Abstract
Background:
Hyperuricemia is implicated in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases and metabolic disorders. Metabolic syndrome (MetS) in childhood is one of the most important causes of different noncommunicable diseases in adulthood. This study aimed to systematically review the association between serum uric acid (UA) concentration and components of pediatric MetS.
Materials and Methods:
In this meta-analysis and systematic review, related articles were gathered by searching English databases including PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and Google Scholar. We used the following keywords: uric acid, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, fasting blood sugar (FBS), hyperglycemia; the search was limited to English language and included observational and cohort studies performed among children or adolescents. Pooled relative risks (odds ratio [OR]) and corresponding 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were extracted. A random-effect model was used.
Results:
On the basis of 34 eligible studies, the pooled correlation between UA with metabolic components including FBS (r = 0.24, 95% CI = 0.09–0.40), fasting insulin (r = 0.26, 95% CI = 0.15–0.37), and hyperglycemia (r for triglyceride and UA = 0.23, 95% CI = 0.19–0.38) (r for high-density lipoprotein and UA = −0.28, 95% CI = −0.37 to −0.20) was statistically significant. The association of both diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and systolic blood pressure (SBP) was statistically significant with UA (r for SBP and UA = 0.34, 95% CI = 0.24–0.43; r for DBP and UA = 0.18, 95% CI = 0.11–0.25). The OR between risk of abdominal obesity with UA was statistically significant (OR = 2.62, 95% CI = 1.41–3.84).
Conclusion:
Serum UA concentration is associated with major components of the pediatric MetS. Its measurement and control should be underscored in at-risk children and adolescents.
Keywords: Abdominal obesity, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, hypertension, hyperuricemia, metabolic syndrome, uric acid
INTRODUCTION
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a group of adverse cardiometabolic risk factors.[1,2,3,4,5,6,7] It was first considered as a condition of adults and linked to their morbidity and mortality.[8] More recently, children have been identified to have MetS.[9] Data from the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey indicate that the prevalence of pediatric MetS increased from 4% to 9% from 1988 to 2006, with a prevalence of 30%–50% in obese children.[9,10,11,12] By rapid lifestyle change, pediatric MetS has also become a problem in developing countries.[10,11,12] Given the escalating trend of childhood obesity, pediatric MetS would become more prevalent in future years.[13] The process of atherosclerosis origins from early life and is linked to the MetS components even from childhood.[14] In addition to related health burden, it would also lead to a large economic burden in terms of hospital costs for chronic diseases.[15,16] Moreover, MetS would result in various disorders, including fibrinolysis, thrombosis, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction, as well as chronic noncommunicable diseases.[1,9,17,18,19,20]
MetS is a cluster of factors that include general or central adiposity, elevated blood pressure (BP), dyslipidemia, low level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), hyperglycemia, and hypertension. As obesity is the main factor of MetS, rapid increase in the prevalence of pediatric MetS and its long-term consequences in adulthood are anticipated.[21,22]
Uric acid (UA) is produced by liver as the last item in the dietary and endogenous purine metabolism mechanisms; it is excreted by the kidneys.[23] Although UA can be effective in the human body for its neuroprotective effects, it destroys free radicals and applies an antioxidant. Moreover, its role as the induction of platelet aggregation and chronic systemic inflammation has adverse health effects.[24,25,26] Hyperuricemia is a pathologic description of increased serum UA levels (SUALs). There are several mechanisms considered for hyperuricemia; it may occur exogenously from purine-rich diet or endogenously from increased production, as in malignancies and inborn errors of metabolism, as well as in decreased renal clearance.[27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34] Hyperuricemia increases the risk of comorbidities such as hypertension, renal diseases, and cardiovascular diseases.[35]
Multiple mechanisms are involved in the relationship between UA and obesity.[36] Obesity, especially its abdominal type, increases the activity of xanthine oxidase in the adipose tissues and would result in higher UA production and lower UA renal clearance.[33,37,38,39] Considering that gout is associated with elevated triglyceride (TG) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) in the gout, it can be suggested that dyslipidemia, as a MetS component, might be related to UA.[40,41,42,43] Furthermore, human hypertension may be developed by the key role of hyperuricemia; therefore, UA might increase the risk of MetS by rising another component of this inflammatory cluster.[44,45] Based on epidemiological and observational studies, MetS is highly prevalent in adults.[46,47] Carbone et al. have described the results from four longitudinal and 12 cross-sectional studies regarding the association between UA levels and MetS in adults.[48] The meta-analysis of Yuan et al. included 11 studies on the relationship between UA levels and the MetS in adults. It showed that elevated UA level was an important factor for increasing the risk of MetS.[49] MetS also commonly has been seen in children.[1,14] Moreover, many cross-sectional and longitudinal investigations showed the relation between UA and MetS in both children and adults in different ethnic populations.[2,3,4] Besides, the importance of the role of UA in MetS in the group of obese children was shown.[5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13] Both of the review articles on relation between MetS and UA included studies on adults and did not investigate the components of MetS separately. The current study aims to systematically review the relationship between SUAL and components of MetS in the pediatric age group.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This systematic review has been guided by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses statement.[50,51] The review focuses on the relation between SUAL and MetS in children and adolescents.
Search strategy and data sources
In July 2019, a systematic literature search was performed in the electronic databases of Web of Science, PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar; then, the search was updated in September 2019. The detailed search strategy for PubMed is presented in Supplementary Material 1. The following MeSH keywords were used: (“Uric acid” [Mesh]) OR “Uric acid” OR Hyperuricemia OR UA OR SUAL AND (“Metabolic Syndrome” [Mesh] OR “Metabolic Syndrome” OR “Metabolic Syndromes” OR “metabolic syndrome” OR “syndrome x” OR “insulin Resistance” OR “dysmetabolic Syndrome” OR “obesity” OR “diabetes mellitus” OR “Hypertriglyceridemia” OR “hyperlipidemia” OR “hypercholesterolemia” OR “hypocholesterolemia” OR “dyslipidemia” OR “hyperinsulinism” OR “hyperglycemia” OR “hypertension”) AND (“Child AND adolescent” [Mesh]) OR “child AND adolescent” OR “children AND adolescent.”
Supplementary Material 1.
Data sheet I search strategy
| Data bases | Number of searched articles |
|---|---|
| Scopus | 143 |
| Web of Science | 1230 |
| PubMed | 407 |
| Google Scholar | 300 |
| Total | 2080 |
Study selection
All identified articles were initially imported into Endnote X8 software [Clarivate Analytics (formerly Thomson Reuters), Philadelphia, PA, USA], and the duplicate records were removed. Two reviewers (PG and RR), a physician and a biostatistician, then independently screened each abstract and full-text article against the predefined inclusion/exclusion criteria. Only those records that were included by both reviewers were considered for the final review step. In the case of disagreement, a third researcher (ShD) specialist in Health Education and Health Promotion was consulted; the consensus was negotiated with a pediatrician, as the senior researcher of the study (RK). Discrepancies were resolved by discussion and consensus among the researchers. Reference lists of the eligible studies were also checked manually to ensure no potentially relevant article would be missed.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) studies conducted in children and adolescents; (2) observational/cohort studies; (3) investigating the association of UA with MetS and its components including BP, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and/or obesity; (4) available full-text article; (5) written in English; and (6) published before September 2019. If study populations overlapped between studies, only the most extensively described study was included. Interventional studies were excluded.
Outcome variables
The outcome variables consisted of pediatric MetS and its components (qualitative and quantitative variables) based on the WHO definition including abdominal obesity, hyper-TG, low HDL-cholesterol (HDL-C), elevated systolic or diastolic BP (SBP or DBP), and elevated fasting blood sugar (FBS).
