Abstract
A number of neuromuscular and muscular diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) and several myopathies, are associated to mutations in related RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), including TDP-43, FUS, MATR3 or hnRNPA1/B2. These proteins harbor similar modular primary sequence with RNA binding motifs and low complexity domains, that enables them to phase separate and create liquid microdomains. These RBPs have been shown to critically regulate multiple events of RNA lifecycle, including transcriptional events, splicing and RNA trafficking and sequestration. Here, we review the roles of these disease-related RBPs in muscle and motor neurons, and how their dysfunction in these cell types might contribute to disease.
Keywords: RNA-Binding Protein (RBP), Muscle, Dystrophy, Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), Inclusion body myopathy (IBM), Fragile X-associated tremor / ataxia syndrome (FXTAS), Multisystem proteinopathy (MSP), Huntington's disease
INTRODUCTION
Key Concepts. KEY CONCEPTS.
Neuromuscular diseases collectively affect muscle function, either by directly impairing muscle structure or function, or by affecting muscle control by motor neurons. As a consequence of impaired muscle function, patients develop weakness that can be progressive and lead to paralysis and early death. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) are two typical diseases of the motor neurons, in which muscle weakness is primarily caused by the degeneration of motor neurons [1]. In contrast, myopathies primarily affect muscle structure and/or function with clinically affected muscles either proximal, such as in limb girdle muscle dystrophy, and/or distal in distal myopathies. Although the distinction between primary muscle and primary neuronal neuromuscular diseases might a priori seem obvious, there are significant clinical and genetic overlaps between these diseases [2–4]. In this review, we describe how mutations in functionally related RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are associated with both muscle and motor neuron diseases, and how these mutations participate in compromising the neuromuscular system. The most important neuromuscular diseases considered are presented in BOX 1.
Box 1. BOX 1: Clinical definition of the major neuromuscular diseases reviewed here.
In recent years, genetics uncovered a large number of causes of neuromuscular diseases. Interestingly, a subset of genes causing either motor neuron diseases or myopathies encode proteins that bind RNA (hence RNA-binding proteins, RBPs) and share a number of biochemical and functional properties. RBPs associated to neuromuscular diseases are part of a large group of proteins involved in mRNAs lifecycle, that are collectively termed heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs). Many of these hnRNPs also display a low complexity domain that resembles yeast prions and is called “prion-like domain” (PrLD). Most of these PrLD containing RBPs are associated with human diseases [5–9], in particular neuromuscular diseases.
In this review, we describe the general properties of disease associated RBPs. We then provide specific examples for the involvement of RBPs in neuromuscular diseases.
MODULAR STRUCTURE AND GENERAL CELLULAR FUNCTIONS OF RBPs
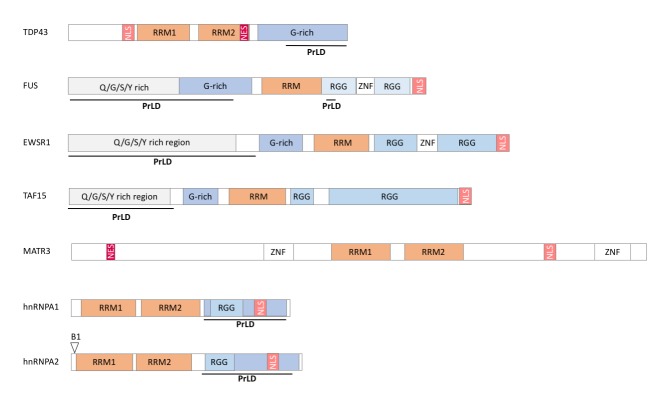
RBPs associated to neuromuscular diseases display a modular structure with well identified subdomains. First, interaction of RBPs with RNA occurs through relatively limited sets of protein modules [10] in particular RNA recognition domains (RRM) and/or hnRNPK homology domain (KH). Other protein domains are variably present in RBPs and include Arginine-Glycine-Glycine rich domain (RGG), double-stranded RNA binding motifs (dsRBM), DEAD box, A2 recognition element (A2RE), AU rich element (ARE), Zinc fingers domain (Zn), Zn-knuckle motifs, S1 domain, PAZ and PIWI domains [10, 11]. (Figure 1).
Figure 1. FIGURE 1: Domain organization of RBPs with prion like domains.
NLS: nuclear localization signal, NES: nuclear export signal, RRM: RNA recognition motif, RGG:arginine/glycine-rich region, G-rich: glycine-rich region, ZNF: Zinc finger motif, Q/G/S/Y rich region: glutamine, glycine, serine and tyrosine-rich region, B1: B1 isoform of hnRNPA2, PrLD : prion like domain.
This interaction with various RNA species, as well as their capacity to shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm allow RBPs to participate in all steps of the mRNA cycle, from transcription, maturation, transport, translation, stability to degradation [11–14]. RBPs also contribute to translational and post translational regulation through binding to 3' untranslated regions (UTR) of mRNAs [15]. Besides mRNAs, a number of these RBPs are also critical in the life cycle of small RNA species, in particular microRNA biogenesis [16–18].
The so-called PrLD is typically found in most disease associated RBPs. It consists of a domain of low primary sequence complexity, rich in uncharged polar amino acids (asparagine, glutamine, and tyrosine) and in glycine [19, 20] and displays high similarity to yeast proteins with prion properties [21]. In the human genome, more than 200 encoded proteins display a PrLD, and a large proportion of these also include RNA binding motifs [14, 19, 20]. The combination of RNA binding properties with PrLDs allows RBPs to phase separate in liquid compartments. Liquid Liquid Phase Separation (LLPS) is a disassembly mechanism of two liquids resulting in the appearance of two phases [22]. This leads to the rapid and reversible creation of liquid microdomains (so called membrane-less organelles), physically separated from the rest of the cell, and allowing specialized functions. [14]. In this respect, RBPs are required for the generation and maintenance of key nuclear subdomains such as nucleoli, paraspeckles, gems, Cajal bodies, P-bodies or cytoplasmic stress granules through LLPS. Disease associated mutations in RBPs compromise LLPS, leading to the appearance of solids aggregates [23–26].
In the next sections, major RBPs are reviewed for their involvement in neuromuscular diseases (Table 1).
TABLE 1.
Summary of selected RBP with prion like domain in neuromuscular disease.
| RBP | Reported RNA motifs | Functions in muscle | Pathological alterations | RBP-associated muscular disease |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MATR3 | UC-rich motif [136, 176] | Proliferation | Mutations | VCPDM |
| Differentiation | Aggregates | ALS | ||
| hnRNP | UAGG motifs [177] | Muscle development | Mutations | FXTAS |
| Contraction | Aggregates | ALS | ||
| FTD | ||||
| LGMD1 | ||||
| OPMD | ||||
| MP | ||||
| SMA | ||||
| TDP43 | (GU)n repeat | Muscle development | Mutations | ALS |
| UG motifs [178, 179] | NMJ formation | Aggregates | FTD | |
| Mitochondrial functions | MD | |||
| IBM | ||||
| SMA | ||||
| FUS | Several motifs reported, including GGUG, GU-rich and CU rich hexamers [170, 180–184] | Muscle development | Mutations | SMA |
| Differentiation | Aggregates | ALS | ||
| NMJ formation | FTD | |||
| Mitochondrial functions | MG | |||
| HD | ||||
| EWSR1 | G-rich motif [181] | Muscle development | Mutations | ALS |
| Differentiation | Aggregates | FTD | ||
| Proliferation | SMA | |||
| Mitochondrial functions | ||||
| TAF15 | GGUAAGU [181, 185] | Mitochondrial fusion | Mutations | ALS |
| Aggregates | FTD |
ALS: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, DM: Distal myopathy, FXTAS: Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome, HD: Huntington disease, IBM: Inclusion body myopathy, LGMD1: limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 1D, MD: Muscular dystrophy, MG: Myasthenia gravis, MP: Multisystem proteinopathy, OPMD: Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy, SMA: Spinal muscular atrophy, VCPDM: Vocal cord and pharyngeal weakness with distal myopathy.
TDP43
TAR DNA-binding protein of 43 kDa (TDP43) is an RBP able to bind to single stranded DNA and RNA in order to modulate splicing, RNA stability and biogenesis [27–29]. TDP43 was initially characterized as a protein binding to the retroviral protein Tar [30] and later shown to modulate the splicing of key exon 9 in the CFTR gene associated with cystic fibrosis [28]. In 2006, a landmark study identified TDP43 protein as the major ubiquinated protein in aggregates present in patients with ALS and fronto-temporal dementia (FTD), two major neurodegenerative diseases (BOX 1) [31]. Indeed, TDP43 inclusions have been found in approximatively 95% of all ALS cases (sporadic and familial) and half of the FTD cases [31]. Subsequently, mutations in the TARDBP gene, encoding TDP43, were found to account for 3% of familial cases and 1.5% of sporadic cases of ALS [32–34].
How TDP43 aggregates are linked to neurodegeneration in ALS and FTD is complex and still not completely understood. First, TDP43 aggregates are cytoplasmic and associated with complete nuclear clearance of TDP43 [35], and cells with TDP43 aggregates thus display loss of TDP43 nuclear function. Indeed, loss of function of TDP43 in motor neurons is sufficient to trigger motor neuron degeneration [36–38], that is likely due to defective repression of splicing of cryptic exons [39, 40] and defective autophagy [38]. Gain of function mechanisms are also likely to participate as expression at physiological levels of mutant TDP43 is able to drive neurodegeneration [41–45]. It is likely that the function of TDP43 in splicing in motor neurons is critical in this mutant gain of function [43, 45, 46]. A potential critical target is the Tardbp mRNA (encoding TDP43) itself whose autoregulation is disrupted upon the expression of a mutant TDP43 [43, 45]. Altered TDP43 function might also be involved in other motor neuron diseases, such as SMA. In this disease, caused by loss of the survival of motor neurons (SMN) protein, TDP43 might contribute to the splicing dysfunction caused by loss of SMN. Indeed, TDP43 promotes the inclusion of exon 7 of the SMN2 pre-mRNA in vitro [47] and depletion of TDP43 leads to reduction and loss of gems, thereby strengthening the role of TDP43 in SMA [48–50]. Thus, TDP43 might participate directly or indirectly in the pathophysiology of a number of neurodegenerative disorders.
Beyond neurons, TDP43 has been shown to be critical for skeletal muscle function, pointing towards a potential involvement of TDP43 in muscle diseases. TDP43 is required for muscle regeneration [51] and forms cytoplasmic granules sequestering sarcomeric RNAs to facilitate regeneration. Furthermore, TDP43 is required for expression of critical regulators of myogenesis such as MYOD or MYOG [52] and key myogenic microRNAs such as miR-1 and 206 [53]. Consistently, TDP43 loss of function [54, 55] or muscle overexpression of TDP43 is highly detrimental for muscle structure and function [56, 57]. TDP43 also participates in neuromuscular junction (NMJ) formation at least in Drosophila [58, 59]. This importance of TDP43 in muscle function indirectly suggests that this protein could be involved in muscle dysfunction in human diseases. Indeed, muscle cytoplasmic aggregates of TDP43 were observed in patients with ALS, muscle dystrophy and inclusion body myositis (IBM) [60–68]. TDP43 might also indirectly participate in muscle pathology developed during inherited peripheral neuropathies of myofibrillar myopathies [69] (Figure 2).
