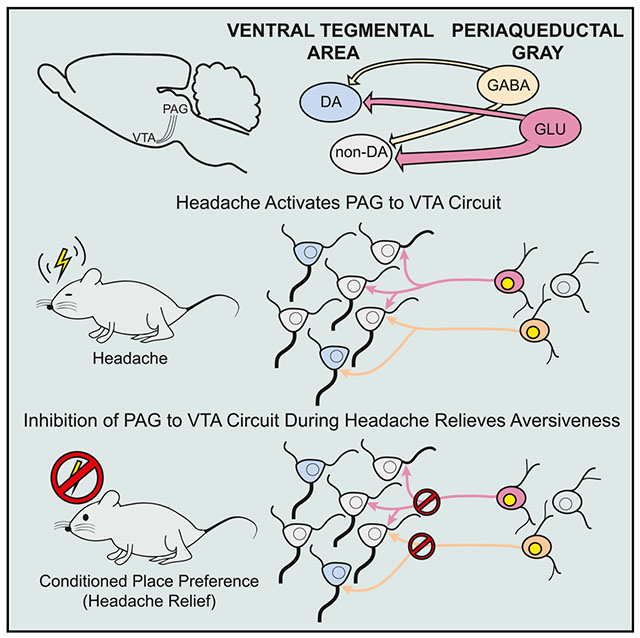
SUMMARY
Migraines are a major health burden, but treatment is limited because of inadequate understanding of neural mechanisms underlying headache. Imaging studies of migraine patients demonstrate changes in both pain-modulatory circuits and reward-processing regions, but whether these changes contribute to the experience of headache is unknown. Here, we demonstrate a direct connection between the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray (vlPAG) and the ventral tegmental area (VTA) that contributes to headache aversiveness in rats. Many VTA neurons receive monosynaptic input from the vlPAG, and cranial nociceptive input increases Fos expression in VTA-projecting vlPAG neurons. Activation of PAG inputs to the VTA induces avoidance behavior, while inactivation of these projections induces a place preference only in animals with headache. This work identifies a distinct pathway that mediates cranial nociceptive aversiveness.
Graphical Abstract
In Brief
Migraine headache is a common and debilitating disorder, yet its brain-activation patterns are poorly understood. Waung et al. discover that headache activates a connection between the periaqueductal gray and the ventral tegmental area in rats. Turning off this connection has no effect normally but decreases unpleasantness during headaches.
INTRODUCTION
Migraine is a chronic relapsing disorder that results in significant health and socioeconomic loss (Bonafede et al., 2018). The World Health Organization ranks migraine headache as the 2nd leading global cause of years lived with disability (GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators, 2017). Despite the significant clinical impact of migraine, a deeper understanding of its neurobiology remains elusive. Human imaging data have implicated several diencephalic and brainstem regions in the pathogenesis of idiopathic headache. Areas including the periaqueductal gray (PAG) are activated early during migraine (Weiller et al., 1995) and may even be active before the onset of headache pain (Maniyar et al., 2014). Surgical manipulation of the PAG can trigger headaches (Raskin et al., 1987), and MRI consistently demonstrates altered functional connectivity between the PAG and other brain regions in migraine patients (Chen et al., 2017; Li et al., 2016b; Mainero et al., 2011).
The PAG is a heterogeneous region that mediates various pain and stress responses. Activation of the dorsolateral PAG triggers defensive behaviors in rats (Bandler and Depaulis, 1988), while stimulation of the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray (vlPAG) promotes quiescence (Depaulis et al., 1994) and analgesia (Fardin et al., 1984). Many of these effects involve descending vlPAG efferents (Behbehani and Fields, 1979; Lovick, 1993; Morgan and Whitney, 2000), but the vlPAG also projects rostrally to limbic midbrain structures (Cameron et al., 1995; Mantyh, 1983) including the ventral tegmental area (VTA), which is also activated early in migraine episodes (Maniyar et al., 2014). The VTA can generate both appetitive and aversive signals (Lammel et al., 2012; Qi et al., 2016; van Zessen et al., 2012), raising the possibility that inputs from the vlPAG could generate either headache relief or aversiveness.
Although this connection has been largely overlooked, the vlPAG has reciprocal connections with the VTA (Geisler et al., 2007; Omelchenko and Sesack, 2010; Suckow et al., 2013), and a study reported monosynaptic PAG inputs onto VTA dopamine and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurons in mice (Ntamati et al., 2018). The behavioral role of the PAG-VTA circuit is unknown; how this connection between the PAG, a hub for central pain modulation, and the VTA, a critical region for motivation and reinforcement, contributes to headache is also unknown. Here we provide evidence that the vlPAG can relay an aversive signal through the VTA that is necessary for the aversiveness of headache.
RESULTS
Most VTA Neurons Receive Synaptic Inputs from the vlPAG
To better understand the nature of PAG inputs within the VTA, we labeled PAG projections with bilateral injections of AAV2-hSynapsin (hSyn)-hChR2(H134R)-mCherry into the vlPAG (Figures 1A–1C). We observed moderately dense fiber staining in the VTA, distributed evenly throughout its medial-lateral and rostral-caudal extent (Figure 1D), with axons and bouton-like appositions among tyrosine hydroxylase-positive (TH(+)) neurons (Figures 1E and 1F).
Figure 1. Fibers from the vlPAG Are Distributed throughout the VTA.
(A) Schematic of AAV2-hSyn-ChR2-mCherry injections into bilateral vlPAG.
(B) Sample horizontal slice with bilateral virus injection sites into the vlPAG marked in magenta (Aq, aqueduct; DR, dorsal raphe; scale bar, 500 μm).
(C) Cell bodies in the PAG with mCherry expression (magenta; scale bar, 250 μm).
(D) Sample horizontal brain slice with mCherry-fiber expression and TH immunocytochemical labeling, acquired and stitched with 2D slide scan in MBF Stereoinvestigator (green; scale bar, 250 μm).
(E and F) Confocal images at high magnification of TH(+) neurons (green) in the VTA surrounded by mCherry bouton-like profiles (E) and axon fibers (F) from the vlPAG (magenta; scale bar, 20 μm).
