Abstract
Background
Carbon utilization and metabolism are fundamental to every living organism for cellular growth. For intracellular human fungal pathogens such as Candida glabrata, an effective metabolic adaptation strategy is often required for survival and pathogenesis. As one of the host defence strategies to combat invading pathogens, phagocytes such as macrophages constantly impose restrictions on pathogens’ access to their preferred carbon source, glucose. Surprisingly, it has been reported that engulfed C. glabrata are able to survive in this harsh microenvironment, further suggesting alternative carbon metabolism as a potential strategy for this opportunistic fungal pathogen to persist in the host.
Main text
In this review, we discuss alternative carbon metabolism as a metabolic adaptation strategy for the pathogenesis of C. glabrata. As the glyoxylate cycle is an important pathway in the utilization of alternative carbon sources, we also highlight the key metabolic enzymes in the glyoxylate cycle and its necessity for the pathogenesis of C. glabrata. Finally, we explore the transcriptional regulatory network of the glyoxylate cycle.
Conclusion
Considering evidence from Candida albicans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, this review summarizes the current knowledge of the glyoxylate cycle as an alternative carbon metabolic pathway of C. glabrata.
Keywords: Candida; Candida glabrata; Carbon metabolism; Glyoxylate cycle; Metabolic adaptation; Pathogenesis; virulence, yeast.
Introduction
Fungi are a group of eukaryotic organisms that can provoke a broad range of infectious diseases in humans, ranging from mild superficial infections to potentially life-threatening systemic infections. Candida species, such as Candida albicans and Candida glabrata, are ubiquitous and are considered benign residential microflora in the human body. However, an increased presence of immunocompromised individuals in human populations can contribute to the spread of candidiasis infections [1–3]. Invasive candidiasis is common among intensive care unit (ICU) and organ transplant patients and is often associated with increased costs of care, significant reductions in lifespan and prolonged hospitalization even after receiving antifungal treatments [4–8].
Bloodstream infections (BSIs) caused by Candida species or candidaemia are the most common manifestation of invasive candidiasis. In recent years, a shift of predominance from C. albicans to non-C. albicans Candida (NCAC) species has been observed, and C. albicans now accounts for only half of the invasive candidiasis cases reported [9]. Notably, C. glabrata has been recognized as either the second or third most common cause of invasive candidiasis after C. albicans [10], and similar epidemiological data have also been highlighted in global surveillance programmes such as SENTRY, ARTEMIS and TRANSNET [11–14]. Pfaller et al. (2014) reported that invasive candidiasis caused by C. glabrata is most commonly associated with patients who receive treatment for solid tumours or undergo solid organ transplantation (SOT) [15]. Among the patients with solid tumours and infections caused by NCAC species, 53.8% were caused by C. glabrata. In addition, C. glabrata was the main aetiological agent of 63.7% of SOT patients with NCAC infections. Overall, the increasing prevalence of NCAC species, particularly C. glabrata, is alarming due to the high mortality rates associated with such infections; thus, there is an urgent need to improve the current diagnostic and therapeutic options for better management of fungal BSIs [16].
Host immunity was believed to be the main factor responsible for the establishment of opportunistic fungal infections caused by yeast pathogens. However, this concept has changed, and it is now agreed that the pathogenicity of these yeast pathogens also plays a crucial role in infection [17]. For instance, virulence factors and fitness attributes such as metabolic flexibility, adherence to the host epithelia, biofilm formation, phenotypic switching, filamentation, secretion of hydrolytic enzymes, production of haemolysin and production of extracellular hydrolase are all associated with Candida species [18, 19]. Relative to C. albicans, the virulence factors and fitness attributes of C. glabrata are not well known, particularly in its natural niche.
The invasion strategy of C. glabrata is believed to be independent of phenotypic switching, as opposed to C. albicans, which employs invasion mechanisms that involve active penetration through hyphae extension and induced endocytosis [20, 21]. Despite being a relatively less virulent Candida species and generally having a weaker tissue-damaging ability compared to C. albicans, C. glabrata is still able to breach the natural barriers, invade the human bloodstream and cause systemic infection, presumably through SOT, parenteral nutrition, trauma, surgical or indwelling medical devices [8, 22]. In addition, C. glabrata uses a co-infection approach in infecting the human bloodstream, often by exploiting the tissue invasion and damage of the natural barriers caused by other Candida species, such as C. albicans [21, 23, 24].
Upon entering the human bloodstream, C. glabrata triggers a weaker polymorphonuclear neutrophil activation that primarily induces the recruitment of monocytic cells to the site of infection and triggers monocyte engulfment [25]. Since C. glabrata can survive and propagate within macrophages but not in neutrophils [26, 27], this fungal pathogen could use monocytes or macrophages as “Trojan horses” to gain protection against host defence mechanisms, particularly against neutrophil attack [25, 26]. In fact, C. glabrata clearly pursues different immune evasion and persistence strategies compared to C. albicans, as escape from the macrophages upon engulfment is not the priority of this fungal pathogen. Unlike C. albicans, C. glabrata can persist and replicate within macrophages without causing any significant damage to the host until the host cells eventually burst and release the fungal cells [26].
While trapped within macrophages, C. glabrata must rely on endogenous resources for survival because macrophages are often depicted as glucose-deficient [28, 29]. It has been shown that the ability of C. glabrata to mobilize intracellular resources through autophagy serves as a major contributor to sustaining the viability of this pathogen during carbon starvation [30, 31]. In addition to recycling intracellular resources via autophagy, the ability to utilize carbon sources other than glucose could potentially assist in the survival of engulfed C. glabrata. This review aims to discuss the metabolic adaptation and alternative carbon metabolism in C. glabrata. Taking cues from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and C. albicans, this review also discusses the role of the glyoxylate cycle in alternative carbon metabolism as well as the transcriptional regulation of this anabolic pathway in C. glabrata.
Metabolic adaptation strategy in C. glabrata
Nutrients are crucial for all living organisms, including fungi. Since Candida species often inhabit host niches with different nutrient availability, these fungal pathogens must be equipped with a high degree of metabolic flexibility and possess metabolic adaptation mechanisms that are required for effective nutrient acquisition [32]. Despite being a common human pathogen and rarely being found in environmental niches, Candida species such as C. albicans and C. glabrata still retain an impressive degree of metabolic flexibility [33, 34]. In addition, the virulence factors and fitness attributes of these fungal pathogens are firmly dependent on fungal metabolism, strengthening the truism of “you are what you eat” [35].
