Abstract
Elucidation of the structure and function of biomolecules provides us knowledge that can be transferred into the generation of new materials and eventually applications in e.g., catalysis or bioassays. The main problems, however, concern the complexity of the natural systems and their limited availability, which necessitates utilization of simple biomimetic analogues that are, to a certain degree, similar in terms of structure and thus behaviour. We have, therefore, devised a small library of six tridentate N-heterocyclic coordinating agents (L1–L6), which, upon complexation, form two groups of artificial, monometallic non-heme iron species. Utilization of iron(III) chloride leads to the formation of the 1:1 (Fe:Ln) ‘open’ complexes, whereas iron(II) trifluoromethanosulfonate allows for the synthesis of 1:2 (M:Ln) ‘closed’ systems. The structural differences between the individual complexes are a result of the information encoded within the metallic centre and the chosen counterion, whereas the organic scaffold influences the observed properties. Indeed, the number and nature of the external hydrogen bond donors coming from the presence of (benz)imidazole moieties in the ligand framework are responsible for the observed biological behaviour in terms of mimicking phenoxazinone synthase activity and interaction with DNA.
Keywords: iron, Schiff base, DNA binding, 2-aminophenol, biomimetic activity
1. Introduction
Nature exhibits an astonishing ability to construct sophisticated molecular machineries to target selected, otherwise hardly approachable by synthetic chemists, molecular transformations [1]. Metalloenzymes were recognized as one class of such species, with judiciously chosen transition metal ions and enzyme active sites being able to facilitate various redox processes in a catalytic and selective manner [2]. Knowledge gained from studies of their structure and function is of prime importance that renders chemistry the hallmark of modern science [3]. Nevertheless, the natural systems’ complexity necessitates the use of artificially constructed biomimetic analogues for further advancement of this discipline [4]. This solution provides access to simple, readily accessible species that retain certain structural features of enzymes, and so their chemical behaviour and function may become mimicked.
From transition metal cations that constitute the redox-active part of enzymes like copper, manganese, or iron, the latter one is of particular importance due to its low biotoxicity, wide availability in nature and electronic states that favour binding of O2 [5,6]. In particular, one may discriminate heme [7] and non-heme [8] Fe-based enzymes, classification, and functions that depend on the structural framework of its active site. The seminal, most widely studied examples of the former group involve studies on the families of horseradish peroxidases [9] and cytochromes P450 [10]. The second group is a much broader class of molecular species, which can be divided in accordance to the number of iron centres [8,11]. Notable representative examples include the bimetallic methane monooxygenase (MMO), which catalyses oxidation of hydrocarbons [12] or the monometallic ‘2-His-1-carboxylate facial triad’ of relevance for various oxidative transformations [13].
These oxidations are a result of the reductive dioxygen activation, which are dependent on the structural features of the artificial biomimetic analogue, specifically the coordination environment around the metallic centre(s) and its redox characteristics [14]. It is thus possible to generate small groups of structurally similar coordinating agents, where one could incorporate the chosen structural motif into the ligands scaffold and evaluate its effect on the biological outcome. Schiff base ligands were recognized as very potent candidates for the construction of such libraries due to their robustness and stability, facile synthetic methodologies and rich complexation behaviour [15,16]. Specifically, iron(II/III) complexes were investigated as DNA binding agents [17,18,19] or as phenoxazinone synthase (PHS) artificial analogues [16,20,21,22,23,24,25]. Interestingly, in Nature it is the copper(II) ion that catalyses oxidation of o-aminophenols to phenoxazinones [26,27], which means that PHS-active iron systems could be used to gain additional insight into the oxidative biological mechanisms [20,28].
Owing to our experience in the construction of the imine-scaffolded metallosupramolecular architectures [29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37] and bioassays [30,36,38,39,40], we designed and synthesized a small library of Schiff base ligands (Scheme 1), where the main structural difference involves the different number and disposition of the hydrogen bond donors.
Scheme 1.
Schematic representation of ligands synthesized for the purpose of this work; green frame denotes the family of benzimidazole-scaffolded ligands whereas blue frame shows the family of pyridine-scaffolded coordinating agents.
Coordination with iron(II)/(III) metallic centres led to the formation of two families of complexes (‘open’ and ‘closed’ species) depending on the applied counterion, which were in turn investigated as artificial phenoxazinone synthase analogues and DNA-binding agents. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report that studies the effect of H-bonding on the multifunctional behaviour of library of Schiff base iron agents in terms of bioassays.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization
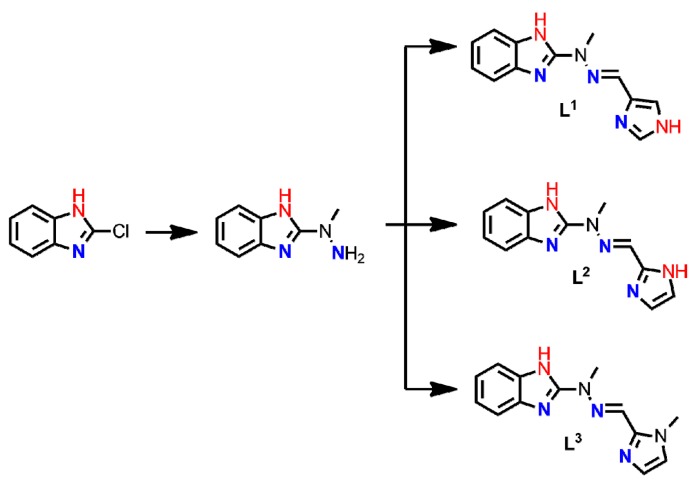
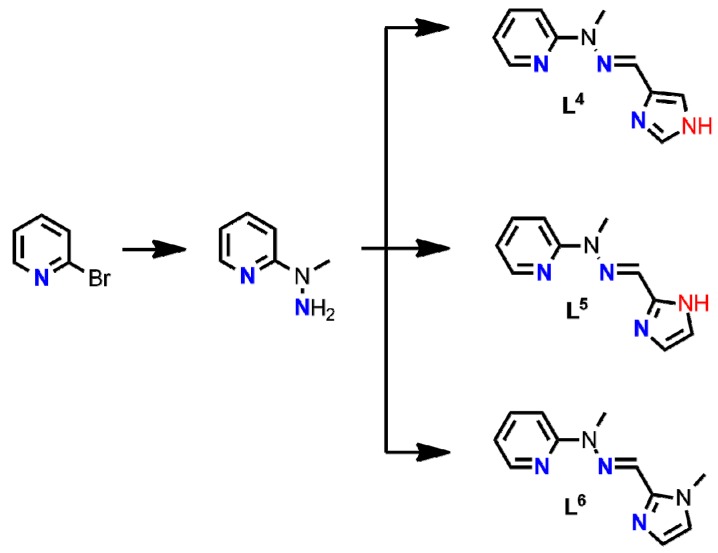
A series of six hydrazone Schiff base ligands L1–L6 was successfully synthesized in a two-step synthetic protocol. [31] Commercially available 2-chlorobenzimidazole (in L1–L3) or 2-bromopyridine (in L4–L6) were subjected to nucleophilic substitution reaction with an excess of methylhydrazine and the product was reacted with the corresponding imidazolecarboxaldehyde. As a result, two sets of coordinating agents were obtained in 41.1–90% yields, with the common N3-tridentate meridional binding subunit which differed in the number (0–2) and topology (axial vs. equatorial) of donor hydrogen bonds (Scheme 1).
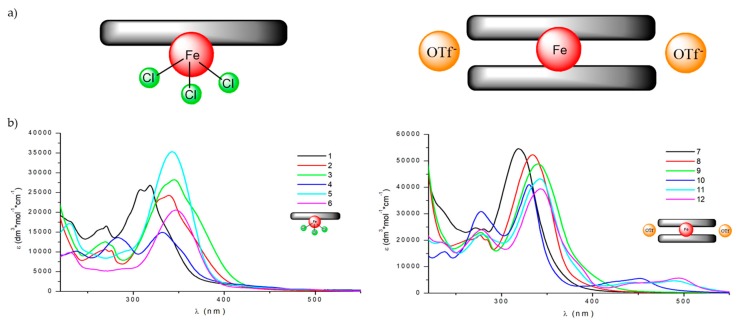
Their UV-Vis and NMR (when possible) solution studies (Figure 1b, Figures S11–S13) indicate stability of synthesized complexes in solution, indicating that the organic Schiff base ligands do not decoordinate. Interestingly, from the family of ‘closed’ species, the ones with the pyridine moiety 10–12 were found to be diamagnetic, whereas the benzimidazole-scaffolded ones 7–9 are paramagnetic at room temperature.
Figure 1.
a) Schematic representation of compounds A: [Fe(Lx)Cl3] ‘open’ (left) and B: [Fe(Lx)2](OTf)2 ‘closed’ systems (right). b) UV-Vis spectra of ‘open’ 1–6 (left) and ‘closed’ system complexes 7–12 (right) recorded in MeOH at c = 2 × 10−5 M.
2.2. Description of Crystal Structures
The structures of iron complexes with six different ligands (L1–L6, cf. Scheme 1) were obtained. The crystal structures confirmed that these complexes can be formed either with one or two tridentate ligand molecules, therefore confirming our initial assumptions. Out of 12 possible compounds studied, we were able to determine crystal structures for nine complexes (cf. Experimental Section, Electronic Supplementary Information Figures S32–S35.
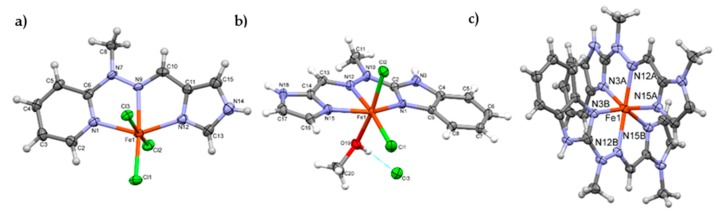
The first group consists of neutral complexes with the general formula [Fe(Lx)Cl3] (with one exception of 2, which is ionic and contains one coordinated methanol molecule instead of one of the chloride anions, additional Cl acts as a counterion). Figure 2 shows a representative example of these complexes.
Figure 2.
Representative perspective views of ‘open’ (4—a, 2—b)) and ‘closed’ complexes (9—c); ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level, hydrogen atoms are shown as spheres of arbitrary radii. Thin blue line in 2 represents the O–H···Cl− hydrogen bond.
In all these complexes Fe(III) cations are six coordinated, by three nitrogen atoms from ligand molecule and three Cl− anions (in case of 2, two Cl− and methanol oxygen, Figure 2b) in a slightly distorted octahedral fashion. The distortion is mainly caused by trans-coordination of two nitrogen atoms of Lx molecule, appropriate N1-Fe-N15 angles differ significantly from 180°, they are in a range 147–148°. Table S1 lists the relevant geometrical features for all the complexes. In this group of complexes, the crystal structures are determined mainly by N-H···Cl (C-H···Cl) hydrogen bonds, and often by secondary π···π or C-H···π interactions (hydrogen bond data are listed in Table S2).
Second group contains cationic complexes of general formula [Fe(Lx)2]2+, with two triflate anions balancing the charge. Also in these cases Fe(II) is six coordinated, by six nitrogen atoms from two ligand molecules, but distortions from ideal octahedral geometry are larger than in former group (cf. Table 1). Figure 2c shows example of the member of this group (9). In the crystal structures of this group the N-H···O (triflate) or C-H···O hydrogen bonds are always present. Probably due to more complicated packing of different moieties, in almost all examples the voids filled by solvent molecules. Table S1 contains also information of the size of the voids, determined as a part of the unit cell. All ligand molecules are almost or approximately planar, as may be seen by analyzing the dihedral angles between planar fragments of the molecules (Table S1).
Table 1.
