Abstract
Recombinant Escherichia coli cells engineered for the expression of the xylB gene in conjunction with genes of the nonmevalonate pathway were supplied with 13C-labeled 1-deoxy-d-xylulose. Cell extracts were analyzed directly by NMR spectroscopy. 13C-labeled 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate was detected at high levels in cells expressing xylB, ispC, ispD, ispE, and ispF. The additional expression of the gcpE gene afforded 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate as an intermediate of the nonmevalonate pathway. Hypothetical mechanisms involving conserved cysteine residues are proposed for the enzymatic conversion of 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate into 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate catalyzed by the GcpE protein.
Keywords: isoprenoid biosynthesis‖1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate
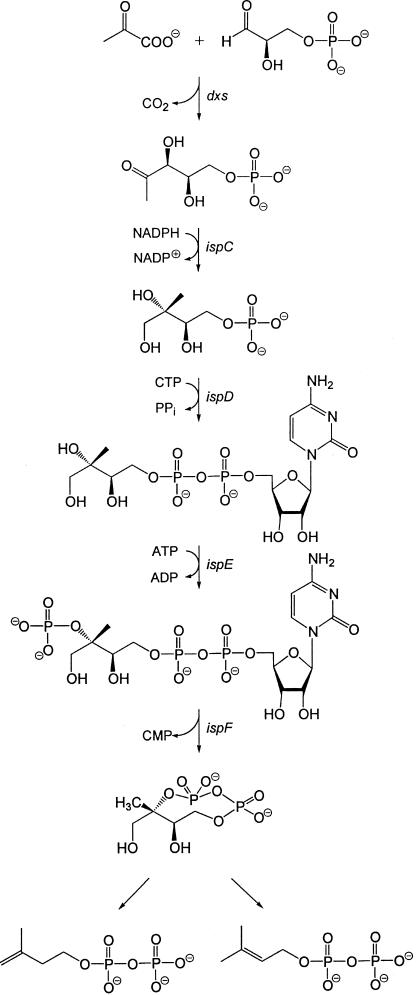
Terpenoids are one of the largest groups of natural products, with more than 30,000 known representatives (1). They are all assembled from the universal precursors dimethylallyl diphosphate and isopentenyl diphosphate, whose biosynthesis via the mevalonate pathway has been studied in considerable detail in animal cells and yeast (reviewed in refs. 2–5). An alternative biosynthetic route conducive to these universal terpene precursors via 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate and 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate has been discovered only recently in certain bacteria (6, 7) and plants (8) (reviewed in refs. 9–12). The available evidence requires a branching point between 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate and isopentenyl diphosphate (respectively, dimethylallyl diphosphate) (Fig. 1) (13–16).
Figure 1.
The nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis.
Clusters of orthologous groups of genes involved in the mevalonate or nonmevalonate pathway show a mutually exclusive distribution in the genomes of completely sequenced microorganisms (12, 17–19). Orthologs of the lytB and gcpE genes follow the distribution of the established genes of the nonmevalonate pathway (20). From this fact and from the established metabolic function of dxs, ispC, ispD, ispE, and ispF for the conversion of pyruvate and d-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate into 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate, it was deduced that gcpE and lytB specify enzymes for the conversion of 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate into isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate (20). Subsequently, the involvement of these genes in the nonmevalonate pathway has been confirmed by gene-targeting studies (21–23), but their metabolic roles are still unknown.
The incorporation rates of free 1-deoxy-d-xylulose into growing cultures of Escherichia coli were shown to be extraordinarily high (7, 13). More recently, we have shown that d-xylulokinase of E. coli specified by the xylB gene phosphorylates the 5-hydroxy group of 1-deoxy-d-xylulose at a high rate (24). In this article we report on recombinant E. coli strains engineered for overexpression of the xylB gene in conjunction with ispCDEF and gcpE or lytB genes. Incorporation experiments with 13C-labeled 1-deoxy-d-xylulose have now enabled us to identify 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate, an intermediate of the nonmevalonate pathway.
