Highlights
-
•
Overall confidence of reviews of exercise for low back pain was very low.
-
•
Higher confidence was found in Cochrane reviews and reviews with registered protocol.
-
•
Confidence in the results is important to generate unbiased clinical recommendations.
Keywords: Physical therapy, Musculoskeletal pain, Methodological quality, Decision-making
Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the overall confidence in the results of systematic reviews of exercise therapy for chronic non-specific low back pain using the AMSTAR 2 tool.
Methods
PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, PEDro and CINAHL was searched up to February 2017. Two independent reviewers selected systematic reviews of randomized controlled trials that investigated exercise therapy in patients with low back pain. AMSTAR 2 assessment was performed by pairs of reviewers, and the overall confidence in the results of the systematic reviews were rated as ‘High’, ‘Moderate’, ‘Low’ and ‘Critically low’. Descriptive analysis was used to summarize the characteristics of included systematic reviews. The percentage of systematic reviews achieving each item from the AMSTAR 2 and the overall confidence in the results were tabulated.
Results
The search identified 38 systematic reviews. Most of the reviews included a median of 10 clinical trials and total sample size of 813 participants per review. Five of 38 (13%) reviews were Cochrane reviews, and 8 (21%) systematic reviews had a protocol published or registered prospectively. The overall confidence in the results of 28 reviews (74%) was rated as ‘Critically low’, 6 (16%) as ‘Low’, 1 (2%) as Moderate, while 3 of 38 reviews (8%) were rated as ‘High’.
Conclusion
The results demonstrate very low confidence in the results of most systematic reviews of exercise in chronic non-specific low back pain. Clinicians are more likely to deliver the most efficacious interventions to patients by critically appraising systematic reviews using AMSTAR 2 before making their decisions.
Introduction
Low back pain (LBP) is a common condition and a significant public health problem across the globe.1, 2, 3, 4 Although a large proportion of patients with an acute episode of non-specific LBP tend to improve spontaneously over time, a large proportion of these people develop chronic LBP,5 which is disabling and is usually treated with exercise therapy and psychosocial interventions.6 There are several therapeutic interventions available for treating non-specific LBP and exercise therapy is probably the most commonly used and effective intervention for these people.6, 7, 8, 9
The effectiveness of exercise for chronic non-specific LBP has been tested in several systematic reviews, including Cochrane10, 11, 12 and non-Cochrane reviews.13, 14 Although these systematic reviews are considered as level 1 evidence and reliable sources for decision making,15 little attention has been given to their methodological quality and how confident readers can be in their results. As clinicians have been evaluating the quality of clinical trials to interpret the available evidence to determine if findings are relevant to clinical practice, the same needs to be performed for systematic reviews.16 The quality of systematic reviews can vary substantially, even when different reviews aim to answer the same research/clinical.17 Therefore, it is necessary to appraise the quality of systematic reviews before the results are implemented into clinical or public health practice. Policymakers have also expressed interest for understanding if systematic reviews are consistent enough from a methodological perspective, to support decision-making.18 Methodological flaws in systematic reviews could potentially affect results of reviews and introduce bias to conclusions. As biased results from systematic reviews can mislead clinical practice,19 it is important to assess and report the overall confidence in the findings of systematic reviews of exercise therapy for chronic non-specific LBP.
The Assessing the Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews (AMSTAR) instrument, published in 2007, is a freely accessible critical appraisal tool for assessing the overall confidence in the results of systematic reviews.19 Validation studies have shown that AMSTAR has good measurement properties.20, 21 The original instrument has been revised and updated, resulting in the AMSTAR 2, published in 2017.22 The main modifications include better consideration of risk of bias within included studies and how this is integrated into interpretation of the review; better alignment with the PICO (population/problem; intervention; comparison; outcome) format to frame a clinical question; and more information on studies excluded from the review. The AMSTAR 2 tool could provide an overview of the overall confidence in the results of systematic reviews of exercise therapy for chronic non-specific LBP, and suggestions for future improvements and recommendations can be made.
AMSTAR 2 scores can also help clinicians and researchers to distinguish high quality reviews from those that were poorly conducted. As an example, we can cite the use of Kinesiotaping in LBP treatment. While one systematic review with some methodological limitations recommends the use of this technique as an additional therapy,23 a more recent review with better methodological quality concluded that the current evidence does not support its use in clinical practice for patients with LBP.24 Another example is about the effectiveness of laser therapy in patients with LBP. There is a Cochrane review that stated that the clinical effect of laser therapy is inconclusive,25 whereas another review reported that the same intervention is effective in reducing pain in LBP treatment.26 In these cases, clinicians should evaluate the confidence in the results of the reviews through the AMSTAR 2 assessment to make an adequate clinical decision making.
This study aims to assess the overall confidence in the results of systematic reviews of exercise therapy for chronic non-specific low back pain using the AMSTAR 2 tool.
Methods
Study design
This study was a methodological survey of systematic reviews.
Search
An electronic search for systematic reviews of exercise therapy for non-specific LBP was conducted in the following databases from their inception up to February 2017: PubMed, Embase (via OvidSP), Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, CINAHL and PEDro. The full search strategy for each database is described in Appendix A. We did not search for grey literature. Two reviewers (MOA; BTS) screened for study eligibility, and disagreements resolved through discussion or by arbitration of a third reviewer (TPY).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria used in our study were:
-
1.
Systematic reviews of randomized controlled trials that investigated exercise therapy in patients with chronic non-specific LBP (>3 months of symptoms).
-
2.
If the reviews included studies conducted on patients with different duration of symptoms (i.e., acute and subacute), we included if most studies included in the review reported on chronic LBP.
-
3.
Systematic reviews that included any type of exercise therapy (e.g., Pilates, Yoga, general exercise, aerobic exercise, specific exercises) compared with other active intervention, minimal interventions (e.g., advice, placebo) or no treatment.
-
4.
For updated reviews (e.g., updated Cochrane review) we included only the most recent version of the review.
-
5.
Systematic reviews written in English, Portuguese, Spanish, or Dutch, as the authors are able to read these languages.
-
6.
Full texts published on peer-review journals.
We excluded from our study overviews of systematic reviews.
Data extraction
The following data were extracted from the included reviews:
-
1.
Bibliometric data (authors, location of corresponding author, year of publication, language, journal impact factor).
-
2.
Characteristics of the review (Cochrane review or not, prospective registration or protocol publication, funding for conducting the review, sample size (n studies/n participants)).
-
3.
Characteristics of the participants included (gender and age).
-
4.
Description of the interventions.
Pairs of reviewers (MOA; BTS; TPY; PP) with experience in systematic reviews (including Cochrane reviews)10, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35 performed the data extraction, disagreements were resolved by discussion or arbitration from a third reviewer (LOPC).
