Abstract
Purpose
Multi-gene signatures provide biological insight and risk stratification in breast cancer. Intrinsic molecular subtypes defined by mRNA expression of 50 genes (PAM50) are prognostic in hormone-receptor positive postmenopausal breast cancer. Yet, for 25–40% in the PAM50 intermediate risk group, long-term risk remains uncertain. Our study aimed to (i) test the long-term prognostic value of the PAM50 signature in pre- and post-menopausal breast cancer; (ii) investigate if the PAM50 model could be improved by addition of other mRNAs implicated in oncogenesis.
Methods
We used archived FFPE samples from 1723 breast cancer survivors; high quality reads were obtained on 1253 samples. Transcript expression was quantified using a custom codeset with probes for > 100 targets. Cox models assessed gene signatures for breast cancer relapse and survival.
Results
Over 15 + years of follow-up, PAM50 subtypes were (P < 0.01) associated with breast cancer outcomes after accounting for tumor stage, grade and age at diagnosis. Results did not differ by menopausal status at diagnosis. Women with Luminal B (versus Luminal A) subtype had a > 60% higher hazard. Addition of a 13-gene hypoxia signature improved prognostication with > 40% higher hazard in the highest vs lowest hypoxia tertiles.
Conclusions
PAM50 intrinsic subtypes were independently prognostic for long-term breast cancer survival, irrespective of menopausal status. Addition of hypoxia signatures improved risk prediction. If replicated, incorporating the 13-gene hypoxia signature into the existing PAM50 risk assessment tool, may refine risk stratification and further clarify treatment for breast cancer.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1007/s10549-019-05446-y) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Breast cancer, Long-term survival, Gene signatures, Hypoxia, PAM50 subtypes, Prognostic modeling
Introduction
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease with large variations in relapse rates even among patients with similar clinical profiles. Several multi-gene prognostic tests are included in national and international guidelines to assist in determining risk of relapse and to better inform treatment decisions [1–7]. Even so, more information is needed regarding how these tests perform in well-characterized cohorts of breast cancer patients with long-term follow-up [8].
The breast cancer intrinsic molecular subtypes, defined by mRNA expression of 50 genes (PAM50), have been shown to improve prognostication significantly compared to standard tumor characteristics and other genomic signatures [3, 9–15]. The related proprietary Prosigna gene signature, FDA-approved in 2013, was validated to estimate relapse risk in postmenopausal women with early stage, hormone-receptor positive breast tumors, but has not been validated in pre-menopausal women [16]. In addition, for the research-based PAM50 signature and the Prosigna test [16, 17], an estimated 25–40% of patients are characterized as having “intermediate risk,” and for these patients, the long-term risk of relapse remains uncertain.
Gene expression studies have identified hundreds of mRNAs implicated in breast cancer. One approach to improving predictive accuracy of existing signatures, such as PAM50, is to evaluate the added prognostic value of independent biomarkers. However, given the large number of potential candidate biomarkers, false positives pose a serious obstacle. Consideration of a priori genes with known oncogenic function could partially mitigate these problems. Hypoxia impacts tumor progression, and hypoxia-related genes are prognostic in breast cancer [18, 19]; hence addition of hypoxia genes to a PAM50 model could elucidate their added prognostic value. Another approach to reduce false discoveries is to use modern statistical methods, such as penalized regression [20], to select prognostic markers from a large candidate list. These methods reduce overfitting of prognostic models and improve future model performance, especially for models with a large number of candidate markers.
Women with ER+ breast cancer continue to relapse 15 years after their primary diagnosis [21, 22]. Treatment options and survival for women with Her2+ tumors have vastly improved since the approval of trastuzumab [23]. However, the Her2+ subgroup comprises < 25% of breast cancers, while women with ER+/Her2− tumors constitute a majority of all breast cancers. Recent research has focused on this ER+/Her2− group to evaluate biomarker-driven treatment approaches in this subgroup [14, 24–27]. Thus, evaluating long-term prognostic value of PAM50 subtypes in the ER+/Her2− subgroup could further clarify its clinical utility. Similarly, although the PAM50-Prosigna signature was originally validated in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors, it may also be prognostic in pre-menopausal breast cancer. Thus it is important to test if the prognostic value of this signature varies by menopausal status at diagnosis.
In this study, using > 1200 archived tumor samples from a large breast cancer cohort with 15 + years of follow-up [28], we investigated genomic predictors of long-term disease-free survival and breast cancer mortality. We previously examined an a priori set of microRNA targets in this sample [29]. The focus in the current work was to examine mRNA expression and breast cancer outcomes, and as a first step we investigated the original research-use PAM50 signature which classified tumors into five distinct subtypes: Luminal A, Luminal B, Basal, Her2-enriched, and normal-like [10]. We also tested a refinement [30], which adds a sixth subtype, the claudin-low cluster. This claudin subtype is characterized by low luminal, Her2, proliferation expression, high immune response, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition expression. Second, we tested if addition of other mRNAs improved prediction via (i) a targeted approach with two a priori hypoxia signatures [18, 19] (ii) an unbiased approach with penalized regression used to select the most prognostic features from among clinical factors, PAM50 subtypes, and 61 individual mRNAs. Third, we investigated PAM50-prognostic value in the ER+/Her2− subgroup, and if subtype-outcome associations differed by menopausal status at diagnosis.
