Abstract
Background
Chlorops oryzae is an important pest of rice crops. There have been frequent outbreaks of this pest in recent years and it has become the main rice pest in some regions. To elucidate the molecular mechanism of frequent C. oryzae outbreaks, we estimated the genetic diversity and genetic differentiation of 20 geographical populations based on a dataset of ISSR markers and COI sequences.
Results
ISSR data revealed a high level of genetic diversity among the 20 populations as measured by Shannon’s information index (I), Nei’s gene diversity (H), and the percentage of polymorphic bands (PPB). The mean coefficient of gene differentiation (Gst) was 0.0997, which indicates that only 9.97% genetic variation is between populations. The estimated gene flow (Nm) value was 4.5165, indicating a high level of gene flow and low, or medium, genetic differentiation among some populations. The results of a Mantel test revealed no significant correlation between genetic and geographic distance among populations, which means there is no evidence of significant genetic isolation by distance. An UPGMA (unweighted pair-group method with arithmetic averages) dendrogram based on genetic identity, did not indicate any major geographic structure for the 20 populations examined. mtDNA COI data indicates low nucleotide (0.0007) and haplotype diversity (0.36) in all populations. Fst values suggest that the 20 populations have low, or medium, levels of genetic differentiation. And the topology of a Neighbor-Joining tree suggests that there are no independent groups among the populations examined.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that C. oryzae populations have high genetic diversity at the species level. There is evidence of frequent gene flow and low, or medium, levels of genetic differentiation among some populations. There is no significant correlation between genetic and geographic distance among C. oryzae populations, and therefore no significant isolation by distance. All results are consistent with frequent gene exchange between populations, which could increase the genetic diversity, and hence, adaptability of C. oryzae, thereby promoting frequent outbreaks of this pest. Such knowledge may provide a scientific basis for predicting future outbreaks.
Keywords: Chlorops oryzae, Mitochondrial DNA, ISSR, Genetic diversity, Genetic differentiation
Background
Chlorops oryzae (Diptera, Chloropidae) is an important pest of paddy rice plants, which inflicts significant economic damage to rice crops throughout Asia. However, the dispersal ability, potential for long-distance dispersal, pattern of migration, ecological amplitude, and population size of C. oryzae are still uncertain. Most research on this species has focused on the physiology and ecology [1–3], and its genetics is relatively unstudied [4].
Frequent C. oryzae outbreaks in recent years have caused the species to become a major pest in some regions. The propensity for outbreaks may itself play an important role in homogenizing genetic variation and intensifying gene flow between pest populations [5, 6]. We hypothesized that frequent gene flow between populations enhances the species’ overall adaptability, promoting the frequent outbreaks that occur today. In other words, the frequent outbreaks of C. oryzae are associated with the species’ genetic diversity, population demography and high rate of gene flow between populations.
To test this hypothesis, we evaluated the genetic structure of different geographic populations of C. oryzae and the level of gene flow between them. We quantified the genetic diversity and degrees of genetic differentiation of 20 different geographical populations, which may provide a scientific basis for predicting future outbreaks.
We used two effective and promising DNA markers, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR), to examine between-population differences. Studies of genetic variation between pest populations can not only provide information on their population structure in different geographical regions, but also deduce the demographic history of this species [7–9]. Yi et al. used microsatellite and mtDNA loci to investigate the genetic divergence and dispersal ability of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) on six offshore islands in South China, which results indicated that these populations have high genetic diversity, frequent gene flow and low, or medium, levels of genetic differentiation. Thus, the geographic isolation of the six islands is no barrier to the dispersal of B. dorsalis [10]. Research on the genetic diversity and population structure of Leucinodes orbonalis collected from a variety of agro-climatic conditions found almost no genetic diversity and no significant genetic variation among the mitochondrial gene Cytochrome Oxidase I (COI) gene sequences of the populations examined. However, a few genetically distinct populations were associated with some specific habitat requirements [11]. Similarly, genetic differentiation in ISSR markers and the COI gene among Iranian populations of Hishimonus phycitis may have been induced by geographical and ecological isolation and may have an impact on the vectoring capability of this insect [12].
Our results not only provide information on the genetic structure and phylogeography research of C. oryzae, but also provide a potential scientific basis for monitoring and controlling this pest.
Results
COI gene analysis
Genetic diversity and differentiation
In total, 432 individuals collected from different locations were used to amplify 684 bp of the COI gene sequence, which defined 47 haplotypes. All 47 haplotypes had 43 variable sites, including 26 singleton variable sites and 17 parsimony informative sites. The mean total nucleotide frequencies of A, T, C and G in the nucleotide sequences from the 20 different populations were 29.98%, 36.56%, 16.95% and 16.51%, respectively, which shows an obvious AT bias (66.54%). The transition/transversion rate ratio was observed to be higher with purines (36.158) than pyrimidines (19.381). The overall transition/transversion bias was 12.022.
Genetic diversity parameters of the 20 populations and the results of neutrality tests are shown in Table 1. Haplotype diversity (Hd) for each population ranged from 0 to 0.71739 and the average number of differences (k) ranged from 0 to 1.35145. Nucleotide diversity (Π) for each population ranged from 0 to 0.00198. Tajima’s D and Fu’s Fs test of neutrality of 19 populations showed a negative value. When all samples were calculated as one population, Tajima’s D and Fu’s Fs values were negative and 1‰ significant, which is strong evidence of population expansion.
Table 1.
Genetic diversity of 20 C. oryzae populations
| populations | n | h | Hd | K | Pi | Tajima’s D | P-value | Fu’s Fs | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TY | 24 | 4 | 0.23913 | 0.25000 | 0.00037 | − 1.73253 | 0.10 > P > 0.05 | − 3.021 | 0.039 |
| ZZ | 24 | 3 | 0.16304 | 0.16667 | 0.00024 | − 1.51469 | > 0.10 | − 2.078 | 0.094 |
| LS | 24 | 4 | 0.23913 | 0.25000 | 0.00037 | − 1.73253 | 0.10. > P > 0.05 | − 3.021 | 0.039 |
| YS | 24 | 3 | 0.16304 | 0.25000 | 0.00037 | − 1.73253 | 0.10 > P > 0.05 | − 1.355 | 0.159 |
| XT | 24 | 3 | 0.23551 | 0.24275 | 0.00035 | − 1.20229 | > 0.10 | − 1.407 | 0.153 |
| HS | 24 | 3 | 0.23551 | 0.24275 | 0.00035 | − 1.20229 | > 0.10 | − 1.407 | 0.153 |
| HD | 16 | 5 | 0.60833 | 1.07500 | 0.00157 | − 1.38795 | > 0.10 | − 1.243 | 0.145 |
| JS | 16 | 4 | 0.35000 | 0.37500 | 0.00055 | − 1.69654 | 0.10 > P > 0.05 | − 2.449 | 0.065 |
| SM | 24 | 5 | 0.31159 | 0.33333 | 0.00049 | − 1.88381 | < 0.05 | − 3.974 | 0.016 |
| DC | 24 | 6 | 0.49638 | 0.64493 | 0.00094 | − 1.81040 | < 0.05 | − 3.383 | 0.026 |
| XX | 24 | 8 | 0.56159 | 0.65942 | 0.00096 | − 2.02600 | < 0.05 | − 6.535 | 0.001 |
| YL | 8 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | N | N | N | N |
| YX | 24 | 3 | 0.30072 | 0.31159 | 0.00046 | − 0.91964 | > 0.10 | − 0.960 | 0.200 |
| SS | 24 | 4 | 0.23913 | 0.33333 | 0.00049 | − 1.88381 | < 0.05 | − 2.331 | 0.070 |
| LL | 24 | 7 | 0.71739 | 1.15942 | 0.00170 | − 1.19233 | > 0.10 | − 2.620 | 0.047 |
| TJ | 24 | 4 | 0.23913 | 0.25000 | 0.00037 | − 1.73253 | 0.10 > P> 0.05 | − 3.021 | 0.039 |
| LH | 24 | 6 | 0.38043 | 0.41667 | 0.00061 | − 1.99611 | < 0.05 | − 4.976 | 0.006 |
| GZ | 8 | 2 | 0.25000 | 0.25000 | 0.00037 | − 1.05482 | > 0.10 | − 0.182 | 0.354 |
| ZJ | 24 | 5 | 0.37681 | 0.48551 | 0.00071 | − 1.49528 | > 0.10 | − 2.842 | 0.043 |
| NX | 24 | 9 | 0.66304 | 1.35145 | 0.00198 | − 1.98791 | < 0.05 | − 4.496 | 0.008 |
| Total | 432 | 47 | 0.36000 | 0.48000 | 0.00070 | − 2.56478 | < 0.001 | − 100.982 | 0.000 |
n: Number of individual, h: Number of haplotype, Hd: Haplotype diversity, K: Average number of differences, Pi: Nucleotide diversity
Based on our sequence database, inter- and intraspecific genetic distances of C. oryzae populations were 0.00012–0.00184 and 0–0.00198 (Table 2) respectively, which indicates no significant genetic differentiation. The Fst values between populations ranged from − 0.0595 to 0.1174 (Table 3), indicating that inter-population differences are relatively low. AMOVA results suggest that 97.28% of all genetic variation is within, and only 2.72% between, populations (Table 4).
