Abstract
The RecBCD complex plays key roles in phage DNA degradation, CRISPR array acquisition (adaptation) and host DNA repair. The switch between these roles is regulated by a DNA sequence called Chi. We report cryo-EM structures of the Escherichia coli RecBCD complex bound to several different DNA forks containing a Chi sequence, including one in which Chi is recognised and others in which it is not. The Chi-recognised structure shows conformational changes in regions of the protein that contact Chi and reveals a tortuous path taken by the DNA. Sequence specificity arises from interactions with both the RecC subunit and the sequence itself. These structures provide molecular details for how Chi is recognised and insights into the changes that occur in response to Chi binding that switch RecBCD from bacteriophage destruction and CRISPR spacer acquisition, to constructive host DNA repair.
Introduction
The RecBCD complex, and its close relatives AddAB and AdnAB, plays a critical role in bacterial DNA double-strand break repair (1,2). These complexes load onto DNA ends resulting from a DNA break and are highly processive helicase/nucleases that digest the duplex until they encounter a special sequence called Chi (Crossover hotspot instigator) (3) at which they load RecA protein to initiate repair by homologous recombination (1,2). In E.coli, approximately 75% of Chi sequences are present in the leading strand with an orientation bias in the direction of DNA replication (4). This arrangement has been proposed to favour activity towards the replication origin (4).
However, the complexes are voracious DNA degrading machines and a major defence system against bacteriophages (as their genomes typically lack Chi sequences), digesting the viral DNA starting from breaks created by restriction enzyme cleavage (5,6). Indeed, the default mode of action of RecBCD and AddAB is DNA destruction; that is only modified to a benign DNA repair mode upon interaction with Chi. Furthermore, phage DNA fragments that are produced by both RecBCD and AddAB digestion are incorporated into CRISPR arrays to recognise and respond rapidly to subsequent phage infection, thus providing a mechanism to avoid incorporation of “self” DNA into these arrays via Chi recognition (7,8). Although structural, genetic and biochemical studies of RecBCD have contributed considerably to our understanding of the role of RecBCD in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (1), how Chi regulates the switch between bacteriophage digestion mode and DNA repair has remained enigmatic for almost half a century.
Here, using gel mobility shift assays, we probed specificity of RecBCD for unwound DNA forks containing a Chi sequence in the 3'-tail to determine the requirements of the complex for Chi recognition. In this way, we identified a DNA fork with the Chi sequence spaced appropriately for recognition and response. Using this substrate, we were able to obtain high-resolution structural information of the complex by cryo-EM. The structure revealed a surprisingly compact and twisted conformation of the Chi sequence, which is bound and recognised quite differently compared to an equivalent structure of AddAB bound to its Chi sequence (9). This different mode of binding explains a conundrum, in that the final cleavage of the 3'-tail after Chi recognition by each enzyme occurs at a different distance from the Chi sequence. Furthermore, the structure reveals an on-enzyme equilibrium between Chi recognised and unrecognised states that explains a mechanism to prevent phage escape from these destructive enzymes.
Results
DNA substrate optimisation and cryo-EM analyses
The recognition of Chi by E. coli RecBCD requires the sequence to enter the enzyme complex as a DNA duplex, which is then unwound to present the Chi sequence (GCTGGTGG) in a single-stranded DNA context in the 3'-terminated strand (10). Previous studies on both RecBCD and the related AddAB system have shown that the RecBCD complex is more highly regulated than AddAB and that this control emanates from the RecD subunit (11–15). Indeed, the nuclease activity of the RecB subunit1 (14) is controlled by the RecD subunit (11,13) by a mechanism that involves binding of the 5'-tail to RecD to induce a conformational change in RecB, releasing an α-helix that blocks the nuclease active site (15,16). Interactions of RecD with the 5'-tail also alter the conformation of domains of the RecC subunit, the subunit proposed to interact with Chi (15–22), indicating that a 5'-tail of around 15 bases or more would be required to activate the enzyme.
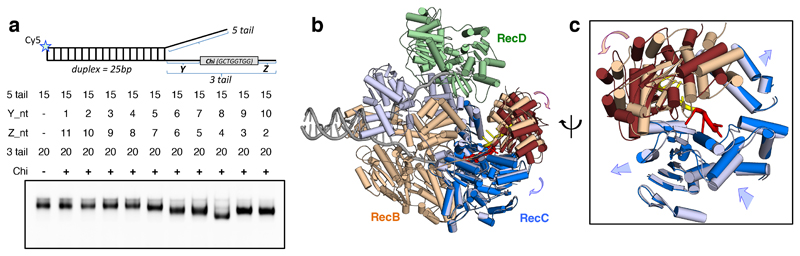
Based on those previous observations, we conducted experiments to determine the specificity requirements for the 3'-tail and to design a synthetic DNA fork that would mimic an encounter with Chi on a physiological substrate (Figure 1a). A Chi site was positioned along the 3'-tail at increasing distance in bases from the fork junction to mimic steps in unwinding a fork. At a spacing of eight bases from the junction, an altered gel mobility shift was observed suggesting a specific response to the Chi sequence at that position (Figure 1a). We thus designed a DNA fork substrate with 25 base pair duplex, a 15 base 5'-tail and a 20 base 3'-tail comprising eight T bases, followed by the eight base Chi sequence (GCTGGTGG), and terminated with four T residues (Figure 1a).
Fig. 1. Structural changes associated with Chi binding.
a, Native gel mobility shift assays (bottom) show an altered shift of the RecBCD-DNA complex band when the substrate contained eight bases between the fork junction and the Chi sequence (Y = 8), suggesting a Chi-specific conformational change. In the schematic on top, the star indicates position of the Cy5 fluorescent label. b, Overview of the conformational changes between the Chi-recognised and the Chi-unrecognised states. The two structures were superimposed on the RecB motor domains. The unchanged domains of both structures are shown in the same colours: RecB in wheat, RecC in light blue and RecD in pale green. The areas that undergo large conformational changes in the Chi-recognised state are coloured darker: RecB nuclease domain in brown and RecC helicase-like domains in blue. The Chi sequence is coloured red and the four bases after Chi are yellow, with the rest of the DNA in grey. c, Expanded and rotated view to emphasise the conformational changes in RecC and RecB nuclease domain around Chi (red). Arrows indicate direction of movements.
