Abstract
Background
Understanding the mechanisms of implementation strategies (i.e., the processes by which strategies produce desired effects) is important for research to understand why a strategy did or did not achieve its intended effect, and it is important for practice to ensure strategies are designed and selected to directly target determinants or barriers. This study is a systematic review to characterize how mechanisms are conceptualized and measured, how they are studied and evaluated, and how much evidence exists for specific mechanisms.
Methods
We systematically searched PubMed and CINAHL Plus for implementation studies published between January 1990 and August 2018 that included the terms “mechanism,” “mediator,” or “moderator.” Two authors independently reviewed title and abstracts and then full texts for fit with our inclusion criteria of empirical studies of implementation in health care contexts. Authors extracted data regarding general study information, methods, results, and study design and mechanisms-specific information. Authors used the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool to assess study quality.
Results
Search strategies produced 2277 articles, of which 183 were included for full text review. From these we included for data extraction 39 articles plus an additional seven articles were hand-entered from only other review of implementation mechanisms (total = 46 included articles). Most included studies employed quantitative methods (73.9%), while 10.9% were qualitative and 15.2% were mixed methods. Nine unique versions of models testing mechanisms emerged. Fifty-three percent of the studies met half or fewer of the quality indicators. The majority of studies (84.8%) only met three or fewer of the seven criteria stipulated for establishing mechanisms.
Conclusions
Researchers have undertaken a multitude of approaches to pursue mechanistic implementation research, but our review revealed substantive conceptual, methodological, and measurement issues that must be addressed in order to advance this critical research agenda. To move the field forward, there is need for greater precision to achieve conceptual clarity, attempts to generate testable hypotheses about how and why variables are related, and use of concrete behavioral indicators of proximal outcomes in the case of quantitative research and more directed inquiry in the case of qualitative research.
Keywords: Mechanism, Moderator, Mediator, Determinant, Implementation, Causal model, Theory
Contributions to the literature statement.
This is the first systematic review of implementation mechanisms across health that assesses the quality of studies and the extent to which they offer evidence in support of establishing mechanisms of implementation.
We summarize nine examples of models for evaluating mechanisms.
We offer conceptual, theoretical, and methodological guidance for the field to contribute to the study of implementation mechanisms.
Background
Implementation research is the scientific evaluation of strategies or methods used to support the integration of evidence-based practices or programs (EBPs) into healthcare settings to enhance the quality and effectiveness of services [1]. There is mounting evidence that multi-faceted or blended implementation strategies are necessary (i.e., a discrete strategy is insufficient) [2, 3], but we have a poor understanding of how and why these strategies work. Mechanistic research in implementation science is in an early phase of development. As of 2016, there were only nine studies included in one systematic review of implementation mediators1 specific to the field of mental health. Mediators are an intervening variable that may statistically account for the relation between an implementation strategy and outcome. We define the term mechanism as a process or event through which an implementation strategy operates to affect one or more implementation outcomes (see Table 1 for key terms and definitions used throughout this manuscript). Mechanisms offer causal pathways explaining how strategies operate to achieve desired outcomes, like changes in care delivery. Some researchers conflate moderators, mediators, and mechanisms [6], using the terms interchangeably [7]. Mediators and moderators can point toward mechanisms, but they are not all mechanisms as they typically are insufficient to explain exactly how change came about.
Table 1.
Terms and definitions
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Mechanism | Process or event through which an implementation strategy operates to affect desired implementation outcomes. |
| Precondition | Factor that is necessary in order for an implementation mechanism to be activated. |
| Strategy | Methods used to promote the implementation of an evidence-based practice or program |
| Determinant | Also commonly referred to as “barriers” and “facilitators,” a factor that enables or hinders the implementation strategy from eliciting the desired effect. |
| Mediator | Intervening variable that may account for the relationship between the implementation strategy and the implementation outcome. |
| Moderator | Factor that increase or decrease the level of influence of an implementation strategy. |
| Proximal outcome | The product of the implementation strategy that is realized because of its specific mechanism of action, the most immediate, observable outcome in the causal pathway. |
| Distal outcome | Outcome that the implementation processes is ultimately intended to achieve, not the most immediate outcome in the causal pathway. |
In addition to these linguistic inconsistencies and lack of conceptual clarity, there is little attention paid to the criteria for establishing a mechanistic relation. Originally, Bradford-Hill [8], and more recently Kazdin offers [4] at least seven criteria for establishing mechanisms of psychosocial treatments that are equally relevant to implementation strategies: strong association, specificity, consistency, experimental manipulation, timeline, gradient, plausibility, or coherence (see Table 2 for definitions). Taken together, these criteria can guide study designs for building the case for mechanisms over time. In lieu of such criteria, disparate models and approaches for investigating mechanisms are likely to exist that make synthesizing findings across studies quite challenging. Consequently, the assumption that more strategies will achieve better results is likely to remain, driving costly and imprecise approaches to implementation.
Table 2.
Kazdin’s criteria for establishing a mechanism
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Strong association | Association between implementation strategy and mechanism AND between mechanism and behavior change. |
| Specificity | One plausible construct accounts for behavior change. |
| Consistency | Replication of observed results across studies, samples, and conditions. |
| Experimental manipulation | Direct manipulation of implementation strategy or proposed mediator or mechanism shows impact on outcomes. |
| Timeline | Causes and mediators temporally precede effects and outcomes. |
| Gradient | Dose response relationship between mediator and outcome. |
| Plausibility or coherence | Explanation invokes other info and steps in a process-outcome relation that are reasonable or supported by other research. |
Understanding the mechanisms of implementation strategies, defined as the processes by which strategies produce desired effects [4, 8], is important for both research and practice. For research, it is important to specify and examine mechanisms of implementation strategies, especially in the case of null studies, in order to understand why a strategy did or did not achieve its intended effect. For practice, it is crucial to understand mechanisms so that strategies are designed and selected to directly target implementation determinants or barriers. In the absence of this kind of intentional, a priori matching (i.e., strategy targets determinant), it is possible that the “wrong” (or perhaps less potent) strategy will be deployed. This phenomenon of mismatched strategies and determinants was quite prevalent among the 22 tailored improvement intervention studies included in Bosch et al.’s [9] multiple case study analysis. Upon examining the timing of determinant identification and the degree to which included studies informed tailoring of the type versus the content of the strategies using determinant information, they discovered frequent determinant-strategy mismatch across levels of analysis (e.g., clinician-level strategies were used to address barriers that were at the organizational level) [9]. Perhaps what is missing is a clear articulation of implementation mechanisms to inform determinant-strategy matching. We argue that, ultimately, knowledge of mechanisms would help to create a more rational, efficient bundle of implementation strategies that fit specific contextual challenges.
Via a systematic review, we sought to understand how mechanisms are conceptualized and measured, how they are studied (by characterizing the wide array of models and designs used to evaluate mechanisms) and evaluated (by applying Kazdin’s seven criteria), and how much evidence exists for specific mechanisms. In doing so, we offer a rich characterization of the current state of the evidence. In reflecting on this evidence, we provide recommendations for future research to optimize their contributions to mechanistic implementation science.
Methods
Search protocol
The databases, PubMed and CINAHL Plus, were chosen because of their extensive collection of over 32 million combined citations of medical, nursing and allied health, and life science journals, as well as inclusiveness of international publications. We searched both databases in August 2018 for empirical studies published between January 1990 and August 2018 testing candidate mechanisms of implementation strategies. This starting date was selected given that the concept of evidence-based practice/evidence-based treatment/evidence-based medicine first gained prominence in the 1990’s with the field of implementation science following in response to a growing consciousness of the research to practice gap [10, 11]. The search terms were based on input from all authors who represent a variety of methodological and content expertise related to implementation science and reviewed by a librarian; see Table 3 for all search terms. The search string consisted of three levels with terms reflecting (1) implementation science, (2) evidence-based practice (EBP), and (3) mechanism. We adopted Kazdin’s [4] definition of mechanisms, which he indicates are the basis of an effect. Due to the diversity of definitions that exist in the literature, the term “mechanism” was supplemented with the terms “mediator” and “moderator” to ensure all relevant studies were collected.
Table 3.
Search strategy
| Search terms | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Implement* OR disseminate* OR “knowledge translation” | These terms were chosen to target Implementation Science literature. |
| AND | |
| “empirically supported treatment” OR “evidence-based practice” OR “evidence-based treatment” OR innovation OR guideline | These terms were chosen to target the implementation evidence-based practices |
| AND | |
| Mediate* OR moderator OR mechanism* | These terms were chosen to target mechanisms explaining the implementation of evidence-based practices |
| NOT | |
| Biology OR microbiology | These terms were chosen to exclude mechanistic studies in biology and microbiology |
Study inclusion and exclusion criteria
Studies were included if they were considered an empirical implementation study (i.e., original data collection) and statistically tested or qualitatively explored mechanisms, mediators, or moderators. We did not include dissemination studies given the likely substantive differences between strategies, mechanisms, and outcomes. Specifically, we align with the distinction made between dissemination and implementation put forth by the National Institutes of Health program announcement for Dissemination and Implementation Research in Health that describes dissemination as involving distribution of evidence to a target audience (i.e., communication of evidence) and implementation as involving use of strategies to integrate evidence into target settings (i.e., use of evidence in practice) [12]. However, the word “dissemination” was included in our search terms because of the tendency of some researchers to use “implementation” and “dissemination” interchangeably. Studies were excluded if they were not an implementation study, used the terms “mediator,” “moderator,” or “mechanism” in a different context (i.e., conflict mediator), did not involve the implementation of an EBP, or were a review, concept paper, or opinion piece rather than original research. All study designs were considered. Only studies in English were assessed. See Additional File 1 for exclusion criteria and definitions. We strategically cast a wide net and limited our exclusions so as to characterize the broad range of empirical studies of implementation mechanisms.
Citations generated from the search of PubMed and CINAHL were loaded into EPPI Reviewer 4, an online software program used for conducting literature reviews [13]. Duplicate citations were identified for removal via the duplicate checking function in EPPI and via manual searching. Two independent reviewers (MRB, CWB) screened the first ten citations on title and abstract for inclusion. They then met to clarify inclusion and exclusion criteria with the authorship team, as well as add additional criteria if necessary, and clarify nuances of the inclusion/exclusion coding system (see Additional File 1 for exclusion criteria and definitions). The reviewers met once a week to compare codes and resolve discrepancies through discussion. If discrepancies could not be easily resolved through discussion among the two reviewers, the first author (CCL) made a final determination. During full text review, additional exclusion coding was applied for criteria that could not be discerned from the abstract; articles were excluded at this phase if they only mentioned the study of mechanisms in the discussion or future directions. Seven studies from the previous systematic review of implementation mechanisms [14] were added to our study for data extraction; these studies likely did not appear in our review due to differences in the search strategy in that the review undertaken by Williams hand searched published reviews of implementation strategies in mental health.
Study quality assessment
The methodological quality of included studies was assessed using the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT-version 2018) [15]. This tool has been utilized in over three dozen systematic reviews in the health sciences. The MMAT includes two initial screening criteria that assess for the articulation of a clear research question/objective and for the appropriateness of the data collected to address the research question. Studies must receive a “yes” in order to be included. The tool contains a subset of questions to assess for quality for each study type—qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods. Table 4 summarizes the questions by which studies were evaluated, such as participant recruitment and relevance and quality of measures. Per the established approach to MMAT application, a series of four questions specific to each study design type are assigned a dichotomous “yes” or “no” answer. Studies receive 25 percentage points for each “yes” response. Higher percentages reflect higher quality, with 100% indicating all quality criteria were met. The MMAT was applied by the third author (CWB). The first author (CCL) checked the first 15% of included studies and, based on reaching 100% agreement on the application of the rating criteria, the primary reviewer then applied the tool independently to the remaining studies.
Table 4.
