Abstract
Background: Thyroid hormone (triiodothyronine [T3]) is essential for the development throughout vertebrates. Anuran metamorphosis mimics mammalian postembryonic development, a period around birth when plasma T3 level peaks and many organs/tissues mature into their adult forms. Compared with the uterus-enclosed mammalian embryos, tadpoles can be easily manipulated to study the roles of T3 and T3 receptors (TRs) in tissue remodeling and adult organ development. We and others have previously knocked out TRα or TRβ in the diploid anuran Xenopus tropicalis and reported distinct effects of the two receptor knockouts on metamorphosis. However, animals lacking either TRα or TRβ can complete metamorphosis and develop into reproductive adults.
Methods: We have generated TRα and TRβ double knockout animals and carried out molecular and morphological analyses to determine if TR is required for Xenopus development.
Results: We found that the TR double knockout tadpoles do not respond to T3, supporting the view that there are no other TR genes in X. tropicalis and that TR is essential for mediating the effects of T3 in vivo. Surprisingly, the double knockout tadpoles are able to initiate metamorphosis and accomplish many metamorphic changes, such as limb development. However, all double knockout tadpoles stall and eventually die at stage 61, the climax of metamorphosis, before tail resorption takes place. Analyses of the knockout tadpoles at stage 61 revealed various developmental abnormalities, including precocious ossification and extra vertebrae.
Conclusions: Our data indicate that TRs are not required for the initiation of metamorphosis but is essential for the completion of metamorphosis. Furthermore, the differential effects of TR knockout on different organs/tissues suggest tissue-specific roles for TR to control temporal coordination and progression of metamorphosis in various organs.
Keywords: Xenopus tropicalis, Xenopus laevis, thyroid hormone receptor, transcriptional regulation, amphibian metamorphosis
Introduction
Anuran metamorphosis is the most dramatic morphological transformation that is controlled by thyroid hormone (triiodothyronine [T3]) during vertebrate development. This process mimics postembryonic development in mammals, a period around birth when T3 level also peaks and many organs/tissues mature into their adult forms (1,2). Anuran metamorphosis, however, offers several major advantages for studying the role of T3 and the underlying mechanism in the formation/maturation of the adult organs during postembryonic development, most noticeably the easiness to manipulate this process without any maternal influence.
Earlier transgenic studies in the anuran Xenopus laevis have shown that T3 receptors (TRs) are both necessary and sufficient to mediate the causative effects of T3 on amphibian metamorphosis (3). Like all other vertebrates, there are two types of TRs, TRα and TRβ, in both the pseudotetraploid X. laevis and the highly related but diploid species Xenopus tropicalis (4,5). These receptors are nuclear transcription factors that can repress or activate T3-inducible genes in the presence or absence of T3, respectively, even in the context of chromatin (2,6–11). These molecular properties and the expression profiles of the TRα and TRβ genes have led to the proposal of a dual function model for TRs during X. laevis development (12,13). According to the dual function model, during premetamorphosis when plasma T3 level is low or absent, TR is mainly unliganded and functions to repress the expression of T3-inducible genes to prevent precocious metamorphosis. When T3 becomes available, T3 binds to TR and liganded TR in turn activates the target genes to induce metamorphosis. Over the years, studies from different laboratories have provided strong molecular and transgenic evidence to support this model (3,13–27). However, the pseudotetraploid nature of the X. laevis genome and the lack of good technologies to inactivate the endogenous genes had long prevented the analysis of function of the endogenous TR genes during X. laevis development.
With the advent of gene editing technologies that are applicable to amphibians, we and others have begun to investigate the role of endogenous TRs by using the diploid anuran X. tropicalis, which is highly related to X. laevis, especially with regard to metamorphosis (4,28–32). Both TRα and TRβ have been knocked out individually, and analyses of the single knockout animals have revealed interesting but distinct phenotypes (33–42). Knocking out TRα leads to derepression of T3-inducible genes in premetamorphic tadpoles and premature initiation of metamorphosis, as reflected by limb morphogenesis, and also decreased response to exogenous T3 and reduced rate of metamorphic progression during natural metamorphosis (33,34,37–41). However, it has no detectable effect on tail resorption with overall time from fertilization to the completion of metamorphosis similar between wild-type (WT) and knockout animals. However, knocking out TRβ has little effect on premetamorphic development and limb metamorphosis but delays tail resorption (35,36,42). Interestingly, both TRα and TRβ individual knockout animals can complete metamorphosis with no apparently morphological defects in the resulting froglets, raising an interesting question whether TR is required for metamorphosis, especially considering that inactivating both TRα and TRβ does not impair mouse embryonic development (43,44).
In this study, we have knocked out the X. tropicalis TRβ gene by using clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/Cas9 genome editing technology in TRα-knockout animals and generated homozygous TR-null (TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−)) animals. Our analyses of the WT and knockout animals show that T3 target gene expression was derepressed in TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) premetamorphic tadpoles, and such tadpoles were completely resistant to T3 treatment. Developmentally, homozygous TR double knockout led to tadpole lethality at stage 61, the climax of metamorphosis, with little tail resorption and gill repression taking place. Examination of the tadpoles at stage 61 revealed various developmental abnormalities in the TR double knockout (TRDKO) animals, which include precocious ossification. Analysis of keratin gene expression in the back skin revealed that TRDKO prevented the repression of larval keratin gene expression normally occurring at stage 61 without affecting the activation of adult keratin gene expression. Our data suggest that TR is not required for the initiation of metamorphosis but is essential for the temporal coordination of the transformation of different organs to ensure the completion of metamorphosis via repression of T3 target genes during premetamorphosis and activation of these genes when bound by T3.
Materials and Methods
Experimental animals
WT adult X. tropicalis were purchased from Nasco. Embryos and tadpoles were staged according to the study by Nieuwkoop and Faber (45). TRα mutation frog (TRα (+/−)TRβ (+/+) and TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/+)) was generated and reared in the 9-L plastic container (37,38). All animal care and treatments were performed as approved by the Animal Use and Care Committee of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
Generation of TRβ-knockout X. tropicalis animals by using CRISPR-Cas9, genome editing technology and genotyping
CRISPR-short guide RNA (sgRNA) was designed, as described (46), to target exon 2 of the TRβ gene, upstream of the DNA binding domain (Supplementary Table S1 and Fig. 1). CRISPR-sgRNA-injected embryos generated from mating of TRα (+/−)TRβ (+/+) and TRα (+/+)TRβ (+/+) animals were reared to sexual maturity (F0-generation frogs). A sexually mature F0 frog was mated with a TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/+) frog, and their offspring were screened to identify TRα homozygous and TRβ heterozygous mutant tadpoles (TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−)). After TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−) mutants were sexually mature (F1 frogs), female and male mutant frogs were primed with 20 U of human chorionic gonadotropin (Novarel), one day before egg laying. They were then boosted with another injection of 200 U of human chorionic gonadotropin on the second day for natural mating to obtain the TR total knockout (TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−)) animals (F2 generation). The resulting fertilized eggs/embryos were collected and reared for 3–4 days at 25°C to reach the onset feeding stage (stage 45). The tadpoles were then transferred to a 4-L container and fed.
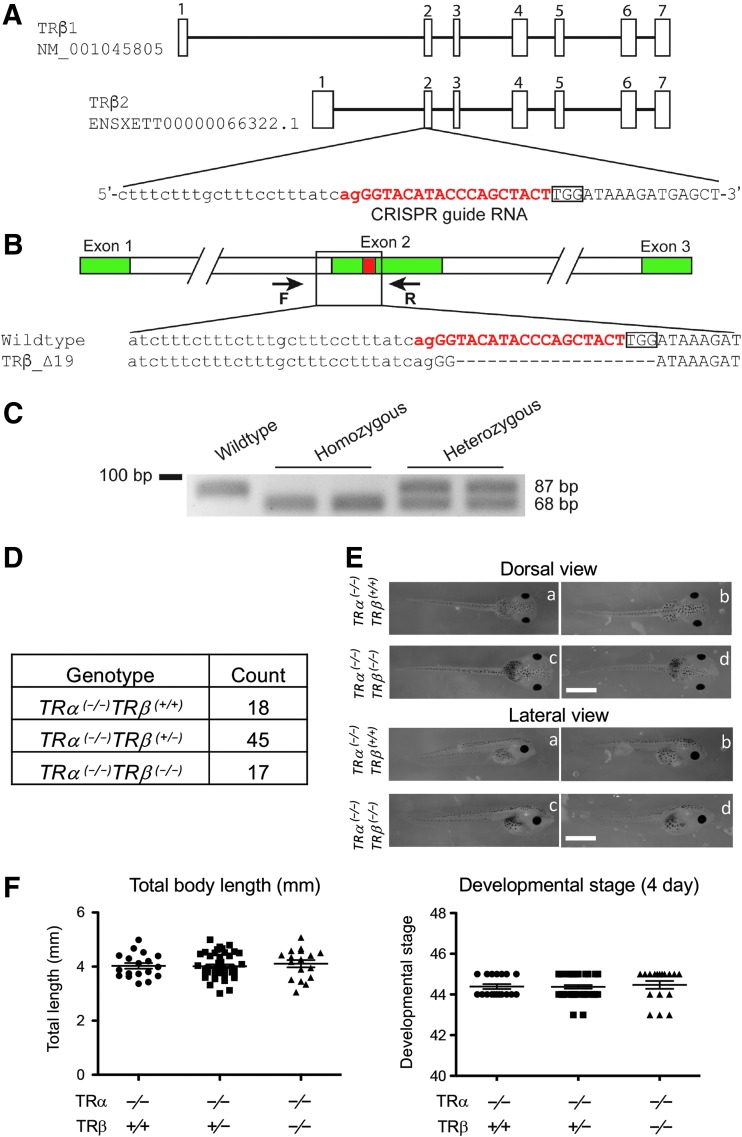
FIG. 1.
