Abstract
The need to calibrate to correct for sensor-to-sensor fabrication variation and sensor drift has proven a significant hurdle in the widespread use of biosensors. To maintain clinically relevant (±20% for this application) accuracy, for example, commercial continuous glucose monitors require recalibration several times a day, decreasing convenience and increasing the chance of user errors. Here, however, we demonstrate a “dual-frequency” approach for achieving the calibration-free operation of electrochemical biosensors that generate an output by using square-wave voltammetry to monitor binding-induced changes in electron transfer kinetics. Specifically, we use the square-wave frequency dependence of their response to produce a ratiometric signal, the ratio of peak currents collected at responsive and non- (or low) responsive square-wave frequencies, which is largely insensitive to drift and sensor-to-sensor fabrication variations. Using electrochemical aptamer-based (E-AB) biosensors as our test bed, we demonstrate the accurate and precise operation of sensors against multiple drugs, achieving accuracy in the measurement of their targets of within better than 20% across dynamic ranges of up to 2 orders of magnitude without the need to calibrate each individual sensor.
Graphical Abstract
INTRODUCTION
The need to calibrate has proven one of several significant hurdles limiting the clinical use of biosensors. Consider, for example, the ex vivo “home glucose meter,” which is typically calibrated either “on-strip,” in which each test run is calibrated against the response generated by a standard sample present in the capillary sample chamber,1 or at the factory prior to shipment.2 Following calibration, these sensors do achieve clinically relevant accuracy (±20%) across a 30-fold concentration range covering the 4−9 mM span of physiological glucose concentrations,3–6 but only at the expense of increased sensor complexity and cost. The situation is still worse for continuous, in vivo glucose monitoring; in-factory calibration has proven insuffcient to ensure their clinical accuracy due to the drift invariably seen in vivo,7 and reagent-using on-device autocalibration is impractical for a sensor operating in situ within the body over many days. Continuous glucose monitors are thus instead calibrated several times a day against finger prick blood samples measured using factory calibrated ex vivo devices,8 decreasing convenience and leading to relatively low adoption rates despite their clear clinical value.7,9 The need for calibration likewise introduces opportunities for error, leading in turn to inappropriate clinical action.10 Driven by the relative ease of collecting finger-prick samples, for example, the calibration of continuous glucose monitors is performed using whole blood, which does not always accurately reflect the interstitial glucose concentration that the sensor is actually monitoring.11
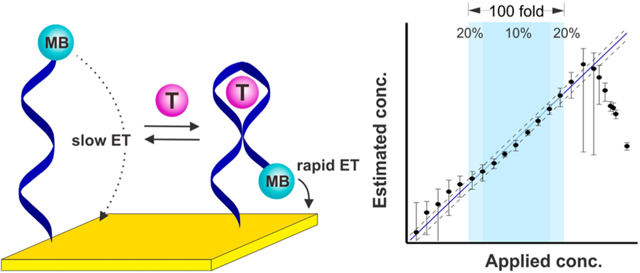
Motivated by a desire to increase the adaptation of biosensors to clinical practice, we present here a means of achieving calibration-free operation for a broad class of electrochemical biosensors employing an increasingly widely used signaling mechanism: binding-induced changes in electron transfer kinetics. As our test bed, we have employed electrochemical aptamer-based (E-AB) sensors (Figure 1), a sensing platform that we,12–15 and others,16–18 have developed to support the measurement of a wide range of molecular targets. E-AB sensors are comprised of a redox-reporter-modified DNA or RNA “probe” that is covalently attached to a self-assembled monolayer deposited on an interrogating electrode (Figure 1A).19 The binding of target to this probe alters the kinetics with which electrons exchange to/from the redox reporter via either binding-induced conformational changes or due to the steric bulk of the target,20 producing an easily measurable change in current when the sensor is interrogated, for example, using square wave voltammetry (Figure 1B). Among their potentially important attributes, EAB sensors are rapid, specific and selective enough to be deployed directly in complex clinical samples and even in situ within the living body.21,22 As is nearly universally true for the electrochemical biosensors reported to date, however, E-AB sensors require calibration in order to achieve acceptable accuracy in the face of sensor-to-sensor fabrication variation. Here, however, we describe a “dual-frequency” calibration-free method of operating E-AB sensors that renders their output “ratiometric”; i.e., a unit-less value that is largely independent of sensor-to-sensor fabrication variation and sensor degradation, thus obviating the need to calibrate each individual sensor. We postulate this will significantly improve the ease of use of both E-AB sensors and other sensors that, like E-AB sensors, rely on binding-induced changes in electron transfer kinetics to generate their output signal.
