Abstract
Background
The increase and spread of virulent-outbreak associated, methicillin and vancomycin resistant (MRSA/VRSA) Staphylococcus aureus require a better understanding of the resistance and virulence patterns of circulating and emerging strains globally. This study sought to establish the resistance phenotype, and strains of 32 non-duplicate clinical MRSA and MSSA S. aureus isolates from four Kenyan hospitals, identify their resistance and virulence genes and determine the genetic relationships of MRSA with global strains.
Methods
Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles were determined on a Vitek 2, genomic DNA sequenced on an Illumina Miseq and isolates typed in-silico. Resistance and virulence genes were identified using ARIBA and phylogenies generated using RAxML.
Results
The MRSA isolates were 100% susceptible to vancomycin, teicoplanin, linezolid, and tigecycline. Nine distinct CC, 12 ST and 15 spa types including the novel t17826 and STs (4705, 4707) were identified with CC8 and CC152 predominating. MRSA isolates distributed across 3 CCs; CC5-ST39 (1), CC8 – ST241 (4), a novel CC8-ST4705 (1), ST8 (1) and CC152 (1). There was > 90% phenotype-genotype concordance with key resistance genes identified only among MRSA isolates: gyrA, rpoB, and parC mutations, mecA, ant (4′)-lb, aph (3′)-IIIa, ermA, sat-4, fusA, mphC and msrA. Kenyan MRSA isolates were genetically diverse and most closely related to Tanzanian and UK isolates. There was a significant correlation between map, hlgA, selk, selq and cap8d virulence genes and severe infections.
Conclusion
The findings showed a heterogeneous S. aureus population with novel strain types. Though limited by the low number of isolates, this study begins to fill gaps and expand our knowledge of S. aureus epidemiology while uncovering interesting patterns of distribution of strain types which should be further explored. Although last-line treatments are still effective, the potential for outbreaks of both virulent and resistant strains remain, requiring sustained surveillance of S. aureus populations.
Keywords: MRSA, MSSA, Kenya, Virulence, Resistance, Genome
Background
Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive bacterium responsible for a broad spectrum of clinical infections ranging from benign skin rashes to necrotizing tissue and pulmonary lesions. The increasing prevalence of multidrug-resistant methicillin and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus strains (MRSA and VRSA) limit available therapeutic options making these infections challenging to manage. Since the emergence of methicillin resistance (MRSA) in the 1940s, epidemics caused by successful MRSA [1, 2] have been observed, e.g. USA 300, a highly virulent MRSA strain that emerged in the USA and is currently associated with community outbreaks globally [3] and E-MRSA 15 which emerged in the UK and caused various hospital outbreaks [4]. The clonal success is attributed to factors that enhance binding to host tissues and the acquisition of virulence genes, e.g., USA 300 which has acquired the arginine catabolic mobile element, sek and seq virulence genes [5–7]. Nosocomial outbreaks of MRSA are frequent in daycare centers, nursing homes, and critical care units [8] and with the emergence of more virulent CA-MRSA [9], S. aureus outbreaks can significantly increase morbidity and mortality.
S. aureus can exhibit resistance to several antibiotics due to genes encoded on the chromosome and the acquisition of resistance genes by horizontal transfer of individual genes or resistance islands from other S. aureus isolates and other bacterial species, e.g., Van genes acquired from Vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) on mobile elements [10]. The implications of acquired drug resistance in bacteria to public health are profound. In Kenya, previously manageable diseases such as typhoid and cholera have caused health crises due to the emergence of highly drug-resistant strains of H58 Salmonella typhi [11] and Vibrio cholera [12, 13] that quickly dominate endemic antibiotic sensitive strains both locally and globally [14]. Monitoring of emerging resistance patterns and genes is therefore essential for the management of new resistant strains with outbreak potential.
Phenotypic testing is the gold standard for determining the antibiotic susceptibility of a bacterium [15] but is limited by the number of antibiotics one can reasonably test in the laboratory. Genomic analysis is ideal for detecting resistance against multiple antibiotics, identifying new resistance genes, mutations or new synergistic relationships affecting resistance genes. Genomic testing is best when used in tandem with existing phenotypic data since it can be challenging to predict resistance based solely only on the presence or absence of resistance genes [16, 17] due to redundant antibiotic resistance mechanisms and the impact of mutations in resistance genes, modifiers of gene expression and accessory genes on phenotypic resistance.
Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) and typing of the staphylococcal protein A (spa) gene have been widely used to identify different S. aureus strain types [18, 19]. For MRSA, typing of the staphylococcal cassette chromosome (SCCmec) which harbors the gene encoding methicillin resistance provides additional strain discrimination [20–22]. Studies on S. aureus isolates from Kenya have focused mainly on antimicrobial susceptibility testing [23, 24] and strain typing with limited testing for resistance genes and virulence determinants which can influence infection severity. The virulence genes reported in the few Kenyan studies looking at both S. aureus infections and carriage include Panton-Valentine leukocidin (pvl), Toxic shock syndrome (tsst-1), exfoliative toxin A and enterotoxin A with a notably high prevalence of pvl reported [25, 26]. These studies were, however, limited to four healthcare institutions in close geographic proximity. Therefore, there is limited information on the genomic diversity and distribution of the S. aureus population across Kenya.
This study sought to fill this gap by characterizing both resistance and virulence determinants of clinical isolates from different geographical areas in Kenya and identifying the relationships between Kenyan MRSA strains and known global strains. By broadening our understanding of the S. aureus population in Kenya, this study provides baseline epidemiological data on the type distribution, drug resistance patterns and emerging virulent strains in Kenya.
Results
Of the 17 antibiotics tested only 16 had complete results for all isolates. All isolates were resistant to at least one of the drugs in the panel of 16 antibiotics analyzed. No resistance was detected against vancomycin, teicoplanin, tigecycline or nitrofurantoin in any isolate while all isolates were resistant to penicillin (Additional file 1). Eight isolates were classified as MRSA and confirmed to possess the mecA gene by PCR.
There was high sensitivity to vancomycin, linezolid, teicoplanin, nitrofurantoin and tigecycline among all isolates. The MRSA isolates were multidrug resistant with 100% resistance to erythromycin, oxacillin, cefoxitin and had varied susceptibilities to rifampicin (50%) and < 25% susceptibility to the remaining drugs tested. In contrast, among the 24 MSSA isolates, > 70% were susceptible to a majority of antibiotics tested with reduced susceptibility (< 75%) to trimethoprim (71%) and rifampicin (67%) (Additional file 1).
