Abstract
Background
Raw second-generation (2G) lignocellulosic biomass materials have the potential for development into a sustainable and renewable source of energy. Poplar is regarded as a promising 2G material (P. davidiana Dode×P. bolleana Lauch, P. bolleana, P. davidiana, P. euphratica, et al). However, their large-scale commercialization still faces many obstacles. For example, drought prevents sufficient irrigation or rainfall, which can reduce soil moisture and eventually destroy the chloroplast, the plant photosynthetic organelle. Heterosis is widely used in the production of drought-tolerant materials, such as the superior clone “Shanxinyang” selected from the offspring of Populus davidiana Dode×Populus bolleana Lauch. Because it produces good wood and is easily genetically transformed, “Shanxinyang” has become a promising material for use in tree genetics. It is also one of the most abundant biofuel plants in northern China. Understanding the genetic features of chloroplasts, the cp transcriptome and physiology is crucial to elucidating the chloroplast drought-response model.
Results
In this study, the whole genome of “Shanxinyang” was sequenced. The chloroplast genome was assembled, and chloroplast structure was analysed and compared with that of other popular plants. Chloroplast transcriptome analysis was performed under drought conditions. The total length of the “Shanxinyang” chloroplast genome was 156,190 bp, the GC content was 36.75%, and the genome was composed of four typical areas (LSC, IRa, IRb, and SSC). A total of 114 simple repeats were detected in the chloroplast genome of “Shanxinyang”. In cp transcriptome analysis, we found 161 up-regulated and 157 down-regulated genes under drought, and 9 cpDEGs was randomly selected to conduct reverse transcription (RT)–qPCR., in which the Log2 (fold change) was significantly consistent with the qPCR results. The analysis of chloroplast transcription under drought provided clues for understanding chloroplast function under drought. The phylogenetic position of “Shanxinyang” within Populus was analysed by using the chloroplast genome sequences of 23 Populus plants, showing that “Shanxinyang” belongs to Sect. Populus and is sister to Populus davidiana. Further, mVISTA analysis showed that the variation in non-coding (regulatory) regions was greater than that in coding regions, which suggests that further attention should be paid to the chloroplast in order to obtain new evolutionary or functional insights related to aspects of plant biology.
Conclusions
Our findings indicate that complex prokaryotic genome regulation occurs when processing transcripts under drought stress. The results not only offer clues for understanding the chloroplast genome and transcription features in woody plants but also serve as a basis for future molecular studies on poplar species.
Keywords: Poplar, Chloroplast genome, Cp Transcriptome, Drought stress, Polymorphism
Summary
The Populus davidiana Dode×Populus bolleana Lauch chloroplast genome, Populus chloroplast phylogeny and differentially expressed cpDEGs induced by drought stress examined here offer clues for understanding the regulatory mechanisms of the cp transcriptome.
Background
Short-rotation period (SRC, SRF) poplar is widely considered to be a promising lignocellulosic material for second-generation biofuel production. It grows rapidly and is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisphere. “Shanxinyang” originated in northern China and is one of the most widely distributed trees in urban areas and forests. The ubiquity of popular varieties symbolizes their ability to adapt to different environmental conditions [1, 2]. Drought causes irrigation or rainfall to be insufficient, thus reducing soil moisture and ultimately harming plants, usually accompanied by a higher transpiration rate through the root than through the plant surface [3]. Aspects of plant physiology, water pressure, water pressure resistance and reclaimed water reuse efficiency in relation to these negative effects are widely researched [4]. Although poplar trees have more and deeper roots than agricultural plants, they are still affected by continuous drought. Different crops respond to drought stress, such as corn [5], potato [6], wheat [7], sugarcane [8] and other woody plants, including poplar, pine and oak [9]. These studies provide useful information for identifying potential mechanisms and managing possible problems, while studies of the chloroplast genome and transcriptome of drought-tolerant species are less common.
It has long been known that multiple cis and trans transcripts are produced by the chloroplast and processed into small mature RNA, which may indicate that chloroplast participation in the behaviour of the organism is limited to only basic functions [10, 11]. However, there are many untranslatable areas in the chloroplast genome (for example, the areas between transcription units, accounting for 40% or more of the total genome), and the operon transcription pattern was found to lead to a stable, fixed-size transcript, showing that chloroplast gene transcription is also regulated. Furthermore, this transcription has been confirmed to participate in many defence reactions and counter-reactions. Previous research has shown that the chloroplast genome expression pattern is similar to the prokaryotic genome expression pattern. However, recent studies have shown that chloroplast genes are mostly functional and regulated [12] and participate in a variety of anti-stress responses [13–16]. A transcription pause phenomenon has been reported in plants, which is regulated by transcription pause factors in chloroplasts [17]. It is of far-reaching significance to explore whole-plastid transcription level changes triggered by drought stress, not only because the whole plastid transcriptome has not been reported in many plants but also because such information would provide a potential mechanistic understanding at the transcriptome level. This information might also provide insight into the functional evolutionary strategy of Populus, and phylogenetic analysis may in turn provide a new understanding of why “Shanxinyang” is a drought-tolerant clone.
The relationship between the taxonomy and phylogeny of Populus has always been controversial. Scholars generally consider Populus to be composed of five factions, which was confirmed by the recent Angiosperm Phylogeny Group IV system [18–20]. In Populus, the main basis for the division of the five factions is a morphological classification system and a molecular system based on chloroplast gene fragments. Related scientific research has been carried out in recent years, but it is mostly limited to model species that have been sequenced. In addition, there are many disputes regarding the division of species in this family. Unclear species boundaries directly lead to difficulty in identifying some species in this family [10], and structural analysis of chloroplasts may provide new insights.
DNA barcoding is a technique that uses a standard DNA sequence to identify species quickly. However, for species with close relationships, the resolution of DNA barcodes is relatively low. Recently, research has shown that DNA barcoding cannot completely solve the problem of related species identification [21, 22]. The average length of chloroplast genomes of angiosperms is approximately 150 kb, and the variation is much higher than that in a single DNA barcode sequence, which reveals close relationships. In addition, the evolutionary rates of coding and non-coding regions of the chloroplast genome are quite different, which makes them suitable for the study of different taxonomic levels. With the development of second-generation high-throughput sequencing technology, more chloroplast genomes are being sequenced. However, chloroplast genomic data are still lacking. Currently, there are only 1100 complete chloroplast genomes in the NCBI genome database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/organelle/). More extensive transcriptome data are rarely used in chloroplast research, and analysing the differences between chloroplast coding and non-coding regions is key to understanding chloroplasts.
Only 23 chloroplast genomes have been sequenced in Populus and hybrid Populus, chloroplast sequences from stress-resistant species are even less reported, and reports of chloroplast transcription under drought conditions are unavailable. In this study, the chloroplast genome of “Shanxinyang” was sequenced, and its structural characteristics and transcriptional behaviour under drought conditions were analysed. Such information will not only offer clues for understanding the chloroplast genome and transcription features in woody plants but also serve as a basis for future molecular studies on poplar species.
Results
Genome assembly and structural analysis of the chloroplast
According to the sequencing results obtained with the Illumina platform, a total of 34,780,120 reads were generated. Through comparison with the Populus chloroplast genome, approximately 1,887,236 chloroplast genome reads were mapped, the mapping ratio was 5.43, the coverage was 100%, and 3471.03 coverage (depth) was reached. After the chloroplast genome assembly was qualified, it was submitted to the GenBank database under accession number MN190025.