Experimental Procedures
Materials.
[U-13C5] and [3,4,5-13C3]1-deoxy-d-xylulose were obtained as described (24, 25). Oligonucleotides were custom synthesized by MWG Biotec (Ebersberg, Germany).
Bacterial Strains and Plasmids.
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strain or plasmid | Genotype or relevant characteristic | Ref. or source |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli | ||
| XL1-Blue | RecA1, endA1, gyrA96, thi-1, hsdR17, supE44, relA1, lac, [F′, proAB, lac1qZΔM15, Tn10 (tet′)] | 27, Stratagene |
| Plasmids | ||
| pBluescript SKII− | High copy cloning vector | Stratagene |
| pBSxylB | Expression of xylB from E. coli | This study |
| pBSxylBispC | Expression of xylB and ispC from E. coli | This study |
| pBSxylBispCDF | Expression of xylB, ispC, ispD, and ispF from E. coli | This study |
| pBScyclo | Expression of xylB, ispC, ispD, ispE, and ispF from E. coli | This study |
| pBSxispC-G | Expression of xylB, ispC, ispD, ispE, ispF, and ispG from E. coli | This study |
DNA Sequence Determination.
DNA was sequenced by the automated dideoxynucleotide method (26) with a 377 Prism sequencer from Perkin–Elmer.
Construction of Vectors with Synthetic Operons Comprising the xylB,ispC,ispD,ispE,ispF, and ispG Genes of E. coli.
Vector constructs for the in vivo utilization of 1-deoxy-d-xylulose into recombinant E. coli strains were synthesized in consecutive cloning steps as follows. The E. coli xylB gene (GenBank accession no. AE000433) was amplified from bp position 8596 to 10144 by PCR with the use of chromosomal E. coli DNA as template and the oligonucleotides xylBEcoRI and xylBHindIII as primers (Table 2). The amplificate was purified, treated with EcoRI and HindIII, and ligated into the plasmid vector pBluescript SKII− (Stratagene), which had been treated with the same restriction enzymes. The resulting plasmid, pBSxylB, was electrotransformed into E. coli strain XL1-Blue (Stratagene) (27), yielding the recombinant strain XL1-pBSxylB.
Table 2.
Oligonucleotides used in this study
| Designation | 5′-Sequence-3′ |
|---|---|
| xylBEcoRI | CCGTCGGAATTCGAGGAGAAATTAACCATGTATATCGGGATAGATCTTGG |
| xylBHindIII | GCAGTGAAGCTTTTACGCCATTAATGGCAGAAGTTGC |
| dxrHindIII | CTAGCCAAGCTTGAGGAGAAATTAACCATGAAGCAACTCACCATTCTGG |
| dxrSalI | GGAGATGTCGACTCAGCTTGCGAGACGC |
| ygbPBSalI | CCGGGAGTCGACGAGGAGAAATTAACCATGGCAACCACTCATTTGGATG |
| ygbPBXhoI | TATCAACTCGAGTCATTTTGTTGCCTTAATGAG |
| ychBXhoI | GCGAACCTCGAGGAGGAGAAATTAACCATGCGGACACAGTGGCCC |
| ychBKpnI | CCTGACGGTACCTTAAAGCATGGCTCTGTGC |
| gcpESacII | GCGGGAGACCGCGGGAGGAGAAATTAACCATGCATAACCAGGCTCCAATTCAACG |
| gcpENotI | CGCTTCCCAGCGGCCGCTTATTTTTCAACCTGCTGAACG |
The E. coli ispC gene (GenBank accession no. AE000126) was amplified from bp position 9887 to 11083 by PCR with the use of chromosomal E. coli DNA as template and the oligonucleotides dxrHindIII and dxrSalI as primers (Table 2). The amplificate was purified, treated with HindIII and SalI, and ligated into the plasmid vector pBSxylB, which had been treated with the same restriction enzymes. The resulting plasmid, pBSxylBispC, was electrotransformed into E. coli strain XL1-Blue, yielding the recombinant strain XL1-pBSxylBispC.