MMAT
| Bardosh et al. 2017 [16] | Brewster et al. 2015 [17] | Carrera et al. 2015 [18] | Frykman et al. 2014 [19] | Wiener-Ogilvie et al. 2008 [20] | Atkins et al. 2008 [21] | Baer et al. 2009 [22] | Bonetti et al. 2005 [23] | Garner et al. 2011 [24] | Glisson et al. 2010 [25] | Holth et al. 2011 [26] | Lee et al. 2018 [27] | Lochman et al. 2009 [28] | Rapkin et al. 2017 [29] | Rohrbach et al. 1993 [30] | Seys et al. 2018 [31] | Williams et al. 2014 [32] | Williams et al. 2017 [33] | |||
| 1. Qualitative | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Data sources relevant? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||
| Data analysis process relevant? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||
| Findings relate to context? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||
| Findings relate to researchers' influence? | N | N | N | Y | N | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||
| 2. Quantitative randomized | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Clear description of the randomization? | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | N | Y | N | Y | N | Y | ||
| Clear description of allocation or concealment? | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | ||
| Complete outcome data? | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y | ||
| Low withdrawal/drop-out? | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N | Y | Y | ||
| Total score (%) | 75 | 75 | 75 | 100 | 75 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 75 | 50 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 25 | 25 | ||
| Aarons et al. 2009 [34] | Becker et al. 2016 [35] | Beenstock et al. 2012 [36] | Beets et al. 2008 [37] | Bonetti et al. 2009 [38] | Chou et al. 2011 [39] | Cummings et al. 2017 [40] | David and Schiff 2017 [41] | Edmunds et al. 2014 [42] | Gnich et al. 2018 [43] | Guerrero et al. 2018 [44] | Huis et al. 2013 [45] | Little et al. 2015 [46] | Llasus et al. 2014 [47] | Nelson and Steele 2007 [48] | Potthoff et al. 2017 [49] | Presseau et al. 2016 [50] | Simmonds et al. 2012 [51] | Stockdale et al. 2018 [52] | Wanless et al. 2015 [53] | |
| 3. Quantitative - non-randomized | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Recruitment minimizes selection bias? | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Measurements appropriate? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Comparable groups or control for differences? | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Complete outcome data, acceptable response rate, or acceptable follow-up rate? | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N |
| Total score (%) | 75 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 75 | 25 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 100 | 50 | 75 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 75 | 75 |
| Armson et al. 2018 [54] | Birken et al. 2015 [55] | Kauth et al. 2010 [56] | Lukas et al. 2009 [57] | Panzano et al. 2012 [58] | Rangachari et al. 2015 [59] | Shrubsole et al. 2018 [60] | ||||||||||||||
| 1. Qualitative | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Data sources relevant? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | |||||||||||||
| Data analysis process relevant? | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | |||||||||||||
| Findings relate to context? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | |||||||||||||
| Findings relate to researchers' influence? | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||||||||||||
| 2. Quantitative randomized | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Clear description of the randomization? | N/A | N/A | N | N/A | N/A | N/A | Y | |||||||||||||
| Clear description of allocation or concealment? | N/A | N/A | N | N/A | N/A | N/A | Y | |||||||||||||
| Complete outcome data? | N/A | N/A | Y | N/A | N/A | N/A | Y | |||||||||||||
| Low withdrawal/drop-out? | N/A | N/A | Y | N/A | N/A | N/A | N | |||||||||||||
| 3. Quantitative non-randomized | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Recruitment minimizes selection bias? | Y | Y | N/A | Y | N | Y | N/A | |||||||||||||
| Measurements appropriate? | Y | Y | N/A | Y | Y | Y | N/A | |||||||||||||
| Comparable groups or control for differences? | N | N | N/A | N | N | N | N/A | |||||||||||||
| Complete outcome data, acceptable response rate, or acceptable follow-up rate? | Y | N | N/A | N | Y | Y | N/A | |||||||||||||
| 4. Mixed methods | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Research design relevant? | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | |||||||||||||
| Integration of qualitative and quantitative data relevant? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | |||||||||||||
| Appropriate consideration given to limitations associated with integration? | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | |||||||||||||
| Total score (%) | 75 | 50 | 50 | 25 | 25 | 75 | 75 | |||||||||||||
Data extraction and synthesis
Data extraction focused on several categories: study information/ background (i.e., country, setting, and sample), methods (i.e., theories that informed study, measures used, study design, analyses used, proposed mediation model), results (i.e., statistical relations between proposed variables of the mediation model tested), and criteria for establishing mechanisms (based on the seven listed in Table 2 [4];). All authors contributed to the development of data extraction categories that were applied to the full text of included studies. One reviewer (MRB) independently extracted relevant data and the other reviewer (CWB) checked the results for accuracy, with the first author (CCL) addressing any discrepancies or questions, consistent with the approach of other systematic reviews [61]. Extracted text demonstrating evidence of study meeting (or not meeting) each criterion for establishing a mechanism was further independently coded as “1” reflecting “criterion met” or “0” reflecting “criterion not met” by MRB and checked by CWB. Again, discrepancies and questions were resolved by the first author (CCL). Technically, mechanisms were considered “established” if all criteria were met. See Additional File 2 for PRISMA checklist for this study.
Results
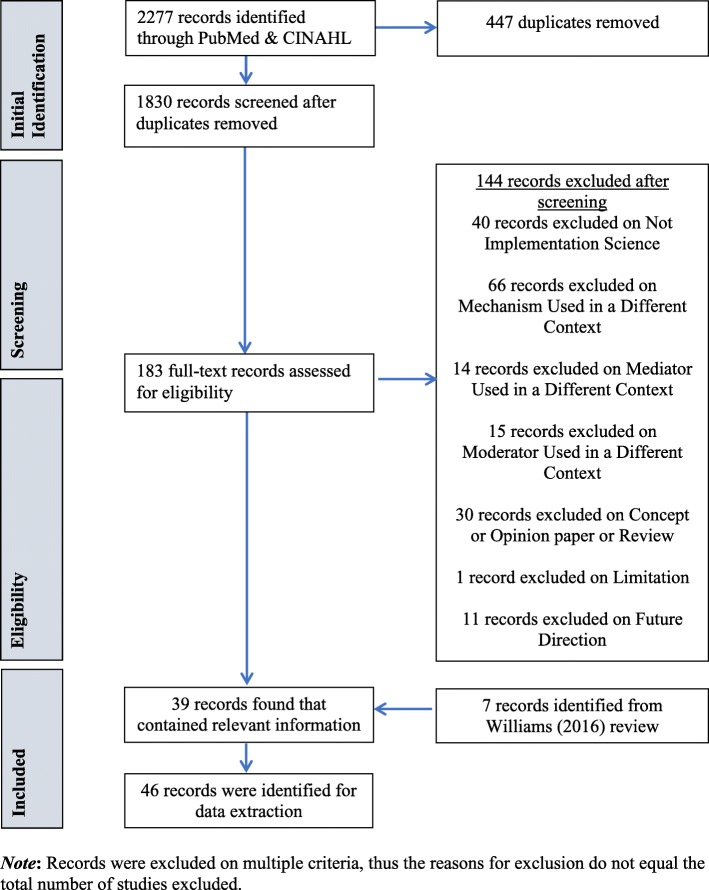
The search of PubMed and CINAHL Plus yielded 2277 studies for title and abstract screening, of which 447 were duplicates, and 183 moved on to full-text review for eligibility. Excluded studies were most frequently eliminated due to the use of mechanism in a different context (i.e., to refer to a process, technique, or system for achieving results of something other than implementation strategies). After full article review, 39 studies were deemed suitable for inclusion in this review. Two of the included studies appeared in the only other systematic review of implementation mechanisms in mental health settings [14]. For consistency and comprehensiveness, the remaining seven studies from the previously published review were added to the current systematic review for a total of 46 studies.2 See Fig. 1 for a PRISMA Flowchart of the screening process and results.
Fig. 1.
Mechanisms of Implementation Systematic Review PRISMA Flowchart
Study characteristics
Setting, sampling, and interventions
Table 5 illustrates the characteristics of the 46 included studies. Twenty-five studies (54.3%) were completed in the USA, while 21 studies were conducted in other countries (e.g., Australia, Canada, Netherlands, UK). Settings were widely variable; studies occurred in behavioral health (e.g., community mental health, residential facilities) or substance abuse facilities most frequently (21.7%), followed by hospitals (15.2%), multiple sites across a health care system (15.2%), schools (15.2%), primary care clinics (10.9%), and Veteran’s Affairs facilities (8.7%). Sampling occurred at multiple ecological levels, including patients (17.4%), providers (65.2%), and organizations (43.5%). Seventeen (40.0%) studies examined the implementation of a complex psychosocial intervention (e.g., Cognitive behavioral therapy [42, 56];, multisystemic therapy [25, 26, 58]).
Table 5.