Kinetic parameters for complexes 1–12.
| Catalyst | Vmax (10−3Ms−1) | KM (10−3M) | kcat (h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Fe(L1)Cl3] (1) | 3.71 | 1.45 | 185.25 |
| [Fe(L2)Cl3] (2) | 2.55 | 2.16 | 127.30 |
| [Fe(L3)Cl3] (3) | 3.45 | 1.95 | 172.30 |
| [Fe(L4)Cl3] (4) | 2.68 | 2.02 | 134.05 |
| [Fe(L5)Cl3] (5) | 2.07 | 2.02 | 103.34 |
| [Fe(L6)Cl3] (6) | 3.01 | 2.19 | 150.49 |
| [Fe(L1)2](OTf)2 (7) | 3.98 | 1.56 | 199.40 |
| [Fe(L2)2](OTf)2 (8) | 1.96 | 2.08 | 97.68 |
| [Fe(L3)2](OTf)2 (9) | 3.68 | 1.86 | 183.80 |
| [Fe(L4)2](OTf)2 (10) | 0.86 | 1.79 | 42.76 |
| [Fe(L5)2](OTf)2 (11) | 1.30 | 1.89 | 65.14 |
| [Fe(L6)2](OTf)2 (12) | 2.13 | 2.08 | 106.53 |
In the crystal structures, Coulombic interactions between ions and directional N-H···O hydrogen bonds between cations and anions (Table S2) are important factors for final crystals architectures.
2.3. Catalysis and DNA Binding Affinity
The structural similarities present within each group of iron complexes represent a great starting point for determination of the structure/properties dependencies, specifically an influence of the number and disposition of H-bonding within the ligands framework on their biomimetic behavior as: (i) artificial phenoxazinone synthase analogues; (ii) DNA-recognition binders.
2.3.1. Phenoxazinone Synthase (PHS) Activity
Oxidation of 2-aminophenol can be done using dioxygen or hydrogen peroxide [21], using different solvent as an environment [24] and what is the most important using a wide variety of complexes. Examples in the literature include: cobalt(II) [21,22,23], manganese(II) [21] or iron(III) compounds [20,28].
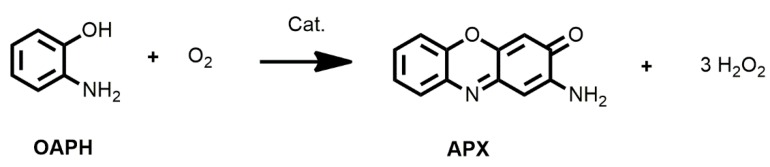
At room temperature and in the presence of air, the present series of iron(II)/(III) complexes catalyze the aerobic oxidative dehydrogenation of o-aminophenol (OAPH) to the corresponding light-absorbing 2-aminophenoxazine-3-one chromophore (APX) (Scheme 2) and the process is strongly dependent on the chosen complex.
Scheme 2.
Schematic representation of oxidation of 2-aminophenol (OAPH) to 2-aminophenoxazine-3-one chromophore (APX).
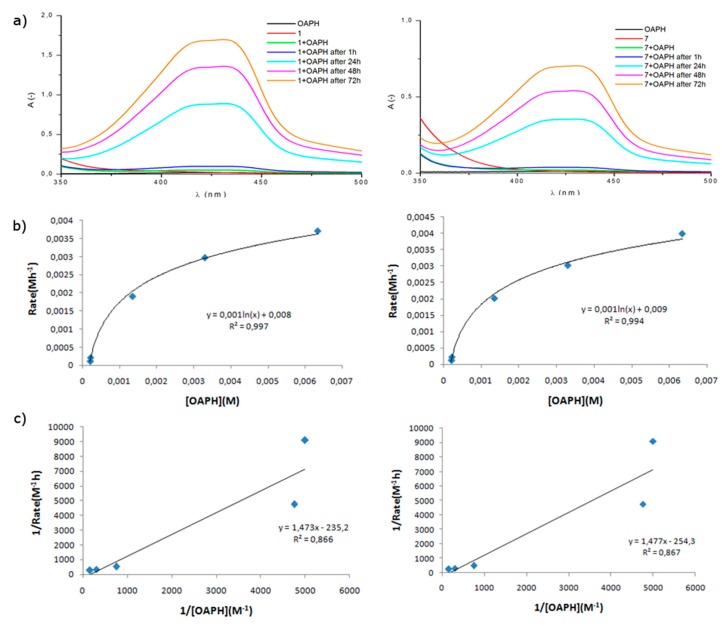
First of all, a ten-fold excess of o-aminophenol solution (2 × 10−4 M) was added to methanolic solutions of the chosen iron complex (2 × 10−5 M), so that an excess of substrate is present and first-order kinetic reaction mechanism could be maintained. The reaction was carried out at room temperature in the presence of air, without any base to minimize the possibility of auto-oxidation of OAPH [41] and in methanol for solubility issues. The catalytic properties of the complexes were monitored spectrophotometrically by observing the increasing intensity of the absorption band at 433 nm, which corresponds to the formation of APX chromophore. Measurements were made separately for the complex, o-aminophenol and also immediately after mixing of the substrates as a function of time. The chosen measurement time intervals (1 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h) are a result of minimal spectroscopic changes at first hours, most probably associated with high iron(III) oxidation state for ‘open’ complexes and sterically blocked ‘closed’ complexes. Spectra registered for complexes 1–12 are gathered in the Supplementary Information (Figures S37–S46) and the most catalytically active complexes from each of the two groups (1 for ‘open’ and 7 for ‘closed’), are shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3.
a) The spectral profile showing the growth of 2-aminophenoxazine-3-one at 433 nm due to addition of complex 1 (left) and 7 (right) to 2-aminophenol dissolved in methanol. The spectra were recorded under aerobic conditions during the three days. b) Plot of rate vs. concentration for complex 1 (left) and 7 (right). c) Linewear–Burk plot of phenoxazinone synthase-like activity for complex 1 (left) and 7 (right).
Thanks to observation of changes in the intensity of bands, it is possible to confirm the catalytic properties of the studied complexes, since blank tests without catalyst (Figure S36) confirm that the latter is necessary to obtain the observed conversion of OAPH to APX.
To gain deeper mechanistic insight into oxidation of OAPH with studied iron(II/III) complexes, kinetic studies were performed at room temperature for each system by varying the relative concentration of complexes from 2 × 10−4 M–2 × 10−6 M and measurement of the reaction initial rates at 433 nm. By ensuring an excess of the substrate with regard to the complex, the initial rates method exhibits a first-order dependence on complex concentration and was treated with the Michaelis–Menten model, in which linearization affords a double reciprocal Lineweaver–Burk plot allowing analysis of the following parameters: the maximum velocity (Vmax), binding constant (KM), and rate constant (kcat) (Figure 3b,c) and Figures S37–S46, Supplementary information). Indeed, rate saturation kinetics was observed, which confirms the validity of the applied kinetic model and also indicates that the reaction involves the formation of complex-substrate intermediate in a pre-equilibrium stage and its subsequent irreversible oxidation is associated as the rate-determining step of the catalytic cycle [25].
Table 1 includes all kinetic parameters determined for twelve iron complexes under study used in oxidation of OAPH, with the range of corresponding values being: Vmax = 0.86–3.98 [10−3Ms−1], KM = 1.45–2.08 [10−3 M] and kcat = 42.76–199.40 [h−1].
Comparison of different catalysts can be done by kcat, which is also expressed as the turnover number and can be related to its activity in a given time unit. Table 2 compares our compounds with different ones found in the literature and shows that our systems can be regarded as functional models of phenoxazinone synthase (PHS) which is involved in the biosynthesis of Actinomycin D, the latter of which is a naturally occurring nontrivial APX derivative exhibiting anti-cancer properties [42,43,44]. We did observe however that activity of each complex is an interplay of its ‘primary’ (open vs. closed) and ‘secondary’ (number and disposition of H-bonds) structural features.
Table 2.
Catalytic oxidation of o-aminophenol with transition metal complexes.
| Catalyst | Solvent | kcat (h−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Fe(L1)Cl3] (1) | Methanol | 185.25 | This work |
| [Fe(L1)2](OTf)2 (7) | Methanol | 199.40 | This work |
| [FeCl2(La)] | DMF | 137.0 | [28] |
| [Fe(Lb)Cl3] | Methanol | 56.0 | [20] |
| [{Fe(Lc)(4,4′-byp)ClO4}]n | Methanol | 32.36 | [42] |
| [FeLcCl]2 | Methanol | 196.18 | [42] |
| [Co(Ld)(N3)3] | Methanol | 33.26 | [23] |
| [Co(Le)(N3)2] | Methanol | 54.0 | [45] |
| [Co(Lf)Cl(H2O)]Cl·H2O | Methanol | 13.68 | [46] |
| [LgCo(Lh)2]ClO4 | Methanol | 11.48 | [47] |
La = 1,3-bis(5′-methyl-2′-thiazolylimino)isoindoline; Lb = N,N’-Bis(2-Methylbenzimidazolyl) pyridinediamide; Lc = N,N’-Disalicylidene-1,2-propylenediamine; Ld = (2-pyridylmethyl)(2-pyridylethyl)amine; Le = 2-{[3-(3-Dimethylaminopropylamino)-propylimino]-methyl}-6-methoxy-phenol; Lf = N,N’-bis(pyridin-2-ylmethylene)-2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diamine; Lg = N,N’-bis(3-methoxysalicylidehydene)cyclohexane-1,2-diamine; Lh = 4-aminopyridine.
Supplementary Table S3, which helps in following the structural features as a function of catalytic parameters is provided in Supplementary Information. It must be noted that whereas higher kcat denotes higher activity of a given complex, lower KM values indicate stronger binding of complex to OAPH which is related to TON, yet might be limited by further reaction processes.
Within the group of ‘open’ complexes 1–6, KM decreases in the order of L6 > ~L2 > L5 = L4 > L3 > L1 and seems to be affected by the ligands H-bonding scaffold. Indeed, whereas the highest value is found for L6 with no H-bond donors, ca. 10% decrease was observed for complexes with scaffold comprising one NH moiety. Interestingly, its relative disposition (L5 vs. L4) does not seem to have relevant influence herein. Further decrease in the series exhibits iron(III) complex coordinated to benzimidazole-imidazole ligand L1 of a mixed axial/equatorial H-bond disposition. Quite unexpectedly, isomeric ligand L2 from iron complex interacts with OAPH in a similar fashion as L6, though their TON values differ. Since coordination number 6 of Fe(III) metal ion can be safely termed as saturated, its interaction with OAPH is possible by assuming exchange of at least one coordinated chloride anion with solvent molecules. Indeed, X-ray structure that we provide for complex 2 proves that it was possible to isolate such species in the solid state as [Fe(L2)Cl2(MeOH)]Cl. Consequently, OAPH can be assumed to coordinate to iron(III) via phenoxo anion, with concomitant exchange of coordinated methanol molecule. This is where non-binding NH2 moiety from coordinated OAP group could additionally interact with NH units of ligand scaffold. (compare with proposed mechanism in Section 2.3.2). TONs change within the order of L1 > L3 > L6 > L4~L2 > L5 and seem to not be dependent on H-bonding moieties (specifically compare KM and TONs of 4 and 6), which also prove that the rate-determining step would be associated with irreversible oxidation of the OAP-catalyst complex, not the binding of OAPH with catalyst per se.
Interesting comparison comes with studies of the ‘closed’ complexes. One could expect that they would not be catalytically active, since it should be hard to dissociate one of the tridentate imine ligands. In addition, 1HNMR studies of diamagnetic 10–12 complexes do not show formation of multiple species in solution. It turns out that TONs decrease in the following order L1 > L3 > L6 > L2~L5 > L4, with the most active complexes being ones based on L1 and L3 ligands – similarly as in the ‘open’ class. Intriguingly, KM decreases in exactly the same order, which would imply that appropriate number and disposition of H-bonding between OAPH and coordinated ligand should be responsible for generation of OAPH···complex interactions. NH on imidazole moiety seems to influence such an interaction more significantly than the benzimidazole unit, however since TONs and KM follow the same trend, redox Fe(II/III) oxidation changes would explain oxidation of OAPH in spite of binding of the latter one via H—bonding and not cationic centre. All in all, ‘closed’ species are somewhat less efficient for oxidation of OAPH than ‘open’ species.