Table 2.
Genetic distances between (below diagonal) and within C. oryzae populations (on diagonal) based on COI sequences
| TY | ZZ | LS | YS | XT | HS | HD | JS | SM | DC | XX | YL | YX | SS | LL | TJ | LH | GZ | ZJ | NX | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TY | 0.00037 | |||||||||||||||||||
| ZZ | 0.00031 | 0.00024 | ||||||||||||||||||
| LS | 0.00037 | 0.00031 | 0.00037 | |||||||||||||||||
| YS | 0.00037 | 0.00031 | 0.00036 | 0.00037 | ||||||||||||||||
| XT | 0.00037 | 0.00030 | 0.00037 | 0.00037 | 0.00036 | |||||||||||||||
| HS | 0.00037 | 0.00031 | 0.00036 | 0.00036 | 0.00037 | 0.00036 | ||||||||||||||
| HD | 0.00101 | 0.00093 | 0.00101 | 0.00101 | 0.00098 | 0.00101 | 0.00158 | |||||||||||||
| JS | 0.00046 | 0.00040 | 0.00046 | 0.00046 | 0.00046 | 0.00046 | 0.00110 | 0.00055 | ||||||||||||
| SM | 0.00043 | 0.00037 | 0.00043 | 0.00043 | 0.00043 | 0.00043 | 0.00105 | 0.00052 | 0.00049 | |||||||||||
| DC | 0.00067 | 0.00059 | 0.00067 | 0.00067 | 0.00064 | 0.00067 | 0.00127 | 0.00076 | 0.00073 | 0.00095 | ||||||||||
| XX | 0.00067 | 0.00060 | 0.00067 | 0.00067 | 0.00065 | 0.00067 | 0.00127 | 0.00076 | 0.00073 | 0.00094 | 0.00097 | |||||||||
| YL | 0.00018 | 0.00012 | 0.00018 | 0.00018 | 0.00018 | 0.00018 | 0.00083 | 0.00028 | 0.00024 | 0.00049 | 0.00048 | 0.00000 | ||||||||
| YX | 0.00042 | 0.00035 | 0.00043 | 0.00043 | 0.00040 | 0.00043 | 0.00102 | 0.00052 | 0.00049 | 0.00068 | 0.00070 | 0.00024 | 0.00046 | |||||||
| SS | 0.00043 | 0.00037 | 0.00043 | 0.00043 | 0.00043 | 0.00043 | 0.00105 | 0.00052 | 0.00048 | 0.00073 | 0.00073 | 0.00024 | 0.00049 | 0.00049 | ||||||
| LL | 0.00116 | 0.00109 | 0.00116 | 0.00116 | 0.00116 | 0.00116 | 0.00167 | 0.00125 | 0.00119 | 0.00146 | 0.00142 | 0.00098 | 0.00122 | 0.00119 | 0.00170 | |||||
| TJ | 0.00037 | 0.00030 | 0.00037 | 0.00037 | 0.00037 | 0.00037 | 0.00098 | 0.00046 | 0.00042 | 0.00065 | 0.00066 | 0.00018 | 0.00041 | 0.00042 | 0.00113 | 0.00037 | ||||
| LH | 0.00049 | 0.00043 | 0.00049 | 0.00049 | 0.00049 | 0.00048 | 0.00113 | 0.00058 | 0.00055 | 0.00079 | 0.00079 | 0.00031 | 0.00055 | 0.00055 | 0.00128 | 0.00049 | 0.00061 | |||
| GZ | 0.00037 | 0.00031 | 0.00035 | 0.00035 | 0.00035 | 0.00035 | 0.00101 | 0.00046 | 0.00043 | 0.00066 | 0.00067 | 0.00018 | 0.00043 | 0.00043 | 0.00116 | 0.00037 | 0.00049 | 0.00037 | ||
| ZJ | 0.00055 | 0.00049 | 0.00055 | 0.00055 | 0.00055 | 0.00055 | 0.00117 | 0.00064 | 0.00061 | 0.00086 | 0.00085 | 0.00037 | 0.00061 | 0.00061 | 0.00122 | 0.00055 | 0.00067 | 0.00055 | 0.00071 | |
| NX | 0.00122 | 0.00116 | 0.00122 | 0.00122 | 0.00121 | 0.00122 | 0.00177 | 0.00131 | 0.00126 | 0.00151 | 0.00148 | 0.00104 | 0.00127 | 0.00126 | 0.00184 | 0.00120 | 0.00134 | 0.00122 | 0.00140 | 0.00198 |
Table 3.