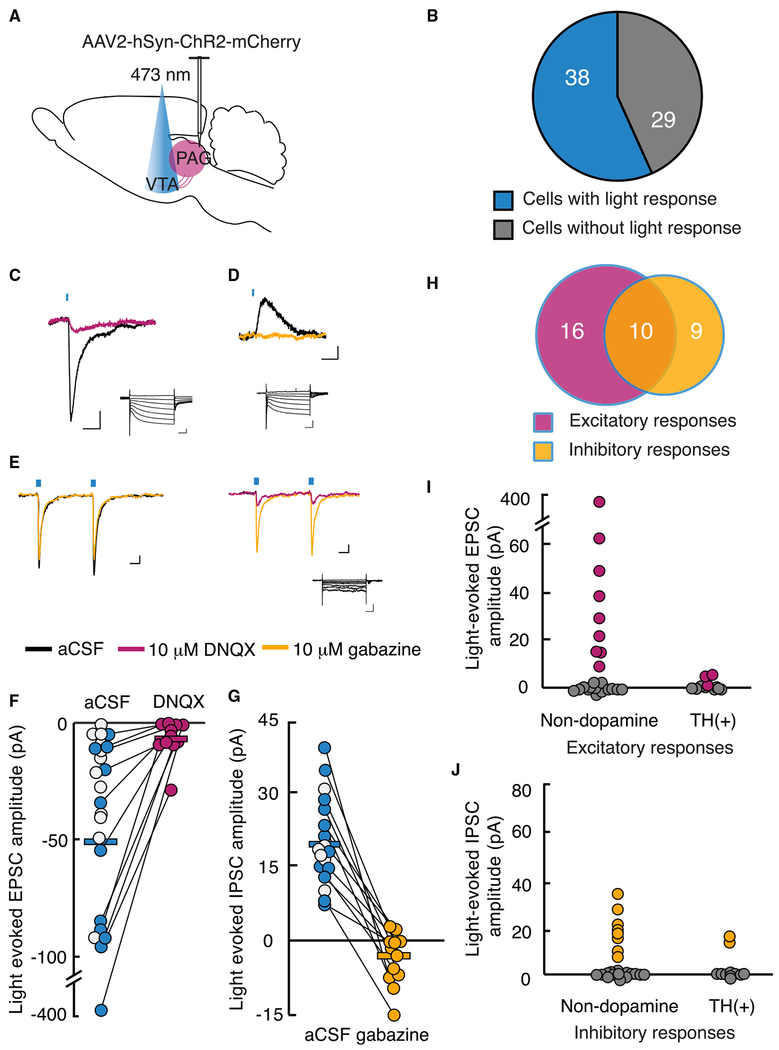
We examined synaptic connections in this circuit using whole-cell recordings in horizontal slices containing the VTA by selective activation of channelrhodopsin (ChR2)-expressing vlPAG inputs with light pulses (λ = 473 nm, 1-10 ms) (Figure 2A). Most VTA neurons (38/67, 57%) exhibited light-activated post-synaptic currents (Figures 2B and S1). Most experiments were completed using a physiological chloride concentration internal solution (Figures 2C and 2D), while a few recordings were made with a high-chloride internal solution to improve detection of inhibitory inputs (Figure 2E). Sixty-eight percent of light-activated responses had an excitatory, inward current component (26/38). Among recordings made with a normal internal chloride concentration and Vholding = −60 mV, the mean light-evoked event amplitude was −51 ± 16 pA (n = 23) (Figures 2C and 2F). These light-evoked excitatory post-synaptic currents (EPSCs) exhibited short latency from onset of the light stimulus (2.0 ± 0.2 ms) and were confirmed to be glutamate receptor mediated, because they were blocked with the AMPA receptor antagonist 6,7-Dinitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (DNQX; −6 ± 2 pA, paired t test, t(10) = −2.40, p = 0.04, tested in 11/23 cells) (Figures 2C and 2F). A subset of cells (n = 6) demonstrated light-evoked EPSCs with slower rise times, which were markedly reduced by the NMDA receptor antagonist D-(-)-2-Amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (APV) in 2 of 2 cells tested (−21 ± 1 pA in artificial cerebrospinal fluid [aCSF] versus −5 ± 2 pA in APV) (Figures S2A and S2B), with the remaining current blocked by DNQX.
Figure 2. Most VTA Neurons Receive Synaptic Inputs from the vlPAG.
(A) Schematic of bilateral injection of AAV2-hSyn-ChR2-mCherry into vlPAG. 4-6 weeks after injection, acute VTA slice from 20 animals were prepared for whole-cell recordings.
(B) Graphical representation of the number of VTA neurons with light-stimulated synaptic potentials following ChR2 expression in vlPAG neurons.
(C and D) Example responses to brief, 470 nm light pulses recorded in voltage clamp. Magenta trace (C); after bath application of 10 μM DNQX at holding potential of −60 mV (scale bar, 20 pA, 10 ms). Yellow trace (D); after 10 μM gabazine at holding potential of −40 mV (scale bar, 5 pA, 10 ms). Insets: responses to voltage steps demonstrating Ih (scale bar, 200 pA, 100 ms).
(E) Sample traces from an individual neuron receiving both excitatory and inhibitory light-evoked post-synaptic currents with holding potential at −60 mV using a high-chloride (KCI) internal solution (scale bar, 20 pA, 10 ms). Inset: response to voltage steps (scale bar, 100 pA, 100 ms).
(F) EPSC amplitudes recorded at −60 mV using K-gluconate internal solution, plotted before and after DNQX application. Each circle represents one neuron; white circles represent presumed glutamatergic responses, but DNQX was not bath applied.
(G) IPSC amplitudes recorded at −40 mV holding potential reduced with gabazine (white circles not tested with gabazine).
(H) Excitatory (magenta) and inhibitory (yellow) inputs from the vlPAG converge onto a proportion of VTA neurons from 35 neurons in which EPSCs and IPSCs could be differentiated.
(I) EPSC amplitudes in confirmed non-dopamine neurons compared with TH(+) neurons.
(J) IPSC amplitudes in confirmed non-dopamine neurons compared with TH(+) neurons.
See also Figures S1 and S2.
A slightly smaller proportion of connected VTA neurons received inhibitory synaptic input from the vlPAG (19/38, 50%). Light-evoked inhibitory post-synaptic currents (IPSCs) had an average amplitude of 20 ± 2 pA (recorded at −40 mV, with a latency of 2.2 ± 0.1 ms from light onset) and were blocked by the selective GABAA receptor antagonist gabazine (−4 ± 2 pA, paired t test, t(11) = 7.30, p = 0.00002, tested in 12/19 cells) (Figures 2D and 2G). Because the VTA has local GABAergic neurons, we investigated whether light-activated inhibitory currents were direct by showing that they are recovered with the potassium channel blocker 4-aminopyridine after being abolished with tetrodotoxin (TTX) (Petreanu et al., 2009). This demonstrates that these are monosynaptic GABAergic responses from the vlPAG (Figures S2C and S2D). Of 38 tested VTA neurons with detected vlPAG input, 10 (26%) received both excitatory and inhibitory connections (Figures 2E and 2H).
Some neurons with electrophysiologically confirmed vlPAG synaptic input were labeled with biocytin and recovered (n = 20); three of these demonstrated co-labeling with TH immunocytochemistry. Furthermore, only 27% of all confirmed dopamine neurons (3/11) received synaptic input from the vlPAG (Figures 2I and 2J). Neurons lacking (1) TH co-labeling, (2) an /h (Margolis et al., 2006), or (3) inhibition by the GABAB receptor agonist baclofen (Margolis et al., 2012) were classified as non-dopamine neurons. A significantly greater proportion of these VTA non-dopamine neurons, 20 of 31 (65%), received direct synaptic input from the vlPAG (Fisher’s exact test, p = 0.04) (Figures 2I and 2J). Overall these data indicate that the vlPAG-to-VTA connection is predominantly excitatory and preferentially targets non-dopamine neurons.
A Subset of vlPAG Neurons Projecting to the VTA Is Activated with Headache
Dural application of inflammatory mediators (IMs), an established model of headache in rats, activates meningeal nociceptors (Strassman et al., 1996) and increases Fos expression in the trigeminal nucleus caudalis (TNC) (Edelmayer et al., 2009). Dural IMs cause a reduction in periorbital mechanical withdrawal thresholds for 2-4 h (Oshinsky and Gomonchareonsiri, 2007), mimicking allodynia in humans with migraine.
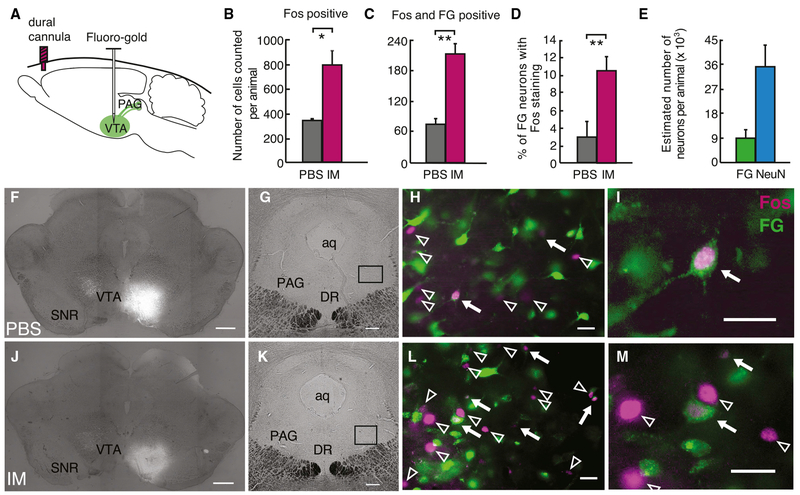
We used dural IMs to determine whether the vlPAG-VTA circuit is activated by headache (Figure 3A). Dural IMs led to significant periorbital allodynia, measured 5 min after infusion, compared with PBS (Figure S3A). Fos activation in the TNC and vlPAG was examined 2 h after dural IMs using stereological counting methods (West and Gundersen, 1990); Fos(+) neurons increased in both the TNC (Figures S3B–S3F) and the vlPAG (Figures 3B and 3F–3M) with headache. To specifically examine Fos activation in vlPAG neurons projecting to the VTA, we injected the retrograde tracer Fluoro-Gold (FG) into the VTA 1 week before dural IMs (Figures 3A, 3F, and 3J). Approximately 24% of vlPAG neurons (indicated by NeuN) were labeled by VTA FG (Figure 3E), with similar numbers of FG-labeled vlPAG neurons in dural PBS- and IM-treated animals (2,500 ± 400 versus 2,000 ± 400 neurons, n = 3 per condition, t(4) = 0.83, p = 0.45). Two hours after headache induction with IMs, we found an increase in Fos and FG co-labeled neurons in the vlPAG of animals treated with IMs compared with those treated with PBS (t(4) = −6.20, p = 0.003, n = 3 animals per condition) (Figures 3C, 3D, and 3F–3M). These data demonstrate that headache induction activates vlPAG neurons, including a significant subpopulation of neurons that project to the VTA.
