Summary
Nearly all classes of coding and non-coding RNA undergo post-transcriptional modification including RNA methylation. Methylated nucleotides belong to the evolutionarily most conserved features of tRNA and rRNA.1,2 Many contemporary methyltransferases use the universal cofactor S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) as methyl group donor. This and other nucleotide-derived cofactors are considered as evolutionary leftovers from an RNA World, in which ribozymes may have catalysed essential metabolic reactions beyond self-replication.3 Chemically diverse ribozymes seem to have been lost in Nature, but may be reconstructed in the laboratory by in vitro selection. Here, we report a methyltransferase ribozyme that catalyses the site-specific installation of 1-methyladenosine (m1A) in a substrate RNA, utilizing O6-methylguanine (m6G) as a small-molecule cofactor. The ribozyme shows a broad RNA sequence scope, as exemplified by site-specific adenosine methylation in tRNAs. This finding provides fundamental insights into RNA’s catalytic abilities, serves a synthetic tool to install m1A in RNA, and may pave the way to in vitro evolution of other methyltransferase and demethylase ribozymes.
More than 70 different methylated nucleotides play important functional roles in present-day RNA.4,5 Mostly known for shaping the structures and tuning the functions of non-coding rRNA, tRNA, and snRNA, some modifications also influence gene expression programmes by regulating the fate and function of mRNA.6–8 The majority of methylated nucleotides currently known in RNA are installed by post-synthetic (i.e., post- or co-transcriptional) methylation by protein enzymes that use S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) as the universal methyl group donor. Methyl transferases are considered ancient enzymes, and methylated nucleotides are also discussed as molecular fossils of the early Earth produced by prebiotic methylating agents.9,10 In an era preceding modern life based on DNA and proteins, RNA was thought to function both as primary genetic material and as catalyst.11 Ribozymes have been discovered in Nature, where they catalyse RNA cleavage and ligation reactions, mostly in the context of RNA splicing and retrotransposition.12–14 In vitro selected ribozymes have been evolved as RNA ligases and replicases that are able to reproduce themselves or their ancestors, and are able to produce functional RNAs, including ribozymes and aptamers.15–17 Self-alkylating ribozymes have been described using reactive iodo- or chloroacetyl derivatives,18–20 or electrophilic epoxides,21 but the design of earlier in vitro selection strategies prevented the emergence of catalysts capable of transferring a one-carbon unit. Thus, ribozymes that catalyse RNA methylation have so far remained elusive. This lack of methyltransferase ribozymes seems surprising, since numerous natural aptamers are known to specifically bind nucleotide-derived metabolites associated with methyl group transfer or one-carbon metabolism, including SAM, methylene tetrahydrofolate (THF), and adenosylcobalamin (vitamin B12)).22,23 These aptamers are found as components of riboswitches that regulate the expression of associated genes, often involved in the biosynthesis of the respective metabolite or its transport across membranes.24 Interestingly, six different classes of SAM-binding riboswitches accommodate the ligand with its reactive methyl group in various different conformations.25,26 However, these RNAs apparently avoid self-methylation.
Therefore, it remained an open question if RNA can catalyse site-specific methylation reactions to produce defined methylated RNA products. Previously, in vitro selection efforts have identified SAM-binding aptamers, but methyl transfer reactions were not observed, likely because the aptamer established a binding site for the adenine moiety of the cofactor but did not specifically interact with the 5’ substituent.27
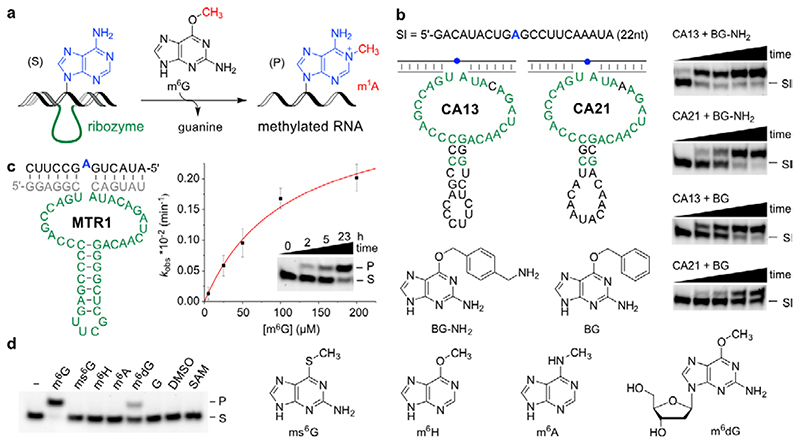
We speculated that alternative methyl group donors other than SAM or methylene-THF could be substrates for RNA-catalysed RNA methylation, and took inspiration from an enzyme class that is responsible for repair of alkylated DNA, i.e. catalyses demethylation of DNA. The O 6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) releases unmodified guanine, accompanied with irreversible methylation of the protein.28 In analogy, we hypothesized that RNA-catalysed methyl transfer would result in methylated RNA upon release of guanine. Using in vitro selection, we identified a ribozyme that utilizes O 6-methylguanine (m6G) as a small molecule methyl group donor and catalyses site-specific methylation of adenosine at position N1, resulting in position-specific installation of 1-methyladenosine (m1A) in the target RNA (Fig. 1a).
Fig. 1. Methyltransferase ribozyme-catalysed synthesis of m1A in RNA using m6G as methyl group donor.
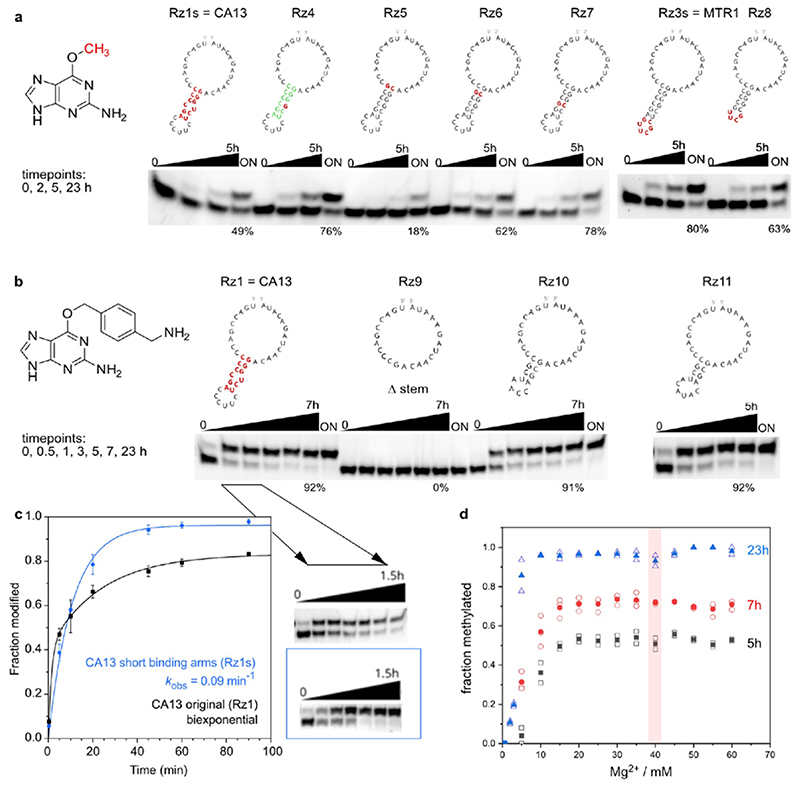
a. Reaction scheme with intermolecular hybridization of ribozyme to target RNA. b. Sequences and predicted secondary structure of CA13 and CA21 ribozymes identified by in vitro selection, and their trans-activity for modification of a 22-nt RNA (Sl) with BG-NH2 or BG, analysed by 20% denaturing PAGE (100 µM guanine derivative, 40 mM MgCl2, pH 7.5, 37°C, timepoints 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 5 h). Representative images of three independent experiments with similar results. c. Methyltransferase ribozyme MTR1 with stabilized stem-loop shows efficient methyl group transfer. The insert shows a gel image of a 3'-fluorescein-labeled 13-mer RNA substrate (S) reacted with MTR1 and m6G (100 µM). k obs was determined with a 3'-fluorescein-labeled 17-mer RNA at five m6G concentrations ranging from 5–200 µM. The red line represents a curve fit to k obs = k max[m6G]/(k m,app+[m6G]). Individual data points (white, n = 3), mean ± s.e.m. (black). d. Structures of m6G analogues tested. Gel image shows that product formation only occurs with m6G, and to a minor extent with m6dG (24 h reaction time, 25°C, with 100 µM m6G or analog). Representative image from two independent experiments. DMSO = dimethyl sulfoxide, G = guanine, SAM = S-adenosylmethionine.
Search for methyltransferase ribozymes
In vitro selection is a powerful method to enrich functional RNAs by repeated cycles of selection and amplification from a random RNA library. We used a structured RNA pool containing 40 random nucleotides that was designed according to our previously used strategy to direct RNA-catalysed labeling of a specific adenosine in a target RNA.29,30 RNA methylation would most likely occur at an O or N nucleobase heteroatom, on the 2'-OH group or on the phosphate backbone. In either case, attachment of a single methyl group would hardly enable physical separation of the active sequences based on size or charge.
