Abstract
Arterial thrombosis is in part contributed by excessive platelet aggregation, which can lead to blood clotting and subsequent heart attack and stroke. Platelets are sensitive to the haemodynamic environment. Rapid haemodynamcis and disturbed blood flow, which occur in vessels with growing thrombi and atherosclerotic plaques or is caused by medical device implantation and intervention, promotes platelet aggregation and thrombus formation. In such situations, conventional antiplatelet drugs often have suboptimal efficacy and a serious side effect of excessive bleeding. Investigating the mechanisms of platelet biomechanical activation provides insights distinct from the classic views of agonist-stimulated platelet thrombus formation. In this work, we review the recent discoveries underlying haemodynamic force-reinforced platelet binding and mechanosensing primarily mediated by three platelet receptors: glycoprotein Ib (GPIb), glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GPIIb/IIIa) and glycoprotein VI (GPVI), and their implications for development of antithrombotic ‘mechano-medicine’ .
Keywords: Blood Flow, Stenosis, Platelets, Stroke, Vessel Wall
Introduction
Thrombotic diseases, which include the acute coronary syndromes, ischaemic stroke and peripheral vascular disease, remain the leading causes of death and disability worldwide.1 2 Platelets play a central role in the pathogenesis of arterial thrombosis. However, despite intensive investigations over the last 40 years into the discovery and development of antiplatelet therapies, the impact of these therapies on the mortality rate remains disappointingly low: <1 in 6 patients taking antiplatelet therapies avoided a fatal thrombotic event.1 This situation is likely to worsen in the next few decades due to the rapidly growing incidence of obesity, diabetes and metabolic syndrome, which all enhance the resistance of arterial thrombosis to conventional antiplatelet drugs.3
The development of more effective antithrombotic approaches requires a better understanding of the molecular events underlying platelet hyperactivity and excessive thrombus growth. To date, most of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved antithrombotic agents target agonist pathways of platelet activation, including the purinergic P2Y12 receptor antagonists (clopidogrel, prasugrel, ticagrelor), inhibitors of thromboxane A2 (TxA2) generation (aspirin, triflusal) or protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR1) antagonists (vorapaxar).1 Increasing the dose of these agents, especially aspirin and clopidogrel, has been employed to dampen the platelet thrombotic functions. However, this also increases the risk of excessive bleeding.4 It has long been recognized that arterial thrombosis is regulated by biomechanical factors, particularly pathological shear stress and flow disturbance associated with vessel stenosis induced by atherosclerotic plaques or medical device implants.1 5 These variations in blood haemodynamics can be sensed by platelets, upregulating platelet adhesive functions and inducing platelet activation via a process called ‘mechanosensing’.6 7 Recent technology advancements in microfluidics, molecular imaging and live-cell dynamic force spectroscopy enabled the investigation of platelet mechanosensing at single-cellular and single-molecular levels. These studies looked into how platelets sense and react to the extracellular haemodynamic forces, and defined the mechanosensing functions of receptors GPIb, GPIIb/IIIa and possibly GPVI, in mediating shear-dependent platelet adhesion,8–10 spreading11 and aggregation.5 12 These insights provided new targets for the next-generation antithrombotic strategies.
Biomechanical versus biochemical activation in platelet adhesion and aggregation
Thrombosis requires platelet adhesion, but also heavily relies on platelet aggregation to form occlusive thrombi. Platelet adhesion and aggregation are both complex processes that involve the binding between multiple receptor–ligand pairs.13 In veins where shear rates are low (300–800 s–1), initial platelet adhesion is mainly mediated by GPVI interaction with collagen and GPIIb/IIIa with fibrinogen in subendothelium (figure 1). The subsequent platelet aggregation is primarily mediated by the GPIIb/IIIa binding to divalent or multivalent ligands for crosslinking. These include von Willebrand factor (VWF), which adopts a structure of a colloid concatemer,14–16 and fibrinogen, which has a total of six motifs to interact with GPIIb/IIIa.17–19 In addition, fibronectins can attach to two ends of a fibrinogen molecule and crosslink platelet GPIIb/IIIa as well.20–22 In arteries and arterioles where shear rate is relatively high (>800 s–1), both GPIb and GPIIb/IIIa serve as the primary mediators of platelet adhesion23 24 and aggregation.5 25 In particular, at pathologically high shear rates (>5000 s–1) that occur in arteries with severe stenosis, the GPIb–VWF interaction alone can achieve large-scale platelet aggregation independent of integrin and platelet activation.26
Figure 1.
