Abstract
Background
Fibromyalgia is characterized by chronic widespread pain that leads to reduced physical function. Exercise training is commonly recommended as a treatment for management of symptoms. We examined the literature on resistance training for individuals with fibromyalgia. Resistance training is exercise performed against a progressive resistance with the intention of improving muscle strength, muscle endurance, muscle power, or a combination of these.
Objectives
To evaluate the benefits and harms of resistance exercise training in adults with fibromyalgia. We compared resistance training versus control and versus other types of exercise training.
Search methods
We searched nine electronic databases (The Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, PEDro, Dissertation Abstracts, Current Controlled Trials, World Health Organization (WHO) International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, AMED) and other sources for published full‐text articles. The date of the last search was 5 March 2013. Two review authors independently screened 1856 citations, 766 abstracts and 156 full‐text articles. We included five studies that met our inclusion criteria.
Selection criteria
Selection criteria included: a) randomized clinical trial, b) diagnosis of fibromyalgia based on published criteria, c) adult sample, d) full‐text publication, and e) inclusion of between‐group data comparing resistance training versus a control or other physical activity intervention.
Data collection and analysis
Pairs of review authors independently assessed risk of bias and extracted intervention and outcome data. We resolved disagreements between the two review authors and questions regarding interpretation of study methods by discussion within the pairs or when necessary the issue was taken to the full team of 11 members. We extracted 21 outcomes of which seven were designated as major outcomes: multidimensional function, self reported physical function, pain, tenderness, muscle strength, attrition rates, and adverse effects. We evaluated benefits and harms of the interventions using standardized mean differences (SMD) or mean differences (MD) or risk ratios or Peto odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CI). Where two or more studies provided data for an outcome, we carried out a meta‐analysis.
Main results
The literature search yielded 1865 citations with five studies meeting the selection criteria. One of the studies that had three arms contributed data for two comparisons. In the included studies, there were 219 women participants with fibromyalgia, 95 of whom were assigned to resistance training programs. Three randomized trials compared 16 to 21 weeks of moderate‐ to high‐intensity resistance training versus a control group. Two studies compared eight weeks of progressive resistance training (intensity as tolerated) using free weights or body weight resistance exercise versus aerobic training (ie, progressive treadmill walking, indoor and outdoor walking), and one study compared 12 weeks of low‐intensity resistance training using hand weights (1 to 3 lbs (0.45 to 1.36 kg)) and elastic tubing versus flexibility exercise (static stretches to major muscle groups).
Statistically significant differences (MD; 95% CI) favoring the resistance training interventions over control group(s) were found in multidimensional function (Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ) total decreased 16.75 units on a 100‐point scale; 95% CI ‐23.31 to ‐10.19), self reported physical function (‐6.29 units on a 100‐point scale; 95% CI ‐10.45 to ‐2.13), pain (‐3.3 cm on a 10‐cm scale; 95% CI ‐6.35 to ‐0.26), tenderness (‐1.84 out of 18 tender points; 95% CI ‐2.6 to ‐1.08), and muscle strength (27.32 kg force on bilateral concentric leg extension; 95% CI 18.28 to 36.36).
Differences between the resistance training group(s) and the aerobic training groups were not statistically significant for multidimensional function (5.48 on a 100‐point scale; 95% CI ‐0.92 to 11.88), self reported physical function (‐1.48 units on a 100‐point scale; 95% CI ‐6.69 to 3.74) or tenderness (SMD ‐0.13; 95% CI ‐0.55 to 0.30). There was a statistically significant reduction in pain (0.99 cm on a 10‐cm scale; 95% CI 0.31 to 1.67) favoring the aerobic groups.
Statistically significant differences were found between a resistance training group and a flexibility group favoring the resistance training group for multidimensional function (‐6.49 FIQ units on a 100‐point scale; 95% CI ‐12.57 to ‐0.41) and pain (‐0.88 cm on a 10‐cm scale; 95% CI ‐1.57 to ‐0.19), but not for tenderness (‐0.46 out of 18 tender points; 95% CI ‐1.56 to 0.64) or strength (4.77 foot pounds torque on concentric knee extension; 95% CI ‐2.40 to 11.94). This evidence was classified low quality due to the low number of studies and risk of bias assessment. There were no statistically significant differences in attrition rates between the interventions. In general, adverse effects were poorly recorded, but no serious adverse effects were reported. Assessment of risk of bias was hampered by poor written descriptions (eg, allocation concealment, blinding of outcome assessors). The lack of a priori protocols and lack of care provider blinding were also identified as methodologic concerns.
Authors' conclusions
The evidence (rated as low quality) suggested that moderate‐ and moderate‐ to high‐intensity resistance training improves multidimensional function, pain, tenderness, and muscle strength in women with fibromyalgia. The evidence (rated as low quality) also suggested that eight weeks of aerobic exercise was superior to moderate‐intensity resistance training for improving pain in women with fibromyalgia. There was low‐quality evidence that 12 weeks of low‐intensity resistance training was superior to flexibility exercise training in women with fibromyalgia for improvements in pain and multidimensional function. There was low‐quality evidence that women with fibromyalgia can safely perform moderate‐ to high‐resistance training.
Keywords: Adult, Female, Humans, Exercise, Fibromyalgia, Fibromyalgia/rehabilitation, Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic, Resistance Training, Resistance Training/methods
Plain language summary
Resistance training (such as weight‐lifting) for fibromyalgia
Research question
What are the effects of resistance exercise training for people with fibromyalgia on wellness, symptoms, fitness, and adverse effects?
Background
What problems does fibromyalgia cause? People with fibromyalgia have chronic, widespread body pain, and often have fatigue (feeling tired), stiffness, depression and problems sleeping.
What is resistance training? Resistance training is exercise that involves lifting weights, or using machines or elastic bands that provide resistance to movement.
‐ This review only looked at resistance training programs supervised by a trained professional.
‐ We compared resistance training to no exercise and to other types of exercise.
Study characteristics
After looking for all related studies in March 2013, we found 5 studies with 219 women with fibromyalgia. Ninety‐five (95) of these women did resistance training.
Only three studies looked at wellness, symptoms, and fitness in 54 women with fibromyalgia who did resistance training and 53 women with fibromyalgia who did not do resistance training.
The 54 women with fibromyalgia who did resistance training:
‐ did supervised resistance training sessions using exercise equipment, free weights, and body weight
‐ exercised 2 to 3 times a week
‐ exercised for 16 to 21 weeks.
Key results: what happened to women with fibromyalgia who took part in resistance training for 16 to 21 weeks compared to those who did not do resistance training during this time period?
Overall well‐being (multidimensional function) on a scale of 0 to 100 units
Women who did resistance training rated their well‐being 25 units better while women who did not do resistance training rated their well‐being 8 units better.
Therefore, women who did resistance training rated their well‐being 17 units better at the end of the studies than those who did not do resistance training.
Physical function (ability to do normal activities) on a scale of 0 to 100 units
Women who did resistance training rated their ability to do normal activities 8 units better while women who did not do resistance training rated their ability to do normal activities 2 units better.
Therefore, women who did resistance training rated their ability to function 6 units better at the end of the studies than women who did not do resistance training.
Pain on a scale of 0 to 10 units
Women who did resistance training rated their pain 3.5 units better while women who did not do resistance training rated their pain 1 unit better.
Therefore, women who did resistance training rated their pain 2.5 units better at the end of the studies than women who did not do resistance training.
Tenderness estimated by number of points (out of 18) perceived as painful with 4 kilograms of pressure
Women who did resistance training had 4 fewer tender points while women who did not do resistance training had 2 fewer tender points.
Therefore, women who did resistance training had 2 fewer tender points at the end of the studies than women who did not do resistance training.
Muscle strength
Women who did resistance training could lift 28 kilograms more while women who did not do resistance training could lift 1 kilogram more.
Therefore, women who did resistance training could lift 27 kilograms more at the end of the studies than women who did not do resistance training.
Dropping out (number of women out of 100 who dropped out of the studies)
Thirteen women who did resistance training dropped out while 4 women who did not do resistance training dropped out.
Therefore, 9 more women out of 100 who did resistance training dropped out of the studies than women who did not do resistance training.
Conclusions
For women with fibromyalgia, resistance training for 16 to 21 weeks likely improves
‐ ability to do normal activities
‐ pain, tenderness, muscle strength and overall well‐being.
Quality of the evidence
‐ Because so few studies have been done so far, more research is likely to change these results.
‐ While we do not have exact information about side effects experienced by women with fibromyalgia during the studies, no injuries were reported.
‐ We do not know if the results would be the same for men, because only women took part in the studies.
Summary of findings
Summary of findings for the main comparison. Resistance training compared with control for fibromyalgia.
| Resistance training compared with control for fibromyalgia | ||||||
|
Patient or population: Individuals with fibromyalgia. Settings: Finland, Brazil. Intervention: Resistance training ‐ supervised group exercise. Comparison: Control. | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | No of Participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Resistance training | |||||
|
Multidimensional function
FIQ Total Score. Scale 0‐100 (lower scores indicate greater health) Follow‐up: 16 weeks |
The mean change (post minus pre) in multidimensional function in the control group was ‐8.16 FIQ units1 | The mean change (post minus pre) in multidimensional function in the intervention group was ‐24.91 FIQ units1 | ‐ | 60 (1 study2) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low3,4 | SMD ‐1.27 (95% CI ‐1.83 to ‐0.72)8 Absolute difference5 ‐16.75 FIQ units (95% CI ‐23.31 to ‐10.19) Relative per cent change6 26% (95% CI 15.96% to 36.51%) better in exercise group7 NNTB 2 (95% CI 1 to 3) |
|
Self reported physical function
Health Assessment Questionnaire and SF‐36 Physical Function Score Scale 0‐100 (converted so lower scores indicate better health) Follow‐up: 16‐21 weeks |
The mean change (post minus pre) in self reported physical function in the control groups was ‐2.01 units1 | The mean change (post minus pre) in self reported physical function in the intervention groups was ‐7.67 units1 | ‐ | 107 (3 studies2) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low9,10 | SMD ‐0.5 (95% CI ‐0.89 to ‐0.11) 11 Absolute difference ‐6.29 units (95% CI ‐10.45 to ‐2.13) Relative per cent change 14.48% (95% CI 4.9% to 24.1%) better in exercise groups NNTB 5 (95% CI 3 to 22) |
|
Pain
Visual analog scale Scale 0‐10 cm (lower scores indicate less pain) Follow‐up: 16‐21 weeks. |
The mean change (post minus pre) in pain in the control groups was ‐0.99 cm1 | The mean change (post minus pre) in pain in the intervention groups was ‐3.53 cm1 | 81 (2 studies2) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low9,10,12 | SMD ‐1.89 (95% CI ‐3.86 to 0.07)8 Absolute difference ‐3.33 cm (95% CI ‐6.35 to ‐0.26) Relative per cent change 44.6% (95% CI 3.5% to 85.9%) better in exercise groups7 NNTB 2 (95% CI 1 to 34) |
|
|
Tenderness
Tender point count and myalgic scores Scores converted to tender points, 0‐18 (lower scores indicate less tenderness) Follow‐up: 16‐21 weeks |
The mean change (post minus pre) in tenderness in the control groups was ‐2.0 tender points1 | The estimated mean change (post minus pre) in tenderness in the intervention groups was ‐3.5 tender points1 |
‐ | 107 (3 studies2) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low9,10,12 | SMD ‐0.73 (95% CI ‐1.12 to ‐0.33)8 Absolute difference ‐1.84 tender points (95% CI ‐2.6 to ‐1.08). Relative per cent change 12.8% (95% CI 7.49 to 18.0%) better in the exercise groups NNTB 4 (95% CI 3 to 7) |
| Muscle strength Maximum concentric leg extension (load measured in kg). Follow‐up: 21 weeks | The mean change (post minus pre) in muscle strength in control groups was 0.44 kg1 | The mean change (post minus pre) in muscle strength in the intervention groups was 27.71 kg1 | ‐ | 47 (2 studies2) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low9,10,12 | SMD 1.67 (95% CI 0.98 to 2.35).8 Absolute difference 27.32 kg (95% CI 18.28 to 36.36) Relative per cent change 25% (95% CI 17% to 33%) better in exercise groups7 NNTB 2 (95% CI 1 to 3) |
| Adverse effects | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | ‐ | See comment | No complaints of any unusual exercise‐induced pain or muscle soreness. No instances of attrition due to adverse effects (2 studies) |
| All‐cause attrition Dropout rates. Follow‐up: 16‐21 weeks | 39 per 1000 |
134 per 1000 (95% CI 30 to 439) |
RR 3.50 (0.79 to 15.49) | 107 (3 studies2) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low9 | Absolute difference 9% (95% CI ‐2% to 20%) Relative per cent change 250% (95% CI ‐21% to 1449%) Not statistically significant |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (eg, the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; FIQ: Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire;NNTB: number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome; RR: risk ratio;SF: Short Form;SMD: standardized mean difference. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence
High quality: Further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect. Moderate quality: Further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate. Low quality: Further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate. Very low quality: We are very uncertain about the estimate. | ||||||
1 Improvement.
2 Only women were studied. 3 Low risk of bias. 4 Evidence based on one small study. 5 Absolute difference = mean change in resistance training group(s) minus mean change in control group(s). 6 Relative change = absolute difference divided by mean of baseline scores in both groups: (∆eg ‐ ∆cg) / {[(μeg • neg ) + (μcg • ncg )]/ N}.
7 Clinically relevant difference (> 15%).
8 Large effect (SMD > 0.80) favoring the resistance training group(s).
9 At least one study had from incomplete documentation of study methods. 10 Wide confidence intervals.
11Moderate effect (SMD 0.50 to 0.79) favoring the resistance training group(s).
12 Statistical heterogeneity (I2 > 50%).
Summary of findings 2. Resistance training compared with aerobic training for fibromyalgia.
| Resistance training compared with aerobic training for fibromyalgia | ||||||
|
Patient or population: Individuals with fibromyalgia. Settings: Brazil and Turkey. Intervention: Resistance training, supervised group exercise. Comparison: Aerobic training, supervised group exercise. | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | No of Participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments7 | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Aerobic Training | Resistance Training | |||||
| Multidimensional function FIQ Total Score. Scale 0‐100 (lower scores indicate greater health) Follow‐up: 8 weeks | The mean change (post minus pre) in multidimensional function in the aerobic training group was ‐21.33 FIQ units1 | The mean change (post minus pre) in multidimensional function in the resistance training group was ‐15.85 FIQ units1 | ‐ | 60 (1 study2) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low3,4 | SMD 0.43 (95% CI ‐0.08 to 0.94)6 Absolute difference5 5.48 FIQ units (95% CI ‐0.92 to 11.88) Not statistically significant |
| Self reported physical function SF‐36 Physical Function Scale. Scale 0‐100 (higher scores indicate greater health) Follow‐up: 8 weeks | The mean change (pre to post) in self reported physical function in the aerobic training groups was 5.81 SF‐36 units1 | The mean change (post minus pre) in self reported physical function in the resistance training groups was 4.54 SF‐36 units1 | ‐ | 86 (2 studies2) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low4 | SMD ‐0.11 (95% CI ‐0.53 to 0.31). 6 Absolute difference ‐1.48 SF‐36 units (95% CI ‐6.69 to 3.74)6 Not statistically significant |
| Pain Visual analog scale. Scale 0‐10 cm (lower scores indicate less pain) Follow‐up: 8 weeks | The mean change (post minus pre) in pain in the aerobic training groups was ‐3.57 cm1,2 | The mean change (post minus pre) in pain in the resistance training groups was ‐2.7 cm1 | ‐ | 86 (2 studies2) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low4 | SMD 0.53 (95% CI 0.10 to 0.97)8 Absolute difference 0.99 cm (95% CI 0.31 to 1.67) Relative per cent change7 12.9% (95% CI 4.05% to 24.05%) better in the aerobic training groups NNTB 5 (95% CI 3 to 24) |
| Tenderness Tender point count and myalgic scores. Scores converted to tender points, 0 to 18 (lower scores indicate less tenderness) Follow‐up: 8 weeks | The mean change (post minus pre) in tenderness in the aerobic training groups was ‐5.15 tender points1 | The mean change (post minus pre) in tenderness in the resistance training groups was ‐4.9 tender points1 | ‐ | 86 (2 studies2) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low4 | SMD ‐0.13 (95% CI ‐0.55 to 0.3)6 Absolute difference ‐0.67 tender points (95% CI ‐1.68 to 0.33) Not statistically significant |
| Adverse effects | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | See comment | See comment | No "worsening of pain or fear of exercise‐induced pain", "no patient experienced musculoskeletal injury...during the intervention" (2 studies) |
| All‐cause attrition Dropout rates Follow‐up: 8 weeks | 89 per 1000 | 89 per 1000 (22 to 296) | Peto OR 1 (0.24 to 4.23) | 90 (2 studies2) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low | Absolute difference 0% (95% CI ‐12% to 12%) Relative per cent change 0% Not statistically significant |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (eg, the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; FIQ: Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire;OR: odds ratio; RR: risk ratio;SF: Short Form;SMD: standardized mean difference. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence High quality: Further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect. Moderate quality: Further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate. Low quality: Further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate. Very low quality: We are very uncertain about the estimate. | ||||||
1 Improvement pretest to post‐test. 2 Only women were studied.
3 Evidence derived from one study.
4 Wide confidence intervals.
5 Absolute difference = mean change in resistance training group(s) minus mean change in control group(s). 6 Not statistically significant.
7 Relative change = absolute difference divided by mean of baseline scores in both groups: (∆eg ‐ ∆cg) / {[(μeg • neg ) + (μcg • ncg )]/ N}.
8 Moderate effect (SMD 0.5 to 0.79) favoring aerobic exercise.
Summary of findings 3. Resistance training compared with flexibility exercise for fibromyalgia.
| Resistance training compared with flexibility exercise for fibromyalgia | ||||||
|
Patient or population: Individuals with fibromyalgia. Settings: USA. Intervention: Resistance training. Comparison: Flexibility exercise. | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | No of Participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Flexibility exercise | Resistance training | |||||
| Multidimensional function FIQ Total. Scale 0‐100 (lower scores indicate greater health) Follow‐up: 12 weeks | The mean change in multidimensional function in the flexibility group was ‐3.78 FIQ units 1 | The mean change in multidimensional function in the resistance training group was ‐10.27 units 1 | ‐ | 56 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low2, 3 | SMD ‐0.55 (95% CI ‐1.09 to ‐0.02) 6 Absolute difference 4 ‐6.49 FIQ units (95% CI ‐12.57 to ‐0.41) Relative per cent change5 13.6% (95% CI 0.9% to 26.4%) better in resistance group Not statistically significant |
| Pain VAS 0‐10 cm (lower scores indicate less pain) Follow‐up: 12 weeks | The mean change (post minus pre) in pain in the flexibility group was ‐1.01 cm 1 | The mean change (post minus pre) in pain in the resistance training group was ‐1.89 cm 1 | ‐ | 56 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low2,3 | SMD ‐0.66 (95% CI ‐1.2 to ‐0.12)6 Absolute difference ‐0.88 cm (95% CI ‐1.57 to ‐0.19)1,2 Relative per cent change 14% (95% CI 3.0% to 24.8%) better in the resistance group Not statistically significant |
| Tenderness Tender point count, scores 0‐18 (lower scores indicate less tenderness) Follow‐up: 12 weeks | The mean change in tenderness in the flexibility group was ‐1 tender points 1 | The mean change in tenderness in the resistance training group was ‐1.46 tender points 1 | ‐ | 56 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low2,3 | SMD ‐0.22 (95% CI ‐0.74 to 0.31)7 Absolute difference ‐0.46 tender points (95% CI ‐1.56 to 0.64) Not statistically significant |
| Strength Maximal isokinetic strength of nondominant knee extension measured in foot‐pounds8 Follow‐up: 12 weeks | The mean change in strength in the flexibility group was 9.7 foot‐pounds 1 | The mean change in strength in the resistance training group was 14.47 foot‐pounds 1 |
‐ | 56 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low2,3 | SMD 0.34 (95% CI ‐0.18 to 0.87).7 Absolute difference 4.77 foot‐ pounds (95% CI ‐2.40 to 11.94) Not statistically significant |
| Adverse effects | "No adverse events or injuries during the intervention" but "six participants (3 per group) experienced a worsening of one or more of the following pain measures: FIQ VAS for pain, total myalgic score, and number of tender points" (1 study) | |||||
| All‐cause attrition Dropout rates Follow‐up: 12 weeks | 214 per 1000 | 214 per 1000 | RR 1.00 (0.37 to 2.73) | 56 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low2,3 | Absolute difference 0% Relative per cent change 0% Not statistically significant |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (eg, the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; FIQ: Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire; RR: risk ratio; SMD: standardized mean difference; VAS: visual analog scale. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence High quality: Further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect. Moderate quality: Further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate. Low quality: Further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate. Very low quality: We are very uncertain about the estimate. | ||||||
1 Improvement 2 Evidence based on one small study 3 Refer to 'Risk of bias' assessment 4 Absolute difference = mean change in resistance training group(s) minus mean change in control group(s). 5 Relative change = absolute difference divided by mean of baseline scores in both groups: (∆eg ‐ ∆cg) / {[(μeg • neg ) + (μcg • ncg )]/ N}.
6 Moderate effect (SMD 0.5 to 0.79) favoring the resistance exercise group.
7 Not statistically significant.
8 A foot‐pound is a unit of force used to rotate an object about an axis (1 foot‐pound = 1.3558 Newton meters).
Background
Description of the condition
Fibromyalgia is a chronic syndrome marked by widespread muscular tenderness and pain (Mease 2005; Wolfe 1990). Most people with fibromyalgia experience concurrent gastrointestinal (eg, abdominal pain, irritable bowel syndrome) and somatosensory symptoms (eg, hyperalgesia, allodynia, paresthesias) in addition to disturbances in sleep, mood, and cognition (Burckhardt 2005; Mease 2005). The myriad of symptoms significantly affects quality of life and results in both physical and psychosocial disability with far‐reaching implications for family, employment, and independence (Burckhardt 1993; Burckhardt 2005; Mease 2005). Moreover, people with fibromyalgia are often intolerant of physical activity and tend to have a sedentary lifestyle that increases the risk of additional morbidity (Park 2007; Raftery 2009). Because of the presence of extensive somatic complaints and disability, people with fibromyalgia have a greater number of physician visits yearly and more specialists enlisted in their care (Park 2007).
The prevalence of fibromyalgia in the US has been estimated at 2% of the population with a greater representation among females than males (3.4% female to 0.5% male) (Wolfe 1995). The Canadian statistics are similar to the US wherein the self reported prevalence of fibromyalgia has been estimated at 1.1% across all ages, again with female diagnoses outnumbering male diagnoses (1.83% female to 0.33% male) (McNalley 2006). Prevalence rates among some European countries (France, Germany, Italy, Portugal, Spain) are estimated to range between 1.4% (France) and 3.7% (Italy) with fibromyalgia diagnoses being twice as common in females (Branco 2010). However, similar to other rheumatologic conditions, the prevalence of fibromyalgia in China is substantially lower than in Western countries at about 0.05% (Zeng 2008).
To date, there is no definitive etiology or pathophysiology for fibromyalgia. However, current evidence supports the model of central amplification of pain perception that is both developed and maintained by a variety of factors influencing neurotransmitter and neurohormone dysregulation (Bennett 1999; Clauw 2011; Desmeules 2003). Based on this theory, treatment and management of fibromyalgia requires multiple modalities and an integrative multidisciplinary approach that includes pharmacologic and other therapies (eg, exercise, cognitive therapy, relaxation, education) (Bernardy 2013; Birse 2012; Burckhardt 2005; Carville 2008; Häuser 2013; Moore 2012; Seidel 2013; Tort 2012; Williams 2012).
Until recently, the standard for diagnosing fibromyalgia has been the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 1990 criteria (Wolfe 1990). According to this method, a diagnosis of fibromyalgia is appropriate when a person has experienced widespread pain lasting more than three months and pain can be elicited at 11 of 18 specific tender points (TP) on the body using 4‐kg tactile pressure. In recent years, the utility of this method has been criticized for failing to address the extent of other key somatic complaints and secondary symptoms of fibromyalgia related to sleep, mood, cognition, and physical function (Mease 2005; Mease 2009).
A newer preliminary diagnostic tool also shows promise in improving upon current ACR standards and eliminates the need for the physical TP exam (Wolfe 2010). This measure, the ACR 2010 criteria, includes a Widespread Pain Index (WPI, 19 areas representing the anterior and posterior axis and limbs) and a Symptom Severity scale (SS, 0 to 12 scale) containing items related to secondary symptoms such as fatigue, sleep disturbances, cognition, and somatic complaints. Scores on both measures are used to determine whether a person qualifies with a 'case definition' of fibromyalgia. An individual is classified as having fibromyalgia when a) WPI > 7 and the SS > 5, or b) WPI = 3 to 6 and SS > 9. This tool has been found to classify 88.1% of cases that meet ACR criteria correctly, and it allows for ongoing monitoring of symptom change in people with current or previous fibromyalgia diagnoses (Wolfe 2010). Although the measures focusing on TP counts have been widely applied in clinic and research settings, the method described by Wolfe 2010 shows promise to classify people with fibromyalgia more efficiently while allowing for improved monitoring of disease status over time. Wolfe and colleagues have further developed the ACR 2010 criteria by eliminating the physicians's estimate of the extent of somatic symptoms and substituting the sum of three specific self reported symptoms (Wolfe 2011).
Description of the intervention
This review focuses on resistance‐training‐only interventions (hereafter referred to as resistance training), which has been found to have numerous benefits including increased muscle strength, muscle endurance, and muscle power in healthy individuals throughout the lifespan (ACSM 2009b; Chodzko‐Zajko 2009; Faigenbaum 2009; Nelson 2007). Resistance training may be especially important to protect individuals against the loss of lean body mass and subsequent impairments and activity limitations that occur with aging (Chodzko‐Zajko 2009; Nelson 2007). In addition, parameters such as balance, coordination, speed, and agility may also be enhanced with this form of training (ACSM 2009b; Asikainen 2004).
Resistance training is frequently administered concurrently with other types of exercise training (aerobic and flexibility training); we only selected studies describing resistance‐training‐only interventions. All types of resistance training (ie, prescriptions that target muscle strength, endurance, power, or a combination of these) were included in this review. The intensity and duration needed to produce adaptations depend on a variety of factors including the fitness level of the individual starting a resistance training intervention and the desired adaptation; typically neuromuscular resistance training adaptations are apparent by 12 weeks or less in healthy novices. By definition, training interventions include a progressive component; as the body adapts to a given stimulus, an increase in the stimulus is required for further adaptations and improvements. Thus, if the load or volume is not increased over time, progress will be limited.
The resistance load can be applied using various types of equipment (eg, free weights, elastic bands/tubing, weight machines), or simply by using the weight of a body segment or segments against gravity to provide resistance. Training for improvements in strength (ie, the ability to produce force), typically involves prescription of higher loads (eg, 60% to 70% of one repetition maximum (RM, see Table 4 ‐ Glossary) for novices, 80% to 100% of 1 RM for more advanced individuals) and fewer repetitions (8 to 12 repetitions for novices and six repetitions or fewer for individuals accustomed to training) (ACSM 2009b; Garber 2011; Appendix 1). In comparison, for muscle endurance (ie, the ability to produce force repetitively), training involves relatively light loads (40% to 60% of 1 RM) and greater repetitions (15 or more). Training to improve muscle power (ie, the ability to produce force quickly) involves exercise using light‐to‐moderate loads (60% or less of 1 RM) over one to six repetitions with high movement velocities.
1. Glossary of terms.
| Term | Definition |
| Allodynia | A painful response to a normally innocuous stimulus. |
| Endurance | 2 forms of endurance that refer to health‐related physical fitness are: (1) cardiorespiratory endurance (also known as cardiovascular endurance, aerobic fitness, aerobic endurance, exercise tolerance) which "relates to the ability of the circulatory and respiratory systems to supply fuel during sustained physical activity and to eliminate waste products after supplying fuel", and (2) muscle endurance, which relates to the ability of muscle groups to exert external force for many repetitions" (Caspersen 1985). |
| Exercise | Planned, structured, and repetitive activities designed to improve or maintain strength or fitness. |
| Hyperalgesia | An increased response to a painful stimulus. |
| Maximum voluntary contraction (MVC) | A measure of muscle strength; the maximum muscle contraction that a person can generate voluntarily as measured in units of force (pounds, kilograms, Newtons) or as a moment around a joint (eg, Newton‐meter, foot‐pounds, kilograms‐meters). |
| Mental health | 1 score derived from set of questions or questionnaire that attempts to summarize the individual's level of psychologic well‐being or an absence of a mental disorder. |
| Multidimensional function (health‐related quality of life) | 1 score derived from either a general health questionnaire (eg, Short‐Form (SF)‐36, EuroQol 5D) or a disease‐specific questionnaire (Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire) that attempts to summarize the many components of health. |
| Muscle strength | A physical test of the amount of force a muscle can generate. |
| Paresthesia | Abnormal sensory symptoms such as pins and needles, burning, and tingling. |
| Physical activity | Any bodily movement produced by skeletal muscles that results in energy expenditure (ie, active work, housework, gardening, leisure, or hobbies). |
| Repetition maximum (1 RM) | The maximum amount of weight one can lift in 1 repetition for a given exercise. |
| Sleep disturbance | A score derived from a questionnaire that measures sleep quantity and quality. The Medical Outcomes Survey Sleep Scale measures 6 dimensions of sleep (initiation, staying asleep, quantity, adequacy, drowsiness, shortness of breath, and snoring). |
| Somatosensory | Of or relating to the perception of sensory stimuli from the skin and internal organs. |
| Tenderness | Pain evoked by tactile pressure. |
How the intervention might work
Although the precise etiology of fibromyalgia is not known, physical deconditioning is believed to play a role in the susceptibility to fibromyalgia. People with fibromyalgia typically present with reduced muscular strength and endurance, which is accompanied by greater levels of muscle fatigue compared with healthy sedentary women (Kingsley 2009). This may contribute to the substantial level of physical disability noted in fibromyalgia (Hawley 1991; Raftery 2009). Improved muscular performance (strength, endurance, and power), coordination, and posture are recognized benefits of regular resistance training (ACSM 2009b), and can enhance a person's ability to perform daily activities and counteract disability.