Knocking out both TR genes does not affect Xenopus tropicalis embryogenesis. (A) Genomic structure of the X. tropicalis TRβ gene and the CRISPR-sgRNA against X. tropicalis TRβ. There are two known transcripts for X. tropicalis TRβ, each with seven exons (boxes). The TRβ-specific sgRNA was designed to target exon 2, and the sgRNA sequences are shown in red. (B) Schematic diagram depicting the sequence of the sgRNA-targeted region in the WT and a TRβ-mutant (19 bases deletion) animals. Arrows represent primers used for genotyping: the forward primer F and the reverse primer R, respectively. (C) Representative examples of genotyping by PCR. Genotyping PCR was carried out on genomic DNA by using a common primer set, primer F and primer R. The presence of only upper (105 bp) or lower (86 bp) band in the gel indicates a WT or homozygous mutant animal, respectively, while the presence of both upper and lower band indicates a heterozygous mutant. (D) Mendelian distribution of four-day-old tadpoles from mating of two TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−) animals. Genotyping PCR was carried out by using tail tip genomic DNA of four-day-old tadpoles, which were at stage 45/46, the onset of tadpole feeding, and the result was close to the expected Mendelian ratio. (E) Representative photos of four-day-old tadpoles of the WT or homozygous TRβ-knockout genotype in the homozygous TRα mutant background. The upper column is the dorsal view and the lower column is the lateral view. Lowercase letters in both columns indicate the same tadpole. Note that no obvious difference was present between the WT or homozygous TRβ tadpoles in the homozygous TRα mutant background. Scale bars: 1 mm. (F) Knocking out TRβ in the homozygous TRα mutant background does not affect the body length and developmental stage of four-day-old tadpoles. The data are shown as the mean, marked as a line, and SE. No significant difference was observed in both parameters for the three genotypes, indicating that removing TRβ has no effect on X. tropicalis embryogenesis. CRISPR, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; SE, standard error; sgRNA, short guide RNA; T3, thyroid hormone; TR, T3 receptor; WT, wild type.
Tadpoles were anesthetized with MS222 for photography, tail clipping, and body length measurement. For genotyping, the tadpole tail tip (about 5 mm or less) was clipped and lysed in 20 μL QuickExtract DNA extraction solution (Epicentre) at 65°C for 20 minutes. After incubating at 95°C for five minutes, 1 μL of the DNA extraction solution was immediately used for genotyping by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). For the F1 animals, genotyping was performed with PCR amplification of the TRα-transcriptional activator–like effector nuclease (TALEN)-targeted (37,38) and TRβ-CRISPR-targeted regions (Supplementary Table S1). This led to the identification of F1 animals with a homozygous mutation for TRα and out-of-frame mutations for TRβ. A 19 base out-of-frame deletion TRβ line (Fig. 1) was chosen for further studies. Genotyping the offspring of this F1 line for TRα was subsequently performed by PCR as described (38). TRβ mutants were identified by PCR with the forward primer 1, 5′-TCAATGGAACCCTTTGGAGCTG-3′ and the reverse primer 1, 5′-ACAGTTACAGGCATTTCCAGGC-3′ for 35 cycles of 94°C for 10 seconds, 60°C for 5 seconds, and 72°C for 45 seconds. The PCR products were analyzed by gel electrophoresis and purified by using QIAGEN PCR purification kit (Qiagen), followed by sequencing (Eurofins genomics). For the F2 generation, the genotyping of TRβ was performed by PCR with the forward primer 2, 5′-GGACAACATTAGATCTTTCTTTCTTTG-3′ and the reverse primer 2, 5′-CACACCACGCATAGCTCATC-3′ for 33 cycles of 94°C for 30 seconds, 60°C for 30 seconds, and 72°C for 20 seconds. The PCR products were analyzed by gel electrophoresis.
T3 treatment
Randomly selected stage 54 tadpoles were treated with 10 nM T3 for 18 hours at 25°C. The tadpole tail tip (about 5 mm or less) was cut for genotyping, and the rest of each animal was frozen in liquid nitrogen. The frozen tadpoles of the same genotype were combined together for RNA extraction. For the long-term T3 treatment, 17–27 tadpoles of different genotypes at stage 54 were pooled together in 4-L plastic container and treated with or without 5 nM T3 for five days at 25°C.
RNA extraction and quantitative real-time PCR
Total RNA of the intestine, tail, or limb was extracted with RNeasy® Mini Kit 250 (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The homogenates of individual tissues from at least five animals, or five whole animals, of each genotype were combined together for RNA extraction. The RNA concentration was measured by using a NanoDrop (Thermo Scientific). The same amount of RNA from each of the three genotypes (TRβ: WT, heterozygous, and homozygous) was reverse-transcribed with the QuantiTect Reverse Transcription Kit (Qiagen). The cDNA was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR by using the SYBR Green method. The PCR primers for the internal control genes ef1α and rpl8 were described previously (37,38) (note that ef1α and rpl8 mRNA expression was similar in all genotypes; data not shown). All expression data were normalized against that of the internal control gene ef1α or rpl8. The expression analyses were performed at least twice, with similar results. The primer sequences are listed in Supplementary Tables S1 and S2.
Staining for ossification
Whole mount staining was carried out according to the study by Inouye (47), with slight modifications. In brief, tadpoles at stages 54–66 were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde/phosphate-buffered saline for one day at 4°C. After dehydration with 95% ethanol for four days, the specimens were deskinned and eviscerated and then delipidated with acetone for one day. The specimens were stained in 0.015% Alcian blue 8GS (Sigma)–0.005% Alizarin red S (Acros Organics), 5% acetic acid, and 70% ethanol at 37°C for one day. The stained specimens were put stepwise into 30% saturated borate–0.5% Trypsin (Sigma) at 37°C for one day, 1% KOH and 20% glycerol for one day, and 50%, 80% glycerol for two hours. The cleared specimens were stored in 100% glycerol. The cartilage was then stained blue, and the calcified bone stained red.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard error. The significance of differences between groups was evaluated by one-way analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni multiple comparison test or Student's t-test using Prism 5 (GraphPad Software).
Results
Generation of X. tropicalis TR total knockout animals via genome editing
To investigate the role of endogenous TRs during vertebrate development, we adapted the genome editing technologies to knockout both TR genes in X. tropicalis. We previously generated TRα-knockout animals by using TALEN technology. To generate TRDKO animals, we used CRISPR technology to generate mosaic TRβ-knockdown frogs (F0) (46). First, we designed a CRISPR guide RNA targeting in exon 2, which encodes part of the DNA binding domain, of X. tropicalis TRβ (Fig. 1A). Then, we microinjected the mRNAs encoding the CRISPR sgRNA and Cas9 into one-cell stage embryos generated from a TRα heterozygous frog (TRα (+/−)TRβ (+/+)) and a WT frog (TRα (+/+)TRβ (+/+)). The resulting F0 animals had mosaic mutations in the target region of the TRβ gene. We raised some of these F0 animals of the TRα (+/−)TRβ mosaic genotype to sexual maturity and then crossed them with TRα homozygous knockout animals (TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/+)) to generate F1, TRβ heterozygous animals (TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−)). We selected one heterozygous mutant line with a 19 base out-of-frame deletion in the target region of TRβ gene for further analysis (Fig. 1B). We finally produced TRβ homozygous knockout F2 generation animals (TRDKO, TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−)) by intercrossing the F1 frogs and confirmed genotype by PCR (Fig. 1C).