The AMSTAR 2 checklist
The AMSTAR 2 checklist aims to assess the overall confidence in the results of a systematic review. AMSTAR 2 is composed of 16 items scored: “yes”, “partial yes”, “no”, and “no meta-analysis”. Of the 16 items, seven are considered as critical domains:
-
•
protocol registered before commencement of the review (item 2);
-
•
adequacy of the literature search (item 4);
-
•
justification for excluding individual studies (item 7);
-
•
risk of bias of included individual studies (item 9);
-
•
appropriateness of meta-analytical methods (item 11);
-
•
consideration of risk of bias when interpreting the results (item 13);
-
•
assessment of presence and likely impact of publication bias (item 15).22
The overall confidence in the results of the systematic reviews proposed by the AMSTAR 2 tool22 was defined as:
-
1.
high (no, or one non-critical weakness: the systematic review provides an accurate and comprehensive summary of the results);
-
2.
moderate (more than one non-critical weakness but no critical flaws: the systematic review provides an accurate summary of the results;
-
3.
low (one critical flaw, with or without non-critical weaknesses: the systematic review may not provide an accurate and comprehensive summary of the results);
-
4.
critically low (more than one critical flaw, with or without non-critical weaknesses: the review should not be relied on to provide an accurate and comprehensive summary of the results).
Pairs of reviewers (MOA; BTS; TPY; PP) performed the AMSTAR 2 assessment, disagreements were resolved by discussion or arbitration from a third reviewer (LOPC).
Data analysis
Descriptive analysis was used to summarize the characteristics of all included systematic reviews, as well as separately according to the overall confidence in the results (High, Moderate, Low and Critically low). The percentage of systematic reviews achieving each item from the AMSTAR 2 and the overall confidence in the results were tabulated. Inter-rater agreement of the AMSTAR 2 assessment was calculated using the Cohen's Kappa coefficient. The software STATA 10 was used for all analyses.
Results
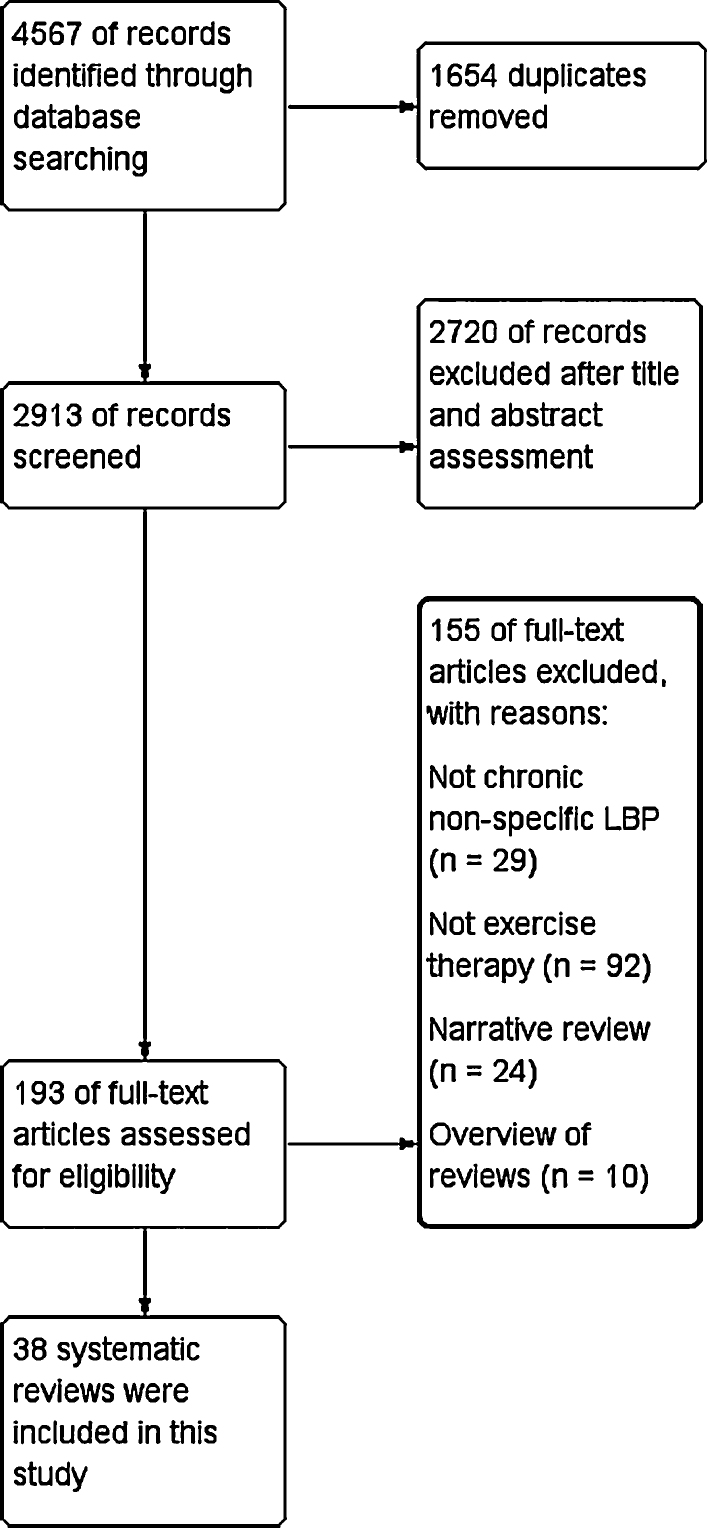
The search identified 193 systematic reviews, of these, 38 fulfilled our inclusion criteria (Fig. 1).10, 11, 13, 29, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69 Most of the reviews were conducted in Europe and Oceania, included a median of 10 clinical trials and a total sample size of 813 per review. Five of 38 (13%) reviews were Cochrane reviews, and 8 (21%) systematic reviews had a protocol published or registered prospectively. Nineteen (50%) of the reviews evaluated pain as the primary outcome, 18 (47%) evaluated disability as the primary outcome, 5 (13%) evaluated other primary outcomes and 18 (47%) did not define a primary outcome. Some reviews reported more than one primary outcome (e.g., pain and function). Table 1 describes the characteristics of the included systematic reviews in our study and separately according to the overall confidence in the results. In Table 1, we detailed the characteristics and the AMSTAR 2 assessment of each included systematic review.
Figure 1.
Study flow diagram (search period to February 7th 2017).
Table 1.