Methods
Study sample
The Women’s Healthy Eating and Living (WHEL) Study, a randomized controlled trial of 3088 breast cancer survivors, tested whether a high fruit/vegetable diet reduced recurrence rates in early stage breast cancer [28, 31]. Women within 4 years of diagnosis with primary operable invasive Stage I (≥ 1 cm), Stage II or Stage III breast carcinoma [32], aged 18 to 70 years at diagnosis, and completed primary treatment for breast cancer were recruited between 1995 and 2000. We obtained IRB approval from participating institutions, and written informed consent from all participants, including for genomic analyses. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue samples from the primary tumor were available for 60% (n = 1723) of the WHEL cohort. The final analysis for this investigation was based on 1253 participants. As the dietary intervention produced no group effect [28], we treated the study population as a single cohort.
Study endpoints
In this study, we evaluated two outcomes (i) a breast cancer event (locoregional recurrence, metastasis, or contralateral), and (ii) death from breast cancer. Events were independently adjudicated by two breast oncologists. Carcinoma in situ was not counted as a breast cancer event. The WHEL study ceased active surveillance for cancer events in 2010. Since then, deaths were ascertained by annual searches of the National Death Index. Time from diagnosis to a second breast cancer event defined the disease-free survival outcome; time from diagnosis to breast cancer death defined the breast cancer survival outcome. Time-to-event was censored at death (from non-breast cancer causes), last contact or end of follow-up (2010 for breast cancer events, 2015 for death).
Nucleic acid extraction
Details on our assay were previously published [29]; for the sake of completeness, we briefly summarize the approach here. Archival tumor blocks were prepared into histological sections. (5 µm each). One slide was stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histopathological review and to guide tumor macrodissection from four unstained sections. The remaining unstained slides from samples with ≥ 40% tumor cellularity were incubated at 65 °C for 30 min and deparaffinized using Citrisolv (Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA) followed by ethanol wash. Tumor tissues were macrodissected into RNAse-free microfuge tubes, and nucleic acids isolated using the Qiagen AllPrep FFPE kit (#80234). Manufacturer’s instructions were followed with the exception that the proteinase K digestion step was extended to an overnight incubation for DNA isolation. Total RNA and DNA were quantified using the Invitrogen Qubit and corresponding quantification kits. DNA pellets were stored at − 80° C for future use.
mRNA quantification
Transcript expression was quantified with 250 ng total RNA using the NanoString nCounter analysis system with a custom miRGE CodeSet containing probes for 123 gene expression targets (see Table S1). This gene set was chosen primarily to include targets in the PAM50, claudin-low, VEGF13 and VEGF15 signatures. Assay reactions were assembled per manufacturer’s specifications (NanoString Technologies, INC Seattle, WA).
Gene signatures
PAM50: Expression of the PAM50 (Table S1) genes were normalized to negative and positive controls, and standardized to five housekeepers, as per standard practice [10]. The published PAM50 algorithm [10] was used to classify each subject into an intrinsic subtype: Luminal A, Luminal B, basal-like, Her2-enriched, normal-like. Prior to implementing this algorithm, mRNA values were platform-adjusted [33]. Risk-of-recurrence scores incorporating tumor size and proliferation index (ROR-PT) were calculated, and categorized into low, medium and high risk strata [10].
Claudin-low
A 30-gene set was used to classify tumors to the claudin-low versus non-claudin subtypes. Centroids were derived using publicly available microarray data [30] previously used to train the claudin-low signature. Spearman correlations between these centroids and the 30-gene expression values for each tumor were calculated. Tumors with correlation ≥ 0.4 with the claudin-low centroid were classified as claudin-low; else they were classified as non-claudin-low type. Non-claudin-low tumors were assigned their PAM50 class as per the research-based subtype call [10]. Again, Zhao’s method [33] was used for platform adjustment.
Hypoxia signatures
We evaluated two hypoxia signatures. A 13-gene VEGF signature [19], VEGF13, and a 15-gene network-based hypoxia metagene [18], VEGF15 (Table S1). After standardizing to housekeepers, VEGF13 and VEGF15 were calculated as the average of log-transformed 13- and 15- gene expression values, respectively. Tertiles of these scores were used to create low, medium or high risk groups. The VEGF13 and VEG15 signatures have only three mRNAs in common, thus potentially provide independent prognostic information.
Other genes
We also obtained mRNA expression for six genes (Table S1) implicated in tumor invasion, proliferation, or other oncogenic function.