Several researchers have described metabolic findings in muscle tissue from individuals with fibromyalgia that are consistent with physical deconditioning (Bengtsson 1986a; Bengtsson 1986b; Bennett 1989; Elvin 2006; Jubrias 1994; Lund 1986; Park 1998). Deconditioning could be linked to the etiology of fibromyalgia by increasing an individual's vulnerability to microtrauma during daily exposure to mechanical strain related to posture or physical activity (Smythe 1981). The metabolic adaptations induced by resistance training that have been observed in healthy individuals (Costill 1979; Deschenes 2002; Holloszy 1984), may normalize some of these findings (Mizelle 2011), thus contributing to improvements in pain. Therefore, exercise may contribute to a reduction in pain through improving resilience to the process of muscle microtrauma, repair, and adaptation during exercise. Resistance exercise also affects pain in healthy individuals. Koltyn 1998 has demonstrated a transient increase in pain threshold (ie, lower pain ratings) immediately after one bout of resistance exercise in healthy individuals and Knutzen 2007 reported that progressive resistance training may reduce pain in older adults.
Other adaptations to long‐term resistance training include decreased cortisol response to stress (Braith 2006), along with decreased anxiety, depression, and insomnia in clinical depression (Brosse 2002; Dunn 2001; King 1997; Singh 1997). Singh 1997 speculated that the improvements in depression may be due to the effects that exercise has on "the hormonal milieu, neurotransmitter levels and sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system activity". If indeed, resistance training can normalize the response to stress, and reduce pain perception, anxiety, depression and insomnia, this would be valuable for individuals with fibromyalgia.
Exercise training, including resistance training that is being examined in this review, should be considered not only for disorder‐specific effects but also from the perspective of whether training affects overall health. Muscle strengthening activity is important in preventing age‐related loss of muscle mass, bone, and physical function (Chodzko‐Zajko 2009; Nelson 2007). Some research also suggests that in the general population, muscle strength and power capabilities are predictive of all‐cause and cardiovascular mortality, independent of an individual's aerobic fitness level (Braith 2006; FitzerGerald 2004; Katzmarzyk 2002). Therefore, individuals with fibromyalgia may improve their overall health and reduce risks associated with other chronic diseases by engaging in resistance training on a regular basis.
Why it is important to do this review
It is important to evaluate whether resistance training has beneficial effects on fibromyalgia symptoms and whether resistance training will result in neuromuscular adaptations seen in healthy individuals. It is also important to document what harms may be associated with resistance training interventions in people with fibromyalgia and to determine whether resistance training should be recommended as a safe, effective component of fibromyalgia management. It is also important to evaluate whether resistance training is more or less effective than other types of exercise training. Some researchers have suggested that resistance training may be feared by individuals with fibromyalgia (van Koulil 2007), and that special care may be needed to avoid delayed‐onset muscle soreness (DOMS) when designing exercise protocols in this population (Jones 2002). In addition to reporting on injuries and other adverse events, this review will report on attrition rates and adherence to training protocols as these may indicate the acceptability of this form of intervention for individuals with fibromyalgia.
Objectives
To evaluate the benefits and harms of resistance training in adults with fibromyalgia. Specific comparisons that were assessed in this review included:
resistance training versus control conditions (eg, treatment as usual, wait list control, physical activity as usual);
resistance training versus other physical activity intervention.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
We selected randomized clinical trials (RCT) that compared a resistance training intervention versus another exercise training protocol, versus an untreated control, or versus a non‐exercise intervention. We included studies if the words randomly, random or randomization were used to describe the method of assignment of subjects to groups (see protocol: Busch 2001a).
Types of participants
We included studies that examined adults with fibromyalgia in the review. We selected those studies that used published criteria for the diagnosis of fibromyalgia (Smythe 1981; Yunus 1981; Yunus 1982; Yunus 1984; Wolfe 1990). Although some differences exist between the diagnostic criteria, for the purpose of this review all were considered acceptable and comparable.
Types of interventions
Intervention: We defined resistance training as exercise performed against a progressive resistance on a minimum of two days per week (on nonconsecutive days) with the intention of improving muscle strength, muscle endurance, muscle power or a combination of these. We did not set a specific minimum intervention duration. We placed no restriction on the type of equipment used to produce the load; included studies could use a variety of equipment for resistance training including free weights, elastic bands or tubing, and exercise machines, as well as calisthenics that use the weight of a body segment or segments moving against gravity as the load for the exercise.
Comparators: We were interested in comparisons in three categories: a) untreated control conditions (treatment as usual, activity as usual, wait list control, and placebo), b) other types of exercise or physical activity interventions (eg, aerobic, flexibility), and c) other resistance training interventions (head‐to‐head comparisons).
Types of outcome measures
Until recently, there was no consensus on outcomes to guide research on the effectiveness of interventions for fibromyalgia. In 2004, a group of clinicians and researchers under the auspices of the Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials (OMERACT) initiative, set about to improve outcome measurement in fibromyalgia through a data‐driven interactive consensus process used previously for other rheumatic diseases (Mease 2009). Over the course of the next five years, patient focus groups (Arnold 2008), patient and clinician Delphi exercises (Mease 2008), a systematic literature review and analysis of outcomes used in fibromyalgia intervention trials (Carville 2008a), and analyses of psychometric properties of outcomes (ie, face, construct, content and criterion validity in fibromyalgia) (Choy 2009a), were conducted. Based on these efforts, OMERACT has recommended the following core set of outcomes for inclusion in all fibromyalgia clinical trials: pain, fatigue, multidimensional function, tenderness, and quality of sleep (Choy 2009b; Mease 2009). OMERACT designated two additional outcomes, depression and dyscognition, as important but not core, and placed anxiety, morning stiffness, imaging, and biomarkers on the agenda for further research (Choy 2009b).
In this review, we have extracted data for 24 outcomes, which include all the outcomes considered important by OMERACT (Choy 2009b). We categorized the 24 outcomes into four main categories: wellness, fibromyalgia symptoms, physical fitness, and safety and acceptability.
In the wellness category, we extracted six outcomes: multidimensional function, patient rated global, clinician rated global, self‐reported physical function, self‐regulation efficacy, and mental health.
In the symptom category of outcomes, we extracted data for eight symptoms experienced by individuals with fibromyalgia: pain, fatigue, sleep disturbance, stiffness, tenderness, depression, anxiety, and dyscognition.
In the physical fitness category, we extracted eight outcomes associated with physiologic adaptation to exercise training: muscle strength, muscle endurance, muscle power, muscle/joint flexibility, muscle fiber activation, muscle size, maximum cardiorespiratory function, and submaximal cardiorespiratory function.
The final category of outcomes was conceptualized as safety and acceptance of resistance training. This category consisted of one outcome associated with possible harms ‐ injuries, exacerbations of fibromyalgia or other adverse effects; while another outcome ‐ attrition rates, served as a proxy for lack of acceptability of resistance training.
1. Outcomes representing wellness
This category of outcomes relates to generalized health or functioning. Tools used to measure outcomes in this category included both broad‐spectrum indices designed to capture an array of tasks or characteristics to yield one summary score (eg, Short Form ‐ 36 items (SF‐36)), and single‐item tests on which the respondent is asked to rate their status in an area of health using one item (eg, a visual analog scale (VAS) on which the respondent places a mark on a 10‐cm line between worst health at one end and best health at the other).
Multidimensional function ‐ The outcome multidimensional function consisted of multidimensional indices used to measure general health status or health‐related quality of life, or both. Similar to Choy 2009b, we collapsed measures to measure general health status or health‐related quality of life (or both) into one outcome. When included studies used more than one instrument to measure multidimensional function, we preferentially extracted data for Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire ‐ Total (FIQ‐total), followed by the SF‐36 total, the SF‐12 total, the EuroQol‐5D, the Arthritics Impact Measurement Scales total (AIMS total), the Quality of Life Scale, and the Illness Intrusiveness questionnaire.
Self reported physical function ‐ Self reported physical function focuses the basic actions and complex activities considered "essential for maintaining independence, and those considered discretionary that are not required for independent living, but may have an impact on quality of life" (Painter 1999). We classified this outcome in the wellness category of outcomes because it is dependent on several factors (physical, sensory, environmental, and behavioral factors) (Painter 1999), and as a self report measure, represents the impact of these multiple factors on the individual's ability to meet the physical demands of daily life. Because cardiorespiratory fitness; neuromuscular attributes such as muscular strength, endurance, and power; and muscle and joint flexibility are important determinants of physical function, this outcome is highly relevant as an outcome of exercise interventions. We preferentially extracted data for the FIQ (English or translated) physical impairment scale followed by the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) disability scale, the SF‐36/Rand 36 Physical Function; the Sickness Impact Profile ‐ Physical Disability, and the Multidimensional Pain Inventory household chores scale.
Patient‐rated global ‐ Patients' rating of global well‐being are commonly assessed by Likert or VAS. They are highly sensitive to change (Choy 2009a; Mease 2009), and appear to be reliable. We extracted data preferentially for self‐perceived change ‐ VAS; followed by self perceived change ‐ numeric rating scale; self perceived disease severity VAS; self perceived disease severity ‐ numeric rating scale; self perceived sense of well‐being ‐ VAS; and self perceived health status ‐ numeric rating scale.
Clinician rated global ‐ Global assessments of disease severity by physicians and other health professionals using a Likert or VAS are commonly used clinical settings. We used clinician‐rated disease severity (VAS).
Self efficacy ‐ We used self efficacy‐physical function. Instruments found in this review were: the Arthritis Self‐Efficacy Scale (Lorig 1989), the chronic Pain Self‐Efficacy (Anderson 1995), the Fibromyalgia Attitudes Index (Callahan 1988), and the Freiburg Mindfulness Inventory (Buchheld 2001).
Mental health ‐ The US Surgeon General has defined mental health as "a state of successful performance of mental function, resulting in productive activities, fulfilling relationships with people, and the ability to adapt to change and to cope with adversity" (www.medicinenet.com/mental_health_psychology/page2.htm). In focus groups conducted by Arnold 2008, participants reported that their physical and emotional ability to complete tasks of daily living was severely limited by fibromyalgia because of pain, lack of energy, fatigue, and depression. Participants also expressed feelings of embarrassment, frustration, guilt, isolation, and shame. We used: SF‐36/Rand 36 Mental Health; psychosocial scale (Sickness Impact Profile); Global Severity Index of the Symptom Checklist 90 ‐ revised (SCL‐90‐R); Profile Mood States (POMS); Psychological General Well‐being (PGWB) total score.
2. Outcomes representing fibromyalgia symptoms
This category of outcomes includes nine symptoms associated with fibromyalgia.
Pain ‐ The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage" (Merskey 1994). For the purpose of this review, we focused on one aspect of the pain experience ‐ pain intensity. When more than one measure of pain was reported in one study, we preferentially extracted: pain VAS (FIQ Pain, FIQ‐Translated, McGill pain VAS, current pain) followed by the Numerical Pain Rating Scale, the SF‐36/Rand 36 Bodily Pain scale, and the Pain Severity scale of the Multidimensional Pain Inventory.
Tenderness ‐ Tenderness was defined as discomfort produced as an evoked response to mechanical pressure (Dadabhoy 2008; Gracely 2003). Although there are concerns that measures of tenderness can be biased by cognitive and emotional aspects of pain perception, many studies have supported the utility of measurement of tenderness in fibromyalgia using either TP counts or pain pressure threshold (Dadabhoy 2008). A TP is identified when pressure of 4 kg is perceived as painful. When included studies used more than one instrument to measure tenderness, we preferentially extracted the TP count followed by pain pressure threshold (dolorimetry score, based on at least six of the 18 ACR TPs) and the total myalgic score (sum/mean of ordinal rating of response to thumb pressure across 18 TPs).
Fatigue ‐ Fatigue is recognized by individuals with fibromyalgia and clinicians alike as an important symptom in fibromyalgia. Fatigue can be measured in a global manner as when an individual rates their fatigue on a single‐item scale, or as a multidimensional tool that breaks the experience of fatigue down into two or more dimensions such as general fatigue, physical fatigue, mental fatigue, reduced motivation, reduced activity, and degree of interference with activities of daily living (Boomershine 2012). We accepted both unidimensional and multidimensional measures for this outcome. When included studies used more than one instrument to measure fatigue, we preferentially extracted the fatigue VAS (FIQ/FIQ‐Translated Fatigue, or single‐item fatigue VAS), followed by the SF‐36/Rand 36 Vitality subscale, the Chalder Fatigue Scale (total), the Fatigue Severity Scale and the Multidimensional Fatigue Inventory.
Sleep disturbance ‐ Sleep problems are almost universal in fibromyalgia, occurring in 95% of people (Boomershine 2012). Measurement of sleep disturbance is challenging and there has been a lack of consensus on the most valid measures (Choy 2009a; Choy 2009b). When included studies used more than one instrument to measure sleep, we preferentially extracted the Pittsburg Sleep Quality Index followed by the Sleep Quality VAS, Sleep Quantity: nights/week, hour/night, hours of good‐to‐disturbed sleep, and the Hamilton Depression Sleep Items.
Stiffness ‐ In focus groups conducted by Arnold 2008, individuals with fibromyalgia "...remarked that their muscles were constantly tense. Participants alternately described feeling as if their muscles were 'lead jelly' or 'lead Jell‐O', and this resulted in a general inability to move with ease and a feeling of stiffness". The only measure we encountered for stiffness was the FIQ stiffness VAS.
Depression ‐ Depression is a common mental disorder characterized by depressed mood, loss of interest or pleasure, feelings of guilt or low self worth, disturbed sleep or appetite, low energy, and poor concentration. These problems can become chronic or recurrent and lead to substantial impairments in an individual's ability to take care of his or her everyday responsibilities (WHO 2012). In focus groups conducted by Arnold 2008, the emotional disturbances most commonly experienced by participants with fibromyalgia included depression and anxiety. A complete understanding of depression and how best to assess it in fibromyalgia trials is still uncertain and is an active research issue (Mease 2009). However, because people with significant depression are commonly excluded from fibromyalgia intervention studies, the discriminatory power of these instruments is underestimated (Choy 2009b). We preferentially extracted Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) Cognitive/Affective subscale scores followed by BDI total, BDI without fibromyalgia Symptoms; Beck Depression Scale, short form translated SF; Hamilton Depression Scale; Center for Epidemiologic Studies‐Depression (CES‐D) FIQ/FIQ translated ‐ depression; Mental Health Inventory subscale depression; AIMS ‐ depression subscale; Hospital Anxiety and Depression Q‐depression; Symptom Checklist 90 ‐ depression; and the PGWB depression score.
Anxiety ‐ Anxiety is a feeling of apprehension and fear characterized by physical symptoms such as palpitations, sweating, irritability, and feelings of stress (www.medicinenet.com/anxiety/article.htm). Some participants in OMERACT focus groups exploring key symptoms in fibromyalgia reported that acute anxiety and panic were disruptive to activities that they were trying to complete (Choy 2009b). We preferentially extracted data for anxiety using the anxiety scale of the AIMS, followed by the State Anxiety Inventory; the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Q‐anxiety; the Beck Anxiety Inventory; the Mental Health Inventory anxiety subscale; the SC‐90 ‐ anxiety scale; PGWB anxiety score; and the FIQ anxiety scale.
Dyscognition ‐ Dyscognition pertains to difficulty with cognitive tasks especially memory and thought processes. Although this outcome was identified as important as an outcome on fibromyalgia trials by OMERACT (Choy 2009b), it is rarely measured in studies of physical activity interventions for individuals with fibromyalgia.
3. Outcomes representing physical fitness/neuromuscular adaptation
This category consisting of eight outcomes is associated with physiologic adaptation to exercise training. There are several facets to physical fitness including: cardiovascular endurance, body composition, muscle strength, muscle endurance, flexibility, agility, coordination, balance, power, reaction time, and speed (ACSM 2009a). Given the nature of the intervention, outcomes reflecting physical fitness are highly relevant.
Muscle strength ‐ Muscular strength is a measure of a muscle's ability to generate force. It is generally expressed as maximal voluntary contraction (MVC) for isometric measurements and as the 1RM for dynamic isotonic measurements (Howley 2001), and peak torque for isokinetic measurements. For the purpose of this review, when more than one measure of strength was reported we preferentially extracted dynamic tests over isometric tests, lower limb over upper limb tests, and contraction of extensor muscles over flexor muscles.
Muscle endurance ‐ Muscular endurance is the ability of a muscle group to exert submaximal force for extended periods; it can be assessed for static or dynamic muscular contractions (Heyward 2010). For the purpose of this review, when more than one measure of muscle endurance was reported we preferentially extracted: lower extremity dynamic endurance (stair step; sit to stand chair tests or fatigue curve), followed by lower extremity static endurance including fatigue curve, number of squats performed in 60 seconds, fatigue index (the ratio of mean power in last five repetitions to the mean power in first five during a test of 60 repetitions), and upper extremity dynamic endurance measured using a fatigue curve and grip endurance test.
Muscle power ‐ Power (the explosive aspect of strength) is defined as rate of doing muscle work (Trew 2005). Power is the product of force (torque) and speed of movement [power = (force x distance)/time] (ACSM 2009b). For the purpose of this review, when more than one measure of power was reported, we preferentially extracted: the vertical jump test (m), horizontal jump, isokinetic power (lower extremity before upper extremity) and maximum power test (maximum power in watts on best of three repetitions doing squats).
Muscle/joint flexibility ‐ Flexibility is the ability of a joint or a series of joints to move fluidly through its complete range of motion (ROM) (Heyward 2010). It is important in the ability to carry out activities of daily living. Flexibility depends on several specific variables, including joint geometry, and the distensibility of the joint capsule, ligaments, tendon, and muscles spanning the joint (Heyward 2010). Flexibility is joint specific, so no single test can evaluate total body flexibility. For the purpose of this review, the following were used: sit and reach test, forward reach test, and ROM measures (when there were multiple ROM measures we took the first measure in the researcher's data table).
Muscle fiber activation ‐ Muscle fiber activation (recruitment) occurs progressively; the level of activation is related to the degree of effort required (Sale 1987). For this review, we extracted data from electromyographic recordings during isometric contractions of lower extremity contractions.
Muscle size ‐ One effect of strength training is an increase in the size of the muscle tissue. Muscle size and strength are often positively correlated. The increase in size of the muscle (also known as exercise‐induced hypertrophy) results from an increase in the total amount of contractile proteins, the number and size of myofibrils per fiber amount of connective tissue surrounding the muscle fibers (Heyward 2010). For this review, we extracted data on cross‐sectional area (cm2) of the quadriceps muscle.
Maximum cardiorespiratory function ‐ Cardiorespiratory endurance is the ability of the heart, lungs and circulatory system to supply oxygen and nutrients to working muscles efficiently. Rhythmic, aerobic‐type exercises involving large muscle groups are recommended for improving cardiovascular fitness. Maximal oxygen uptake (VO2 max) is accepted as the best criterion to measure cardiorespiratory fitness. Maximal oxygen uptake is the product of the maximal cardiac output (liters of blood/minute) and arterial‐venous oxygen difference (milliliters O2/liter of blood). Maximal tests have the disadvantage of requiring the participant to exercise to the point of volitional fatigue and often require medical supervision and emergency equipment. For this reason, maximal exercise testing is not always feasible in health and fitness settings. For this review, we preferentially extracted data from maximal or symptom‐limited treadmill or cycle ergometer tests in units of milliters/kilogram/minute, energy expended, peak workload or test duration. We also accepted data from exercise tests that yielded predicted maximum oxygen uptake.
Submaximal cardiorespiratory function ‐ Measuring VO2 max requires expensive laboratory equipment and considerable amounts of time as well as a high level of motivation on the part of the participant. Submaximal tests to predict or estimate VO2 max are similar except that they are terminated at some predetermined point (usually based on heart rate intensity or perceived exertion). Assumptions associated with submaximal exercise testing include: a) a steady‐state heart rate is reached at each exercise intensity, and there is a linear relationship between heart rate, oxygen uptake and work intensity; b) the mechanical efficiency on the cycle or treadmill is constant for all individuals; and c) the maximum heart rate for participants of a given age is similar (Heyward 1998). In this review, we preferentially extracted data from work completed at a specified exercise heart rate (eg, PWC170 test), followed by distance walked in six minutes (meters), the two‐minute walk test (meters), walking time for a set distance (seconds), anaerobic threshold test, and timed walking distance (eg, Quarter Mile Walk Test).
Major outcomes
We designated seven of the 24 outcomes as major outcomes:
multidimensional function (wellness);
self reported physical function (wellness);
pain (symptoms);
tenderness (symptoms);
muscle strength (fitness);
attrition rates;
adverse effects (injuries, exacerbations of pain and other symptoms, other adverse events).
Minor outcomes
We designated the 17 remaining outcomes as minor outcomes. There were four wellness outcomes, six symptom outcomes, and seven physical fitness outcomes.
Minor wellness outcomes:
patient‐rated global;
mental health;
self efficacy;
clinician‐rated (single‐item instrument).
Minor symptom outcomes:
fatigue;
sleep disturbance;
stiffness;
depression;
anxiety;
dyscognition.
Minor physical fitness outcomes:
muscle endurance;
muscle power;
muscle fiber activation (EMG);
muscle size (cross‐sectional area of muscle);
maximum cardiorespiratory function;
submaximal cardiorespiratory function;
muscle/joint flexibility.
Search methods for identification of studies
Interventions in this review are part of a comprehensive search for all physical activity interventions. The citations found in the electronic searches were screened and then classified by type of exercise training (eg, aerobic, resistance, flexibility and yoga, aquatic exercise, mixed exercise and composite interventions, and innovative exercise interventions).
Electronic searches
We searched the following databases from database inception to 5 March 2013 using current methods outlined in Chapter 6 of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Lefebvre 2011). We applied no language restrictions. Full search strategies for each database are found in the appendices as indicated in the list.
MEDLINE (Ovid) 1946 to 5 March 2013 (Appendix 2);
EMBASE (Ovid) EMBASE Classic + EMBASE 1947 to 4 March 2013 (Appendix 3);
-
The Cochrane Library 2013 Issue 2 (www.thecochranelibrary.com/view/0/index.html) (Appendix 4):
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews;
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE);
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL);
Health Technology Assessment Database (HTA);
NHS Economic Evaluation Database (EED).
CINAHL (EBSCO) 1982 to 5 March 2013 (Appendix 5);
PEDro (www.pedro.org.au/), accessed 5 March 2013 (Appendix 6);
Dissertation Abstracts (Proquest), accessed 5 March 2013 (Appendix 7);
Current Controlled Trials, accessed 5 March 2013 (Appendix 8);
World Health Organization (WHO) International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (www.who.int/ictrp/), accessed 5 March 2013 (Appendix 9);
AMED (Allied and Complementary Medicine) (Ovid) 1985 to February 2013 (accessed 5 March 2013) (Appendix 10).
Searching other resources
Two review authors independently searched reference lists from key journals, identified articles, meta‐analyses and reviews of all types of treatment for fibromyalgia with all promising or potential references scrutinized and appropriate titles added to the search output.
Data collection and analysis
Review team
The review team was made up of 11 members, including two consumers, and one librarian, and nine review authors. Review authors came from the following backgrounds: physical therapy, kinesiology, and dietetics. Review authors were trained in data extraction using a standardized orientation program designed for this review. Review authors worked in pairs (with at least one physical therapist in each pair) to extract data. The team met monthly to discuss progress, to clarify procedures, and to make decisions regarding inclusion/exclusion and classification of outcome variables and to work collaboratively in the production of this review.
Selection of studies
Two review authors independently examined the titles and reviewed abstracts of studies generated from searches using a set of criteria (see Appendix 11 ‐ Screening and Classification Criteria ‐ Level 1 and Level 2). We retrieved full‐text publications for all potential abstracts. We translated the methods and results sections for all non‐English reports. Two review authors then independently examined the full‐text reports and translations to determine if the study met the selection criteria (see Appendix 11 ‐ Screening and Classification Criteria ‐ Level 3). We resolved disagreements and questions regarding interpretation of inclusion criteria by discussion with partners unless the pair agreed to take the issue to the team.
Data extraction and management
We developed electronic data extraction forms to facilitate independent data extraction and consensus. Pairs of review authors worked independently to extract the descriptive and quantitative data from the studies. After the data were extracted, the review authors reviewed the data together and reached a consensus. We frequently encountered questions regarding the acceptability of outcome measures used in the studies; we referred these questions to the team for resolution if not solved with partners.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
We followed the procedure to assess bias recommended in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Two review authors independently evaluated the risk of bias in each included study using a customized form based on the Cochrane 'Risk of bias' tool (Higgins 2011c). The tool addresses seven specific domains: sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel, blinding of outcome assessment, incomplete outcome data, selective outcome reporting, and other sources of bias. For other sources of bias, we considered potential sources of bias such as baseline inequities despite randomization, or inequities in the duration of interventions being compared. Each criterion was rated as low risk of bias, high risk of bias or unclear risk of bias (either lack of information or uncertainty over the potential for bias). In a consensus meeting, we discussed and resolved disagreements among the review authors. If we could not reach consensus, we referred the issue to the review team who made the final decision. Due to the nature of the intervention, blinding of study participants and care providers is very difficult.
Measures of treatment effect
The outcome measures of interest were most often presented as continuous data with pre‐test means, post‐test means, and standard deviations. We calculated change scores and estimated standard deviations for the change scores using the formula described in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Figure 1). We used Review Manager 5 (RevMan 2012) analysis software to (1) calculate effect sizes in the form of mean differences (MD), standardized mean differences (SMD) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for continuous outcomes; risk ratios (RR) and Peto odds ratio (OR) and 95% CI for dichotomous outcomes, and (2) generate forest plots to display the results.
1.
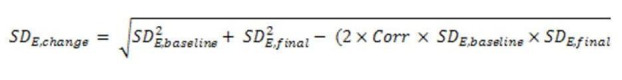
Formula for calculating standard deviations of change scores based on pre‐ and post‐test standard deviations (see Section 16.1.3.2 in Higgins 2011c).
Unit of analysis issues
This review of RCTs included studies with two or more parallel groups. We preferentially used data (mean change scores) from intention‐to‐treat analysis, so that the number of observations in the analyses matched the number of individuals that were randomized. However, in some cases, the researchers presented data for completers only, in which case, the number of individuals whose data were analyzed was less than the number of individuals that were randomized. In trials with three arms, if the control group was used as a comparator twice within the same analysis, we halved the sample size of the control group.
Dealing with missing data
When numerical data were missing, we contacted the authors of studies, requesting additional data required for analysis. When data were available only in graphic form, we used Engauge version. 4.1 (Mitchell 2002), to extrapolate means and standard deviations by digitizing data points on the graphs. When unavailable, we calculated the standard deviations of the change scores using the formulae in Higgins 2011c (see Figure 1). The correlation between baseline and end of study measurements was estimated at 0.8.
We contacted authors using open‐ended questions to obtain the information needed to assess risk of bias or the treatment effect (Bircan 2008; Hakkinen 2001; Jones 2002).
Assessment of reporting biases
We found too few studies to assess reporting bias.
Data synthesis
When two or more sets of data were available for the same outcome, we used the Review Manager analyses to pool the data (meta‐analysis, fixed‐effect model) (RevMan 2012). In order to carry out meta‐analysis, we performed transformation of the point estimates of outcomes: a) to express results in the same units (eg, centimeters were transformed to millimeters), or b) to resolve differences in the direction of the scale (when scores derived from scales with higher score indicating greater health were combined with scores derived from scales with high scores indicating greater disease). To evaluate the magnitude of the effect, we used Cohen's guidelines (small effect = 0.2 to 0.49, moderate effect = 0.5 to 0.79, large effect > 0.79) (Cohen 1988).
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
We found too few studies to conduct subgroup analysis. We assessed statistical heterogeneity among the trials using the heterogeneity statistics (Chi2 test and I2 statistic). We considered P values < 0.10 or I2 > 50% to be indicative of significant heterogeneity. Where P value < 0.10 or I2 > 50% (or both), we used a random‐effects model instead of the fixed‐effect model for meta‐analysis. In addition, in the case of statistical heterogeneity, we scrutinized the studies for sources of clinical heterogeneity and methodologic differences.
Sensitivity analysis
We found too few studies to conduct sensitivity analysis.
'Summary of findings' tables
We used Grade‐Pro (version 3.6) (Schünermann 2009) to prepare 'Summary of findings' tables with the seven major outcomes for each of the three comparisons ‐ resistance training versus control, resistance training versus aerobic training, and resistance training versus flexibility exercise. In the 'Summary of findings' tables, we integrated analysis concerning the quality of evidence and the magnitude of effect of the interventions. We applied the GRADE Working Group grades of evidence, which considers the risk of bias and the body of literature to rate quality into one of four levels.
High quality: Further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect.
Moderate quality: Further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate.
Low quality: Further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate.
Very low quality: We are very uncertain about the estimate.
Quality ratings were made separately for each of the seven major outcomes. Because of the comprehensive nature of the outcome variable ‐ 'multidimensional function', we gave it primacy over all the other variables and chose it as the variable to highlight in the 'Summary of findings' table and the lay summary. We carried out calculations based on the guidelines of the Cochrane Musculoskeletal Review Group.