Summary of the characteristics of the 38 included systematic reviews.
| Total | AMSTAR rating |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Moderate | Low | Critically Low | ||
| Number of reviews (%) | 38 | 3 (8) | 1 (2) | 6 (16) | 28 (74) |
| Location, n (%) | |||||
| North America | 4 (11) | 1 (25) | 1 (25) | 0 (0) | 2 (50) |
| South America | 4 (11) | 1 (25) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (75) |
| Europe | 14 (37) | 1 (7) | 0 (0) | 3 (21) | 10 (71) |
| Asia | 4 (11) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4 (100) |
| Oceania | 12 (32) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (25) | 9 (75) |
| Impact factor of the journal, mean (SD) | 2.3 (1.7) | 5.9 (0.2) | 2.8 | 3.2 (1.5) | 1.7 (1.2) |
| Cochrane review, n (%) | 5 (13) | 3 (60) | 1 (20) | 1 (20) | 0 (0) |
| Funding, n (%) | 10 (26) | 1 (10) | 0 (0) | 2 (20) | 7 (70) |
| Protocol published, n (%) | 8 (21) | 3 (38) | 1 (12) | 3 (38) | 1 (12) |
| Number of included trials in the review, median (IQR) | 10 (6–15) | 12 (11–19) | 61 | 11 (6–17) | 9 (5–14) |
| Total sample size, median (IQR) | 813 (502–1585) | 1080 (795–2742) | 6390 | 966 (493–1586) | 777 (479–1277) |
| Type of exercise therapy, n (%) | |||||
| General exercise | 13 (34) | 0 (0) | 1 (8) | 2 (15) | 10 (77) |
| Motor control | 7 (18) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (29) | 5 (71) |
| Pilates | 7 (18) | 1 (14) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 6 (86) |
| McKenzie | 5 (13) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (20) | 4 (80) |
| Yoga | 3 (8) | 1 (33) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (67) |
| Aerobic | 3 (8) | 1 (33) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (67) |
| Graded activity | 2 (5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (50) | 1 (50) |
IQR, Interquartile range.
Overall confidence in the results of the systematic reviews
The overall confidence in the results of 28 reviews (74%) was rated as ‘Critically low’,13, 36, 37, 39, 40, 42, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 65, 66, 67, 69 6 reviews were rated as ‘Low’,29, 41, 43, 53, 63, 68 1 review was rated as ‘Moderate’,38 while 3 of 38 reviews (8%) were rated as ‘High’10, 11, 64 (Table 2). The assessment of the 16 items of AMSTAR 2 from each included systematic review is demonstrated in Table 3. The three systematic reviews rated as ‘High’ and the one rated as ‘Moderate’38 are Cochrane reviews and had a protocol prospectively published. The mean journal impact factor of the systematic reviews rated as ‘Critically low’ (1.7) was the lowest compared to the other reviews rated as ‘Low’ (3.2), ‘Moderate’ (2.8) and ‘High’ (5.9). The kappa coefficient for the inter-rater agreement of the AMSTAR 2 assessment was 0.73, which indicates substantial agreement.
Table 2.
Characteristics detailed of each included systematic review.
| Study | Country (location of corresponding author) | Cochrane (if it is a Cochrane review or not) | Funding (funding for conducting the review) | Protocol (if there is prospective registration or protocol publication) | Number of included studies in the review | Total sample size (number of participants included) | Meta analysis (if meta-analyses were performed or not) | Intervention | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bystrom 201345 | Sweden | No | No | No | 16 | 2675 | Yes | Motor control exercise | General exercise, spinal manual therapy, multimodal physical therapy and minimal intervention |
| Chang 201536 | Taiwan | No | Yes | No | 4 | 173 | No | Core strength training | Typical resistance training |
| Dunsford 201146 | Australia | No | No | No | 4 | 758 | No | McKenzie therapy | Exercise, manual therapy, education and heat |
| Dvorak 201137 | United States | No | No | No | 4 | 682 | No | Exercise therapy | Manual therapy |
| Gomes-Neto 201747 | Brazil | No | No | No | 11 | 1013 | Yes | Motor control | General exercise and manual therapy |
| Gordon 201648 | United Kingdom | No | Yes | No | 14 | 743 | No | Aerobic, motor control and flexibility exercises | Passive and active treatments |
| Hayden 200538 | Canada | Yes | No | Yes | 61 | 6390 | Yes | Exercise therapy | No treatment, placebo, Other conservative therapies and other exercises |
| Hendrick 201049 | New Zealand | No | No | No | 4 | 311 | No | Walking | Conventional therapy and No treatment |
| Hettinga 200750 | United Kingdom | No | Yes | No | 31 | 3953 | No | Exercise therapy | Other treatments |
| Hilde 201351 | Norway | No | No | No | 9 | 932 | No | Flexion and extension exercises | Standard treatments and No treatment |
| Hill 201352 | United Kingdom | No | No | No | 4 | 711 | No | Yoga | Minimal intervention and physical therapy interventions |
| Kalin 201653 | Switzerland | No | No | No | 6 | 257 | No | Sensory discrimination training | No treatment, placebo, exercise and passive treatment |
| Kool 200454 | Netherlands | No | No | No | 14 | 2796 | Yes | Exercises | Usual care and passive therapies |
| Laird 201239 | Australia | No | No | No | 12 | 696 | No | Movement based intervention | General exercise, spinal manipulation and No treatment |
| Lawford 201656 | Australia | No | No | Yes | 7 | 869 | No | Walking | Inactive interventions and Non-pharmacologic intervention |
| Lewis 200886 | Australia | No | No | No | 15 | 1695 | No | Rehabilitation exercises, stabilization and other exercises | Manual therapy, surgery and other treatments |
| Liddle 200458 | United Kingdom | No | Yes | No | 16 | 1730 | No | Strengthening, flexibility and cardiovascular exercises | No treatment, passive therapies, medication and other exercises |
| Lim 201159 | Singapore | No | Yes | No | 7 | 194 | Yes | Pilates | Minimal or other interventions |
| Lin 201640 | Taiwan | No | No | No | 8 | 500 | No | Pilates | Minimal intervention, No intervention and other exercises |
| Macedo 201041 | Australia | No | No | Yes | 15 | 1654 | No | Graded activity | Minimal intervention and other exercises |
| Machado 200642 | Australia | No | No | No | 29 | 2431 | Yes | McKenzie therapy | Passive therapies, advice, exercises, spinal manipulation and back school |
| McCaskey 201443 | Switzerland | No | No | Yes | 18 | 1380 | No | Proprioceptive exercises | Inactive treatments, usual care, home based training, endurance, strengthening and stretching exercises |
| Merepeza 201444 | Canada | No | No | No | 3 | 796 | No | Exercise therapy | Spinal manipulation |
| Miyamoto 201360 | Brazil | No | No | No | 8 | 363 | Yes | Pilates | No treatment, minimal intervention and other interventions |
| Patti 201561 | Italy | No | No | No | 29 | 1373 | No | Pilates | No treatment, minima intervention and other exercises |
| Pereira 201262 | Brazil | No | Yes | No | 5 | 139 | Yes | Pilates | Lumbar stabilization exercises |
| Rackwitz 200663 | Germany | No | Yes | No | 7 | 551 | No | Stabilizing exercises alone or combined with other therapies | Other physical therapy interventions |
| Saragiotto 201629 | Australia | Yes | Yes | No | 29 | 2431 | Yes | Motor control exercises | Minimal intervention, manual therapy and other exercises |
| Schaafsma 201364 | Netherlands | Yes | No | Yes | 25 | 4404 | Yes | Physical conditioning exercises | Usual care |
| Searle 201565 | Australia | No | No | No | 45 | 4462 | Yes | Exercise therapy | Wait list, usual care, electrotherapies, manual therapy |
| Slade 200666 | Australia | No | No | No | 15 | 903 | Yes | Strengthening exercises | No exercises, other exercises and surgeries |
| Slade 200767 | Australia | No | No | No | 6 | 830 | Yes | Unloaded movement facilitation exercises | Stabilization exercises, education, chiropractic and usual care |
| Surkitt 201268 | Australia | No | No | Yes | 6 | 474 | No | Directional preference exercises | No treatment and other conservative treatments |
| Touche 200855 | Spain | No | No | No | 3 | 141 | No | Pilates | Back school and No treatment |
| Van der Giessen 201269 | Netherlands | No | No | No | 10 | 680 | No | Graded activity | Usual care, active physical treatments and wait list |
| Wang 201213 | China | No | Yes | No | 5 | 414 | Yes | Core stability exercise | General exercise |
| Wieland 201711 | United States | Yes | No | Yes | 12 | 1080 | Yes | Yoga | No exercise and other exercises |
| Yamato 201510 | Brazil | Yes | Yes | Yes | 10 | 510 | Yes | Pilates | Minimal interventions and other exercises |
Table 3.