Figure 2. FIGURE 2: TDP43 and FUS alterations in neuromuscular diseases.
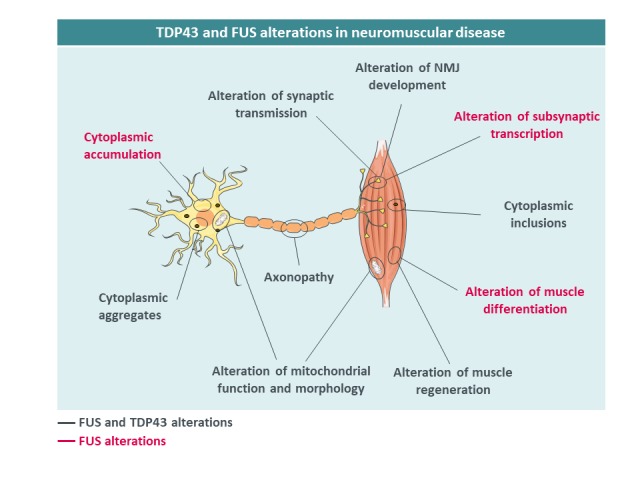
Mutant TDP43 aggregates are found in motor neurons and muscles of patients. TDP-43 mislocalization causes axonopathy and mitochondrial alterations, alters synaptic transmission, NMJ development and muscle regeneration. Similar observations are made for FUS, which is also involved in subsynaptic transcription.
FUS
FUS is an RBP belonging to the FET family, that also includes EWS and TAF15. The FET proteins are predominantly localized in the nucleus where they control DNA/RNA metabolism [70, 71]. Multiple results demonstrate a pleiotropic function of FUS in regulating mRNA expression, stability, maturation in multiples cells including muscle cells.
Mutations in the FUS gene have been identified in patients with ALS in 2009 [72, 73] and currently more than 50 mutations in this gene have been described. ALS patients with FUS mutations show generally an earlier age at onset, sometimes in their 20's, and aggressive progression [74]. Most of these mutations are in or around the C-terminal nuclear localization signal (NLS) [73, 75–78], and severity is correlated with the degree of impairment of FUS nuclear import [76]. FUS aggregates are also found in a subset of FTD patients, yet in the absence of germline mutations, with different post-translational modifications [79, 80] and with co-deposition of other proteins including TAF15, EWS and TNPO1 [81–83]. In a manner similar to TDP43, both gain and loss of FUS function have been postulated to participate in FUS-related neurodegeneration. First, FUS cytoplasmic accumulation, due to loss of nuclear import, might lead to neuronal death through a so-called cytoplasmic gain of function. In particular, cytoplasmic FUS might sequester proteins of importance, such as SMN [49, 84–87] or PRMT1 [88, 89] and lead to the accumulation of toxic stress granules and cytoplasmic aggregates [79, 88, 90]. Second, clearance of FUS from the nucleus might lead to alterations in the many nuclear FUS functions, including transcription, splicing or DNA damage repair [91, 92]. Importantly, accumulation of cytoplasmic FUS is necessary to lead to motor neuron degeneration in mice [93–96]. For instance, we and others have shown that heterozygous Fus knock-in mouse models with truncated mutations develop mild, late onset muscle weakness and motor neuron degeneration, but not haploinsufficient Fus knock-out mice, demonstrating that the presence of the protein in the cytoplasm is necessary to trigger motor neuron toxicity [93, 94, 97]. Loss of FUS function might contribute to FTD symptoms, through alterations of splicing of key neuronal mRNAs such as MAPT, encoding the TAU protein, or of stability of mRNAs encoding synaptic proteins such as GluA1 and SynGAP1 [98–102]. Although less studied than its function in neurons, FUS plays important roles in the muscle. Indeed, muscles of sporadic IBM [64, 65] can display FUS aggregates, while mutations in FUS were found in one patient with myositis [103]. In the muscle, FUS regulates alternative splicing and differentiation through its action on DUX4 and PTBP1 [104, 105] but also hnRNPA1 and MATR3, two proteins involved in muscle development [106] and ALS [20, 107, 108]. Furthermore, FUS has been shown to be important for the function of PGC1α, a key regulator of muscle mitochondrial function [109]. FUS also exerts critical roles in neuromuscular junction development. Animal models of FUS-ALS show alteration of synaptic transmission and modification of NMJ numbers and size [110–114], and we recently demonstrated that FUS is required for the post-synaptic development of the NMJ [115]. Indeed, both knock-in and knock-out mice for Fus developed NMJ morphology defects. Newborn homozygous Fus mutant mice displayed predominantly postsynaptic NMJ defects whereas adult heterozygous Fus mutant mice displayed constitutively smaller neuromuscular endplates that denervate. Importantly, FUS was enriched in muscular subsynaptic nuclei and this enrichment depended on innervation and was perturbed in heterozygous Fus mutant mice. Mechanistically, FUS binds to the promoter region and stimulates transcription of acetylcholine receptor (AchR) subunit genes involved in NMJ formation through the transcription factor ERM. In induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived myotube cultures and motor neuron/myotube co-cultures from FUS-ALS patients, endplate maturation was impaired and AChR expression reduced. Finally, in motor neuron/myotube co-cultures, ALS-mutant FUS was intrinsically toxic to both motor neurons and myotubes. Altogether, these data show that FUS plays a key role in regulating selective expression of AChR genes in subsynaptic nuclei and indicate that intrinsic toxicity of ALS-mutant FUS in the muscle may be critical for ALS [115].
FUS is also involved in SMA, through a direct interaction between FUS and SMN through the U1-snRNP. Similar as TDP43, FUS is associated with gems, that are affected by ALS causing mutations [49, 113]. Furthermore, snRNAs seem to be trapped by cytoplasmic FUS [116, 117].
Besides motor neuron diseases, FUS is also associated with other neuromuscular diseases such as myasthenia gravis and Huntington's disease. Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder of the NMJ inducing skeletal muscle weakness. In this disease, an increase of FUS transcript is observed in the blood of myasthenic patients [118]. Its significance remains unknown. In Huntington's disease, mutant huntingtin (HTT) protein sequesters FUS in neuronal inclusions [99, 119, 120].
EWS
EWS is the second member of the FET family, encoded by the EWSR1 gene. This oncogenic protein is involved in proliferation and cell differentiation [121–123]. In analogy with FUS mutations, Couthouis and collaborators identified three EWSR1 missense mutations in ALS patients able to lead to EWS mislocalization in the cytoplasm of motor neurons. Indeed, EWS appears to be mislocalized in the cytoplasm of motor neurons in sporadic ALS in the absence of EWS mutations [19, 124] and FUS-FTD [81]. Like for FUS and TDP43, EWS interacts with SMN and is required for its function in splicing, suggesting a role of EWS in SMA [125, 126].
In muscle, EWS may participate to myogenesis through its regulation of the transcriptional co-activator PGC1α. Indeed, EWS loss leads to PGC1α degradation due to impaired stability [127]. Consistently, the loss of EWSR1 causes abnormalities in mitochondrial structure and a decrease in DNA and mitochondrial density.
TAF15
TAF15, the last member of FET family, shares similar structure and functions as FUS and EWS and appears associated with ALS.
In 2011, Couthouis et al. identified three missenses mutations in TAF15, whereas Ticozzi et al. discovered four other mutations in ALS patients [19, 128]. These mutations affect mainly the RGG domain [128] and promote cytoplasmic foci in primary rat embryonic neuron cultures [19]. In human post-mortem spinal cord tissue of control patients TAF15 is nuclear while TAF15 in ALS patients is nuclear and forms cytoplasmic aggregates. Furthermore, neurodegeneration and abnormal mitochondrial fragmentation in muscle and motor neurons were observed in TAF15 ALS fly models [19, 129]. These mitochondrial abnormalities are mediated by mitofusins as mutant TAF15 decreases mitofusin protein expression and mitochondrial defects can be rescued upon rescue of mitofusin in Taf15 mutant flies [129].
MATR3
Matrin 3 (MATR3) is a 125 kDA nuclear matrix protein [130] of 845 amino acids [131]. MATR3 binds and stabilizes RNA [132] in multiple tissues especially skeletal muscle. Contrary to previous examples, MATR3 has no prion-like domain per se, but several intrinsically disordered regions.
In myotubes, MATR3 is present in the nuclear matrix and nuclear membrane [133] and its localization is dependent upon the expression of the muscle specific transcription factor Myogenin [133].
MATR3 has been found to be critical in multiple gene expression events related to muscle function and differentiation. First, MATR3 is required for normal myoblast proliferation and differentiation since its overexpression increases the expression of myogenic related genes [134]. Conversely, MATR3 depletion decreases protein levels of myogenin and decreases the differentiation status. MATR3 regulates alternative splicing through its interaction with the Polypyrimidine Tract Binding Protein (PTBP) that is critical in muscle differentiation [135, 136]. Furthermore, MATR3 binds to and regulates long non-coding RNA in muscles [134]. Last, MATR3 binds directly to Lamin A, a protein required for muscle differentiation [133, 137, 138]. Interestingly, mutations in LMNA gene encoding lamin A/C lead to skeletal and cardiac myopathy [139] and disrupt lamin A/MATR3 interaction [133].
Mutations in MATR3 have been first associated with muscular diseases. First, a MATR3 missense mutation p.Ser85Cys (chr5:138643358, C>G) was associated with vocal cord and pharyngeal weakness with distal myopathy (weakness and atrophy of the hands and feet) [140, 141]. The distal myopathy associated with MATR3 mutation usually begins within the fourth decade, and is characterized by heterogeneous involvement of distal limb muscles, pharyngeal and respiratory muscles, leading to proximal and axial weakness, vocal cord dysfunction with mild voice abnormalities, dysphagia and decreased respiratory function [141–144].
More recently, mutations in MATR3 have been associated with ALS. Johnson et al. performed exome sequencing and identified novel missense mutations associated with ALS in MATR3: p.Phe115Cys (chr5:138643448, T>G) and p.Thr622Ala (chr5:138658372, A>G) [107]. Interestingly, the p.Phe115Cys mutation caused a respiratory form of ALS leading to death within five years of symptom onset whereas the p.Ser85Cys mutation (identified in distal myopathy) induced a slowly progressive form of ALS. MATR3 immunostaining showed a partial mislocalization in the cytoplasm of motor neurons and surrounding glial cells in ALS patients but no cytoplasmic inclusions were observed. MATR3 and TDP43 co-aggregated in skeletal muscles of patients and a direct interaction was observed between MATR3 and TDP43, another RBP linked to ALS. Recently a novel missense mutation p.Ser610Phe was discovered in one patient and three missense variants p.Ala313Gly, p.Arg147Lys, and p.Gln347Lys were observed in three healthy subjects [145]. Thus, similar to several other RBPs, mutations in MATR3, can lead to a broad spectrum of neuromuscular diseases, from pure muscle involvement to severe motor neuron disease.