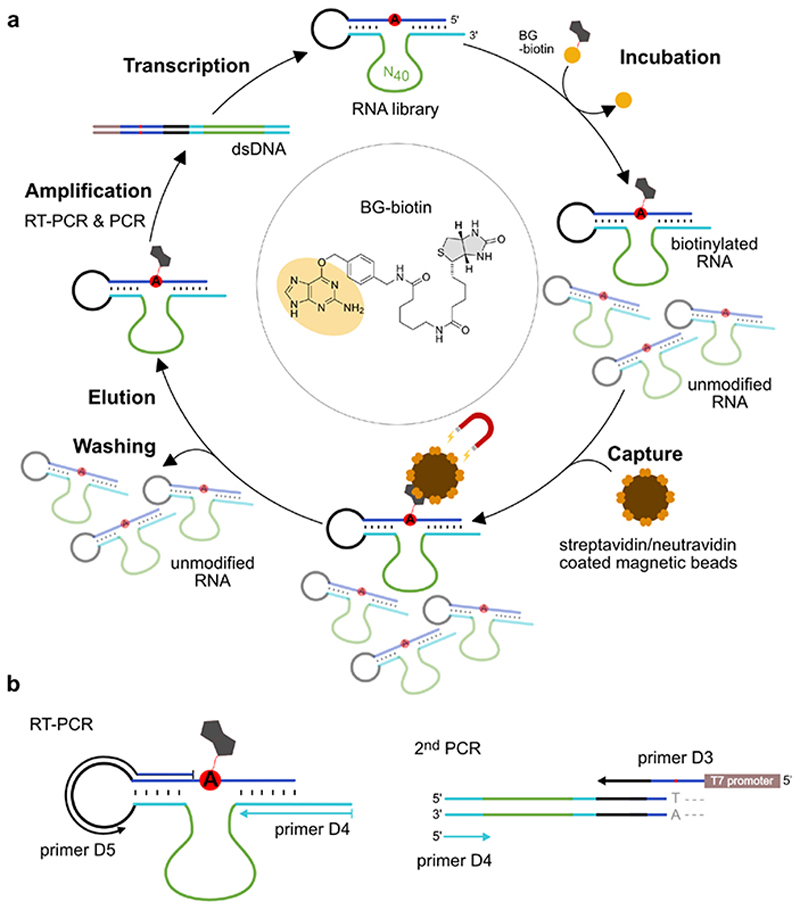
Therefore, we searched for alkylating ribozymes that catalysed the transfer of a biotin group attached via a benzyl linker to the target RNA, and speculated that resulting ribozymes could later be engineered to enable RNA methylation. After incubation with biotinylated O 6-benzylguanine, the biotinylated products were separated via streptavidin/neutravidin affinity purification on magnetic beads, and the enriched candidates were amplified by reverse transcription and PCR. Then, in vitro transcription with T7 RNA polymerase provided the enriched library that was used in the next round of selection (the in vitro selection scheme is shown in Extended Data Fig. 1). Two alkyltransferase ribozyme candidates were identified after 11 rounds of in vitro selection, named CA13 and CA21 that contained a predicted internal hairpin structure with a partially complementary stem, and showed high sequence similarity in the flanking regions (Fig. 1b). Both ribozymes were able to catalyse alkylation of the target RNA in a bimolecular setup (referred to as trans activity), in which the ribozyme and the target RNA interacted via Watson-Crick base pairing. Moreover, the biotin moiety was not essential: fast and efficient alkylation of the target RNA was achieved with O 6-(4-aminomethylbenzyl)guanine (BG-NH2) as well as with O 6-benzylguanine (BG) (Fig. 1b). Inspired by the natural or engineered promiscuity of protein methyltransferases that tolerate SAM cofactors with extended alkyl groups,31,32 we examined the opposite direction for the in vitro selected ribozyme and asked if the transferred alkyl group could be a simple methyl group, i.e. if O 6-methylguanine could serve as cofactor for the new ribozyme. The target RNA (and the Watson-Crick binding arms of the ribozyme) were shortened to simplify the analysis of the reaction product. The predicted stem in the ribozyme core was stabilized and an extrastable UUCG tetraloop was introduced. The engineered ribozyme (called MTR1, Fig. 1c) used a 13-nt or a 17-nt RNA as target and m6G as cofactor to generate methylated RNA products in >80-90% yield after 23 h incubation at 37°C, pH 7.5. The reaction rate was dependent on m6G concentration with an apparent K m of ca 100 µM. The presence of the stem-loop in the core of MTR1 was confirmed by compensatory mutations of individual base-pairs, which retained catalytic activity. The stem was shortened with only slightly reduced activity while deletion of the stem resulted in inactive ribozymes (Extended Data Fig. 2). RNA structure probing (by DMS and SHAPE chemistry) also confirmed the overall architecture of the ribozyme (Extended Data Fig. 3).
The RNA-catalysed reaction was strictly dependent on m6G as demonstrated by control experiments in which m6G was replaced by DMSO or guanine (Fig. 1d). Residual activity was observed with O 6-methyl-2'-deoxyguanosine (m6dG), while S 6-methylthioguanine (ms6G), O6- methylhypoxanthin (m6H), N 6-methyladenine (m6A), and SAM could not serve as methyl group donors under the conditions tested. Surprisingly, the methylated product (P) was easily separable from the unmodified RNA (S) by denaturing PAGE (Fig. 1c,d) and anion exchange HPLC (Fig 2a). Addition of a single methyl group to the target RNA was confirmed by high resolution electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry (HR-ESI-MS, Fig. 2b).
Fig. 2. Reaction product characterization.
a. Anion exchange HPLC analysis of MTR1-catalysed reaction of 13-mer RNA substrate S (5'-AUACUGAGCCUUC-3') with m6G at 25°C for 23 h; 10 μM RNA (S), 12 μM MTR1, 100 μM m6G, 40 mM MgCl2, pH 7.5. The ribozyme is labeled with Rz, the substrate RNA S and the reaction product P. HPLC traces of reference oligonucleotide S (= ref A), and the corresponding m6A and m1A-modified synthetic RNAs are shown for comparison. m1A-RNA elutes earlier, while A and m6A-RNAs cannot be distinguished. b. HR-ESI-MS of S* (top) and P* (bottom). Shown are the measured m/z spectra, the deconvoluted mass spectrum in red, and the simulated isotope pattern in grey (* denotes 3'-aminohexyl RNA) c. RNase T1 digestion and alkaline hydrolysis of reaction product P in comparison to S, m6A and m1A references demonstrate that P contains m1A. d. Atomic mutagenesis of RNA substrate. Individual data points (n = 6 for A, n = 2 for all others) and average (grey bar) shown. white: 17 nt RNAs, blue: 13 nt RNAs. Gel images and detailed description in Extended Data Fig. 4. e. Incubation under Dimroth rearrangement conditions (pH 10, 65°C, 1 h) produced m6A from m1A, as seen in the + lanes of m1A reference and MTR1 reaction product P.
Identification of the methylation product
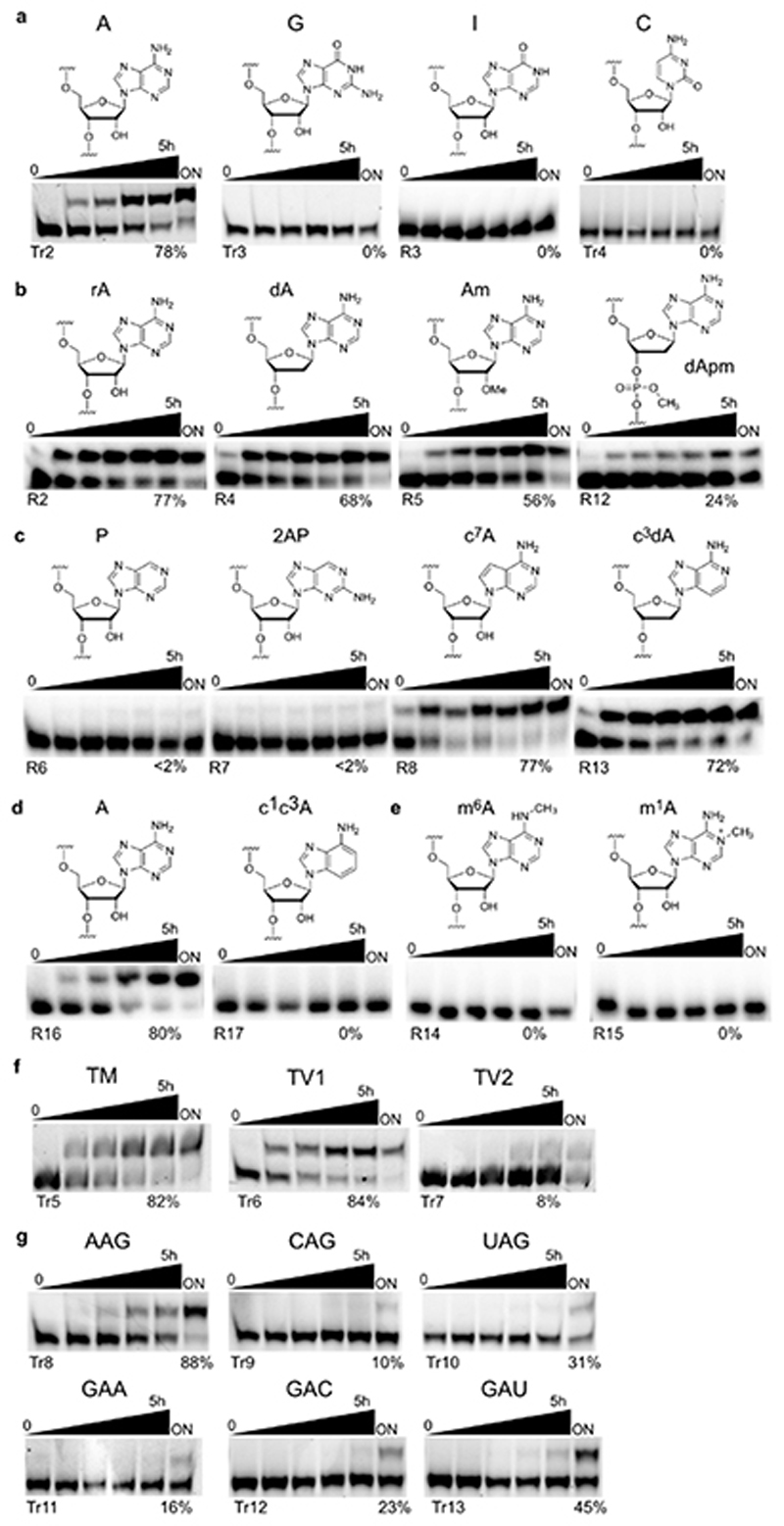
The next goal was to identify the chemical constitution of the methylated RNA product. The first indication that the reaction happened at the bulged adenosine was obtained with mutated target RNAs, since RNA substrates with adenosine changed to guanosine, inosine or cytidine were not modified (Extended Data Fig. 4). Adenosine has several possible nucleophilic positions, and several isomeric methylated adenosines are known as native RNA modifications, including N 6-methyladenosine (m6A), 1-methyladenosine (m1A), and 2'-O-methyladenosine (Am). Other possible methylation sites are N7, N3 and the non-bridging oxygen atoms of the phosphodiester backbone. Atomic mutagenesis with various modified adenosines in the target RNA revealed the substrate requirements (Fig. 2d). These reactions were performed with BG-NH2, since the larger electrophoretic shift upon transfer of a 4-aminomethylbenzyl group simplified the analysis. RNA oligonucleotides with 2'-deoxyadenosine (dA) or 2'-O-methyladenosine (Am), as well as 3'-methylphosphate (P-OCH3) and 3'-methylphosphonate (P-CH3) linkages were tolerated, and disclosed that the reaction occurred on the nucleobase. This conclusion was further corroborated by alkaline hydrolysis and RNase T1 digestion of the isolated product P, which revealed the presence of the cleavage product at the bulged adenosine and up-shifted digestion products beyond this position (Fig. 2c), while alkylation at the 2'-OH would have caused a missing band in the hydrolysis pattern. Instead, an extra hydrolysis band was observed close to the adenosine position, which could not be explained by counting the number of nucleotides. To solve this puzzle, additional hints were collected from the analysis of ribozyme-catalysed alkylation of RNAs containing different nucleobase analogues (Fig. 2d, Extended Data Fig. 4).
