Understanding the biosynthetic and regulatory mechanisms of heat-stable antifungal factor (HSAF) could improve the yield in Lysobacter enzymogenes. Here, we report that RpfB1 and RpfB2 encode acyl coenzyme A (CoA) ligases. Our research shows that RpfB1 and RpfB2 affect free fatty acid metabolism via fatty acyl-CoA ligase (FCL) activity to reduce the substrate for HSAF synthesis and, thereby, block HSAF production in L. enzymogenes. Furthermore, these findings reveal new roles for the fatty acyl-CoA ligases RpfB1 and RpfB2 in antibiotic biosynthesis in L. enzymogenes. Importantly, the novelty of this work is the finding that RpfB2 lies outside the Rpf gene cluster and plays a key role in HSAF production, which has not been reported in other diffusible signaling factor (DSF)/Rpf-producing bacteria.
KEYWORDS: heat-stable antifungal factor (HSAF), Lysobacter enzymogenes OH11, fatty acyl-CoA ligase (FCL), intracellular free fatty acids
ABSTRACT
In Lysobacter enzymogenes OH11, RpfB1 and RpfB2 were predicted to encode acyl coenzyme A (CoA) ligases. RpfB1 is located in the Rpf gene cluster. Interestingly, we found an RpfB1 homolog (RpfB2) outside this canonical gene cluster, and nothing is known about its functionality or mechanism. Here, we report that rpfB1 and rpfB2 can functionally replace EcFadD in the Escherichia coli fadD mutant JW1794. RpfB activates long-chain fatty acids (n-C16:0 and n-C18:0) for the corresponding fatty acyl-CoA ligase (FCL) activity in vitro, and Glu-361 plays critical roles in the catalytic mechanism of RpfB1 and RpfB2. Deletion of rpfB1 and rpfB2 resulted in significantly increased heat-stable antifungal factor (HSAF) production, and overexpression of rpfB1 or rpfB2 completely suppressed HSAF production. Deletion of rpfB1 and rpfB2 resulted in increased L. enzymogenes diffusible signaling factor 3 (LeDSF3) synthesis in L. enzymogenes. Overall, our results showed that changes in intracellular free fatty acid levels significantly altered HSAF production. Our report shows that intracellular free fatty acids are required for HSAF production and that RpfB affects HSAF production via FCL activity. The global transcriptional regulator Clp directly regulated the expression of rpfB1 and rpfB2. In conclusion, these findings reveal new roles of RpfB in antibiotic biosynthesis in L. enzymogenes.
IMPORTANCE Understanding the biosynthetic and regulatory mechanisms of heat-stable antifungal factor (HSAF) could improve the yield in Lysobacter enzymogenes. Here, we report that RpfB1 and RpfB2 encode acyl coenzyme A (CoA) ligases. Our research shows that RpfB1 and RpfB2 affect free fatty acid metabolism via fatty acyl-CoA ligase (FCL) activity to reduce the substrate for HSAF synthesis and, thereby, block HSAF production in L. enzymogenes. Furthermore, these findings reveal new roles for the fatty acyl-CoA ligases RpfB1 and RpfB2 in antibiotic biosynthesis in L. enzymogenes. Importantly, the novelty of this work is the finding that RpfB2 lies outside the Rpf gene cluster and plays a key role in HSAF production, which has not been reported in other diffusible signaling factor (DSF)/Rpf-producing bacteria.
INTRODUCTION
Lysobacter enzymogenes strain OH11, originally isolated from the rhizosphere of green pepper, is a nonpathogenic strain that was used to control crop fungal diseases (1–4). Heat-stable antifungal factor (HSAF), a polycyclic tetramate macrolactam, is a newly identified broad-spectrum antifungal antibiotic isolated from the biocontrol species L. enzymogenes and is regarded as an attractive agent for the biological control of fungal diseases of agriculturally important plants (5–8). HSAF exhibits inhibitory activity against a wide range of fungal species, and its chemical structure and mode of action are distinct from those of existing antifungal drugs or fungicides (1, 7). Therefore, the identification of genes and growth conditions that regulate HSAF production is of significant interest.
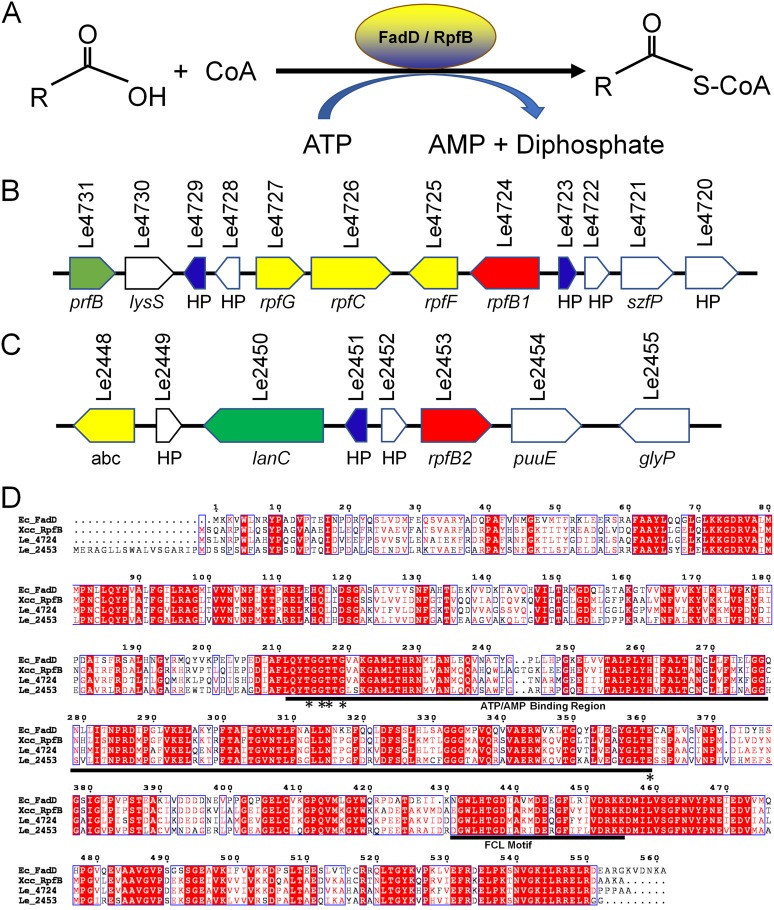
The diffusible signaling factor (DSF) represents a new class of widely conserved quorum sensing (QS) signals that regulate various biological functions in pathogenic and beneficial environmental bacteria (9, 10). The Rpf gene cluster is important for the DSF signaling network in bacteria, and the role of RpfF and RpfB in this gene cluster in DSF production and turnover has been well documented (11–13). A previous study revealed that L. enzymogenes diffusible signaling factor 3 (LeDSF3)-mediated QS positively regulates the biosynthesis of HSAF in L. enzymogenes (10, 14). However, whether RpfB can also affect HSAF synthesis in L. enzymogenes remains unknown. RpfB is annotated as a gene encoding a fatty acyl coenzyme A (CoA) ligase (FCL), also known as fatty acid CoA synthetase (15), which plays a crucial role in fatty acid β-oxidation to yield acyl-CoAs for membrane lipid synthesis in bacteria (Fig. 1A) (16). RpfB acts strongly on short- (C8), medium- (C10 to C14), and long-chain (C16 to C18) fatty acids, which indicates that this protein is a broad chain-length FCL. In contrast, RpfB FCL activity was very low with DSF fatty acid substrates (15).
FIG 1.
Identification and sequence characterization of RpfB in L. enzymogenes OH11. (A) Chemical equation of the acyl-CoA ligase reaction. (B) Chromosomal region of L. enzymogenes surrounding the rpfB1 gene. prfB, peptide chain release factor 2; lysS, lysyl-tRNA synthetase; HP, hypothetical protein; rpfG, two-component system, response regulator; rpfC, two-component system, sensor histidine kinase; rpfF, enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase family; rpfB1, long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase; szfP, SWIM zinc finger protein. (C) Chromosomal region of L. enzymogenes surrounding the rpfB2 gene. abc, ABC transporter, ATP-binding protein; lanC, lanthionine synthetase C-like protein; rpfB2, long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase; puuE, 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase; glyP, glyoxalase family protein. (D) Alignment of L. enzymogenes, X. campestris, and E. coli RpfBs. The alignment was performed with Clustal W based on identical residues. The ATP/AMP and FCL motifs are underlined. The sites that were experimentally confirmed in E. coli are denoted by asterisks.
Two RpfB homologs encoding an FCL were identified in the genome of L. enzymogenes OH11. Interestingly, there exists an RpfB homolog (Le2453) outside the canonical Rpf gene cluster, and nothing is known about its functionality or mechanistic action. To distinguish these two genes, rpfB (Le4724), located immediately upstream of rpfGCF within the rpf gene cluster, was named rpfB1, and the other rpfB gene, located upstream of puuE (4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase), was named rpfB2 (Le2453) (Fig. 1B and C). We hypothesized that RpfB can regulate the synthesis of HSAF, but the regulatory mechanism of RpfB remains unknown. Whether the RpfB1 and RpfB2 homologs synergistically or differentially regulate the synthesis of HSAF in L. enzymogenes remains unknown.
In the present study, we demonstrated that two long-chain acyl-CoA ligases, namely, RpfB1 and RpfB2, play a role in fatty acid β-oxidation in L. enzymogenes. Either RpfB1 or RpfB2 effectively operates in HSAF synthesis by affecting intracellular free fatty acid metabolism in L. enzymogenes. The global transcription regulator Clp directly positively regulates RpfB expression.
RESULTS
Two conserved rpfB genes in the L. enzymogenes genome.
To investigate the function of RpfB in L. enzymogenes OH11, alignments of RpfB with FadD proteins from Escherichia coli (17) and Xanthomonas campestris (15) were examined (Fig. 1D). The results showed that the RpfB1 protein shares 58% and 75% identity with E. coli FadD and X. campestris RpfB, respectively. We also aligned RpfB2 with E. coli FadD and X. campestris RpfB, and the respective identity values were 58% and 62%, respectively. The RpfB1 protein shares 64% identity with RpfB2 (Fig. 1D). Our sequence alignments (Fig. 1D) showed that the ATP/AMP and FCL signature motifs identified for E. coli FadD and X. campestris RpfB are highly conserved in L. enzymogenes RpfB1 and RpfB2 (17, 18). Based on these criteria, it seems reasonable that RpfB1 and RpfB2 could be functional acyl-CoA ligases that play crucial roles in L. enzymogenes.