OTHER hnRNPs
A number of other hnRNPs has been associated with various neuromuscular diseases.
First, hnRNPA3 was found to bind to mutant C9ORF72 RNA in ALS and could mediate some of its toxic effects [146, 147]. Furthermore, hnRNPA3 was also reported to be present in TDP43, p62 immunoreactive dipeptide repeat (DPR) inclusions in C9orf72 cases [148, 149] further linking hnRNPA3 to C9orf72 ALS/FTD. Second, mutations in hnRNPA1 and hnRNPA2B1 have been identified in multisystem proteinopathy, a disorder combining IBM, FTD, ALS or Paget's disease of the bone (PDB) [20]. Disease mutations impact C-terminal regions of hnRNPA2 (residues 185–341) and hnRNPA1 (residues 186–320) which are located in the PrLD, essential for RNA granule formation. Indeed, disease associated mutations of hnRNPA2B1 and hnRNPA1 alter stress granule formation through cytoplamic mislocalization and accelerated fibrillization of the mutant protein. Interestingly hnRNPA1 and hnRNPA2B1 co-localize in stress granule with TDP43 and VCP, two proteins involved in ALS. hnRNAPA1 could be involved in ALS and was shown to be mislocalized in post-mortem samples of ALS patients [150]. Moreover, hnRNPA1 interacts and co-localizes with wild type but not mutant FUS.
hnRNPA2B1 could be involved in Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS), a late onset disorder inducing a form of mental retardation. This disease is caused by expansion of more than 200 CGG in the FMR1 gene and provokes tremor, ataxia and cognitive defects [151]. In 2007, Sofola and collaborators identified an interaction between hnRNPA2/B1 and the mutant RNA carrying CGG repeats in mouse cerebellar lysates [152]. Consistent with RNA toxicity, overexpression of hnRNPA2/B1 prevents the neurodegenerative eye phenotype induced in CGG transgenic flies. In muscles, Liu and collaborators showed that hnRNPA1 depletion causes muscle developmental defects associated with an increase of myofibers in the heart, a decrease in diaphragm and tongue [106] and dysregulated expression of the genes involved in the development and muscular contraction. Indeed, hnRNPA1 and hnRNPA2/B1 are also involved in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 1D (LGMD1D). This skeletal and cardiac myopathy, can be caused by missense mutations in DNAJB6, induces ambulation problems and is characterized by myofibrillar protein aggregation and autophagic rimmed vacuoles. Recently, Bengoechea and collaborators reported an accumulation and co-localization of hnRNPA1 and hnRNPA2/B1 with DNAJB6 in sarcoplasmic stress granules [67]. Further strengthening the link between hnRNPs and LGMD, hnRNPDL mutations were observed in LGMD1G [153], and are thought to cause disease through aggregation in muscle and loss of function [154].
hnRNPs are also associated with oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD) an adult-onset disease characterized by droopy eyelids, external ophthalmoplegia, dysphagia and proximal limb weakness. OPMD is caused by a GCG repeat expansion in PABPN1 (poly(A)-binding protein N1) and induces inclusions. These contain insoluble intranuclear aggregates of PABPN1 but also hnRNPA1 and A/B [155]. Finally, hnRNPs are also involved SMA, a juvenile neuromuscular disorder characterized by a loss of motor neurons, muscular weakness and wasting. The disease is caused by a mutation in the SMN1 gene and several studies revealed an interaction between SMN and hnRNPA1, HnRNPC1/C2, hnRNPG, hnRNPM, hnRNPQ, hnRNPR [156–163].
A NETWORK OF RBPs TO FINE TUNE NEUROMUSCULAR HEALTH
The occurrences of mutations in multiple functionally related RBPs leading to a vast array of neuromuscular diseases suggest that RBPs are involved in a tight network to regulate neuromuscular health (Figure 3). This RBP network is illustrated by the existence of multiple binary protein-protein interactions between RBPs. For instance, MATR3 interacts with TDP43 [132, 164] as well as with a number of splicing regulators including hnRNPK [132] and hnRNPL [165]. MATR3 and FUS interaction is known to regulate splicing and transcription in vitro [166], while FUS and TDP43 interaction is modulated by disease associated mutations [164]. In addition, RBPs appear to regulate levels of other RBPs through splicing. A clear example is provided by TDP43-mediated regulation of HNRNPA1 splicing, leading to altered hnRNPA1 content, and subsequent protein aggregation and cellular toxicity [167].
Figure 3. FIGURE 3: RBP with prion like domain network in neuromuscular disease.
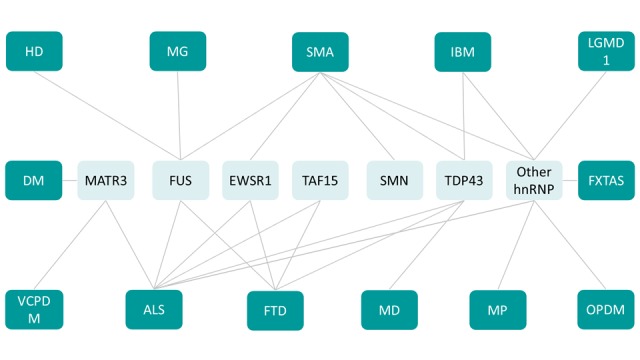
ALS: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, DM: Distal myopathy, FXTAS: Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome, HD: Huntington disease, IBM: Inclusion body myopathy, LGMD1: limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 1D, MD: Muscular dystrophy, MG: Myasthenia gravis, MP: Multisystem proteinopathy, OPMD: Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy, SMA: Spinal muscular atrophy, VCPDM: Vocal cord and pharyngeal weakness with distal myopathy.
The functions of RBPs are partially overlapping, as exemplified for instance by the common regulation of MAPT splicing by FUS and TDP43 [29, 98, 168] or of HDAC6 mRNA [169]. However, this overlap is only partial, and TDP43 and FUS share only a subset of their mRNA targets [170].
Similarly, while FUS, TAF15, EWS and MATR3 are all required for the function of the U1 snRNP/RNA polymerase II complex, they appear to exert distinct, non-overlapping molecular functions in this complex [171].
Thus, mutations or loss of function of one RBP might alter the whole network, and lead to disease. Consistently, a recent study showed that mutation in FUS has an impact on the homeostasis of a number of RBPs, and that the toxicity of FUS mutations could be mitigated by other RBPs [172]. Similar evidence has been published in zebrafish, with epistatic interactions between FUS and TDP43 [173]. In all, RBP homeostasis should be considered globally and a number of secondary consequences on multiple RBPs could be expected from a mutation in one single member.
CONCLUSIONS
The different examples reviewed here convincingly demonstrate a strong involvement of RBPs in neuromuscular diseases. Importantly, the pathogenic roles of these proteins go far beyond the rare cases associated with germline mutations, as shown by the widespread aggregation of TDP43 or FUS in ALS and FTD.
However, many questions remain open. First, the relative role of loss of nuclear function versus gain of cytoplasmic function remains an open question. Indeed, while it is clear that the cytoplasmic accumulation is necessary for toxicity, it cannot be excluded that associated loss of nuclear function contributes to the toxicity. Furthermore, if cytoplasmic toxicity appears critical, it is unclear whether toxicity of the mutant proteins occur through aggregation or their soluble forms. Indeed, aggregation of these proteins is generally not observed in knock-in animal models, which correlates with a mild phenotype. In general, biophysical properties of these proteins in the cytoplasm remains to be studied.
Most importantly, the identification of critical pathogenic events downstream of RBP mutation or aggregation remains to be done. In this respect, recent studies demonstrated that loss of nuclear TDP43 in motor neurons triggers loss of stathmin 2 in turn possibly responsible of axonal degeneration [174, 175]. The identification of a limited number of critical events downstream RBPs dysfunction could help to identify relevant targets. Importantly, as the toxicity of mutant RBPs extends beyond motor neurons, including muscles or other cell types, it will be necessary to study such critical events in different cell types to better define possible targets either common to several cell types or cell specific. We would like to specifically stress that the mechanisms underlying toxicity in skeletal muscles should be further investigated, especially given the large body of literature reviewed here showing a critical role of RBPs in muscle development, function and pathologies. It is very likely that the extent of RBP involvement in neuromuscular diseases will grow in the next years.
Acknowledgments
Our laboratory regularly receives funds from American Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Association (ALSA), Association Française contre les Myopathies (AFM), Association de Recherche sur la Sclérose Latérale Amyotrophique (ARsla), Fondation Thierry Latran (HypotALS), Fondation pour la recherche médicale (DEQ20180339179 to LD), agence nationale de la recherche (ToFU, EpiFUS, SpreadALS to LD). LD is an USIAS research fellow.
Abbreviatons:
- AchR
– acetylcholine receptor;
- ALS
– amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;
- FTD
– fronto-temporal dementia;
- hnRNP
– heterogenous nuclear ribo-nucleoprotein;
- IBM
– Inclusion body myositis;
- NMJ
– neuromuscular junction;
- OPMD
– oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy;
- PrLD
– prion-like domain;
- RBP
– RNA binding protein;
- RGG
– Arginine-Glycine-Glycine rich domain;
- SMA
– spinal muscular atrophy;
- SMN
– survival of motor neurons.