TR is not required for frog embryogenesis
To analyze the effects of TR knockout on embryogenesis, we measured the body length and determined the developmental stage of individual animals according to their external morphology four days after fertilization (45). Genotyping of 80 F2 siblings from mating two TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−) animals revealed a Mendelian distribution of the three expected genotypes (Fig. 1D). Furthermore, there was no significant difference in body length or developmental stage among the three genotypes: TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/+), TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−), and TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) (Fig. 1E, F) and all animals reached stage 45, the onset of feeding. These results indicate that removing TRβ in the TRα knockout background had no effect on embryogenesis. In addition, earlier studies have shown that TRα single knockout also had no detectable gross developmental defects on embryogenesis (38). Thus, TR is not essential for Xenopus embryogenesis.
TRβ represses T3 target genes in premetamorphic tadpoles and upregulates them in the presence of exogenous T3 to facilitate precocious tissue transformations in premetamorphic tadpoles
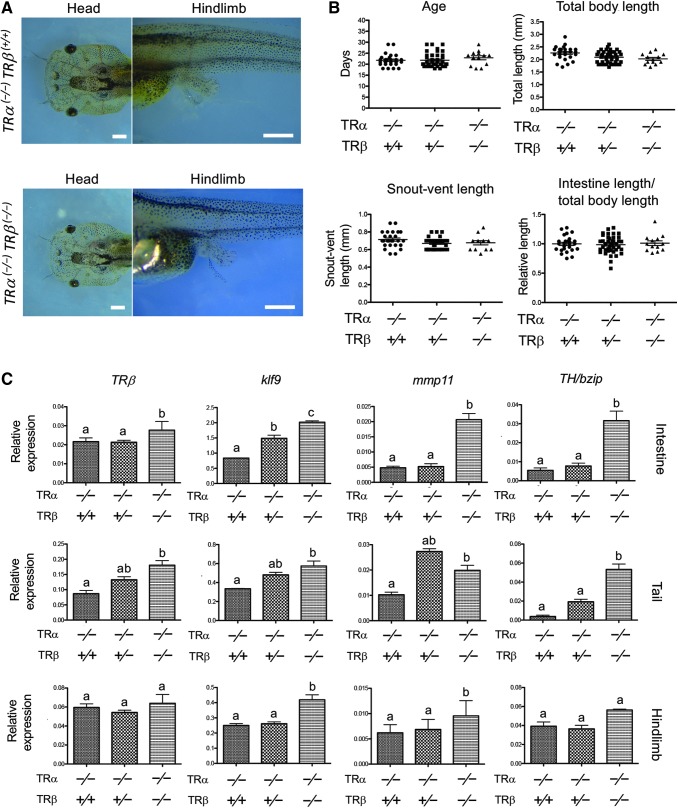
To investigate the effect of TRβ knockout on premetamorphic tadpoles in the absence of TRα, we first measured the age in days for the animals to reach stage 54, commonly considered to be the onset of metamorphosis. Eighty F2 siblings as generated above were randomly selected when individual tadpoles reached stage 54 based on morphology (Fig. 2A), and their ages were recorded (Fig. 2B). After measuring the total body length, snout-vent length and intestine length, the genotype of each tadpole was determined by PCR, showing the presence of 26 TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/+), 41 TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−), and 13 TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) tadpoles among them (Fig. 2B). Interestingly, no difference was observed for any of the four parameters among the three genotypes (Fig. 2B), suggesting that TRβ knockout in the background of TRα knockout does not affect premetamorphic tadpole development.
FIG. 2.
Knocking out TRβ in the homozygous TRα mutant background derepresses the expression of T3-inducible genes in premetamorphic tadpoles with little effect on premetamorphic development. (A) Representative photos of tadpoles at stage 54. Note that the TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/+) and TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) tadpoles at stage 54 have a similar head (dorsal view) and hind limb morphology (lateral view). Scale bars: 1 mm. (B) TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/+) and TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) tadpoles have similar developmental rates (age, days to stage 54), total body length, snout-vent length, and intestinal length (normalized against the total body length) at stage 54. These results are plotted as the mean, marked as a line, and SE. (C) Increased basal expression of known T3 target genes due to TRβ knockout in premetamorphic tadpoles. Total RNA from three different organs, intestine, tail, and hind limb, of stage 54 tadpoles of the three genotypes, was used for qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of four well-known T3 direct target genes: TRβ, klf9, mmp11, and TH/bzip. The expression levels were normalized against that of ef1α. Different lowercase letters denote statistically significant differences (p < 0.05). qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time PCR.
We next investigated the expression of several known direct T3 target genes, TRβ (48), klf9 (49), mmp11 (50), and TH/bzip (51) in three different organs: intestine, tail, and hind limb of premetamorphic tadpoles. The results show that the expression of all these genes was increased in TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) tadpoles, although few changes were observed in most cases in TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−) heterozygous animals (Fig. 2C). Thus, in the absence of TRα, TRβ repressed the expression of the target genes in premetamorphic tadpoles.
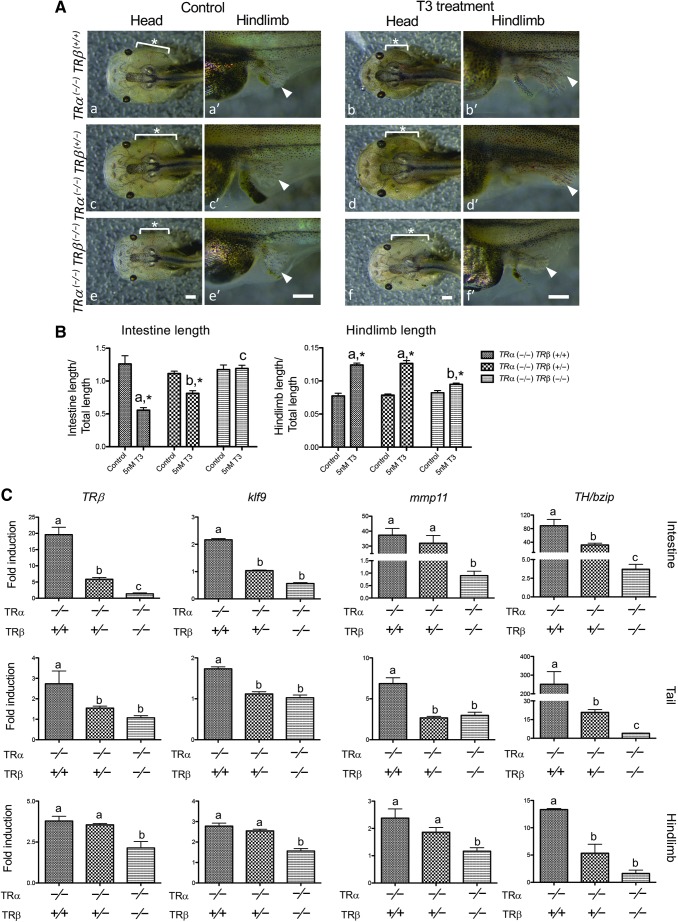
To investigate whether TRβ can activate target gene expression in the absence of endogenous TRα and if gene activation by T3 requires any TR, we treated stage 54 premetamorphic tadpoles containing all three genotypes together with or without 5 nM T3 for five days, a long-term treatment known to induce external morphological changes in WT tadpoles. As shown in Figure 3A, TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/+) tadpoles had most dramatic responses to T3 treatment, with obvious gill resorption, reshaping of the head to a pointy structure, and hind limb development (Fig. 3A). However, the double knockout (TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−)) tadpoles had little noticeable changes, while the TRβ heterozygous (TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−)) animals were in between (Fig. 3A). Quantitative measurement of the lengths of the intestine and hind limbs, normalized against the total body length, showed that the T3-induced changes were essentially abolished in the TRDKO tadpoles (Fig. 3B).
FIG. 3.