L. enzymogenes rpfB1 and rpfB2 complemented the growth of an E. coli fadD mutant strain.
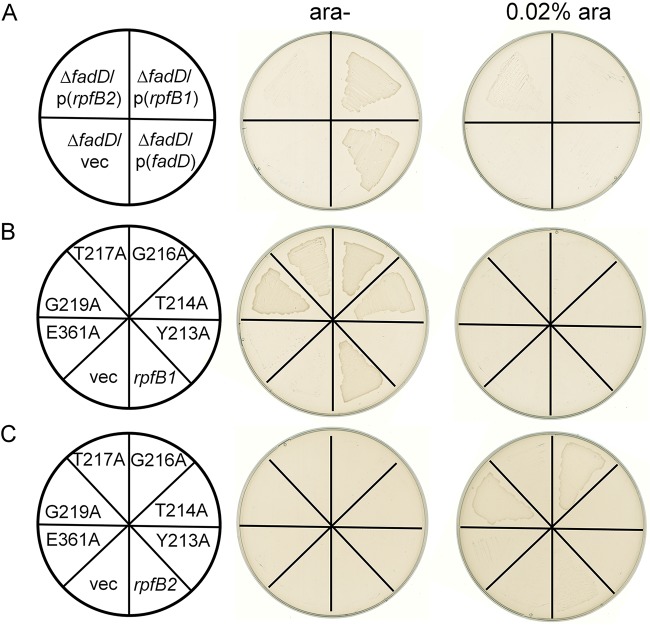
The E. coli JW1794 strain is a fadD mutant that cannot survive in minimal medium when exogenous fatty acids are the sole source of carbon (19). This deficiency can be complemented by a plasmid carrying a gene encoding acyl-CoA ligase. To test whether RpfB can function as an acyl-CoA ligase, we expressed rpfB1 and rpfB2 in the E. coli ΔfadD strain (JW1794). The vector plasmid pBAD24M and an EcFadD complementation vector were used as a negative control and a positive control, respectively. The resulting transformants were tested on M9 medium plates supplemented with oleic acid as the sole carbon source. rpfB1 functionally complemented the E. coli ΔfadD strain and allowed growth on oleic acid as the sole carbon source without arabinose as an inducer, whereas JW1794 carrying rpfB2 exhibited growth on oleic acid as the sole carbon source but needed arabinose as an inducer (Fig. 2A). The results showed that either rpfB1 or rpfB2 functions as an acyl-CoA ligase, which is consistent with the results obtained for X. campestris RpfB (15).
FIG 2.
Expression of L. enzymogenes RpfBs restored the growth of the E. coli fadD mutant JW1794. Transformants of the E. coli fadD mutant JW1794 were grown on M9 minimal medium plates with oleic acid as the sole carbon source. Growth was tested in either the presence or absence of arabinose. The strains tested were as follows: (A) JW1794 carrying the plasmid pBAD24M-EcD, pBAD24M-rpfB1, or pBAD24M-rpfB2, encoding E. coli fadD (EcfadD), L. enzymogenes rpfB1, or L. enzymogenes rpfB2, respectively, or the vector plasmid pBAD24M. (B) Strain JW1794 carrying the plasmid pBAD24M-rpfB1, pBAD24M-rpfB1 Y213A, pBAD24M-rpfB1 T214A, pBAD24M-rpfB1 G216A, pBAD24M-rpfB1 T217A, pBAD24M-rpfB1 G219A, or pBAD24M-rpfB1 E361A, encoding L. enzymogenes rpfB1 or the Y213A, T214A, G216A, T217A, G219A, or E361A rpfB1 mutant, respectively, or the vector plasmid pBAD24M. (C) Strain JW1794 carrying the plasmid pBAD24M-rpfB2, pBAD24M-rpfB2 Y213A, pBAD24M-rpfB2 T214A, pBAD24M-rpfB2 G216A, pBAD24M-rpfB2 T217A, pBAD24M-rpfB2 G219A, or pBAD24M-rpfB2 E361A, encoding L. enzymogenes rpfB2 or the Y213A, T214A, G216A, T217A, G219A, or E361A rpfB2 mutant, respectively, or the vector plasmid pBAD24M.
A previous study revealed that E. coli FCL (FadD) contains two sequence elements, namely, an ATP/AMP signature motif and an FCL motif, the residues of which are critical for catalytic activity (17). To test whether this motif was important for catalytic activity in RpfB1 or RpfB2, we substituted the RpfB1 and RpfB2 residues Tyr-213, Thr-214, Gly-216, Thr-217, Gly-219, and Glu-361 of the ATP/AMP signature motif and FCL motif with alanine (Ala) by site-directed mutagenesis. The growth of the E. coli strain JW1794 carrying plasmids encoding these mutant proteins was tested with oleic acid as the sole carbon source on M9 medium plates. Our results showed that point mutations of the Tyr-213 and Glu-361 residues in RpfB1 abolished FCL activity. The strains expressing the RpfB2 Y213A, T214A, T217A, and E361A mutant proteins failed to grow either in the presence or in the absence of arabinose, whereas the strains expressing the RpfB2 G216A and G219A mutant proteins grew better in the presence of arabinose than the strain expressing the RpfB2 wild-type protein (Fig. 2B and C). These results demonstrated that Tyr-213 and Glu-361 are required for RpfB1 FCL activity and that Tyr-213, Thr-214, Thr-217, and Glu-361 are critical for RpfB2 FCL activity. To confirm this phenotype, these strains were grown in M9 broth, and similar results were obtained (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). Altogether, these results indicate that RpfB1 and RpfB2 have acyl-CoA ligase activity in vivo.
Biochemical properties of the two L. enzymogenes RpfBs.
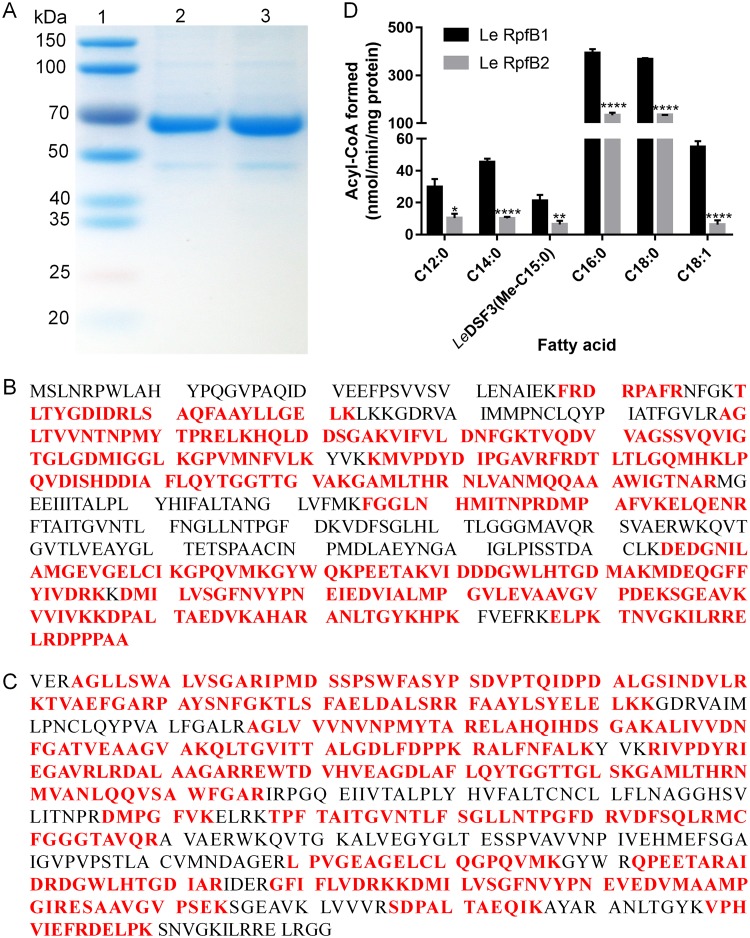
To further characterize the RpfB1- and RpfB2-encoded acyl-CoA ligases, recombinant N-terminal hexahistidine-tagged RpfB1 and RpfB2 were produced. The proteins had a monomeric molecular weight of 61 kDa and were purified by nickel chelation chromatography to obtain preparations that exhibited single bands by SDS-gel electrophoresis (Fig. 3A); the molecular weight and purity were verified by mass analysis (Fig. 3B and C). The fatty acid substrate specificity of RpfB1 and RpfB2 was determined in vitro. RpfB1 and RpfB2 exhibited a high level of activity toward C16:0 and C18:0 substrates, but the acyl-CoA ligase enzymatic activity of RpfB2 was significantly weaker than that of RpfB1. In contrast, the FCL activity of RpfB1 and RpfB2 was very low with LeDSF3 fatty acid substrates (Fig. 3D). These results showed that RpfB1 and RpfB2 are long-chain (C16 to C18) FCLs.
FIG 3.
Fatty acyl chain-length specificity of the two L. enzymogenes RpfBs. (A) Purification of L. enzymogenes RpfB1 and RpfB2 by native nickel-chelation chromatography. Lane 1, molecular mass markers; lane 2, purified RpfB1; lane 3, purified RpfB2. (B) Mass spectrometric identification of L. enzymogenes RpfB1. (C) Mass spectrometric identification of L. enzymogenes RpfB2. The matching peptides are shown in bold and marked in red. (D) Activities of RpfB1 and RpfB2 using fatty acids with different chain lengths (at 500 μM) as the substrates. Error bars, means ± standard deviations (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001; assessed by one-way ANOVA. All experiments were repeated three times with similar results.
RpfB1 and RpfB2 were required for the utilization of free fatty acids.
Since RpfB functionally replaced the E. coli FadD β-oxidation protein, we asked whether RpfB could function in L. enzymogenes fatty acid utilization. We tested the growth of the ΔrpfB1, ΔrpfB2, and ΔrpfB1B2 strains on various fatty acids as sole carbon sources (Table 1). The ΔrpfB1 and ΔrpfB2 strains grew well on glucose, sucrose, and fatty acids, but the ΔrpfB1B2 double-mutant strain completely failed to grow on any fatty acid tested. When the strain was complemented with a rpfB1 or rpfB2 plasmid, it had a growth phenotype similar to that of the wild-type L. enzymogenes, which grew well on fatty acids C10:0 or longer. These results indicated that RpfB1 and RpfB2 are required for the utilization of fatty acids as a sole carbon source and that RpfB1 and RpfB2 are functionally interchangeable in terms of the utilization of fatty acids of L. enzymogenes.
TABLE 1.