Genetic differentiation (pairwise FST) of 20 C. oryzae populations based on nucleotide sequences of mitochondrial DNA. Lower left diagonal represents the
| TY | ZZ | LS | YS | XT | HS | HD | JS | SM | DC | XX | YL | YX | SS | LL | TJ | LH | GZ | NX | ZJ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TY | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | + | – | |
| ZZ | 0.0000 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | + | – | |
| LS | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | + | – | |
| YS | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | − 0.0141 | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | + | – | |
| XT | 0.0145 | − 0.0165 | 0.0145 | 0.0145 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | |
| HS | 0.0145 | 0.0174 | 0.0006 | 0.0006 | 0.0290 | + | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | + | – | |
| HD | 0.0555 | 0.0442 | 0.0555 | 0.0555 | 0.0284 | 0.0616 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | |
| JS | 0.0044 | 0.0089 | 0.0044 | 0.0044 | 0.0168 | 0.0168 | 0.0333 | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | |
| SM | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0124 | 0.0124 | 0.0347 | 0.0013 | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | |
| DC | 0.0163 | − 0.0075 | 0.0163 | 0.0163 | − 0.0145 | 0.0242 | 0.0112 | 0.0146 | 0.0217 | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | + | – | |
| XX | 0.0003 | − 0.0167 | 0.0079 | 0.0079 | − 0.0150 | 0.0158 | 0.0022 | 0.0011 | 0.0003 | − 0.0153 | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | |
| YL | − 0.0595 | − 0.0595 | − 0.0595 | − 0.0595 | − 0.0381 | − 0.0381 | − 0.0140 | − 0.0503 | − 0.0595 | − 0.0354 | − 0.0515 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| YX | 0.0257 | 0.0019 | 0.0373 | 0.0373 | − 0.0234 | 0.0497 | 0.0204 | 0.0332 | 0.0326 | − 0.0279 | − 0.0132 | − 0.0108 | + | – | – | – | + | + | ||
| SS | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0124 | 0.0124 | 0.0347 | 0.0013 | − 0.0105 | 0.0217 | 0.0003 | − 0.0595 | 0.0326 | + | – | – | – | – | – | |
| LL | 0.1098 | 0.1118 | 0.1098 | 0.1098 | 0.1144 | 0.1144 | 0.0151 | 0.0846 | 0.0774 | 0.0947 | 0.0612 | 0.0400 | 0.1174 | 0.0774 | + | + | – | – | + | |
| TJ | 0.0000 | − 0.0170 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | − 0.0137 | 0.0145 | 0.0221 | 0.0044 | − 0.0121 | − 0.0068 | − 0.0152 | − 0.0595 | 0.0016 | − 0.0121 | 0.0816 | – | – | – | – | |
| LH | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0109 | − 0.0102 | 0.0452 | − 0.0011 | 0.0000 | 0.0201 | 0.0067 | − 0.0595 | 0.0290 | 0.0000 | 0.0994 | 0.0000 | – | + | – | |
| GZ | 0.0000 | 0.0189 | − 0.0435 | − 0.0435 | 0.0158 | − 0.0272 | − 0.0024 | − 0.0123 | − 0.0116 | − 0.0309 | − 0.0255 | 0.0000 | 0.0269 | − 0.0116 | 0.0480 | 0.0000 | − 0.0194 | – | – | |
| NX | 0.0351 | 0.0370 | 0.0391 | 0.0391 | 0.0354 | 0.0435 | − 0.0064 | 0.0224 | 0.0217 | 0.0288 | 0.0066 | − 0.0253 | 0.0382 | 0.0217 | 0.0012 | 0.0187 | 0.0356 | − 0.0137 | + | |
| ZJ | 0.0193 | 0.0217 | 0.0193 | 0.0193 | 0.0290 | 0.0290 | 0.0309 | 0.0135 | 0.0174 | 0.0311 | 0.0186 | − 0.0381 | 0.0435 | 0.0174 | 0.0890 | 0.0193 | 0.0158 | − 0.0068 | 0.0346 |
FST value and upper diagonal showing the significance (+, P < 0.05)
Table 4.
AMOVA analysis of mtDNA COI gene sequences in 20 C. oryzae populations
| Source of variation | df | Sum of squares | Variance components | Percentage of variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among populations | 19 | 7.116 | 0.00654Va | 2.72 |
| Within populations | 412 | 96.250 | 0.23362Vb | 97.28 |
| Total | 431 | 103.366 | 0.24016 | 100 |
Fst = 0.02724 (P = 0.000)
Haplotype network and population tree
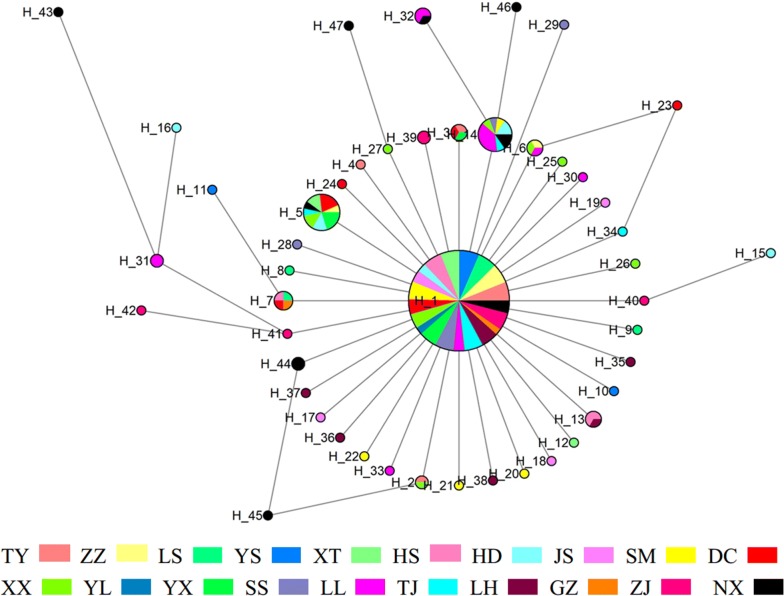
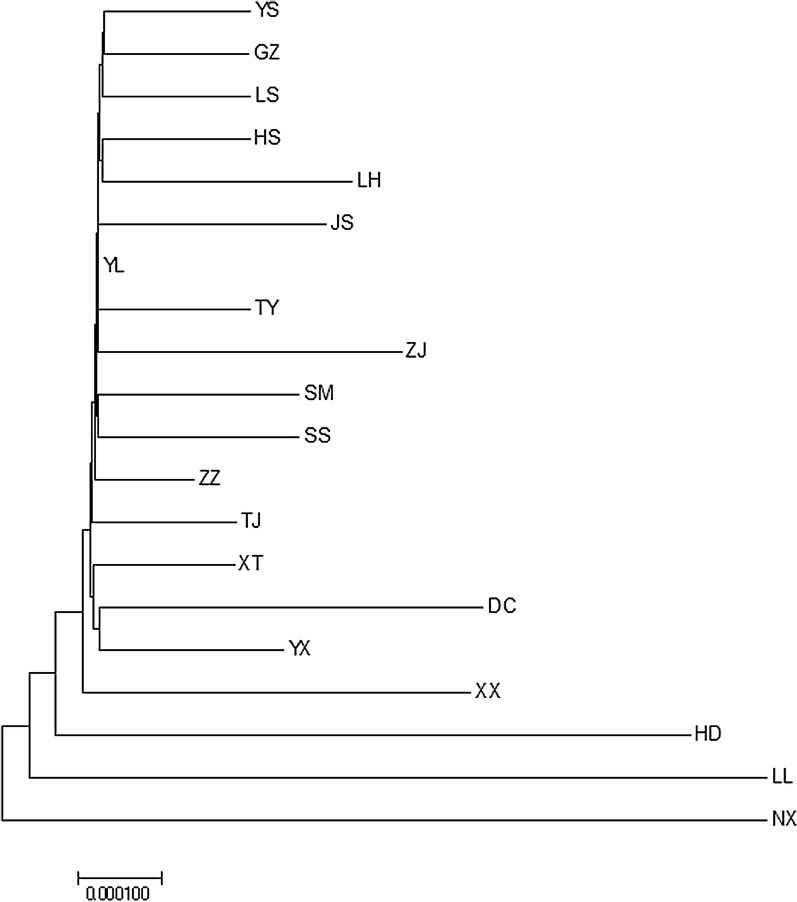
Evolutionary relationships among the haplotypes were depicted using the median-joining network method (Fig. 1). Among the 47 haplotypes, H1 was the most frequent haplotype, which occupied a central position of the network and was diversified by 46 haplotypes. Especially, H23 and H45 can be derived from two different haplotypes with just one mutational step, respectively. The topology of the C. oryzae population Neighbor-Joining tree suggested that there were no independent groups in all populations (Fig. 2). It is worth mentioning that NX population is most distant on the haplotype network and population tree, however, there is no certain landscape features around the NX location. The reason for preventing emigration of individuals is still unknown.
Fig. 1.
Median-joining network based on the single gene of COI haplotypes. Each circle represents a haplotype, and the area of a circle is proportional to the number of individuals with that haplotype. Colors within nodes refer to C. oryzae sampling regions
Fig. 2.