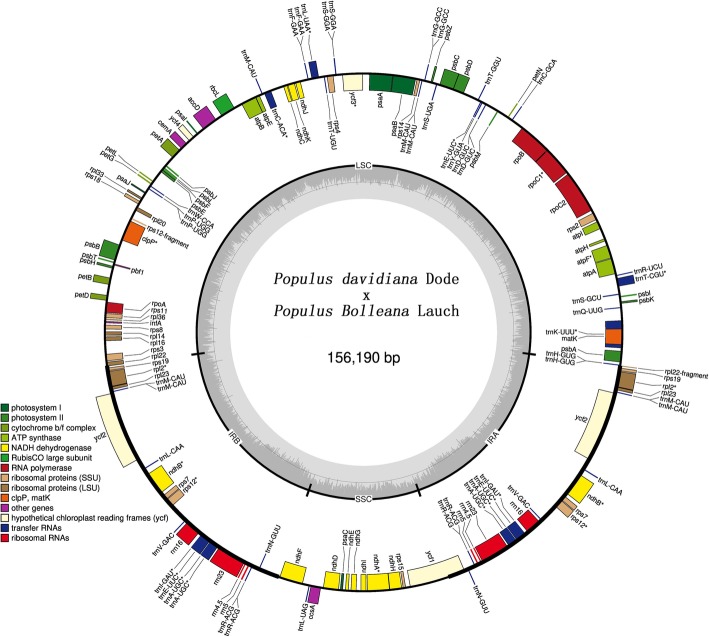
The total length of the “Shanxinyang” chloroplast genome was 156,190 bp, and the GC content was 36.75%. Its structure was similar to that of most angiosperm genomes, and it was composed of four typical regions: the LSC region, the SSC region and a pair of separated IR regions, with lengths of 84,612, 16,498 and 27,540 bp, respectively (Fig. 1). The GC content was unevenly distributed along the “Shanxinyang” chloroplast genome, with that in the IR region being the highest, which may be responsible for IR region conservation. The total length of the coding region was 78,407 bp, covering approximately 50.20% of the whole chloroplast genome.
Fig. 1.
Assembly and annotation of the chloroplast genome of “Shanxinyang”. Genes located outside the outer rim are transcribed in a counterclockwise direction, whereas genes inside the outer rim are transcribed in a clockwise direction. The coloured bars indicate different known functional groups. The dashed grey area in the inner circle shows the GC content percentage of the corresponding genes. LSC, SSC, and IR denote large single copy, small single copy, and inverted repeat, respectively
There were 131 annotated genes in the “Shanxinyang” chloroplast genome, including 86 protein-coding genes, 37 tRNA genes and 8 rRNA genes, among which 23 tRNA genes, 14 protein-coding genes and 4 rRNA genes were located in the two IR regions (Fig. 1).
Introns play an important role in gene selective splicing. In the “Shanxinyang” chloroplast genome, a total of 16 intron-containing genes, including 8 tRNA genes and 8 protein-coding genes, were inserted and released. Except for the clpP and ycf3 genes containing two introns, the genes contained only one intron (Table 1). The trnK-UUU gene had the longest intron, which was 2578 bp. The rps12 gene had a trans-spliced structure, with the 5′ end and 3′ end located in the LSC region and IR region, respectively, and the rpl22 gene had similar structural characteristics.
Table 1.
Introns and exons in genes in the chloroplast genome of “Shanxinyang”
| Gene name | Exon | Intron | Exon | Intron | Exon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ndhB | 755 | 681 | 776 | – | – |
| clpPa | 227 | 630 | 291 | 797 | 70 |
| rpl2 | 433 | 668 | 390 | – | – |
| ycf3a | 154 | 725 | 225 | 732 | 125 |
| rpoC1 | 1618 | 790 | 429 | – | – |
| atpF | 410 | 725 | 143 | – | – |
| ndhA | 546 | 1072 | 550 | – | – |
| rps12 | 26 | 535 | 231 | – | – |
| trnA-UGC | 35 | 801 | 36 | – | – |
| trnE-UUC | 39 | 947 | 31 | – | – |
| trnK-UUU | 35 | 2578 | 37 | – | – |
| trnT-CGU | 34 | 693 | 42 | – | – |
| trnL-UAA | 34 | 599 | 49 | – | – |
| trnC-ACA | 55 | 581 | 38 | – | – |
| trnI-GAU | 35 | 15 | 35 | – | – |
| trnA-UGC | 36 | 39 | 27 | – | – |
Note: a indicates that there are 2 introns in this gene
Repeat sequence analysis
According to the characteristics of the genome repeats, they could be divided into two categories: tandem repeats and interspersed repeats. The second category mainly consists of transposable elements (TEs). The first type of tandem repeat consists of microsatellites or simple sequence repeats (1–9 bases composing a repeat unit) and minisatellites (10–60 bases composing a repeat unit). In this study, 72 SSRs were detected in the “Shanxinyang” chloroplast genome, including 8 mononucleotide SSRs, 4 dinucleotide SSRs, 8 trinucleotide SSRs, 8 tetranucleotide SSRs, 13 pentanucleotide SSRs, 22 hexanucleotide SSRs, 7 heptanucleotide SSRs, 1 octonucleotide SSR and 1 nonanucleotide SSR (Table 2). Most SSRs were located in non-coding regions, and only a few SSRs were located in CDSs. Twenty-one pairs were detected in the “Shanxinyang” chloroplast genome (Table 2).
Table 2.
Repeat sequence of the chloroplast genome of “Shanxinyang”
| Repeat type | Subtype | Category: start-stop |
|---|---|---|
| SSR | 1 | (A)n:63961–63,979,98,244-98,268,73,696-73,721,73,480–73,506;(T)n:92750–92,768,74,999-75,023,49,077-49,105,110,784–110,815 |
| 2 | (AT)n:149467–149,490,90,969-90,996,55,839–55,888;(TA)n:62786–62,864 | |
| 3 | (AAT)n:74499–74,548;(ATA)n:102256–102,285;(ATT)n:140391–140,419;(CTT)n:1437–1467;(TAA)n:70134–70,169;(TAT)n:54868–54,916,36,241–36,351;(TTT)n:82352–82,389 | |
| 4 | (AAAC)n:74209–74,231;(AATA)n:86940–86,976;(ATTT)n:156029–156,084,42,745–42,828;(TAAA)n:96056–96,078;(TATT)n:17554–17,592,104,656–104,727;(TTAA)n:108558–108,614 | |
| 5 | (AATGG)n:1766–1807;(AATTC)n:55169–55,234;(AATTT)n:2510–2537;(CATAT)n:95486–95,524;(TAACT)n:86305–86,367;(TCCAT)n:137687–137,728;(TCTAA)n:94997–95,064;(TGATA)n:20401–20,454;(TTATT)n:91555–91,597;(TTTAT)n:56856–56,898,99,816–99,902;(TTTTA)n:110753–110,814;(TTTTG)n:90467–90,497 | |
| 6 | (AATATA)n:72201–72,248;(AATCAA)n:31871–31,900;(ACTAAT)n:11422–11,466;(ATAATG)n:93151–93,186;(ATAGAA)n:1684–1723;(ATATAG)n:105068–105,122;(ATATTA)n:97585–97,658;(ATTAAG)n:36305–36,369;(ATTAAT)n:59132–59,174;(TAAGAG)n:27396–27,435;(TATTAG)n:128028–128,072;(TATTTT)n:92995–93,038;(TCTTTC)n:79848–79,887;(TGTTTC)n:813–877;(TTAATA)n:33386–33,431;(TTTATA)n:136950–136,956;(TTTATT)n:127492–127,541;(TTTCTA)n:137771–137,810;(TTTGTT)n:75579–75,618;(TTTTAT)n:84635–84,674;(TTTTGC)n:70652–70,685;(TTTTTG)n:78823–78,863 | |
| 7 | (AATATTA)n:95525–95,537,95,464–95,485;(ATAATAA)n:93187–93,196;(ATTCTAA)n:63445–63,546;(TAATAGG)n:63677–63,711;(TTATTAT)n:27333–27,389;(TTATTTT)n:39270–39,354 | |
| 8 | (TATTTGTA)n:109761–109,843 | |
| 9 | (AATAAATAG)n:58568–58,608 | |
| Low_complexity | A-rich | < 30:2538–2557,11,957–12,005;30–80:27674–27,709,44,037-44,073,49,380-49,446,54,158-54,193,57,311-57,358,74,380-74,429,92,835-92,880,93,954-94,030,94,879-94,922,99,929-99,969,112,105-112,161,121,902-121,940,136,957–136,984; > 80:139622–139,711,146,459–146,569 |
| GA-rich | 30–40:138027–138,057,139,634–139,678 | |
| LTR/Gypsy | Atlantys3_I-int | 37: 24992–25,029,114,465–114,502 |
| rRNA | LSU-rRNA_Ath | 30–80:3674–3910; > 80:4349–4462,4612-4659,5526-5687,5829-5931,6090–6217 |
| SSU-rRNA_Ath | 73:8893–8966,9062–9417; 134:9482–9616,129,878–130,012; 355:130077–130,432,130,528–130,601 | |
| LSU-rRNA_Ath | 47:133277–133,404; > 80:133563–133,665,133,807-133,968,134,835-134,882,135,032-135,145,135,584–135,820 |
Note: All the repeat positions are listed with the start and stop positions
The second type of TEs includes two types: retroelements of class-I TEs transposed by RNA-mediated mechanisms and DNA transposons of class-II TEs transposed by DNA. Class I TEs are mainly composed of LTRs (long terminal repeats). Some sequences of LTRs may have encoding functions. Two LTR/Gypsy elements were found in the chloroplast genome, and 18 rRNA-like repeats were found (Table 2).