Data extraction
The following study characteristics were collected in Excel: authors, year of publication, location, participants’ characteristics (gender, age, number of participants), study type, and covariate variables. Appropriate effect size (odds ratio [OR], regression coefficient, and correlation coefficient) or standard error were extracted from the different adjusted models of included studies in this meta-analysis. In the case which used regression coefficient, it was changed to correlation coefficient.
Risk of bias and quality assessment
Risk of bias and quality of studies in the eligible criteria was assessed using The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) checklist[52] by two reviewers (PG and ShD) with regard to selection bias, detection bias, performance bias, and loss to follow-up. Three categories for quality assessment were established arbitrarily: (1) when the study fulfilled more than 80% criteria stated in STROBE; (2) when 50%–80% of STROBE criteria were fulfilled; and (3) if less than 50% criteria could be achieved.
Statistical analysis
The desired pooled effect size was considered as a correlation coefficient and OR with 95% confidence interval (CI). We used the forest plot to investigate the association between serum UA and MetS components in the pediatric age group. The fixed-effect model was used according to the nonexistence of significant heterogeneity. The Z-test was used to assess the significance of the pooled effect size; P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Heterogeneity between the included studies was assessed by Cochran’s Q statistic, which was quantified by calculating the inconsistency index (I2). In cases with high heterogeneity among studies (substantial heterogeneity considered as I2 > 50%), the random-effect model with DerSimonian and Laird method was used.[53] In addition, we used the meta-regression analysis (based on the age and body mass index [BMI]) to identify the source of heterogeneity. We assessed potential publication bias using funnel plots (not shown) and both Begg’s and Egger’s tests. The sensitivity analysis was conducted to assess the extent of the influence of omitting individual studies on the pooled OR. A P < 0.05 from both Begg’s and Egger’s tests and asymmetrical shape of the funnel plot showed statistically significant publication bias. The analysis was conducted by the Stata software, version 11.2 (STATA Corp, College Station, TX, USA).
RESULTS
Description of the studies
Of 1480 titles and abstracts screened, 370 studies were extracted for detailed evaluation, of which 34 adhered to our inclusion criteria [Figure 1]. They comprised seven prospective and 24 cross-sectional studies including 50,150 participants aged 2–18 years. The number of participants ranged from 128 to 6768. The WHO criteria were used in 33 studies, whereas the criteria of Adult Treatment Panel III modified for the pediatric age group were used in one study. The characteristics of all included studies are presented in Table 1.
Figure 1.
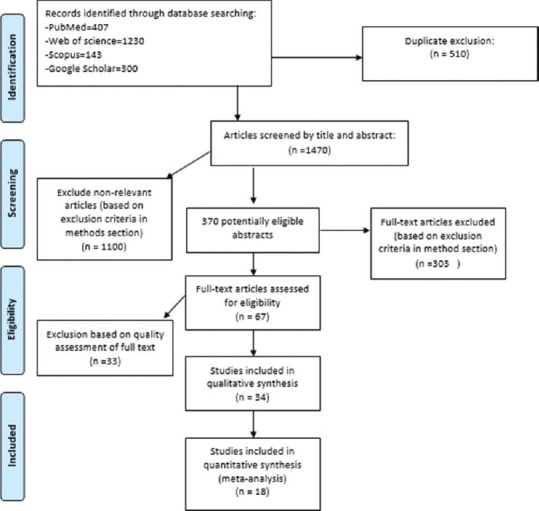
Flow diagram of the inclusion process
Table 1.
Characteristics of studies included in the review
| ID | First author name, publish year/location | Type of study | Sample size | Age group (years) | Gender | Outcome | Adjusted covariates | Finding |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | D Kızılay (2019), Turkey | Cross-sectional | 128 | 8-18 | Girl/boy | WC, HC, insulin/FBS, HDL-LDL, TG, total cholesterol, BP, AST, ALT, UA | Age and sex | ↑SUAL was correlated with ↑TG, ↑WC, ↓HDL. Not related to BP |
| 2 | E Lurbe (2018), European origin | Cross-sectional | 333 | 5-18 | Girl/boy | BP, HDL, TG, insulin, BMI, WC, UA, LDL | Age and pubertal stage | Participants with three or more metabolic risk factors showed ↑SUAL. and ↑SUAL is related to ↑WC |
| 3 | E Patrícia (2018), Germany | Cross-sectional | 458 | 6-18 | Girl/boy | FBS, TG, HDL, BP, cysteine, C-peptide | Sex, age | ↑SUAL was associated with, ↑SBP; ↓HDL |
| 4 | L Reis (2018), Brazil | Cross-sectional | 2335 | 7-17 | Girl/boy | BP, UA, BMI | Sex, age | ↑SUL was related to↑SBP and↑DBP |
| 5 | B Park (2017), South Korea | Cohort | 449 | * | Girl/boy | UA, BMI, BP | Sex, current height, and body mass index | The group with a↑SUL had significantly increased SBP (96.4 mmHg [95% CI: 94.7-98.0] vs. 93.3 mm Hg [95% CI: 91.8-94.8]; P<0.01) and DBP (62.3 mm Hg [95% CI: 60.9-63.7] vs. 59.5 mm Hg [95% CI: 58.2-60.8]; P<0.01) at 3 years of age |
| 6 | E Perez (2017), Mexico | Cross-sectional | 59 | 6-9 | Girl/boy | BP, BMI, TG, HDL, LDL, UA, WC, tanner stage, total cholesterol | Gender-age-BMI | The results show that with one unit difference (1 unit=1 mg/dL) in UA, there were 3.9 times more likely to have a MetS diagnosis. ↑SUAL are associated with↑WC, ↑TG and↓HDL |
| 7 | L Scheepers (2017), Germany | Cross-sectional | 246 | 6-7 | Girl/boy | BP, BMI, UA, xanthine, hypoxanthine | Age, sex, and BMI Z-scores and place and mode of delivery, maternal smoking during pregnancy (active and passive), total physical activity, and nutrition intake at 4 years of age (total energy intake [kcal], energy from carbohydrates [%] and energy from protein [%] and fiber intake [g]) | Multivariable analysis showed that a 1 SD (38 mmol/l) ↑SUAL was associated with↑DBP, no association was found with SBP |
| 8 | B Jones (2017), Indiana | Cross-sectional | 57 | Preadolescents | Girl/boy | Salivary UA, salivary C, peptide, BP | Age, gender, family income, and education level | These analyses did not yield any significant associated with HTN risk for children |
| 9 | N Li (2017), Tianjin | Cross-sectional | 4073 | 3-6 | Girl/boy | SUA, BP, TG | History of mother and father regarding gout, education of mother and father, family income, and health history of parents in addition to all variables listed in the model | The prevalence of hyperuricemia increased among children with overweight (9.9%) and obesity (18.9%) (P for trend <0.001). Children with↑DBP or↑TG (≥1.70 mmol/L) had higher prevalence of hyperuricemia |
| 10 | R Luciano (2017), Italy | Cross-sectional | 1364 | 4.1-17.9 | Girl/boy | SUA, BMI, WC, glucose, insulin, total cholesterol, HDL | Age, sex | There were statistically significant even weak correlations between SUA and WC (ρ=0.467). ↑SUA was also correlated with ↑TG (ρ=0.165), ↓HDL (ρ=−0.149), ↑FBS (ρ=−0.107, P<0.001) |