AMSTAR 2 assessment of each included systematic review.
| Study | AMSTAR 2 ITENS |
Overall rating | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | ||
| Bystrom 201345 | Yes | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes | Critically low |
| Chang 201536 | No | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | No | No | No MA | Yes | Critically low |
| Dunsford 201146 | Yes | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Partial Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | No | No | No MA | Yes | Critically low |
| Dvorak 201137 | Yes | No | No | Partial Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | No | No | No MA | No | Critically low |
| Gomes-Neto 201747 | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Partial Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | Critically low |
| Gordon 201648 | No | No | No | Partial Yes | No | No | No | Partial Yes | No | No | No MA | No MA | No | No | No MA | Yes | Critically low |
| Hayden 200538 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Moderate |
| Hendrick 201049 | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | Yes | No | No MA | No | Critically low |
| Hettinga 200750 | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | Partial Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | Yes | No | No MA | Yes | Critically low |
| Hilde 201351 | No | No | No | Partial Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Partial Yes | No | No MA | No MA | Yes | Yes | No MA | No | Critically low |
| Hill 201352 | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Partial Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | No | No | No MA | No | Critically low |
| Kalin 201653 | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No MA | No MA | No | Yes | No MA | Yes | Low |
| Kool 200454 | No | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | Critically low |
| Laird 201239 | No | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Partial Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | No | No | No MA | Yes | Critically low |
| Lawford 201656 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Partial Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | No | Yes | No MA | Yes | Critically low |
| Lewis 200886 | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | No | No | No MA | No | Critically low |
| Liddle 200458 | No | No | Yes | Partial Yes | No | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | Yes | No | No MA | Yes | Critically low |
| Lim 201159 | Yes | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Critically low |
| Lin 201640 | No | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | Yes | Partial Yes | Partial Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | No | No | No MA | No | Critically low |
| Macedo 201041 | Yes | Yes | No | Partial Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Low |
| Machado 200642 | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Partial Yes | Partial Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Critically low |
| McCaskey 201443 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | Yes | Yes | No MA | Yes | Low |
| Merepeza 201444 | Yes | No | No | Partial Yes | No | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | No | No | No MA | No | Critically low |
| Miyamoto 201360 | Yes | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | Critically low |
| Patti 201561 | Yes | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No MA | No MA | No | No | No MA | Yes | Critically low |
| Pereira 201262 | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes | Critically low |
| Rackwitz 200663 | Yes | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Partial Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | Yes | Yes | No MA | Yes | Low |
| Saragiotto 201629 | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Schaafsma 201364 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | High |
| Searle 201565 | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Partial Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Critically low |
| Slade 200666 | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Critically low |
| Slade 200767 | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Partial Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes | Critically low |
| Surkitt 201268 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | Yes | Yes | No MA | No | Low |
| Touche 200855 | No | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Partial Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | No | No | No MA | No | Critically low |
| Van der Giessen 201269 | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Partial Yes | Yes | No | No MA | No MA | No | No | No MA | Yes | Critically low |
| Wang 201213 | Yes | No | No | Partial Yes | Yes | Yes | Partial Yes | Partial Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Critically low |
| Wieland 201711 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | High |
| Yamato 201510 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | High |
Items: (1) Did the research questions and inclusion criteria for the review include the components of PICO?; (2) Did the report of the review contain an explicit statement that the review methods were established prior to the conduct of the review and did the report justify any significant deviations from the protocol?; (3) Did the review authors explain their selection of the study designs for inclusion in the review?; (4) Did the review authors use a comprehensive literature search strategy?; (5) Did the review authors perform study selection in duplicate?; (6) Did the review authors perform data extraction in duplicate?; (7) Did the review authors provide a list of excluded studies and justify the exclusions?; (8) Did the review authors describe the included studies in adequate detail?; (9) Did the review authors use a satisfactory technique for assessing the RoB in individual studies that were included in the review?; (10) Did the review authors report on the sources of funding for the studies included in the review?; (11) If MAs was performed did the review authors use appropriate methods for statistical combination of results?; (12) If MAs was performed, did the review authors assess the potential impact of RoB in individual studies on the results of the MAs or other evidence synthesis?; (13) Did the review authors account for RoB in individual studies when interpreting/ discussing the results of the review?; (14) Did the review authors provide a satisfactory explanation for, and discussion of, any heterogeneity observed in the results of the review?; (15) If they performed quantitative synthesis did the review authors carry out an adequate investigation of publication bias and discuss its likely impact on the results of the review?; (16) Did the review authors report any potential sources of conflict of interest, including any funding they received for conducting the review?
AMSTAR, Assessing the Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews; MA, meta-analysis; RoB, risk of bias.
Full details of the AMSTAR 2 assessment appear in Table 4. Reviews performed most poorly with respect to:
-
•
explaining selection of the study designs (8%);
-
•
reporting sources of funding for included studies (11%);
-
•
assessing potential impact of risk of bias in individual studies on the results of the meta-analyses (13%);
-
•
investigation of publication bias (21%); and
-
•
establishing review methods prior to conduct of the review (21%).
Table 4.