Knocking out TRβ in the homozygous TRα mutant background abolishes tadpole response to exogenous T3. (A) Representative photos of tadpoles treated with 5 nM T3 for five days. Age-matched stage 54 tadpoles were randomly collected and kept in a 4-L plastic container. They were genotyped after treatment with (b, d, f) or without (a, c, e) 5 nM T3 for five days and photographed dorsally (a–f) or laterally (a′–f′). Note that after T3 treatment, TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/+) tadpoles (b) were morphologically distinct from TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) tadpoles (f). The former have pointy heads and more developed hind limbs, while the latter are similar to those without T3 treatment (e). The TRβ heterozygous tadpoles (d) show a morphologically intermediate phenotype. Lowercase letter in the panels indicates the same tadpoles. Asterisks (*) indicate the position of the gills. Arrowheads: hind limb. Scale bars: 1 mm. (B) TRDKO tadpoles show little or no response to T3. The lengths of the intestine and hind limb of the tadpoles treated with or without T3 as in (A) were measured and normalized against the total body length. Note that after T3 treatment, the intestine is significantly shortened, while the hind limbs are larger except in the TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) tadpoles, which show essentially no response to T3 (although a very small increase in hind limb length was observed). No significant difference was observed in both parameters for the three genotypes in the absence of T3. Different lowercase letters denote statistically significant differences (p < 0.01), and asterisks (*) indicate a significant difference when compared with the control group without T3 treatment (p < 0.01). (C) T3 treatment fails to induce target gene expression in TRDKO tadpoles. Age-matched tadpoles at stage 54 were treated with 10 nM T3 for 18 hours. The expression of several known T3 target genes, TRβ, klf9, mmp11, and TH/bzip, was analyzed by qRT-PCR in the intestine, tail, and hind limb, respectively, and the expression levels were normalized against that of ef1α. The results are shown as fold-induction in response to T3. Note that in the double knockout tadpoles, the fold induction was about 1 for all genes in all organs, that is, there was no T3 response. Different lowercase letters denote statistically significant differences (p < 0.05). TRDKO, TR double knockout.
Molecularly, we found that T3 was able to induce the expression of target genes, such as TRβ, klf9, mmp11, and TH/bzip, in the intestine, tail, and hind limb of TRβ WT (TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/+)) and heterozygous (TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−)) animals even in the absence of TRα (Fig. 3C). In contrast, the fold induction by T3 was close to 1 for most of the genes in different organs in TRDKO (TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−)) tadpoles (Fig. 3C). It is interesting to note that the fold induction by T3 was above 1 for some genes in some organs in the TRDKO tadpoles, for example, TH/bzip in the intestine and TRβ in the hind limb (Fig. 3C). This small residual effect is likely due to nongenomic action of T3, although it had no detectable effect on tadpole development (Fig. 3B). In addition, earlier transgenic studies with dominant negative and dominant positive TRs have shown that T3 signaling via TRs is both necessary and sufficient for Xenopus metamorphosis, suggesting that nongenomic action of T3 is not required for Xenopus development (14,16,17). Thus, our results suggest that the endogenous TRα and TRβ are responsible for mediating gene activation and metamorphic effects of T3 in X. tropicalis.
Complete TR knockout is lethal at climax of metamorphosis
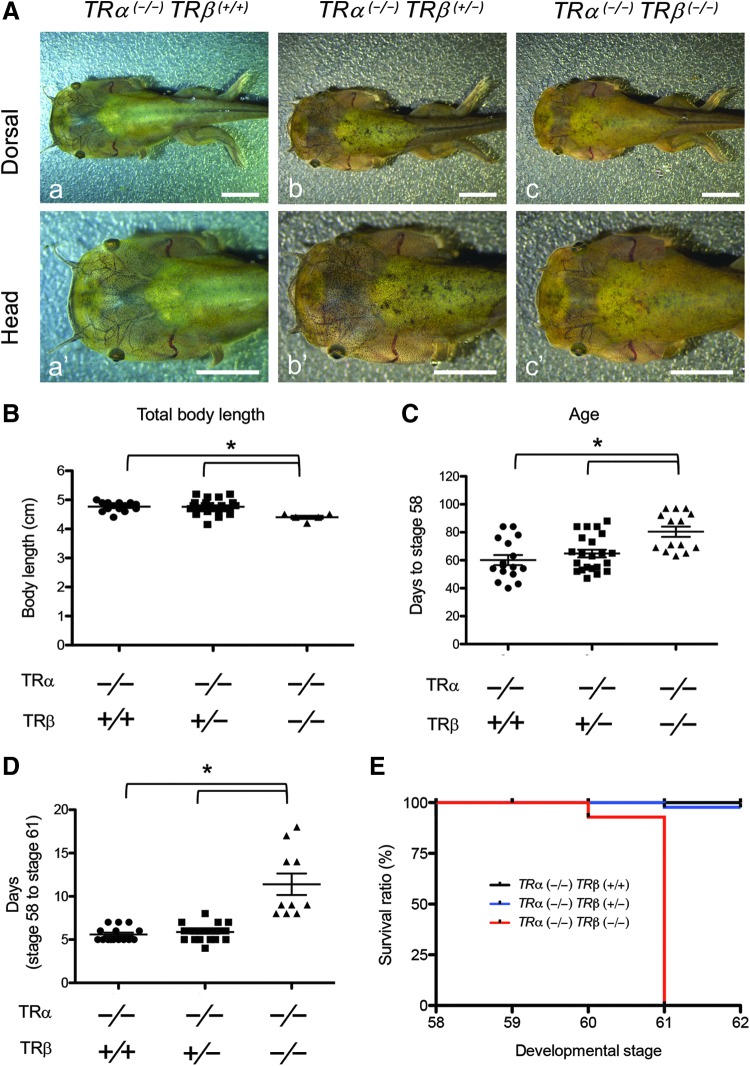
Having shown that TRβ knockout in the TRα knockout background did not affect premetamorphic tadpole development, we next investigated whether TR double knockout tadpoles could undergo metamorphosis. We reared F2 siblings from mating of TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−) heterozygous frogs together and found that all animals were able to develop beyond stage 54, suggesting that all could initiate metamorphosis. We recorded the body length and age of each animal when it reached stage 58, the stage of forelimb emergence and onset of metamorphic climax (Fig. 4A) (45), and genotyped the animal. We found that in the TRα knockout background, TRβ knockout slightly reduced the body length of the tadpoles at stage 58 (Fig. 4B) and also slowed the tadpole development to stage 58 (Fig. 4C). There were no significant differences in either parameter between the TRβ WT and heterozygous knockout tadpoles.
FIG. 4. .
Total knockout of TRs reduces the rate of natural metamorphic progression and causes tadpoles lethality at the climax of metamorphosis. (A) Representative photos of tadpoles for three TRβ genotypes at the stage of forelimb emergence (stage 58). Adult TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−) animals were mated, and the resulting tadpoles were euthanized when their forelimbs broke through the membrane-enclosure, photographed, and genotyped to identify the three genotypes [(a) TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/+), (b) TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−), and (c) TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−)]. Lowercase letters indicate the same tadpole with two different views: dorsal view (upper) and a higher magnification from the dorsal side for the head (lower: a′–c′). Scale bars: 5 mm. (B) TRDKO tadpoles have shorter body length at the onset of metamorphic climax (stage 58). The body length of individual tadpoles at stage 58 as identified in (A) was measured and plotted with the mean, marked as a line, and SE. The asterisks (*) indicate a significant difference for the three genotypes (p < 0.01). (C) TRDKO tadpoles have delayed onset of metamorphic climax (stage 58). The age of individual tadpoles at stage 58 as identified in (A) was recorded and plotted with the mean, marked as a line, and SE. The asterisks (*) indicate a significant difference for the three genotypes (p < 0.01). (D) TRDKO tadpoles have a reduced rate of metamorphic progression at the climax stages. The time in days for the tadpoles as identified in (A) to go from stage 58 to stage 61 [as judged by the length of NO and BO. At stage 61, NO = BO (Fig. 6A)] was recorded and plotted with the mean, marked as a line, and SE. The asterisks (*) indicate a significant difference for the three genotypes (p < 0.01). (E) TRDKO leads to lethality at metamorphic climax. The tadpoles as identified in (A) were allowed to develop from stage 58 or stage 62, or when they died and were then genotyped. The survival rate for each of the three genotypes, TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/+) (n = 17), TRα (−/−)TRβ (+/−) (n = 21), and TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) (n = 15), was determined and plotted. Note that no double knockout tadpoles developed to stage 62. BO, bulbus olfactorius; NO, nervus olfactorius.
When individual tadpoles at stage 58 were allowed to develop further to stage 61, the climax stage when the lengths of the nervus olfactorius (NO) and bulbus olfactorius (BO) are the same (45), we found that the TRDKO tadpoles took twice as long (10 days vs. 5 days) to develop from stage 58 to stage 61 compared with the TRβ WT and heterozygous knockout tadpoles (Fig. 4D). Furthermore, we observed that TRDKO tadpoles remained at stage 61 for 1–2 weeks (data not shown) and died before reaching stage 62, while all tadpoles of the other two genotypes developed to stage 62 as expected (Fig. 4E). Thus, in the absence of TRα, TRβ knockout not only delays metamorphic progression but also leads to tadpole lethality at the climax of metamorphosis, indicating that TR is essential for anuran metamorphosis.