The observation that 2-aminopurine (2AP) and purine (P) could not be efficiently alkylated suggested that the N 6-amino group is essential, in contrast to N7 and N3, both of which could be removed individually without compromising the alkylation efficiency. In contrast, the RNA with N1,N3-dideaza-adenosine was not alkylated. These results narrowed down the possible reaction sites to N 6 or N1 of adenosine. This conclusion was supported by the observation that synthetic RNAs that contained either m6A or m1A could not be further alkylated by the ribozyme (Fig. 2d). The retarded electrophoretic mobility of m1A-RNA compared to m6A-RNA is attributed to the positive charge on the m1A nucleobase. Indeed, m6A-modified and unmodified 13-nt RNA could not be separated by PAGE or anion exchange HPLC, in contrast to the reaction product, which was observed as a separated band/peak in both assays, suggesting that the MTR1 reaction product indeed contained m1A. The presence of m1A also explained the extra band in the alkaline hydrolysis lane: m1A is susceptible to Dimroth rearrangement under alkaline conditions, resulting in partial formation of m6A and an additional hydrolysis band with distinctly different migration. Comparison of the alkaline hydrolysis patterns of the MTR1 product with authentic reference RNAs containing m6A and m1A confirmed this conclusion (Fig. 2c). Furthermore, Dimroth rearrangement was induced by incubation of the MTR1 reaction product at pH 10, 65°C for 1 h, resulting in >60% conversion to m6A without concomitant hydrolysis of the RNA backbone (Fig. 2e). In combination, these results firmly establish m1A as the sole product of MTR1-catalysed RNA methylation using m6G as methyl group donor.
RNA-catalysed tRNA methylation
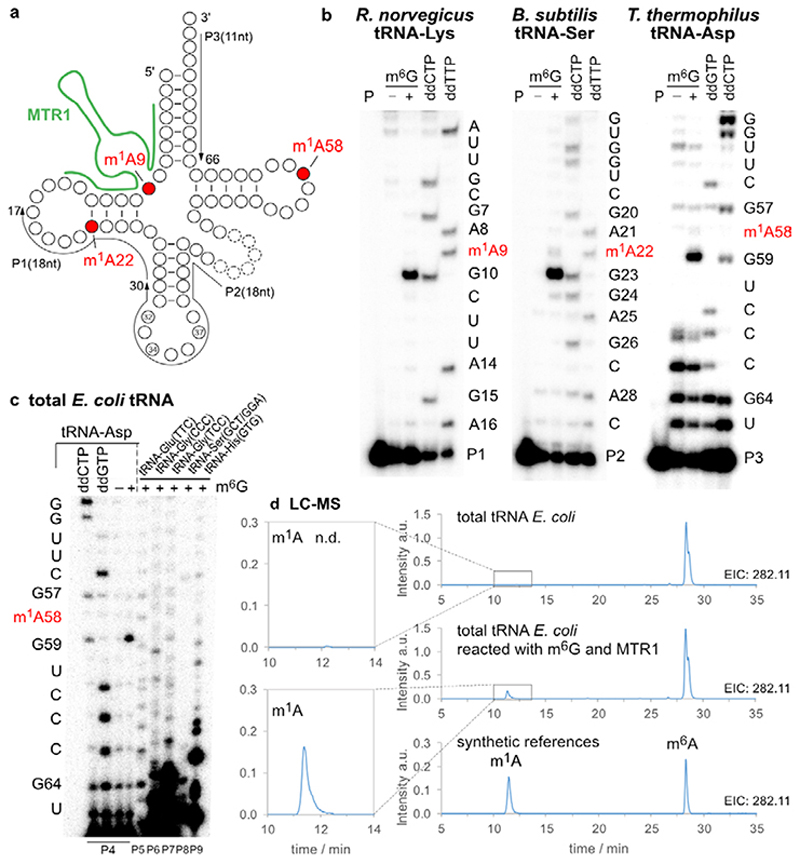
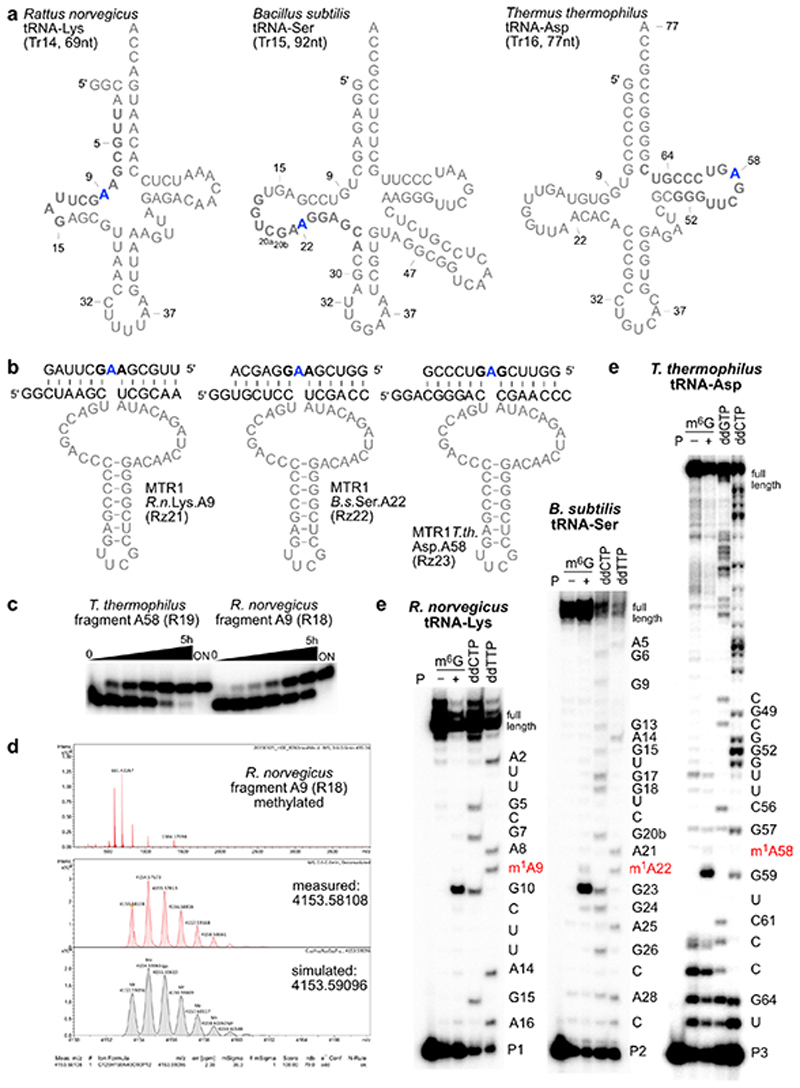
The methylated nucleoside m1A is a native tRNA modification that is found in all domains of life at positions 9, 14, 22, 57/58, and is installed by two distinct families of methyltransferases that use SAM as cofactor (SPOUT family and Rossman-fold MTases).33 We asked if the methyltransferase ribozyme MTR1 could install m1A on in vitro transcribed tRNA. The prerequisite for such an application is a general RNA sequence scope of the ribozyme. Therefore, we first examined the ability of MTR1 to catalyse alkylation of transition and transversion mutants of the parent target RNA, and checked if the flanking guanosines could also be mutated (Extended data Fig. 4). All tested RNA substrates were alkylated, although with varying efficiency between 10 and 90%, suggesting GAG and AAG as preferred methylation sites. Next, we chose three natural tRNA sequences that contain m1A flanked by purines and synthesized 13-nt tRNA fragments enclosing the m1A site. Utilizing MTR1 derivatives with binding arms complementary to these tRNA fragments, the corresponding methylated RNAs were obtained upon incubation with m6G (Extended Data Fig. 5). These results encouraged us to test MTR1 on full-length tRNAs which were prepared by in vitro transcription. We chose to target m1A at position 9 of Rattus norvegicus tRNALys, m1A at position 22 of Bacillus subtilis tRNASer, and m1A at position 58 of Thermus thermophilus tRNAAsp (Extended Data Fig. 5). The synthetic tRNAs were annealed with the corresponding ribozymes, and the incubation with m6G was carried out for 22 h. All three synthetic tRNAs were successfully methylated by the corresponding MTR1 ribozymes (Fig. 3b), as revealed by the strong abort bands in primer extension experiments, in which m1A blocks the reverse transcriptase (RT).