Overall confidence assessment (AMSTAR 2 tool) of the 38 included systematic review.
| AMSTAR 2 ITEMS | Yes n (%) | Partial yes n (%) | No n (%) | No MA n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Did the research questions and inclusion criteria for the review include the components of PICO? | 27 (71) | – | 11 (29) | – |
| 2. Did the report of the review contain an explicit statement that the review methods were established prior to the conduct of the review and did the report justify any significant deviations from the protocol? | 8 (21.1) | 0 (0) | 30 (78.9) | – |
| 3. Did the review authors explain their selection of the study designs for inclusion in the review? | 3 (7.9) | – | 35 (82.1) | – |
| 4. Did the review authors use a comprehensive literature search strategy? | 19 (50) | 18 (47.4) | 1 (2.6) | – |
| 5. Did the review authors perform study selection in duplicate? | 28 (73.7) | – | 10 (26.3) | – |
| 6. Did the review authors perform data extraction in duplicate? | 23 (60.5) | – | 15 (39.5) | – |
| 7. Did the review authors provide a list of excluded studies and justify the exclusions? | 16 (42.1) | 4 (10.5) | 18 (47.4) | – |
| 8. Did the review authors describe the included studies in adequate detail? | 14 (36.8) | 17 (44.7) | 7 (18.5) | – |
| 9. Did the review authors use a satisfactory technique for assessing the RoB in individual studies that were included in the review? | 35 (82.1) | 1 (2.6) | 2 (5.3) | – |
| 10. Did the review authors report on the sources of funding for the studies included in the review? | 4 (10.5) | – | 34 (89.5) | – |
| 11. If MAs was performed did the review authors use appropriate methods for statistical combination of results? | 17 (44.7) | – | – | 21 (55.3) |
| 12. If MAs was performed, did the review authors assess the potential impact of RoB in individual studies on the results of the MAs or other evidence synthesis? | 5 (13.2) | – | 12 (31.6) | 21 (55.3) |
| 13. Did the review authors account for RoB in individual studies when interpreting/ discussing the results of the review? | 15 (39.5) | – | 23 (60.5) | – |
| 14. Did the review authors provide a satisfactory explanation for, and discussion of, any heterogeneity observed in the results of the review? | 16 (42.1) | – | 22 (57.9) | – |
| 15. If they performed quantitative synthesis did the review authors carry out an adequate investigation of publication bias and discuss its likely impact on the results of the review? | 8 (21.1) | – | 9 (23.6) | 21 (55.3) |
| 16. Did the review authors report any potential sources of conflict of interest, including any funding they received for conducting the review? | 25 (65.8) | – | 13 (34.2) | – |
AMSTAR, Assessing the Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews; MA, meta-analysis; RoB, risk of bias.
Items in bold are the item considered as critical domains in the AMSTAR 2.
Discussion
The overall confidence in the results of systematic reviews that evaluated the effectiveness of exercise for people with chronic non-specific low back pain was ‘critically low’. Specifically, reviews frequently lacked details on the selection of study designs for inclusion, often did not report the source of funding for included trials and did not assess the potential impact of the risk of bias on the results.
The motivation to conduct this study was that we expected to find a large number of systematic reviews of exercise for low back pain, but we were not sure about the overall confidence in the results of these reviews and consequently if their conclusions are reliable. Unfortunately, as demonstrated by our findings, the overall confidence of the included reviews of exercise for chronic low back pain was very low in general. This scenario is worrying, since exercise is one of the most consistently recommended interventions,70, 71, 72, 73 in the treatment of this high costly and disabling condition.74 Clinical practice guidelines often base their recommendations in findings from systematic reviews. So, the overall confidence in the results of the systematic reviews is very important to generate unbiased estimates of treatment effects for decision making, alerting clinicians to based their conducts only on high-quality reviews. Understanding how well a systematic review has been conducted is essential for clinicians to determine if the findings are relevant and can be applied to clinical practice.16
In our study, the overall confidence in the results were rated as ‘High’ based on the AMSTAR 2 tool in only three (8%) systematic reviews.10, 11, 64 This is consistent with the findings from Martins et al.75 that reported only 7.5% of the reviews on surgical treatment of low back pain rated as ‘Excellent’ based on the original AMSTAR tool. In contrast to our findings, the study by Martins et al.75 reported that, only 22.5% of the reviews were rated as ‘very poor’. Oliveira et al.76 evaluated the methodological quality of systematic reviews of physical therapy interventions using the AMSTAR tool, most of the reviews were rated as ‘low’ (median 3, 0–11 scale) for the orthopaedics PEDro subdiscipline.
The three systematic reviews in which the overall confidence in the results were rated as ‘High” in our study evaluated the effectiveness of physical conditioning exercises,64 Yoga11 and Pilates10 in LBP patients. In the review about physical conditioning, authors stated that the effect of intervention on sick leave for workers with LBP remains uncertain.64 On the other hand, the reviews on Yoga and Pilates conclude that these types of exercises are effective in reducing pain and improving function in patients with LBP, but there is no robust evidence that they are superior to other forms of exercises.10, 11 These reviews highlighted that the decision to use any type of exercise may be based on patient's or clinician's preferences and costs. The only included systematic review rated as ‘moderate’ evaluated the effects of exercise therapy in general and also concluded that exercise was effective at reducing pain and improving function in patients with LBP.38
Our descriptive analysis showed that the systematic reviews with higher overall confidence in the results are Cochrane reviews and reviews with a registered protocol. This is consistent with previous studies that found that Cochrane reviews are generally better than non-Cochrane reviews.77, 78 Cochrane reviews typically use more rigorous methods, and consequently, are less vulnerable to bias and generally more conservative in their conclusions.79, 80 Further, reviews with protocol registration also generally yielded higher scores using the AMSTAR tool.76, 81, 82 The proportion of reviews with protocol registration in our study was low (21%), which is in line with the low proportion (19%) of systematic review registered in the physical therapy field.76 As occurred with randomized clinical trials, journal editors should stimulate change in editorial policies, requiring review authors to prospectively register their protocols on a database such as PROSPERO. Prospective registration of systematic reviews reduces the probability of bias in the review, since the authors report their methods and statistical analysis a priori, and improve the transparency of the research.83 It is important to point out that some systematic reviews38, 42, 54, 55, 58, 63, 66, 67 with no registered protocol were performed before the publication of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) statement in 2009,84 which first proposed the registry for protocol of systematic reviews. Subsequently of PRISMA statement, PROSPERO was developed and implemented.
Despite a high proportion (82%) of reviews using appropriate methods for the risk of bias assessment, few of them considered the impact of the quality of included trials on their results. As trials with high risk of bias may overestimate the treatment effect, the results of these reviews should be interpreted with caution. Systematic reviewers should be aware that simply assessing risk of bias is not sufficient, its impact on the reviews’ results should be assessed. It is important to say that that the quality of primary studies does not influence the quality of systematic reviews. The AMSTAR 2 does not look for the quality of primary studies. Its objective is to evaluate the methodological quality of systematic reviews, considering how well the systematic review was conducted (literature searching, pooling of data, etc.). Therefore, if a systematic review included primary studies with high risk of bias, but it was well conducted, this review tends to be rated as ‘high quality’. Another important finding was the low proportion (21%) of systematic reviews that carried out an adequate investigation of publication bias. Studies with positive results are published more frequent and quickly than negative studies.85 Systematic reviewers should always investigate if this kind of bias is present, decreasing the possibility of overestimation of treatment effects.
Strengths of included systematic reviews should also be highlighted. Around 70% of the reviews defined adequately the research questions and inclusion criteria, using the PICO (problem, intervention, comparison and outcomes) components. Most of reviews also performed study selection (74%) and data extraction (60%) in duplicate, and only 1 review50 did not use a comprehensive literature search strategy.