Figure 1.
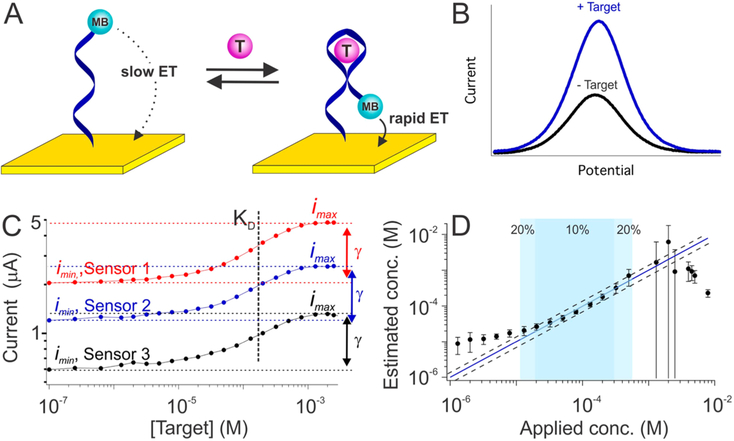
Electrochemical aptamer-based (E-AB) biosensors. (A) E-AB sensors are comprised of an electrode-bound, redox reporter-modified aptamer that undergoes a binding-induced conformational change. (B) This conformational change upon target binding alters the kinetics with which the reporter (here methylene blue, MB) exchanges electrons with the electrode, producing a target-dependent change in current when the sensor is interrogated via electrochemical methods, such as square wave voltammetry, that are sensitive to changes in electron transfer kinetics. (C) Because of variations in electrode surface area and aptamer packing density, the absolute currents output by E-AB sensors vary dramatically from sensor to sensor. Shown, for example, are titrations of three independently hand-fabricated cocaine-detecting sensors interrogated in undiluted blood serum. Though both the maximum and minimum observed currents observed (imax and imin) vary significantly from sensor to sensor, however, their ratio (denoted as γ) remains constant, as does aptamer affinity, KD. (D) To correct for such sensor-to-sensor variation we have historically used calibration (to determine imin) in a target-free reference sample, which works because the relative output of E-AB sensors (i/imin) is quite reproducible (Figure S1). Using such calibration (and prior knowledge of the constants γ and KD), E-AB sensors achieve excellent accuracy and precision over a broad range of target concentrations. The three cocaine-detecting sensors from panel C, for example, produce concentration estimates (eq 3) within ±10% of the actual (spiked) concentration over the range from 20 to 300 μM (dark blue) and within ±20% over the range from 10 to 600 μM (light blue). The dashed lines represent ±20% accuracy bands. The binding-versus relative occupancy curve becomes quite flat at very high or very low target concentrations (panel C), thus accounting for the poor accuracy and precision seen at target concentrations below 10 μM and above 1 mM. The error bars shown in panel D and in the following figures represent the standard deviation of at least three independently hand-fabricated sensors. Additional data for individual sensors (illustrating, for example, the good precision of calibrated sensors) is presented in Figure S2.
RESULTS
Provided the aptamer binds a single molecule of its target the relationship between target concentration and the voltammetric peak current, i, output by an E-AB sensor is given by23
| (1) |
where KD is the aptamer’s dissociation constant, and imin and imax are the peak currents that would be seen in the absence of target and in the presence of saturating target, respectively. The former parameter, KD, is a constant for all sensors employing a given aptamer under a given set of measurement conditions (Figure 1C) and is only very weakly dependent on packing density.24 The ratio of imax to imin, denoted here as γ, is likewise constant (Figure 1C), and thus eq 1 simplifies to
| (2) |
From this, we see that target concentration is related to four parameters, one of which, i, is the sensor output in the sample, and two more of which, γ and KD, are constants only needing to be determined once during the original design and validation of a given type of sensors, rather than for each individual sensor. In contrast, the fourth parameter, imin, varies dramatically from one individual sensor to the next due to significant variation in the microscopic surface area of the sensing electrode and (to a much lesser extent) the density with which the reporter-modified aptamers are packed onto it. This variation is so great that we cannot derive target concentrations from measurements of peak current alone (Figure 1C). Fortunately, however, relative E-AB signal change (e.g., i/imin) is well correlated with target concentration irrespective of sensor-to-sensor variation in imin (Figure S1). Thus, after determining imin for an individual sensor via calibration we can use the ratio i/imin to determine target concentrations accurately and precisely via a relationship (recast from eq 2):
| (3) |
Applying this approach, for example, to a previously described25,26 cocaine-detecting E-AB sensor deployed in undiluted blood serum, we achieve concentration estimates within ±10% of the actual (spiked) concentration of the drug over the range from 20 to 300 μM and within ±20% over the range from 10 to 600 μM (Figure 1D). This success not withstanding, however, the required calibration for each individual sensor is inconvenient, motivating us to develop a calibration-free approach to E-AB sensing.