Complete TR knockout alters and/or accelerates some metamorphic events while preventing others
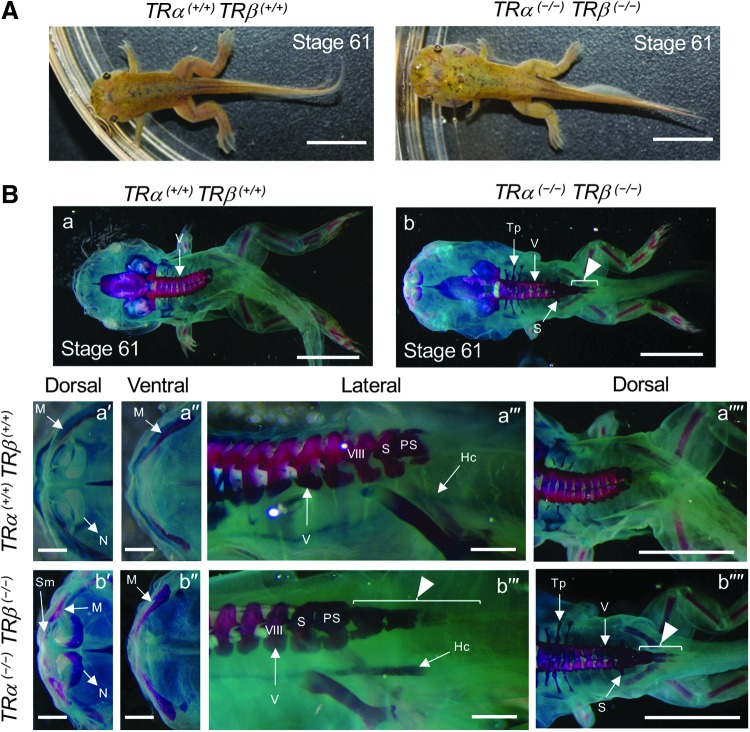
The above results indicate that TR is not required for initiation of metamorphosis and progression up to stage 61. However, all TRDKO tadpoles died at stage 61. This lethal phenotype may be due to the failure of one or more tissues to undergo proper metamorphic progression or mis-coordination of temporal progressions in different organs/tissues. To determine the developmental defects due to total TR knockout, we next focused on stage 61 tadpoles of two genotypes: total TR knockout (TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−)) and TR WT (TRα (+/+)TRβ (+/+)). Total TR knockout tadpoles had normal forelimbs and hind limbs but an abnormal head structure (Fig. 5A, also see below). Interestingly, Alizarin red (for ossification) and Alcian blue (for cartilages) whole mount staining revealed more advanced bone development in the TR-knockout tadpoles, such as advanced maxilla and nasal ossification in cranial bone (red color: Fig. 5B-a′, a′′, b′, and b′′). Additionally, in WT animals, there are nine vertebrae and their ossification occurs gradually during metamorphosis, with the vertebra IX (sacral vertebra) fused to the illium by stage 65/66 (Supplementary Fig. S1). The hypochord begins to ossify around stage 61 and the process ends after metamorphosis (Supplementary Fig. S2). The TRDKO tadpoles at stage 61 had several additional ossified vertebrae at the body–tail junction and appeared to have completed hypochord ossification and developed a sacral vertebra structure fused with vertebra VIII (Fig. 5B-a′′′, a′′′′, b′′′, and b′′′′) (52). In WT animals at the end of metamorphosis, the hypochord comes into contact with the anterior end of the coccyx to form the urostyle (Supplementary Fig. S1) (53). Unexpectedly, longer vertebra bones (arrowheads in Fig. 5B-b, b′′′, and b′′′′) were found in the TR-knockout tadpoles at stage 61 (Supplementary Fig. S1) (53). Developmentally, we observed that these abnormalities were present as early as stage 58 in the TRDKO animals (Supplementary Figs. S1 and S2). Thus, removal of TR leads to precocious ossification and abnormal vertebra development.
FIG. 5.
Total knockout of TRs alters skeletal development and ossification at the climax of metamorphosis. (A) Representative photos of a WT (TRα (+/+)TRβ (+/+)) (left panel) and TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) (right panel) tadpoles at stage 61. The tadpoles were allowed to develop to stage 61 regardless of age and were then photographed. Scale bars: 5 mm. (B) TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) tadpoles have increased ossification and additional ossified vertebrae at the end of the body at stage 61. Alizarin red (for ossification) and Alcian blue (for cartilages) whole mount staining of tadpoles at stage 61. (a) TRα (+/+)TRβ (+/+) and (b) TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−). (a′, b′) are dorsal views and (a′′, b′′) are ventral views of high magnification of the mouth region. (a′′′, b′′′) High magnification of the body. Note the increased ossification in the head region and extra ossified vertebrae (arrow heads in b′′′, b′′′′) at the body–tail junction. Scale bars: 1 cm (a, a′, b, b′), 1 mm (a′′, a′′′, b′′, b′′′), 5 mm (a′′′′, b′′′′). Hc, hypochord; M, maxilla; N, nasal; PS, postsacral vertebra; S, sacral vertebra; Sm, septomaxilla; Tp, transverse process; V, vertebra; VIII, eighth vertebra.
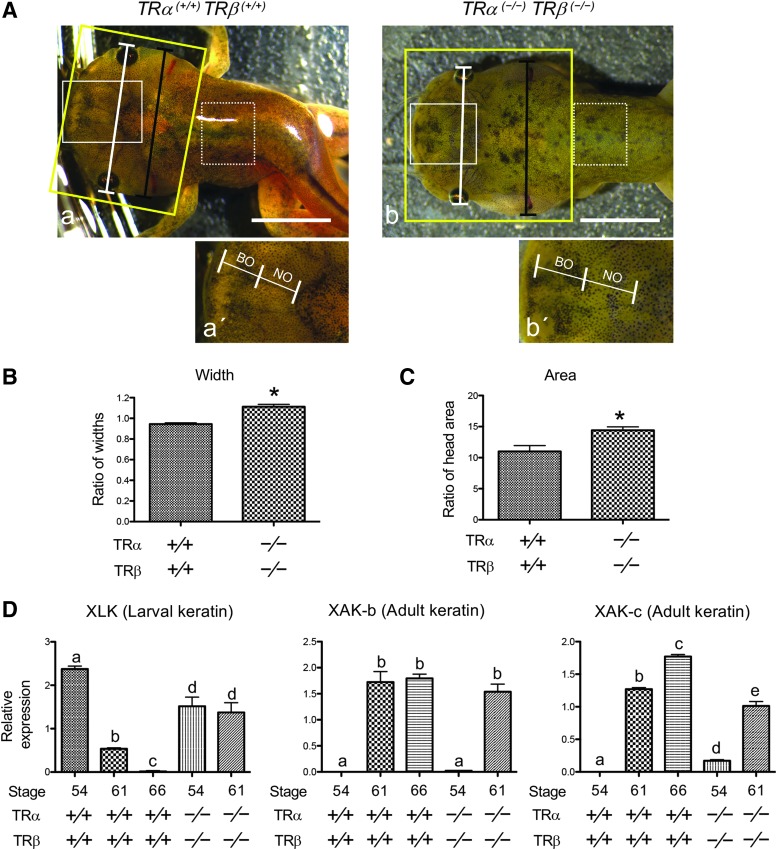
As indicated above (Fig. 5A), at stage 61, when the lengths of the NO and the BO are equal (Fig. 5A) (45), TRDKO animals have an abnormal head structure and their gills appeared to be largely intact until the animals eventually died (Fig. 5; data not shown). To analyze this further, we determined the ratio of the width at the gill position (Fig. 6A, black line) to the width at the eye position (Fig. 6A, white lines), as well as the head area (Fig. 6A, the region within the yellow rectangle) by using the Image J Software. The results show that TRDKO tadpoles at stage 61 have a larger ratio of the two widths (Fig. 6B) and a larger head area (Fig. 6C) compared with those in WT stage 61 tadpoles. These were consistent with the obviously larger gill areas in the knockout tadpoles (Fig. 6A), indicating that TR is required for gill resorption.
FIG. 6.