2.3.2. Proposed Mechanism of OAPH Oxidation
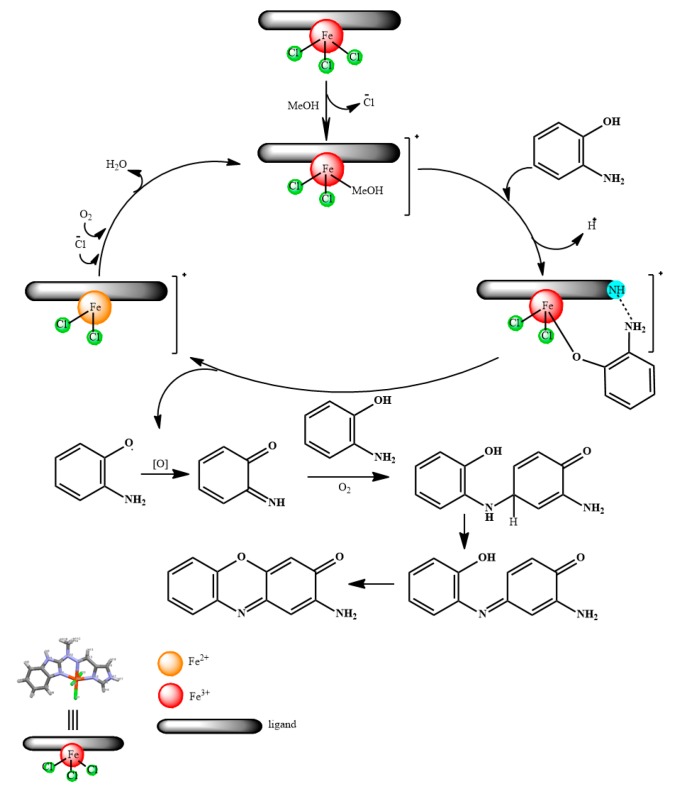
On the basis of obtained results and literature data [25,41], we would like to show proposed mechanism of oxidation of 2-aminophenol (OAPH) to 2-aminophenoxazine-3-one (APX) with ‘open’ iron complexes investigated herein (Scheme 3).
Scheme 3.
Proposed mechanism of phenoxazinone synthase like activity of complex 1 in methanolic environment of reaction.
As was noted earlier, ‘open’ species are prone to ligand exchange and this is what happens in the first step between chloride and methanol molecule. Such a configuration allows the molecule of complex to interact with molecule of 2-aminophenol (OAPH), which results in coordination of the latter one to the metallic centre in its deprotonated form, with simultaneous extrusion of the methanol solvent molecule to the environment and additional interactions from the ligand/H-bond moieties. Subsequent oxidation is presumed to be the rate-determining step, which could explain certain time-lag associated with the initial reaction times. Obtained 2-aminophenoxazinone (APX) is formed on the basis of quinone imine intermediate, reacting with second molecule of OAPH and a series of subsequent redox transformations [25,41].
2.3.3. DNA Binding Affinity
The compounds may interact with DNA in a variety of ways: they can combine by electrostatic interaction with a phosphate sugar backbone, intercalate between pairs of bases, covalently bind with nucleobases or attach in major or minor grooves [48]. Binding ability of metal complexes to DNA can be studied by using spectroscopic methods such as: electronic absorption titration [49], fluorescence competitive binding with ethidium bromide (EB) [50] and circular dichroism (CD) measurements [51]. Based on the observed changes in the spectrum the type of interaction may be specified.
Absorption Titration
The absorption titration experiment provides basic information concerning the presence and strength of interactions between compounds and DNA. The most important and straightforward indication is hypochromism in the spectrum of compound that increases together with the increase of concentration of CT-DNA in the sample solution [52,53]. Monitoring of this phenomenon allows one to evaluate the ability of compounds to interact with DNA double helix.
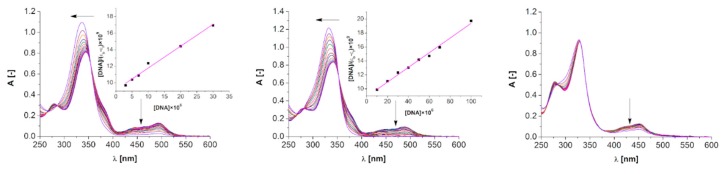
Absorption spectra of all complexes in the presence of CT-DNA were measured in the range of 250–600 nm (Figures S47–S49). Interestingly, neither of ‘open’ complexes interact with CT-DNA, and only three ‘closed’ complexes did show spectral changes attributable to specific complex-nucleic acid interactions (10, 11, 12—Figure 4). It shows the significance of the “secondary” structure of potential metallodrugs (if we say that the ligand framework and metal salt are the “primary” structure, then their mutual arrangement in the space may be called the “secondary” structure of the system). Interestingly, 10–12 employ pyridine moiety in the ligands “primary” structure, which would imply that introduction of additional H-bonding through benzimidazole moiety hampers such process. However, not only the pyridine/benzimidazole bias in the ligand scaffold is visible, since the topology and substitution pattern of imidazole is relevant for DNA binding as well. Compounds 11 and 12 with 2-imidazole substituent interact with DNA much stronger (hypochromism of MLCT band at ca. 485 nm of 96% and 79%, respectively) than 10 with 4-imidazole substituent (hypochromism of MLCT band of 45%). At the same time blocking of hydrogen bonding donor site N-H as N-CH3 in imidazole unit facilitates the DNA binding (comparison of L5 and L6 in complexes 11 and 12). One may say that two-level recognition in the presented case is observed and is crucial for the DNA binding phenomenon: (i) lack of hydrogen bonding donors in the “primary” structure and (ii) ‘closed’ composition of the “secondary” structure of complex.
Figure 4.
Absorption titration of 12 (left), 11 (middle) and 10 (right) with increasing concentrations of CT-DNA (0–100 µM). Arrows show hypsochromic and hypochromic changes upon increasing CT-DNA concentration. Inset: plot of [DNA]/(εa − εf) versus [DNA]; ▪,experimental data points; solid line, linear fitting of the data.
As mentioned before, interaction of complexes 10, 11 and 12 with DNA is visible as a decrease of the intensity of the MLCT band at ca. λ = 485 nm. In general, a strong hypochromism in the absorption spectra is an indication of intercalative binding mode, since the distance between intercalated compound and DNA bases decreases and the π electrons of both combine [54]. Only for 11 and 12 the binding constants (Kb) were calculated, since the diminution of the MLCT band in case of 10 did not reach 50%. In the face of this fact, we focused in our further discussion on 11 and 12. Both complexes 11 and 12, as well as the corresponding ligands (L5 and L6), are stable in the biological medium employed in this study (10 mM TrisHCl, 5 mM NaCl, 50 mM pH 7.5) as shown in Figure S50. In general, 12 binds to the DNA twice more efficiently than 11 what is reflected in the intrinsic binding constants Kb = 2.8797 × 104 (R2 = 0.98602 for 6 points, inset Figure 4) and Kb = 1.1820 × 104 (R2 = 0.99087 for 8 points, inset Figure 4), for 12 and 11, respectively. In case of both complexes, a hypsochromic shifts of ca. 8 nm of ILCT bands (ca. 335 nm) were observed. Changes in the intensity and position of the ligand-derived bands may suggest electrostatic interaction with CT-DNA. On the other hand, there is an isobestic point at 353 nm for complex 11 and 354 nm for complex 12 as well as hypochromism of MLCT bands at 488 nm and 493 nm for complexes 11 and 12, respectively, indicating intercalative binding to DNA [15,55]. The standard Gibb’s free energy for DNA binding is −25.03 and −22.86 for 12 and 11, respectively, which indicates the spontaneous binding of both compounds with DNA. Also, the ability of ligands L5 and L6 to bind with CT-DNA was examined (Figure S51). Since no significant changes in the intensity of bands as increasing amounts of DNA were added, one may assume that they do not interact with DNA in non-coordinated form.
Competitive Binding Fluorescence Experiment
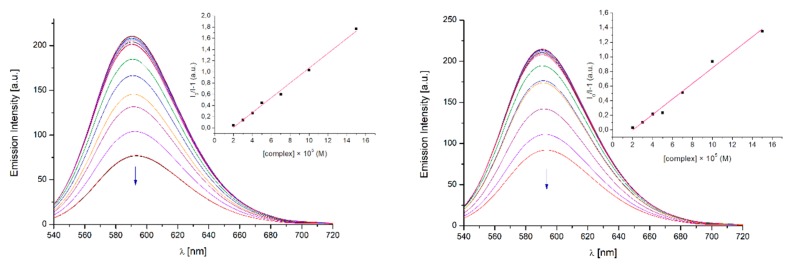
In order to further investigate the strength of intercalation mode of synthesized complexes with DNA the competitive binding experiments with ethidium bromide (EB) as a probe were carried out. EB is a weak luminescent compound exhibiting high affinity to the DNA helix. Formation of a DNA–EB complex enhances its emission at λmax = 590 nm (λexc = 467 nm) due to strong intercalation of EB planar phenanthridine rings between adjacent base pairs of the DNA helix. Displacement of EB from its DNA–EB complex due to gradual titration by a competing molecule results in subsequent quenching of its emission band.
Competitive binding experiments with DNA-EB complex showed that compounds 11 and 12 are able to bind with the DNA scaffold and release EB from its complex. Significant decrease in emission intensity was observed for both complexes, which indicates that complexes bind with DNA in spaces occupied by EB or EB is released due to conformational changes in the double helix. The quenching constants are: KSV = 1.32 × 104 and KSV = 1.06 × 104 for 12 and 11 (Figure 5), respectively. Based on quenching constants, it can be concluded that complex 12 is slightly better binder than complex 11, which is consistent with the results obtained in the electronic absorption titration experiments. This could be explained by the fact that lack of hydrogen bonds in the “primary” structure of 12 results in easier insertion between the base pairs of the DNA helix than 11. Both complexes act on the principle of intercalation with DNA due to the “secondary” ’closed’ structure.
Figure 5.
Emission spectra of ethidium bromide (EB) bound to CT DNA in the presence of increasing amount of 12 (left) and 11 (right). Arrow shows the hypochromic changes upon increasing 12 or 11 concentration. Inset: Stern–Volmer plot of I0/I − 1 versus [12] or [11] for the titration of EB-CT DNA complex; ▪, experimental data points; solid line, linear fitting of the data.
DNA Binding Investigation via CD
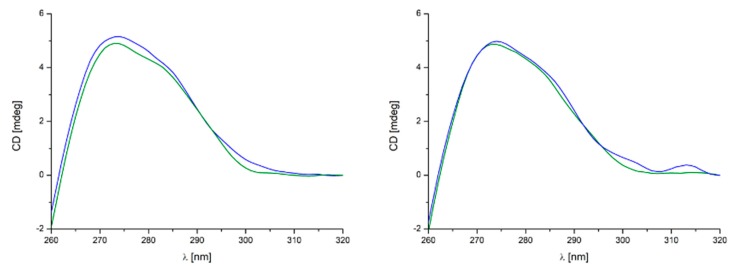
The study of morphological changes of DNA structure caused by the interaction of DNA with compounds can be observed using circular dichroism (CD) measurements. This technique is a very sensitive and informative method for studying the structural changes of the secondary structure of nucleic acids and proteins. The B-DNA helix exhibits two conservative bands due to its helicity—negative one at ca. 250 nm and a positive one at ca. 270 nm [50]. CD experiments were performed on the 12-mer oligo DNA of composition d(GTTAATCGCTGG) in the presence of different amounts of compounds 11 and 12 in the 1–30 eq. range. No significant CD perturbation under the above conditions was observed. However, after thermal treatment (70 °C) and subsequent slow cooling down of the sample solution, DNA underwent conformational changes in the presence of 12 corresponding to the variations observed in the positive band at 270 nm and are more pronounced for this ‘hydrogen bond free’ complex than in the case of 11. Based on CD studies one may hypothesize that 12 is more effective than 11 (Figure 6) in interacting with DNA by preventing its correct annealing. Such findings from CD spectra correspond well with the results from DNA titration and EB competitive binding. Moreover, the differences observed in the CD DNA spectrum due to 12, and in particular, the decrease of intensity of the positive band at 270 nm, resemble similar effects previously associated to well-characterized ligand-induced DNA conformational perturbations [16].
Figure 6.
