Abstract
Cyanobactins are a large family of cyanobacterial ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs) often associated with biological activities, such as cytotoxicity, antiviral, and antimalarial activities. They are traditionally described as cyclic molecules containing heterocyclized amino acids. However, this definition has been recently challenged by the discovery of short, linear cyanobactins containing three to five amino acids as well as cyanobactins containing no heterocyclized residues. Here, we report the discovery of scytodecamide (1) from the freshwater cyanobacterium Scytonema sp. UIC 10036. Structural elucidation based on mass spectrometry, 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy, and Marfey’s method revealed 1 to be a linear decapeptide with an N-terminal N-methylation and a C-terminal amidation. The genome of Scytonema sp. UIC 10036 was sequenced and bioinformatic analysis revealed a cyanobactin-like biosynthetic gene cluster consistent with the structure of 1. The discovery of 1 as a novel linear peptide containing an N-terminal N-methylation and a C-terminal amidation expands the chemical and genetic diversity of the cyanobactin family of compounds.
Keywords: cyanobacteria, natural products, biosynthesis, RiPP, cyanobactin
Graphical Abstract
Scytodecamide is a novel N- and C-protected peptide. Isolated from the freshwater cyanobacterium Scytonema sp. UIC 10036, it is a linear decapeptide featuring N-terminal N-methylation, and a C-terminal amidation. Genome sequencing and bioinformatics analysis revealed a cyanobactin biosynthetic gene cluster consistent with the structure of scytodecamide.
Introduction
Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic prokaryotes that produce chemically diverse and biotechnologically relevant natural products, such as polyketides, non-ribosomal peptides, and a wide range of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs).[1–3] Cyanobactins encompass a large family of RiPPs, often associated with biological activities, such as cytotoxicity, multidrug reversing, antiviral, and antimalarial activities.[4–6] They were traditionally described as cyclic peptides of ribosomal origin that contain heterocyclized amino acid (aa) residues.[6,7] However, this definition has been recently challenged. Genome mining of cyanobacterial strains has resulted in novel cyanobactins that did not fit the classic definition. Anacyclamides and prenylagaramides are cyclic peptides containing no heterocyclized residues.[8,9] In 2013, Leikoski and colleagues discovered the first linear cyanobactins, aeruginosamides B and C and viridisamide.[10] These short peptides (three to five aa residues) contain N-terminal N-prenylations and methylated C-termini connected to thiazole rings.[10] Enzymatic modifications of peptides, such as cyclizations, methylations, prenylations, epimerizations, and amidations, have been shown to increase the functional diversity of peptidic natural products.[11,12]
The canonical biosynthetic pathway for cyanobactins, as recently reviewed,[13,14] is ribosomal synthesis of the precursor peptide (E gene), followed by heterocyclization (D gene, if the product contains heterocycles), proteolytic cleavage of the leader peptide (A gene), and macrocyclization/cleavage of the C-terminal follower peptide (G gene). Heterocyclizing enzymes (D protein) recognize the precursor peptide at recognition sequence I (RSI), whereas proteases (A protein) cleave the leader peptide at RSII, and macrocyclases/proteases (G protein) recognize RSIII. Tailoring enzymes such as oxidases, methyltransferases and prenyltransferases may also be involved in cyanobactin pathways usually leading to late-stage modifications.[15–18]
In a previous study, strain Scytonema sp. UIC 10036 was found to produce scytophycin C and tolytoxin.[19] Scytophycins and tolytoxin were first characterized by the Patterson group. [20,21] Tolytoxin was later shown to be a potent actin inhibitor.[22] Potential uses of these compounds as chemical probes or as anticancer agents inspired further studies into their biosynthesis,[23] total chemical synthesis,[24] and production under different culture conditions.[25,26] The chemical potential of strain Scytonema sp. UIC 10036 encouraged us to perform media studies to challenge its growth and production of secondary metabolites.[19] In short, strain UIC 10036 was cultured under various levels of nitrate and phosphate. Untargeted comparative metabolomics was applied to assess the influence of these media components on its metabolomic profile. Results obtained for strain Scytonema sp. UIC 10036 revealed a) changes in tolytoxin production under the different conditions, b) increased heterocyst glycolipid production under nitrate starvation, and c) increased production of a potentially novel compound of m/z [M - H]- 994 in low nitrate and high phosphate in comparison to the standard Z medium.[19] The latter was investigated in this work.
Herein we present the isolation and complete structural elucidation of scytodecamide (1), a N- and C-protected linear decapeptide. Moreover, we report the genome sequence of the producing strain Scytonema sp. UIC 10036 and the bioinformatics identification of a cyanobactin-like biosynthetic gene cluster consistent with the structure of 1.
Results and Discussion
In order to isolate and elucidate the structure of the potentially novel compound, cell mass from large-scale cultures (18 L) of Scytonema sp. UIC 10036 was harvested, lyophilized, and extracted with MeOH:DCM 1:1 (v/v). Dry extract was subjected to fractionation using Diaion® HP-20SS as solid phase and a step gradient of water and isopropyl alcohol (IPA). The target compound was found to be enriched in the fraction eluting at 40:60 IPA:H2O (F3) by LC-MS analysis. Further purification by semi-preparative HPLC afforded scytodecamide (1).