Statistical approach
Prognostic modeling
Associations between PAM50 subtypes and tumor characteristics were investigated via ANOVA and Chi square tests. Prognostic value of PAM50 subtypes and ROR-PT risk categories for breast cancer outcomes were assessed via Kaplan–Meier plots, and unadjusted and adjusted Cox models, adjusted for clinical variables, namely age at diagnosis, tumor stage, and grade. The VEGF13 or VEGF15 signatures were then added to the model which included clinical variables (age at diagnosis, stage, grade) and PAM50 subtypes. We used delayed entry models [34] to account for varying times from cancer diagnosis to study entry. Likelihood ratio tests and Akaike information criteria (AIC) were used to compare models.
Variable selection
We used penalized regression for unbiased variable selection. We included all variables, namely, clinical factors, PAM50 subtypes, and 61 individual mRNAs (including 25 hypoxia, 30 claudin-low genes) in the model and used penalized Cox regression implemented via a lasso penalty [20]. The tuning parameter λ, which controls overfitting, was chosen by 10-fold cross-validation to minimize model deviance.
The statistical software package R [35] was used for all statistical analysis.
Results
PAM50 and clinical and demographic characteristics
Of the 1723 FFPE samples, 25% had low tumor cellularity or low RNA content and could not be assayed. Gene expression was obtained on 1291 samples; of these 38 were eliminated due to outliers or poor-quality reads. The final WHEL-PAM50 sample comprised of N = 1253 breast cancer survivors. Study characteristics were similar to the parent WHEL Study (N = 3088) [28]. Women were at an average of 50 years at cancer diagnosis: 85% were White, 36% had Stage I, and 46% had Stage II tumors, three-quarters had ER+ histopathology, and 16% had triple negative histopathology (Table 1). In addition, 78.5% of them were post-menopausal. There were 303 breast cancer events (locoregional recurrence, metastasis, or contralateral breast cancer) and 219 deaths due to breast cancer.
Table 1.
Participant demographic and clinical characteristics at study entry (N = 1253)
| Age at breast cancer diagnosis | |
| Median (range) | 50 (27–70) |
| Race/Ethnicity N (%) | |
| White | 1060 (84.6%) |
| Black | 45 (3.6%) |
| Hispanic | 85 (6.8%) |
| Asian | 31 (2.5%) |
| Other | 32 (2.6%) |
| Stage N (%) | |
| I | 453 (36.2%) |
| IIA | 432 (34.5%) |
| IIB | 144 (11.5%) |
| IIIA | 166 (13.2%) |
| IIIC | 58 (4.6%) |
| Nodal status N (%) | |
| Negative | 702 (56%) |
| Positive | 551 (44%) |
| Tumor size (cm) | |
| Mean (SD) | 2.3 (1.44) |
| Grade N (%) | |
| Poorly differentiated | 497 (39.7%) |
| Moderately differentiated | 496 (39.6%) |
| Well differentiated | 159 (12.7%) |
| Unspecified | 101 (8.1%) |
| Histopathology N (%) | |
| ER+ | 909 (73.7%) |
| PR+ | 809 (66.4%) |
| Her2+ | 217 (17.3%) |
| Triple negative | 199 (15.9%) |
| Years diagnosis to study entry | |
| Median (25th, 75th %-iles) | 1.8 (1.03, 2.8) |
| Chemotherapy and Anti-estrogen therapy N (%) | |
| Yes, yes | 590 (47.1%) |
| Yes, no | 314 (25.1%) |
| No, yes | 258 (20.6%) |
| No, no | 76 (6.1%) |
| Yes, unknown | 5 (0.4%) |
| No, unknown | 9 (0.7%) |
| Outcomes | |
| Breast cancer events (N) | 303 |
| Disease-free survival (years) | |
| Median (25th, 75th)%-iles | 9.5 (6.7, 11.3) |
| Breast cancer deaths (N) | 219 |
| Breast cancer survival (years) | |
| Median (25th, 75th)%-iles | 16.8 (15.3, 18.2) |
PAM50 subtype distributions were 45% Luminal A, 23% Luminal B, 18% basal, 11% Her2-enriched, and 3% normal-like. Subtypes were significantly associated with clinical characteristics and menopausal status at diagnosis (Table 2). The proportion of Luminal A tumors decreased with increasing tumor stage (56% Stage 1, 29% Stage IIIC). Also, 25% Stage IIIC vs 16% Stage I tumors were basal. Poorly differentiated tumors had a high proportion of basal subtype. Luminal A subtype tumors were more prevalent, while basal and Luminal B subtypes were less prevalent in women who were postmenopausal at diagnosis compared to women who were pre-menopausal at diagnosis (Table 2). As expected (Table S2), basal subtype constituted 77% of triple negative tumors, while ER+ tumors were predominantly luminal (55% Luminal A, 29% Luminal B). The subtype distribution for ER+/Her2− tumors was similar to ER+ tumors, whereas ER+/Her2+ tumors were split across Her2-enriched (34%), Luminal A (29%) and B subtypes (31%). Due to low prevalence, the “normal-like” subtype was excluded from the outcome analysis.
Table 2.