Our results are limited to systematic reviews in the field of exercise therapy for patients with chronic low back pain. Therefore, the scenario for other types of interventions for a wide range of health conditions is still unknown. More studies are needed in order to externally validate our findings using different sets of reviews, conditions and interventions.
In conclusion, the findings of our study demonstrate very low overall confidence in the results of most systematic reviews of exercise in chronic non-specific low back pain. Our study highlights the need to improve the quality of systematic reviews in this field, to avoid biased recommendations for clinical decision making.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Search strategy for each database
Pubmed
1 dorsalgia.ti,ab,kw.
2 exp Back Pain/
3 “backache” ti,ab
4 (lumbar adj pain) ti,ab
5 coccyx.ti,ab
6 coccydynia.ti,ab
7 sciatica.ti,ab
8 exp sciatic neuropathy/
9 “spondylosis” ti,ab
10 “lumbago” ti,ab
11 lumbago.ti,ab,kw.
12 (disc adj degeneration) ti,ab
13 (disc adj prolapse) ti,ab
14 (disc adj herniation) ti,ab
15 OR / #1-14
16 systematic review /
17 meta-analysis /
18 (#16 OR #17)
19 (#15 AND #19)
Embase
1 dorsalgia.ti,ab,kw.
2 (back pain or backache or back ache).ti,ab,kw.
3 exp LOW BACK PAIN/
4 exp BACKACHE/
5 (lumb$ adj3 pain).ti,ab,kw.
6 coccyx.ti,ab,kw.
7 coccydynia.ti,ab,kw.
8 sciatica.ti,ab,kw.
9 sciatica/
10 exp ISCHIALGIA/
11 spondylosis.mp.
12 lumbago.ti,ab,kw.
13 back disorder$.ti,ab,kw.
14 or/1-13
15 systematic review /
16 meta-analysis /
17 (#15 OR #16)
-
18
(#14 AND #17)
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
#1 MeSH descriptor: [Back Pain] explode all trees
#2 dorsalgia
#3 backache or back ache
#4 MeSH descriptor: [Back Pain] explode all trees
#5 lumb* near pain or coccyx or coccydynia or sciatica or spondylosis
#6 MeSH descriptor: [Spine] explode all trees
#7 MeSH descriptor: [Spinal Diseases] explode all trees
#8 lumbago or discitis or disc near herniat*
#9 spinal fusion
#10 facet near joint*
#11 MeSH descriptor: [Intervertebral Disk] explode all trees
#12 postlaminectomy
#13 arachNoiditis
#14 failed near back
#15 MeSH descriptor: [Cauda Equina] explode all trees
#16 lumb* near vertebra*
#17 spinal near steNosis
#18 slipped near (disc* or disk*)
#19 degenerat* near (disc* or disk*)
#20 steNosis near (spine or root or spinal)
#21 displace* near (disc* or disk*)
#22 prolap* near (disc* or disk*)
#23 MeSH descriptor: [Sciatic Neuropathy] explode all trees
#24 sciatic*
#25 back disorder*
#26 back near pain
#27 (#1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 or #13 or #14 or #15 or #16 or #17 or #18 or #19 or #20 or #21 or #22 or #23 or #24 or #25 or #26)
#28 systematic review
#29 meta-analysis
#30 (#28 or #29)
#31 (#27 AND #30)
PEDro
Problem: Pain
AND
Body Part: lumbar spine, sacro-iliac joint or pelvis
AND
Method: systematic review
CINAHL
S1 “lumbago”
S2 (MH “Spondylolisthesis”) OR (MH “Spondylolysis”)
S3 (MH “Thoracic Vertebrae”)
S4 S1 or S2 or S3
S5 lumbar N2 vertebra
S6 (MH “Lumbar Vertebrae”)
S7 “coccydynia”
S8 “coccyx”
S9 “sciatica”
S10 (MH “Sciatica”)
S11 (MH “Coccyx”)
S12 S5 or S6 or S7or S8 or S9 or S10 or S11
S13 backache or “back ache”
S14 lumb* W3 pain
S15 back pain
S16 (MH “Low Back Pain”)
S17 (MH “Back Pain+”)
S18 “dorsalgia”
S19 S13 S14 or S15 or S16 or S17 or S18 or S34
S20 S4 or S12 or S19
S21 systematic review
S22 meta-analysis
S23 S21 or S22
S24 S20 and S23
References
- 1.van Tulder M., Becker A., Bekkering T. Chapter 3 European guidelines for the management of acute nonspecific low back pain in primary care. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(suppl 2):S169–S191. doi: 10.1007/s00586-006-1071-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Airaksinen O., Brox J.I., Cedraschi C. Chapter 4. European guidelines for the management of chronic nonspecific low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(suppl 2):S192–S300. doi: 10.1007/s00586-006-1072-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ferreira G., Costa L.M., Stein A., Hartvigsen J., Buchbinder R., Maher C.G. Tackling low back pain in Brazil: a wake-up call. Braz J Phys Ther. 2018 doi: 10.1016/j.bjpt.2018.10.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bento T.P.F., Genebra C., Maciel N.M., Cornelio G.P., Simeao S., Vitta A. Low back pain and some associated factors: is there any difference between genders? Braz J Phys Ther. 2019 doi: 10.1016/j.bjpt.2019.01.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Costa L.C.M., Maher C.G., Hancock M.J., McAuley J.H., Herbert R.D., Costa L.O. The prognosis of acute and persistent low-back pain: a meta-analysis. Can Med Assoc J. 2012;184(11):E613–E624. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.111271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Foster N.E., Anema J.R., Cherkin D. Prevention and treatment of low back pain: evidence, challenges, and promising directions. Lancet. 2018 doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30489-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hayden J.A., Cartwright J.L., Riley R.D., Vantulder M.W. Exercise therapy for chronic low back pain: protocol for an individual participant data meta-analysis. Syst Rev. 2012;1:64. doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-1-64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Qaseem A., Wilt T.J., McLean R.M., Forciea M.A. Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of P. Noninvasive Treatments for Acute Subacute, and Chronic Low Back Pain: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2017 doi: 10.7326/M16-2367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Saragiotto B.T., Maher C.G., Yamato T.P. Motor control exercise for nonspecific low back pain: a cochrane review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016;41(16):1284–1295. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000001645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yamato T.P., Maher C.G., Saragiotto B.T. Pilates for low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(7):CD010265. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010265.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wieland L.S., Skoetz N., Pilkington K., Vempati R., D’Adamo C.R., Berman B.M. Yoga treatment for chronic non-specific low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;1:CD010671. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010671.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Saragiotto B.T., Maher C.G., Yamato T.P. Motor control exercise for chronic non-specific low-back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;1:CD012004. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wang X.Q., Zheng J.J., Yu Z.W. A meta-analysis of core stability exercise versus general exercise for chronic low back pain. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(12):e52082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hall A.M., Maher C.G., Lam P., Ferreira M., Latimer J. Tai chi exercise for treatment of pain and disability in people with persistent low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2011;63(11):1576–1583. doi: 10.1002/acr.20594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Herbert R., Jamtvedt G., Mead J., Hagen K.B. 2nd ed. Elsevier; Edinburgh: 2011. Practical Evidence-Based Physiotherapy. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Harrison J.K., Reid J., Quinn T.J., Shenkin S.D. Using quality assessment tools to critically appraise ageing research: a guide for clinicians. Age Ageing. 2017;46(3):359–365. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afw223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mullen P.D., Ramirez G. The promise and pitfalls of systematic reviews. Annu Rev Public Health. 2006;27:81–102. doi: 10.1146/annurev.publhealth.27.021405.102239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jansen J.P., Trikalinos T., Cappelleri J.C. Indirect treatment comparison/network meta-analysis study questionnaire to assess relevance and credibility to inform health care decision making: an ISPOR-AMCP-NPC Good Practice Task Force report. Value Health. 2014;17(2):157–173. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2014.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shea B.J., Grimshaw J.M., Wells G.A. Development of AMSTAR: a measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2007;7:10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-7-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Shea B.J., Bouter L.M., Peterson J. External validation of a measurement tool to assess systematic reviews (AMSTAR) PLoS ONE. 2007;2(12):e1350. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shea B.J., Hamel C., Wells G.A. AMSTAR is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62(10):1013–1020. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2008.