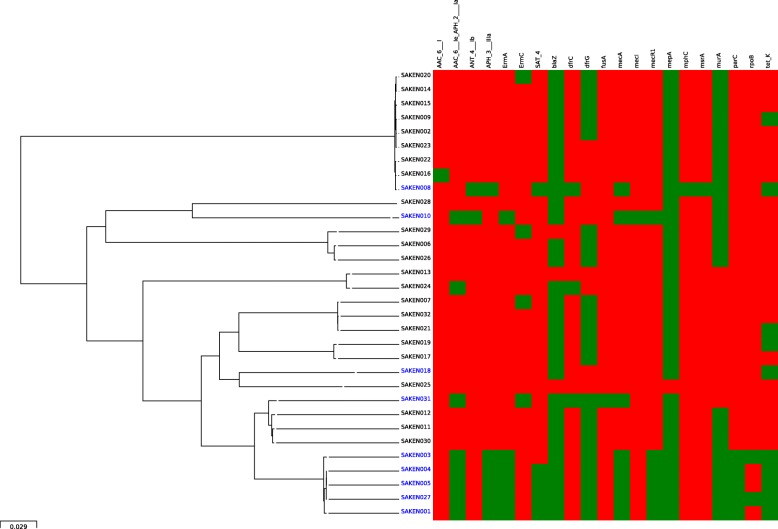
Resistance genes identified are listed in Additional file 1, and their distribution is shown on the heat map in Fig. 1. Phenotype-genotype concordance of 90–99% was observed. Discordance was observed for rifampicin and aminoglycosides drug classes. The genes 23S rRNA and tet38, important in macrolides and tetracycline resistance [27, 28] and the multigene regulators important for multidrug resistance and virulence gene expression arlR/arlS, mgrA [29–31] were ubiquitously expressed among the isolates and are not indicated on the figure. All the MRSA isolates had mecA mediated methicillin resistance. The multidrug resistant phenotype of the MRSA isolates was supported by the presence of multiple antibiotic resistance genes which varied in number and composition by the MRSA lineages (Fig. 1). The resistance genes detected among MRSA ranged from 9 to 14 compared to 1–5 for MSSA isolates. The genes associated only with MRSA isolates were the ant (4′)-lb, aph (3′)-IIIa, ermA, sat-4, fusA, mphC, msrA genes, the quinolone resistance-conferring mutations on parC (S80F) and gyrA (S84 L) and the rifampicin resistance mutations in rpoB. TetK, dfrG, and dfrC were found among both MSSA and MRSA.
Fig. 1.
Core genome SNP phylogeny and heat map of antibiotic resistance genes identified. MRSA isolates are shown in blue and MSSA isolates are in black. Green denotes the presence and red the absence of the genes listed. Ubiquitously expressed genes are not indicated (S. aureus 23S, arlR, arlS, mgrA, and tet38)
Isolate typing using the various methods indicated great diversity among the isolates with identification of 9 distinct clonal complexes (CC5, 8, 15, 22, 80, 88, 121, 152, 580), 12 ST types (ST8, 15, 22, 39, 80, 121, 152, 241, 580, 1633, 4705, 4707), 15 spa types (t005, t007, t037, t064, t084, t186, t272, t314, t355, t1476, t2029, t4198, t5941, t13194 and a novel spa type, assigned t17826) (Table 1). Among the MRSA, three known staphylococcal cassette chromosome types, SCCmec_type2A, 3A and 2B and a novel divergent SCCmec element were identified.
Table 1.
Table of isolate characteristics
| Isolate ID | Clonal complex | ST | spa type | SSC mec | REGION | CAI/HAIb | IP/OP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRSA | SAKEN001 | 8 | 241 | 37 | SCC mec _type_III (3A) | Kisumu | CAI | In-patient |
| SAKEN003 | 8 | 4705 a | 2029 | SCC mec _type_III (3A) | Kisumu | CAI | Outpatient | |
| SAKEN004 | 8 | 241 | 37 | SCC mec _type_III (3A) | Kisumu | HAI | In-patient | |
| SAKEN005 | 8 | 241 | 37 | SCC mec _type_III (3A) | Kisumu | CAI | In-patient | |
| SAKEN008 | 152 | 152 | 355 | SCC mec _type_IVa (2B) | Nairobi | CAI | Out-patient | |
| SAKEN010 | 5 | 39 | 7 | SCC mec _type_II (2A) | Kisumu | CAI | Out-patient | |
| SAKEN027 | 8 | 241 | 37 | SCC mec _type_III (3A) | Kisumu | HAI | In-patient | |
| SAKEN031 | 8 | 8 | 1476 | novel cassette: mecA present | Nairobi | CAI | Out-patient | |
| MSSA | SAKEN017 | 15 | 15 | 84 | n/a | Kericho | CAI | Out-patient |
| SAKEN024 | 22 | 22 | 5 | n/a | Kericho | CAI | Out-patient | |
| SAKEN032 | 80 | 80 | 13,194 | n/a | Kericho | CAI | Out-patient | |
| SAKEN026 | 121 | 121 | 314 | n/a | Kericho | CAI | Out-patient | |
| SAKEN009 | 152 | 152 | 355 | n/a | Kericho | CAI | In-patient | |
| SAKEN016 | 152 | 152 | 355 | n/a | Kericho | CAI | Out-patient | |
| SAKEN025 | 5 | 4707a | 17826a | n/a | Kisumu | CAI | Out-patient | |
| SAKEN030 | 8 | 8 | unknown | n/a | Kisumu | CAI | In-patient | |
| SAKEN019 | 15 | 15 | unknown | n/a | Kisumu | CAI | In-patient | |
| SAKEN018 | 88 | 88 | 186 | n/a | Kisumu | CAI | Out-patient | |
| SAKEN029 | 121 | 121 | 272 | n/a | Kisumu | CAI | Out-patient | |
| SAKEN002 | 152 | 152 | 355 | n/a | Kisumu | CAI | Out-patient | |
| SAKEN011 | 8 | 8 | 64 | n/a | Kisumu | CAI | In-patient | |
| SAKEN012 | 8 | 8 | 64 | n/a | Kisumu | CAI | In-patient | |
| SAKEN021 | 80 | 80 | 13,194 | n/a | Kisumu | CAI | Out-patient | |
| SAKEN020 | 152 | 152 | 355 | n/a | Kisumu | CAI | In-patient | |
| SAKEN028 | 580 | 580 | unknown | n/a | Malindi | CAI | Out-patient | |
| SAKEN013 | 22 | 22 | 84 | n/a | Nairobi | CAI | Out-patient | |
| SAKEN007 | 80 | 80 | 5941 | n/a | Nairobi | CAI | In-patient | |
| SAKEN006 | 121 | 121 | 4198 | n/a | Nairobi | CAI | In-patient | |
| SAKEN014 | 152 | 152 | 355 | n/a | Nairobi | HAI | In-patient | |
| SAKEN015 | 152 | 1633 | 355 | n/a | Nairobi | HAI | In-patient | |
| SAKEN022 | 152 | 152 | 355 | n/a | Nairobi | CAI | Out-patient | |
| SAKEN023 | 152 | 152 | 355 | n/a | Nairobi | CAI | In-patient |
adenotes a novel ST and spa type. bCAI community-acquired infection, HAI hospital-acquired infection. MRSA isolates are shown in bold
A majority of the isolates belonged to CC152 (9/32) and CC8 (9/32). MRSA in this study classified as CC5, 8 and 152 with a majority (4/9) belonging to ST241 and spa type t037. Two novel STs assigned ST4705 (CC8, MRSA) and ST4707 (CC5, MSSA) by PubMLST [32] were reported. Spa typing indicated t355 as the dominant spa type (9/32; 28.1%). The eight MRSA isolates belonged to 5 spa types; t007 (1), t037 (4), t2029 (1), t1476 (1) and t2029 (1). MSSA isolates had greater spa diversity than MRSAs with t005, t186, t314, t4198, t5941 represented by single isolates.