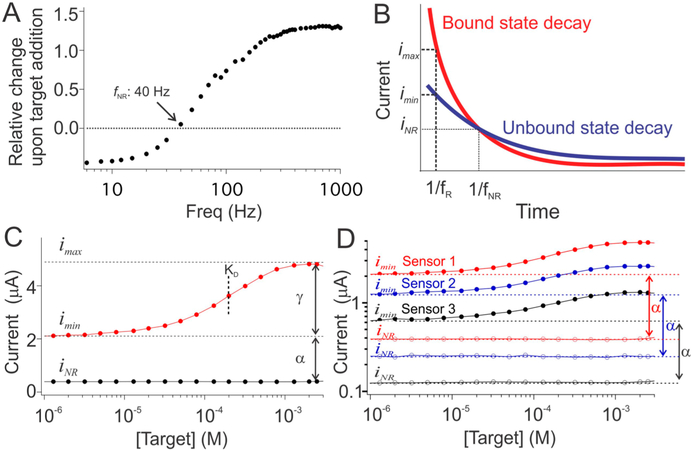
To avoid the need to calibrate against a reference sample for each individual sensor, we exploit the strong square-wave frequency dependence of E-AB signaling, using it to generate a signal that is (i) proportional to imin, and (ii) constant irrespective of whether or not target is present. Specifically, because E-AB signaling arises due to binding-induced changes in electron transfer kinetics the output current of E-AB sensors is sensitive to square-wave frequency.27 Enough so that there is a frequency (the value of which depends on the aptamer and redox reporter employed27,28) at which the sensor does not respond to its target (Figure 2A). The origins of this nonresponsive frequency, f NR, lie in the interplay between the electron transfer kinetics of the bound and unbound states of the aptamer. To see this, it is helpful to assume a two-state binding model in which electron transfer from/to the redox reporter is the sum of two exponential decays, one associated with the bound state and a second associated with the unbound state (Figure 2B). As must be true for single exponential decays differing in time constant the two curves cross at a single, specific point. At this instant, the currents produced by the bound and unbound states are equal, and thus the observed current is independent of the relative populations of the two states, rendering it independent of target concentration. Conveniently, the current in square wave voltammetry is sampled at a specific time after the initiation of the square-wave pulse. If this time delay, which is set by the square-wave frequency, matches the crossing time of the exponential decays, the output of the square-wave voltammogram will also prove independent of target concentration, thus accounting for the existence of iNR.
Figure 2.
Calibration-free means of estimating imin using a nonresponsive square-wave frequency. (A) E-AB signaling arises due to a binding-induced change in electron transfer kinetics, and thus the relative change in peak current observed upon the addition of saturating target is strongly dependent on the square-wave frequency used to interrogate the sensor. Enough so that there is a specific frequency (40 Hz for the cocaine-detecting sensor shown here) at which sensors of a given type do not respond to target. (B) The origins of this nonresponsive frequency are as follows. When subject to a potential pulse, E-AB sensors produce an exponentially decaying current, the lifetime of which depends on whether or not the aptamer is bound to its target. At the instant the “bound” and “unbound” current decay curves cross (t = 1/f NR) the currents produced by the two states are the same irrespective of which state (or mixture of states) the aptamer is populating. (C) Square wave voltammetry can be used to sample the current at this specific time by setting its frequency to f NR (for the cocaine-detecting sensors shown here, 40 Hz; black curve), at which the sensor’s output, iNR, is constant irrespective of target concentration. In contrast, at a responsive frequency, f R (here 500 Hz; red trace), the output is strongly dependent on the binding state of the aptamer. (D) The proportionality constant, α, which relates imin to iNR, is quite reproducible from sensor to sensor for a given type of sensor, as shown here for the same three cocaine-detecting sensors employed in Figure 1.