Transcriptional analyses of macrophage-engulfed C. albicans and C. glabrata revealed extensive metabolic reprogramming that reflects nutrient deprivation [28, 29]. These effects include the upregulation of genes that encode key metabolic enzymes in three interconnected anabolic pathways for alternative carbon metabolism, i.e., gluconeogenesis (PCK1 and FBP1), glyoxylate cycle (ICL1 and MLS1) and β-oxidation of fatty acids (FOX2, POT1 and POX1), coupled with the downregulation of genes related to glycolysis and translational machinery (e.g., elongation factors, ribosomal protein genes, translation initiation and tRNA synthetases). The induction of these key enzyme genes suggests that the microenvironment within macrophages is deficient in glucose; however, the confined C. glabrata cells are still able to utilize endogenous resources such as alternative carbon sources for their growth and survival. Furthermore, Rai et al. (2012) reported that engulfed C. glabrata cells primarily utilize acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) from the breakdown of fatty acids via the glyoxylate cycle as the main carbon source for the production of cellular building blocks [36].
Other than macronutrients, fungal pathogens are also dependent on micronutrients for the full functionality of proteins and enzymes, which are essential for survival and host colonization [32]. Trace metals such as iron are usually sequestered from fungal pathogens via nutritional immunity, forcing these fungal pathogens to employ iron acquisition mechanisms during iron starvation. In Candida species, C. albicans is able to obtain xenosiderophores from other microorganisms through iron parasitism using the Sit1 siderophore transporter [37]. Iron parasitism and the Sit1 transporter are well conserved in many fungal species, such as S. cerevisiae, Cryptococcus and Aspergillus [38]. Nevertheless, C. glabrata is unable to use siderophores of bacterial origin for iron uptake. In fact, C. glabrata can only exploit fungal xenosiderophores via the Sit1 homologue transporter, which is critical for its survival in macrophages [39]. To date, the uptake of other important trace metals in C. glabrata, such as copper and manganese, remains uncharacterized.
In addition to reprogramming its metabolic activity, C. glabrata obtains nutrients through mobilization of intracellular resources via a specialized autophagy known as pexophagy. Deletion of the genes required for pexophagy, ATG11 and ATG17, rendered C. glabrata more susceptible to macrophage killing. Therefore, pexophagy could potentially assist trapped C. glabrata in overcoming transient periods of nutrient deprivation in the phagosome and facilitate disseminated infection [30].
Alternative carbon metabolism in C. glabrata
Glucose remains the preferred carbon source for Candida species, and it is an important carbon and energy source for cell growth and development. Generally, glucose sensing and uptake in Candida species involve three main pathways, including the sugar receptor-repressor pathway, adenylate cyclase pathway and glucose repression pathway [40]. However, the availability of glucose varies in many host niches and anatomical sites, ranging from 0.05–0.1% in vaginal secretion to 0.1–0.2% in the blood [41, 42]. Apart from glucose, yeast cells are able to utilize alternative carbon sources, including but not limited to lactate, acetate, ethanol, glycerol and oleate [43]. Organic and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as acetate and lactate, are produced by intestinal bacteria from the degradation of complex carbohydrates [42–44]. Acetate and lactate can also be found in other host niches, such as the vaginal environment, which is dominated by vaginal microflora. Previously, it has been shown that C. glabrata can survive in carbon starvation conditions upon macrophage engulfment [30]; therefore, it is likely that alternative carbon metabolism plays a major role in the survival of C. glabrata trapped within macrophages.
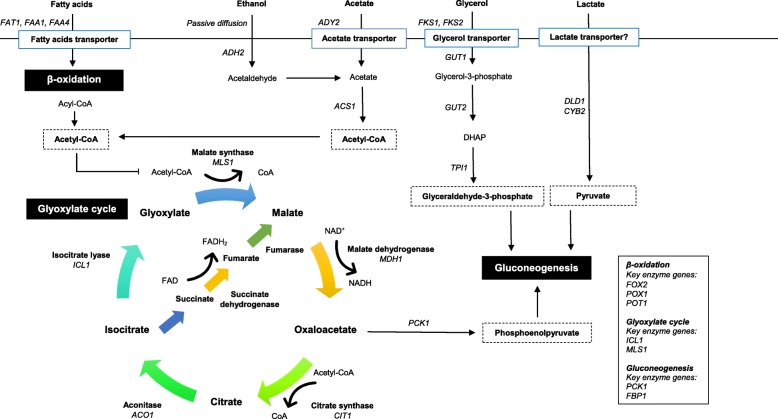
Glycerol is utilized by yeast cells as an important carbon source as well as for osmoregulation [45]. In fact, glycerol is also one of the alternative carbon sources that can be utilized by C. glabrata, and the uptake process is probably mediated by the glycerol transporter encoded by FPS1 and FPS2 [46]. Glycerol is first converted to glycerol-3-phosphate by the glycerol kinase Gut1, followed by conversion to dihydroacetone phosphate (DHAP), catalysed by glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Fig. 1). Subsequently, DHAP can enter gluconeogenesis through conversion into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate by triose phosphate isomerase. On the other hand, lactate is transported through a monocarboxylate permease encoded by JEN1 in yeast such as S. cerevisiae and C. albicans. The presence of glucose represses the expression of JEN1, and the degradation of protein-coding mRNA is also observed when induced JEN1 is exposed to glucose [47, 48]. Lactate is converted to pyruvate by two different oxidoreductases encoded by CYB2 and DLD1 [49], which serves as an intermediate for gluconeogenesis. Although JEN1 is absent in C. glabrata [50], lactate dehydrogenase-mediated lactate assimilation has been shown to be vital for the survival and adaptation of C. glabrata in the mouse intestine [51].
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of glyoxylate cycle and its involvement in alternative carbon metabolism. In the absence of glucose, alternative carbon sources acids are transported and utilized by C. glabrata, converted to the central metabolite acetyl-CoA to fuel glyoxylate cycle and gluconeogenesis for glucose and energy production [23, 38, 52, 53]
Ethanol is believed to enter the cells through passive diffusion, whereas acetate is transported to the cells through the carboxylate transporter acetate permease [54–56]. Both carbon sources are ultimately converted to acetyl-CoA by acetyl-CoA synthetase (Acs1) in the cytosol (Fig. 1). It has been shown that C. glabrata are able to utilize acetate, even in the presence of glucose [57, 58]. In addition, the putative acetate permease gene ADY2 was induced in C. glabrata in response to engulfment by macrophages [29] and neutrophils [59]. These observations suggest that acetate is relevant in vivo and that C. glabrata may assimilate acetate or other SCFAs in microenvironments with poor glucose availability. In addition, transporters such as Fat1, Faa1 and Faa4 are believed to be involved in the uptake of fatty acids in yeast cells [60]. Orthologous genes that encode these fatty acid transporters have been identified in C. glabrata, although they have not been fully characterized. Unlike ethanol and acetate, fatty acids are broken down to acetyl-CoA via β-oxidation in the peroxisomes, which involves the enzymes fatty acyl-CoA oxidase, 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase and 3-oxoacyl-CoA thiolase. Acetyl-CoA generated from the breakdown of acetate, ethanol and fatty acids fuels the glyoxylate cycle and gluconeogenesis for glucose production when glucose availability is scarce (Fig. 1) [28, 43].