When we found statistically significant results, we calculated numbers needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) and for an additional harmful outcome (NNTH). We also evaluated the clinical relevance of the effects in major outcomes by calculating the absolute and relative difference in change from a pooled baseline in the intervention group as compared with the change from a pooled baseline in the control or comparison group. We calculated the pooled baseline as follows:
Pooled baseline = (X1 pren1 + X2 pre n2) / (n1 + n2)
Relative difference (%) = MD/pooled baseline
where the MD was calculated by Review Manager (RevMan 2012), X1 pre and X2 pre are the pre‐test means in the experimental and the control groups, respectively, and n1 and n2 are the number of participants in the experimental and control groups, respectively. In keeping with the practice of the Philadelphia Panel, we used 15% as the level for clinical relevance (Philadelphia 2001).
Results
Description of studies
Results of the search
The search resulted in 1856 citations. We excluded 1090 studies on citation screening and 605 studies based on abstract screening (see Figure 2). On examination of full‐text articles, we excluded 58 studies because they did not meet the selection criteria related to: a) diagnosis of fibromyalgia (five studies), b) physical activity intervention (10 studies), c) study design (34 studies), or d) outcomes (nine studies). Ninety‐eight research publications described 84 RCTs with physical activity interventions for individuals with fibromyalgia. We screened the 84 RCTs to identify studies that compared interventions that were exclusively resistance training interventions versus control groups or other interventions with the result that an additional 79 trials were screened out (see Table 5). Five additional studies are awaiting classification.
2.
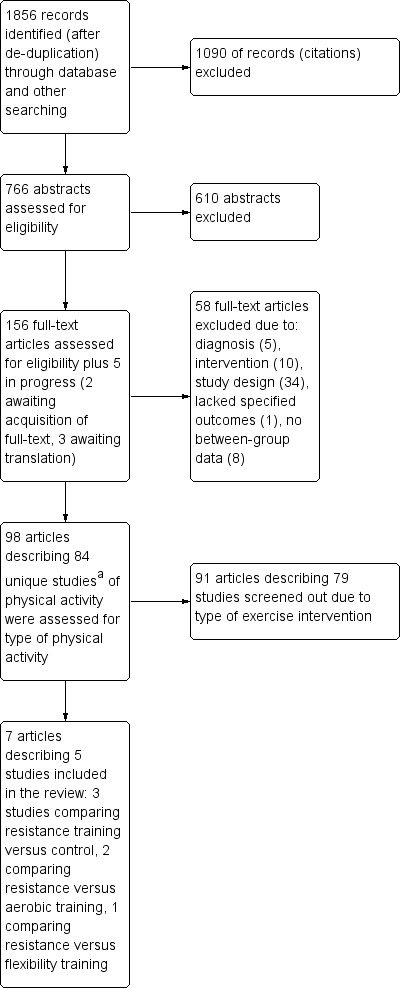
Study flow diagram (note: a Discrepancy between the number of articles and studies denotes that multiple papers have described the same study).
2. RCTs of exercise interventions screened out of resistance training review.
| Study (primary and secondary citations)* | Number of groups | Interventions |
| Alentorn‐Geli 2008 | 3 | MX, Comp (Vib+MX), Control |
| Altan 2004 | 2 | AQ‐MX, Bal |
| Altan 2009 | 2 | MX, Relax+FX |
| Arcos‐Carmona 2011 | 2 | AQ+LD MX, Control (placebo magnet therapy) |
| Assis 2006 | 2 | AE, AQ‐AE |
| Astin 2003 | 2 | Mindfulness Meditation; Control |
| Baptista 2012 | 2 | Dance; Wait List Control |
| Bojner Horwitz 2006 | 2 | Dance/Movement; Control |
| Bressan 2008 | 2 | 2 groups: FX, AE |
| Buckelew 1998 | 4 | 4 groups: Biof+Relax, MX, Comp (Biof+Relax+MX), Control (Educ/Attention) |
| Burckhardt 1994 | 3 | Comp (ED+MX), ED, Control (Delayed treatment) |
| Calandre 2009 | 2 | FX, AiChi |
| Carson 2010; Carson 2012 | 2 | COMP (Yoga, meditation, breathing exercises, ED), Control (Wait List) |
| Cedraschi 2004 | 2 | Comp (AQ+Land AE, Relax, ED), Control |
| Demir‐Gocmen 2013 | 2 | MX (FX+Coord)/HPrg (FX) |
| Da Costa 2005 | 2 | AQ+LD MX, Control (TAU) |
| De Andrade 2008 | 2 | AQ‐(AE), AQ‐(AE) SPA |
| de Melo Vitorino 2006 | 2 | AQ‐MX, LD‐MX |
| Etnier 2009 | 2 | MX, Control ‐ Delayed Entry |
| Evcik 2008 | 2 | AQ‐MX, MX |
| Field 2003 | 2 | COMP (Self Massage+FX), Relax |
| Fontaine 2007 | 2 | LPA (likely mostly aerobic), ED |
| Fontaine 2010; Fontaine 2011 | 2 | LPA (likely mostly aerobic), ED |
| Garcia‐Martinez 2012 | 2 | MX (AE+ST+FX); Control |
| Genc 2002 | 2 | MX, COMP (Non ex intervention, Remedial Ex, Relax, Mobil) |
| Gowans 1999 | 2 | Comp (AQ‐AE+ED), Control (Wait List) |
| Gowans 2001; Gowans 2002 | 2 | AQ‐AE+LD AE, Control (TAU) |
| Gusi 2010; Olivares 2011 | 2 | VIB, Control (TAU) |
| Gusi 2006; Tomas‐Carus 2007a; Tomas‐Carus 2007b; Tomas‐Carus 2007 | 2 | AQ‐MX , Control |
| Hammond 2006 | 2 | COMP (Educ+SMP+MX), Relax |
| Hecker 2011 | 2 | AQ MX, MX |
| Hooten 2012 | 2 | COMP (MX+pain prg), COMP (MX+pain prg) |
| Hunt 2000 | 2 | MX, Control |
| Ide 2008 | 2 | AQ‐COMP (AE+Relax), Control (Supervised ˜PA Recreational Activities) |
| Isomeri 1993 | 3 | AE, ST+Meds, AE+Meds |
| Jentoft 2001 | 2 | AQ‐MX, MX |
| Jones 2007; Jones 2008 | 4 | Comp Meds+MX, Meds+Placebo (Diet Recall), Placebo Med+MX, Control: Placebo Med+Placebo Diet Recall |
| Jones 2012 | 2 | Tai Chi; Educ |
| Joshi 2009 | 2 | MX; Med |
| Keel 1998 | 2 | Comp (MX, ED, Relax), Relax |
| King 2002 | 4 | AE (AQ ± LD), ED, Comp (AE AQ ± LD+ED), Control |
| Lemstra 2005 | 2 | Comp (MX+Educ+SMP+Massage), Control |
| Liu 2012 | 2 | Qi Gong/sham QiGong |
| Lopez‐Rodriguez 2012 | 2 | AQ Biodance |
| Lynch 2012 | 2 | Qi Gong/Wait List Control |
| Mannerkorpi 2000 | 2 | AQ‐MX, Edu |
| Mannerkorpi 2009 | 2 | COMP AQ‐MX+ED, ED |
| Mannerkorpi 2010 | 2 | AE (moderate intensity), AE (low intensity) |
| Martin 1996 | 2 | MX, Relax |
| Martin‐Nogueras 2012 | 2 | MX (FX+FX+Relax)/Control |
| Matsutani 2007 | 2 | COMP (Educ+Laser+FX), COMP (Educ+FX) |
| Matsutani 2012 | 2 | AE, FX |
| McCain 1988 | 2 | AE, FX |
| Mengshoel 1992; Mengshoel 1993 | 2 | AE‐Dance, Control |
| Munguia‐Izquierdo 2007; Munguia‐Izquierdo 2008 | 3 | AQ‐MX, Control (fibromyalgia), Control (Healthy) |
| Nichols 1994 | 2 | AE, Control |
| Norregaard 1997 | 2 | AE, MX, Thermotherapy |
| Ramsay 2000 | 2 | AE, AE (CV) |
| Richards 2002 | 2 | AE, Comp Relax+FX |
| Rivera Redondo 2004 | 2 | AQ+LD MX, CBT |
| Rooks 2007 | 4 | MX1, MX2, FSHC, FSHC+MX |
| Sanudo 2010 | 2 | MX, Comp (MX+Vib) |
| Sanudo 2010a | 3 | AE, MX, Control (TAU) |
| Sanudo 2010c | 2 | AE, Control |
| Sanudo 2011 | 2 | MX, Control (TAU, AAU) |
| Sanudo 2012 | 2 | MX (Vib+AE+ST+FX); MX (AE+ST+FX) |
| Schachter 2003 | 3 | AE ‐ long bout, AE ‐ short bout, Control (TAU) |
| Schmidt 2011 | 3 | Comp (Meditation Yoga), Comp (Relax+FX), Control (Wait List) |
| Sencan 2004 | 3 | AE, Meds, Control |
| Tomas‐Carus 2008; Tomas‐Carus 2007c; Gusi 2008 | 2 | AQ‐MX, Control |
| Valencia 2009 | 2 | COMP (Relax+MX) , FX (Meziere Method) |
| Valim 2003 | 2 | AE, FX |
| Valkeinen 2008 | 2 | MX, C (AAU) |
| van Koulil 2010 | 2 | Comp CBT1 + AQ/LD MX, Comp CBT2 + AQ/LD MX |
| vanSanten 2002a | 3 | MX, Biofeedback, Control |
| vanSanten 2002 | 2 | MX (self selected intensity), AE (moderate to vigorous intensity) |
| Verstappen 1997 | 2 | MX, Control |
| Wang 2010 | 2 | Tai Chi, Comp (FX + ED) |
| Wigers 1996 | 3 | AE, SMT, Control (TAU) |
| Yuruk 2008 | 2 | MX1, MX2 |
AAU: activity as usual; AE: aerobics; AQ: aquatics; Biof: biofeedback; spa: balneotherapy; CBT: cognitive behavior therapy; Comp: composite; ED: education; FX: flexibility; LD: land; LPA: leisure time physical activity; LifePA: lifestyle physical activity; Meds: medication; Multi: multidisciplinary program; ˜: not, or non; MX: mixed exercise; Relax: relaxation; SMP: self management program; ST: strength; SM: stress management; Spa: thelassotherapy; TAU: treatment as usual; TENS: transcutaneous electrical stimulation; Vib: whole body vibration.
* Seven trials had more than one publication. In total, there were 73 trials with 14 additional publications.
Included studies
Seven research publications met our selection criteria and were included for analysis (Bircan 2008; Hakkinen 2001 (Primary); Hakkinen 2002 (Secondary); Jones 2002; Kayo 2011; Valkeinen 2004 (Primary); Valkeinen 2005 (Secondary)). As Hakkinen 2002 (Secondary) reported on additional variables from the Hakkinen 2001 (Primary) study, the two reports were counted as one study for analysis (hereafter both reports are identified as Hakkinen 2001). Likewise, Valkeinen 2005 (Secondary) reported on additional variables to the Valkeinen 2004 (Primary) study and this pair was also counted as one study (hereafter both reports are identified as Valkeinen 2004). Thus, although there were seven separate publications, there were only five included studies. In total, there were 241 participants in the included studies and of these, there were 219 women with fibromyalgia (note: two studies, Hakkinen 2001 and Valkeinen 2004, had comparison groups consisting of healthy women). One hundred and sixty‐six of the 219 women with fibromyalgia were assigned to exercise interventions: 95 to resistance training, 43 to aerobic training, and 28 to flexibility training. We were hampered by missing data pertaining to characteristics of the study, assessment of risk of bias, assessment of exercise interventions, outcome data, or a combination of these, in all included studies. We requested additional information from all authors and received responses to our queries from four of the five authors (Bircan 2008; Hakkinen 2001; Jones 2002; Kayo 2011).
Excluded studies
Following screening of citations and abstracts, we excluded 106 studies based on examination of full‐text reports. We based exclusions on unmet criteria (44 studies) related to: a) diagnosis (seven studies), b) study design (26 studies), c) intervention (five studies), d) lack parallel data (six studies) (see Characteristics of excluded studies), and e) duplicate studies identified progressively across multiple searches (62 studies).
Risk of bias in included studies
Results of the risk of bias assessment are provided in the Characteristics of included studies table and in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
3.
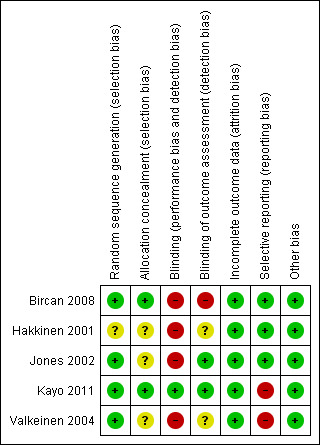
Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgments about each risk of bias item for each included study.
4.
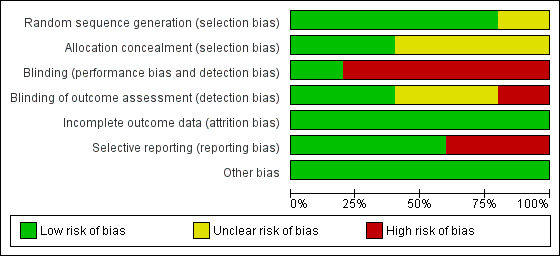
Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgments about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.
Allocation
Four of the five included studies used an acceptable method of random sequence generation (computer‐generated sequence, coin toss, drawing of cards or lots) and were rated low risk (Bircan 2008; Jones 2002; Kayo 2011; Valkeinen 2004). Although two studies (Bircan 2008; Kayo 2011) used opaque sealed envelopes to conceal allocation and were rated as low risk, the remaining three included studies were rated as unclear risk as they did not provide sufficient information to determine allocation methods and whether treatment allocation was concealed.
Blinding
No specific information regarding blinding of the care provider or participants was provided in any of the included studies; however, in exercise studies, blinding of participants and care providers is very rare. Performance and detection bias were rated as high risk for the five studies. Two studies blinded outcome assessors to participant group assignment (Jones 2002; Kayo 2011), one study did not (Bircan 2008), and the other included studies did not provide specific information about blinding of outcome assessors: the studies were rated as low (Jones 2002; Kayo 2011), high (Bircan 2008), and unclear risk (Hakkinen 2001; Valkeinen 2004).
Incomplete outcome data
Three studies were rated as low risk related to incomplete outcome data; two studies had no dropouts (Hakkinen 2001; Valkeinen 2004), and one study used an intention‐to‐treat analysis (Kayo 2011). There was insufficient information provided by Jones 2002 to determine whether incomplete outcome data were adequately addressed. Missing outcome data were balanced in numbers across intervention groups, with similar reasons for missing data across groups, suggesting low risk of bias in Bircan 2008. Attrition rates were reported to be 18% (6/34 participants) in Jones 2002 and 13% (2/15 participants) in Bircan 2008.
Selective reporting
It was difficult to assess selective reporting bias because a priori research protocols were not available for any of the reviewed studies. Three studies were rated as having a high risk of selective reporting because some of the reported outcome measures were not prespecified and point/variability estimates were not provided for all outcomes (Hakkinen 2001; Kayo 2011; Valkeinen 2004). Another study was also rated as high risk because it compared the effects of resistance training and aerobic training yet did not evaluate results for muscle strength, muscle endurance, or muscle power (Bircan 2008).
Other potential sources of bias
The studies appear to be free of other serious potential sources of bias. Only one of the included studies reported differences between intervention groups at baseline that could have biased final results; Kayo 2011 reported a significantly longer disease duration in the control group. Kayo 2011 included the greatest number of participants (analyzed 30 per group). Small sample sizes are associated with low power and it is possible that detection of treatment effects were missed. Poor adherence is also a potential source of bias in exercise studies. Two studies reported attendance at organized exercise sessions (Bircan 2008; Jones 2002), but none of the included studies reported detailed results of systematic data collection and analysis of participant adherence to exercise performance in a way that would allow the review authors to understand the amount of training actually performed by participants. Overall, we rated the risk due to other sources as low.
Effects of interventions
See: Table 1; Table 2; Table 3
All studies but one (Kayo 2011) used the end of the intervention as the final data collection point. None of the interventions extended beyond 21 weeks. Kayo 2011 measured the effects of physical activity midway through the intervention (eight weeks), immediately following the intervention (16 weeks) and followed study participants for an additional period of 12 weeks after the supervised intervention concluded. The results related to effects of the interventions have been grouped below to correspond to objectives of the review.
Resistance training versus control
Two of the three studies that compared resistance training versus control were very similar in structure ‐ both studies (Hakkinen 2001; Valkeinen 2004) described 21‐week resistance training interventions that were congruent with American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) guidelines (Garber 2011). Both studies had three arms: a) women with fibromyalgia carrying out the resistance training intervention, b) women with fibromyalgia in a control group, and c) healthy women carrying out resistance the training intervention. Both studies used similar resistance machines and intensities (moderate‐ to high‐intensity levels). Sample sizes for the fibromyalgia exercise group, the fibromyalgia control group, and the healthy control group were 11, 10, and 12, respectively, in Hakkinen 2001; and 13, 13, and 11, respectively, in Valkeinen 2004. The fibromyalgia control group in Valkeinen 2004 continued with their normal medication and daily activities; however, Hakkinen 2001 did not describe the fibromyalgia control group conditions with respect to medications or activity. A key difference between the two studies was age of the study participants ‐ in Hakkinen 2001 the participants were premenopausal women, while Valkeinen 2004 studied older women (mean age of participants in the exercise group was 60.2 ± 2.5 years). The results of the comparisons of the fibromyalgia training groups and the fibromyalgia control groups will be considered in this section.
The third study, Kayo 2011, compared three 16‐week interventions: a resistance training group who used body weight against gravity and free weights as resistance with exercise load and intensity increased every two weeks to tolerance (n = 30), an aerobic exercise group who did moderate‐intensity indoor and outdoor walking (n = 30), and an untreated control group (n = 30). Outcomes were measured at baseline, eight weeks, 16 weeks (post‐intervention), and 28 weeks (follow‐up). The results of the comparison between the resistance training group and the control group at 16 weeks will be considered in this section.
Hakkinen 2001 provided data for five major outcomes (self reported physical function, pain, tenderness, muscle strength, and attrition), and seven minor outcomes (patient‐rated global, fatigue, sleep, depression, muscle power, muscle size and muscle activation). Valkeinen 2004 presented data on five major outcomes (self reported physical function, tenderness, muscle strength, adverse effects, and attrition) and two minor outcomes (muscle size and muscle activation). In their published report, Kayo 2011 provided data for four major outcomes (multidimensional function, pain, adverse effects, and attrition), but upon request, they supplied data for two additional major outcomes (self reported physical function and tenderness). Kayo 2011 provided data for two minor outcomes (mental health and fatigue). Kayo 2011 was the only study to include a follow‐up point after the resistance training protocol was completed (12 weeks). Thus, meta‐analyses were carried out on five major outcomes (self reported physical function, pain, tenderness, muscle strength, and attrition) and three minor outcomes (fatigue, muscle size, and muscle activation) and were restricted to postintervention analysis only.
Major outcomes: Among the major outcomes, large effects (SMD > 0.79) favoring resistance training were found for multidimensional function (MD ‐16.75 FIQ units on a 100‐point scale, 95% CI ‐23.31 to ‐10.19, 1 study, 60 of 60 participants analyzed, Analysis 1.1), pain (MD ‐3.30 cm on 10‐cm VAS, 95% CI ‐6.35 to ‐0.26, 2 studies, 81 participants, Analysis 1.3), and muscle strength (MD 27.32 kg, 95% CI 18.28 to 36.36, 2 studies, 47 of 47 participants analyzed, Analysis 1.5); while a moderate effects favoring resistance training were found in self reported physical function (MD ‐6.29 less on 100‐point scale, 95% CI ‐10.45 to ‐2.13, 3 studies, 107 of 107 participants analyzed, Analysis 1.2) and tenderness (MD ‐1.84 out of 18 TPs, 95% CI ‐2.6 to ‐1.08, 3 studies, 107 of 107 participants analyzed, Analysis 1.4). Relative to the control groups these represented incremental improvements of 26% in multidimensional function, 15.9% in self reported physical function, 44.6% in pain, 12.6% in tenderness, and 25% in muscle strength in the resistance groups.
1.1. Analysis.
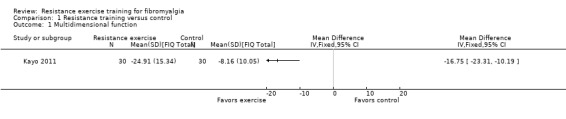
Comparison 1 Resistance training versus control, Outcome 1 Multidimensional function.
1.3. Analysis.
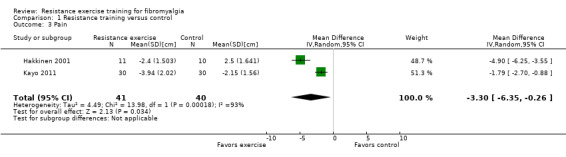
Comparison 1 Resistance training versus control, Outcome 3 Pain.
1.5. Analysis.
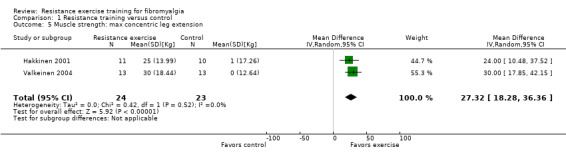
Comparison 1 Resistance training versus control, Outcome 5 Muscle strength: max concentric leg extension.
1.2. Analysis.
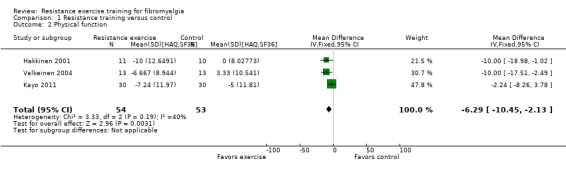
Comparison 1 Resistance training versus control, Outcome 2 Physical function.
1.4. Analysis.
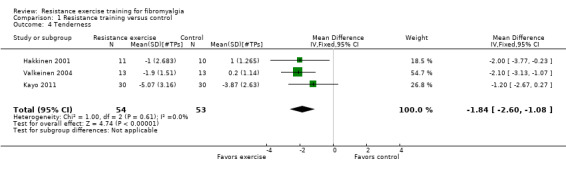
Comparison 1 Resistance training versus control, Outcome 4 Tenderness.
Only two of the three studies provided information on adverse effects of resistance training (eg, injuries, exacerbations or other adverse effects related to exercise). Valkeinen 2004 reported, "after the initial phase of training, the patients did not complain of any unusual exercise‐induced pain or muscle soreness" (page 227). Although Kayo 2011 expected to find "worsening of pain or fear of exercise‐induced pain", they reported that no instances of attrition due to adverse effects were observed during the study. While Hakkinen 2001 did not report on adverse effects, the lack of dropouts among the women who undertook this high‐intensity resistance exercise regimen suggests that individuals with fibromyalgia can tolerate resistance training exercise. All‐cause attrition rates for the resistance groups (n1/N1) versus control groups (n2/N2) were 0/11 versus 0/10 (Hakkinen 2001), 0/13 versus 0/13 (Valkeinen 2004), and 7/30 versus 2/30 (Kayo 2011). The pooled RR for attrition in the intervention groups compared with the control groups at the end of the intervention was 3.50 (95% CI 0.79 to 15.49). Minor outcomes: Large effects favoring resistance training were found for several minor outcomes: patient‐rated global well‐being (MD ‐40.00 mm on a 100‐mm scale, 95% CI ‐54.31 to ‐25.69, relative difference 91%, 1 study, 21 of 21 participants analyzed, Analysis 1.7), fatigue (MD ‐14.66 on a 100‐unit scale, 95% CI ‐20.55 to ‐8.77, relative difference 22.4%, 2 studies, 81 of 81 participants analyzed, Analysis 1.6), depression (MD ‐3.70, 95% CI ‐6.37 to ‐1.03, relative difference 57%, 1 study, 21 participants of 21 analyzed, Analysis 1.9), muscle power (MD 2 cm higher on a squat jump, 95% CI 1 to 3, relative difference 12%, 1 study, 21 of 21 participants analyzed, Analysis 1.10), and muscle activation (MD 40.92 μVs more on integrated EMG, 95% CI 33.5 to 48.34, relative difference 35.2%, 2 studies, 47 of 47 participants analyzed, Analysis 1.13). No differences were found in mental health (Analysis 1.8), sleep (Analysis 1.11), or muscle size (Analysis 1.12). Although the SMD for muscle size was 0.48, due to the high variability in these data, this was not statistically significant. Regarding effects on fitness, Valkeinen 2004 stated that their results "clearly show changes in fitness and the trainability of muscles" in people with fibromyalgia. In addition, Hakkinen 2001 and Valkeinen 2004 found no differences in magnitude and timing of adaptations of the neuromuscular system to strength training during the 21‐week resistance training program in women with fibromyalgia compared with healthy women performing the same routine. The researchers also found a similar response in systemic growth hormone levels during an acute bout of exercise in participants with fibromyalgia and healthy controls.
1.7. Analysis.
Comparison 1 Resistance training versus control, Outcome 7 Patient‐rated global.
1.6. Analysis.
Comparison 1 Resistance training versus control, Outcome 6 Fatigue.
1.9. Analysis.
Comparison 1 Resistance training versus control, Outcome 9 Depression.
1.10. Analysis.
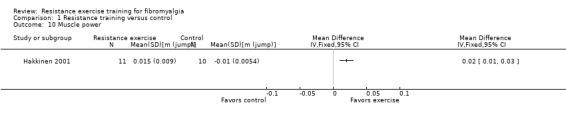
Comparison 1 Resistance training versus control, Outcome 10 Muscle power.
1.13. Analysis.
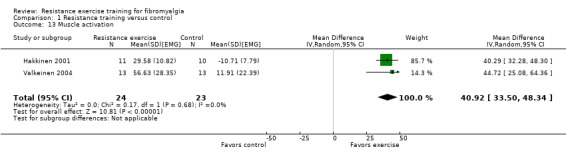
Comparison 1 Resistance training versus control, Outcome 13 Muscle activation.
1.8. Analysis.
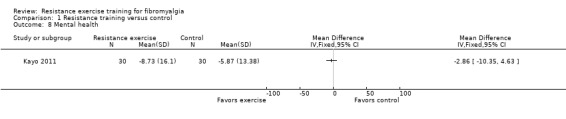
Comparison 1 Resistance training versus control, Outcome 8 Mental health.
1.11. Analysis.
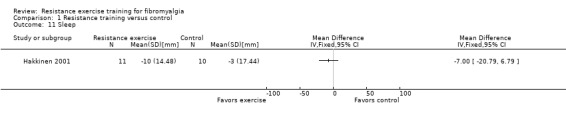
Comparison 1 Resistance training versus control, Outcome 11 Sleep.
1.12. Analysis.
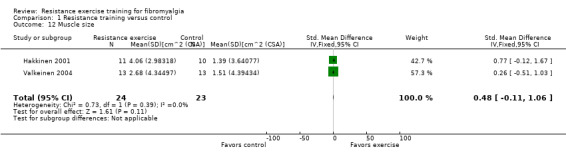
Comparison 1 Resistance training versus control, Outcome 12 Muscle size.
Quality of evidence: These data indicate that resistance training has positive effects on wellness, symptoms, and physical fitness without serious adverse effects, but due to the limited number of studies, the paucity of study participants, and the risk of bias findings for these studies, this evidence is categorized as low‐quality evidence (see Table 1). Long‐term effects:Kayo 2011 was the only study to investigate retention of effects following the intervention. Kayo 2011 did not report any details about the activities of the participants during the follow‐up period. They found that differences favoring resistance training in multidimensional function (MD ‐10.67 on a 100‐point scale, 95% CI ‐17.88 to ‐3.46), fatigue (MD ‐9.11 on a 100‐point scale, 95% CI ‐16.18 to ‐2.04), and pain (MD ‐0.85 cm on 10‐cm scale, 95% CI ‐1.77 to 0.07) were retained at week 28 (12 weeks after end of intervention). No differences were found at follow‐up in tenderness (MD ‐1.92 tenderness rating, 95% CI ‐7.06 to 3.22), self reported physical function (MD 1.00 on a 100‐point scale, 95% CI ‐5.04 to 7.04) or mental health (MD 0.54 on a 100‐point scale, 95% CI ‐7.01 to 8.09).
Resistance training versus aerobic training
Bircan 2008 compared the effects of eight weeks of resistance training (n = 13) involving free weights and body weight resistance to major muscle groups versus aerobic interventions (n = 13, treadmill walking). Both the aerobic training group and resistance training groups met three times per week. Women in the aerobic group walked on a treadmill for 20 to 30 minutes each session at 60% to 70% of predicted maximum heart rate, while those in the resistance training group used body segment loads, free weights, or both to perform exercises, progressing from four to five repetitions to 12 repetitions over the course of the program. Attendance was not reported to be a problem with participants attending all supervised exercise sessions over the eight‐week program. Kayo 2011 compared the effects of resistance training (n = 30, free weights and body weight resistance to major muscle groups) versus aerobic training (n = 30, indoor and outdoor walking) at eight weeks (mid‐test), 16 weeks (post‐test), and 26 weeks (12 weeks after the conclusion of the intervention).
Since both Bircan 2008 and Kayo 2011 provided data at eight weeks, we used eight‐week data in our assessment of resistance versus aerobic training. Bircan 2008 provided data for five major outcome measures: self reported physical function, pain, tenderness, adverse effects, and attrition; and six minor outcome measures: mental health, fatigue, sleep, depression, anxiety, and cardiorespiratory submaximal. Kayo 2011 provided data for six major outcomes: multidimensional function, self reported physical function, pain, tenderness, adverse effects, and attrition; and two minor outcomes: mental health and fatigue. Thus, meta‐analyses were carried out on four major outcomes (self reported physical function, pain, tenderness, and attrition) and two minor outcomes (fatigue and mental health). Kayo 2011 included a follow‐up point after the exercise training protocols were completed (12 weeks).