Scytodecamide (1) was obtained as a white, amorphous powder. HRMS data (m/z 996.6450 [M + H]+) was consistent with the formula C47H85N11O12, requiring 11 degrees of unsaturation. MS/MS fragmentation of 1 showed a sequential loss of ten aa residues (Supplementary Information S3). The peptidic nature of 1 was further confirmed by the inspection of DEPTQ and 1H NMR spectra (Table 1). The DEPTQ spectrum of 1 in methanol-d4 contained ten amide carbonyl signals (δC 172–178) as well as resonances typical of α-carbons in aa (δC 53–70) and aliphatic methyl, methylene and methine groups (δC 12–42). Methylene signals at δC 62.2 and 63.0 ppm suggested the presence of two Ser residues. The 1H NMR spectrum of 1 in methanol-d4 exhibited resonances characteristic of aa α-protons (δH 3.8–4.4), aliphatic methylene and methine groups (δH 1.2–2.5), and 13 aliphatic methyl signals (δH 0.8–1.5). The methyl doublets at δH 1.41 and 1.48 ppm suggested the presence of two Ala residues. A deshielded methyl singlet at δH 2.34 ppm was also observed. Comparison of 1H NMR spectra of 1 in methanol-d4 and -d3 showed only six exchangeable amide signals (δH 7.5–8.2). Additional 1H NMR spectra acquired in pyridine-d5 with TFA vapor revealed a total of 11 exchangeable signals between δH 8.1–9.3 ppm.
Table 1.
NMR spectroscopic data of scytodecamide (1)a
| Methanol-d3b and -d4 | Pyridine-d5 with TFA vapor | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | δC, mult | δH, mult (J in Hz) | COSY | HMBC | δC, mult | δH, mult (J in Hz) | COSY | HMBC | |
| Val amide | 1 | 176.7, C | 175.4, C | ||||||
| 2 | 60.9, CH | 4.17, m | 2-NH, 3 | 1, 3 | 60.4, CH | 5.05, m | 2-NH, 3 | 1, 3, 4 | |
| 3 | 31.4, CH | 2.23, o (6.8) | 2, 3-Me, 4 | 2, 4 | 31.2, CH | 2.8, m | 2, 3-Me, 4 | 2, 4 | |
| 3-Me | 19.8, CH3 | 0.98, d (6.8) | 3 | 3 | 20.5, CH3 | 1.25, d (6.8) | 3 | 2, 3 | |
| 4 | 18.8, CH3 | 1.01, d (6.8) | 3 | 3 | 19.1, CH3 | 1.38, d (6.8) | 3 | 2, 3, 3-Me | |
| 1-NHa | nd | 8.08, br | 1 | ||||||
| 1-NHb | nd | 8.14, br | 2 | ||||||
| 2-NH | 7.56, d (8.8) | 2 | 1Leu1 | 8.23, d (8.8) | 2 | 2, 3, 1Leu1 | |||
| Leu1 | 1 | 175.7, C | 174.4, C | ||||||
| 2 | 54.8, CH | 4.33, dd (11.0, 3.8) | NH, 3 | 1, 3 | 54.7, CH | 5.05, m | 3 | 1, 2 | |
| 3 | 41.5, CH2 | 1.58, m | 2 | 2, 4 | 41.6, CH2 | 2.12, ddd (13.8, 9.8, 4.0) | 2 | 2, 4 | |
| 1.93, m | 2.39, ddd (13.8, 11.2, 4.3) | ||||||||
| 4 | 25.4, CH | 1.93, m | 4-Me, 5 | 5 | 25.3, CH | 2.34, m | 4-Me, 5 | 3 | |
| 4-Me | 22.7, CH3 | 0.91, d (6.3) | 4 | 5 | 24.1, CH3 | 1.04, d (6.6) | 4 | 3, 5 | |
| 5 | 21.2, CH3 | 0.89, d (6.3) | 4 | 21.7, CH3 | 0.92, d (6.6) | 4 | 3 | ||
| NH | 7.69, d (6.4) | 2 | 1Ser1 | 8.30, d (7.4) | 2 | 2, 3, 1Ser1 | |||
| Ser1 | 1 | 173.2, C | 172.4, C | ||||||
| 2 | 59.7, CH | 4.22, dd (6.6, 3.6) | NH, 3 | 1 | 59.9, CH | 4.95, m | NH, 3 | ||
| 3 | 62.2, CH2 | 3.94, dd (11.9, 3.6) | 2 | 1, 2 | 62.7, CH2 | 4.47, dd (11.6, 3.8) | 2 | 1 | |
| 4.04, dd (11.9,6.6) | 4.61, dd (11.6, 6.4) | ||||||||
| OH | nd | nd | |||||||
| NH | 7.69, d (6.4) | 2 | 1Ala1 | 8.32, d (4.4) | 2 | 2, 3, 1Ala1 | |||
| Ala1 | 1 | 177.56, C | 176.2, C | ||||||
| 2 | 53.5, CH | 4.09, q (7.3) | 2-Me | 1, 2-Me | 52.9, CH | 4.64, m | NH, 2-Me | 2-Me | |
| 2-Me | 16.8, CH3 | 1.41, d (7.3) | 2 | 1, 2 | 17.3, CH3 | 1.71, d (7.3) | 2 | 1, 2 | |
| NH | 8.24, d (4.14) | 2 | 8.66, br | 2 | 1Leu2 | ||||
| Leu2 | 1 | 176.9, C | 176.0, C | ||||||
| 2 | 56.6, CH | 4.06, m | NH, 3 | 1, 3, 4 | 55.9, CH | 4.62, m | NH, 3 | 3, 4 | |