The E. coli ispDF operon (GenBank accession no. AE000358) was amplified from bp position 6275 to 7464 by PCR with the use of chromosomal E. coli DNA as template and the oligonucleotides ygbPBSalI and ygbPBXhoI as primers (Table 2). The amplificate was purified, treated with SalI and XhoI, and ligated into the plasmid vector pBSxylBispC, which had been treated with the same restriction enzymes. The resulting plasmid pBSxylBCDF was electrotransformed into E. coli strain XL1-Blue, yielding the recombinant strain XL1-pBSxylBispCDF.
The E. coli ispE gene (GenBank accession no. AE000219) was amplified from bp position 5720 to 6571 by PCR with the use of chromosomal E. coli DNA as template and the oligonucleotides ychBXhoI and ychBKpnI as primers (Table 2). The amplificate was purified, treated with XhoI and KpnI, and ligated into the plasmid vector pBSxylBispCDF, which had been treated with the same restriction enzymes. The resulting plasmid pBScyclo was electrotransformed into E. coli strain XL1-Blue, yielding the recombinant strain XL1-pBScyclo.
The E. coli ispG (formerly gcpE) gene (GenBank accession no. AE000338) was amplified from bp position 372 to 1204 by PCR with the use of chromosomal E. coli DNA as template and the oligonucleotides gcpESacII and gcpENotI as primers (Table 2). The amplificate was purified, treated with SacII and NotI, and ligated into the plasmid vector pBScyclo, which had been treated with the same restriction enzymes. The resulting plasmid pBSxispC-G was electrotransformed into E. coli strain XL1-Blue, yielding the recombinant strain XL1-pBSxispC-G.
Feeding of 13C-Labeled 1-Deoxy-d-Xylulose to Recombinant Cells of E. coli Overexpressing the xylB Gene in Conjunction with the Genes of the Nonmevalonate Pathway.
Terrific Broth medium (0.2 liter containing 36 mg of ampicillin) (28) was inoculated with recombinant E. coli XL1-Blue cells carrying plasmid pBSxylB or pBScyclo or pBSxispC-G. The cells were grown with shaking at 37°C overnight. At an optical density (600 nm) of 5.0, 30 mg (0.1 mmol) of cytidine and, in the case of plasmid XL1-pBSxispC-G, 25 mmol of lithium lactate in 20 ml of 100 mM Tris hydrochloride (pH 7.2), were added. After 30 min, 0.1 mmol of [U-13C5]- or [3,4,5-13C3]1-deoxy-d-xylulose was added. Aliquots of 40 ml were retrieved in intervals of 1 h. The cells were harvested, centrifuged for 10 min at 5,000 rpm and 4°C, washed with 0.9% NaCl, and centrifuged. The cells were resuspended in 600 μl of 10 mM NaF/D2O in 50% (vol/vol) methanol-d4, cooled on ice, and subjected to ultrasonic treatment. The suspension was centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 15 min. To avoid degradation during work-up, the supernatants were subjected to NMR analysis without further purification.
NMR Spectroscopy.
1H, 13C, and 31P NMR spectra were recorded with an AVANCE 500 spectrometer from Bruker Instruments (Karlsruhe, Germany).
Results
A suspension of recombinant E. coli cells engineered for overexpression of the xylB gene was supplied with [U-13C5]1-deoxy-d-xylulose as described under Experimental Procedures (Fig. 2). 13C NMR analysis of the cell-free extract obtained after cell disruption showed intense signals for 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate (25), indicating that exogenous 1-deoxy-d-xylulose is rapidly purged from the culture medium and accumulated into intracellular 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate in substantial concentrations (data not shown).