Major outcomes: Our analyses showed a moderate difference between resistance and aerobic training favoring aerobic training for pain (MD 0.99 cm on a 10‐cm VAS, 95% CI 0.31 to 1.67, relative difference 12.94%, 2 studies, 86 of 90 participants analyzed, Analysis 2.3). No significant differences were found between the resistance training interventions and the aerobic interventions for multidimensional function measured by FIQ total (MD 5.48 on a 100‐point scale, 95% CI ‐0.92 to 11.88, 1 study, 60 of 60 participants analyzed, Analysis 2.1), self reported physical function measured by SF‐36 Physical Function Scale (MD ‐1.48 on a 100‐point scale, 95% CI ‐6.69 to 3.74, 2 studies, 86 of 90 participants analyzed, Analysis 2.2) or tenderness measured using TP counts and myalgic scores (SMD ‐0.13, 95% CI ‐0.55 to 0.30, 2 studies, 86 of 90 participants analyzed, Analysis 2.4).
2.3. Analysis.
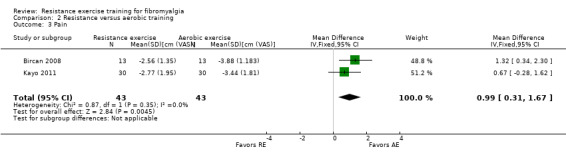
Comparison 2 Resistance versus aerobic training, Outcome 3 Pain.
2.1. Analysis.
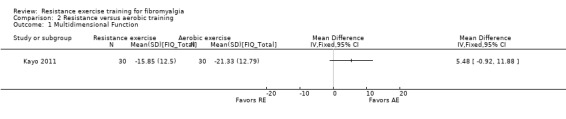
Comparison 2 Resistance versus aerobic training, Outcome 1 Multidimensional Function.
2.2. Analysis.
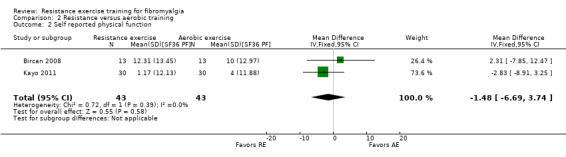
Comparison 2 Resistance versus aerobic training, Outcome 2 Self reported physical function.
2.4. Analysis.
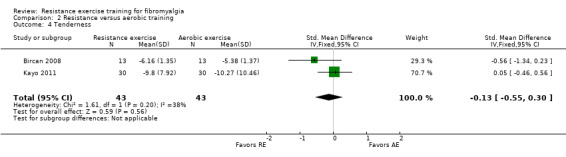
Comparison 2 Resistance versus aerobic training, Outcome 4 Tenderness.
Although Kayo 2011 expected to find "worsening of pain or fear of exercise‐induced pain", they reported that no instances of attrition due to adverse effects were observed during the study. Likewise, Bircan 2008 stated, "no patient experienced musculoskeletal injury...during the intervention" (page 529). All‐cause attrition‐rates for the resistance training groups (n1/N1) versus aerobic training groups (n2/N2) in the included studies were: 2/15 versus 2/16 (Bircan 2008) and 7/30 versus 8/30 (Kayo 2011) to yield a Peto OR of 1.00 (95% CI 0.24 to 4.23, Analysis 2.11).
2.11. Analysis.
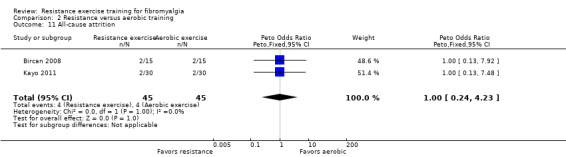
Comparison 2 Resistance versus aerobic training, Outcome 11 All‐cause attrition.
Minor outcomes: A large effect (SMD > 0.79) was found favoring aerobic training for sleep (Analysis 2.7), but no differences were found between resistance and aerobic training for fatigue (Analysis 2.5), mental health (Analysis 2.6), depression (Analysis 2.8), or anxiety (Analysis 2.9).
2.7. Analysis.
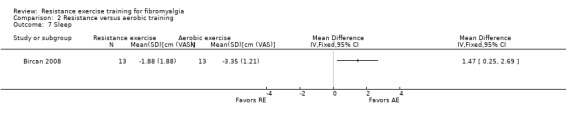
Comparison 2 Resistance versus aerobic training, Outcome 7 Sleep.
2.5. Analysis.
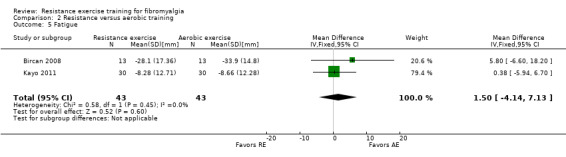
Comparison 2 Resistance versus aerobic training, Outcome 5 Fatigue.
2.6. Analysis.
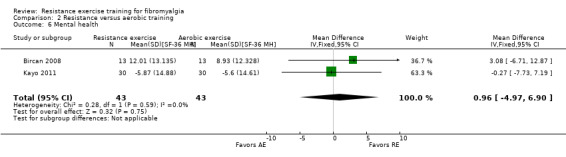
Comparison 2 Resistance versus aerobic training, Outcome 6 Mental health.
2.8. Analysis.
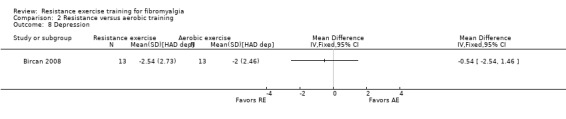
Comparison 2 Resistance versus aerobic training, Outcome 8 Depression.
2.9. Analysis.
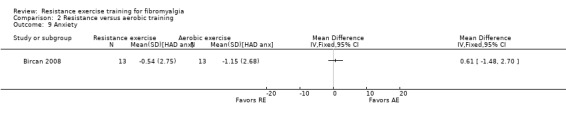
Comparison 2 Resistance versus aerobic training, Outcome 9 Anxiety.
Long‐term effects: Based on Kayo 2011, positive effects favoring aerobic training emerged at 12 weeks after the conclusion of the intervention for self reported physical function (SMD 0.68, 95% CI 0.16 to 1.20) and mental health (SMD 0.58, 95% CI 0.06 to 1.10). However, the positive effects for pain favoring aerobic training found after eight weeks were no longer statistically significant (SMD 0.41, 95% CI ‐0.10 to 0.92) 12 weeks after the conclusion of the intervention.
Quality of evidence: Although these data indicate that aerobic training may have advantages over resistance training in pain (short term) and physical function (short term) and mental health (emerging 12 weeks post‐intervention), this evidence is categorized as low‐quality evidence (see Table 2).
Resistance training versus flexibility exercise
Jones 2002 compared a 12‐week resistance training program (n = 28) designed to be sensitive to peripheral and central dysfunctions versus a stretching intervention (n = 28) consisting of static stretching exercises; the same 12 muscle groups were targeted in both programs. Resistance training utilized hand weights (up to 3 lb (1.4 kg)) and elastic tubing. Jones 2002 provided data for six major outcomes ‐ multidimensional function, pain, tenderness, strength, adverse effects, and attrition, and five minor outcomes ‐ self efficacy, sleep, depression, anxiety, and muscle/joint flexibility. No meta‐analyses were possible for this comparison.
Major outcomes:Jones 2002 found a moderate‐sized effect favoring resistance training for multidimensional function using FIQ total (scale 0 to 100) (MD ‐6.49, 95% CI ‐12.57 to, ‐0.04, 1 study, 56 of 68 participants analyzed, Analysis 3.1, relative difference 13.6%) and VAS pain (MD ‐0.88 cm on a 10‐cm scale, 95% CI ‐1.57 to ‐0.19, 1 study, 56 of 68 participants analyzed, Analysis 3.2, relative difference 14%). No between‐group differences were found for tenderness (number of TPs) (MD ‐0.46, 95% CI ‐1.56 to 0.64, 1 study, 56 of 68 participants analyzed, Analysis 3.3) or muscle strength (MD 4.77, 95% CI ‐2.40 to 11.94, 1 study, 56 of 68 participants analyzed, Analysis 3.4). Jones 2002 indicated that there were "no adverse events or injuries during the intervention" (page 1045). However, Jones 2002 further stated "six participants (3 per group) experienced a worsening of one or more of the following pain measures: FIQ VAS for pain, total myalgic score, and number of tender points" (page 1045). All‐cause attrition‐rates for the resistance group (n1/N1) versus flexibility group (n2/N2) were: 6/28 versus 6/28, RR 1.00 (95% CI 0.37 to 2.73, Analysis 3.11).
3.1. Analysis.
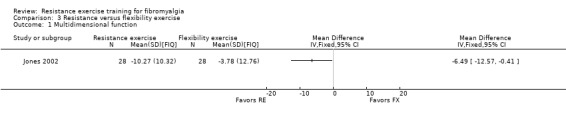
Comparison 3 Resistance versus flexibility exercise, Outcome 1 Multidimensional function.
3.2. Analysis.
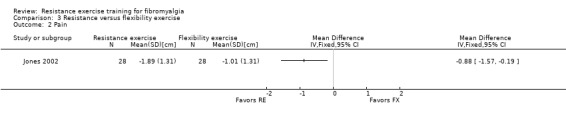
Comparison 3 Resistance versus flexibility exercise, Outcome 2 Pain.
3.3. Analysis.
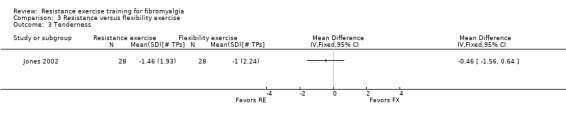
Comparison 3 Resistance versus flexibility exercise, Outcome 3 Tenderness.
3.4. Analysis.
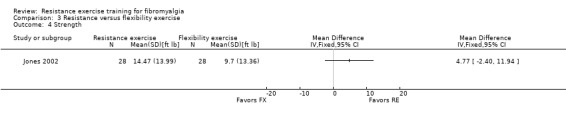
Comparison 3 Resistance versus flexibility exercise, Outcome 4 Strength.
3.11. Analysis.
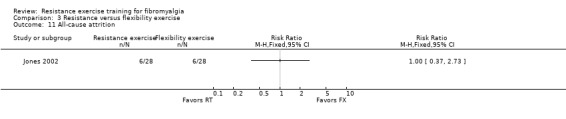
Comparison 3 Resistance versus flexibility exercise, Outcome 11 All‐cause attrition.
Minor outcomes:Jones 2002 found a large effect favoring resistance training on fatigue (Analysis 3.6) and sleep (Analysis 3.7). However, there was a moderate effect favoring the flexibility group on the hand‐to‐scapula test reflecting muscle and joint flexibility (MD 0.30 on a 4‐point scale, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.59, 1 study, 56 of 68 participants analyzed, Analysis 3.10). No differences were found in self efficacy (Analysis 3.5), depression (Analysis 3.8), or anxiety (Analysis 3.9).
3.6. Analysis.
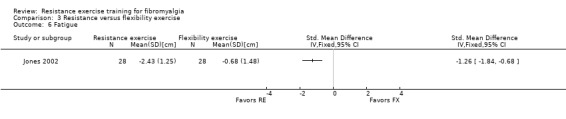
Comparison 3 Resistance versus flexibility exercise, Outcome 6 Fatigue.
3.7. Analysis.
Comparison 3 Resistance versus flexibility exercise, Outcome 7 Sleep.
3.10. Analysis.
Comparison 3 Resistance versus flexibility exercise, Outcome 10 Muscle/joint flexibility.
3.5. Analysis.
Comparison 3 Resistance versus flexibility exercise, Outcome 5 Self efficacy.
3.8. Analysis.
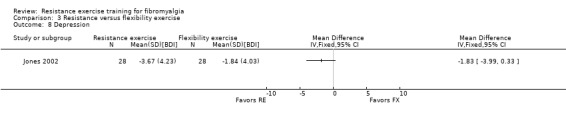
Comparison 3 Resistance versus flexibility exercise, Outcome 8 Depression.
3.9. Analysis.
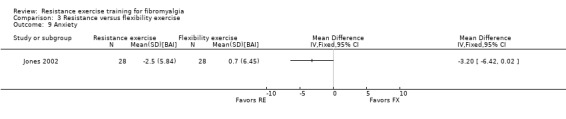
Comparison 3 Resistance versus flexibility exercise, Outcome 9 Anxiety.
Quality of evidence: Considering there is only one study in this category, there was very‐low‐quality evidence that 12 weeks of low‐intensity resistance training yielded greater improvements in wellness, and symptoms, fitness, safety, and acceptability than does flexibility exercise (see Table 3).
Discussion
Summary of main results
This review was one part of a larger review examining the effects of physical activity interventions for individuals with fibromyalgia. Of the 78 studies that we found that examined the effects of physical activity, only five provided resistance training‐only interventions. The paucity of such studies makes this review particularly important. With the emphasis on multidisciplinary management for fibromyalgia, this review provides a valuable opportunity to isolate the effects of resistance training and delivers factual information about the benefits and risks regarding an important type of exercise to healthcare professionals and people with fibromyalgia. The main results of our review were as follows.
Resistance training compared with control. There was low‐quality evidence that resistance training using moderate‐ to high‐intensity levels for 16 to 21 weeks has positive effects on wellness (multidimensional function, self reported physical function, and patient‐rated global well‐being), symptoms (pain, tenderness, fatigue, and depression) and physical fitness (muscle strength, muscle power, and muscle activation). There was low‐quality evidence that some improvement was retained for an additional 12 weeks following the conclusion of the supervised intervention in wellness (multidimensional function) and some symptoms (fatigue, but not pain and tenderness).
Resistance training compared with aerobic training. Low‐quality evidence suggested that moderate‐intensity resistance training was not as effective as aerobic training; there were greater improvements in the aerobic training groups in symptoms (pain and sleep but not tenderness, depression or anxiety) than in the resistance training group.
Resistance training compared with flexibility training. Low‐quality evidence suggested that low‐intensity resistance training was more effective than flexibility exercise in wellness (multidimensional function) and symptoms (pain, fatigue, sleep, but not tenderness, depression or anxiety). There was also low‐quality evidence that 12 weeks of low‐intensity resistance training does not result in differences in muscle strength compared with flexibility training; however, flexibility training appeared to yield greater improvement in muscle and joint flexibility than did resistance training.
Safety and acceptability. Based on evidence across all included studies, there was low‐quality evidence that suggested that resistance training was acceptable (attrition rates were not higher for resistance intervention than for comparators), and that women with fibromyalgia could safely perform resistance training (no serious adverse effects were reported).
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
Completeness: There were only five studies included in this review; with only 95 women (and no men) with fibromyalgia in total assigned to resistance training exercise. Given the lack of agreement on core outcomes to evaluate in trials examining interventions for fibromyalgia until recently, researchers have not been consistent in reporting on wellness and symptom outcomes. For example, multidimensional function was only measured in two of the five studies. Indeed one study did not report effects on pain and no studies measured stiffness, clinician‐rated global or dyscognition.
Given the nature of the intervention, an additional set of outcomes focusing on physical fitness must be considered. One would expect that muscle strength would have been universally assessed; however, only three of the five studies addressed this important outcome. Neither Bircan 2008 nor Kayo 2011 measured outcomes related to muscle performance (ie, muscle strength, endurance or power) in their trials designed to compare the effects of resistance training and aerobic exercise.
In terms of physical fitness outcomes, the most thorough appraisals were carried out by Hakkinen 2001 and Valkeinen 2004. Hakkinen 2001 found that women in the fibromyalgia training group demonstrated gains in muscle strength and power and increases in neuromuscular activity to the same degree as women in the healthy training group, indicating comparable ability to train the neuromuscular system in women with fibromyalgia. Similarly, Valkeinen 2004 demonstrated that resistance training among postmenopausal women with fibromyalgia led to improvements in physical fitness outcomes (strength, muscle activation, muscle size) in an equivalent manner to healthy postmenopausal women.
Unaccustomed resistance exercise is frequently accompanied by delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS), even in healthy individuals (Cheung 2003). This phenomenon can result in symptoms on palpation or with movement ranging from insignificant muscle tenderness to severe debilitating muscle pain that usually peaks 24 to 72 hours post‐exercise (Cheung 2003). The etiology of DOMS is thought to be multifactorial (Lewis 2012), and related to the repair process in response to microscopic exercise‐induced muscle damage (Cheung 2003). Some clinicians have suggested that exercise prescription for individuals with fibromyalgia should avoid eccentric exercise (Jones 2002), as eccentric exercise is known to produce greater levels of DOMS (Cheung 2003). Indeed, Jones 2002 designed their program to minimize eccentric work for this reason. Unfortunately, measurements that would clarify the presence or absence of DOMS in response to exercise were not carried out in these five studies, thus this review cannot contribute to our understanding of DOMS or eccentric exercise causing DOMS in individuals with fibromyalgia. Nevertheless, since exercise that emphasizes or overloads eccentric contractions causes more DOMS than concentric does, it would be wise to minimize this type of exercise (eg, plyometrics) or loads specifically chosen to train muscle eccentrically.
Clinicians and patients alike would like to know the optimal features of resistance training protocols. Given the research available, we are unable to make specific recommendations about optimal protocols for resistance training (types of resistance, intensities, frequencies, progression schemes) or to compare the effectiveness of resistance training versus other forms of exercise training.
General applicability of the findings: All included studies in this review involved supervised group exercise. It is not known if unsupervised individuals with fibromyalgia would get the same results as seen in these studies. This review deals with exercise protocols composed entirely of resistance exercise; the review does not address the effects of mixed exercise interventions that include other types of exercise (eg, aerobic, flexibility) for more than purposes of warm‐up or cool‐down.
There are many factors that need to be considered in determining important change including: a) the perspective of the audience ‐ individuals with fibromyalgia, clinicians, policy makers all may have unique interpretations, b) the impact that baseline status has on the interpretation of change, c) the sensitivity and stability of the measure, d) the application to individual versus groups (Dworkin 2008; Philadelphia 2001). A consensus statement that offers guidance in this area is the Initiative on Methods, Measurement, and Pain Assessment in Clinical Trials (IMMPACT). This initiative recommended the following benchmarks for interpreting changes in pain intensity on a 0 to 10 numerical rating scale in chronic pain clinical trials: a) 10% to 20% decrease is minimally important, b) greater than 30% decrease is moderately important, and c) greater than 50% decrease is substantial (Dworkin 2008). In keeping with this categorization, resistance training yields clinically important differences in pain intensity that fall between minimal and moderate (29%), and if we apply similar standards to the other outcomes, important improvements are noted in several outcomes reflecting wellness and symptoms. The Philadelphia Panel developed the standard of 15% relative benefit based on extensive input by rheumatology and biostatistics experts (Philadelphia 2001). This is consistent with Bennett 2009, who indicated that a minimal clinically important change in the FIQ total score (multidimensional function) was at least a 14% reduction. Despite the paucity of data, our results suggest that 16 to 21 weeks of moderate‐ to high‐intensity resistance training provides clinically relevant effects for wellness (multidimensional function 26%, patient‐rated global 91%), symptoms (pain 29%, fatigue greater than 33%) and muscle strength (25%) as compared with usual treatment. Using the 15% relative difference as the standard, clinically important differences were found between 12 weeks of low‐intensity resistance training and flexibility training in one primary outcome: fatigue (23%); in contrast, no clinically important differences were found when comparing eight weeks of moderate‐intensity resistance training versus aerobic training.
The absence of injuries or adverse events observed in high‐intensity (Valkeinen 2004), moderate‐intensity (Bircan 2008), and intensity‐as‐tolerated (Kayo 2011) interventions suggests that women with fibromyalgia can safely perform resistance training. The lack of dropouts in Hakkinen 2001 (moderate‐ to high‐intensity exercise regimen, n = 10) also support this conclusion. Kingsley 2011, who examined the cardiovascular and autonomic effects of a 12‐week resistance training program in premenopausal women with fibromyalgia (n = 9), also suggests that resistance training is "a safe and effective modality for increasing maximal strength without adversely altering vascular function in women with and without fibromyalgia" (page 261). One of the included studies involved postmenopausal women, so there is some evidence that older women with fibromyalgia can also safely tolerate high‐intensity resistance training (Valkeinen 2004). Not surprisingly, Hakkinen 2001 and Valkeinen 2004 support the use of supervised resistance training programs as a safe and effective means of improving outcomes in both pre‐ and postmenopausal women with fibromyalgia.
Despite the low‐quality evidence, the large effect sizes for a number of outcome measures reflecting wellness, symptoms, and physical fitness reach the standard for clinical importance, and in the absence of serious adverse events, we believe resistance training is a promising treatment for individuals with fibromyalgia. Recognizing that resistance training may yield improvements in wellness and symptoms can help promote this type of exercise as part of a balanced conditioning program for people with fibromyalgia, and decrease fear avoidance for this group with respect to possible increases in muscular tenderness post exercise. It is especially relevant to note that older (postmenopausal) women with fibromyalgia have the neuromuscular capability to make strength gains, which can help to improve and maintain functional mobility with aging and reduce fall risk (Jones 2009). A balanced conditioning program can also help to reduce the risk of comorbidity and promote a more active lifestyle (Jones 2008; Jones 2009).
Because the sample sizes of these studies were very small, it was unclear whether the people recruited represent all people with fibromyalgia. It is possible that many people will not consider or tolerate resistive exercise and, therefore, intervention may only benefit a subset of people (ie, selection bias).
Specific questions regarding applicably of resistance training: Overall, the comparison between low‐intensity resistance training and flexibility training demonstrated more favorable effects related to resistance training, despite the absence of improvement in muscle strength. It is possible that the resistance or progression of resistance was too low to achieve a training stimulus. As well, testing methods were not specific to the type of training exercises used so that strength gains could be obscured (Morrissey 1995). In addition, because participants did not receive a familiarization session on the dynamometer prior to initial testing, there may have been a learning effect that resulted in improvements in strength in both groups on their second tests. We believe that low attendance may also have contributed to the lack of difference in strength between the groups. Jones 2002 commented that "85% of the participants attended 13 or more classes"; however, this could mean that the majority of participants attended only slightly more than 50% of the 24 supervised sessions.
In this review we encountered statistical heterogeneity when meta‐analyzing two of the major outcomes (pain and tenderness) in the resistance training versus control comparison; however, there was consistency in the direction of the effect (all studies favored the resistance training). The day‐to‐day variability in pain in individuals with fibromyalgia may partially explain the statistical heterogeneity (I2 = 93%), but the resistance training programs used in Hakkinen 2001 and Kayo 2011 were different in several ways including duration (21 versus 16 weeks), type of resistance used (isokinetic exercise machine versus free weights) and nature of exercise (strength progressing to strength and power training versus strength training throughout). Despite these differences, both were well‐supervised, progressive high‐intensity interventions and we deemed them similar enough to meta‐analyze. The statistical heterogeneity in the meta‐analysis of tenderness (I2 = 58%) between Hakkinen 2001 and Valkeinen 2004 cannot be attributed to the exercise programs as they were identical, but may relate to the difference in age of the participants ‐ Hakkinen 2001 included only premenopausal women whereas Valkeinen 2004 included only postmenopausal women.
Quality of the evidence
There were limitations inherent in the included studies including incomplete description of the exercise protocols, inadequate small sample sizes, and inadequate documentation of adherence to exercise prescriptions. Concerns about small sample sizes and the small number of RCTs is partially counterbalanced by the magnitude of the SMDs for several important outcomes.
Potential biases in the review process
In our review process, we attempted to control for biases as follows:
we did not limit our search to English‐only publications;
we contacted primary authors for clarification and additional information where indicated, although responses were not always obtained. Our questions were asked in an open‐ended fashion so as to avoid leading questions or answers;
our multidisciplinary team had a range of expertise: ie, in library science, critical appraisal, pain, clinical rheumatology, exercise physiology, and knowledge translation;
two members of our multidisciplinary team also had the perspective of consumers (ie, one team member had fibromyalgia and another team member had another rheumatic disease);
intention‐to‐treat data were used preferentially.
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
Since the early 2000s, there have been several reviews and clinical practice guidelines regarding exercise for fibromyalgia. Based on their relevancy, we have chosen to comment on four: Brosseau 2008; Busch 2008; Jones 2009; and Winkelmann 2012.
Using rigorous methodology (The Cochrane Collaboration methods and Ottawa methods group procedures), Brosseau 2008 found and evaluated clinical trials examining the effects of resistance (strengthening) exercises in the management of fibromyalgia. In their review, five trials were evaluated; however, Hakkinen 2002 (Secondary) and Valkeinen 2005 (Secondary) were counted as separate trials. Due to this classification, the number of subjects across all trials was over‐reported in Brousseau. Using their methodology, the following Grade A evidence‐based clinical practice guidelines related to strengthening exercises were generated: benefits in muscle strength, pain relief, physical disability, and depression (all classed as clinically important benefits) at the end of 21 weeks (strengthening versus control); and benefits in quality of life (clinically important benefit) at the end of 12 weeks (strengthening versus flexibility training). Our results were consistent with Brosseau 2008.
Jones 2009 provides a synopsis on current evidence related to exercise and fibromyalgia, with a focus on guidelines for clinicians with respect to exercise prescription and exercise resources for people with fibromyalgia. Jones 2009 describes one strength study where subjects with fibromyalgia (n = 10) performed resistance training twice per week for 16 weeks (Figueroa 2008). They were compared with a control group of sedentary health individuals (n = 9) and results showed people with fibromyalgia had perturbed heart rate variability (no further definition provided); however, after the intervention, the subjects with fibromyalgia improved in total power, cardiac parasympathetic tone, pain, and muscle strength. In terms of recommendations for resistance exercise for people with fibromyalgia, Jones 2009 advises the importance of minimizing eccentric loading in order to reduce unnecessary strain and possible discomfort for people with fibromyalgia (Gibson 2006 as cited by Jones 2009). In addition, Jones 2009 advise that strength training loads be less than 50% of one‐repetition maximum using weights that are lighter than age‐predicted norms and that loads be kept close to midline and work done on a 'parallel plane', with reduced repetitive movements for smaller muscle groups. They advise doing single sets of six repetitions to begin and increasing this slowly. In our review, all five included studies applied progressive resistance exercise starting at a lower level and progressing, but Jones 2002 probably started with low resistance and did not progress to intensity levels attained in the other studies. Although all studies in this review employed dynamic exercises, Jones 2002 was the only study in which the resistance exercises were modified to reduce the eccentric phase. Our review does not support the Jones 2009 recommendation regarding eccentric exercise. Although avoiding the eccentric phase could potentially minimize DOMS, eccentric contractions may have particular advantages for connective tissue and are specifically recommended in exercise regimens designed to prevent and manage tendonopathy (Crosier 2002; Hibbert 2008). In addition, it should be noted that eccentric contractions are an inherent component of most activities of daily living.
Our group previously conducted a broad review of the effects of exercise for fibromyalgia (Busch 2008). Although there were 34 research publications included in this previous review, only three separate investigations dealt specifically with resistance training for people with fibromyalgia (Hakkinen 2001; Jones 2002; Valkeinen 2004). Analyses of these three studies resulted in the following findings in favor of resistance training: large reductions in pain, the number of TPs, and depression; large improvements in global well‐being; and moderate (non‐significant) effects on objective measures of physical function. Results of the current review, which took advantage of upgraded methodology and focused on seven major outcomes, similarly found favorable large effects for resistance training (versus control) on pain and patient‐rated global well‐being. However, the current analysis also revealed a small effect for self reported physical function favoring resistance training (over a control group) and large effects for muscle strength and muscle power. The current investigation included information about the effects of resistance training compared with aerobic training and flexibility exercises, which was not included in our previous review. In addition, the current study used the GRADE evaluation to rate included papers, which was not available when the last review was published.
As part of a scheduled update to the German S3 guidelines on fibromyalgia syndrome by the Association of the Scientific Medical Societies ('Arbeitsgemeinschaft der Wissenschaftlichen Medizinischen Fachgesellschaften'), Winkelmann 2012 reviewed the effectiveness of resistance training for fibromyalgia. They identified six RCTs (Altan 2009; Hakkinen 2001; Jones 2002; Kingsley 2005; Rooks 2007; Valkeinen 2008), and generated the following recommendation: Low‐ to moderate‐intensity strength training should be employed and indicated that there is evidence for a training frequency of 60 minutes twice a week. Although we do not dispute the recommendation, the mismatch between our included studies and those of Winkelmann 2012 is interesting. Altan 2004 was excluded from our review because we determined that pilates are better classified as a mixed exercise because they contain substantial aerobic and stretching components. Likewise, Rooks 2007 and Valkeinen 2008 had a substantial aerobic component included in the intervention. All three studies have been earmarked for a review on mixed exercise interventions, which our team plans to conduct. Kingsley 2005 was excluded because we were unable to verify that a published criteria for the diagnosis of fibromyalgia had been used. Our review included three studies (Bircan 2008; Kayo 2011; Valkeinen 2004), which were not included by Winkelmann 2012.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
We have found evidence in outcomes representing wellness, symptoms, and physical fitness favoring resistance training over usual treatment and over flexibility exercise, and favoring aerobic training over resistance training. Despite large effect sizes for many outcomes, the evidence has been decreased to low quality based on small sample sizes, small number of randomized clinical trials (RCTs), and the problems with description of study methods in some of the included studies.
This review provides evidence that 16 to 21 weeks of moderate‐ to high‐intensity supervised group resistance training using resistance machines or free weights and body weight for resistance has several large and clinically important positive effects on wellness, symptoms, and physical fitness of women with fibromyalgia. There is evidence that eight weeks of aerobic exercise may be superior to moderate‐intensity resistance training for reducing pain and improving sleep in women with fibromyalgia. There is evidence that 12 weeks of low‐intensity resistance training results in greater improvements than flexibility exercise in women with fibromyalgia in multidimensional function, pain, fatigue, and sleep. There is evidence that women with fibromyalgia can tolerate and benefit from resistance training.