| 3 | 40.5, CH2 | 1.69, m | 2 | 1, 2, 4 | 40.4, CH2 | 2.01, m | 2 | 1, 2, 4 | |
| 1.77, m | 2.08, m | ||||||||
| 4 | 25.7, CH | 1.74 m | 4-Me, 5 | 3 | 25.5, CH | 2.02, m | 4-Me, 5 | 3 | |
| 4-Me | 23.9, CH3 | 0.92, d (6.3) | 4 | 3 | 23.3, CH3 | 1.01, d (6.1) | 4 | 3 | |
| 5 | 22.3, CH3 | 0.88, d (6.3) | 4 | 3 | 22.4, CH3 | 0.91, d (6.1) | 4 | ||
| NH | 7.98, d (4.83) | 2 | 8.39, br | 2 | 2, 3, 1Leu3 | ||||
| Leu3 | 1 | 177.2, C | 176.7, C | ||||||
| 2 | 55.9, CH | 4.19, t (7.9) | NH, 3 | 1, 3, 4 | 55.5, CH | 4.63, m | NH, 3 | 3, 4 | |
| 3 | 40.5, CH2 | 1.75, m | 2 | 1, 2, 4 | 40.3, CH2 | 1.95, m | 2 | 1, 2, 4 | |
| 1.81, m | 1.99, m | ||||||||
| 4 | 26.3, CH | 1.70, m | 4-Me, 5 | 5 | 25.8, CH | 1.88, m | 4-Me, 5 | 4-Me | |
| 4-Me | 23.0, CH3 | 1.02, d (6.7) | 4 | 3 | 23.0, CH3 | 0.95, d (6.5) | 4 | 3 | |
| 5 | 22.9, CH3 | 0.97, d (6.7) | 4 | 3 | 22.5, CH3 | 0.84, d (6.5) | 4 | 3 | |
| NH | 7.62, d (6.4) | 2 | 1Ala2 | 8.15, br | 2 | 1Ala2 | |||
| Ala2 | 1 | 177.8, C | 176.8, C | ||||||
| 2 | 53.3, CH | 4.06, m | NH, 2-Me | 1, 2-Me | 53.2, CH | 4.43, m | NH, 2-Me | 1, 2-Me | |
| 2-Me | 16.5, CH3 | 1.48, d (7.3) | 2 | 1, 2 | 17.2, CH3 | 1.52, d (7.3) | 2 | 1, 2 | |
| NH | nd | 8.78, d (4.4) | 2 | 1Pro | |||||
| Pro | 1 | 176.0, C | 175.2, C | ||||||
| 2 | 64.1, CH | 4.29, t (8.2) | 3 | 1, 3 | 63.4, CH | 4.68, m | 3 | 1, 3 | |
| 3 | 30.6, CH2 | 2.01, m | 2, 4 | 1, 2, 5 | 30.3, CH2 | 2.13, m | 2, 4 | 2, 5 | |
| 2.43, m | 2.35, m | ||||||||
| 4 | 26.4, CH2 | 2.06, m | 3, 5 | 5, 3 | 25.9, CH2 | 1.77, m | 3, 5 | 3, 5 | |
| 2.18, m | 1.98, m | ||||||||
| 5 | 49.3, CH2 | 4, dt (9.2, 6.8) | 4 | 4, 2Ser2 | 49.0, CH2 | 4.11, m | 4 | 3, 4 | |
| 4.07, m | 4.14, m | ||||||||
| Ser2 | 1 | 172.7, C | 172.7, C | ||||||
| 2 | 53.5, CH | 4.94, dd (6.4, 4.9) | 3 | 1, 3 | 53.7, CH | 5.51, m | NH, 3 | 1, 3 | |
| 3 | 63.0, CH2 | 3.83, dd (10.2, 6.4) | 2 | 1, 2 | 63.1, CH2 | 4.25, m | 2 | 1, 2 | |
| 4.14, dd (10.2, 4.7) | 4.54, dd (10.4, 5.4) | ||||||||
| OH | nd | nd | |||||||
| NH | nd | 9.3, br | 2 | ||||||
| N-Me-Ile | 1 | 175.2, C | nd | ||||||
| 2 | 70.1, CH | 2.94, d (5.2) | 3 | 1, 3, N-Me, 4 | 69.1, CH | 3.63, br | 3 | ||
| 3 | 39.5, CH | 1.72, m | 2, 3-Me, 4 | 38.5, CH | 2.11, m | 2, 3-Me, 4 | |||
| 3-Me | 15.9, CH3 | 0.94, d (6.9) | 3 | 3, 4, 2 | 16.1, CH3 | 1.13, d (6.8) | 3 | 2, 3, 4 | |
| 4 | 26.7, CH2 | 1.22, m | 3, 5 | 3, 3-Me, 5 | 26.5, CH2 | 1.44, m | 3, 5 | 3, 3-Me, 5 | |
| 1.55, m | 1.83, m | ||||||||
| 5 | 12.1, CH3 | 0.91, t (7.6) | 4 | 12.2, CH3 | 0.88, d (7.4) | 4 | 3, 4 | ||
| N-Me | 35.6, CH3 | 2.34, s | 2 | 35.0, CH3 | 2.67, s | 2 | |||
| NH | nd | nd | |||||||
Frequency of 900 MHz for 1H and 226 MHz for 13C.
Methanol-d3 was used for the assignment of NH protons as well as their COSY correlations to α-protons and HMBC correlations to carbonyl carbons.
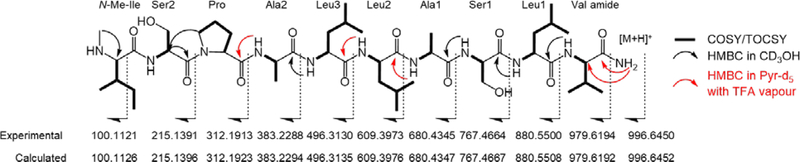
Interpretation of COSY and TOCSY spectra allowed for the assignment of ten aa residues: two Ser, two Ala, three Leu, one Ile, one Pro, and one Val. The methyl singlet at δH 2.34 (methanol-d4) showed a single HMBC correlation with the α-carbon of the Ile residue (δC 69.1), revealing this to be an N-Me-Ile. HBMC correlations between the broad exchangeable signals at δH 8.08 and 8.14 ppm (pyridine-d5 with TFA vapor) with the Val carbonyl (δC 175.4) and α-carbon (δC 60.4), respectively, suggested this residue to be a terminal Val amide.