Chloroplast transcriptome analysis
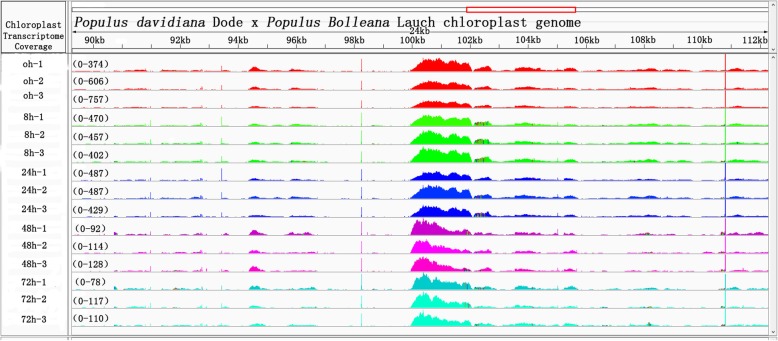
Sequence data were collected from the samples 0, 8, 24, 48 and 72 h after 20% PEG treatment and mapped to the chloroplast genome as shown in Fig. 2. Bowtie2 was used to compare the reads obtained from each sample with the chloroplast genome. Then, the read counts were used to calculate the expression level.
Fig. 2.
Comparison of the “Shanxinyang” transcriptome to the chloroplast
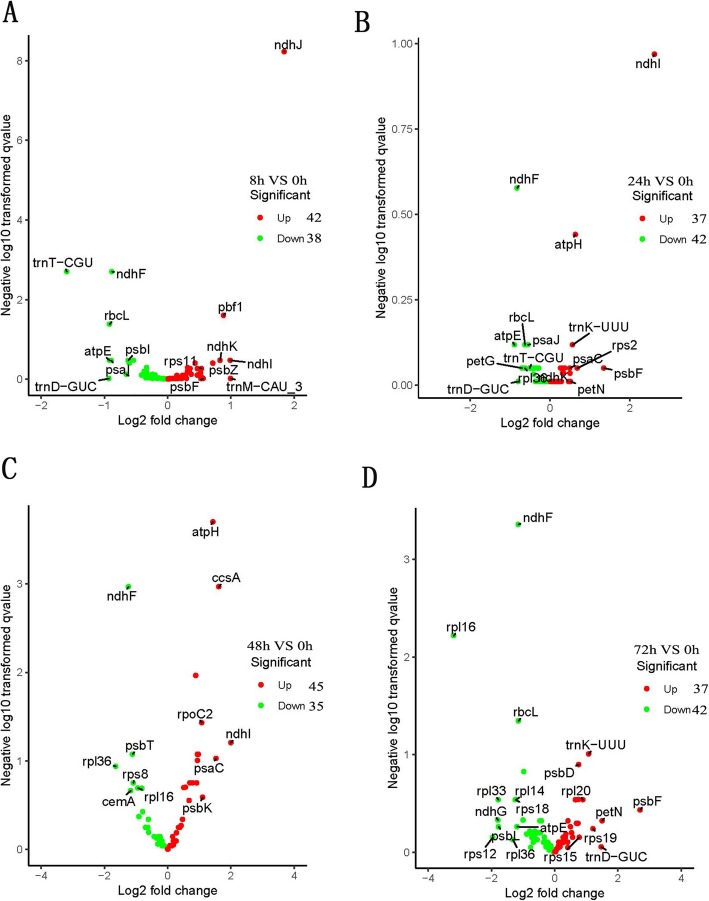
According to the comparison results, the expression level was estimated. Log2 (fold change) was used to express the expression abundance of the transcripts. Volcano plots were used to examine differences between groups, and statistical significance was estimated by DESeq (fold change (> 2); FDR < 0.01). Volcano plots of the 4 groups are shown in Fig. 3a, b, c and d. In total, we found 42 up-regulated and 38 down-regulated genes in the 8 h VS 0 h group comparison (Fig. 3a); 37 up-regulated and 42 down-regulated genes in the 24 h VS 0 h group comparison (Fig. 3b); 45 up-regulated and 35 down-regulated genes in the 48 h VS 0 h group comparison (Fig. 3c); and 37 up-regulated and 42 down-regulated genes in the 72 h VS 0 h group comparison (Fig. 3d). Drought stress regulation of key genes was found in further analyses, in which the cpDEGs were involved in drought responses. Moreover, we sumarized the detail information of the up regulated and down regulated cp DEGs in Table S2, which may be functional to the drought defence. Further more, the lasting regulated cp DEGs was shown in the Venn maps (Figure S1). Among these genes, most were the key genes to form the photosynthetic systems, and some tRNAs were also found. In which, the rpl16, petG, atpE, psaI, rps18, psbL, rps19, rpl14, trnL-UAA, rpl22, rbcL, trnT-CGU and psaB were found lasting down regulated. While, the psbF, petN, psbM, rpoC1, rps11, ndhC, rps19, ndhK, trnK-UUU, psbB, atpI and ycf3 were found up regulated.
Fig. 3.