| 11 | S Safiri (2016), Iran | Cross-sectional | 367 | 10-18 | Girl/boy | BMI, WC, BP, HDL, LDL, SUA, TG, FBS | Age, living area, sex, PA, ST, and SES | The higher frequency of ↑BP associated with the ↑SUA tertiles. There were no significant differences in the number of metabolic syndrome components between tertiles of SUA, either. A↓HDL-C was associated with↑SUA |
| 12 | V Hirschler (2016), Argentina | Cross-sectional | 354 | 9.6±2.3 | Girl/boy | WC, serum magnesium, phosphorus | Age and gender | There was a significant association between WC and UA |
| 13 | H Sun (2015), Taiwan | Cohort | 8005 | 10-15 | Girl/boy | WC, BMI, BP, FBS, TG, HDL, LDL, UA | * | ↑SUAL was either the second or third best predictor of HTN in both genders. HTN was the most important predictor for MetS in these adolescents, and a↑SUAL only predicted future MetS in males |
| 14 | F Viazzi (2015), Sangerado Hospital | Cross-sectional cohort | 501 | 6-18 | Girl/boy | WC, pubertal stage, BP, glucose, insulin, total cholesterol, UA, HDL, BMI | Pubertal status, gender, BMI Z-score, and HOMA index | Children showed↑SUAL along with↑SBP (Z-score, r=0.21, P=0.001) and↑DBP (Z-score, r=0.11, P=0.02), ↑TG (r=0.23, P=0.001), ↑LDL, ↑cholesterol (r=−0.26, P=0.001) |
| 15 | A Alper (2015), Bogalusa | Cohort | 577 | 5-17 | Girl/boy | UA, BP, BMI | age, sex, race, childhood body mass index, childhood UA levels, and change in levels of UA | ↑SUAL was associated with↑SBP (r=0.31; P=0.0001) and↑DBP (r=0.20; P=0.0001) |
| 16 | Z Wang (2015), China | Cross-sectional | 936 | 11-16 | Boy/girl | BP, WC, TG, HDL, LDL, FBS, HbA1c, insulin, UA | * | BMI, WC, SBP, TG, were significantly higher in the highest SUA quartile (Q4) for both sexes. In all subjects, prevalence of MetS was higher in Q4 than Q1. No significant difference was observed between quartiles for SUA, FBS, or HbA1c in either gender. ↑SUAL was significantly associated with the↑abdominal obesity, ↑dyslipidaemia and↑HTN in Q4 in boys, and↑abdominal obesity and↑dyslipidaemia only in girls. The ORs (95% CI) of the highest quartile of SUA for MetS were 7.67 (95% CI=2.58-22.78) for boys and 4.77 (95% CI=1.01-22.60) for girls |
| 17 | E Ford (2014), US | Cross-sectional | 1370 | 12-17 | Girl/boy | TG, HDL, WC, glucose, SUA | Age, sex, race or ethnicity, and concentrations of C-reactive protein | ↑SUAL was associated with↑abdominal obesity, ↑hypertriglyceridemia, ↑hyperglycaemia. In addition, the association between high BP and concentrations of UA was of borderline significance. Concentrations of UA were significantly higher among teens with the metabolic syndrome (387.6 mol/L) than among those without the syndrome (319.7 mol/L) (P=0.001) |
| 18 | D Sun (2014), US | Cohort | 2614 | 4-18 | Girl/boy | BMI, MAP, TG, HDL, insulin, UA | Age | ↑SUAL was associated with↑BMI consistently whereas UA was associated with other MetS components in selected subgroups. UA showed associations with MetS (OR=1.53-2.59, P=0.01) across race-gender groups. The risk of MetS associated with an increase of one unit (mg/dL) of UA was 1.74 times higher in children |
| 19 | S Pan (2014), China | Cross-sectional | 3778 | 10-15 | Girl/boy | BP, WC, total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, BUN, Cr | Age, sex, ethnicity, total cholesterol, HDL, LDL, TGs, GFR, fasting glucose, BMI | Age, DBP, BMI, LDL, HDL, TG, fasting glucose, the incidence of high BP, and hyperglycaemia showed an increasing trend as the UA level increased |
| 20 | J Wang (2012), Taiwan | Cohort | 613 | <18 | Girl/boy | UA, BMI, WC, BP, TG, HDL, LDL, FBS | Age, for each component of the MetS | The variables including WC, BMI, SBP, DBP, HDL, and log TG were significantly different among the UA quartiles |
| 21 | S Civantos (2012), Madrid, Spain | Cross-sectional | 148 | 5-19 | Girl/boy | BMI, WC, BP, glucose, HDL, TG, insulin, UA | Age, sex | Patients with hyperuricemia had more WC (101.4 vs. 91.1 cm, P<0.001) and higher BP both systolic (123.4 vs. 111.9 mm Hg, P<0.001) and diastolic (78.2 vs. 68.7 mmHg, P<0.001). HDL levels were significantly lower in patients with hyperuricemia (49.5 vs. 54.4 mg/dl P=0.02) and TG levels were higher (110.7 vs. 97.6 mg/dl, P=0.1). There were no statistically significant differences in the levels of cholesterol or LDL. It was found that patients diagnosed with metabolic syndrome had higher levels of UA, (5.8 vs. 5.1 mg/dl, P=0.006). There were not statistically significant differences between hyperuricemia and waist size, TGs, fasting glucose |
| 22 | A Kong (2012), Hong Kong | Cross-sectional | 2067 | 6-20 | Girl/boy | BMI, LDL, HDL, BP, WC, glucose, LFT, TG, UA | Age, sex, and body mass index | High levels of UA (75th percentile) were associated with cardiovascular risk factors including overweight/obesity and high BP |
| 23 | L Loeffler (2012), US | Cross-sectional | 6036 | 12-17 | Girl/boy | SUA, BMI, BP | Age, sex, race/ethnicity, and BMI percentile | Participants with elevated BP had a mean UA of 5.6 mg/dL, compared to 5.0 mg/dL in the normal BP group (P=0.004). As UA quintile increased, participants were more likely to, have higher weight, height, BMI and systolic BP percentiles and have elevated BP |
| 24 | A Cardoso (2012), State of Paraíba, Brazil | Cross-sectional | 129 | 2 and 18 | Girl/boy | BMI, WC, BP, TG, HDL, insulin, UA | * | ↑SUAL were significantly associated with SBP, hypertriglyceridemia, and MetS. Also 4th quartile (percentile >75th for UA values) showed significantly higher values of BMI, WC, SBP, DBP, TG, and HOMA-IR, and lower mean of HDL-C |
| 25 | M Krzystek-Korpacka (2011), Poland | - | 184 | <17 | Girl/boy | WC, BP, puberty stage, C-peptide, glucose | Age, gender, BMI | Mean UA concentrations were significantly higher in patients who were overweight or obese, had MetS, ↑BP, hypertriglyceridemia, and low HDL-C |
| 26 | M DeBoer (2011), US | Cross-sectional | 3296 | 12-19 | Girl/boy | WC, BP, TG, HDL, glucose, SUA | Race, gender | Regarding MetS components commonly associated with elevated UA, HTN status, obesity status, and insulin status as each of these indices has been particularly tightly linked to UA elevations. ↑WC and↑insulin had↑SUAL |
| 27 | L Tang (2010), Amagasaki | Cross-sectional | 1027 | 6-14 | Girl/boy | BMI, WC, BP, TG, glucose, HDL, UA | Gender, age | Analysis revealed that hyperuricemia was independently associated with systolic BP, and HDL-C. On the other hand, no association was found between hyperuricemia and WC, DBP, TG, or fasting blood glucose |