CD spectra relative to DNA duplex (2 µM) in the presence of 30 equiv. of 12 (left) and 11 (right) in Tris HCl 5 mM NaCl 50 mM (pH 7.5) at 20 °C (blue line) and after thermal treatment at 70 °C (5 min.) and subsequent cooling to 20 °C over 1 h in the same buffer (green line).
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Methods
All reagent and solvent were purchased form commercial sources and used as received.
Elemental analyses for C, H, and N were carried out using an Elementar Analyser Vario EL III (Elementar Analysensysteme GmbH, Hanau, Germany). Infrared spectra were recorded on an iS50 FT-IR, ThermoScientific Nicolet (Thermo Fisher Scientific wissenschaftliche Geräte GmbH, Wien, Austria). Electrospray ionisation mass spectroscopy (ESI-MS) was performed using Mass Spectrometer ZQ Waters (Miromass&Waters; Milford, USA) by dissolving the powder samples of compounds in methanol at ~10−4 M. The cone voltage values are depicted in each spectrum in Electronic Supplementary Material. 1H and 13C-NMR spectra were run on a Bruker Ultrashield 300 MHz spectrometer (Bruker, Karlsruhe, Germany) or Varian Gemini 400 MHz spectrometer (L1) (Varian, Darmstadt, Germany) and were calibrated against the residual protonated solvent signals with chemical shifts represented in ppm ((CD3)2SO: 2.50 ppm, water: 3.33 ppm; CD3CN: 1.94 ppm, water: 2.13 ppm; CDCl3: 7.26 ppm, water: 1.56 ppm; CD3OD: 3.31 ppm, water: 4.87 ppm). Each time ca. 2 mg of sample was dissolved in 0.6 mL of deuterated solvent.
CT-DNA, ethidium bromide, Tris and NaCl were supplied from Sigma Aldrich (Sigma Aldrich, Poznań, Poland) and used without further purification. CT-DNA was dissolved in Tris Buffer (5 mM TrisHCl, 50 mM NaCl, pH 7.25) prior to use. The CT-DNA solution gave a ratio of UV absorbance of 1.82:1 at 260 and 280 nm, indicating that the CT-DNA sample was sufficiently free from protein [56,57]. CT-DNA concentration per nucleotide was determined from the UV absorbance at 260 nm using the extinction coefficient ε260= 6600 dm3·mol−1·cm−1 [58]. Oligo DNA was supplied from Genomed S.A. (Genomed S.A., Warsaw, Poland) and used without further purification. Electronic absorption titrations of compounds were performed on Jasco V-770 spectrophotometer (Jasco Europe S.R.L., Cremella, Italy) equipped with a Peltier at a temperature of 20 °C between 600 and 250 nm, in 10 × 10 mm quartz cells. Emission spectra in the competitive fluorescence titration experiments were measured at room temperature on a JASCO FP-6200 spectrofluorimeter (Jasco, Tokyo, Japan) in the range 540–720 nm with excitation and emission slits of 10 nm and excitation wavelength λexc = 467 nm. CD experiments were performed by a Jasco J-810 spectropolarimeter (Jasco Europe S.R.L., Cremella, Italy) equipped with a Peltier PTC-423S/15 (Jasco Europe S.R.L., Cremella, Italy) with a response time of 4 s, a scanning speed of 50 nm/min and a bandwidth of 1.0 nm. Freshly prepared stock solutions of complexes (at concentration 2 × 10−3 M) were taken for all spectroscopic investigations of the binding mode with DNA. It needs to be emphasized that compounds are stable in this medium for several days. After this time some precipitate starts to occur.
3.2. Synthesis of Ligands
3.2.1. Synthesis of Ligands L1–L3
Synthesized ligands (Scheme 4 and Scheme 5) were obtained as yellow, crystalline solids and their identity and purity were confirmed by routine analytical methods (1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, melting points, ESI-MS, Figures S1–S10, S14–S19). These species were subsequently reacted in equimolar ratio with iron(III) chloride and 2:1 (Lx:M) iron(II) trifluoromethanesulfonate salts, respectively to obtain two classes of iron-based coordination compounds: A: [Fe(Lx)Cl3] ‘open’ and B: [Fe(Lx)2](OTf)2 ‘closed’ systems (Figure 1a). In general, weakly coordinating triflates do not form coordination bonds with Fe(II) ions, therefore two, tridentate Schiff base ligands fill its coordination sphere to form octahedrally coordinated ‘closed’ species. In the presence of chlorides the octahedral binding mode is preserved, nonetheless Fe(III) ions are bound by only one chelate imine ligand; the remaining coordination sites are potentially labile and are filled by three chlorides, hence ‘open’ species. Names refer to the coordination sites of the central metal ion, since chlorides are in fact more susceptible to exchange in the solvent medium than the chelating Schiff base ligand, which is also readily visible upon comparison of X-ray structures (e.g., 2 vs. 4). We managed to successfully synthesize and characterize all 12 complexes (Figures S20–S31), 9 of which also by means of X-ray crystallography, and confirmed their structural character within each group, that is amenable to both the oxidation state of iron and the coordinative strength of the anion chosen during the synthesis. Details are included in Section 3.
Scheme 4.
Schematic representation of ligands L1–L3.
Scheme 5.
Schematic representation of ligands L4–L6.
The first step:
At two-necked round-bottomed flask 2-chlorobenzimidazole (8.00 g, 0.05 mol) was weighed and placed under argon atmosphere. Methylhydrazine (11.9 g, 0.25 mol) in five-fold excess was dissolved in a anhydrous ethanol and was added to the reaction mixture, which was warmed to 80 °C and stirred for 2 h. The white, crystalline product was filtered on Büchner funnel and dried under vacuum. Yield 68.2% (5.8 g, 0.036 mol).
The next step:
-
-
for L1: condensation of 4-imidazolecarboxyaldehyde with 2-(1-methyl-hydrazine)-benzimidazole was performed. At two-necked round-bottomed flask 2-(1- methylhydrazine)benzimidazole (1.00 g, 6.16 mmol) was placed under argon atmosphere. The 4-imidazolecarboxyaldehyde (0.591 g, 6.16 mmol) was dissolved in a anhydrous ethanol and was added to the reaction mixture. Yellow suspension was formed and the reaction mixture was stirred for 24 h at 60 °C. Yellow clear solution was cooled to room temperature and the precipitate appeared, which was filtered by vacuum filtration, washed with anhydrous ethanol and dried under vacuum. Yield 80% (1.184 g, 4.9 mmol.)
ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 241 (100) [HL1]+, 263 (10) [NaL1]+; ESI-MS(−): 239 (100) [L1 − H]−. IR: ν(N-H)br 3300–2500; ν(C=C)ar 1596, 1560; ν(C-N) 1451; ν(C=N)ar 1277; ρ(C-H)ar. 1162, 1091; γ(C-H)ar. 942, 737, 623 cm−1. 1H-NMR ((CD3)2SO, 300 MHz): δ (ppm) 12.38 (s, 0.7H, NH(i/j)); 11.53 (s, 0.7H, NH(i/j)); 7.89 (s, 1H, Hh); 7.78 (s, 1H, Hf); 7.31 (s, 3H, Hb,c,g); 7.01 (s, 2H, Ha,d); 4.37 (s, 0.7H, NH(i/j)); 3.56 (s, Me(e)). 1H-NMR ((CD3)2SO + K2CO3, 400 MHz): δ (ppm) 7.80 (s, 1H, Hh); 7.77 (s, 1H, Hf); 7.38 (s, 1H, Hg); 7.32–7.28 (dd, 2H, J = 5.8, 3.2 Hz, Hb, c); 7.00–6.96 (dd, 2H, J = 5.9, 3.2 Hz, Ha,d); 3.56 (s, Me(e)). 13C-NMR ((CD3)2SO + K2CO3, 75 MHz): δ (ppm) 154.5, 138.7, 137.3, 131.9 (2C), 128.9, 125.2, 119.9 (2C), 112.7 (2C), 31.1. Melting temperature: 176–179 °C.
-
-
for L2: condensation of 2-imidazolecarboxyaldehyde with 2-(1-methyl-hydrazine)-benzimidazole was performed. At two-necked round-bottomed flask 2-(1- methylhydrazine)benzimidazole (1.00 g, 6.16 mmol)was weighed and placed under argon atmosphere. 2-Imidazolecarboxyaldehyde (0.591 g, 6.16 mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous ethanol and was added to the reaction mixture. Yellow suspension was formed, and the reaction mixture was stirred for 24 h at 60 °C. Yellow clear solution was cooled to room temperature and evaporated to dryness. The resulting solid was dissolved in methanol and boiling acetonitrile was added to the flask. Cooling of the reaction mixture resulted in formation of pale pink crystalline product. The precipitate was filtered by vacuum filtration, washed with anhydrous ethanol and dried under vacuum to give 1.24 g (5.16 mmol) of ligand. The supernatant was concentrated to minimal amount of volume and the next part of precipitate was obtained 0.140 g (0.58 mmol). Total yield is 91% (1.38 g, 5.74 mmol).
ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 241 (40) [HL2]+, 263 (100) [NaL2]+; ESI-MS(−): 239 (100) [L2 − H]−. IR: ν(N-H)br 3400–2400; ν(C=C)ar. 1552; ν(C-N) 1452; ν(C=N)ar 1271; ρ(C-H)ar. 1145, 1040; γ(C-H)ar. 945, 737 cm−1. 1H-NMR ((CD3)2SO, 300 MHz): δ (ppm) 12.33 (s, 1H, NH(i)); 11.66 (s, 1H, NH(j)); 7.70 (s, 1H, Hf); 7.45–7.28 (m, 3H, Hb, c, g); 7.10–6.99 (m, 3H, Ha, d, h); 3.59 (s, Me(e)). 13C-NMR ((CD3)2SO, 75 MHz): δ (ppm) 154.2, 144.9, 143.3, 134.1, 129.8, 127.8, 121.2, 120.4, 118.2, 116.9, 109.7, 31.7. Melting temperature: 295–306 °C. At 295 °C ligand started to become darker and decomposed at 306 °C.
-
-
for L3: condensation of 1-methyl-2-imidazolecarboxyaldehyde with 2-(1-methyl-hydrazine)-benzimidazole was performed. At two-necked round-bottomed flask 2-(1- methylhydrazine)benzimidazole (1.00 g, 6.16 mmol)was weighed and placed under argon atmosphere. The 1-methyl-2-imidazolecarboxyaldehyde (0.704 g, 6.16 mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous ethanol and was added to the reaction mixture. Yellow suspension was formed and the reaction mixture was stirred for 24 h at 60 °C. Clear yellow solution was cooled to room temperature and kept in fridge. Yellow crystals were filtered by vacuum filtration, washed with anhydrous ethanol and dried under vacuum. Yield is 80% (1.26 g, 4.96 mmol).
ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 255 (30) [HL3]+, 277 (100) [NaL3]+; ESI-MS(−): 253 (100) [L3 − H]−. IR: ν(N-H)br 3500-2450; ν(C=C)ar. 1573; ν(C-N) 1445; ν(C=N)ar 1284; ρ(C-H)ar. 1170, 1038; γ(C-H)ar. 944, 743 cm−1. 1H-NMR ((CD3)2SO, 300 MHz): δ (ppm) 11.25 (s, 1H, H(j)), 7.81 (s, 1H, H(f)), 7.36–7.29 (m, 3H, Hb, c, h), 7.04–6.99 (m, 3H, Ha, d, i), 4.01 (s, Me(g)), 3.65 (s, Me(e)). 13C-NMR ((CD3)2SO, 75 MHz): δ (ppm) 153.4, 142.6, 144.1, 134.1, 129.8, 128.4, 124.3, 120.8, 119.8, 116.2, 110.1, 35.1, 31.6.
3.2.2. Synthesis of Ligands L4–L6
The first step:
At two-necked round-bottomed flask 2-bromopyrridine (8.00 g, 0.05 mmol) was weighed and placed under argon atmosphere. Methylhydrazine (11.6 g, 0.25 mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous ethanol and was added to the reaction mixture. Then the reaction mixture was warmed to 80 °C and stirred for 24 h. The oil residue was purified by column chromatography (SiO2; 5% MeOH in CH2Cl2). Yield 52% (3.24 g).