The breakdown of alternative carbon sources, such as fatty acids, ethanol and acetate, leads to the generation of the central metabolite acetyl-CoA in different subcellular compartments [52]. Specifically, breakdown of fatty acids generates acetyl-CoA that is solely peroxisomal, while breakdown of ethanol and acetate produces cytosolic acetyl-CoA. Due to its bulkiness and amphiphilic nature, transport of peroxisomal and cytosolic acetyl-CoA to the glyoxylate cycle often requires a functional acetyl unit transport system [52, 61]. In general, S. cerevisiae appears to use two parallel modes of acetyl unit transportation systems, namely, the carnitine shuttle and citrate synthase pathway, while C. albicans exclusively depends on the carnitine shuttle [reviewed in [52]]. The genome of C. glabrata also encodes three still uncharacterized, putative carnitine acetyltransferase orthologues, Cat2, Yat1 and Yat2, which are similar to those in S. cerevisiae and C. albicans [62, 63], suggesting that a functional carnitine shuttle also exists in C. glabrata for acetyl-CoA transportation. It has been shown that C. albicans is fully dependent on the carnitine shuttle for transportation of acetyl-CoA due to the absence of peroxisomal citrate synthase (Cit2), and this is further underlined by the fact that C. albicans also possesses a complete carnitine biosynthesis pathway [64–66]. In contrast to C. albicans, a putative Cit2 orthologue exists in C. glabrata (60% similarity to S. cerevisiae Cit2), suggesting that C. glabrata may utilize two modes of acetyl unit transportation, similar to the phylogenetically more closely related S. cerevisiae. Nonetheless, further investigation is needed to fully decipher the carnitine shuttle and potential peroxisomal citrate synthase pathway in C. glabrata.
Glyoxylate cycle: an overview
The glyoxylate cycle is an anaplerotic variant of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and is an anabolic pathway occurring in most protists, plants, bacteria and fungi. The glyoxylate cycle is assumed to be absent in animals and human tissues, with nematodes at the early stages of embryogenesis being the only known exception [67, 68]. The primary function of the glyoxylate cycle is to allow growth when glucose is not available and two-carbon compounds, such as ethanol and acetate, are the only sources of carbon [69]. The glyoxylate cycle is basically a shunt in the TCA cycle, with which it shares many metabolic enzymes, including malate dehydrogenase, citrate synthase, and aconitase [70]. The two decarboxylation steps involve isocitrate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in the TCA cycle and are essentially excluded from the glyoxylate cycle. Alternatively, the glyoxylate cycle contains two additional key enzymes: isocitrate lyase and malate synthase (Fig. 1). In brief, isocitrate lyase catalyses the breakdown of isocitrate (C6) into glyoxylate (C2) and succinate (C4), followed by condensation of glyoxylate with acetyl-CoA (C2) catalysed by malate synthase to generate malate (C4) and a free CoA (Fig. 1). Therefore, malate produced from C2 compounds (e.g., ethanol and acetate) can serve as an intermediate to replenish the TCA cycle in the absence of glucose [71]. In addition, malate serves as the precursor of oxaloacetate, an essential substrate for gluconeogenesis. Oxaloacetate is converted to phosphoenolpyruvate by the gluconeogenesis enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and eventually leads to glucose production with the help of another gluconeogenesis enzyme, fructose-1,6-biphosphate (Fig. 1) [71]. In short, the glyoxylate cycle bypasses the two decarboxylation steps in the TCA cycle to allow for the anabolism of simpler carbon compounds in gluconeogenesis.
The glyoxylate cycle and its key metabolic enzymes, isocitrate lyase and malate synthase, are believed to be highly conserved across different organisms [67, 72]. The glyoxylate cycle plays an important role in the growth of plant seedlings and is involved in the conversion of stored lipids to carbohydrates, which serve as the main nutritional resource for the plant before the commencement of photosynthesis [73]. The glyoxylate cycle is also well studied in bacterial pathogens, especially in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Honer Zu Bentrup et al. (1999) showed that M. tuberculosis possesses a second copy of the functional ICL1 gene (aceA) [53]. The glyoxylate cycle is reported to be essential for M. tuberculosis survival in the host because deletion of ICL1 and aceA genes leads to complete impairment of intracellular replication and rapid elimination of this pathogen from the lungs of C57BL/6 mice in vivo [74]. In addition, the glyoxylate cycle is essential for the pathogenicity of other intracellular bacterial pathogens, namely, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, Rhodococcus equi and Pseudomonas aeruginosa [75–77].
Inactivation of the ICL1 gene in the fungus Leptosphaeria maculans, a causal agent of the blackleg of crucifers, causes low germination rates of pycnidiospores, thus reducing the pathogenicity of this fungal pathogen on canola cotyledons [78]. In addition, the glyoxylate cycle is required for the full virulence of Magnaporthe grisea, the rice blast fungus. Disruption of ICL1 in M. grisea causes a reduction in appressorium formation, conidiogenesis and cuticle penetration, leading to an overall decrease in damage to rice and barley leaves [79]. Furthermore, disruption of MLS1 in the glyoxylate cycle also causes a reduction in the pathogenicity of certain plant pathogenic fungi, such as Rhodococcus fascians, Stagonospora nodorum and Xanthomonas campestris [80–82]. For intracellular human fungal pathogens, upregulation of glyoxylate cycle genes has been observed in Paracoccidioides brasiliensis, Penicillium marneffei, C. albicans, A. fumigatus and C. neoformans in response to macrophages [28, 83–86]. While the glyoxylate cycle is required for the full virulence of C. albicans, it is not essential for the full virulence of A. fumigatus and C. neoformans in vivo [87–89].
Glyoxylate cycle and the virulence of C. glabrata: what we know so far
The glyoxylate cycle enzymes isocitrate lyase and malate synthase are highly similar in C. glabrata and S. cerevisiae, with protein sequence identities of approximately 84 and 86%, respectively. In contrast, both enzymes of C. glabrata and C. albicans have protein identities between 58 and 68%, respectively. The subcellular localizations of isocitrate lyase and malate synthase have been inferred in the peroxisomes of C. albicans [90]. However, the isocitrate lyase of S. cerevisiae is localized in the cytosol, while malate synthase is compartmentalized in both the peroxisomes and the cytosol [70]. For C. glabrata, the subcellular localizations of both enzymes still remain to be determined, although WoLF PSORT predicts that these enzymes are localized in the peroxisomes, similar to C. albicans [91]. This result implies that C. glabrata could potentially regulate the localization of isocitrate lyase and malate synthase in a way that is similar to C. albicans, albeit with glyoxylate cycle enzymes that resemble those of baker’s yeast.