The current output at the nonresponsive frequency provides a means of estimating imin (Figure 2C). Specifically, iNR is proportional to imin with a proportionality factor, α, that is a constant for all sensors of a given type under a given set of measurement conditions (Figure 2D). Thus, given knowledge of the constants α, γ, and KD we can estimate the concentration of the target molecule from the sensor’s output at both a responsive frequency and at the nonresponsive frequency via the relationship:
| (4) |
without the need to calibrate each individual sensor.
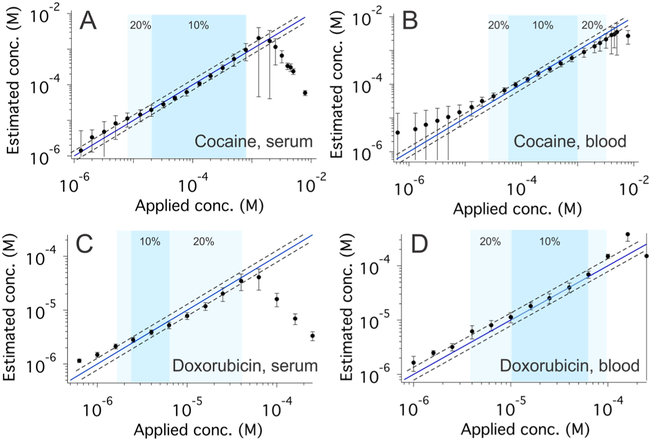
As our first proof-of-principle for this “dual-frequency” approach to calibration-free E-AB sensing, we applied it to the cocaine-detecting E-AB sensor.25,26 To do so, we first used a training set of individually hand-fabricated sensors to identify a responsive square-wave frequency, 500 Hz, and a frequency at which the sensor is not responsive to its target, 40 Hz (Figure 2A and Figure S3). We then challenged these sensors with increasing concentrations of target while interrogating them at these responsive and nonresponsive frequencies to generate a titration data that we globally fit to eq 4 to determine α, γ, and KD (Figures S4–7 and Table S1). (Note that these parameters are dependent on the nature of the sample; e.g., serum versus whole blood, but they remain effectively constant for different batches of the same sample matrix; for example, testing our sensors in different batches of bovine blood produces effectively identical sensor parameters.) With this prior knowledge of these parameters in hand, we then applied eq 4 to measurements of i and iNR obtained from another set of sensors that were not used to define the relevant parameters and that were interrogated in a new (and different) batch of serum or whole blood. In undiluted blood serum, the estimated concentrations we obtained were accurate to within ±10% (relative to the concentration spiked into the sample) across a 40-fold concentration range and within ±20% across a 100-fold range (Figure 3A, Figure S8). Estimated target concentrations in undiluted whole blood were accurate to within ±10% across a 15-fold concentration range and within ±20% across a 100-fold range (Figure 3B, Figure S8). These results compare quite favorably to the accuracy observed for (calibrated) commercial glucose sensors, which can measure across a 30-fold concentration range (1 to 30 mM) with relative error of ±20%.6
Figure 3.
Accurate, calibration-free measurement for cocaine and doxorubicin. The use of iNR to normalize E-AB sensor outputs (eq 4) produces excellent accuracy and precision. (A and B) Shown are cocaine-detecting sensors interrogated in undiluted blood serum and whole blood, respectively. Under the former conditions, sensor-estimated concentrations are accurate to within ±10% (i.e., the estimated concentration is within 10% of the spiked concentration) over the concentration range 20 to 800 μM (dark blue) and ±20% over the range 8 to 800 μM (light blue). Under the latter conditions, we observe likewise excellent accuracy, achieving accuracy within ±10% over the range 60 μM to 1 mM (dark blue) and ±20% over the range 20 μM to 2 mM (light blue). The dashed lines in all four panels represent ±20% error bands. (C and D) Shown are doxorubicin-detecting sensors interrogated in undiluted blood serum and whole blood, respectively. Under the former conditions, we achieved excellent accuracy within ±10% over the range 2.5 to 6 μM (dark blue) and 20% over the range 2 to 40 μM (light blue). Under the latter conditions, once again, these sensors produced excellent accuracy, achieving accuracy within ±10% over the range 10 to 60 μM (dark blue) and within ±20% over the range 4 to 100 μM (light blue). Additional data for individual sensors (illustrating, for example, the good precision of these sensors) are presented in Figures S8 and S14.