Typically, management of fibromyalgia is multidisciplinary. In the studies included in this review, emphasis was placed on exercise. In one study (Kayo 2011), exercise was administered as a single modality (medication use was discontinued during the study). Bircan 2008 and Valkeinen 2004 allowed participants to continue their medication at entry, and Valkeinen 2004 also allowed participants to continue their normal daily activities and visit medical professionals if needed. In the two remaining studies, no information was provided about co‐interventions (Hakkinen 2001; Jones 2002). Uncontrolled co‐interventions act as a threat to validity in two ways ‐ first, the effects attributed to the experimental intervention may in fact be produced by the co‐intervention, and second, the co‐intervention may interact with the experimental intervention to modify its effects. It is hoped that the use of a control group helped to reduce the former and the consistency of the findings of Hakkinen 2001, Kayo 2011, and Valkeinen 2004 provides reassurance that the exercise is an effective treatment with or without other co‐interventions.
Aside from very general recommendations, we cannot make specific recommendations about the optimal design of resistance training protocols (types of resistance, intensities, frequencies, progression schemes).
Implications for research.
Several implications for further research arose from this review. We have used the EPICOT approach to describing implications for future research (Brachaniec 2009).
Evidence: There are insufficient high‐quality studies to allow adequate meta‐analysis of the effects of resistance training on symptoms, and physical function in individuals with fibromyalgia. A better description of research procedures or training protocols, or both, is needed in future research to address all aspects of potential bias more adequately.
Population: The five studies included in this review recruited only women; research is needed to clarify the effects of resistance training on males with fibromyalgia. Researchers undertaking exercise interventions are encouraged to describe physical fitness levels and physical activity participation of participants recruited to these studies. Population was mainly formed by middle‐aged white women living in developed countries (Europe n = 3, Brazil n = 1, and US n=1), which make results difficult to generalize to other populations and settings while at the same time brings awareness of the need for studies coming from other parts of the world.
Intervention: More detail with respect to exercise frequency, duration, intensity, and mode is needed to identify exercise volume more precisely and to determine if the prescribed exercise protocols meet current recommendations.
Comparators: In this review, resistance training was compared with aerobic exercise and flexibility exercise; however, there was only one study in each of these grouping. More research of this type is needed.
Outcomes: Improved documentation is needed in the area of adverse effects (injuries, exacerbations of fibromyalgia, and other associated adverse effects). Assessment of adherence to frequency and intensity of exercise should be an integral part of the results section of all RCTs studying effects of exercise interventions. Further research is needed to elucidate a dose‐response relationship. Formal follow‐up periods are needed to assess stability of responses. In addition, further work to validate a set of outcome measures for fibromyalgia research, such as has been initiated by OMERACT, is needed to allow comparisons across studies and elucidation of the more effective interventions. Determination of the minimum clinically important difference (MCID) and responsiveness of the core measures is also needed.
Timestamp: The need for an update of this review should be reviewed in three to five years.
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 4 July 2014 | Amended | Plain language summary amended |
History
Review first published: Issue 12, 2013
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 25 February 2013 | Amended | Update and restructuring of the Exercise for treating fibromyalgia review. The Exercise for treating fibromyalgia review has been split into several reviews, each focusing on a particular type of exercise training or physical activity. This review addresses resistance exercise training. The others are: ‐ Aquatic exercise training for fibromyalgia ‐ Aerobic exercise for fibromyalgia ‐ Composite exercise for fibromyalgia ‐ Flexibility exercise for fibromyalgia ‐ Mixed exercise for fibromyalgia ‐ Whole body vibration exercise for fibromyalgia |
| 14 June 2008 | Amended | Converted to new review format. CMSG ID C036‐R |
| 17 August 2007 | New citation required and conclusions have changed | Substantive amendment. See published notes for details |
Notes
This review is a major update of the previous reviews completed in 2002 and 2007. Methodologic differences between the 2007 review and this update included:
small revisions to the search terms;
changes in the membership of the review team (addition of new review authors and two consumers);
use of the 'Risk of bias' tool (Higgins 2011b) to assess the quality of the evidence instead of the van Tulder 2003 methodologic criteria that were used in the earlier version of the review;
revisions to Cochrane methods described in Version 5.1.0 of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011a) including Summary of findings, Grade;
use of electronic data extraction methods (Google docs) as opposed to paper‐based methods used in earlier versions of the review.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the following:
Mary Brachaniec and Janet Gunderson for contributing to team discussions, reviewing outcome measures, and drafting and reviewing the common language summary;
Louise Falzon for help with the literature search;
Christopher Ross for help with the manuscript, data entry, analysis, and administrative support for review team;
Tanis Kershaw, Joelle Harris, and Saf Malleck for administrative support for the review team;
Beliz Acan for assistance with translations from Turkish, which permitted screening and extraction for Yuruk 2008 (not used in this review);
Nora Chavarria for assistance translating a symptom checklist (from German) used in Keel 1998;
Patrícia Luciano Mancini for assistance with translations from Portuguese, which permitted screening of Matsutani 2012 and Santana 2010 , and data extraction for Hecker 2011 and Matsutani 2012 (not used in this review);
Winfried Hauser for assistance with translations from German, which permitted screening of Uhlemann 2007, Keel 1990, and Hillebrand 1969;
Silas Wieflspuett for assistance with translations from German, which permitted screening of Lange 2011 and Sigl‐Erkel 2011;
Julia Bidonde for translation of Arcos‐Carmona 2011, Tomas‐Carus 2007, Tomas‐Carus 2007b, Tomas‐Carus 2007c, and Sanudo 2010c from Spanish to English.
Appendices
Appendix 1. 2011 American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) position stand: guidance for prescribing exercise
The following recommendations are from Garber 2011.
Recommendations for cardiorespiratory fitness
Moderate‐intensity cardiorespiratory exercise training for ≥ 30 minutes/day on ≥ five days/week for a total of ≥ 150 minutes/week, vigorous‐intensity cardiorespiratory exercise training for ≥ 20 minutes/day on ≥ three days/week (≥ 75 minutes/week), or a combination of moderate‐ and vigorous‐intensity exercise to achieve a total energy expenditure of ≥ 500‐1000 MET (metabolic energy) minute/week.
Recommendations for muscular fitness
On two to three days/week, adults should also perform resistance exercises for each of the major muscle groups, and neuromotor exercise involving balance, agility, and coordination.
Two to four sets of resistance exercise per muscle group are recommended but even one set of exercise may significantly improve muscle strength and size.
Rest interval between sets if more than one set is performed: two to three minutes
Resistance equivalent of 60% to 80% of one repetition max (1 RM) effort. For novices 60% to 70% of 1 RM is recommended, for experienced exercises ≥ 80% may be appropriate.
The selected resistance should permit the completion of 8 to 12 repetitions per set or the number needed to induce muscle fatigue but not exhaustion.
For people who wish to focus on improving muscular endurance, a lower intensity (< 50% of 1 RM) can be used with 15 to 25 repetitions in no more than two sets.
Recommendations for flexibility
A series of flexibility exercises for each the major muscle‐tendon groups with a total of 60 seconds per exercise on ≥ two days/week is recommended. A series of exercises targeting the major muscle‐tendon units of the shoulder girdle, chest, neck, trunk, lower back, hops, posterior and anterior legs, and ankles are recommended. For most individuals, this routine can be completed within 10 minutes.
Stretches should be held for 1 to 30 seconds at the point of tightness or slight discomfort. Older people may realize greater improvements in range of motion with longer durations (30‐60 seconds) of stretching. A 20% to 75% maximum contraction held for three to six seconds followed by a 10‐ to 30‐second assisted stretch is recommended for proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) techniques.
Repeating each flexibility exercise two to four times is effective.
Appendix 2. MEDLINE (Ovid) search strategy
1. Fibromyalgia/
2. Fibromyalgi$.tw.
3. fibrositis.tw.
4. or/1‐3
5. exp Exercise/
6. Physical Exertion/
7. Physical Fitness/
8. exp Physical Endurance/
9. exp Sports/
10. Pliability/
11. exertion$.tw.
12. exercis$.tw.
13. sport$.tw.
14. ((physical or motion) adj5 (fitness or therapy or therapies)).tw.
15. (physical$ adj2 endur$).tw.
16. manipulat$.tw.
17. (skate$ or skating).tw.
18. jog$.tw.
19. swim$.tw.
20. bicycl$.tw.
21. (cycle$ or cycling).tw.
22. walk$.tw.
23. (row or rows or rowing).tw.
24. weight train$.tw.
25. muscle strength$.tw.
26. exp Yoga/
27. yoga.tw.
28. exp Tai Ji/
29. tai chi.tw.
30. Ai Chi.tw.
31. exp Vibration/
32. vibration.tw.
33. pilates.tw.
34. or/5‐33
35. 4 and 34
Appendix 3. EMBASE (Ovid) search strategy
1. FIBROMYALGIA/
2. fibromyalgi$.tw.
3. fibrositis.tw.
4. or/1‐3
5. exp exercise/
6. fitness/
7. exercise tolerance/
8. exp sport/
9. pliability/
10. exertion$.tw.
11. exercis$.tw.
12. sport$.tw.
13. ((physical or motion) adj5 (fitness or therapy or therapies)).tw.
14. (physical$ adj2 endur$).tw.
15. manipulat$.tw.
16. (skate$ or skating).tw.
17. jog$.tw.
18. swim$.tw.
19. bicycl$.tw.
20. (cycle$ or cycling).tw.
21. walk$.tw.
22. (row or rows or rowing).tw.
23. weight train$.tw.
24. muscle strength$.tw.
Appendix 4. The Cochrane Library search strategy
#1 MeSH descriptor Fibromyalgia explode all trees
#2 fibromyalgia
#3 fibrositis
#4 (#1 OR #2 OR #3)
#5 MeSH descriptor Exercise explode all trees
#6 MeSH descriptor Physical Exertion explode all trees
#7 MeSH descriptor Physical Fitness explode all trees
#8 MeSH descriptor Exercise Tolerance explode all trees
#9 MeSH descriptor Sports explode all trees
#10 MeSH descriptor Pliability explode all trees
#11 exertion*
#12 exercis*
#13 sport*
#14 (physical or motion) near/5 (fitness or therapy or therapies)
#15 physical* near/2 endur*
#16 manipulat*
#17 skate* or skating
#18 jog*
#19 swim*
#20 bicycl*
#21 cycle*
#22 walk*
#23 row or rows or rowing
#24 weight next train*
#25 muscle next strength*
#26 MeSH descriptor Yoga explode all trees
#27 yoga
#28 tai chi
#29 MeSH descriptor Tai Ji explode all trees
#30 MeSH descriptor Vibration explode all trees
#31 vibration
#32 pilates
#33 (#5 OR #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11 OR #12 OR #13 OR #14 OR #15 OR #16 OR #17 OR #18 OR #19 OR #20 OR #21 OR #22 OR #23 OR #24 OR #25 OR #26 OR ( # AND 27 ) OR #28 OR #29 OR #30 OR #31 OR #32)
#34 (#33 AND #4)
Appendix 5. CINAHL (EbscoHost) search strategy
S41 (S27 and (S28 or S40)
S40 S31 or S32 or S33 or S34 or S35 or S36 or S37 or S38 or S39
S39 TX vibration
S38 (MH "Vibration")
S37 (MH "Pilates") OR "pilates"
S36 TX pilates
S35 TX tai ji
S34 (MM "Tai Chi")
S33 TX tai chi
S32 TX yoga
S31 (MH "Yoga Pose") OR (MH "Yoga")
S30 S27 and S28
S29 S27 and S28
S28 S4 or S5 or S6 or S7 or S8 or S9 or S10 or S11 or S12 or S13 or S14 or S15 or S16 or S17 or S18 or S19 or S20 or S21 or S22 or S23 or S24 or S25 or S26
S27 S1 or S2 or S3
S26 TI manipulat* or AB manipulat*
S25 TI muscle strength* or AB muscle strength*
S24 TI weight train* or AB weight train*
S23 TI ( row or rows or rowing ) or AB ( row or rows or rowing )
S22 TI walk* or AB walk*
S21 TI ( (cycle* or cycling) ) or AB ( (cycle* or cycling) )
S20 TI bicycl* or AB bicycl*
S19 TI swim* or AB swim*
S18 jog* or AB jog*
S17 ( skate* or skating ) or AB ( skate* or skating )
S16 TI physical* N2 endur* or AB physical* N2 endur*
S15 TI motion N5 fitness or TI motion N5 therapy or TI motion N5 therapies or AB motion N5 fitness or AB motion N5 therapy or AB motion N5 therapies
S14 TI physical N5 fitness or TI physical N5 therapy or TI physical N5 therapies or AB physical N5 fitness or AB physical N5 therapy or AB physical N5 therapies
S13 TI sport* or AB sport*
S12 TI exercis* or AB exercis*
S11 TI exertion* or AB exertion*
S10 (MH "Physical Endurance+")
S9 (MH "Pliability")
S8 (MH "Sports+")
S7 (MH "Exercise Test+")
S6 (MH "Physical Fitness")
S5 (MH "Exertion+")
S4 (MH "Exercise+")
S3 TI fibrositis or AB fibrositis
S2 TI fibromyalgia or AB fibromyalgia
S1 (MH "Fibromyalgia")
Appendix 6. PEDro Physiotherapy Evidence Database (www.pedro.org.au/) search strategy
Terms searched:
fibromyalg* AND fitness training
fibromyalg* AND strength training
fibrositis
Appendix 7. Dissertation Abstracts (ProQuest) search strategy
Terms searched fibromyalg* or fibrositis (in citation or abstract)
Appendix 8. Current Controlled Trials (www.controlled‐trials.com/) search strategy
Terms searched fibromyalg* or fibrositis
Appendix 9. WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (www.who.int/ictrp/en/) search strategy
Terms searched fibromyalg* or fibrositis in Condition
Appendix 10. AMED (Ovid) Allied and Complementary Medicine search strategy
Ovid AMED (Allied and Complementary Medicine) <1985 to Jan 2012>
Search strategy:
‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐
1 Fibromyalgia/ (1453)
2 Fibromyalgi$.tw. (1626)
3 fibrositis.tw. (20)
4 or/1‐3 (1631)
5 exp Exercise/ (7293)
6 Physical Fitness/ (1655)
7 exp Physical Endurance/ (747)
8 exp Sports/ (3576)
9 Pliability/ (32)
10 exertion$.tw. (1129)
11 exercis$.tw. (18,675)
12 sport$.tw. (4952)
13 ((physical or motion) adj5 (fitness or therapy or therapies)).tw. (8773)
14 (physical$ adj2 endur$).tw. (629)
15 manipulat$.tw. (4038)
16 (skate$ or skating).tw. (81)
17 jog$.tw. (158)
18 swim$.tw. (552)
19 bicycl$.tw. (972)
20 (cycle$ or cycling).tw. (3530)
21 walk$.tw. (7139)
22 (row or rows or rowing).tw. (174)
23 weight train$.tw. (149)
24 muscle strength$.tw. (5651)
25 exp pilates/ (22)
26 exp Yoga/ (345)
27 exp Tai chi/ (204)
28 Tai ji.tw. (6)
29 yoga.tw. (448)
30 (hatha or kundalini or ashtunga or bikram).tw. (26)
31 pilates.tw. (62)
32 exp Exercise therapy/ (4945)
33 or/5‐32 (43,624)
34 4 and 33 (328)
Appendix 11. Selection criteria
Level one screen
Based solely on the title of the report:
Does the study deal exclusively with fibromyalgia? No ‐ exclude, Yes or uncertain ‐ go to step two
Does it include exercise? No ‐ exclude, Yes or uncertain ‐ go to step three
Does the study deal exclusively with adults? No ‐ exclude, Yes or uncertain ‐ go to step four
Is it an RCT? No ‐ exclude, Yes or uncertain ‐ Include
Level two screen
Based solely on the abstract of the report:
Does the study deal exclusively with fibromyalgia? No ‐ exclude, Yes or uncertain ‐ go to step two
Does it include exercise? No ‐ exclude, Yes or uncertain ‐ go to step three
Does the study deal exclusively with adults? No ‐ exclude, Yes or uncertain ‐ go to step four
Is it an RCT? No ‐ exclude, Yes or uncertain ‐ Include
Level three screen
Based on the full text of the report:
Does the study deal exclusively with fibromyalgia? No ‐ exclude, Yes ‐ go to step two, Uncertain ‐ add to list of questions for author and proceed to step two
Is the diagnosis of fibromyalgia based on published criteria? No ‐ exclude, Yes ‐ go to step three, Uncertain ‐ add to list of questions for author and proceed to step three
Does the study deal exclusively with adults? No ‐ exclude, Yes ‐ go onto step four, Uncertain ‐ add to list of questions for author and proceed to step four
Is it an RCT (the study uses terms such as "random", "randomized", "RCT", or "randomization" to describe the study design or assignment of subjects to groups)? No ‐ exclude, Yes ‐ go onto step five, Uncertain ‐ add to list of questions for author and proceed to step five,
Does it include at least one physical activity or exercise intervention? No ‐ exclude, Yes ‐ go onto step six, Uncertain ‐ add to list of questions for author and proceed to step six
Is between group data provided for the outcomes? No (the study does not contain ONLY fibromyalgia, or results are reported such that effects on fibromyalgia cannot be isolated) ‐ exclude, Yes ‐ include the study, Uncertain about one or more of steps 1 ‐ 5 ‐ reserve judgment until authors are contacted
Level four screen (classification of interventions in the included studies)
-
Classification of design
Number of interventions
-
Type of comparisons
Head to head comparison?
Exercise to control?
Composite to control?
-
Control group
Classify type of control
-
Exercise
Enter the type of exercise interventions used in the study
Complete the naming of the intervention groups
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. Resistance training versus control.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Multidimensional function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2 Physical function | 3 | 107 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐6.29 [‐10.45, ‐2.13] |
| 3 Pain | 2 | 81 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐3.30 [‐6.35, ‐0.26] |
| 4 Tenderness | 3 | 107 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.84 [‐2.60, ‐1.08] |
| 5 Muscle strength: max concentric leg extension | 2 | 47 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 27.32 [18.28, 36.36] |
| 6 Fatigue | 2 | 81 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐14.66 [‐20.55, ‐8.77] |
| 7 Patient‐rated global | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 8 Mental health | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 9 Depression | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 10 Muscle power | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 11 Sleep | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 12 Muscle size | 2 | 47 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.48 [‐0.11, 1.06] |
| 13 Muscle activation | 2 | 47 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 40.92 [33.50, 48.34] |
| 14 All‐cause attrition | 3 | 107 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.5 [0.79, 15.49] |
1.14. Analysis.
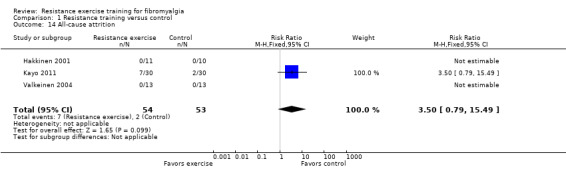
Comparison 1 Resistance training versus control, Outcome 14 All‐cause attrition.
Comparison 2. Resistance versus aerobic training.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Multidimensional Function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2 Self reported physical function | 2 | 86 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.48 [‐6.69, 3.74] |
| 3 Pain | 2 | 86 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.31, 1.67] |
| 4 Tenderness | 2 | 86 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.13 [‐0.55, 0.30] |
| 5 Fatigue | 2 | 86 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.50 [‐4.14, 7.13] |
| 6 Mental health | 2 | 86 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [‐4.97, 6.90] |
| 7 Sleep | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 8 Depression | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 9 Anxiety | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 10 Cardio respiratory submax | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 11 All‐cause attrition | 2 | 90 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.24, 4.23] |
2.10. Analysis.
Comparison 2 Resistance versus aerobic training, Outcome 10 Cardio respiratory submax.
Comparison 3. Resistance versus flexibility exercise.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Multidimensional function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2 Pain | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3 Tenderness | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4 Strength | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5 Self efficacy | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 6 Fatigue | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7 Sleep | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 8 Depression | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 9 Anxiety | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 10 Muscle/joint flexibility | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 11 All‐cause attrition | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
Comparison 4. Acceptability ‐ Attrition.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Attrition | 5 | 253 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.49, 1.83] |
| 1.1 RT vs. control | 3 | 107 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.30, 3.31] |
| 1.2 RT vs. AE | 2 | 90 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.31, 2.43] |
| 1.3 RT vs. flexibility | 1 | 56 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.28, 3.58] |
4.1. Analysis.
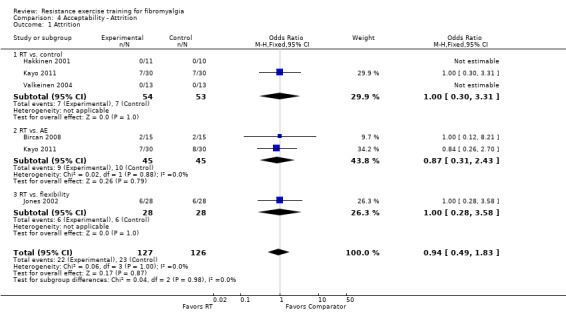
Comparison 4 Acceptability ‐ Attrition, Outcome 1 Attrition.
Comparison 5. Follow‐up resistance training versus control.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Multidimensional function | 1 | 180 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐12.43 [‐16.25, ‐8.61] |
| 1.1 8 weeks (wk) | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐9.87 [‐16.07, ‐3.67] |
| 1.2 16 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐16.75 [‐23.31, ‐10.19] |
| 1.3 28 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐10.67 [‐17.88, ‐3.46] |
| 2 Physical function | 1 | 180 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.64 [‐4.11, 2.83] |
| 2.1 8 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.67 [‐6.63, 5.29] |
| 2.2 16 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐2.24 [‐8.26, 3.78] |
| 2.3 28 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [‐5.04, 7.04] |
| 3 Pain | 1 | 180 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.12 [‐1.65, ‐0.58] |
| 3.1 8 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.68 [‐1.62, 0.26] |
| 3.2 16 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.79 [‐2.70, ‐0.88] |
| 3.3 28 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.85 [‐1.77, 0.07] |
| 4 Tenderness | 1 | 180 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.82 [‐4.37, 0.74] |
| 4.1 8 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.26 [‐4.21, 3.69] |
| 4.2 16 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐3.69 [‐8.11, 0.73] |
| 4.3 28 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.92 [‐7.06, 3.22] |
| 5 Fatigue | 1 | 180 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐6.53 [‐10.47, ‐2.59] |
| 5.1 8 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.65 [‐4.96, 8.26] |
| 5.2 16 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐12.85 [‐19.67, ‐6.03] |
| 5.3 28 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐9.11 [‐16.18, ‐2.04] |
| 6 Mental health | 1 | 180 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.95 [‐5.21, 3.32] |
| 6.1 8 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.54 [‐7.69, 6.61] |
| 6.2 16 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐2.86 [‐10.35, 4.63] |
| 6.3 28 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.54 [‐7.01, 8.09] |
5.1. Analysis.
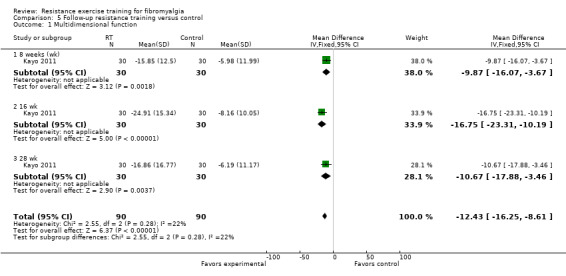
Comparison 5 Follow‐up resistance training versus control, Outcome 1 Multidimensional function.
5.2. Analysis.
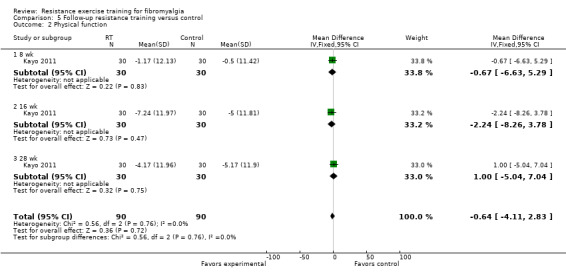
Comparison 5 Follow‐up resistance training versus control, Outcome 2 Physical function.
5.3. Analysis.
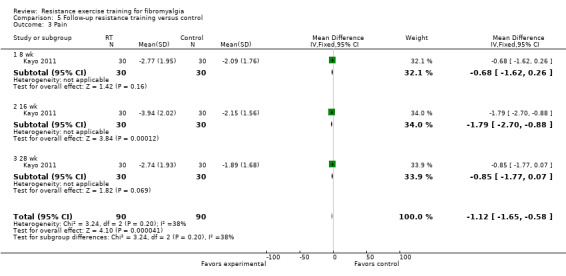
Comparison 5 Follow‐up resistance training versus control, Outcome 3 Pain.
5.4. Analysis.
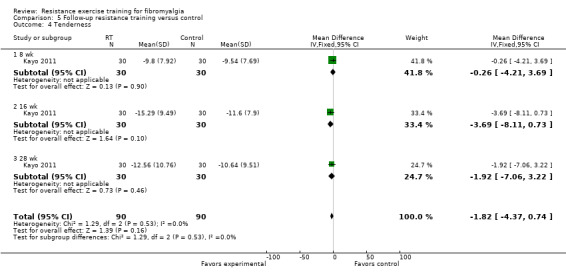
Comparison 5 Follow‐up resistance training versus control, Outcome 4 Tenderness.
5.5. Analysis.
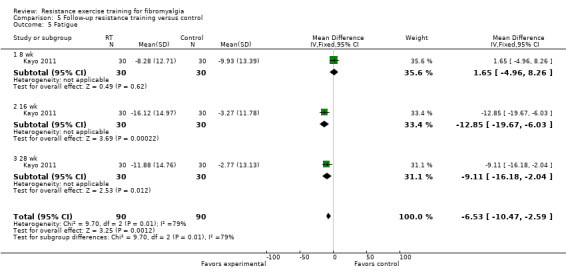
Comparison 5 Follow‐up resistance training versus control, Outcome 5 Fatigue.
5.6. Analysis.
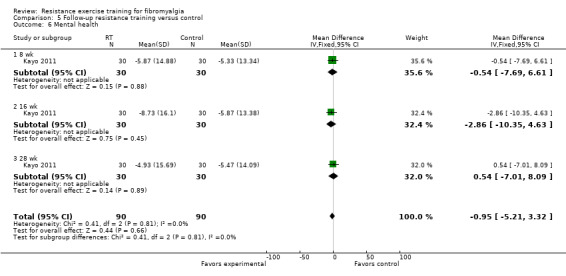
Comparison 5 Follow‐up resistance training versus control, Outcome 6 Mental health.
Comparison 6. Follow‐up resistance training versus aerobic training.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Multidimensional function | 1 | 180 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.82 [0.69, 8.95] |
| 1.1 8 weeks (wk) | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.48 [‐0.92, 11.88] |
| 1.2 16 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.39 [‐6.02, 8.80] |
| 1.3 28 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 7.71 [‐0.19, 15.61] |
| 2 Physical function | 1 | 180 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.22 [1.61, 8.83] |
| 2.1 8 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.83 [‐3.25, 8.91] |
| 2.2 16 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.43 [‐1.76, 10.62] |
| 2.3 28 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.83 [2.33, 15.33] |
| 3 Pain | 1 | 180 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.28 [‐0.28, 0.85] |
| 3.1 8 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.67 [‐0.28, 1.62] |
| 3.2 16 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.67 [‐1.67, 0.33] |
| 3.3 28 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.83 [‐0.18, 1.84] |
| 4 Tenderness | 1 | 180 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.64 [‐2.23, 3.51] |
| 4.1 8 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.47 [‐4.22, 5.16] |
| 4.2 16 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.36 [‐6.48, 3.76] |
| 4.3 28 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.84 [‐2.28, 7.96] |
| 5 Fatigue | 1 | 180 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.47 [‐4.27, 3.33] |
| 5.1 8 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.38 [‐5.94, 6.70] |
| 5.2 16 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐3.56 [‐10.30, 3.18] |
| 5.3 28 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.62 [‐5.08, 8.32] |
| 6 Mental health | 1 | 180 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.38 [‐0.03, 8.78] |
| 6.1 8 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.27 [‐7.73, 7.19] |
| 6.2 16 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.74 [‐3.03, 12.51] |
| 6.3 28 wk | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.94 [1.26, 16.62] |
6.1. Analysis.
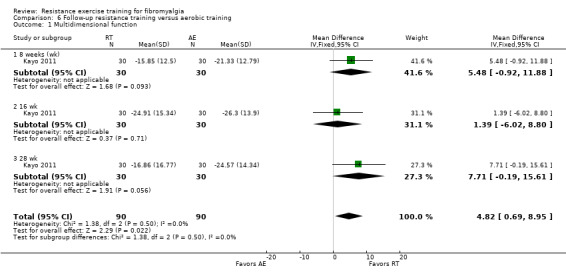
Comparison 6 Follow‐up resistance training versus aerobic training, Outcome 1 Multidimensional function.
6.2. Analysis.
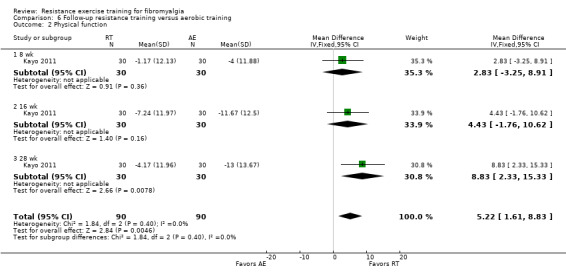
Comparison 6 Follow‐up resistance training versus aerobic training, Outcome 2 Physical function.