Aerobic growth of L. enzymogenes strains on fatty acids of various chain lengthsa
| C source | Growth result by strain |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OH11 | ΔrpfB1 | ΔrpfB1/B1 | ΔrpfB1/B2 | ΔrpfB2 | ΔrpfB2/B1 | ΔrpfB2/B2 | ΔrpfB1B2 | ΔrpfB1B2/B1 | ΔrpfB1B2/B2 | |
| Glucose | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ |
| Sucrose | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| C4:0 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C6:0 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C8:0 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C10:0 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | − | − | − |
| C12:0 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | − | − | − |
| C14:0 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | − | + | ++ |
| C16:0 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | − | + | ++ |
| C18:0 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | − | + | ++ |
| C18:1 | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | − | + | ++ |
L. enzymogenes strains were grown at 28°C on M813 modified medium plates supplemented with 0.4% glucose, 0.4% sucrose, or 0.1% fatty acids with Brij58. The fatty acid was butyrate (C4:0), hexanoate (C6:0), octanoate (C8:0), decanoate (C10:0), dodecanoate (C12:0), tetradecanoate (C14:0), hexadecanoic acid (C16:0), octadecanoic acid (C18:0), or oleate (C18:1). Growth was usually obvious after 4–8 days of aerobic growth. Growth was scored “+” if growth after 6 days was obvious or “−” when no colonies were apparent after 8 days of incubation. Aerobic growth (after 4 days) on a given carbon source was given a score of “++++.”
RpfBs were responsible for LeDSF3 production.
Zhou et al. found that the deletion of rpfB resulted in increased DSF production compared with that in X. campestris (12). To investigate whether RpfB modulated LeDSF3 production in L. enzymogenes, we generated rpfB1 and rpfB2 deletion or overexpression strains and measured LeDSF3 production in the LB medium supernatant. We found that the amount of LeDSF3 signal produced by the ΔrpfB1, ΔrpfB2, and ΔrpfB1B2 mutant strains was significantly higher than that produced by the wild-type strain OH11. The rpfB1- or rpfB2-complemented strains (ΔrpfB1/B1, ΔrpfB1/B2, ΔrpfB2/B1, ΔrpfB2/B2, ΔrpfB1B2/B1, and ΔrpfB1B2/B2) yielded LeDSF3 signals at the level observed with the wild-type strain OH11 (Fig. 4). These findings indicated that RpfB1 and RpfB2 are responsible for affecting the synthesis of the LeDSF3 signal in L. enzymogenes.
FIG 4.
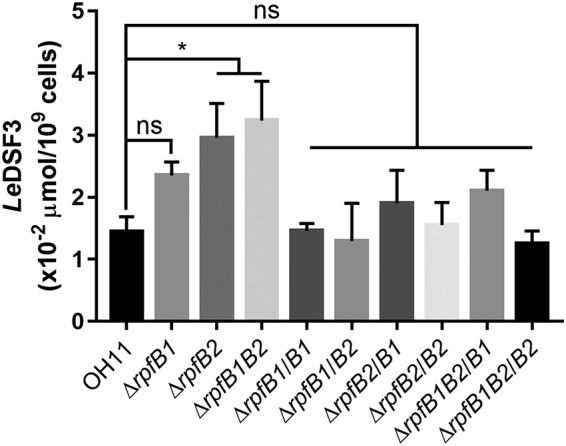
Deletion of rpfB1 and rpfB2 affects the synthesis of the LeDSF3 signal in L. enzymogenes. Error bars, means ± standard deviations (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; as assessed by one-way ANOVA. All experiments were repeated three times with similar results.
L. enzymogenes Clp directly positively regulated RpfB1 and RpfB2 expression.
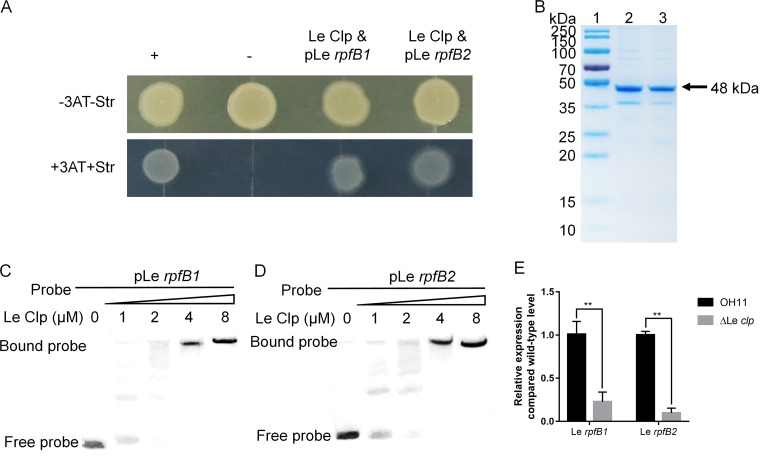
Previously, Zhou et al. showed that Clp binds to the upstream region of X. campestris rpfB (12). Based on the DNA consensus sequence 5′-ATGC-N6-GCAT-3′, which was identified for X. campestris Clp (12), we identified the following two potential binding sites of L. enzymogenes Clp in the upstream region of rpfB1 and rpfB2: 5′-ATGC-N22-CGAT-3′ and 5′-ATCG-N22-GCAT-3′ (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material). We, therefore, hypothesized that L. enzymogenes Clp mediates the effects of rpfB1 and rpfB2 on HSAF biosynthesis. To test this hypothesis, we performed an E. coli-based one-hybrid assay and found that Clp could directly bind to the promoters of L. enzymogenes rpfB1 and rpfB2 (Fig. 5A). To further verify this binding, an electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) was performed. The putative promoter DNA fragments covering 451 bp or 486 bp upstream of the L. enzymogenes rpfB1 or rpfB2 translational start site, namely, pLe rpfB1 or pLe rpfB2, respectively, were cloned and analyzed using EMSA. The addition of purified glutathione S-transferase (GST)-Clp protein (Fig. 5B) at concentrations ranging from 0 μM to 8 μM to the reaction mixtures (20 μl, 28°C, 25 min) caused a shift in the mobility of the pLe rpfB1 or pLe rpfB2 DNA fragment, which suggests that Clp directly binds to the promoter regions of rpfB1 and rpfB2 (Fig. 5C and D). Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis showed that the expression of L. enzymogenes rpfB1 or rpfB2 in the ΔLe clp mutant strain resulted in decreased RpfB1 and RpfB2 expression (Fig. 5E). Thus, the above results collectively suggest that L. enzymogenes Clp directly binds to the promoters of rpfB1 and rpfB2 to promote expression.
FIG 5.
L. enzymogenes Clp directly bound the promoters of rpfB1 and rpfB2. (A) Direct physical interaction between Clp and the rpfB1 and rpfB2 promoter regions was detected in E. coli. Experiments were performed according to the procedures described in the Materials and Methods. +, cotransformant containing pBX-R2031 and pTRG-R3133, used as a positive control; −, cotransformant containing pBXcmT and the empty pTRG, used as a negative control; Clp and pLe rpfB1, cotransformant harboring pTRG-clp and pBXcmT-pLe rpfB1. Clp and pLe rpfB2, cotransformant harboring pTRG-Clp and pBXcmT-pLe rpfB2. −3AT-Str, plate with no selective medium (3AT, 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole and Str, streptomycin); +3AT+Str, plate with M9-based selective medium. (B) The purified protein was analyzed by 12% SDS-PAGE. Lane 1, molecular mass markers; lanes 2 to 3, Clp protein. (C and D) Gel shift assay showing that Clp directly regulates rpfB1 or rpfB2. Clp (0, 1, 2, 4, or 8 μM) was added to reaction mixtures containing 50 ng of probe DNA, and the reaction mixtures were separated on polyacrylamide gels. (E) Relative expression of rpfB1 and rpfB2, as determined by qRT-PCR. All experiments were repeated three times with similar results.
Deletion of rpfB1 and rpfB2 resulted in increased HSAF production.
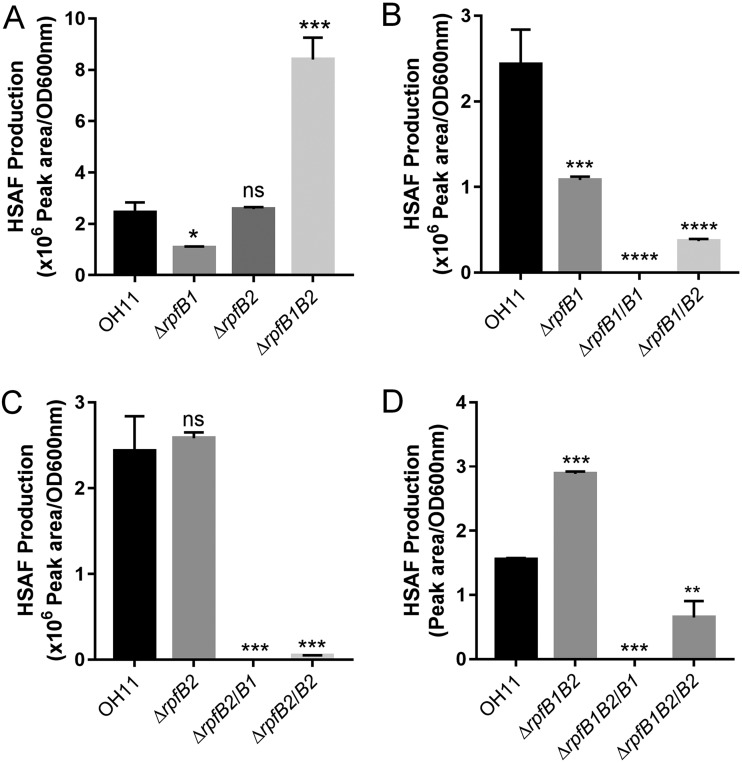
L. enzymogenes is known for its synthesis of the antifungal antibiotic HSAF (20). To identify the physiological functions of L. enzymogenes RpfB1 and RpfB2 in HSAF production, the knockout strains ΔrpfB1 and ΔrpfB2 and the double-mutant strain ΔrpfB1B2, in which the rpfB1 (Le4724) and rpfB2 (Le2453) genes were deleted, were constructed by a two-step homologous recombination approach. We quantified HSAF production in the ΔrpfB1 and ΔrpfB2 single mutants and in the double-mutant strain ΔrpfB1B2 by use of a high-performance liquid chromatograph (HPLC). We found that ΔrpfB1 exhibited decreased HSAF levels and that the deletion of rpfB2 did not affect HSAF levels. However, ΔrpfB1B2 exhibited a significant increase in HSAF levels compared with the wild-type levels (Fig. 6A). To determine the role of RpfB1 and RpfB2 in the regulation of HSAF biosynthesis, we complemented the ΔrpfB1, ΔrpfB2, and ΔrpfB1B2 mutants with plasmid-borne rpfB1 and rpfB2. HSAF production in the rpfB1-complemented strains (ΔrpfB1/B1, ΔrpfB2/B1, and ΔrpfB1B2/B1) was completely suppressed, and in the rpfB2-complemented strains (ΔrpfB1/B2, ΔrpfB2/B2, and ΔrpfB1B2/B2), HSAF production was significantly decreased (Fig. 6B, C, and D). Importantly, the rpfB1, rpfB2, and rpfB1B2 mutations did not impair bacterial growth (see Fig. S3 in the supplemental material), implying that L. enzymogenes RpfB1 and RpfB2 play a specific role in regulating HSAF production. In previous work, Glu-361 was found to be critical for the FCL activity of RpfB1 and RpfB2 (Fig. 2); therefore, we expected the rpfB1 E361A and rpfB2 E361A mutants to not reduce HSAF production in the ΔrpfB1, ΔrpfB2, and ΔrpfB1B2 mutant strains. To test this prediction, we complemented the ΔrpfB1, ΔrpfB2, and ΔrpfB1B2 mutants with the plasmid-borne rpfB1 E361A and rpfB2 E361A mutants. We found that mutation of Glu-361 to Ala-361 did not significantly reduce HSAF production compared with that in the ΔrpfB1, ΔrpfB2, and ΔrpfB1B2 mutant strains (see Fig. S4 in the supplemental material).