Our approach to performing calibration-free E-AB sensing also holds for sensors employing other aptamers. To show this, we first employed a sensor against the cancer chemotherapeutic doxorubicin,21,22 defining α, γ, and KD via the global fitting of data collected from a training set of individually hand-fabricated sensors (Figures S9–13 and Table S1). Applying these values to data collected from sensors excluded from the training set, we once again obtained excellent accuracy. Specifically, when making measurements in undiluted serum the estimated target concentrations, we obtained are accurate to within ±10% of the spiked concentrations across an approximate 3-fold concentration range and within ±20% across a 20-fold range (Figure 3C, Figure S14), with these ranges expanding to a 6-fold and a 25-fold concentration spans (Figure 3D, Figure S14), respectively, when the sensors were deployed in undiluted whole blood.
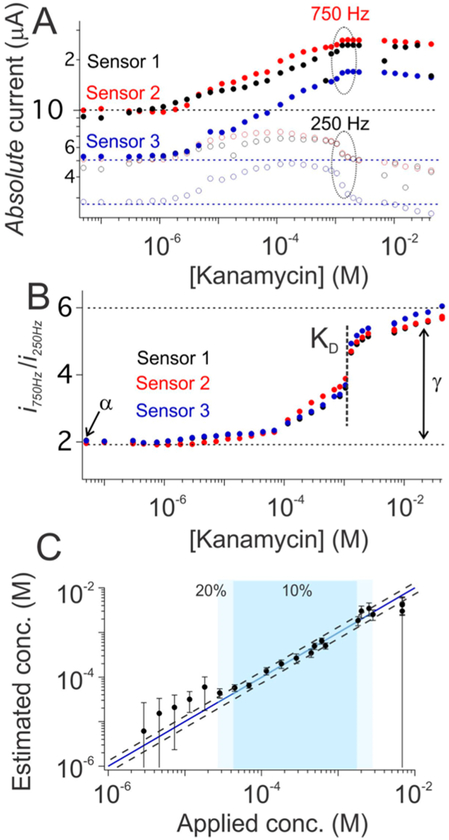
Both of the examples we explored above are sensors that exhibit nonresponsive frequencies. That is, sensors employing aptamers that bind in a two-state manner (unbound and singly bound), and for which there exists a square-wave frequency at which the peak currents of these two states are identical (the exponential decay curves cross, Figure 2B), thus rendering the output current a constant irrespective of the target concentration. If, in contrast, some third state (e.g., a state in which more than one copy of the target molecule is bound to each aptamer) was significantly populated, it would unlikely be the case that all the three exponential current decays would cross at a single point (Figure S15A), reducing the likelihood of there being a nonresponsive frequency at which the sensor output is independent of target concentration (Figure S15B). Even for such “multi-phase” binding, however, we can still achieve accurate, calibration-free operation. To demonstrate this, we employed an aminoglycoside-detecting E-AB sensor29 that, presumably due to the presence of an additional binding event at high target concentrations (Figures 4A, Figure S16), does not exhibit a nonresponsive frequency (Figure S15). To perform the calibration-free operation of this sensor, we replaced the nonresponsive frequency with a “low-response” frequency (here 250 Hz). Again we find that, though the absolute currents obtained from such sensors vary dramatically from sensor to sensor (Figure 4A), the ratio of the currents seen at a high-responsive frequency (here 750 Hz) and this low-response frequency is quite reproducible and maintains a binding isotherm (Figure 4B). Using this ratio as sensor output, we can derive target concentration without the need for the calibration of each individual sensor via the relationship:
| (5) |
Here, α is given by , instead of imin/iNR for previous two examples, where imin and are the currents seen at the high-responsive and low-response frequency in the absence of target, respectively. The constant γ is, likewise, the ratio of the maximum value of the i/iLR output (i.e., at saturating target) to its minimum value (Figure 4B), and KD is the midpoint of the i/iLR versus target concentration curve. As is true for previous two examples, these three parameters for all sensors of a given type, here for kanamycin-detecting sensors, are constant and can be determined during the design process. Using α, γ, and KD defined via global fitting to data collected from a training set of individually hand-fabricated sensors (Figures S17–S18 and Table S1) and then applied to an out-of-training set collection of sensors we achieved accuracy within ±10% of the spiked kanamycin concentration across a 25-fold concentration range and within ±20% across a 100-fold concentration range (Figure 4C).
Figure 4.