Neighbor-joining tree (model Kimura-2 parameter) of the phylogenetic relationships among 20 C. oryzae populations based on COI gene variation (1000 bootstrap replicates)
ISSR-PCR analysis
Genetic diversity
197 fragments were generated from the 9 primers, ranging in size from 250 to 2000 bp, and with an average of 21.89 fragments per primer. The percentage of polymorphic bands was 100% showing high genetic diversity at the species level. Among the 20 populations, PPB values ranged from 89.85% to 99.49%. The Na and Ne were 2.0000 ± 0.0000 (1.8985 ± 0.3028 to 1.9949 ± 0.0712 among populations) and 1.6460 ± 0.2373 (1.4992 ± 0.3270 to 1.6908 ± 0.2784 among populations), respectively. The H and I were 0.3785 ± 0.0984 (0.2992 ± 0.1588 to 0.3893 ± 0.1196) and 0.5609 ± 0.1151 (0.4547 ± 0.2091 to 0.5692 ± 0.1457), respectively, within all samples (Table 5).
Table 5.
Genetic variation among C. oryzae populations
| Population | Number of polymorphic bands | PPB (%) | Na | Ne | H | I |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TY | 189 | 95.94 | 1.9594 ± 0.1979 | 1.5564 ± 0.2981 | 0.3307 ± 0.1428 | 0.4970 ± 0.1848 |
| ZZ | 194 | 98.48 | 1.9848 ± 0.1228 | 1.5755 ± 0.2915 | 0.3410 ± 0.1342 | 0.5119 ± 0.1683 |
| LS | 192 | 97.46 | 1.9746 ± 0.1577 | 1.6440 ± 0.2820 | 0.3704 ± 0.1275 | 0.5460 ± 0.1612 |
| YS | 190 | 96.45 | 1.9645 ± 0.1856 | 1.5740 ± 0.2886 | 0.3404 ± 0.1355 | 0.5101 ± 0.1736 |
| XT | 189 | 95.94 | 1.9594 ± 0.1979 | 1.6300 ± 0.3049 | 0.3604 ± 0.1431 | 0.5309 ± 0.1855 |
| HS | 194 | 98.48 | 1.9848 ± 0.1228 | 1.6908 ± 0.2784 | 0.3893 ± 0.1196 | 0.5692 ± 0.1457 |
| HD | 191 | 96.95 | 1.9695 ± 0.1723 | 1.5777 ± 0.2993 | 0.3403 ± 0.1395 | 0.5095 ± 0.1773 |
| JS | 187 | 94.92 | 1.9492 ± 0.2201 | 1.5680 ± 0.3006 | 0.3360 ± 0.1403 | 0.5036 ± 0.1817 |
| SM | 194 | 98.48 | 1.9848 ± 0.1228 | 1.6039 ± 0.2831 | 0.3545 ± 0.1278 | 0.5287 ± 0.1584 |
| DC | 196 | 99.49 | 1.9949 ± 0.0712 | 1.5609 ± 0.2835 | 0.3367 ± 0.1272 | 0.5091 ± 0.1556 |
| XX | 195 | 98.98 | 1.9898 ± 0.1005 | 1.5200 ± 0.2769 | 0.3193 ± 0.1283 | 0.4881 ± 0.1596 |
| YL | 177 | 89.85 | 1.8985 ± 0.3028 | 1.5646 ± 0.3245 | 0.3289 ± 0.1578 | 0.4893 ± 0.2113 |
| YX | 192 | 97.46 | 1.9746 ± 0.1577 | 1.5377 ± 0.2914 | 0.3243 ± 0.1370 | 0.4916 ± 0.1737 |
| SS | 187 | 94.92 | 1.9492 ± 0.2201 | 1.5917 ± 0.3165 | 0.3426 ± 0.1501 | 0.5087 ± 0.1955 |
| LL | 192 | 97.46 | 1.9746 ± 0.1577 | 1.6025 ± 0.2834 | 0.3539 ± 0.1281 | 0.5275 ± 0.1615 |
| TJ | 195 | 98.98 | 1.9898 ± 0.1005 | 1.5816 ± 0.2890 | 0.3443 ± 0.1310 | 0.5167 ± 0.1621 |
| LH | 195 | 98.98 | 1.9898 ± 0.1005 | 1.5947 ± 0.2691 | 0.3536 ± 0.1172 | 0.5300 ± 0.1420 |
| GZ | 180 | 91.37 | 1.9137 ± 0.2815 | 1.5762 ± 0.3268 | 0.3342 ± 0.1551 | 0.4969 ± 0.2048 |
| ZJ | 185 | 93.91 | 1.9391 ± 0.2398 | 1.4992 ± 0.3270 | 0.2992 ± 0.1588 | 0.4547 ± 0.2091 |
| NX | 190 | 96.45 | 1.9645 ± 0.1856 | 1.5801 ± 0.2966 | 0.3416 ± 0.1393 | 0.5106 ± 0.1791 |
| Total | 197 | 100.00 | 2.0000 ± 0.0000 | 1.6460 ± 0.2373 | 0.3785 ± 0.0984 | 0.5609 ± 0.1151 |
PPB the percentage of polymorphic bands, Na Observed number of alleles, Ne effective number of alleles
H = Nei’s (1973) gene diversity, I = Shannon’s information index
Genetic differentiation
The Gst was 0.0997, which indicates that 90.03% genetic variation is within populations and only 9.97% between populations. The estimated Nm value was 4.5165 (Table 6). These results suggest that genetic differentiation among populations of C. oryzae is impeded by high gene flow. Table 7 lists the genetic identity (above diagonal) and genetic distance (below diagonal) among populations.
Table 6.
Population genetic differentiation coefficients and gene flow among C. oryzae populations
| Total genetic diversity (Ht) | Genetic diversity within populations (Hs) | Coefficient of gene differentiation (Gst) | Gene flow (Nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 0.3799 | 0.3421 | 0.0997 | 4.5165 |
| Standard deviation | 0.0095 | 0.0074 |
Table 7.