The glyoxylate cycle in Candida species has been mainly studied in C. albicans, the predominant Candida species that causes invasive candidiasis in humans. Lorenz and Fink (2001) reported that the glyoxylate cycle genes ICL1 and MLS1 were significantly upregulated in C. albicans that were grown in the presence of macrophages [87]. In addition, the ICL1 gene is required for the full virulence of this fungal pathogen. Homozygous deletion of ICL1 rendered C. albicans avirulent in an in vivo mouse model of invasive candidiasis, while reintroducing ICL1 restored the virulence of this fungal pathogen in vivo. Genetic characterization of the glyoxylate cycle genes ICL1 and MLS1 revealed high homologies to other fungal species, particularly S. cerevisiae and C. tropicalis [92]. In addition, ICL1 and MLS1 were repressed in the presence of glucose and only induced in the presence of alternative carbon sources, which is very similar to the regulation of the glyoxylate cycle in S. cerevisiae.
Global gene expression analysis of C. albicans showed that ICL1 and MLS1 were also highly upregulated (> 20-fold) in response to human blood [93], which is in concordance with the data obtained from a previous study [87]. In 2004, transcriptional profiling of C. albicans in response to murine macrophages was investigated by using a microarray approach [28]. Microarray analyses revealed a reprogramming event in C. albicans in response to nutrient starvation in macrophages. In fact, genes related to alternative carbon metabolism, including genes from gluconeogenesis, glyoxylate cycles and β-oxidation of fatty acids, were found to be induced upon macrophage engulfment.
Barelle et al. (2006) revisited the role of the glyoxylate cycle in the virulence of C. albicans by using a green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion approach instead of transcript profiling, which allows for the monitoring of individual C. albicans within host niches [94]. Indeed, ICL1-GFP fusion was repressed at physiologically relevant glucose concentrations (0.1%) and only expressed in the presence of amino acids. Furthermore, induction of ICL1-GFP was observed in phagocytosed C. albicans in neutrophils and macrophages, but not in the non-phagocytosed cells. While most of the C. albicans cells expressed glycolytic genes PYK1 and PFK2 in the infected mouse kidneys, only half of the C. albicans cells expressed ICL1-GFP in the early stage of infection. This result implies that ICL1 is essential for the virulence of C. albicans in the early stage of infection in response to macrophages. However, a glycolytic mechanism is required for the disease progression of invasive candidiasis in the later stage of infection.
In addition, Ramírez and Lorenz (2007) reported that mutants lacking the glyoxylate cycle enzyme gene ICL1 displayed more extensive growth defects than initially predicted [95]. In addition to fatty acids, ethanol and acetate, ICL1 mutants of C. albicans are unable to grow in medium with citrate or glycerol as the sole carbon source. This finding suggests that the regulation of alternative carbon metabolism in C. albicans may be different compared to other fungi, such as S. cerevisiae. Ramírez and Lorenz (2007) also reconfirmed that ICL1 is required for the virulence of C. albicans by using a newly engineered strain that accounts for the positional effects of the URA3 disruption marker used in a previous study [87, 96]. Fernández-Arenas et al. (2007) used a proteomic approach to show that the glyoxylate cycle in C. albicans is upregulated in response to challenges from murine macrophages [97]. The glyoxylate cycle enzymes isocitrate lyase and malate synthase are localized to the peroxisome in a Pex5p-dependent manner. However, peroxisomal localizations of these enzymes are not essential for the functioning of the glyoxylate cycle, as this metabolic pathway works equally well in the cytosol of the cells [90].
Sandai et al. (2012) reported that there is significant disagreement between the proteome and transcriptome profiles of C. albicans [98]. Although the presence of glucose triggers the degradation of the ICL1 transcript, isocitrate lyase is stable and not destabilized, in contrast to the rapid destabilization of isocitrate lyase in S. cerevisiae following exposure to glucose. In fact, the isocitrate lyase of C. albicans lacks the main ubiquitination sites essential for targeted degradation of the transcript. These findings suggest that C. albicans underwent post-translational rewiring as it co-evolved with its host and thereby gained the ability to utilize alternative carbon sources and glucose simultaneously during systemic infection. Childers et al. (2016) investigated the impact of ubiquitin-mediated catabolite inactivation on the virulence of C. albicans [99]. The addition of ubiquitination sites in C. albicans leads to the destabilization of isocitrate lyase in response to glucose. Reduced metabolic flexibility following the addition of a ubiquitination site rendered C. albicans unable to use alternative carbon sources, more susceptible to macrophage killing, and unable to cause systemic and gastrointestinal tract infections in vivo.
As for C. glabrata, Kaur et al. (2007) have reported that the transcriptional response of C. glabrata co-incubated with macrophages is very similar to the response described in C. albicans [29]. Genes involved in gluconeogenesis, the glyoxylate cycle, β-oxidation of fatty acids and the methylcitrate cycle were induced upon macrophage engulfment. In addition, Rai et al. (2012) revealed that alternative carbon remained the main intracellular carbon source in macrophages, and C. glabrata utilized acetyl-CoA via the glyoxylate cycle and gluconeogenesis for energy production [36]. Our previous work showed that the ICL1 gene is indeed crucial for the metabolism of alternative carbon sources in C. glabrata [100]. In fact, disruption of ICL1 rendered C. glabrata unable to utilize acetate, ethanol or oleic acid as the sole carbon source for growth and survival. In addition, ICL1 is also required for the intracellular survival of C. glabrata upon macrophage engulfment, potentially through the utilization of alternative carbon sources found within macrophages. Most importantly, ICL1 is essential for the virulence of C. glabrata in vivo, as disruption of ICL1 confers a severe attenuation in the virulence of C. glabrata in the mouse model of invasive candidiasis.
Regulation of the glyoxylate cycle
Most of the transcriptional regulators in yeast belong to a subclass of proteins known as zinc cluster proteins. These proteins are characterized by a well-conserved motif (CysX2CysX6CysX5–12CysX2CysX6–8Cys) and are fungal specific [101]. As most zinc cluster proteins bind to DNA, they are essential for the regulation of yeast transcriptional and translational machineries [102]. To date, transcriptional regulation of alternative carbon metabolism has not been well studied in C. glabrata. In S. cerevisiae, Snf1 kinase is the main activator of downstream glucose-repressed genes and is important for the activation of alternative carbon metabolism. Generally, Snf1 kinase is induced in response to glucose-deficient conditions and deactivates the transcriptional repressor Mig1 by phosphorylation [43]. Dissociation of Mig1 from the co-repressor protein complex Ssn6-Tup1 leads to increased expression of Cat8, a transcriptional regulator that binds the carbon source-responsive element (CSRE) located at the promoter region of many glyoxylate cycle and gluconeogenic genes such as ICL1, MLS1, FBP1 and PCK1 [43, 103, 104].