Figure 3. A Subset of PAG Neurons that Project to the VTA Is Activated with Headache.
(A) Schematic of retrograde marker Fluoro-Gold (FG) injection into the VTA. 5-7 days after injections, animals were treated with dural PBS or IMs. Two hours later, animals underwent intracardiac perfusion with 4% paraformaldehyde, and coronal slices of the PAG were systematically collected and labeled with a Fos antibody.
(B and C) Number of Fos(+) cells (B) and double-labeled Fos- and FG-positive cells (C) counted using stereological methods in the vlPAG using an optical fractionator probe (n = 3 animals per condition, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).
(D) Percentage of FG-positive cells that were also Fos(+) (**p < 0.005).
(E) Estimated number of FG- and NeuN-positive cells in the vlPAG (n = 3 animals). All plots represent mean ± SEM.
((F-M) Example coronal slices in animals treated with dural PBS (F, G, H, and I) or IM (J, K, L, and M).
(F and J) Images in (F) and (J), demonstrating unilateral VTA injection sites, were acquired and stitched with 2D slide scan in MBF Stereoinvestigator (scale bar, 500 μm).
(G and K) Coronal vlPAG slices, with indication of the locations of higher-magnification images in (H) and (L), respectively (scale bar, 250 μm).
(H and L) Fos(+) cells (magenta) and FG-positive cells (green) in the vlPAG. White arrows indicate Fos-labeled cells, and arrowheads indicate double-labeled neurons (scale bar, 25 μm).
(I and M) High magnification of Fos(+) cells with and without FG double-labeling (scale bar, 25 μm).
Targeted Activation of vlPAG-to-VTA Afferents Is Aversive in Control Animals
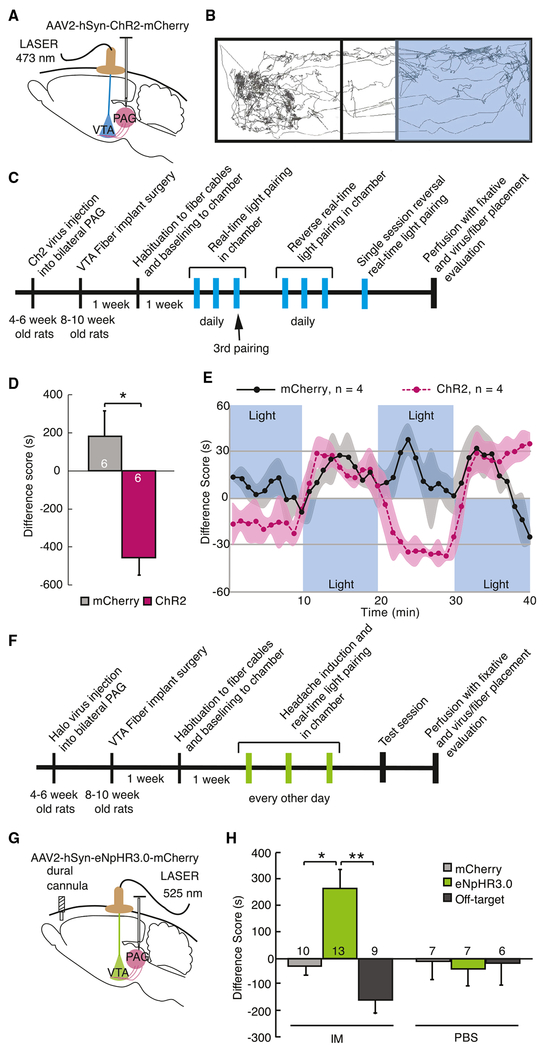
To determine whether activation of this vlPAG-VTA circuit in awake animals affects behavior, we optogenetically manipulated activity of vlPAG-originating axons in the VTA (Figures 4A and S4A–S4C). Animals were trained in a chamber with two contexts with different tactile and visual cues separated by a vestibule. Upon entry into one side (randomized across animals), vlPAG-VTA terminals expressing ChR2 were activated using pulsed blue light (λ = 473 nm, 20 Hz, 5 ms, 10-12 mW) delivered bilaterally through optic fibers. A stimulation frequency of 20 Hz was chosen based on published data from in vivo single-unit recordings reporting sustained 20 Hz firing rates in many PAG neurons during fear conditioning with foot shock (Johansen et al., 2010). By the third 20-min training session, activation of the vlPAG-VTA circuit resulted in a real-time place aversion, while rats injected with control virus expressing mCherry demonstrated no preference for either the laser or the no-laser paired side (p = 0.003, n = 6 rats per condition) (Figure 4D). Reversal of the animal’s side preference could be achieved repeatedly within a single session by alternating light stimulation between chambers (Figure 4E). There was a significant interaction of virus injection with light stimulation over time within individual animals (mixed ANOVA, F(39, 234) = 3.89, p = 0.0001) and a significant effect of ChR2 virus compared with mCherry virus between subjects (F(1,6) = 20.9, p = 0.004).
Figure 4. Activation of vlPAG-to-VTA Afferents Is Aversive and Required for Headache Aversiveness.
(A) Schematic of surgical preparation using ChR2 to selectively activate vlPAG axon terminals in the VTA in 3 replicate groups. Control animals were injected with sham virus, AAV2-hSyn-mCherry. 6-8 weeks later, optical fibers were implanted, bilaterally aimed at the VTA. Animals showed no chamber bias at baseline.
(B) Example track tracing of an animal during testing in which blue light (473 nm, 20 Hz, 5 ms pulse, 10-12 mW) commenced when the rat entered the right side of the chamber and was turned off when animal exited that side of the chamber.
(C) Timeline of the real-time optical stimulation place pairing protocol. Animals were placed in the test chamber for 20-min sessions daily in which blue light stimulation was paired with one side of the chamber. After 3 sessions with light paired with one side of the chamber, light was then paired to the opposite chamber for 3 daily 20-min sessions for reversal training. After 6 sessions, 4 animals underwent a 40-min session in which light pairing was reversed every 10 min.
(D) During the 3rd training session, animals with active ChR2 virus infection avoided the chamber with light stimulation compared with animals injected with sham virus. The difference score is calculated as the time spent in the stimulation-paired chamber minus the time spent in the nostimulation chamber (*p < 0.05). Plot represents mean ± SEM.
(E) Averaged real-time difference score from 4 animals during the last session, with stimulation alternating between chambers every 10 min.
(F) Timeline of the real-time optical inhibition place pairing protocol. Animals from 5 replicate groups received either intradural IMs or PBS 5 min before being placed into the test chamber. After 3 daily 20-min sessions of green light pairing (525 nm, 16-18 mW) with one side of the chamber, animals were tested the following day in the chamber without light inhibition.
(G) Schematic of surgical preparation for the behavioral experiment using halorhodopsin to selectively silence vlPAG inputs to the VTA after dural IMs to induce headache. Sham virus or AAV2-hSyn-eNpHR3.0-mCherry was injected into the vlPAG. Bilateral optical fibers were implanted directed to the VTA 6-8 weeks later.
(H) Difference scores were measured during the testing session with no stimulation (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01), demonstrating that inactivation of the vlPAG-to-VTA connection was appetitive only in rats that received IMs, suggesting it relievesthe aversive state induced by dural IMs. Plot represents mean ± SEM. See also Figure S4.