The aa sequence in 1 was established with the combined analysis of the HMBC spectra in methanol-d3 and pyridine-d5 with TFA vapor and HRMS/MS fragmentation (Figure 1, Table 1). In methanol-d3, HMBC correlations from Val amide NH (δH 7.56) to Leu1 C-1 (δC 175.7), from Leu1 NH (δH 7.69) to Ser1 C-1 (δC 173.2), from Ser1 NH (δH 7.69) to Ala1 C-1 (δC 177.6), from Leu3 NH (δH 7.62) to Ala2 C-1 (δC 177.8), and from Pro H-4 (δH 4.00 and 4.07) to Ser2 C-2 (δC 53.5) were observed. In pyridine-d5 with TFA vapor, additional correlations from Ala1 NH (δH 8.66) to Leu2 C-1 (δC 176.0), from Leu2 NH (δH 8.39) to Leu3 C-1(δC 176.7), and from Ala2 NH (δH 8.78) to Pro C-1 (δC 175.2) supported the sequence of Ser2-Pro-Ala2-Leu3-Leu2-Ala1-Ser1-Leu1-Val-CONH2. Despite extensive efforts, no NMR correlations were observed between Ser2 and the terminal N-Me-Ile. The placement of N-Me-Ile as the N-terminal aa was confirmed by HRMS/MS fragmentation of 1 (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
HRMS/MS fragmentation and key NMR correlations of 1
The absolute configuration of the aa in 1 was determined by acid hydrolysis followed by the advanced Marfey’s method. All residues were assigned the l configuration based on the comparison with aa standards (Supplementary Information S20). The final structure of 1 was established as l-N-Me-Ile-l-Ser-l-Pro-l-Ala-l-Leu-l-Leu-l-Ala-l-Ser-l-Leu-l-Val-CONH2.
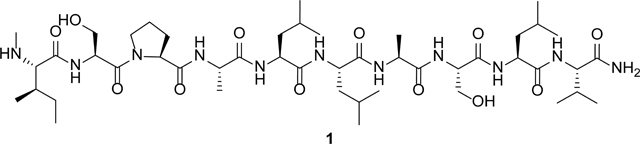
Scytodecamide (1) features two terminal modifications. N-methylation and C-terminal amidation have been associated with improved membrane permeability and resistance to peptidases, respectively.[12,27,28] The unusual structural features of 1 increased our interest in investigating its biosynthetic pathway. Either a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) or a RiPP pathway can be envisioned for biosynthesis of 1.
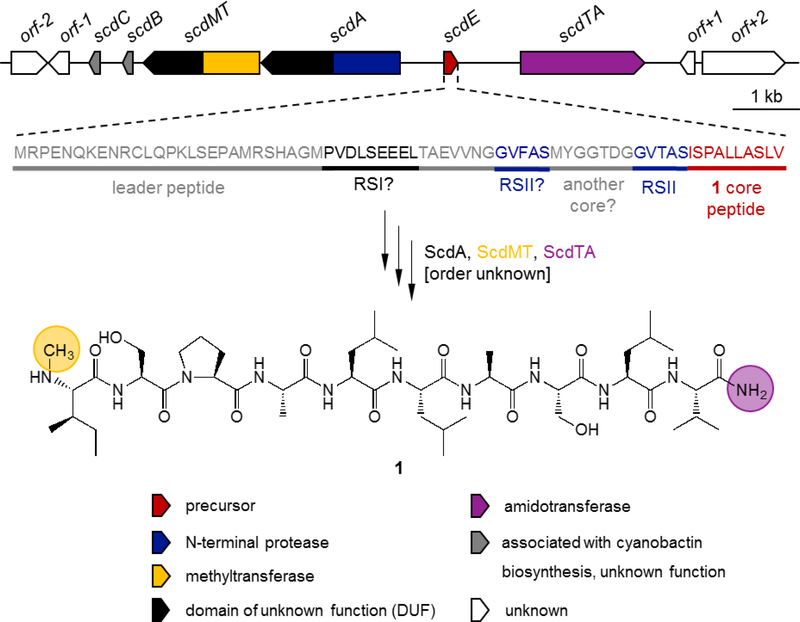
The genome of Scytonema sp. UIC 10036 was sequenced with short-read Illumina and long-read PacBio technologies. None of the NRPS gene clusters detected were in agreement with the structure of 1. Instead, bioinformatic analysis revealed a putative cyanobactin gene cluster. Open reading frames (ORFs) within the gene cluster were annotated and subsequently analyzed for sequence similarity to known proteins (Supplementary Information S21). The putative scd biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC) consisted of six genes spanning approx. 8.3 kb (Figure 2, Table 2). It was positively identified by the presence of the precursor gene scdE encoding the exact peptide sequence found in scytodecamide (1) (Figure 2). ScdE as shown in Figure 2 is composed of 70 aa including the leader peptide, recognition site II (RSII), and the ten aa core sequence. Although there are alternative methionines in the leader peptide sequence that could function as start codons, the one shown in Figure 2 and leading to the 60-aa leader sequence has the best ribosome biding site consensus (GGAG), followed by the first internal methionine leading to a 40-aa leader sequence (GAG). A comparison of known cyanobactin precursor peptides and ScdE is shown in Supplementary Information S22. A second core peptide can be tentatively predicted, however we did not detect this peptide in cultures of strain UIC 10036. A potential RSI sequence can also be predicted, although the sequence is not very well conserved (Figure 2 and Supplementary Information S22).
Figure 2.
The putative scd biosynthetic gene cluster from Scytonema sp. UIC 10036 and the hypothetical biosynthetic pathway of 1, with an expansion showing the amino acid sequence of the precursor peptide ScdE, the substrate of the biosynthetic enzymes. The N-terminal protease ScdA would cleave off the leader peptide of ScdE at recognition sequence II (RSII), and ScdMT and ScdTA would catalyze methylation and transamidation, respectively. The substrates and timing of reactions catalyzed by Scd enzymes remain to be elucidated. For example, it is conceivable that transamidation by ScdTA could happen either before or after cleavage of the leader sequence by ScdA. Genes of the scd BGC are named according to Gu et al.[13]
Table 2.