Fig. 3. MTR1-catalysed methylation of tRNA.
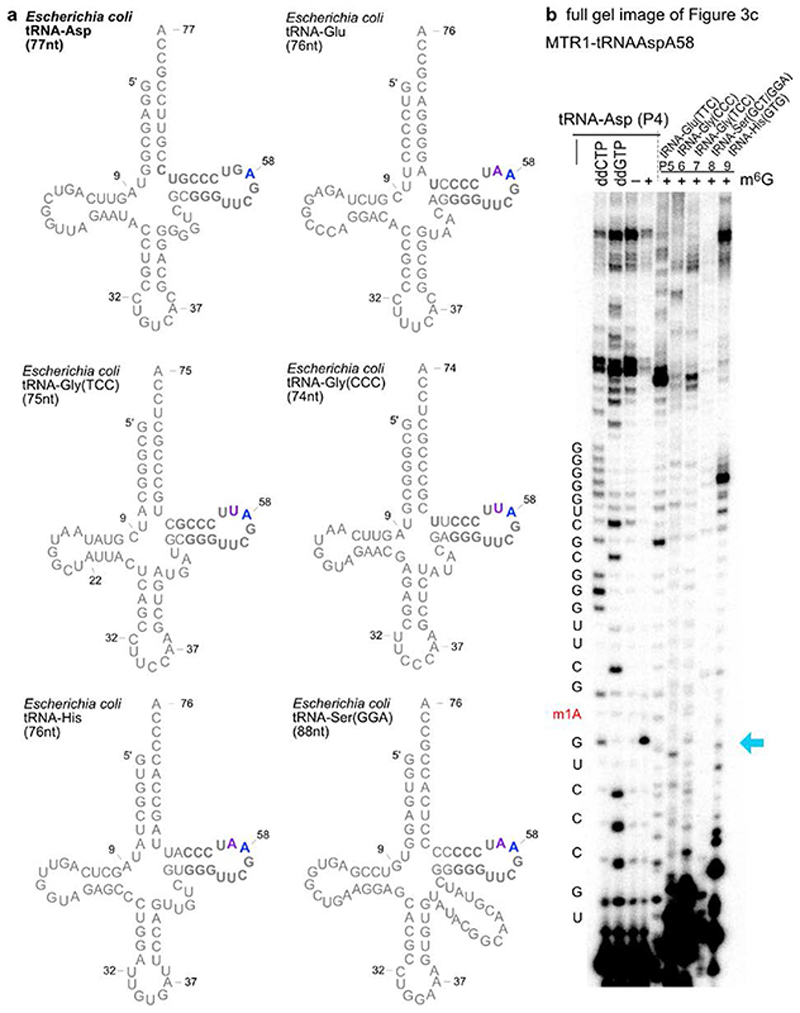
a. Native m1A sites at positions 9, 22 and 58 are shown in a generic tRNA scaffold. b. In vitro transcribed tRNAs were incubated with the corresponding complementary ribozymes in presence (+) or absence (−) of m6G. The installation of m1A was probed by primer extension experiments. Primer binding sites are indicated on the tRNA scheme. Sequencing reactions were run in parallel to assign the position of the abort bands. c. Total E.coli tRNA was incubated with a tRNAAsp-A58-specific MTR1, and specific methylation of tRNAAsp was probed by primer extension with six tRNA-specific primers P4-P9. Sequences of tRNAs are given in Extended Data Fig. 6. d. LC-MS analysis of MTR1-catalyzed methylation of total E.coli tRNA. Extracted ion chromatograms (EIC, detecting MH+ (m/z 282.11±0.05), corresponding to methylated adenosines) are shown for digested tRNAs (before and after treatment with MTR1), and for synthetic m1A and m6A nucleosides.
Successful methylation of in vitro transcribed tRNA stimulated the test of MTR1 for specific methylation of one target tRNA in total E. coli tRNA, since m1A has not been found as natural modification in E.coli tRNAs.34,35 After treatment with MTR1 and m6G, primer extension assays with six different tRNA-specific primers confirmed methylation of the target tRNAAsp at A58, while other tRNAs with highly similar TΨC-stem-loop sequences (tRNAGlu, two tRNAsGly, tRNASer, and tRNAHis) were not methylated (Fig. 3c, Extended Data Fig. 6). Additionally, m1A was unequivocally detected by LC-MS in the total tRNA nucleosides of MTR1-treated total E.coli tRNA, but not in native E.coli tRNA (Fig. 3d).
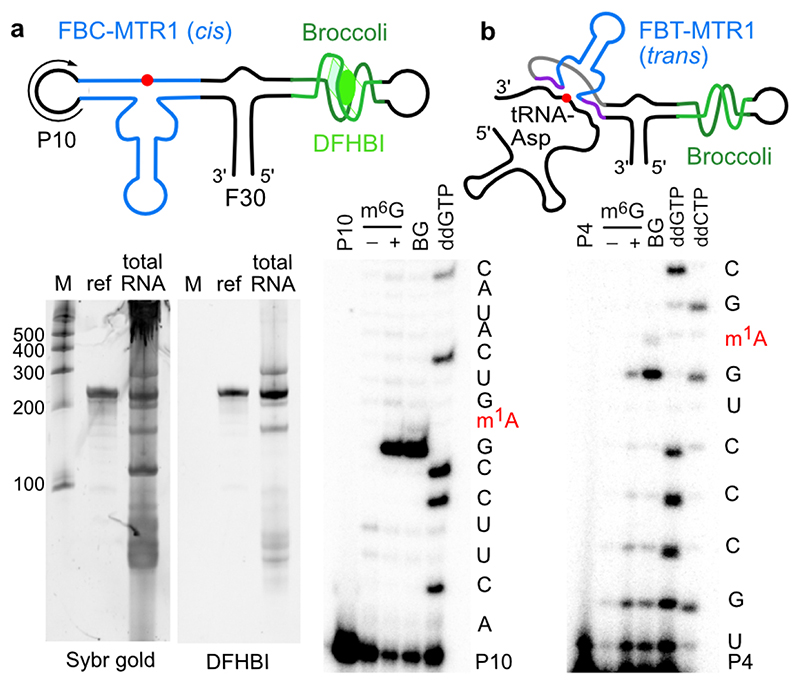
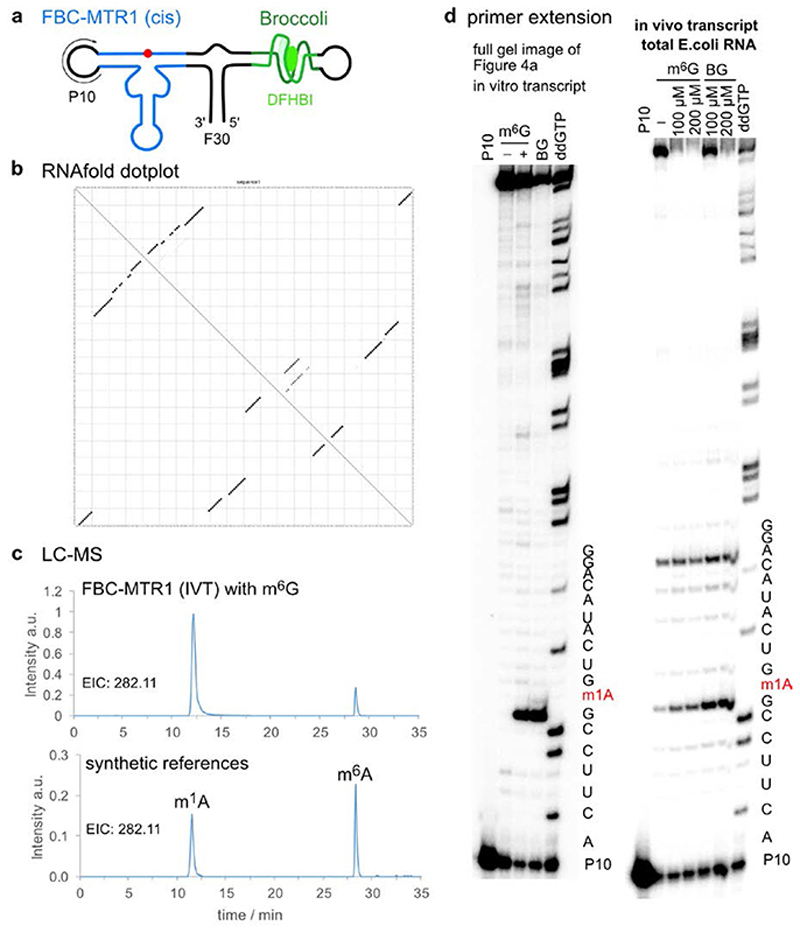
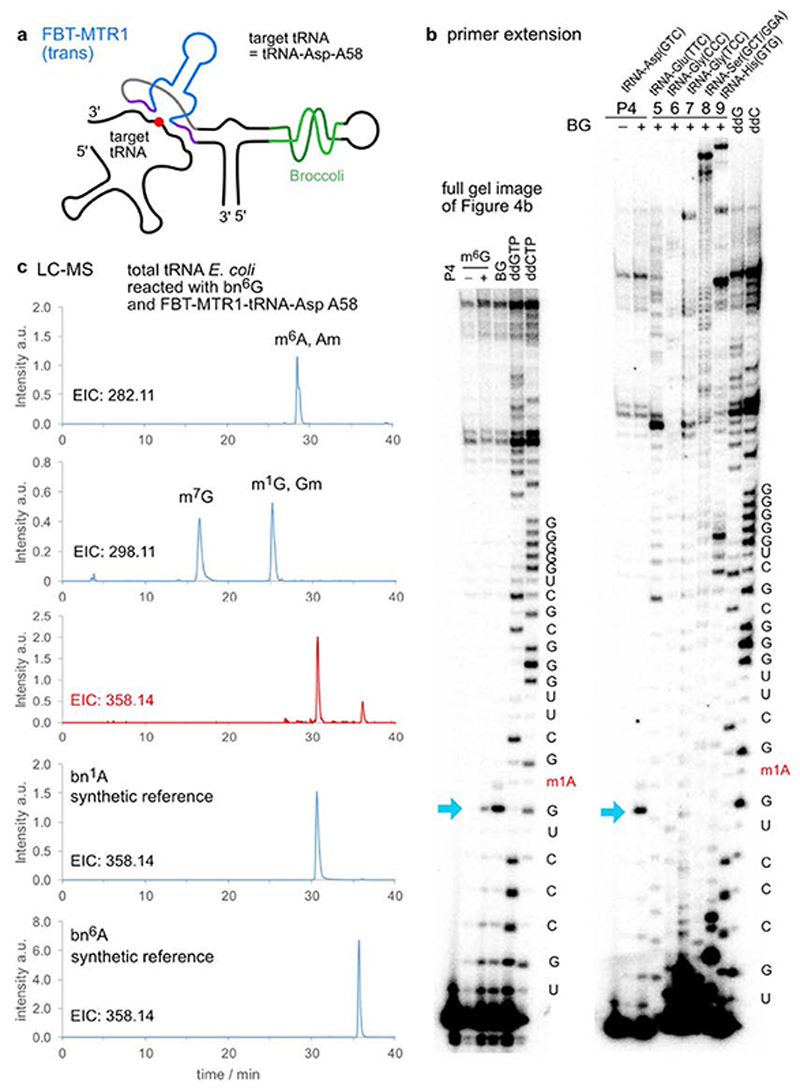
To investigate the potential for future application of MTR1 in vivo, we designed plasmids for expression of MTR1 in E. coli. One construct contained the cis-active MTR1 ribozyme in the stabilizing F30 scaffold together with the fluorogenic aptamer Broccoli,36 which was used to confirm ribozyme expression by staining with DFHBI (Fig. 4a). Successful methylation was shown by primer extension and LC-MS after incubation of isolated total E.coli RNA with m6G (Extended Data Fig. 7). These results confirm the correct folding of the ribozyme in the Broccoli-F30 construct. Direct in situ methylation was limited by the availability of m6G and the required Mg2+ level in E.coli. A second plasmid contained a trans-reactive F30-Broccoli-MTR1 construct that was targeted against E.coli tRNAAsp and the corresponding transcript was tested on total E.coli tRNA (Fig. 4b). Primer extension assays with the E. coli tRNA-specific primers mentioned above confirmed that the specificity of the MTR1 ribozyme was maintained when incorporated into the F30 scaffold (Extended Data Fig. 8). These results establish the MTR1 ribozyme as a promising tool for installation of m1A at a specific target RNA, and may thereby aid in the validation of predicted and controversially discussed m1A sites in eukaryotic mRNAs,37,38 and enable studying of m1A biology (readers and erasers) in RNAs for which corresponding methyltransferase enzymes have not yet been identified.39,40 Moreover, we notice that these ribozymes could serve as highly promising tools for site-specific labeling of RNA, using fluorescently labeled benzylguanine derivatives as cofactors for RNA-catalysed RNA alkylation.
Fig. 4. Plasmid-encoded cis- and trans-active MTR1.
a. F30-Broccoli-cis (FBC)-MTR1 (modification site indicated as red dot) is transcribed in E.coli. Total RNA isolated 1h after IPTG induction, analysed on PAGE next to an in vitro transcribed reference and a size marker, and stained by DFHBI (10% denaturing PAGE, 20 μM DFHBI) and Sybr gold. Both the in vitro and in vivo transcripts contain an active MTR1 ribozyme, as revealed by the primer extension stops after incubation with m6G or BG (here with in vitro transcript and primer P10, data with in vivo transcript shown in Extended Data Fig. 7). b. F30-Broccoli-trans (FBT)- MTR1 with binding arms specific for hybridization to E.coli tRNAAsp. The activity was reduced with m6G but retained with BG. Formation of 1-benzyladenosine was confirmed by LC-MS and specifically detected only in tRNAAsp (Extended Data Fig. 8).
Conclusions