TR is required for larval tissue resorption. (A) Representative photos of the heads of TRα (+/+)TRβ (+/+) and TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) tadpoles at stage 61, the climax of metamorphosis. The developmental stage was determined based on the length of the NO and BO with NO = BO at stage 61 (note that the boundaries of NO and BO could be easily determined based on morphological differences by microscopy). (a) TRα (+/+)TRβ (+/+) and (b) TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−). The black line in the top panel spans the width from the outer edge of the gills, and the white line spans the width from the outer edge of the eyes. The yellow box encloses the head region. Higher magnification of areas boxed with white lines in (a, b) is shown in (a′, b′). An area of the dorsal skin used for gene expression studies in D is shown in the dashed box. Scale bars: 5 mm. (B) TRDKO inhibits gill repression at the metamorphic climax. The ratio of the width at the gill position [black line in the top panel of (A)] to the width at the eye position [white line in the top panel of (A)] was calculated as a measure of the relative gill size. Data are expressed as mean plus SE (TRα (+/+)TRβ (+/+) [n = 9] and TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) [n = 6]). The asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference when compared with that for TRα (+/+)TRβ (+/+) (p < 0.01). (C) TRDKO inhibits the reduction in head size associated with jaw remodeling and gill resorption. The head area, enclosed by yellow box in the top panel of (A), was measured by the ImageJ software and is presented as mean plus SE (TRα (+/+)TRβ (+/+) [n = 9] and TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−) [n = 6]). The asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference when compared with that for TRα (+/+)TRβ (+/+) (p < 0.01). (D) TRDKO blocks the downregulation of larval keratin genes but allows the expression of adult keratin genes at the metamorphic climax. The dorsal skin, as shown in the area enclosed by dashed boxes in A, of the WT (TRα (+/+)TRβ (+/+)) at stages 54, 61, and 66, and TRDKO (TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−)) tadpoles stages 54 and 61 were dissected for total RNA extraction and qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of a larval skin marker, larval keratin (xlk), and two adult skin markers, adult keratins b and c (xak-b and xak-c). The qRT-PCR for all genes and on all samples was performed simultaneously. The expression levels were normalized against that of rpl8. The groups included 5, 3, 3 WT (TRα (+/+)TRβ (+/+)) tadpoles at stage 54, 61, and 66; and 5 TRβ homozygous (TRα (−/−)TRβ (−/−)) tadpoles each at stages 54 and 61, respectively. Note that, as expected, the larval keratin gene was repressed by stage 61, while adult keratin genes were upregulated by stage 61 in WT animals. Interestingly, in the double knockout animals at stage 61, no repression of the larval keratin gene was observed, although the adult keratin genes were activated as in the WT animals. Different lowercase letters denote statistically significant differences (p < 0.05).
Next, we analyzed the transformation of the skin, which involves the transition from the expression of larval keratin (xlk) in tadpoles to the expression of adult keratins (xak-b and xak-c) during/after metamorphosis (54,55). We determined the expression of keratin genes in WT tadpoles at stages 54, 61, and 66 and in TRDKO tadpoles at stages 54 and 61. As expected, in WT tadpoles, xlk expression was reduced by stage 61 and completely repressed by the end of metamorphosis (Fig. 6D). In contrast, both adult keratin genes were not expressed in premetamorphic WT tadpoles but activated by stage 61 and remained highly expressed in postmetamorphic frogs (Fig. 6D). Interestingly, in the TRDKO tadpoles at stage 61, no repression of the larval keratin gene was observed, while both adult keratin genes were activated (Fig. 6D), suggesting that TRDKO prevents the degeneration of larval keratinocytes but allows the development of adult keratinocytes.
Discussion
Since the discovery over a century ago that frog metamorphosis could be accelerated by feeding tadpoles with thyroid (56,57), anurans have been used as a model to study vertebrate development, particularly the role of hormones. This has contributed to the discovery of T3 and the study of the role of T3 during vertebrate development. Earlier studies, particularly in X. laevis, have led to a dual function model for TRs during frog development, but the roles of endogenous TRs have been investigated only more recently with the development of gene editing technologies and the use of the diploid anuran X. tropicalis. Individual TRα and TRβ knockout studies have indeed demonstrated critical and distinct involvement of the two TRs in metamorphosis (33–42). However, neither TRα nor TRβ appears to be essential for anuran metamorphosis as individual knockout animals complete metamorphosis with no obvious morphological defects, although the overall developmental rate is affected. Our double knockout studies shown here demonstrate unambiguously that TRs are essential for anuran metamorphosis and reveal broad roles of both unliganded and liganded TR in coordinating the development of different organs/tissues to ensure normal tadpole development and survival of the animal through metamorphosis.
TRα and TRβ are the only receptors mediating gene regulation by T3 in X. tropicalis
Studies on T3-inducible promoters in vitro and in cell cultures have shown that TRs can bind to T3 response elements constitutively to activate the promoters in the presence and repress them in the absence of T3, respectively. Consistent with this, TRα knockout in X. tropicalis leads to upregulation of known T3-inducible genes in premetamorphic tadpoles when little T3 is present and most or all the receptors are likely unliganded (37–39). Our results here show that disrupting TRβ in the TRα knockout background further increases the expression of these T3-inducible genes in premetamorphic tadpoles, suggesting that both receptors participate in the repression of target genes when T3 is not available. Similarly, T3 treatment of premetamorphic tadpoles shows that TRα knockout reduces the induction of these genes by T3 (37–39), and additional knockout of TRβ completely abolishes the induction of these genes by T3 (Fig. 3). Thus, there are no other nuclear receptors for T3 in X. tropicalis, and all developmental effects of T3 are mediated by TRα and TRβ.
Diverse metamorphic changes in many organs do not require TR
TRDKO tadpoles can develop up to stage 61, indicating that TRs are not required for many of the metamorphic transformations. There are three types of tissue transformations during metamorphosis: adult organ development, larval organ resorption, and organ remodeling. Both adult organ development and organ remodeling take place for at least some organs in TRDKO tadpoles. The most dramatic is limb development, which is essentially complete by stage 61 and does not require TR. Among the organs undergoing remodeling, the development of the bones, including vertebrae and jaw, takes place and appears even more advanced in TRDKO tadpoles at stage 61 compared with that in the WT animals. The remodeling of the head, leading to a more pointed structure, also occurs without TR. In addition, adult keratin genes are activated in the TRDKO tadpoles at stage 61, just like in WT animals (Fig. 6), suggesting that the development of the adult skin can occur in the absence of TR. While the exact cause of these TR-independent metamorphic changes remains to be determined, it is very likely that the removal of TR leads to derepression of T3-inducible genes, which in turn facilitates metamorphosis. Thus, unliganded TRs are critical to maintain normal tadpole development and prevent premature metamorphosis in different organs/tissues.
TRDKO inhibits metamorphic changes in most organs and causes abnormal development and lethality at climax of metamorphosis
While many metamorphic processes can occur without TRs, many others require TR-mediating T3 signaling. Most notably, there are two tadpole-specific organs, the tail and gills, which are completely resorbed by the end of metamorphosis. The gills are mostly resorbed in the WT tadpoles by stage 61. However, little gill resorption occurs in stage 61 TRDKO tadpoles (Figs. 5 and 6). In addition, tail resorption takes place mostly from stage 62 on. All knockout tadpoles are developmentally stalled at stage 61 and die before tail resorption, suggesting that larval organ resorption requires T3 action through TRs. In addition, in the body skin, while the adult skin appears to form as reflected by the expression of adult keratin genes in the TRDKO tadpoles at stage 61, the larval keratin gene is not suppressed at stage 61 in the TRDKO animals, in contrast to that observed in the WT tadpoles (Fig. 6), suggesting that larval keratinocyte death is inhibited or delayed in the absence of TR. Thus, TR appears to be required for larval cell death in many, if not all, organs during metamorphosis.
The TR double knock phenotypes that we observed bear similarities to those of TR-knockout mice. Mice with the knockout of either TRα or TRβ knockout can develop into adulthood, although with various abnormalities (58–60). Similarly, double knockout mice for both TRα and TRβ knocked out are born alive (43,44,61). Interestingly, two studies found that the double knockout mice developed into adults (44,61), while another found that the double knockout mice stopped growing and eventually died around five weeks of age (43). This latter phenotype is similar to what we have observed here for the double knockout tadpoles. While the exact cause for the different findings in mouse is unclear, it has been suggested that different knockout strategies may have different effects on the truncated TRα isoforms derived from a promoter located in the intron 7 of the TRα gene, consequently leading to different outcomes (61). It remains to be determined if such TRα isoforms exist in X. tropicalis and contribute to tadpole lethality that we have observed for the TRDKO tadpoles.