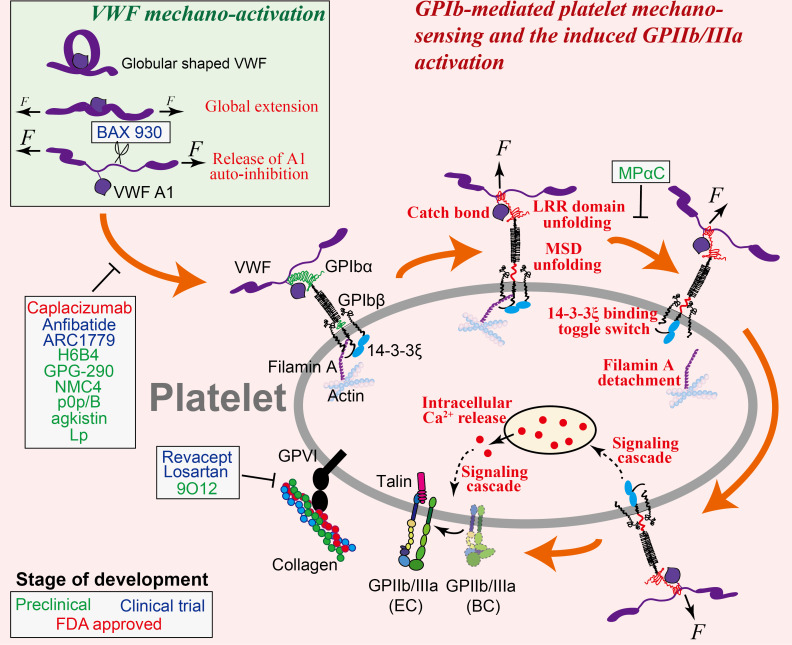
Illustration of VWF mechanoactivation (inset) and the step-by-step process of GPIb-mediated platelet mechanosensing. VWF is activated by shear flow in two steps: it is first globally elongated from a globular to an extended conformation, followed by the relief of its A1 domain autoinhibition that enables binding to platelet GPIbα. Once VWF is bound to a platelet, force from the shear flow transmits from VWF to GPIbα and triggers a series of GPIbα conformational changes and allosteric effects. These events would result in the reinforcement of VWF–GPIb interaction as well as the initiation of a mechanosignaling pathway that eventually leads to intracellular calcium release and GPIIb/IIIa activation. Note: platelet GPVI and its interaction with collagen are also depicted in this graph. Agents and drugs that have the potential to inhibit arterial thrombosis by targeting GPIb-mediated or GPVI-mediated platelet binding and mechanosensing, and their respective targets, are indicated, corresponding to table 1.
Platelet adhesion and aggregation are heavily dependent on platelet activation, mainly due to the fact that platelet activation primes GPIIb/IIIa to achieve stronger binding capacity.13 23 Additionally, platelet activation also results in platelet spreading and granule release to allow ligand deposition as well as surface expression of extra receptors for binding.11 27–29 Platelets can be activated by soluble agonists via G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling pathways. For instance, ADP (by binding to P2Y1 and P2Y12),30 31 thromboxane A2 (by binding to thromboxane A2 receptor)32 and thrombin (by binding to PAR1 and PAR4)33 can induce GPIIb/IIIa inside-out activation at various levels to trigger cytoskeletal remodelling, granule release, degranulation and cell death,1 34 35 while the inhibition of these interactions or their subsequent signaling pathways has been employed to develop antithrombotic drugs like clopidogrel,36 aspirin,37 warfarin38 and heparin.39 In parallel, platelets can be biomechanically activated via binding to its extracellular ligands under shear.7 In this process, force pulling on a platelet receptor triggers ‘mechanosignals’ across the membrane and results in intracellular signal transduction.6 Platelet GPIb and GPIIb/IIIa together form an important mechanosensing axis.40 GPIb initiates platelet mechanosignaling by binding to immobilised VWF under force, which is followed by the mechanosignaling of GPIIb/IIIa while binding to its own ligands, eventually allowing rapid shear-dependent thrombus formation.12 Importantly, the intensity and timing of GPIb mechanosignaling is quantitatively correlated with the level of subsequent GPIIb/IIIa activation in both affinity and avidity,12 which highlights the role of GPIb as a mechanosensor in shear-dependent platelet thrombus formation.
The role of VWF–GPIb axis in platelet binding and mechanosensing
VWF contains binding sites for both platelet GPIb and GPIIb/IIIa, respectively, in its A1 and C4 domains.41 The VWF molecule itself is mechanosensitive, which undergoes conformational activation under shear force. The inactive form of VWF in plasma adopts a globular, irregularly coiled shape, with its functional epitopes buried. In particular, its A1 domain is autoinhibited by the adjacent N-terminal D′D3 domain42 and C-terminal A2 domain,43 44 which prevents the accessibility of VWF-A1 to GPIb. Under high-shear laminar flow or high-shear gradient disturbed flow, VWF is mechanically extended by shear force to expose its platelet-binding epitopes.41 45 Further exertion of force on the extended VWF unmasks its A1 domain and relieves the autoinhibition of its GPIb-binding site, thereby allowing platelet GPIb binding46–49 (figure 1). Besides, shear can facilitate the self-association of VWF into fibres, which further enhances platelet adhesion and activation.50 51
The VWF A1 domain autoinhibition was suggested to be controlled by the C1669–C1670 disulfide bond plug in the A2 domain.52 Three different redox forms of this disulfide plug were discovered to exist in circulating human VWF: reduced, glutathionylated and oxidized. The oxidized form has high affinity for platelet GPIb, whereas the reduced and glutathionylated forms have low affinity. Clinically, most of heart failure patients who have received extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) support have markedly more oxidized VWF in the circulation,53 which seems to result from the dysregulated blood shear associated with the device but not the disease or therapy variations.52 This result explains the thrombotic complications associated with ECMO device, and suggests that reducing this disulfide plug might provide protection to patients against thrombosis.