| 28 | M Hongo (2010), Japan | Cross-sectional | 958 | 12.1-15.0 | Girl/boy | WC, BP, HDL, total cholesterol, TG, FBS, HbA1c, LDL, UA | Age, POW, and HbA1c | ↑SUAL was significantly associated with abdominal obesity, HTN, dyslipidemia and with HTN in the third quartile in boys, and it was associated with abdominal obesity in the highest quartile in girls. No significant association was found between quartiles of SUA and increased FBS in both genders. There were no correlations between percentage change in SUA and percentage changes in SBP, DBP, HDL-C, TG, or FBS |
| 29 | L Pacifico (2009), Italy | - | 120 | 10-11.2 | Girl/boy | Total cholesterol, HDL, Cr, UA, BMI, BP, FBS, insulin | Age, sex | ↑SUAL was associated with SBP, TGs, HDL-C. No correlation was found between UA and total cholesterol. When the association was restricted to the control group, UA levels were significantly correlated with BMI only. The mean concentrations of UA were significantly higher in the obese patients with MS compared with those without (0.32 [95% CI=0.30-0.34] vs. 0.27 [0.26-0.29]; P=0.0001) |
| 30 | M Gil-Campos (2009), Spain | - | 54 | 6-12 | Girl/boy | BMI, TS, SS, WC, BP, leptin, adiponectin, TNF, sex hormone (FSH, LH), glucose, C-peptide, insulin, UA | Sex, age | ↑SUAL was significantly higher in the obese children than in the normal weight controls. SUAL was correlated with↑SBP, DBP, ↑plasma insulin, ↑TG and↓HDL-C |
| 31 | P Muntner (2008), Bogalusa, Louisiana | Cohort | 517 | 5-17 | Girl/boy | BMI, BP, TG, HDL | Race and follow-up age, cigarette smoking, alcohol consumption, microalbuminuria | The mean SUAL was 6.56 mg/dL and 6.36 mg/dL for males with and without the metabolic syndrome, respectively, and 4.95 and 4.43 for females with and without the metabolic syndrome, the metabolic syndrome was associated with a 2.60 (1.08-6.27) and 3.01 (1.34-6.75) higher odds of elevated SUA for both gender |
| 32 | D Jones (2008), Tennessee | - | 104 | 6-18 | Girl/boy | SUA, BP | Age, race, gender BMI Z-score, 24-h and night-time SBP and DBP | Mean SUAL were significantly higher among individuals with diastolic HTN. There were no significant differences in mean SUA between subjects with and without systolic HTN |
| 33 | D Feig (2003), Houston, TX, US | Cohort | 125 | 6-18 | Girl/boy | BP, SUA, BMI | BMI | A SUAL >5.5 mg/dL was useful in identifying children with primary HTN. A correlation is also present in secondary HTN between UA and SBP (r=0.4357, P=0.002) and between UA and DBP (r=0.3076, P=0.005) but is weak relative to that in primary HTN (graphical data not shown) |
| 34 | H Goldstein (1992), New Jersey | Cross-sectional | 6768 | 12-17 | Girl/boy | Weight, height, SBP, DBP, UA | Age, height, weight, sexual maturity | In White males, UA was a significant predictor of SBP (F1, 2854=11.41, P=0.0007) and SBP (F1, 2855=10.85, P<0.0001). In black males it is predictor of SBP (F1, 405=3.27, P=0.0713) only. For females UA was not a significant predictor of SBP. The subgroup analyses revealed a significant UA predictor effect for white males (F1, 2854=12.06, P=0.0005) and a trend for DBP (F1, 2845=4.74, P=0.0295) |
ALT=Alanine aminotransferase; G/B=Girl/boy, FBS=Fasting blood sugar; HDL-C=High-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; LDL=Low density lipoprotein; WC=Waist circumference; ↑=High; ↓=Low; UA=Uric acid; SUA=Serum UA; SUAL=SUA level; BMI=Body mass index; BP=Blood pressure; DBP=Diastolic BP; SBP=Systolic BP; TGs=Triglycerides; HTN=Hypertension; CI=Confidence interval; MeTS=Metabolic syndrome; HbA1c=Hemoglobin A1c; ORs=Odds ratios; POW=Percentage of overweight; AST=Aspartate aminotransferase; Cr=Creatinine; BUN=Blood urea nitrogen; HOMA-IR=Homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance; FSH=Follicle-stimulating hormone; ST=Screen time; PA=Physical activity; LFT=Liver function tests; ↑=High; ↓=Low
The association of uric acid with metabolic syndrome components
The correlation between SUAL and some MetS components was equivocal.[54] Some studies did not show any significant correlation between UA and fasting blood glucose; for instance, Tang et al. investigated a group of 6–14-year-old children and adolescents, Hongo et al. assessed a group of Japanese juniors, Wang et al. studied a group of high-school students, and Civantos Modino et al. investigated on 10–16-year-old adolescents.[54,55,56,57,58] On the other hand, some studies reported strong significant association between these factors.[59,60,61] Regarding waist circumference and abdominal obesity, except two cross-sectional studies, others reported that it had significant association with SUAL.[54,56] Studies on the association of BP with UA did not have enough agreement; for instance, Ford et al. reported borderline relationship, while Jones et al. and Goldstein and Manowitz did not find significant association between UA and SBP.[33,44,62] Some other studies showed significant relationship of UA with SBP, but not with DBP.[26,63,64]
Meta-analysis results
Correlation between metabolic syndrome components and uric acid
The forest plot with correlation coefficient (95% CI) for the associations between MetS components and serum UA in children and adolescents is shown in Figures 2 and 3.
Figure 2.
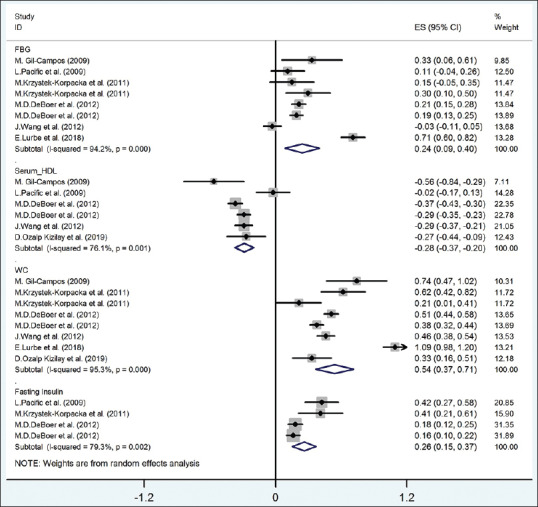
The forest plot of the correlation between metabolic syndrome components (FBG-HDL-fasting insulin) with serum uric acid. FBG = Fasting blood glucose; HDL = High-density lipoprotein; WC = Waist circumference
Figure 3.
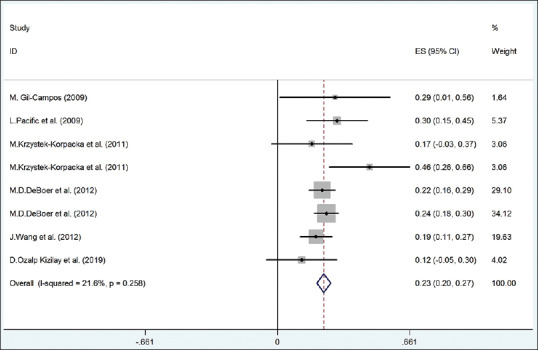
The forest plot of the correlation between metabolic syndrome components (TG) with serum uric acid. TG = Triglyceride
The pooled correlation between fasting blood glucose and UA, according to random-effect model, was significant (r = 0.24, 95% CI = 0.09–0.40) with 94.2% heterogeneity (I2 = 94.2%; P < 0.001). Results of meta-regression on age and BMI revealed that the correlation between fasting blood glucose with UA was significantly different according to BMI (β = 0.077, P = 0.002); the residual variation due to heterogeneity was equal to 54.25%. The pooled correlation between fasting insulin and UA (according to random-effect model) was statistically significant (r = 0.26, 95% CI = 0.15–0.37) with 79.3% heterogeneity (I2 = 79.3%; P < 0.001). As presented in Figure 2, the meta-regression did not show any correlation between fasting insulin and UA with was not significantly different according to age and BMI (P > 0.05).