The cpDEGs in the cp transcriptome of “Shanxinyang”. All the treatment groups (8, 24, 48 and 72 h) was compared with the CK group (0 h); The cp DEGs of each group were shown by the volcano maps; a: 8 h VS 0 h; b: 24 h VS 0 h; c: 48 h VS 0 h; d: 72 h VS 0 h
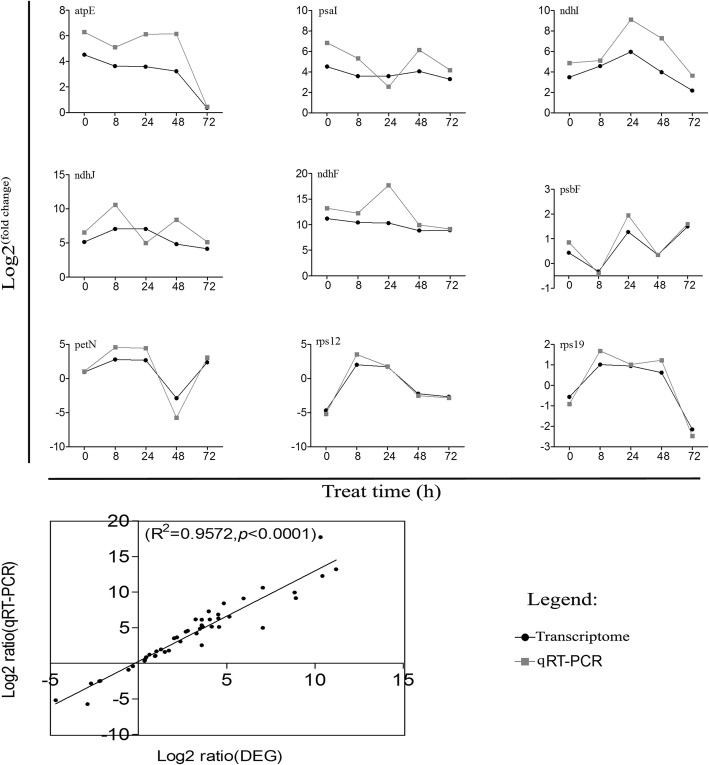
To further validate this approach, we selected 9 cpDEGs to conduct reverse transcription (RT)–qPCR (Fig. 4), which indicated that the results were reliable because the Log2 (fold change) was significantly consistent with the qPCR results.
Fig. 4.
RT–qPCR of cpDEGs in the chloroplast transcriptome of “Shanxinyang”
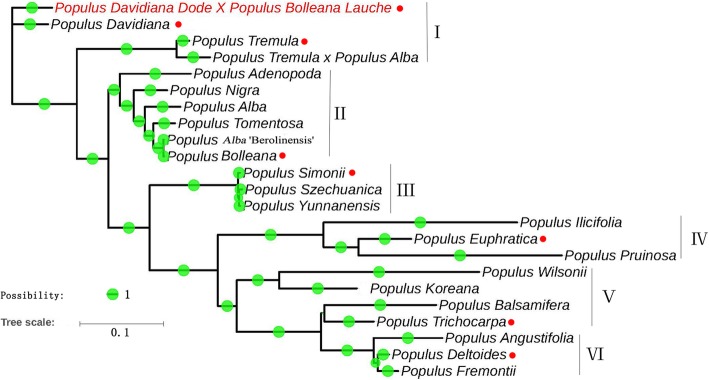
Phylogenetic analysis
In this study, published chloroplast genomes of 23 Populus species were used for phylogenetic analysis. The phylogenetic position of “Shanxinyang” in Populus was determined by constructing a phylogenetic tree. The phylogenetic tree had 6 branches, labelled clades I - VI (Fig. 5). Clades I and II belonged to Sect. Populus. Clades III and V belonged to Sect. Tacamahaca. Clade IV belonged to Sect. Turanga, and clade VI belonged to Sect. Aigeiros. “Shanxinyang” and Populus davidiana were on sister branches that belonged to clade I. At the same time, we fould differences between “Shanxinyang” and Populus species in phylogenetic analysis, which guide us to think the sequences details of the chloroplasts IRs, non-coding and coding regions, which may explaine the unique systematic and evolutionary positions of “Shanxinyang” and partly explained its superior stress tolerance compared with that of other Populus plants and may guide insight to the further drought stress regulation of key cpDEGs.
Fig. 5.
Phylogenetic tree of Populus plants. Red dot: 7 representative species from 4 sections
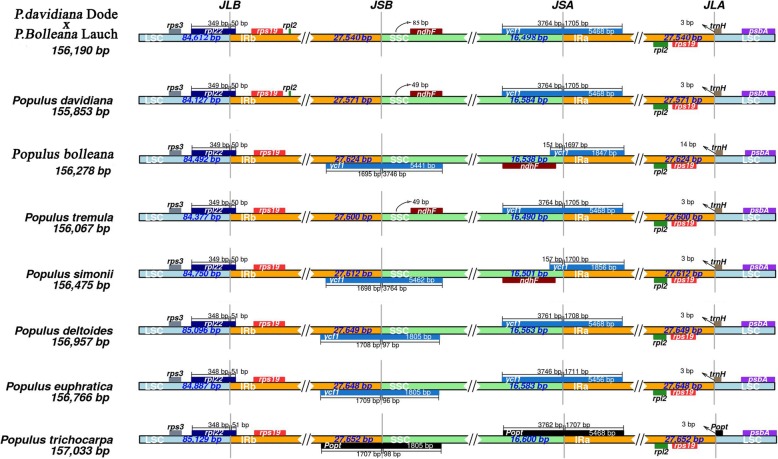
Analysis of IR region contraction and expansion
The contraction and expansion of the IR regions may be the main reasons for the diversity of chloroplast genome length in angiosperms (Kim and Lee, 2004). Comparing the IR regions of “Shanxinyang” and other poplar chloroplast genomes with the boundaries of the LSC and SSC regions, it was found that four junctions (JLA, JLB, JSA and JSB) were located between the two IRs (IRB and IRA) and the two single-copy regions (LSC and SSC), and the IR region of the chloroplast genome in Populus was found to have experienced contraction and expansion (Fig. 6). The LSC-IRb junction of all 8 plants was between the rps19 and rpl22 genes. The LSC-IRa junction was between the rps19 and trnH genes because the IR region did not expand at the IRa-LSC junction, such that the trnH gene was still in the LSC region, but most of them were close to the boundary (< 10 bp). The IR region of Populus plants shrank obviously at the LSC-IRb junction, which led to the generation of a ycf1 pseudogene in the IRa region of these species.
Fig. 6.
Analysis of IR regions of Populus chloroplast genomes
Comparative analysis of Populus chloroplast genomes
To determine the differences between “Shanxinyang” and other Populus species, the chloroplast genome of “Shanxinyang” was compared with that of 7 representative species from 4 sections. The sequence and composition of the chloroplast genome of “Shanxinyang” were most similar to those of P. davidiana. The chloroplast genome lengths of the Populus species were significantly different, with an average length of 157,727 bp. P. deltoides had the longest chloroplast genome, at 156,957 bp, and P. davidiana had the shortest chloroplast genome, with a difference of 1101 bp (Table 3). “Shanxinyang” had the most similar chloroplast genome to Populus davidiana, with the largest difference from P. deltoides.
Table 3.