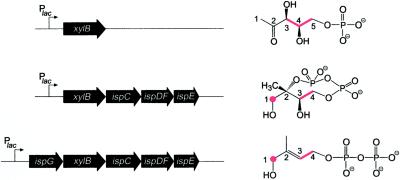
Figure 2.
Expression vectors comprising synthetic operons of xylB together with genes of the nonmevalonate pathway used for the in vivo production of intermediates in the nonmevalonate pathway. 13C-labeled compounds detected in cell extracts obtained from E. coli cells overexpressing the indexed genes and supplied with [3,4,5-13C3]1-deoxy-d-xylulose are indicated (the 13C label is in red).
Capitalizing on this observation, we then constructed synthetic operons comprising the xylB gene and various terpenoid pathway genes endowed with artificial ribosomal binding sites under the control of a lac promoter/operator (Fig. 2) on high-copy plasmids (see Experimental Procedures). Bacterial suspensions with an OD600 of about 5 were incubated with [3,4,5-13C3]- or [U-13C5]-labeled 1-deoxy-d-xylulose for 2 h, harvested, disrupted by ultrasonic treatment in 10 mM NaF/D2O in 50% (vol/vol) methanol-d4, and centrifuged. To minimize the decomposition of potentially unstable metabolites, the supernatants were analyzed by one- and two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy without any pretreatment. This experimental strategy was expected to enhance the sensitivity and selectivity of the NMR analysis, and, indeed, 13C NMR spectra of the crude extracts showed signals for products derived from the proffered 13C-labeled 1-deoxy-d-xylulose, whereas the concentrations of unlabeled metabolites from the cell background turned out to be too low for 13C NMR detection.
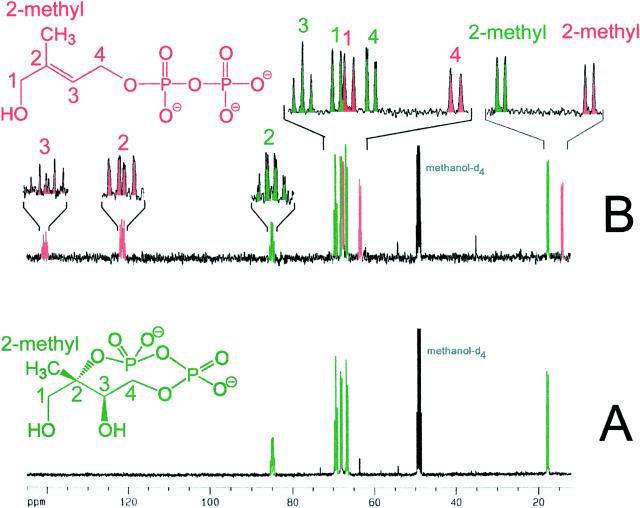
When [U-13C5]1-deoxy-d-xylulose was incubated with a recombinant strain engineered for hyperexpression of xylB, ispC, ispD, ispE, and ispF (experiment A), the 13C NMR spectrum of the cell extract was dominated by the known (19) signals of 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate (Fig. 3A, signals in green). In an analogous experiment (experiment B) with a recombinant E. coli strain expressing xylB, ispC, ispD, ispE, ispF, and, in addition, gcpE (29) (subsequently designated ispG), the 13C NMR spectrum of the cell extracts displayed, in addition to the signature of 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate, a set of 13C-coupled signals with comparable intensities belonging to a five-carbon compound (Fig. 3B, signals in red).
Figure 3.
13C NMR spectra of crude extracts obtained from the feeding of [U-13C5]1-deoxy-d-xylulose to recombinant cells of E. coli overexpressing (A) the xylB, ispC, ispD, ispE, and ispF genes and (B) the xylB, ispC, ispD, ispE, ispF, and ispG (gcpE) genes.