The pooled correlation between serum TG and serum HDL with UA (according to random-effect model) was statistically significant (r for TG and UA = 0.23, 95% CI = 0.20–0.27 [from fixed-effect model]; r for HDL and UA = −0.28, 95% CI = −0.37 to − 0.20) with 21.6% (I2 = 21.6%; P = 0.258) and 76.1% heterogeneity (I2 = 76.1%; P < 0.001), respectively [Figures 2 and 3]. In meta-regression analysis, the correlation between serum HDL-C and UA was not significantly different according to age and BMI with (P > 0.05).
The pooled correlation between waist circumference and UA (according to random-effect model) was statistically significant (r = 0.54, 95% CI = 0.37–0.71) with 95.3% heterogeneity (I2 = 95.3%; P < 0.001) [Figure 2]. In meta-regression analysis, the correlation between waist circumference and UA was not significantly different according to age and BMI with P > 0.05.
The pooled correlation between SBP and DBP with UA (according to random-effect model) was statistically significant (r for SBP and UA = 0.34, 95% CI = 0.24–0.43; r for DBP and UA = 0.18, 95% CI = 0.11–0.25) with 96.2% (I2 = 96.2%; P < 0.001) and 92.5% heterogeneity (I2 = 92.5%; P < 0.001), respectively [Figure 4]. Based on the meta-regression analysis, the correlation between SBP, DBP, and UA was not significantly different according to age and BMI (P > 0.05).
Figure 4.
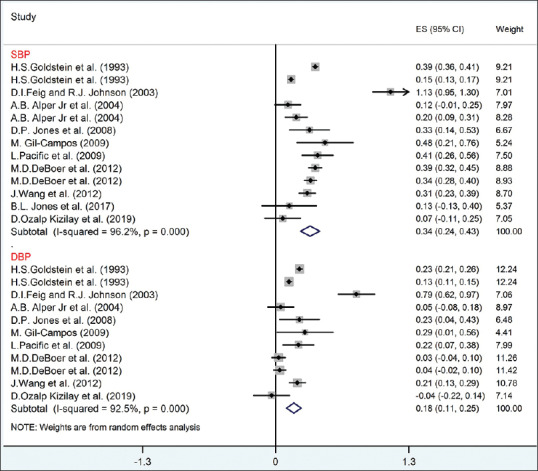
The forest plot of the correlation between metabolic syndrome components (SBP-DBP) with serum uric acid. DBP = Diastolic blood pressure; SBP = Systolic blood pressure
Association between uric acid and the risk of metabolic syndrome components
Figure 5 shows that the pooled OR between risk of elevated FBS with high UA (according to fixed-effect model) was not significant (OR = 1.06, 95% CI = 0.60–1.52) without any significant heterogeneity (I2 = 25.4%; P = 0.24).
Figure 5.
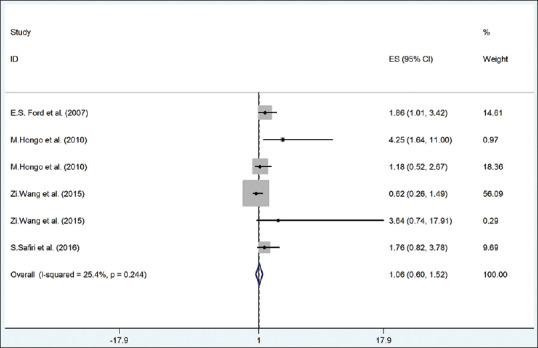
The forest plot of the association between serum uric acid with risk of high fast blood sugar. DBP = Diastolic blood pressure; SBP = Systolic blood pressure
As presented in Figure 6, the pooled OR between risk of abdominal obesity with UA (according to random-effect model) was statistically significant (OR = 2.62, 95% CI = 1.41–3.84) with 68.7% heterogeneity (I2 = 68.7%; P = 0.004).
Figure 6.
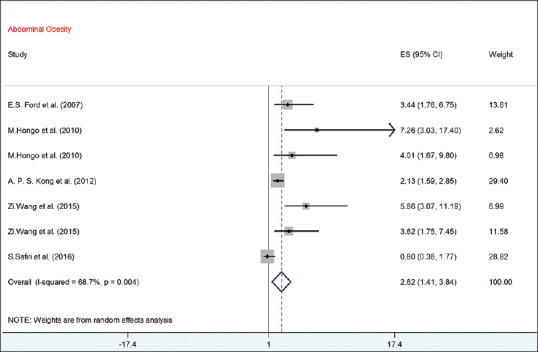
The forest plot of the association between serum uric acid with risk of abdominal obesity
As depicted in Figure 7, the risk of hyper-TG (OR = 1.38, 95% CI = 0.90–1.86) and low HDL-C (OR = 1.63, 95% CI = 0.97–2.28) with UA (according to fixed-effect model) was not significant without significant heterogeneity (P > 0.004).
Figure 7.
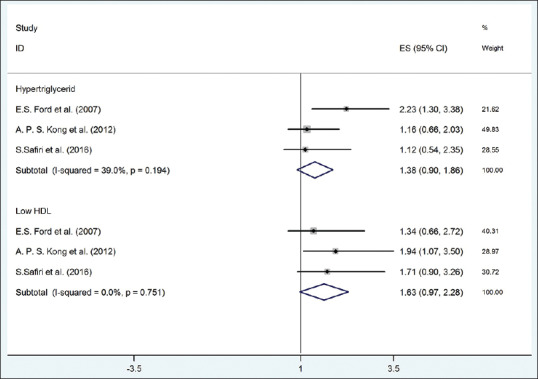
The forest plot of the association between serum uric acid with risk of high lipids. HDL = High-density lipoprotein
The risk of hypertension in individuals with elevated UA was 53% higher than others (according to fixed-effect model, OR = 1.38, 95% CI = 1.03–1.74) without significant heterogeneity (I2 = 31.5%, P = 0.177) [Figure 8].
Figure 8.
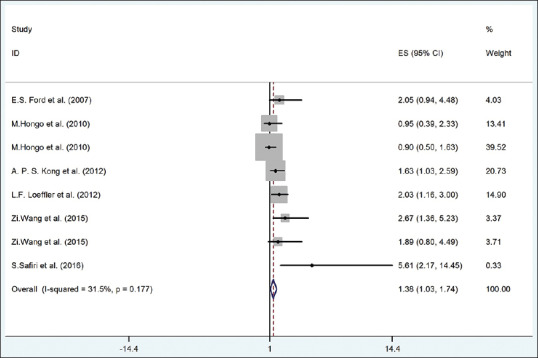
The forest plot of the association between serum uric acid with risk of hypertension
Sensitivity analysis
The sensitivity analysis showed that elimination of any individual studies did not result in significant change in the pooled effect size (P = 0.26)
Publication bias
Based on both Begg’s and Egger’s tests, there was no evidence of publication bias (P > 0.05). Results are shown in Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Table 1.
Results of publication studies according to Begg's and Egger's tests
| Studies for association between UA and the risk of MetS components (P) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Begg's test | Egger's test | |
| High FBS | 0.999 | 0.655 |
| Abdominal obesity | 0.764 | 0.340 |
| HTN | 0.734 | 0.436 |
| Hyper-TG | 0.721 | 0.411 |
| Low HDL-C | 0.296 | 0.075 |
| FBS | 0.450 | 0.731 |
| Serum TG | 0.405 | 0.637 |
| Serum HDL-C | 0.308 | 0.301 |
| WC | 0.450 | 0.640 |
| Fasting insulin | 0.700 | 0.341 |
| SBP | 0.454 | 0.643 |
| DBP | 0.998 | 0.587 |
FBS=Fasting blood sugar; HDL-C=High-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; TG=Triglyceride; WC=Waist circumference; BP=Blood pressure; DBP=Diastolic BP; SBP=Systolic BP; MetS=Metabolic syndrome; HTN=Hypertension
DISCUSSION
In this systematic review and meta-analysis of the relationship between SUAL and MetS components, we found consistent evidence on significant association between elevated levels of UA and different components of pediatric MetS. Significant association was also documented between SUAL and elevated BP in children and adolescents.