The vlPAG-to-VTA Circuit Is Required for Headache Aversiveness
Because vlPAG-VTA activation is aversive in controls (Figures 4D and 4E), we used optogenetic inhibition of vlPAG terminals in the VTA to determine their contribution to headache aversiveness. Inhibition of vlPAG-to-VTA projections was accomplished with bilateral injections of AAV2-hSyn-eNpHR3.0-mCherry into the vlPAG and optic fibers implanted in the VTA (Figures 4G and S4D–S4F). Five minutes before each training session, one group was given dural IMs, while the other group received PBS. Light stimulation in the VTA (λ = 525 nm, continuous stimulation, 16-18 mW) was paired with one chamber for three training sessions in the real-time apparatus every other day, followed by a test session without dural IMs or light stimulation. There were significant main effects of difference scores in IM-treated animals compared with PBS controls (two-way independent ANOVA, F(1,33) = 6.38, p = 0.02) and in animals infected with eNpHR3.0 compared with sham virus (F(1,33) = 8.64, p = 0.006), as well as a significant interaction between active eNpHR3.0 virus and dural treatment (F(1,33) = 5.72, p = 0.02) (Figure 4H). Bonferroni post hoc tests revealed a conditioned preference for the light-paired chamber with IMs and vlPAG eNpHR3.0 compared with IMs and vlPAG mCherry-only infection (p = 0.001). In addition, eNpHR3.0-infected animals with dural IMs exhibited a significant preference for the light-paired side, while eNpHR3.0-infected animals treated with PBS developed no preference (p = 0.01), indicating that the vlPAG-VTA circuit contributed strongly to aversion in headache animals but did not confer an ongoing aversion in control, non-headache animals. More specifically, control eNpHR3.0-infected animals treated with dural PBS did not demonstrate a conditioned preference or aversion for the light-paired chamber compared with sham-infected animals (p = 0.7). Furthermore, in animals with off-target eNpHR3.0 virus expression that were treated with dural IMs, there was no impact on behavior, with no differences compared with off-target sham virus injections (p > 0.2) (Figure 4H), but these animals were significantly distinct from animals with on-target eNpHR3.0 infections (p = 0.0003). Therefore, specific inactivation of vlPAG-VTA axons with eNpHR3.0 leads to a conditioned place preference in animals treated with dural IMs but had no impact in animals without headache. Together with Fos activation in VTA-projecting vlPAG neurons by induction of headache, these results are consistent with a significant contribution of the vlPAG-VTA circuit to the aversiveness of headache.
DISCUSSION
Our studies demonstrate that a direct connection from the vlPAG to the VTA produces an aversive signal that is activated during headache. After induction of headache, the number of Fos-expressing vlPAG neurons that project to the VTA doubles. Optogenetic activation of this circuit in awake, behaving rats is aversive, while inactivation is appetitive—but only in the context of ongoing headache. Clearly, this circuit is necessary for cranial pain aversiveness, and its activation sufficient to produce an aversive state.
We found that the direct vlPAG-to-VTA inputs are predominantly glutamatergic but also include GABA synapses. These direct connections are predominantly onto non-dopamine neurons. These findings are consistent with anatomical studies showing that a subset of PAG neurons projecting to the VTA expresses the vesicular glutamate transporter Vglut2 mRNA (Geisler et al., 2007), and approximately one-third of cells in the vlPAG are immunoreactive for glutamate decarboxylase, the enzyme that converts glutamate to GABA (Barbaresi and Manfrini, 1988). Ultrastructural studies demonstrate asymmetric and symmetric synapses from PAG axons onto both GABA and dopamine VTA neurons (Omelchenko and Sesack, 2010). These putative excitatory and inhibitory synapses appear to arise from separate PAG neurons (Omelchenko and Sesack, 2010), and Vglut2 and Vgat, the vesicular GABA transporters, do not appear to co-localize in PAG neurons (Samineni et al., 2017).
Our findings also generally agree with a report by Ntamati and colleagues showing both glutamate and GABA PAG input onto VTA dopamine and GABA neurons in DAT-Cre and GAD65-Cre transgenic mice, respectively (Ntamati et al., 2018). However, we found that a higher percentage of VTA neurons receive GABA input, and a quarter of VTA neurons with input from the vlPAG receive converging excitatory and inhibitory input. Furthermore, we found that non-dopamine neurons in the VTA were more likely than dopamine neurons to receive direct vlPAG synaptic connections, while Ntamati et al. (2018) found that VTA dopamine and GABA neurons in mice had similar connectivity rates. We did not directly test whether our non-dopamine VTA neurons were GABA or glutamate, but this will be essential in future studies examining downstream VTA targets.
The PAG also contains dopamine neurons that play a role in pain and reward behaviors (Li et al., 2016a; Taylor et al., 2019). Omelchenko and Sesack (2010) found that only 3% of PAG axons in the VTA contain dopamine (Omelchenko and Sesack, 2010). Although these could be fibers of passage, dopamine release in the VTA from the PAG could be modulating headache aversiveness. In our slice recordings, optically evoked currents from PAG axons in the VTA were abolished by a combination of glutamate and/or GABA receptor antagonists. However, it is possible that we did not sample enough neurons in the VTA to find a sparse dopamine-mediated synaptic effect. We may also not have detected a direct dopaminergic response if dopamine-releasing varicosities from the vlPAG are not synaptic like the local VTA dopamine connections (Ford et al., 2009). In addition, TH(+) neurons can co-release glutamate, which has been demonstrated in the PAG projection to the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (Li et al., 2016a). Activation of PAG dopamine neurons have overall demonstrated antinociceptive effects (Li et al., 2016a; Taylor et al., 2019), but we cannot rule out the possibility that a small subset projecting to the VTA might participate in a pronociceptive, projection-specific effect.
The population of vlPAG neurons sending projections to the VTA is distinct from the PAG neuron population with descending projections to the rostral ventromedial medulla (RVM) (Suckow et al., 2013), where they synapse onto ON and OFF cells to bidirectionally modulate nociception. This organization allows the different PAG neurons to differentially control sensory, motor, and autonomic responses to incoming stimuli and influence behavior. Classically, the PAG is involved in a range of adaptive functions, including modulation of pain, response to fear, and autonomic regulation (Bandler and Depaulis, 1988; Behbehani, 1995). Activation of the vlPAG by focal electrical stimulation or local application of excitatory amino acids results in analgesia (Fardin et al., 1984), transient freezing (Morgan et al., 1998), quiescence (Depaulis et al., 1994), and bradycardia (Carrive and Bandler, 1991). Fanselow (1991) proposed a model in which the vlPAG mediates post-encounter defensive responses to a predator, including opioid-dependent analgesia, to enable inhibition of reflexive motor responses to pain, thus maintaining freezing behavior.
More recent studies have demonstrated a role for ascending PAG projections in aversive teaching signals during fear conditioning (Johansen et al., 2010; McNally and Cole, 2006). Human imaging studies also indicate that PAG activity encodes an aversive prediction error (Roy et al., 2014), and this information may be transmitted through the limbic system. Consistent with this human work, Johansen and colleagues demonstrated that an aversive prediction error is encoded in a subset of rodent PAG neurons: pharmacological inactivation of the PAG attenuates acquisition of fear conditioning, partly via downstream disruption of neural responses to aversive cues in the lateral amygdala (Johansen et al., 2010). The VTA sends dopamine (Breton et al., 2019; Swanson, 1982), GABA, and glutamate (Breton et al., 2019; Taylor et al., 2014) projections to the amygdala; therefore, one might speculate that the PAG promotes an aversive teaching signal in the amygdala via the VTA. Prolonged activation of the PAG-to-VTA pathway during headache may maintain and promote aversive learning, favoring the hypersensitivity and aversiveness of sensory stimuli (allodynia, photophobia, phono-phobia, and movement sensitivity) observed in headache states.
This aversive circuit from the vlPAG to the VTA can be contrasted with the neighboring appetitive, glutamatergic pathway from the dorsal raphe to the VTA in mice that triggers dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens (Qi et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2019). Focal electrical stimulation of the dorsal raphe can also elicit analgesia (Cannon et al., 1982). Therefore, these two adjacent midbrain regions provide opposing input to the limbic system.