The VWF–GPIb interaction features fast bond association and dissociation, which plays a primary role in platelet recruitment from rapid blood circulation.54–56 A counterintuitive phenomenon was discovered in this interaction: increasing the shear rate would enhance, rather than reduce, platelet adhesion onto a VWF-coated surface.23 55 57 Using single-cell force spectroscopies, this phenomenon was explained by a ‘catch bond’ behaviour55 57 and a force-induced unfolding of the GPIb leucine rich repeat (LRR) domain,58 in both of which mechanical force reinforces VWF–GPIb bond strength (figure 1). Taken together, the mechanosensitivity of VWF and the force reinforcement of VWF–GPIb interaction work cooperatively to allow platelets to resist high-shear forces in the arteries while being recruited to the vascular injury site. However, they also promote thrombus development under pathological shear conditions59: as shear rate increases to 5000 s–1, the VWF–GPIb interaction starts to mediate large platelet aggregate formation (>100 µm2), and this effect becomes more pronounced as the shear rate increases to 10 000 s–1 and above.26
VWF–GPIb interaction not only mediates platelet binding but also triggers the outside-in mechanosignals of platelets independent of other receptors, leading to intraplatelet calcium flux60 and GPIIb/IIIa activation.8 10 Inhibition of the GPIb-triggered Ca2+ prevents platelet firm adhesion, suggesting that Ca2+ is an obligatory signaling molecule on the pathway to GPIIb/IIIa activation.8 9 61 62 Although how the transmission of the mechanical signal across the membrane and its transduction into cytoplasmic chemical signals are fulfilled remains elusive, a juxtamembrane mechanosensitive domain (MSD) in the GPIbα subunit was found to correlate with intraplatelet Ca2+ triggering (figure 1): force-induced MSD unfolding is well correlated with an α-type Ca2+ signal8 9 and the subsequent GPIIb/IIIa intermediate activation, whereas failing to unfold MSD will most likely result in β-type or null-type Ca2+ signals and limit GPIIb/IIIa activation.60 63 Intracellularly, a scaffold protein that binds to GPIb cytoplasmic tail, 14-3-3ζ, was also found to play a pivotal role in GPIb mechanosignaling (figure 1), as the inhibition of 14-3-3ζ–GPIb association strongly inhibited GPIb-triggered Ca2+ flux and subsequent GPIIb/IIIa activation.60 64 Filamin A, another cytoplasmic protein that links GPIb with the cytoskeleton, was also speculated to participate in GPIb mechanosignaling65 (figure 1). At the downstream of this signal transduction pathway, the phosphorylation of kinases (including Akt and focal adhesion kinase (FAK)) is required, which involves the Src family kinases66 as well as the activation of several signaling pathways including the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt and cGMP-dependent protein kinase pathway, mitogen-activated protein kinase (ERK1/2 and p38) pathway and LIM kinase 1 pathway.67
Targeting VWF–GPIb axis as a novel antithrombotic strategy
Many works have explored the potential of inhibiting VWF–GPIb interaction to reduce arterial thrombosis.68 For instance, Chen et al discovered a ‘hot spot’ residue R1326 on murine VWF-A1.69 Mutating this residue to histidine weakens both the association and endurance of VWF–GPIb binding, thereby diminishing thrombus formation in arterioles in a laser-injury thrombosis model.70 The autoinhibitory effect of the N-terminal sequence Q1238-E1260 of VWF-A1 on its own binding to platelet GPIb inspires another potential antithrombotic approach: the soluble polypeptide Lp of the same sequence was shown to inhibit platelet binding to VWF under shear.57 A humanized anti-VWF-A1 blocking nanobody named ALX-0081 (caplacizumab) inhibited acute thrombosis without compromising haemostasis in baboons,71 and induced the reperfusion of a thrombus-occluded cerebral artery without provoking cerebral bleeding in guinea pigs.72 Besides, an inhibitory monoclonal antibody against VWF-A1, NMC4,73 a recombinant mimetics of human GPIbα, GPG-290,74 and an anti-VWF aptamer, ARC1779,75 were also found to inhibit thrombosis (table 1; figure 1). Similarly, the inhibition of GPIb binding by monoclonal antibodies H6B476 and p0p/B,77 or by chemicals purified from snake venom like agkistin78 and anfibatide,79 were found to reduce platelet aggregation and thrombus formation under arterial shear conditions (table 1; figure 1). The anti-GPIb blockade has displayed a strong protective effect in the mouse stroke models without inducing significant intracranial bleeding.77 80 Notably, unpublished phase IIa human clinical trials have shown the promise of anfibatide as a novel antiplatelet agent without significantly affecting haemostasis in patients with non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (MI).81 Additionally, anfibatide was also shown as a promising candidate to treat ischaemic stroke and spontaneous or bacterial shigatoxin-induced acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) in experimental animal models.82 83
Table 1.