Predicted function of ORFs in the scd BGC.
| Protein | Length (aa) | Predicted function |
|---|---|---|
| ORF-2 | 188 | hypothetical protein |
| ORF-1 | 119 | hypothetical protein |
| ScdC | 56 | unknown (PatC homolog) |
| ScdB | 65 | unknown (PatB homolog) |
| ScdMT | 587 | didomain protein methyltransferase/DUF |
| ScdA | 697 | didomain protein N-terminal protease/DUF (PatA homolog) |
| ScdE | 70 | precursor protein |
| ScdTA | 627 | transamidase |
| ORF+1 | 82 | hypothetical protein |
| ORF+2 | 415 | tRNA nucleotidyltransferase |
Overall, the structure of 1 conforms to the current definition of the cyanobactins. However, as a decapeptide, it is larger than the linear cyanobactins reported to date. Moreover, N-terminal N-methylation and C-terminal amidation have been previously described in RiPPs, but not for a cyanobactin.[29]
The scd BGC encodes a homolog of the N-terminal protease PatA from the patellamide biosynthetic pathway (ScdA, 83% similarity at the aa level; Figure 2, Table 2).[30,31] PatA catalyzes the cleavage of the N-terminal protease site RSII of the precursor peptide, removing the leader peptide sequence.[30] PatA contains two domains, an N-terminal serine protease domain and a C-terminal domain of unknown function (DUF). Besides an A protease, cyanobactin gene clusters may encode a macrocyclase/C-terminal protease which is related to PatG/AgeG.[4,10,30] PatG catalyzes macrocyclization[30] while AgeG from the aeruginosamide pathway cleaves off a C-terminal peptide sequence leading to linear products.[16] G enzymes also contain a DUF domain[32] and recognize the precursor peptide C-terminal protease signature RSIII.[33] No homologs for G enzymes were found in the putative scd gene cluster, which is consistent with the lack of an RSIII in the precursor protein sequence (Figure 2 and Supplementary Information S22). Lack of RSIII is an unusual feature of precursor peptide ScdE since reported cyanobactin precursor peptides all contain RSIII (Supplementary Information S22).
Furthermore, genes with sequence similarity to the short conserved proteins PatB and PatC, were identified (ScdB and ScdC; Figure 2, Table 2).[5,6] Despite being conserved among nearly all cyanobactin gene clusters, their function remains unknown, and studies have shown that these genes are non-essential for in vivo production of patellamides.[34] Consistent with the structure of 1, no homologs of PatD (heterocyclase) or PatF (prenyltransferase) were found.[30,31]
The scd BGC contains one gene, scdMT, with a N-terminal S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase domain and a C-terminal region that shows sequence similarity to the DUF domain of proteases and macrocyclases [32] (Supplementary Information S23-S25). Genes containing methyltransferase domains were previously found in six out of 30 cyanobactin BGCs identified by genome mining, of which four encode unknown compounds.[10] The two known compounds are aeruginosamide and viridisamide, featuring N-terminal N-prenylations and C-terminal O-methylations. The only cyanobactin featuring N-methylation is the cyclic cyanobactin microcyclamide in which the nitrogen of a histidine residue is methylated. However, a methyltransferase could not be identified in the microcyclamide BGC.[35] In five out of six cases, methyltransferases identified by genome mining[10] are fused with other functions such as prenyltransferase, and the DUF domain of proteases and macrocyclases. The only characterized cyanobactin methyltransferase is AgeMTPT, which contains methyltransferase and prenyltransferase domains.[16] AgeMTPT was shown to N-prenylate a peptide precursor containing RSIII, after which AgeG cleaves off the RSIII and AgeMTPT O-methylates the C-terminal carboxyl group towards biosynthesis of aeruginosamides. The scdMT gene potentially expands the genetic diversity for N-protection in cyanobactins by putatively encoding a N-terminal N-methyltransferase. The substrate and timing of methylation remains to be elucidated.
Finally, the structure of scytodecamide features an unusual C-terminal amide. A protein BLAST analysis of the scd gene cluster revealed the gene scdTA to encode a putative transamidase (= amidotransferase, Supplementary Information S21). Li et al. recently showed that TtmN, an amidotransferase from Streptomyces afghaniensis NRRL 5621, catalyzes the amidation of the carboxylated intermediate prethiotetraamide C to yield thiotetroamide C.[36] ScdTA shows 29% identity and 57% similarity, respectively, to TtmN at the aa level. We, therefore, hypothesize that ScdTA is responsible for the C-terminal amidation of scytodecamide.
Scytodecamide (1) was tested for cytotoxicity against MDA-MB-435 human melanoma, MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer, and OVCAR3 human ovarian cancer cells, but no activity was detected up to 25 μM.
Conclusion
Media studies analyzed by untargeted comparative metabolomics led to the discovery of scytodecamide (1), a new linear decapeptide featuring an N-terminal N-methylation and a C-terminal amidation. The genome of Scytonema sp. UIC 10036 was sequenced using Illumina and PacBio technologies. Bioinformatic analysis revealed an 8.3-kb cyanobactin-like biosynthetic gene cluster consistent with the structure of 1. Novel modes of N- and C-terminal protection – N-methylation and C-terminal amidation, respectively – expand the chemical and genetic diversity of cyanobactins.