UA has a role as an eminent biomarker of lifestyle-dependent diseases that would dispose individuals to MetS, hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and renal disorders.[33,65,66] These findings suggest that measuring serum UA in the pediatric age group and improving lifestyles, such as limiting purine-rich foods and high fructose diets, might reduce the risk of chronic diseases from childhood and mitigate the deleterious effect of noncommunicable diseases on adulthood.
Our findings showed that the association of SUAL with MetS could be explained by several potential underlying mechanisms.[20,67] The first mechanism is related to the effect of high UA on endothelial dysfunction by reducing nitric oxide level. The bioavailability of nitric oxide can be inhibited by UA. Nitric oxide acts as an antioxidant factor in the blood vessels, and it is necessary for glucose uptake, so increasing UA will increase blood glucose.[3] The second mechanism is related to the fact that UA might accelerate the adipogenesis process that would lead to oxidative and inflammatory alterations in the adipocytes, by expressing xanthine oxidoreductase, i.e., the enzyme that generates UA from xanthine.[65,68] Based on experimental studies, MetS in obese mice origins from these inflammatory and oxidative changes.[11]
Our results are in line with previous findings in adult populations. We found significant associations between serum UA concentrations and various anthropometric indexes of generalized and abdominal obesity in children and adolescents.
Our findings demonstrated strong positive relationship between fasting blood glucose and SUALs. However, some previous studies did not show such association.[57,58] Results of the current meta-regression showed that by increase in BMI and age, the relationship of FBS and UA became stronger. The results obtained are in line with the previous studies. Those studies showed that, although moderate FBS level was related to high level of UA, it was not seen with high level of FBS.[69,70,71,72] Based on the evidence, glycosuria increases the excretion of urinary UA, so this biological mechanism may justify the relation of hyperglycemia with a low level of UA.[69,73]
Regarding abdominal obesity, we found a significant relationship between abdominal obesity and high SUAL. In obese individuals, fluxed free fatty acid from omental fat would lead to increasing hepatic nocturnal gluconeogenesis and increase in fasting glucose. Therefore, individuals with abdominal obesity would have overnight increase in keto acid formation from fatty acid. It can be suggested that UA along with lactic acid and redox status is important for gluconeogenesis in the adipose tissues. Then, in competition between acids for renal excretion, UA excretion will decrease.[74,75,76] Thus, it is possible to consider elevated fasting blood glucose as a prerequisite for hyperuricemia in children with abdominal obesity.[77] We also found that hyperuricemia induced a higher risk of 68.7% for abdominal obesity compared to other MetS components. Furthermore, waist circumference had an interpretation for the biggest variance in the SUAL. This finding is also supported by the findings in experimental studies that showed, hyperuricemia in rats increase the risk of insulin resistance. Based on research, insulin resistance is one of the risk factor for MetS.[3,78] Based on the fact that insulin increases renal tubular sodium and urate excretion, decreased renal excretion of UA is one of the potential pathophysiologic mechanisms linking hyperuricemia with insulin resistance in humans.[79] It can justify the underlying process for our finding on the association between UA and fasting insulin.
We found that dyslipidemia, as a MetS component, was associated with hyperuricemia. Our results revealed strong association of elevated TG and LDL-cholesterol, as well as low HDL-C with high SUALs. Some previous studies showed that rise in the serum leptin levels was simultaneous with UA accumulation. Therefore, it can be suggested that renal reabsorption of UA was affected by leptin.[80,81,82] Previous studies reported that the relationship between TGs and SUAL existed even in the normal population.[83] Therefore, the relationship between UA and dyslipidemia might be determined by a variation in a few critical genes more than it would be expected by chance.[24] A biological explanation of this event might be related to a high concentration of adenosine.[80] Adenosine is produced in the situation of impaired oxidative phosphorylation, which occurs in the process of MetS. Thereafter, adenosine could increase the renal reabsorption of sodium, urate, and water.[84,85,86] Thus, over time, the increase in UA due to adenosine might increase the production of urate.[87]
According to our results, interrelationships between SUAL and BP showed a strong positive association in children and adolescents. Both DBP and SBP were affected by a high level of UA. Our finding is in line with the previous assertion, which revealed that high UA has a key role in the pathogenesis of early life hypertension.[27,88,89] The results of an experimental study also vindicated the probability of the relationship between BP and UA. There are possible biological mechanisms for this association; moreover, as high UA concentration reduces nitric oxide in the macula densa, UA directly activates the renin-angiotensin system; both of these mechanisms would cause hypertension by vasoconstriction.[80] Previous studies among children supposed that UA can be considered as a useful and diagnostic factor for preventing hypertension in later life. These studies emphasized on the importance of early recognition of the MetS by measuring UA and assessment of hyperuricemia in children and adolescents.[26,27,74] The early elevation of UA concentration could act as the main risk factor for MetS by developing hypertension.[44]
A previous study also mentioned that there is a significant genetic correlation between serum level of UA and MetS components such as: abdominal obesity or hyperglycemia.[54]
The limitation of the current study is the restriction of search to English-language publications, to the selected database sources. This study had some strength points: According to the STROBE checklist, all studies were classified as two categories of moderate (76.5%) and high (23.5%) quality. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first meta-analysis and systematic review to determine the relationship between MetS components and hyperuricemia in children and adolescents. The generalizability of the current review is strengthened by a large number of included studies, as well as by a very large and diverse baseline population with different ethnicities.
CONCLUSION
Considering all evidence, hyperuricemia has the ability for worsening MetS and it has a close relationship with its major components. SUAL increased the risk of abdominal obesity, hypertension, and FBS. Therefore, measurement and control of UA should be emphasized in at-risk children; it can be useful in the primary prevention of noncommunicable diseases.
Financial support and sponsorship
The study was supported by Isfahan University of Medical Sciences.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the research team working on this review.