Cat8 is also an activator of Sip4, another important CSRE-binding transcriptional regulator found in S. cerevisiae. Although Cat8 and Sip4 have similar functions in regulating the glyoxylate cycle and gluconeogenic genes, Cat8 appears to be the primary regulator, because the removal of Cat8 significantly reduced the expression of CSRE-dependent genes, while the absence of Sip4 only caused a minor reduction in the expression of these genes [105, 106]. Furthermore, activation of Sip4 requires a functional CAT8, whereas activation of Cat8 is not dependent on SIP4. Unlike Mig1-regulated Cat8, activation of Sip4 is regulated by Snf1 Kinase and Rds2, another transcriptional regulator [43, 107]. Like Cat8 and Sip4, Rds2 also binds to the promoter region of CSRE-dependent genes from the glyoxylate cycle and gluconeogenesis following exposure to alternative carbon sources [107]. In short, CSRE-dependent genes from the glyoxylate cycle are at least recognized and regulated by three transcriptional regulators, namely, Cat8, Sip4 and Rds2, in S. cerevisiae.
Interestingly, removal of CAT8 did not alter the expression of CSRE-dependent genes that encode enzymes for the glyoxylate cycle, gluconeogenesis and β-oxidation of fatty acids in C. albicans [108]. Additionally, disruption of CAT8 did not lead to any noticeable attenuation in the virulence of C. albicans in vivo. This result suggests that Cat8 is not involved in the transcriptional regulation of glyoxylate cycle genes and is also not required for the full virulence of C. albicans. This observation could potentially be attributed to the substantial reassignment of the function of some transcriptional regulators between C. albicans and S. cerevisiae, which are reported to be highly divergent [109]. Therefore, it remains to be seen whether the regulation of the glyoxylate cycle in C. glabrata follows the more phylogenetically related S. cerevisiae or other Candida species from the CTG clade, such as C. albicans. Moreover, orthologous genes of SIP4 and RDS2 have been found in both C. albicans and C. glabrata [110, 111]; however, their involvement in the regulation of alternative carbon metabolism, particularly the glyoxylate cycle, remains unclear.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rapid and effective metabolic adaptation within the host is crucial for human fungal pathogens to thrive. The present review discussed the importance of alternative carbon metabolism as a metabolic adaptation strategy for intracellular C. glabrata to survive and propagate in carbon starvation. Considering the essential role of the glyoxylate cycle, particularly ICL1, in the virulence of C. glabrata, further studies should be conducted to investigate other key metabolic enzymes involved in alternative carbon metabolism, notably those from gluconeogenesis and β-oxidation of fatty acids. Moreover, little is known about the transcriptional regulation and post-translation modification of these key metabolic enzymes in C. glabrata. Given the rapid emergence of invasive candidiasis caused by NCAC species, especially C. glabrata, it is envisaged that the knowledge generated from investigating this metabolic adaptation strategy will provide some basic insights into devising novel and innovative strategies for reducing the severity of invasive candidiasis caused by C. glabrata worldwide.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Abbreviations
- BSIs
Bloodstream infections
- CoA
Coenzyme A
- CSRE
Carbon sources responsive element
- DHAP
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
- GFP
Green fluorescent protein
- ICU
Intensive care unit
- NCAC
Non-C. albicans Candida
- SCFAs
Short-chain fatty acids
- SOT
Solid organ transplantation
- TCA
Tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Authors’ contributions
SY, WC and LT reviewed the literature and co-wrote the manuscript. All authors listed gave final approval for publication.
Funding
This work was supported by Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) from Ministry of Education (MOE), Malaysia (Grant number: 01–01-14-1456FR). S.Y. was supported by MyBrain15 Scholarship from MOE, Malaysia. W.C. was supported by Graduate Research Fellowship (GRF) from Universiti Putra Malaysia.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Shu Yih Chew, Email: shuyih87@gmail.com.
Wallace Jeng Yang Chee, Email: wallace_1024@hotmail.com.
Leslie Thian Lung Than, Email: leslie@upm.edu.my.
References
- 1.Mayer FL, Wilson D, Hube B. Candida albicans pathogenicity mechanisms. Virulence. 2013;4:119–128. doi: 10.4161/viru.22913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Munoz-Duarte AR, Castrejon-Jimenez NS, Baltierra-Uribe SL, et al. Candida glabrata survives and replicates in human osteoblasts. Pathog Dis. 2016;74:ftw030. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftw030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sadeghi G, Ebrahimi-Rad M, Mousavi SF, et al. Emergence of non-Candida albicans species: epidemiology, phylogeny and fluconazole susceptibility profile. J Mycol Med. 2018;28:51–58. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2017.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ. Epidemiology of invasive candidiasis: a persistent public health problem. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007;20:133–163. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00029-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Andes DR, Safdar N, Baddley JW, et al. Impact of treatment strategy on outcomes in patients with candidemia and other forms of invasive candidiasis: a patient-level quantitative review of randomized trials. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54:1110–1122. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Falcone M, Concia E, Iori I, et al. Identification and management of invasive mycoses in internal medicine: a road-map for physicians. Intern Emerg Med. 2014;9:501–511. doi: 10.1007/s11739-014-1077-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yapar N. Epidemiology and risk factors for invasive candidiasis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014;13:95–105. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S40160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Taimur S. Yeast infections in solid organ transplantation. Infect Dis Clin N Am. 2018;32:651–666. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2018.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kullberg BJ, Arendrup MC. Invasive candidiasis. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1445–1456. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1315399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fidel PL, Vazquez JA, Sobel JD. Candida glabrata: review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, and clinical disease with comparison to Candida albicans. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999;12:80–96. doi: 10.1128/CMR.12.1.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Messer SA, Jones RN, Fritsche TR. International surveillance of Candida spp. and Aspergillus spp.: report from the SENTRY antimicrobial surveillance program (2003) J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:1782–1787. doi: 10.1128/JCM.44.5.1782-1787.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Messer SA, Moet GJ, Kirby JT, et al. Activity of contemporary antifungal agents, including the novel echinocandin anidulafungin, tested against Candida spp., Cryptococcus spp., and Aspergillus spp.: report from the SENTRY antimicrobial surveillance program (2006 to 2007) J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:1942–1946. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02434-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ, Gibbs DL, et al. Results from the ARTEMIS DISK global antifungal surveillance study, 1997 to 2007: a 10.5-year analysis of susceptibilities of Candida species to fluconazole and voriconazole as determined by CLSI standardized disk diffusion. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48:1366–1377. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02117-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Andes DR, Safdar N, Baddley JW, et al. The epidemiology and outcomes of invasive Candida infections among organ transplant recipients in the United States: results of the transplant-associated infection surveillance network (TRANSNET) Transpl Infect Dis. 2016;18:921–931. doi: 10.1111/tid.12613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pfaller MA, Andes DR, Diekema DJ, et al. Epidemiology and outcomes of invasive candidiasis due to non-albicans species of Candida in 2,496 patients: data from the prospective antifungal therapy (PATH) registry 2004-2008. PLoS One. 2014;9:e101510. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Doi AM, Pignatari ACC, Edmond MB, et al. Epidemiology and microbiologic characterization of nosocomial candidemia from a Brazilian National Surveillance Program. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0146909. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Silva S, Negri M, Henriques M, et al. Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis and Candida tropicalis: biology, epidemiology, pathogenicity and antifungal resistance. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2012;36:288–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sardi JC, Scorzoni L, Bernardi T, et al. Candida species: current epidemiology, pathogenicity, biofilm formation, natural antifungal products and new therapeutic options. J Med Microbiol. 2013;62:10–24. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.045054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wan L, Luo G, Lu H, et al. Changes in the hemolytic activity of Candida species by common electrolytes. BMC Microbiol. 2015;15:171. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0504-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Goyer M, Loiselet A, Bon F, et al. Intestinal cell tight junctions limit invasion of Candida albicans through active penetration and endocytosis in the early stages of the interaction of the fungus with the intestinal barrier. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0149159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Galocha M, Pais P, Cavalheiro M, et al. Divergent approaches to virulence in C albicans and C glabrata: two sides of the same coin. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:2345. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Perlroth J, Choi B, Spellberg B. Nosocomial fungal infections: epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Med Mycol. 2007;45:321–346. doi: 10.1080/13693780701218689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Alves CT, Wei XQ, Silva S, et al. Candida albicans promotes invasion and colonisation of Candida glabrata in a reconstituted human vaginal epithelium. J Inf Secur. 2014;69:396–407. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2014.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tati S, Davidow P, McCall A, et al. Candida glabrata binding to Candida albicans hyphae enables its development in oropharyngeal candidiasis. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:e1005522. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Duggan S, Essig F, Hünniger K, et al. Neutrophil activation by Candida glabrata but not Candida albicans promotes fungal uptake by monocytes. Cell Microbiol. 2015;17:1259–1276. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Seider K, Brunke S, Schild L, et al. The facultative intracellular pathogen Candida glabrata subverts macrophage cytokine production and phagolysosome maturation. J Immunol. 2011;187:3072–3086. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Seider K, Gerwien F, Kasper L, et al. Immune evasion, stress resistance, and efficient nutrient acquisition are crucial for intracellular survival of Candida glabrata within macrophages. Eukaryot Cell. 2014;13:170–183. doi: 10.1128/EC.00262-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lorenz Michael C., Bender Jennifer A., Fink Gerald R. Transcriptional Response ofCandida albicansupon Internalization by Macrophages. Eukaryotic Cell. 2004;3(5):1076–1087. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.5.1076-1087.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kaur R, Ma B, Cormack BP. A family of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked aspartyl proteases is required for virulence of Candida glabrata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:7628–7633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611195104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Roetzer A, Gratz N, Kovarik P, et al. Autophagy supports Candida glabrata survival during phagocytosis. Cell Microbiol. 2010;12:199–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01391.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Shimamura S, Miyazaki T, Tashiro M, et al. Autophagy-inducing factor Atg1 is required for virulence in the pathogenic fungus Candida glabrata. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:27. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ene IV, Brunke S, Brown AJ, et al. Metabolism in fungal pathogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014;4:a019695. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a019695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Brown AJ, Odds FC, Gow NA. Infection-related gene expression in Candida albicans. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007;10:307–313. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2007.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wilson D, Thewes S, Zakikhany K, et al. Identifying infection-associated genes of Candida albicans in the postgenomic era. FEMS Yeast Res. 2009;9:688–700. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2009.00524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Brown AJ, Brown GD, Netea MG, et al. Metabolism impacts upon Candida immunogenicity and pathogenicity at multiple levels. Trends Microbiol. 2014;22:614–622. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2014.07.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rai MN, Balusu S, Gorityala N, et al. Functional genomic analysis of Candida glabrata-macrophage interaction: role of chromatin remodelling in virulence. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8:e1002863. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Heymann P, Gerads M, Schaller M, et al. The siderophore iron transporter of Candida albicans (Sit1p/Arn1p) mediates uptake of ferrichrome-type siderophores and is required for epithelial invasion. Infect Immun. 2002;70:5246–5255. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.9.5246-5255.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Schrettl M, Haas H. Iron homeostasis - Achilles' heel of Aspergillus fumigatus? Curr Opin Microbiol. 2011;14:400–405. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2011.06.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nevitt T, Thiele DJ. Host iron withholding demands siderophore utilization for Candida glabrata to survive macrophage killing. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1001322. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sabina J, Brown V. Glucose sensing network in Candida albicans: a sweet spot for fungal morphogenesis. Eukaryot Cell. 2009;8:1314–1320. doi: 10.1128/EC.00138-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ehrström S, Yu A, Rylander E. Glucose in vaginal secretions before and after oral glucose tolerance testing in women with and without recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:1432–1437. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000246800.38892.fc. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Miramón P, Lorenz MC. A feast for Candida: metabolic plasticity confers an edge for virulence. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13:e1006144. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Turcotte B, Liang XB, Robert F, et al. Transcriptional regulation of nonfermentable carbon utilization in budding yeast. FEMS Yeast Res. 2010;10:2–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2009.00555.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yamaguchi N, Sonoyama K, Kikuchi H, et al. Gastric colonization of Candida albicans differs in mice fed commercial and purified diets. J Nutr. 2005;135:109–115. doi: 10.1093/jn/135.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hohmann S. Osmotic stress signaling and osmoadaptation in yeasts. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2002;66:300–372. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.66.2.300-372.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Beese-Sims SE, Pan SJ, Lee J, et al. Mutants in the Candida glabrata glycerol channels are sensitized to cell wall stress. Eukaryot Cell. 2012;11:1512–1519. doi: 10.1128/EC.00231-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Casal M, Paiva S, Andrade RP, et al. The lactate-proton symport of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is encoded by JEN1. J Bacteriol. 1999;181:2620–2623. doi: 10.1128/jb.181.8.2620-2623.