The 13C NMR chemical shifts of the unknown metabolite suggested a double bond (signals at 122.7 and 139.5 ppm), a methyl group (signal at 14.7 ppm), and two carbon atoms (signals at 64.5 and 68.6 ppm) connected to a heteroatom. Because the compound had been biosynthesized from uniformly 13C-labeled 1-deoxy-d-xylulose, the carbon connectivity could be established by 13C,13C coupling analysis. The three signals accounting for carbon atoms with sp3 hybridization (14.7, 64.5, and 68.5 ppm) showed 13C coupling to one adjacent 13C atom with coupling constants of 40–50 Hz (Table 3). The signal at 122.7 ppm showed 13C coupling to two adjacent 13C neighbors (coupling constants, 74 and 50 Hz), whereas the signal at 141.5 ppm showed 13C coupling to three neighboring 13C atoms (coupling constants, 74, 43, and 43 Hz).
Table 3.
NMR data of 1-hydroxy-2-(E)-methyl-2-butenyl 4-diphosphate
| Position | Chemical
shifts, ppm
|
Coupling constants, Hz
|
NMR
correlation pattern
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1H* | 13C* | 31P† | JPC | JPP | JCC | HMQC-TOCSY | HMBC | |
| 1 | 3.91 | 68.6‡§ | 43.0,§ 5.5,‡ 3.5‡ | 1 | 2-Methyl, 2, 3 | |||
| 2 | 139.5‡§ | 74.3,§ 43.3,§ 43.3§ | ||||||
| 2-Methyl | 1.51 | 14.7§ | 42.2,§ 4.0,§ 4.0§ | 2-Methyl | 1, 3, 2 | |||
| 3 | 5.57 | 122.7§ | 8.0‡ | 73.9,§ 49.8,‡ 4.0‡ | 3, 4 | |||
| 4 | 4.46 | 64.5‡§ | 5.5‡ | 49.3,‡ 5.5‡ | 4, 3 | 3, 2 | ||
| Pβ | −9.2 | 20.9 | ||||||
| Pα | −10.6 | 5.8,‡ 7.4‡ | 20.9 | |||||
HMQC, Heteronuclear multiple quantum correlation spectroscopy; TOCSY, total correlation spectroscopy; HMBC, heteronuclear multiple bond correlation spectroscopy. The solvent was a mixture of deuterated water and methanol (1:1, vol/vol).
Referenced to external trimethylsilylpropane sulfonate.
Referenced to external 85% orthophosphoric acid.
Observed with [1,3,4-13C3]1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate.
Observed with [U-13C5]1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate.
1H,13C correlation experiments (heteronuclear multiple quantum correlation, heteronuclear multiple quantum correlation–total correlation spectroscopy, and heteronuclear multiple bond correlation) revealed the 1H NMR chemical shifts, as well as the 13C,1H and 1H,1H spin systems summarized in Table 3. Together with the carbon connectivities, these data demonstrate the presence of a 1,4-dihydroxy-2-methyl-2-butenyl derivative.
In a similar experiment with proffered [3,4,5-13C3]1-deoxy-d-xylulose, only enriched signals accounting for C-1, C-3, and C-4 of the novel metabolite were observed (compare Fig. 2). Because the complexity of the 13C,13C coupling pattern was lower by comparison with the earlier experiment, it could be established beyond doubt that C-4 and C-3 resonating at 64.5 and 122.7 ppm show 13C,31P coupling with coupling constants of 5.5 and 8.0 Hz, respectively, thus suggesting the presence of a phosphate or diphosphate group at position 4.
The 1H-decoupled 31P NMR spectrum of the compound displayed a doublet at −9.2 (31P,31P coupling constant, 20.9 Hz) and a double-double doublet at −10.6 ppm (31P,31P coupling constant, 20.9 Hz; 31P,13C coupling constants, 5.8 and 7.4 Hz). Without 1H decoupling, the 31P NMR signal at −10.6 ppm was broadened, whereas the signal at −9.2 ppm was not affected by 1H decoupling. The chemical shifts as well as the observed coupling patterns confirmed the presence of a diphosphate group at position 4. Conclusive proof for the structure of the compound was eventually obtained by comparison with the NMR data of a synthetic specimen of 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate, in which the geometry of the double bond was established by nuclear Overhauser effect (spectroscopy) experiments (data to be published elsewhere). Whereas this compound had not yet been isolated from natural sources, the structurally related 1-O-β-d-glucoside of 1,4-dihydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butene has been detected in Ornithogalum montanum (30).