Experimental Section
General Experimental Procedures:
Optical rotation was recorded using a PerkinElmer 241 polarimeter. UV spectrum was acquired on a Varian Cary 5000 spectrophotometer. IR spectrum was obtained using a Thermo-Nicolet 6700 with Smart iTR™ accessory. 1D and 2D NMR spectra were acquired on Bruker AVII 900 MHz spectrometer equipped with a 5 mm TCI cryoprobe (Supplementary Information S4–19). NMR chemical shifts were referenced to residual solvent peaks (CD3OD/CD3OH δH 3.31 and δC 49.0; Pyr-d5 δH 8.74 and δC 150.35). LC-UV-HRMS experiments were performed on a Shimadzu LCMS-IT-TOF equipped with a UPLC C18 column (2.1 × 50 mm x 1.7 μm). Mobile phases consisted of H2O (A) and CH3CN (B), both acidified with 0.1% formic acid, flowing at a total rate of 0.5 mL/min. The gradient program was set as follows: 5–100% B for 7 minutes,1-min wash, and 2-min re-equilibration. PDA acquisition ranged from 190 to 450 nm at 4.17 Hz sampling rate. HRMS data were recorded in positive and negative modes from 150 to 3000 m/z. Additional HRMS/MS spectra were acquired at the University of North Carolina at Greensboro using a Thermo QExactive Plus MS (Thermo-Fisher). HRMS/MS spectra were obtained by automatic data-dependent fragmentation with a collision energy of 35 eV.
Biological Material and Culture Conditions:
Scytonema sp. UIC 10036 was isolated from a sample collected in December of 2006 at Homestead, Florida (N 25°24.2′, W 80°33.4′). Unialgal strain isolation was accomplished by micropipette isolation techniques.[37] Scytonema sp. UIC 10036 was cultured for 6 weeks in 18 L of liquid Z medium[19] (one 13 L flask containing 10 L of medium and four 2.8 L Fernbach flasks, with 2 L of medium each). Cultures were grown at 22 oC under fluorescent lights (2.6 klx) in an 18/6 h light/dark cycle. Sterile air was continuously passed into cultures. Cells were harvested by centrifugation and ~500 mg of wet cell mass was set aside for genomic DNA isolation. The remaining cells were lyophilized to allow for the isolation of 1.
Morphological Identification:
Cultured UIC 10036 was analyzed under a Zeiss Axiostar Plus light microscope with a Moticam 5 microscope camera (Supplementary Information S1). Observed morphological features were: cylindrical and isopolar trichomes, monoseriate, homogeneous width along the filament, thin sheaths, common false branching, cells shorter than wide, rounded apical cells, solitary heterocysts of quadrangular shape, no akinetes, hormogonia arising terminally by trichome disintegration. Preliminary morphological identification of UIC 10036 was based on the taxonomic systems by Komarek et al.[38,39]
Phylogenetic Analysis and Genome Sequencing:
For genomic DNA isolation, ~250 mg of wet cell mass was resuspended in 2.5 mL of lysis buffer (10mM Tris, 0.1 M EDTA, and 0.5% w/v SDS) and lysozyme (Sigma-Aldrich, final concentration of 1 mg/mL). The mixture was incubated in a water bath at 37 oC for 30 min. Subsequently, proteinase K (Thermo Fisher Scientific) was added at a final concentration of 100 μg/mL. After incubating the mixture in a water bath for 1 h at 50 oC, the sample was centrifuged and the supernatant was removed. Subsequently, the Nucleospin® soil kit (Macherey-Nagel) was used to extract genomic DNA from the pretreated cells according to the manufacturers’ instructions. The 16S rRNA gene was amplified by PCR on an Applied Biosystems 2720 Thermal Cycler using the cyanobacteria specific primers 109F (5’-CGGACGGGTGAGTAACGCGTGA-3’) and 1509R (5’-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3’). The 50 μL PCR reaction consisted of 100 ng of genomic DNA, 0.4 μM of each primer, 0.2 mM of each dNTP, and 0.05 U/μL Taq DNA polymerase (New England Biolabs) in the buffer supplied with the enzyme. The following thermal cycling conditions were used: 2 min at 95 oC, 35 cycles of 95 oC for 30 s, 49 oC for 30 s, 72 oC for 120 s, and a final hold for 5 min at 72 oC. PCR products were submitted for Sanger sequencing using the primers 109F, 359F (5’-GGGGAATTTTCCGCAATGGG-3’), and 1509R. The partial 16S rRNA sequence of Scytonema sp. UIC 10036 has been deposited at GenBank under accession no. MH780925.
Phylogenetic analysis of Scytonema sp. UIC 10036 was performed using Mega 7.0.[40] Muscle was used to create a multiple sequence alignment containing strains from the Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology[41] as well as other strains available on NCBI. The evolutionary history was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining tree building method and 1000 bootstrap replicates were performed to determine the consistency of the tree. The bootstrap values are shown next to the branches of the tree and any branches with bootstrap values less than 75% were removed from the tree. Evolutionary distances were computed using the Kimura 2-parameter method with a gamma distribution of 0.55 (Supplementary Information S2).
For genomic DNA isolation for genome sequencing, ~250 mg of cell mass was washed with nuclease-free water and resuspended in 500 μL cell lysis solution (Promega) and lysozyme solution (Sigma-Aldrich, final concentration of 1 mg/mL). After incubating the mixture in a water bath at 37 oC for 30 min, the sample was centrifuged and the supernatant was removed. The pellet was washed with nuclease-free water, centrifuged, and the supernatant was removed. Subsequently, the Nucleospin® soil kit (Macherey-Nagel) was used to extract genomic DNA from the pretreated cells according to the manufacturers’ instructions. Genomic DNA was prepared for sequencing using a Nextera XT DNA library preparation kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Sequencing was performed on an Illumina Miseq system. Genomic DNA was also subjected to one RSII single-molecule real-time (SMRT) DNA sequencing on the Pacific Biosciences (PacBio) system with a 6-hour movie capture using P6-PC4 chemistry. Samples were prepped using standard PacBio templated protocol for 10kb libraries and size selected using Blue Pippin (Sage Science) instrument starting at 4kb. De novo hybrid assembly of Illumina and PacBio reads was performed using SPAdes v3.9.[42,43]
Bioinformatic Analysis:
The genome of UIC 10036 was annotated using RAST.[44–46] Biosynthetic gene clusters were roughly predicted with antiSMASH version 4.[47] The identified putative scytodecamide (scd) biosynthetic gene cluster was further annotated using FgenesB (http:/www.softberry.com) and BLAST[48] followed by manual curation. The putative scd biosynthetic gene cluster has been deposited at Genbank under accession no. MN265868, and at MiBIG under accession code BGC0001880. The genome of Scytonema sp. UIC 10036 has been deposited at GenBank under accession code WJFC00000000.