In summary, we report the first ribozyme with methyltransferase activity for the site-specific methylation of adenosine. Surprisingly, the methyl group donor for the MTR1 methyltransferase ribozyme is a simple methylated nucleobase. Conceptually, the ribozyme mimics RNA-guided RNA methylation by RNA-protein complexes, such as CD box RNPs involved in 2'-O-methylation of ribosomal RNA.41 Here, the ribozyme combines both functions - guide and enzyme - in a single molecule of RNA. The cofactor binding site in the catalytic core of the in vitro selected ribozyme may imitate the binding site of guanine / m6G in purine riboswitches.42,43 Thus, it is conceivable that methyltransferase ribozymes could be evolved from riboswitch RNAs that are known to bind modern methyltransferase cofactors, including SAM and THF derivatives. Given the activity of MTR1 with m6dG, it seems likely that an analogous ribozyme activity can be evolved to catalyse removal of a methyl group from RNA (or DNA), thus mimicking repair enzymes of alkylation damage response pathways. Such imaginary RNA repair ribozymes could have been beneficial catalysts in an RNA world, aiding the evolution of RNA replicases by releasing mutagenic methylation blocks that originated from environmental damage and interfered with faithful Watson-Crick base pairing. Our work also demonstrated that MTR1 enables site-specific synthesis of m1A in defined RNA targets. Thus, the reported findings have implications for scrutinizing the evolution of catalytic RNA as well as studying fundamental aspects of RNA methylation in contemporary biology.
Methods
RNA synthesis
RNA oligonucleotides were prepared by solid-phase synthesis using phosphoramidite chemistry (2'-O-TOM-protected) on controlled-pore glass solid supports.44 RNA/DNA sequences are given in Supplementary Table 1. Modified phosphoramidites for atomic mutagenesis and synthesis of reference oligonucleotides were purchased or prepared in house, following published procedures.45–47 RNA oligonucleotides were deprotected with ammonia/methyl amine (AMA), followed by 1M tetrabutylammonium fluoride in THF, desalted and purified by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Mild deprotection conditions were used for m1A RNA (3.5 M NH3 in MeOH, at 25°C for 72 h) to avoid Dimroth rearrangement during deprotection, and for methylphosphate-modified RNA (0.05 M K2CO3 in MeOH at 25°C for 7 h) to avoid loss of the phosphotriester. Quality of RNAs (purity and identity) was analysed by anion exchange HPLC (Dionex DNAPac PA200, 2x250 mm, at 60 °C. Solvent A: 25 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 6 M Urea. Solvent B: 25 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 6 M Urea, 0.5 M NaClO4. Gradient: linear, 0–40% solvent B, 4% solvent B per 1 CV) and HR-ESI-MS (micrOTOF-Q III, negative mode, direct injection). Measured and calculated masses are listed in Supplementary Table 2.
Unmodified RNA substrates and tRNAs were prepared by in vitro transcription with T7 RNA polymerase (prepared according to ref48 with minor modifications) from synthetic DNA templates (purchased from Microsynth), following standard procedures with 4 mM NTPs and 30 mM MgCl2.29
In vitro selection
The DNA template for in vitro transcription of the initial RNA library was assembled from two DNA oligonucleotides (D2+D3, N40: A:C:G:T=1:1:1:1) by overlap extension using Klenow fragment with the sequence of the connecting loop acting as the overlapping region. The dsDNA template (450 pmol) was used for in vitro transcription with T7 RNA polymerase in a final volume of 450 μl. For the first selection round, 3.3 nmol RNA pool (containing 10% 3'-fluorescently labeled RNA, obtained by sodium periodate oxidation and reaction with Lucifer yellow carbohydrazide, according to ref25) were folded in selection buffer (120 mM KCl, 5 mM NaCl, 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5; 3 minutes at 95 °C, then 10 minutes at 25 °C). Biotinylated O 6-benzylguanine (SNAP-biotin, New England Biolabs) and MgCl2 were added (100 μM and 40 mM final concentrations, respectively) to a final reaction volume of 60 μL and the reaction mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 16 h. In subsequent rounds, the incubation time, the amount of RNA, and the concentration of the biotinylated substrate were reduced in order to increase the selection pressure. After precipitation by ethanol, the biotinylated RNA were captured using either neutravidin- or streptavidin-coated magnetic beads (Dynabeads, Thermo Fisher Scientific, ca 1 nmol RNA per mg of beads), eluted with formamide, and amplified by RT-PCR, following established procedures.29,30 In vitro transcription was performed (total volume of 100 μL), followed by PAGE purification to prepare the enriched RNA library for the next selection round. After 11 rounds of selection, the library was cloned (TOPO-TA cloning), and ribozymes generated from randomly picked colonies were examined for catalytic activity (by streptavidin gel shift assay on native PAGE) and sequenced. Three sequence families were identified (Supplementary Data Table 3), two of which retained catalytic activity in trans (i.e. in an intermolecular setup upon removing the connecting loop between binding arm and substrate sequence), named CA13 and CA21.