Novel antiplatelet agents targeting GPIb, GPIIb/IIIa and GPVI mechanosensing axes
| Axis | Target | Agent | Description | Antithrombotic effect | Phase of development | Clinical trials gov identifier | References |
| GPIb | VWF | Lp (Q1238-E1260) | The N-terminal polypeptide sequence of VWF-A1 that autoinhibits VWF-A1 binding to platelet GPIb. | Inhibits platelet attachment on VWF in whole blood perfusion in vitro. | Preclinical | 57 | |
| 14-3-3ζ | MPαC | Designed based on the 14-3-3ζ-binding sequence in GPIbα. Blocks 14-3-3ζ binding to GPIbα. | Weakens GPIbα-VWF interaction and inhibits GPIbα mechanosignalling. | Preclinical | 92 93 | ||
| VWF | BAX 930 | Recombinant ADAMTS13; cleaves VWF at A2 domain to weaken its activity. | Inhibits arterial thrombosis. | III | NCT03393975 | 88 89 | |
| VWF | NMC4 | A monoclonal antibody against VWF-A1. | Inhibits arterial thrombosis. | Preclinical | 73 | ||
| VWF | Caplacizumab | A nanobody against VWF-A1. | Showed inhibitory effects on thrombosis in primate models without causing adverse side effects. | FDA approved | 71 72 | ||
| VWF | ARC1779 | An anti-VWF aptamer. | Showed encouraging results in inhibiting thrombosis. | II (terminated) | NCT00742612 | 75 85 | |
| GPIbα | p0p/B | An antibody against GPIbα. | Dramatically reduces infarct volumes in cerebral ischaemia model. | Preclinical | 77 | ||
| GPIbα | H6B4 | An antibody against GPIbα. | Inhibits high-shear arterial thrombosis in baboons without causing adverse side effects. | Preclinical | 76 | ||
| GPIbα | GPG-290 | A recombinant human GPIbα chimeric protein which blocks GPIbα binding to VWF. | Inhibits coronary artery thrombosis in a canine model. | Preclinical | 74 | ||
| GPIbα | agkistin | Blocks GPIbα binding to VWF. | Reduces thrombus formation under arterial shear conditions. | Preclinical | 78 | ||
| GPIbα | Anfibatide | Inhibits both VWF and α-thrombin binding to GPIbα. | In experimental models, inhibits platelet adhesion, aggregation and thrombus formation without increasing bleeding time. | I, II | NCT01585259 | 79 | |
| GPIIb/IIIa | PI3Kβ | AZD6482 | Inhibits PI3Kβ downstream GPIIb/IIIa mechanosignaling and shear-induced platelet activation. | Inhibits thrombus formation in vivo in preclinical models with minimal effects on bleeding. | I | NCT00853450 | 138 |
| Gα13 | mP6 | A myristoylated peptide (Myr-FEEERA) that inhibits association of Gα13 with integrin β3 cytoplasmic tail and suppresses the early phase of GPIIb/IIIa outside-in signalling. | Inhibits platelet spreading and thrombus formation in preclinical models with no effects on bleeding time. | Preclinical | 104 | ||
| PDI | Isoquercetin | Inhibits PDI activity in plasma and decreases platelet-dependent thrombin generation; also reduces levels of coagulation markers at higher doses. | Inhibits platelet thrombus formation and fibrin formation in preclinical models. Partial inhibition does not cause serious bleeding. | II–III | NCT02195232 | 141 | |
| Active GPIIb/IIIa | scFv SCE5 | Single-chain antibody that specifically inhibits the active conformation of GPIIb/IIIa; can also be used to deliver clot-directed thrombolytic, antiplatelet and anticoagulant agents. | Inhibits platelet aggregation and thrombus formation in preclinical models without major increase in bleeding time. | Preclinical | 145 | ||
| GPIIb/IIIa | RUC-4 | A small molecule that binds to the metal ion-binding site on the GPIIIa without causing major conformational changes; specific to GPIIb/IIIa (αIIbβ3) over αVβ3 integrins. | Inhibits platelet aggregation and thrombus formation in preclinical models; effects on bleeding not yet evaluated. | I | NCT03844191 | 150 | |
| GPIIb/IIIa | PSI A1, PSI B1, PSI C1, PSI E1 | Antibodies against GPIIIa PSI domain, inhibiting its thiol isomerase function. | Inhibits platelet aggregation and thrombus formation in preclinical models. | Preclinical | 128 | ||
| GPVI | GPVI | 9O12 | A monoclonal antibody Fab that blocks the collagen/fibrin-binding site of GPVI with high affinity. The recombinant scFv version is also available. | Inhibits thrombosis and appears to maintain haemostasis in preclinical models. | Preclinical | 163 | |
| Collagen | Revacept | Dimeric GPVI-Fc that blocks vascular collagen at sites of plaque or vascular erosion and collagen-induced platelet activation | Inhibits platelet thrombus formation at sites of vascular injury in preclinical models; no effect on bleeding time. | I, II | NCT01645306 | 165 | |
| GPVI | Losartan (DuP-753) | An angiotensin II (Ang II) type I receptor (AT1R) antagonist that has been reported to exert an anti-platelet activity besides its antihypertensive effect. | Inhibits platelet adhesion to collagen and subsequent collagen induced platelet activation and aggregation via GPVI. | IV | NCT00805311 | 169 |
PDI, protein disulfide isomerase; scFv, single-chain variable fragment.