Accurate, calibration-free kanamycin measurements. Dual-frequency calibration-free operation can be achieved even for sensors that lack a nonresponsive frequency. (A) The kanamycin-detecting EAB sensor, for example, does not exhibit a frequency at which its output is independent of target concentration (Figure S15), likely because the binding of its aptamer is not two-state (e.g., the sensor output trends downward at high kanamycin concentrations, presumably reflecting a second binding event). The sensor’s output at a low-response frequency (250 Hz; open circles) nevertheless parallels its output at a more responsive frequency (750 Hz; solid circles). (B) That is, despite the modest target-concentration-dependence of the output current, iLR, observed at the low-response frequency the ratio i/iLR is both indicative of target concentration and largely independent of sensor-to-sensor variation. (C) Exploiting this (eq 5) we obtain calibration-free estimates of kanamycin concentration in buffer that are accurate to within ±10% over the range 40 μM to 1 mM (dark blue) and within ±20% over the range 30 μM to 3 mM (light blue). Additional data for individual sensors (illustrating, for example, the good precision of these sensors) are presented in Figure S19.
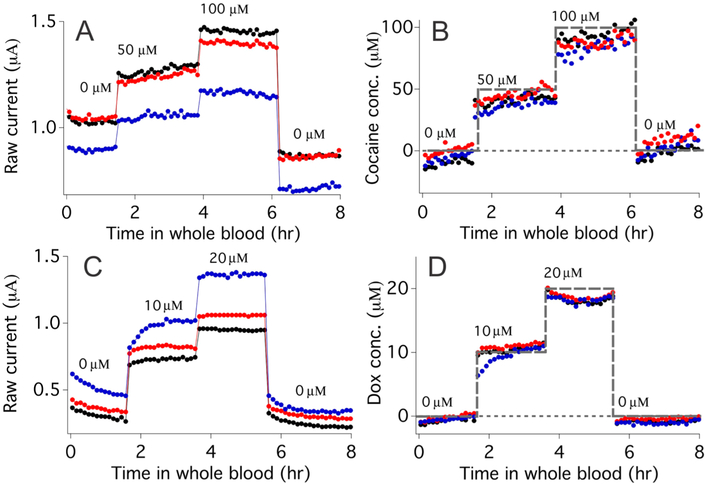
To further test the scope of dual-frequency calibration-free EAB sensing, we also challenged both cocaine- and doxorubicin-detecting sensors in flowing whole blood. Under these very demanding conditions, the absolute currents generated by cocaine-detecting sensors vary significantly, not only from one sensor to the next but also for a single sensor over the course of a few hours (Figure 5A). After correction using eq 4, however, we obtained accurate estimates of the applied cocaine concentration and good return to baseline (Figure 5B). Similar results likewise hold for doxorubicin-detecting sensors in flowing whole blood, with dual-frequency measurements once again producing good accuracy over several hours (Figure 5C,D). Of course, the need to collect two voltammograms per data point reduces the time resolution of our dual-frequency approach relative to that of (calibration-requiring) single-scan approaches, it nevertheless remains just seconds. Here, for example, we complete the necessary scan pairs in just 10.6 s, representing time resolution more than sufficient here for the real-time monitoring of small molecule drugs in bloodstream.
Figure 5.
Continuous, calibration-free measurement of cocaine and doxorubicin in flowing whole blood. (A) When challenged in vitro in flowing, undiluted whole blood the absolute peak currents of cocaine-detecting E-AB sensors vary significantly from sensor to sensor and even for a single sensor over several hours (compare the zero-target baselines of individual sensors at 1 and 6 h). (B) Dual-frequency calibration-free sensing nevertheless produces reasonably accurate concentration estimations of cocaine (spiked concentrations shown as a gray dashed line) even under these demanding conditions. (C) Doxorubicin-detecting sensors exhibit similar variability when placed in flowing whole blood. (D) Dual-frequency calibration-free measurements, however, once again suppress this variability, producing concentration estimates in close agreement with the spiked concentration (gray dashed line).
DISCUSSION
Here we have demonstrated a dual-frequency approach to achieving calibration-free operation of E-AB sensors. Using it, we produce target concentration estimates for three drugs within ±20% of the spiked target concentration across concentration ranges of 20- to 100-fold. We have also used this approach to perform the continuous measurements of two drugs in flowing, undiluted whole blood over the course of many hours, again achieving good accuracy and precision despite the significant drift seen in absolute sensor current under these more challenging conditions. Together, these results compare favorably with the performance of commercial glucose sensors, which are typically accurate to of order ±20% across a 30-fold concentration range.6 Moreover, unlike the case for commercial glucose sensors, we achieve this level of performance without the use of calibration, suggesting that our approach may prove to be particular user-friendly. Indeed, dual-frequency calibration-free operation may even enable accurate measurements under conditions in which calibration is difficult to perform, such as for sensors employed directly in situ in the living body.