The next step:
-
-
for L4: condensation of 4-imidazolecarboxyaldehyde with 2-(1-methylhydrazine)pyridine was performed. At two-necked round-bottomed flask the 2-(1-methylhydrazine)pyridine (0.510g, 4.15 mmol) was weighed and placed under argon atmosphere. 4-imidazolecarboxyaldehyde (0.399 g, 4.15 mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous ethanol and was added to the reaction mixture. Yellow solution formed immediately and the reaction mixture was stirred for 24 h at 60 °C. The clear and orange solution was concentrated to minimal amount of volume, then Et2O was added and it was left in the refrigerator. The subsequent pale pink precipitate was filtered by vacuum filtration, washed with anhydrous ethanol and dried under vacuum to give 0.607 g (3.01 mmol) of ligand. 10 mL of Et2O was added to the supernatant and next part of precipitate was obtained 0.053 g (0.27 mmol). Total yield is 79.2% (0.660 g, 3.28 mmol).
ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 202 (20) [HL4]+, 224 (25) [NaL4]+; ESI-MS(−): 200 (100) [L4 − H]−. IR: ν(N-H)br 3300–2600; ν(C-H)imin. 3011; ν(CH3) 2951; ν(C=C)ar. 1588, 1565, 1542; ν(C-N) 1475, 1440; ν(C=N)ar 1309; ρ(C-H)ar. 1199, 1121; γ(C-H)ar. 891, 768, 644, 594 cm−1. 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz): δ (ppm) 8.18 (d, 1H, J = 4.3 Hz, Ha); 7.66 (s, 1H, Hf); 7.61 (s, 1H, Hh); 7.56–7.47 (m, 2H, Hc, d); 7.23 (s, 1H, Hg); 6.73 (t, 1H, J = 5.0 Hz, Hb); 6.40 (s, broad, NH); 3.59 (s, Me(e)). 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 75 MHz): δ (ppm) 157.4, 147.0, 137.7, 136.0, 131.6, 125.6, 125.4, 115.6, 109.7, 29.7. Melting temperature: 163–165 °C.
-
-
for L5: condensation of 2-imidazolecarboxyaldehyde with 2-(1-methylhydrazine)pyridine was performed. At two-necked round-bottomed flask the 2-(1-methylhydrazine)pyridine (0.525 g, 4.26 mmol) was weighed and placed under argon atmosphere. 2-Imidazolecarboxyaldehyde (0.469 g, 4.26 mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous ethanol and was added to the reaction mixture. Yellow solution formed immediately and the reaction mixture was stirred for 24 h at 60 °C. The clear and yellow solution was concentrated to minimal amount of volume and left in the refrigerator. The subsequent yellow precipitate was filtered by vacuum filtration, washed with anhydrous ethanol and dried in the vacuum to give 0.301 g (1.49 mmol). The supernatant was concentrated to minimal amount of volume and left in the refrigerator. The next part of precipitate was obtained 0.052 g (0.26 mmol). Total yield is 41.1% (0.353 g, 1.75 mmol).
ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 202 (30) [HL5]+, 224 (100) [NaL5]+; ESI-MS(−): 200 (100) [L5 − H]−. IR: ν(N-H) 3149; ν(C-H)imin. 3075; ν(CH3) 3002; ν(C=C)ar. 1591, 1566; ν(C-N) 1475, 1448; ν(C=N)ar. 1288; ρ(C-H)ar 1213, 1124; γ(C-H)ar. 852, 773, 751, 738 cm−1. 1H-NMR (CD3OD, 300 MHz): δ (ppm) 8.18 (d, 1H, J = 5.0 Hz, Ha); 7.83 (d, 1H, J = 8.6 Hz, Hd); 7.67 (t, 1H, J = 7.9 Hz, Hc); 7.62 (s, 1H, Hf); 7.10 (s, 2H, Hg, Hh); 6.87 (t, 1H, J = 5.5 Hz, Hb); 3.61 (s, Me(e)). 13C-NMR (CD3OD, 75 MHz): δ (ppm) 157.2, 149.9, 146.5, 145.1, 137.6, 124.2, 115.9, 109.9, 99.9, 28.6. Melting temperature: 191–193 °C.
-
-
for L6: synthesized according to our previous work [31]
3.3. Synthesis of Complexes
3.3.1. Synthetic Method for ‘Open’ Complexes
For complexes 1, 4–6 [Fe(Lx)]Cl3 the molar ratio of the ligand to the corresponding salt was 1:1. To a solution of L1, L4, L5, L6 in MeOH the methanolic solution of FeCl3∙6H2O was added. Mixture was stirred for 24h at room temperature. Then solvents were evaporated under vacuum to minimal amount of them and Et2O was added. Obtained precipitate was filtrated and washed twice with Et2O (10 mL in total) and dried in vacuum. Yields based on ligands are shown in Table 3.
Table 3.
The amount of substrate used to prepare complexes and information about yield and crystals of them.
| Complex | Ligand (mg) | Fe(II/III) Salt (mg) | Precipitation Color/Solid | Yield a | Crystals From | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg | % | |||||
| 1 | 26.7 | 30.0 | very dark green | 50.4 | 88.9 | iPr2O |
| 2 | 402.9 | 453.6 | dark green | 693.7 | 81 | tBuOMe |
| 3 | 60.0 | 63.8 | dark green | 66.2 | 67.3 | - |
| 4 | 22.3 | 30.0 | dark green | 46.8 | 89.4 | iPr2O |
| 5 | 23.9 | 30.0 | black | 47.3 | 87.7 | - |
| 6 | 21.9 | 30.0 | dark green | 39.8 | 76.8 | iPr2O |
| 7 | 70.0 | 51.6 | cinnamon | 87.9 | 72.3 | Et2O |
| 8 | 70.0 | 51.6 | hot chocolate | 104.0 | 72.3 | iPr2O |
| 9 | 70.0 | 48.7 | raspberry | 89.0 | 75.0 | tBuOMe |
| 10 | 70.0 | 61.6 | red | 121.0 | 91.9 | Et2O |
| 11 | 70.0 | 61.6 | warm brown | 117.0 | 88.8 | - |
| 12 | 55.0 | 45.3 | dark chocolate | 90.0 | 89.2 | PhMe |
a yield based on powder.
For complexes 2 and 3 reaction system was evacuated on the vacuum/gas line. To a solution of L2 and L3 in dry MeCN (dried on molecular sieves) FeCl3 ∙ 6H2O was added. Dark-green solution formed instantly and the reaction mixture was stirred for 48 h at room temperature. The green precipitate was filtered via suction filtration and dried in the vacuum. Yields based on ligands are shown in Table 3.
Crystals suitable for X-ray characterization were grown by vial-to-vial diffusion of different external precipitating co-solvents into the methanolic solutions of complexes at 4 °C. Please note that thoroughly dried samples were used for catalytic and biological studies, hence elementary analysis does not account for crystallization solvents that were found in the X-ray structures.
1 [FeL1Cl3]: ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 241 (100) [HL1]+; ESI-MS(−) m/z (%): 239 (100) [L1 − H]−. Anal. calc. for [Fe(C12H12N6)(Cl)3] (402.48): C: 35.81; H, 3.01; N, 20.88; found: C: 35.77; H, 3.31; N, 20.30%. IR: ν(C-H)arom 3125, 3093; νas(C-H)alif 2992, 2924; νs(C-H)alif 2849; ν(C=C) 1788, 1578, 1473; ν(C=N) 1437, 1350 δ(CH3) 1327, ν(C-O) 1289, 1245, 1214, 1148 γ(C-H)arom 1085, 1048, 1008, 972, 931, 907, 850, 806, 756, 675, 615 cm−1.
2 [FeL2Cl2(MeOH)]Cl: ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 241 (70) [HL2]+, 366 (30) [FeL2Cl2]+; ESI-MS(−) m/z (%): 198 (100) [FeCl4]−. Anal. calc. for [Fe(C12H12N6)(Cl)2(MeOH)]Cl (434.52): C: 35.93, H: 3.71, N: 19.34%; found: C: 35.70, H: 3.45, N: 19.77%. IR: v(N-H) 3419, ν(C-H)arom 3145, 3057; νas(C-H)alif 2973; νs(C-H)alif 2938; ν(C=C) 1611, 1577, 1552, 1476, 1462; ν(C=N) 1438 δ(CH3) 1421, 1364 ν(C-O) 1314, 1287, 1255, 1216, 1180 γ(C-H)arom 1119, 1083, 1054, 1008, 971, 883, 810, 753, 710, 651, 603 cm−1.
3 [FeL3Cl3]: ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 255 (40) [HL3]+, 277 (5) [NaL3]+, 344 (30) [Fe(L3 − H)Cl]+. Anal. calc. for [Fe(C13H14N6)(Cl)3] (416.49): C: 37.49, H: 3.39, N: 20.18%; found: C: 37.75, H: 3.39, N: 20.41%. IR: ν(N-H) 3546,ν(C-H)ar 3011; ν (C=C) 1575, 1495, 1476, 1463; ν(C=N) 1315 ρ(C-H) 1258, 1057, 1043, 1004, 979; γ(C-H) 869, 756 cm−1.
4 [FeL4Cl3]: ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 202 (100) [HL4]+; ESI-MS(−) m/z (%): 200 (100) [L4 − H]−. Anal. calc. for [Fe(C10H11N5)(Cl)3] (363.44): C, 33.05; H, 3.05; N, 19.27; found: C, 32.96; H, 3.09; N, 19.90%. IR: ν(C-H)arom 3125, 3096, 3026; νas(C-H)alif 2913; νs(C-H)alif 2862; ν(C=C) 1596, 1560, 1470; ν(C=N) 1430 δ(CH3) 1321, ν(C-O) 1261, 1217, 1174 γ(C-H)arom 1084, 995, 958, 918, 906, 846, 774, 648, 610 cm−1.
5 [FeL5Cl3]·CH3CN: ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 202 (40) [HL5]+, 327 (20) [FeL5Cl2]+; ESI-MS(−) m/z (%): 198 (40) [FeCl4]−. Anal. calc. for [Fe(C10H11N5)(Cl)3]·CH3CN (404.49): C, 35.63; H, 3.49; N, 20.78; found: C, 35.55; H, 3.40; N, 20.65%. IR: v(N-H) 3505 ν(C-H)arom 3154, 3128, 3078, 3044; νas(C-H)alif 2917; νs(C-H)alif 2892; ν(C=C) 1608, 1574, 1481; ν(C=N) 1420, 1388 δ(CH3) 1310, ν(C-O) 1255, 1224, 1165 γ(C-H)arom 1083, 1015, 869, 848, 767, 710, 626 cm−1.
6 [FeL6Cl3]: ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 216 (100) [HL6]+. Anal. calc. for [Fe(C11H13N5)(Cl)3] (377.46): C, 35.00; H, 3.47; N, 18.55; found: C, 33.96; H, 3.51; N, 18.30%. IR: v(N-H) 3552 ν(C-H)arom 3149, 3097; νas(C-H)alif 2917; νs(C-H)alif 2846; ν(C=C) 1636, 1593, 1520, 1488; ν(C=N) 1442 δ(CH3) 1325 ν(C-O) 1300, 1219, 1166 γ(C-H)arom 1116, 1016, 871, 778, 710, 621 cm−1.
3.3.2. Synthesis Method for ‘Closed’ Complexes
For complexes 7–12 [Fe(Lx)2](OTf)2 the molar ratio of the ligand to the corresponding salt was 2:1. To a solution of L1–L6 in MeOH (MeCN/MeOH; 1:1, v:v; in case of ligand L1) the methanolic solution of Fe(OTf)2 was added. Mixture was stirred for 48h at room temperature. Then solvents were evaporated under vacuum to the minimal amount and Et2O was added. Obtained precipitate was filtrated via suction filtration and washed twice with Et2O (10 mL in total) and dried under vacuum. Yields based on ligands are shown in Table 3.
Crystals suitable for X-ray characterization were grown by vial-to-vial diffusion of different external precipitating co-solvents into the methanolic 7–10, 12 solution of complexes at 4 °C.