Nonetheless, due to the indispensable role of VWF–GPIb interaction in initiating platelet haemostatic functions, inhibiting this axis can easily trigger a strong side effect of excessive bleeding. Historically, this has caused the failure of several clinical trials.4 84 For instance, although a phase II trial demonstrated that ARC1779 reduced cerebral thromboembolism after carotid endarterectomy, two-thirds of patients receiving ARC1779 experienced haemorrhagic complications.85 As another example, caplacizumab was trialled in combination with aspirin, clopidogrel and heparin in high-risk patients with acute MI undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).86 However, its development was discontinued in 2011 because of a severe bleeding profile.84 Instead, it received FDA approval following phase III HERCULES trials for the treatment of acute episode of acquired TTP in adult patients in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.87 We argue that similar outcome may hold true for other drug candidates that generally inhibit VWF–GPIb interaction, which deserve careful consideration and further investigation.
On a separate note, considering the distinct haemodynamic conditions associated with arterial thrombosis and haemostasis, a potential strategy to selectively inhibit arterial thrombosis without compromising haemostasis is to target the biomechanical activation of VWF and/or the biomechanical reinforcement of VWF–GPIb interaction. For instance, inhibiting the LRR domain unfolding of GPIbα may serve to suppress VWF–GPIb interaction under high forces,58 thereby hampering thrombosis in stenosed arteries where shear rate is pathologically high. As another example, shear force unfolds the A2 domain of ultra-large VWF to allow its cleavage by ADAMTS13 into normal sizes.88 It was found that under pathologically high-shear flow, shear force becomes sufficiently large to trigger cleavage of normal-sized VWF by ADAMTS13 in a growing thrombus, thereby inhibiting thrombosis.88 89 This makes recombinant ADAMTS13 (BAX 930) a promising antithrombotic agent90 (table 1; figure 1): in preclinical tests, infusing recombinant ADAMTS13 before reperfusion significantly reduced the infarct volume and other stroke effects.91 Moreover, the mechanoredox regulation of VWF reactivity suggests that using antioxidative agents or more specific disulfide isomerases to reverse plasma VWF from oxidized to its reduced form can reduce platelet binding and thereby suppress thrombosis.52
Since GPIb mechanosignaling leads to GPIIb/IIIa activation,12 the GPIb signaling pathway serves as another target to inhibit thrombosis. However, blocking housekeeping cytoplasmic adaptors and signaling kinases would most likely affects physiological functions of other cell types. Considering this, targeting certain steps of the GPIb mechanosignaling process seems more promising due to higher specificity. Previous works have identified that a small peptide, MPαC, which inhibits the association of 14-3-3ζ with GPIb, suppresses mouse arterial thrombosis with minor consequences of bleeding92 93 (table 1; figure 1). Inhibiting the unfolding of MSD should also suppress the mechanosignaling of GPIb. The current development of bispecific antibody technology94 provides a possible approach to achieve this: by making a bispecific antibody with two antigen binding fragments respectively targeting the two ends of MSD, it can potentially constrain MSD in its folded conformation even under force pulling.
The role of GPIIb/IIIa in platelet binding and mechanosensing
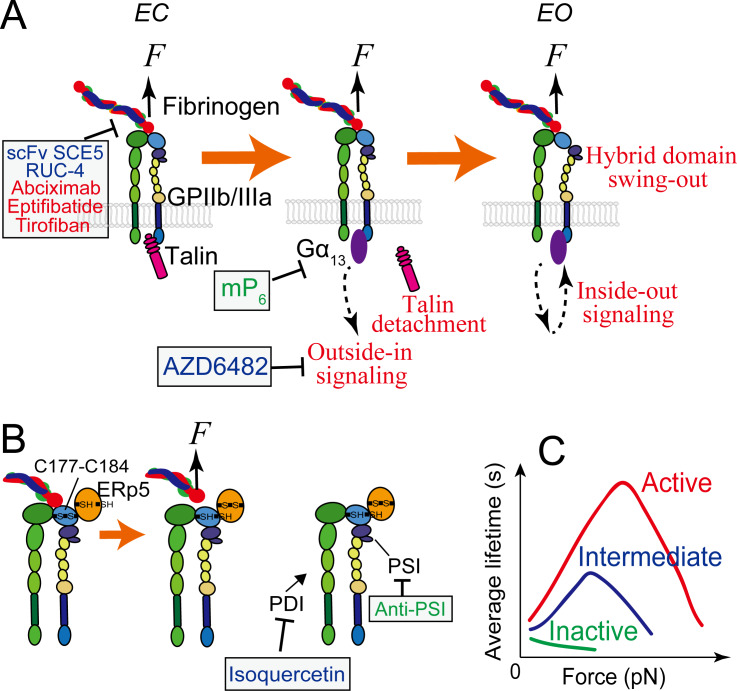
A good amount of works have substantially characterized GPIIb/IIIa as a platelet receptor in structure,95–100 binding activity101–103 and signaling.8 9 11 62 104 105 GPIIb/IIIa regulates its ligand-binding affinity with conformational changes.106–108 Inactive GPIIb/IIIa adopts a bent conformation (B) with closed headpiece (C) (or called hybrid domain swung-in); its ligand binding site is inactive and barely binds any ligand. On activation, the GPIIb/IIIa extends its ectodomain to achieve an extended-closed (EC) conformation, followed by headpiece opening to reach extended-open (EO)95 98 109–112 (figure 2A). The EO conformation of GPIIb/IIIa is extensively correlated with active ligand binding,98 113 whereas the EC conformation was recently found to be associated with an intermediate affinity state.12
Figure 2.