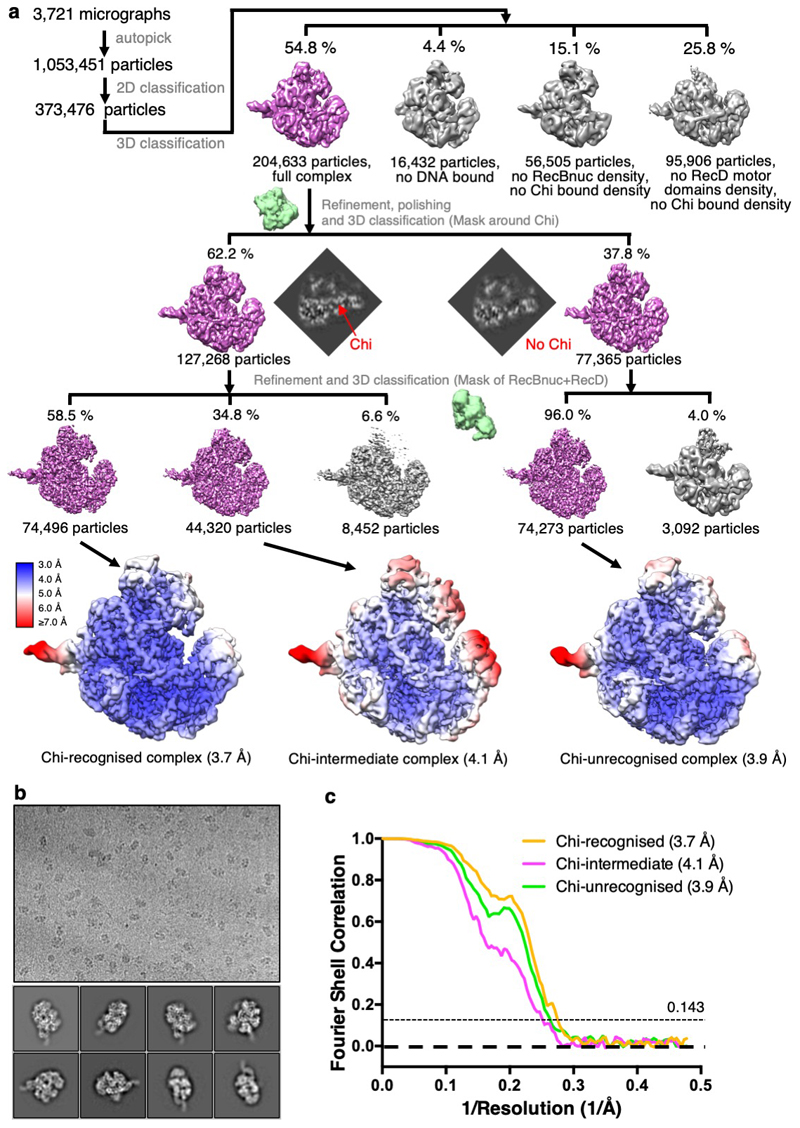
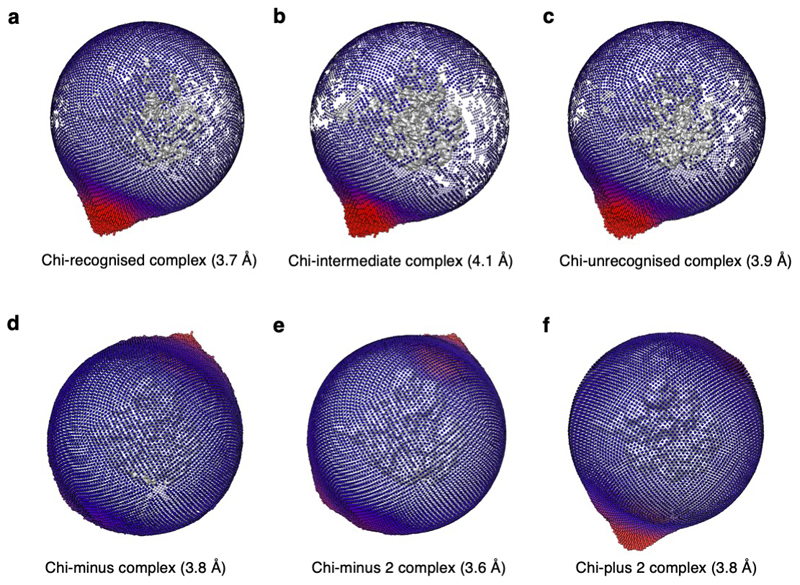
Cryo-EM analysis of RecBCD in complex with this DNA fork substrate resulted in three main structures – a 3.7Å structure of the Chi-recognised complex, a 3.9Å structure with a DNA fork bound but in which Chi has not been recognised, and an intermediate structure at 4.1Å (Figures 1b & 1c, Table 1, Extended Data Figures 1 – 3, Supplementary Movie 1).
Table 1. Cryo-EM data collection, refinement and validation statistics.
| Chi-recognised (EMD-10214,PDB 6SJB) |
Chi-intermediate (EMD-10215, PDB 6SJE) |
Chi-unrecognised (EMD-10216,PDB 6SJF) |
Chi-minus (EMDB-10217,PDB 6SJG) |
Chi-minus 2 (EMD-10369, PDB-6T2U) |
Chi-plus 2 (EMD-10370, PDB-6T2V) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data collection and processing | ||||||
| Magnification | 47,755 | 47,755 | 47,755 | 47,710 | 75,000 | 75,000 |
| Voltage (kV) | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| Detector | Gatan K2 | Gatan K2 | Gatan K2 | Gatan K2 | Falcon3 (Integrating) | Falcon3 (Integrating) |
| Electron exposure (e–/Å2) | 45 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 75.9 | 75.9 |
| Dose rate (e–/pixel/s) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 5 |
| Pixel size (Å) | 1.047 | 1.047 | 1.047 | 1.048 | 1.085 | 1.085 |
| Defocus range (μm) | -1.0 to -3.0 | -1.0 to -3.0 | -1.0 to -3.0 | -1.0 to -2.5 | -1.2 to -2.7 | -1.2 to -2.7 |
| Initial particle images (no.) | 373,476 | 373,476 | 373,476 | 99,545 | 754,150 | 795,810 |
| Final particle images (no.) | 74,496 | 44,320 | 74,273 | 62,812 | 379,790 | 380,912 |
| Symmetry imposed | C1 | C1 | C1 | C1 | C1 | C1 |
| Map resolution (Å) | 3.7 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 3.6 | 3.8 |
| FSC threshold | 0.143 | 0.143 | 0.143 | 0.143 | 0.143 | 0.143 |
| Refinement | ||||||
| Initial model used (PDB code) | 5LD2 | 6SJB | 5LD2 | 6SJF | 5LD2 | 5LD2 |
| Model resolution (Å) | 3.7 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 3.6 | 3.8 |
| FSC threshold | 0.143 | 0.143 | 0.143 | 0.143 | 0.143 | 0.143 |
| Refinement program | Phenix 1.12-2829 | Phenix 1.12-2829 | Phenix 1.12-2829 | Phenix 1.12-2829 | Phenix 1.12-2829 | Phenix 1.12-2829 |
| Model to map CC (masked) | 0.80 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.73 |
| Map sharpening B factor (Å2) | -50 | -50 | -50 | -50 | -100 | -100 |
| Model composition | ||||||
| Non-hydrogen atoms | 24,115 | 24,115 | 23,826 | 23,826 | 23,826 | 23,826 |