The metabolite was not formed in detectable amounts with the recombinant strain of experiment A lacking the overexpressed IspG protein, nor was it formed when the ispG gene of the recombinant strain used in experiment B was replaced by lytB (data not shown). Because 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate appears to be formed at the expense of 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate, we propose that it represents one of the missing links in the formation of isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate.
Discussion
The available genetic and biochemical data show that the formation of the metabolite 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate requires the IspG protein. Enzymes involved in the transformation of 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate into 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate, in addition to IspG protein, if any, must have been specified in sufficient amounts by chromosomal genes in our experimental system, because the hyperexpression of ispG is sufficient for the formation of 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate in relatively large amounts.
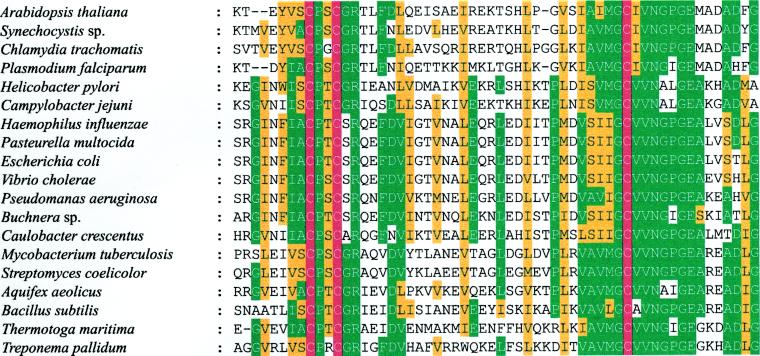
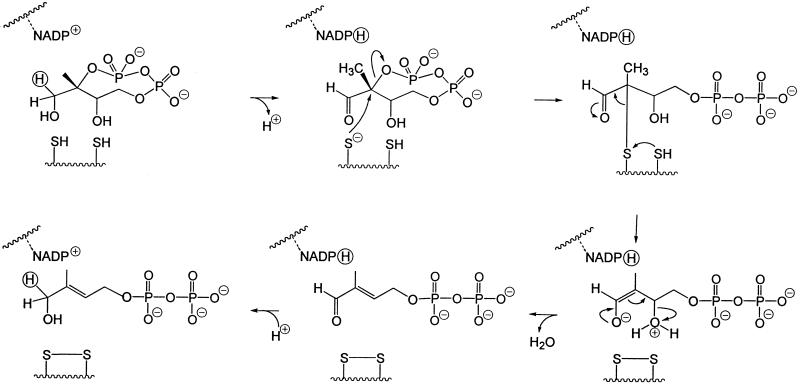
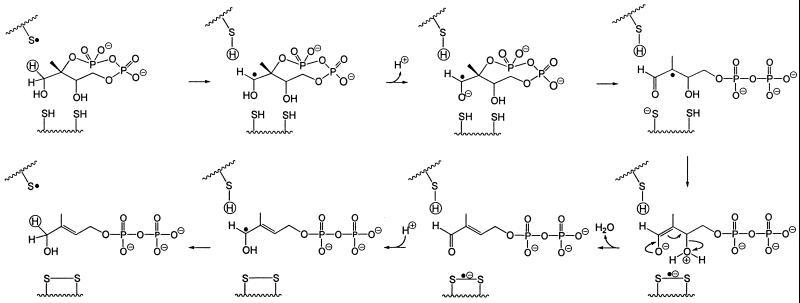
The cluster of the orthologous IspG (GcpE) group is characterized by three absolutely conserved cysteines (residues 269, 272, and 305 of the E. coli enzyme; Fig. 4). Although these residues might be part of a transition metal-binding site (e.g., for iron or zinc), no direct evidence for metal binding has been obtained. The overall reaction catalyzed by the IspG protein is a two-electron reduction process involving the cleavage of two carbon–oxygen bonds. From previous work on the E. coli pathway to terpenes it can be inferred that all of the carbon-bonded hydrogen atoms of the cyclodiphosphate precursor are preserved in the reaction product (16, 31, 32). This stringent requirement puts severe limitations on the choice of a plausible reaction mechanism for the unusual biochemical transformation; among the remaining possibilities, we would like to focus attention on the two hypothetical reaction sequences summarized in Figs. 5 and 6, both of which critically depend on the presence of at least two cysteinyl residues.