GPIIb/IIIa mediated platelet mechanosensing. (A) The extended-close (EC) GPIIb/IIIa receives mechanosignals from its bound ligand and mediates outside-in signaling, which can subsequently upregulate GPIIb/IIIa themselves towards the active state with an extended-open (EO) conformation. During the process, the adaptor protein talin that is originally associated with the cytoplasmic tail of GPIIIa will detach and be replaced by a Gα13 molecule, which will be ensued by a second wave of talin attachment to in turn replace Gα13 (not depicted here). (B) Redox regulation of GPIIb/IIIa binding via ERp5, PSI and PDI. Force pulling on the GPIIb/IIIa headpiece via a bound Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD)-bearing ligand can facilitate ERp5 to reduce the C177–C184 disulfide bond in the βI domain, which in turn accelerates ligand dissociation from GPIIb/IIIa. PSI domain has endogenous thiol isomerase function, which reinforces GPIIb/IIIa binding. Extracellular PDI can also induce thiol-disulfide exchange in GPIIb/IIIa and enhances its binding capacity. (C) In the resting bent-closed (BC) state, GPIIb/IIIa binding to fibronectin manifests a slip bond (a small catch bond if against fibrinogen). Once upregulated to the intermediate extended-closed (EC) state, GPIIb/IIIa binding to both ligands will adopt a strong catch bond, which will become even stronger when the integrin is further activated to the EO state. Agents and drugs (green: preclinical phase; blue: undergoing clinical trials; red: FDA approved) that have the potential to inhibit arterial thrombosis by targeting GPIIb/IIIa mechanosensing, and their respective targets, are indicated, corresponding to table 1. ‘Anti-PSI’ represents antibodies PSI A1, PSI B1, PSI C1 and PSI E1. ERp5, endoplasmic reticulum 5; PDI, protein disulfide isomerase.
GPIIb/IIIa plays critical roles in platelet adhesion, activation and aggregation, which altogether define it as the primary mediator of both thrombosis and haemostasis.114–117 As first observed in mouse stenosed blood vessels and in varied arterial injury models, GPIIb/IIIa can mediate platelet aggregation in a biomechanical pathway,25 where the platelets mainly remain discoid.5 In the biomechanical platelet aggregation, the interaction between GPIb and VWF initiates platelet mechanosensing and results in the EC conformation, intermediate affinity activation of GPIIb/IIIa.8 9 12 60 Once upregulated to this intermediate state, GPIIb/IIIa starts to receive mechanosignals to undergo outside-in signaling, which leads to its own activation to the high affinity, EO state (figure 2A) as well as platelet spreading, extracellular Ca2+ influx and granule secretion.8 12 27 104 118 119 Remarkably, the above process does not require the external supplement of soluble agonists. Therefore, the activation of GPIIb/IIIa via this pathway was named ‘mechanical affinity maturation’.12 Likely serving as a self-inhibitory mechanism to avoid overly activation of platelets, only the intermediate state, but not inactive state GPIIb/IIIa can undergo outside-in mechanosignaling.12 Importantly, the biomechanically driven activation (via sequential GPIb and GPIIb/IIIa mechanosignaling) and agonist-stimulated activation (via stimulation of soluble agonists) of GPIIb/IIIa are essentially distinctive and probably via differential signaling pathways.12
Mechanoredox coupling has been unravelled as a new mechanism by which GPIIb/IIIa biomechanically regulates platelet thrombosis.120–122 Thiol isomerases, including protein disulfide isomerase (PDI),123 124 endoplasmic reticulum 5 (ERp5)121 125 and ERp57,126 127 are enzymes which regulate the function of platelets by reducing or oxidising disulfide bonds of their cell surface proteins, such as GPIIb/IIIa. Importantly, the regulation of these thiol isomerases can either strengthen or weaken GPIIb/IIIa binding. For example, the PSI domain of GPIIb/IIIa contains an endogenous thiol isomerase function, the inhibition of which suppressed platelet aggregation.128 On the other hand, another thiol isomerase ERp5 is secreted by activated platelets and binds to GPIIIa.121 129 Via reducing the βI domain C177–C184 disulfide bond nearby the fibrinogen binding pocket of GPIIb/IIIa, ERp5 results in the premature release of fibrinogen.125 Importantly, Passam et al identified this process to be force sensitive: RGD-ligand binding to the integrin and shear force can facilitate ERp5 to reduce the disulfide bond, thereby accelerating fibrinogen dissociation125 (figure 2B). This intriguing finding provides a new concept on how platelets harness force to balance haemostatic versus thrombotic functions from a redox perspective.