6.3. Analysis.
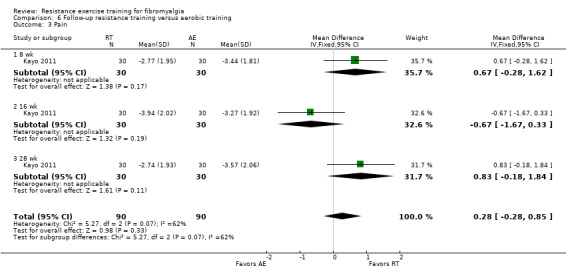
Comparison 6 Follow‐up resistance training versus aerobic training, Outcome 3 Pain.
6.4. Analysis.
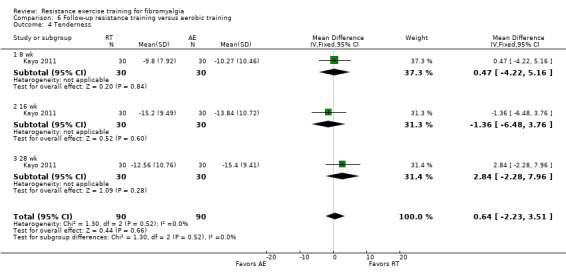
Comparison 6 Follow‐up resistance training versus aerobic training, Outcome 4 Tenderness.
6.5. Analysis.
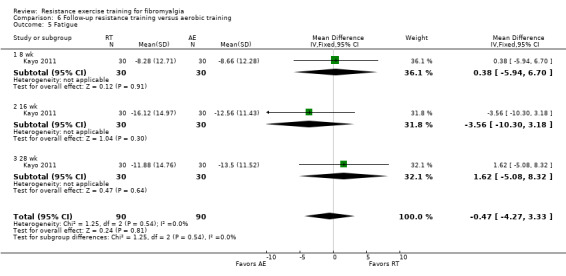
Comparison 6 Follow‐up resistance training versus aerobic training, Outcome 5 Fatigue.
6.6. Analysis.
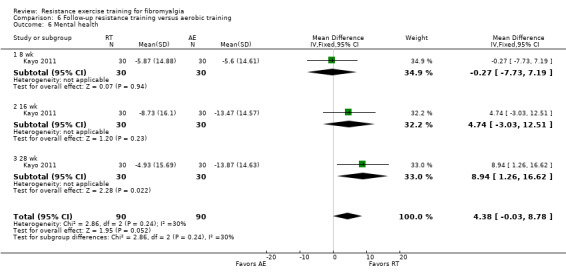
Comparison 6 Follow‐up resistance training versus aerobic training, Outcome 6 Mental health.
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Bircan 2008.
| Methods | Randomized trial, 2 groups (aerobic exercise group, resistance exercise group), LENGTH: 8 wk. | |
| Participants | FEMALE:MALE = 26:0, AGE (yrs (SD)): 46 (8.5) to 48.3 (5.3). DURATION OF ILLNESS (yrs (SD)): 3.85 (3.31) to 4.62 (5.22). INCLUSION: Women who met ACR 1990 diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia (Wolfe 1990). EXCLUSION: Presence of serious cardiovascular, pulmonary, endocrine, neurologic or renal disease, inflammatory rheumatic disease, or participation in a physical therapy or exercise program in the last 6 months. |
|
| Interventions |
1) Resistance training group (randomized n = 15, completed and analyzed n = 13): frequency: 3/wk, duration: 40 min (30‐min resistance exercise), intensity: unspecified 4‐5 reps progressed to 12 reps, method: free weights or body weight resistance exercise in standing, sitting, and lying for upper and lower limb muscles and trunk muscles. 2) Aerobic training group (randomized n = 15, completed and analyzed n = 13): frequency: 3/wk; duration: 20 min progressing to 30 min; intensity: low to moderate; method: treadmill walking. |
|
| Outcomes | Measurements: Pre‐ and post‐intervention (8 wks): sleep disturbance (VAS), fatigue (VAS), tenderness (tender point count), cardio‐respiratory function submaximal (6‐min walk), anxiety (HAD Anxiety scale), depression (HAD Depression scale), self reported physical function (SF‐36 Physical functioning scale), mental health (SF‐36 Mental Health Scale), pain (VAS) | |
| Congruence with ACSM Guidelines for Resistance Training (yes/no) |
Guidelines for healthy adults: No (frequency ‐ yes, type ‐ yes, rep ‐ no, starts too low, sets ‐ unclear, intensity ‐ unclear, progression ‐ yes). Guidelines for older adults: Unclear (frequency ‐ yes, type ‐ yes, rep ‐ yes, intensity ‐ unclear, progression ‐ yes) |
|
| Notes | Adverse effects: page 529: "No patient experienced musculoskeletal injury or exacerbation of fibromyalgia related symptoms during the intervention". Attrition: Resistance training: n = 2 (13.33%), aerobic training: n = 2 (13.33%). Adherence: Not specified. Co‐interventions: Both groups "were allowed to continue their medication at entry; however treatment had to remain stable for 1 month prior to entry to the study" (p. 528). Communication with author: Correction to data in table 2 confirming data for pain, sleep, fatigue are in centimeters (email 8 May 2013). Country: Turkey (paper published in English). Funding, conflict of interest: No information was available. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Participants were randomly assigned to an AE group or a SE group" (AE: aerobic exercise; SE: strengthening exercise) Bircan 2008 (p. 528). In email communication with the author (29 June 2012), the authors clarified as follows, "The patients were assigned to groups by the random allocation rule. As the sample size was planned to be 30, special cards were prepared for each treatment (15 were labelled as A and 15 as B), the cards were inserted into opaque envelopes, and the envelopes were shuffled. Patients were assigned to groups during the study by drawing lots among these envelopes after the initial evaluations were done." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Although no information was provided in the publication, in email communication with the author (29 June 2012), we learned that, "The patient's group was determined after all initial evaluations of the patient were done. The investigators did not know what the next treatment allocation would be." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | Although no information was provided in the publication, in email communication with the author (29 June 2012), we learned, "Participants, outcome assessors and people that delivered the intervention were not blind to study groups." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Only 1 variable was measured by an assessor (6‐min walk) ‐ in email communication (29 June 2012), we learned that this outcome was not blinded (see above). |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Missing outcome data balanced in numbers across intervention groups, with similar reasons for missing data across groups. It is unclear why intention‐to‐treat analysis was not used. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All outcomes specified on Bircan 2008, page 528 appear in data tables. According to email communication with the authors: "There were not any outcomes measured but not reported in the paper." (29 June 2012). |
| Other bias | Low risk | Based on the data provided, there is no indication that there are other important risks of bias. |
Hakkinen 2001.
| Methods | Randomized trial, 3 groups (fibromyalgia resistance exercise group, fibromyalgia control group, healthy resistance training group). LENGTH: 4‐wk baseline control phase for all groups followed by a 21‐wk intervention phase. | |
| Participants | FEMALE:MALE = 33:0, AGE (yrs (SD)): 37 (6) to 39 (6). DURATION OF ILLNESS (yrs (SD)): 12 (4). INCLUSION: Diagnosis: fibromyalgia (ACR criteria; Wolfe 1990), pre‐menopausal women. EXCLUSION: Unspecified. |
|
| Interventions |
1) Fibromyalgia resistance training group (fibromyalgia: n = 11) frequency: 2/wk; duration: duration of each session not provided, intensity: moderate‐to‐heavy progressive resistance (15‐20 reps at 40‐60% of 1 RM progressing to 5‐10 reps at 70‐80% of 1 RM; from wk 7 on: 30% of leg exercise performed rapidly with 40‐60% RM); method: 6‐8 dynamic resisted exercises using David 200 dynamometer to upper extremity, lower extremity, and trunk muscle groups. 2) Fibromyalgia control group (fibromyalgia: n = 10) Controls maintained their normal low‐intensity recreational physical activities but did not participate in the strength training. 3) Healthy resistance training control group (healthy: n = 12) A training group made up of sedentary healthy women (without fibromyalgia) was also a part of this study. Data from this group were not analyzed in this review. |
|
| Outcomes | Measurements: 4 wks pre‐intervention, immediately pre‐intervention, immediately postintervention (21 wks). Patient‐rated global well‐being (VAS), pain (VAS), tenderness (tender point count), fatigue (VAS), muscle strength (maximum bilateral (1 RM) concentric leg extension), sleep (VAS), self reported physical function (Health Assessment Questionnaire), muscle power (squat jump), muscle fiber activation (EMG), muscle size (cross‐sectional area), depression (Beck Depression Index). | |
| Congruence with ACSM Guidelines for Resistance Training (yes/no) |
Guidelines for healthy adults: Yes (frequency ‐ yes, type ‐ yes, reps ‐ yes, sets ‐ yes, intensity ‐ yes, progression ‐ yes). Guidelines for older adults: Yes (frequency ‐ yes, type ‐ yes, reps ‐ yes, intensity ‐ yes, progression ‐ yes). |
|
| Notes |
Adverse effects: None reported. Attrition: n = 0 (0%), aerobic training: n = 0 (0%) Adherence to exercise protocol: Not specified Data for this study were extracted from 2 reports: Hakkinen 2001 (Primary); Hakkinen 2002 (Secondary). Additional data were obtained from the authors on the following outcome measures: maximum bilateral (1 RM) concentric leg extension, squat jump vertical, and tender points. The authors also clarified the timing of the assessments. The researcher reported that there were no dropouts. The author attributed this to intensive process for habituating participants to the study methods and cultural values unique to Finland where the study took place (personal communication). Also of note, prior to entry into the study, the "subjects in all groups were habitually active (such as walking, swimming, biking, skiing) but they had no background in strength training" (page 1288, Hakkinen 2002 (Secondary)). Co‐interventions: No information was provided about co‐interventions. Country: Finland. Funding, conflict of interest: As reported by the authors: "This study was supported in part by grants from Finnish Social Insurance Institution and the Yrjö Jahnsson Foundation". No information was available regarding conflict of interest. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No information regarding how participants were randomized. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No procedure was described. |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | Insufficient information, but it is unlikely that participants and care providers were blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No information on blinding of outcome assessors was provided. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No dropouts reported. Table 4 in Hakkinen 2001 showed the sample size for both groups. We assume that these values are consistent for before and after treatment. Data on tenderness, which was not available in the research report, was provided by the study authors upon request. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Although the study protocol was unavailable, between the primary, the companion paper and the response from the authors, all the variables measured have been accounted for. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Based on the data provided, there is no indication that there are other important risks of bias. |
Jones 2002.
| Methods | Randomized trial, 2 groups (resistance exercise group, flexibility exercise group). LENGTH: 12 wk. | |
| Participants | FEMALE:MALE = 56:0, AGE (yrs (SD): 46.4 (8.6) to 49.2 (6.3). DURATION OF ILLNESS (yrs (SD)): 6.9 (6.6) to 7.7 (5.5). INCLUSION: Diagnosis: fibromyalgia (ACR criteria; Wolfe 1990), women only, ages 20‐60 yrs. EXCLUSION: Current or past history of cardiovascular, pulmonary, neurologic, endocrine, or renal disease that would preclude exercise program; current use of medications that would affect normal physiologic response to exercise; current cigarette smoking, score = 29 on Beck Depression Scale modified for fibromyalgia, current participant in a regular exercise program. |
|
| Interventions | 1) Resistance exercise group (n = 28): frequency: 2/wk; duration: 60 min; intensity: progressed from 4 to 12 reps; method: supervised dynamic resistance exercise for lower and upper limbs and trunk using hand weight (1‐3 lb (0.45‐1.36 kg)) and elastic tubing; minimization of eccentric work (a videotape to guide home practice of the strengthening exercise regimen was provided to participants). 2) Flexibility exercise group (n = 28): frequency: 2/wk; duration: 60 min; flexibility for lower limbs and trunk; intensity: n/a, method: supervised static stretches (a videotape to guide home practice of the flexibility exercise regimen was provided to participants). | |
| Outcomes | Measurement pre‐ and post‐intervention (12 wks). Multidimensional function (FIQ total score), pain (FIQ VAS), tenderness (tender point count), fatigue (FIQ VAS), muscle strength (maximum isokinetic strength of nondominant knee extension), sleep (FIQ VAS), muscle/joint flexibility (hand‐to‐neck, hand‐to‐scapula movement), depression (Beck Depression Inventory), anxiety (Beck Anxiety Inventory), coping/self efficacy (Arthritis Self Efficacy Scale). | |
| Congruence with ACSM Guidelines for Resistance Training (yes/no) |
Guidelines for healthy adults: No (F ‐ yes, type ‐ yes, reps ‐ unclear, sets ‐ unclear, I ‐ no, progression ‐ unclear). Guidelines for older adults: No (F‐ yes, type ‐ yes, repetitions ‐ unclear, I ‐ unclear). |
|
| Notes |
Adverse effects: There were no occurrences of adverse events or injury during the intervention and incidence of worsening of pain or tenderness was the same in both groups (n = 3 in each group) (page 1045). Attrition: Authors stated that they had a low attrition rate (9%) (page 1045); however, following analysis of the data and communication with author (email 19 July 2010), the attrition from each group was not specified. The data were: 12/68 (17.64%) either dropped out or did not meet adherence criteria for inclusion. Resistance training n = 6 (17.64%), flexibility training n = 6 (17.64%). Adherence to exercise protocol: "Class attendance records by the exercise instructor indicated that 85% of the participants (n = 58) attended 13 or more classes" (page 1043); however, "the strengthening intervention was not monitored to assure that subjects progressively increased the load throughout the 12 weeks. Instead, participants were encouraged to listen to their bodies and increase the intensity as they thought they could tolerate it." (pages 1045, 1046). Co‐interventions: No information was provided about co‐interventions. Country: US. Communication with author: Additional data were obtained from the authors to clarify the content and delivery of the intervention (eg, videotapes, education, the exercise level at completion), the number randomized, and specifics related to dropouts. Funding, conflict of interest: As reported by the authors: "Supported by an Individual National Research Service Award (#1F31NR07337‐01A1) from the National Institutes of Health, a doctoral dissertation grant (#2324938) from the Arthritis Foundation, and funds from the Oregon Fibromyalgia Foundation". No information was available regarding conflict of interest. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Randomization was accomplished with a coin flip" (page 1042). |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information in the research report. |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | Insufficient information, but it is unlikely that participants and care providers were blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | "Data were collected by an exercise science technician (strength and body fat) or the principal investigator (all other measures). Both were blinded to group assignment" (Jones 2002, page 1042). |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Reasons for missing outcome data unlikely to be related to true outcome (for survival data, censoring unlikely to be introducing bias). Authors stated that the participants who dropped out lived far from the fitness center (page 1045). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The study protocol was not available but it was clear that the published reports included all expected outcomes, including those that were prespecified. |
| Other bias | Low risk | There may be a risk related to poor adherence to the exercise regimen. "85% of the participants attended only slightly more than 50% of the 24 supervised sessions" (Jones 2002, page 1043). The low attendance may have contributed to low power (ie, type 2 error). |
Kayo 2011.
| Methods | Randomized trial, 3 groups (walking group, strengthening exercise group, control group). LENGTH: 16 wks with follow‐up for an additional 12 wks. | |
| Participants | FEMALE:MALE = 90:0, AGE (yrs (SD)): 46.1 (6.4) to 47.7 (5.3). DURATION OF ILLNESS (yrs (SD)): 4 (3.1) to 5.4 (3.5). INCLUSION: women ages 30‐55 yrs and agreed to participate in an exercise program 3 times/wk for 16 wks and to discontinue medications for fibromyalgia 4 wks before the start of the study and who had at least 4 yrs of schooling. EXCLUSION: women with any contraindications to exercise on the basis for clinical rheumatologic examination, and those involved in cases of medical litigation. |
|
| Interventions |
1) Progressive aerobic exercise (n = 30): frequency: 3 times/wk x 16 wks; duration: ˜ 60 min (warm‐up (5‐10 min) conditioning stimulus, cool down (5 min); intensity: moderate to high intensity (40‐50% to 60‐70% heart rate reserve by wk 16); method: supervised indoor or outdoor walking monitored using heart rate monitor. 2) Resistance exercise training (n = 30): frequency: 3 times/wk x 16 wk; duration: ˜ 60 min; intensity: high intensity (4 on 10‐point Borg scale)b, exercise load and intensity were increased every 2 wks (reps ‐ wks 1 + 2: 3 sets of 10 reps with rest intervals of 1 min between sets, wks 3‐16; load ‐ wks 1‐4, no load, wks 5‐16 load was included), "The training load was individually and systematically adjusted every time the participant performed more than 15 repetitions with successfully"b; M: supervised exercise protocol consisting of 11 free active exercises for upper and lower limbs and trunk muscles, using free weights and body weight performed in the standing, sitting, and lying positions. 3) Control group (n = 30): control conditions not specified, except authors stated participants in all 3 groups were asked to discontinue tricyclic antidepressants but were allowed to use acetaminophen (paracetamol) for pain. |
|
| Outcomes | Measurement pre‐intervention, mid‐intervention (8 wks), immediately post‐intervention (16 wks), and follow‐up (12 wks post‐intervention). As reported in paper: multidimensional function (FIQ total), pain (VAS). As provided by author on request: fatigue (SF‐36 ‐ Vitality scale), tenderness (tender point pain), self reported physical function (SF‐36 Physical Function scale), mental health (SF36 Mental Health). |
|
| Congruence with ACSM Guidelines for Resistance Training (yes/no) |
Guidelines for healthy adults: No (frequency ‐ yes, type ‐ yes, reps ‐ no, sets ‐ yes, intensity ‐ yes, according to description provided by authors regarding the scale, progression ‐ yes). Guidelines for older adults: Yes (frequency ‐ yes, type ‐ yes, reps ‐ yes, intensity ‐ yes, progression ‐ yes). |
|
| Notes |
Adverse effects: "No complications or adverse effects were observed during the study period among patients who completed the treatment protocols." Attrition: Aerobics training n = 1 (3.3%), resistance training n = 5 (16.6%), control n = 5 (16.6%). Adherence to exercise protocol: "We adopted Borg Scale (0‐10) and the recommended intensity was 4 (somewhat severe) and all participants complied." From email communication (19 July 2012). 80% attendance rate ‐ excluding those who dropped out for reasons of work or family illness, with only 1 participant assigned to the resistance training group that did not meet the attendance requirements of the study. Co‐interventions: Exercise was administered in this study as a single modality; the timing of restarting medication was monitored. Country: Brazil Funding, conflict of interest: No information on funding of the study was found, but the authors stated there was no conflict of interest. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "The allocation sequence was based on a random number list (GraphPad Statmate version 1.0), which was organized by an investigator (MSP)" (online page 2). |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Opaque sealed envelopes were used. |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No details provided in the report. "There was no contact among the groups"b. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | The study authors stated: "all patients were clinically examined by the same rheumatologist (CSM), who was blinded to group assignment throughout the study" (online page 2). |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Intention‐to‐treat analysis was used. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Outcome data for important variables (eg, tender points, SF‐36 Physical Functioning, SF‐36 Vitality, SF‐36 Mental Health) were not provided in the published report, but the study authors provided these on requestb. An important shortcoming was that there were no performance tests for physical function applied in this study. |
| Other bias | Low risk | There did not appear to be any other serious sources of bias. Although the researchers found differences between groups in duration of disease at baseline (P value = 0.04, longer duration in control group than the intervention groups), no between‐group differences were found in baseline levels of age, pain, tenderness, multidimensional function, SF‐36 subscales, so we did not consider this a serious problem. |
Valkeinen 2004.
| Methods | Randomized trial, 3 groups (fibromyalgia resistance exercise group, fibromyalgia control group, healthy resistance exercise control group). LENGTH: 21 wk. | |
| Participants | FEMALE:MALE = 36:0, AGE (yrs (SD)): 59.1 (3.5) to 60.2 (2.5). DURATION OF ILLNESS (yrs (SD)): 8.5 (4.3) to 6.6 (4.1). INCLUSION: Diagnosis: fibromyalgia (ACR criteria; Wolfe 1990), age = 55 yrs, women. EXCLUSION: No other diseases, no injuries, no experience of regular strength training exercises, willingness to participate in study protocol. |
|
| Interventions |
1) Fibromyalgia resistance exercise group (fibromyalgia: n = 13): frequency: 2/wk; duration: 60‐90 min, 80% strength 20% power, I: light‐ to high‐intensity progressive resistance from 3 sets of 15‐20 reps at 40‐60% 1 RM to 3‐5 sets of 5‐10 reps at 70‐80% 1 RM, for power (legs only) 2 sets of 8‐12 reps at 40‐50% 1 RM; method: resisted dynamic exercise to knee extensors x 2 plus 5‐6 exercises for other main muscle groups of body (exercise equipment not specified). 2) Fibromyalgia control group (fibromyalgia: n = 13): Control conditions were treatment as usual and physical activity as usual. 3) Healthy resistance exercise control group (healthy: n = 10): A group made up of sedentary women without fibromyalgia (n = 12) who carried out the exercise protocol was also a part of this study. Data from this group were not analyzed in this review. |
|
| Outcomes | Measurements 4 wks pre‐intervention, immediately pre‐intervention, immediately post‐intervention (21 wks). Tenderness (tender point count), muscle strength (Max concentric leg extension), self reported function (Health Assessment Questionnaire), muscle fiber activation (EMG), muscle size (cross‐sectional area). The study authors stated they measured 5 other variables (pain, fatigue, patient‐rated global, depression, and sleep) but the data were not available in the report and they did not respond to our emails. |
|
| Congruence with ACSM Guidelines for Resistance Training (yes/no) |
Guidelines for healthy adults: Yes (frequency ‐ yes, type ‐ yes, reps ‐ yes, sets ‐ yes, intensity ‐ yes). Guidelines for older adults: Yes (frequency ‐ yes, type ‐ yes, reps ‐ yes, intensity ‐ yes). |
|
| Notes |
Adverse effects: "After the initial phase of training, the patients did not complain of any unusual exercise‐induced pain or muscle soreness" (Valkeinen 2004 (Primary) page 227). Attrition: Fibromyalgia resistance training n = 0 (0%), fibromyalgia control n = 0 (0%), healthy resistance training n = 0 (0%) Adherence to exercise protocol: The researchers did not specify if or how adherence to the exercise protocol was monitored; however, muscular function was measured at 7, 14, and 21 wks. They did state all fibromyalgia subjects "completed training". Co‐interventions: "All subjects were allowed to continue their normal daily activities, to use their normal medication ... and to visit medical professionals if needed" (page 226). Country: Finland. Data for this study was extracted from 2 reports: Valkeinen 2004 (Primary), Valkeinen 2005 (Secondary). Funding, conflict of interest: As reported by the authors: "This study was supported in part by grants from the Central Hospital of Central Finland; Kuopio University Hospital, Peurunka‐Medical Rehabilitation Foundation and The Ministry of Education, Finland". No information was available regarding conflict of interest. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Described on page 225 Valkeinen 2004: "After inclusion, the fibromyalgia patients were randomly allocated by draw ..." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No mention of allocation concealment. |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | Insufficient information, but it is unlikely that participants and care providers were blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No information available. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Missing outcome data balanced in numbers across interventions groups, with similar reasons for missing data across groups. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Outcome of statistical analyses are reported for pain, fatigue, sleep, depression, perceived health (all non‐significant) but point estimates for these outcome measures were not reported. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Based on the data provided, there is no indication that there are other important risks of bias. |
a intention‐to‐treat analysis.
b based on email communication with the study author.
ACR: American College of Rheumatology, EMG: electromyography; FIQ: Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire; HAD: Hospital Anxiety and Depression; min: minute; rep: repetition; RM: repetition maximum; SD: standard deviation; SF: Short Form; VAS: visual analog scale; wk: week; yr: year.
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Ahlgren 2001 | Diagnosis ‐ trapezius myalgia. |
| Alentorn‐Geli 2009 | The study did not provide data on outcomes used in this review ‐ focus was on serum insulin‐like growth factor. |
| Astin 2003 | Did not meet exercise criteria (QiGong). |
| Bailey 1999 | Not an RCT (1 group design). |
| Bakker 1995 | Between‐group analysis not done. |
| Carbonell‐Baeza 2011 | A study proposal (no data). |
| Casanueva‐Fernandez 2012 | Insufficient exercise component (treadmill 5 min, cycle ergometer 5 min, once/wk, 8 weeks). |
| da Silva 2007 | This study did not present data allowing isolation of effects of physical activity ‐ focus of study was on a manipulative intervention called Tui Na. |
| Dal 2011 | Not an RCT. |
| Dawson 2003 | Not randomized. A 1‐group before‐after design. |
| Finset 2004 | This report did not provide data for parallel groups. |
| Gandhi 2000 | Not randomized, 3‐group design: (1) non‐exercising control (n = 12), (2) hospital‐based exercise group (n = 10), (3) home‐based videotaped exercise program (n = 10). |
| Geel 2002 | Not randomized. |
| Gowans 2002 | Focused on measurement issues of selected variables already reported in an included study; new variables did not include standard deviations. |
| Gowans 2004 | This report described an uncontrolled follow‐up of a physical activity intervention. |
| Guarino 2001 | Diagnosis ‐ Gulf War syndrome. |
| Han 1998 | Not randomized (geographic control). |
| Huyser 1997 | Not an RCT. |
| Karper 2001 | Not randomized (program evaluation). |
| Kendall 2000 | Did not meet exercise criteria (body awareness). |
| Khalsa 2009 | Not an RCT. |
| Kingsley 2005 | Diagnosis of fibromyalgia made by physician or rheumatologist but when contacted, the authors did not verify the use of published criteria (eg, ACR criteria; Wolfe 1990). |
| Lange 2011 | Not randomized. |
| Lorig 2008 | Arthritis Self‐Management Program internet‐based instruction. Content included exercise design but no explanation was given. |
| Mannerkorpi 2002 | Not an RCT. |
| Mason 1998 | Not randomized (subjects enrolled in a multimodal treatment compared with subjects who were unable to participate due to insurance reasons). |
| McCain 1986 | This study appears to present preliminary results of the McCain 1988 study and was, therefore, excluded. |
| Meiworm 2000 | Not randomized (subjects self selected their group). |
| Meyer 2000 | Problem with implementation of study design ‐ randomization lost. |
| Mobily 2001 | Not an RCT (a case study). |
| Mutlu 2013 | Study compared exercise + Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) versus exercise; effects of exercise cannot be isolated in this RCT. |
| Nielen 2000 | Not randomized (cross‐sectional case‐control study of fitness). |
| Offenbacher 2000 | Non‐experimental ‐ narrative review. |
| Oncel 1994 | Insufficient description of exercise (1 group received "medical therapy and exercise"; no further information about the exercise intervention given). |
| Peters 2002 | Diagnosis ‐ persistent unexplained symptoms. |
| Pfeiffer 2003 | Not an RCT (1 group before‐and‐after design). |
| Piso 2001 | Not randomized ‐ our translator reported: "The authors wrote only how they recruited nine of the patients. They wrote nothing about if and how the patients were allocated to the two groups." We were unsuccessful on several attempts to contact the authors for clarification. |
| Rooks 2002 | Not an RCT (1‐group design). |
| Santana 2010 | Could not confirm that diagnosis was made using published criteria. |
| Sigl‐Erkel 2011 | A commentary on research by other investigators. |
| Thieme 2003 | Did not meet exercise criteria (passive physical therapy with light movement in water ‐ the active exercise was too small a component, not described or quantified sufficiently). |
| Tiidus 1997 | Not an RCT (1 group repeated measures design). |
| Uhlemann 2007 | Not an RCT (cross‐over design ‐ no parallel data reported). |
| Vlaeyen1996 | Insufficient description of the mode of exercise. "Each session ended with a physical exercise such as swimming or bicycling, excluding systematic physical or fitness training." |
| Williams 2010 | The study did not present data allowing isolation of effects of physical activity ‐ focused on internet‐based management system to increase adherence. |
| Worrel 2001 | Not an RCT (1‐group design). |
RCT: randomized clinical trial, wk: week.
Characteristics of studies awaiting assessment [ordered by study ID]
Adsuar 2012.
| Methods | Unknown. |
| Participants | |
| Interventions | Vibration exercise versus control. |
| Outcomes | |
| Notes | Awaiting acquisition of full‐text article. |
Amanollahi 2013.
| Methods | Unknown. |
| Participants | |
| Interventions | Ibuprofen versus massage versus stretching. |
| Outcomes | |
| Notes | Awaiting translation. |
Aslan 2001.
| Methods | RCT. |
| Participants | 14 people with fibromyalgia. |
| Interventions | Classical massage combined with superficial heating and exercise in KMG. |
| Outcomes | Visual analog scale (VAS), number of trigger points and Neck Pain and Disability (NPAD) VAS. |
| Notes | In Turkish ‐ awaiting translation. |
Bland 2010.
| Methods | |
| Participants | |
| Interventions | |
| Outcomes | |
| Notes |
Ekici 2008.
| Methods | RCT. |
| Participants | 51 women with fibromyalgia (ACR criteria; Wolfe 1990). |
| Interventions | Pilates versus connective tissue massage. |
| Outcomes | Pain, depression. |
| Notes | In Turkish ‐ awaiting translation. |
Thijssen 1992.
| Methods | Unknown. |
| Participants | Patienten met fibromyalgie (people with fibromyalgia). |
| Interventions | Zwemprogramma. |
| Outcomes | Unknown. |
| Notes | In Dutch ‐ awaiting acquisition. |
Wright 2012.
| Methods | |
| Participants | |
| Interventions | |
| Outcomes | |
| Notes |
ACR: American College of Rheumatology; RCT: randomized clinical trial.
Contributions of authors
AJB: Designing and reviewing protocol for review, screening data extraction, methodologic analysis, and writing and reviewing manuscript.
SW: Participating in discussion regarding methods, screening studies, data extraction, methodologic analysis, and writing and reviewing manuscript.
RR: Participating in discussion regarding methods, screening studies, data extraction, methodologic analysis, and writing and reviewing manuscript.