Descriptive summary
| Study | Setting | Sample | Intervention/Innovation | Complex psychosocial intervention | Design |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qualitative | |||||
| Bardosh et al. 2017 [16] | Health care facilities, multiple countries | Key informants (researchers, Mhealth staff, clinic staff, government officials; n = 32) | Mobile health application | N | Qualitative, cross sectional, comparative case study, non-randomized |
| Brewster et al. 2015 [17] | Hospitals | Hospitals (k = 10); hospital employees (hospital staff, n = 82; state hospital representatives n = 8) | Initiative to reduce rehospitalization rates | N | Qualitative, descriptive, cross sectional, non-randomized |
| Carrera and Lambooij 2015 [18] | Primary care | Patients (n = 12); health care providers (n = 4) | Blood pressure monitoring guidelines | N | Qualitative descriptive, cross sectional, non-randomized |
| Frykman et al. 2014 [19] | Emergency departments | Departments (k = 2), health care providers (n = 11) | Multi-professional teamwork guideline | N | qualitative, longitudinal (2 assessment points, 21 months), comparative case study, non-randomized |
| Wiener-Ogilvie et al. 2008 [20] | Primary care | Health care providers (n = 9) | Asthma management guideline | N | qualitative, cross sectional, comparative case study, non-randomized |
| Quantitative randomized | |||||
| Atkins et al. 2008 [21] | Schools | Teachers (n = 127); mental health providers (n = 21) | Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder guidelines | Y | quantitative, longitudinal (5 assessment points, 2 years), randomized |
| Baer et al. 2009 [ | Substance abuse treatment facilities | Substance abuse treatment facilities (k = 6); Mental health providers (n = 118) | Motivational Interviewing | Y | quantitative, longitudinal (3 assessment points, 6 months), randomized |
| Bonetti et al. 2005 [23] | Primary care | Health care providers (n = 152) | Spinal X-ray referral guidelines | N | quantitative, longitudinal (2 assessment points, 2 months), randomized control trial |
| Garner et al. 2011 [24] | Substance abuse treatment facilities | Substance abuse treatment facilities (k = 29); mental health providers (n = 95) | Adolescent Community Reinforcement Approach and Assertive Continuing Care | Y | quantitative, longitudinal (2 assessment points, 3 years), randomized control trial |
| Glisson et al. 2010 [25] | Juvenile courts | Counties (k = 14); patients (n = 615) | Multisystemic Therapy | Y | quantitative, longitudinal (weekly, quarterly, 4 years), randomized control trial |
| Holth et al. 2011 [26] | Behavioral health facilities | Mental health providers (n = 21); families (youth and primary caregiver; n = 41) | Multisystemic Therapy, Cognitive Behavior Therapy | Y | quantitative, longitudinal (monthly, 17 months), block randomized control trial |
| Lee et al. 2018 [27] | Schools, child care facilities | Organizations (n = 121) | Nutritional guidelines | N | quantitative, longitudinal (two time points; 2 studies at 6 months, 1 study at 12 months), analysis of aggregated datasets from three randomized control trials |
| Lochman et al. 2009 [28] | Schools | Schools (k = 57); patients (n = 531); mental health providers (n = 49) | Coping Power Program | Y | quantitative, longitudinal (2 assessment points, 2 years), randomized |
| Rapkin et al. 2017 [29] | Public library system | Communities (k = 20); community members (n = 9374) | Cancer screening and prevention education programs | N | quantitative, randomized, stepped-wedge, longitudinal |
| Rohrbach et al. 1993 [30] | Schools | Schools (k = 25); administrators (n = 25); teachers (n = 60); patients (n = 1147) | Adolescent Alcohol Prevention Trial | Y | quantitative, longitudinal (3 assessment points, 2 years), randomized control trial |
| Seys et al. 2018 [31] | Hospitals | Care teams (k = 19); care team members (n = 284); patients (n = 257) | Care pathway for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | N | quantitative, longitudinal (two assessment points, 30 days), randomized |
| Williams et al. 2014 [32] | Behavioral health facilities | Behavioral health facilities (k = 92); administrators (n = 311) | Motivational Interviewing | Y | quantitative, longitudinal (3 assessment points, 3 months), randomized control trial |
| Williams et al. 2017 [33] | Behavioral health facilities | Organizations (k = 14); clinicians (n = 475) | Evidence-based practice (not specified) | Evidence-based practice implemented not reported | quantitative, longitudinal, randomized (4 assessment points, 4 years) |
| Quantitative non-randomized | |||||
| Aarons et al. 2009 [34] | Behavioral health facilities | Mental health care providers (n = 174) | 31 child or family evidence-based practices | Ya | quantitative, cross-sectional, survey, non-randomized |
| Becker et al. 2016 [35] | Substance abuse treatment facilities | Clinics (k = 15); treatment providers (n = 60) | Contingency management treatment | Y | quantitative, longitudinal (biweekly, 12 months), non-randomized |
| Beenstock et al. 2012 [36] | Hospitals | Hospitals (k = 8); health care providers (n = 364) | Smoking cessation guideline | N | quantitative, cross sectional, survey, non-randomized |
| Beets et al. 2008 [37] | Schools | Teachers (n time 1 = 171, n time 2 = 191) | Positive Action Program | Y | quantitative, cross sectional at two time points, survey, non-randomized |
| Bonetti et al. 2009 [38] | Dentist offices | Health care providers (n = 133) | Fissure sealant evidence-based practice | N | quantitative, longitudinal, predictive cohort study (3 assessment points, 28 months), non-randomized |
| Chou et al. 2011 [39] | Veterans Affairs | Hospitals (k = 132), health care providers (n = 2,438) | Major depressive disorder screening guideline | N | quantitative, cross sectional, survey, randomized |
| Cummings et al. 2017 [40] | Nursing homes | Nursing homes (k = 7); nursing home staff (n = 333) | Coaching for Impressive Care | N | quantitative, , non-randomized two-group crossover |
| David and Schiff 2017 [41] | Health care system, multiple sites | Health care providers (n = 77) | Child-Parent Psychotherapy | Y | quantitative, cross sectional, survey, non-randomized |
| Edmunds et al. 2014 [42] | Behavioral health facilities | Mental health providers (n = 50) | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy | Y | quantitative, longitudinal, non-randomized |
| Gnich et al. 2018 [43] | Dentist offices | Health care providers (n = 709) | Fluoride varnish application | N | quantitative, longitudinal (2 assessment points, 18 months), non-randomized |
| Guerrero et al. 2018 [44] | Behavioral health facilities | Behavioral health facilities (k = 112), mental heal providers (n = 427) | Contingency management treatment and medicationassisted treatment | Y | quantitative, longitudinal (2 assessment points), survey, non-randomized |
| Huis et al. 2013 [45] | Hospitals | Hospitals (k = 3); departments (k = 67): health care providers (k = 2733) | Hand hygiene guidelines | N | quantitative, longitudinal, process evaluation of a cluster randomized controlled trial |
| Little et al. 2015 [46] | Schools | School districts (k = 183); departments (k = 22) | Tobacco Use Prevention Education | N | quantitative, cross sectional, survey, non-randomized |
| Llasus et al. 2014 [47] | University nursing programs | Nursing students (n = 174) | Evidence-based practices (not specified) | N | quantitative, descriptive, correlational, cross sectional, survey, non-randomized |
| Nelson and Steele 2007 [48] | Health care system, multiple sites | Mental health providers (n = 214) | Evidence-based practices (not specified) | N | quantitative, cross sectional, survey, non-randomized |
| Potthoff et al. 2017 [49] | Primary care | Organizations (k = 99); health care providers (n = 489) | Type 2 diabetes management guideline | N | quantitative, longitudinal (2 assessment points, 1 year), correlational, survey, non-randomized |
| Presseau et al. 2016 [50] | Primary care | Family physicians (time 1 n = 632; time 2 n = 426) | Prescription of hypertension medication | N | quantitative, longitudinal (2 assessment points, approximately 8 months), 2X3 factorial |
| Simmonds et al. 2012 [51] | Health care system, multiple sites | Health care providers (n = 108) | Lower back pain management guidelines | N | quantitative, cross sectional, survey, non-randomized |
| Stockdale et al. 2018 [52] | Veterans Affairs | Health care providers (n = 149), patients (n = 3329) | Patient Centered Medical Home | N | quantitative, cross sectional, survey, non-randomized |
| Wanless et al. 2015 [53] | Schools | Schools (k = 13); teachers (n = 1114) | Responsive Classroom | Y | quantitative, longitudinal, non-randomized (focuses on one condition in an RCT) |
| Yamada et al. 2017 [62] | Hospitals | Care units (k = 32); nurses (n = 779); patients (n = 1,604) | Instrumental and conceptual research use, evidence-based pain assessment | N | quantitative, cross sectional, non-randomized |
| Mixed Methods | |||||
| Armson et al. 2018 [54] | Health care system, multiple sites | Health care providers (n = 70) | Breast cancer screening guideline | N | mixed method, longitudinal, observational/ naturalist field study, non-randomized |
| Birken et al. 2015 [55] | Health care system, multiple sites | Organizations (k = 149); administrators (n = 223) | Quality improvement initiative based on Chronic Care Model | N | mixed method sequential, cross sectional, non-randomized |
| Kauth et al. 2010 [56] | Veterans Affairs | Clinics (k = 21); mental health providers (n = 23) | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy | Y | mixed method, quasi-experimental, longitudinal (2 assessment points, 6 months), randomized |
| Lukas et al. 2009 [57] | Veterans Affairs | Organizations (k = 78); health care providers, non-clinical staff (n = 3870) | Advance Clinic Access | N | mixed method, cross sectional, observational, non-randomized |
| Panzano et al. 2012 [58] | Behavioral health facilities | Consultants (n = 34); mental health providers (n = 70) | Multisystemic Therapy, Dual Disorder Treatment, Ohio medication algorithms, Cluster-based Outcomes Management | Y | mixed method, longitudinal, observational/ naturalist field study, non-randomized |
| Rangachari et al. 2015 [59] | Hospitals | Departments (k = 2); health care providers (n = 101); administrators (n = 6) | Central line bundle catheter insertion evidence-based practice | N | prospective, longitudinal, exploratory field study, mixed-method analysis |
| Shrubsole et al. 2018 [60] | Hospitals | Hospitals (k = 4); health care providers (n = 37); patients (n = 107) | Aphasia management practices | N | mixed method, longitudinal, cross-over, cluster randomized control trial |
aMultiple EBPs, some of which were complex psychosocial interventions
Study design
Our review included six qualitative (10.9%), seven mixed methods (15.2%), and 34 quantitative studies (73.9%). The most common study design was quantitative non-randomized/observational (21 studies; 45.7%), of which 11 were cross-sectional. There were 13 (28.3%) randomized studies included in this review. Twenty-nine studies (63.0%) were longitudinal (i.e., included more than one data collection time point for the sample).
Study quality
Table 4 shows the results of the MMAT quality assessment. Scores for the included studies ranged from 25 to 100%. Six studies (13.0%) received a 25% rating based on the MMAT criteria [15], 17 studies (40.0%) received 50%, 21 studies (45.7%) received 75%, and only three studies (6.5%) scored 100%. The most frequent weaknesses were the lack of discussion on researcher influence in qualitative and mixed methods studies, lack of clear description of randomization approach utilized in the randomized quantitative studies, and subthreshold rates for acceptable response or follow-up in non-randomized quantitative studies.
Study design and evaluation of mechanisms theories, models, and frameworks
Twenty-seven (58.7%) of the studies articulated their plan to evaluate mechanisms, mediators, or moderators in their research aims or hypotheses; the remaining studies included this as a secondary analysis. Thirty-five studies (76.1%) cited a theory, framework, or model as the basis or rationale for their evaluation. The diffusion of innovations theory [63, 64] was most frequently cited, appearing in nine studies (19.6%), followed by the theory of planned behavior [65], appearing in seven studies (15.2%). The most commonly cited frameworks were the theoretical domains framework (five studies; 10.9%) [66] and Promoting Action on Research in Health Services (PARiHS) [67] (three studies; 6.5%).
Ecological levels
Four studies (8.7%) incorporated theories or frameworks that focused exclusively on a single ecological level; two focusing on leadership, one at the organizational level, and one at the systems level. There was some discordance between the theories that purportedly informed studies and the potential mechanisms of interest, as 67.4% of candidate mechanisms or mediators were at the intrapersonal level, while 30.4% were at the interpersonal level, and 21.7% at the organizational level. There were no proposed mechanisms at the systems or policy level. Although 12 studies (26.1%) examined mechanisms or mediators across multiple ecological levels, few explicitly examined multilevel relationships (e.g., multiple single-level mediation models were tested in one study).
Measurement and analysis
The vast majority of studies (38, 82.6%) utilized self-report measures as the primary means of assessing the mechanism, and 13 of these studies (28.3%) utilized focus groups and/or interviews as a primary measure, often in combination with other self-report measures such as surveys. Multiple regression constituted the most common analytic approach for assessing mediators or moderators, utilized by 25 studies (54.3%), albeit this was applied in a variety of ways. Twelve studies (26.1%) utilized hierarchical linear modeling (HLM) and six studies (13.0%) utilized structural equation modeling (SEM); see Table 6 for a complete breakdown. Studies that explicitly tested mediators employed diverse approaches including Baron and Kenny’s (N = 8, 17.4 causal steps approach [78], Preacher and Hayes’ (N = 3, 6.5%) approach to conducting bias-corrected bootstrapping to estimate the significance of a mediated effect (i.e., computing significance for the product of coefficients) [95, 126], and Sobel’s (N = 4, 8.9%) approach to estimating standard error for the product of coefficients often using structural equation modeling [79]. Only one study tested a potential moderator, citing Raudenbush’s [80, 82]. Two other studies included a potential moderator in their conceptual frameworks, but did not explicitly test moderation.
Table 6.