Comparison of Populus chloroplast genomes
| Species | Size (bp) | G + C (%) |
Number of genes | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | LSC | IR | SSC | Protein-coding genes | rRNAs | tRNAs | Coding ratio (%) |
GenBank accessions | ||
|
P. davidiana Dode× P. bolleana Lauch |
156,190 | 84,612 | 27,540 | 16,498 | 36.75 | 86 | 8 | 37 | 50.20 | MN190025 |
| P. bolleana | 156,278 | 84,492 | 27,624 | 16,538 | 37.00 | 86 | 8 | 37 | 51.78 | MK267319 |
| P. davidiana | 155,853 | 84,127 | 27,571 | 16,584 | 36.98 | 88 | 8 | 37 | 50.17 | KX306825 |
| P. tremula | 156,067 | 84,377 | 27,600 | 16,490 | 36.80 | 86 | 8 | 37 | 65.65 | KP861984 |
| P. simonii | 156,475 | 84,750 | 27,612 | 16,501 | 36.99 | 86 | 8 | 37 | 46.96 | MK267304 |
| P. deltoides | 156,957 | 85,096 | 27,649 | 16,563 | 36.87 | 86 | 8 | 37 | 51.55 | MK267316 |
| P. euphratica | 156,766 | 84,888 | 27,642 | 16,593 | 36.40 | 84 | 8 | 36 | 65.63 | KJ624919 |
| P. trichocarpa | 157,033 | 85,129 | 27,652 | 16,600 | 36.70 | 100 | 8 | 37 | 68.97 | EF489041 |
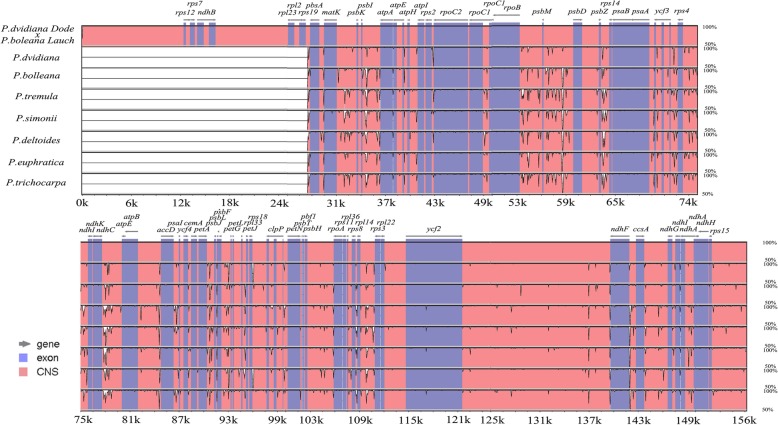
To study the similarities of and differences in cp genome sequences between “Shanxinyang” and related species, a comparison program was used to compare these sequences. “Shanxinyang” was used as the reference genome in the mVISTA tool (Fig. 7). In general, the cp genome sizes of these related materials were not significantly different, but partially incomparable regions were also found, which indicated the unique phylogenetic position of “Shanxinyang”. The overall pattern of similarity among these sequences was very high, with homology greater than 90%. As shown in Fig. 7, the structure of these cp genomes was conserved, with neither translocation nor inversion in the sequence. As expected, the coding regions were more conserved than the non-coding regions. More specifically, most of the highly polymorphic regions were located in the intergenic regions (such as matK- psbI/K-atpA, rpoB-psbM-psbD, ycf2-ndhF and ndhC-atpE), but ycf genes had higher variability. These regions may be undergoing more rapid nucleotide substitution at the species level, which indicates the potential regulatory differences in the non-coding regions of the Populus chloroplast genome.
Fig. 7.
Sequence alignment of 8 related chloroplast genomes using the mVISTA program with “Shanxinyang” as a reference. Grey arrows above the alignment indicate the transcriptional directions of genes. Genome regions are colour coded as exons and conserved non-coding sequences (CNSs). A 50% identity cut-off was used for the plots. The Y-axis indicates the percent identity between 50 and 100%
Discussion
With the development of sequencing technology, research on the chloroplast genome has entered a new stage. An in-depth understanding of the chloroplast genome will undoubtedly lead to a better understanding of plants. The chloroplast is an important organelle for photosynthesis and provides the material necessary for life activities. Due to its maternal genetic inheritance, the chloroplast genome can allow maternal characteristics to remain unchanged in offspring. The chloroplast genome is the second largest genome after the nuclear genome, and its structural complexity is far lower than that of the nuclear genome.
Cp genome sequence analysis of Populus davidiana Dode×Populus bolleana Lauch
The chloroplast genome in “Shanxinyang” is similar to that in other Populus plants, which to some extent reflects the high conservation of the angiosperm chloroplast genome [23]. Interestingly, it has been reported that the ycf15 gene exists in most angiosperms. In contrast, we found that the ycf15 gene was absent in the “Shanxinyang” and Populus davidiana chloroplast genomes, which showed that the ycf15 gene can be transcribed as one of the precursors of polycistronic transcripts, but its function is still unclear [24]. Loss of protein-coding genes in chloroplast genomes is common in angiosperms [25]. In the Myrsinaceae s. str. Clade, Yan et al. (2019) [26] reported that the ycf15 gene was absent from five taxa (Elingamita johnsonii, Tapeinosperma netor, Tapeinosperma multiflorum, Parathesis donnell-smithii and Parathesis chiapensis).
SSRs have been widely used as gene markers in DNA fingerprinting, phylogenetics, species identification and population genetic diversity analysis due to their co-dominant inheritance and high polymorphism [27–29]. Herein, a total of 72 SSRs were identified in the “Shanxinyang” chloroplast genome, most of which were located in non-coding regions and a few of which were located in CDSs. A similar pattern was also observed in the Loropetalum subcordatum [30] and Quercus bawanglingensis chloroplast genomes [31].
In most angiosperms, the A/T content of SSRs is higher than the G/C content [32, 33]. A similar pattern was observed in “Shanxinyang”, with 8 single-A/T SSRs. In contrast to other plants, “Shanxinyang” has a higher A/T content. In this study, two LTR/Gypsy and 18 rRNA-like repeats were found in the “Shanxinyang” chloroplast genome. The long repeat sequence had a length greater than or equal to 30 bp and may function to promote the rearrangement of the chloroplast genome and increase genetic diversity [34].
Phylogenetic tree based on Populus cp genomes
The chloroplast genome is of great value for understanding plant evolution [35]. In this investigation, “Shanxinyang” and Populus davidiana were located on sister branches, belonging to clade I (Sect. Populus), which was similar to the pattern in the APG IV classification system [11]. In addition, some studies have suggested that Populus simonii is located on a sister branch of Populus trichocarpa [9]; however, the results of this study showed that Populus trichocarpa was on a new branch (clade V), which was similar to the pattern in the APG IV classification system [11, 36]. The angiosperm Populus trichocarpa has long been considered to have originated in North America. In recent years, most studies have shown that Populus trichocarpa and Populus simonii are sister to each other, which together constitute Sect. Tacamahaca. The results of this study support “Shanxinyang” as belonging to Sect. Populus (clade I).
IR region variation
The chloroplast genome has a high gene conversion ability, which ensures the consistency and stability of the two IR reverse-replication regions, thereby enhancing its own stability and conservation. Therefore, contractions and expansions of IR regions represent important evolutionary events that are responsible for the size variation in the cpDNA genome [37, 38]. During the continuous evolution of species, a large degree of variation remains in the IR regions of some species [39, 40]. In this study, the IR regions had a higher GC content than the other regions due to the presence of eight rRNA sequences in the IR regions [41, 42], and the lengths of the IR regions in Populus chloroplast genomes were generally similar. Therefore, IR region length is an important factor affecting the length of the chloroplast genome and is relatively conserved, which may be due to the copy correction caused by gene transformation between IR region sequences [39].
The IR regions are known to maintain the stability of the other regions in the chloroplast genome because of the intramolecular recombination between IR copies, therefore limiting recombination between the two single-copy regions [43]. Compared with that in other Populus chloroplast genomes, the IR region in the “Shanxinyang” chloroplast genome has expanded obviously, and rpl22 and other genes are close to the LSC region. A similar pattern also occurs in the chloroplast genomes of other plants [44]. IR region expansion has been reported in many studies, and its mechanism has been discussed. It is believed that slight IR expansion may be caused by gene transfer, consistent with the pseudogenes found in the “Shanxinyang” and P. davidiana IR regions in this study, and greater IR expansion may be achieved through a double-strand break repair (DSBR) mechanism [45, 46]. However, there are few reports on IR region contraction, and at present, it is mainly believed that the IR region contraction mechanism is also a DSBR mechanism [44]. One of the reasons for a change in IR region length is recombination between repeat sequences or poly structures and tRNA [47].