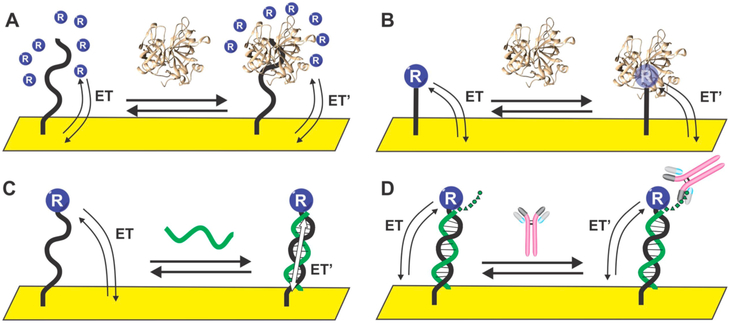
Given the nature of our dual-frequency calibration-free approach, we postulate it should be adaptable to nearly any electrochemical system that undergoes a change in its electron transfer kinetics in response to a target binding. Examples include sensors based on binding-induced changes linked to changes in the diffusion of solution-phase redox-reporter (Figure 6A);30,31 on binding-induced displacement of ligands on the reporter32,33 or binding-induced changes in redox-reporter’s reorganizational energy (Figure 6B);34–36 on bind-ing-induced changes in the coupling constant that defines how rapidly electrons can transfer between the electrode and the reporter (Figure 6C);37–39 or on sterically induced changes in the efficiency with which a scaffold-attached redox reporter approaches an underlying electrode surface (Figure 6D).40,41 Given these arguments, we postulate that calibration-free approach described here will benefit a wide variety of electrochemical sensor architectures and may significantly improve the clinical utility of many biosensors.
Figure 6.
Examples of electrochemical biosensors that are thought to signal via binding-induced changes in electron transfer kinetics. These include sensors based on binding-induced changes in (A) a redox reporter’s ability to diffuse to the electrode surface; (B) redox-reporter reorganization energy, which in turn alters electron transfer kinetics; (C) through-DNA charge transfer; and (D) sterically induced changes in the efficiency with which a “scaffold mounted” redox reporter approaches the electrode surface.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the Institute for Collaborative Biotechnologies through US Army Research Office Grant W911NF-09–0001 and the National Institutes of Health (Grant R01AI107936). H.L. acknowledges support from an “Early Postdoc Mobility fellowship” from the Swiss National Science Foundation, P.D.-D. from Fonds de recherche du Quebec -Nature et Technologies and Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council, and G.O. via a Postdoc Fellowship from the Government of the Basque Country, Spain.
Footnotes
Supporting Information
The Supporting Information is available free of charge on the ACS Publications website at DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b05412.
Experimental details (PDF)
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): K.W.P. discloses service on the scientific advisory boards of Diagnostic Biochips Inc., Ilumi Health, and Eccrine Systems. H.L., P.D.-D, G.O., and K.W.P have filed a provisional patent based on the work presented in this paper.
REFERENCES
- (1).Noble M; Rippeth J; Edington D; Rayman G; Brandon-Jones S; Hollowood Z; Kew SJ Diabetes Sci. Technol 2014, 8, 766–775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (2).Yue X-Y; Zheng Y; Cai Y-H; Yin N-N; Zhou J-X PLoS One 2013, 8, e60070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (3).Kilo C Sr.; Dickey WT Jr.; Joynes JO; Pinson MB; Baum JM; Parkes JL; Parker DR Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract 2006, 74, 66–74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (4).International Organization for Standardization. Determination of performance criteria for in vitro blood glucose monitoring systems for management of human diabetes mellitus. ISO 15197:2003. Geneva, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- (5).U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Review criteria for assessment of portable invasive blood glucose monitoring in vitro diagnostic devices which use glucose oxidase, dehydrogenase, or hexokinase methodology; Food and Drug Administration: Rockville, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- (6).Heller A; Feldman B Chem. Rev 2008, 108, 2482–2505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (7).Hovorka R Nat. Rev. Endocrinol 2011, 7, 385–395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (8). https://www.dexcom.com/get-started-cgm?utm_source= adwords&utm_campaign=b&sfc=70133000001LlpgAAC&gclid= CO3fwIK419MCFRSDfgod2nwEiw.