Distribution of PAM50 subtypes by clinical characteristics
| Luminal A % | Luminal B % | Basal-like % | Her2% | Normal % | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 564 | 284 | 225 | 139 | 41 | ||
| Cancer stage | < 0.0001 | ||||||
| I | 453 | 55.6 | 17.7 | 15.9 | 8.2 | 2.6 | |
| IIA | 432 | 42.4 | 22.9 | 20.1 | 11.1 | 3.5 | |
| IIB | 144 | 34.7 | 26.4 | 20.1 | 15.3 | 3.5 | |
| IIIA | 166 | 37.4 | 31.3 | 13.3 | 13.9 | 4.2 | |
| IIIC | 58 | 29.3 | 25.9 | 25.9 | 15.5 | 3.5 | |
| Tumor grade | < 0.0001 | ||||||
| Well-differentiated | 159 | 80.5 | 12 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 3.8 | |
| Moderately-diff | 496 | 57.3 | 26.6 | 4.8 | 7.9 | 3.4 | |
| Poorly diff | 497 | 17.9 | 23.9 | 37.4 | 18.1 | 2.6 | |
| Unspecified | 101 | 62.4 | 13.9 | 10.9 | 7.9 | 5 | |
| Mean age at diagnosis (SE) | 52.8 (0.4) | 50.8 (0.5) | 48.2 (0.6) | 50.5 (0.8) | 49.6 (1.2) | <0.0001 | |
| Menopausal status at diagnosis | 0.02 | ||||||
| Pre-menopausal | 40.3 | 25 | 19.9 | 10.9 | 3.9 | ||
| Post-menopausal | 49.7 | 20.3 | 16.3 | 11.3 | 2.7 |
PAM50 and breast cancer outcomes
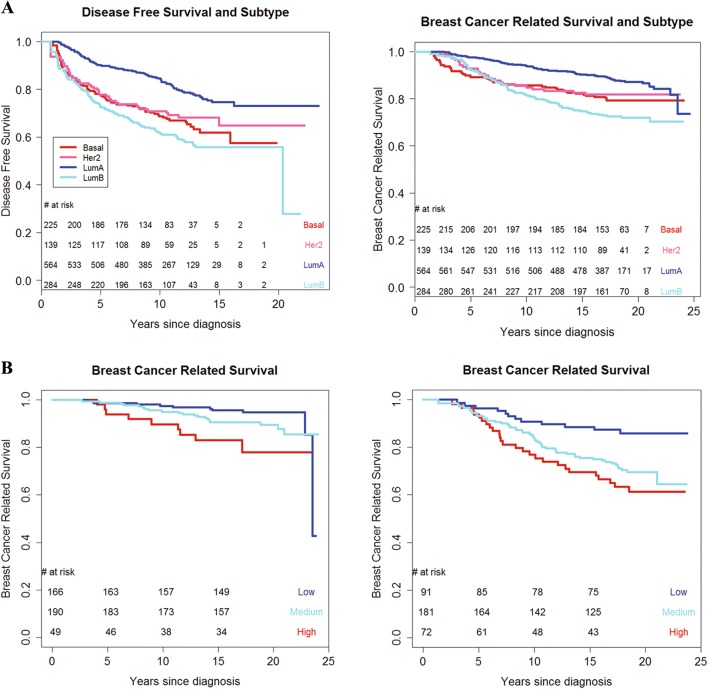
Kaplan–Meier curves (Fig. 1) for the four subtypes were well separated (P < 0.001 for disease-free and breast cancer survival). Luminal A subtype had the best outcomes with 10-year rate of 0.85 (95% CI 0.81–0.88). Interestingly, the 10-year rate was the lowest in the Luminal B group—0.61 (95% CI 0.55–0.69), and basal and Her2-enriched tumors had intermediate rates of 0.69 (95% CI 0.62–0.76) and 0.71 (95% CI 0.60–0.84), respectively.
Fig. 1.
a Kaplan–Meier curve of PAM50 subtype and Disease-free survival (left, P < 0.001) and Breast cancer survival (right P < 0.001). b Kaplan–Meier curve of ROR-PT category and Breast cancer survival by nodal status (left node-negative P = 0.007; right node-positive P = 0.003). P-value based on likelihood ratio test comparing null (unadjusted) to PAM50 model
Multivariable adjusted Cox models (Table 3) showed similar effects, with a 60% higher hazard of a breast cancer event or death for the Luminal B versus Luminal A subtype. Likelihood ratio tests confirmed the prognostic value of the PAM50 signature over clinical factors (P < 0.01).
Table 3.