Some strain types were found in only particular geographical regions, for example, ST88 and ST241 detected in Kisumu County only, in contrast to CC152 which showed a wide geographic distribution. Isolates from Kericho County were the most heterogeneous based on CC/ST types.
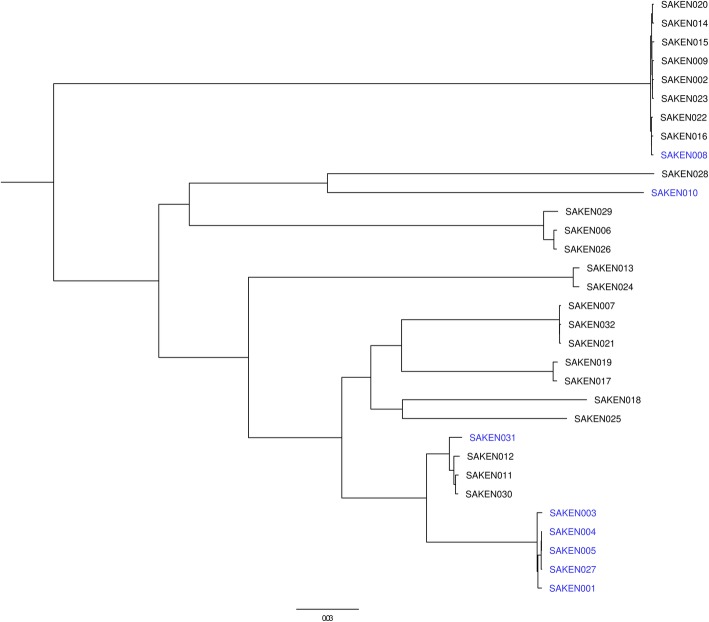
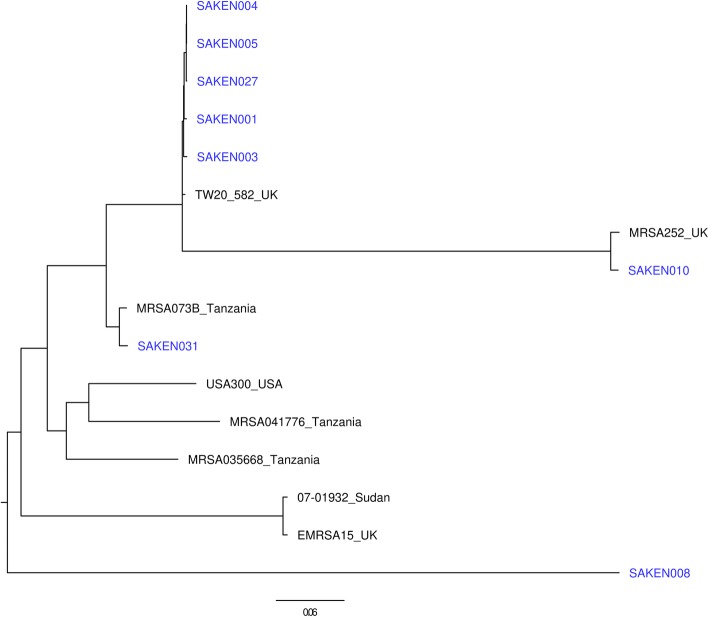
Phylogenetic analysis of the Kenyan isolates indicated SNP differences of 5–27,562 SNPs and clustered the isolates by ST or CC types. MRSA isolates were distributed across four clusters. The largest MRSA cluster consisting of SAKEN1, 3, 4, 5, and 27 clustered within CC8 with MSSA isolates. SAKEN004 and SAKEN005 isolates had only 5 SNP differences and were from patients admitted in the same hospital at the same time. SAKEN004, 005,027 had SNP differences between 5 and 34 SNPs, an indication that they were closely related but distinct isolates (Fig. 2). Kenyan MRSA isolates were genetically diverse and most closely related to MRSA073B from Tanzania, MRSA252 UK, and TW20_582_UK (Fig. 3).
Fig. 2.
Core genome SNP phylogeny of Kenyan S. aureus isolates. MRSA isolates are in blue, and MSSA isolates are in black. MRSA isolates are distributed across four clusters
Fig. 3.