- (9).Kim J; Kim M; Lee M-S; Kim K; Ji S; Kim Y-T; Park J; Na K; Bae KH; Kyun Kim H; Bien F; Young Lee C; Park J-U Nat. Commun 2017, 8, 14997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (10).Klonoff DC Diabetes Spectr. 2014, 27, 174–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (11).Waltz E Nat. Biotechnol 2017, 35, 11–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (12).Lubin AA; Lai RY; Baker BR; Heeger AJ; Plaxco KW Anal. Chem 2006, 78, 5671–5677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (13).Xiao Y; Lubin AA; Heeger AJ; Plaxco KW Angew. Chem., Int. Ed 2005, 44, 5456–5459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (14).Ferguson BS; Hoggarth DA; Maliniak D; Ploense K; White RJ; Woodward N; Hsieh K; Bonham AJ; Eisenstein M; Kippin TE; Plaxco KW; Soh HT Sci. Transl. Med 2013, 5, 213ra165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (15).Li H; Arroyo-Curras N; Kang D; Ricci F; Plaxco KW J. Am. Chem. Soc 2016, 138, 15809–15812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (16).Ferapontova EE; Olsen EM; Gothelf KV J. Am. Chem. Soc 2008, 130, 4256–4258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (17).Zuo X; Song S; Zhang J; Pan D; Wang L; Fan CJ Am. Chem. Soc 2007, 129, 1042–1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (18).Liu Y; Yan J; Howland MC; Kwa T; Revzin A Anal. Chem 2011, 83, 8286–8292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (19).Lubin AA; Plaxco KW Acc. Chem. Res 2010, 43, 496–505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (20).Bonham AJ; Paden NG; Ricci F; Plaxco KW Analyst 2013, 138, 5580–5583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (21).Arroyo-Currás N; Somerson J; Vieira PA; Ploense KL; Kippin TE; Plaxco KW Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2017, 114, 645–650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (22).Li H; Dauphin-Ducharme P; Arroyo-Curras N; Tran CH; Vieira PA; Li S; Shin C; Somerson J; Kippin TE; Plaxco KW Angew. Chem., Int. Ed 2017, 56, 7492–7495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (23).Demchenko AP Lab Chip 2005, 5, 1210–1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (24).White RJ; Phares N; Lubin AA; Xiao Y; Plaxco KW Langmuir 2008, 24, 10513–10518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (25).Baker BR; Lai RY; Wood MS; Doctor EH; Heeger AJ; Plaxco KW J. Am. Chem. Soc 2006, 128, 3138–3139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (26).Stojanovic MN; de Prada P; Landry DW J. Am. Chem. Soc 2001, 123, 4928–4931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (27).White RJ; Plaxco KW Anal. Chem 2010, 82, 73–76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (28).Dauphin-Ducharme P; Plaxco KW Anal. Chem 2016, 88, 11654–11662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (29).Rowe AA; Bonham AJ; White RJ; Zimmer MP; Yadgar RJ; Hobza TM; Honea JW; Ben-Yaacov I; Plaxco KW PLoS One 2011, 6, e23783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (30).Katayama Y; Ohuchi Y; Higashi H; Kudo Y; Maeda M Anal. Chem 2000, 72, 4671–4674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (31).Le Floch F; Ho HA; Leclerc M Anal. Chem 2006, 78, 4727–4731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (32).Prasad E; Knettle BW; Flowers RA J. Am. Chem. Soc 2004, 126, 6891–6894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (33).Chan J; Dodani SC; Chang CJ Nat. Chem 2012, 4, 973–984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (34).Plumb K; Kraatz H-B Bioconjugate Chem. 2003, 14, 601–606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (35).Orlowski GA; Chowdhury S; Kraatz H-B Langmuir 2007, 23, 12765–12770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (36).Feld DJ; Hsu H-T; Eckermann AL; Meade TJ Langmuir 2012, 28, 939–949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (37).Uzawa T; Cheng RR; White RJ; Makarov DE; Plaxco KW J. Am. Chem. Soc 2010, 132, 16120–16126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (38).Genereux JC; Barton JK Chem. Rev 2010, 110, 1642–1662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (39).Boon EM; Ceres DM; Drummond TG; Hill MG; Barton JK Nat. Biotechnol 2000, 18, 1096–1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (40).Ge B; Huang YC; Sen D; Yu H-Z Angew. Chem., Int. Ed 2010, 49, 9965–9967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (41).Cash KJ; Ricci F; Plaxco KW J. Am. Chem. Soc 2009, 131, 6955–6957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.