FIG 6.
Deletion of rpfB1B2 resulted in increased HSAF production, and HSAF production in the rpfB1- and rpfB2-complemented strains was completely suppressed. (A) Quantification of HSAF in the rpfB mutant strains. (B) Quantification of HSAF in the rpfB1 mutant strains complemented with the rpfB1 gene. (C) Quantification of HSAF in the rpfB2 mutant strains complemented with the rpfB2 gene. (D) Quantification of HSAF in the rpfB1B2 double-mutant strains complemented with the rpfB1 or rpfB2 gene. Error bars, means ± standard deviations (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; assessed by one-way ANOVA. All experiments were repeated three times with similar results.
Intracellular free fatty acids were critical for HSAF production.
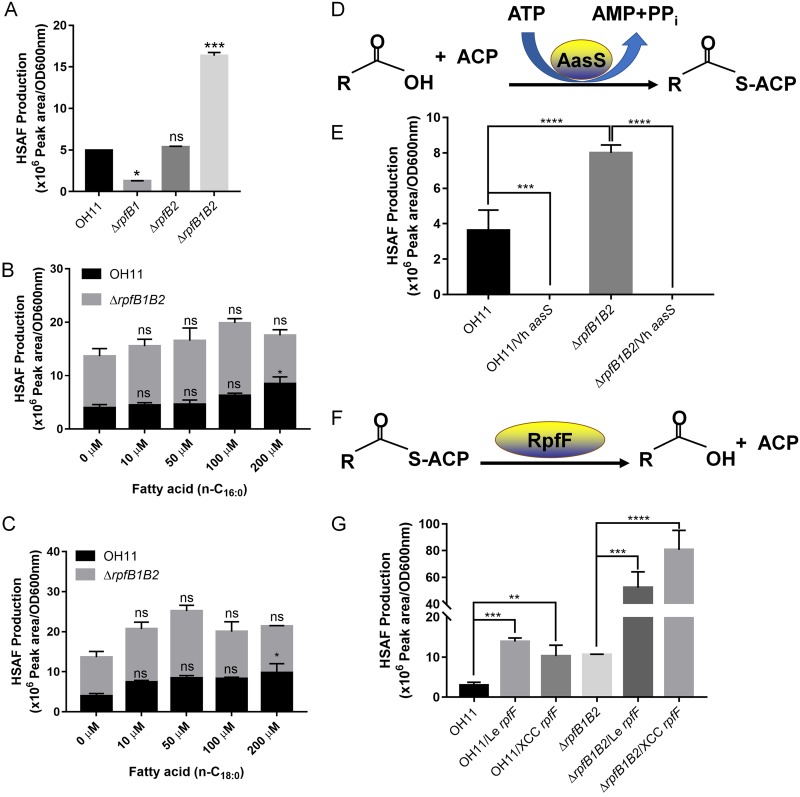
The above studies also found that HSAF production in the rpfB1- and rpfB2-complemented strains was completely suppressed compared with that in the ΔrpfB1, ΔrpfB2, and ΔrpfB1B2 mutants (Fig. 6B, C, and D). RpfB is an acyl-CoA ligase that catalyzes the synthesis of acyl-CoA from free fatty acids and coenzyme A (CoA) (Fig. 2 and 3). We hypothesized that the in-frame deletion of rpfB1 and rpfB2 affected HSAF production due to the influence of the free fatty acid content. To test this hypothesis, we first determined the effect of 10% Trypticase soy broth (TSB) medium without free fatty acids on the synthesis of HSAF in L. enzymogenes. We found that extracellular free fatty acids do not affect HSAF synthesis in L. enzymogenes (Fig. 7A). To further investigate the function of extracellular free fatty acids in HSAF production, we examined HSAF synthesis in L. enzymogenes grown in 10% TSB medium supplemented with free fatty acids (n-C16:0 or n-C18:0). As shown in Fig. 7B and C, these conditions weakly promoted HSAF production by wild-type OH11, but none of these conditions significantly promoted HSAF production by the ΔrpfB1B2 mutant strain. These results indicated that extracellular free fatty acids were not key for HSAF production in L. enzymogenes. To further determine the importance of intracellular free fatty acids for HSAF synthesis in L. enzymogenes, we overexpressed a Vibrio harveyi acyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP) ligase-encoding gene (Vh aasS) that catalyzes the synthesis of acyl-ACP from free fatty acids and ACP (Fig. 7D) (21) in both the wild-type OH11 and ΔrpfB1B2 mutant backgrounds, and the resulting decreased levels of intracellular free fatty acids can completely suppress HSAF production (Fig. 7E). To ultimately determine whether RpfBs affect intracellular free fatty acid metabolism to regulate the synthesis of HSAF, we overexpressed L. enzymogenes and X. campestris acyl-ACP thioesterases (rpfF of both species), which cleave acyl-ACP thioester bonds to yield free fatty acids plus holo-ACP (Fig. 7F) (13, 22), in both the wild-type OH11 and ΔrpfB1B2 mutant strains, and the resulting increase in intracellular free fatty acids significantly increased HSAF production (Fig. 7G). We quantified the cellular fatty acid content and found that ΔrpfB1 exhibited decreased cellular fatty acid levels and that the deletion of rpfB2 did not affect the cellular fatty acid content. However, ΔrpfB1B2 exhibited a significant increase in cellular fatty acid content compared with that of the wild type. This result is consistent with HSAF production (see Fig. S5 in the supplemental material). These findings suggested that RpfBs affect intracellular free fatty acid metabolism to block HSAF biosynthesis.
FIG 7.
Intracellular free fatty acids were required for HSAF biosynthesis. (A) Quantification of HSAF produced by the ΔrpfB1, ΔrpfB2, and ΔrpfB1B2 mutant strains grown in 10% TSB medium without free fatty acids. (B) Quantification of HSAF produced by the rpfB mutant strains grown in 10% TSB medium supplemented with hexadecanoic acid (n-C16:0). (C) Quantification of HSAF produced by the rpfB mutant strains grown in 10% TSB medium supplemented with octadecanoic acid (n-C18:0). (D) Chemical equation of the acyl-ACP synthetase reaction. (E) Quantification of HSAF produced by the wild-type OH11 and rpfB1B2 double-mutant strains complemented with the V. harveyi aasS gene. (F) Chemical equation of the acyl-ACP thioesterase reaction. (G) Quantification of HSAF produced by the wild-type OH11 and the rpfB1B2 double-mutant strains complemented with the L. enzymogenes rpfF or X. campestris rpfF gene. Error bars, means ± standard deviations (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; assessed by one-way ANOVA. All experiments were repeated three times with similar results.
DISCUSSION
Previous studies have indicated that FCL is widespread in a variety of bacterial species and that RpfB encodes an acyl-CoA ligase (15, 17, 23, 24). Recent studies have shown that RpfB represents a naturally occurring signal turnover system that targets DSF-family QS signals in X. campestris (12). LeDSF3-mediated QS plays critical roles in regulating the biosynthesis of HSAF in L. enzymogenes (10, 14). However, the mechanism through which RpfB coordinates the synthesis of HSAF remains unknown. In this study, we investigated the RpfB-dependent regulation of the biosynthesis of the antibiotic HSAF in L. enzymogenes.
Unlike many other bacteria, L. enzymogenes has two FCLs for long-chain fatty acid activation (Fig. 1). The present study demonstrated that RpfB1 and RpfB2 affect the synthesis of the LeDSF3 signal in L. enzymogenes (Fig. 4). The FCLs RpfB1 and RpfB2 exhibited a low level of activity toward LeDSF3 fatty acid substrates (Fig. 3D). These results are indicative of the presence of a RpfB-dependent signal turnover system in L. enzymogenes.
Our data show that the in-frame deletion of the rpfB1 or rpfB2 coding sequence does not significantly affect HSAF production (Fig. 6). However, surprisingly, the deletion of both the rpfB1 and rpfB2 genes resulted in a significant increase in HSAF production (Fig. 6A and D), and the overexpression of rpfB1 or rpfB2 in the wild-type OH11 strain and the ΔrpfB1, ΔrpfB2, and ΔrpfB1B2 mutant strains completely suppressed HSAF production (Fig. 6B, C, and D). RpfB1 and RpfB2 have been shown to exhibit long-chain (n-C16:0 and n-C18:0) FCL activity and harbor a key catalytic glutamine residue (Glu-361) that is required for the FCL activity of RpfB1 and RpfB2 (Fig. 2). This activity is different from the catalytic activity of E. coli FadD and X. campestris RpfB with n-C12:0 and n-C14:0 free fatty acids as the substrates (15, 17). Apparently, RpfB1 and RpfB2 use their FCL activity to affect free fatty acid metabolism and, thus, block HSAF biosynthesis in L. enzymogenes. Therefore, we tested the effect of inactive RpfB1 and RpfB2 on HSAF synthesis; RpfB1 and RpfB2 with point mutations of the E-361 residue were expressed in the wild-type OH11 strain and in the ΔrpfB1, ΔrpfB2, and ΔrpfB1B2 mutant strains. Our analysis revealed that residue Glu-361 in RpfB1 and RpfB2 was essential for blocking HSAF biosynthesis (see Fig. S4 in the supplemental material). Importantly, we found that RpfB2 is outside the Rpf gene cluster and plays a key role in HSAF production, which has not been reported in other DSF/Rpf-producing bacteria (11, 12, 15).