Kinetic assays of RNA-catalysed RNA methylation reactions
Single-turnover assays were performed as described previously with a 10-fold excess of ribozyme over the target RNA.29 Briefly, 10 pmol (32P- or fluorescein-labeled) RNA target were mixed with 100 pmol of the corresponding ribozyme in 10 μL of selection buffer (120 mM KCl, 5 mM NaCl, 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5) including 100 μM of substrate (BG-NH2, BG or m6G) and 40 mM MgCl2. To ensure proper folding and formation of the ribozyme-substrate RNA complex, an annealing step (3 min at 95°C, 10 min at 25 °C) was performed prior to addition of MgCl2 and the small molecule substrate. The mixture was incubated at 37 °C and 1 μL aliquots were taken at desired time points and quenched immediately by adding 4 μL of stop solution. Half of each time point sample was analysed by PAGE (20% polyacrylamide), and band intensities were quantified by Phosphorimaging or by Fluorescence imaging using blue epi illumination and 530/28 nm emission filter. The yield versus time data were fit to (fraction reacted) = Y(1 – e−kt), where k = k obs and Y= final yield using KaleidaGraph (4.3) or Origin (2019). All kinetic assays were carried out as three independent replicates, and representative gel images are shown. Source data are given in the supplementary information.
Analysis of the RNA methylation products
From a 20 μL methylation reaction with 1 nmol target RNA, 1.2 nmol ribozyme, 100 μM m6G and 40 mM MgCl2 at pH 7.5 (120 mM KCl, 5 mM NaCl, 50 mM HEPES) for 21 h at 37°C, the methylated RNA product was isolated by PAGE, and subjected to HR-ESI-MS (Bruker microOTOF-Q III, direct injection), RNase T1 digestion (150 IPS of 5'-32P-RNA were digested with 0.5 U RNase T1 in 5 μL 50 mM Tris (pH 7.5) for 30 sec at 37 °C), and alkaline hydrolysis (250 IPS of 5'-32P-RNA in 5 μL 25 mM NaOH were incubated at 95°C for 5 min). Dimroth rearrangement was examined in a volume of 5 μL with 90 IPS of 5'-32P-RNA in 25 mM Na2CO3 buffer (pH 10) with 1 mM EDTA at 65 °C or 1 h. After quenching with high dye gel loading buffer, the samples were resolved on denaturing PAGE and visualized by autoradiography.
tRNA methylation and primer extension assays
In vitro transcribed tRNA (10 pmol) was annealed with the corresponding ribozyme (100 pmol) and optional disruptor oligo (25 pmol), and then incubated in a final volume of 10 μL of 1x selection buffer (120 mM KCl, 5 mM NaCl, 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5) including 100 μM of m6G and 40 mM MgCl2, at 25°C for 22 h. Disruptor oligos were used for B. subtilis tRNA-Ser and R. norvegicus tRNA-Lys. The unmodified tRNA reference samples were prepared analogously, but without addition of m6G. Primer extension stop experiments were carried out with 4 pmol of the methylated or the unmodified tRNA, and the appropriate 5'-32P-labeled primer (100 IPS, ca 4 pmol). After annealing in 5 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) and 0.1 mM EDTA, the sample was combined with 5 mM DTT, 0.5 mM of each dNTP and 50 U of SuperScript III RT (ThermoFisher Scientific) in 1x first strand buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.3), 75 mM KCl, 3 mM MgCl2) to yield a final reaction volume of 10 μL. After incubation at 55°C for 1 h, the reaction was stopped by adding 1 μL of 2 N NaOH and incubation at 95 °C for 5 min. RT primer extension on total E. coli tRNA was carried out for 105 min at 42 °C using 1 μg total E. coli tRNA, followed by workup as above. The primer extension products were recovered by ethanol precipitation, dissolved in high dye solution and resolved on 15% or 20% denaturing PAGE. Sequencing ladders were prepared in analogy with suitable dNTP/ddNTP mixtures (0.5 mM ddNTP, 0.05 mM corresponding dNTP, 0.5 mM each of the other three dNTPs), and analyzed in parallel.
RNA structure probing by DMS and SHAPE
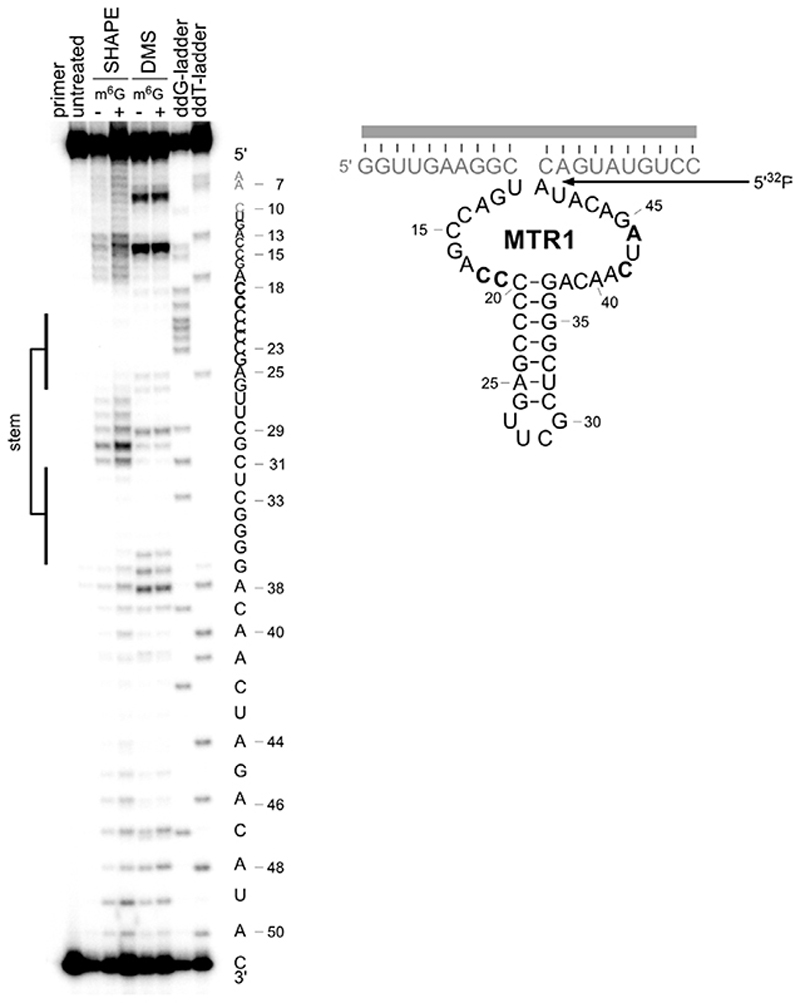
MTR1 (Rz3) hybridized to unreactive 17-nt RNA (R6) in 10 μL selection buffer with MgCl2 (40 mM) was treated with DMS or 1M7 in absence or presence of m6G (100 μM). For DMS probing, 0.5 μL DMS solution (5% in EtOH) was added and incubated for 1 h at 25 °C. The reaction was quenched by the addition of 10 μL of 1 M 2-mercaptoethanol and 1.5 M NaCl. SHAPE probing was performed by addition of 1 μL 1M7 solution (130 mM in dry DMSO; synthesized according to ref49) and 50 min incubation at 37 °C. After ethanol precipitation, the modification pattern was analyzed by primer extension as described above, using 5'-32P-labeled primer (D4).
Construction of F30-Broccoli-MTR1-containing plasmids and expression in E.coli
The F30-Broccoli-MTR1 constructs were prepared by overlap extension of synthetic DNA oligonucleotides, amplified by PCR and inserted into a pET14 vector using restriction enzymes BglII and BlpI. The sequence of the insert and successful ligation into the plasmid was confirmed by Sanger Sequencing. The F30-Broccoli-MTR1 plasmid was transformed into E. coli BL21(DE3) cells, and expression was induced by addition of 1 mM IPTG. After 1 h incubation at 37°C, total E.coli RNA was extracted as previously reported.30 A fraction (0.5 μg) was analysed by 10% denaturing PAGE, that was stained with a solution of 20 μM DFHBI in 100 mM KCl, 5 mM Mg2+, 40 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, for 15 min, and imaged on a ChemiDoc imager. Afterwards the gel was stained with Sybr gold and imaged again to visualize all RNA and the size marker.
For testing the activity of the F30-Broccoli-MTR1 constructs, 200 ng of total cellular RNA was incubated in vitro at 37 °C for 4 h in 10 μL of selection buffer (120 mM KCl, 5 mM NaCl, 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5) including 100 μM m6G or BG and 40 mM MgCl2. Primer extension experiments were then performed as described above for probing of the modification site.