7[Fe(L1)2](CF3SO3)2·C4H10O: ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 241 (40) [HL1]+, 263 (5) [NaL1]+, 268 (80) [FeL12]2+, 535 (35) [FeL1(L1 − H)]+; ESI-MS(−): 149 (100) [CF3SO3]−. Anal. calc. for [Fe(C12H12N6)2](CF3SO3)2·C4H10O (908.66): C: 39.66, H: 3.77, N: 18.50%; found: C: 39.59, H: 3.84, N: 19.05%. IR: ν(C-H)ar 3200, 3056; ν(C=C) 1640, 1575, 1480, 1475; ν(C=N) 1354, 1340; νas(CF3SO3) 1240, 1225; νs(CF3SO3) 1180; ρ(C-H) 1134, 1104; γ(C-H) 750, 640 cm−1.
8[Fe(L2)2](CF3SO3)2: ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 241 (75) [HL2]+, 263 (5) [NaL2]+, 268 (80) [FeL22]2+, 535 (95) [FeL2(L2 − H)]+. Anal. calc. for [Fe(C12H12N6)2](CF3SO3)2 (834.54): C: 37.42, H: 2.90, N: 20.14%; found: C: 37.60, H: 2.98, N: 20.70%. IR: ν(N-H) 3492; ν(C-H)ar 3154, 3100, 2948; ν(C=C) 1640, 1575, 1480, 1475; ν(C=N) 1390; νas(CF3SO3) 1248, 1225; νs(CF3SO3) 1160; ρ(C-H) 1118, 1052, 1030, 1008; γ(C-H) 750, 640 cm−1.
9[Fe(L3)2](CF3SO3)2·C5H12O: ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 282 (95) [FeL32]2+, 563 (70) [FeL3(L3 − H)]+; ESI-MS(−): 149 (100) [CF3SO3]−. Anal. calc. for [Fe(C13H14N6)2](CF3SO3)2·C5H12O (950.74): C: 41.69, H: 4.24, N: 17.68%; found: C: 41.52, H: 4.41, N: 17.25%. IR: ν(N-H) 3475; ν(C-H)ar 3120, 2954; ν(C=C) 1640, 1560, 1480, 1475; ν(C=N) 1370; νas(CF3SO3) 1250, 1238; νs(CF3SO3) 1152; ρ(C-H) 1054, 1030; γ(C-H) 750, 642 cm−1.
10[Fe(L4)2](CF3SO3)2·C4H10O: ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 229 (100) [FeL42]+, 457 (35) [FeL4(L4 − H)]+; ESI-MS(−): 149 (100) [CF3SO3]−. Anal. calc. for [Fe(C10H11N5)2](CF3SO3)2·C4H10O (830.56): C: 37.60, H: 3.88, N: 16.86 %; found: C: 37.71, H: 3.57, N: 16.54%. IR: ν(N-H) 3208, 3185; ν(C-H)ar 3118, 2910; ν(C=C) 1608, 1575, 1550, 1500; ν(C=N) 1315; νas(CF3SO3) 1248, 1230; νs(CF3SO3) 1151; ρ(C-H) 1090, 1032; γ(C-H) 765, 647 cm−1. 1H-NMR (CD3CN, 300 MHz): δ (ppm) 10.85 (s, 2H); 9.12 (s, 2H); 7.64–7.40 (m, 6H); 7.10 (s, 2H); 7.01 (d, 2H); 6.71 (t, 2H); 4.18 (s, 6H).
11[Fe(L5)2](CF3SO3)2: ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 229 (100) [FeL52]2+, 457 (20) [FeL5(L5 − H)]+; ESI-MS(−): 149 (100) [CF3SO3]−. Anal. calc. for [Fe(C10H10N5)2](CF3SO3)2 (756.44): C: 34.93, H: 2.93, N: 18.52 %; found: C: 34.10, H: 3.09, N: 18.02%. IR: ν(N-H) 3540, 3480; ν(C-H)ar 3175, 3110, 3055; ν (C=C) 1610, 1576, 1540, 1500, 1418; ν(C=N) 1352; νas(CF3SO3−) 1248; νs(CF3SO3) 1151; ρ(C-H) 1030; γ(C-H) 850, 759 cm−1. 1H-NMR (CD3CN, 300 MHz): δ (ppm) 9.28 (s, 2H); 7.69–7.52 (m, 4H); 7.06 (d, 2H); 7.01 (s, 2H); 6.77 (t, 2H); 6.37 (s, 2H); 4.28 (s, 6H).
12[Fe(L6)2](CF3SO3)2·CH3OH: ESI-MS(+) m/z (%): 243 (100) [FeL62]2+, 635 (30) [FeL62(CF3SO3)]+; ESI-MS(−): 149 (100) [CF3SO3]−. Anal. calc. for [Fe(C11H13N5)2](CF3SO3)2·CH3OH (816.56): C: 36.77, H: 3.70, N: 17.15%; found: C: 36.66, H: 3.38, N: 17.50%. IR: ν(C-H)ar 3120, 2958; ν(C=C) 1612, 1570, 1546, 1500, 1448; ν(C=N) 1338; νas(CF3SO3) 1254, 1237; νs(CF3SO3) 1151; ρ(C-H) 1125, 1035; γ(C-H) 760, 648 cm−1. 1H-NMR (CD3CN, 300 MHz): δ (ppm) 9.26 (s, 2H); 7.69 (t, 2H); 7.56 (d, 2H); 7.03 (d, 2H); 6.89 (s, 2H); 6.75 (t, 2H); 6.29 (s, 2H); 4.28 (s, 6H); 3.92 (s, 6H).
3.4. X-ray Crystallography
Diffraction data were collected by the ω-scan technique at 100(1)K (2, 6–10,12) on Rigaku XCalibur four-circle diffractometer with EOS CCD detector and graphite-monochromated MoKα radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å) and at 130(1)K (1, 4) on Rigaku SuperNova four-circle diffractometer with Atlas CCD detector and mirror-monochromated CuKα radiation (λ = 1.54178 Å). The data were corrected for Lorentz-polarization as well as for absorption effects [59]. Precise unit-cell parameters were determined by a least-squares fit of the reflections of the highest intensity, chosen from the whole experiment. The structures were solved with SHELXT-2013 [60] and refined with the full-matrix least-squares procedure on F2 by SHELXL-2013 [61]. All non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically, hydrogen atoms were placed in idealized positions and refined as ‘riding model’ with isotropic displacement parameters set at 1.2 (1.5 for CH3) times Ueq of appropriate carrier atoms. The crystals of 1 were of very poor quality, and the diffraction was measurable only for low angles. Therefore the number of data is low and the C and N atoms were refined isotropically. However, as this was the only example of the complex of its class, and the geometry looks quite reasonable, we decided to include this structure in the manuscript. Structures of five other complexes (generally, with large voids with unidentified electron density) were deposited in the CDB and attached as Supplementary material. Alerts B in 7, 8, 9, 10 and 12 are related to the lack of certain (small) number of reflections, caused by the experimental conditions, or (for 12) by high value of Flack parameter. In this case, we have tried the twin/basf refinement but the results are slightly inferior (even though the Alert vanishes). Crystallographic data for the structural analysis has been deposited with the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, deposition numbers are included in Table 4, which is shown below. Copies of this information may be obtained free of charge from: The Director, CCDC, 12 Union Road, Cambridge, CB2 1EZ, UK; e-mail: deposit@ccdc.cam.ac.uk, or www: www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk.
Table 4.
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement.
| Compound | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formula | C12H12Cl3FeN6 | C13H16Cl2FeN6O+·Cl− | C10H11Cl3FeN5 | C11H13Cl3FeN5 | C24H24FeN122+·2(CF3SO3)−·C4H10O | C24H24FeN122+·2(CF3SO3)−·solvent | C26H28FeN122+·2(CF3SO3) −·C5H12O | C20H22FeN102+·2(CF3SO3)−·C4H10O | C22H26FeN102+·2(CF3SO3)−·CH4O |
| FeL1Cl3 | [FeL2Cl2(CH3OH)]+·Cl− | FeL4Cl3 | FeL6Cl3 | (FeL12)2+·2(CF3SO3)−·C4H10O | (FeL22)2+·2(CF3SO3)−·solvent | (FeL32)2+·2(CF3SO3)−·C5H12O | (FeL42)2+·2(CF3SO3)−·C4H10O | (FeL62)2+·2(CF3SO3)−·CH3OH | |
| Formula weight | 402.48 | 434.52 | 363.44 | 377.46 | 908.66 | 834.54 | 950.74 | 830.58 | 816.56 |
| Crystal system | triclinic | monoclinic | triclinic | monoclinic | monoclinic | monoclinic | triclinic | monoclinic | orthorhombic |
| Space group | P-1 | P21/n | P-1 | P21/c | C2/c | P21/c | P-1 | P21/c | Pca21 |
| a (Å) | 7.459(2) | 7.6840(4) | 7.5198(4) | 7.2144(2) | 23.1912(8) | 12.9879(7) | 12.4297(8) | 15.5382(2) | 22.3563(6) |
| b (Å) | 9.055(2) | 13.9429(6) | 8.1040(6) | 12.4684(3) | 17.0021(5) | 13.0532(8) | 13.0407(7) | 12.55315(14) | 8.3830(2) |
| c (Å) | 12.460(3) | 16.8684(6) | 12.4702(10) | 16.7244(4) | 22.3107(8) | 21.9024(19) | 13.4814 (7) | 18.1225 (2) | 17.5420(6) |
| α (°) | 75.69(2) | 90 | 75.205(6) | 90 | 90 | 90 | 88.870(4) | 90 | 90 |
| β (°) | 87.94(2) | 98.281(4) | 84.655(5) | 99.730(2) | 116.163(4) | 91.711(6) | 74.131(5) | 91.2230(13) | 90 |
| γ (°) | 66.12(3) | 90 | 66.519(6) | 90 | 90 | 90 | 75.262(5) | 90 | 90 |
| V(Å3) | 743.7(4) | 1788.39(14) | 673.87(9) | 1482.75(7) | 7895.8(5) | 3711.5(4) | 2029.9(2) | 3534.05(7) | 3287.60(16) |
| Z | 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| Dx(g cm−3) | 1.797 | 1.614 | 1.791 | 1.691 | 1.529 | 1.493 | 1.556 | 1.561 | 1.650 |
| F(000) | 406 | 884 | 366 | 764 | 3728 | 1696 | 980 | 1704 | 1672 |
| μ (mm−1) | 13.136 | 1.305 | 14.392 | 1.553 | 0.577 | 0.604 | 0.565 | 0.634 | 0.680 |
| Reflections: | |||||||||
| collected | 1450 | 7518 | 4550 | 6161 | 18337 | 13346 | 30279 | 15200 | 17885 |
| unique (Rint) | 917 (0.042) | 3576 (0.024) | 2666 (0.054) | 3106 (0.022) | 7987 (0.031) | 6526 (0.059) | 7129 (0.083) | 7095 (0.015) | 5695 (0.029) |
| with I>2σ(I) | 716 | 2958 | 2319 | 2688 | 6243 | 3623 | 5726 | 6301 | 5323 |
| R(F) [I>2σ(I)] | 0.078 | 0.033 | 0.075 | 0.029 | 0.058 | 0.081 | 0.059 | 0.030 | 0.063 |
| wR(F2) [I>2σ(I)] | 0.233 | 0.081 | 0.196 | 0.059 | 0.174 | 0.153 | 0.156 | 0.072 | 0.165 |
| R(F) [all data] | 0.104 | 0.044 | 0.084 | 0.037 | 0.077 | 0.146 | 0.070 | 0.035 | 0.067 |
| wR(F2) [all data] | 0.233 | 0.087 | 0.204 | 0.063 | 0.188 | 0.174 | 0.169 | 0.075 | 0.169 |
| Goodness of fit | 1.05 | 1.05 | 1.14 | 1.04 | 1.24 | 1.02 | 1.07 | 1.02 | 1.08 |
| max/min Δρ (e·Å−3) | 0.77/−0.98 | 0.50/−0.29 | 1.75/−0.79 | 0.32/−0.31 | 1.68/−0.67 | 0.87/−0.45 | 1.14/−0.62 | 0.34/−0.39 | 0.83/−0.92 |
| CCDC number | 1851825 | 1851824 | 1851829 | 1851826 | 1871758 | 1871759 | 1871760 | 1871763 | 1871761 |
3.5. Catalytic Oxidation of 2-Aminophenol
Catalytic oxidation of o-aminophenol Phenoxazinone synthase like activity of our synthesized ‘open’ and ‘close’ system complexes was investigated by the reaction of 2.0 × 10−5 M methanolic solutions of the complexes with 2.0 × 10−4 M methanolic solution of o-aminophenol (OAPH) at room temperature and in the presence of air. The reactions were monitored on spectrophotometer by increasing absorbance at ca. 433 nm which correspond to band from the product of reaction, phenoxazinone chromophore (2-aminophenoxazine-3-one). Each measurement was performed three times and given values represent a representative average.