| Protein residues | 2,847 | 2,847 | 2,847 | 2,847 | 2,847 | 2,847 |
| DNA residues | 68 | 68 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 |
| B factors (Å2) | ||||||
| Protein | 105 | 118 | 106 | 109 | 94 | 135 |
| DNA | 155 | 172 | 199 | 241 | 147 | 208 |
| R.m.s. deviations | ||||||
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| Bond angles (°) | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.52 | 0.54 | 0.46 | 0.43 |
| Validation | ||||||
| Clashscore | 4.4 | 4.3 | 4.4 | 4.3 | 4.5 | 4.6 |
| Poor rotamers (%) | 2.6 | 3.1 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Ramachandran plot | ||||||
| Favored (%) | 97.7 | 97.9 | 98.0 | 97.8 | 98.0 | 98.0 |
| Allowed (%) | 2.3 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 2.2 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Disallowed (%) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
FSC = Fourier shell correlation, R.m.s = root means squared, CC = correlation coefficient as calculated by phenix.real_space_refine
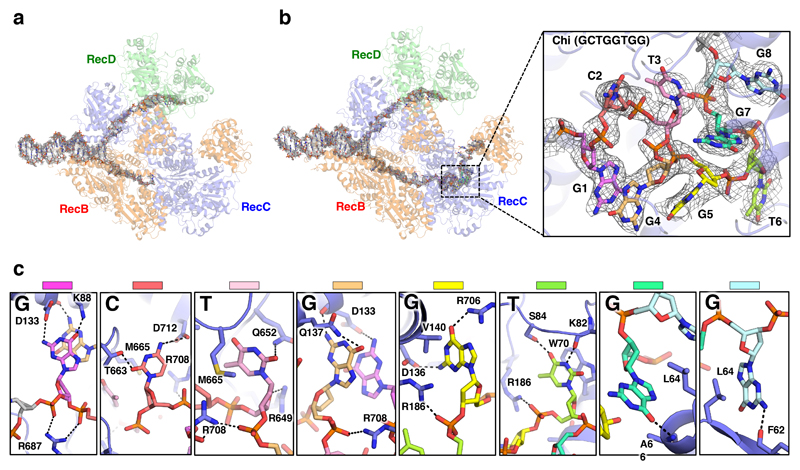
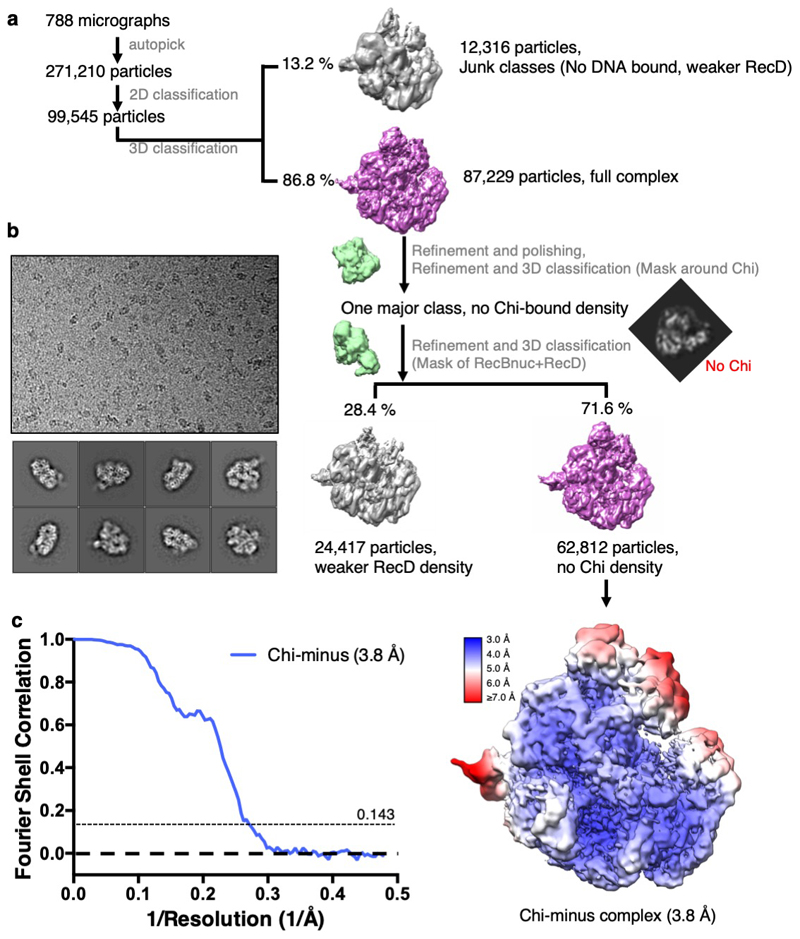
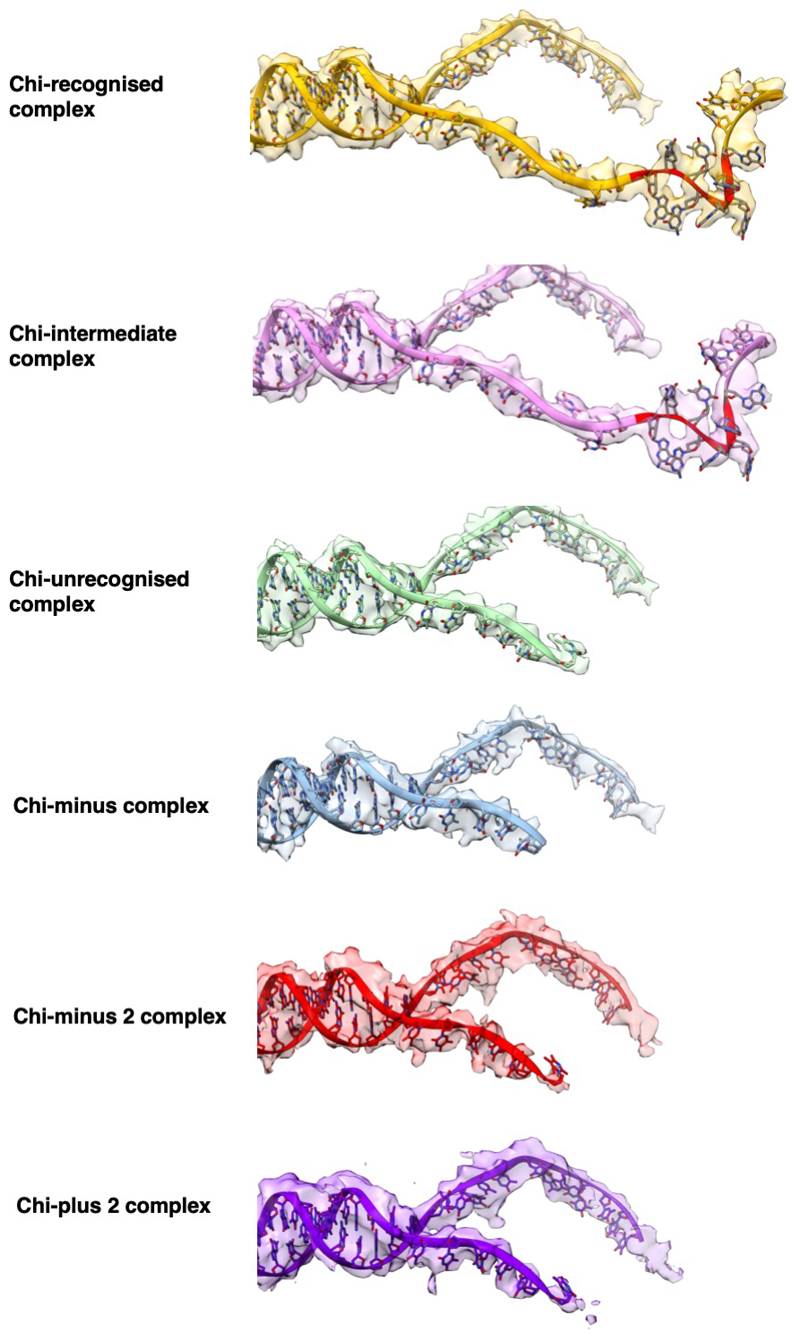
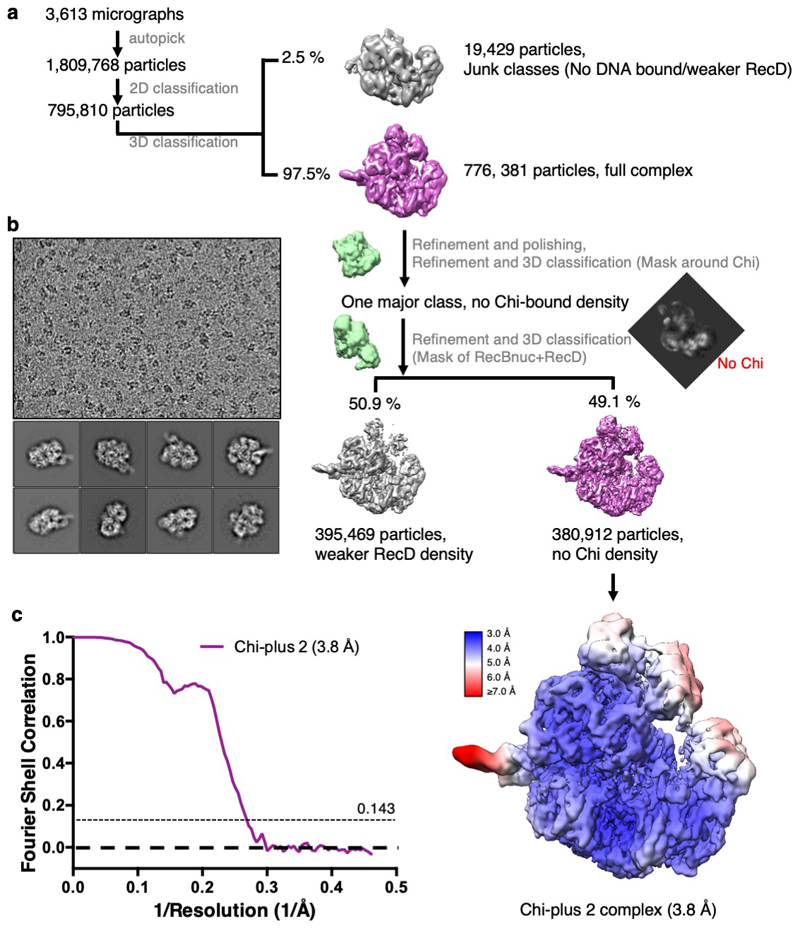
The structure in which Chi is not recognised is indistinguishable from our previous structure with a long 5'-tail (16). Density corresponding to the bound DNA fork is visible for the duplex region, the 5'-tail, and for the 3'-tail across the RecB subunit, although it is disordered beyond the sixth base so the Chi sequence is not visible (Figure 2a). Consequently, this structure provides a high resolution internal control to delineate which conformational changes are specific to the Chi response. As further confirmation, the structure of a complex with an equivalent substrate that lacks a Chi sequence (Chi-minus) and does not induce an altered gel mobility shift (Figure 1a), was determined at 3.8Å resolution and shows no density in the Chi-binding site (Table 1, Supplementary Figures 2 & 3). Similarly, structures of complexes with forks in which the 3'-tail contained either six (Chi-minus 2, 3.6Å resolution) or ten (Chi-plus 2, 3.8Å resolution) bases between the junction and the Chi site also revealed no density in the Chi site (Table 1, Extended Data Figures 3 – 5). Consequently, we can be confident that the changes we observe in the Chi-bound complexes are a result of specific interactions with that sequence and that a spacer of eight residues is required between the fork junction and the start of the Chi site.