The Cp transcriptome and Populus cp genome comparison
Volcano plots of the 4 groups showed that approximately 35–50 cp genes were up-regulated or down-regulated in each group. Including 13 lasting down regulated and 12 up regulated genes. Among which, most were the key genes to form the photosynthetic systems, which partly explain the loss of green when the plants was drought, and some tRNAs were also found, which was important to the whole chloroplast biology. Some of these related proteins were also found to regulate plant defence [13–16]. These cp DEGs may be the potential ones to understand the chloroplast evolutionary biology to the drought in the further study. To further understand potential regulatory differences, plant systematic and evolutionary analyses should be performed with the sequences showing the greatest differences. According to mVISTA analysis, the structure of these cp genomes is conserved, and there is neither translocation nor inversion in the sequence. As expected, the coding regions are more conserved than the non-coding regions. More specifically, most of the highly polymorphic regions are located in intergenic regions. These regions may be undergoing more rapid nucleotide substitution at the species level, which indicates potential regulatory differences in the non-coding regions of the Populus chloroplast, explains the unique systematic and evolutionary positions of “Shanxinyang” and partly explains its superior stress tolerance compared with that of other Populus taxa. Drought stress regulation of key cpDEGs should be explored in further research.
Conclusion
In this study, we completed the sequencing, assembly and annotation of the “Shanxinyang” chloroplast genome and analysed its structure, GC content, gene structure and repeat sequences. The results showed that the genome structure and gene composition of the “Shanxinyang” chloroplast were similar to those of most angiosperm chloroplasts, but the ycf15 gene was missing. Compared with that in most Populus chloroplast genomes, the IR region in the “Shanxinyang” chloroplast genome was contracted. Through analysis of chloroplast genes that were differentially expressed under drought conditions, the expression mode of chloroplast genes under drought conditions was summarized. Through phylogenetic analysis of the chloroplast genome, the phylogenetic position of “Shanxinyang” was confirmed. Differences in chloroplast non-coding regions explained the unique systematic and evolutionary positions of “Shanxinyang” and partly explained its superior stress tolerance compared with that of other Populus plants and may guide further drought stress regulation of key cpDEGs. As a 2G plant, “Shanxinyang” has important scientific and economic value. The sequencing and analysis of its chloroplast genome also provide data for phylogenetic studies, species identification and stress resistance research in Populus.
Methods
Plant growth and material preparation
The Populus davidiana Dode×Populus bolleana Lauch materials used in the study were preserved in our laboratory and planted on the campus of Northeast Forestry University (latitude: 45°39′48.58″N, longitude: 126°36′59.77″E). As researchers in the laboratory, we performed hybridization and formal identification of the plant material used in this study, and we were allowed to use these materials for research. Sampling of these materials was performed in compliance with institutional, national, and international guidelines.
Populus davidiana Dode×Populus bolleana Lauch clones were surface sterilized in 3% H2O2, rinsed several times with sterile water, and germinated on rooting medium (4.4 g Murashige and Skoog medium, 3% sucrose, 0.7% agar, pH 5.8, 0.5 ppm NAA) for 4 weeks. Four-week-old plants were explanted on the rooting medium for another 4 weeks in a controlled environment (22–23 °C, 16 h light and 8 h dark). At this stage, the lines had grown to the same degree. Four-week-old plants were used for DNA isolation and stress treatment. Drought stress was induced by treatment with 20% polyethylene glycol (PEG 6000) as described by Kwon et al. (2014) [48]. The samples were collected 0, 8, 24, 48 and 72 h after 20% PEG 6000 treatments. Each group included 3 plantlets, which were quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen for DNA/RNA extraction and sequencing.
DNA/RNA preparation, cDNA synthesis, library preparation and sequencing
DNA/RNA was isolated by plant kits (Qiagen, http,//www.qiagen.com). The total DNA/RNA was quantified by an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent, http,//www.agilent.com). A DNA library was constructed, and read quality was evaluated according to Sharon et al. 2013 and Tilgner et al. 2014 [49, 50]. Further, RNA libraries were generated using a TruSeq RNA Library Prep Kit v2 (Illumina, USA), and cDNA was synthesized through freshly isolated mRNA. A HiSeq 2500 sequencer (Illumina, USA) was used for RNA-seq. At the same time, the Illumina RNA-seq data from 15 samples were evaluated by NGS QC Toolkit [51].
Chloroplast genome assembly and annotation
With Illumina data, the genome was assembled using Velvet (version 1.2.10) [52] and NOVOPlasty (version 2.7.2) [53] software. Combining the two results, the optimal contig assembly was obtained. Then, SSPACE (version 3.0) [54] software was used to align the reads from all libraries to the contig sequence, and the scaffold sequence was further assembled by paired-end reads. Finally, GapFiller (1000 Genomes Project Consortium, 2012) (version 1–10) [55] software was used to align the reads of all libraries to the scaffold sequence, and the reads in the alignment were used to complement the gaps in the scaffold sequence. The scaffold sequence was extended. Finally, a scaffold sequence with a lower proportion of unknown (N) bases and a greater sequence length was obtained.
The chloroplast genome was annotated by GeSeq, an online tool. By BLAT with the reference genome, protein-coding genes, rRNA genes and tRNA genes were searched, and tRNA genes were annotated by tRNAscan-SE (v2.0) [56] and ARAGORN (v1.2) [57]. The online tool OGDRAW v1.2 (https://chlorobox.mpimp-golm.mpg.de/OGDraw.html) was used to draw a genome Circos map. For PCR validation, we designed PCR primers that covered boundary regions. The primers for each element are listed in Supplementary Table S1. PCR fragments were then sequenced.
RepeatModeler (version 1.0.8) software was used to predict repetitive sequences in the genome from scratch. The analysis was divided into two steps. The first step was to identify possible repetitive sequences by calling RECON (version 1.08) software and RepeatScout (version 1.0.5) software and then optimizing and constructing the results of the first step by using RepeatModeler software. The second step was to use RepeatMasker (version 4.0.5) software to search for and analyse repetitive sequences in the target genome. At the same time, NUCmer (NUCleotide MUMmer; version 3.1) was used to further detect the internal repeat sequence of the genome, and long repeat regions with lengths greater than or equal to 100 bp were screened.
Chloroplast transcriptome and cpDEG qRT–PCR validation
The filtered RNA-seq reads were mapped to the corresponding plastome using Bowtie2. The following stringent alignment parameters were applied to properly align reads to the chloroplast genome: 1) reads that aligned to multiple genomic locations were ignored, and 2) for the uniquely mapped reads, tolerances were set to allow at most one mismatch. Then, the SAMtools package (version 1.9) was employed to index the alignment results as BAM files. The coverage and base depth were calculated by converting the BAM alignments into pileup files, which were then used for further statistical analyses of plastome transcription and visualisation in IGV 2.4.9.
Based on the plastome annotation files, we calculated the transcription of the different plastome genes. Position information for all coding regions (protein-coding, rRNA, and tRNA genes) and non-coding regions (intergenic regions and introns) was extracted from the annotation file. The transcription level for every genomic base-pair position was assigned on the basis of the number of sequence reads covering each position by HT-SEQ (version 0.11.2). Gene expression levels were estimated by DESeq2 (version 3.9) based on the reads from HT-SEQ [58]. The log2 of the score for each base-pair position of all the genes was calculated (Table S2), and volcano plots were created with R/Bioconductor.
Further, to verify the statistical significance and accuracy of the expression levels, cpDEGs were selected to conduct reverse-transcription PCR ((q)RT–PCR). First-strand cDNA was synthesized by a reverse transcription kit (TaKaRa). qRT-PCR primers were designed with SnapGene 2.0 (https,//www.snapgene.com/) (Table S1). qRT-PCR analysis was conducted in triplicate with TdACTIN (GenBank number MK273079) as a reference gene [59] by the qTOWER 2.0 platform (Analytic Jena, Germany). The reaction system for real-time PCR contained 10 μL of SYBR Green Real-time PCR Master Mix (TaKaRa), 0.5 μmol/L each forward and reverse primer, and 1 μL of template for a total volume of 20 μL. The PCR and 2-ΔΔCt expression level calculations were performed according to Livak and Schmittgen (2001) [60].
Polymorphism in the Populus chloroplast genome
Based on the APG IV system and the reported Populus chloroplast genomes, 23 complete chloroplast genomes of angiosperms were selected. A phylogenetic tree was constructed to identify the phylogenetic position of Populus davidiana Dode x Populus bolleana Lauche. Sequences were compared with ClustalW software. Phylogenetic trees were constructed by using MrBayes 3.2.2 of the XSEDE tools from the CIPRES Science Gateway server (http://www.phylo.org/). Phylogenetic trees were viewed by iTol2 (http://itol2.embl.de/upload.cgi). The similarity between chloroplast boundaries was analysed by IRscope (https://irscope.shinyapps.io/irapp/). The differences between chloroplast genomes were analysed by mVISTA (http://genome.lbl.gov/vista/mvista/submit.shtml).
Statistical analysis
Data analysis was performed using SPSS version 11.5 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Correlation analysis was performed to test for correlations between qRT-PCR and RNA-Seq data, the log2-fold change values of transcripts were plotted in GraphPad Prism 5, and corresponding R2 and p values were calculated. All plots were created using R packages and GraphPad Prism 5.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1 Table S1. The sequences of primers used in boundary PCR and cpDEG qRT-PCR.
Additional file 2 Table S2. The information of cp DEGs and the expression levels.
Additional file 3 Figure S1. The Venn maps of the cp DEGs. A: up regulated genes; B: down regulated genes.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- APG
Angiosperm phylogeny group
- CNS
Conserved non-coding sequence
- cp
Chloroplast
- IR
Inverted repeat
- LSC
Large single copy
- ML
Maximum likelihood
- NCBI
National center for biotechnology information
- SSC
Small single copy
- SSR
Simple sequence repeat
Authors’ contributions
XZ assembled, annotated and analysed the cp genome and transcriptome of Populus davidiana Dode×Populus bolleana Lauch. XZ wrote the manuscript. CRG, TXZ, BTT, HZ, YLW and CPY revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 30571513), Overseas Expertise Introduction Project for Discipline Innovation (B16010) and Heilongjiang Touyan Innovation Team Program (Tree Genetics and Breeding Innovation Team). The funding bodies played no role in the design of the study; collection, analysis, or interpretation of data or writing of the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
Illumina HiSeq 2500 data have been submitted to the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) under accession number PRJNA534167. The complete cp genome of Populus davidiana Dode×Populus bolleana Lauch was submitted to GenBank under accession number MN190025.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Populus davidiana Dode×Populus bolleana Lauch materials used in the study were preserved in our laboratory and planted on the campus of Northeast Forestry University (latitude: 45°39′48.58″N, longitude: 126°36′59.77″E). As researchers in the laboratory, we were allowed to use these materials for research. Sampling of these materials was performed in compliance with institutional, national, and international guidelines.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12862-020-01622-7.
References
- 1.Li BS, Qin YR, Duan H, Yin WL, Xia XL. Genome-wide characterization of new and drought stress responsive microRNAs in Populus euphratica. J Exp Bot. 2011;62:3765–3779. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tang S, Liang HY, Yan DH, Zhao Y, Han X, Carlson JE. Populus euphratica, the transcriptomic response to drought stress. Plant Mol Biol. 2013;83:539–557. doi: 10.1007/s11103-013-0107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jordan WR, Ritchie JT. Influence of soil water stress on evaporation, root absorption, and internal water status of cotton. Plant Physiol. 1971;48:783–788. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.6.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Osakabe Y, Osakabe K, Shinozaki K, Tran LSP. Response of plants to water stress. Front Plant Sci. 2014;5:86. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Avramova V, Abdelgawad H, Asard H, Beemster GT. The growth zone of maize leaves subjected to drought stress offers unique possibilities to confirm transcriptome analysis with cellular, physiological and biochemical measurements. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci. 2014;79:111–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gong L. Transcriptome profiling of the potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) plant under drought stress and water-stimulus conditions. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0128041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Okay S, Derelli E, Unver T. Transcriptome-wide identification of bread wheat WRKY transcription factors in response to drought stress. Mol Genet Genom MGG. 2014;289:765–781. doi: 10.1007/s00438-014-0849-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kido EA, Neto JRCF, Silva RLD, Pandolfi V, Guimaraes ACR, Veiga DT. New insights in the sugarcane transcriptome responding to drought stress as revealed by superSAGE. The ScientificWorld Journal. 2012;82:1062. doi: 10.1100/2012/821062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dong Y, Wang C, Han X, Tang S, Liu S, Xia X. A novel bHLH transcription factor PebHLH35 from Populus euphratica confers drought tolerance through regulating stomatal development, photosynthesis and growth in Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;450:453–458. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Saunders RMK. Monograph of Schisandra (Schisandraceae) Syst Bot Monographs. 2000;58:1–149. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang YH, Zhang SZ, Gao JP, Chen DF. Phylogeny of the Schisandraceae based on cpDNA mat-K and rpL16 intron data. Chem Biodivers. 2006;3:359–369. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.200690039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rojas M, Yu QG, Carrier R, Pal M, Barkan A. Engineered PPR proteins as inducible switches to activate the expression of chloroplast transgenes. Nat Plants. 2019;5:505–11. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 13.Wang Z, Fuxing W, Hong Y, Huang J, Shi HZ, Zhu JK. Two chloroplast proteins suppress drought resistance by affecting ROS production in guard cells. Plant Physiol. 2016;172:2491–503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 14.Hong Y, Wang Z, Liu X, Yao JJ, Kong XF, Shi HZ, Zhu JK. Two chloroplast proteins negatively regulate plant drought resistance through separate pathways. Plant Physiol. 2019;182:1007–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Lei L. Chloroplast proteins: fight drought. Nat Plants. 2017;3:16214. doi: 10.1038/nplants.2016.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Alexia TF. Chloroplasts navigate towards the pathogen interface to counteract infection by the Irish potato famine pathogen. BioRxiv. 2019;10:1101.