Core genome phylogeny of MRSA isolates from this study (in blue) and known global and regional strains. Although the isolates are genetically diverse, Kenyan MRSA isolates are closely related to Tanzanian ad UK strains
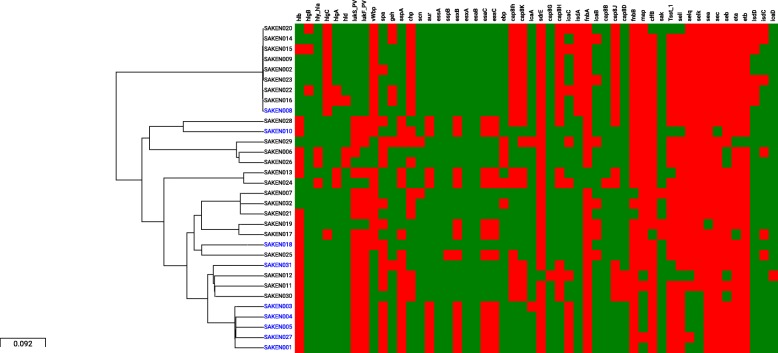
The virulence genes identified among the isolates are indicated in Fig. 4 and grouped according to function; pore formers, immune evasion, toxins, and adhesins. There was no significant difference in the numbers of virulence genes between MRSA and MSSA isolates (p = 0.09), but there was a significant association (p < 0.05) between the severity of the infection and the five virulence genes; map, hlgA, selk, selq, and cap8d. Map, selk, selq, hlgC, vwbp virulence genes were significantly associated with CC8 (p < 0.00005) but showed varied distribution within the CC. There was a strong association between isolates in CC152 and the presence of LukS_PV, LukF_PV and hlb and the absence of hlgc, vwbp, capIh, chp, isdA, isdD, cap8h and cap8K (p < 0.00005).
Fig. 4.
Core genome phylogeny and a heat map showing the distribution of virulence genes among study isolates. Green denotes the presence and red indicates the absence of the gene. Virulence factors are grouped according to function. Genes that were ubiquitously expressed among the isolates are not shown. MRSA isolates are shown in blue and MSSA isolates are in black
Discussion
In this study, antimicrobial resistance phenotypes and genotypes and strain types of S. aureus isolates from diverse geographical areas in Kenya were investigated and phylogenetic relationships inferred between the isolates and known global and regional strains based on whole genome sequences. Virulence genes were identified, and their presence relative to the clonal complexes and clinical presentation examined for possible correlations to identify genetic predictors of hyper-virulence.
Phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility testing indicated high sensitivity to vancomycin, linezolid, teicoplanin, nitrofurantoin and tigecycline among all isolates consistent with previous observations by Gitau et al. [33]. High levels of resistance to benzylpenicillin, sulfamethoxazole, rifampicin, tetracycline, and erythromycin have been reported by previous Kenyan [23, 25] and African [34] studies. The high levels of resistance to these commonly used antibiotics could be linked to Kenya having a high prevalence of tuberculosis (TB), HIV and malaria. Rifampicin is among the first-line agents for the treatment of TB [35] infections in Kenya which is linked to HIV infection [36] and is also used as an antimalarial drug. The MRSA isolates bearing the mutation in the rpoB gene conferring resistance to rifampicin were from Kisumu County which is endemic for malaria and has a high prevalence of HIV [37]. Previous Kenyan studies have reported SXT resistance rates of 40% [25] and 62% [23]. In this study, the high-level resistance (75%) to sulfamethoxazole (SXT), mediated by both chromosomally encoded dfrC and plasmid-borne dfrG genes may be driven by the use of SXT in HIV prophylaxis [37–39].
MSSA isolates were 100% susceptible to quinolones consistent with the high susceptibility rates indicated in other Kenyan studies [40–42] while MRSA isolates were 25% susceptible, markedly lower than a previous study that reported a susceptibility of 55.9% to ciprofloxacin among Kenyan MRSA [43] suggesting growing resistance of MRSA to quinolones in Kenya. Quinolone resistance was mediated by the resistance-conferring mutations on parC (S80F) and gyrA (S84 L) [44].
This study reports 62.5% susceptibility to tetracyclines which is higher than the 20–50.3% reported in Kenya, and other African studies [42, 45]. The previously observed increase in resistance to tetracycline in Africa (< 75%) was linked to increased use of tetracycline in animal husbandry [46], but the reduction in resistance observed in this study among human clinical isolates could be an indicator that tetracycline is being used less to treat human infections. TetK and TetM genes are reported [42] to be predominant in Sub-Saharan Africa, but this study has shown that TetK is the principal mediator of resistance and could be useful as a marker to monitor tetracycline resistance in Kenya.
Strain typing revealed 12 STs and 9 CCs among the isolates confirming the considerable heterogeneity previously described among S. aureus both regionally and globally [25, 34, 47, 48]. Spa typing showed higher discriminatory power than ST with multiple spa types belonging to the same STs. Of the major lineages described for MRSA, MRSA isolates in the present study belonged to CC8 and CC5, both of which are associated with global outbreaks [1]. CC8 was composed of both MSSA and MRSA isolates. CC5/ST241, t037 and ST 239, t037 are the predominant MRSA clones described in previous studies on Kenyan isolates from Nairobi and its environs [25, 47]. In this study, a majority of MRSA isolates also belonged to ST241, t037 even though they were from sites in Western Kenya situated ~ 300 km from Nairobi suggesting a widespread geographical distribution of the CC5/ST241 MRSA strain in Kenya. Schaumburg et al. [34] reported ST 241 MRSA clone to also be prevalent in Africa though with varying SSCmec types; Senegal (SSCmec III), Tunisia (SSCmec III), Niger (SSCmec III and V) Nigeria (SSCmec III and IV) and Algeria (SSCmec III) [49]. Even though globally most HAI-MRSA are SCCmec type I-III and CAI-MRSA SCCmec types IV and V [50, 51], the hospital associated strain ST 241 SCCmec III [49] was identified in both HAI and CAI infections in the present study and a previous Kenyan study [47]. SCCmec typing may, therefore, have limited utility as a marker of CAI or HAI in the region.
The Kenyan isolates grouped distinctly into several clonal complexes. The CC8 cluster was composed of two clades ST8 (MSSA) and ST241 (MRSA) with the two clades sharing a recent common ancestor. Studies have shown that MSSA isolates of CC8 act as reservoirs for MRSA pending acquisition of the staphylococcal cassette [52, 53]. Relationships between isolates of this study and known global strains using core genome SNPs revealed close clustering of a majority of MRSA strains in this study with the well-known strains. The predominant CC8 MRSA isolates in this study were closely related to the CC8 TW20 strain 582, which is a successful HAI MRSA clone from London [4], known for its high transmissibility and multi-drug resistant properties due to a plethora of resistance genes carried on mobile elements [54]. CC8 MRSA strains have been linked to community-acquired infections and include other well-known strains such as USA 300 which is a lineage-linked to the acquisition of SSCmec IV, pvl and seq and sek genes [5, 55]. MRSA isolates in this study were also closely related to MRSA252 from UK and MRSA_0411776 from Tanzania indicating the ease of spread of S. aureus strains across regional and international borders.