Fig. 2. Details of the Chi-binding site interactions.
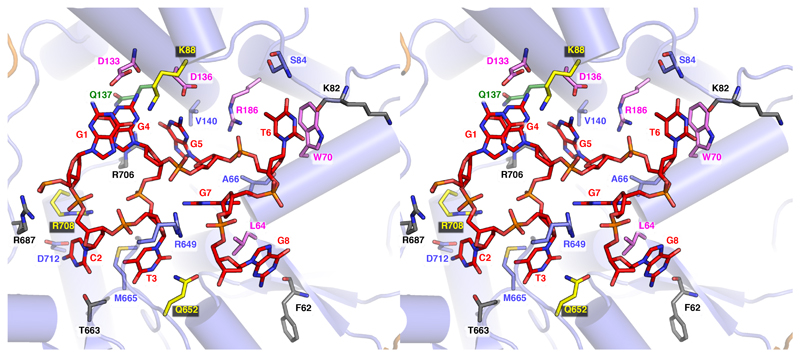
a, Density corresponding to the bound DNA fork substrate in the Chi-unrecognised state with the protein complex shown as a faint cartoon. Strong density is observed for the duplex and 5’-tail regions. Density is also observed for the first six bases of the 3’-tail, but is disordered beyond that. b, Density corresponding to the bound DNA fork substrate in the Chi-recognised state. The density is similar to that observed in the Chi-unrecognised state except that additional density is observed for the entire 20 bases of the 3’-tail, including the Chi sequence. Inset, Expanded view of the density (contoured at 2.5 σ) for the eight Chi bases with the Chi bases individually coloured as in panel (c) demonstrating the highly twisted conformation of the DNA. c, Details of the interactions with each base of the Chi sequence. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines.
Conformational changes in response to Chi recognition
In the Chi-recognised complex, density for the bound DNA is visible for all twenty bases of the 3'-tail, including the Chi sequence (Figure 2b, Extended Data Figures 3 & 4, Supplementary Movie 1). Furthermore, the overall structure of the protein component showed Chi-dependent domain shifts that likely explain the altered gel mobility (Figures 1b & 1c, Supplementary Movie 2). Conformational changes in the RecB nuclease and RecC domains were observed as well as smaller changes in specific regions of the RecC subunit, many of which make direct interactions with the Chi sequence (Figures 2 - 4). The conformational changes in RecC that are induced by the 5'-tail binding to RecD (15) appear to facilitate Chi recognition and bring several residues into proximity of the Chi-binding site prior to Chi binding, switching the subunit into a Chi-recognition mode. Binding to Chi induces a rotation of the 1A and 1B domains of RecC. The 1A domain of RecC forms a significant part of the interface with the RecB nuclease domain and the largest Chi-dependent movement is of the nuclease domain that rotates towards the Chi-binding site as part of a rigid-body movement with domain 1A of RecC (Supplementary Movie 2). The active site residues of the nuclease domain are now located close to the terminal T residue of the 3'-tail (Figure 5). The final cleavage of the 3'-tail is located 4-6 bases after the Chi sequence (23), suggesting the structure is that after the final cleavage event following Chi recognition.
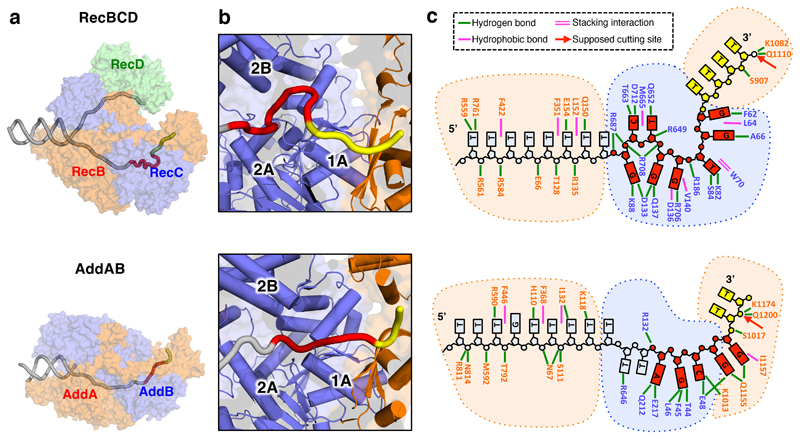
Fig. 4. Comparison of RecBCD and AddAB Chi-bound complexes.
a, Transparent surfaces of RecBCD (above) and AddAB (below) coloured by subunit with the DNA fork backbones overlaid as a cartoon in grey with their respective Chi sequences depicted in red and the bases between Chi and the nuclease active site in yellow. b, Expanded cartoon view of the Chi-binding region in each structure with the RecC domains labelled to highlight the different Chi-binding surfaces utilised by the two enzymes. c, Cartoon representation detailing the contacts between the proteins and DNA.
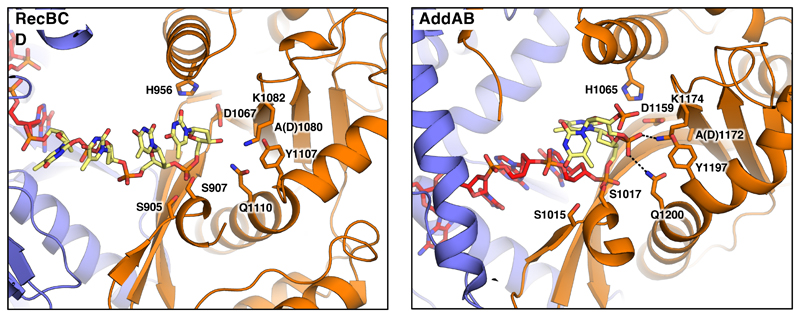
Fig. 5. The nuclease active site in the Chi-bound RecBCD and AddAB complexes.
The nuclease domains of RecBCD and AddAB are shown as cartoons. Key residues participating in DNA binding and catalysis are shown as sticks. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines. The DNA forks used for both enzymes represent substrates after the final cleavage, with four bases after Chi for RecBCD but just a single base for AddAB (in each case depicted in yellow). The difference in the final cleavage site relates to the distance between the end of the Chi-binding site and the nuclease even though the relative position of the nuclease, relative to RecC or AddB, are similar. The normal cleavage of DNA after Chi in RecBCD would result in a terminal 3’-phosphate but this was not added to the substrate synthesised for the structure determination.