Determination of different kinetic parameters for the catalytic activity was done using the procedure reported earlier [25,41] based on Michaelis– Menten model. It gave a double reciprocal Lineweaver–Burk plots on which values of Vmax were interpreted, values of KM were from ½ Vmax on x-axis, while values of kcat is results of Vmax/[catalyst].
3.6. DNA Binding Assays
3.6.1. Absorption Titration
The absorbance titrations were performed in fixed concentration of metal complexes (20 µM) while gradually increasing the concentration of CT-DNA within the range from 0 to 100 µM. Each sample solution was allowed to equilibrate 5 min. before the spectra were recorded. Using the absorption titration data, the binding constant Kb was determined according to the equation [62]:
| [DNA]/(εa − εf) = [DNA]/(εb − εf) +1/Kb (εb − εf) |
where [DNA] is the concentration of CT-DNA in the base pairs, εa corresponds to the extinction coefficient observed (Aobsd/[M]), εf corresponds to coefficient of free compound, εb is the extinction coefficient of the compound fully bound to CT-DNA, and Kb is the intrinsic binding constant. The Kb value was given by the ratio of slope to intercept in the plot of [DNA]/(εa − εf) versus [DNA].
The standard Gibb’s free energy for DNA binding was calculated based on the equation [63]:
where is the standard Gibb’s free energy, R corresponds to gas constant, T is temperature and Kb stands for binding constant of the appropriate complex.
3.6.2. Competitive Binding Fluorescence Experiment
The competitive binding of compounds with ethidium bromide (EB) has been investigated by the fluorescence emission spectroscopy in order to evaluate its ability to displace EB from its DNA–EB fluorescent complex. The solution of EB (20 µM) and CT-DNA (26 µM) was allowed to equilibrate for 30 min. at 25 °C before the measurements were taken. While increasing the concentration of investigated complexes, the fluorescence spectra were recorded in the range of 540–720 nm at λexc = 467 nm. The ability of compounds to quench the emission of DNA-EB complex was evaluated by the Stern–Volmer equation [64]:
| I0/I = 1 + KSV |
were I0 and I are fluorescence intensities in absence and presence of compound, respectively, and KSV is the Stern–Volmer constant. KSV depends on the ratio of bound EB to the concentration of CT-DNA.
3.6.3. Circular Dichroism Studies
For the CD experiments 2 µM oligo DNA d(GTTAATCGCTGG) as a solution in Tris Buffer (10 mM TrisHCl, 5 mM NaCl, 50 mM pH 7.5) was used. 1–30 eq. of complexes were added to the solution 5 min. before measurements. At 1:30 molar ratio the samples were annealed at 70 °C for 5 min. and then slowly cooled down to room temperature. Quartz cuvettes with a path length of 1 cm were used with the sample volumes of 2 mL. Spectra were collected in the range 320–220 nm at 20 °C and were averaged over three scans.
4. Conclusions
Synthesis of a small library of Schiff base ligands is presented, which were designed so as to behave as efficient tridentate chelators with simultaneous incorporation of different number and disposition of non-coordinating NH moieties. Information encoded within iron(II/III) metallic centres and counterions allowed for generation of two families of complexes, which we term as ‘open’: [Fe(Lx)Cl3] and ‘closed’: [[Fe(Lx)2](OTf)2. Complexes were studied as phenoxazinone synthase activity mimics and DNA-binders, with the aim to see if there is an effect of hydrogen bonding on the studied biological activity.
Catalytic studies and derived kinetic parameters of 2-aminophenol (OAPH) oxidation with synthesized complexes show that the number and disposition of NH moieties influences the initial binding of OAPH to the complex. Nonetheless, its subsequent oxidation to 2-aminophenoxazine-3-one chromophore (APX) and thus catalytic activity is an outcome of additional factors. Consequently, attributing their activity solely to H-bonding is inaccurate. We postulate however that the mechanism of action differs within the ‘open’ and ‘closed’ families, and effect of non-covalent interactions is more important in the latter case.
The more straightforward effect of employing benzimidazole and imidazole moieties in the ligands scaffold was observed for DNA-binding studies. Intriguingly, the family of ‘open’ [Fe(Lx)Cl3] complexes do not interact with studied nucleic acid, which can be attributed to the effect of negatively charged chlorides, which may repel the complex from the sugar-phosphate backbone of CT-DNA. In contrast, ‘closed’ [Fe(Lx)2](OTf)2 complexes exhibit the behavior of bulky cations that are able to interact with the negatively charged backbone of DNA. Electronic absorption titration, fluorescence competitive binding with EB and CD titration allowed one to confirm that from the group of triflate analogues 7–12, only the pyridine-scaffolded ‘closed’ species 11 and 12 effectively bind with DNA, most probably by the intercalation-type mode. This shows that the benzimidazole moiety effectively precludes the remaining species from intercalation or any other significant interaction with nucleic acids and the imidazole substituent can be used for tuning of the interaction strength. In our previous works [38,40,65], a similar phenomenon was observed, where complexes without hydrogen bonding donors in the “primary” structure bind to DNA scaffold—such as helical and “open” complexes with terpyridine-type and quaterpyridine-type ligands [66].
We are currently working on ways to introduce H-bonding moieties in the immediate vicinity of the compounds’ coordination sphere as well as for utilization of the above-demonstrated phenomenon on aspects of crystal engineering and spin-crossover magnetic properties.
Acknowledgments
We thank Justyna Pachla for assistance in synthesis of ligand L6.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online: Ms PDF document with all supplementary Figures and Tables.
Author Contributions
A.B.: repeated synthesis and full characterization of ligands, synthesis and characterization of ‘open’ 1–6 and ‘closed’ 7–12 iron complexes, writing—original draft preparation, catalytic measurements; M.S. and G.N.R.: biological measurements and their description, writing—original draft preparation; D.B.: catalytic measurements; M.K.: X-ray measurements and description of crystal structures; M.W.-C.: first synthesis of ligands L4 and L5; M.A.F.-J.: planning of DNA binding assays, biological measurements and their description, writing—final version of paragraphs concerning DNA binding, review and editing; A.G.: conceptualization, first synthesis of ligands L1–L3 and complexes 1–6, writing—final manuscript, review and editing, V.P.: supervision, writing—review and editing.
Funding
A.G. thanks to the National Science Centre in Cracow, Poland (grant PRELUDIUM no. 2015/17/N/ST5/01973) for financial support. Supported by the Foundation for Polish Science (FNP). M.A.F.J. thanks to the National Science Centre in Cracow, Poland (grant SONATINA no. 2017/24/C/ST5/00181) for financial support. A.B.: the work was supported by the grant no. POWR.03.02.00-00-I023/17 co-financed by the European Union through the European Social Fund under the Operational Program Knowledge Education Development. M.S.: the work was supported by the grant no. POWR.03.02.00-00-I026/16 co-financed by the European Union through the European Social Fund under the Operational Program Knowledge Education Development.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds: L1–L6, 1–12 are available from the authors.
References
- 1.Berg J.M., Tymoczko J.L., Gatto G.J., Stryer L. Biochemistry. 8th ed. W. H. Freeman and Company; New York, NY, USA: 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nastri F., Chino M., Maglio O., Bhagi-Damodaran A., Lu Y., Lombardi A. Design and engineering of artificial oxygen-activating metalloenzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016;45:5020–5054. doi: 10.1039/C5CS00923E. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Whitesides G.M. Reinventing Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015;54:3196–3209. doi: 10.1002/anie.201410884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schwizer F., Okamoto Y., Heinisch T., Gu Y., Pellizzoni M.M., Lebrun V., Reuter R., Köhler V., Lewis J.C., Ward T.R. Artificial Metalloenzymes: Reaction Scope and Optimization Strategies. Chem. Rev. 2018;118:142–231. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Abbaspour N., Hurrell R., Kelishadi R. Review on iron and its importance for human health. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014;19:174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hohenberger J., Ray K., Meyer K. The biology and chemistry of high-valent iron–oxo and iron–nitrido complexes. Nat. Commun. 2012;3:720. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Poulos T.L. Heme Enzyme Structure and Function. Chem. Rev. 2014;114:3919–3962. doi: 10.1021/cr400415k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bruijnincx P.C.A., van Koten G., Klein Gebbink R.J.M. Mononuclear non-heme iron enzymes with the 2-His-1-carboxylate facial triad: Recent developments in enzymology and modeling studies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008;37:2716–2744. doi: 10.1039/b707179p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Krainer F., Glieder A. An updated view on horseradish peroxidases: Recombinant production and biotechnological applications. Appl. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015;99:1611–1625. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6346-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Denisov I.G., Makris T.M., Sligar S.G., Schlichting I. Structure and Chemistry of Cytochrome P450. Chem. Rev. 2005;105:2253–2278. doi: 10.1021/cr0307143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Solomon E.I., Brunold T.C., Davis M.I., Kemsley J.N., Lee S.-K., Lehnert N., Neese F., Skulan A.J., Yang Y.-S., Zhou J. Geometric and Electronic Structure/Function Correlations in Non-Heme Iron Enzymes. Chem. Rev. 2000;100:235–350. doi: 10.1021/cr9900275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tinberg C.E., Lippard S.J. Dioxygen Activation in Soluble Methane Monooxygenase. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011;44:280–288. doi: 10.1021/ar1001473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hegg E.L., Que L., Jr. The 2-His-1-Carboxylate Facial Triad—An Emerging Structural Motif in Mononuclear Non-Heme Iron(II) Enzymes. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997;250:625–629. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.t01-1-00625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Solomon E.I., Goudarzi S., Sutherlin K.D. O2 Activation by Non-Heme Iron Enzymes. Biochemistry. 2016;55:6363–6374. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tabassum S., Amir S., Arjmand F., Pettinari C., Marchetti F., Masciocchi N., Lupidi G., Pettinari R. Mixed-ligand Cu(II)–vanillin Schiff base complexes; effect of coligands on their DNA binding, DNA cleavage, SOD mimetic and anticancer activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013;60:216–232. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.08.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Krishnamurthy G., Ding W.-d., O’Brien L., Ellestad G.A. Circular dichroism studies of calicheamicin-DNA interaction: Evidence for calicheamicin-induced DNA conformational change. Tetrahedron. 1994;50:1341–1349. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)80622-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Abdel-Rahman L.H., El-Khatib R.M., Nassr L.A.E., Abu-Dief A.M. DNA binding ability mode, spectroscopic studies, hydrophobicity, and in vitro antibacterial evaluation of some new Fe(II) complexes bearing ONO donors amino acid Schiff bases. Arab. J. Chem. 2017;10:S1835–S1846. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.07.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Joseph J., Ayisha Bibin Rani G. Metal based SOD mimetic therapeutic agents: Synthesis, characterization and biochemical studies of metal complexes. Arab. J. Chem. 2017;10:S1963–S1972. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.07.024. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Abdel-Rahman L.H., Ismail N.M., Ismael M., Abu-Dief A.M., Ahmed E.A.-H. Synthesis, characterization, DFT calculations and biological studies of Mn(II), Fe(II), Co(II) and Cd(II) complexes based on a tetradentate ONNO donor Schiff base ligand. J. Mol. Struct. 2017;1134:851–862. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.01.036. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bakshi R., Kumar R., Mathur P. Bis-benzimidazole diamide iron(III) complexes as mimics of phenoxazinone synthase. Catal. Commun. 2012;17:140–145. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2011.10.017. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.El-Khalafy S.H., Hassanein M. Oxidation of 2-aminophenol with molecular oxygen and hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by water soluble metalloporphyrins. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2012;363–364:148–152. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2012.06.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hassanein M., Abdo M., Gerges S., El-Khalafy S. Study of the oxidation of 2-aminophenol by molecular oxygen catalyzed by cobalt(II) phthalocyaninetetrasodiumsulfonate in water. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2008;287:53–56. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2008.03.