Extraction and Isolation:
After lyophilization, dry cell mass of UIC 10036 was extracted with 1 L CH2Cl2/MeOH 1:1 three times (24 h each time) at 4 oC with occasional agitation. Cell material was filtered and the extraction solution was concentrated in a rotatory evaporator to yield 1.3 g of dry extract. Extract was fractionated using a chromatographic column containing Diaion® HP-20SS and applying a step gradient of IPA/H2O (0:100, 20:80, 40:60, 70:30, 90:10, and 100:0). LC-MS analysis detected 1 in the fraction eluting at 40:60 IPA/H2O (F3). Compound isolation was accomplished by semipreparative HPLC using an Agilent C18 column (250 × 10.0 mm), with a flow rate of 4 mL/min, and a gradient of H2O (A) and ACN (B), both acidified with 0.1% formic acid. Gradient program was set as follows: 20% B for 5 min, 20–100% B for 35 min, 100% B for 10 min, 100–20% B for 5 min, 20% B for 4 min. Compound 1 (~1.1 mg) eluted at rt 16.1 min.
Scytodecamide (1): white amorphous powder; [α]25D none detected (c 0.09, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 213 (3.65), 262 (3.58) nm; IR (neat) ʋmax 3303 (br), 2960, 2931, 2873, 1663, 1543, 1436, 1387, 1369, 1311, 1205, 1185, 1138, 1058, 840, 801, 723 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR (CD3OD/CD3OH and Pyr-d5 with TFA vapour) see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 996.6450 [M + H]+, calcd for C47H86N11O12, 996.6457.
Acid Hydrolysis and Marfey’s Analysis:
Approximately 0.2 mg of 1 was subjected to hydrolysis with 6 N HCl (1 mL) at 110 oC for about 18h. Residual HCl was removed by resuspending the sample with water (0.5 mL) and applying repeated evaporation. The hydrolysate of 1 was split into two equal portions (~0.1 mg each) prior to derivatization. Hydrolysate as well as amino acid standards were derivatized with l- and dl-Advanced Marfey’s reagent (l-FDLA and dl-FDLA). Approximately 0.1 mg of the hydrolysate or standards were mixed with 110 μL of acetone, 50 μL of H2O, 20 μL of 1 N NaHCO3, and 20 μL of l-FDLA or dl-FDLA solution (10 mg/mL in acetone). The mixtures were stirred at 40 oC for 1h. After 1h, the mixtures were removed from heat and quenched with 20 μL of 1 N HCl. Reaction mixtures were evaporated and resuspended in CH3CN for LC-MS analysis. LC-MS analyses were performed on a Shimadzu LCMS-IT-TOF with a Phenomenex Kinetex C18 column (50 × 2.1 mm, 1.7 μm) and a gradient of H2O (A) and CH3CN (B) both with 0.1% formic acid. Flow rate was kept at 0.5 mL/min and gradient program went from 25 to 65 %B over 9 min. Extracted ion chromatograms and retention times were compared for each Marfey’s derivative for the assignment of absolute configuration (Supplementary Information S20).
Antiproliferative Assay:
Cytotoxicity assays were performed following established protocols.[49] Tested cell lines included MDA-MB-435 (human melanoma), MDA-MB-231 (human breast cancer), and OVCAR3 (human ovarian cancer).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank K. Mathes for assisting with DNA extraction, Dr. D. May for phylogenetic analysis, R. Ahadi and S. Romanowski for cyanobacterial strain culture, and the UIC Research Resources Center Genome Research Division for genome sequencing and assembly. We thank Dr. N. Oberlies for access to the Thermo QExactive Plus mass spectrometer and Dr. J. Burdette for antiproliferative assays. This research was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) under grant PO1CA125066 (to J.O), by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the NIH under grant KL2TR002002 (to A.S.E.), and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES)/Science without Borders under award number BEX 13055–13-5 (to C.M.C). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this article is given via a link at the end of the document
References
- [1].Tidgewell K, Clark BR, Gerwick WH, in Compr. Nat. Prod. II (Eds.: Liu H.-W. (Ben), Mander L), Elsevier, Oxford, 2010, pp. 141–188. [Google Scholar]
- [2].Dittmann E, Gugger M, Sivonen K, Fewer DP, Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 642–652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Singh RK, Tiwari SP, Rai AK, Mohapatra TM, J. Antibiot 2011, 64, 401–412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Martins J, Vasconcelos V, Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6910–6946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Donia MS, Schmidt EW, in Compr. Nat. Prod. II, Elsevier, 2010, pp. 539–558. [Google Scholar]
- [6].Sivonen K, Leikoski N, Fewer DP, Jokela J, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2010, 86, 1213–1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Donia MS, Ravel J, Schmidt EW, Nat. Chem. Biol 2008, 4, 341–343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Leikoski N, Fewer DP, Jokela J, Wahlsten M, Rouhiainen L, Sivonen K, Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2010, 76, 701–709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Donia MS, Schmidt EW, Chem. Biol 2011, 18, 508–519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Leikoski N, Liu L, Jokela J, Wahlsten M, Gugger M, Calteau A, Permi P, Kerfeld CA, Sivonen K, Fewer DP, Chem. Biol 2013, 20, 1033–1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Ortega MA, Van Der Donk WA, Cell Chem. Biol 2016, 23, 31–44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Wang G, Curr. Biotechnol 2011, 1, 72–79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Gu W, Dong S-H, Sarkar S, Nair SK, Schmidt EW, in Methods Enzymol. (Ed.: Moore BS), Elsevier, Cambridge, 2018, pp. 113–163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Czekster CM, Ge Y, Naismith JH, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol 2016, 35, 80–88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Morita M, Hao