Associations between PAM50 subtypes and hypoxia signatures with breast cancer outcomes: Multiple regression survival analysis*
| Disease-free survival (N = 295 relapse events)* |
Breast cancer survival (N = 212 breast cancer deaths)* |
|
|---|---|---|
| PAM50 subtypea | HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) |
| Luminal A (ref) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Basal | 1.24 (0.87, 1.78) | 1.01 (0.65, 1.55) |
| Her2 | 0.98 (0.65, 1.49) | 0.91 (0.56, 1.49) |
| Luminal B | 1.60 (1.19, 2.13) | 1.68 (1.20, 2.35) |
| Model comparison: clinical vs (PAM50 + clinical) | ||
| Likelihood ratio test: Chi square statistic | 11.7 | 12.9 |
| Degrees of freedom | 3 | 3 |
| P-value | 0.009 | 0.005 |
| VEGF13 signatureb | ||
| Low (ref) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Medium | 1.33 (0.99, 1.78) | 1.27 (0.90, 1.79) |
| High | 1.48 (1.08, 2.02) | 1.41 (0.98, 2.03) |
| Model comparison: (PAM50 + clinical) vs (PAM50 + clinical +VEGF13) | ||
| Likelihood ratio test: chi square statistic | 6.2 | 3.6 |
| Degrees of freedom | 2 | 2 |
| P-value | 0.04 | 0.16 |
| VEGF15 signatureb | ||
| Low (ref) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Medium | 0.92 (0.68, 1.24) | 0.92 (0.65, 1.31) |
| High | 1.33 (0.99, 1.78) | 1.33(0.94,1.87) |
| Model comparison: (PAM50 + clinical) vs (PAM50 + clinical +VEGF15) | ||
| Likelihood ratio test: chi square statistic | 6.7 | 4.8 |
| Degrees of freedom | 2 | 2 |
| P-value | 0.03 | 0.09 |
*Subjects who were classified as normal-like subtype were excluded from this analysis
aModel adjusted for age at diagnosis, tumor grade, tumor stage
bModel adjusted for age at diagnosis, tumor grade, tumor stage, PAM50 subtype
Hypoxia gene signatures and prognosis
Adding VEGF13 to the PAM50 model improved prognostication (likelihood ratio test P = 0.04), with > 40% higher hazard of breast cancer events for the highest vs lowest tertile (Table 3). Hazard ratios were similar for VEGF13 and breast cancer deaths, although results were not statistically significant (Table 3). The results for VEGF15 were similar to VEGF13 (Table 3).
Identifying individual prognostic mRNAs
The penalized regression [20] analysis for disease-free survival identified tumor stage and PAM50 subtype as the most prognostic variables. Additional selected features were FLVCR2, which encodes a calcium transporter protein, and FABP5, implicated in fatty acid binding, both in the VEGF13 signature, justifying our a priori models. These four variables were also selected in the breast cancer mortality model, in addition to ANGPTL4, a VEGF-13 marker implicated in angiogenesis, and SPINT1, a claudin-low feature involved in epithelial cell differentiation. The estimated hazard ratios with 95% CIs of the selected features are presented Table 4; the 95% CIs do not account for the selection process, and should be interpreted with caution.
Table 4.
Transcripts associated with breast cancer outcomes: results of penalized regression
| Selected mRNAs | Disease-free survivala Hazard ratiob (95% CI) |
Breast cancer mortalitya Hazard ratiob (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| FLVCR2 | 0.85 (0.77, 0.93) | 0.8 (0.70, 0.90) |
| FABP5 | 1.14 (1.06, 1.23) | 1.13 (1.04, 1.24) |
| ANGPTL4 | Not selected | 1.09 (1.02, 1.17) |
| SPINT1 | Not selected | 1.11 (1.01, 1.22) |
aModels also adjusted for tumor stage, grade, and PAM50 subtype
bHazard ratio represents increase in hazard per unit increase in (log2)-mRNA
Subgroups and refinements
Results did not differ by menopausal status at diagnosis (subtype*menopausal interaction P value ≥ 0.3). Among pre-menopausal women, adjusted hazard ratios for disease-free survival were: 1.24 for basal, 0.96 for Her2-enriched, and 1.55 for Luminal B subtypes compared to Luminal A subtypes, and for postmenopausal women the corresponding hazard ratios were 1.25 for basal, 1.05 for Her2-enriched, and 1.63 for Luminal B subtypes. Hazard ratios for PAM50 subtypes also did not differ by age categories: < 50 versus ≥ 50 years at diagnosis.
With the inclusion of 30 claudin genes, 5% (N = 64) were classified as claudin-low. Of these, 59% were previously classified as basal, 22% as luminal A, and 11% as normal-subtype. The 10-year disease-free survival rate (95% CI) for the claudin-low group (Fig S1) was 0.81 (0.71, 0.94); 10-year rates for the other subtypes, after incorporation of the claudin-low subtype, were similar to the original PAM50 calls. Inclusion of the claudin-low subtype did not improve model fit: Akaike information criterion statistic was 3839.5 for the claudin-low-added versus 3837.9 for the standard PAM50 signatures.
Further investigation of PAM50 risk scores in the ER+/Her2− subgroup confirmed that ROR-PT risk categories were associated with disease-free survival and breast cancer death (Fig. 1b). We stratified plots by nodal status given its established prognostic value and key role in determining course of breast cancer treatment [8]. Ten-year breast cancer mortality rates were 3%, 5%, and 10% for the low, medium, high ROR-PT categories among node-negative (P = 0.007), and 10%, 16% and 23% in the low, medium, high ROR-PT groups among node-positive (P = 0.003) survivors. Similarly, for disease-free survival in the node-negative stratum, 10-year event rates were 10%, 13%, and 32% (P = 0.05) for the low, medium, and high risk groups, respectively. For node-positive patients, the corresponding 10-year event rates were 19%, 36%, and 44% (P = 0.02). These results are concordant with previous findings on risk separation by ROR-PT categories and breast cancer outcomes in ER+/Her2− breast cancer [36].