JB: Participating in discussion regarding methods, screening studies, data extraction, methodologic analysis, writing and reviewing drafts, and approving the final manuscript.
LS: Participating in discussion regarding methods, screening studies, data extraction, reviewing drafts, and approving the final draft of the manuscript.
AD: Participating in discussion regarding methods, screening studies, data extraction, reviewing drafts, and approving the final draft of the manuscript.
AS: Participating in discussion regarding methods, screening studies, data extraction, reviewing drafts, and approving the final draft of the manuscript.
VDBH: Participating in discussion regarding methods, screening studies, data extraction, reviewing drafts, and approving the final draft of the manuscript.
TR: Designing and implementing the search strategy, designing the study selection protocol, writing the clay text summary, reviewing drafts, and approving the final draft of the manuscript.
CLS: Designing and reviewing protocol for review, screening studies, data extraction, providing expert opinion on exercise physiology, reviewing drafts, and approving the final draft of the manuscript.
TO: Designing and reviewing protocol for review, screening studies, data extraction, providing expert opinion on exercise physiology, reviewing drafts, and approving the final draft of the manuscript.
Sources of support
Internal sources
School of Physical Therapy, University of Saskatchewan, Canada.
Department of Medicine, University of Saskatchewan, Canada.
Institute of Health and Outcomes Research, University of Saskatchewan, Canada.
Institute for Work and Health, Canada.
External sources
No sources of support supplied
Declarations of interest
We confirm that any present or past affiliations or other involvement in any organization or entity with an interest in the review that might lead us to have a real or perceived conflict of interest are listed below.
None known.
Edited (no change to conclusions)
References
References to studies included in this review
Bircan 2008 {published data only}
- Bircan C, Karasel SA, Akgun B, El O, Alper S. Effects of muscle strengthening versus aerobic exercise program in fibromyalgia. Rheumatology International 2008;28(6):527‐32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hakkinen 2001 {published data only}
- Hakkinen A, Hakkinen K, Hannonen P, Alen M. Strength training induced adaptations in neuromuscular function of premenopausal women with fibromyalgia: comparison with healthy women. Annals of Rheumatic Diseases 2001;60(1):21‐6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakkinen K, Pakarinen A, Hannonen P, Hakkinen A, Airaksinen O, Valkeinen H, et al. Effects of strength training on muscle strength, cross‐sectional area, maximal electromyographic activity, and serum hormones in premenopausal women with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(6):1287‐95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jones 2002 {published data only}
- Jones KD, Burckhardt CS, Clark SR, Bennett RM, Potempa KM. A randomized controlled trial of muscle strengthening versus flexibility training in fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(5):1041‐8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kayo 2011 {published data only}
- Kayo AH, Peccin MS, Sanches CM, Trevisani VF. Effectiveness of physical activity in reducing pain in patients with fibromyalgia: a blinded randomized clinical trial. Rheumatology International 2011;32(8):2285‐92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Valkeinen 2004 {published data only}
- Valkeinen H, Alen M, Hannonen P, Hakkinen A, Airaksinen O, Hakkinen K. Changes in knee extension and flexion force, EMG and functional capacity during strength training in older females with fibromyalgia and healthy controls. Rheumatology 2004;43(2):225‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valkeinen H, Hakkinen K, Pakarinen A, Hannonen P, Hakkinen A, Airaksinen O, et al. Muscle hypertrophy strength development, and serum hormones during strength training in elderly women with fibromyalgia. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 2005; Vol. 34, issue 4:309‐14. [DOI] [PubMed]
References to studies excluded from this review
Ahlgren 2001 {published data only}
- Ahlgren C, Waling K, Kadi F, Djupsjobacka M, Thornell L, Sundelin G. Effects on physical performance and pain from three dynamic training programs for women with work‐related trapezius myalgia. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2001;33(4):162‐9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Alentorn‐Geli 2009 {published data only}
- Alentorn‐Geli E, Moras G, Padilla J, Fernandez‐Sola J, Bennett RM, Lazaro‐Haro C, et al. Effect of acute and chronic whole‐body vibration exercise on serum insulin‐like growth factor‐1 levels in women with fibromyalgia. Journal of Alternative & Complementary Medicine 2009;15(5):573‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Astin 2003 {published data only}
- Astin JA, Berman BM, Bausel B, Lee WL, Hochberg M, Forys KL. The efficacy of mindfulness meditation plus Qigong movement therapy in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Rheumatology Journal of Rheumatology 2003;30(10):2257‐62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bailey 1999 {published data only}
- Bailey A, Starr L, Alderson M, Moreland J. A comparative evaluation of a fibromyalgia rehabilitation program. Arthritis Care & Research 1999;12(5):336‐40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bakker 1995 {published data only}
- Bakker C, Rutten M, Santen‐Hoeufft M, Bolwijn P, Doorslaer E, Linden S. Patient utilities in fibromyalgia and the association with other outcome measures. Journal of Rheumatology 1995;22:1536‐43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Carbonell‐Baeza 2011 {published data only}
- Carbonell‐Baeza A, Ruiz JR, Aparicio VA, Ortega FB, Munguía‐Izquierdo D, Alvarez‐Gallardo IC, et al. Land‐ and water‐based exercise Intervention in women with fibromyalgia: the Al‐Andalus physical activity randomised control trial. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2012:18. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-13-18.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Casanueva‐Fernandez 2012 {published data only}
- Casanueva‐Fernandez B, Llorca J, Rubio JBI, Rodero‐Fernandez B, Gonzalez‐Gay MA. Efficacy of a multidisciplinary treatment program in patients with severe fibromyalgia. Rheumatology International 2012;32(8):2497‐502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dal 2011 {published data only}
- Dal U, Cimen OB, Incel NA, Adim M, Dag F, Erdogan AT, et al. Fibromyalgia syndrome patients optimize the oxygen cost of walking by preferring a lower walking speed. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 2011;19(4):212‐7. [Google Scholar]
da Silva 2007 {published data only}
- Silva GD, Lorenzi‐Filho G, Lage LV. Effects of yoga and the addition of Tui Na in patients with fibromyalgia. Journal of Alternative & Complementary Medicine 2007;13(10):1107‐13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dawson 2003 {published data only}
- Dawson KA, Tiidus PM, Pierrynowski M, Crawford JP, Trotter J. Evaluation of a community‐based exercise program for diminishing symptoms of fibromyalgia. Physiotherapy Canada 2003;55:17‐22. [Google Scholar]
Finset 2004 {published data only}
- Finset A, Wigers SH, Gotestam KG. Depressed mood impedes pain treatment response in patients with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2004;31(5):976‐80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gandhi 2000 {published data only}
- Gandhi N. Effect of an Exercise Program on Quality of Life of Women with Fibromyalgia. Washington: Washington State University, 2000. [Google Scholar]
Geel 2002 {published data only}
- Geel SE, Robergs RA. The effect of graded resistance exercise on fibromyalgia symptoms and muscle bioenergetics: a pilot study. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2002;47:82‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gowans 2002 {published data only}
- Gowans SE, deHueck A, Abbey SE. Measuring exercise‐induced mood changes in fibromyalgia: a comparison of several measures. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2002;47:603‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gowans 2004 {published data only}
- Gowans SE, deHueck A, Voss S, Silaj A, Abbey SE. Six‐month and one‐year followup of 23 weeks of aerobic exercise for individuals with fibromyalgia. Arthritis Care & Research 2004;51(6):890‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Guarino 2001 {published data only}
- Guarino P, Peduzzi P, Donta ST, Engel CC, Clauw DJ, Williams DA, et al. A multicenter two by two factorial trial of cognitive behavioral therapy and aerobic exercise for Gulf War veterans' illnesses: design of a Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study (CSP #470). Controlled Clinical Trials 2001;22:310‐32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Han 1998 {published data only}
- Han SS. Effects of a self‐help program including stretching exercise on symptom reduction in patients with fibromyalgia. Taehan Kanho 1998;37:78‐80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Huyser 1997 {published data only}
- Huyser B, Buckelew SP, Hewett JE, Johnson JC. Factors affecting adherence to rehabilitation interventions for individuals with fibromyalgia. Rehabilitation Psychology 1997;42:75‐91. [Google Scholar]
Karper 2001 {published data only}
- Karper WB, Hopewell R, Hodge M. Exercise program effects on women with fibromyalgia syndrome. Clinical Nurse Specialist 2001;15:67‐75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kendall 2000 {published data only}
- Kendall SA, Brolin MK, Soren B, Gerdle B, Henriksson KG. A pilot study of body awareness programs in the treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome. Arthritis Care and Research 2000;13:304‐11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Khalsa 2009 {published data only}
- Khalsa KPS. Bodywork for fibromyalgia: alternative therapies soothe the pain. Massage & Bodywork 2009;online(May/June):80. [Google Scholar]
Kingsley 2005 {published data only}
- Kingsley JD, Panton LB, Toole T, Sirithienthad P, Mathis R, McMillan V. The effects of a 12‐week strength‐training program on strength and functionality in women with fibromyalgia. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2005;86(9):1713‐21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lange 2011 {published data only}
- Lange M, Krohn‐Grimberghe B, Petermann F. Medium‐term effects of a multimodal therapy on patients with fibromyalgia. Results of a controlled efficacy study [Mittelfristige Effekte einer multimodalen Behandlung bei Patienten mit Fibromyalgiesyndrom]. Schmerz (Berlin, Germany) 2011; Vol. 25, issue 1:55‐61. [DOI] [PubMed]
Lorig 2008 {published data only}
- Lorig KR, Ritter PL, Laurent DD, Plant K, Lorig KR, Ritter PL. The internet‐based arthritis self‐management program: a one‐year randomized trial for patients with arthritis or fibromyalgia. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2008;59(7):1009‐17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mannerkorpi 2002 {published data only}
- Mannerkorpi K, Ahlmen M, Ekdahl C. Six‐ and 24‐month follow‐up of pool exercise therapy and education for patients with fibromyalgia. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 2002;31(5):306‐10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mason 1998 {published data only}
- Mason LW, Goolkasian P, McCain GA. Evaluation of multimodal treatment program for fibromyalgia. Journal of Behavioral Medicine 1998;21(2):163‐78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
McCain 1986 {published data only}
- McCain GA. Role of physical fitness training in the fibrositis/fibromyalgia syndrome. American Journal of Medicine 1986;81(3A):73‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Meiworm 2000 {published data only}
- Meiworm L, Jakob E, Walker UA, Peter HH, Keul J. Patients with fibromyalgia benefit from aerobic endurance exercise. Clinical Rheumatology 2000;19(4):253‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Meyer 2000 {published data only}
- Meyer BB, Lemley KJ. Utilizing exercise to affect the symptomology of fibromyalgia: a pilot study. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2000;32(10):1691‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mobily 2001 {published data only}
- Mobily KE, Verburg MD. Aquatic therapy in community‐based therapeutic recreation: pain management in a case of fibromyalgia. Therapeutic Recreation Journal 2001;35:57‐69. [Google Scholar]
Mutlu 2013 {published data only}
- Mutlu B, Paker N, Bugdayci D, Tekdos D, Kesiktas N. Efficacy of supervised exercise combined with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in women with fibromyalgia: a prospective controlled study. Rheumatology International 2013;33(3):649‐55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nielen 2000 {published data only}
- Nielens H, Boisset V, Masquelier E. Fitness and perceived exertion in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Clinical Journal of Pain 2000;16:209‐13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Offenbacher 2000 {published data only}
- Offenbacher M, Stucki G. Physical therapy in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 2000;113(Suppl):78‐85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Oncel 1994 {published data only}
- Oncel A, Eskiyurt N, Leylabadi M. The results obtained by different therapeutic measures in the treatment of generalized fibromyalgia syndrome. Tip Fakultesi Mecmuasi 1994;57(4):45‐9. [Google Scholar]
Peters 2002 {published data only}
- Peters S, Stanley I, Rose M, Kaney S, Salmon P. A randomized controlled trial of group aerobic exercise in primary care patients with persistent, unexplained physical symptoms. Family Practice 2002;19:665‐74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pfeiffer 2003 {published data only}
- Pfeiffer AT. Effects of a 1.5‐day multidisciplinary outpatient treatment program for fibromyalgia: a pilot study. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2003;82:186‐91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Piso 2001 {published data only}
- Piso U, Kuther G, Gutenbrunner C, Gehrke A. Analgesic effects of sauna in fibromyalgia. [German]. Physikalische Medizin Rehabilitationsmedizin Kurortmedizin 2001;11(3):94‐9. [Google Scholar]
Rooks 2002 {published data only}
- Rooks DS, Silverman CB, Kantrowitz FG. The effects of progressive strength training and aerobic exercise on muscle strength and cardiovascular fitness in women with fibromyalgia: a pilot study. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2002;47:22‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Santana 2010 {published data only}
- Santana JS, Almeida AP, Brandao PM. The effect of Ai Chi method in fibromyalgic patients [Os efeitos do método Ai Chi em pacientes portadoras da síndrome fibromiálgica]. Ciência & Saúde Coletiva 2010;15 Suppl 1:1433‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sigl‐Erkel 2011 {published data only}
- Sigl‐Erkel T. A randomized trial of tai chi for fibromyalgia [Studienbesprechung zu tai chi (taiji) bei fibromyalgie]. Chinesische Medizin 2011;26(2):ns. [Google Scholar]
Thieme 2003 {published data only}
- Thieme K, Gronica‐Ihle E, Flor H. Operant behavioral treatment of fibromyalgia: a controlled study. Arthritis Care & Research Arthritis Care & Research 2003;49:314‐20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tiidus 1997 {published data only}
- Tiidus PM. Manual massage and recovery of muscle function following exercise: a literature review. Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy 1997;25:107‐12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Uhlemann 2007 {published data only}
- Uhlemann C, Strobel I, Muller‐Ladner U, Lange U. Prospective clinical trial about physical activity in fibromyalgia. Aktuelle Rheumatologie 2007;32(1):27‐33. [Google Scholar]
Vlaeyen1996 {published data only}
- Vlaeyen JW, Teeken‐Gruben NJ, Goossens ME, Rutten‐van Molken MP, Pelt RA, Eek H, et al. Cognitive‐educational treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized clinical trial. I Clinical effects. Journal of Rheumatology 1996;23(7):1237‐45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Williams 2010 {published data only}
- Williams DA, Kuper D, Segar M, Mohan N, Sheth M, Clauw DJ. Internet‐enhanced management of fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Pain 2010; Vol. 151, issue 3:694‐702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Worrel 2001 {published data only}
- Worrel LM, Krahn LE, Sletten CD, Pond GR. Treating fibromyalgia with a brief interdisciplinary program: initial outcomes and predictors of response. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2001;76:384‐90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies awaiting assessment
Adsuar 2012 {published data only}
- Adsuar JC, Pozo‐Cruz B, Parraca JA, Olivares PR, Gusi N. Whole body vibration improves the single‐leg stance static balance in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Sports Medicine & Physical Fitness 2012;52(1):85‐91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Amanollahi 2013 {published data only}
- Amanollahi A, Naghizadeh J, Khatibi A, Hollisaz MT, Shamseddini AR, Saburi A. Comparison of impacts of friction massage, stretching exercises and analgesics on pain relief in primary fibromyalgia syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. Tehran University Medical Journal 2013;70(10):616‐22. [Google Scholar]
Aslan 2001 {published data only}
- Aslan Ub, Yuksel I, Yazici M. A comparison of classical massage and mobilization techniques treatment in primary fibromyalgia. Fizyoterapi Rehabilitasyon 2001;12(2):50‐4. [Google Scholar]
Bland 2010 {published data only}
- Bland P. Tai chi of benefit in fibromyalgia. Practitioner 2010;254(1735):8‐10. [Google Scholar]
Ekici 2008 {published data only}
- Ekici G, Yakut E, Akbayrak T. Effects of Pilates exercises and connective tissue manipulation on pain and depression in females with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Fizyoterapi Rehabilitasyon 2008;19(2):47‐54. [Google Scholar]
Thijssen 1992 {published data only}
- Thijssen Ej, Klerk E. Evaluatie van een zwemprogramma voor patienten met fibromyalgie. Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Fysiotherapie 1992;102(3):71‐5. [Google Scholar]
Wright 2012 {published data only}
- Wright C, Carson J, Carson K, Bennett R, Mist S, Jones K. Yoga of awareness: a randomized trial in fibromyalgia: post intervention and 3 month follow up results. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2012;12:P249. [Google Scholar]
Additional references
ACSM 2009a
- American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM's Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. 8th Edition. Philadelphia, PA: LippenWilliams and Wilkins, 2009. [Google Scholar]
ACSM 2009b
- American College of Sports Medicine. Progression models in resistance training for healthy adults. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2009;41(3):687‐708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Alentorn‐Geli 2008
- Alentorn‐Geli E, Padilla J, Moras G, Lazaro Haro C, Fernandez‐Sola J. Six weeks of whole‐body vibration exercise improves pain and fatigue in women with fibromyalgia. Journal of Alternative & Complementary Medicine 2008;14(8):975‐81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Altan 2004
- Altan L, Bingol U, Aykac M, Koc Z, Yurtkuran M. Investigation of the effects of pool‐based exercise on fibromyalgia syndrome. Rheumatology International 2004;24(5):272‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Altan 2009
- Altan L, Korkmaz N, Bingol U, Gunay B. Effect of pilates training on people with fibromyalgia syndrome: a pilot study. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2009;90:1983‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Anderson 1995
- Anderson KO, Dowds BN, Pelletz RE, Edwards WT, Peeters Asdourian C. Development and initial validation of a scale to measure self‐efficacy beliefs in patients with chronic pain. Pain 1995;63(1):77‐84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Arcos‐Carmona 2011
- Arcos‐Carmona IM, Castro‐Sanchez AM, Mataran‐Penarrocha GA, Gutierrez‐Rubio AB, Ramos‐Gonzalez E, Moreno‐Lorenzo C. Effects of aerobic exercise program and relaxation techniques on anxiety, quality of sleep, depression, and quality of life in patients with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Medicina Clinica 2011;137(9):398‐491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Arnold 2008
- Arnold LM, Crofford LJ, Mease PJ, Burgess SM, Palmer SC, Abetz L, et al. Patient perspectives on the impact of fibromyalgia. Patient Education and Counseling 2008;73(1):114‐20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Asikainen 2004
- Asikainen TM, Kukkonen‐Harjula K, Miilunpalo S. Exercise for health for early postmenopausal women: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Sports Medicine 2004;34(11):753‐78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Assis 2006
- Assis MR, Silva LE, Alves AM, Pessanha AP, Valim V, Feldman D, et al. A randomized controlled trial of deep water running: clinical effectiveness of aquatic exercise to treat fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatology 2006;55(1):57‐65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Baptista 2012
- Baptista AS, Villela AL, Jones A, Natour J. Effectiveness of dance in patients with fibromyalgia: a randomized, single‐blind, controlled study. Clinical & Experimental Rheumatology 2012;30(6 Suppl 74):18‐23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bengtsson 1986a
- Bengtsson A, Henriksson KG, Larsson J. Muscle biopsy in primary fibromyalgia. Light‐microscopical and histochemical findings. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 1986;15(1):1‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bengtsson 1986b
- Bengtsson A, Henriksson KG, Jorfeldt L, Kagedal B, Lennmarken C, Lindstrom F. Primary fibromyalgia. A clinical and laboratory study of 55 patients. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 1986;15(3):340‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bennett 1989
- Bennett RM, Clark SR, Goldberg L, Nelson D, Bonafede RP, Porter J, et al. Aerobic fitness in patients with fibrositis. A controlled study of respiratory gas exchange and 133xenon clearance from exercising muscle. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1989;32(4):454‐60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bennett 1999
- Bennett RM. Emerging concepts in the neurobiology of chronic pain: evidence of abnormal sensory processing in fibromyalgia. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 1999;74(4):385‐98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bennett 2009
- Bennett RM, Bushmakin AG, Cappelleri JC, Zlateva G, Sadosky AB. Minimal clinically important difference in the Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire. Journal of Rheumatology 2009;36(6):1304‐11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bernardy 2013
- Bernardy K, Klose P, Busch AJ, Choy EHS, Häuser W. Cognitive behavioural therapies for fibromyalgia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 9. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009796.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Birse 2012
- Birse F, Derry S, Moore RA. Phenytoin for neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 5. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009485.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bojner Horwitz 2006
- Bojner Horwitz E, Kowalski J, Theorell T, Anderberg UM. Dance/movement therapy in fibromyalgia patients: changes in self‐figure drawings and their relation to verbal self‐rating scales. Arts in Psychotherapy 2006;33(1):11‐25. [Google Scholar]
Boomershine 2012
- Boomershine CS. A comprehensive evaluation of standardized assessment tools in the diagnosis of fibromyalgia and in the assessment of fibromyalgia severity. Pain Research and Treatment 2012;2012:653714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Brachaniec 2009
- Brachaniec M, DePaul V, Elliott M, Moor L, Sherwin P. Partnership in action: an innovative knowledge translation approach to improve outcomes for persons with fibromyalgia (Editorial). Physiotherapy Canada 2009;61(3):123‐7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Braith 2006
- Braith RW, Stewart KJ. Resistance exercise training: its role in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2006;113(22):2642‐50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Branco 2010
- Branco JC, Bannwarth B, Failde I, Abello Carbonell J, Blotman F, Spaeth M, et al. Prevalence of fibromyalgia: a survey in five European countries. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 2010;39(6):448‐53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bressan 2008
- Bressan LR, Matsutani LA, Assumpcao A, Marques AP, Cabral CMN. Effects of muscle stretching and physical conditioning as physical therapy treatment for patients with fibromyalgia [in Portuguese]. Revista Brasileira de Fisioterapia/Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy 2008;12(2):88‐93. [Google Scholar]
Brosse 2002
- Brosse AL, Sheets ES, Lett HS, Blumenthal JA. Exercise and the treatment of clinical depression in adults: recent findings and future directions. Sports Medicine 2002;32(12):741‐60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Brosseau 2008
- Brosseau L, Wells GA, Tugwell P, Egan M, Wilson KG, Dubouloz CJ, et al. Ottawa Panel evidence‐based clinical practice guidelines for strengthening exercises in the management of fibromyalgia: part 2. Physical Therapy 2008;88(7):873‐86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Buchheld 2001
- Buchheld N, Grossman P, Walach H. Measuring mindfulness in insight meditation (Vipassana) and meditation‐based psychotherapy: the development of the Freiburg Mindfulness Inventory (FMI). Journal for Meditation and Meditation Research 2001;1(1):11‐34. [Google Scholar]
Buckelew 1998
- Buckelew SP, Conway R, Parker J, Deuser WE, Read J, Witty TE, et al. Biofeedback/relaxation training and exercise interventions for fibromyalgia: a prospective trial. Arthritis Care and Research 1998;11(3):196‐209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Burckhardt 1993
- Burckhardt CS, Clark SR, Bennett RM. Fibromyalgia and quality of life: a comparative analysis. Journal of Rheumatology 1993;20:475‐9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Burckhardt 1994
- Burckhardt CS, Mannerkorpi K, Hedenberg L, Bjelle A. A randomized, controlled clinical trial of education and physical training for women with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 1994;21(4):714‐20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Burckhardt 2005
- Burckhardt CS, Goldenberg D, Crofford L, Gerwin RD, Gowans SE, Jackson K, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: guideline for the management of fibromyalgia syndrome pain in adults and children. American Pain Society (APS). Glenview (IL): American Pain Society, 2005, issue 4:109.