Mechanism analysis
| Study | Aims | Theory, framework, model | Mechanism measurement | Mediation testing citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qualitative | ||||
| Bardosh et al. 2017 [16] | N | Consolidated framework for implementation research [68] | Interviews | None |
| Brewster et al. 2015 [17] | Y | Implementation innovation framework [69] | Interviews | None |
| Carrera and Lambooij 2015 [18] | N | Technology acceptance model [70]; Theory of planned behavior [65]; Model of personal computing utilization [71] | Focus groups | None |
| Frykman et al. 2014 [19] | N | Direction, competence, opportunity and motivation (DCOM) [72, 73] | Interviews; observations | None |
| Wiener-Ogilvie et al. 2008 [20] | N | None reported | Interviews; focus groups | None |
| Quantitative- randomized | ||||
| Atkins et al. 2008 [21] | Y | Diffusion of innovation theory [63] | Interviews; self-report | [74] |
| Baer et al. 2009 [22] | Y | None reported | interviews; self-report | [75] |
| Bonetti et al. 2005 [23] | N | Theory of planned behavior [65]; Social cognitive theory [76, 77] | Self-report | [78, 79] |
| Garner et al. 2011 [24] | N | Theory of planned behavior [65] | Self-report | [80, 81] |
| Glisson et al. 2010 [25] | N | None reported | Self-report, audiotape coding and interviews | [82] |
| Holth et al. 2011 [26] | Y | None reported | Interviews; self-report | [83] |
| Lee et al. 2018 [27] | Y | Theoretical domains framework [84] | Self-report, secondary analysis | [85, 86] |
| Lochman et al. 2009 [28] | N | Diffusion of innovation theory [87] | Coder ratings | [88] |
| Rapkin et al. 2017 [29] | Y | None reported | Self-report | [89] |
| Rohrbach et al. 1993 [30] | N | Diffusion of innovation theory [64] | Interviews; self-report; observations | None |
| Seys et al. 2018 [31] | Y | None reported | Chart review; self-report | [78] |
| Williams et al. 2014 [32] | Y | Diffusion of innovation theory [87] | Self-report | [90, 91] |
| Williams et al., 2017 (66) | Y | Organizational culture theory [32] and Theory of planned behavior [65] | Self-report | [92] |
| Quantitative- non-randomized | ||||
| Aarons et al. 2009 [34] | Y | Institutional theory [93], Theory of planned behavior [65], Theory of perceived organizational support [94] | Self-report | [78] |
| Becker et al. 2016 [35] | Y | Diffusion of innovation theory [64] | Self-report | None |
| Beenstock et al. 2012 [36] | N | Theoretical domains framework [66] | Self-report | [95] |
| Beets et al. 2008 [37] | Y | Theory driven evaluation [96]; Diffusion of innovation theory [63] | Self-report | [97, 98] |
| Bonetti et al. 2009 [38] | N | Theory of planned behavior [65]; Social cognitive theory [99]; Operant learning theory [100]; Action planning [101]; Common sense self-regulation model [102]; Precaution adoption process model [103]; Stage theory [103, 104] | Self-report; objective measure | [78, 79] |
| Chou et al. 2011 [39] | N | Goal setting theory [105]; Goal commitment theory [106] | Self-report | [80, 107] |
| Cummings et al. 2017 [40] | N | Promoting action on research in health services (PARiHS) [67] | Self-report | [108] |
| David and Schiff 2017 [41] | Y | Diffusion of innovation theory [87, 109] | Self-report | [110] |
| Edmunds et al. 2014 [42] | Y | EPIS framework [111] | Self-report | [80, 112] |
| Gnich et al. 2018 [43] | Y | Theoretical domains framework [66] | Self-report | None |
| Guerrero et al. 2018 [44] | Y | Theory on middle manager s[69] | Self-report | [113] |
| Huis et al. 2013 [45] | N | None reported | Observations; self-report; website visitor registration; logs; field Notes; effect evaluation; quiz | none |
| Little et al. 2015 [46] | N | Diffusion of innovation theory [64] | Self-report | [114–116] |
| Llasus et al. 2014 [47] | N | Knowledge to action conceptual framework [117] | Self-report | [78, 79, 95] |
| Nelson and Steele 2007 [48] | N | None reported | Self-report | None |
| Potthoff et al. 2017 [49] | Y | Dual process model of behavior [118] | Self-report | [79] |
| Presseau et al. 2016 [50] | Y | Theory of planned behavior [65] | Self-report | None |
| Simmonds et al. 2012 [51] | Y | None reported | Self-report | [78] |
| Stockdale et al. 2018 [52] | Y | None reported | Self-report | [119] |
| Wanless et al. 2015 [53] | Y | None reported | Self-report, observation | [110] |
| Yamada et al. 2017 [62] | Y | Promoting action on research in health services (PARiHS) [120] | Self-report, chart review | None |
| Mixed methods | ||||
| Armson et al. 2018 [54] | Y | Theoretical domains framework [66] | Interviews; self-report | None |
| Birken et al. 2015 [55] | N | Hierarchical taxonomy of leader behavior [121] | Interviews; self-report | [95, 122] |
| Kauth et al. 2010 [56] | Y | Fixsen model [123]; Promoting action on research in health services (PARiHS) [120] | Self-report; logs | None |
| Lukas et al. 2009 [57] | Y | Diffusion of Innovations Theory [63, 124] | Interviews | [78] |
| Panzano et al. 2012 [58] | Y | None reported | Self-report | [78] |
| Rangachari et al. 2015 [59] | N | Complex systems theory [125] | Infection rate; chart review; hospital records; logs | None |
| Shrubsole et al. 2018 [60] | N | Theoretical domains framework [66] | Chart review; self-report | none |
Emergent mechanism models
There was substantial variation in the models that emerged from the studies included in this review. Table 7 represents variables considered in mediating or moderating models across studies (or identified as candidate mediators, moderators, or mechanisms in the case of qualitative studies). Additional file 3 depicts the unique versions of models tested and their associated studies. We attempted to categorize variables as either (a) an independent variable (X) impacting a dependent variable; (b) a dependent variable (Y), typically the outcome of interest for a study; or (c) an intervening variable (M), a putative mediator in most cases, though three studies tested potential moderators. We further specified variables as representing a strategy, determinant, and outcome; see Table 1 for definitions.3
Table 7.
Model tested
| Study | Independent variable (X) | Intervening variable (M) | Dependent variable (Y) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qualitative | |||
| Bardosh et al. 2017 [16] | Mobile and text follow up with patients | Service organization at clinic level, clinician norms and practices, availability of local champions staff, adaptability and co-design of strategy, receptivity and capacity of local management | Culture of care |
| Brewster et al. 2015 [17] | Patient education, follow-up phone calls to patients after discharge, discharge planning, collaboration with post-acute providers | Intrinsic reward to staff --> shift in norms and attitudes | Reduced hospital readmissions |
| Carrera and Lambooij 2015 [18] | None reported |
Mediators: perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, self-efficacy, attitudes,social norm Moderator: enabling conditions |
Intervention acceptability (providers and patients) |
| Frykman et al. 2014 [19] | Senior manager and consultant-driven teamwork strategy, senior manager and staff-driven teamwork strategy | Direction, communication, opportunity, motivation | Change in staff behavior |
| Wiener-Ogilvie et al. 2008 [20] | Guideline implementation | Practice organization (delegation of work to nurses) | Compliance with guidelines |
| Quantitative—randomized | |||
| Atkins et al. 2008 [21] | Training and consultation | Key opinion leader instrumental supportmental health professional instrumental support | Teacher self-reported used of ADHD guidelines |
| Baer et al. 2009 [22] | Climate for organizational change | Post training agency activities to support use of Motivational Interviewing | Fidelity to intervention (Motivational Interviewing spirit and response to question ratio) |
| Bonetti et al. 2005 [23] | Audit and feedback | Decision difficulty, behavioral control | Simulated behavior |
| Garner et al. 2011 [24] | Pay for performance |
1. Subjective norms 2. Attitudes toward intervention 3. Perceived control |
1. Therapists’ intention to achieve monthly competence 2. Therapists’ intention to achieve targeted threshold |
| Glisson et al. 2010 [25] | Availability responsiveness and continuity (ARC) Intervention + Multisystemic Therapy quality assurance, pay for performance | Fidelity to multisystemic therapy | Rate of change in child behavior out of home placements |
| Holth et al. 2011 [26] | Workshop + manual, intensive quality assurance + workshop + manual | Adherence to contingency management and cognitive behavioral therapy techniques | Youth cannabis use |
| Lee et al. 2018 [27] | Implementation strategy bundles (varied across studies) | Knowledge, skills, social/professional role and identity, environmental resources | Nutrition guideline implementation |
| Lochman et al. 2009 [28] | Intensive training + feedback, basic training | # of sessions attended, # of objectives completed, # of contacts with trainers, counselor engagement w/clients | Client externalizing behaviors, client social skills, client study skills, client expectancies re: aggression, consistent parenting, client assaultive acts |
| Rapkin et al. 2017 [29] | Indicators of program activities: cumulative local programs, attendance at local programs, time since most recent local program, personal awareness of programs, cumulative outside programs | Mediators: awareness of free/low cost cancer screening, cancer knowledge, cancer information seeking, having health insurance, annual physical moderator: frequency of library use | Cancer screening attempts to quit smokingtobacco cessation |
| Rohrbach et al. 1993 [30] |
1. Teacher training 2. Principal support intervention |
1a. Teacher self-efficacy, 1b. enthusiasm, 1c. preparedness 2a. Principal encouragement, 2b. Principal beliefs about program |
Quantity of program implementation |
| Seys et al. 2018 [31] | Care pathway implementation | Adherence to evidence-based recommendations, level of competence, team climate for innovation, burnout, level of organized care | 30-day hospital readmission |
| Williams et al. 2014 [32] | Information packets and Motivational Interviewing webinar | Attitudes towards EBPs, pressure for change, barriers to EBPs, resources, organizational climate, management support | Motivational Interviewing adoption |
| Williams et al. 2017 [33] | Availability,Responsiveness, and Continuity (ARC) intervention implementation | Proficiency culture --> evidence-based practice intention, barrier reduction | EBP adoption, EBP use |
| Quantitative—non-randomized | |||
| Aarons et al. 2009 [34] | Agency type |
1. organizational support for EBP --> provider attitudes towards EBP 2, 3 organizational support for EBP organizational support for EBP |
1,3 provider EBP use2. provider EBP attitudes |
| Becker et al. 2016 [35] | Training as usual, training + ongoing technical assistance, support from in-house champion, specialized training on change process, monthly conference calls and online forum to support change | Organizational readiness to change (motivation for change, adequacy of resources, staff attributes, organizational climate),perceived intervention characteristics (relative advantage, observability, trialability, compatibility, and complexity) | Adoption |
| Beenstock et al. 2012 [36] | Main place of work | Propensity to act | Referral of women to smoking cessation services |
| Beets et al. 2008 [37] | Perception of school climate |
1. Beliefs about responsibility to teach program 2. beliefs about responsibility to teach program --> attitudes towards program --> curriculum delivered |
1. Attitudes towards program 2. curriculum delivered to schoolwide material usage |
| Bonetti et al. 2009 [38] | Behavioral intention | Action planning | Placing fissure sealants |
| Chou et al. 2011 [39] | Receipt of individual performance feedback, clinician input into guideline implementation and quality improvement, clinician expectancy, clinician self-efficacy | Agreement with guidelines, adherence to guidelines, improved knowledge, practice delivery | Fidelity to screening patients for depression |
| Cummings et al. 2017 [40] | Culture, feedback, leadership and resources | Manager support, coaching conversations, job satisfaction | Conceptual research use, persuasive research use, instrumental research use |
| David and Schiff 2017 [41] |
Child-parent psychotherapy social network Child-parent psychotherapy supervision |
Self-efficacy | Number of child-parent psychotherapy cases, intention to use child-parent psychotherapy |
| Edmunds et al. 2014 [42] | Time following training | Time spent in consultation | Knowledge of cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety, attitudes towards EBPs |
| Gnich et al. 2018 [43] | Pay-per item financial incentive | Knowledge, skills, social/professional role and identity, beliefs about consequences, motivation and goals (intention), environmental context and resources, social influences (norms), emotion, behavioral regulation | Fluoride varnish delivery |
| Guerrero et al. 2018 [44] | Top manager transformational leadership | Middle managers’ implementation leadership | Employee attitudes towards EBPs, EBP implementation |
| Huis et al. 2013 [45] | individual and organization targeted strategies (education, reminders, feedback), individual and organizational targeted strategies + team and leader strategy | Social influence, leadership, performance feedback | Handwashing fidelity |
| Little et al. 2015 [46] | Community priority, organizational support, program champion | beliefs about effectiveness of interventions --> funding to adopt program | Adoption |
| Llasus et al. 2014 [47] | EBP knowledge | Self confidence in one's EBP competencies (defined as readiness) | EBP implementation behaviors |
| Nelson and Steele 2007 [48] | EBP training, openness of clinical setting to EBPs | Positive attitudes towards treatment research, negative attitudes towards treatment research | EBP use |
| Potthoff et al. 2017 [49] | Action planning, coping planning | Habit | Clinical behaviors (prescribing, advising, examining) |
| Presseau et al. 2016 [50] | Printed informational materials | Attitudes toward prescribing, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, intention to prescribe | Self-reported prescribing behavior |
| Simmonds et al. 2012 [51] | Intolerance of uncertainty | Treatment orientation toward back pain |
Recommendations to return to work 2. recommendations to return to usual activities,estimated risk of back pain disability |
| Stockdale et al. 2018 [52] | Health care team communication | Patient-provider communication | Patient satisfaction with primary care provider |
| Wanless et al. 2015 [53] | Use of responsive classroom practices, global emotional support, self-efficacy, collective responsibility | Teacher training engagement | Fidelity to intervention |
| Yamada et al. 2017 [62] | Instrumental research use, conceptual research use |
Organizational context: leadership, culture, evaluation, social capital, informal interactions, formal interactions, resources, slack space, slack staff, slack time |
Pain assessment, evidence-based pain procedure use, pain intensity |
| Mixed methods | |||
| Armson et al. 2018 [54] | Implementation tools (printed education materials, informational video, decision aid) | Evidence-based information in guideline, evidence-based information in screening module, discussions with peers, application of implementation tools, discussions with patients, lack of evidence about benefits, patients' screening expectations, fear of misdiagnosis, problems with having patient materials available | Use of breast cancer screening guidelines |
| Birken et al. 2015 [55] |