Discussion
In this study, we confirmed the prognostic value of PAM50 subtypes over clinical factors in an independent breast cancer cohort with long-term follow-up. Our results did not differ by age or menopausal status at diagnosis, suggesting that PAM50 subtypes are prognostic across the age spectrum. In recent years, a plethora of gene markers implicated in breast cancer have been identified. Hypoxia impacts tumor progression, and hence we investigated two hypoxia-related gene signatures [18, 19]. These signatures added significant prognostic value to the model with clinical variables (age at diagnosis, stage, grade) and PAM50 subtypes: participants with high levels of the hypoxia signature (i.e., highest tertile) had 30–40% increased hazard for relapse compared to those with lower levels (bottom tertile). Replication of this finding in independent cohorts and additional research on incorporating these signatures for clinical use is needed.
We evaluated the claudin-low subtype [30] and found that incorporation of this refinement did not improve prognostication for disease-free or breast cancer survival in our sample. Our results are similar to Dias [37], but differ from other studies [30], which found worse survival in the claudin-low group. There are clinical and treatment differences between studies, which could explain these discrepancies. Only 5% (N = 64) of tumors in our study were classified as claudin-low, limiting our ability to conduct further sensitivity analysis on this subgroup.
An important finding is the consistently worse survival rates in the Luminal B subtype irrespective of menopausal status. Women with this subtype, which constitutes ~ 25% of breast cancers, continued to experience poor outcomes even 15 years after diagnosis. Identifying genomic markers, treatments and modifiable risk factors specific to this subgroup could improve long-term outcomes for a large proportion of breast cancer survivors.
Our study has many strengths. The study sample comprised a large well-characterized clinical cohort with over 15 years follow-up including both pre-and post-menopausal women of all hormonal and Her2 subtypes. We obtained high-quality assays using the validated Nanostring platform, and derived subtype calls of > 95% confidence for 90% of our sample. We used rigorous statistical approaches for model development and implemented modern penalized regression methods for unbiased variable selection. There are limitations. Our study cohort was diagnosed with breast cancer between 1991 and 2000, and did not receive current standard of care: women with Her2+ tumors did not receive adjuvant trastuzumab, few postmenopausal women received adjuvant aromatase inhibitors. Women entered the WHEL Study on average of 2 years after cancer diagnosis. While we used left-truncated survival models to account for this delayed entry, there could nevertheless have been a selection bias, whereby women who recurred early would not have been eligible to enter our study. Women with the basal, Her2-overexpressed and claudin-low subtypes could have been most susceptible to this selection bias, a possible explanation for the attenuated hazard ratios observed for these groups in our study.
In summary, we confirmed the prognostic value of PAM50 subtypes for breast cancer outcomes in pre- and post-menopausal women in a large independent cohort with 15-year follow-up. Addition of hypoxia signatures further improved prognostication. Relapse and breast cancer mortality rates for women with Luminal B tumors were the highest, especially over the long-term. Future research and clinical trial innovation should focus on this high-risk group.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
Supported by National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Awards No. R01CA166293 (KM, LN, MP, JP, BP, SF, ERM, ME, SD, TV), P30CA023100 (KM, LN, MP, EP) and F32CA220859 (CRM).