There was a significant correlation between the five virulence genes: map, hlgA, selk, selq and cap8d and severe infections indicating their potential usefulness as markers of infection severity in the region. While CC8 isolates were strongly associated with the presence of multiple virulence genes, CC152 was in contrast associated with an absence of these virulence genes but the presence of pvl, a bi-component leukocidin (lukF_PV and lukS_PV) destroying leukocytes and causing tissue necrosis. Pvl predominant ST152 clones have been described in Nigeria [56] and Mali [57] and Europe [58] indicating a global distribution of this clone. The MRSA prevalence in Kenya ranges widely from 3 to 30% [24, 33], and although, as this study has shown, most S. aureus infections remain relatively easy to treat, the morbidity associated with hypervirulent strains could be managed better by understanding the circulating strains and their virulence gene profiles.
Despite the low sample numbers, this study does begin to fill gaps and expand our understanding of the epidemiology of S. aureus by providing data on clinical isolates of S. aureus from other parts of the country as previous studies in Kenya have been limited to four healthcare institutions within close geographic proximity. The isolates in this study, collected over a 3-year period (2015 to Aug 2018), uncover patterns of distribution of different strain types that are interesting and will be explored further as part of the ongoing surveillance to examine whether the observed S. aureus distribution patterns hold and other patterns emerge over time with more isolates.
Conclusion
This study provides insight into the diversity, distribution and resistance profiles of Kenyan MSSA and MRSA isolates and their relatedness to global MRSA strains. Although limited by the low numbers of isolates this study provides a baseline for monitoring S. aureus strain types and associated resistance and virulence patterns to create risk maps for S. aureus infections in Kenya. The study has identified multidrug resistance genes carried by Kenyan S. aureus isolates and provided a basis to track trends in drug resistance and identify emerging resistance patterns and novel strain types. The evidence of co-occurrence of methicillin resistance and virulence genes portend the emergence of highly virulent MRSA infections that could be outbreak-associated. In the advent of increasing drug resistance in Kenya, continued surveillance using both phenotype and genotype data is recommended to identify country-specific data on drugs effective for treatment for both MRSA and MSSA to reduce morbidity given the unique backdrop of other endemic diseases.
Materials and methods
Bacterial isolates identification and drug susceptibility testing
Non- duplicate clinical S. aureus isolates from patients enrolled in an ongoing surveillance study (WRAIR#2089, KEMRI#2767) in four hospitals in Kisumu, Kericho, Malindi, and Nairobi counties in Kenya were analyzed for this study. S. aureus isolates were identified based on characteristic beta hemolysis, catalase, and coagulase positive phenotypes. Isolate identity was confirmed and antimicrobial susceptibility testing performed on the Vitek 2 platform (bioMérieux, Hazelwood, MO, USA) using the GP identification and the P580 antibiotic susceptibility card which tests a panel of 17 drugs (Benzylpenicillin, oxacillin, gentamicin, tobramycin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, erythromycin, clindamycin, linezolid, teicoplanin, vancomycin, tetracycline, tigecycline, nitrofurantoin, fusidic acid, rifampicin, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole). MRSA was identified using CLSI break-points for oxacillin MIC and cefoxitin screen and validated by PCR for the presence of the mecA gene using published primers [22]. All MRSA isolates identified between April 2015 and August 2018 and a selection of methicillin susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) isolates from each county totaling 32 isolates (8 MRSA, 24 MSSA) were included in this study. The isolates were from both in- and out-patients. The infections were classified as severe if the patient was admitted in the hospital (17/32, 53.2%) or as mild if they were treated in the out-patient department (15/32, 46.9%). 87.5% (28/32) of the isolates were from patients with community-acquired infections and 12.5% (4/32) with hospital-acquired infections as per the CDC classification [59] (Table 1).
Whole genome sequencing and sequence analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted from freshly cultured S. aureus isolates using the ZR Fungal/Bacterial DNA MiniPrep Kit (Zymo research, California, United States). DNA concentrations were determined using the Qubit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Massachusetts, United States) and 1 ng of DNA used for library preparation with the Nextera XT kit (Illumina Inc. San Diego, California, United States) as per manufacturer’s instructions to generate 300 bp paired-end libraries. Libraries were sequenced on an Illumina MiSeq platform (Illumina Inc. San Diego, California, United States). Raw reads were trimmed for quality and de-novo assembly performed using Newbler [60]. Genome assemblies were uploaded onto NCBI under BioProject ID PRJNA481322.
Isolate typing
In-silico spa typing was performed on assembled genomes using SpaTyper 1.0 hosted on the Centre for Genome Epidemiology (CGE) https://cge.cbs.dtu.dk/services/spatyper/ [61]. In-silico MLST sequence type (ST) were obtained on https://cge.cbs.dtu.dk/services/MLST/ [62] at the Centre for Genomic Epidemiology and isolates grouped into clonal complexes using the BURST clustering algorithm available on http://eburst.mlst.net/, allowing a minimum of 6 identical loci for group definition. Sequences of novel STs were submitted to https://pubmlst.org/saureus/ for ST assignment [63]. Staphylococcal cassette types for the MRSA isolates were determined in-silico using SCCmecFinder 1.2 hosted on https://cge.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SCCmecFinder/ [64].
Antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes identification
Genes coding for antimicrobial resistance and virulence were identified using ARIBA [65] (version 2.11.1) employing CARD [66] (version 3.0.1) https://card.mcmaster.ca as the reference database. To investigate the presence of virulence factors, the whole genomes of the Kenyan isolates were screened for 85 known virulence genes using the Virulence Factors Database (VFDB). AMR gene distribution and heat maps were generated and visualized on Microreact at https://microreact.org/ [67].
Phylogenetic analysis was performed to infer relationships between the eight Kenyan MRSA and eight known global strains; selected to include at least one whole genome for all the sequence types identified in the Kenyan isolates. The reference strains used in the phylogenetic analysis are listed in the Additional file 2. High-quality SNPs were called, and maximum likelihood phylogeny inferred using RAxML [68].