Targeting GPIIb/IIIa as a novel antithrombotic strategy
Just like GPIb, antagonists that directly block GPIIb/IIIa extracellular binding have been developed for antithrombotic use.81 130 Among them, abciximab, eptifibatide and tirofiban are approved by FDA for acute cardiac ischaemic events. However, these antagonists would compromise haemostasis and induce profound thrombocytopenia with mechanisms incompletely understood.117 131 Clinicians have to heavily rely on the fine tuning of dosage to prevent these side effects from being life-threatening, which often fails.132 As a result, these GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors seem to be restricted to particular high-risk subgroups, such as MI patients undergoing PCI without pretreatment with a P2Y12 antagonist.133 134 In the case of acute/moderate ischaemic stroke, their use is not recommended until multicentre analyses of endovascular stroke therapy necessitating adjunctive GPIIb/IIIa inhibitions are conducted.135
For the last decades, breakthroughs from basic research suggest new antithrombotic therapeutic targets underlying the early phases of GPIIb/IIIa intracellular signaling pathway.92 104 128 136 137 For instance, selectively targeting GPIIb/IIIa downstream signaling molecules PI3Kβ138 and Gα13 104 was shown to inhibit arterial thrombosis without affecting haemostasis under certain doses (table 1; figure 2A). The PI3Kβ inhibitor AZD6482, which suppresses GPIIb/IIIa mechanosignaling in particular, has completed preclinical and phase I clinical trials, and was demonstrated in multiple species including mice, rats, rabbits, dogs and humans for its good tolerance without prolonging skin bleeding time, even when administered at high doses. AZD6482 also demonstrated high efficiency in reducing the disturbed flow enhanced thrombotic response in a diabetic mouse model, which displayed resistance to co-administered aspirin and clopidogrel,139 suggesting that targeting platelet mechanosensing pathways provides a potentially more effective antithrombotic approach for patients with diabetes. On the other hand, inhibiting the interaction between GPIIb/IIIa and Gα13 with a myristoylated peptide ExE peptide motif (mP6) selectively inhibits GPIIb/IIIa mediated platelet spreading but not agonist induced inside-out signaling or fibrinogen ligation104 (figure 2A). This peptide was shown to suppress occlusive arterial thrombosis without affecting bleeding. To explain this, our single-platelet analyses suggested that Gα13 binding is needed for the active EO state activation of GPIIb/IIIa, but not for the intermediate EC state activation12 (unpublished data). As such, preventing GPIIb/IIIa from the EC–EO transition might be a promising strategy to differentiate occlusive thrombosis from haemostasis.
The regulation of thiol isomerases was also suggested for antithrombotic application. For instance, inhibiting the thiol isomerase function of GPIIb/IIIa PSI domain by anti-PSI antibodies was demonstrated to inhibit murine thrombus formation without significantly affecting bleeding128 (figure 2B; table 1). Furthermore, inhibitors of PDI have been identified by high-throughput screening of 350 000 compounds.122 140 Isoquercetin, a first-generation flavonoid anti-PDI drug derived from this screening, demonstrated good efficacy for reducing venous thrombosis in cancer patients in a phase II clinical trial141 (figure 2B; table 1). These exciting results corroborate the rationale of targeting disulfide redox states of GPIIb/IIIa via thiol isomerase inhibitors. Importantly, patients with diabetes and metabolic syndrome have increased thiol isomerase activity in their blood,142 143 which raises the possibility of applying these inhibitors to these patients in the future.
Another promising antithrombotic strategy is to inhibit, but not eliminate, the ligand-binding capacity of GPIIb/IIIa. Catch bond mechanism was demonstrated to reinforce the ligand binding of activated GPIIb/IIIa12; in particular, compared with the EC intermediate state, the lifetime of EO GPIIb/IIIa is not only globally prolonged under all forces but also stretches its ‘catch’ regime with a wider force range12 (figure 2C). Such conformation-specific binding attributes of GPIIb/IIIa leads to steady development of thrombi even under pathologically shear rates in stenosed arteries.5 Taking advantage of this, a potential antithrombotic approach could be to downregulate the catch bond behaviour of activated GPIIb/IIIa at large forces. As a proof-of-concept, we demonstrated that a variant (R77H) in another integrin, αMβ2, suppresses the integrin catch bond at 5–12 pN, but causes no effect to the bond lifetime at lower forces (<5 pN).144 Noting that R77 is located in the β-propeller domain distal to the ligand-binding site, this discovery highlights an allosteric effect in integrin binding regulation by integrin α-subunit, which may also be applied to platelet GPIIb/IIIa. The conformation-specific targeting of GPIIb/IIIa represents another promising approach to partially inhibit GPIIb/IIIa.145 The selective targeting of the active EO conformation of GPIIb/IIIa should inhibit the propagation and stabilisation of thrombi, but not the formation of an initial haemostatic platelet plug on vascular injury—a process that relies on GPIIb/IIIa being in the low-activating BC/EC state.4 12 146 Indeed, this concept has been proven in principle where a single-chain variable fragment (scFv) SCE5 directed against the active conformation of GPIIb/IIIa markedly inhibited thrombosis on both human and mouse platelets (figure 2A),145 but did not prolong bleeding time in mouse models.145 Moreover, conformation-specific scFvs have been used to deliver targeted antithrombotic agents such as the ADP-hydrolysing enzyme CD39,147 the potent factor Xa inhibitor tick anticoagulant peptide148 and the fibrinolytic agent urokinase149 to the selective sites of developing clots, which all displayed potent antithrombotic effects in preclinical models without affecting haemostasis.4
One caveat of GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors is that most of them can potentially induce the receptor to undergo a major conformational change that either exposes neoepitopes for platelet clearance or trigger high-affinity state when the drug dissociates from the receptor, facilitating instead of inhibiting its binding to ligand.150 This could cause the paradoxical increase in mortality on treatment for MI patients. As an alternative, a small-molecule GPIIb/IIIa antagonist, known as RUC-4, binds to the metal ion-binding site on the GPIIb/IIIa. It inhibits ligand binding but does not induce GPIIb/IIIa conformational change or activation (figure 2A). Furthermore, in preclinical studies, RUC-4 showed potent antithrombotic efficacy (table 1).150 An interesting aspect of RUC-4 is its suitability for intramuscular injection, which raises the prospect of administration in prehospital emergency settings.150 However, the bleeding risk profile of this agent remains to be evaluated.