1. Top manager support 2. Performance reviews 3. Human resources |
Mediators: 1a. Performance reviews 1b. Human resources 1c. Training 1d. Funding 1e. Local social network involvement Moderator: 2/3. top manager support |
1, 2, 3 middle manager commitment to innovation |
| Kauth et al. 2010 [56] | Facilitation + workshop, workshop |
Job-related barriers, # of contacts with facilitator, time spent in facilitation |
% time conducting Cognitive Behavioral Therapy |
| Lukas et al. 2009 [57] | Higher management support, group culture, hierarchical culture | Team effectiveness | Extent of implementation |
| Panzano et al. 2012 [58] |
1. Strategic fit of intervention 2. Climate for innovation |
1. Climate for innovation2. Fidelity to intervention |
1. Fidelity to intervention 2. Assimilation |
| Rangachari et al. 2015 [59] | Emails containing intervention information and unit level adherence feedback + brief weekly training | Proactive communication between nurses and physicians emergence of champions | Number of catheter days |
| Shrubsole et al. 2018 [60] | Tailored training intervention targeting information provision |
Mechanisms of Intervention 1 targeting information provision implementation): knowledge, beliefs about consequences, social influence, beliefs about capabilities, environmental context and resources Mechanisms of Intervention 2 targeting implementation of goal setting): beliefs about consequences, social influences, beliefs about capabilities, environmental context and resources |
Information provisiongoal setting |
Numbering is used to denote match variables across models; not all models tested the same sets of variables
Common model types
The most common model type (29; 63.0%) was one in which X was a determinant, M was also a determinant, and Y was an implementation outcome variable (determinant ➔ determinant ➔ implementation outcome). For example, Beenstock et al. [36] tested a model in which propensity to act (determinant) was evaluated as a mediator explaining the relation between main place of work (determinant) and referral to smoking cessation services (outcome). Just less than half the studies (22; 47.8%) included an implementation strategy in their model, of which 16 (34.8%) evaluated a mediation model in which an implementation strategy was X, a determinant was the candidate M, and an implementation outcome was Y (strategy ➔ determinant ➔ implementation outcome); ten of these studies experimentally manipulated the relation between the implementation strategy and determinant. An example of this more traditional mediation model is a study by Atkins and colleagues [21] which evaluated key opinion leader support and mental health practitioner support (determinants) as potential mediators of the relation between training and consultation (strategy) and adoption of the EBP (implementation outcome). Five studies included a mediation model in which X was an implementation strategy, Y was a clinical outcome, and M was an implementation outcome (strategy ➔ implementation outcome ➔ clinical outcome) [25, 26, 28, 29, 31].
Notable exceptions to model types
While the majority of quantitative studies tested a three-variable model, there were some notable exceptions. Several studies tested multiple three variable models that held the independent variable and mediator constant but tested the relation among several dependent variables. Several studies tested multiple three variable models that held the independent variable and dependent variables constant but tested several mediators.
Qualitative studies
Five studies included in this review utilized qualitative methods to explore potential mechanisms or mediators of change, though only one explicitly stated this goal in their aims [17]. Three studies utilized a comparative case study design incorporating a combination of interviews, focus groups, observation, and document review, whereas two studies employed a cross-sectional descriptive design. Although three of the five studies reported their analytic design was informed by a theory or previously established model, only one study included an interview guide in which items were explicitly linked to theory [19]. All qualitative studies explored relations between multiple ecological levels, drawing connections between intra and interpersonal behavioral constructs and organization or system level change.
Criteria for establishing mechanisms of change
Finally, with respect to the seven criteria for establishing mechanisms of change, the plausibility/coherence (i.e., a logical explanation of how the mechanism operates that incorporates relevant research findings) was the most frequently fulfilled requirement, met by 42 studies (91.3%). Although 20 studies (43.5%), of which 18 were quantitative, provided statistical evidence of a strong association between the dependent and independent variables, only 13 (28.2%) studies experimentally manipulated an implementation strategy or the proposed mediator or mechanism. Further, there was only one study that attempted to demonstrate a dose-response relation between mediators and outcomes. Most included studies (39; 84.8%) fulfilled three or fewer criteria, and only one study fulfilled six of the seven requirements for demonstrating a mechanism of change; see Table 8.
Table 8.
Kazdin criteria
| Association | Specificity | Consistency | Manipulation | Timeline | Gradient | Plausibility | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qualitative | ||||||||
| Bardosh et al. 2017 [16] | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Brewster et al. 2015 [17] | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Carrera and Lambooij 2015 [18] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Frykman et al. 2014 [19] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Wiener-Ogilvie et al. 2008 [20] | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Quantitative—randomized | ||||||||
| Atkins et al. 2008 [21] | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Baer et al. 2009 [22] | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Bonetti et al. 2005 [23] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 5 |
| Garner et al. 2011 [24] | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Glisson et al. 2010 [25] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Holth et al. 2011 [26] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 |
| Lee et al. 2018 [27] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Lochman et al. 2009 [28] | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Rapkin et al. 2017 [29] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Rohrbach et al. 1993 [30] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Seys et al. 2018 [31] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 5 |
| Williams et al. 2014 [32] | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 |
| Williams et al. 2017 [33] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| Quantitative—non-randomized | ||||||||
| Aarons et al. 2009 [34] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 |
| Becker et al. 2016 [35] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Beenstock et al. 2012 [36] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Beets et al. 2008 [37] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Bonetti et al. 2009 [38] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Chou et al. 2011 [39] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Cummings et al., 2017 [40] | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| David and Schiff 2017 [41] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Edmunds et al. 2014 [42] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Gnich et al. 2018 [43] | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Guerrero et al. 2018 [44] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Huis et al. 2013 [45] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Little et al. 2015 [46] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Llasus et al. 2014 [47] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Nelson and Steele 2007 [48] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Potthoff et al. 2017 [49] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Presseau et al. 2016 [50] | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Simmonds et al. 2012 [51] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Stockdale et al. 2018 [52] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Wanless et al. 2015 [53] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Mixed methods | ||||||||
| Armson et al. 2018 [54] | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Birken et al. 2015 [55] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Kauth et al. 2010 [56] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Lukas et al. 2009 [57] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Panzano et al. 2012 [58] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Rangachari et al. 2015 [59] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Shrubsole et al. 2018 [60] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
Studies that only tested mediation relationships are not included in this table
Discussion
Observations regarding mechanistic research in implementation science
Mechanism-focused implementation research is in an early phase of development, with only 46 studies identified in our systematic review across health disciplines broadly. Consistent with the field of implementation science, no single discipline is driving the conduct of mechanistic research, and a diverse array of methods (quantitative, qualitative, mixed methods) and designs (e.g., cross-sectional survey, longitudinal non-randomized, longitudinal randomized, etc.) have been used to examine mechanisms. Just over one-third of studies (N = 16; 34.8%) evaluated a mediation model with the implementation strategy as the independent variable, determinant as a putative mediator, and implementation outcome as the dependent variable. Although this was the most commonly reported model, we would expect a much higher proportion of studies testing mechanisms of implementation strategies given the ultimate goal of precise selection of strategies targeting key mechanisms of change. Studies sometimes evaluated models in which the determinant was the independent variable, another determinant was the putative mediator, and an implementation outcome was the dependent variable (N = 11; 23.9%). These models suggest an interest in understanding the cascading effect of changes in context on key outcomes, but without manipulating or evaluating an implementation strategy as the driver of observed change. Less common (only 5, 10.9%) were more complex models in which multiple mediators and outcomes and different levels of analyses were tested (e.g., [37, 39]), despite that this level of complexity is likely to characterize the reality of typical implementation contexts. Although there were several quantitative studies that did observe significant relations pointing toward a mediator, none met all criteria for establishing a mechanism.
Less than one-third of the studies experimentally manipulated the strategy-mechanism linkage. As the field progresses, we anticipate many more tests of this nature, which will allow us to discern how strategies exert their effect on outcomes of interest. However, implementation science will continue to be challenged by the costly nature of the type of experimental studies that would be needed to establish this type of evidence. Fortunately, methodological innovations that capitalize on recently funded implementation trials to engage in multilevel mediation modeling hold promise for the next iteration of mechanistic implementation research [14, 127] As this work unfolds, a number of scenarios are possible. For example, it is likely the case that multiple strategies can target the same mechanism; that a single strategy can target multiple mechanisms; and that mechanisms across multiple levels of analysis must be engaged for a given strategy to influence an outcome of interest. Accordingly, we expect great variability in model testing will continue and that more narrowly focused efforts will remain important contributions so long as shared conceptualization of mechanisms and related variables is embraced, articulated, and rigorously tested. As with other fields, we observed great variability in the degree to which mechanisms (and related variables of interest) were appropriately specified, operationalized, and measured. This misspecification coupled with the overall lack of high-quality studies (only three met 100% of the quality criteria), and the diversity in study methods, strategies tested, and mediating or moderating variables under consideration, we were unable to synthesize the findings across studies to point toward promising mechanisms.
The need for greater conceptual clarity and methodological advancements
Despite the important advances that the studies included in this review represent, there are clear conceptual and methodological issues that need to be addressed to allow future research to more systematically establish mechanisms. Table 1 offers a list of key terms and definitions for the field to consider. We suggest the term “mechanism” be used to reflect a process or event through which an implementation strategy operates to affect desired implementation outcomes. Consistent with existing criteria [4], mechanisms can only be confidently established via carefully designed (i.e., longitudinal; experimentally manipulated) empirical studies demonstrating a strong association, and ideally a dose-response relation, between an intervening variable and outcome (e.g., via qualitative data or mediation or moderator analyses) that are supported by very specific theoretical propositions observed consistently across multiple studies. We found the term “mediator” to be most frequently used in this systematic review, which can point toward a mechanism, but without consideration of these full criteria, detection of a mediator reflects a missed opportunity to contribute more meaningfully to the mechanisms literature.
Interestingly, the nearly half of studies (43.5%) treated a variable that many would conceptualize as a “determinant” as the independent variable in at least one proposed or tested mediation pathway. Presumably, if researchers are exploring the impact of a determinant on another determinant and then on an outcome, there must be a strategy (or action) that caused the change in the initial determinant. Or, it is possible that researchers are simply interested in the natural associations among these determinants to identify promising points of leverage. This is a prime example where the variable or overlapping use of concepts (i.e., calling all factors of interest “determinants”) becomes particularly problematic and undermines the capacity of the field to accumulate knowledge across studies in the service of establishing mechanisms. We contend that it is important to differentiate among concepts to use more meaningful terms like preconditions, putative mechanisms, proximal and distal outcomes, all of which were under-specified in the majority of the included studies. Several authors from our team have articulated an approach to building causal pathway diagrams [128] that clarifies that preconditions are necessary factors for a mechanism to be activated and proximal outcomes are the immediate result of a strategy that is realized only because the specific mechanism was activated. We conceptualize distal outcomes as the eight implementation outcomes articulated by Proctor and colleagues [129]. Disentangling these concepts can help characterize why strategies fail to exert an impact on an outcome of interest. Examples of each follow in the section below.