The aasS gene of V. harveyi B392 is a unique gene that encodes acyl-ACP synthetase, which catalyzes the synthesis of acyl-ACP from free fatty acids and ACP (21). Thus, to verify the importance of intracellular free fatty acids for HSAF synthesis, we overexpressed V. harveyi acyl-ACP synthetase (AasS) and successfully showed that this protein could recapture intracellular fatty acids in L. enzymogenes and completely suppress HSAF production (Fig. 7E). In addition, we found that extracellular free fatty acids do not affect HSAF production in L. enzymogenes (Fig. 7A, B, and C). Expression of acyl-ACP thioesterase could increase intracellular free fatty acid production (22). Thus, we overexpressed L. enzymogenes and X. campestris acyl-ACP thioesterases (rpfF of both species), which increased HSAF production in L. enzymogenes (Fig. 7G). These data clearly show that increasing or decreasing the levels of intracellular free fatty acids can significantly increase or decrease the synthesis of HSAF, suggesting that RpfBs affect intracellular free fatty acid metabolism to block HSAF biosynthesis via FCL activity in L. enzymogenes. However, the detailed mechanism underlying the effect of intracellular free fatty acids on HSAF production remains to be studied. Li et al. speculated that the synthetic precursor of HSAF may be a polyene-hexaketide fatty acid (8). Therefore, we speculated that compared with RpfB1, RpfB2 has higher enzymatic activity when using polyene-hexaketide fatty acid as a substrate. However, we cannot obtain the polyene-hexaketide fatty acid, so the ultimate mechanism still needs to be studied in the future. The present study demonstrated that free fatty acids are usually converted to acyl-ACP or acyl-CoA, which are involved in cellular metabolism in bacteria (25–28). However, our study found that acyl-ACP and acyl-CoA are not required for HSAF synthesis in L. enzymogenes. Therefore, we speculate that L. enzymogenes can synthesize HSAF using intracellular free fatty acids as potential substrates. Further clarification of these possible mechanisms will help elucidate the mechanism underlying the use of intracellular free fatty acids as potential substrates for HSAF synthesis.
Clp has been well studied as a cyclic di-GMP-responsive transcriptional regulator that plays essential roles in virulence factor production and in the DSF signaling network (29, 30). Previous findings have demonstrated that Clp is the major regulator of HSAF biosynthesis gene expression in L. enzymogenes (20, 31). The present study revealed that Clp acts as a transcriptional activator to directly positively regulate RpfB1 and RpfB2 expression (Fig. 5), which is different from observations in X. campestris (12). We can only speculate that L. enzymogenes Clp not only directly regulates the biosynthesis of HSAF but also indirectly regulates other factors, such as RpfB, to affect HSAF production.
Overall, L. enzymogenes Clp positively regulated RpfB1 and RpfB2 expression via direct binding to their promoters. RpfBs could affect intracellular free fatty acid metabolism to block the biosynthesis of HSAF via FCL activity in L. enzymogenes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials.
The antibiotics used in this study were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). TaKaRa Biotechnology Co. (Dalian, Liaoning, China) provided the molecular biology reagents, and Novagen (Madison, WI, USA) provided the pET vectors. Ni-agarose columns were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich, and Bio-Rad (Hercules, CA, USA) provided the Quick Start Bradford dye reagent. All other reagents used in this study were of the highest purity available. Genscript (Nanjing, Jiangsu, China) synthesized the oligonucleotide primers.
Bacterial strains, plasmids, and growth conditions.
The strains and plasmids used in this study are shown in Table 2. E. coli strains were grown in Luria-Bertani medium (10 g/liter tryptone, 5 g/liter yeast extract, and 10 g/liter NaCl [pH 7.0]) at 37°C. L. enzymogenes strains were grown at 28°C in Luria-Bertani medium and 10% TSB. M813 modified medium (4 g glucose, 3 g K2HPO4, 1.2 g NaH2PO4, 1 g NH4Cl, 0.3 g MgSO4, 0.15 g KCl, 10 mg CaCl2, and 2.8 mg FeSO4·7H2O, per liter) was used for the growth of L. enzymogenes OH11 (32). For the preparation of culture medium, tryptone, peptone, beef extract, and yeast extract were purchased from Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China). When required, antibiotics were added (100 μg/ml sodium ampicillin, 30 μg/ml kanamycin sulfate, and 50 μg/ml gentamicin) to the E. coli or L. enzymogenes cultures. The bacterial growth in liquid medium was determined by measuring the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) using a Bioscreen-C automated growth curves analysis system (Oy Growth Curves, Helsinki, Finland).
TABLE 2.
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study
| Bacterial strain or plasmid | Relevant characteristicsa | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | ||
| E. coli | ||
| BL21(DE3) | F− dcm ompT hsdS(rB−mB−) gal (λDE3) | Lab collection |
| DH5α | F− deoR endA1 gyrA96 hsdR17(rK−mK+) recA1 relA1 supE44 thi-1 Δ(lacZYA-argF)U169(φ80lacZΔM15) | Lab collection |
| JW1794 | BW25113 ΔfadD::KanR | 19 |
| XL1-Blue MRF′ kan | Δ(mcrA)183, Δ(mcrCB-hsdSMR-mrr)173, endA1, supE44, thi-1, recA1 gyrA96, relA1, lac, [F′ proAB lacIqZΔM15 Tn5 (KmR)] | 42 |
| L. enzymogenes | ||
| OH11 | KanR, wild-type strain | Lab stock |
| ΔrpfB1 | KanR, the L. enzymogenes rpfB1 in-frame deletion mutant of strain OH11 | This study |
| ΔrpfB2 | KanR, the L. enzymogenes rpfB2 in-frame deletion mutant of strain OH11 | This study |
| ΔrpfB1B2 | KanR, the L. enzymogenes rpfB1 and rpfB2 in-frame deletion mutant of strain OH11 | This study |
| ΔrpfB1/B1 | KanR, GmR, the rpfB1 in-frame deletion mutant harboring the rpfB1 expression plasmid pBBR1-rpfB1 | This study |
| ΔrpfB1/B2 | KanR, GmR, the rpfB1 in-frame deletion mutant harboring the rpfB2 expression plasmid pBBR1-rpfB2 | This study |
| ΔrpfB2/B1 | KanR, GmR, the rpfB2 in-frame deletion mutant harboring the rpfB1 expression plasmid pBBR1-rpfB1 | This study |
| ΔrpfB2/B2 | KanR, GmR, the rpfB2 in-frame deletion mutant harboring the rpfB2 expression plasmid pBBR1-rpfB2 | This study |
| ΔrpfB1B2/B1 | KanR, GmR, the rpfB1 and rpfB2 double-mutant strain harboring the rpfB1 expression plasmid pBBR1-rpfB1 | This study |
| ΔrpfB1B2/B2 | KanR, GmR, the rpfB1 and rpfB2 double-mutant strain harboring the rpfB2 expression plasmid pBBR1-rpfB2 | This study |
| ΔrpfB1/B1 E361A | KanR, GmR, the rpfB1 in-frame deletion mutant harboring the rpfB1 E361A expression plasmid pBBR1-rpfB1 E361A | This study |
| ΔrpfB2/B2 E361A | KanR, GmR, the rpfB2 in-frame deletion mutant harboring the rpfB2 E361A expression plasmid pBBR1-rpfB2 E361A | This study |
| ΔrpfB1B2/B1 E361A | KanR, GmR, the rpfB1 and rpfB2 double-mutant strain harboring the rpfB1 E361A expression plasmid pBBR1-rpfB1 E361A | This study |
| ΔrpfB1B2/B2 E361A | KanR, GmR, the rpfB1 and rpfB2 double-mutant strain harboring the rpfB2 E361A expression plasmid pBBR1-rpfB2 E361A | This study |
| OH11/Vh aasS | KanR, GmR, the wild-type strain OH11 harboring the V. harveyi aasS expression plasmid pBBR1-Vh aasS | This study |
| ΔrpfB1B2/Vh aasS | KanR, GmR, the rpfB1 and rpfB2 double-mutant strain harboring the V. harveyi aasS expression plasmid pBBR1-Vh aasS | This study |
| OH11/Le rpfF | KanR, GmR, the wild-type strain OH11 harboring the L. enzymogenes rpfF expression plasmid pBBR1-Le rpfF | This study |
| OH11/XCC rpfF | KanR, GmR, the wild-type strain OH11 harboring the X. campestris rpfF expression plasmid pBBR1-XCC rpfF | This study |
| ΔrpfB1B2/Le rpfF | KanR, GmR, the rpfB1 and rpfB2 double-mutant strain harboring the L. enzymogenes rpfF expression plasmid pBBR1-Le rpfF | This study |
| ΔrpfB1B2/XCC rpfF | KanR, GmR, the rpfB1 and rpfB2 double-mutant strain harboring the L. enzymogenes rpfF expression plasmid pBBR1-Le rpfF | This study |
| ΔLe clp | KanR, the L. enzymogenes clp in-frame deletion mutant of strain OH11 | 40 |
| Plasmids | ||
| pET28b | KmR, T7 promoter-based expression vector | Lab collection |
| pBAD24M | AmpR; PBAD promoter-based expression vector | 34 |
| pEX18GM | GmR, sacB-based gene replacement vector | 37 |
| pBBR1MCS5 | GmR, broad host range cloning vector | 38 |
| pET-rpfB1 | KmR, L. enzymogenes rpfB1 in pET-28b | This study |
| pET-rpfB2 | KmR, L. enzymogenes rpfB2 in pET-28b | This study |
| pBAD24M-rpfB1 | AmpR, L. enzymogenes rpfB1 in pBAD24M | This study |
| pBAD24M-rpfB2 | AmpR, L. enzymogenes rpfB2 in pBAD24M | This study |
| pBAD24M-rpfB1 Y213A | AmpR, RpfB1 Y213A in pBAD24M-rpfB1 | This study |
| pBAD24M-rpfB1 T214A | AmpR, RpfB1 T214A in pBAD24M-rpfB1 | This study |
| pBAD24M-rpfB1 G216A | AmpR, RpfB1 G216A in pBAD24M-rpfB1 | This study |
| pBAD24M-rpfB1 T217A | AmpR, RpfB1 T217A in pBAD24M-rpfB1 | This study |
| pBAD24M-rpfB1 G219A | AmpR, RpfB1 G219A in pBAD24M-rpfB1 | This study |
| pBAD24M-rpfB1 E361A | AmpR, RpfB1 E361A in pBAD24M-rpfB1 | This study |
| pBAD24M-rpfB2 Y213A | AmpR, RpfB2 Y213A in pBAD24M-rpfB2 | This study |
| pBAD24M-rpfB2 T214A | AmpR, RpfB2 T214A in pBAD24M-rpfB2 | This study |
| pBAD24M-rpfB2 G216A | AmpR, RpfB2 G216A in pBAD24M-rpfB2 | This study |
| pBAD24M-rpfB2 T217A | AmpR, RpfB2 T217A in pBAD24M-rpfB2 | This study |
| pBAD24M-rpfB2 G219A | AmpR, RpfB2 G219A in pBAD24M-rpfB2 | This study |
| pBAD24M-rpfB2 E361A | AmpR, RpfB2 E361A in pBAD24M-rpfB2 | This study |
| pBBR1-rpfB1 | GmR, L. enzymogenes rpfB1 in pBBR1MCS5 | This study |
| pBBR1-rpfB2 | GmR, L. enzymogenes rpfB2 in pBBR1MCS5 | This study |
| pBBR1-rpfB1 E361A | GmR, RpfB1 E361A in pBBR1-rpfB1 | This study |
| pBBR1-rpfB2 E361A | GmR, RpfB2 E361A in pBBR1-rpfB2 | This study |
| pBBR1-Vh aasS | GmR, V. harveyi aasS in pBBR1MCS5 | This study |
| pBBR1-Le rpfF | GmR, L. enzymogenes rpfF in pBBR1MCS5 | This study |
| pBBR1-XCC rpfF | GmR, X. campestris rpfF in pBBR1MCS5 | This study |
| pEX18-ΔrpfB1 | GmR, L. enzymogenes rpfB1 in-frame deletion fragment inserted into pEX18GM vector between HindIII/XbaI sites | This study |
| pEX18-ΔrpfB2 | GmR, L. enzymogenes rpfB2 in-frame deletion fragment inserted into pEX18GM vector between HindIII/XbaI sites | This study |
| pGEX-6p-1 | AmpR, vector for protein expression | 45 |
| pGEX-6p-1-Clp | AmpR, pGEX-6p-1 with the coding region of Clp | 40 |
| pTRG | TetR, plasmid used for protein expression in bacterial one-hybrid assay | 42 |
| pTRG-Clp | TetR, pTRG with the coding region of Clp | 45 |
| pBXcmT | CmR, plasmid used for DNA cloning in bacterial one-hybridization assay | 40 |
| pBXcmT-pLe rpfB1 | CmR, pBXcmT with the L. enzymogenes rpfB1 promoter region | This study |
| pBXcmT-pLe rpfB2 | CmR, pBXcmT with the L. enzymogenes rpfB2 promoter region | This study |
KmR, kanamycin resistance; GmR, gentamicin resistance; AmpR, ampicillin resistance; CmR, chloramphenicol resistance.