Consistent with its role in generating an aversive signal, we demonstrate that inhibition of vlPAG inputs to the VTA is rewarding, but only in rats experiencing headache. When these inputs are inhibited in control animals, there is no obvious behavioral effect, but when these inputs are inhibited during headache, animals display approach behavior, likely because of the negative reinforcing effect of decreasing an aversive signal. Similarly, De Felice and colleagues found that inhibiting descending facilitation of pain transmission at the level of the RVM during headache generates conditioned place preference (CPP), which is accompanied by increased Fos expression in VTA dopamine neurons and requires dopamine signaling in the nucleus accumbens, a major VTA output (De Felice et al., 2013). Based on these studies, we propose that the vlPAG-VTA circuit produces an aversive effect by indirectly inhibiting dopamine VTA neurons projecting to the nucleus accumbens. Alternatively, optogenetically driving neural activity in lateral habenula-projecting VTA glutamatergic neurons (Root et al., 2014) or nucleus accumbens (NAc)-projecting glutamate VTA neurons (Qi et al., 2016) produces conditioned place aversion in mice. Other non-dopamine VTA neurons, as well as projections to the amygdala (de la Mora et al., 2010) and/or the anterior cingulate cortex (Narita et al., 2010), may also encode aversive signals.
A limitation to our behavioral inhibition studies is uncertainty about whether activation of eNpHR3.0-containing fibers in the VTA leads to sustained inhibition. While inhibition of cell bodies with eNpHR3.0 photoactivation has been demonstrated (Gradinaru et al., 2010), inhibition of terminal fibers may also generate a rebound excitation once light activation is discontinued (Mahn et al., 2016), potentially because of accumulation of intracellular CI−. Although the CPP we observe with activation of eNpHR3.0 may result from inhibition of PAG-to-VTA fibers, one alternative explanation is that rebound excitation of these fibers results in aversiveness associated with exiting the chamber paired with optical stimulation. However, given the current data, the simplest interpretation, that eNpHR3.0 activation is inhibiting this input, is consistent with all other observations reported here.
Further studies will be needed to determine whether the vlPAG-VTA circuit is sensitive to therapeutic manipulations that ameliorate headache. Relieving the aversiveness of headache is a critical unmet need for many patients. Here we show that the projection from the vlPAG to the VTA contributes to this signal and that inhibiting this connection is sufficient to produce relief.
STAR★METHODS
LEAD CONTACT AND MATERIALS AVAILABILITY
Further information and requests for resources, reagents, and protocols should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the Lead Contact, Maggie Waung (Maggie.waung@ucsf.edu). This study did not generate new unique reagents.
EXPERIMENTAL MODEL AND SUBJECT DETAILS
Animals
Male Sprague Dawley rats obtained from Charles River Laboratories (South San Francisco, CA) were used in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals under protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the University of California, San Francisco. Animals were maintained on a 12-hour light-dark cycle with lights on at 10:00 PM and allowed access to food and water ad libitum. Animals were group housed until undergoing intracranial surgery, after which they were single housed.
METHOD DETAILS
Viral Constructs and Antibodies
AAV2-hSyn-hChR2(H134R)-mCherry (titer: 2.9e12), AAV2-hSyn-mCherry (titer: 4.7e12), and AAV2-hSyn-eNpHR3.0-mCherry (1.5e12) were obtained from the University of North Carolina Vector Core with available stock constructs from the laboratory of K. Deisseroth at Stanford University.
C-Fos antibody (1:5000, Cell Signaling Technology Cat# 4384, RRID:AB_2106617) was a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against a synthetic peptide corresponding to amino acids near the carboxy-terminus of human c-Fos protein. TH antibody (1:250, Millipore Cat# AB152, RRID:AB_390204) was a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against denatured tyrosine hydroxylase from rat pheochro-mocytoma. NeuN antibody (1:1000, EMD Millipore Cat# MAB377, RRID:AB_2298772) was a mouse monoclonal antibody, clone A60, selected from immunoglobulins formed against purified cell nuclei from mouse brain. Secondary antibodies used were purchased from Jackson Immuno Research (Westgrove, PA): Cy5 Goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:500, Cat# 111-175-144, RRID:AB_2338013), Alexafluor 594 Donkey anti-rabbit IgG (1:500, Cat# 711-585-152, RRID:AB_2340621), Cy5 Goat anti-mouse IgG (1:500, Cat# 115-175-146, RRID:AB_2338713), and FITC streptavidin (1:200, Cat# 016-010-084, RRID:AB_2337236).
Stereotaxic injections
Rats weighing 100-120 g were anesthetized with 5% isofluorane via inhalation and placed into a stereotaxic frame. Bilateral craniotomies were created with a dental drill above the injection site. Injections of either AAV2-hSyn-hChR2(H134)-mCherry, AAV2-hSyn-eNpHR3.0-mCherry, or AAV2-hSyn-mCherry were made into the vlPAG (AP −7.8, DV −5.8, ML ± 0.6 mm from bregma) using a Nanoject II (Drummond Scientific, Broomall, PA). A volume of approximately 504 nanoliters was injected per side over a period of 4.5 min. The glass injector tip was left in place for 2 additional min before slow withdrawal to prevent backflow and infection of tissue dorsal to the vlPAG.
Dural cannula and optic fiber implant surgeries
Four to six weeks later, animals underwent a second cranial surgery to implant 200 mm optic fibers at a 12° angle off sagittal midline into the bilateral VTA (coordinates AP −5.8, DV −8.6, ML ± 2.4 mm from bregma). For induction of headache, a craniotomy was created above the superior sagittal sinus, under guidance of a dissecting microscope, with care to not disrupt the underlying dura. A dural guide cannula (20 gauge, 2mm pedestal, PlasticsOne, Roanoke, VA) was placed over the dura and a stylet inserted to maintain patency of the cannula. Optic fibers and cannulas were anchored with flat point screws and dental cement.
Animals were treated with subcutaneous carprofen 5 mg/kg and topical 2% lidocaine during the surgery for pain control. After surgery, animals had access to Tylenol in their drinking water for 3-5 days. Animals were allowed to recover for 1-2 weeks prior to behavioral studies and pain measurements with periorbital Von Frey testing. All virus injections, as well as fiber and cannula placements, were verified post mortem according to a rat brain atlas (Paxinos and Watson, 1998).
Electrophysiology
Rats were deeply anesthetized with isoflurane, decapitated, and brains were quickly removed into ice-cold artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF) consisting of (in mM): 119 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 1.0 NaH2PO4, 26.2 NaHCO3, 11 glucose, 1.3 MgSO4, 2.5 CaCl2, saturated with 95% O2-5% CO2, with a measured osmolarity 310-320 mOsm/L. 150-200 μm horizontal sections through the VTA were cut with a Leica VT1000 vibratome. Slices were incubated in oxygenated aCSF at 33 °C and allowed to recover for at least one hour. A single slice was placed in the recording chamber where it was continuously superfused at a rate of 2-3 mL/min with oxygenated aCSF. Neurons were visualized with an upright microscope (Olympus BX51WI or Zeiss Axioskop FS 2 plus) equipped with infrared-differential interference contrast and fluorescent optics. Whole cell recordings were made at 33°C using borosilicate glass microelectrodes (3-5 MΩ) filled with either K-gluconate internal solution containing (in mM): 123 K-gluconate, 10 HEPES, 8 NaCl, 0.2 EGTA, 2 MgATP, 0.3 Na3GTP, and 0.1% biocytin or KCl internal solution containing (in mM): 120 KCl, 10 HEPES, 1 EGTA, 0.3 CaCl2, 2 MgATP, 0.3 Na3GTP, and 0.1% biocytin (pH 7.2 adjusted with KOH; 275 mOsm/L). Liquid junction potentials were not corrected during recordings. Input and series resistance were monitored throughout the experiment with a hyperpolarizing step of 4 mV every 10-15 s. Series resistance was required to be 5-30 MΩ and cells with series resistance changes > 25% were excluded.