LC-MS analysis of MTR1-catalyzed methylation
For LC-MS analysis, 30 μg total E. coli tRNA were mixed with 5.4 μg (300 pmol) of tRNA-Asp-A58-specific ribozyme in 10 μL of selection buffer (120 mM KCl, 5 mM NaCl, 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5) including 100 μM m6G and 40 mM MgCl2. An annealing step (2 min at 95°C, 10 min at 25 °C) was performed prior to addition of m6G and MgCl2. After 22 h incubation at 25 °C the RNA was digested for 18 h at 37°C using 7.5 U bacterial alkaline phosphatase and 2.0 U snake venom phosphodiesterase in 40 mM Tris.HCl, pH 7.5 in the presence of 20 mM MgCl2. The unmodified reference was generated by digestion of 30 μg unmodified E. coli tRNA. After extracting the sample twice with chloroform, the aqueous layer was concentrated, and an aliquot was analysed by LC-MS, using an RP-18 column (Synergi, 4 μm Fusion-RP C18 80 Å, 250 x 2 mm; Phenomenex) at 25°C with aqueous mobile phase A (5 mM NH4OAc, pH 5.3) and organic mobile phase B (100% acetonitrile). The flow rate was 0.2 mL/min with a gradient of 0-5% B in 15 min, followed by 5-70% B in 30 min. The micrOTOF-Q III with an ESI ion source was operated in positive ion mode, with capillary voltage of 4.5 kV, end plate offset of 500 V, nitrogen nebulizer pressure 1.4 bar, dry gas flow 9 L/min, and dry temperature 200 °C. Data were analyzed with Data Analysis software DA 4.2 (Bruker Daltonics).
Analysis of F30-Broccoli-cis-MTR1 and F30-Broccoli-trans-tRNA-Asp-MTR1 were performed analogously using 200 pmol of in vitro transcribed constructs that were incubated at 37°C for 22 h in the presence of 100 μM m6G (cis) or BG (trans). Synthetic reference nucleosides m1A, m6A, bn1A and bn6A (synthesized in analogy to literature-known procedures),47,50 were injected at a concentration of 50 nM.
Statistics and reproducibility statement
Kinetic experiments for characterization of ribozyme core sequence requirements, to determine k obs, m6G and Mg2+-concentration dependence were run as three independent experiments. Kinetic experiments for atomic mutagenesis of RNA substrates were repeated twice. All primer extension experiments with in vitro transcribed tRNA were repeated three times with similar results. Experiments with isolated E.coli tRNA and total E.coli RNA were performed two times with freshly extracted RNA from independent cultures and gave similar results. Representative gel images and LC-MS traces are shown in the Figures. Full scans of polyacrylamide gels for kinetic analyses are given in Supporting Figure 1.
Extended Data
Figure 1. Extended Data Figure 1.
a. In vitro selection scheme consisting of incubation, capture, wash, elution, amplification and transcription steps. The RNA substrate (blue) contains an unpaired adenosine (red, A) and is connected to the RNA library via the single-stranded loop (black). The library contains 40 random nucleotides (green) and two constant binding arms (cyan) complementary to the RNA substrate upstream and downstream of the bulged A. Incubation: 50 μM RNA, 100 μM SNAP-biotin, 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 120 mM KCl, 5 mM NaCl, 40 mM MgCl2, 37°C. (Round 1-8: 16 h; Round 9-11: 4 h; Round 11: 50 μM SNAPbiotin). Capture: Beads were blocked with E. coli tRNA; streptavidin and neutravidin beads were switched every other round. Denaturing wash buffer: 8 M urea, 10 mM Tris.HCl, pH 7.5, 1 mM EDTA, 0.01% tween-20; Elution: 95% formamide, 1 mM EDTA, 95°C, 5 min. b. RT-PCR: 42°C, 30 min, 10 cycles PCR with 1 μM primer D4 and 0.5 μM primer D5. 2nd PCR: 25 cycles, 5% (v/v) RT-PCR product as template, 1 μM D4 and 0.5 μM D3, 10% (v/v) DMSO, annealing temp. 65°C. In vitro transcription: dsDNA template from 200 μL PCR reaction, 100 μL reaction volume with 4 mM each NTP, followed by PAGE purification.
Figure 2. Extended Data Figure 2.
Activity of methyltransferase ribozymes: Examination of mutations in the stem-loop. a. 3'-Fluorescein-labeled R10a tested with 100 μM m6G, b. 5'-Fluorescein-labeled R1 tested with 100 μM BG-NH2. ON = over night (23 h) c. Kinetics of CA13 (Rz1/Rz1s)-catalysed alkylation of R1 using BG-NH2 cofactor. Fraction modified is shown as mean ± stdev (n = 3), and fit to a monexponential model (Y = Ymax (1 – e–kt), blue), or a biexponential model (Y = Ymax (a (1 – e–k1t) + (1 – a) (1 – e–k2t)), black). d. Dependence of MTR1 methylation yield on Mg2+ concentration, reactions performed with 100 μM m6G (on R2 with Rz3) at 37°C. Individual data points are shown as empty symbols (n = 2 for 5 h and 23 h, n = 3 for 7 h timpoints), and mean is depicted as filled symbol.
Figure 3. Extended Data Figure 3.
RNA structure probing by DMS and SHAPE. MTR1 (Rz3) was annealed with 17-nt RNA (R6), treated with dimethylsulfate (DMS) or 1-methyl-7-nitroisatoic anhydride (1M7), in presence (+) or absence (−) of m6G, and the modification pattern was analysed by primer extension (5'-32P-labeled D4) with Superscript III. DMS probes the accessibility of the Watson-Crick face of A and C, while SHAPE with 1M7 probes the flexibility of the backbone. Both probing methods confirm the central base-paired stem and reveal the protection of several additional nucleotides (bold). The experiment was repeated three times with similar results.
Figure 4. Extended Data Figure 4.
Representative gel images of RNA-catalysed alkylation reactions of RNA substrate mutants by their corresponding ribozymes with complementary binding arms as listed in Supplementary Table 1. a. adenosine point mutations. b. atomic mutagenesis of backbone. c, d. atomic mutagenesis of adenosine. e. reactions sites blocked by methylation. f. binding arm mutations outside of GAG. g. point mutations next to target nucleoside A. Reactions were performed with 100 μM BG-NH2 (a - e) or SNAP-biotin (f - g) at pH 7.5, 40 mM MgCl2, 37°C and repeated two times for each substrate. The parent reaction with adenosine was performed with fluorescently labelled and radioactively labelled RNA independently for six times.
Figure 5. Extended Data Figure 5.
RNA-catalyzed methylation of tRNAs. a. tRNA sequences studied. b. Synthetic fragments and corresponding ribozymes. c. Exemplary gel images for kinetic analysis of MTR1-catalysed fragment methylation showing quantitative formation of m1A. d. Exemplary HR-ESI MS of isolated methylated R.norvegicus RNA fragment. e. Full gel images of primer extension analyses shown in Fig 3. Representative gel images of three independent experiments with similar results.
Figure 6. Extended Data Figure 6.
Specificity of ribozyme for the target tRNA. a. Secondary structure schemes of six E.coli tRNAs, with very similar TΨC-stem-loop sequences (drawn without natural modifications). Target tRNAAsp in top left corner, with A58 indicated in blue. The nucleotides complementary to the binding arms of MTR1-tRNAAsp-A58 (Rz23) are shown in bold. The purple nucleotides indicate mismatched positions with the binding arms. b. Full gel image of primer extension analysis on total E.coli tRNA with six different primers, shown in Fig. 3c. Primer extension analyses were repeated twice.
Figure 7. Extended Data Figure 7.
Plasmid-encoded cis-active ribozyme. a. Schematic depiction of F30-Broccoli-cis (FBC)-MTR1 construct. b. Dot plot for FBC-MTR1 generated by Vienna RNAfold (http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at/), indicates high probability of folding into the designed structure. c. LC-MS analysis of SVPD/BAP-digested FBC-MTR1 in vitro transcript after reaction with m6G. Extracted ion chromatogram (EIC) for detection of MH+ 282.11±0.05 (methylated adenosines) shows production of m1A, and m6A to a small extent (due to partial Dimroth rearrangement during digestion). Bottom trace for synthetic references m1A and m6A (50 nM each), is same as shown in Fig 3d. d. Primer extension stop assays also confirm activity of FBC-MTR1 transcribed in vitro and in vivo, in the presence of total E.coli RNA. Left: full gel image shown in Fig. 4a for in vitro transcribed FBC-MTR1. Right: primer extension on total E.coli RNA, isolated 1 h after IPTG induction, and incubated with indicated m6G or BG concentration in vitro. These experiments were independently repeated two times with similar results.
Figure 8. Extended Data Figure 8.
Plasmid-encoded trans-active ribozyme. a. Schematic depiction of F30-Broccoli-trans (FBT)-MTR1 with specific binding arms for E.coli tRNA-Asp (A58). b. Primer extension stop assays confirm the activity and specificity of the FBT-MTR1 in vitro transcript. Left: full gel image shown in Fig. 4b for FBT-MTR1 reacted with m6G and BG on total E.coli tRNA. Right: primer extension on BG-treated sample with six different E.coli tRNA-specific primers (P4-P9), repeated twice. c. LC-MS analysis after digestion of total E.coli tRNA treated with FBT-MTR1 and BG (same sample as for right gel image). EIC for MH+ 282.11 (methylated adenosines) and 298.11 (methylated guanosines) demonstrate the presence of natural tRNA modifications. EIC 358.11 in comparison to reference nucleosides bn1A and bn6A shows bn-modified adenosines produced by FBT-MTR1.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the European Research Council (ERC-CoG 682586) and by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG; SPP1784 Chemical Biology of native nucleic acid modifications). We thank Juliane Adelmann and Sebastian Mayer for help with mass spectrometric analyses, Christian Steinmetzger for synthesis of 1M7, and Surjendu Dey for providing m6dG.