Complementation of an E. coli ΔfadD strain.
An E. coli ΔfadD strain complementation assay was performed as previously described (33). An fadD mutant strain of E. coli (JW1794) was used for the complementation studies (19). L. enzymogenes rpfB genes were amplified from the genomic DNA of the wild-type OH11 strain using the primers listed in Table 3, which contained NdeI and HindIII sites. PCR fragments were purified and cloned into pBAD24M (34). The rpfB sequences were verified by sequencing. The two recombinant vectors were introduced into the E. coli strain JW1794 for complementation. An empty vector was also transformed into JW1794 and used as a negative control in the complementation experiments. The E. coli fadD gene was also employed as a control for the complementation study. These strains were inoculated into M9 minimal medium supplemented with 0.1% fatty acids with Brij58 (0.02% arabinose was added if required), and the complementation results were determined after the cells were incubated for 72 h at 37°C.
TABLE 3.
Sequences of the PCR primers used in this work
| Primer name by use | Primer sequence (5′ to 3′)a | Digestion site |
|---|---|---|
| For deletion | ||
| rpfB1 HindIII | ATCCAAGCTTCATCCTGCAACTGGGTCATC | HindIII |
| rpfB1 up1 | TGACGATCACCACCTTGACCTAGGTCAGTGTCTTGCCGAA | |
| rpfB1 down1 | TTCGGCAAGACACTGACCTAGGTCAAGGTGGTGATCGTCA | |
| rpfB1 XbaI | CTAGTCTAGAATGTCTTCCATCAGCGGTGT | XbaI |
| rpfB2 HindIII | ACCCAAGCTTGCAGACCGAACTCAACTTCA | HindIII |
| rpfB2 up1 | CACCTTGTACCCCGTGAGATGGTCTTGCCGAAATTGCTGT | |
| rpfB2 down1 | ACAGCAATTTCGGCAAGACCATCTCACGGGGTACAAGGTG | |
| rpfB2 XbaI | CTAGTCTAGACCATCTTGATCCTGCCGTTG | XbaI |
| For in trans expression | ||
| pBBR1-rpfB1-F | ATGGGGTACCCATCCTGCAACTGGGTCATC | KpnI |
| pBBR1-rpfB1-R | ACCCAAGCTTTTGCCTGTTTCGCTGCAGGA | HindIII |
| pBBR1-rpfB2-F | ATGGGGTACCGCAGAAGACCATGTACGGC | KpnI |
| pBBR1-rpfB2-R | ACCCAAGCTTCCACCAAGACAACAAAGGCA | HindIII |
| 24M-rpfB1 F | GAATTCCATATGATGAGTTTGAACCGTCCGTG | NdeI |
| 24M -rpfB1 R | ACCCAAGCTTTTGCCTGTTTCGCTGCAGGA | HindIII |
| 24M -rpfB2 F | GAATTCCATATGGTGGAGCGCGCCGGCTTGCT | NdeI |
| 24M -rpfB2 R | ACCCAAGCTTCCACCAAGACAACAAAGGCA | HindIII |
| Le rpfB1 Y213A F | ACATCGCGTTCCTGCAGGCAACCGGCGGCACCACCGGC | |
| Le rpfB1 Y213A R | GCCGGTGGTGCCGCCGGTTGCCTGCAGGAACGCGATGT | |
| Le rpfB1 T214A F | TCGCGTTCCTGCAGTACGCAGGCGGCACCACCGGCGTG | |
| Le rpfB1 T214A R | CACGCCGGTGGTGCCGCCTGCGTACTGCAGGAACGCGA | |
| Le rpfB1 G216A F | TCCTGCAGTACACCGGCGCAACCACCGGCGTGGCCAAG | |
| Le rpfB1 G216A R | CTTGGCCACGCCGGTGGTTGCGCCGGTGTACTGCAGGA | |
| Le rpfB1 T217A F | TGCAGTACACCGGCGGCGCAACCGGCGTGGCCAAGGG | |
| Le rpfB1 T217A R | CCCTTGGCCACGCCGGTTGCGCCGCCGGTGTACTGCA | |
| Le rpfB1 G219A F | ACACCGGCGGCACCACCGCAGTGGCCAAGGGCGCCATG | |
| Le rpfB1 G219A F | ACACCGGCGGCACCACCGCAGTGGCCAAGGGCGCCATG | |
| Le rpfB1 E361A F | AGGCCTACGGCCTGACCGCAACCTCGCCGGCGGCGTGC | |
| Le rpfB1 E361A R | GCACGCCGCCGGCGAGGTTGCGGTCAGGCCGTAGGCCT | |
| Le rpfB2 Y213A F | ACCTCGCGTTCCTGCAGGCAACCGGCGGCACCACCGGC | |
| Le rpfB2 Y213A R | GCCGGTGGTGCCGCCGGTTGCCTGCAGGAACGCGAGGT | |
| Le rpfB2 T214A F | TCGCGTTCCTGCAGTACGCAGGCGGCACCACCGGCCT | |
| Le rpfB2 T214A R | AGGCCGGTGGTGCCGCCTGCGTACTGCAGGAACGCGA | |
| Le rpfB2 G216A F | TCCTGCAGTACACCGGCGCAACCACCGGCCTGTCCAAG | |
| Le rpfB2 G216A R | CTTGGACAGGCCGGTGGTTGCGCCGGTGTACTGCAGGA | |
| Le rpfB2 T217A F | TGCAGTACACCGGCGGCGCAACCGGCCTGTCCAAGGGC | |
| Le rpfB2 T217A R | GCCCTTGGACAGGCCGGTTGCGCCGCCGGTGTACTGCA | |
| Le rpfB2 G219A F | ACACCGGCGGCACCACCGCACTGTCCAAGGGCGCGATG | |
| Le rpfB2 G219A R | CATCGCGCCCTTGGACAGTGCGGTGGTGCCGCCGGTGT | |
| Le rpfB2 E361A F | AAGGCTACGGCCTGACCGCAAGTTCGCCGGTGGCGGTG | |
| Le rpfB2 E361A R | CACCGCCACCGGCGAACTTGCGGTCAGGCCGTAGCCTT | |
| For protein expression | ||
| 28b-rpfB1 P1 | GAATTCCATATGATGAGTTTGAACCGTCCGTG | NdeI |
| 28b-rpfB1 P2 | ACCCAAGCTTTTGCCTGTTTCGCTGCAGGA | HindIII |
| 28b-rpfB2 P1 | GAATTCCATATGGTGGAGCGCGCCGGCTTGCT | NdeI |
| 28b-rpfB2 P2 | ACCCAAGCTTCCACCAAGACAACAAAGGCA | HindIII |
| For bacterial one-hybrid assays and EMSA | ||
| prpfB1 P1 | CCGCTCGAGCATCCTGCAACTGGGTCATC | XhoI |
| prpfB1 P2 | TGCTCTAGACACGGACGGTTCAAACTCAT | XbaI |
| prpfB2 P1 | CCGCTCGAGGCAGAAGACCATGTACGGC | XhoI |
| prpfB2 P2 | TGCTCTAGAAGCAAGCCGGCGCGCTCCAC | XbaI |
| For RT-PCR | ||
| RT-rpfB1-F | AGAAGATGGTGCCCGACTAC | |
| RT-rpfB1-R | GATGATCTCTTCGCCCATGC | |
| RT-rpfB2-F | GTCAATCCGATGTACACCGC | |
| RT-rpfB2-R | GACGTACTTGAGCGCGAAAT | |
| RT-16S rRNA-F | ACGGTCGCAAGACTGAAACT | |
| RT-16S rRNA-R | AAGGCACCAATCCATCTCTG |
Underlined sequences represent restriction endonuclease sites.
Site-directed mutagenesis and essentiality testing.
Site-directed mutagenesis and essentiality testing were performed as described previously (33). To obtain the rpfB1 and rpfB2 site-directed mutant strains, a mutation plasmid was constructed; for example, to obtain the Y213A mutation in RpfB1, the approximately 500-bp DNA fragments flanking the L. enzymogenes rpfB1 gene were amplified with Pfu DNA polymerase using L. enzymogenes genomic DNA as the template and either rpfB1 NdeI and rpfB1 Y213A P1 (for the up rpfB1 Y213A mutant) or rpfB1 Y213A P1 and rpfB1 HindIII (for the down rpfB1 Y213A mutant) as the primers (Table 3). The fragments were connected by overlap PCR using the primers rpfB1 NdeI and rpfB1 HindIII. The fused fragment was digested with NdeI and HindIII and inserted into pBAD24M to obtain the plasmid pBAD24M-rpfB1 Y213A. The other five site-directed mutant plasmids (T214A, G216A, T217A, G219A, and E361A) and rpfB2 site-directed mutant plasmids were constructed using a similar method. These RpfB mutant plasmids were then introduced into E. coli strain JW1794 for the complementation study.
Protein expression and purification.
Protein expression and purification were performed as described previously (35). To clone the L. enzymogenes rpfB1 and rpfB2 genes, genomic DNA extracted from L. enzymogenes was used for PCR amplification using Pfu DNA polymerase, and the primers are listed in Table 3. The PCR products were inserted into pET-28b (+) to produce the plasmids pET-rpfB1 and pET-rpfB1. The L. enzymogenes rpfB1 and rpfB2 genes were verified by nucleotide sequencing by Genscript (Nanjing, Jiangsu, China). rpfB1 and rpfB2 with a vector-encoded His6-tagged N terminus were expressed in E. coli BL21(DE3) and purified with Ni-nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) agarose (Qiagen, Chatsworth, CA, USA) using a nickel-ion affinity column (Qiagen). The protein purity was monitored by SDS-PAGE and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry.
Assay of acyl-CoA ligase activity.
The assay was performed as described previously (36). Briefly, the reaction buffer mixture contained 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.2), 5 mM MgCl2, 5 mM ATP, 0.125 mM reduced CoA, and 0.5 mM fatty acid substrate. The total reaction volume was 500 μl and included 5 μg of purified protein. For the reaction, a mixture containing all of the components listed above (excluding CoA) was assembled, and 475 μl of the mixture was preincubated at 28°C for 3 min. The reaction was initiated through the addition of 25 μl of 5 mM reduced CoA (diluted to a final concentration of 0.5 mM), which was preincubated at 28°C for 3 min, rapidly mixed, and incubated at 28°C throughout the reaction. Immediately after mixing, a reading was obtained at the zero time point by removing 100 μl from the 500-μl reaction mixture, adding it to 100 μl of 0.4 mM 5,5′-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB; dissolved in 0.1 M potassium phosphate at pH 8.0), and measuring the absorbance at 412 nm. Subsequently, 100-μl aliquots of the reaction mixture were collected at 5-min intervals and mixed with DTNB to obtain additional measurements. The extinction coefficient of CoA was assumed to be 1.36 × 104 M−1 cm−1. All reactions involving RpfBs were repeated to obtain triplicate data for each fatty acid at each concentration. The maximum velocity (Vmax) of the enzymes and affinity for the different substrates (Michaelis constant, Km) were then determined using Hanes-Woolf plots.
Deletion of L. enzymogenes rpfB genes and complementation.
To disrupt the L. enzymogenes rpfB1 and rpfB2 genes, the pEX18GM based suicide plasmids pEX18-ΔrpfB1 and pEX18-ΔrpfB2 were constructed for in-frame deletion. The approximately 500-bp DNA fragments flanking the rpfB1 and rpfB2 genes were amplified with Pfu DNA polymerase using L. enzymogenes genomic DNA as the template and either rpfB1 HindIII and rpfB1 up1 (for up rpfB1) and rpfB1 down1 and rpfB1 XbaI (for down rpfB1) or rpfB2 HindIII and rpfB2 up1 (for up rpfB2) and rpfB2 down1 and rpfB2 XbaI (for down rpfB2) as the primers (Table 3). The fragments were purified and joined by overlap PCR. The fused fragments were digested with HindIII and XbaI and inserted into pEX18GM (37) to obtain the plasmids pEX18-ΔrpfB1 and pEX18-ΔrpfB2. The resulting constructs were transferred into L. enzymogenes by electroporation, and gentamicin was used to select for integration of the nonreplicating plasmid into the recipient chromosome. A single-crossover integrant colony was spread on LB medium without gentamicin and incubated at 28°C for 3 days, and after appropriate dilution, the culture was spread onto LB plates containing 15% sucrose. Colonies sensitive to gentamicin were screened by PCR using the primers listed in Table 3, and the L. enzymogenes rpfB1 and rpfB2 deletion strains (ΔrpfB1 and ΔrpfB2) were obtained. For complementation of the rpfB1 and rpfB2 mutants, the coding regions of rpfB1 and rpfB2 were PCR amplified and cloned into the versatile pBBR1MCS5 plasmid (38). The resulting plasmids were transferred into the L. enzymogenes strain by electroporation and rpfB1 and rpfB2 complementation strains were obtained.
Quantitative real-time PCR.
Quantitative real-time PCR was carried out according to previous studies (39). The bacterial cells were collected when the cellular optical density (OD600) reached 1.0 in 10% TSB. Total RNA was extracted using a TRIzol-based method (Life Technologies, CA, USA). RNA quality control was performed via the following steps: (i) the degree of RNA degradation and potential contamination were monitored on 1% agarose gels, (ii) the RNA purity (OD260/OD280, OD260/OD230) was checked using a NanoPhotometer spectrophotometer (Implen, CA, USA), and (iii) the RNA integrity was measured using the Bioanalyzer 2100 (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The primers used in this assay are listed in Table 3. cDNA was then synthesized from each RNA sample (400 ng) using the TransScript all-in-one first-strand cDNA synthesis supermix for qPCR (one-step genomic DNA [gDNA] removal) kit (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. qRT-PCR was performed using the TransStart top green qPCR supermix (TransGen Biotech) on a QuantStudio TM 6 flex real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) with the following thermal cycling parameters: denaturation at 94°C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of 94°C for 5 s, and 60°C for 34 s. Gene expression analyses were performed using the 2–ΔΔCT method with the 16S rRNA gene as the endogenous control, and the expression level in the wild type was set to a value of 1. The experiments were performed three times, and three replicates were examined in each run.
Bacterial one-hybrid assays.
Bacterial one-hybrid assays were performed as previously described (40, 41). In brief, the bacterial one-hybrid reporter system contains three components, namely, the plasmids pBXcmT and pTRG, which are used to clone the target DNA and to express the target protein, respectively; and the E. coli XL1-Blue MRF′ kan strain, which is the host strain for the propagation of pBXcmT and pTRG recombinants (42). In this study, the L. enzymogenes rpfB1 (451 bp) and rpfB2 (486 bp) promoter regions were cloned into pBXcmT to generate the recombinant vectors pBXcmT-prpfB1 and pBXcmT-prpfB2, respectively. Similarly, the coding region of Clp (690 bp) was cloned into pTRG to create the final construct pTRG-Clp. The two recombinant vectors were transformed into the XL1-Blue MRF′ kan strain. If direct physical binding occurred between Clp and the L. enzymogenes rpfB1 or rpfB2 promoter, the positive-transformant E. coli strain containing both pBXcmT-prpfB1 and pTRG-Clp or both pBXcmT-prpfB2 and pTRG-Clp would grow well on selective medium, that is, minimal medium containing 5 mM 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole, 8 μg/ml streptomycin, 12.5 μg/ml tetracycline, 34 μg/ml chloramphenicol, and 30 μg/ml kanamycin. Furthermore, cotransformants containing pBX-R2031/pTRG-R3133 served as a positive control (42), and cotransformants containing empty pTRG and either pBXcmT-prpfB1 or pBXcmT-prpfB2 were used as a negative control. All cotransformants were spotted onto selective medium, grown at 28°C for 3 to 4 days, and then photographed.
Electrophoretic mobility gel shift assays.
EMSA was performed as previously described (43, 44). For L. enzymogenes Clp gel shift assays, we used DNA fragments that included the L. enzymogenes rpfB1 (451 bp) or rpfB2 (486 bp) promoter region as a probe. The probe DNA (50 ng) was mixed with protein in a 20-μl reaction mixture containing 10 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 50 mM KCl, 1 mM dithiothreitol, and 0.4% glycerol. After incubation for 30 min at 28°C, samples were electrophoresed on a 5% nondenaturing acrylamide gel in 0.5× Tris-borate-EDTA (TBE) buffer at 4°C. The gel was soaked in 10,000-fold-diluted SYBR green I nucleic acid dye (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China), and the DNA was visualized at 300 nm.
HSAF extraction and quantification.
HSAF was extracted from 50-ml L. enzymogenes cultures grown in 10% TSB for 48 h at 28°C with shaking (at 180 rpm). HSAF was detected via HPLC and quantified per unit of OD600 as described previously (10, 20, 31). Three biological replicates were used, and each was examined with three technical replicates.
Detection of DSF signal components in the L. enzymogenes culture supernatant.
The protocols used for the extraction and purification of DSF family components were described previously (12). L. enzymogenes strains were cultured in liquid medium for 24 h, and 50 ml of the bacterial supernatant was collected by centrifugation at 4000 × g and 4°C for 15 min. The pH of the supernatants was adjusted to 4.0 by adding hydrochloric acid prior to two extractions with an equal volume of ethyl acetate. Ethyl acetate fractions were collected, and the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to dryness at 42°C. The residue was dissolved in 100 μl of methanol. Crude extract was subjected to 0.22-μm Mini-Star filtration, and the filtrate was concentrated to 100 μl for liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis. The extract (2 μl) was injected into a C18 reversed-phase column (2.1 × 100 mm; Agilent Poroshell SB-C18) and eluted with water in methanol (20:80 [vol/vol]) at a flow rate of 0.3 ml/minute in a QTRAP 6500 LC-MS/MS system (AB Sciex, USA).
Statistical analyses.
The experimental data sets were subjected to analyses of variance using GraphPad Prism 7.0. The significance of the treatment effects was determined by the F value (P = 0.05). If a significant F value was obtained, a separation of means was accomplished by Fisher’s protected least significant difference at a P value of ≤0.05.
Data availability.
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in GenBank under accession numbers RCTY01000033 (Lysobacter enzymogenes strain OH11 scffold34, whole-genome shotgun sequence; Le4724/Le RpfB1, and locus tag D9T17_13860) and RCTY01000001 (Lysobacter enzymogenes strain OH11 scffold1, whole-genome shotgun sequence, Le2453/Le RpfB2, locus tag D9T17_00210).
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872018).
K.L. and F.L. conceived and designed the experiments. K.L., R.H., H.X., and G.W. carried out experiments. K.L., R.H., H.X., and G.W. analyzed the data and prepared the figures. K.L. and F.L. wrote the manuscript draft. G.Q. and H.W. revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
We declare that we have no competing financial interests.
Footnotes
Supplemental material is available online only.
REFERENCES
- 1.Zhao Y, Cheng C, Jiang T, Xu H, Chen Y, Ma Z, Qian G, Liu F. 2019. Control of wheat fusarium head blight by heat-stable antifungal factor (HSAF) from Lysobacter enzymogenes. Plant Dis 103:1286–1292. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-09-18-1517-RE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhao Y, Qian G, Chen Y, Du L, Liu F. 2017. Transcriptional and antagonistic responses of biocontrol strain Lysobacter enzymogenes OH11 to the plant pathogenic oomycete Pythium aphanidermatum. Front Microbiol 8:1025. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Qian GL, Hu BS, Jiang YH, Liu FQ. 2009. Identification and characterization of Lysobacter enzymogenes as a biological control agent against some fungal pathogens. Agr Sci China 8:68–75. doi: 10.1016/S1671-2927(09)60010-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Odhiambo BO, Xu G, Qian G, Liu F. 2017. Evidence of an unidentified extracellular heat-stable factor produced by Lysobacter enzymogenes (OH11) that degrade Fusarium graminearum PH1 hyphae. Curr Microbiol 74:437–448. doi: 10.1007/s00284-017-1206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lou L, Qian G, Xie Y, Hang J, Chen H, Zaleta-Rivera K, Li Y, Shen Y, Dussault PH, Liu F, Du L. 2011. Biosynthesis of HSAF, a tetramic acid-containing macrolactam from Lysobacter enzymogenes. J Am Chem Soc 133:643–645. doi: 10.1021/ja105732c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yu F, Zaleta-Rivera K, Zhu X, Huffman J, Millet JC, Harris SD, Yuen G, Li XC, Du L. 2007. Structure and biosynthesis of heat-stable antifungal factor (HSAF), a broad-spectrum antimycotic with a novel mode of action. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:64–72. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00931-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Li S, Du L, Yuen G, Harris SD. 2006. Distinct ceramide synthases regulate polarized growth in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Biol Cell 17:1218–1227. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-06-0533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Li Y, Wang H, Liu Y, Jiao Y, Li S, Shen Y, Du L. 2018. Biosynthesis of the polycyclic system in the antifungal HSAF and analogues from Lysobacter enzymogenes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 57:6221–6225. doi: 10.1002/anie.201802488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Deng Y, Wu J, Tao F, Zhang LH. 2011. Listening to a new language: DSF-based quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria. Chem Rev 111:160–173. doi: 10.1021/cr100354f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Qian G, Wang Y, Liu Y, Xu F, He YW, Du L, Venturi V, Fan J, Hu B, Liu F. 2013. Lysobacter enzymogenes uses two distinct cell-cell signaling systems for differential regulation of secondary-metabolite biosynthesis and colony morphology. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:6604–6616. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01841-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang XY, Zhou L, Yang J, Ji GH, He YW. 2016. The RpfB-dependent quorum sensing signal turnover system is required for adaptation and virulence in rice bacterial blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 29:220–230. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-09-15-0206-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhou L, Wang XY, Sun S, Yang LC, Jiang BL, He YW. 2015. Identification and characterization of naturally occurring DSF-family quorum sensing signal turnover system in the phytopathogen Xanthomonas. Environ Microbiol 17:4646–4658. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bi H, Christensen QH, Feng Y, Wang H, Cronan JE. 2012. The Burkholderia cenocepacia BDSF quorum sensing fatty acid is synthesized by a bifunctional crotonase homologue having both dehydratase and thioesterase activities. Mol Microbiol 83:840–855. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.07968.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Han Y, Wang Y, Tombosa S, Wright S, Huffman J, Yuen G, Qian G, Liu F, Shen Y, Du L. 2015. Identification of a small molecule signaling factor that regulates the biosynthesis of the antifungal polycyclic tetramate macrolactam HSAF in Lysobacter enzymogenes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:801–811. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6120-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bi H, Yu Y, Dong H, Wang H, Cronan JE. 2014. Xanthomonas campestris RpfB is a fatty acyl-CoA ligase required to counteract the thioesterase activity of the RpfF diffusible signal factor (DSF) synthase. Mol Microbiol 93:262–275. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhang YM, Rock CO. 2008. Thematic review series: glycerolipids. Acyltransferases in bacterial glycerophospholipid synthesis. J Lipid Res 49:1867–1874. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R800005-JLR200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Weimar JD, DiRusso CC, Delio R, Black PN. 2002. Functional role of fatty acyl-coenzyme A synthetase in the transmembrane movement and activation of exogenous long-chain fatty acids. Amino acid residues within the ATP/AMP signature motif of Escherichia coli FadD are required for enzyme activity and fatty acid transport. J Biol Chem 277:29369–29376. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107022200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Black PN, DiRusso CC. 2003. Transmembrane movement of exogenous long-chain fatty acids: proteins, enzymes, and vectorial esterification. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:454–472. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.67.3.454-472.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Baba T, Ara T, Hasegawa M, Takai Y, Okumura Y, Baba M, Datsenko KA, Tomita M, Wanner BL, Mori H. 2006. Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: the Keio collection. Mol Syst Biol 2:2006.0008. doi: 10.1038/msb4100050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Xu G, Han S, Huo C, Chin KH, Chou SH, Gomelsky M, Qian G, Liu F. 2018. Signaling specificity in the c-di-GMP-dependent network regulating antibiotic synthesis in Lysobacter. Nucleic Acids Res 46:9276–9288. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jiang Y, Chan CH, Cronan JE. 2006. The soluble acyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase of Vibrio harveyi B392 is a member of the medium chain acyl-CoA synthetase family. Biochemistry 45:10008–10019. doi: 10.1021/bi060842w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Li M, Zhang X, Agrawal A, San KY. 2012. Effect of acetate formation pathway and long chain fatty acid CoA-ligase on the free fatty acid production in E. coli expressing acy-ACP thioesterase from Ricinus communis. Metab Eng 14:380–387. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2012.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Stanley SA, Kawate T, Iwase N, Shimizu M, Clatworthy AE, Kazyanskaya E, Sacchettini JC, Ioerger TR, Siddiqi NA, Minami S, Aquadro JA, Grant SS, Rubin EJ, Hung DT. 2013. Diarylcoumarins inhibit mycolic acid biosynthesis and kill Mycobacterium tuberculosis by targeting FadD32. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:11565–11570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1302114110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Black PN, Zhang Q, Weimar JD, DiRusso CC. 1997. Mutational analysis of a fatty acyl-coenzyme A synthetase signature motif identifies seven amino acid residues that modulate fatty acid substrate specificity. J Biol Chem 272:4896–4903. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.8.4896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Morgan-Kiss RM, Cronan JE. 2004. The Escherichia coli fadK (ydiD) gene encodes an anerobically regulated short chain acyl-CoA synthetase. J Biol Chem 279:37324–37333. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405233200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Knoll LJ, Gordon JI. 1993. Use of Escherichia coli strains containing fad mutations plus a triple plasmid expression system to study the import of myristate, its activation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae acyl-CoA synthetase, and its utilization by S. cerevisiae myristoyl-CoA:protein N-myristoyltransferase. J Biol Chem 268:4281–4290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ma JC, Wu YQ, Cao D, Zhang WB, Wang HH. 2017. Only acyl carrier protein 1 (acpp1) functions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa fatty acid synthesis. Front Microbiol 8:2186. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Agarwal V, Lin S, Lukk T, Nair SK, Cronan JE. 2012. Structure of the enzyme-acyl carrier protein (ACP) substrate gatekeeper complex required for biotin synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:17406–17411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1207028109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.He YW, Ng AY, Xu M, Lin K, Wang LH, Dong YH, Zhang LH. 2007. Xanthomonas campestris cell-cell communication involves a putative nucleotide receptor protein Clp and a hierarchical signalling network. Mol Microbiol 64:281–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tao F, He YW, Wu DH, Swarup S, Zhang LH. 2010. The cyclic nucleotide monophosphate domain of Xanthomonas campestris global regulator Clp defines a new class of cyclic di-GMP effectors. J Bacteriol 192:1020–1029. doi: 10.1128/JB.01253-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang Y, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Shen Y, Su Z, Xu G, Du L, Huffman JM, Venturi V, Qian G, Liu F. 2014. Transcriptomic analysis reveals new regulatory roles of Clp signaling in secondary metabolite biosynthesis and surface motility in Lysobacter enzymogenes OH11. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:9009–9020. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6072-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Palumbo JD, Sullivan RF, Kobayashi DY. 2003. Molecular characterization and expression in Escherichia coli of three beta-1,3-glucanase genes from Lysobacter enzymogenes strain N4-7. J Bacteriol 185:4362–4370. doi: 10.1128/jb.185.15.4362-4370.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Feng S, Xu C, Yang K, Wang H, Fan H, Liao M. 2017. Either fadD1 or fadD2, which encode acyl-CoA synthetase, is essential for the survival of Haemophilus parasuis SC096. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:72. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Guzman LM, Belin D, Carson MJ, Beckwith J. 1995. Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter. J Bacteriol 177:4121–4130. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.14.4121-4130.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Li KH, Yu YH, Dong HJ, Zhang WB, Ma JC, Wang HH. 2017. Biological functions of ilvC in Branched-chain fatty acid synthesis and diffusible signal factor family production in Xanthomonas campestris. Front Microbiol 8:2486. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kang Y, Zarzycki-Siek J, Walton CB, Norris MH, Hoang TT. 2010. Multiple FadD acyl-CoA synthetases contribute to differential fatty acid degradation and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS One 5:e13557. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hoang TT, Karkhoff-Schweizer RR, Kutchma AJ, Schweizer HP. 1998. A broad-host-range Flp-FRT recombination system for site-specific excision of chromosomally-located DNA sequences: application for isolation of unmarked Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. Gene 212:77–86. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(98)00130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kovach ME, Elzer PH, Hill DS, Robertson GT, Farris MA, Roop RM II, Peterson KM. 1995. Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 166:175–176. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00584-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cui C, Yang C, Song S, Fu S, Sun X, Yang L, He F, Zhang LH, Zhang Y, Deng Y. 2018. A novel two-component system modulates quorum sensing and pathogenicity in Burkholderia cenocepacia. Mol Microbiol 108:32–44. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Xu H, Chen H, Shen Y, Du L, Chou SH, Liu H, Qian G, Liu F. 2016. Direct regulation of extracellular chitinase production by the transcription factor LeClp in Lysobacter enzymogenes OH11. Phytopathology 106:971–977. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-01-16-0001-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wang B, Wu G, Zhang Y, Qian G, Liu F. 2018. Dissecting the virulence-related functionality and cellular transcription mechanism of a conserved hypothetical protein in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Mol Plant Pathol 19:1859–1872. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Guo M, Feng H, Zhang J, Wang W, Wang Y, Li Y, Gao C, Chen H, Feng Y, He ZG. 2009. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res 19:1301–1308. doi: 10.1101/gr.086595.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hirakawa H, Hirakawa Y, Greenberg EP, Harwood CS. 2015. BadR and BadM proteins transcriptionally regulate two operons needed for anaerobic benzoate degradation by Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:4253–4262. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00377-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Shao X, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Zhu M, Yang P, Yuan J, Xie Y, Zhou T, Wang W, Chen S, Liang H, Deng X. 2018. RpoN-dependent direct regulation of quorum sensing and the type VI secretion system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J Bacteriol 200:e00205-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00205-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Deng Y, Schmid N, Wang C, Wang J, Pessi G, Wu D, Lee J, Aguilar C, Ahrens CH, Chang C, Song H, Eberl L, Zhang LH. 2012. Cis-2-dodecenoic acid receptor RpfR links quorum-sensing signal perception with regulation of virulence through cyclic dimeric guanosine monophosphate turnover. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:15479–15484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1205037109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in GenBank under accession numbers RCTY01000033 (Lysobacter enzymogenes strain OH11 scffold34, whole-genome shotgun sequence; Le4724/Le RpfB1, and locus tag D9T17_13860) and RCTY01000001 (Lysobacter enzymogenes strain OH11 scffold1, whole-genome shotgun sequence, Le2453/Le RpfB2, locus tag D9T17_00210).