Calandre 2009
- Calandre EP, Rodriguez‐Claro ML, Rico‐Villademoros F, Vilchez JS, Hidalgo J, Gado‐Rodriguez A. Effects of pool‐based exercise in fibromyalgia symptomatology and sleep quality: a prospective randomised comparison between stretching and Ai Chi. Clinical & Experimental Rheumatology 2009;27(5 Suppl 56):S21‐8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Callahan 1988
- Callahan LF, Brooks RH, Pincus T. Further analysis of learned helplessness in rheumatoid arthritis using a "Rheumatology Attitudes Index". Journal of Rheumatology 1988;15(3):418‐26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Carson 2010
- Carson JW, Carson KM, Jones KD, Bennett RM, Wright CL, Mist SD. A pilot randomized controlled trial of the Yoga of Awareness program in the management of fibromyalgia. Pain 2010; Vol. 151, issue 2:530‐9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Carson 2012
- Carson JW, Carson KM, Jones KD, Mist SD, Bennett RM. Follow‐up of Yoga of Awareness for Fibromyalgia: results at 3 months and replication in the wait‐list group. Clinical Journal of Pain 2012;28(9):804‐13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Carville 2008
- Carville SF, Arendt‐Nielsen S, Bliddal H, Blotman F, Branco JC, Buskila D, et al. EULAR evidence‐based recommendations for the management of fibromyalgia syndrome. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2008;67(4):536‐41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Carville 2008a
- Carville SF, Choy EH. Systematic review of discriminating power of outcome measures used in clinical trials of fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2008;35(11):2094‐105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Caspersen 1985
- Caspersen CJ, Powell KE, Christenson GM. Physical activity, exercise, and physical fitness: definitions and distinctions for health‐related research. Public Health Reports 1985;100(2):126‐31. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cedraschi 2004
- Cedraschi C, Desmeules J, Rapiti E, Baumgartner E, Cohen P, Finckh A, et al. Fibromyalgia: a randomised, controlled trial of a treatment programme based on self management. Annals of Rheumatic Diseases 2004;63(3):290‐6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cheung 2003
- Cheung K, Hume P, Maxwell L. Delayed onset muscle soreness: treatment strategies and performance factors. Sports Medicine 2003;33(2):145‐64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chodzko‐Zajko 2009
- Chodzko‐Zajko WJ, Proctor DN, Fiatarone Singh MA, Minson CT, Nigg CR, Salem GJ, et al. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Exercise and physical activity for older adults. Medicine and Science in Sports Exercise 2009;41(7):1510‐30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Choy 2009a
- Choy EH, Arnold LM, Clauw DJ, Crofford LJ, Glass JM, Simon LS, et al. Content and criterion validity of the preliminary core dataset for clinical trials in fibromyalgia syndrome. Journal of Rheumatology 2009;36(10):2330‐4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Choy 2009b
- Choy EH, Mease PJ. Key symptom domains to be assessed in fibromyalgia (outcome measures in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials). Rheumatic Diseases Clinics of North America 2009;35(2):329‐37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Clauw 2011
- Clauw DJ, Arnold LM, McCarberg BH. The science of fibromyalgia. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2011;86(9):907‐11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cohen 1988
- Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. 2nd Edition. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1988. [ISBN: 0 8058 0283 5] [Google Scholar]
Costill 1979
- Costill DL, Coyle EF, Fink WF, Lesmes GR, Witzmann FA. Adaptations in skeletal muscle following strength training. Journal of Applied Physiology 1979;46(1):96‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Crosier 2002
- Crosier JL, Forthomme B, Namurois MH, Vanderthomme M, Crielaard JM. Hamstring muscle strain recurrence and strength performance disorders. American Journal of Sports Medicine 2002;30(2):199‐203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Da Costa 2005
- Costa D, Abrahamowicz M, Lowensteyn I, Bernatsky S, Dritsa M, Fitzcharles MA, et al. A randomized clinical trial of an individualized home‐based exercise programme for women with fibromyalgia. Rheumatology 2005;44(11):1422‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dadabhoy 2008
- Dadabhoy D, Crofford LJ, Spaeth M, Russell IJ, Clauw DJ. Biology and therapy of fibromyalgia. Evidence‐based biomarkers for fibromyalgia syndrome. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2008;10(4):211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
De Andrade 2008
- Andrade SC, Carvalho RFPP, Soares AS, Abreu Freitas RP, Madeiros Guerra LM, Vilar MJ. Thalassotherapy for fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial comparing aquatic exercises in sea water and water pool. Rheumatology International 2008;29(2):147‐52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
de Melo Vitorino 2006
- Melo Vitorino DF, Carvalho LBC, do Prado GF. Hydrotherapy and conventional physiotherapy improve total sleep time and quality of life of fibromyalgia patients: randomized clinical trial. Sleep Medicine 2006;7(3):293‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Demir‐Gocmen 2013
- Demir‐Gocmen D, Altan L, Korkmaz N, Arabaci R. Effect of supervised exercise program including balance exercises on the balance status and clinical signs in patients with fibromyalgia. Rheumatology International 2013;33(3):743‐50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Deschenes 2002
- Deschenes MR, Kraemer WJ. Performance and physiologic adaptations to resistance training. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2002;81(11 Suppl):S3‐16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Desmeules 2003
- Desmeules JA, Cedraschi C, Rapiti E, Baumgartner E, Finckh A, Cohen P, et al. Neurophysiologic evidence for a central sensitization in patients with fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2003;48(5):1420‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dunn 2001
- Dunn AL, Trivedi MH, O'Neal HA. Physical activity dose‐response effects on outcomes of depression and anxiety. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2001;33(6 Suppl):S587‐97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dworkin 2008
- Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Wyrwich KW, Beaton D, Cleeland CS, Farrar JT, et al. Interpreting the clinical importance of treatment outcomes in chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain 2008;9(2):105‐21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Elvin 2006
- Elvin A, Siosteen AK, Nilsson A, Kosek E. Decreased muscle blood flow in fibromyalgia patients during standardised muscle exercise: a contrast media enhanced colour Doppler study. European Journal of Pain 2006;10(2):137‐44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Etnier 2009
- Etnier JL, Karper WB, Gapin JI, Barella LA, Chang YK, Murphy KJ. Exercise, fibromyalgia, and fibrofog: a pilot study. Journal of Physical Activity & Health 2009;6(2):239‐46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Evcik 2008
- Evcik D, Yugit I, Pusak H, Kavuncu V. Effectiveness of aquatic therapy in the treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome: a randomized controlled open study. Rheumatology International 2008;28(9):885‐90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Faigenbaum 2009
- Faigenbaum AD, Kraemer WJ, Blimkie CJ, Jeffreys I, Micheli LJ, Nitka M, et al. Youth resistance training: updated position statement paper from the national strength and conditioning association. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 2009;23(5 Suppl):S60‐79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Field 2003
- Field T, Delage J, Hernandez‐Reif M. Movement and massage therapy reduce fibromyalgia pain. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies 2003;7(1):49‐52. [Google Scholar]
Figueroa 2008
- Figueroa A, Kingsley JD, McMillan V, Panton LB. Resistance exercise training improves heart rate variability in women with fibromyalgia. Clinical Physiology and Functional Imaging 2008;28(1):49‐54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
FitzerGerald 2004
- FitzerGerald SJ, Barlow CE, Kampert JB, Morrow JR Jr, Jackson AW, Blair SN. Muscular fitness and all‐cause mortality: prospective observations. Journal of Physical Activity and Health 2004;1:7‐18. [Google Scholar]
Fontaine 2007
- Fontaine KR, Haas S. Effects of lifestyle physical activity on health status, pain, and function in adults with fibromyalgia syndrome. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 2007;15(1):3‐9. [Google Scholar]
Fontaine 2010
- Fontaine KR, Conn L, Clauw DJ. Effects of lifestyle physical activity on perceived symptoms and physical function in adults with fibromyalgia: results of a randomized trial. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2010;12(2):R55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fontaine 2011
- Fontaine KR, Conn L, Clauw DJ. Effects of lifestyle physical activity in adults with fibromyalgia: results at follow‐up. Journal of Clinical Rheumatology 2011;17(2):64‐8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Garber 2011
- Garber C, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR, Franklin BA, Lamonte MJ, Lee IM, et al. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2011; Vol. 43, issue 7:1334‐59. [DOI] [PubMed]
Garcia‐Martinez 2012
- Garcia‐Martinez AM, Paz JA, Marquez S. Effects of an exercise programme on self‐esteem, self‐concept and quality of life in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Rheumatology International 2012;32(7):1869‐76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Genc 2002
- Genc A, Sagiroglu E. Comparison of two different exercise programs in fibromyalgia treatment [in Turkish]. Fizyoterapi Rehabilitasyon 2002;13(2):90‐5. [Google Scholar]
Gibson 2006
- Gibson W, Arendt‐Nielsen L, Graven‐Nielsen T. Delayed onset muscle soreness at tendon‐bone junction and muscle tissue is associated with facilitated referred pain. Experimental Brain Research 2006;174(2):351‐60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gowans 1999
- Gowans SE, Hueck A, Voss S, Richardson M. A randomized, controlled trial of exercise and education for individuals with fibromyalgia. Arthritis Care and Research 1999;12(2):120‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gowans 2001
- Gowans SE, Hueck A, Voss S, Silaj A, Abbey SE, Reynolds WJ. Effect of a randomized, controlled trial of exercise on mood and physical function in individuals with fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2001;45(6):519‐29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gracely 2003
- Gracely RH, Grant MA, Giesecke T. Evoked pain measures in fibromyalgia. Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology 2003;17(4):593‐609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gusi 2006
- Gusi N, Tomas‐Carus P, Hakkinen A, Hakkinen K, Ortega‐Alonso A. Exercise in waist‐high warm water decreases pain and improves health‐related quality of life and strength in the lower extremities in women with fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2006;55(1):66‐73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gusi 2008
- Gusi N, Tomas‐Carus P. Cost‐utility of an 8‐month aquatic training for women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2008;10(1):R24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gusi 2010
- Gusi N, Parraca JA, Olivares PR, Leal A, Adsuar JC. Tilt vibratory exercise and the dynamic balance in fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Care & Research (Hoboken) 2010;62(8):1072‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hakkinen 2001 (Primary)
- Hakkinen A, Hakkinen K, Hannonen P, Alen M. Strength training induced adaptations in neuromuscular function of premenopausal women with fibromyalgia: comparison with healthy women. Annals of Rheumatic Diseases 2001;60(1):21‐6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hakkinen 2002 (Secondary)
- Hakkinen K, Pakarinen A, Hannonen P, Hakkinen A, Airaksinen O, Valkeinen H, et al. Effects of strength training on muscle strength, cross‐sectional area, maximal electromyographic activity, and serum hormones in premenopausal women with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(6):1287‐95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hammond 2006
- Hammond A, Freeman K. Community patient education and exercise for people with fibromyalgia: a parallel group randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2006;20(10):835‐46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hawley 1991
- Hawley DJ, Wolfe F. Pain, disability, and pain/disability relationships in seven rheumatic disorders: a study of 1,522 patients. Journal of Rheumatology 1991;18(10):1552‐7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hecker 2011
- Hecker CD, Melo C, Tomazoni SS, Lopes‐Martins RAB, Leal Junior ECP. Analysis of effects of kinesiotherapy and hydrokinesiotherapy on the quality of patients with fibromyalgia ‐ a randomized clinical trial [in Portuguese]. Fisioterapia em Movimento 2011;24(1):57‐64. [Google Scholar]
Heyward 1998
- Heyward VH. Advanced fitness assessment and exercise prescription.. 3. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics, 1998. [Google Scholar]
Heyward 2010
- Heyward VH. Advanced Fitness Assessment and Exercise Prescription. 6th Edition. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics, 2010. [Google Scholar]
Hibbert 2008
- Hibbert O, Cheong K, Grant A, Beers A, Moizumi T. A systematic review of the effectiveness of eccentric strength training in the prevention of hamstring muscle strains in otherwise healthy individuals. North American Journal of Sports Physical Therapy 2008;3(2):67‐81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011a
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011c
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Holloszy 1984
- Holloszy JO, Coyle EF. Adaptations of skeletal muscle to endurance exercise and their metabolic consequences. Journal of Applied Physiology: Respiratory, Environmental & Exercise Physiology 1984;56(4):831‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hooten 2012
- Hooten WM, Qu W, Townsend CO, Judd JW. Effects of strength vs aerobic exercise on pain severity in adults with fibromyalgia: a randomized equivalence trial. Pain 2012;153(4):915‐23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Howley 2001
- Howley ET. Type of activity: resistance, aerobic and leisure versus occupational physical activity. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2001;33(6 Suppl):S364‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hunt 2000
- Hunt J, Bogg J. An evaluation of the impact of a fibromyalgia self‐management programme on patient morbidity and coping. Advancing in Physiotherapy 2000;2(4):168‐75. [Google Scholar]
Häuser 2013
- Häuser W, Urrútia G, Tort S, Üçeyler N, Walitt B. Serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) for fibromyalgia syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010292] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ide 2008
- Ide MR, Laurindo LMM, Rodrigues‐Junior AL, Tanaka C. Effect of aquatic respiratory exercise‐based program in patients with fibromyalgia. APLAR Journal of Rheumatology 2008;11(2):131‐40. [Google Scholar]
Isomeri 1993
- Isomeri R, Mikkelsson M, Latikka P, Kammonen K. Effects of amitriptyline and cardiovascular fitness training on pain in patients with primary fibromyalgia. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 1993;1:253‐60. [Google Scholar]
Jentoft 2001
- Jentoft ES, Kvalvik AG, Mengshoel AM. Effects of pool‐based and land‐based aerobic exercise on women with fibromyalgia/chronic widespread muscle pain. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2001;45(1):42‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jones 2007
- Jones KD, Deodhar AA, Burckhardt CS, Perrin NA, Hanson GC, Bennett RM. A combination of 6 months of treatment with pyridostigmine and triweekly exercise fails to improve insulin‐like growth factor‐I levels in fibromyalgia, despite improvement in the acute growth hormone response to exercise. Journal of Rheumatology 2007;34(5):1103‐11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jones 2008
- Jones KD, Burckhardt CS, Deodhar AA, Perrin NA, Hanson GC, Bennett RM. A six‐month randomized controlled trial of exercise and pyridostigmine in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2008;58(2):612‐22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jones 2009
- Jones KD, Liptan GL. Exercise interventions in fibromyalgia: clinical applications from the evidence. Rheumatics Diseases Clinics of North America 2009;35(2):373‐91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jones 2012
- Jones K, Sherman C, Mist S, Carson J, Bennett R, Li F. A randomized controlled trial of 8‐form Tai chi improves symptoms and functional mobility in fibromyalgia patients. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2012;12:1205‐14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Joshi 2009
- Joshi MN, Joshi R, Jain AP. Effect of amitriptyline vs. physiotherapy in management of fibromyalgia syndrome: what predicts a clinical benefit?. Journal of Postgraduate Medicine 2009;55(3):185‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jubrias 1994
- Jubrias SA, Bennett RM, Klug GA. Increased incidence of a resonance in the phosphodiester region of 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectra in the skeletal muscle of fibromyalgia patients. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1994;37(6):801‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Katzmarzyk 2002
- Katzmarzyk PT, Craig CL. Musculoskeletal fitness and risk of mortality. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2002;34(5):740‐4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Keel 1998
- Keel PJ, Bodoky C, Gerhard U, Muller W. Comparison of integrated group therapy and group relaxation training for fibromyalgia. Clinical Journal of Pain 1998;14(3):232‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
King 1997
- King AC, Oman RF, Brassington GS, Bliwise DL, Haskell WL. Moderate‐intensity exercise and self‐rated quality of sleep in older adults. A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1997;277(1):32‐7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
King 2002
- King SJ, Wessel J, Bhambhani Y, Sholter D, Maksymowych W. The effects of exercise and education, individually or combined, in women with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(12):2620‐7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kingsley 2009
- Kingsley JD, Panton LB, McMillan V, Figueroa A. Cardiovascular autonomic modulation after acute resistance exercise in women with fibromyalgia. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2009;90(9):1628‐34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kingsley 2011
- Kingsley JD, McMillan V, Figueroa A. Resistance exercise training does not affect postexercise hypotension and wave reflection in women with fibromyalgia. Applied Physiology Nutrition and Metabolism 2011;36(2):254‐63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Knutzen 2007
- Knutzen KM, Pendergrast BA, Lindsey B, Brilla LR. The effect of high resistance weight training on reported pain in older adults. Journal of Sports Science and Medicine 2007;6:455‐60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Koltyn 1998
- Koltyn KF, Arbogast RW. Perception of pain after resistance exercise. British Journal of Sports Medicine 1998;32(1):20‐4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lefebvre 2011
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Lemstra 2005
- Lemstra M, Olszynski WP. The effectiveness of multidisciplinary rehabilitation in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Journal of Pain 2005;21(2):166‐74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lewis 2012
- Lewis PB, Ruby D, Bush‐Joseph CA. Muscle soreness and delayed‐onset muscle soreness. Clinical Sports Medicine 2012;31(2):255‐62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Liu 2012
- Liu W, Zahner L, Cornell M, Le T, Ratner J, Wang Y, et al. Benefit of Qigong exercise in patients with fibromyalgia: a pilot study. International Journal of Neuroscience 2012;122(11):657‐64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lopez‐Rodriguez 2012
- Lopez‐Rodriguez MM, Castro‐Sanchez AM, Fernandez‐Martinez M, Mataran‐Penarrocha GA, Rodriguez‐Ferrer ME. Comparison between aquatic‐biodanza and stretching for improving quality of life and pain in patients with fibromyalgia. Atencion Primaria 2012;44(11):641‐9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lorig 1989
- Lorig K, Chastain RL, Ung E, Shoor S, Holman HR. Development and evaluation of a scale to measure perceived self‐efficacy in people with arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1989;32(1):37‐44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lund 1986
- Lund N, Bengtsson A, Thorborg P. Muscle tissue oxygen pressure in primary fibromyalgia. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 1986;15(2):165‐73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lynch 2012
- Lynch M, Sawynok J, Hiew C, Marcon D. A randomized controlled trial of qigong for fibromyalgia. Arthritis Research and Therapy 2012;14(4):R178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mannerkorpi 2000
- Mannerkorpi K, Nyberg B, Ahlmen M, Ekdahl C. Pool exercise combined with an education program for patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. A prospective, randomized study. Journal of Rheumatology 2000;27(10):2473‐81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mannerkorpi 2009
- Mannerkorpi K, Nordeman L, Ericsson A, Arndorw M. Pool exercise for patients with fibromyalgia or chronic widespread pain: a randomized controlled trial and subgroup analyses. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2009;41(9):751‐60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mannerkorpi 2010
- Mannerkorpi K, Nordeman L, Cider A, Jonsson G. Does moderate‐to‐high intensity Nordic walking improve functional capacity and pain in fibromyalgia? A prospective randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2010;12(5):R189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Martin 1996
- Martin L, Nutting A, MacIntosh BR, Edworthy SM, Butterwick D, Cook J. An exercise program in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 1996;23(6):1050‐3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Martin‐Nogueras 2012
- Martin‐Nogueras AM, Calvo‐Arenillas JI. Efficacy of physiotherapy treatment on pain and quality of life in patients with fibromyalgia [in Spanish]. Rehabilitacion 2012;46(3):199‐206. [Google Scholar]
Matsutani 2007
- Matsutani LA, Marques AP, Ferreira EA, Assumpcao A, Lage LV, Casarotto RA, et al. Effectiveness of muscle stretching exercises with and without laser therapy at tender points for patients with fibromyalgia. Clinical & Experimental Rheumatology 2007;25(3):410‐5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Matsutani 2012
- Matsutani LA, Assumpcao A, Marques AP. Stretching and aerobic exercises in the treatment of fibromyalgia: pilot study [in Portuguese]. Fisioterapia em Movimento 2012;25(2):411‐8. [Google Scholar]
McCain 1988
- McCain GA, Bell DA, Mai FM, Halliday PD. A controlled study of the effects of a supervised cardiovascular fitness training program on the manifestations of primary fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1988;31(9):1135‐41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
McNalley 2006
- McNalley JD, Matheson DA, Bakowshy VS. The epidemiology of self‐reported fibromyalgia in Canada. Chronic Diseases in Canada 2006;27(1):9‐16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mease 2005
- Mease P. Fibromyalgia syndrome: review of clinical presentation, pathogenesis, outcome measures, and treatment. Journal of Rheumatology ‐ Supplement 2005;75:6‐21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mease 2008
- Mease PJ, Arnold LM, Crofford LJ, Williams DA, Russell IJ, Humphrey L, et al. Identifying the clinical domains of fibromyalgia: contributions from clinician and patient Delphi exercises. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2008;59(7):952‐60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mease 2009
- Mease P, Arnold LM, Choy EH, Clauw DJ, Crofford LJ, Glass JM, et al. Fibromyalgia syndrome module at OMERACT 9: domain construct. Journal of Rheumatology 2009;36(10):2318‐29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mengshoel 1992
- Mengshoel AM, Komnaes HB, Forre O. The effects of 20 weeks of physical fitness training in female patients with fibromyalgia. Clinical & Experimental Rheumatology 1992;10(4):345‐9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mengshoel 1993
- Mengshoel AM, Forre O. Physical fitness training in patients with fibromyalgia. Musculoskeletal pain 1993;1(4):267‐72. [Google Scholar]
Merskey 1994
- Merskey H, Bogduk N. Classifications of Chronic Pain: Descriptions and Definitions of Chronic Pain Syndromes and Definitions of Pain Terms. Seattle, WA: IASP, 1994. [Google Scholar]
Mitchell 2002
- Mitchell M. Engauge digitizer ‐ digitizing software. digitizer.sourceforge.net/ 2002; Vol. (accessed 20 October 2013).
Mizelle 2011
- Mizelle K, Fontaine KR. Exercise and physical activity for fibromyalgia. Journal of Musculoskeletal Medicine 2011;28(8):310‐6. [Google Scholar]
Moore 2012
- Moore RA, Derry S, Aldington D, Cole P, Wiffen PJ. Amitriptyline for neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 12. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008242.pub2] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Morrissey 1995
- Morrissey MC, Harman EA, Johnson MJ. Resistance training modes: specificity and effectiveness. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 1995;27(5):648‐60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Munguia‐Izquierdo 2007
- Munguia‐Izquierdo D, Legaz‐Arrese A. Exercise in warm water decreases pain and improves cognitive function in middle‐aged women with fibromyalgia. Clinical & Experimental Rheumatology 2007;25(6):823‐30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Munguia‐Izquierdo 2008
- Munguia‐Izquierdo D, Legaz‐Arrese A. Assessment of the effects of aquatic therapy on global symptomatology in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2008;89(12):2250‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nelson 2007
- Nelson ME, Rejeski WJ, Blair SN, Duncan PW, Judge JO, King AC, et al. Physical activity and public health in older adults: recommendation from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Circulation 2007;116(9):1094‐105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nichols 1994
- Nichols DS, Glenn TM. Effects of aerobic exercise on pain perception, affect, and level of disability in individuals with fibromyalgia. Physical Therapy 1994;74:327‐32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Norregaard 1997
- Norregaard J, Lykkegaard JJ, Mehlsen J, Danneskiold Samsoe B. Exercise training in treatment of fibromyalgia. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 1997;5(1):71‐9. [Google Scholar]
Olivares 2011
- Olivares PR, Gusi N, Parraca JA, Adsuar JC, Pozo‐Cruz B. Tilting whole body vibration improves quality of life in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2011;17(8):723‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Painter 1999
- Painter P, Stewart AL, Carey S. Physical functioning: definitions, measurement, and expectations. Advances in Renal Replacement Therapy 1999;6(2):110‐23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Park 1998
- Park JH, Phothimat P, Oates CT, Hernanz Schulman M, Olsen NJ. Use of P‐31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy to detect metabolic abnormalities in muscles of patients with fibromyalgia. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1998;41(3):406‐13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Park 2007
- Park J, Knudson S. Medically unexplained physical symptoms. Health Reports 2007;18(1):43‐7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Philadelphia 2001
- Philadelphia Panel. Philadelphia Panel evidence‐based clinical practice guidelines on selected rehabilitation interventions: overview and methodology. Physical Therapy 2001;81(10):1629‐40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Raftery 2009
- Raftery G, Bridges M, Heslop P, Walker DJ. Are fibromyalgia patients as inactive as they say they are?. Clinical Rheumatology 2009;28(6):711‐4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ramsay 2000
- Ramsay C, Moreland J, Ho M, Joyce S, Walker S, Pullar T. An observer‐blinded comparison of supervised and unsupervised aerobic exercise regimens in fibromyalgia. Rheumatology 2000;39(5):501‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
RevMan 2012 [Computer program]
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.2. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Richards 2002
- Richards SC, Scott DL. Prescribed exercise in people with fibromyalgia: parallel group randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2002;325(7357):185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rivera Redondo 2004
- Rivera Redondo J, Moratalla Justo C, Valdepenas Moraleda F, Garcia Velayos Y, Oses Puche JJ, Ruiz Zubero J, et al. Long‐term efficacy of therapy in patients with fibromyalgia: a physical exercise‐based program and a cognitive‐behavioral approach. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2004;51(2):184‐92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rooks 2007
- Rooks DS, Gautam S, Romeling M, Cross ML, Stratigakis D, Evans B, et al. Group exercise, education, and combination self‐management in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2007;167(20):2192‐200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sale 1987
- Sale DG. Influence of exercise and training on motor unit activation. Exercise and Sport Science Reviews 1987;15:95‐151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sanudo 2010
- Sanudo B, Hoyo M, Carrasco L, McVeigh JG, Corral J, Cabeza R, et al. The effect of 6‐week exercise programme and whole body vibration on strength and quality of life in women with fibromyalgia: a randomised study. Clinical & Experimental Rheumatology 2010;28(6 Suppl 63):S40‐5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sanudo 2010a
- Sanudo B, Galiano D, Carrasco L, Blagojevic M, Hoyo M, Saxton J. Aerobic exercise versus combined exercise therapy in women with fibromyalgia syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2010;91(12):1838‐43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sanudo 2010c
- Sanudo Corrales B, Galiano Orea D, Carrasco Paez L, Saxton J. Autonomic nervous system response and quality of life on women with fibromyalgia after a long‐term intervention with physical exercise [in Spanish]. Rehabilitacion 2010;44(3):244‐9. [Google Scholar]
Sanudo 2011
- Sanudo B, Galiano D, Carrasco L, Hoyo M, McVeigh JG. Effects of a prolonged exercise program on key health outcomes in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2011;43(6):521‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sanudo 2012
- Sanudo B, Hoyo M, Carrasco L, Rodriguez‐Blanco C, Oliva‐Pascual‐Vaca A, McVeigh JG. Effect of whole‐body vibration exercise on balance in women with fibromyalgia syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2012;18(2):158‐64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schachter 2003
- Schachter CL, Busch AJ, Peloso P, Sheppard MS. The effects of short versus long bouts of aerobic exercise in sedentary women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Physical Therapy 2003;83(4):340‐58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schmidt 2011
- Schmidt S, Grossman P, Schwarzer B, Jena S, Naumann J, Walach H. Treating fibromyalgia with mindfulness‐based stress reduction: Results from a 3‐armed randomized controlled trial. Pain 2011;152(2):1838‐43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schünermann 2009
- Schünemann H, Brożek J, Oxman A, editors. GRADE handbook for grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendation. Version 3.2 [updated March 2009]. The GRADE Working Group, 2009. Available from www.cc‐ims.net/gradepro..
Seidel 2013
- Seidel S, Aigner M, Ossege M, Pernicka E, Wildner B, Sycha T. Antipsychotics for acute and chronic pain in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 8. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004844.pub3] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sencan 2004
- Sencan S, Ak S, Karan A, Muslumanoglu L, Ozcan E, Berker E. A study to compare the therapeutic efficacy of aerobic exercise and paroxetine in fibromyalgia syndrome. Journal of Back & Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation 2004;17(2):57‐61. [Google Scholar]
Singh 1997
- Singh NA, Clements KM, Fiatarone MA. A randomized controlled trial of the effect of exercise on sleep. Sleep 1997;20(2):95‐101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Smythe 1981
- Smythe HA. Fibrositis and other diffuse musculoskeletal syndromes. In: Kelley WN, Harris ED, Jr, Ruddy S, Sledge CB editor(s). Textbook of Rheumatology. 1st Edition. Oxford: WB Saunders, 1981. [Google Scholar]
Tomas‐Carus 2007
- Tomas‐Carus P, Gusi N, Leal A, Garcia Y, Orega‐Alonso A. The fibromyalgia treatment with physical exercise in warm water reduces the impact of the disease on female patients'' physical and mental health. [Spanish]. Reumatologia Clinica 2007;3(1):33‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tomas‐Carus 2007a
- Tomas‐Carus P, Hakkinen A, Gusi N, Leal A, Hakkinen K, Ortega‐Alonso A. Aquatic training and detraining on fitness and quality of life in fibromyalgia. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2007;39(7):1044‐50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tomas‐Carus 2007b
- Tomas‐Carus P, Raimundo A, Adsuar JC, Olivares P, Gusi N. Effects of aquatic training and subsequent detraining on the perception and intensity of pain and number [in Spanish]. Apunts Medicina de l'Esport 2007;154:76‐81. [Google Scholar]
Tomas‐Carus 2007c
- Tomas‐Carus P, Raimundo A, Timon R, Gusi N. Exercise in warm water decreases pain but no the number of tender points in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial [in Spanish]. Seleccion 2007;16(2):98‐102. [Google Scholar]
Tomas‐Carus 2008
- Tomas‐Carus P, Gusi N, Hakkinen A, Hakkinen K, Leal A, Ortega‐Alonso A. Eight months of physical training in warm water improves physical and mental health in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2008;40(4):248‐52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tort 2012
- Tort S, Urrútia G, Nishishinya MB, Walitt B. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) for fibromyalgia syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009807] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Trew 2005
- Trew M, Everett T. Human Movement: An Introductory Text. 5th Edition. Edinburgh: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, 2005. [Google Scholar]
Valencia 2009
- Valencia M, Alonso B, Alvarez MJ, Barrientos MJ, Ayan C, Sanchez VM. Effects of 2 physiotherapy programs on pain perception, muscular flexibility, and illness impact in women with fibromyalgia: a pilot study. Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics 2009;32(1):84‐92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Valim 2003
- Valim V, Oliveira L, Suda A, Silva L, Assis M, Barros Neto T, et al. Aerobic fitness effects in fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2003;30(5):1060‐9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Valkeinen 2004 (Primary)
- Valkeinen H, Alen M, Hannonen P, Hakkinen A, Airaksinen O, Hakkinen K. Changes in knee extension and flexion force, EMG and functional capacity during strength training in older females with fibromyalgia and healthy controls. Rheumatology 2004;43(2):225‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Valkeinen 2005 (Secondary)
Valkeinen 2008
- Valkeinen H, Alen M, Hakkinen A, Hannonen P, Kukkonen‐Harjula K, Hakkinen K. Effects of concurrent strength and endurance training on physical fitness and symptoms in postmenopausal women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial; futures. Archives of Physical and Medical Rehabilitation 2008;89(9):1660‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
van Koulil 2007
- Koulil S, Effting M, Kraaimaat FW, Lankveld W, Helmond T, Cats H, et al. Cognitive‐behavioural therapies and exercise programmes for patients with fibromyalgia: state of the art and future directions. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2007;66(5):571‐81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
van Koulil 2010
- Koulil S, Lankveld W, Kraaimaat FW, Helmond T, Vedder A, Hoorn H, et al. Tailored cognitive‐behavioral therapy and exercise training for high‐risk patients with fibromyalgia. Arthritis Care & Research 2010;62(10):1377‐85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
van Tulder 2003
- Tulder MW, Furlan A, Bombardier C, Bouter L. Updated method guidelines for systematic reviews in the Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group. Spine 2003;28(12):1290‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
vanSanten 2002
- vanSanten M, Bolwijn P, Landewe R, Verstappen F, Bakker C, Hidding A, et al. High or low intensity aerobic fitness training in fibromyalgia: does it matter?. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(3):582‐7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
vanSanten 2002a
- vanSanten M, Bolwijn P, Verstappen F, Bakker C, Hidding A, Houben H, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing fitness and biofeedback training versus basic treatment in patients with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(3):575‐81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Verstappen 1997
- Verstappen FTJ, Santen‐Hoeuftt HMS, Bolwijn PH, Linden S, Kuipers H. Effects of a group activity program for fibromyalgia patients on physical fitness and well being. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 1997;5(4):17‐28. [Google Scholar]
Wang 2010
- Wang C, Schmid CH, Rones R, Kalish R, Yinh J, Goldenberg DL, et al. A randomized trial of tai chi for fibromyalgia. New England Journal of Medicine 2010;363(8):743‐54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
WHO 2012
- World Health Organization. Depression. www.who.int/topics/depression/en/ (accessed 22 October 2013).
Wigers 1996
- Wigers SH, Stiles TC, Vogel PA. Effects of aerobic exercise versus stress management treatment in fibromyalgia. A 4.5 year prospective study. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 1996;25(2):77‐86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Williams 2012
- Williams AC, Eccleston C, Morley S. Psychological therapies for the management of chronic pain (excluding headache) in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 11. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007407] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Winkelmann 2012
- Winkelmann A, Hauser W, Friedel E, Moog‐Egan M, Seeger D, Settan M, et al. Physiotherapy and physical therapies for fibromyalgia syndrome: systematic review, meta‐analysis and guideline [in German]. Schmerz 2012;26(3):276‐86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wolfe 1990
- Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, Bennett RM, Bombardier C, Goldenberg DL, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of fibromyalgia. Report of the Multicenter Criteria Committee. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1990;33(2):160‐72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wolfe 1995
- Wolfe F, Ross K, Anderson J, Russell IJ, Hebert L. The prevalence and characteristics of fibromyalgia in the general population. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1995;38(1):19‐28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wolfe 2010
- Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles MA, Goldenberg DL, Katz RS, Mease P, et al. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia and measurement of symptom severity. Arthritis Care & Research 2010;62(5):600‐10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wolfe 2011
- Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles MA, Goldenberg DL, Hauser W, Katz RS, et al. Fibromyalgia Criteria and Severity Scales for Clinical and Epidemiological Studies: A Modification of the ACR Preliminary Diagnostic Criteria for Fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2011;38(6):1113‐22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Yunus 1981
- Yunus M, Masi AT, Calabro JJ, Miller KA, Feigenbaum SL. Primary fibromyalgia (fibrositis): clinical study of 50 patients with matched normal controls. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 1981;11:151‐71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Yunus 1982
- Yunus M, Masi AT, Calabro JJ, Shah IK. Primary fibromyalgia. American Family Physician 1982;25(5):115‐21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Yunus 1984
- Yunus MB. Primary fibromyalgia syndrome: current concepts. Comprehensive Therapy 1984;10:21‐8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Yuruk 2008
- Yuruk OB, Gultekin Z. Comparison of two different exercise programs in women with fibromyalgia syndrome [in Turkish]. Fizyoterapi Rehabilitasyon 2008;19(1):15‐23. [Google Scholar]
Zeng 2008
- Zeng QY, Chen R, Darmawan J, Xiao ZY, Chen SB, Wigley R, et al. Rheumatic diseases in China. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2008;10(1):R17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to other published versions of this review
Busch 2001
- Busch AJ, Schachter CL, Peloso PM. Fibromyalgia and exercise training: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Physical Therapy Review 2001;6:287‐306. [Google Scholar]
Busch 2001a
- Busch AJ, Schachter CL, Bombardier C, Peloso P. Exercise for treating fibromyalgia syndrome (Protocol for a Cochrane Review). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003786] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Busch 2002
- Busch AJ, Schachter CL, Peloso P, Bombardier C. Exercise for treating fibromyalgia syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2002, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003786] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Busch 2007
- Busch AJ, Barber KA, Overend TJ, Peloso PM, Schachter CL. Exercise for treating fibromyalgia syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003786] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Busch 2008
- Busch AJ, Schachter CL, Overend TJ, Peloso PM, Barber KA. Exercise for fibromyalgia: a systematic review. Journal of Rheumatology 2008;35(6):1130‐44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