Footnotes
Author contributions
In vitro selection was carried out by CPMS, RNA solid-phase synthesis was performed by AKL and CH, ribozymes were characterized by CPMS, MGM and AKL. Plasmids were constructed by MGM, AKL and CPMS. RNA structure probing and detection of RNA methylation by primer extension was performed by CPMS, LC-MS analyses were run by CPMS and CH. CPMS, MGM and CH designed experiments, CPMS and CH wrote the paper, all authors analysed data and commented on the manuscript.
The authors declare no competing financial interest. Reprints and permissions information is available at www.nature.com/reprints.
Data availability statement
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its Supplementary information files.
References
- 1.Motorin Y, Helm M. RNA nucleotide methylation. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011;2:611–631. doi: 10.1002/wrna.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Waddell TG, Eilders LL, Patel BP, Sims M. Prebiotic methylation and the evolution of methyl transfer reactions in living cells. Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2000;30:539–548. doi: 10.1023/a:1026523222285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jadhav VR, Yarus M. Coenzymes as coribozymes. Biochimie. 2002;84:877–888. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(02)01404-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Frye M, Jaffrey SR, Pan T, Rechavi G, Suzuki T. RNA modifications: what have we learned and where are we headed? Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17:365–372. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2016.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Traube FR, Carell T. The chemistries and consequences of DNA and RNA methylation and demethylation. RNA Biol. 2017;14:1099–1107. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1318241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zaccara S, Ries RJ, Jaffrey SR. Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20:608–624. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Frye M, Harada BT, Behm M, He C. RNA modifications modulate gene expression during development. Science. 2018;361:1346–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.aau1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bohnsack KE, Höbartner C, Bohnsack MT. Eukaryotic 5-methylcytosine (m(5)C) RNA Methyltransferases: Mechanisms, Cellular Functions, and Links to Disease. Genes. 2019;10:E102. doi: 10.3390/genes10020102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Becker S, Schneider C, Crisp A, Carell T. Non-canonical nucleosides and chemistry of the emergence of life. Nat Commun. 2018;9:5174. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07222-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schneider C, et al. Noncanonical RNA Nucleosides as Molecular Fossils of an Early Earth-Generation by Prebiotic Methylations and Carbamoylations. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2018;57:5943–5946. doi: 10.1002/anie.201801919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Higgs PG, Lehman N. The RNA World: molecular cooperation at the origins of life. Nat Rev Genet. 2015;16:7–17. doi: 10.1038/nrg3841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Doudna JA, Cech TR. The chemical repertoire of natural ribozymes. Nature. 2002;418:222–228. doi: 10.1038/418222a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pyle AM. Group II Intron Self-Splicing. Annu Rev Biophys. 2016;45:183–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-062215-011149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ren A, Micura R, Patel DJ. Structure-based mechanistic insights into catalysis by small self-cleaving ribozymes. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2017;41:71–83. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2017.09.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Attwater J, Raguram A, Morgunov AS, Gianni E, Holliger P. Ribozyme-catalysed RNA synthesis using triplet building blocks. Elife. 2018;7 doi: 10.7554/eLife.35255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wachowius F, Attwater J, Holliger P. Nucleic acids: function and potential for abiogenesis. Q Rev Biophys. 2017;50:e4. doi: 10.1017/S0033583517000038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tjhung KF, Shokhirev MN, Horning DP, Joyce GF. An RNA polymerase ribozyme that synthesizes its own ancestor. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2020;117:2906–2913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1914282117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wilson C, Szostak JW. In vitro evolution of a self-alkylating ribozyme. Nature. 1995;374:777–782. doi: 10.1038/374777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sharma AK, et al. Fluorescent RNA labeling using self-alkylating ribozymes. ACS Chem Biol. 2014;9:1680–1684. doi: 10.1021/cb5002119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ameta S, Jäschke A. An RNA catalyst that reacts with a mechanistic inhibitor of serine proteases. Chem Sci. 2013;4:957–964. [Google Scholar]
- 21.McDonald RI, et al. Electrophilic activity-based RNA probes reveal a self-alkylating RNA for RNA labeling. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10:1049–1054. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Peselis A, Serganov A. Themes and variations in riboswitch structure and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1839:908–918. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.02.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.McCown PJ, Corbino KA, Stav S, Sherlock ME, Breaker RR. Riboswitch diversity and distribution. RNA. 2017;23:995–1011. doi: 10.1261/rna.061234.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Breaker RR. Riboswitches and Translation Control. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018;10 doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a032797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Batey RT. Recognition of S-adenosylmethionine by riboswitches. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011;2:299–311. doi: 10.1002/wrna.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sun A, et al. SAM-VI riboswitch structure and signature for ligand discrimination. Nat Commun. 2019;10:5728. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13600-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Burke DH, Gold L. RNA aptamers to the adenosine moiety of S-adenosyl methionine: structural inferences from variations on a theme and the reproducibility of SELEX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:2020–2024. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.10.2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lindahl T, Demple B, Robins P. Suicide inactivation of the E. coli O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase. EMBO J. 1982;1:1359–1363. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01323.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ghaem Maghami M, Scheitl CPM, Höbartner C. Direct in Vitro Selection of Trans-Acting Ribozymes for Posttranscriptional, Site-Specific, and Covalent Fluorescent Labeling of RNA. J Am Chem Soc. 2019;141:19546–19549. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b10531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ghaem Maghami M, Dey S, Lenz AK, Höbartner C. Repurposing antiviral drugs for orthogonal RNA-catalyzed labeling of RNA. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2020;59 doi: 10.1002/anie.202001300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Keppler A, et al. A general method for the covalent labeling of fusion proteins with small molecules in vivo. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:86–89. doi: 10.1038/nbt765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dalhoff C, Lukinavicius G, Klimasauskas S, Weinhold E. Direct transfer of extended groups from synthetic cofactors by DNA methyltransferases. Nat Chem Biol. 2006;2:31–32. doi: 10.1038/nchembio754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Oerum S, Degut C, Barraud P, Tisne C. m1A Post-Transcriptional Modification in tRNAs. Biomolecules. 2017;7:20. doi: 10.3390/biom7010020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chujo T, Suzuki T. Trmt61B is a methyltransferase responsible for 1-methyladenosine at position 58 of human mitochondrial tRNAs. RNA. 2012;18:2269–2276. doi: 10.1261/rna.035600.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Reichle VF, Weber V, Kellner S. NAIL-MS in E. coli Determines the Source and Fate of Methylation in tRNA. ChemBioChem. 2018;19:2575–2583. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201800525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Filonov GS, Kam CW, Song W, Jaffrey SR. In-gel imaging of RNA processing using broccoli reveals optimal aptamer expression strategies. Chem Biol. 2015;22:649–660. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.04.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Xiong X, Li X, Yi C. N1-methyladenosine methylome in messenger RNA and non-coding RNA. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018;45:179–186. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.06.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Grozhik AV, et al. Antibody cross-reactivity accounts for widespread appearance of m1A in 5'UTRs. Nat Commun. 2019;10:5126. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13146-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Safra M, et al. The m1A landscape on cytosolic and mitochondrial mRNA at single-base resolution. Nature. 2017;551:251–255. doi: 10.1038/nature24456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhou H, et al. Evolution of a reverse transcriptase to map N1-methyladenosine in human messenger RNA. Nat Methods. 2019;16:1281–1288. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0550-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Terns MP, Terns RM. Small nucleolar RNAs: versatile trans-acting molecules of ancient evolutionary origin. Gene Expr. 2002;10:17–39. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Serganov A, et al. Structural basis for discriminative regulation of gene expression by adenine- and guanine-sensing mRNAs. Chem Biol. 2004;11:1729–1741. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.11.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gilbert SD, Reyes FE, Edwards AL, Batey RT. Adaptive ligand binding by the purine riboswitch in the recognition of guanine and adenine analogs. Structure. 2009;17:857–868. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2009.04.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pitsch S, Weiss PA, Jenny L, Stutz A, Wu X. Reliable Chemical Synthesis of Oligoribonucleotides (RNA) with 2'-O-[(Triisopropylsilyl)oxy]methyl(2’-O-tom)-Protected Phosphoramidites. Helv Chim Acta. 2001;84:3773–3795. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wachowius F, Höbartner C. Probing Essential Nucleobase Functional Groups in Aptamers and Deoxyribozymes by Nucleotide Analogue Interference Mapping of DNA. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:14888–14891. doi: 10.1021/ja205894w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kosutic M, et al. A Mini-Twister Variant and Impact of Residues/Cations on the Phosphodiester Cleavage of this Ribozyme Class. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2015;54:15128–15133. doi: 10.1002/anie.201506601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Höbartner C, et al. The Synthesis of 2’-O-[(Triisopropylsilyl)oxy] methyl (TOM) Phosphoramidites of Methylated Ribonucleosides (m1G, m2G, m2 2G, m1I, m3U, m4C, m6A, m6 2A) for Use in Automated RNA Solid-Phase Synthesis. Monatshefte für Chemie / Chemical Monthly. 2003;134:851–873. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rio DC. Expression and purification of active recombinant T7 RNA polymerase from E. coli. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2013 doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot078527. 2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Mortimer SA, Weeks KM. A fast-acting reagent for accurate analysis of RNA secondary and tertiary structure by SHAPE chemistry. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:4144–4145. doi: 10.1021/ja0704028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Fujii T, Itaya T, Saito T. Purines. 18. Kinetic Studies of Base-Catalysed Conversion of 1-Alkyladenosines into N-Alkyladenosines - Effect of Substituents on Rearrangement Rate. Chem Pharm Bull. 1975;23:54–61. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its Supplementary information files.