Signals were recorded using a patch clamp amplifier (Axopatch 1D, Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA). Signals were filtered at 5 kHz and collected at 20 kHz using IGOR Pro (Wavemetrics). Light evoked EPSCs and IPSCs were driven with paired blue light pulses (473 nm, 1-10 ms) administered 50 ms apart. Light was delivered by either an LED coupled to an optic fiber aimed at the recorded cell (10-15 mW) or a Xenon Arc laser light source guided onto the back aperture of the microscope objective for widefield exposure of the recorded slice (2-3 mW). Photostimulation sweeps were collected every 10-15 s. Recordings were made in voltage-clamp mode, with membrane potential clamped at Vm = −60 mV and −40 mV, for EPSCs and IPSCs, respectively. EPSCs and IPSCs with an amplitude at least 2 standard deviations above noise that were time-locked with short latency (< 5 ms) and repeatable were considered light-evoked. Latency was calculated as time from start of light pulse to 10% of the peak amplitude. Where possible, DNQX (10 μM) or gabazine (10 μM) was bath applied to identify currents as AMPA or GABAA receptor mediated, respectively. All recordings were analyzed offline using IGOR Pro with 10-20 sequential stimulations averaged together to estimate synaptic amplitude. After recordings, slices were drop fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 2 hours at 4°C and processed for TH immunocyto-chemistry and biocytin labeling.
Inflammatory mediators headache model
After at least one week of recovery following implant surgery, animals were treated with dural inflammatory mediators (IMs, comprised of 1 mM histamine, serotonin, bradykinin, and 0.1 mM prostaglandin E2 in HEPES-buffered saline, pH 7.4). Animals were gently restrained while a microinjector was inserted into the dural guide cannula. 10 μL of phosphate buffered saline (PBS) or IMs was slowly infused over 2 minutes with a KD Scientific (Holliston, MA) microinjection pump fitted with a 25 μL Hamilton syringe. A 1 min refractory period followed the injection to allow for diffusion of the injected solution. Five to ten minutes following infusions, mechanical withdrawal thresholds were evaluated.
Periorbital Von Frey testing
Mechanical threshold testing in the V1 dermatome was conducted using eight Touch Test ® fibers (North Coast Medical & Rehabilitation Products, Gilroy, CA, USA) ranging from 0.06 to 15 g. Fibers were pressed perpendicularly to the periorbital region above the eye and held for 2-3 s. A positive response was noted if the head was withdrawn. The 50% withdrawal threshold was obtained and calculated according to the up-down method (Chaplan et al., 1994).
Retrograde tracing
Similar to virus injections, Fluoro-gold (FG, 55.2 nL 4% in H20, Biotium, Fremont, CA) was injected into the right VTA (AP −5.8, DV −8.5, ML 0.5 mm from bregma) of animals weighing 275-300 g. In the same surgery, a dural cannula was placed for IM infusions as described above. One week after FG injection, animals underwent microinjection of PBS or IMs into dural cannulas. Two hours after injection, animals were deeply anesthetized and perfused.
Brain removal for immunohistochemistry
Animals were deeply anesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of Euthasol (0.5 mg/kg). After becoming unresponsive to noxious stimuli, the animals were transcardially perfused with 100 mL of normal saline, followed by 400 mL of 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (PFA). The brains were extracted and immersion-fixed in PFA for 2 h at room temperature, then washed two times with PBS to remove excess PFA, and stored in PBS at 4°C until they were subsequently sectioned (50 μm slices) using a vibratome (Leica VT 1000 S).
Histology and immunohistochemistry
Slices were washed three times for 5 minutes each with PBS (GIBCO, Waltham, MA), then blocked with a solution containing: bovine serum albumin (0.2%), normal goat serum (5%) and Tween20 (0.3%; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) for 2 h at room temperature. For Fos staining, normal donkey serum (5%) was used in place of normal goat serum. Slices were incubated in primary antibodies diluted in PBS + 0.3% Tween20 (PBST) for 48 hours at 4°C. After 6 10-minute rinses in PBST, slices were incubated with secondary antibody overnight at 4°C. After 5, 10-min rinses, brain slices were mounted onto glass slides with Vectashield (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA). Slices were imaged using a Zeiss Axioskop upright microscope (2.5X, NA = 0.075 or Olympus Plan Apochromat 20X, NA = 0.75).
Stereological neuron counting
Coronal vlPAG slices with a section thickness of 50 μm were collected from each animal. Three animals were used per condition and counting was performed blinded to treatment. The optical fractionator method was used for cell counting: the first slice was chosen at random from the first 4 slices and every 4th slice thereafter was sampled to ensure random and systematic sampling throughout the rostral-caudal axis of the vlPAG, with 16 vlPAG slices collected per animal. For each slice, the vlPAG ipsilateral to the Fluorogold injection was traced using the 2.5X objective. Z stacks of the entire vlPAG were taken using the 20X objective. For counting of Fos and FG double-labeling, the entire area was counted (area sampling fraction, asf = 1). For NeuN counting, the area sampling fraction was set at 0.05. An estimate of the total number of neurons in the vlPAG (N = 35,200) can be calculated by the equation, N = ∑Q−•(t /h)•(1 /asf)•(1 /ssf), where Q− is the number of NeuN neurons counted (330), t is the section mounted thickness, which accounts for slice shrinkage (40 μm), h is the counting frame height (30 μm), asf (0.05), and ssf is the section sample fraction (0.25). Fos staining in the TNC (or Sp5C) was counted in the same manner. The coefficient of error calculated by the Gunderson method was less than 0.1 for region sections from each animal. Statistics between conditions were calculated based on total cell counts obtained from each animal.
Real-time place preference assay
Two-sided chambers with distinct visual (horizontal versus vertical stripes) and textural (thick versus thin mesh flooring) cues separated by a central vestibule were used. Prior to testing, animals were acclimated to handling and attachment of fiber cables to intracranial fiber implants in a neutral environment. Animals were allowed up to 3 opportunities to explore the test chambers for 15-minute baseline sessions. Only animals that spent similar time within 15% of the total time in both chambers by the 3rd session were included. On testing days, fiber implants were connected to optic fiber cables attached to a 1× 2 fiber optic rotary joint (Doric Lenses, Quebec, Canada).
For ChR2 activation studies, a laser light source (MBL 473, OEM Laser Systems, East Lansing, MI) was used with light intensity at the end of the output fiber adjusted to 80-120 mW/mm2 at the fiber tip. One side of the chamber was paired with a light stimulation pattern of 5 ms pulses at 20 Hz, which commenced when the animal’s head crossed the threshold into the paired chamber and discontinued when the animal’s head exited the paired chamber. The side of the chamber used for light-pairing was chosen randomly for each animal and counterbalanced between all animals. Light stimulation was controlled via a custom-made program interface run on a Raspberry Pi (Cambridge, UK) using a Pixy camera (Charmed Labs, Pittsburgh, PA) to track the animal in real time, triggering the laser via an Arduino pulse generator (SparkFun, Niwat, CO). Animals were initially placed in the vestibule and allowed to ambulate freely in the chamberfor20 minutes while receiving light stimulation in the paired side. Animals underwent once daily light-stimulation pairing sessions 3 times on one side followed by 3 sessions with light-pairing to the opposite chamber. The day after the last training session, animals were placed in the CPP apparatus for 40 minutes, and light stimulation was alternated every 10 minutes between the 2 chambers (Figure S4).
For in vivo terminal fiber inhibition studies, a laser light source (MSL-III-532, λ = 525 nm, CNI Optoelectronics, Changchun, China) was used with intensity of the output fiber adjusted to 120-160 mW/mm2 at the fiber tip. On testing days, rats were infused with PBS or IMs. 10-20 minutes later, they were placed in the central vestibule of the testing chamber. One side was paired with continuous light stimulation. Animals spent 20 minutes in the chamber per training day, interleaved with no treatment days to allow recovery from headache between infusions. Two days after the last infusion, rats were placed in the chamber allowed to roam freely without any light stimulation. Time spent in each chamber was recorded using Viewer software (Biobserve, Bonn, Germany).
General Experimental Design
For immunohistological and behavioral experiments, subject numbers were determined by pilot studies and power analyses (power = 0.80, significance level = 0.05, effect size = 15-30%). All behavioral experiments were performed blinded to experimental condition.