Figure 4.
Highly conserved amino acid region of 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-butenyl 4-diphosphate synthases (IspG proteins) from various organisms. Identical and similar residues conserved in more than 60% of the sequences are shown in green and yellow, respectively. Conserved cysteine residues (corresponding to residues 269, 272, and 304 of the E. coli protein) are shown in red.
Figure 5.
Hypothetical mechanism of the IspG protein-mediated reaction patterned after the mode of action of vitamin K epoxyquinone reductase (30).
Figure 6.
Hypothetical mechanism of the IspG protein-mediated reaction patterned after the mode of action of ribonucleotide reductase (31).
The mechanism illustrated in Fig. 5 is patterned after the mode of action of vitamin K epoxyquinone reductase (34). The aldehydo group generated in the first step with NADP+ as a putative cofactor is expected to accelerate the subsequent nucleophilic displacement of the pyrophosphate group at C-2 by a thiolate ion and provides the necessary electron sink in the step that leads to the formation of a disulfide bond. After β-elimination of water from the resulting enolate, the original oxidation state of C-1 is then restored by back transfer from the cofactor of the hydride ion removed in the first step.
The alternative presented in Fig. 6 is a radical process akin to the one exploited by ribonucleotide reductase (35), in which the role of the immediate initiator is assigned, by analogy, to a thiyl radical derived from the third conserved cysteine residue of the enzyme. Participation of such a radical without or with negligible exchange of the resulting thiol group with solvent protons is well precedented (34).
In both schemes reductive cleavage of the disulfide bond is necessary for multiple turnover. No clues are yet available concerning the nature of the reducing agent. An unusual sensitivity of the latter may explain why 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate is accumulated in certain bacteria under conditions of oxidative stress (35).
Acknowledgments
We thank Katrin Gärtner, Manja Weinhold, Fritz Wendling, and Ingrid Obersteiner for their skillful assistance. We thank the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie, and the Hans-Fischer Gesellschaft for support. Financial support by Novartis International AG, Basel (to D.A.) is gratefully acknowledged.
Footnotes
Data deposition: The sequence reported in this paper has been deposited in the GenBank database (accession no. AY033515).