Y, Jokela JK, Sardar D, Lin Z, Sivonen K, Nair SK, Schmidt EW, J. Am. Chem. Soc 2018, 140, 6044–6048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Sardar D, Hao Y, Lin Z, Morita M, Nair SK, Schmidt EW, J. Am. Chem. Soc 2017, 139, 2884–2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Dalponte L, Parajuli A, Younger E, Mattila A, Jokela J, Wahlsten M, Leikoski N, Sivonen K, Jarmusch SA, Houssen WE, et al. , Biochemistry 2018, 57, 6860–6867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Gao S, Ge Y, Bent AF, Schwarz-Linek U, Naismith JH, Biochemistry 2018, 57, 5996–6002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [19].Crnkovic CM, May DS, Orjala J, J. Appl. Phycol 2018, 30, 375–384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [20].Ishibashi M, Moore RE, Patterson GM, Xu C, Clardy J, J. Org. Chem 1986, 51, 5300–5306. [Google Scholar]
- [21].Carmeli S, Moore RE, Patterson GML, J. Nat. Prod 1990, 53, 1533–1542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [22].Patterson GML, Smith CD, Kimura LH, Britton BA, Carmeli S, Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 1993, 24, 39–48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Carmeli S, Moore RE, Patterson GML, Yoshida WY, Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 5571–5574. [Google Scholar]
- [24].Paterson I, Watson C, Yeung K-S, Wallace PA, Ward RA, J. Org. Chem 1997, 62, 452–453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [25].Patterson GML, Bolis CM, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 1993, 40, 375–381. [Google Scholar]
- [26].Patterson GML, Bolis CM, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 1995, 43, 692–700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Chatterjee J, Rechenmacher F, Kessler H, Angew. Chemie - Int. Ed 2013, 52, 254–269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [28].Brinckerhoff LH, Kalashnikov VV, Thompson LW, Yamshchikov GV, Pierce RA, Galavotti HS, Engelhard VH, Slingluff CL, Int. J. Cancer 1999, 83, 326–334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [29].Arnison PG, Bibb MJ, Bierbaum G, Bowers AA, Bugni TS, Bulaj G, Camarero JA, Campopiano DJ, Challis GL, Clardy J, et al. , Nat. Prod. Rep 2013, 30, 108–160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [30].Schmidt EW, Nelson JT, Rasko DA, Sudek S, Eisen JA, Haygood MG, Ravel J, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 2005, 102, 7315–7320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [31].Long PF, Dunlap WC, Battershill CN, Jaspars M, ChemBioChem 2005, 6, 1760–1765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [32].Mann G, Koehnke J, Bent AF, Graham R, Houssen W, Jaspars M, Schwarz-Linek U, Naismith JH, Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Commun 2014, 70, 1597–1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Koehnke J, Bent AF, Houssen WE, Mann G, Jaspars M, Naismith JH, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2014, 29, 112–121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [34].Donia MS, Hathaway BJ, Sudek S, Haygood MG, Rosovitz MJ, Ravel J, Schmidt EW, Nat. Chem. Biol 2006, 2, 729–735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [35].Ziemert N, Ishida K, Quillardet P, Bouchier C, Hertweck C, de Marsac NT, Dittmann E, Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2008, 74, 1791–1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [36].Li J, Tang X, Awakawa T, Moore BS, Angew. Chemie Int. Ed 2017, 56, 12234–12239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [37].Stein JR, Handbook of Phycological Methods: Culture Methods and Growth Measurements, Cambridge University Press, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- [38].Komárek J, Kling H, Komárková J, in Freshw. Algae North Am. (Eds.: Wehr JD, Sheath RG), Academic Press, Burlington, 2003, pp. 117–196. [Google Scholar]
- [39].Komárek J, Kaštovský J, Mareš J, Johansen JR, Preslia 2014, 86, 295–335. [Google Scholar]
- [40].Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K, Mol. Biol. Evol 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [41].Castenholz RW, Wilmotte A, Herdman M, Rippka R, Waterbury JB, Iteman I, Hoffmann L, in Bergey’s Manual® Syst. Bacteriol, Springer New York, New York, NY, 2001, pp. 473–599. [Google Scholar]
- [42].Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, et al. , J. Comput. Biol 2012, 19, 455–477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [43].Antipov D, Korobeynikov A, McLean JS, Pevzner PA, Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1009–1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [44].Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M, et al. , BMC Genomics 2008, 9, 75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [45].Overbeek R, Olson R, Pusch GD, Olsen GJ, Davis JJ, Disz T, Edwards RA, Gerdes S, Parrello B, Shukla M, et al. , Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D206–D214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [46].Brettin T, Davis JJ, Disz T, Edwards RA, Gerdes S, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Overbeek R, Parrello B, Pusch GD, et al. , Sci. Rep 2015, 5, 8365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [47].Blin K, Wolf T, Chevrette MG, Lu X, Schwalen CJ, Kautsar SA, Suarez Duran HG, De Los Santos ELC, Kim HU, Nave M, et al. , Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W36–W41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [48].Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ, J. Mol. Biol 1990, 215, 403–410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [49].Ren Y, Chen W-L, Lantvit DD, Sass EJ, Shriwas P, Ninh TN, Chai H-B, Zhang X, Soejarto DD, Chen X, et al. , J. Nat. Prod 2017, 80, 648–658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.