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shea B.J., Reeves B.C., Wells G. AMSTAR 2 a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. 2017;358:j4008. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j4008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Nelson N.L. Kinesio taping for chronic low back pain: a systematic review. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2016;20(3):672–681. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2016.04.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Luz Junior M.A.D., Almeida M.O., Santos R.S., Civile V.T., Costa L.O.P. Effectiveness of kinesio taping in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2019;44(1):68–78. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000002756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yousefi-Nooraie R., Schonstein E., Heidari K. Low level laser therapy for nonspecific low-back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;(2):CD005107. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005107.pub4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Huang Z., Ma J., Chen J., Shen B., Pei F., Kraus V.B. The effectiveness of low-level laser therapy for nonspecific chronic low back pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:360. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0882-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Saragiotto B.T., Machado G.C., Ferreira M.L., Pinheiro M.B., Abdel Shaheed C., Maher C.G. Paracetamol for low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;(6):CD012230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Macedo L.G., Saragiotto B.T., Yamato T.P. Motor control exercise for acute non-specific low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2:CD012085. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Saragiotto B.T., Maher C.G., Yamato T.P. Motor control exercise for chronic non-specific low-back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;(1):CD012004. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yamato T.P., Maher C.G., Traeger A.C., Wiliams C.M., Kamper S.J. Do schoolbags cause back pain in children and adolescents? A systematic review. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(19):1241–1245. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2017-098927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Parreira P., Heymans M.W., van Tulder M.W. Back Schools for chronic non-specific low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;8:CD011674. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011674.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Parreira P.C.S., Maher C.G., Megale R.Z., March L., Ferreira M.L. An overview of clinical guidelines for the management of vertebral compression fracture: a systematic review. Spine J. 2017;17(12):1932–1938. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2017.07.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Parreira Pdo C., Costa Lda C., Hespanhol L.C., Jr., Lopes A.D., Costa L.O. Current evidence does not support the use of Kinesio Taping in clinical practice: a systematic review. J Physiother. 2014;60(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2013.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Almeida M.O., Davis I.S., Lopes A.D. Biomechanical differences of foot-strike patterns during running: a systematic review with meta-analysis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2015;45(10):738–755. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2015.6019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Almeida M.O., Silva B.N., Andriolo R.B., Atallah A.N., Peccin M.S. Conservative interventions for treating exercise-related musculotendinous, ligamentous and osseous groin pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(6):CD009565. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009565.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chang W.D., Lin H.Y., Lai P.T. Core strength training for patients with chronic low back pain. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015;27:619–622. doi: 10.1589/jpts.27.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dvorak H., Kujat C., Brumitt J. Effect of therapeutic exercise versus manual therapy on athletes with chronic low back pain. J Sport Rehabil. 2011;20:494–504. doi: 10.1123/jsr.20.4.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hayden J., van Tulder M.W., Malmivaara A., Koes B.W. Exercise therapy for treatment of non-specific low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;(3):CD000335. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000335.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Laird R.A., Kent P., Keating J.L. Modifyng patterns of movement in people with low back pain – does it help?. A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:169. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-13-169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lin H.T., Hung W.C., Hung J.L., Wu P.S., Liaw L.J., Chang J.H. Effects of Pilates on patients with chronic non-specific low back pain: a systematic review. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28:2961–2969. doi: 10.1589/jpts.28.2961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Macedo L.G., Smeet R.J., Maher C.G., Latimer J., McAuley J.H. Graded activity and graded exposure for persistent nonspecific low back pain: a systematic review. Phys Therapy. 2010;90:860879. doi: 10.2522/ptj.20090303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Machado L.C., Souza M.C., Ferreira P.H., Ferreira M.L. The McKenzie method for low back pain: a systematic review of the literature with a meta-analysis approach. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006;31(9):254–262. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000214884.18502.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.McCaskey M.A., Amft C.S., Wirth B., Suica Z., Bruin E.D. Effects of proprioceptive exercises on pain and function in chronic neck- and low back pain rehabilitation: a systematic literature review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:382. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Merepeza A. Effects of spinal manipulation versus therapeutic exercise on adults with chronic low back pain: a literature review. J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2014;58(4):456–466. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bystrom M.G., Rasmussen-Barr E., Grooten W.J. Motor control exercises reduces pain and disability in chronic and recurrent low back pain: a meta-analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013;38(6):E350–E358. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31828435fb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Dunsford A., Kumar S., Clarke S. Integrating evidence into practice: use of McKenzie-based treatment for mechanical low back pain. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2011;4:393–402. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S24733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gomes-Neto M., Lopes J.M., Conceicao C.S. Stabilization exercise compared to general exercises or manual therapy for the management of low back pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Phys Ther Sport. 2017;23:136–142. doi: 10.1016/j.ptsp.2016.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gordon R., Bloxham S. A systematic review of the effects of exercise and physical activity on non-specific chronic low back pain. Healthcare (Basel) 2016;4(2) doi: 10.3390/healthcare4020022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hendrick P., Te Wake A.M., Tikkisetty A.S., Wulff L., Yap C., Milosavljevic S. The effectiveness of walking as an intervention for low back pain: a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(10):1613–1620. doi: 10.1007/s00586-010-1412-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hettinga D.M., Jackson A., Moffett J.K., May S., Mercer C., Woby S.R. A systematic review and synthesis of higher quality evidence of the effectiveness of exercise interventions for non-specific low back pain of at least 6 weeks’ duration. Phys Therapy Rev. 2013;12(3):221–232. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hilde G., Bø K. Effect of exercise in the treatment of chronic low back pain: a systematic review, emphasising type and dose of exercise. Phys Therapy Rev. 2013;3(2):107–117. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hill C. Is yoga an effective treatment in the management of patients with chronic low back pain compared with other care modalities – a systematic review. J Complement Integr Med. 2013:10. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2012-0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kalin S., Rausch-Osthoff A.K., Bauer C.M. What is the effect of sensory discrimination training on chronic low back pain?. A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:143. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-0997-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kool J., de Bie R., Oesch P., Knüsel O., Brandt Pvd, Bachmann S. Exercise reduces sick leave in patients with non-acute non-specific low back pain: a meta-analysis. J Rehabil Med. 2004;36(2):49–62. doi: 10.1080/16501970310020104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.La Touche R., Escalante K., Linares M.T. Treating non-specific chronic low back pain through the Pilates Method. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2008;12(4):364–370. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2007.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lawford B.J., Walters J., Ferrar K. Does walking improve disability status, function, or quality of life in adults with chronic low back pain?. A systematic review. Clin Rehabil. 2016;30(6):523–536. doi: 10.1177/0269215515590487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lewis A., Morris M.E., Walsh C. Are physiotherapy exercises effective in reducing chronic low back pain? Phys Therapy Rev. 2013;13(1):37–44. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Liddle S.D., Baxter D.G., Gracey J.H. Exercise and chronic low back pain: what works? Pain. 2004;107(1):176–190. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2003.10.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Lim E.C., Poh R.L., Low A.Y., Wong W.P. Effects of Pilates-based exercises on pain and disability in individuals with persistent nonspecific low back pain: a systematic review with meta-analysis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2011;41(2):70–80. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2011.3393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Miyamoto G.C., Costa L.O., Cabral C.M. Efficacy of the Pilates method for pain and disability in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Braz J Phys Ther. 2013;17(6):517–532. doi: 10.1590/S1413-35552012005000127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Patti A., Bianco A., Paoli A. Effects of Pilates exercise programs in people with chronic low back pain: a systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore) 2015;94(4):e383. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Pereira L.M., Obara K., Dias J.M. Comparing the Pilates method with no exercise or lumbar stabilization for pain and functionality in patients with chronic low back pain: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2012;26(1):10–20. doi: 10.1177/0269215511411113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Rackwitz B., de Bie R., Limm H., von Garnier K., Ewert T., Stucki G. Segmental stabilizing exercises and low back pain What is the evidence?. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Clin Rehabil. 2006;20(7):553–567. doi: 10.1191/0269215506cr977oa. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Schaafsma F.G., Whelan K., van der Beek A.J., van der Es-Lambeek L.C., Ojajarvi A., Verbeek J.H. Physical conditioning as part of a return to work strategy to reduce sickness absence for workers with back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(8):CD001822. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001822.pub3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Searle A., Spink M., Ho A., Chuter V. Exercise interventions for the treatment of chronic low back pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Clin Rehabil. 2015;29(12):1155–1167. doi: 10.1177/0269215515570379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Slade S.C., Keating J.L. Trunk-strengthening exercises for chronic low back pain: a systematic review. J Manip Physiol Ther. 2006;29(2):163–173. doi: 10.1016/j.jmpt.2005.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Slade S.C., Keating J.L. Unloaded movement facilitation exercise compared to no exercise or alternative therapy on outcomes for people with nonspecific chronic low back pain: a systematic review. J Manip Physiol Ther. 2007;30(4):301–311. doi: 10.1016/j.jmpt.2007.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Surkitt L.D., Ford J.J., Hahne A.J., Pizzari T., McMeeken J.M. Efficacy of directional preference management for low back pain: a systematic review. Phys Ther. 2012;92(5):652–665. doi: 10.2522/ptj.20100251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.van der Giessen R.N., Speksnijder C.M., Helders P.J. The effectiveness of graded activity in patients with non-specific low-back pain: a systematic review. Disabil Rehabil. 2012;34(13):1070–1076. doi: 10.3109/09638288.2011.631682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . 2016. Low Back Pain and Sciatica in Over 16s: Assessment and Management. NICE guideline [NG59]. London. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Qaseem A., Wilt T.J., McLean R.M., Forciea M.A. Noninvasive treatments for acute, subacute, and chronic low back pain: a clinical practice guideline from the American college of physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166(7):514–530. doi: 10.7326/M16-2367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Stochkendahl M.J., Kjaer P., Hartvigsen J. National Clinical Guidelines for non-surgical treatment of patients with recent onset low back pain or lumbar radiculopathy. Eur Spine J. 2017 doi: 10.1007/s00586-017-5099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Van Wambeke P., Desomer A., Ailliet L. Belgian Health Care Knowledge Centre (KCE); 2017. Low Back Pain and Radicular Pain: Assessment and Management – Summary. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1211–1259. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Martins D.E., Astur N., Kanas M., Ferretti M., Lenza M., Wajchenberg M. Quality assessment of systematic reviews for surgical treatment of low back pain: an overview. Spine J. 2016;16(5):667–675. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2016.01.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Oliveira C.B., Elkins M.R., Lemes I.R. A low proportion of systematic reviews in physical therapy are registered: a survey of 150 published systematic reviews. Braz J Phys Ther. 2017;22(3):177–183. doi: 10.1016/j.bjpt.2017.09.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Fleming P.S., Seehra J., Polychronopoulou A., Fedorowicz Z., Pandis N. Cochrane and non-Cochrane systematic reviews in leading orthodontic journals: a quality paradigm? Eur J Orthod. 2013;35(2):244–248. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjs016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Moseley A.M., Elkins M.R., Herbert R.D., Maher C.G., Sherrington C. Cochrane reviews used more rigorous methods than non-Cochrane reviews: survey of systematic reviews in physiotherapy. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62(10):1021–1030. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2008.09.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Tricco A.C., Tetzlaff J., Pham B., Brehaut J., Moher D. Non-Cochrane vs Cochrane reviews were twice as likely to have positive conclusion statements: cross-sectional study. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62(4) doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2008.08.008. 380–386.e1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Useem J., Brennan A., LaValley M. Systematic differences between cochrane and non-cochrane meta-analyses on the same topic: a matched pair analysis. PLOS ONE. 2015;10(12):e0144980. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Ge L., Tian J.H., Li Y.N. Association between prospective registration and overall reporting and methodological quality of systematic reviews: a meta-epidemiological study. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;93:45–55. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Sideri S., Papageorgiou S.N., Eliades T. Registration in the international prospective register of systematic reviews (PROSPERO) of systematic review protocols was associated with increased review quality. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018 doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Higgins J.P.T., Green S. 2011. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011) [Google Scholar]
- 84.Liberati A., Altman D.G., Tetzlaff J. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Dwan K., Gamble C., Williamson P.R., Kirkham J.J., Reporting Bias G. Systematic review of the empirical evidence of study publication bias and outcome reporting bias – an updated review. PLOS ONE. 2013;8(7):e66844. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Lewis A., Morris M.E., Walsh C. Are physiotherapy exercises effective in reducing chronic low back pain? Phys Therapy Rev. 2008;13(1):37–44. [Google Scholar]