Nei’s genetic identity (above diagonal) and genetic distance (below diagonal) among C. oryzae populations
| TY | ZZ | LS | YS | XT | HS | HD | JS | SM | DC | XX | YL | YX | SS | LL | TJ | LH | GZ | ZJ | NX | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TY | 0.9644 | 0.9643 | 0.9690 | 0.9543 | 0.9680 | 0.9770 | 0.9630 | 0.9614 | 0.9665 | 0.9638 | 0.9545 | 0.9533 | 0.9583 | 0.9633 | 0.9630 | 0.9521 | 0.9216 | 0.9473 | 0.9616 | |
| ZZ | 0.0362 | 0.9657 | 0.9800 | 0.9430 | 0.9547 | 0.9627 | 0.9494 | 0.9494 | 0.9533 | 0.9510 | 0.9342 | 0.9439 | 0.9406 | 0.9632 | 0.9580 | 0.9456 | 0.9025 | 0.9157 | 0.9388 | |
| LS | 0.0363 | 0.0349 | 0.9652 | 0.9694 | 0.9643 | 0.9698 | 0.9606 | 0.9566 | 0.9505 | 0.9624 | 0.9444 | 0.9568 | 0.9556 | 0.9680 | 0.9553 | 0.9558 | 0.9259 | 0.9209 | 0.9589 | |
| YS | 0.0315 | 0.0202 | 0.0354 | 0.9493 | 0.9560 | 0.9712 | 0.9555 | 0.9508 | 0.9593 | 0.9592 | 0.9362 | 0.9523 | 0.9428 | 0.9676 | 0.9604 | 0.9460 | 0.9131 | 0.9273 | 0.9415 | |
| XT | 0.0468 | 0.0586 | 0.0311 | 0.0520 | 0.9770 | 0.9643 | 0.9565 | 0.9475 | 0.9472 | 0.9620 | 0.9477 | 0.9512 | 0.9593 | 0.9599 | 0.9406 | 0.9457 | 0.9198 | 0.9239 | 0.9516 | |
| HS | 0.0325 | 0.0463 | 0.0363 | 0.0450 | 0.0232 | 0.9730 | 0.9582 | 0.9607 | 0.9636 | 0.9544 | 0.9572 | 0.9487 | 0.9721 | 0.9684 | 0.9514 | 0.9567 | 0.9406 | 0.9357 | 0.9628 | |
| HD | 0.0233 | 0.0380 | 0.0306 | 0.0292 | 0.0364 | 0.0274 | 0.9778 | 0.9599 | 0.9619 | 0.9695 | 0.9568 | 0.9617 | 0.9710 | 0.9714 | 0.9609 | 0.9585 | 0.9261 | 0.9420 | 0.9608 | |
| JS | 0.0377 | 0.0519 | 0.0402 | 0.0455 | 0.0444 | 0.0427 | 0.0225 | 0.9481 | 0.9632 | 0.9790 | 0.9569 | 0.9738 | 0.9554 | 0.9705 | 0.9563 | 0.9672 | 0.9221 | 0.9407 | 0.9630 | |
| SM | 0.0394 | 0.0519 | 0.0444 | 0.0505 | 0.0539 | 0.0401 | 0.0409 | 0.0533 | 0.9553 | 0.9580 | 0.9390 | 0.9453 | 0.9489 | 0.9599 | 0.9594 | 0.9599 | 0.9398 | 0.9426 | 0.9728 | |
| DC | 0.0341 | 0.0479 | 0.0508 | 0.0415 | 0.0543 | 0.0371 | 0.0389 | 0.0375 | 0.0457 | 0.9678 | 0.9350 | 0.9681 | 0.9446 | 0.9773 | 0.9778 | 0.9765 | 0.9332 | 0.9301 | 0.9600 | |
| XX | 0.0368 | 0.0502 | 0.0384 | 0.0416 | 0.0387 | 0.0467 | 0.0309 | 0.0212 | 0.0429 | 0.0327 | 0.9497 | 0.9816 | 0.9541 | 0.9726 | 0.9588 | 0.9666 | 0.9258 | 0.9361 | 0.9616 | |
| YL | 0.0466 | 0.0681 | 0.0572 | 0.0659 | 0.0537 | 0.0437 | 0.0441 | 0.0441 | 0.0629 | 0.0672 | 0.0516 | 0.9446 | 0.9532 | 0.9433 | 0.9263 | 0.9312 | 0.9090 | 0.9350 | 0.9385 | |
| YX | 0.0479 | 0.0577 | 0.0442 | 0.0489 | 0.0500 | 0.0526 | 0.0390 | 0.0266 | 0.0563 | 0.0324 | 0.0185 | 0.0569 | 0.9460 | 0.9692 | 0.9622 | 0.9706 | 0.9279 | 0.9395 | 0.9557 | |
| SS | 0.0426 | 0.0613 | 0.0454 | 0.0589 | 0.0416 | 0.0283 | 0.0295 | 0.0457 | 0.0525 | 0.0570 | 0.0470 | 0.0479 | 0.0555 | 0.9568 | 0.9435 | 0.9378 | 0.9203 | 0.9300 | 0.9487 | |
| LL | 0.0374 | 0.0375 | 0.0325 | 0.0329 | 0.0409 | 0.0321 | 0.0290 | 0.0299 | 0.0409 | 0.0229 | 0.0278 | 0.0583 | 0.0313 | 0.0442 | 0.9645 | 0.9694 | 0.9349 | 0.9301 | 0.9606 | |
| TJ | 0.0377 | 0.0429 | 0.0457 | 0.0404 | 0.0612 | 0.0498 | 0.0399 | 0.0447 | 0.0414 | 0.0224 | 0.0420 | 0.0765 | 0.0385 | 0.0582 | 0.0362 | 0.9755 | 0.9334 | 0.9322 | 0.9557 | |
| LH | 0.0490 | 0.0560 | 0.0452 | 0.0555 | 0.0558 | 0.0443 | 0.0424 | 0.0333 | 0.0409 | 0.0237 | 0.0339 | 0.0713 | 0.0299 | 0.0642 | 0.0311 | 0.0248 | 0.9524 | 0.9445 | 0.9691 | |
| GZ | 0.0816 | 0.1026 | 0.0770 | 0.0909 | 0.0835 | 0.0612 | 0.0768 | 0.0811 | 0.0621 | 0.0691 | 0.0771 | 0.0954 | 0.0749 | 0.0831 | 0.0673 | 0.0689 | 0.0487 | 0.9345 | 0.9551 | |
| ZJ | 0.0541 | 0.0881 | 0.0825 | 0.0754 | 0.0792 | 0.0664 | 0.0597 | 0.0612 | 0.0591 | 0.0724 | 0.0661 | 0.0672 | 0.0624 | 0.0726 | 0.0724 | 0.0702 | 0.0571 | 0.0678 | 0.9583 | |
| NX | 0.0392 | 0.0631 | 0.0419 | 0.0603 | 0.0496 | 0.0379 | 0.0400 | 0.0377 | 0.0275 | 0.0408 | 0.0392 | 0.0634 | 0.0453 | 0.0527 | 0.0402 | 0.0453 | 0.0314 | 0.0459 | 0.0426 |
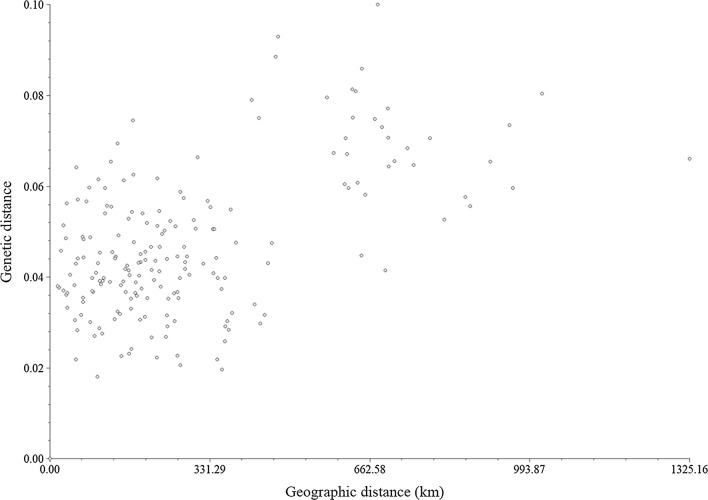
The relationship between genetic and geographic distance was shown in Fig. 3. A Mantel test revealed no significant correlation between genetic and geographic distance (r = 0.54675, p = 0.9992) among C. oryzae populations, and there was therefore no evidence of significant isolation by distance.
Fig. 3.