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Andrade RP, Kötter P, Entian KD, et al. Multiple transcripts regulate glucose-triggered mRNA decay of the lactate transporter JEN1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;332:254–262. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.04.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lodi T, Ferrero I. Isolation of the DLD gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encoding the mitochondrial enzyme D-lactate ferricytochrome c oxidoreductase. Mol Gen Genet. 1993;238:315–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00291989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lodi T, Diffels J, Goffeau A, et al. Evolution of the carboxylate Jen transporters in fungi. FEMS Yeast Res. 2007;7:646–656. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2007.00245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ueno K, Matsumoto Y, Uno J, et al. Intestinal resident yeast Candida glabrata requires Cyb2p-mediated lactate assimilation to adapt in mouse intestine. PLoS One. 2011;6:e24759. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Strijbis K, Distel B. Intracellular acetyl unit transport in fungal carbon metabolism. Eukaryot Cell. 2010;9:1809–1815. doi: 10.1128/EC.00172-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lorenz MC, Fink GR. Life and death in a macrophage: role of the glyoxylate cycle in virulence. Eukaryot Cell. 2002;1:657–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 54.Paiva S, Devaux F, Barbosa S, et al. Ady2p is essential for the acetate permease activity in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 2004;21:201–210. doi: 10.1002/yea.1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Casal M, Paiva S, Queirós O, et al. Transport of carboxylic acids in yeasts. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008;32:974–994. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Vieira N, Casal M, Johansson B, et al. Functional specialization and differential regulation of short-chain carboxylic acid transporters in the pathogen Candida albicans. Mol Microbiol. 2010;75:1337–1354. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.07003.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Mota S, Alves R, Carneiro C, et al. Candida glabrata susceptibility to antifungals and phagocytosis is modulated by acetate. Front Microbiol. 2015;6:919. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Cunha DV, Salazar SB, Lopes MM, et al. Mechanistic insights underlying tolerance to acetic acid stress in vaginal Candida glabrata clinical isolates. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:259. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Fukuda Y, Tsai HF, Myers TG, et al. Transcriptional profiling of Candida glabrata during phagocytosis by neutrophils and in the infected mouse spleen. Infect Immun. 2013;81:1325–1333. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00851-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Black PN, DiRusso CC. Yeast acyl-CoA synthetases at the crossroads of fatty acid metabolism and regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1771;2007:286–298. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Rottensteiner H, Theodoulou FL. The ins and outs of peroxisomes: co-ordination of membrane transport and peroxisomal metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1763;2006:1527–1540. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Swiegers JH, Dippenaar N, Pretorius IS, Bauer FF. Carnitine-dependent metabolic activities in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: three carnitine acetyltransferases are essential in a carnitine-dependent strain. Yeast. 2001;18:585–595. doi: 10.1002/yea.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Prigneau O, Porta A, Maresca B. Candida albicans CTN gene family is induced during macrophage infection: homology, disruption and phenotypic analysis of CTN3 gene. Fungal Genet Biol. 2004;41:783–793. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2004.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Strijbis K, van Roermund CW, Visser WF, et al. Carnitine-dependent transport of acetyl coenzyme a in Candida albicans is essential for growth on nonfermentable carbon sources and contributes to biofilm formation. Eukaryot Cell. 2008;7:610–618. doi: 10.1128/EC.00017-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Strijbis K, van Roermund CW, Hardy GP, et al. Identification and characterization of a complete carnitine biosynthesis pathway in Candida albicans. FASEB J. 2009;23:2349–2359. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-127985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Zhou H, Lorenz MC. Carnitine acetyltransferases are required for growth on non-fermentable carbon sources but not for pathogenesis in Candida albicans. Microbiology. 2008;154:500–509. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/014555-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Kondrashov FA, Koonin EV, Morgunov IG, et al. Evolution of glyoxylate cycle enzymes in Metazoa: evidence of multiple horizontal transfer events and pseudogene formation. Biol Direct. 2006;1:31. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-1-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Kunze M, Hartig A. Permeability of the peroxisomal membrane: lessons from the glyoxylate cycle. Front Physiol. 2013;4:204. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kornberg HL. The role and control of the glyoxylate cycle in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1966;99:1–11. doi: 10.1042/bj0990001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Kunze M, Pracharoenwattana I, Smith SM, et al. A central role for the peroxisomal membrane in glyoxylate cycle function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1763;2006:1441–1452. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Dunn M. F., Ramirez-Trujillo J. A., Hernandez-Lucas I. Major roles of isocitrate lyase and malate synthase in bacterial and fungal pathogenesis. Microbiology. 2009;155(10):3166–3175. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.030858-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Eastmond P. J., Germain V., Lange P. R., Bryce J. H., Smith S. M., Graham I. A. Postgerminative growth and lipid catabolism in oilseeds lacking the glyoxylate cycle. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2000;97(10):5669–5674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.10.5669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Honer Zu Bentrup K, Miczak A, Swenson DL, et al. Characterization of activity and expression of isocitrate lyase in Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1999;181:7161–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 74.Muñoz-Elías EJ, McKinney JD. Mycobacterium tuberculosis isocitrate lyases 1 and 2 are jointly required for in vivo growth and virulence. Nat Med. 2005;11:638–644. doi: 10.1038/nm1252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Fang FC, Libby SJ, Castor ME, et al. Isocitrate lyase (AceA) is required for Salmonella persistence but not for acute lethal infection in mice. Infect Immun. 2005;73:2547–2549. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.4.2547-2549.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Wall DM, Duffy PS, Dupont C, et al. Isocitrate lyase activity is required for virulence of the intracellular pathogen Rhodococcus equi. Infect Immun. 2005;73:6736–6741. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.10.6736-6741.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lindsey TL, Hagins JM, Sokol PA, et al. Virulence determinants from a cystic fibrosis isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa include isocitrate lyase. Microbiol. 2008;154:1616–1627. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/014506-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Idnurm A, Howlett BJ. Isocitrate lyase is essential for pathogenicity of the fungus Leptosphaeria maculans to canola (Brassica napus) Eukaryot Cell. 2002;1:719–724. doi: 10.1128/EC.1.5.719-724.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Wang ZY, Thornton CR, Kershaw MJ, et al. The glyoxylate cycle is required for temporal regulation of virulence by the plant pathogenic fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Microbiol. 2003;47:1601–1612. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Vereecke D, Cornelis K, Temmerman W, et al. Chromosomal locus that affects pathogenicity of Rhodococcus fascians. J Bacteriol. 2002;184:1112–1120. doi: 10.1128/jb.184.4.1112-1120.