Our study also reveals that removal of TRs leads to accelerated endochondral ossification in the skull and the notochord, and additional vertebra formation by stage 58, if not earlier (Fig. 5B and Supplementary Fig. S2) during early metamorphosis when plasma T3 levels are still relatively low (45). This suggests that unliganded TRs not only temporally control the timing of endochondral ossification but are also important for spatial development of the vertebrae. Similarly, T3 and TRs are critical for normal endochondral ossification and bone development in mice (44,61–64). TRα single or TRDKO mice have impaired bone development and lower ossification (43,44,61), and a dominant negative TRα-knockin mutation in heterozygous mice causes dwarfism and delayed endochondral and intramembranous ossification (65). However, the dominant negative knockin mutation in the TRβ locus leads to advanced endochondral and intramembranous ossification in homozygous mice, accompanied by very high levels of circulating T3 (65,66). These findings suggest that unliganded TRs also inhibit ossification during mouse development. It is tempting to speculate that TRs have conserved roles in regulated temporal coordination of tissue remodeling and adult organ maturation during postembryonic development.
In summary, the findings shown here reveal broad roles of TRs that are essential for tadpole development and survival through anuran metamorphosis. TRDKO affects diverse processes during Xenopus development. Embryogenesis is the only developmental period with no obvious alterations due to TR knockout. It has been shown earlier that TRα knockout leads to premature initiation of metamorphosis (i.e., reaching stage 54 at younger age) (33–39), and TRDKO tadpoles behave similarly as TRα-knockout animals in this respect (Fig. 2), indicating that unliganded TR, mainly TRα, controls metamorphic timing. During the first half of metamorphosis (from onset at stage 54 to the early climax at stage 58), TR controls the rate of metamorphic progression, with TRα knockout dramatically slowing down this process (33,34,37–39) and additional TRβ knockout further reducing the developmental rate (Fig. 4C). During the second half of metamorphosis (stage 58–stage 66), TRα knockout has little effect (33,34,37–39) while TRβ knockout delays this process (35,36). TRDKO tadpoles also delay their development from stage 58 onward and stall at stage 61 before eventual death (Fig. 4D, E). The ability of double knockout animals to reach stage 61 strongly suggests that the removal of the repression caused by unliganded TRs in tadpoles is sufficient for many metamorphic events to take place. The metamorphic lethal phenotype at stage 61 caused by TRDKO, however, is likely due to the incomplete and/or uncoordinated transformations of many organs due to the lack of T3 signaling by liganded TRs. Thus, anuran metamorphosis involves sophisticated spatiotemporal coordination of the transformation of different organs by employing both unliganded and T3-bound TRs via the control of T3 availability. The unliganded TRs prevent precocious metamorphosis in different organs by repressing T3-inducible genes. With the rising concentration of plasma T3, T3-inducible genes are first derepressed and then further activated to even higher levels. The ability of TRDKO animals to develop to stage 61 suggests that most of the metamorphic changes up to this stage simply require the derepression. The metamorphic changes that fail to occur in the TRDKO animals likely require additional activation beyond derepression. These distinct requirements of T3-TR signaling suggest that a precise regulation of the levels of TR and T3 in different organs is important for metamorphosis. Given all organs are exposed to the same plasma T3 levels, it is very likely that other factors influencing T3 signaling, such as transporters and deiodinases, are involved in this process. Clearly, future studies on this are needed. In addition, in light of the findings reported here, it may also be interesting to determine whether TRDKO in mouse also leads to incomplete maturation of adult organs and/or defects in temporal coordination of adult organ development and to identify the molecular mechanisms underlying these alterations/defects during metamorphosis or postembryonic development in mammals.
Supplementary Material
Author Disclosure Statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Funding Information
This work was supported in part by the Intramural Research Programs of National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and National Cancer Institutes, National Institutes of Health (NIH). Y.S. was supported in part by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (NIH) Fellowship.
Supplementary Material
References
- 1. Tata JR. 1993. Gene expression during metamorphosis: an ideal model for post-embryonic development. Bioessays 15:239–248 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Shi Y-B. 1999. Amphibian Metamorphosis: From Morphology to Molecular Biology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York [Google Scholar]
- 3. Buchholz DR, Paul BD, Fu L, Shi YB. 2006. Molecular and developmental analyses of thyroid hormone receptor function in Xenopus laevis, the African clawed frog. Gen Comp Endocrinol 145:1–19 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Wang X, Matsuda H, Shi Y-B. 2008. Developmental regulation and function of thyroid hormone receptors and 9-cis retinoic acid receptors during Xenopus tropicalis metamorphosis. Endocrinology 149:5610–5618 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Yaoita Y, Shi YB, Brown DD. 1990. Xenopus laevis alpha and beta thyroid hormone receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87:7090–7094 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Wong J, Shi YB, Wolffe AP. 1995. A role for nucleosome assembly in both silencing and activation of the Xenopus TR beta A gene by the thyroid hormone receptor. Genes Dev 9:2696–2711 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Lazar MA. 1993. Thyroid hormone receptors: multiple forms, multiple possibilities. Endocr Rev 14:184–193 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Yen PM. 2001. Physiological and molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. Physiol Rev 81:1097–1142 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Evans RM. 1988. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science 240:889–895 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Tsai MJ, O'Malley BW. 1994. Molecular mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily members. Ann Rev Biochem 63:451–486 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Laudet V, Gronemeyer H. 2002. The Nuclear Receptor FactsBook. Academic Press, San Diego [Google Scholar]
- 12. Shi Y-B, Wong J, Puzianowska-Kuznicka M, Stolow M. 1996. Tadpole competence and tissue-specific temporal regulation of amphibian metamorphosis: roles of thyroid hormone and its receptors. BioEssays 18:391–399 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Sachs LM, Damjanovski S, Jones PL, Li Q, Amano T, Ueda S, Shi YB, Ishizuya-Oka A. 2000. Dual functions of thyroid hormone receptors during Xenopus development. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 126:199–211 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Schreiber AM, Das B, Huang H, Marsh-Armstrong N, Brown DD. 2001. Diverse developmental programs of Xenopus laevis metamorphosis are inhibited by a dominant negative thyroid hormone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:10739–10744 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Brown DD, Cai L. 2007. Amphibian metamorphosis. Dev Biol 306:20–33 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Buchholz DR, Hsia VS-C, Fu L, Shi Y-B. 2003. A dominant negative thyroid hormone receptor blocks amphibian metamorphosis by retaining corepressors at target genes. Mol Cell Biol 23:6750–6758 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Buchholz DR, Tomita A, Fu L, Paul BD, Shi Y-B. 2004. Transgenic analysis reveals that thyroid hormone receptor is sufficient to mediate the thyroid hormone signal in frog metamorphosis. Mol Cell Biol 24:9026–9037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Shi Y-B. 2009. Dual functions of thyroid hormone receptors in vertebrate development: the roles of histone-modifying cofactor complexes. Thyroid 19:987–999 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Nakajima K, Yaoita Y. 2003. Dual mechanisms governing muscle cell death in tadpole tail during amphibian metamorphosis. Dev Dyn 227:246–255 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Denver RJ, Hu F, Scanlan TS, Furlow JD. 2009. Thyroid hormone receptor subtype specificity for hormone-dependent neurogenesis in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol 326:155–168 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Bagamasbad P, Howdeshell KL, Sachs LM, Demeneix BA, Denver RJ. 2008. A role for basic transcription element-binding protein 1 (BTEB1) in the autoinduction of thyroid hormone receptor beta. J Biol Chem 283:2275–2285 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Schreiber AM, Mukhi S, Brown DD. 2009. Cell-cell interactions during remodeling of the intestine at metamorphosis in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol 331:89–98 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Shi Y-B. 1994. Molecular biology of amphibian metamorphosis: a new approach to an old problem. Trends Endocrinol Metab 5:14–20 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Shi YB, Matsuura K, Fujimoto K, Wen L, Fu L. 2012. Thyroid hormone receptor actions on transcription in amphibia: the roles of histone modification and chromatin disruption. Cell Biosci 2:42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Grimaldi A, Buisine N, Miller T, Shi YB, Sachs LM. 2013. Mechanisms of thyroid hormone receptor action during development: lessons from amphibian studies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830:3882–3892 