Conceptual and methodological recommendations for future research
Hypothesis generation
With greater precision among these concepts, the field can also generate and test more specific hypotheses about how and why key variables are related. This begins with laying out mechanistic research questions (e.g., How does a network intervention, like a learning collaborative, influence provider attitudes?) and generating theory-driven hypotheses. For instance, a testable hypothesis may be that learning collaboratives [strategy] operate through sharing [mechanism] of positive experiences with a new practice to influence provider attitudes [outcome]. As another example, clinical decision support [strategy] may act through helping the provider to remember [mechanism] to administer a screener [proximal outcome] and flagging this practice before an encounter may not allow the mechanism to be activated [precondition]. Finally, organizational strategy development [strategy] may have an effect because it means prioritizing competing demands [mechanism] to generate a positive implementation climate [proximal outcome]. Research questions that allow for specific mechanism-focused hypotheses have the potential to expedite the rate at which effective implementation strategies are identified.
Implementation theory
Ultimately, theory is necessary to drive hypotheses, explain implementation processes, and effectively inform implementation practice by providing guidance about when and in what contexts specific implementation strategies should or should not be used. Implementation theories can offer mechanisms that extend across levels of analysis (e.g., intrapersonal, interpersonal, organizational, community, macro policy [130]). However, there is a preponderance of frameworks and process models, with few theories in existence. Given that implementation is a process of behavior change at its core, in lieu of implementation-specific theories, many researchers draw upon classic theories from psychology, decision science, and organizational literatures, for instance. Because of this, the majority of the identified studies explored intrapersonal-level mechanisms, driven by their testing of social psychological theories such as the theory of planned behavior [65] and social cognitive theory [76, 77, 99]. Nine studies cited the diffusion of innovations [63, 64] as a theory guiding their mechanism investigation, which does extend beyond intrapersonal to emphasize interpersonal, and to some degree community level mechanisms, although we did not see this materialize in the included study analyses [63–65, 76, 77]. Moving forward, developing and testing theory is critical for advancing the study of implementation mechanisms because theories (implicitly or explicitly) tend to identify putative mechanisms instead of immutable determinants.
Measurement
Inadequate measurement has the potential to undermine our ability to advance this area of research. Our coding indicated that mechanisms were assessed almost exclusively via self-report (questionnaire, interview, focus group) suggesting that researchers conceptualize the diverse array of mechanisms to be latent constructs and not directly observable. This may indeed be appropriate, given that mechanisms are typically processes like learning and reflecting that occur within an individual and it is their proximal outcomes that are directly observable (e.g., knowledge acquisition, confidence, perceived control). However, conceptual, theoretical, and empirical work is needed to (a) articulate the theorized mechanisms for the 70+ strategies and proximal outcomes [128], (b) identify measures of implementation mechanisms and evaluate their psychometric evidence base [131] and pragmatic qualities [132], and (c) attempt to identify and rate or develop objective measures of proximal outcomes for use in real-time experimental manipulations of mechanism-outcome pairings.
Quantitative analytic approaches
The multilevel interrelations of factors implicated in an implementation process also call for sophisticated quantitative and qualitative methods to uncover mechanisms. With respect to quantitative methods, it was surprising that the Baron and Kenny [78] approach to mediation testing remains most prevalent despite that most studies are statistically underpowered to use this approach, and the other most common approach (i.e., the Sobel test [79]) relies on an assumption that the sampling distribution of the mediation effect is normal [14, 133], neither of which were reported on in any of the 12 included studies that used these methods. Williams [14] suggests the product of coefficients approach [134, 135] is more appropriate for mediation analysis because it is a highly general approach to both single and multi-level mediation models that minimizes type I error rates, maximizes statistical power, and enhances accuracy of confidence intervals [14]. The application of moderated mediation models and mediated moderator models will allow for a nuanced understanding of the complex interrelations among factors implicated in an implementation process.
Qualitative analytic approaches
Because this was the first review of implementation mechanisms across health disciplines, we believed it was important to be inclusive with respect to methods employed. Qualitative studies are important to advancing research on implementation mechanisms in part because they offer a data collection method in lieu of having an established measure to assess mechanisms quantitatively. Qualitative research is important for informing measure development work, but also for theory development given the richness of the data that can be gleaned. Qualitative inquiry can be more directive by developing hypotheses and generating interview guides to directly test mechanisms. Diagramming and tracing causal linkages can be informed by qualitative inquiry in a structured way that is explicit with regard to how the data informs our understanding of mechanisms. This kind of directed qualitative research is called for in the United Kingdom’s MRC Guidance for Process Evaluation [136]. We encourage researchers internationally to adopt this approach as it would importantly advance us beyond the descriptive studies that currently dominate the field.
Limitations
There are several limitations to this study. First, we took an efficient approach to coding for study quality when applying the MMAT. Although it was a strength that we evaluated study quality, the majority of studies were assessed only by one research specialist. Second, we may have overlooked relevant process evaluations conducted in the UK where MRC Guidance stipulates inclusion of mechanisms that may have been described using terms not included in our search string. Third, although we identified several realist reviews, we did not include them in our systematic review because they conceptualize mechanisms differently than how they are treated in this review [137]. That is, realist synthesis posits that interventions are theories and that they imply specific mechanisms of action instead of separating mechanisms from the implementation strategies/interventions themselves [138]. Thus, including the realist operationalization would have further confused an already disharmonized literature with respect to mechanisms terminology but ultimately synthesizing findings from realist reviews with standard implementation mechanism evaluations will be important. Fourth, our characterization of the models tested in the identified studies may not reflect those intended by researchers given our attempt to offer conceptual consistency across studies, although we did reach out to corresponding authors for whom we wished to seek clarification on their study. Finally, because of the diversity of study designs and methods, and the inconsistent use of relevant terms, we are unable to synthesize across the studies and report on any robustly established mechanisms.
Conclusion
This study represents the first systematic review of implementation mechanisms in health. Our inclusive approach yielded 46 qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods studies, none of which met all seven criteria (i.e., strong association, specificity, consistency, experimental manipulation, timeline, gradient, plausibility or coherence) that are deemed critical for empirically establishing mechanisms. We found nine unique versions of models that attempted to uncover mechanisms, with only six exploring mediators of implementation strategies. The results of this review indicated inconsistent use of relevant terms (e.g., mechanisms, determinants) for which we offer guidance to achieve precision and encourage greater specificity in articulating research questions and hypotheses that allow for careful testing of causal relations among variables of interest. Implementation science will benefit from both quantitative and qualitative research that is more explicit in their attempt to uncover mechanisms. In doing so, our research will allow us to test the idea that more is better and move toward parsimony both for standardized and tailored approaches to implementation.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Figure S1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria and Definitions.
Additional file 2. PRISMA 2009 Checklist.
Additional file 3. Emergent Mechanism Models.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
The authors are willing to share the raw data tables that informed the summary tables included in this manuscript.
Abbreviations
- EBPs
Evidence-based practice
- MMAT
Mixed methods appraisal tool
- PARiHS
Promoting Action on Research in Health Services
- HLM
Hierarchical linear modeling
- SEM
Structural equation modeling
Authors’ contributions
CCL conceptualized the larger study and articulated the research questions with all coauthors. CCL, MRB, and CWB designed the approach with feedback from all coauthors. MRB and CWB executed the systematic search with oversight and checking by CCL. MRB led the data extraction and CWB led the study appraisal. All authors contributed to the discussion and reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Funding
This project was supported by grant number R13HS025632 from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
A mediator can point toward a mechanism as it is an intervening variable that may account (statistically) for the relation between the independent variable (strategy) and the dependent variable (implementation outcome), revealing one possible causal pathway for the observed effect [4]. Compared to mediators, mechanisms are conceptualized as more precise in their description of the operations underlying causal processes [5].
Key differences in Williams’ [14] search method are important to note. Williams first conducted a broad search for randomized controlled trials concerning implementation or dissemination of evidence-based therapies. Only after screening references for these criteria, did Williams narrow the search to studies that specifically addressed mediators. Conversely, the present method included mediators/moderators/mechanisms as terms in the initial search string. Additionally, Williams hand searched references included in four previous reviews of implementation strategies in mental health.
We refer to variables in the ways the study authors did, even if we might have a different way in which we would approach their conceptualization.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Cara C. Lewis, Email: cara.c.lewis@kp.org
Meredith R. Boyd, Email: meredithboyd@ucla.edu
Callie Walsh-Bailey, Email: callie.w@wustl.edu.
Aaron R. Lyon, Email: lyona@uw.edu
Rinad Beidas, Email: rbeidas@upenn.edu.
Brian Mittman, Email: brian.s.mittman@kp.org.
Gregory A. Aarons, Email: gaarons@ucsd.edu
Bryan J. Weiner, Email: bjweiner@uw.edu
David A. Chambers, Email: dchamber@mail.nih.gov
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s13012-020-00983-3.
References
- 1.Eccles MP, Mittman BS. Welcome to implementation science. Implement Sci. 2006;1(1):1. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-1-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Powell BJ, McMillen JC, Proctor EK, Carpenter CR, Griffey RT, Bunger AC, et al. A compilation of strategies for implementing clinical innovations in health and mental health. Med Care Res Rev. 2012;69(2):123–157. doi: 10.1177/1077558711430690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Powell BJ, Waltz TJ, Chinman MJ, Damschroder LJ, Smith JL, Matthieu MM, et al. A refined compilation of implementation strategies: results from the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) project. Implement Sci. 2015;10:21. doi: 10.1186/s13012-015-0209-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kazdin AE. Mediators and mechanisms of change in psychotherapy research. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2007;3(1):1–27. doi: 10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.3.022806.091432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kraemer HC, Wilson GT, Fairburn CG, Agras WS. Mediators and moderators of treatment effects in randomized clinical trials. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2002;59(10):877–883. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.59.10.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gerring J. Social science methodology: a criterial framework. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Frazier PA, Tix AP, Barron KE. Testing moderator and mediator effects in counseling psychology research. US: American Psychological Association; 2004. pp. 115–134. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hill AB. The Environment and Disease: Association or Causation? Proc R Soc Med. 1965;58:295–300. doi: 10.1177/003591576505800503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bosch M, van der Weijden T, Wensing M, Grol R. Tailoring quality improvement interventions to identified barriers: a multiple case analysis. J Eval Clin Pract. 2007;13(2):161–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2006.00660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Claridge JA, Fabian TC. History and development of evidence-based medicine. World J Surg. 2005;29(5):547–553. doi: 10.1007/s00268-005-7910-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cook SC, Schwartz AC, Kaslow NJ. Evidence-Based psychotherapy: advantages and challenges. Neurotherapeutics. 2017;14(3):537–545. doi: 10.1007/s13311-017-0549-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dissemination and Implementation Research in Health (R01 Clinical Trial Optional). National Institutes of Health (NIH); 2019. https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/pa-files/PAR-19-274.html.
- 13.Thomas J, Brunton J, Graziosi S. EPPI-Reviewer 4: software for research synthesis. EPPI-Centre Software. London: Social Science Research Unit, UCL Institute of Education; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Williams NJ. Multilevel mechanisms of implementation strategies in mental health: integrating theory, research, and practice. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2016;43(5):783–798. doi: 10.1007/s10488-015-0693-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hong QN, Pluye P, Fabregues S, Bartlett G, Boardman F, Cargo M, et al. Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) Montreal, Canada: McGill University; 2018 [Available from: http://mixedmethodsappraisaltoolpublic.pbworks.com/w/file/fetch/127916259/MMAT_2018_criteria-manual_2018-08-01_ENG.pdf.