QUANTIFICATION AND STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean in figures and text. Unless otherwise stated, two-tailed t tests were performed. Significance was set at p < 0.05. Repeated-measures ANOVAs were conducted in SPSS version 25 (IBM Analytics, Armonk, NY) to compare across greater than 2 independent variables. Replicates are reported in figure captions and sample numbers are included in the text.
DATA AND CODE AVAILABILITY
Source data for Figures 2, 3, and 4 in the paper are available on Mendeley https://doi.org/10.17632/yhtnjnf2jf.1. Tracking software code used for this study is available at https://github.com/charmedlabs/pixy. The user interface code used for this study is not central to generation of the results, but will be made available from the corresponding author upon request.
Supplementary Material
KEY RESOURCES TABLE
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| C-Fos antibody | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#4384; RRID: AB_2106617 |
| TH antibody | Millipore | Cat#AB152; RRID: AB_390204 |
| NeuN antibody | EMD Millipore | Cat#MAB377; RRID: AB_2298772 |
| Cy5 Goat anti-rabbit IgG | Jackson Immuno Research | Cat#111-175-144; RRID: AB_2338013 |
| Alexafluor 594 Donkey anti-rabbit IgG | Jackson Immuno Research | Cat#711-585-152; RRID: AB_2340621 |
| Cy5 Goat anti-mouse IgG | Jackson Immuno Research | Cat#115-175-146; RRID: AB_2338713 |
| FITC streptavidin | Jackson Immuno Research | Cat#016-010-084; RRID: AB_2337236 |
| Bacterial and Virus Strains | ||
| AAV2-hSyn-hChR2(H134R)-mCherry | University of North Carolina Vector Core, stock constructs from the laboratory of K. Deisseroth at Stanford University | n/a |
| AAV2-hSyn-mCherry | University of North Carolina Vector Core, stock constructs from the laboratory of K. Deisseroth at Stanford University | n/a |
| AAV2-hSyn-eNpHR3.0-mCherry | University of North Carolina Vector Core, stock constructs from the laboratory of K. Deisseroth at Stanford University | n/a |
| Chemicals, Peptides, and Recombinant Proteins | ||
| Fluoro-Gold | Biotium | Cat#80023 CAS 223769-64-0 |
| Biocytin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#B4261 CAS 576-19-2 |
| Histamine | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#H7250 CAS 56-92-8 |
| Serotonin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#H9523 CAS 153-98-0 |
| Bradykinin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#B3259 CAS 6846-03-3 |
| Prostaglandin E2 | Millipore | Cat#538904 CAS 363-24-6 |
| 4-Aminopyridine | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#275875 CAS 504-24-5 |
| Tetrodotoxin | Tocris | Cat#1078 CAS 4368-28-9 |
| Gabazine (SR 95531) | Tocris | Cat#1262 CAS 104104-50-9 |
| DNQX | Tocris | Cat#0189 CAS 2379-57-9 |
| Paraformaldehyde | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#158127 CAS 30525-89-4 |
| Vectashield | Vector Labs | Cat#H-1000 |
| AP-5 | Tocris | Cat#0106 CAS 79055-68-8 |
| Deposited Data | ||
| A midbrain circuit that mediates headache aversiveness | Mendeley Data | https://doi.org/10.17632/yhtnjnf2jf.1 |
| Experimental Models: Organisms/Strains | ||
| Model organism: Sprague Dawley rat | Charles River Laboratories | n/a |
| Software and Algorithms | ||
| Igor Pro 6 | WaveMetrics | RRID: SCR_000325 |
| Viewer II software | Biobserve | RRID: SCR_014337 |
| Stereoinvestigator | MBF | n/a |
| SPSS 25 | IBM | RRID: SCR_002865 |
| Other | ||
| Nanoject II | Drummond Scientific | Cat#3-000-204 |
| PixyCam | Charmed Labs | n/a |
| Arduino Uno | SparkFun Electronics | Cat#DEV-11021 |
Highlights.
Ventrolateral periaqueductal gray (vlPAG) sends inputs to ventral tegmental area (VTA)
vlPAG projections to VTA are both excitatory and inhibitory
vlPAG neurons that project to VTA are activated during headache in rats
Inhibition of the vlPAG-VTA circuit relieves the aversive state elicited during headache
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Samuel Chia, Ryan Carothers, Michelle Lee, Benjamin Snyder, and Gabrielle Mintz for technical assistance. We also thank Frederic W. Hopf, Jennifer M. Mitchell, and Allan I. Basbaum for helpful discussions. This work was supported by the NIH (grant numbers K08 NS097632 to M.W.W. and R01 DA030529 to E.B.M.) and a Weill Scholar Award to M.W.W. from the UCSF Weill Innovation Fund.
Footnotes
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
Supplemental Information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.08.009.
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
REFERENCES
- Bandler R, and Depaulis A (1988). Elicitation of intraspecific defence reactions in the rat from midbrain periaqueductal grey by microinjection of kainic acid, without neurotoxic effects. Neurosci. Lett 88, 291–296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbaresi P, and Manfrini E (1988). Glutamate decarboxylase-immunoreactive neurons and terminals in the periaqueductal gray of the rat. Neuroscience 27, 183–191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behbehani MM (1995). Functional characteristics of the midbrain periaqueductal gray. Prog. Neurobiol 46, 575–605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behbehani MM, and Fields HL (1979). Evidence that an excitatory connection between the periaqueductal gray and nucleus raphe magnus mediates stimulation produced analgesia. Brain Res. 170, 85–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonafede M, Sapra S, Shah N, Tepper S, Cappell K, and Desai P (2018). Direct and Indirect Healthcare Resource Utilization and Costs Among Migraine Patients in the United States. Headache 58, 700–714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breton JM, Charbit AR, Snyder BJ, Fong PTK, Dias EV, Himmels P, Lock H, and Margolis EB (2019). Relative contributions and mapping of ventral tegmental area dopamine and GABA neurons by projection target in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol 527, 916–941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron AA, Khan IA,Westlund KN, Cliffer KD, and Willis WD (1995). The efferent projections of the periaqueductal gray in the rat: a Phaseolus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin study. I. Ascending projections. J. Comp. Neurol 351, 568–584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon JT, Prieto GJ, Lee A, and Liebeskind JC (1982). Evidence for opioid and non-opioid forms of stimulation-produced analgesia in the rat. Brain Res. 243, 315–321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrive P, and Bandler R (1991). Viscerotopic organization of neurons subserving hypotensive reactions within the midbrain periaqueductal grey: a correlative functional and anatomical study. Brain Res. 541, 206–215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, and Yaksh TL (1994). Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J. Neurosci. Methods 53, 55–63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z, Chen X, Liu M, Liu S, Ma L, and Yu S (2017). Disrupted functional connectivity of periaqueductal gray subregions in episodic migraine. J. Headache Pain 18, 36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Felice M, Eyde N, Dodick D, Dussor GO, Ossipov MH, Fields HL, and Porreca F (2013). Capturing the aversive state of cephalic pain preclinically. Ann. Neurol 74, 257–265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Mora MP, Gallegos-Cari A, Arizmendi-García Y, Marcellino D, and Fuxe K (2010). Role of dopamine receptor mechanisms in the amygdaloid modulation of fear and anxiety: Structural and functional analysis. Prog. Neurobiol 90, 198–216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depaulis A, Keay KA, and Bandler R (1994). Quiescence and hyporeactivity evoked by activation of cell bodies in the ventrolateral midbrain periaqueductal gray of the rat. Exp. Brain Res 99, 75–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelmayer RM, Vanderah TW, Majuta L, Zhang ET, Fioravanti B, De Felice M, Chichorro JG, Ossipov MH, King T, Lai J, et al. (2009). Medullary pain facilitating neurons mediate allodynia in headache-related pain. Ann. Neurol 65, 184–193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanselow MS (1991). The midbrain periaqueductal gray as a coordinator of action in response to fear and anxiety In The Midbrain Periaqueductal Gray Matter, Depaulis A and Bandler R, eds. (Springer; ), pp. 151–173. [Google Scholar]