Relationship between genetic distance and geographic distance of 20 C. oryzae populations
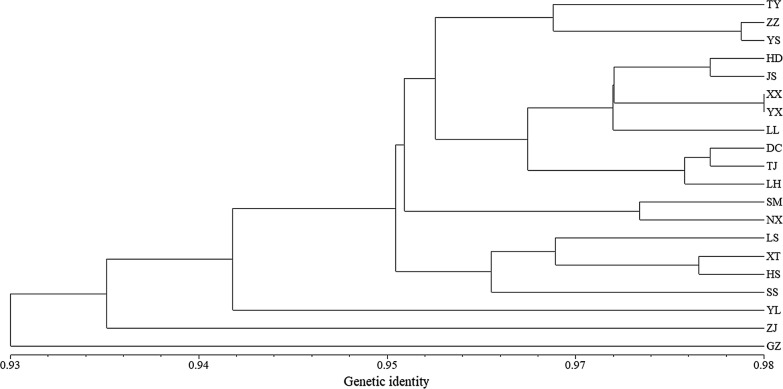
An UPGMA dendrogram constructed based on genetic identity (Fig. 4) grouped the 20 populations into two major clusters. The dendrogram did not reveal any major geographic structure for these populations.
Fig. 4.
UPGMA dendrogram of 20 C. oryzae populations
Discussion
The rapid development of molecular techniques has made it possible to directly measure genetic differentiation and genetic diversity among populations [13]. The faster mutation rate and relatively conserved sequence of the mtDNA COI gene is ideally suited to species identification via DNA barcoding [14]. Analysis of mtCOI gene variation is regarded as an important and reliable tool for defining cryptic species [15], evaluating biodiversity [16], identifying samples [17], and distinguishing closely related species [18].
Various surveys have demonstrated the reliability of ISSR markers, which can generate more polymorphisms than either RAPD or RFLP, [19]. For example, Dioscorea hispida were grouped into 10 vital groups based on information that provided by ISSR markers, proving the existence of significant variation among germplasm specimens. D. hispida shows a high level of genetic diversity among accessions, which suggests that ISSR markers have been very effective in detecting polymorphism in this species [20]. ISSR primers have been used to determine the potential for the diversification of cassava crops in Angola, revealing genetic diversity within populations and genetic information sharing among the three main taxa [21]. The ISSR molecular marker technique has also been used to distinguish between citrus rootstock species, and to reveal the broad genetic base and high genetic variability among these [22].
Genetic diversity
Genetic diversity, also known as gene diversity, is the foundation of biodiversity that guarantees the evolution of species. The percentage of polymorphism, haplotype diversity and nucleotide diversity are used to evaluate population genetic diversity [10]. High levels of genetic diversity are indicative of the strong viability and adaptability of populations [23]. Results from this study indicate that the genetic diversity of C. oryzae was high between populations that were sampled. This may increase fitness in populations to changing conditions. Crawford and Whitney [24] also showed that genetic diversity increases the ability of species to colonize on a short-term ecological timescale by increasing the possibility of population survival, growth and reproduction under novel environments. Episyrphus balteatus and Sphaerophoria scripta European populations successfully adapt to changing environmental conditions and have great colonization abilities due to the high genetic diversity [25]. The Tajima’s D and Fu’s Fs test of neutrality values for 19 populations were negative. When all samples were calculated as one population, Tajima’s D and Fu’s Fs values were negative and 1‰ significant, strongly indicating population expansion. This result is consistent with the idea that the negative Tajima’s D and Fu’s Fs test values demonstrated demographic expansion has occurred in these populations.
Genetic differentiation
Fst values between C. oryzae populations ranged from − 0.0595 to 0.1174, and the Gst value was 0.0997, both of which are indicative of low genetic differentiation between populations. This suggests frequent gene flow between populations, which may increase the species’ adaptability to environmental change [26]. Moreover, gene flow can not only demonstrate the probable genetic differentiation and genetic infiltration among populations, but also reduce the genetic differences among populations [27]. In this research, the Nm value of C. oryzae was 4.5165 which indicates high gene flow and low, or medium, genetic differentiation among some populations. High gene flow may impede genetic differentiation in C. oryzae. Gene flow (or lack of gene flow) plays a crucial role in genetic differentiation, affects the overall adaption of entire species and adaptative divergence between populations [28]. It has been traditionally considered as a homogeneous force that limits adaptive differences [29, 30], and recent studies have shown that it can also promote adaptation to local environmental conditions [31, 32]. For example, moderate gene flow increases the adaptation capabilities of Rhagoletis cerasi populations (which occupy different habitates in fragmented landscapes) to local habitates, thus preventing them from becoming extinct due to genetic processes [33, 34].
An AMOVA based on Fst values indicates that most of the genetic variation was resulted from the difference within populations. Furthermore, a Mantel test indicates no significant correlation between genetic and geographic distance. This result is consistent with the findings of Yang et al. [35] who compared correlation of the symmetric matrix constituted by geographic and genetic distances to analyze the existence of isolation among populations of Odontotermes formosanus in different regions. These authors found no significant correlation between geographic distance and genetic distance and no significant isolation by distance. Overall, we found a high level of genetic diversity and a low degree of population differentiation among populations of C. oryzae, and the gene flow was unaffected by geographic distance. Similarly, geographic distance did not appear to affect gene flow between 10 geographically separated populations Oedaleus infernalis [36]. Fst and Gst values for these populations are low, and the gene flow is high, indicating a low level of genetic differentiation and high gene flow among populations [36]. The correlation between genetic and geographic distance was insignificant [36].
Our results provide important, new information on the genetic diversity and genetic differentiation of C. oryzae, and suggest that high gene flow between populations contributes to the now frequent outbreaks of this pest. However, further research on both additional geographical populations and different genetic markers are necessary before definitive conclusions can be reached. Furthermore, future work can focus on doing a more comprehensive ecological and behavioural research to understand the natural history of C. oryzae in greater detail.
Conclusions
This study showed that the now frequent outbreaks of C. oryzae may due to high gene flow between populations. We have found that these populations have high genetic diversity at the species level, whereas exhibited low genetic differentiation. High genetic diversity and frequent gene flow between populations may enhance the tolerance of populations to environmental variability and increase the adaptability to novel environmental pressures, leading to frequent outbreaks what had happened and what will happen in a large scale.
Methods
Sample collection and DNA extraction
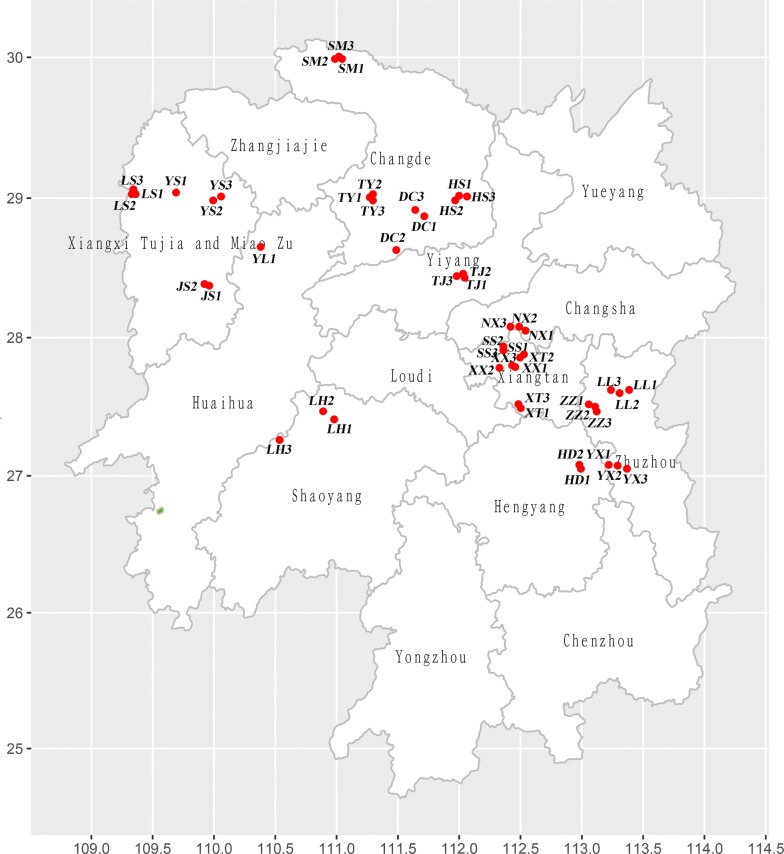
400 specimens of C. oryzae were collected from different parts of Hunan province, China, and an additional 32 specimens from Zhejiang and Guizhou provinces (Fig. 5, Additional file 1: Table S1). Samples were soaked in 100% ethanol and stored at − 20 °C until their genomic DNA (gDNA) was isolated. After removing the residual ethanol, DNA was extracted from each individual using an Ezup Column Animal Genomic DNA Extraction Kit as per the manufacturer’s instructions (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China).