- 16.Bardosh KL, Murray M, Khaemba AM, Smillie K, Lester R. Operationalizing mHealth to improve patient care: a qualitative implementation science evaluation of the WelTel texting intervention in Canada and Kenya. Global Health. 2017;13(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12992-017-0311-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Brewster AL, Curry LA, Cherlin EJ, Talbert-Slagle K, Horwitz LI, Bradley EH. Integrating new practices: a qualitative study of how hospital innovations become routine. Implement Sci. 2015;10:168. doi: 10.1186/s13012-015-0357-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Carrera PM, Lambooij MS. Implementation of out-of-office blood pressure monitoring in the netherlands: from clinical guidelines to patients’ adoption of innovation. Medicine. 2015;94(43):e1813. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Frykman M, Hasson H, Muntlin Athlin Å, von Thiele Schwarz U. Functions of behavior change interventions when implementing multi-professional teamwork at an emergency department: a comparative case study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14:218. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-14-218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wiener-Ogilvie S, Huby G, Pinnock H, Gillies J, Sheikh A. Practice organisational characteristics can impact on compliance with the BTS/SIGN asthma guideline: qualitative comparative case study in primary care. BMC Fam Pract. 2008;9:32. doi: 10.1186/1471-2296-9-32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Atkins MS, Frazier SL, Leathers SJ, Graczyk PA, Talbott E, Jakobsons L, et al. Teacher key opinion leaders and mental health consultation in low-income urban schools. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2008;76(5):905–908. doi: 10.1037/a0013036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Baer JS, Wells EA, Rosengren DB, Hartzler B, Beadnell B, Dunn C. Agency context and tailored training in technology transfer: a pilot evaluation of motivational interviewing training for community counselors. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2009;37(2):191–202. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2009.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bonetti D, Eccles M, Johnston M, Steen N, Grimshaw J, Baker R, et al. Guiding the design and selection of interventions to influence the implementation of evidence-based practice: an experimental simulation of a complex intervention trial. Soc Sci Med. 2005;60(9):2135–2147. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2004.08.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Garner BR, Godley SH, Bair CML. The impact of pay-for-performance on therapists’ intentions to deliver high quality treatment. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2011;41(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2011.01.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Glisson C, Schoenwald SK, Hemmelgarn A, Green P, Dukes D, Armstrong KS, et al. Randomized trial of MST and ARC in a two-level evidence-based treatment implementation strategy. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2010;78(4):537–550. doi: 10.1037/a0019160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Holth P, Torsheim T, Sheidow AJ, Ogden T, Henggeler SW. Intensive quality assurance of therapist adherence to behavioral interventions for adolescent substance use problems. J Child Adolesc Subst Abuse. 2011;20(4):289–313. doi: 10.1080/1067828X.2011.581974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lee H, Hall A, Nathan N, Reilly KL, Seward K, Williams CM, et al. Mechanisms of implementing public health interventions: a pooled causal mediation analysis of randomised trials. Implement Sci. 2018;13(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13012-018-0734-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lochman JE, Boxmeyer C, Powell N, Qu L, Wells K, Windle M. Dissemination of the coping power program: importance of intensity of counselor training. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2009;77(3):397–409. doi: 10.1037/a0014514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rapkin BD, Weiss E, Lounsbury D, Michel T, Gordon A, Erb-Downward J, et al. Reducing Disparities in cancer screening and prevention through community-based participatory research partnerships with local libraries: a comprehensive dynamic trial. Am J Community Psychol. 2017;60(1-2):145–159. doi: 10.1002/ajcp.12161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rohrbach LA, Graham JW, Hansen WB. Diffusion of a school-based substance abuse prevention program: predictors of program implementation. Prev Med. 1993;22(2):237–260. doi: 10.1006/pmed.1993.1020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Seys D, Bruyneel L, Sermeus W, Lodewijckx C, Decramer M, Deneckere S, et al. Teamwork and adherence to recommendations explain the effect of a care pathway on reduced 30-day readmission for patients with a COPD exacerbation. COPD. 2018;15(2):157–164. doi: 10.1080/15412555.2018.1434137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Williams NJG, C. The role of organizational culture and climate in the dissemination and implementation of empirically-supported treatments for youth. Dissemination and implementation of evidence based practices in child and adolescent mental health. New York: Oxford University Press; 2014. p. 61-81.
- 33.Williams NJ, Glisson C, Hemmelgarn A, Green P. Mechanisms of change in the ARC Organizational strategy: increasing mental health clinicians' EBP adoption through improved organizational culture and capacity. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2017;44(2):269–283. doi: 10.1007/s10488-016-0742-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Aarons GA, Sommerfeld DH, Walrath-Greene CM. Evidence-based practice implementation: the impact of public versus private sector organization type on organizational support, provider attitudes, and adoption of evidence-based practice. Implement Sci. 2009;4:83. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-4-83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Becker SJ, Squires DD, Strong DR, Barnett NP, Monti PM, Petry NM. Training opioid addiction treatment providers to adopt contingency management: a prospective pilot trial of a comprehensive implementation science approach. Subst Abus. 2016;37(1):134–140. doi: 10.1080/08897077.2015.1129524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Beenstock J, Sniehotta FF, White M, Bell R, Milne EMG, Araujo-Soares V. What helps and hinders midwives in engaging with pregnant women about stopping smoking? A cross-sectional survey of perceived implementation difficulties among midwives in the North East of England. Implement Sci. 2012;7:36. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-7-36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Beets MW, Flay BR, Vuchinich S, Acock AC, Li KK, Allred C. School climate and teachers' beliefs and attitudes associated with implementation of the positive action program: a diffusion of innovations model. Prev Sci. 2008;9(4):264–275. doi: 10.1007/s11121-008-0100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bonetti D, Johnston M, Clarkson J, Turner S. Applying multiple models to predict clinicians' behavioural intention and objective behaviour when managing children's teeth. Psychol Health. 2009;24(7):843–860. doi: 10.1080/08870440802108918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chou AF, Vaughn TE, McCoy KD, Doebbeling BN. Implementation of evidence-based practices: applying a goal commitment framework. Health Care Manage Rev. 2011;36(1):4–17. doi: 10.1097/HMR.0b013e3181dc8233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chambers D, Simpson L, Neta G, UvT S, Percy-Laurry A, Aarons GA, et al. Proceedings from the 9th annual conference on the science of dissemination and implementation. Implementation Sci. 2017;12(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13012-017-0575-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.David P, Schiff M. Self-efficacy as a mediator in bottom-up dissemination of a Research-supported intervention for young, traumatized children and their families. J Evid Inf Soc Work. 2017;14(2):53–69. doi: 10.1080/23761407.2017.1298072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Edmunds JM, Read KL, Ringle VA, Brodman DM, Kendall PC, Beidas RS. Sustaining clinician penetration, attitudes and knowledge in cognitive-behavioral therapy for youth anxiety. Implement Sci. 2014;9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 43.Gnich W, Sherriff A, Bonetti D, Conway DI, Macpherson LMD. The effect of introducing a financial incentive to promote application of fluoride varnish in dental practice in Scotland: a natural experiment. Implement Sci. 2018;13(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13012-018-0775-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Guerrero EG, Frimpong J, Kong Y, Fenwick K. Aarons GA. Health Care Manage Rev: Advancing theory on the multilevel role of leadership in the implementation of evidence-based health care practices; 2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Huis A, Holleman G, van Achterberg T, Grol R, Schoonhoven L, Hulscher M. Explaining the effects of two different strategies for promoting hand hygiene in hospital nurses: a process evaluation alongside a cluster randomised controlled trial. Implement Sci. 2013;8:41. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-8-41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Little MA, Pokhrel P, Sussman S, Rohrbach LA. The process of adoption of evidence-based tobacco use prevention programs in California schools. Prev Sci. 2015;16(1):80–89. doi: 10.1007/s11121-013-0457-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Llasus L, Angosta AD, Clark M. Graduating baccalaureate students' evidence-based practice knowledge, readiness, and implementation. J Nurs Educ. 2014;53(Suppl 9):S82–S89. doi: 10.3928/01484834-20140806-05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Nelson TD, Steele RG. Predictors of practitioner self-reported use of evidence-based practices: practitioner training, clinical setting, and attitudes toward research. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2007;34(4):319–330. doi: 10.1007/s10488-006-0111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Potthoff S, Presseau J, Sniehotta FF, Johnston M, Elovainio M, Avery L. Planning to be routine: habit as a mediator of the planning-behaviour relationship in healthcare professionals. Implement Sci. 2017;12(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s13012-017-0551-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Presseau J, Grimshaw JM, Tetroe JM, Eccles MP, Francis JJ, Godin G, et al. A theory-based process evaluation alongside a randomised controlled trial of printed educational messages to increase primary care physicians' prescription of thiazide diuretics for hypertension [ISRCTN72772651] Implement Sci. 2016;11(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s13012-016-0485-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Simmonds MJ, Derghazarian T, Vlaeyen JW. Physiotherapists' knowledge, attitudes, and intolerance of uncertainty influence decision making in low back pain. Clin J Pain. 2012;28(6):467–474. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e31825bfe65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Stockdale SE, Rose D, Darling JE, Meredith LS, Helfrich CD, Dresselhaus TR, et al. Communication among team members within the patient-centered medical home and patient satisfaction with providers: the mediating role of patient-provider communication. Med Care. 2018;56(6):491–496. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0000000000000914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wanless SB, Rimm-Kaufman SE, Abry T, Larsen RA, Patton CL. Engagement in training as a mechanism to understanding fidelity of implementation of the responsive classroom approach. Prev Sci. 2015;16(8):1107–1116. doi: 10.1007/s11121-014-0519-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Armson H, Roder S, Elmslie T, Khan S, Straus SE. How do clinicians use implementation tools to apply breast cancer screening guidelines to practice? Implement Sci. 2018;13(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13012-018-0765-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Birken SA, Lee S-YD, Weiner BJ, Chin MH, Chiu M, Schaefer CT. From strategy to action: how top managers’ support increases middle managers’ commitment to innovation implementation in healthcare organizations. Health Care Manage Rev. 2015;40(2):159–168. doi: 10.1097/HMR.0000000000000018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kauth MR, Sullivan G, Blevins D, Cully JA, Landes RD, Said Q, et al. Employing external facilitation to implement cognitive behavioral therapy in VA clinics: a pilot study. Implement Sci. 2010;5(1):75. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-5-75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lukas CV, Mohr DC, Meterko M. Team effectiveness and organizational context in the implementation of a clinical innovation. Qual Manag Health Care. 2009;18(1):25–39. doi: 10.1097/01.QMH.0000344591.56133.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Panzano PC, Sweeney HA, Seffrin B, Massatti R, Knudsen KJ. The assimilation of evidence-based healthcare innovations: a management-based perspective. J Behav Health Serv Res. 2012;39(4):397–416. doi: 10.1007/s11414-012-9294-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Rangachari P, Madaio M, Rethemeyer RK, Wagner P, Hall L, Roy S, et al. The evolution of knowledge exchanges enabling successful practice change in two intensive care units. Health Care Manage Rev. 2015;40(1):65–78. doi: 10.1097/HMR.0000000000000001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Shrubsole K, Worrall L, Power E, O'Connor DA. The acute aphasia implementation study (AAIMS): a pilot cluster randomized controlled trial. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2018;53(5):1021–1056. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Scott SD, Albrecht L, O'Leary K, Ball GD, Hartling L, Hofmeyer A, et al. Systematic review of knowledge translation strategies in the allied health professions. Implement Sci. 2012;7:70. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-7-70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yamada J, Squires JE, Estabrooks CA, Victor C, Stevens B, Pain CTiCs The role of organizational context in moderating the effect of research use on pain outcomes in hospitalized children: a cross sectional study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12913-017-2029-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Rogers E. Diffusion of innovations. 4. New York: Free Press; 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Rogers E. Diffusion of Innovations. 3. New York: Free Press; 1983. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ajzen I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process. 1991;50(2):179–211. doi: 10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Michie S, Johnston M, Abraham C, Lawton R, Parker D, Walker A, et al. Making psychological theory useful for implementing evidence based practice: a consensus approach. Qual Saf Health Care. 2005;14(1):26–33. doi: 10.1136/qshc.2004.011155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Kitson A, Harvey G, McCormack B. Enabling the implementation of evidence based practice: a conceptual framework. Qual Health Care. 1998;7(3):149–158. doi: 10.1136/qshc.7.3.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Damschroder LJ, Aron DC, Keith RE, Kirsh SR, Alexander JA, Lowery JC. Fostering implementation of health services research findings into practice: a consolidated framework for advancing implementation science. Implement Sci. 2009;4:50. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-4-50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Klein KJ, Sorra JS. The challenge of innovation implementation. Acad Manage Rev. 1996;21(4):1055–1080. doi: 10.5465/amr.1996.9704071863. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Davis FD. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly. 1989;13(3):319–340. doi: 10.2307/249008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Thompson RS, Higgins CA, Howell JM. Personal computing: toward a conceptual model of utilization. MIS Quarterly. 1991;15(1):125–143. doi: 10.2307/249443. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Braksick LW. Unlock behavior, unleash profits: developing leadership behavior that drives profitability in your organization. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Johnson J, Dakens L, Edwards P, Morse N. SwitchPoints: culture change on the fast track to business success. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Hedeker D, Gibbons RD. Longitudinal data analysis. New York, NY: Wiley; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 75.Krull JL, MacKinnon DP. Multilevel modeling of individual and group level mediated effects. Multivariate Behav Res. 2001;36(2):249–277. doi: 10.1207/S15327906MBR3602_06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bandura A. Self-efficacy: the exercise of control. New York: Macmillan; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Bandura A. Exercise of human agency through collective efficacy. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2000;9(3):75–78. doi: 10.1111/1467-8721.00064. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1986;51(6):1173–1182. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.51.6.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Sobel ME. Asymptotic confidence intervals for indirect effects in structural equation models. In: Leinhart S, editor. Sociological Methodology. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass; 1982. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Raudenbush SW, Bryk AS, Cheong YF, Congdon RT. HLM7: hierarchical linear and nonlinear modeling. Chicago: Scientific Software International; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S. Applied logistic regression. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- 82.Raudenbush SW, Bryk A, Congdon RT. HLM 6. Scientific Software International: Lincolnwood, IL; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Singer JD, Willet JB. Applied longitudinal data analysis: modeling change and event occurrence. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 84.Cane J, O'Connor D, Michie S. Validation of the theoretical domains framework for use in behaviour change and implementation research. Implement Sci. 2012;7:37. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-7-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Imai K, Keele L, Tingley D. A general approach to causal mediation analysis. Psychol Methods. 2010;15(4):309–334. doi: 10.1037/a0020761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.van Buuren SG-O, K. Mice: multivariate imputation by chained equations in R. J Stat Softw. 2010:1–68.