REFERENCES
- 1.Boillée S, Yamanaka K, Lobsiger CS, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Kassiotis G, Kollias G, Cleveland DW. Onset and progression in inherited ALS determined by motor neurons and microglia. Science. 2006;312(5778):1389–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.1123511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Komlósi K, Hadzsiev K, Garbes L, Martínez Carrera LA, Pál E, Sigur∂sson JH, Magnusson O, Melegh B, Wirth B. Exome sequencing identifies Laing distal myopathy MYH7 mutation in a Roma family previously diagnosed with distal neuronopathy. Neuromuscul Disord. 2014;24(2):156–161. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2013.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Boyer JG, Ferrier A, Kothary R. More than a bystander: the contributions of intrinsic skeletal muscle defects in motor neuron diseases. Front Physiol. 2013;4:356. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Agrawal PB, Joshi M, Marinakis NS, Schmitz-Abe K, Ciarlini PDSC, Sargent JC, Markianos K, De Girolami U, Chad DA, Beggs AH. Expanding the Phenotype Associated With the NEFL Mutation Neuromuscular Disease in a Family with Overlapping Myopathic and Neurogenic Findings. JAMA Neurol. 2014;71(11):1413–1420. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dash S, Siddam AD, Barnum CE, Janga SC, Lachke SA. RNA-binding proteins in eye development and disease: implication of conserved RNA granule components. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016;7(4):527–557. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.de Bruin RG, Rabelink TJ, van Zonneveld AJ, van der Veer EP. Emerging roles for RNA-binding proteins as effectors and regulators of cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. 2017;38(18):1380–1388. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pereira B, Billaud M, Almeida R. RNA-Binding Proteins in Cancer: Old Players and New Actors. Trends Cancer. 2017;3(7):506–528. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2017.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhou H, Mangelsdorf M, Liu J, Zhu L, Wu JY. RNA-binding proteins in neurological diseases. Sci China Life Sci. 2014;57(4):432–444. doi: 10.1007/s11427-014-4647-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hanson KA, Kim SH, Tibbetts RS. RNA-binding proteins in neurodegenerative disease: TDP–43 and beyond. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012;3(2):265–285. doi: 10.1002/wrna.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lunde BM, Moore C, Varani G. RNA-binding proteins: modular design for efficient function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(6):479–490. doi: 10.1038/nrm2178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lukong KE, Fatimy RE. Implications of RNA-binding Proteins for Human Diseases. In: eLS. John Wiley & Sons. 2012. [DOI]
- 12.Dreyfuss G, Matunis MJ, Piñol-Roma S, Burd CG. hnRNP proteins and the biogenesis of mRNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:289–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Marchand V, Gaspar I, Ephrussi A. An intracellular transmission control protocol: assembly and transport of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012;24(2):202–210. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2011.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gomes E, Shorter J. The molecular language of membraneless organelles. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(18):7115–7127. doi: 10.1074/jbc.TM118.001192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mayr C, Bartel DP. Widespread shortening of 3'UTRs by alternative cleavage and polyadenylation activates oncogenes in cancer cells. Cell. 2009;138(4):673–684. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dreyfuss G, Kim VN, Kataoka N. Messenger-RNA-binding proteins and the messages they carry. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3(3):195–205. doi: 10.1038/nrm760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Morlando M, Dini Modigliani S, Torrelli G, Rosa A, Di Carlo V, Caffarelli E, Bozzoni I. FUS stimulates microRNA biogenesis by facilitating co-transcriptional Drosha recruitment. EMBO J. 2012;31(24):4502–4510. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Treiber T, Treiber N, Plessmann U, Harlander S, Daiβ J-L, Eichner N, Lehmann G, Schall K, Urlaub H, Meister G. A Compendium of RNA-Binding Proteins that Regulate MicroRNA Biogenesis. Mol Cell. 2017;66(2):270–284.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Couthouis J, et al. A yeast functional screen predicts new candidate ALS disease genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(52):20881–20890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1109434108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kim HJ, et al. Mutations in prion-like domains in hnRNPA2B1 and hnRNPA1 cause multisystem proteinopathy and ALS. Nature. 2013;495(7442):467–473. doi: 10.1038/nature11922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Alberti S, Halfmann R, King O, Kapila A, Lindquist S. A systematic survey identifies prions and illuminates sequence features of prionogenic proteins. Cell. 2009;137(1):146–158. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hyman AA, Weber CA, Jülicher F. Liquid-liquid phase separation in biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:39–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100913-013325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lin Y, Protter DSW, Rosen MK, Parker R. Formation and Maturation of Phase-Separated Liquid Droplets by RNA-Binding Proteins. Mol Cell. 2015;60(2):208–219. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.08.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Molliex A, Temirov J, Lee J, Coughlin M, Kanagaraj AP, Kim HJ, Mittag T, Taylor JP. Phase separation by low complexity domains promotes stress granule assembly and drives pathological fibrillization. Cell. 2015;163(1):123–133. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.09.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Murakami T, et al. ALS/FTD Mutation-Induced Phase Transition of FUS Liquid Droplets and Reversible Hydrogels into Irreversible Hydrogels Impairs RNP Granule Function. Neuron. 2015;88(4):678–690. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.10.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Patel A, Lee HO, Jawerth L, Maharana S, Jahnel M, Hein MY, Stoynov S, Mahamid J, Saha S, Franzmann TM, Pozniakovski A, Poser I, Maghelli N, Royer LA, Weigert M, Myers EW, Grill S, Drechsel D, Hyman AA, Alberti S. A Liquid-to-Solid Phase Transition of the ALS Protein FUS Accelerated by Disease Mutation. Cell. 2015;162(5):1066–1077. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Buratti E, Baralle FE. Characterization and functional implications of the RNA binding properties of nuclear factor TDP-43, a novel splicing regulator of CFTR exon 9. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(39):36337–36343. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M104236200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Buratti E, Dörk T, Zuccato E, Pagani F, Romano M, Baralle FE. Nuclear factor TDP-43 and SR proteins promote in vitro and in vivo CFTR exon 9 skipping. EMBO J. 2001;20(7):1774–1784. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.7.1774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lagier-Tourenne C, Polymenidou M, Cleveland DW. TDP-43 and FUS/TLS: emerging roles in RNA processing and neurodegeneration. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19(R1):R46–64. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ou SH, Wu F, Harrich D, García-Martínez LF, Gaynor RB. Cloning and characterization of a novel cellular protein, TDP-43, that binds to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 TAR DNA sequence motifs. J Virol. 1995;69(6):3584–3596. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.6.3584-3596.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT, Bruce J, Schuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM, McCluskey LF, Miller BL, Masliah E, Mackenzie IR, Feldman H, Feiden W, Kretzschmar HA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science. 2006;314(5796):130–133. doi: 10.1126/science.1134108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kabashi E, Valdmanis PN, Dion P, Spiegelman D, McConkey BJ, Vande Velde C, Bouchard J-P, Lacomblez L, Pochigaeva K, Salachas F, Pradat P-F, Camu W, Meininger V, Dupre N, Rouleau GA. TARDBP mutations in individuals with sporadic and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Genet. 2008;40(5):572–574. doi: 10.1038/ng.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sreedharan J, Blair IP, Tripathi VB, Hu X, Vance C, Rogelj B, Ackerley S, Durnall JC, Williams KL, Buratti E, Baralle F, de Belleroche J, Mitchell JD, Leigh PN, Al-Chalabi A, Miller CC, Nicholson G, Shaw CE. TDP-43 mutations in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science. 2008;319(5870):1668–1672. doi: 10.1126/science.1154584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lattante S, Rouleau GA, Kabashi E. TARDBP and FUS mutations associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: summary and update. Hum Mutat. 2013;34(6):812–826. doi: 10.1002/humu.22319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tamaki Y, Shodai A, Morimura T, Hikiami R, Minamiyama S, Ayaki T, Tooyama I, Furukawa Y, Takahashi R, Urushitani M. Elimination of TDP-43 inclusions linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by a misfolding-specific intrabody with dual proteolytic signals. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):1–16. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24463-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wu L-S, Cheng W-C, Shen C-KJ. Targeted depletion of TDP-43 expression in the spinal cord motor neurons leads to the development of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-like phenotypes in mice. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(33):27335–27344. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.359000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Iguchi Y, Katsuno M, Niwa J, Takagi S, Ishigaki S, Ikenaka K, Kawai K, Watanabe H, Yamanaka K, Takahashi R, Misawa H, Sasaki S, Tanaka F, Sobue G. Loss of TDP-43 causes age-dependent progressive motor neuron degeneration. Brain. 2013;136(Pt 5):1371–1382. doi: 10.1093/brain/awt029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Donde A, Sun M, Jeong YH, Wen X, Ling J, Lin S, Braunstein K, Nie S, Wang S, Chen L, Wong PC. Upregulation of ATG7 attenuates motor neuron dysfunction associated with depletion of TARDBP/TDP-43. Autophagy. 2019. pp. 1–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 39.Ling JP, Pletnikova O, Troncoso JC, Wong PC. TDP-43 repression of nonconserved cryptic exons is compromised in ALS-FTD. Science. 2015;349(6248):650–655. doi: 10.1126/science.aab0983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Donde A, Sun M, Ling JP, Braunstein KE, Pang B, Wen X, Cheng X, Chen L, Wong PC. Splicing repression is a major function of TDP-43 in motor neurons. Acta Neuropathol. 2019;138(5):813–826. doi: 10.1007/s00401-019-02042-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Arnold ES, Ling S-C, Huelga SC, Lagier-Tourenne C, Polymenidou M, Ditsworth D, Kordasiewicz HB, McAlonis-Downes M, Platoshyn O, Parone PA, Da Cruz S, Clutario KM, Swing D, Tessarollo L, Marsala M, Shaw CE, Yeo GW, Cleveland DW. ALS-linked TDP-43 mutations produce aberrant RNA splicing and adult-onset motor neuron disease without aggregation or loss of nuclear TDP-43. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(8):E736–745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222809110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Mitchell JC, Constable R, So E, Vance C, Scotter E, Glover L, Hortobagyi T, Arnold ES, Ling S-C, McAlonis M, Da Cruz S, Polymenidou M, Tessarolo L, Cleveland DW, Shaw CE. Wild type human TDP-43 potentiates ALS-linked mutant TDP-43 driven progressive motor and cortical neuron degeneration with pathological features of ALS. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2015;3:36. doi: 10.1186/s40478-015-0212-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fratta P, et al. Mice with endogenous TDP-43 mutations exhibit gain of splicing function and characteristics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. EMBO J. 2018;37(11) doi: 10.15252/embj.201798684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rouaux C, Gonzalez De Aguilar J-L, Dupuis L. Unmasking the skiptic task of TDP-43. EMBO J. 2018;37(11) doi: 10.15252/embj.201899645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.White MA, Kim E, Duffy A, Adalbert R, Phillips BU, Peters OM, Stephenson J, Yang S, Massenzio F, Lin Z, Andrews S, Segonds-Pichon A, Metterville J, Saksida LM, Mead R, Ribchester RR, Barhomi Y, Serre T, Coleman MP, Fallon JR, Bussey TJ, Brown RH, Sreedharan J. TDP-43 gains function due to perturbed autoregulation in a Tardbp knock-in mouse model of ALS-FTD. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21(4):552–563. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0113-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ditsworth D, Maldonado M, McAlonis-Downes M, Sun S, Seelman A, Drenner K, Arnold E, Ling S-C, Pizzo D, Ravits J, Cleveland DW, Cruz SD. Mutant TDP-43 within motor neurons drives disease onset but not progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathologica. 2017;133(6):907. doi: 10.1007/s00401-017-1698-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bose JK, Wang I-F, Hung L, Tarn W-Y, Shen C-KJ. TDP-43 overexpression enhances exon 7 inclusion during the survival of motor neuron pre-mRNA splicing. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(43):28852–28859. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M805376200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ishihara T, Ariizumi Y, Shiga A, Kato T, Tan C-F, Sato T, Miki Y, Yokoo M, Fujino T, Koyama A, Yokoseki A, Nishizawa M, Kakita A, Takahashi H, Onodera O. Decreased number of Gemini of coiled bodies and U12 snRNA level in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22(20):4136–4147. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Tsuiji H, Iguchi Y, Furuya A, Kataoka A, Hatsuta H, Atsuta N, Tanaka F, Hashizume Y, Akatsu H, Murayama S, Sobue G, Yamanaka K. Spliceosome integrity is defective in the motor neuron diseases ALS and SMA. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5(2):221–234. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201202303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Shan X, Chiang P-M, Price DL, Wong PC. Altered distributions of Gemini of coiled bodies and mitochondria in motor neurons of TDP-43 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(37):16325–16330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1003459107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Vogler TO, Wheeler JR, Nguyen ED, Hughes MP, Britson KA, Lester E, Rao B, Betta ND, Whitney ON, Ewachiw TE, Gomes E, Shorter J, Lloyd TE, Eisenberg DS, Taylor JP, Johnson AM, Olwin BB, Parker R. TDP-43 and RNA form amyloid-like myo-granules in regenerating muscle. Nature. 2018;563(7732):508–513. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0665-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Militello G, Hosen MR, Ponomareva Y, Gellert P, Weirick T, John D, Hindi SM, Mamchaoui K, Mouly V, Döring C, Zhang L, Nakamura M, Kumar A, Fukada S-I, Dimmeler S, Uchida S. A novel long non-coding RNA Myolinc regulates myogenesis through TDP-43 and Filip1. J Mol Cell Biol. 2018;10(2):102–117. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjy025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.King IN, Yartseva V, Salas D, Kumar A, Heidersbach A, Ando DM, Stallings NR, Elliott JL, Srivastava D, Ivey KN. The RNA-binding protein TDP-43 selectively disrupts microRNA-1/206 incorporation into the RNA-induced silencing complex. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(20):14263–14271. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.561902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Diaper DC, Adachi Y, Sutcliffe B, Humphrey DM, Elliott CJH, Stepto A, Ludlow ZN, Vanden Broeck L, Callaerts P, Dermaut B, Al-Chalabi A, Shaw CE, Robinson IM, Hirth F. Loss and gain of Drosophila TDP-43 impair synaptic efficacy and motor control leading to age-related neurodegeneration by loss-of-function phenotypes. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22(8):1539–1557. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Schmid B, Hruscha A, Hogl S, Banzhaf-Strathmann J, Strecker K, van der Zee J, Teucke M, Eimer S, Hegermann J, Kittelmann M, Kremmer E, Cruts M, Solchenberger B, Hasenkamp L, van Bebber F, Van Broeckhoven C, Edbauer D, Lichtenthaler SF, Haass C. Loss of ALS-associated TDP-43 in zebrafish causes muscle degeneration, vascular dysfunction, and reduced motor neuron axon outgrowth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(13):4986–4991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218311110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Diaper DC, Adachi Y, Lazarou L, Greenstein M, Simoes FA, Di Domenico A, Solomon DA, Lowe S, Alsubaie R, Cheng D, Buckley S, Humphrey DM, Shaw CE, Hirth F. Drosophila TDP-43 dysfunction in glia and muscle cells cause cytological and behavioural phenotypes that characterize ALS and FTLD. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22(19):3883–3893. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Tawara N, Yamashita S, Kawakami K, Kurashige T, Zhang Z, Tasaki M, Yamamoto Y, Nishikami T, Doki T, Zhang X, Matsuo Y, Kimura E, Tawara A, Maeda Y, Hauschka SD, Maruyama H, Ando Y. Muscle-dominant wild-type TDP-43 expression induces myopathological changes featuring tubular aggregates and TDP-43-positive inclusions. Exp Neurol. 2018;309:169–180. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Godena VK, Romano G, Romano M, Appocher C, Klima R, Buratti E, Baralle FE, Feiguin F. TDP-43 regulates Drosophila neuromuscular junctions growth by modulating Futsch/MAP1B levels and synaptic microtubules organization. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(3):e17808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Romano G, Klima R, Buratti E, Verstreken P, Baralle FE, Feiguin F. Chronological requirements of TDP-43 function in synaptic organization and locomotive control. Neurobiol Dis. 2014;71:95–109. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Weihl CC, Temiz P, Miller SE, Watts G, Smith C, Forman M, Hanson PI, Kimonis V, Pestronk A. TDP-43 accumulation in inclusion body myopathy muscle suggests a common pathogenic mechanism with frontotemporal dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79(10):1186–1189. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2007.131334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Salajegheh M, Pinkus JL, Taylor JP, Amato AA, Nazareno R, Baloh RH, Greenberg SA. Sarcoplasmic redistribution of nuclear TDP-43 in inclusion body myositis. Muscle Nerve. 2009;40(1):19–31. doi: 10.1002/mus.21386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Sorarú G, Orsetti V, Buratti E, Baralle F, Cima V, Volpe M, D'ascenzo C, Palmieri A, Koutsikos K, Pegoraro E, Angelini C. TDP-43 in skeletal muscle of patients affected with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2010;11(1–2):240–243. doi: 10.3109/17482960902810890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.D'Agostino C, Nogalska A, Engel WK, Askanas V. In sporadic inclusion body myositis muscle fibres TDP-43-positive inclusions are less frequent and robust than p62 inclusions, and are not associated with paired helical filaments. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2011;37(3):315–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.2010.01108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Hernandez Lain A, Millecamps S, Dubourg O, Salachas F, Bruneteau G, Lacomblez L, LeGuern E, Seilhean D, Duyckaerts C, Meininger V, Mallet J, Pradat P-F. Abnormal TDP-43 and FUS proteins in muscles of sporadic IBM: similarities in a TARDBP-linked ALS patient. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011;82(12):1414–1416. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2010.208868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yamashita S, Kimura E, Tawara N, Sakaguchi H, Nakama T, Maeda Y, Hirano T, Uchino M, Ando Y. Optineurin is potentially associated with TDP-43 and involved in the pathogenesis of inclusion body myositis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2013;39(4):406–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.2012.01297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Cortese A, Plagnol V, Brady S, Simone R, Lashley T, Acevedo-Arozena A, de Silva R, Greensmith L, Holton J, Hanna MG, Fisher EMC, Fratta P. Widespread RNA metabolism impairment in sporadic inclusion body myositis TDP43-proteinopathy. Neurobiol Aging. 2014;35(6):1491–1498. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.12.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bengoechea R, Pittman SK, Tuck EP, True HL, Weihl CC. Myofibrillar disruption and RNA-binding protein aggregation in a mouse model of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 1D. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24(23):6588–6602. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Cykowski MD, Powell SZ, Appel JW, Arumanayagam AS, Rivera AL, Appel SH. Phosphorylated TDP-43 (pTDP-43) aggregates in the axial skeletal muscle of patients with sporadic and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2018;6(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s40478-018-0528-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Cortese A, Laurà M, Casali C, Nishino I, Hayashi YK, Magri S, Taroni F, Stuani C, Saveri P, Moggio M, Ripolone M, Prelle A, Pisciotta C, Sagnelli A, Pichiecchio A, Reilly MM, Buratti E, Pareyson D. Altered TDP-43-dependent splicing in HSPB8-related distal hereditary motor neuropathy and myofibrillar myopathy. Eur J Neurol. 2018;25(1):154–163. doi: 10.1111/ene.13478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Tan AY, Manley JL. The TET family of proteins: functions and roles in disease. J Mol Cell Biol. 2009;1(2):82–92. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjp025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Svetoni F, Frisone P, Paronetto MP. Role of FET proteins in neurodegenerative disorders. RNA Biology. 2016;13(11):1089. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1211225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kwiatkowski TJ, Bosco DA, Leclerc AL, Tamrazian E, Vanderburg CR, Russ C, Davis A, Gilchrist J, Kasarskis EJ, Munsat T, Valdmanis P, Rouleau GA, Hosler BA, Cortelli P, de Jong PJ, Yoshinaga Y, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Yan J, Ticozzi N, Siddique T, McKenna-Yasek D, Sapp PC, Horvitz HR, Landers JE, Brown RH. Mutations in the FUS/TLS gene on chromosome 16 cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science. 2009;323(5918):1205–1208. doi: 10.1126/science.1166066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Vance C, Rogelj B, Hortobágyi T, De Vos KJ, Nishimura AL, Sreedharan J, Hu X, Smith B, Ruddy D, Wright P, Ganesalingam J, Williams KL, Tripathi V, Al-Saraj S, Al-Chalabi A, Leigh PN, Blair IP, Nicholson G, de Belleroche J, Gallo J-M, Miller CC, Shaw CE. Mutations in FUS, an RNA processing protein, cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 6. Science. 2009;323(5918):1208–1211. doi: 10.1126/science.1165942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Waibel S, Neumann M, Rosenbohm A, Birve A, Volk AE, Weishaupt JH, Meyer T, Müller U, Andersen PM, Ludolph AC. Truncating mutations in FUS/TLS give rise to a more aggressive ALS-phenotype than missense mutations: a clinico-genetic study in Germany. Eur J Neurol. 2013;20(3):540–546. doi: 10.1111/ene.12031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Vance C, Scotter EL, Nishimura AL, Troakes C, Mitchell JC, Kathe C, Urwin H, Manser C, Miller CC, Hortobágyi T, Dragunow M, Rogelj B, Shaw CE. ALS mutant FUS disrupts nuclear localization and sequesters wild-type FUS within cytoplasmic stress granules. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22(13):2676–2688. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Dormann D, Rodde R, Edbauer D, Bentmann E, Fischer I, Hruscha A, Than ME, Mackenzie IRA, Capell A, Schmid B, Neumann M, Haass C. ALS-associated fused in sarcoma (FUS) mutations disrupt Transportin-mediated nuclear import. EMBO J. 2010;29(16):2841–2857. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Rademakers R, Stewart H, Dejesus-Hernandez M, Krieger C, Graff-Radford N, Fabros M, Briemberg H, Cashman N, Eisen A, Mackenzie IRA. Fus gene mutations in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve. 2010;42(2):170–176. doi: 10.1002/mus.21665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Zhou Y, Liu S, Liu G, Oztürk A, Hicks GG. ALS-associated FUS mutations result in compromised FUS alternative splicing and autoregulation. PLoS Genet. 2013;9(10):e1003895. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Dormann D, Madl T, Valori CF, Bentmann E, Tahirovic S, Abou-Ajram C, Kremmer E, Ansorge O, Mackenzie IRA, Neumann M, Haass C. Arginine methylation next to the PY-NLS modulates Transportin binding and nuclear import of FUS. EMBO J. 2012;31(22):4258–4275. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Suárez-Calvet M, Neumann M, Arzberger T, Abou-Ajram C, Funk E, Hartmann H, Edbauer D, Kremmer E, Göbl C, Resch M, Bourgeois B, Madl T, Reber S, Jutzi D, Ruepp M-D, Mackenzie IRA, Ansorge O, Dormann D, Haass C. Monomethylated and unmethylated FUS exhibit increased binding to Transportin and distinguish FTLD-FUS from ALS-FUS. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131(4):587–604. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1544-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Neumann M, Bentmann E, Dormann D, Jawaid A, DeJesus-Hernandez M, Ansorge O, Roeber S, Kretzschmar HA, Munoz DG, Kusaka H, Yokota O, Ang L-C, Bilbao J, Rademakers R, Haass C, Mackenzie IRA. FET proteins TAF15 and EWS are selective markers that distinguish FTLD with FUS pathology from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with FUS mutations. Brain. 2011;134(9):2595–2609. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Neumann M, Valori CF, Ansorge O, Kretzschmar HA, Munoz DG, Kusaka H, Yokota O, Ishihara K, Ang L-C, Bilbao JM, Mackenzie IRA. Transportin 1 accumulates specifically with FET proteins but no other transportin cargos in FTLD-FUS and is absent in FUS inclusions in ALS with FUS mutations. Acta Neuropathol. 2012;124(5):705–716. doi: 10.1007/s00401-012-1020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Hofweber M, Hutten S, Bourgeois B, Spreitzer E, Niedner-Boblenz A, Schifferer M, Ruepp M-D, Simons M, Niessing D, Madl T, Dormann D. Phase Separation of FUS Is Suppressed by Its Nuclear Import Receptor and Arginine Methylation. Cell. 2018;173(3):706–719.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Yamazaki T, Chen S, Yu Y, Yan B, Haertlein TC, Carrasco MA, Tapia JC, Zhai B, Das R, Lalancette-Hebert M, Sharma A, Chandran S, Sullivan G, Nishimura AL, Shaw CE, Gygi SP, Shneider NA, Maniatis T, Reed R. FUS-SMN protein interactions link the motor neuron diseases ALS and SMA. Cell Rep. 2012;2(4):799–806. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.08.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Groen EJN, Fumoto K, Blokhuis AM, Engelen-Lee J, Zhou Y, van den Heuvel DMA, Koppers M, van Diggelen F, van Heest J, Demmers JAA, Kirby J, Shaw PJ, Aronica E, Spliet WGM, Veldink JH, van den Berg LH, Pasterkamp RJ. ALS-associated mutations in FUS disrupt the axonal distribution and function of SMN. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22(18):3690–3704. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Sun S, Ling S-C, Qiu J, Albuquerque CP, Zhou Y, Tokunaga S, Li H, Qiu H, Bui A, Yeo GW, Huang EJ, Eggan K, Zhou H, Fu X-D, Lagier-Tourenne C, Cleveland DW. ALS-causative mutations in FUS/TLS confer gain and loss of function by altered association with SMN and U1-snRNP. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6171. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Mirra A, Rossi S, Scaricamazza S, Di Salvio M, Salvatori I, Valle C, Rusmini P, Poletti A, Cestra G, Carrì MT, Cozzolino M. Functional interaction between FUS and SMN underlies SMA-like splicing changes in wild-type hFUS mice. Sci Rep. 2017;7 doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02195-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Tradewell ML, Yu Z, Tibshirani M, Boulanger M-C, Durham HD, Richard S. Arginine methylation by PRMT1 regulates nuclear-cytoplasmic localization and toxicity of FUS/TLS harbouring ALS-linked mutations. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21(1):136–149. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Tibshirani M, Tradewell ML, Mattina KR, Minotti S, Yang W, Zhou H, Strong MJ, Hayward LJ, Durham HD. Cytoplasmic sequestration of FUS/TLS associated with ALS alters histone marks through loss of nuclear protein arginine methyltransferase 1. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24(3):773–786. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Bosco DA, Lemay N, Ko HK, Zhou H, Burke C, Kwiatkowski TJ, Sapp P, McKenna-Yasek D, Brown RH, Hayward LJ. Mutant FUS proteins that cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis incorporate into stress granules. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19(21):4160–4175. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Wang W-Y, Pan L, Su SC, Quinn EJ, Sasaki M, Jimenez JC, Mackenzie IRA, Huang EJ, Tsai L-H. Interaction of FUS and HDAC1 Regulates DNA Damage Response and Repair in Neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2013;16(10):1383–1391. doi: 10.1038/nn.3514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Singatulina AS, Hamon L, Sukhanova MV, Desforges B, Joshi V, Bouhss A, Lavrik OI, Pastré D. PARP-1 Activation Directs FUS to DNA Damage Sites to Form PARG-Reversible Compartments Enriched in Damaged DNA. Cell Reports. 2019;27(6):1809–1821.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.04.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Scekic-Zahirovic J, Sendscheid O, El Oussini H, Jambeau M, Sun Y, Mersmann S, Wagner M, Dieterlé S, Sinniger J, Dirrig-Grosch S, Drenner K, Birling M-C, Qiu J, Zhou Y, Li H, Fu X-D, Rouaux C, Shelkovnikova T, Witting A, Ludolph AC, Kiefer F, Storkebaum E, Lagier-Tourenne C, Dupuis L. Toxic gain of function from mutant FUS protein is crucial to trigger cell autonomous motor neuron loss. EMBO J. 2016;35(10):1077–1097. doi: 10.15252/embj.201592559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Devoy A, Kalmar B, Stewart M, Park H, Burke B, Noy SJ, Redhead Y, Humphrey J, Lo K, Jaeger J, Mejia Maza A, Sivakumar P, Bertolin C, Soraru G, Plagnol V, Greensmith L, Acevedo Arozena A, Isaacs AM, Davies B, Fratta P, Fisher EMC. Humanized mutant FUS drives progressive motor neuron degeneration without aggregation in “FUSDelta14” knockin mice. Brain. 2017;140(11):2797–2805. doi: 10.1093/brain/awx248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.López-Erauskin J, Tadokoro T, Baughn MW, Myers B, McAlonis-Downes M, Chillon-Marinas C, Asiaban JN, Artates J, Bui AT, Vetto AP, Lee SK, Le AV, Sun Y, Jambeau M, Boubaker J, Swing D, Qiu J, Hicks GG, Ouyang Z, Fu X-D, Tessarollo L, Ling S-C, Parone PA, Shaw CE, Marsala M, Lagier-Tourenne C, Cleveland DW, Da Cruz S. ALS/FTD-Linked Mutation in FUS Suppresses Intra-axonal Protein Synthesis and Drives Disease Without Nuclear Loss-of-Function of FUS. Neuron. 2018;100(4):816–830.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.09.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ling S-C, Dastidar SG, Tokunaga S, Ho WY, Lim K, Ilieva H, Parone PA, Tyan S-H, Tse TM, Chang J-C, Platoshyn O, Bui NB, Bui A, Vetto A, Sun S, McAlonis-Downes M, Han JS, Swing D, Kapeli K, Yeo GW, Tessarollo L, Marsala M, Shaw CE, Tucker-Kellogg G, La Spada AR, Lagier-Tourenne C, Da Cruz S, Cleveland DW. Overriding FUS autoregulation in mice triggers gain-of-toxic dysfunctions in RNA metabolism and autophagy-lysosome axis. Elife. 2019;8 doi: 10.7554/eLife.40811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Scekic-Zahirovic J, Oussini HE, Mersmann S, Drenner K, Wagner M, Sun Y, Allmeroth K, Dieterlé S, Sinniger J, Dirrig-Grosch S, René F, Dormann D, Haass C, Ludolph AC, Lagier-Tourenne C, Storkebaum E, Dupuis L. Motor neuron intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms contribute to the pathogenesis of FUS-associated amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2017;133(6):887–906. doi: 10.1007/s00401-017-1687-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Orozco D, Edbauer D. FUS-mediated alternative splicing in the nervous system: consequences for ALS and FTLD. J Mol Med. 2013;91(12):1343–1354. doi: 10.1007/s00109-013-1077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Kino Y, Washizu C, Kurosawa M, Yamada M, Doi H, Takumi T, Adachi H, Katsuno M, Sobue G, Hicks GG, Hattori N, Shimogori T, Nukina N. FUS/TLS acts as an aggregation-dependent modifier of polyglutamine disease model mice. Sci Rep. 2016;6:35236. doi: 10.1038/srep35236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Ishigaki S, Fujioka Y, Okada Y, Riku Y, Udagawa T, Honda D, Yokoi S, Endo K, Ikenaka K, Takagi S, Iguchi Y, Sahara N, Takashima A, Okano H, Yoshida M, Warita H, Aoki M, Watanabe H, Okado H, Katsuno M, Sobue G. Altered Tau Isoform Ratio Caused by Loss of FUS and SFPQ Function Leads to FTLD-like Phenotypes. Cell Rep. 2017;18(5):1118–1131. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Yokoi S, Udagawa T, Fujioka Y, Honda D, Okado H, Watanabe H, Katsuno M, Ishigaki S, Sobue G. 3'UTR Length-Dependent Control of SynGAP Isoform α2 mRNA by FUS and ELAV-like Proteins Promotes Dendritic Spine Maturation and Cognitive Function. Cell Rep. 2017;20(13):3071–3084. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.08.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Ishigaki S, Sobue G. Importance of Functional Loss of FUS in FTLD/ALS. Front Mol Biosci. 2018;5:44. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Brown JA, Min J, Staropoli JF, Collin E, Bi S, Feng X, Barone R, Cao Y, O'Malley L, Xin W, Mullen TE, Sims KB. SOD1, ANG, TARDBP and FUS mutations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a United States clinical testing lab experience. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2012;13(2):217–222. doi: 10.3109/17482968.2011.643899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Meissner M, Lopato S, Gotzmann J, Sauermann G, Barta A. Proto-oncoprotein TLS/FUS is associated to the nuclear matrix and complexed with splicing factors PTB, SRm160, and SR proteins. Exp Cell Res. 2003;283(2):184–195. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(02)00046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Ansseau E, Eidahl JO, Lancelot C, Tassin A, Matteotti C, Yip C, Liu J, Leroy B, Hubeau C, Gerbaux C, Cloet S, Wauters A, Zorbo S, Meyer P, Pirson I, Laoudj-Chenivesse D, Wattiez R, Harper SQ, Belayew A, Coppée F. Homologous Transcription Factors DUX4 and DUX4c Associate with Cytoplasmic Proteins during Muscle Differentiation. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(1):e0146893. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Liu T-Y, Chen Y-C, Jong Y-J, Tsai H-J, Lee C-C, Chang Y-S, Chang J-G, Chang Y-F. Muscle developmental defects in heterogeneous nuclear Ribonucleoprotein A1 knockout mice. Open Biol. 2017;7(1):e99645. doi: 10.1098/rsob.160303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Johnson JO, et al. Mutations in the Matrin 3 gene cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Neurosci. 2014;17(5):664–666. doi: 10.1038/nn.3688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Kamelgarn M, Chen J, Kuang L, Arenas A, Zhai J, Zhu H, Gal J. Proteomic analysis of FUS interacting proteins provides insights into FUS function and its role in ALS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1862(10):2004–2014. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.07.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Sánchez-Ramos C, Tierrez A, Fabregat-Andrés O, Wild B, Sánchez-Cabo F, Arduini A, Dopazo A, Monsalve M. PGC-1α regulates translocated in liposarcoma activity: role in oxidative stress gene expression. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(2):325–337. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Xia R, Liu Y, Yang L, Gal J, Zhu H, Jia J. Motor neuron apoptosis and neuromuscular junction perturbation are prominent features in a Drosophila model of Fus-mediated ALS. Mol Neurodegener. 2012;7:10. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-7-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Armstrong GAB, Drapeau P. Loss and gain of FUS function impair neuromuscular synaptic transmission in a genetic model of ALS. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22(21):4282–4292. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Machamer JB, Collins SE, Lloyd TE. The ALS gene FUS regulates synaptic transmission at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(14):3810–3822. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Sharma A, Lyashchenko AK, Lu L, Nasrabady SE, Elmaleh M, Mendelsohn M, Nemes A, Tapia JC, Mentis GZ, Shneider NA. ALS-associated mutant FUS induces selective motor neuron degeneration through toxic gain of function. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10465. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.So E, Mitchell JC, Memmi C, Chennell G, Vizcay-Barrena G, Allison L, Shaw CE, Vance C. Mitochondrial abnormalities and disruption of the neuromuscular junction precede the clinical phenotype and motor neuron loss in hFUSWT transgenic mice. Hum Mol Genet. 2018;27(3):463–474. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Picchiarelli G, Demestre M, Zuko A, Been M, Higelin J, Dieterlé S, Goy M-A, Mallik M, Sellier C, Scekic-Zahirovic J, Zhang L, Rosenbohm A, Sijlmans C, Aly A, Mersmann S, Sanjuan-Ruiz I, Hübers A, Messaddeq N, Wagner M, van Bakel N, Boutillier A-L, Ludolph A, Lagier-Tourenne C, Boeckers TM, Dupuis L, Storkebaum E. FUS-mediated regulation of acetylcholine receptor transcription at neuromuscular junctions is compromised in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22(11):1793–1805. doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0498-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Gerbino V, Carrì MT, Cozzolino M, Achsel T. Mislocalised FUS mutants stall spliceosomal snRNPs in the cytoplasm. Neurobiol Dis. 2013;55:120–128. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Reber S, Stettler J, Filosa G, Colombo M, Jutzi D, Lenzken SC, Schweingruber C, Bruggmann R, Bachi A, Barabino SM, Mühlemann O, Ruepp M-D. Minor intron splicing is regulated by FUS and affected by ALS-associated FUS mutants. EMBO J. 2016;35(14):1504–1521. doi: 10.15252/embj.201593791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Barzago C, Lum J, Cavalcante P, Srinivasan KG, Faggiani E, Camera G, Bonanno S, Andreetta F, Antozzi C, Baggi F, Calogero RA, Bernasconi P, Mantegazza R, Mori L, Zolezzi F. A novel infection- and inflammation-associated molecular signature in peripheral blood of myasthenia gravis patients. Immunobiolog. 2016;221(11):1227–1236. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2016.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Doi H, Okamura K, Bauer PO, Furukawa Y, Shimizu H, Kurosawa M, Machida Y, Miyazaki H, Mitsui K, Kuroiwa Y, Nukina N. RNA-binding protein TLS is a major nuclear aggregate-interacting protein in huntingtin exon 1 with expanded polyglutamine-expressing cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(10):6489–6500. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705306200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Doi H, Koyano S, Suzuki Y, Nukina N, Kuroiwa Y. The RNA-binding protein FUS/TLS is a common aggregate-interacting protein in polyglutamine diseases. Neurosci Res. 2010;66(1):131–133. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2009.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Eliazer S, Spencer J, Ye D, Olson E, Ilaria RL. Alteration of mesodermal cell differentiation by EWS/FLI-1, the oncogene implicated in Ewing's sarcoma. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(2):482–492. doi: 10.1128/mcb.23.2.482-492.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Rorie CJ, Thomas VD, Chen P, Pierce HH, O'Bryan JP, Weissman BE. The Ews/Fli-1 fusion gene switches the differentiation program of neuroblastomas to Ewing sarcoma/peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Cancer Res. 2004;64(4):1266–1277. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-3274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Kang H-J, Park JH, Chen W, Kang SI, Moroz K, Ladanyi M, Lee SB. EWS-WT1 oncoprotein activates neuronal reprogramming factor ASCL1 and promotes neural differentiation. Cancer Res. 2014;74(16):4526–4535. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Couthouis J, Hart MP, Erion R, King OD, Diaz Z, Nakaya T, Ibrahim F, Kim H-J, Mojsilovic-Petrovic J, Panossian S, Kim CE, Frackelton EC, Solski JA, Williams KL, Clay-Falcone D, Elman L, McCluskey L, Greene R, Hakonarson H, Kalb RG, Lee VMY, Trojanowski JQ, Nicholson GA, Blair IP, Bonini NM, Van Deerlin VM, Mourelatos Z, Shorter J, Gitler AD. Evaluating the role of the FUS/TLS-related gene EWSR1 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21(13):2899–2911. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Young PJ, Francis JW, Lince D, Coon K, Androphy EJ, Lorson CL. The Ewing's sarcoma protein interacts with the Tudor domain of the survival motor neuron protein. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2003;119(1):37–49. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2003.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Chi B, O'Connell JD, Iocolano AD, Coady JA, Yu Y, Gangopadhyay J, Gygi SP, Reed R. The neurodegenerative diseases ALS and SMA are linked at the molecular level via the ASC-1 complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(22):11939–11951. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Park JH, Kang H-J, Lee YK, Kang H, Kim J, Chung JH, Chang JS, McPherron AC, Lee SB. Inactivation of EWS reduces PGC-1α protein stability and mitochondrial homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(19):6074–6079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504391112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Ticozzi N, Vance C, Leclerc AL, Keagle P, Glass JD, McKenna-Yasek D, Sapp PC, Silani V, Bosco DA, Shaw CE, Brown RH, Landers JE. Mutational analysis reveals the FUS homolog TAF15 as a candidate gene for familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2011;156B(3):285–290. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.31158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Altanbyek V, Cha S-J, Kang G-U, Im DS, Lee S, Kim H-J, Kim K. Imbalance of mitochondrial dynamics in Drosophila models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;481(3–4):259–264. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Nakayasu H, Berezney R. Nuclear matrins: identification of the major nuclear matrix proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991;88(22):10312–10316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Belgrader P, Dey R, Berezney R. Molecular cloning of matrin 3. A 125-kilodalton protein of the nuclear matrix contains an extensive acidic domain. J Biol Chem. 1991;266(15):9893–9899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Salton M, Elkon R, Borodina T, Davydov A, Yaspo M-L, Halperin E, Shiloh Y. Matrin 3 binds and stabilizes mRNA. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(8):e23882. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Depreux FF, Puckelwartz MJ, Augustynowicz A, Wolfgeher D, Labno CM, Pierre-Louis D, Cicka D, Kron SJ, Holaska J, McNally EM. Disruption of the lamin A and matrin-3 interaction by myopathic LMNA mutations. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24(15):4284–4295. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Banerjee A, Vest KE, Pavlath GK, Corbett AH. Nuclear poly(A) binding protein 1 (PABPN1) and Matrin3 interact in muscle cells and regulate RNA processing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(18):10706–10725. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Hall MP, Nagel RJ, Fagg WS, Shiue L, Cline MS, Perriman RJ, Donohue JP, Ares M. Quaking and PTB control overlapping splicing regulatory networks during muscle cell differentiation. RNA. 2013;19(5):627–638. doi: 10.1261/rna.038422.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Coelho MB, Attig J, Bellora N, König J, Hallegger M, Kayikci M, Eyras E, Ule J, Smith CWJ. Nuclear matrix protein Matrin3 regulates alternative splicing and forms overlapping regulatory networks with PTB. EMBO J. 2015;34(5):653–668. doi: 10.15252/embj.201489852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Frock RL, Kudlow BA, Evans AM, Jameson SA, Hauschka SD, Kennedy BK. Lamin A/C and emerin are critical for skeletal muscle satellite cell differentiation. Genes Dev. 2006;20(4):486–500. doi: 10.1101/gad.1364906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Dubinska-Magiera M, Zaremba-Czogalla M, Rzepecki R. Muscle development, regeneration and laminopathies: how lamins or lamina-associated proteins can contribute to muscle development, regeneration and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(15):2713–2741. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1190-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Bertrand AT, Chikhaoui K, Yaou RB, Bonne G. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity in laminopathies. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011;39(6):1687–1692. doi: 10.1042/BST20110670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Feit H, Silbergleit A, Schneider LB, Gutierrez JA, Fitoussi RP, Réyès C, Rouleau GA, Brais B, Jackson CE, Beckmann JS, Seboun E. Vocal cord and pharyngeal weakness with autosomal dominant distal myopathy: clinical description and gene localization to 5q31. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;63(6):1732–1742. doi: 10.1086/302166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Senderek J, Garvey SM, Krieger M, Guergueltcheva V, Urtizberea A, Roos A, Elbracht M, Stendel C, Tournev I, Mihailova V, Feit H, Tramonte J, Hedera P, Crooks K, Bergmann C, Rudnik-Schöneborn S, Zerres K, Lochmüller H, Seboun E, Weis J, Beckmann JS, Hauser MA, Jackson CE. Autosomal-dominant distal myopathy associated with a recurrent missense mutation in the gene encoding the nuclear matrix protein, matrin 3. Am J Hum Genet. 2009;84(4):511–518. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.03.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Udd B. Distal muscular dystrophies. Handb Clin Neurol. 2011;101:239–262. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-08-045031-5.00016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Müller TJ, Kraya T, Stoltenburg-Didinger G, Hanisch F, Kornhuber M, Stoevesandt D, Senderek J, Weis J, Baum P, Deschauer M, Zierz S. Phenotype of matrin-3-related distal myopathy in 16 German patients. Ann Neurol. 2014;76(5):669–680. doi: 10.1002/ana.24255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Kraya T, Schmidt B, Müller T, Hanisch F. Impairment of respiratory function in late-onset distal myopathy due to MATR3 Mutation. Muscle Nerve. 2015;51(6):916–918. doi: 10.1002/mus.24603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Xu L, Li J, Tang L, Zhang N, Fan D. MATR3 mutation analysis in a Chinese cohort with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol Aging. 2016;38:218.e3–218.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.11.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Mori K, Lammich S, Mackenzie IRA, Forné I, Zilow S, Kretzschmar H, Edbauer D, Janssens J, Kleinberger G, Cruts M, Herms J, Neumann M, Van Broeckhoven C, Arzberger T, Haass C. hnRNP A3 binds to GGGGCC repeats and is a constituent of p62-positive/TDP43-negative inclusions in the hippocampus of patients with C9orf72 mutations. Acta Neuropathol. 2013;125(3):413–423. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Mori K, Nihei Y, Arzberger T, Zhou Q, Mackenzie IR, Hermann A, Hanisch F, German Consortium for Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration, Bavarian Brain Banking Alliance, Kamp F, Nuscher B, Orozco D, Edbauer D, Haass C. Reduced hnRNPA3 increases C9orf72 repeat RNA levels and dipeptide-repeat protein deposition. EMBO Rep. 2016;17(9):1314–1325. doi: 10.15252/embr.201541724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Davidson YS, Flood L, Robinson AC, Nihei Y, Mori K, Rollinson S, Richardson A, Benson BC, Jones M, Snowden JS, Pickering-Brown S, Haass C, Lashley T, Mann DMA. Heterogeneous ribonuclear protein A3 (hnRNP A3) is present in dipeptide repeat protein containing inclusions in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration and Motor Neurone disease associated with expansions in C9orf72 gene. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2017;5(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s40478-017-0437-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Fifita JA, Zhang KY, Galper J, Williams KL, McCann EP, Hogan AL, Saunders N, Bauer D, Tarr IS, Pamphlett R, Nicholson GA, Rowe D, Yang S, Blair IP. Genetic and Pathological Assessment of hnRNPA1, hnRNPA2/B1, and hnRNPA3 in Familial and Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurodegener Dis. 2017;17(6):304–312. doi: 10.1159/000481258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Honda H, Hamasaki H, Wakamiya T, Koyama S, Suzuki SO, Fujii N, Iwaki T. Loss of hnRNPA1 in ALS spinal cord motor neurons with TDP-43-positive inclusions. Neuropathology. 2015;35(1):37–43. doi: 10.1111/neup.12153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Koukoui SD, Chaudhuri A. Neuroanatomical, molecular genetic, and behavioral correlates of fragile X syndrome. Brain Res Rev. 2007;53(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2006.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Sofola OA, Jin P, Qin Y, Duan R, Liu H, de Haro M, Nelson DL, Botas J. RNA-binding proteins hnRNP A2/B1 and CUGBP1 suppress fragile X CGG premutation repeat-induced neurodegeneration in a Drosophila model of FXTAS. Neuron. 2007;55(4):565–571. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.07.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Vieira NM, Naslavsky MS, Licinio L, Kok F, Schlesinger D, Vainzof M, Sanchez N, Kitajima JP, Gal L, Cavaçana N, Serafini PR, Chuartzman S, Vasquez C, Mimbacas A, Nigro V, Pavanello RC, Schuldiner M, Kunkel LM, Zatz M. A defect in the RNA-processing protein HNRPDL causes limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 1G (LGMD1G). Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(15):4103–4110. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Batlle C, Yang P, Coughlin M, Messing J, Pesarrodona M, Szulc E, Salvatella X, Kim HJ, Taylor JP, Ventura S. hnRNPDL Phase Separation Is Regulated by Alternative Splicing and Disease-Causing Mutations Accelerate Its Aggregation. Cell Rep. 2020;30(4):1117–1128.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.12.080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Fan X, Messaed C, Dion P, Laganiere J, Brais B, Karpati G, Rouleau GA. HnRNP A1 and A/B interaction with PABPN1 in oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy. Can J Neurol Sci. 2003;30(3):244–251. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100002675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Kashima T, Rao N, David CJ, Manley JL. hnRNP A1 functions with specificity in repression of SMN2 exon 7 splicing. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16(24):3149–3159. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Chen H-H, Chang J-G, Lu R-M, Peng T-Y, Tarn W-Y. The RNA binding protein hnRNP Q modulates the utilization of exon 7 in the survival motor neuron 2 (SMN2) gene. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28(22):6929–6938. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01332-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Irimura S, Kitamura K, Kato N, Saiki K, Takeuchi A, Gunadi, Matsuo M, Nishio H, Lee MJ. HnRNP C1/C2 may regulate exon 7 splicing in the spinal muscular atrophy gene SMN1. Kobe J Med Sci. 2009;54(5):E227–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Cho S, Moon H, Loh TJ, Oh HK, Cho S, Choy HE, Song WK, Chun J-S, Zheng X, Shen H. hnRNP M facilitates exon 7 inclusion of SMN2 pre-mRNA in spinal muscular atrophy by targeting an enhancer on exon 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1839(4):306–315. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Dombert B, Sivadasan R, Simon CM, Jablonka S, Sendtner M. Presynaptic localization of Smn and hnRNP R in axon terminals of embryonic and postnatal mouse motoneurons. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(10):e110846. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Moursy A, Allain FH-T, Cléry A. Characterization of the RNA recognition mode of hnRNP G extends its role in SMN2 splicing regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(10):6659–6672. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Geuens T, Bouhy D, Timmerman V. The hnRNP family: insights into their role in health and disease. Hum Genet. 2016;135:851–867. doi: 10.1007/s00439-016-1683-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Beusch I, Barraud P, Moursy A, Cléry A, Allain FH-T. Tandem hnRNP A1 RNA recognition motifs act in concert to repress the splicing of survival motor neuron exon 7. Elife. 2017;6 doi: 10.7554/eLife.25736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Ling S-C, Albuquerque CP, Han JS, Lagier-Tourenne C, Tokunaga S, Zhou H, Cleveland DW. ALS-associated mutations in TDP-43 increase its stability and promote TDP-43 complexes with FUS/TLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(30):13318–13323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008227107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Zeitz MJ, Malyavantham KS, Seifert B, Berezney R. Matrin 3: chromosomal distribution and protein interactions. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108(1):125–133. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Yamaguchi A, Takanashi K. FUS interacts with nuclear matrix-associated protein SAFB1 as well as Matrin3 to regulate splicing and ligand-mediated transcription. Sci Rep. 2016;6:35195. doi: 10.1038/srep35195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Deshaies J-E, Shkreta L, Moszczynski AJ, Sidibé H, Semmler S, Fouillen A, Bennett ER, Bekenstein U, Destroismaisons L, Toutant J, Delmotte Q, Volkening K, Stabile S, Aulas A, Khalfallah Y, Soreq H, Nanci A, Strong MJ, Chabot B, Vande Velde C. TDP-43 regulates the alternative splicing of hnRNP A1 to yield an aggregation-prone variant in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain. 2018;141(5):1320–1333. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Gu J, Chen F, Iqbal K, Gong C-X, Wang X, Liu F. Transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) regulates alternative splicing of tau exon 10: Implications for the pathogenesis of tauopathies. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(25):10600–10612. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.783498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Kim SH, Shanware NP, Bowler MJ, Tibbetts RS. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-associated proteins TDP-43 and FUS/TLS function in a common biochemical complex to co-regulate HDAC6 mRNA. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(44):34097–34105. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.154831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Lagier-Tourenne C, Polymenidou M, Hutt KR, Vu AQ, Baughn M, Huelga SC, Clutario KM, Ling S-C, Liang TY, Mazur C, Wancewicz E, Kim AS, Watt A, Freier S, Hicks GG, Donohue JP, Shiue L, Bennett CF, Ravits J, Cleveland DW, Yeo GW. Divergent roles of ALS-linked proteins FUS/TLS and TDP-43 intersect in processing long pre-mRNAs. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15(11):1488–1497. doi: 10.1038/nn.3230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Chi B, O'Connell JD, Yamazaki T, Gangopadhyay J, Gygi SP, Reed R. Interactome analyses revealed that the U1 snRNP machinery overlaps extensively with the RNAP II machinery and contains multiple ALS/SMA-causative proteins. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):8755. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27136-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Marrone L, Drexler HCA, Wang J, Tripathi P, Distler T, Heisterkamp P, Anderson EN, Kour S, Moraiti A, Maharana S, Bhatnagar R, Belgard TG, Tripathy V, Kalmbach N, Hosseinzadeh Z, Crippa V, Abo-Rady M, Wegner F, Poletti A, Troost D, Aronica E, Busskamp V, Weis J, Pandey UB, Hyman AA, Alberti S, Goswami A, Sterneckert J. FUS pathology in ALS is linked to alterations in multiple ALS-associated proteins and rescued by drugs stimulating autophagy. Acta Neuropathol. 2019;138(1):67–84. doi: 10.1007/s00401-019-01998-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Kabashi E, Bercier V, Lissouba A, Liao M, Brustein E, Rouleau GA, Drapeau P. FUS and TARDBP but not SOD1 interact in genetic models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS Genet. 2011;7(8):e1002214. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Melamed Z, López-Erauskin J, Baughn MW, Zhang O, Drenner K, Sun Y, Freyermuth F, McMahon MA, Beccari MS, Artates JW, Ohkubo T, Rodriguez M, Lin N, Wu D, Bennett CF, Rigo F, Da Cruz S, Ravits J, Lagier-Tourenne C, Cleveland DW. Premature polyadenylation-mediated loss of stathmin-2 is a hallmark of TDP-43-dependent neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22(2):180–190. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0293-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Klim JR, Williams LA, Limone F, Guerra San Juan I, Davis-Dusenbery BN, Mordes DA, Burberry A, Steinbaugh MJ, Gamage KK, Kirchner R, Moccia R, Cassel SH, Chen K, Wainger BJ, Woolf CJ, Eggan K. ALS-implicated protein TDP-43 sustains levels of STMN2, a mediator of motor neuron growth and repair. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22(2):167–179. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0300-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Uemura Y, Oshima T, Yamamoto M, Reyes CJ, Costa Cruz PH, Shibuya T, Kawahara Y. Matrin3 binds directly to intronic pyrimidine-rich sequences and controls alternative splicing. Genes Cells. 2017;22(9):785–798. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Burd CG, Dreyfuss G. Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins. Science. 1994;265(5172):615–621. doi: 10.1126/science.8036511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Tollervey JR, Curk T, Rogelj B, Briese M, Cereda M, Kayikci M, König J, Hortobágyi T, Nishimura AL, Zupunski V, Patani R, Chandran S, Rot G, Zupan B, Shaw CE, Ule J. Characterizing the RNA targets and position-dependent splicing regulation by TDP-43. Nat Neurosci. 2011;14(4):452–458. doi: 10.1038/nn.2778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Polymenidou M, Lagier-Tourenne C, Hutt KR, Huelga SC, Moran J, Liang TY, Ling S-C, Sun E, Wancewicz E, Mazur C, Kordasiewicz H, Sedaghat Y, Donohue JP, Shiue L, Bennett CF, Yeo GW, Cleveland DW. Long pre-mRNA depletion and RNA missplicing contribute to neuronal vulnerability from loss of TDP-43. Nat Neurosci. 2011;14(4):459–468. doi: 10.1038/nn.2779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Lerga A, Hallier M, Delva L, Orvain C, Gallais I, Marie J, Moreau-Gachelin F. Identification of an RNA binding specificity for the potential splicing factor TLS. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(9):6807–6816. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008304200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Hoell JI, Larsson E, Runge S, Nusbaum JD, Duggimpudi S, Farazi TA, Hafner M, Borkhardt A, Sander C, Tuschl T. RNA targets of wild-type and mutant FET family proteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011;18(12):1428–1431. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Masuda A, Takeda J, Okuno T, Okamoto T, Ohkawara B, Ito M, Ishigaki S, Sobue G, Ohno K. Position-specific binding of FUS to nascent RNA regulates mRNA length. Genes Dev. 2015;29(10):1045–1057. doi: 10.1101/gad.255737.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Wang T, Birsoy K, Hughes NW, Krupczak KM, Post Y, Wei JJ, Lander ES, Sabatini DM. Identification and characterization of essential genes in the human genome. Science. 2015;350(6264):1096–1101. doi: 10.1126/science.aac7041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Rogelj B, Easton LE, Bogu GK, Stanton LW, Rot G, Curk T, Zupan B, Sugimoto Y, Modic M, Haberman N, Tollervey J, Fujii R, Takumi T, Shaw CE, Ule J. Widespread binding of FUS along nascent RNA regulates alternative splicing in the brain. Sci Rep. 2012;2:603. doi: 10.1038/srep00603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Kapeli K, Pratt GA, Vu AQ, Hutt KR, Martinez FJ, Sundararaman B, Batra R, Freese P, Lambert NJ, Huelga SC, Chun SJ, Liang TY, Chang J, Donohue JP, Shiue L, Zhang J, Zhu H, Cambi F, Kasarskis E, Hoon S, Jr MA, Burge CB, Ravits J, Rigo F, Yeo GW. Distinct and shared functions of ALS-associated proteins TDP-43, FUS and TAF15 revealed by multisystem analyses. Nat Commun. 2016;7(1):1–14. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]