Fig. 5.
Collection sites of populations. ZJ and GZ are populations from Zhejiang and Guizhou province, about 900 km and 810 km from Hunan province, respectively. They are not shown on the figure. The figure was created by Ailin Zhou
COI PCR amplification and sequencing
The COI was amplified with the COIF (5′-CTAGGTGCTCCAGATATAGCATTTC-3′) and COIR (5′-GGCTAAAACAACTCCTGTTAATCC-3′) primers from isolated DNA. PCR was performed in 20 μL volumes comprised of 10 μL PrimeSTAR Max DNA Polymerase (TaKaRa, Tokyo, Japan), 1 μL of each primer (10 mmol/L), 1 μL of template DNA solution (70 ng/μL), and 7 μL double distilled water. Amplifications were conducted as follows: 34 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 59 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 1 min. All the PCR products were checked by electrophoresis on a 1.2% agarose gel and bidirectional sequencing was completed by TSINGKE (Beijing, China).
ISSR PCR amplification
A total of sixteen primers from the University of British Columbia Biotechnology Laboratory Primer kit No.9 were tested for PCR and nine (Additional file 1: Table S2) that could produce reproducible, clear, polymorphic electrophoretic bands were chosen for further analysis. PCR was performed in 20 μL volumes comprised of 10 μL Premix Taq™ (Ex Taq™ Version 2.0 plus dye) (TaKaRa, Tokyo, Japan), 2 μL of primer (10 mmol/L), 1 μL of template DNA solution (70 ng/μL), and 7 μL double distilled water. Amplifications were carried out as follows: an initial denaturing at 94 °C for 3 min, followed by 34 cycles of denaturing at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at an optimized temperature for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 1 min, with a final extension 7 min at 72 °C. All PCR products were electrophoretically separated on 2% agarose.
Data analysis
COI gene data analysis
COI sequences were edited manually with BioEdit v.7.0.9 to produce consensus sequences of 685 bp for each specimen [37]. All indices for sequence polymorphic sites, DNA polymorphism, genetic differentiation, neutrality tests [Tajima’s D [38] and Fu’s Fs [39] ], and haplotype analyses were executed using DnaSp v.5.10 [40]. A haplotype network, which included haplotype frequencies, was calculated using Network v.4.6 [41]. Intra- and inter-specific genetic distances and transition/transversion ratios in each codon were computed based on COI gene sequences using MEGA v.7.0 [42]. A population phylogenetic tree based on genetic distances was constructed using the Neighbor-Joining tree model in MEGA v.7.0. Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) was performed with Arlequin software v.3.5.2 [43].
ISSR data analysis
Amplified ISSR fragments were scored as present (1) or absent (0) according to the molecular weight (bp) and the resulting matrix of binary values was used for further analyses. The observed number of alleles (Na), effective number of alleles (Ne), Nei’s gene diversity (H), Shannon’s information index (I), the percentage of polymorphic bands (PPB), total gene diversity (Ht), genetic diversity within populations (Hs), coefficient of gene differentiation (Gst), and Gene flow (Nm) were calculated using POPOGENE v.1.31 [44]. Cluster analysis was used to construct dendrograms using the UPGMA (unweighted pair-group method with arithmetic averages) in NTSYSpc v.2.1 [45]. To estimate the existence of isolation among 20 C. oryzae populations, the geographic distances between them were calculated using the google-maps-distance-calculator (www. daftlogic.com/projects-google-maps-distance-calculator. htm) (Additional file 1: Table S3). The correlation between geographic and genetic distances was further analyzed using the MXCOMP program and a Mantel test in NTSYSpc v.2.1.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Zhongcai Li, Xinwen Li, Xiaoping Tan and Zhengbing Zhang for their help in collecting the material in this study.
Abbreviations
- mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA
- ISSR
Inter-simple sequence repeat
- gDNA
Genomic DNA
- COI
Mitochondrial gene Cytochrome Oxidase I
- AMOVA
Analysis of molecular variance
- Na
The observed number of alleles
- Ne
Effective number of alleles
- H
Nei’s gene diversity
- I
Shannon’s information index
- PPB
The percentage of polymorphic bands
- Ht
Total gene diversity
- Hs
Genetic diversity within populations
- Gst
Coefficient of gene differentiation
- Nm
Gene flow
- UPGMA
Unweighted pair-group method with arithmetic averages
- Hd
Haplotype diversity
- k
The average number of differences
- Π
Nucleotide diversity
Authors’ contributions
AZ and PT performed the experiments. ZL, XL, XT, ZZ, WD and YL conceived and designed the experiments. AZ, LQ and HH analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Changsha City Science and Technology Bureau Key Projects, China (kc1701003).
Double first-class construction project of Hunan Agricultural University (SYL2019029)
Availability of data and materials
The authors declare that the data supporting the finding of this study are available in the article and its additional files.
Ethic approval and consent to participate
No permissions were required for sampling. There is no any regional/national legislature/law require ethical approval for sampling.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12898-020-00293-8.