Details of the interactions between RecBCD and the bound Chi sequence (Figures 2 - 4, Supplementary Movies 1 & 3) reveal multiple side chain interactions with residues in RecC, many of which have been identified from mutational studies (19,20,22). Interactions with each of the eight bases of the Chi sequence provide specificity while interactions with the phosphodiester backbone (mainly arginine side chains) help to stabilise the twisted conformation of the DNA, allowing the first and fourth residues (both guanines) of the Chi sequence to stack upon each other which provides additional specificity. It has been determined that mutation of any one of the eight bases in Chi is sufficient to reduce affinity to a level that is not functional in vivo (20).
In addition to the particles we assigned to the Chi-recognised structure, a further group were isolated in a class that also showed good density for Chi (Extended Data Figures 1 & 3). The majority of the structure was the same as the Chi-recognised complex, but the nuclease domain was in a slightly altered location, intermediate between the positions of the recognised and unrecognised complexes, that was slightly misaligned for interaction with the 3'-terminus. The density for the nuclease was also less well ordered (Extended Data Figure 1) suggesting the domain is more mobile. This class appears to have recognised Chi but is not optimally aligned for cleavage so we suggest this may be an intermediate in which Chi has been recognised but the nuclease is not aligned for cleavage and during active translocation may not have time to cleave before the Chi sequence is pushed out. We, therefore, refer to this as the Chi-intermediate structure.
Comparison with AddAB/Chi recognition complex
RecBCD shares many aspects of its activity with AddAB (1,2) and the structure of B.subtilis AddAB bound to its Chi sequence (AGCGG) has been determined (9). However, comparison of the structures reveals that interactions with their respective Chi sequences are very different, even though the structures and conformations of the protein components, and their interactions with the DNA fork, are all very similar (Figure 4). In particular, the conformation of the Chi sequence itself is completely different despite the two sequences sharing some apparent similarity (9) (Figure 4). However, the different interaction modes for Chi with RecC and AddB observed in the structures explains why the final cleavage event for RecBCD is 4-6 bases after Chi (23) but only a single base away for AddAB (24). In each case, the bound ssDNA is presented to the nuclease active site in a manner that is consistent with these differing cleavage sites (Figures 4 & 5). Consistent with our structural data, residues beyond the canonical eight base Chi site may also contribute to specificity, particularly in the 4-7 bases on the 3' side of the Chi sequence (21,22), albeit with reduced specificity. Furthermore, a RecBCD complex that carries a mutation in the RecC protein (17) recognises an extended eleven base Chi sequence (Chi* = GCTGGTGCTCG) that includes this region (25).
Mechanism of RecBCD stalling
Single-molecule studies have shown that, upon encountering Chi, RecBCD pauses for several seconds before recommencing translocation at (usually) a reduced speed (26,27). It is also known that an active RecB motor is required for Chi recognition and response (28). The RecB motor precedes the Chi-binding site in RecC so reactivation would push DNA towards the bound Chi sequence. However, the twisted and compacted Chi sequence would act as a physical block to prevent translocation and the DNA would become compressed within the space at the RecB/RecC interface. The conformational changes that provide additional interactions between RecC and the Chi sequence would tighten this grip even further and prevent translocation across and through the RecC subunit. As described previously (19,20), once translocation by the RecB motor recommences, the only exit for this DNA would be through a protein gate between the RecB and RecC subunits that is operated by an ion pair “latch”.
Such a mechanism has similarities to the “DNA scrunching” mechanism observed for RNA polymerase during initiation of transcription that forces the RNA product out of the enzyme complex (29). Blocking the 3'-channel would also explain why nuclease digestion of the 3'-strand is attenuated after Chi binding (30). Although the structure explains why RecBCD stalls at Chi sites (26,27) it does not provide details of the subsequent steps that precede full conversion to repair mode such as reactivation of translocation or how the RecD subunit becomes inactivated (27).
A mechanism to prevent phage evasion
It is known that RecBCD only cleaves at a Chi sequence in 25-40% of encounters (30,31). There are two explanations for this counter intuitive behaviour. The first is that the rate of translocation by RecBCD is so rapid that the Chi sequence passes over the RecC binding site before the complex has a chance to recognise the sequence. A second alternative is that there is an intrinsic equilibrium between bound and unbound states that is reached at every step of translocation. For this to be the case, at a translocation speed of around 1000 bases per second, this equilibrium would need to be established within 1 ms. For the particles with bound DNA substrate, around 40% had the Chi sequence bound specifically and were in the Chi-recognised state with the nuclease correctly positioned (Extended Data Figure 1), suggesting that the latter explanation is correct. Although an additional 20% have also bound Chi (Chi-intermediate), the nuclease domain does not appear to be correctly positioned for cleavage. The remaining 40% of molecules have failed to recognise Chi. Since single-molecule studies of RecBCD indicate that translocation speeds vary considerably (26,27), this would ensure that Chi is recognised and cleaved with similar frequency, regardless of the translocation speed on the 3’-strand (RecB motor). Furthermore, bacteriophages that infect E. coli, such as lambda, typically lack Chi sequences or have them at very low frequency. Consequently, the reduced recognition frequency is an adaptation mechanism to ensure that even bacteriophages that acquire a Chi sequence will likely fail to escape degradation by RecBCD. By contrast, the elevated frequency of Chi sequences in the E. coli genome (4) ensures DNA repair is initiated within a few kilobases of the break site. Thus, these contradictory requirements for Chi recognition can be achieved simultaneously; allowing RecBCD to make the switch between being friend to the host, yet foe to bacteriophages.
Discussion
The twisted conformation of the Chi sequence when bound to RecBCD was unanticipated in light of the related AddAB/Chi structure reported previously (9). In AddAB, the Chi sequence is extended with each base sitting in a pocket on the surface of the AddB subunit, making side chain contacts with the protein that explain the specificity for the sequence. By contrast, RecC contacts Chi in a quite different manner with fewer base-specific contacts. Instead, the specificity appears to come from an overall interaction with a specific shape of the bound ssDNA that is stabilised, at least in part, by contacts such as the intra-sequence contacts between the first and fourth guanine residues in the sequence. Nonetheless, many side chains have been shown to be essential for Chi recognition (19,20,22) so these are, presumably, assisting in the shape recognition that leads to sequence specificity.
RecBCD has been validated as a target for antibiotic development (32). The differing modes of Chi interaction adopted by AddAB and RecBCD have important implications for drug discovery. Recognition of Chi by AddAB provides opportunities for the design of specific drugs that might interact at any or each of the base specificity pockets to prevent Chi binding. Such interactions could be different in organisms with different Chi sequences creating the potential for narrow spectrum targeting of groups of organisms with similar Chi sequences. By contrast, blocking of Chi recognition in RecBCD may require a different approach to find compounds that interact with a part of the pocket in a different manner. Nevertheless, the twisted conformation of the Chi sequence provides multiple surfaces and pockets that might provide specificity for drug design.
In E.coli, 75% of Chi sequences are located in the leading strand and oriented with a bias to favour activity towards the replication origin (4). Such an arrangement has been proposed to promote DNA repair processes during replication (4,33). Given this property, one would imagine that determination of Chi sequences would be straightforward in different organisms. However, that has proved not to be the case and analysis of bacterial genomic data has had limited success in identifying Chi sequences (34). Indeed, even the notion that Chi sequences have evolved to facilitate repair has been questioned. Instead, it was shown that G-rich sequences are naturally more prevalent and the orientation of G-rich sequences other than Chi also showed an apparent directional bias in E.coli but less so in other organisms (such as H.influenzae) that do not show an intrinsic sequence bias (35). This suggests that, rather than Chi sequences evolving as a regulator of Chi, an alternative is that RecBCD adopted a naturally occurring sequence with appropriate characteristics as a regulator, possibly initially with a higher redundancy but later to be more specific as a co-evolution with the abundance of sequence of Chi itself. Such a proposal might explain why Chi sites have proved to be so hard to identify from bioinformatics analysis alone because under these circumstances there need be no conservation of sequences between organisms. To date, Chi sequences that bind to RecBCD have only been identified in two other organisms (H.influenzae and P.synringae) and these are both very similar to the E.coli sequence (E.coli – GCTGGTGG, H.influenzae – G(G/C)TGGTGG and P.syringae – GCTGGCGC).