REFERENCES
- 1.Lee J, Sparrow D, Vokonas PS, Landsberg L, Weiss ST. Uric acid and coronary heart disease risk: Evidence for a role of uric acid in the obesity-insulin resistance syndrome. The Normative Aging Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1995;142:288–94. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ishizaka N, Ishizaka Y, Toda E, Nagai R, Yamakado M. Association between serum uric acid, metabolic syndrome, and carotid atherosclerosis in Japanese individuals. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:1038–44. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000161274.87407.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nakagawa T, Hu H, Zharikov S, Tuttle KR, Short RA, Glushakova O, et al. A causal role for uric acid in fructose-induced metabolic syndrome. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006;290:F625–31. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00140.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kawamoto R, Tomita H, Oka Y, Ohtsuka N. Relationship between serum uric acid concentration, metabolic syndrome and carotid atherosclerosis. Intern Med. 2006;45:605–14. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.45.1661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med. 1998;15:539–53. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9136(199807)15:7<539::AID-DIA668>3.0.CO;2-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Grundy SM. Metabolic syndrome: Connecting and reconciling cardiovascular and diabetes worlds. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:1093–100. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.11.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120:1640–5. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lakka HM, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, Niskanen LK, Kumpusalo E, Tuomilehto J, et al. The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA. 2002;288:2709–16. doi: 10.1001/jama.288.21.2709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Weiss R, Dziura J, Burgert TS, Tamborlane WV, Taksali SE, Yeckel CW, et al. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2362–74. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa031049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cook S, Weitzman M, Auinger P, Nguyen M, Dietz WH. Prevalence of a metabolic syndrome phenotype in adolescents: Findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988-1994. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2003;157:821–7. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.157.8.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Johnson RJ, Perez-Pozo SE, Sautin YY, Manitius J, Sanchez-Lozada LG, Feig DI, et al. Hypothesis: Could excessive fructose intake and uric acid cause type 2 diabetes? Endocr Rev. 2009;30:96–116. doi: 10.1210/er.2008-0033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dhuper S, Cohen HW, Daniel J, Gumidyala P, Agarwalla V, St Victor R, et al. Utility of the modified ATP III defined metabolic syndrome and severe obesity as predictors of insulin resistance in overweight children and adolescents: A cross-sectional study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2007;6:4. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-6-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ebbeling CB, Pawlak DB, Ludwig DS. Childhood obesity: Public-health crisis, common sense cure. Lancet. 2002;360:473–82. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09678-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kong AP, Choi KC, Ho CS, Chan MH, Ozaki R, Chan CW, et al. Associations of uric acid and gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) with obesity and components of metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. Pediatr Obes. 2013;8:351–7. doi: 10.1111/j.2047-6310.2012.00115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Robinson R. The fetal origins of adult disease: No longer just a hypothesis and may be critically important in South Asia. BMJ. 2001;322:375. doi: 10.1136/bmj.322.7283.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Solomons NW. Programme and policy issues related to promoting positive early nutritional influences to prevent obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular disease in later life: A developing countries view. Matern Child Nutr. 2005;1:204–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1740-8709.2005.00030.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fraile JM, García Puig J. Metabolic syndrome, hyperuricemia and gout. Revista Españla de Obesidad. 2009;7:85–90. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Arsenault BJ, Lemieux I, Després JP, Wareham NJ, Kastelein JJ, Khaw KT, et al. The hypertriglyceridemic-waist phenotype and the risk of coronary artery disease: Results from the EPIC-Norfolk prospective population study. CMAJ. 2010;182:1427–32. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.091276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Choi HK, Ford ES, Li C, Curhan G. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in patients with gout: The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57:109–15. doi: 10.1002/art.22466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hayden MR, Tyagi SC. Uric acid: A new look at an old risk marker for cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes mellitus: The urate redox shuttle. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2004;1:10. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-1-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li C, Hsieh MC, Chang SJ. Metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and hyperuricemia. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013;25:210–6. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32835d951e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J IDF Epidemiology Task Force Consensus Group. The metabolic syndrome – A new worldwide definition. Lancet. 2005;366:1059–62. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67402-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Nakanishi N, Suzuki K, Kawashimo H, Nakamura K, Tatara K. Serum uric acid: Correlation with biological, clinical and behavioral factors in Japanese men. J Epidemiol. 1999;9:99–106. doi: 10.2188/jea.9.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Russo C, Olivieri O, Girelli D, Guarini P, Corrocher R. Relationships between serum uric acid and lipids in healthy subjects. Prev Med. 1996;25:611–6. doi: 10.1006/pmed.1996.0096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ramsay LE. Hyperuricaemia in hypertension: Role of alcohol. Br Med J. 1979;1:653–4. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6164.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Alper AB, Jr, Chen W, Yau L, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS, Hamm LL. Childhood uric acid predicts adult blood pressure: The Bogalusa Heart Study. Hypertension. 2005;45:34–8. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000150783.79172.bb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Feig DI, Johnson RJ. Hyperuricemia in childhood primary hypertension. Hypertension. 2003;42:247–52. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000085858.66548.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Khosla UM, Zharikov S, Finch JL, Nakagawa T, Roncal C, Mu W, et al. Hyperuricemia induces endothelial dysfunction. Kidney Int. 2005;67:1739–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kramer CK, von Mühlen D, Jassal SK, Barrett-Connor E. A prospective study of uric acid by glucose tolerance status and survival: The Rancho Bernardo Study. J Intern Med. 2010;267:561–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2010.02168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wasserman A, Shnell M, Boursi B, Guzner-Gur H. Prognostic significance of serum uric acid in patients admitted to the Department of Medicine. Am J Med Sci. 2010;339:15–21. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e3181bbb647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lin JD, Lin PY, Lin LP, Hsu SW, Yen CF, Fang WH, et al. Serum uric acid, hyperuricemia and body mass index in children and adolescents with intellectual disabilities. Res Dev Disabil. 2009;30:1481–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2009.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Negri AL, Spivacow R, Del Valle E, Pinduli I, Marino A, Fradinger E, et al. Clinical and biochemical profile of patients with “pure” uric acid nephrolithiasis compared with “pure” calcium oxalate stone formers. Urol Res. 2007;35:247–51. doi: 10.1007/s00240-007-0109-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ford ES, Li C, Cook S, Choi HK. Serum concentrations of uric acid and the metabolic syndrome among US children and adolescents. Circulation. 2007;115:2526–32. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.657627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Harlan WR, Cornoni-Huntley J, Leaverton PE. Physiologic determinants of serum urate levels in adolescence. Pediatrics. 1979;63:569–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sui X, Church TS, Meriwether RA, Lobelo F, Blair SN. Uric acid and the development of metabolic syndrome in women and men. Metabolism. 2008;57:845–52. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2008.01.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tsushima Y, Nishizawa H, Tochino Y, Nakatsuji H, Sekimoto R, Nagao H, et al. Uric acid secretion from adipose tissue and its increase in obesity. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:27138–49. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.485094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Krishnan E, Pandya BJ, Chung L, Hariri A, Dabbous O. Hyperuricemia in young adults and risk of insulin resistance, prediabetes, and diabetes: A 15-year follow-up study. Am J Epidemiol. 2012;176:108–16. doi: 10.1093/aje/kws002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Johnson RJ, Lanaspa MA, Gaucher EA, editors . Uric Acid: A Danger Signal from the RNA World that May have a role in the Epidemic of Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Cardiorenal Disease: Evolutionary Considerations. Elsevier: Seminars in Nephrology; 2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Matsuura F, Yamashita S, Nakamura T, Nishida M, Nozaki S, Funahashi T, et al. Effect of visceral fat accumulation on uric acid metabolism in male obese subjects: Visceral fat obesity is linked more closely to overproduction of uric acid than subcutaneous fat obesity. Metabolism. 1998;47:929–33. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(98)90346-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Gibson T, Rodgers AV, Simmonds HA, Toseland P. Beer drinking and its effect on uric acid. Br J Rheumatol. 1984;23:203–9. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/23.3.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Emmerson BT, Knowles BR. Triglyceride concentrations in primary gout and gout of chronic lead nephropathy. Metabolism. 1971;20:721–9. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(71)80001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Mielants H, Veys EM, de Weerdt A. Gout and its relation to lipid metabolism I Serum uric acid, lipid, and lipoprotein levels in gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973;32:501–5. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.6.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Matsubara K, Matsuzawa Y, Jiao S, Takama T, Kubo M, Tarui S. Relationship between hypertriglyceridemia and uric acid production in primary gout. Metabolism. 1989;38:698–701. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Goldstein HS, Manowitz P. Relation between serum uric acid and blood pressure in adolescents. Ann Hum Biol. 1993;20:423–31. doi: 10.1080/03014469300002832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chen JH, Chuang SY, Chen HJ, Yeh WT, Pan WH. Serum uric acid level as an independent risk factor for all-cause, cardiovascular, and ischemic stroke mortality: A Chinese cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61:225–32. doi: 10.1002/art.24164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Deeks J, Higgins J, Altmann D. Incorporating heterogeneity into random-effects models. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. 2013 [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang JY, Chen YL, Hsu CH, Tang SH, Wu CZ, Pei D. Predictive value of serum uric acid levels for the diagnosis of metabolic syndrome in adolescents. J Pediatr. 2012;161:753–600. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.03.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Carbone F, Montecucco F, Mach F, Pontremoli R, Viazzi F. The liver and the kidney: Two critical organs influencing the atherothrombotic risk in metabolic syndrome. Thromb Haemost. 2013;110:940–58. doi: 10.1160/TH13-06-0499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yuan H, Yu C, Li X, Sun L, Zhu X, Zhao C, et al. Serum uric acid levels and risk of metabolic syndrome: A dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100:4198–207. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-2527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and explanation. BMJ. 2015;350:g7647. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g7647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP, et al. The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147:573–7. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-147-8-200710160-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J, Welch VA, Higgins JP, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: A new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;10:ED000142. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Tang W, Hong Y, Province MA, Rich SS, Hopkins PN, Arnett DK, et al. Familial clustering for features of the metabolic syndrome: The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) family heart study. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:631–6. doi: 10.2337/diacare.29.03.06.dc05-0679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wang ZN, Li P, Jiang RH, Li L, Li X, Li L, et al. The association between serum uric acid and metabolic syndrome among adolescents in northeast China. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:21122–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Civantos Modino S, Guijarro de Armas MG, Monereo Mejías S, Montaño Martínez JM, Iglesias Bolaños P, Merino Viveros M, et al. Hyperuricemia and metabolic syndrome in children with overweight and obesity. Endocrinol Nutr. 2012;59:533–8. doi: 10.1016/j.endonu.2012.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hongo M, Hidaka H, Sakaguchi S, Nakanishi K, Ichikawa M, Hirota N, et al. Association between serum uric acid levels and cardiometabolic risk factors among Japanese junior high school students. Circ J. 2010;74:1570–7. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-09-0837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Wang ZN, Li P, Jiang RH, Li L, Li X, Li L, et al. The association between serum uric acid and metabolic syndrome among adolescents in Northeast China. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:21122–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sun D, Li S, Zhang X, Fernandez C, Chen W, Srinivasan SR, et al. Uric acid is associated with metabolic syndrome in children and adults in a community: The Bogalusa Heart Study. PLoS One. 2014;9:e89696. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Reis LN, Reuter CP, Pollo Renner JD, Burgos LT, Rech Franke SI, Burgos MS. High urate concentration is associated with elevated blood pressure in schoolchildren. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018;31:1207–12. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2018-0227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Perez ES, Medina MA, Lomeli ML, González VT, Pérez JZ, Lavalle González FJ, et al. Association between serum uric acid and metabolic syndrome components in prepubertal obese children (Tanner Stage I) from Nuevo León, Mexico – A preliminary study. BMC Obes. 2017;4:25. doi: 10.1186/s40608-017-0160-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Jones DP, Richey PA, Alpert BS, Li R. Serum uric acid and ambulatory blood pressure in children with primary hypertension. Pediatr Res. 2008;64:556–61. doi: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e318183fd7c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Viazzi F, Antolini L, Giussani M, Brambilla P, Galbiati S, Mastriani S, et al. Serum uric acid and blood pressure in children at cardiovascular risk. Pediatrics. 2013;132:e93–9. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-0047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Pacifico L, Cantisani V, Anania C, Bonaiuto E, Martino F, Pascone R, et al. Serum uric acid and its association with metabolic syndrome and carotid atherosclerosis in obese children. Eur J Endocrinol. 2009;160:45–52. doi: 10.1530/EJE-08-0618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Feig DI, Kang DH, Johnson RJ. Uric acid and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1811–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0800885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Coutinho Tde A, Turner ST, Peyser PA, Bielak LF, Sheedy PF, 2nd, Kullo IJ. Associations of serum uric acid with markers of inflammation, metabolic syndrome, and subclinical coronary atherosclerosis. Am J Hypertens. 2007;20:83–9. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2006.06.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Heinig M, Johnson RJ. Role of uric acid in hypertension, renal disease, and metabolic syndrome. Cleve Clin J Med. 2006;73:1059–64. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.73.12.1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Cardoso AS, Gonzaga NC, Medeiros CC, Carvalho DF. Association of uric acid levels with components of metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in overweight or obese children and adolescents. J Pediatr (Rio J) 2013;89:412–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jped.2012.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Cook DG, Shaper AG, Thelle DS, Whitehead TP. Serum uric acid, serum glucose and diabetes: Relationships in a population study. Postgrad Med J. 1986;62:1001–6. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.62.733.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Tuomilehto J, Zimmet P, Wolf E, Taylor R, Ram P, King H. Plasma uric acid level and its association with diabetes mellitus and some biologic parameters in a biracial population of Fiji. Am J Epidemiol. 1988;127:321–36. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Herman JB, Goldbourt U. Uric acid and diabetes: Observations in a population study. Lancet. 1982;2:240–3. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Whitehead TP, Jungner I, Robinson D, Kolar W, Pearl A, Hale A. Serum urate, serum glucose and diabetes. Ann Clin Biochem. 1992;29(Pt 2):159–61. doi: 10.1177/000456329202900206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Lytvyn Y, Škrtić M, Yang GK, Yip PM, Perkins BA, Cherney DZ. Glycosuria-mediated urinary uric acid excretion in patients with uncomplicated type 1 diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015;308:F77–83. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00555.2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Prebis JW, Gruskin AB, Polinsky MS, Baluarte HJ. Uric acid in childhood essential hypertension. J Pediatr. 1981;98:702–7. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80828-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Fam AG. Gout, diet, and the insulin resistance syndrome. J Rheumatol. 2002;29:1350–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Cahill GF., Jr Fuel metabolism in starvation. Annu Rev Nutr. 2006;26:1–22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.26.061505.111258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Randle PJ. Regulatory interactions between lipids and carbohydrates: The glucose fatty acid cycle after 35 years. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1998;14:263–83. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-0895(199812)14:4<263::aid-dmr233>3.0.co;2-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Murphy R, Thornley S, de Zoysa J, Stamp LK, Dalbeth N, Merriman TR. Sugar Sweetened beverage consumption among adults with gout or type 2 diabetes. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0125543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Lippi G, Montagnana M, Franchini M, Favaloro EJ, Targher G. The paradoxical relationship between serum uric acid and cardiovascular disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2008;392:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2008.02.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Choi HK, Ford ES. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in individuals with hyperuricemia. Am J Med. 2007;120:442–7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2006.06.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Fruehwald-Schultes B, Peters A, Kern W, Beyer J, Pfützner A. Serum leptin is associated with serum uric acid concentrations in humans. Metabolism. 1999;48:677–80. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(99)90163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Bedir A, Topbas M, Tanyeri F, Alvur M, Arik N. Leptin might be a regulator of serum uric acid concentrations in humans. Jpn Heart J. 2003;44:527–36. doi: 10.1536/jhj.44.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Hovsepian S, Javanmard SH, Mansourian M, Hashemipour M, Tajadini M, Kelishadi R. Lipid regulatory genes polymorphism in children with and without obesity and cardiometabolic risk factors: The CASPIAN-III study. J Res Med Sci. 2018;23:11. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_911_17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Fransen R, Koomans HA. Adenosine and renal sodium handling: Direct natriuresis and renal nerve-mediated antinatriuresis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1995;6:1491–7. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V651491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Balakrishnan VS, Coles GA, Williams JD. Effects of intravenous adenosine on renal function in healthy human subjects. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:F374–81. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1996.271.2.F374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Balakrishnan VS, Coles GA, Williams JD. A potential role for endogenous adenosine in control of human glomerular and tubular function. Am J Physiol. 1993;265:F504–10. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.4.F504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Bakker SJ, Gans RO, ter Maaten JC, Teerlink T, Westerhoff HV, Heine RJ. The potential role of adenosine in the pathophysiology of the insulin resistance syndrome. Atherosclerosis. 2001;155:283–90. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(00)00745-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Feig DI, Nakagawa T, Karumanchi SA, Oliver WJ, Kang DH, Finch J, et al. Hypothesis: Uric acid, nephron number, and the pathogenesis of essential hypertension. Kidney Int. 2004;66:281–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00729.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Feig DI, editor. Uric acid and Hypertension in Adolescents. Elsevier: Seminars in Nephrology; 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