- Fardin V, Oliveras JL, and Besson JM (1984). A reinvestigation of the analgesic effects induced by stimulation of the periaqueductal gray matter in the rat. I. The production of behavioral side effects together with analgesia. Brain Res. 306, 105–123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford CP, Phillips PE, and Williams JT (2009). The time course of dopamine transmission in the ventral tegmental area. J. Neurosci 29, 13344–13352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators (2017). Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 390, 1211–1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler S, Derst C, Veh RW, and Zahm DS (2007). Glutamatergic afferents of the ventral tegmental area in the rat. J. Neurosci 27, 5730–5743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradinaru V, Zhang F, Ramakrishnan C, Mattis J, Prakash R, Diester I, Goshen I, Thompson KR, and Deisseroth K (2010). Molecular and cellular approaches for diversifying and extending optogenetics. Cell 141, 154–165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen JP, Tarpley JW, LeDoux JE, and Blair HT (2010). Neural substratesforexpectation-modulated fear learning in the amygdala and periaqueductal gray. Nat. Neurosci 13, 979–986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammel S, Lim BK, Ran C, Huang KW, Betley MJ, Tye KM, Deisseroth K, and Malenka RC (2012). Input-specific control of reward and aversion in the ventral tegmental area. Nature 491, 212–217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C, Sugam JA, Lowery-Gionta EG, McElligott ZA, McCall NM, Lopez AJ, McKlveen JM, Pleil KE, and Kash TL (2016a). Mu Opioid Receptor Modulation of Dopamine Neurons in the Periaqueductal Gray/Dorsal Raphe: A Role in Regulation of Pain. Neuropsychopharmacology 41, 2122–2132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z, Liu M, Lan L, Zeng F, Makris N, Liang Y, Guo T, Wu F, Gao Y, Dong M, et al. (2016b). Altered periaqueductal gray resting state functional connectivity in migraine and the modulation effect of treatment. Sci. Rep 6, 20298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovick TA (1993). The periaqueductal gray-rostral medulla connection in the defence reaction: efferent pathways and descending control mechanisms. Behav. Brain Res 58, 19–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahn M, Prigge M, Ron S, Levy R, and Yizhar O (2016). Biophysical constraints of optogenetic inhibition at presynaptic terminals. Nat. Neurosci 19, 554–556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainero C, Boshyan J, and Hadjikhani N (2011). Altered functional magnetic resonance imaging resting-state connectivity in periaqueductal gray networks in migraine. Ann. Neurol 70, 838–845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniyar FH, Sprenger T, Monteith T, Schankin C, and Goadsby PJ (2014). Brain activations in the premonitory phase of nitroglycerin-triggered migraine attacks. Brain 137, 232–241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh PW (1983). Connectionsofmidbrain periaqueductal gray in the monkey. I. Ascending efferent projections. J. Neurophysiol 49, 567–581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis EB, Lock H, Hjelmstad GO, and Fields HL (2006). The ventral tegmental area revisited: is there an electrophysiological marker for dopaminergic neurons? J. Physiol 577, 907–924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis EB, Toy B, Himmels P, Morales M, and Fields HL (2012). Identification of rat ventral tegmental area GABAergic neurons. PLoS ONE 7, e42365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally GP, and Cole S (2006). Opioid receptors in the midbrain periaqueductal gray regulate prediction errors during pavlovian fear conditioning. Behav. Neurosci 120, 313–323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan MM, and Whitney PK (2000). Immobility accompanies the antinociception mediated by the rostral ventromedial medulla of the rat. Brain Res. 872,276–281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan MM, Whitney PK, and Gold MS (1998). Immobility and flight associated with antinociception produced by activation of the ventral and lateral/dorsal regions of the rat periaqueductal gray. Brain Res. 804,159–166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narita M, Matsushima Y, Niikura K, Narita M, Takagi S, Nakahara K, Kurahashi K, Abe M, Saeki M, Asato M, et al. (2010). Implication of dopaminergic projection from the ventral tegmental area to the anterior cingulate cortex in μ-opioid-induced place preference. Addict. Biol 15, 434–447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ntamati NR, Creed M, Achargui R, and Lüscher C (2018). Periaqueductal efferents to dopamine and GABA neurons of the VTA. PLoS ONE 13, e0190297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omelchenko N, and Sesack SR (2010). Periaqueductal gray afferents synapse onto dopamine and GABA neurons in the rat ventral tegmental area. J. Neurosci. Res 88, 981–991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshinsky ML, and Gomonchareonsiri S (2007). Episodic dural stimulation in awake rats: a model for recurrent headache. Headache 47, 1026–1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paxinos G, and Watson C (1998). The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, Fourth Edition (Academic Press; ). [Google Scholar]
- Petreanu L, Mao T, Sternson SM, and Svoboda K (2009). The subcellular organization of neocortical excitatory connections. Nature 457, 1142–1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi J, Zhang S, Wang HL, Wang H, de Jesus Aceves Buendia J, Hoffman AF, Lupica CR, Seal RP, and Morales M (2014). A glutamatergic reward input from the dorsal raphe to ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons. Nat. Commun 5, 5390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi J, Zhang S, Wang HL, Barker DJ, Miranda-Barrientos J, and Morales M (2016). VTA glutamatergic inputs to nucleus accumbens drive aversion by acting on GABAergic interneurons. Nat. Neurosci 19, 725–733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskin NH, Hosobuchi Y, and Lamb S (1987). Headache may arise from perturbation of brain. Headache 27, 416–420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root DH, Mejias-Aponte CA, Qi J, and Morales M (2014). Role of glutamatergic projections from ventral tegmental area to lateral habenula in aversive conditioning. J. Neurosci 34, 13906–13910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy M, Shohamy D, Daw N, Jepma M, Wimmer GE, and Wager TD (2014). Representation of aversive prediction errors in the human periaqueductal gray. Nat. Neurosci 17, 1607–1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samineni VK, Grajales-Reyes JG, Copits BA, O’Brien DE, Trigg SL, Gomez AM, Bruchas MR, and Gereau RW 4th. (2017). Divergent Modulation of Nociception by Glutamatergic and GABAergic Neuronal Subpopulations in the Periaqueductal Gray. eNeuro 4, ENEURO.0129–16.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strassman AM, Raymond SA, and Burstein R (1996). Sensitization of meningeal sensory neurons and the origin of headaches. Nature 384,560–564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suckow SK, Deichsel EL, Ingram SL, Morgan MM, and Aicher SA (2013). Columnardistribution ofcatecholaminergic neurons in theventrolateral periaqueductal gray and their relationship to efferent pathways. Synapse 67, 94–108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson LW (1982). The projections of the ventral tegmental area and adjacent regions: a combined fluorescent retrograde tracer and immunofluorescence study in the rat. Brain Res. Bull 9, 321–353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor SR, Badurek S, Dileone RJ, Nashmi R, Minichiello L, and Picciotto MR (2014). GABAergic and glutamatergic efferents of the mouse ventral tegmental area. J. Comp. Neurol 522, 3308–3334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor NE, Pei J, Zhang J, Vlasov KY, Davis T, Taylor E, Weng FJ, Van Dort CJ, Solt K, and Brown EN (2019). The Role of Glutamatergic and Dopaminergic Neurons in the Periaqueductal Gray/Dorsal Raphe: Separating Analgesia and Anxiety. eNeuro 6, ENEURO.0018–18.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zessen R, Phillips JL, Budygin EA, and Stuber GD (2012). Activation of VTA GABA neurons disrupts reward consumption. Neuron 73, 1184–1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang HL, Zhang S, Qi J, Wang H, Cachope R, Mejias-Aponte CA, Gomez JA, Mateo-Semidey GE, Beaudoin GMJ, Paladini CA, et al. (2019). Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses on VTA Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Neurons. Cell Rep. 26, 1128–1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiller C, May A, Limmroth V, Jüptner M, Kaube H, Schayck RV, Coenen HH, and Diener HC (1995). Brain stem activation in spontaneous human migraine attacks. Nat. Med 1, 658–660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West MJ, and Gundersen HJ (1990). Unbiased stereological estimation of the number of neurons in the human hippocampus. J. Comp. Neurol 296, 1–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Source data for Figures 2, 3, and 4 in the paper are available on Mendeley https://doi.org/10.17632/yhtnjnf2jf.1. Tracking software code used for this study is available at https://github.com/charmedlabs/pixy. The user interface code used for this study is not central to generation of the results, but will be made available from the corresponding author upon request.