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Solomon PS, Lee RC, Wilson TJ, et al. Pathogenicity of Stagonospora nodorum requires malate synthase. Mol Microbiol. 2004;53:1065–1073. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Tamir-Ariel D, Navon N, Burdman S. Identification of genes in Xanthomonas campestris pv. Vesicatoria induced during its interaction with tomato. J Bacteriol. 2007;189:6359–6371. doi: 10.1128/JB.00320-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Fan W, Kraus PR, Boily MJ, et al. Cryptococcus neoformans gene expression during murine macrophage infection. Eukaryot Cell. 2005;4:1420–1433. doi: 10.1128/EC.4.8.1420-1433.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ebel F, Schwienbacher M, Beyer J, et al. Analysis of the regulation, expression, and localization of the isocitrate lyase from Aspergillus fumigatus, a potential target for antifungal drug development. Fungal Genet Biol. 2006;43:476–489. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2006.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Derengowski LS, Tavares AH, Silva S, et al. Upregulation of glyoxylate cycle genes upon Paracoccidioides brasiliensis internalization by murine macrophages and in vitro nutritional stress condition. Med Mycol. 2008;46:125–134. doi: 10.1080/13693780701670509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Thirach S, Cooper CR, Jr, Vanittanakom N. Molecular analysis of the Penicillium marneffei glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase-encoding gene (gpdA) and differential expression of gpdA and the isocitrate lyase-encoding gene (acuD) upon internalization by murine macrophages. J Med Microbiol. 2008;57:1322–1328. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.2008/002832-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Lorenz MC, Fink GR. The glyoxylate cycle is required for fungal virulence. Nature. 2001;412:83–86. doi: 10.1038/35083594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Rude TH, Toffaletti DL, Cox GM, et al. Relationship of the glyoxylate pathway to the pathogenesis of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 2003;70:5684–5694. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.10.5684-5694.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Schöbel F, Ibrahim-Granet O, Avé P, et al. Aspergillus fumigatus does not require fatty acid metabolism via isocitrate lyase for development of invasive aspergillosis. Infect Immun. 2007;75:1237–1244. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01416-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Piekarska K, Hardy G, Mol E, et al. The activity of the glyoxylate cycle in peroxisomes of Candida albicans depends on a functional beta-oxidation pathway: evidence for reduced metabolite transport across the peroxisomal membrane. Microbiol. 2008;54:3061–3072. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2008/020289-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Horton P, Park KJ, Obayashi T, et al. WoLF PSORT: protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:W585–W587. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Eschrich D, Kötter P, Entian KD. Gluconeogenesis in Candida albicans. FEMS Yeast Res. 2002;2:315–325. doi: 10.1016/S1567-1356(02)00087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Fradin C, Kretschmar M, Nichterlein T, et al. Stage-specific gene expression of Candida albicans in human blood. Mol Microbiol. 2003;47:1523–1543. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Barelle CJ, Priest CL, MacCallum DM, et al. Niche-specific regulation of central metabolic pathways in a fungal pathogen. Cell Microbiol. 2006;8:961–971. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ramírez MA, Lorenz MC. Mutations in alternative carbon utilization pathways in Candida albicans attenuate virulence and confer pleiotropic phenotypes. Eukaryot Cell. 2007;6:280–290. doi: 10.1128/EC.00372-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Brand A, MacCallum DM, Brown AJ, et al. Ectopic expression of URA3 can influence the virulence phenotypes and proteome of Candida albicans but can be overcome by targeted reintegration of URA3 at the RPS10 locus. Eukaryot Cell. 2004;3:900–909. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.4.900-909.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Fernández-Arenas E, Cabezón V, Bermejo C, et al. Integrated proteomics and genomics strategies bring new insight into Candida albicans response upon macrophage interaction. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007;6:460–478. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M600210-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Sandai D, Yin Z, Selway L, et al. The evolutionary rewiring of ubiquitination targets has reprogrammed the regulation of carbon assimilation in the pathogenic yeast Candida albicans. mBio. 2012;3:e00495–e00412. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00495-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Childers DS, Raziunaite I, Mol Avelar G, et al. The rewiring of ubiquitination targets in a pathogenic yeast promotes metabolic flexibility, host colonization and virulence. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:e1005566. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Chew SY, Ho KL, Cheah YK, et al. Glyoxylate cycle gene ICL1 is essential for the metabolic flexibility and virulence of Candida glabrata. Sci Rep. 2019;9:2843. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39117-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.MacPherson S, Larochelle M, Turcotte B. A fungal family of transcriptional regulators: the zinc cluster proteins. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006;70:583–604. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00015-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Laity JH, Lee BM, Wright PE. Zinc finger proteins: new insights into structural and functional diversity. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001;11:39–46. doi: 10.1016/S0959-440X(00)00167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Schöler A, Schüller HJ. A carbon source-responsive promoter element necessary for activation of the isocitrate lyase gene ICL1 is common to genes of the gluconeogenic pathway in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14:3613–3622. doi: 10.1128/MCB.14.6.3613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Roth S, Kumme J, Schüller HJ. Transcriptional activators Cat8 and Sip4 discriminate between sequence variants of the carbon source-responsive promoter element in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 2004;45:121–128. doi: 10.1007/s00294-003-0476-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Vincent O, Carlson M. Sip4, a Snf1 kinase-dependent transcriptional activator, binds to the carbon source-responsive element of gluconeogenic genes. EMBO J. 1998;17:7002–7008. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.23.7002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Hiesinger M, Roth S, Meissner E, et al. Contribution of Cat8 and Sip4 to the transcriptional activation of yeast gluconeogenic genes by carbon source-responsive elements. Curr Genet. 2001;39:68–76. doi: 10.1007/s002940000182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Soontorngun N, Larochelle M, Drouin S, et al. Regulation of gluconeogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is mediated by activator and repressor functions of Rds2. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27:7895–7905. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01055-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Ramírez MA, Lorenz MC. The transcription factor homolog CTF1 regulates beta-oxidation in Candida albicans. Eukaryot Cell. 2009;8:1604–1614. doi: 10.1128/EC.00206-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Martchenko M, Levitin A, Hogues H, et al. Transcriptional rewiring of fungal galactose-metabolism circuitry. Curr Biol. 2007;17:1007–1013. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.05.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Maicas S, Moreno I, Nieto A, et al. In silico analysis for transcription factors with Zn (II)(2) C (6) binuclear cluster DNA-binding domains in Candida albicans. Comp Funct Genomics. 2005;6:345–356. doi: 10.1002/cfg.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Klimova N, Yeung R, Kachurina N, et al. Phenotypic analysis of a family of transcriptional regulators, the zinc cluster proteins, in the human fungal pathogen Candida glabrata. G3. 2014;4:931–940. doi: 10.1534/g3.113.010199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable