Abstract
Background & Aims:
The canonical Wnt signaling pathway activates the transcriptional activity of β-catenin. This pathway is often activated in colorectal cancer cells, but strategies to block it in tumors have not been effective. The SAM pointed domain containing ETS transcription factor (SPDEF) suppresses formation of colon tumors by unclear mechanisms. We investigated these mechanisms and the effects of SPDEF on β-catenin activity in mouse models of colorectal cancer (CRC), CRC cell lines, and mouse and human normal and cancer colonoids.
Methods:
We performed studies of Lgr5CreERT2; β-cateninexon3; Rosa26LSL-rtta-ires-EGFP; TRE-Spdef mice, which express an oncogenic form of β-catenin in Lgr5-positive intestinal stem cells upon administration of tamoxifen and SPDEF upon administration of tetracycline. CRC lines (HCT116 and SW480) were engineered to express inducible tagged SPDEF or vector (control) and subcutaneously injected into immunodeficient NSG mice. We generated SPDEF-inducible human colonoids, including a line derived from normal rectal mucosa (control) and an adenocarcinoma line derived from a patient with germline MUTYH mutation. Full-length and truncated forms of SPDEF were expressed in CRC cells; cells were assayed for β-catenin activity and studied in immunoprecipitation and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays.
Results:
Expression of SPDEF was sufficient to inhibit intestinal tumorigenesis by activated β-catenin, block tumor cell proliferation, and restrict growth of established tumors. In tumor cells with activated β-catenin, expression of SPDEF induced a quiescent state, which was reversed when SPDEF expression was stopped. In mouse and human normal and tumor-derived enteroids/colonoids, those that expressed SPDEF for 3 days were significantly smaller. SPDEF inhibited the transcriptional activity of β-catenin via a protein–protein interaction, independent of SPDEF DNA binding capacity. SPDEF disrupted β-catenin binding to TCF1 and TCF3, displacing β-catenin from enhancer regions of genes that regulate the cell cycle but not genes that regulate stem cell activities.
Conclusions:
In studies of mice and human CRC, we found that SPDEF induces a quiescent state in CRC cells, by disrupting binding of β-catenin to TCF1 and TCF3 and regulation of genes that control the cell cycle. In this model, β-catenin activity determines the proliferation or quiescence of CRC cells based on the absence or presence of SPDEF.
Keywords: colon cancer, TCF/LEF factors, xenograft, tumor suppressor
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer in the United States in both men and women. Canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling normally regulates homeostasis and differentiation of the intestinal epithelium, and is frequently hyperactivated in CRC1, 2. Previous studies showed that activation of nuclear β-catenin in intestinal stem cells is sufficient to initiate tumorigenesis; however, there are currently no treatments targeting this pathway3, 4.
SAM Pointed Domain containing ETS transcription Factor (SPDEF) is an ETS family transcription factor reported to play a role in tumor progression and metastasis of several cancers5–7. In the adult intestines, SPDEF is a direct downstream target gene of ATOH1, a master transcription factor that mediates Notch-regulated differentiation of the intestinal epithelium8, 9. Spdef is expressed in goblet cells, Paneth cells, and a subpopulation of progenitors10. Transgenic overexpression of SPDEF in vivo resulted in the expansion of goblet cells without increased cell proliferation11, whereas deletion of Spdef impaired maturation of goblet and Paneth cells10. These results suggest that SPDEF is critical for goblet and Paneth cell terminal differentiation.
SPDEF is progressively lost in human CRC tissues; consistent with a tumor suppressor role for SPDEF in CRC, Spdef deletion enhances intestinal tumor formation, while re-expression of SPDEF inhibits proliferation in several CRC mouse models12, 13. Our studies suggested that SPDEF represses β-catenin signaling, however the detailed molecular mechanism by which SPDEF mediates colorectal tumor repression remains unknown.
Here, we report that SPDEF inhibits β-catenin-driven tumorigenesis, and restricts established tumor growth by enforcing quiescence on intestinal tumor cells. Mechanistically, we find that SPDEF competes with TCF1 and TCF3 for binding to β-catenin, resulting in selective displacement of β-catenin from its targets. As a consequence, SPDEF functionally inhibits the expression of β-catenin-regulated cell cycle genes without affecting intestinal stem cell signature genes. Taken together, we propose a novel molecular mechanism for how SPDEF controls canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling to switch tumor cells from an active to a quiescent state.
Materials and Methods
Detailed Materials and Methods are available as Supplementary Information.
Animals.
Lgr5CreERT2, β-cateninexon3, Rosa26LSL-rtta-ires-EGFP; TRE-Spdef, Fapb1Cre; Atoh1fl/fl, and Atoh1GFP/GFP mice have been described previously9, 11, 14–16. To induce intestinal tumor initiation, mice were given one intraperitoneal injection of 2 mg/mouse tamoxifen (Sigma) dissolved in corn oil. To induce SPDEF expression, mice were feed 2 mg/ml tetracycline in drinking water. For xenograft studies, male NSG mice were randomly divided into experimental groups. Mice were subcutaneously injected with 2.5 × 106 HCT116 or SW480 cells in a 100 μl medium (50% matrigel in RPMI1640 without FBS). To induce SPDEF expression, mice were feed 2 mg/ml tetracycline in drinking water immediately after inoculation of HCT116 or SW480 cells. Tumor volume (mm3) was calculated using the following formula: tumor volume (mm3) = length (mm) × diameter2 (mm2) × 0.5. All mouse studies were approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC).
Antibodies and Chemicals.
The primary and secondary antibodies used in this study are listed in Supplementary Table 1.
Results
SPDEF inhibits human CRC cell growth.
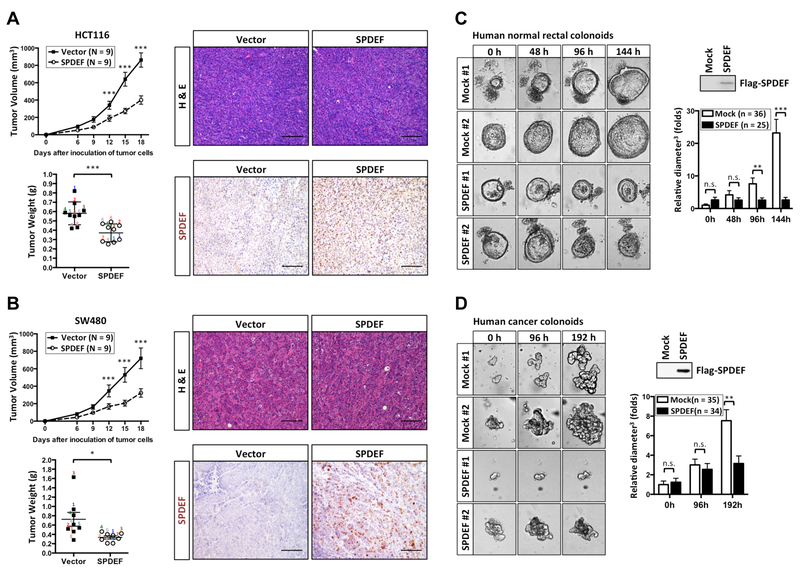
SPDEF expression is absent in most CRCs12. To test whether re-expression of SPDEF can inhibit CRC growth, CRC lines HCT116 and SW480 were engineered to inducibly express Flag-tagged SPDEF or empty vector control, and subcutaneously injected into immunodeficient NSG mice (Figure 1A, Figure 1B, Supplementary Figure 1). We found that SPDEF significantly repressed the growth of human CRC xenografts (Figure 1A, Figure 1B). Immunochemical staining confirmed the nuclear expression of SPDEF in xenografts (Figure 1A, Figure 1B). Next, to test whether SPDEF can inhibit primary human colonoid growth, we generated SPDEF-inducible human colonoids, including a line derived from normal rectal mucosa, and an APC-mutant colon cancer line derived from a patient with germline MUTYH mutation (Figure 1C, Figure 1D). SPDEF significantly inhibited the growth of human cancer colonoids and normal rectal colonoids (Figure 1C, Figure 1D). Immunoblots confirmed the expression of SPDEF (Figure 1C, Figure 1D). Taken together, these results indicate that SPDEF inhibits human CRC growth.
Figure 1. SPDEF inhibits human colon cancer cell growth.
(A) HCT116 or (B) SW480 human colon cancer cell lines stably transduced with pINDUCER20 Flag-SPDEF (SPDEF) and pINDUCER20 empty vector control (Vector) were subcutaneously injected into NSG mice. Immediately following engraftment, mice were provided water with tetracycline (2 mg/ml). SPDEF and Vector xenografts were isolated 18 days after inoculation followed by H&E staining. Immunochemical staining was performed with an anti-FLAG antibody. Freshly dissected numbered 1 – 9. (C) Primary human normal rectal colonoids or (D) cancer colonoids stably transduced with pINDUCER20 Flag-SPDEF (SPDEF) and mock control were generated. Immunoblot with an anti-FLAG antibody confirmed Flag-SPDEF expression after doxycycline (2 μg/ml) induction for 6 days. Bright field images were taken after SPDEF induction as indicated by hours. Quantitated result indicated SPDEF inhibits both normal rectal colonoids and cancer colonoids growth. Colonoids sizes (maximum diameter3) were normalized to the average size (maximum diameter3) of mock control after SPDEF induction at 0h. Error bars, S.E.M.. **, p<0.005. ***, p<0.001. Scale bars: 100 μm.
SPDEF inhibits β-catenin-driven intestinal tumorigenesis.
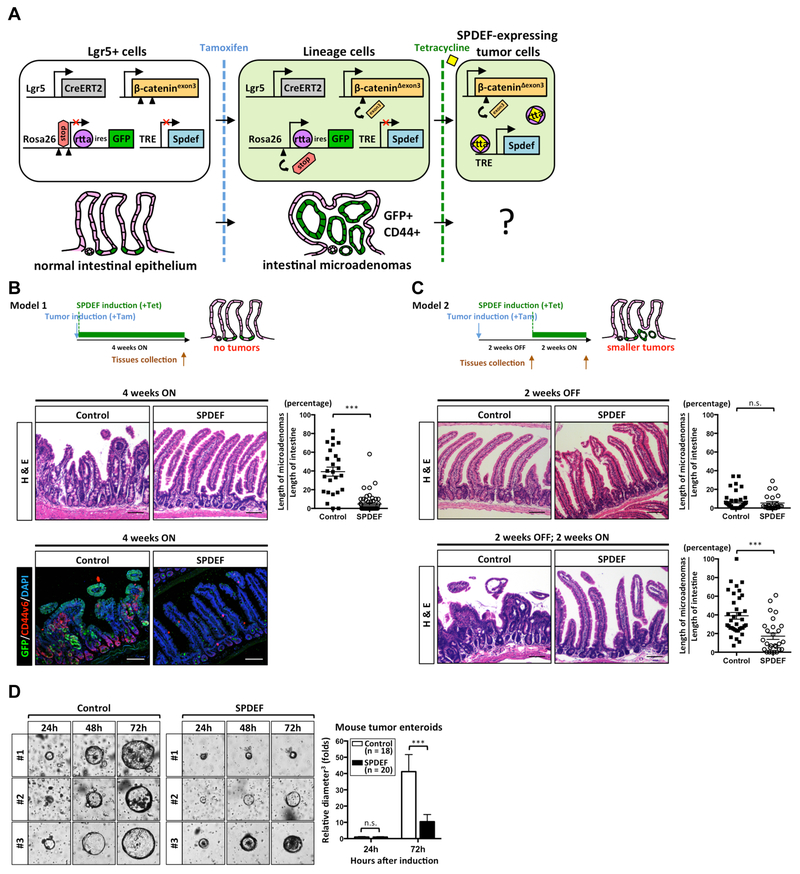
To test whether SPDEF is sufficient to counteract canonical Wnt/β-catenin-driven tumor formation, transgenic mice in which oncogenic β-catenin can be inducibly expressed in Lgr5-positive intestinal stem cells (Lgr5CreERT2; β-cateninexon3) were bred with tetracycline-inducible SPDEF transgenic mice (Rosa26LSL-rtta-ires-EGFP; TRE-Spdef)4, 11. In this de novo tumorigenesis model, constitutively active β-cateninΔexon3 is expressed after Cre-mediated recombination following tamoxifen injection, whereas SPDEF expression is restrictively induced in tumor cells, but not in adjacent normal epithelial cells, by oral tetracycline (Figure 2A).
Figure 2. SPDEF inhibits canonical Wnt/β-catenin-driven tumorigenesis.
(A) Schematic illustration of the experimental strategy using the double inducible mouse model of intestinal tumorigenesis (Lgr5CreERT2; β-cateninexon3; Rosa26LSL-rtta-ires-EGFP; TRE-Spdef). Arrows indicate the direction of transcription. Arrowheads indicate loxP sites. β-catenin-driven tumorigenesis was induced by one tamoxifen injection (2 mg/mouse); SPDEF expression was induced by continuously feeding mice with tetracycline water (2 mg/ml). (B) Intestinal tumorigenesis and SPDEF expression were induced at the same time (Model 1). (C) Intestinal tumorigenesis was induced by tamoxifen and microadenoma were allowed to grow for 2 weeks, followed by treatment with tetracycline to induce SPDEF expression for 2 weeks (Model 2). Intestinal tissues from control mice (Lgr5CreERT2; β-cateninexon3; Rosa26LSL-rtta-ires-EGFP) or SPDEF mice (Lgr5CreERT2; β-cateninexon3; Rosa26LSL-rtta-ires-EGFP; TRE-Spdef) in Model 1 and Model 2 were collected at different time points followed by H&E staining. Immunofluorescent staining was performed with an anti-GFP and an anti-CD44v6 antibodies. Quantitated results were shown. Each dot represents 1 mm length of intestinal epithelium randomly selected from jejunum. Wilcoxin test, Error bars, S.E.M., ***, p<0.001. Scale bars: 100 μm. (D) Mouse tumor enteroids were generated from either control (N=3) or SPDEF mice (N=3) 4 weeks post-tamoxifen induction and grown without Wnt and R-spondin. Doxycycline (2 μg/ml) was added in culture medium to induce SPDEF expression. Bright field view was taken after SPDEF induction. Enteroids sizes (maximum diameter3) were normalized to the average size (maximum diameter3) of control after SPDEF induction at 24h. Error bars, S.E.M.. ***, p<0.001.
We first compared endogenous SPDEF expression to the amount expressed in the TRE-Spdef inducible model. As a target of ATOH1, SPDEF is highly expressed in goblet and Paneth cells10, 11. Spdef mRNA is 9–10 fold higher in purified ATOH1-positive goblet and Paneth cells, compared to total crypt cells, in both ileum and colon (Supplementary Figure 2). Transgenic Spdef expressed by the TRE-Spdef allele is approximately 1.5 fold higher than ATOH1-positive cells, indicating that the TRESpdef allele expresses approximately normal levels of SPDEF (Supplementary Figure 2).
To test SPDEF’s activity in β-catenin-driven tumor initiation, SPDEF expression was induced coincident with recombination-mediated tumor initiation (Model 1; Figure 2B). As expected, hyperproliferating intestinal adenomas were formed 4 weeks after tamoxifen injection in littermate control mice (Lgr5CreERT2; β-cateninexon3; Rosa26LSL-rtta-ires-EGFP) (Figure 2B; control). Immunofluorescence staining for CD44v6, a β-catenin target, indicated activation of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling in these intestinal adenomas (Figure 2B)17. However, in mice (Lgr5CreERT2; β-cateninexon3; Rosa26LSL-rtta-ires-EGFP; TRE-Spdef) simultaneously expressing SPDEF with oncogenic β-catenin, the intestinal epithelium maintained its normal crypt-villus architecture 4 weeks after tumor induction (Figure 2B; SPDEF), and CD44v6 was observed at normal levels at the base of the crypts (Figure 2B)18. These results indicated that SPDEF is sufficient to suppress β-catenin-driven intestinal tumor formation. Next, we asked whether SPDEF is able to inhibit growth of established β-catenin-driven tumors. Here, intestinal microadenomas were allowed to grow for 2 weeks followed by SPDEF induction for another 2 weeks (Model 2; Figure 2C). Before SPDEF induction, small intestinal microadenomas were observed in both groups (Figure 2C; 2 weeks OFF). However, after SPDEF expression for two weeks, intestinal microadenomas were significantly smaller in SPDEF mice compared to control mice (Figure 2C; 2 weeks OFF, 2 weeks ON). Next, we generated β-catenin-driven mouse tumor enteroids from both control and SPDEF mice. After SPDEF induction in vitro for 3 days, the average size of SPDEF-expressing mouse tumor enteroids was significantly smaller (Figure 2D). Taken together, these results indicated that SPDEF is sufficient to inhibit β-catenin-driven tumor growth.
SPDEF promotes tumor cell cycle exit without promoting tumor cell differentiation.
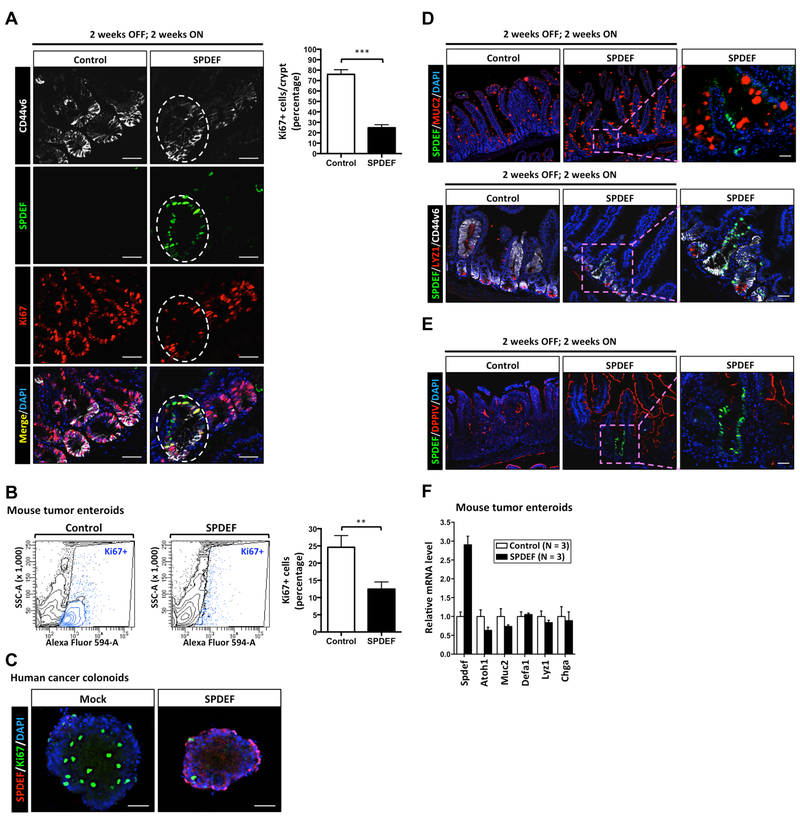
We next tested whether SPDEF can inhibit tumor cell proliferation by co-staining for SPDEF and Ki67, which is present during all active phases of the cell cycle (G1, S, G2 and M phase) but absent from resting cells (in G0 phase). Tissues from control mice showed abundant Ki67-positive cells in microadenomas (Figure 3A; control), indicative of actively cycling tumor cells. In contrast, there were significantly fewer Ki67-positive cells in remnant tumor tissues from mice that had expressed SPDEF for 2 weeks, indicating these cells were no longer actively cycling (Figure 3A; SPDEF). Of note, expression of CD44v6 remains strong in these cells, clearly demarcating SPDEF-expressing microadenomas (Figure 3A). Similar results were observed in mouse tumor enteroids (Figure 3B): fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) indicated that Ki67-positive tumor cells are significantly decreased after SPDEF induction (Figure 3B). Moreover, SPDEF inhibited Ki67 expression in human cancer colonoids (Figure 3C). Taken together, these results suggested that SPDEF inhibits tumor cell proliferation and shifts cells to the G0 phase of the cell cycle.
Figure 3. SPDEF promotes tumor cell cycle exit without promoting tumor cell differentiation.
(A) Mouse intestines from control mice (Lgr5CreERT2; β-cateninexon3; Rosa26LSL-rtta-ires-EGFP) or SPDEF mice (Lgr5CreERT2; β-cateninexon3; Rosa26LSL-rtta-ires-EGFP; TRE-Spdef) were collected at 4 weeks after 2 weeks OFF; 2 weeks ON tetracycline treatment (Model 2) followed by immunofluorescent staining. The expression of Ki67, SPDEF, and CD44v6 were shown as indicated. The white line outlines CD44v6-positive SPDEF-expressing tumor cells. Scale bars: 20 μm. Ki67 quantitated result was shown. (B) Ki67-positive tumor cells from either control (N=3) or SPDEF (N=3) tumor enteroids were quantitated by flow cytometer analysis after SPDEF induction in vitro by doxycycline (2 μg/ml) for 72h. (C) Post-induction by doxycycline (2 μg/ml) for 6 days, immunofluorescent staining was performed by anti-FLAG and anti-Ki67 antibodies in cancer colonoid lines pINDUCER20 Flag-SPDEF (SPDEF) and mock control. (D-E) Immunofluorescent staining was performed by anti-SPDEF, anti-MUC2, anti-LYZ1, and anti-DPPIV antibodies in mouse tumors. (F) Relative mRNA levels of indicated genes from either control (N=3) or SPDEF (N=3) tumor enteroids were quantitated by RT-qPCR after SPDEF induction in vitro by doxycycline (2 μg/ml) for 72h. Error bars, S.E.M.. ***, p<0.001. **, p<0.005.
The G0 phase of the cell cycle is a non-cycling state in which cells are either senescent, terminally differentiated, or quiescent19. Once cells are senescent, they are not capable of future cell division; terminally differentiated cells are resistant to re-entering cell cycle. However, quiescent cells remain poised to re-enter the cell cycle19. Previous studies suggested that SPDEF is critical for intestinal goblet and Paneth cell terminal differentiation10, 11. To test the possibility that the reduction in active cycling among SPDEF-expressing tumor cells was caused by enforced terminal differentiation into goblet-like and Paneth-like cells, we assessed MUC2 (goblet cell marker) and LYZ1 (Paneth cell marker) expression in remnant SPDEF-expressing tumor cells. We did not detect goblet or Paneth cell hyperplasia in SPDEF-expressing tumors (Figure 3D), and SPDEF/MUC2+ or SPDEF/LYZ1+ tumor cells were rarely found in these mice (Figure 3D). Furthermore, SPDEF-expressing tumor cells did not express the enterocyte marker DPPIV (Figure 3E). Consistent with these observation in vivo, the mRNA level of secretory cell specific genes, such as Atoh1, Muc2, Defa1, Lyz1, and Chga, were not increased upon SPDEF induction in mouse tumor enteroids (Figure 3F). Taken together, these results indicated that SPDEF does not promote terminal differentiation of tumor cells.
SPDEF promotes tumor quiescence.
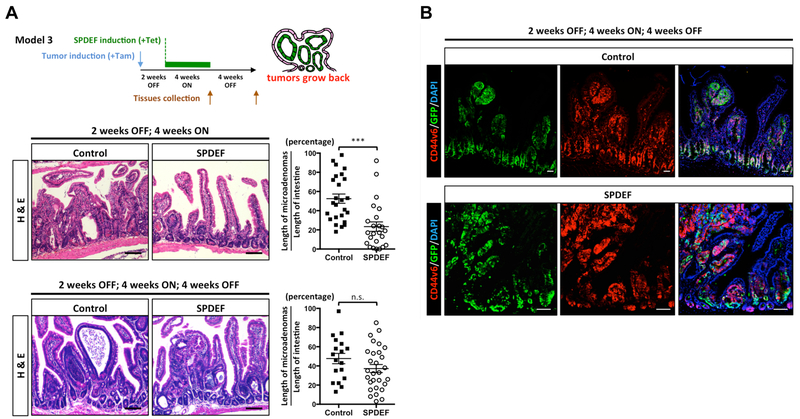
To examine whether these G0 phase SPDEF-expressing tumor cells are truly quiescent, we directly tested whether these cells can re-enter the cell cycle upon SPDEF withdrawal. To this end, we induced tumor formation with tamoxifen, and after 2 weeks controlled SPDEF expression by feeding control mice or SPDEF mice tetracycline water for 4 weeks, then withdrew tetracycline for another 4 weeks (Model 3; Figure 4A). As expected, tumors were significantly smaller after SPDEF expression for 4 weeks (Figure 4A; 2 weeks OFF, 4 weeks ON). However, after withdrawal of tetracycline, hyper-proliferating tumors re-grew in the SPDEF mice (Figure 4A; 2 weeks OFF, 4 weeks ON, 4 weeks OFF). The tumor burden and morphology of the re-grown tumors is highly comparable to those in control mice (Figure 4A). Expression of CD44v6 and GFP confirmed that re-grown tumors were derived from tissues that had previously expressed SPDEF (Figure 4B). Taken together, these results indicated that SPDEF induces in a quiescent state (G0 phase) in colorectal tumor cells, which is reversible after SPDEF withdrawal.
Figure 4. SPDEF promotes tumor quiescence.
(A) Intestinal microadenomas were allowed to grow for 2 weeks, followed by a 4 weeks ON; 4 weeks OFF tetracycline treatment (Model 3). Intestinal tissues from control mice (Lgr5CreERT2; β-cateninexon3; Rosa26LSL-rtta-ires-EGFP) or SPDEF mice (Lgr5CreERT2; β-cateninexon3; Rosa26LSL-rtta-ires-EGFP; TRE-Spdef) were collected at different time points followed by H&E staining. Quantitated result was shown. Each dot represents 1 mm length of intestinal epithelium randomly selected from jejunum. Wilcoxin test, Error bars, S.E.M., ***, p<0.001. Scale bars: 100 μm. (B) Immunofluorescent staining was performed by an anti-GFP and an anti-CD44v6 antibody. Scale bars: 100 μm.
SPDEF interacts with the ARM repeats of nuclear β-catenin via its Pointed domain.
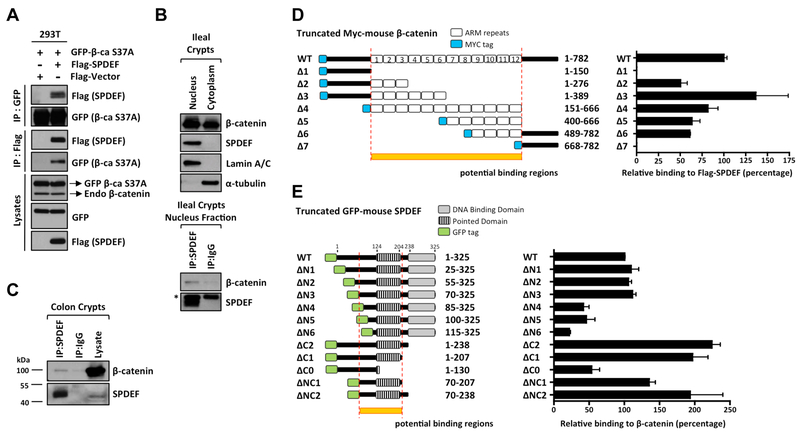
To better understand the role of SPDEF as a tumor suppressor, we next investigated the molecular mechanism underlying SPDEF-mediated tumor quiescence. Besides providing the driving force to intestinal tumorigenesis, the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway is critical for maintaining intestinal stem cell proliferation and self-renewal. β-catenin, as the key executor of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling, regulates Wnt-mediated gene activation20. Our previous studies suggested that SPDEF may physically interact with β-catenin12. Reciprocal immunoprecipitation and immunoblots confirmed the interaction between SPDEF and β-catenin bearing the oncogenic S37A mutation when co-transfected in HEK-293T cells. (Figure 5A). We next tested whether SPDEF could interact with β-catenin under their homeostatic conditions in mouse crypts. We performed nuclear and cytoplasmic fractionation in ileal crypts and found that the SPDEF is exclusively localized in the nuclear fraction (Figure 5B), and that SPDEF coimmunoprecipitated with β-catenin in the nuclear fraction, where β-catenin is in its transcriptionally active form (Figure 5B). Endogenous SPDEF and β-catenin interaction was also confirmed in mouse colonic crypts (Figure 5C). To further examine this protein-protein interaction, we mapped the protein domains required for the interaction between SPDEF and β-catenin. β-catenin is a scaffold molecule that consists of a N-terminal domain (residues 1–150), a central 12 Armadillo (ARM) repeats (residues 151–667), and a C-terminal domain (residues 668–782) (Figure 5D)20. Using a series of MYC-tagged, truncated β-catenin constructs, co-transfected with Flag-tagged full length SPDEF into HEK-293T cells, we found that SPDEF binds the ARM repeats of β-catenin, but not its N-terminal or C-terminal domains (Figure 5D, Supplementary Figure 3A). SPDEF consists of an undefined N-terminal polypeptide (residues 1–124), a central Pointed domain (residues 124–204), a linker region (residues 205–237), and a C-terminal ETS DNA-binding domain (residues 238–325) (Figure 5E). GFP-tagged truncated SPDEF constructs were transiently transfected into human colon cancer cell line HCT116 followed by immunoprecipitation. We found that β-catenin avidly interacts with the central region of SPDEF, especially residues 70–207 encompassing the Pointed domain (Figure 5E, Supplementary Figure 3B). Taken together, these results indicated that SPDEF interacts with the ARM repeats of β-catenin via its central Pointed domain. Of note, SPDEF mutants lacking the ETS DNA-binding domain (SPDEF ΔC1, ΔC2) bind to β-catenin stronger than full-length SPDEF (SPDEF WT), demonstrating that the DNA-binding domain of SPDEF is dispensable for this interaction (Figure 5E).
Figure 5. SPDEF interacts with the ARM repeats of β-catenin.
(A) HEK-293T cells were transiently transfected with the indicated plasmids. Immunoprecipitation was performed with an anti-FLAG or an anti-GFP antibody 48h post-transfection, and the precipitated SPDEF and β-catenin S37A were detected by the corresponding antibodies as indicated. The input lysates were probed for the expression of transfected Flag-SPDEF, GFP-β-catenin S37A and endogenous β-catenin. (B) Ileal crypts were purified from mice followed by nucleus/cytoplasm fractionation. Lamin A/C and α-tubulin were used as the internal control for nucleus and cytoplasm fractions, respectively. Only nuclear fraction was used for the immunoprecipitation of endogenous SPDEF. The asterisk indicates non-specific binding. (C) Colonic crypts were purified from mice and whole crypt lysates were used for the immunoprecipitation of endogenous SPDEF. (D) Schematic illustration of truncated MYC-tagged mouse β-catenin constructs. HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with Flag-tagged full-length SPDEF and MYC-tagged β-catenin mutants. Reciprocal immunoprecipitations were performed by an anti-FLAG or an anti-MYC antibody 48h post-transfection. Quantitation of relative binding of β-catenin mutants to SPDEF derived from three independent experiments was shown. (E) Schematic illustration of truncated GFP-tagged mouse SPDEF constructs. HCT116 were transfected with GFP-tagged SPDEF mutants. The endogenous β-catenin was immunoprecipitated by an anti-β-catenin antibody 48h post-transfection. Quantitated result of relative binding derived from three independent experiments was shown. Error bars, S.E.M..
SPDEF inhibits canonical Wnt/β-catenin transcriptional activity.
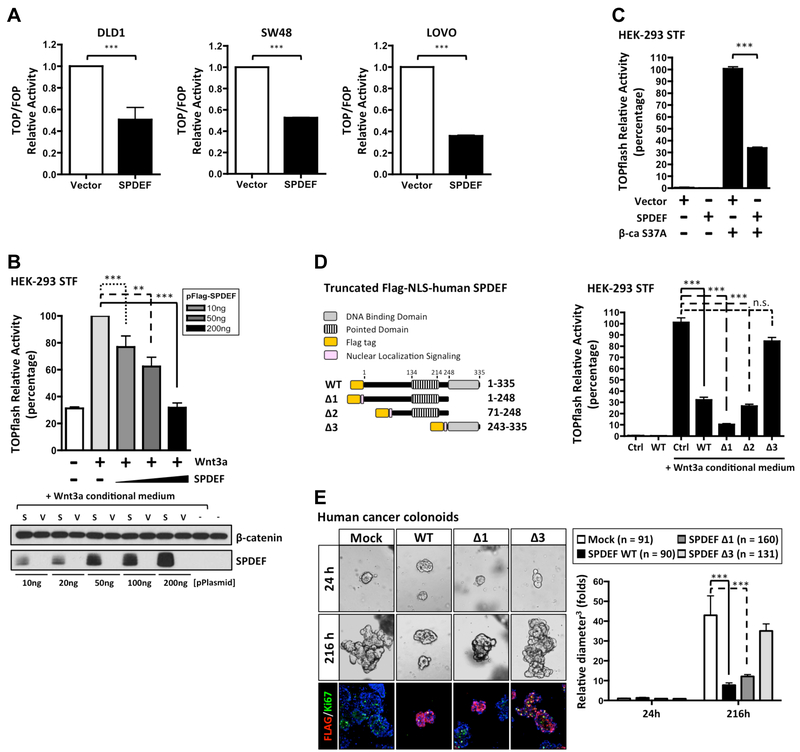
To further test the inhibitory capacity of SPDEF on β-catenin transcriptional activity, we selected three CRC lines, DLD1, LOVO, and SW48, which contain either gain of function β-catenin mutations, or loss of function APC mutations, thus resulting in continuous hyperactivation of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling21. Consistent with our previous studies in SW480 and HCT11612, transient overexpression of SPDEF is sufficient to inhibit β-catenin transcriptional activity (Figure 6A). To test whether SPDEF exhibits dose-dependent inhibitory activity, Flag-tagged SPDEF or empty vector plasmids were co-transfected into HEK-293T Super TOPflash cells (containing a Wnt/β-catenin responsive luciferase reporter). Unlike human CRC lines, in HEK-293T cells canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling is intact and TOPflash-luciferase can be activated by extracellular Wnt ligand. Consistent with our hypothesis, Wnt-activated TOPflash luciferase was inhibited by SPDEF in a dose dependent manner (Figure 6B). Similarly, SPDEF inhibited oncogenic S37A β-catenin induced reporter activity (Figure 6C). Taken together, these results suggested that SPDEF inhibits both ligand- and oncogene-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling transcriptional activity.
Figure 6. SPDEF inhibits β-catenin transcriptional activity through protein-protein interaction.
(A) Human colon cancer lines were co-transfected with TOPflash or FOPflash, with Flag-tagged SPDEF and Renilla plasmids. β-catenin activity was detected by the dual luciferase assay 48h post-transfection. Quantitated result of relative β-catenin activity derived from three independent experiments was shown. (B) HEK-293T Super TOPflash cells were transfected with different amounts of Flag-tagged SPDEF plasmids as indicated. Canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway was activated by Wnt3a conditional medium 24h post-transfection. 48h post-transfection, the β-catenin activity was detected. Quantitated result of relative β-catenin activity derived from three independent experiments was shown. Immunoblot analysis showed the expression level of ectopic SPDEF and endogenous β-catenin. (C) HEK-293T Super TOPflash cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. 48h post-transfection, the β-catenin activity was detected. Quantitated result of relative β-catenin activity derived from three independent experiments was shown. (D) Schematic illustration of truncated Flag-tagged human NLS-SPDEF mutants. HEK-293T Super TOPflash cells were transfected with indicated NLS-SPDEF mutants. Canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway was activated by Wnt3a conditional medium 24h post-transfection. 48h post-transfection, the β-catenin activity was detected. (E) Human cancer colonoids stably transduced with pINDUCER20 expressing Flag-tagged human NLS-SPDEF mutants, and mock control were generated. Bright field images were taken after SPDEF induction as indicated by hours. Quantitated result indicated SPDEF WT and Δ1 inhibit cancer colonoid growth. Colonoid sizes (maximum diameter3) were normalized to the average size (maximum diameter3) of mock control after SPDEF induction at 24h. Error bars, S.E.M.. ***, p<0.001. **, p<0.005.
Because we found that mutant SPDEF lacking the ETS DNA-binding domain exhibits stronger interaction with β-catenin compared to wild type SPDEF (Figure 5E), we tested which SPDEF domains were necessary to inhibit β-catenin transcriptional activity. Full length Flag-tagged SPDEF (SPDEF WT, residues 1–335), truncated SPDEF lacking the DNA-binding domain (SPDEF Δ1, residues 1–248), SPDEF with only the central region (SPDEF Δ2, residues 71–248), and the DNA-binding-domain alone (SPDEF Δ3, residue 243–335) were and assayed for repressive activity (Figure 6D). SPDEF truncation mutants lacking the ETS DNA-binding domain lose their nuclear localization (data not shown). We therefore added a nuclear localization signal (NLS) adjacent to the Flag tag in these constructs, and confirmed the nuclear localization of each SPDEF construct (Supplementary Figure 4). SPDEF Δ1 and SPDEF Δ2 retained the ability to inhibit canonical Wnt-induced β-catenin transcriptional activity, comparable to SPDEF WT (Figure 6D). However, the ETS DNA-binding-domain alone (SPDEF Δ3) exhibited no effect on β-catenin transcriptional activity (Figure 6D). Consistent with this finding, human cancer colonoids engineered to inducibly express full-length SPDEF or SPDEF Δ1 inhibited cancer colonoid growth and Ki67 expression, however SPDEF Δ3 exhibited limited effect (Figure 6E). These results indicate that the inhibitory effect of SPDEF on β-catenin transcriptional activity is most likely mediated by protein-protein interaction, and is distinct from the traditional function of SPDEF as a DNA-binding transcription factor.
SPDEF selectively disrupts the binding between β-catenin and TCF family proteins.
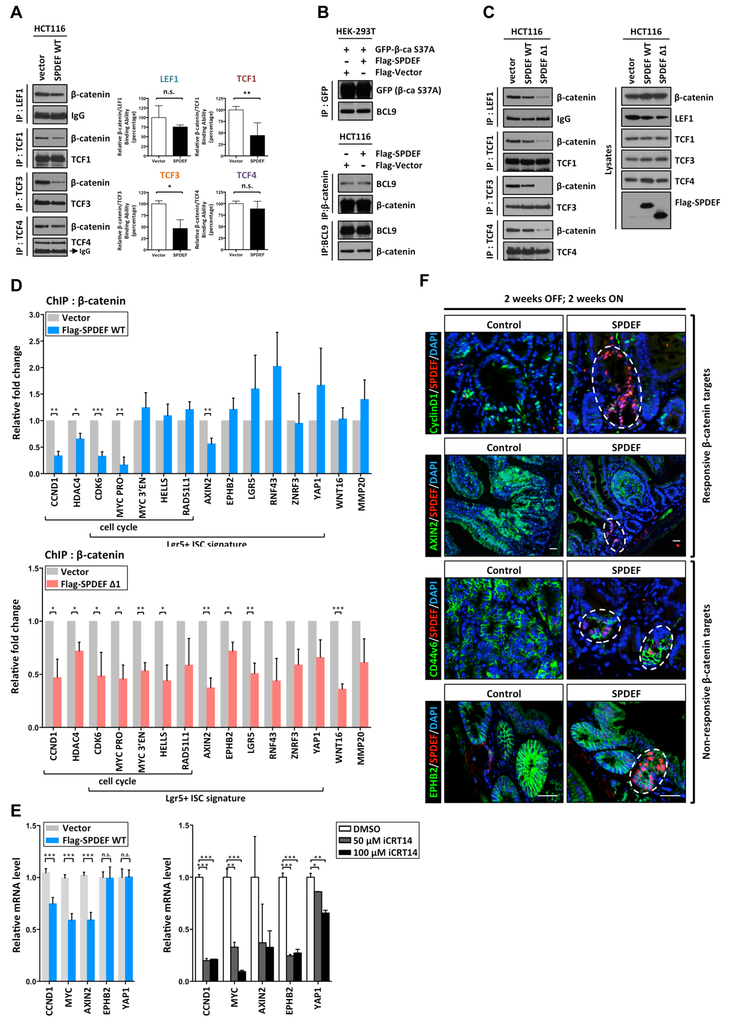
β-catenin contains no DNA-binding domain, and is recruited to chromatin via interaction with DNA-binding T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor (TCF/LEF) family proteins, LEF1, TCF1, TCF3, and TCF422. β-catenin binds to TCF/LEF proteins through ARM repeats 3–10 and then recruits other transcription cofactors, such as BCL9, to its target genes23. SPDEF interacts with ARM repeats 4–6 of β-catenin, which overlaps with the TCF/LEF binding regions (Figure 5D). Therefore, we hypothesized that SPDEF competes with TCF/LEF proteins for binding to β-catenin. To test this hypothesis, binding between TCF/LEF factors and β-catenin was assessed in HCT116 cells that inducibly express SPDEF. Following SPDEF expression, protein complexes containing LEF1, TCF1, TCF3, or TCF4 were immunoprecipitated to determine their binding to endogenous β-catenin (Figure 7A). Quantitative analysis indicated that SPDEF disrupted the binding between β-catenin and TCF1 or TCF3, but did not affect on the binding between β-catenin and LEF1 or TCF4 (Figure 7A). In addition, SPDEF exhibited no effect on the binding between β-catenin and BCL9, which interacts with the ARM repeats 1–2 of β-catenin (Figure 7B)24. Thus, SPDEF disrupts specific β-catenin/TCF1 and β-catenin/TCF3 complexes. Because SPDEF lacking its DNA-binding domain exhibited stronger binding to β-catenin (Figure 5E), we hypothesized that SPDEF Δ1 would show greater activity to competitively inhibit binding between β-catenin and TCF/LEF proteins. Consistent with this, we found that SPDEF Δ1 inhibits the binding between β-catenin and all TCF/LEF proteins (Figure 7C). Taken together, these results suggested that SPDEF selectively disrupts the binding between β-catenin and TCFs through competitive protein-protein interaction.
Figure 7. SPDEF selectively displaces β-catenin binding from the chromatin, resulting in the inhibition of β-catenin-mediated cell cycle machinery.
(A) Immunoprecipitation was performed with an anti-LEF1, an anti-TCF1, anti-TCF3, and an anti-TCF4 antibody respectively in HCT116 pINDUCER20 Flag-SPDEF WT and Vector control cell lines 48h post-doxycycline (1 μg/ml) induction. The precipitated β-catenin and LEF/TCFs interaction was detected by the antibodies as indicated. Quantitated result of relative binding derived from at least three independent experiments was shown. (B) HEK-293T and HCT116 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. The immunoprecipitation was performed 48hr post-transfection, and the precipitated β-catenin and BCL9 were detected by immunoblot analysis by the corresponding antibodies as indicated. (C) Immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-LEF1, anti-TCF1, anti-TCF3, and anti-TCF4 antibodies as indicated in HCT116 pINDUCER20 Flag-SPDEF WT, Flag-SPDEF Δ1 and Vector control cell lines 48h post-doxycycline (1 μg/ml) induction. The precipitated β-catenin and LEF/TCFs interaction was detected by immunoblot analysis. (D) Doxycycline inducible pINDUCER20 Flag-tagged SPDEF (Flag-SPDEF WT), pINDUCER20 Flag-tagged SPDEF Δ1 (Flag-SPDEF Δ1) and pINDUCER20 empty vector control (Vector) HCT116 stable lines were established. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) was performed with an anti-β-catenin antibody 48h post-doxycycline (1 μg/ml) induction. Relative β-catenin binding on chromatin (β-catenin targets) was quantified by qPCR as indicated. Quantitated result of relative binding derived from at least three independent ChIP experiments was shown. (E) Relative mRNA level of β-catenin targets was quantitated by RT-qPCR in Flag-SPDEF WT and Vector HCT116 stable lines 72h post-doxycycline (2 μg/ml) induction. Relative mRNA level of β-catenin targets was quantitated by RT-qPCR in HCT116 treated by DMSO or iCRT14 for 48h. (F) Mouse intestines from control mice or SPDEF mice (Model 2) were collected followed by immunofluorescent staining. The expression of β-catenin targets, CYCLIND1 and AXIN2, but not CD44v6 and EPHB2 were reduced in SPDEF-expressing tumor cells. The white line outlines SPDEF-expressing tumor cells. Scale bars: 20 μm. Error bars, S.E.M., ***, p<0.001; **, p<0.005; *. P<0.05.
SPDEF selectively displaces β-catenin from the promoter/enhancer regions of cell cycle genes without affecting the other ISC signature genes.
Based on the finding that SPDEF physically interacts with activated nuclear β-catenin and competitively inhibits the interaction between β-catenin and TCFs, we hypothesized that SPDEF displaces β-catenin from its targets on chromatin. To test the hypothesis, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiments were performed using HCT116 cells inducibly expressing SPDEF (Flag-SPDEF WT) or empty vector control (Vector) (Supplementary Figure 1). We selected fifteen previously validated β-catenin ChIP-seq targets in HCT116 cells, that were also members of the Lgr5-positive intestinal stem cell (ISC) signature gene set (Figure 7D, Supplementary Figure 5)25, 26. When we examined the effect of SPDEF expression on the interaction between β-catenin and these fifteen targets by anti-β-catenin ChIP-qPCR, we found that SPDEF decreased β-catenin binding to the promoter/enhancer regions of CCND1, HDAC4, CDK6, MYC, and AXIN2 (Figure 7D, upper panel). Of note, these genes are particularly important for Wnt/β-catenin- mediated cell cycle regulation. However, SPDEF did not affect β-catenin binding to other targets including LGR5, EPHB2, RNF43, YAP1, and ZNRF3 (Figure 7D, upper panel). To further extend this finding, HCT116 cells inducibly expressing DNA-binding domain-truncated SPDEF (Flag-SPDEF Δ1) were established to examine the effect of SPDEF Δ1 on the interaction between β-catenin and its targets. Consistent with our findings that SPDEF Δ1 is a stronger competitor of the interaction between β-catenin and all TCF/LEF proteins (Figure 5E, Figure 7C), we found that SPDEF Δ1 displaced β-catenin from all of these targets without selectivity (Figure 7D, bottom panel). Taken together, these results indicated that SPDEF is able to selectively displace β-catenin from the promoter/enhancer regions of cell cycle genes without affecting the other ISC signature genes.
To determine whether this novel molecular mechanism can functionally influence β-catenin-mediated transcription, we assessed the mRNA level of β-catenin targets in inducible Flag-SPDEF and control HCT116 cells. Consistent with our ChIP-qPCR results, the mRNA levels of CCND1, MYC, and AXIN2, but not EPHB2 and YAP1, were decreased after SPDEF expression (Figure 7E). In contrast, the mRNA levels of all β-catenin targets were significantly decreased after Wnt/β-catenin inhibitor (iCRT14) treatment (Figure 7E). These results indicated that SPDEF inhibits transcription of β-catenin-regulated cell cycle machinery without affecting other stem cell signature gene expression. Finally, to test this novel molecular mechanism in vivo, we assessed the protein levels of β-catenin targets in tumors from control and SPDEF-expressing mice (Model 2) (Figure 7F). Consistent with our ChIP- and RT-qPCR results, SPDEF selectively inhibited the expression of β-catenin targets. Compared to control tumors, SPDEF-expressing tumor cells expressed much less CCND1 and AXIN2, but maintained robust expression of CD44v6 and EPHB2 (Figure 7F). Taken together, these results suggested a novel function for SPDEF wherein it represses canonical Wnt/β-catenin transcriptional activity through selectively displacing β-catenin from chromatin targets.
Discussion
The vast majority of CRCs (>90%) have alterations resulting in activation of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which provide the driving force for cancer cell proliferation, migration, and metastasis2. Mutations of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), β-catenin (CTNNB1), AXIN2, or other pathway components cause the inappropriate stabilization and activation of β-catenin. Our previous studies showed that SPDEF is lost in most CRCs, and suggested that SPDEF is a colonic tumor suppressor12. In this study, we unveil for the first time a novel mechanism by which SPDEF directs intestinal tumor cells to switch between active and quiescent states, by shifting the transcriptional targets of activated β-catenin. We demonstrated that SPDEF is sufficient to inhibit β-catenin-driven intestinal tumor initiation and restrict established tumor growth in CRC xenografts, primary human cancer colonoids, and in a transgenic mouse model of intestinal tumorigenesis (Figure 1, Figure 2). In addition, SPDEF promotes cell cycle exit without promoting terminal differentiation of tumor cells, resulting in a quiescent state of β-catenin-driven tumors in vivo (Figure 3, Figure 4). In further exploration of this mechanism, we found that the DNA-binding domain of SPDEF is dispensable for the inhibitory effect of SPDEF on Wnt/β-catenin activity, suggesting that inhibition of β-catenin is mediated by protein-protein interaction, but not SPDEF’s DNA-binding transcriptional activity (Figure 5, Figure 6). Most importantly, we showed that SPDEF selectively displaces β-catenin from the promoter/enhancers of cell cycle genes without affecting genes important for stem cell identity (Figure 7); and this selectivity appears to be dependent on specific disruption of binding between β-catenin and TCF1 and TCF3, but not TCF4 and LEF1 (Figure 7). Taken together, this interaction between SPDEF and β-catenin represents a novel mechanism for modulating canonical Wnt/β-catenin transcriptional machinery, providing deeper insight into the molecular mechanism of β-catenin-driven oncogenesis, as well as SPDEF-mediated tumor suppression.
Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin transcriptional activity can be achieved by several mechanisms, including modified β-catenin degradation, localization, and protein complex formation27. Upon activation of Wnt signaling, β-catenin accumulates in the cytoplasm and then shuttles into the nucleus. We did not observe any change of β-catenin protein level in the nucleus or in the cytoplasm when SPDEF was overexpressed in human colon cancer cell lines, suggesting that SPDEF does not affect either β-catenin nuclear translocation or β-catenin protein stability (data not shown). Rather, SPDEF inhibits β-catenin transcriptional activity driven by intact Wnt-mediated signaling, as well as oncogenic APC/β-catenin mutation (Figure 6), suggesting that SPDEF’s effect is most likely exerted on activated, nuclear β-catenin through protein-protein interaction (Figure 5). This is further supported by results showing that truncated SPDEF lacking the DNA-binding domain retains its ability to inhibit β-catenin transcriptional activity and human cancer colonoid growth (Figure 6). However, we cannot exclude the possibility that the transcriptional function of SPDEF may play additional roles in this inhibitory effect.
Because β-catenin itself has no DNA-binding domain, β-catenin regulates gene expression by interacting with transcription factors of the TCF/LEF proteins. Upon binding to TCF/LEF proteins, β-catenin displaces TLE/Groucho repressor complexes and provides a platform for recruitment of transcriptional co-activators to initiate β-catenin-dependent transcription. Several transcription factors have been reported to share overlapping binding sites on the ARM repeats of β-catenin, including FOXM1, FOXO and KLF4, resulting in either up- or down- regulation of β-catenin transcriptional activity through distinct mechanisms28–30. For example, FOXM1 and β-catenin interaction enhances β-catenin nuclear localization and transcriptional activity29. In contrast, FOXO factors compete for TCF4 binding with β-catenin, thereby inhibiting β-catenin activity28. On the other hand, KLF4 inhibits β-catenin/TCF4 transcriptional activity by blocking the recruitment of co-activators31. Thus, the competition among binding partners for limited amounts of nuclear β-catenin is an important mechanism for regulating canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling and is in part responsible for the diversity of Wnt/β-catenin effects in specific cellular contexts. Unlike these other inhibitors of β-catenin transcriptional activity, SPDEF binds to the ARM repeats of β-catenin and disrupts the binding between β-catenin and specific TCF/LEF proteins, TCF1 and TCF3 (Figure 5, Figure 7). Consistent with this observation, SPDEF is unique in demonstrating specificity in inhibiting a subset of β-catenin targets (Figure 7). We also found that a SPDEF mutant lacking its DNA binding domain exhibits stronger bind to β-catenin (Figure 5), disrupts β-catenin interaction with all TCF/LEFs (Figure 7), and loses the selectivity for displacing β-catenin from specific chromatin targets (Figure 7). Thus, this SPDEF mutant lacking the DNA-binding domain out-competes TCF/LEF family proteins for β-catenin interaction due to its stronger affinity for β-catenin than the full-length SPDEF. Alternatively, SPDEF’s DNA binding domain may confer selectivity for specific promoter/enhancer regions. Further studies to identify SPDEF binding partners and to assess their interaction with β-catenin/TCF transcription complexes at the chromatin level could unveil the mechanism underlying selective repression of β-catenin targets by SPDEF.
Under homeostatic conditions, a gradient of canonical Wnt/β-catenin activity is generated from the bottom of the crypts, where the stem cell reside, to the rapidly cycling transit amplifying cells in the upper crypt32. Among these cells at the small intestinal crypt base, non-cycling Paneth cells, which express SPDEF, are highly specialized intestinal secretory cells that reside intercalated among cycling LGR5-positive crypt base columnar (CBC) intestinal stem cells10, 12, 33. Paneth cells provide essential niche signals to regulate the activity of CBC cells34. Interestingly, previous studies have indicated that active β-catenin, visualized by strong nuclear β-catenin expression in Paneth cells, is essential for Paneth cell maturation, implying that Wnt/β-catenin signals can separately drive a CBC intestinal stem cell program and a Paneth cell gene program through an unknown mechanism35. We have observed endogenous nuclear SPDEF and β-catenin interaction in mouse crypts (Figure 5B); in this context, SPDEF may play an important role in conferring a unique β-catenin transcriptional program to the non-cycling Paneth cells that is distinct from the transcriptional program in adjacent, cycling LGR5-positive CBC cells. We have also noted a recent study suggesting that a subpopulation of pre-Paneth progenitors can revert to CBC cells upon injury, and thus embody quiescent stem cell properties36. We hypothesize that SPDEF may re-target β-catenin to a distinct target gene repertoire, which directs the terminal differentiation of CBCs into Paneth cells. Furthermore, we speculate that loss of the SPDEF-β-catenin interaction allows reversion of Paneth cell progenitors to the CBC fate. Further studies to determine whether SPDEF, or any other transcription factor, has the potential to shift transcriptional targets of activated β-catenin in different cellular contexts will expand our current knowledge on both cancer biology and stem cell biology of the intestinal cells.