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Puzianowska-Kuznicka M, Damjanovski S, Shi Y-B. 1997. Both thyroid hormone and 9-cis retinoic acid receptors are required to efficiently mediate the effects of thyroid hormone on embryonic development and specific gene regulation in Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol 17:4738–4749 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Sachs LM, Shi Y-B. 2000. Targeted chromatin binding and histone acetylation in vivo by thyroid hormone receptor during amphibian development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:13138–13143 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Bilesimo P, Jolivet P, Alfama G, Buisine N, Le Mevel S, Havis E, Demeneix BA, Sachs LM. 2011. Specific histone lysine 4 methylation patterns define TR-binding capacity and differentiate direct T3 responses. Mol Endocrinol 25:225–237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Amaya E, Offield MF, Grainger RM. 1998. Frog genetics: Xenopus tropicalis jumps into the future. Trends Genet 14:253–255 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Matsuura K, Fujimoto K, Fu L, Shi Y-B. 2012. Liganded thyroid hormone receptor induces nucleosome removal and histone modifications to activate transcription during larval intestinal cell death and adult stem cell development. Endocrinology 153:961–972 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Matsuura K, Fujimoto K, Das B, Fu L, Lu CD, Shi YB. 2012. Histone H3K79 methyltransferase Dot1L is directly activated by thyroid hormone receptor during Xenopus metamorphosis. Cell Biosci 2:25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Sterling J, Fu L, Matsuura K, Shi Y-B. 2012. Cytological and morphological analyses reveal distinct features of intestinal development during Xenopus tropicalis metamorphosis. PLoS One 7:e47407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Choi J, Ishizuya-Oka A, Buchholz DR. 2017. Growth, development, and intestinal remodeling occurs in the absence of thyroid hormone receptor alpha in tadpoles of Xenopus tropicalis. Endocrinology 158:1623–1633 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Choi J, Suzuki KI, Sakuma T, Shewade L, Yamamoto T, Buchholz DR. 2015. Unliganded thyroid hormone receptor alpha regulates developmental timing via gene repression as revealed by gene disruption in Xenopus tropicalis. Endocrinology 156:735–744 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Sakane Y, Iida M, Hasebe T, Fujii S, Buchholz DR, Ishizuya-Oka A, Yamamoto T, Suzuki KT 2018. Functional analysis of thyroid hormone receptor beta in Xenopus tropicalis founders using CRISPR-Cas. Biol Open 7:pii: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Nakajima K, Tazawa I, Yaoita Y. 2018. Thyroid hormone receptor alpha- and beta-knockout Xenopus tropicalis tadpoles reveal subtype-specific roles during development. Endocrinology 159:733–743 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Wen L, Shi YB. 2015. Unliganded thyroid hormone receptor alpha controls developmental timing in Xenopus tropicalis. Endocrinology 156:721–734 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Wen L, Shibata Y, Su D, Fu L, Luu N, Shi Y-B. 2017. Thyroid hormone receptor α controls developmental timing and regulates the rate and coordination of tissue specific metamorphosis in Xenopus tropicalis. Endocrinology 158:1985–1998 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Wen L, Shi YB. 2016. Regulation of growth rate and developmental timing by Xenopus thyroid hormone receptor alpha. Dev Growth Differ 58:106–115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Sachs LM. 2015. Unliganded thyroid hormone receptor function: amphibian metamorphosis got TALENs. Endocrinology 156:409–410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Yen PM. 2015. Unliganded TRs regulate growth and developmental timing during early embryogenesis: evidence for a dual function mechanism of TR action. Cell Biosci 5:8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Nakajima K, Tazawa I, Shi YB. 2019. A unique role of thyroid hormone receptor beta in regulating notochord resorption during Xenopus metamorphosis. Gen Comp Endocrinol 277:66–72 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Gauthier K, Chassande O, Plateroti M, Roux JP, Legrand C, Pain B, Rousset B, Weiss R, Trouillas J, Samarut J. 1999. Different functions for the thyroid hormone receptors TRalpha and TRbeta in the control of thyroid hromone production and post-natal development. EMBO J 18:623–631 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Gothe S, Wang Z, Ng L, Kindblom JM, Barros AC, Ohlsson C, Vennstrom B, Forrest D. 1999. Mice devoid of all known thyroid hormone receptors are viable but exhibit disorders of the pituitary-thyroid axis, growth, and bone maturation. Genes Dev 13:1329–1341 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Nieuwkoop PD, Faber J. 1965. Normal table of Xenopus laevis. North Holland Publishing, Amsterdam [Google Scholar]
- 46. Shibata Y, Bao L, Fu L, Shi B, Shi YB. 2019. Functional studies of transcriptional cofactors via microinjection-mediated gene editing in Xenopus. Methods Mol Biol 1874:507–524 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Inouye M. 1976. Differential staining of cartilage and bone in mouse skeleton by Alcian Blue and Alizarin Red S. Congenit Anom 16:171–173 [Google Scholar]
- 48. Ranjan M, Wong J, Shi YB. 1994. Transcriptional repression of Xenopus TR beta gene is mediated by a thyroid hormone response element located near the start site. J Biol Chem 269:24699–24705 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Furlow JD, Kanamori A. 2002. The transcription factor basic transcription element-binding protein 1 is a direct thyroid hormone response gene in the frog Xenopus laevis. Endocrinol 143:3295–3305 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Fu L, Tomita A, Wang H, Buchholz DR, Shi Y-B. 2006. Transcriptional regulation of the Xenopus laevis stromelysin-3 gene by thyroid hormone is mediated by a DNA element in the first intron. J Biol Chem 281:16870–16878 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Furlow JD, Brown DD. 1999. In vitro and in vivo analysis of the regulation of a transcription factor gene by thyroid hormone during Xenopus laevis metamorphosis. Mol Endocrinol 13:2076–2089 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Trueb L, Hanken J. 1992. Skeletal development in Xenopus laevis (Anura: Pipidae). J Morphol 214:1–41 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Pugener LA, Maglia AM. 2009. Skeletal morphogenesis of the vertebral column of the miniature hylid frog Acris crepitans, with comments on anomalies. J Morphol 270:52–69 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Yoshizato K. 2007. Molecular mechanism and evolutional significance of epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in the body- and tail-dependent metamorphic transformation of anuran larval skin. Int Rev Cytol 260:213–260 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Watanabe Y, Kobayashi H, Suzuki K, Kotani K, Yoshizato K. 2001. New epidermal keratin genes from Xenopus laevis: hormonal and regional regulation of their expression during anuran skin metamorphosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1517:339–350 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Gudernatch JF. 1912. Feeding experiments on tadpoles. I. The influence of specific organs given as food on growth and differentiation: a contribution to the knowledge of organs with internal secretion. Arch Entwicklungsmech Org 35:457–483 [Google Scholar]
- 57. Allen BM. 1929. The influence of the thyroid gland and hypophysis upon growth and development of amphibian larvae. Quart Rev Biol 4:325–352 [Google Scholar]
- 58. Forrest D, Erway LC, Ng L, Altschuler R, Curran T. 1996. Thyroid hormone receptor beta is essential for development of auditory function. Nat Genet 13:354–357 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Mai W, Janier MF, Allioli N, Quignodon L, Chuzel T, Flamant F, Samarut J. 2004. Thyroid hormone receptor alpha is a molecular switch of cardiac function between fetal and postnatal life. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:10332–10337 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Wikstrom L, Johansson C, Salto C, Barlow C, Barros AC, Baas F, Forrest D, Thoren P, Vennstrom B. 1998. Abnormal heart rate and body temperature in mice lacking thyroid hormone receptor. EMBO J 17:455–461 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Gauthier K, Plateroti M, Harvey CB, Williams GR, Weiss RE, Refetoff S, Willott JF, Sundin V, Roux JP, Malaval L, Hara M, Samarut J, Chassande O. 2001. Genetic analysis reveals different functions for the products of the thyroid hormone receptor alpha locus. Mol Cell Biol 21:4748–4760 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Kim HY, Mohan S. 2013. Role and mechanisms of actions of thyroid hormone on the skeletal development. Bone Res 1:146–161 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Bassett JH, Nordstrom K, Boyde A, Howell PG, Kelly S, Vennstrom B, Williams G R. 2007. Thyroid status during skeletal development determines adult bone structure and mineralization. Mol Endocrinol 21:1893–1904 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Bassett JH, Williams GR. 2016. Role of thyroid hormones in skeletal development and bone maintenance. Endocr Rev 37:135–187 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. O'Shea PJ, Bassett JH, Sriskantharajah S, Ying H, Cheng SY, Williams GR. 2005. Contrasting skeletal phenotypes in mice with an identical mutation targeted to thyroid hormone receptor alpha1 or beta. Mol Endocrinol 19:3045–3059 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. O'Shea PJ, Harvey CB, Suzuki H, Kaneshige M, Kaneshige K, Cheng SY, Williams GR. 2003. A thyrotoxic skeletal phenotype of advanced bone formation in mice with resistance to thyroid hormone. Mol Endocrinol 17:1410–1424 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.