Supplementary information
Additional file 1. Table of susceptibility testing results obtained from the Vitek 2 platform and genotypes detected using ARIBA. MICs were interpreted using the CLSI guidelines and expert deductions on the Vitek Advanced Expert System (AES). * indicates forced resistance by the AES. **denotes presence of only the ubiquitous resistance genes in the isolates (S. aureus 23S, arlR, arlS, mgrA and tet38). Isolates in bold are confirmed MRSA validated as MecA positive by PCR testing. Fusidic acid is not shown as results were missing for some isolates.
Additional file 2. List of reference genomes used in this study.
Acknowledgments
This study was presented in part at the American Society of Microbiology 2018 meeting in Georgia, Atlanta. We thank Dr. John Waitumbi, Kimita Gathii and Luiser Ingasia (Kisumu basic Science Lab), Patrick Mc Gann and Jason Stam (WRAIR MRSN, Silver Spring, Baltimore USA) for sequencing support. We are grateful for the participation of all the study subjects from the participating healthcare facilities. This work has been published with the permission of the Director KEMRI.
Disclaimers
The material has been reviewed by the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research. There is no objection to its publication. The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the author and are not to be construed as official, or as reflecting true views of the Department of the Army or the Department of Defense. The investigators have adhered to the policies for the protection of human subjects as prescribed in AR 70–25.
Abbreviations
- AES
Advanced Expert System
- AFHSB
Armed Forces Health Surveillance Branch
- ARIBA
Antimicrobial Resistance Identification By Assembly
- CA
Community acquired
- CAI
Community acquired infection
- CARD
Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database
- CC
Clonal complex
- CGE
Center for Genome Epidemiology
- CLSI
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute
- DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- GEIS
Global Emerging Infections Surveillance and Response System
- HAI
Hospital acquired infection
- IRB
Institutional review board
- KEMRI
Kenya Medical Research Institute
- MIC
Minimum inhibitory concentration
- MLST
Multi-locus sequence typing
- MRSA
Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- MRSN
Multidrug Resistance Surveillance Network
- MSSA
Methicillin susceptible Staphylococcus aureus
- PCR
Polymerase chain reaction
- PROMIS
Proposal Management Information System
- Pvl
Panton-Valentine leukocidin
- RAxML
Randomized Axelerated Maximum Likelihood
- SCCmec
Staphylococcal cassette chromosome
- SNPs
Single nucleotide polymorphisms
- Spa
Staphylococcus aureus Protein A
- ST
Sequence type
- SXT
Sulfamethoxazole
- TB
Tuberculosis
- tsst-1
Toxic shock syndrome
- UK
United Kingdom
- Van
Vancomycin
- VFDB
Virulence Factors Database
- VRE
Vancomycin resistant enterococci
- VRSA
Vancomycin resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- WRAIR
Walter Reed Army Institute of Research
Authors’ contributions
Conceptualization: LM. Data Curation: LM, CK. Formal analysis: CK, JN, LM. Funding Acquisition: LM. Investigation: CK, JN, DM, VO, SW. Methodology: LM, CK. Supervision: VO, LM, WS. Validation: LM, CK. Writing- Original draft preparation: CK, LM. Writing- Review and Editing: JN, CK, VO, SW, DM, WS, LM. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work is funded by the Armed Forces Health Surveillance Branch (AFHSB) and its Global Emerging Infections Surveillance (GEIS) Section PROMIS ID: 20160270153 FY17. The funding body had no role in the design of the study, data collection, analysis, and interpretation of data or in writing the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Sequence data is available on NCBI under BioProject ID PRJNA481322.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study is approved by the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research (#2089) and the Kenya Medical Research Institute (#2767) IRBs under which study participants provided written consent for their samples to be used in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12866-019-1597-1.
References
- 1.Chambers HF, Deleo FR. Waves of resistance: Staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009;7(9):629–641. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mediavilla JR, Chen L, Mathema B, Kreiswirth BN. Global epidemiology of community-associated methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) Curr Opin Microbiol. 2012;15(5):588–595. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2012.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nimmo GR. USA300 abroad: global spread of a virulent strain of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18(8):725–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2012.03822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Edgeworth JD, Yadegarfar G, Pathak S, Batra R, Cockfield JD, Wyncoll D, et al. An outbreak in an intensive care unit of a strain of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus sequence type 239 associated with an increased rate of vascular access device-related bacteremia. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44(4):493–501. doi: 10.1086/511034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Diep BA, Gill SR, Chang RF, Phan TH, Chen JH, Davidson MG, et al. Complete genome sequence of USA300, an epidemic clone of community-acquired meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 2006;367(9512):731–739. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68231-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Holden MT, Feil EJ, Lindsay JA, Peacock SJ, Day NP, Enright MC, et al. Complete genomes of two clinical Staphylococcus aureus strains: evidence for the rapid evolution of virulence and drug resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(26):9786–9791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402521101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tenover FC, McDougal LK, Goering RV, Killgore G, Projan SJ, Patel JB, et al. Characterization of a strain of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus widely disseminated in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44(1):108–118. doi: 10.1128/JCM.44.1.108-118.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Layton MC, Hierholzer WJ, Jr, Patterson JE. The evolving epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at a university hospital. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1995;16(1):12–17. doi: 10.2307/30140995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Vandenesch F, Naimi T, Enright MC, Lina G, Nimmo GR, Heffernan H, et al. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying Panton-valentine leukocidin genes: worldwide emergence. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9(8):978–984. doi: 10.3201/eid0908.030089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lester CH, Frimodt-Moller N, Sorensen TL, Monnet DL, Hammerum AM. In vivo transfer of the vanA resistance gene from an Enterococcus faecium isolate of animal origin to an E. faecium isolate of human origin in the intestines of human volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50(2):596–599. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.2.596-599.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kariuki S, Revathi G, Kiiru J, Mengo DM, Mwituria J, Muyodi J, et al. Typhoid in Kenya is associated with a dominant multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi haplotype that is also widespread in Southeast Asia. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48(6):2171–2176. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01983-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Finch MJ, Morris JG, Jr, Kaviti J, Kagwanja W, Levine MM. Epidemiology of antimicrobial resistant cholera in Kenya and East Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988;39(5):484–490. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Saidi SM, Chowdhury N, Awasthi SP, Asakura M, Hinenoya A, Iijima Y, et al. Prevalence of Vibrio cholerae O1 El Tor variant in a cholera-endemic zone of Kenya. J Med Microbiol. 2014;63(Pt 3):415–420. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.068999-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wong KC, Brown AM, Luscombe GM, Wong SJ, Mendis K. Antibiotic use for Vibrio infections: important insights from surveillance data. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-0959-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Piddock LJ. Assess drug-resistance phenotypes, not just genotypes. Nat Microbiol. 2016;1(8):16120. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dantas G, Sommer MO. Context matters - the complex interplay between resistome genotypes and resistance phenotypes. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2012;15(5):577–582. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2012.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.McDermott PF, Tyson GH, Kabera C, Chen Y, Li C, Folster JP, et al. Whole-genome sequencing for detecting antimicrobial resistance in Nontyphoidal Salmonella. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(9):5515–5520. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01030-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Enright MC, Day NP, Davies CE, Peacock SJ, Spratt BG. Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38(3):1008–1015. doi: 10.1128/jcm.38.3.1008-1015.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Strommenger B, Braulke C, Heuck D, Schmidt C, Pasemann B, Nübel U, et al. Spa typing of Staphylococcus aureus as a frontline tool in epidemiological typing. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46(2):574–581. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01599-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.International Working Group on the Classification of Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome Elements (IWG-SCC) Classification of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec): guidelines for reporting novel SCCmec elements. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53(12):4961–4967. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00579-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ito T, Katayama Y, Asada K, Mori N, Tsutsumimoto K, Tiensasitorn C, et al. Structural comparison of three types of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec integrated in the chromosome in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001;45(5):1323–1336. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.5.1323-1336.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhang K, McClure JA, Elsayed S, Louie T, Conly JM. Novel multiplex PCR assay for characterization and concomitant subtyping of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec types I to V in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43(10):5026–5033. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.10.5026-5033.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Maina EK, Kiiyukia C, Wamae CN, Waiyaki PG, Kariuki S. Characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from skin and soft tissue infections in patients in Nairobi, Kenya. Int J Infect Dis. 2013;17(2):e115–e119. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2012.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Omuse G, Kabera B, Revathi G. Low prevalence of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus as determined by an automated identification system in two private hospitals in Nairobi, Kenya: a cross sectional study. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14:669. doi: 10.1186/s12879-014-0669-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Aiken AM, Mutuku IM, Sabat AJ, Akkerboom V, Mwangi J, Scott JA, et al. Carriage of Staphylococcus aureus in Thika level 5 hospital, Kenya: a cross-sectional study. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2014;3:22. doi: 10.1186/2047-2994-3-22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Omuse G, Shivachi P, Kariuki S, Revathi G. Prevalence of Panton Valentine Leukocidin in Carriage and Infective Strains of Staphylococcus aureus at a Referral Hospital in Kenya. Open J Med Microbiol. 2013;03(01):7. doi: 10.4236/ojmm.2013.31002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Truong-Bolduc QC, Villet RA, Estabrooks ZA, Hooper DC. Native efflux pumps contribute resistance to antimicrobials of skin and the ability of Staphylococcus aureus to colonize skin. J Infect Dis. 2014;209(9):1485–1493. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Vester B, Douthwaite S. Macrolide resistance conferred by base substitutions in 23S rRNA. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001;45(1):1–12. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.1.1-12.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fournier B, Aras R, Hooper DC. Expression of the multidrug resistance transporter NorA from Staphylococcus aureus is modified by a two-component regulatory system. J Bacteriol. 2000;182(3):664–671. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.3.664-671.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Truong-Bolduc QC, Zhang X, Hooper DC. Characterization of NorR protein, a multifunctional regulator of norA expression in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 2003;185(10):3127–3138. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.10.3127-3138.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Truong-Bolduc QC, Dunman PM, Strahilevitz J, Projan SJ, Hooper DC. MgrA is a multiple regulator of two new efflux pumps in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 2005;187(7):2395–2405. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.7.2395-2405.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jolley KA, Maiden MC. BIGSdb: scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010;11(1):595. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gitau W, Masika M, Musyoki M, Museve B, Mutwiri T. Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from clinical specimens at Kenyatta National Hospital. BMC Res Notes. 2018;11(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s13104-018-3337-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schaumburg F, Alabi AS, Peters G, Becker K. New epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus infection in Africa. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20(7):589–596. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Agency TUR . Access to multi-drug resistant tuberculosis treatment in Dadaab refugee camps, Kenya. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Likhovole C, Ouma C, Vulule J, Musau S, Khayumbi J, Okumu A, et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistance to isoniazid and rifampicin in a HIV-1 endemic population in Western Kenya in 2014. BMJ Global Health. 2017;2(Suppl 2):A32–A3A. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2016-000260.84. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bwakura-Dangarembizi M, Kendall L, Bakeera-Kitaka S, Nahirya-Ntege P, Keishanyu R, Nathoo K, et al. A randomized trial of prolonged co-trimoxazole in HIV-infected children in Africa. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(1):41–53. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1214901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Egwuatu CC, Iwuafor AA, Egwuatu TO, Akujobi CN, Nnachi AU, Aghanya IN, et al. Effect of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis on faecal carriage rates of resistant isolates of Escherichia coli in hiv-infected adult patients in Lagos. Afr J Infect Dis. 2016;10(2):156–163. doi: 10.21010/ajid.v10i2.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hamel MJ, Greene C, Chiller T, Ouma P, Polyak C, Otieno K, et al. Does cotrimoxazole prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV-associated opportunistic infections select for resistant pathogens in Kenyan adults? Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008;79(3):320–330. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2008.79.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ayoyi AO, Kikuvi G, Bii C, Kariuki S. Prevalence, aetiology and antibiotic sensitivity profile of asymptomatic bacteriuria isolates from pregnant women in selected antenatal clinic from Nairobi, Kenya. Pan Afr Med J. 2017;26:41. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2017.26.41.10975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nyangacha RM, Odongo D, Oyieke F, Ochwoto M, Korir R, Ngetich RK, et al. Secondary bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance among tungiasis patients in Western, Kenya. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11(9):e0005901. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ruffing U, Alabi A, Kazimoto T, Vubil DC, Akulenko R, Abdulla S, et al. Community-associated Staphylococcus aureus from sub-Saharan Africa and Germany: a cross-sectional geographic correlation study. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):154. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00214-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kesah C, Ben Redjeb S, Odugbemi TO, Boye CS, Dosso M, Ndinya Achola JO, et al. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in eight African hospitals and Malta. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2003;9(2):153–156. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0691.2003.00531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Tanaka M, Wang T, Onodera Y, Uchida Y, Sato K. Mechanism of quinolone resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Chemother. 2000;6(3):131–139. doi: 10.1007/s101560070010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Shittu AO, Okon K, Adesida S, Oyedara O, Witte W, Strommenger B, et al. Antibiotic resistance and molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureusin Nigeria. BMC Microbiol. 2011;11(1):92. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Mitema ES, Kikuvi GM, Wegener HC, Stohr K. An assessment of antimicrobial consumption in food producing animals in Kenya. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2001;24(6):385–390. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2885.2001.00360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Omuse G, Van Zyl KN, Hoek K, Abdulgader S, Kariuki S, Whitelaw A, et al. Molecular characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from various healthcare institutions in Nairobi, Kenya: a cross sectional study. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2016;15(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12941-016-0171-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rolo J, Miragaia M, Turlej-Rogacka A, Empel J, Bouchami O, Faria NA, et al. High genetic diversity among community-associated Staphylococcus aureus in Europe: results from a multicenter study. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34768. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Abdulgader SM, Shittu AO, Nicol MP, Kaba M. Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Africa: a systematic review. Front Microbiol. 2015;6:348. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Fang H, Hedin G, Li G, Nord CE. Genetic diversity of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in southern Stockholm, 2000-2005. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008;14(4):370–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Okuma K, Iwakawa K, Turnidge JD, Grubb WB, Bell JM, O’Brien FG, et al. Dissemination of new methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones in the community. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40(11):4289–4294. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.11.4289-4294.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Driebe EM, Sahl JW, Roe C, Bowers JR, Schupp JM, Gillece JD, et al. Using whole genome analysis to examine recombination across diverse sequence types of Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0130955. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Strauss L, Stegger M, Akpaka PE, Alabi A, Breurec S, Coombs G, et al. Origin, evolution, and global transmission of community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus ST8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(49):E10596–E1E604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1702472114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Holden MT, Lindsay JA, Corton C, Quail MA, Cockfield JD, Pathak S, et al. Genome sequence of a recently emerged, highly transmissible, multi-antibiotic- and antiseptic-resistant variant of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, sequence type 239 (TW) J Bacteriol. 2010;192(3):888–892. doi: 10.1128/JB.01255-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Tristan A, Ferry T, Durand G, Dauwalder O, Bes M, Lina G, et al. Virulence determinants in community and hospital meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Hosp Infect. 2007;65(Suppl 2):105–109. doi: 10.1016/S0195-6701(07)60025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Okon KO, Basset P, Uba A, Lin J, Oyawoye B, Shittu AO, et al. Cooccurrence of predominant Panton-valentine leukocidin-positive sequence type (ST) 152 and multidrug-resistant ST 241 Staphylococcus aureus clones in Nigerian hospitals. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47(9):3000–3003. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01119-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ruimy R, Maiga A, Armand-Lefevre L, Maiga I, Diallo A, Koumare AK, et al. The carriage population of Staphylococcus aureus from Mali is composed of a combination of pandemic clones and the divergent Panton-valentine leukocidin-positive genotype ST152. J Bacteriol. 2008;190(11):3962–3968. doi: 10.1128/JB.01947-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Muller-Premru M, Strommenger B, Alikadic N, Witte W, Friedrich AW, Seme K, et al. New strains of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with Panton-valentine leukocidin causing an outbreak of severe soft tissue infection in a football team. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005;24(12):848–850. doi: 10.1007/s10096-005-0048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Horan TC, Andrus M, Dudeck MA. CDC/NHSN surveillance definition of health care-associated infection and criteria for specific types of infections in the acute care setting. Am J Infect Control. 2008;36(5):309–332. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2008.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Silva GG, Dutilh BE, Matthews TD, Elkins K, Schmieder R, Dinsdale EA, et al. Combining de novo and reference-guided assembly with scaffold_builder. Source Code Biol Med. 2013;8(1):23. doi: 10.1186/1751-0473-8-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Bartels MD, Petersen A, Worning P, Nielsen JB, Larner-Svensson H, Johansen HK, et al. Comparing whole-genome sequencing with sanger sequencing for spa typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52(12):4305–4308. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01979-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Larsen MV, Cosentino S, Rasmussen S, Friis C, Hasman H, Marvig RL, et al. Multilocus sequence typing of total-genome-sequenced bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50(4):1355–1361. doi: 10.1128/JCM.06094-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Jolley KA, Maiden MC. BIGSdb: scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010;11:595. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Kaya H, Hasman H, Larsen J, Stegger M, Johannesen TB, Allesoe RL, et al. SCCmecFinder, a Web-Based Tool for Typing of Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec in Staphylococcus aureus Using Whole-Genome Sequence Data. mSphere. 2018;3(1):e00612–e00617. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00612-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Hunt M, Mather AE, Sánchez-Busó L, Page AJ, Parkhill J, Keane JA, et al. ARIBA: rapid antimicrobial resistance genotyping directly from sequencing reads. Microb Genom. 2017;3(10):e000131. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Jia B, Raphenya AR, Alcock B, Waglechner N, Guo P, Tsang KK, et al. CARD 2017: expansion and model-centric curation of the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(D1):D566–DD73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Argimón S, Abudahab K, Goater RJ, Fedosejev A, Bhai J, Glasner C, et al. Microreact: visualizing and sharing data for genomic epidemiology and phylogeography. Microb Genom. 2016;2(11):e000093. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(9):1312–1313. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. Table of susceptibility testing results obtained from the Vitek 2 platform and genotypes detected using ARIBA. MICs were interpreted using the CLSI guidelines and expert deductions on the Vitek Advanced Expert System (AES). * indicates forced resistance by the AES. **denotes presence of only the ubiquitous resistance genes in the isolates (S. aureus 23S, arlR, arlS, mgrA and tet38). Isolates in bold are confirmed MRSA validated as MecA positive by PCR testing. Fusidic acid is not shown as results were missing for some isolates.
Additional file 2. List of reference genomes used in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Sequence data is available on NCBI under BioProject ID PRJNA481322.