- 17.Ding SH, Zhang Y, Hu Z, Huang XH, Zhang BH, Lu QT, Wen XG, Wang YC, Lu CM. mTERF5 acts as a transcriptional pausing factor to positively regulate transcription of chloroplast psbEFLJ. Mol Plant. 2019;9:1259–1277. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2019.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Smith AC. The families Illiciaceae and Schisandraceae. Sargentia. 1947;7:1–224. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bremer B, Bremer K, Chase MW, Fay MF, Reveal JL, Soltis DE. An update of the angiosperm phylogeny group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG III. Bot J Linn Soc. 2009;161:105–121. [Google Scholar]
- 20.The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group An update of the angiosperm phylogeny group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG IV. Bot J Linn Soc. 2016;181:1–20. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hebert PDN, Cywinska A, Ball SL, Dewaard JR. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc R Soc B-Biol Sci. 2003;270:313–321. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2002.2218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhang J, Chen M, Dong XY, Lin RZ, Fan JH, Chen ZD. Evaluation of four commonly used DNA barcoding loci for Chinese medicinal plants of the family Schisandraceae. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0125574. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wicke S, Schneeweiss GM. dePamphilis CW, Muller KF, and Quandt D. the evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant Mol Biol. 2011;76:273–297. doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9762-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shi C, Liu Y, Huang H, Xia EH, Zhang HB, Gao LZ. Contradiction between plastid gene transcription and function due to complex posttranscriptional splicing: an exemplary study of ycf15 function and evolution in angiosperms. PLoS One. 2013;8:e59620. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jansen RK, Ruhlman TA. Plastid genomes of seed plants. In: Bock R, Knoop V, editors. Genomics of Choroplasts and mitochondria. Dordrecht, The Netherlands.: Springer; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yan XK, Liu TJ, Yuan X, Yan HF, Hao G. Chloroplast genomes and comparative analyses among thirteen taxa within Myrsinaceae s.str. Clade (Myrsinoideae, Primulaceae) Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:4534. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bodin SS, Kim JS, Kim J. Complete chloroplast genome of Chionographics japonica (Willd.) maxim. (Melanthiaceae): comparative genomics and evaluation of universal primers for liliales. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 2013;31:1407–1421. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dashnow H, Tan S, Das D, Easteal S, Oshlack A. Genotyping microsatellites in next-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015;16:A5. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chmielewski M, Meyza K, Chybicki I, Dzilauk A, Litkowiec M, Burczyk J. Chloroplast microsatellites as a tool for phylogeographic studies: the case of white oaks in Poland. iForest. 2015;8:765–771. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhang YY, Cai HX, Dong XJ, Dong W, Li P, Wang ZS. The complete chloroplast genome of Loropetalum subcordatum, a natioanal key protected species in China. Conserv Genet Resour. 2018;11:377–380. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Liu X, Chang EM, Liu JF, Huang YN, Wang Y, Yao N. Complete chloroplast genome sequence and phylogenetic analysis of Quercus bawanglingensis Huang, Li et Xing, a vulnerable oak tree in China. Forests. 2019;10:0587. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yang Y, Dang YY, Li Q, Lu JJ, Li XW, Wang YT. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of poisonous and medicinal plant Datura stramonium: organizations and implications for genetic engineering. PLoS One. 2014;9:e110656. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Raveendar S, Na YW, Lee JR, Shim D, Ma KH, Lee SY, et al. The complete chloroplast genome of Capsicum annuum var. glabriusculum using Illumina sequencing. Molecules. 2015;20:13080–13088. doi: 10.3390/molecules200713080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Qian J, Song JY, Gao HH, Zhu YJ, Xu J, Pang XH, et al. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of the medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza. PLoS One. 2013;8:e57607. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wu ML, Lan SR, Cai BR, Chen SP, Chen H, Zhou SL. The complete chloroplast genome of Guadua angustifolia and comparative analyses of neotropical-paleotropical bamboos. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0143792. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Qiu YL, Lee J, Bernasconi-Quadroni F, Soltis DE, Chase MW. The earliest angiosperms: evidence from mitochondrial, plastid and nuclear genomes. Nature. 1999;402:404–407. doi: 10.1038/46536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Terakami S, Matsumura Y, Kurita K, Kanamori H, Katayose Y, Yamamoto T, et al. Complete sequence of the chloroplast genome from pear (Pyrus pyrifolia): genome structure and comparative analysis. Tree Genet Genomes. 2012;8:841–854. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yang Y, Zhou T, Duan D, Yang J, Feng L, Zhao G. Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of five Quercus species. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:959. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Khakhlova O, Bock R. Elimination of deleterious mutations in plastid genomes by gene conversion. Plant J. 2006;46:85–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kang L, Xie DF, Xiao QY, Peng C, Yu Y, He XJ. Sequening and analyses on chloroplast genomes of Tetrataenium candicans and two allies give new insights on structural variants, DNA barcoding and phylogeny in Apiaceae subfamily Apioideae. Peer J. 2019;7:e8063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 41.Huotari T, Korpelainen H. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Elodea Canadensis and comparative analysis with other monocot plastid genomes. Gene. 2012;508:96–105. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.07.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zong D, Gan P, Zhou A, Li J, Xie Z, Duan A, et al. Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of seven Populus species: insights into altermative female parents of Populus tomentosa. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0218455. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Palmer JD, Osorio B, Aldrich J, Thompson WF. Chloroplast DNA evolution among legumes: loss of a large inverted repeat occurred prior to other sequence rear rangerments. Curr Genet. 1987;1987:275–286. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Peery RM. Understanding angiosperm genome interactions and evolution: insights from sacred lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) and the carrot family (Apiaceae). Doctor dissertation. Illinois: University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Goulding SE, Wolfe KH, Olmstead RG, Morden CW. Ebb and flow of the chloroplast inverted repeat. Mol Gen Genet. 1996;252:195–206. doi: 10.1007/BF02173220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wang RJ, Cheng CL, Chang CC, Wu CL, Su TM, Chaw SM. Dynamics and evolution of the inverted repeat-large single copy junctions in the chloroplast genomes of monocots. BMC Evol Biol. 2008;8:36. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-8-36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Plunkett GM, Downie SR. Expansion and contraction of the chloroplast inverted repeat in Apiaceae subfamily Apioideae. Syst Bot. 2000;25:648–667. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kwon, S.H., Kwon, H.K., Kim, W., Noh, E.W., Kwon, M., and Choi., Y.I. (2014). Identification of salt and drought inducible glutathione S-transferase genes of hybrid poplar. J Plant Biotechnol 41, 26–32.
- 49.Sharon D, Tilgner H, Grubert F, Snyder M. A single-molecule longread survey of the human transcriptome. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31:1009–1014. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Tilgner H, Grubert F, Sharon D, Snyder MP. Defining a personal,allele-specific, and single-molecule long-read transcriptome. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111:9869–9874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1400447111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hussain A. Nitric oxide mediated transcriptome profiling reveals activation of multiple regulatory pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 52.Zerbino DR, Birney E. Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008;18:821–829. doi: 10.1101/gr.074492.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Dierckxsens N, Mardulyn P, Smits G. NOVOPlasty: de novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;45:e18. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Boetzer M, Henkel CV, Jansen HJ. Scaffolding pre-assembled contigs using SSPACE. Bioinformatics. 2010;27:578–579. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.1000 Genomes Project Consortium An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature. 2012;491:56. doi: 10.1038/nature11632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lowe TM, Chan PP. tRNAscan-SE on-line: integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:W54–W57. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Laslett D, Canback B. ARAGORN, a program to detect tRNA genes and tmRNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:11–16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Li B, Dewey CN. RSEM, accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12:323. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Yang Y, Tang RJ, Li B, Wang HH, Jin YL, Jiang CM. Overexpression of a Populus trichocarpa h+−pyrophosphatase gene ptvp1.1 confers salt tolerance on transgenic poplar. Tree Physiol. 2015;35:663–677. doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpv027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1 Table S1. The sequences of primers used in boundary PCR and cpDEG qRT-PCR.
Additional file 2 Table S2. The information of cp DEGs and the expression levels.
Additional file 3 Figure S1. The Venn maps of the cp DEGs. A: up regulated genes; B: down regulated genes.
Data Availability Statement
Illumina HiSeq 2500 data have been submitted to the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) under accession number PRJNA534167. The complete cp genome of Populus davidiana Dode×Populus bolleana Lauch was submitted to GenBank under accession number MN190025.