The structures presented here help us to explain the long-standing observation of Chi-regulation and its effects on phage biology. They help explain the switch from destructive to repair mode but several questions remain unanswered. For example, the structures show how the enzyme is stopped in its tracks during degradation but they do not explain how the complex changes in order to recommence translocation after pausing at the Chi site. Several events take place after Chi recognition including inactivation of the RecD motor (27) and loading of RecA protein onto the 3'-tail. Hopefully, future structures will shed light on those processes.
Methods
Purification of RecBCD
To prevent digestion of the single-stranded tails of the DNA substrate, a nuclease-deficient E. coli RecBCD mutant (D1080A in RecB) was used in this work. The complex was produced from three plasmids, pETduet-His6-TEVsite-recBD1080A, pRSFduet-recC and pCDFduet-recD in a ΔrecBD E. coli strain as described previously (12). His-tagged RecBCD complex was expressed and purified as described previously (16, 36) with the His-tag removed by TEV protease. The purified protein was flash-frozen with 15% glycerol and stored at -80 °C until use.
Preparation of forked DNA substrates
The forked DNA substrates used during this work were made by annealing equal molar quantities of two respective ssDNA oligonucleotides to generate forks with 25 bp duplex, 15 base single-stranded 5’-tail and a 20 base single-stranded 3’-tail. The same upper strand, responsible for generating the 5’-tail, was used in all cases and had the sequence: 5’ TTTTTTTTTTTTTTTgagcgactgcactacaacagaacca 3’ (lower case represents the bases that form the duplex region). The variable lower strand, responsible for presenting Chi (GCTGGTGG), contained the sequence: 5’ tggttctgttgtagtgcagtcgctc(Y)GCTGGTGG(Z) 3’. Y and Z represent the variable number of T bases used to alter the position of the Chi sequence whilst keeping the total number of unpaired bases to 20 (see Figure 1). In the Chi-minus negative control substrate, the Chi sequence was replaced by eight T bases to give a 3’-tail of twenty unpaired T bases.
Native gel mobility assays
For native gel mobility assays, all DNA substrates contained the upper strand labelled with fluorophore (Cy5) at the 5’-terminus and for the lower strand Y values of 1-10 with corresponding Z values of 11-2 were used. Typically, 500 nM RecBD1080ACD was incubated with 500 nM DNA substrate in a 5μl binding solution containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 100 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM TCEP and 5% glycerol, which was incubated on ice for 10 min. Samples were separated on 5% native polyacrylamide gels in 1 × TB buffer. Gels were scanned in fluorescence mode (Cy5) on a BIO-RAD ChemiDocTM MP imaging system.
Cryo-electron microscopy grid preparation and data collection
Prior to preparing grids, RecBCD was thawed and desalted into 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 50mM NaCl, 0.5 mM TCEP using Sephadex G25 spintrap columns (GE Healthcare). The protein was mixed with a 1.5 fold excess of DNA substrate for 10 min at room temperature. Final concentrations were 1 μM RecBCD and 1.5 μM DNA substrate. A RecBCD-Chi complex was prepared using a Chi-containing DNA substrate with a Y spacing of 8 and a Z spacing of 4 (see Figure 1). For the Chi-minus dataset, a complex was prepared using the negative control substrate lacking Chi. For the Chi-minus 2 dataset, a complex was prepared using a Chi-containing DNA substrate with a Y spacing of 6 and a Z spacing of 4 (Figure 1). For the Chi-plus 2 dataset, a complex was prepared using a Chi-containing DNA substrate with a Y spacing of 10 and a Z spacing of 4 (Figure 1). Quantifoil R2/2 μm holey carbon film grids (300 mesh) were treated by plasma cleaning for 30 s before being covered with graphene oxide sheets. In order to improve grid preparation reproducibility and hydrophilicity of the graphene oxide, the following method was used: 5μl of graphene oxide solution (Aldrich 763705, 2mg/ml) were mixed with 5μl of 1.5% w/v solution of nonionic detergent n-Dodecyl-β-D-Maltoside. The mixture was diluted 100 times with water and 5ul was applied to the carbon side of the grid. A sharp edge of a piece of filter paper was applied to the centre of the opposite surface of the grid to pull the graphene oxide solution through the grid. Grids were used within 30 minutes of graphene oxide application. Sample (4 μL) was evenly applied to the graphene oxide-coated side of the grid, followed by a 5 s wait time, 1 s blot time, and freezing in liquid ethane using a Vitrobot Mark IV (FEI). The Vitrobot chamber was maintained at close to 100% humidity at 4°C.
The dataset with the Chi substrate was collected using a Titan Krios microscope operated at 300 KV at eBIC, Diamond, UK. Zero loss energy images were collected automatically using EPU (FEI) on a Gatan K2-Summit detector in counting mode with a pixel size of 1.047 Å. A total of 3,721 images were collected with a nominal defocus range of −1.3 to −2.5 μm in 0.3 μm increments. Each image consisted of a movie stack of 40 frames with a total dose of 45 e-/Å2 over 10 s corresponding to a dose rate of 5 e-/pixel/s. The dataset with the Chi-minus control substrate was collected using a similar collection strategy again with a Gatan K2-Summit detector and Titan Krios microscope at eBIC, Diamond, UK. The pixel size was 1.048 Å and a total of 788 images were collected with a similar defocus range to the above. A total dose of 45 e-/Å2 was split into 40 frames over 7 s, corresponding to a dose rate of 7 e-/pixel/s.
The datasets with the Chi-minus 2 and Chi-plus 2 were collected using a Titan Krios microscope operated at 300 KV at eBIC, Diamond, UK. Zero loss energy images were collected automatically using EPU (FEI) on a Falcon3 detector in integrating mode with a pixel size of 1.085 Å. A total of 4,013 images (Chi-minus 2 substrate) and 3,613 images (Chi-plus 2 substrate) were collected with a nominal defocus range of −1.2 to −2.7 μm in 0.3 μm increments. Each image consisted of a movie stack of 39 frames with a total dose of 76 e-/Å2 over 1 s corresponding to a dose rate of 89 e-/pixel/s.
Data processing – The Chi-containing dataset
Movie stacks were aligned and summed using Motioncor2 (37). Template-free particle picking was done in Gautomatch, using a circular diameter of 150 Å and CTF parameters were estimated for each micrograph using Gctf (38). A total of 1,053,451 picked particles were extracted 2x binned from 3,721 images for two rounds of 2D classification in RELION3 (39) in which 373,476 real RecBCD particles were kept and picking artefacts/noise discarded. A consensus refinement was run on all the particles followed by unmasked 3D classification without alignment. From this, 204,633 particles with complete density for the complex were selected and sub-stoichiometric classes discarded (no DNA density, no RecB nuclease domain density or weaker RecD density). These 204,633 particles were re-extracted unbinned, 3D refined and Bayesian polished prior to 3D classification without alignment using a mask of RecC around the prospective Chi-binding site. This separated 127,268 particles with ordered density for the complete ssDNA 3’ tail, including the Chi sequence, from 77,365 particles with no ssDNA density beyond the RecB helicase domains.