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Compliance with ethical standards
Conflicts of interest
SD has stock or other ownership in NanoString Techologies. BAP has a consulting or advisory Role with Bioalta; Research Funding from Genetech, Glaxo Smith Kline, and Novartis; and Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property with Salk Institute Licensed Technology. MJE has a leadership role, Employment of Immediate Family Member, and stock or other ownership, consulting or advisory role, and Honoraria with Bioclassifier, Prosigna, and NanoString Technologies. ERM has a leadership role and stock with Qiagen N.V., and a consulting or advisory role with Regeneron. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For The Women’s Healthy Eating and Living (WHEL) Study, we obtained IRB approval from participating institutions, and written informed consent from all participants, including for genomic analyses. All aspects of this study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at University of California, San Diego. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Buyse M, Loi S, van’t Veer L, Viale G, Delorenzi M, Glas AM, d’Assignies MS, Bergh J, Lidereau R, Ellis P, Harris A, Bogaerts J, Therasse P, Floore A, Amakrane M, Piette F, Rutgers E, Sotiriou C, Cardoso F, Piccart MJ, Consortium T Validation and clinical utility of a 70-gene prognostic signature for women with node-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98(17):1183–1192. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djj329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cardoso F, Piccart-Gebhart M, Van’t Veer L, Rutgers E, Consortium T The MINDACT trial: the first prospective clinical validation of a genomic tool. Mol Oncol. 2007;1(3):246–251. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2007.10.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nielsen TO, Parker JS, Leung S, Voduc D, Ebbert M, Vickery T, Davies SR, Snider J, Stijleman IJ, Reed J, Cheang MCU, Mardis ER, Perou CM, Bernard PS, Ellis MJ. A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(21):5222–5232. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-10-1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Paik S, Shak S, Tang G, Kim C, Baker J, Cronin M, Baehner FL, Walker MG, Watson D, Park T, Hiller W, Fisher ER, Wickerham DL, Bryant J, Wolmark N. A multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(27):2817–2826. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa041588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Prat A, Ellis MJ, Perou CM. Practical implications of gene-expression-based assays for breast oncologists. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2012;9(1):48–57. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tang G, Shak S, Paik S, Anderson S, Costantino J, Geyer CJ, Mamounas E, Wickerham D, Wolmark N. Comparison of the prognostic and predictive utilities of the 21-gene Recurrence Score assay and Adjuvant! for women with node-negative, ER-positive breast cancer: results from NSABP B-14 and NSABP B-20. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;127(1):133–142. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-1331-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.van’t Veer LJ, Dai HY, van de Vijver MJ, He YDD, Hart AAM, Mao M, Peterse HL, van der Kooy K, Marton MJ, Witteveen AT, Schreiber GJ, Kerkhoven RM, Roberts C, Linsley PS, Bernards R, Friend SH. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature. 2002;415(6871):530–536. doi: 10.1038/415530a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sestak I, Cuzick J. Markers for the identification of late breast cancer recurrence. Breast Cancer Res. 2015;17:10. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0516-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ellis MJ, Suman VJ, Hoog J, Lin L, Snider J, Prat A, Parker JS, Luo JQ, DeSchryver K, Allred DC, Esserman LJ, Unzeitig GW, Margenthaler J, Babiera GV, Marcom PK, Guenther JM, Watson MA, Leitch M, Hunt K, Olson JA. Randomized Phase II neoadjuvant comparison between letrozole, anastrozole, and exemestane for postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-rich stage 2 to 3 breast cancer: clinical and biomarker outcomes and predictive value of the baseline PAM50-based intrinsic subtype-ACOSOG Z1031. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(17):2342–2349. doi: 10.1200/Jco.2010.31.6950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Parker JS, Mullins M, Cheang MCU, Leung S, Voduc D, Vickery T, Davies S, Fauron C, He XP, Hu ZY, Quackenbush JF, Stijleman IJ, Palazzo J, Marron JS, Nobel AB, Mardis E, Nielsen TO, Ellis MJ, Perou CM, Bernard PS. Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(8):1160–1167. doi: 10.1200/jco.2008.18.1370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406(6797):747–752. doi: 10.1038/35021093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Thorsen T, Quist H, Matese JC, Brown PO, Botstein D, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(19):10869–10874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.191367098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie T, Marron JS, Nobel A, Deng S, Johnsen H, Pesich R, Geisler S, Demeter J, Perou CM, Lonning PE, Brown PO, Borresen-Dale AL, Botstein D. Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(14):8418–8423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0932692100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Buus R, Sestak I, Kronenwett R, Denkert C, Dubsky P, Krappmann K, Scheer M, Petry C, Cuzick J, Dowsett M. Comparison of EndoPredict and EPclin with oncotype DX recurrence score for prediction of risk of distant recurrence after endocrine therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016 doi: 10.1093/jnci/djw149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sestak I, Buus R, Cuzick J, Dubsky P, Kronenwett R, Denkert C, Ferree S, Sgroi D, Schnabel C, Baehner FL, Mallon E, Dowsett M. Comparison of the performance of 6 prognostic signatures for estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(4):545–553. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.5524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nielsen T, Wallden B, Schaper C, Ferree S, Liu SZ, Gao DX, Barry G, Dowidar N, Maysuria M, Storhoff J. Analytical validation of the PAM50-based prosigna breast cancer prognostic gene signature assay and ncounter analysis system using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded breast tumor specimens. BMC Cancer. 