM. Mtor: From growth signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2011;12:21–35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Dazert E, Hall MN. Mtor signaling in disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2011;23:744–755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Emanuela S, Myriam H, Paul G, Emmanuel V, Gilberto F. Inhibition of mtor signaling in parkinson's disease prevents l‐dopa‐induced dyskinesia. Sci Signal 2009;2:ra36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Wong M. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mtor) pathways in neurological diseases. Biomed J 2013;36:40–50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Chong ZZ, Shang YC, Zhang L, Wang S, Maiese K. Mammalian target of rapamycin: Hitting the bull's‐eye for neurological disorders. Oxid med Cell Longev 2010;3:374–391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Jordi B, Marta MV, Miquel V. Fighting neurodegeneration with rapamycin: Mechanistic insights. Nat Rev Neurosci 2011;12:437–452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Wong M. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mtor) inhibition as a potential antiepileptogenic therapy: From tuberous sclerosis to common acquired epilepsies. Epilepsia 2010;51:27–36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Huang X, Zhang H, Yang J, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway suppresses acquired epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 2010;40:193–199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Zhang B, Wong M. Pentylenetetrazole‐induced seizures cause acute, but not chronic, mtor pathway activation in rat. Epilepsia 2012;53:506–511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Buckmaster PS, Lew FH. Rapamycin suppresses mossy fiber sprouting but not seizure frequency in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci 2011;31:2337–2347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Zeng LH, Rensing NR, Wong M. The mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway mediates epileptogenesis in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci 2009;29:6964–6972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Zeng LH, McDaniel S, Rensing NR, Wong M. Regulation of cell death and epileptogenesis by the mammalian target of rapamycin (mtor): A double‐edged sword? Cell Cycle 2010;9:2281–2285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Chen L, Hu L, Dong JY, et al. Rapamycin has paradoxical effects on s6 phosphorylation in rats with and without seizures. Epilepsia 2012;53:2026–2033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Racine RJ. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation: Cortical areas. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1975;38:1–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Zeng LH, Xu L, Rensing NR, Sinatra PM, Rothman SM, Wong M. Kainate seizures cause acute dendritic injury and actin depolymerization in vivo. J Neurosci 2007;27:11604–11613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Zeng LH, Xu L, Gutmann DH, Wong M. Rapamycin prevents epilepsy in a mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Ann Neurol 2008;63:444–453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Buckmaster PS. Prolonged infusion of tetrodotoxin does not block mossy fiber sprouting in pilocarpine‐treated rats. Epilepsia 2004;45:452–458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Carson RP, Cary F, Peggy W, Ess KC. Deletion of rictor in neural progenitor cells reveals contributions of mtorc2 signaling to tuberous sclerosis complex. Hum Mol Genet 2012;22:140–152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Suzuki F, Makiura Y, Guilhem D, Sørensen JC, Onteniente B. Correlated axonal sprouting and dendritic spine formation during kainate‐induced neuronal morphogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult mice. Exp Neurol 1997;145:203–213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Rice AC, Floyd CL, Lyeth BG, Hamm RJ, DeLorenzo RJ. Status epilepticus causes long‐term nmda receptor‐dependent behavioral changes and cognitive deficits. Epilepsia 1998;39:1148–1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Gastens AM, Brandt C, Bankstahl JP, Loscher W. Predictors of pharmacoresistant epilepsy: Pharmacoresistant rats differ from pharmacoresponsive rats in behavioral and cognitive abnormalities associated with experimentally induced epilepsy. Epilepsia 2008;49:1759–1776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Drexel M, Preidt AP, Sperk G. Sequel of spontaneous seizures after kainic acid‐induced status epilepticus and associated neuropathological changes in the subiculum and entorhinal cortex. Neuropharmacology 2012;63:806–817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Royle SJ, Collins FC, Rupniak HT, Barnes JC, Anderson R. Behavioural analysis and susceptibility to CNS injury of four inbred strains of mice. Brain Res 1999;816:337–349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Rodriguez‐Alvarez N, Jimenez‐Mateos EM, Dunleavy M, Waddington JL, Boylan GB, Henshall DC. Effects of hypoxia‐induced neonatal seizures on acute hippocampal injury and later‐life seizure susceptibility and anxiety‐related behavior in mice. Neurobiol Dis 2015;83:100–114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Cambiaghi M, Cursi M, Magri L, et al. Behavioural and eeg effects of chronic rapamycin treatment in a mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Neuropharmacology 2013;67:1–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Carson RP, Kelm ND, West KL, et al. Hypomyelination following deletion of tsc2 in oligodendrocyte precursors. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2015;2:1041–1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Ma L, Wang L, Yang F, et al. Disease‐modifying effects of rhc80267 and jzl184 in a pilocarpine mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy. CNS Neurosci Ther 2014;20:905–915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Shao JT, Schuman EM. A rapamycin‐sensitive signaling pathway contributes to long‐term synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002;99:467–472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Jacek J, Samantha S, Seeburg DP, Hoogenraad CC, Morgan S. Control of dendritic arborization by the phosphoinositide‐3′‐kinase‐akt‐mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. J Neurosci 2005;25:11300–11312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Ehninger D, Han S, Shilyansky C, et al. Reversal of learning deficits in a tsc2 + /‐ mouse model of tuberous sclerosis. Nat Med 2008;14:843–848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Brewster AL, Lugo JN, Patil VV, et al. Rapamycin reverses status epilepticus‐induced memory deficits and dendritic damage. PLoS One 2013;8:e57808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1 Behaviors studies showed no different in Rptor CKO mice and controls in naïve condition.