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Panja A., Shyamal M., Saha A., Kanti Mandal T. Methylene bridge regulated geometrical preferences of ligands in cobalt(III) coordination chemistry and phenoxazinone synthase mimicking activity. Dalton Trans. 2014;43:5443–5452. doi: 10.1039/c3dt52597j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Simándi L.I., Simándi T.M., May Z., Besenyei G. Catalytic activation of dioxygen by oximatocobalt(II) and oximatoiron(II) complexes for catecholase-mimetic oxidations of o-substituted phenols. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2003;245:85–93. doi: 10.1016/S0010-8545(03)00057-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Adhikary J., Chakraborty A., Dasgupta S., Chattopadhyay S.K., Kruszynski R., Trzesowska-Kruszynska A., Stepanović S., Gruden-Pavlović M., Swart M., Das D. Unique mononuclear MnII complexes of an end-off compartmental Schiff base ligand: Experimental and theoretical studies on their bio-relevant catalytic promiscuity. Dalton Trans. 2016;45:12409–12422. doi: 10.1039/C6DT00625F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chowdhury B., Maji M., Biswas B. Catalytic aspects of a copper(II) complex: Biological oxidase to oxygenase activity. J. Chem. Sci. 2017;129:1–11. doi: 10.1007/s12039-017-1379-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Horváth T., Kaizer J., Speier G. Functional phenoxazinone synthase models: Kinetic studies on the copper-catalyzed oxygenation of 2-aminophenol. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2004;215:9–15. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2004.01.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Szávuly M., Csonka R., Speier G., Barabás R., Giorgi M., Kaizer J. Oxidation of 2-aminophenol by iron(III) isoindoline complexes. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2014;392:120–126. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2014.05.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fik M.A., Löffler M., Weselski M., Kubicki M., Korabik M.J., Patroniak V. New Fe(II) complexes with Schiff base ligand: Synthesis, spectral characterization, magnetic studies and thermal stability. Polyhedron. 2015;102:609–614. doi: 10.1016/j.poly.2015.10.050. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gorczyński A., Pakulski D., Szymańska M., Kubicki M., Bułat K., Łuczak T., Patroniak V. Electrochemical deposition of the new manganese(II) Schiff-base complex on a gold template and its application for dopamine sensing in the presence of interfering biogenic compounds. Talanta. 2016;149:347–355. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2015.11.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gorczyński A., Zaranek M., Witomska S., Bocian A., Stefankiewicz A.R., Kubicki M., Patroniak V., Pawluć P. The cobalt(II) complex of a new tridentate Schiff-base ligand as a catalyst for hydrosilylation of olefins. Catal. Commun. 2016;78:71–74. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2016.02.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fik M.A., Czepa W., Kubicki M., Patroniak V. Formation of non-covalent porous framework with Fe ions and N2O Schiff base ligand: structural and thermal studies. Supramol. Chem. 2017;29:643–650. doi: 10.1080/10610278.2017.1311413. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Czepa W., Fik M.A., Witomska S., Kubicki M., Consiglio G., Pawluć P., Patroniak V. Simple Schiff-Base Cu(II) Complexes as Efficient Catalysts for Benzyl Alcohol Oxidation. ChemistrySelect. 2018;3:9504–9509. doi: 10.1002/slct.201801550. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Marcinkowski D., Fik M.A., Łuczak T., Kubicki M., Patroniak V. New Mn(II) complexes with benzoxazole-based ligands: Synthesis, structure and their electrochemical behavior. Polyhedron. 2018;141:125–132. doi: 10.1016/j.poly.2017.11.039. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gorczyński A., Marcinkowski D., Kubicki M., Löffler M., Korabik M., Karbowiak M., Wiśniewski P., Rudowicz C., Patroniak V. New field-induced single ion magnets based on prolate Er(iii) and Yb(iii) ions: tuning the energy barrier Ueff by the choice of counterions within an N3-tridentate Schiff-base scaffold. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018;5:605–618. doi: 10.1039/C7QI00727B. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gorczyński A., Kubicki M., Szymkowiak K., Łuczak T., Patroniak V. Utilization of a new gold/Schiff-base iron(iii) complex composite as a highly sensitive voltammetric sensor for determination of epinephrine in the presence of ascorbic acid. RSC Adv. 2016;6:101888–101899. doi: 10.1039/C6RA22028B. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wałęsa-Chorab M., Gorczyński A., Kubicki M., Hnatejko Z., Patroniak V. Self-assembly of a tridentate Schiff-base ligand with Zn(II) in the presence of lanthanides: Novel crystal structures and spectroscopic properties. Polyhedron. 2012;31:51–57. doi: 10.1016/j.poly.2011.08.032. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fik M.A., Gorczyński A., Kubicki M., Hnatejko Z., Fedoruk-Wyszomirska A., Wyszko E., Giel-Pietraszuk M., Patroniak V. 6,6″-Dimethyl-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine revisited: New fluorescent silver(I) helicates with in vitro antiproliferative activity via selective nucleoli targeting. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014;86:456–468. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Adamski A., Kruszka D., Dutkiewicz Z., Kubicki M., Gorczyński A., Patroniak V. Novel family of fused tricyclic [1,4]diazepines: Design, synthesis, crystal structures and molecular docking studies. Tetrahedron. 2017;73:3377–3386. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2017.05.015. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Adamski A., Fik M.A., Kubicki M., Hnatejko Z., Gurda D., Fedoruk-Wyszomirska A., Wyszko E., Kruszka D., Dutkiewicz Z., Patroniak V. Full characterization and cytotoxic activity of new silver(i) and copper(i) helicates with quaterpyridine. New J. Chem. 2016;40:7943–7957. doi: 10.1039/C5NJ03601A. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chatterjee S., Sukul D., Banerjee P., Adhikary J. Phenoxazinone synthase activity of two iron(III) complexes comprising the same Schiff base ligand: Biomimetic functional model and mechanistic investigation. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 2018;474:105–112. doi: 10.1016/j.ica.2018.01.024. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Liu X.-F., Xiang L., Zhou Q., Carralot J.-P., Prunotto M., Niederfellner G., Pastan I. Actinomycin D enhances killing of cancer cells by immunotoxin RG7787 through activation of the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2016;113:201611481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611481113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lu D.-F., Wang Y.-S., Li C., Wei G.-J., Chen R., Dong D.-M., Yao M. Actinomycin D inhibits cell proliferations and promotes apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015;8:1904–1911. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lohani N., Singh H., Moganty R. Structural aspects of the interaction of anticancer drug Actinomycin-D to the GC rich region of hmgb1 gene. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016;87:433–442. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.02.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Panja A., Jana N.C., Brandão P. Influence of the first and second coordination spheres on the diverse phenoxazinone synthase activity of cobalt complexes derived from a tetradentate Schiff base ligand. New J. Chem. 2017;41:9784–9795. doi: 10.1039/C7NJ02015E. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Panja A. Syntheses and structural characterizations of cobalt(II) complexes with N4-donor Schiff base ligands: Influence of methyl substitution on structural parameters and on phenoxazinone synthase activity. Polyhedron. 2014;80:81–89. doi: 10.1016/j.poly.2014.02.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mahato M., Mondal D., Nayek H.P. Syntheses, Structures and Phenoxazinone Synthase Activities of Two Cobalt(III) Complexes. ChemistrySelect. 2016;1:6777–6782. doi: 10.1002/slct.201601597. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Strekowski L., Wilson B. Noncovalent interactions with DNA: An overview. Mut. Res. 2007;623:3–13. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2007.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wolfe A., Shimer G.H., Meehan T. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons physically intercalate into duplex regions of denatured DNA. Biochemistry. 1987;26:6392–6396. doi: 10.1021/bi00394a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Li L., Guo Q., Dong J., Xu T., Li J. DNA binding, DNA cleavage and BSA interaction of a mixed-ligand copper(II) complex with taurine Schiff base and 1,10-phenanthroline. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 2013;125:56–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2013.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Woody R.W. Methods in Enzymology. Volume 246. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 1995. Circular dichroism; pp. 34–71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Liu X.-W., Li J., Li H., Zheng K.-C., Chao H., Ji L.-N. Synthesis, characterization, DNA-binding and photocleavage of complexes [Ru(phen)2(6-OH-dppz)]2+ and [Ru(phen)2(6-NO2-dppz)]2+ J. Inorg. Biochem. 2005;99:2372–2380. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2005.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Abdel-Rahman L.H., Abu-Dief A.M., El-Khatib R.M., Abdel-Fatah S.M. Some new nano-sized Fe(II), Cd(II) and Zn(II) Schiff base complexes as precursor for metal oxides: Sonochemical synthesis, characterization, DNA interaction, in vitro antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Bioorg. Chem. 2016;69:140–152. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2016.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sirajuddin M., Ali S., Badshah A. Drug–DNA interactions and their study by UV–Visible, fluorescence spectroscopies and cyclic voltametry. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013;124:1–19. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2013.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Mishra M., Tiwari K., Shukla S., Mishra R., Singh V.P. Synthesis, structural investigation, DNA and protein binding study of some 3d-metal complexes with N′-(phenyl-pyridin-2-yl-methylene)-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid hydrazide. Spectrochim. Acta A. 2014;132:452–464. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2014.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Raman N., Pothiraj K., Baskaran T. DNA interaction, antimicrobial, electrochemical and spectroscopic studies of metal(II) complexes with tridentate heterocyclic Schiff base derived from 2′-methylacetoacetanilide. J. Mol. Struct. 2011;1000:135–144. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2011.06.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Marmur J. A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from micro-organisms. J. Mol. Biol. 1961;3:208–218. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(61)80047-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Reichmann M.E., Rice S.A., Thomas C.A., Doty P. A Further Examination of the Molecular Weight and Size of Desoxypentose Nucleic Acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1954;76:3047–3053. doi: 10.1021/ja01640a067. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Rigaku O.D. CrysAlis PRO (Version 1.171.38.34c) [(accessed on 12 April 2019)];2015 Available online: https://www.rigaku.com/en/products/smc/crysalis.
- 60.Sheldrick G. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A. 2015;71:3–8. doi: 10.1107/S2053273314026370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sheldrick G. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C. 2015;71:3–8. doi: 10.1107/S2053229614024218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Shivakumar L., Shivaprasad K., Revanasiddappa H.D. Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, antimicrobial, DNA binding and oxidative-induced DNA cleavage activities: New oxovanadium(IV) complexes of 2-(2-hydroxybenzylideneamino)isoindoline-1,3-dione. Spectrochim. Acta A. 2012;97:659–666. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2012.07.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Sabolová D., Kožurková M., Plichta T., Ondrušová Z., Hudecová D., Šimkovič M., Paulíková H., Valent A. Interaction of a copper(II)–Schiff base complexes with calf thymus DNA and their antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011;48:319–325. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Baguley B.C., Le Bret M. Quenching of DNA-ethidium fluorescence by amsacrine and other antitumor agents: A possible electron-transfer effect. Biochemistry. 1984;23:937–943. doi: 10.1021/bi00300a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Fik M.A., Gorczyński A., Kubicki M., Hnatejko Z., Wadas A., Kulesza P.J., Lewińska A., Giel-Pietraszuk M., Wyszko E., Patroniak V. New vanadium complexes with 6,6″-dimethyl-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine in terms of structure and biological properties. Polyhedron. 2015;97:83–93. doi: 10.1016/j.poly.2015.05.021. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Gorczyński A., Harrowfield J.M., Patroniak V., Stefankiewicz A.R. Quaterpyridines as Scaffolds for Functional Metallosupramolecular Materials. Chem. Rev. 2016;116:14620–14674. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.