2014 doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wallden B, Storhoff J, Nielsen T, Dowidar N, Schaper C, Ferree S, Liu SZ, Leung S, Geiss G, Snider J, Vickery T, Davies SR, Mardis ER, Gnant M, Sestak I, Ellis MJ, Perou CM, Bernard PS, Parker JS. Development and verification of the PAM50-based Prosigna breast cancer gene signature assay. BMC Med Genom. 2015 doi: 10.1186/s12920-015-0129-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Buffa FM, Harris AL, West CM, Miller CJ. Large meta-analysis of multiple cancers reveals a common, compact and highly prognostic hypoxia metagene. Br J Cancer. 2010;102(2):428–435. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hu Z, Fan C, Livasy C, He X, Oh DS, Ewend MG, Carey LA, Subramanian S, West R, Ikpatt F, Olopade OI, van de Rijn M, Perou CM. A compact VEGF signature associated with distant metastases and poor outcomes. BMC Med. 2009;7:9. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-7-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tibshirani R. The lasso method for variable selection in the Cox model. Stat Med. 1997;16(4):385–395. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0258(19970228)16:4<385::AID-SIM380>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Colleoni M, Sun Z, Price KN, Karlsson P, Forbes JF, Thurlimann B, Gianni L, Castiglione M, Gelber RD, Coates AS, Goldhirsch A. Annual hazard rates of recurrence for breast cancer during 24 years of follow-up: results from the international breast cancer study group trials I to V. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(9):927–935. doi: 10.1200/jco.2015.62.3504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Natarajan L, Pu MY, Parker BA, Thomson CA, Caan BJ, Flatt SW, Madlensky L, Hajek RA, Al-Delaimy WK, Saquib N, Gold EB, Pierce JP. Time-varying effects of prognostic factors associated with disease-free survival in breast cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;169(12):1463–1470. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwp077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Slamon D, Eiermann W, Robert N, Pienkowski T, Martin M, Press M, Mackey J, Glaspy J, Chan A, Pawlicki M, Pinter T, Valero V, Liu MC, Sauter G, von Minckwitz G, Visco F, Bee V, Buyse M, Bendahmane B, Tabah-Fisch I, Lindsay MA, Riva A, Crown J. Adjuvant trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(14):1273–1283. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0910383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bertucci F, Finetti P, Viens P, Birnbaum D. EndoPredict predicts for the response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in ER-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014;355(1):70–75. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.09.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rakha EA, Agarwal D, Green AR, Ashankyty I, Ellis IO, Ball G, Alaskandarany MA. Prognostic stratification of oestrogen receptor-positive HER2-negative lymph node-negative class of breast cancer. Histopathology. 2017;70(4):622–631. doi: 10.1111/his.13108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Suman VJ, Ellis MJ, Ma CX. The ALTERNATE trial: assessing a biomarker driven strategy for the treatment of post-menopausal women with ER +/Her2- invasive breast cancer. Chin Clin Oncol. 2015;4(3):34. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2304-3865.2015.09.01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zanotti G, Hunger M, Perkins JJ, Horblyuk R, Martin M. Treatment patterns and real world clinical outcomes in ER+/HER2− post-menopausal metastatic breast cancer patients in the United States. Bmc Cancer. 2017;17(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3379-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pierce JP, Natarajan L, Caan BJ, Parker BA, Greenberg ER, Flatt SW, Rock CL, Kealey S, Al-Delaimy WK, Bardwell WA, Carlson RW, Emond JA, Faerber S, Gold EB, Hajek RA, Hollenbach K, Jones LA, Karanja N, Madlensky L, Marshall J, Newman VA, Ritenbaugh C, Thomson CA, Wasserman L, Stefanick ML. Influence of a diet very high in vegetables, fruit, and fiber and low in fat on prognosis following treatment for breast cancer—the Women’s Healthy Eating and Living (WHEL) Randomized Trial. J Am Med Assoc. 2007;298(3):289–298. doi: 10.1001/jama298.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Natarajan L, Pu M, Davies SR, Vickery TL, Nelson SH, Pittman E, Parker BA, Ellis MJ, Flatt SW, Mardis ER, Marinac CR, Pierce JP, Messer K. MiRNAs and long-term breast cancer survival: evidence from the WHEL Study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2019 doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.epi-18-1322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Prat A, Parker JS, Karginova O, Fan C, Livasy C, Herschkowitz JI, He X, Perou CM. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of the claudin-low intrinsic subtype of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010 doi: 10.1186/bcr2635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pierce JP, Faerber S, Wright FA, Rock CL, Newman V, Flatt SW, Kealey S, Jones VE, Caan BJ, Gold EB, Haan M, Hollenbach KA, Jones L, Marshall JR, Ritenbaugh C, Stefanick ML, Thomson C, Wasserman L, Natarajan L, Thomas RG, Gilpin EA. A randomized trial of the effect of a plant-based dietary pattern on additional breast cancer events and survival: the Women’s Healthy Eating and Living (WHEL) Study. Control Clin Trials. 2002;23(6):728–756. doi: 10.1016/S0197-2456(02)00241-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.AJCC . American Joint Committee on Cancer: manual for staging of cancer. 6. New York: Spring-Verlag; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhao X, Rodland EA, Tibshirani R, Plevritis S. Molecular subtyping for clinically defined breast cancer subgroups. Breast Cancer Res. 2015 doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0520-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Therneau TM, Grambsch PM. modeling survival data: extending the Cox model. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 35.R DCT (2009) The R project for statistical computing (freeware statistics package R)
- 36.Sestak I, Buus R, Cuzick J, Dudsky P, Kronenwett R, Ferree S, Sgroi D, Schnabel C, Baehner R, Mallon E, Dowsett M (2016) Comprehensive comparison of prognostic signatures for breast cancer recurrence in TransATAC. In: Paper presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, San Antonio, TX, Dec 6–10, 2016
- 37.Dias K, Dvorkin-Gheva A, Hallett RM, Wu Y, Hassell J, Pond GR, Levine M, Whelan T, Bane AL. Claudin-low breast cancer; clinical & pathological characteristics. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(1):e0168669. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.