- 87.Rogers EM. Diffusion of innovations. 5. New York, NY: Free Press; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 88.Raudenbush SW, Liu X. Statistical power and optimal design for multisite randomized trials. Psychol Methods. 2000;5(2):199–213. doi: 10.1037/1082-989X.5.2.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Allison PD. Event history analysis. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications; 1984. [Google Scholar]
- 90.Yuk Fai C, Randall PF, Stephen WR. Efficiency and robustness of alternative estimators for two- and three-level models: the case of NAEP. J Educ Behav Stat. 2001;26(4):411–429. doi: 10.3102/10769986026004411. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Hox JJ, Maas CJM. The accuracy of multilevel structural equation modeling with pseudobalanced groups and small samples. Struct Equ Model. 2001;8(2):157–174. doi: 10.1207/S15328007SEM0802_1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Zhang Z, Zyphur MJ, Preacher KJ. Testing multilevel mediation using hierarchical linear models: problems and solutions. Organizational Research Methods. 2009;12(4):695–719. doi: 10.1177/1094428108327450. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Scott WR. Institutions and Organizations. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 94.Eisenberger R, Huntington R, Hutchison S, Sowa D. Perceived organizational support. Journal of Applied Psychology. 1986;71:500–507. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.71.3.500. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Preacher KJ, Hayes AF. SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effects in simple mediation models. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput. 2004;36(4):717–731. doi: 10.3758/BF03206553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Chen HT. Theory-driven evaluations. In: Reynolds HJ, Walber HJ, editors. Advances in educational productivity: evaluation research for educational productivity. 7. Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Publishing Limited; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 97.Marsh HW, Hau KT, Balla JR, Grayson D. Is More Ever Too Much? The Number of indicators per factor in confirmatory factor analysis. Multivariate Behav Res. 1998;33(2):181–220. doi: 10.1207/s15327906mbr3302_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Bandalos DL, Finney SJ. Item parceling issues in structural equation modeling. In: Marcoulides GA, editor. New developments and techniques in structural equation modeling. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum; 2001. pp. 269–296. [Google Scholar]
- 99.Bandura A. Health promotion from the perspective of social cognitive theory. Psychol Health. 1998;13(4):623–649. doi: 10.1080/08870449808407422. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Blackman D. Operant conditioning: an experimental analysis of behaviour. London, UK: Methuen; 1974. [Google Scholar]
- 101.Gollwitzer PM. Implementation intentions: strong effects of simple plans. Am Psychol. 1999;54:493–503. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.54.7.493. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Leventhal H, Nerenz D, Steele DJ. Illness representations and coping with health threats. In: Baum A, Taylor SE, Singer JE, editors. Handbook of psychology and health, volume 4: social psychological aspects of health. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum; 1984. pp. 219–251. [Google Scholar]
- 103.Weinstein N. The precaution adoption process. Health Psychol. 1988;7:355–386. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.7.4.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Prochaska JO, DiClemente CC. Stages and processes of self-change of smoking: toward an integrative model of change. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1983;51(3):390–395. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.51.3.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Landy FJ, Becker W. Motivation theory reconsidered. In: Cumming LL, Staw BM, editors. Research in organizational behavior. Greenwich, CT: JAI Press; 1987. [Google Scholar]
- 106.Locke EA, Latham GP. Building a practically useful theory of goal setting and task motivation: a 35-year odyssey. Am Psychol. 2002;57(9):705–717. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.57.9.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Kennedy P. A guide to econometrics. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 108.Joreskog KGS, D. LISRELR 8: User’s reference guide. Lincolnwood, IL: Scientific Software International; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 109.Valente TW. Social network thresholds in the diffusion of innovations. Social Networks. 1996;18:69–89. doi: 10.1016/0378-8733(95)00256-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Hayes AF. Beyond Baron and Kenny: Statistical mediation analysis in the new millennium. Communication Monographs. 2009;76:408–420. doi: 10.1080/03637750903310360. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Aarons GA, Hurlburt M, Horwitz SM. Advancing a conceptual model of evidence-based practice implementation in public service sectors. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2011;38(1):4–23. doi: 10.1007/s10488-010-0327-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Raudenbush SW, Bryk AS. Hierarchical linear models. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 113.Bryk AS, Raudenbush SW. Hierarchical linear models. Newbury Park, CA: Sage; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 114.Muthén LK, Muthén BO. Mplus user's guide Los Angeles, CA: Muthén & Muthén 2012 [Seventh Edition:[Available from: https://www.statmodel.com/download/usersguide/Mplus%20user%20guide%20Ver_7_r3_web.pdf.
- 115.Bentler PM. On tests and indices for evaluating structural models. Personal Individ Differ. 2007;42(5):825–829. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2006.09.024. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 116.MacKinnon DP, Fairchild AJ, Fritz MS. Mediation analysis. Annu Rev Psychol. 2007;58:593–614. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.58.110405.085542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Graham I, Logan J, Harrison M, Straus S, Tetroe J, Caswell W, et al. Lost in knowledge translation: time for a map? J Contin Educ Health Prof. 2006;26. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 118.Epstein S. Cognitive-experiential self-theory. In: Pervin LA, editor. Handbook of personality: theory and research. New York: Guilford; 1990. pp. 165–192. [Google Scholar]
- 119.Karlson KB, Holm A, Breen R. Comparing Regression coefficients between same-sample Nested models using logit and probit: a new method. Sociological Methodology. 2012;42(1):274–301. doi: 10.1177/0081175012444861. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Rycroft-Malone J, Kitson A, Harvey G, McCormack B, Seers K, Titchen A, et al. Ingredients for change: revisiting a conceptual framework. BMJ Qual Saf. 2002;11(2):174–180. doi: 10.1136/qhc.11.2.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Yukl G, Gordon A, Taber T. A hierarchical taxonomy of leadership behavior: integrating a half century of behavior research. J Leadersh Organ Stud. 2002;9(1):15–32. doi: 10.1177/107179190200900102. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Shrout PE, Bolger N. Mediation in experimental and nonexperimental studies: new procedures and recommendations. Psychol Methods. 2002;7(4):422–445. doi: 10.1037/1082-989X.7.4.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Fixsen DL, Naoom SF, Blase KA, Friedman RM. Implementation research: a synthesis of the literature. 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 124.Frambach R. An integrated model of organizational adoption and diffusion of innovations. Eur J Mark. 1993;27(5):22–41. doi: 10.1108/03090569310039705. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Institute of Medicine (IOM). Crossing the quality chasm: a new health system for the 21st century. Washington, DC: Institute of Medicine, National Academy Press; 2001.
- 126.Preacher KJ, Hayes AF. Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav Res Methods. 2008;40(3):879–891. doi: 10.3758/BRM.40.3.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Stahmer AC, Suhrheinrich J, Schetter PL, McGee HE. Exploring multi-level system factors facilitating educator training and implementation of evidence-based practices (EBP): a study protocol. Implement Sci. 2018;13(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13012-017-0698-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Lewis CC, Klasnja P, Powell BJ, Lyon AR, Tuzzio L, Jones S, et al. From classification to causality: advancing understanding of mechanisms of change in implementation science. Front Public Health. 2018;6:136. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2018.00136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Proctor E, Silmere H, Raghavan R, Hovmand P, Aarons G, Bunger A, et al. Outcomes for implementation research: conceptual distinctions, measurement challenges, and research agenda. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2011;38(2):65–76. doi: 10.1007/s10488-010-0319-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Weiner BJ, Lewis MA, Clauser SB, Stitzenberg KB. In search of synergy: strategies for combining interventions at multiple levels. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2012;2012(44):34–41. doi: 10.1093/jncimonographs/lgs001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Lewis CC, Weiner BJ, Stanick C, Fischer SM. Advancing implementation science through measure development and evaluation: a study protocol. Implement Sci. 2015;10:102. doi: 10.1186/s13012-015-0287-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Powell BJ, Stanick CF, Halko HM, Dorsey CN, Weiner BJ, Barwick MA, et al. Toward criteria for pragmatic measurement in implementation research and practice: a stakeholder-driven approach using concept mapping. Implement Sci. 2017;12(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13012-017-0649-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Wu AD, Zumbo BD. Understanding and using mediators and moderators. Soc Indic Res. 2007;87(3):367. doi: 10.1007/s11205-007-9143-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 134.MacKinnon DP, Lockwood CM, Hoffman JM, West SG, Sheets V. A comparison of methods to test mediation and other intervening variable effects. Psychol Methods. 2002;7(1):83. doi: 10.1037/1082-989X.7.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Pituch KA, Murphy DL, Tate RL. Three-level models for indirect effects in school- and class-randomized experiments in education. J Exp Educ. 2009;78(1):60–95. doi: 10.1080/00220970903224685. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Moore GF, Audrey S, Barker M, Bond L, Bonell C, Hardeman W, et al. Process evaluation of complex interventions: Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ : British Medical Journal. 2015;350:h1258. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Pawson R, Manzano-Santaella A. A realist diagnostic workshop. Evaluation. 2012;18(2):176–191. doi: 10.1177/1356389012440912. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Pawson R, Greenhalgh T, Harvey G, Walshe K. Realist synthesis: an introduction. Manchester, UK: ESRC Research Methods Programme, University of Manchester; 2004. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Figure S1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria and Definitions.
Additional file 2. PRISMA 2009 Checklist.
Additional file 3. Emergent Mechanism Models.
Data Availability Statement
The authors are willing to share the raw data tables that informed the summary tables included in this manuscript.