References
- 1.Takeda M. Genetic basis of photoperiodic control of summer and winter diapause in geographic ecotypes of the rice stem maggot, Chlorops oryzae. Entomol Exp Appl. 1998;86(1):59–70. doi: 10.1046/j.1570-7458.1998.00265.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Takeda M, Nagata T. Photoperiodic responses during larval development and diapause of two geographic ecotypes of the rice stem maggot, Chlorops oryzae. Entomol Exp Appl. 1992;63(3):273–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1570-7458.1992.tb01584.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Takeda M. Effects of photoperiod and temperature on larval development and summer diapause in two geographic ecotypes of the rice stem maggot, Chlorops oryzae Matsumura (Diptera: chloropidae) Appl Entomol Zool. 1997;32(1):63–74. doi: 10.1303/aez.32.63. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Qiu L, Tao S, He H, Ding W, Li Y. Transcriptomics reveal the molecular underpinnings of chemosensory proteins in Chlorops oryzae. BMC Genom. 2018;19(1):890. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5315-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chapuis MP, Lecoq M, Michalakis Y, Loiseau A, Sword GA, Piry S, Estoup A. Do outbreaks affect genetic population structure? A worldwide survey in Locusta migratoria, a pest plagued by microsatellite null alleles. Mol Ecol. 2008;17(16):3640–3653. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chapuis MP, Loiseau A, Michalakis Y, Lecoq M, Franc A, Estoup A. Outbreaks, gene flow and effective population size in the migratory locust, Locusta migratoria: a regional-scale comparative survey. Mol Ecol. 2009;18(5):792–800. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.04072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Assefa Y, Mitchell A, Conlong DE. Phylogeography of Eldana saccbarina Walker (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) Ann Soc Entomol Fr. 2006;42(3–4):331–337. doi: 10.1080/00379271.2006.10697465. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Assefa Y, Conlong DE, Van Den Berg J, Martin LA. Ecological genetics and host range expansion by Busseola fusca (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) Environ Entomol. 2015;44(4):1265–1274. doi: 10.1093/ee/nvv079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Assefa Y, Goftishu M, Capdevielle-Dulac C, Ru BL. Clarifying the source of Conicofrontia sesamoides Hampson (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) population in South African sugarcane using morphological identification and mitochondrial DNA analysis. Phytoparasitica. 2017;45(1):45–55. doi: 10.1007/s12600-017-0566-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yi C, Zheng C, Zeng L, Xu Y. High genetic diversity in the offshore island populations of the tephritid fruit fly Bactrocera dorsalis. BMC Ecol. 2016;16(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12898-016-0101-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Palraju M, Paulchamy R, Sundaram J. Population genetic structure and molecular diversity of Leucinodes orbonalis based on mitochondrial COI gene sequences. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal. 2018;29(8):1231–1239. doi: 10.1080/24701394.2018.1436169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hemmati C, Moharramipour S, Seyahooei MA, Bagheri A, Mehrabadi M. Population genetic structure of Hishimonus phycitis (Hem.: Cicadellidae), vector of lime witches’ broom phytoplasma. J Agric Sci Technol. 2018;20(5):999–1012. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mutun S, Borst DW. Intraspecific mitochondrial DNA variation and historical biogeography of the eastern lubber grasshopper, Romalea microptera. Ann Entomol Soc Am. 2004;97(4):681–696. doi: 10.1603/0013-8746(2004)097[0681:IMDVAH]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Saccone C, De Giorgi C, Gissi C, Pesole G, Reyes A. Evolutionary genomics in Metazoa: the mitochondrial DNA as a model system. Gene. 1999;238(1):195–209. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00270-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bucklin A, Wiebe PH, Smolenack SB, Copley NJ, Beaudet JG, Bonner KG, Färberlorda J, Pierson JJ. DNA barcodes for species identification of Euphausiids (Euphausiacea, Crustacea) J Plankt Res. 2007;29(6):483–493. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbm031. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Smith MA, Fisher BL, Hebert PD. DNA barcoding for effective biodiversity assessment of a hyperdiverse arthropod group: the ants of Madagascar. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005;360(1462):1825–1834. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lakra WS, Goswami M, Gopalakrishnan A, Singh DP, Singh A, Nagpure NS. Genetic relatedness among fish species of Genus Channa using mitochondrial DNA genes. Biochem Syst Ecol. 2010;38(6):1212–1219. doi: 10.1016/j.bse.2010.12.012. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hebert PD, Ratnasingham S, deWaard JR. Barcoding animal life: cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc Biol Sci. 2003;270(Suppl 1):S96–S99. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2003.0025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Prevost A, Wilkinson MJ. A new system of comparing PCR primers applied to ISSR fingerprinting of potato cultivars. Theor Appl Genet. 1999;98(1):107–112. doi: 10.1007/s001220051046. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nudin NFH, Ali AM, Ngah N, Mazlan NZ, Mat N, Ghani MNA, Alias N, Zakaria AJ, Jahan MS. ISSR marker-assisted genetic diversity analysis of Dioscorea hispida and selection of the best variety for sustainable production. C R Biol. 2017;340(8):359–366. doi: 10.1016/j.crvi.2017.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sandra DJA, Ricardo FCM, Carlos SL, Cláudia FF, Vanderlei SS, Pascoal AM. Genetic structure of cassava populations (Manihot esculenta Crantz) from Angola assessed through (ISSR) markers. Afr J Biotechnol. 2019;18(7):144–154. doi: 10.5897/AJB2018.16720. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Salis C, Papadakis IE, Kintzios S, Hagidimitriou M. In vitro propagation and assessment of genetic relationships of citrus rootstocks using ISSR molecular markers. Not Bot Horti Agrobo. 2017;45(2):383–391. doi: 10.15835/nbha45210900. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Barrett RDH, Schluter D. Adaptation from standing genetic variation. Trends Ecol Evol. 2008;23(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2007.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Crawford KM, Whitney KD. Population genetic diversity influences colonization success. Mol Ecol. 2010;19:1253–1263. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Raymond L, Plantegenes M, Vialatte A. Migration and dispersal may drive to high genetic variation and significant mixing: the case of two agriculturally important, continental hoverflies (Episyrphus balteatus and Sphaerophoria scripta) Mol Ecol. 2013;22:5329–5339. doi: 10.1111/mec.12483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Xu Y, Mai JW, Yu BJ, Hu HX, Yuan L, Jashenko R, Ji R. Study on the genetic differentiation of geographic populations of Calliptamus italicus (Orthoptera: Acrididae) in Sino-Kazakh border areas based on mitochondrial COI and COII genes. J Econ Entomol. 2019;112(4):1912–1919. doi: 10.1093/jee/toz112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Millar CI, Libby WJ, Falk DA, Holsinger KE. Strategies for conserving clinal, ecotypic, and disjunct population diversity in widespread species. Genet Conserv Rare Plants. 1991;149:170. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Garant D, Forde SE, Hendry AP. The multifarious effects of dispersal and gene flow on contemporary adaptation. Funct Ecol. 2007;21(3):434–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2435.2006.01228.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Barton N, Partridge L. Limits to natural selection. BioEssays. 2000;22:1075–1084. doi: 10.1002/1521-1878(200012)22:12<1075::AID-BIES5>3.0.CO;2-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lenormand T. Gene flow and the limits to natural selection. Trends Ecol Evol. 2002;17:183–189. doi: 10.1016/S0169-5347(02)02497-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gandon S, Nuismer SL. Interactions between genetic drift, gene flow, and selection mosaics drive parasite local adaptation. Am Nat. 2009;173:212–224. doi: 10.1086/593706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ribeiro A, Llord P, Bowie RCK. A tight balance between natural selection and gene flow in a southern African arid-zone endemic bird. Evol. 2011;65:3499–3514. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2011.01397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lynch M, Conery J, Burger R. Mutation accumulation and the extinction of small population. Am Nat. 1995;146:485–518. doi: 10.1086/285812. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Crnokrak P, Roff DA. Inbreeding depression in the wild. Heredity. 1999;83:260–270. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6885530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yang YQ, Pu LJ, Wang Q, Wang Z, Pang ZP, Long YH. Population diversity of Odontotermes formosanus (Shiraki) (Termitidae, Macrotermitinae) from different geographic locations in Anhui province. China. Sociobiol. 2018;65(3):497–505. doi: 10.13102/sociobiology.v65i3.1146. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sun W, Dong H, Gao YB, Su QF, Qian HT, Bai HY, Zhang ZT, Cong B. Genetic variation and geographic differentiation among populations of the nonmigratory agricultural pest Oedaleus infernalis (Orthoptera: Acridoidea) in China. J Insect Sci. 2015;15:150. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/iev132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hall TA. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acid Symp Ser. 1999;41:95–98. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tajima F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics. 1989;123(3):585–595. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fu YX. Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics. 1997;147(2):915–925. doi: 10.1093/genetics/147.2.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Librado P, Rozas J. DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(11):1451–1452. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Polzin T, Daneshmand SV. On Steiner trees and minimum spanning trees in hypergraphs. Oper Res Lett. 2003;31:12–20. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6377(02)00185-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33(7):1870–1874. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Excoffier L, Lischer HE. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Resour. 2010;10(3):564–567. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-0998.2010.02847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yeh FC, Yang RC, Boyle T, Ye ZH, Mao JX. Popgene, the user friendly shareware for population genetic analysis. Edmonton: Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Center. University of Alberta; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rohlf FJ. NTSYS-pc Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system’, Version 2.02e. Setauket: Exeter Software; 1997. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The authors declare that the data supporting the finding of this study are available in the article and its additional files.