References
- 1.Sacchettini J C, Poulter C D. Science. 1997;277:1788–1789. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5333.1788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Qureshi N, Porter J W. In: Biosynthesis of Isoprenoid Compounds. Porter J W, Spurgeon S L, editors. Vol. 1. New York: Wiley; 1981. pp. 47–94. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bloch K. Steroids. 1992;57:378–382. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(92)90081-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bach T J. Lipids. 1995;30:191–202. doi: 10.1007/BF02537822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bochar D A, Friesen J A, Stauffacher C V, Rodwell V W. In: Comprehensive Natural Product Chemistry. Cane D, editor. Vol. 2. Oxford: Pergamon; 1999. pp. 15–44. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rohmer M, Knani M, Simonin P, Sutter B, Sahm H. Biochem J. 1993;295:517–524. doi: 10.1042/bj2950517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Broers S T J. Ph.D thesis. Zürich: Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Schwarz M K. Ph.D thesis. Zürich: Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Eisenreich W, Schwarz M, Cartayrade A, Arigoni D, Zenk M H, Bacher A. Chem Biol. 1998;5:R221–R233. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(98)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rohmer M. In: Comprehensive Natural Product Chemistry. Cane D, editor. Vol. 2. Oxford: Pergamon; 1999. pp. 45–68. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Schwarz M, Arigoni D. In: Comprehensive Natural Product Chemistry. Cane D, editor. Vol. 2. Oxford: Pergamon; 1999. pp. 367–399. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Eisenreich W, Rohdich F, Bacher A. Trends Plant Sci. 2001;6:78–84. doi: 10.1016/s1360-1385(00)01812-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Giner J-L, Jaun B, Arigoni D. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1998. 1857–1858. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Leyes A E, Baker J A, Hahn F M, Poulter C D. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1999. 717–718. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rodriguez-Conception M, Campos N, Lois L M, Maldonado C, Hoeffler J F, Grodemnage-Billiard C, Rohmer M, Boronat A. FEBS Lett. 2000;473:328–332. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01552-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Charon L, Hoeffler J F, Pale-Grosdemange C, Lois L M, Campos N, Boronat A, Rohmer M. Biochem J. 2000;346:737–742. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rohdich F, Wungsintaweekul J, Fellermeier M, Sagner S, Herz S, Kis K, Eisenreich W, Bacher A, Zenk M H. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:11758–11763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.21.11758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lüttgen H, Rohdich F, Herz S, Wungsintaweekul J, Hecht S, Schuhr C A, Fellermeier M, Sagner S, Zenk M H, Bacher A, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:1062–1067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.3.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Herz S, Wungsintaweekul J, Schuhr C A, Hecht S, Lüttgen H, Sagner S, Fellermeier M, Eisenreich W, Zenk M H, Bacher A, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:2486–2490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.040554697. . (First Published February 29, 2000; 10.1073/pnas.040554697) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Adam, P., Eisenreich, W., Fellemeier, M., Hecht, S., Rohdich, F., Schuhr, C. A., Wungsintaweekul, J. Zenk, M. H. & Bacher, A. (2000) German Patent Application 10027821.3.
- 21.Cunningham F, Jr, Lafond T P, Gantt E. J Bacteriol. 2000;182:5841–5848. doi: 10.1128/jb.182.20.5841-5848.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Campos N, Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Seemann M, Rohmer M, Boronat A. FEBS Lett. 2001;488:170–173. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)02420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Altincicek B, Kollas A-K, Sanderbrand S, Wiesner J, Hintz M, Beck E, Jomaa H. J Bacteriol. 2001;183:2411–2416. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.8.2411-2416.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wungsintaweekul J, Herz S, Hecht S, Eisenreich W, Feicht R, Rohdich F, Bacher A, Zenk M H. Eur J Biochem. 2001;268:310–316. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2001.01875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hecht S, Kis K, Eisenreich W, Amslinger S, Wungsintaweekul J, Herz S, Rohdich F, Bacher A. J Org Chem. 2001;66:3948–3952. doi: 10.1021/jo0100300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson A R. Biotechnology. 1992;24:104–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bullock W O, Fernandez J M, Short J M. BioTechniques. 1987;5:376–379. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sambrook J, Fritsch E F, Maniatis T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 2nd Ed. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Baker J, Franklin D B, Parker J. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992;94:175–180. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90604-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nicoletti M, Tomassini L, Foddai S. Planta Med. 1992;58:472. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-961519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Giner J-L, Jaun B, Arigoni D. Chem. Commun. 1998. 1857–1858. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Giner J-L, Jaun B. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998;39:8021–8022. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Silverman R B, Nandi D L. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988;155:1248–1254. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81274-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Licht S, Stubbe J. In: Comprehensive Natural Product Chemistry. Poulter C D, editor. Vol. 5. Oxford: Pergamon; 1999. pp. 163–203. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ostrovsky D, Diomina G, Lysak E, Matveeva E, Ogrel O, Trutko S. Arch Microbiol. 1998;171:69–72. doi: 10.1007/s002030050680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]