As a direct target of ATOH1, SPDEF can amplify ATOH1-dependent transcription in a subset of mature secretory cell genes8. Moreover, SPDEF itself is not sufficient to drive these genes’ expression in the absence of ATOH18. This epistatic relationship between ATOH1 and SPDEF might explain why terminal differentiation does not occur after SPDEF re-expression in Wnt/β-catenin-driven tumors because ATOH1 is usually silenced due to either epigenetic regulation or post-translational modification37, 38.
In conclusion, our study has shed light on a novel molecular mechanism underlying SPDEF-mediated colorectal tumor repression. These studies not only improve our current understanding of the modifiable transcriptional network that is initiated by canonical Wnt/β-catenin activation and β-catenin-driven tumorigenesis in the presence or absent of SPDEF, but also provide a potential unexplored strategy to bring the proliferating tumor cells into a quiescent state for tumor prevention or treatment.
Supplementary Material
Grant Support.
NIH U01 DK103117; NIH R01 CA142826; NIH P30 DK056338; NIH R01 DK092306; NIH P30 CA016672; NCI F99CA212433; a gift from the Feinberg Family to E.V.; the Janice Davis Gordon Memorial Postdoctoral Fellowship in Colorectal Cancer Prevention to E.B.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Disclosures. The authors disclose no conflicts.
References
- 1.Borras E, San Lucas FA, Chang K, et al. Genomic Landscape of Colorectal Mucosa and Adenomas. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2016;9:417–27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Clevers H, Nusse R. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 2012;149:1192–205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhu L, Gibson P, Currle DS, et al. Prominin 1 marks intestinal stem cells that are susceptible to neoplastic transformation. Nature 2009;457:603–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Barker N, Ridgway RA, van Es JH, et al. Crypt stem cells as the cells-of-origin of intestinal cancer. Nature 2009;457:608–11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Buchwalter G, Hickey MM, Cromer A, et al. PDEF promotes luminal differentiation and acts as a survival factor for ER-positive breast cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2013;23:753–67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cheng XH, Black M, Ustiyan V, et al. SPDEF inhibits prostate carcinogenesis by disrupting a positive feedback loop in regulation of the Foxm1 oncogene. PLoS Genet 2014;10:e1004656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Horst D, Gu X, Bhasin M, et al. Requirement of the epithelium-specific Ets transcription factor Spdef for mucous gland cell function in the gastric antrum. J Biol Chem 2010;285:35047–55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lo YH, Chung E, Li Z, et al. Transcriptional Regulation by ATOH1 and its Target SPDEF in the Intestine. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;3:51–71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shroyer NF, Helmrath MA, Wang VY, et al. Intestine-specific ablation of mouse atonal homolog 1 (Math1) reveals a role in cellular homeostasis. Gastroenterology 2007;132:2478–88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gregorieff A, Stange DE, Kujala P, et al. The ets-domain transcription factor Spdef promotes maturation of goblet and paneth cells in the intestinal epithelium. Gastroenterology 2009;137:1333–45 e1–3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Noah TK, Kazanjian A, Whitsett J, et al. SAM pointed domain ETS factor (SPDEF) regulates terminal differentiation and maturation of intestinal goblet cells. Exp Cell Res 2010;316:452–65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Noah TK, Lo YH, Price A, et al. SPDEF functions as a colorectal tumor suppressor by inhibiting beta-catenin activity. Gastroenterology 2013;144:1012–1023 e6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Moussa O, Turner DP, Feldman RJ, et al. PDEF is a negative regulator of colon cancer cell growth and migration. J Cell Biochem 2009;108:1389–98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, et al. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature 2007;449:1003–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Harada N, Tamai Y, Ishikawa T, et al. Intestinal polyposis in mice with a dominant stable mutation of the beta-catenin gene. EMBO J 1999;18:5931–42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Flora A, Klisch TJ, Schuster G, et al. Deletion of Atoh1 disrupts Sonic Hedgehog signaling in the developing cerebellum and prevents medulloblastoma. Science 2009;326:1424–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zeilstra J, Joosten SP, van Andel H, et al. Stem cell CD44v isoforms promote intestinal cancer formation in Apc(min) mice downstream of Wnt signaling. Oncogene 2014;33:665–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wielenga VJ, Smits R, Korinek V, et al. Expression of CD44 in Apc and Tcf mutant mice implies regulation by the WNT pathway. Am J Pathol 1999;154:515–23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cheung TH, Rando TA. Molecular regulation of stem cell quiescence. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2013;14:329–40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Valenta T, Hausmann G, Basler K. The many faces and functions of beta-catenin. EMBO J 2012;31:2714–36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ilyas M, Tomlinson IP, Rowan A, et al. Beta-catenin mutations in cell lines established from human colorectal cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1997;94:10330–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cadigan KM, Waterman ML. TCF/LEFs and Wnt signaling in the nucleus. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2012;4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kramps T, Peter O, Brunner E, et al. Wnt/wingless signaling requires BCL9/legless-mediated recruitment of pygopus to the nuclear beta-catenin-TCF complex. Cell 2002;109:47–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sampietro J, Dahlberg CL, Cho US, et al. Crystal structure of a beta-catenin/BCL9/Tcf4 complex. Mol Cell 2006;24:293–300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bottomly D, Kyler SL, McWeeney SK, et al. Identification of {beta}-catenin binding regions in colon cancer cells using ChIP-Seq. Nucleic Acids Res 2010;38:5735–45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Munoz J, Stange DE, Schepers AG, et al. The Lgr5 intestinal stem cell signature: robust expression of proposed quiescent ‘+4’ cell markers. EMBO J 2012;31:3079–91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell 2009;17:9–26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hoogeboom D, Essers MA, Polderman PE, et al. Interaction of FOXO with beta-catenin inhibits beta-catenin/T cell factor activity. J Biol Chem 2008;283:9224–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhang N, Wei P, Gong A, et al. FoxM1 promotes beta-catenin nuclear localization and controls Wnt target-gene expression and glioma tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2011;20:427–42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yang F, Li X, Sharma M, et al. Linking beta-catenin to androgen-signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 2002;277:11336–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Evans PM, Chen X, Zhang W, et al. KLF4 interacts with beta-catenin/TCF4 and blocks p300/CBP recruitment by beta-catenin. Mol Cell Biol 2010;30:372–81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fevr T, Robine S, Louvard D, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin is essential for intestinal homeostasis and maintenance of intestinal stem cells. Mol Cell Biol 2007;27:7551–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Clevers HC, Bevins CL. Paneth cells: maestros of the small intestinal crypts. Annu Rev Physiol 2013;75:289–311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sato T, van Es JH, Snippert HJ, et al. Paneth cells constitute the niche for Lgr5 stem cells in intestinal crypts. Nature 2011;469:415–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.van Es JH, Jay P, Gregorieff A, et al. Wnt signalling induces maturation of Paneth cells in intestinal crypts. Nat Cell Biol 2005;7:381–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Buczacki SJ, Zecchini HI, Nicholson AM, et al. Intestinal label-retaining cells are secretory precursors expressing Lgr5. Nature 2013;495:65–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bossuyt W, Kazanjian A, De Geest N, et al. Atonal homolog 1 is a tumor suppressor gene. PLoS Biol 2009;7:e39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tsuchiya K, Nakamura T, Okamoto R, et al. Reciprocal targeting of Hath1 and beta-catenin by Wnt glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in human colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2007;132:208–20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.