Each class was further refined and classified without alignment, this time using a mask around both RecD and the RecB nuclease. The classifications removed 8,452 and 3,092 particles from the Chi and no Chi classes respectively, which had weaker density for the RecD helicase domains. This left 74,273 homogenous particles from the no Chi class, that were refined to give a 3.9 Å resolution (0.143 FSC cutoff, RELION3) map representing a Chi-unrecognised complex. This structure was very similar a previous RecBCD structure with a forked DNA substrate containing long ssDNA tails (PDB: 5LD2) (16). From the Chi class, two significant conformations were identified. The major state, with 74,496 particles, refined to a resolution of 3.7 Å (0.143 FSC cutoff, RELION3) and represented a Chi-recognised complex with ordered Chi density and significant local conformational changes involving RecC and the RecB nuclease. The second Chi state contained 44,320 particles, refined to 4.1 Å (0.143 FSC cutoff, RELION3) and similarly showed ordered Chi density and the associated local conformational changes in RecC. However, this third state did not show such a substantial movement in the RecB nuclease domain, therefore may represent an intermediate between the Chi-unrecognised and Chi-recognised states, which we have called the Chi-intermediate complex. Work flows for data processing for this and all other structures are presented in Extended Data Figures 1 and 2. An analysis of particle orientations for all structures is presented in Extended Data Figure 6.
Data processing – The Chi-minus control dataset
The Chi-minus movie stacks were initially processed similarly to the Chi dataset. A total of 271,210 particles were extracted 2x binned from 788 images for two rounds of 2D classification in RELION3, resulting in 99,545 RecBCD particles. A consensus 3D refinement was run followed by unmasked 3D classification without alignment from which a homogeneous subset of 87,229 particles with complete density for the complex was selected. The particles were re-extracted unbinned, refined and Bayesian polished prior to 3D classification without alignment using the mask of RecC around the Chi binding site. This time there was only one class, with no DNA density observed in the Chi-binding channel. 3D classification with a mask of RecD plus the RecB nuclease domain separated a class of sub-stoichiometric particles (24,417 particles). The remaining major class (62,812 particles) was refined to produce a 3.8 Å resolution map (0.143 FSC cutoff, RELION3). This represents the Chi-minus complex, which resembles the Chi-unrecognised complex and similarly does not contain ordered 3’ ssDNA beyond the RecB helicase.
Data processing – The Chi-minus 2 dataset
The movie stacks were initially processed similarly to the Chi-containing dataset. A total of 1,694,205 particles were extracted 2x binned from 4,013 images for two rounds of 2D classification in RELION3, resulting in 754,150 RecBCD particles. A consensus 3D refinement was run followed by unmasked 3D classification without alignment from which a homogeneous subset of 687,825 particles with complete density for the complex was selected. The particles were re-extracted unbinned, refined and Bayesian polished prior to 3D classification without alignment using the mask of RecC around the Chi binding site. Only one class, with no DNA density observed in the Chi-binding channel was obtained. 3D classification with a mask of RecD plus the RecB nuclease domain separated a class of sub-stoichiometric particles (308,035 particles). The remaining major class (379,790 particles) was refined to produce a 3.6 Å resolution map (0.143 FSC cutoff, RELION3). This structure resembles the Chi-unrecognised complex and similarly does not contain ordered 3’ ssDNA beyond the RecB helicase.
Data processing – The Chi-plus 2 dataset
The movie stacks were initially processed similarly to the Chi-containing dataset. A total of 1,809,768 particles were extracted 2x binned from 3,613 images for two rounds of 2D classification in RELION3, resulting in 795,810 RecBCD particles. A consensus 3D refinement was run followed by unmasked 3D classification without alignment from which a homogeneous subset of 776, 381 particles with complete density for the complex was selected. The particles were re-extracted unbinned, refined and Bayesian polished prior to 3D classification without alignment using the mask of RecC around the Chi binding site. Only one class, with no DNA density observed in the Chi-binding channel was obtained. 3D classification with a mask of RecD plus the RecB nuclease domain separated a class of sub-stoichiometric particles (395,469 particles). The remaining class (380,912 particles) was refined to produce a 3.8 Å resolution map (0.143 FSC cutoff, RELION3). This structure resembles the Chi-unrecognised complex and similarly does not contain ordered 3’ ssDNA beyond the RecB helicase.
Model building and refinement
The structure of RecBCD in a complex with a DNA fork (PDB 5LD2) (16) was used as a starting model for global docking in Chimera (40) for the Chi-recognised, Chi-unrecognised, Chi-minus 2, and Chi-plus 2 complexes. Once finalised, the Chi-recognised model was then used as a starting template for the Chi-intermediate complex. The Chi-unrecognised model was used a starting template for the Chi minus complex. Each of the six models was edited initially by jelly-body refinement with Refmac (41) in CCP-EM (42) followed by cycles of manual rebuilding in Coot (43) and real-space refinement with PHENIX (44). A 3.7 Å resolution (0.143 FSC cutoff, RELION3) map from a masked focused refinement of the Chi region for the 127,268 Chi-bound particles was used to help build the novel Chi bases and surrounding protein contacts. The six models were finally checked for consistency with one another, apart from where obvious density differences occurred in the maps. A final run of PHENIX real-space refinement with group B-factor refinement was run to generate the final models and model statistics (Table 1).
Extended Data
Extended Data Figure 1.
Extended Data Figure 2.
Extended Data Figure 3.
Extended Data Figure 4.
Extended Data Figure 5.
Extended Data Figure 6.
Supplementary Material
Fig. 3. Details of the full Chi-binding site.
A cross-eye stereo view of the Chi-binding site and interacting residues is shown. Interacting residues are shown as sticks and coloured according to previously published point mutation studies (19,20). Mutations at residues that failed to recognize Chi are in violet, those that showed altered/relaxed Chi recognition specificity are in green, and those that showed little or no influence after mutation are grey. Additional residues which failed to recognize Chi after mutation (22) are coloured in yellow.
Acknowledgements
We thank Diamond for access and support of the cryo-EM facilities at the UK national electron bio-imaging centre (eBIC), funded by the Wellcome Trust, MRC, and BBSRC. The work was funded by the Medical Research Council (MR/N009258/1).
Footnotes
Data Availability
The cryo-electron density maps and coordinates of the final refined models have been deposited at the EMDB wwPDB, respectively, with the following accession codes: EMD-10214 and PDB 6SJB (Chi-recognized); EMD-10215, PDB 6SJE (Chi-intermediate); EMD-10216, PDB 6SJF (Chi-unrecognized); EMD-10369, PDB 6T2U (Chi-minus 2); EMD-10370, PDB 6T2V (Chi-plus 2).
Author Contributions
KC conducted biochemical experiments and prepared samples. KC, MW, & YC collected cryoEM data. KC and MW processed data. KC, MW & DBW analysed data. DBW wrote the manuscript with input from KC & MW.
Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- 1).Dillingham MS, Kowalczykowski S. RecBCD enzyme and the repair of double-stranded DNA breaks. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2008;72:642–71. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00020-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2).Wigley DB. Bacterial DNA repair: recent insights into the mechanism of RecBCD, AddAB and AdnAB. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013;11:9–13. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3).Lam ST, Stahl MM, McMilin KD, Stahl FW. Rec-mediated recombinational hot spot activity in bacteriophage lambda. II. A mutation which causes hot spot activity. Genetics. 1974;77:425–33. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.3.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4).Blattner FR, Plunkett G, Bloch CA, Perna NT, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner JD, Rode CK, Mayhew GF, Gregor J, et al. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science. 1997;277:1453–62. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5331.1453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5).Simmon VF, Lederberg S. Degradation of bacteriophage lambda deoxyribonucleic acid after restriction by Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1972;112:161–9. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.161-169.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6).Dharmalingam K, Goldberg EB. Mechanism localisation and control of restriction cleavage of phage T4 and lambda chromosomes in vivo. Nature. 1976;260:406–10. doi: 10.1038/260406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7).Levy A, Goren MG, Yosef I, Auster O, Manor M, Amitai G, Edgar R, Qimron U, Sorek R. CRISPR adaptation biases explain preference for acquisition of foreign DNA. Nature. 2015;520:505–510. doi: 10.1038/nature14302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8).Modell JW, Jiang W, Marraffini LA. CRISPR-Cas systems exploit viral DNA injection to establish and maintain adaptive immunity. Nature. 2017;544:101–104. doi: 10.1038/nature21719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9).Krajewski WW, Fu X, Wilkinson M, Cronin NB, Dillingham MS, Wigley DB. Structural basis for translocation by AddAB helicase/nuclease and its arrest at Chi sites. Nature. 2014;508:416–9. doi: 10.1038/nature13037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10).Bianco PR, Kowalczykowski SC. The recombination hotspot Chi is recognized by the translocating RecBCD enzyme as the single strand of DNA containing the sequence 5'-GCTGGTGG-3'. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:6706–11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.13.6706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11).Lieberman RP, Oishi M. The recBC deoxyribonuclease of Escherichia coli: isolation and characterization of the subunit proteins and reconstitution of the enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1974;71:4816–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12).Amundsen SK, Taylor AF, Chaudhury AM, Smith GR. RecD: the gene for an essential third subunit of exonuclease V. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986;83:5558–62. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13).Chaudhury AM, Smith GR. A new class of Escherichia coli recBC mutants: implications for the role of RecBC enzyme in homologous recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1984;81:7850–7854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14).Yu M, Souaya J, Julin DA. The 30-kDa C-terminal domain of the RecB protein is critical for the nuclease activity, but not the helicase activity, of the RecBCD enzyme from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:981–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.3.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15).Singleton MR, Dillingham MS, Gaudier M, Kowalczykowski SC, Wigley DB. Crystal structure of RecBCD enzyme reveals a machine for processing DNA breaks. Nature. 2004;432:187–93. doi: 10.1038/nature02988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16).Wilkinson M, Chaban Y, Wigley DB. Mechanism for nuclease regulation by RecBCD. Elife. 2016;5 doi: 10.7554/eLife.18227. pii: e18227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17).Schultz DW, Taylor AF, Smith GR. Escherichia coli RecBC pseudorevertants lacking Chi recombinational hotspot activity. J Bacteriol. 1983;155:664–80. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.664-680.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18).Ponticelli AS, Schultz DW, Taylor AF, Smith GR. Chi-dependent DNA strand cleavage by RecBCD enzyme. Cell. 1985;41:145–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19).Handa N, Yang L, Dillingham MS, Kobayashi I, Wigley DB, Kowalczykowski SC. Molecular determinants responsible for recognition of the single-stranded DNA regulatory sequence, χ, by RecBCD enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:8901–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206076109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20).Yang L, Handa N, Liu B, Dillingham MS, Wigley DB, Kowalczykowski SC. Alteration of χ recognition by RecBCD reveals a regulated molecular latch and suggests a channel-bypass mechanism for biological control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:8907–12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206081109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21).Taylor AF, Amundsen SK, Smith GR. Unexpected DNA context-dependence identifies a new determinant of Chi recombination hotspots. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:8216–28. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22).Amundsen SK, Sharp JW, Smith GR. RecBCD Enzyme "Chi Recognition" Mutants Recognize Chi Recombination Hotspots in the Right DNA Context. Genetics. 2016;204:139–52. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.191056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23).Taylor AF, Schultz DW, Ponticelli AS, Smith GR. RecBC enzyme nicking at Chi sites during DNA unwinding: location and orientation-dependence of the cutting. Cell. 1985;41:153–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24).Chedin F, Ehrlich SD, Kowalczykowski SC. The Bacillus subtilis AddAB helicase/nuclease is regulated by its cognate Chi sequence in vitro. J Mol Biol. 2000;298:7–20. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25).Handa N, Ohashi S, Kusano K, Kobayashi I. χ*, a χ-related 11-mer sequence partially active in an E. coli recC* strain. Genes Cells. 1997;2:525–36. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.1997.1410339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26).Spies M, Bianco PR, Dillingham MS, Handa N, Baskin RJ, Kowalczykowski SC. A Molecular Throttle: The Recombination Hotspot χ Controls DNA Translocation by the RecBCD Helicase. Cell. 2003;114:647–654. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00681-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27).Spies M, Amitani I, Baskin RJ, Kowalczykowski SC. RecBCD enzyme switches lead motor subunits in response to chi recognition. Cell. 2007;131:694–705. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.09.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28).Spies M, Dillingham MS, Kowalczykowski SC. Translocation by the RecB motor is an absolute requirement for χ-recognition and RecA protein loading by RecBCD enzyme. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:37078–87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M505521200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29).Kapanidis AN, Margeat E, Ho SO, Kortkhonjia E, Weiss S, Ehbright RH. Initial transcription by RNA polymerase proceeds through a DNA-scrunching mechanism. Science. 2006;314:1139–43. doi: 10.1126/science.1131399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30).Dixon DA, Kowalczykowski SC. The recombination hotspot chi is a regulatory sequence that acts by attenuating the nuclease activity of the E. coli RecBCD enzyme. Cell. 1993;73:87–96. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90162-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31).Taylor AF, Smith GR. RecBCD enzyme is altered upon cutting DNA at a chi recombination hotspot. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89:5226–30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32).Wilkinson M, Troman L, Wan Nur Ismah WA, Chaban Y, Avison MB, Dillingham MS, Wigley DB. Structural basis for the inhibition of RecBCD by Gam and its synergistic antibacterial effect with quinolones. Elife. 2016;5 doi: 10.7554/eLife.22963. pii: e22963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33).El Karoui M, Biaudet V, Schbath S, Gruss A. Characteristics of Chi distribution on different bacterial genomes. Res Microbiol. 1999;150:579–87. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2508(99)00132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34).Uno R, Nakayama Y, Arakawa K, Tomita M. The orientation bias of Chi sequences is a general tendency of G-rich oligomers. Gene. 2000;259:207–15. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(00)00430-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35).Halpern D, Chiapello H, Schbath S, Robin S, Hennequet-Antier C, Gruss A, El Karoui M. Identification of DNA motifs implicated in maintenance of bacterial core genomes by predictive modeling. PLoS Genet. 2007;3:1614–21. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36).Saikrishnan K, Griffiths SP, Cook N, Court R, Wigley DB. DNA binding to RecD: role of the 1B domain in SF1B helicase activity. EMBO J. 2008;27:2222–9. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37).Zheng SQ, Palovcak E, Armache JP, Verba KA, Cheng Y, Agard DA. MotionCor2: anisotropic correction of beam-induced motion for improved cryo-electron microscopy. Nat Methods. 2017;14:331–2. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38).Zhang K. Gctf: Real-time CTF determination and correction. J Struct Biol. 2016;193:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2015.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39).Zivanov J, Nakane T, Forsberg BO, Kimanius D, Hagen WJ, Lindahl E, Scheres SH. New tools for automated high-resolution cryo-EM structure determination in RELION-3. Elife. 2018;7 doi: 10.7554/eLife.42166. pii:e42166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40).Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE. UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem. 2004;25:1605–1612. doi: 10.1002/jcc.20084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41).Murshudov GN, Vagin AA, Dodson EJ. Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1997;53:240–55. doi: 10.1107/S0907444996012255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42).Burnley T, Palmer CM, Winn M. Recent developments in the CCP-EM software suite. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2017;73:469–477. doi: 10.1107/S2059798317007859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43).Emsley P, Lohkamp B, Scott WG, Cowtan K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2010;66:486–501. doi: 10.1107/S0907444910007493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44).Afonine PV, Poon BK, Read RJ, Sobolev OV, Terwilliger TC, Urzhumtsev A, Adams PD. Real-space refinement in PHENIX for cryo-EM and crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2018;74:531–544. doi: 10.1107/S2059798318006551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45).Kucukelbir A, Sigworth FJ, Tagare HD. Quantifying the local resolution of cryo-EM density maps. Nat Methods. 2014;11:63–5. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.