GPVI: a potential mechanosensor and antithrombotic target
Aside from GPIb and GPIIb/IIIa, many other receptors on platelet surface may also mediate platelet mechanosensing. One topical candidate is GPVI, which is exclusively expressed on platelets and megakaryocytes. It is associated with the Fc receptor γ-chain, which contains an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM). Its engagement with ligands, such as collagen, leads to ITAM-dependent signaling and potent platelet activation.81 GPVI plays an important role in haemostasis and thrombosis, not only via its own binding to collagen but also through the triggering of GPIIb/IIIa and integrin α2β1 activation.151 In this context, GPVI was suggested to play a mechanosensing role.152 However, direct evidence and the detailed mechanosensing mechanism are yet to be revealed. Recently, fibrin was identified as a new GPVI ligand.153 154 GPVI–fibrin interaction seems to stabilize thrombus formation under both low-shear and high-shear conditions.153 Moreover, GPVI was suggested to co-associate with GPIbα to coordinate thrombotic output across these haemodynamic conditions.155 Intriguingly, patients and mice with GPVI deficiency only display a mild bleeding diathesis,155 whereas mice lacking GPVI are protected against arterial thrombosis and subsequent neointima formation156 and demonstrate an impaired thrombus formation under high-shear conditions.157
Platelet GPVI has been gradually recognized to play a role in ischaemic stroke.158–160 Platelet adhesion and activation enhance the infarct growth by promoting an inflammatory response.77 GPVI-mediated platelet activation can lead to the release of IL-1α that induces cerebrovascular inflammation.161 Thus, GPVI may serve as an antithromboinflammation target.162 Currently, two strategies targeting GPVI have reached advanced stages of development. The first is the antibody Fab 9O12, which binds and blocks the collagen/fibrin-binding site of GPVI with high affinity153 163 (figure 1). This approach has demonstrable antithrombotic efficacy in preclinical models of thrombosis and seems to maintain haemostasis (table 1). A humanized scFv form of 9O12 is being prepared to enter early phase clinical trial.164 The second anti-GPVI is the humanized Fc fusion protein of the GPVI ectodomain called revacept165 (figure 1). In animal models, revacept protected against thrombosis, ischaemia-reperfusion injury166 and stroke.167 In phase I clinical trials, revacept inhibited collagen-induced human platelet aggregation.165 Phase II trials of revacept in patients with carotid artery stenosis, transient ischaemic attack, or stroke are ongoing (table 1). Interestingly, this therapeutic seems to be particularly potent at inhibiting thrombus growth under pathological shear conditions ex vivo, suggesting that its antithrombotic effects might be maintained at sites of atherosclerotic plaque rupture,168 consistent with the fact that collagens are highly abundant in atherosclerotic plaques. Some other GPVI targeted agents that are under investigation, such as losartan,169 have been shown to inhibit the binding of GPVI to collagen (table 1; figure 1).
Concluding remarks
Many FDA approved antiplatelet agents are less efficient in relieving arterial thrombosis in severe stenosis,170 in part due to that they only target agonist pathways rather than the biomechanical platelet aggregation mechanisms. Hereby, we propose that targeting platelet mechanosensing pathways may represent a novel strategy to prevent thrombotic complications. This new strategy uses high-shear flow as the ‘trigger’ of effect, and therefore should be specific in preventing occlusive thrombosis in stenosed arteries. In parallel, current inhibitors of GPIb and GPIIb/IIIa extracellular activity were shown to cause adverse effect of bleeding, because they are unable to discriminate the haemostatic versus thrombotic conditions.171 172 From a biomechanical perspective, we highlight that although thrombosis and haemostasis share similarity in most aspects, a key difference is that only thrombosis heavily relies on shear-resistant platelet aggregation for endovascular clot growth. This comparison is supported by an interesting evolutionary perspective: the avian thrombocytes have similar adhesion and signaling behaviours as mammalian platelets, but cannot form shear-resistant aggregates173; in consequence, thrombocytes support haemostasis but cannot form occlusive thrombi in vivo. Therefore, inhibitors that weaken GPIb and GPIIb/IIIa binding under thrombotic haemodynamic conditions, should selectively prevent shear-resistant platelet aggregates towards artery occlusion. The above new antithrombotic strategies, which are under development or yet to be tested, promise a ‘mechano-medicine’ to solve the long lingering question of how to effectively inhibit arterial thrombosis without causing excessive bleeding.
Footnotes
YC and LAJ contributed equally.
Correction notice: This article has been corrected since it was first published. Orcid iD for
author Lining Arnold Ju has been added.
Contributors: Both authors wrote the manuscript and made the table. YC drew the figures.
Funding: This work was supported by grants from Sydney Research Accelerator (SOAR) prize (L.A.J.), The Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia Kanematsu research award (L.A.J.) and the Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand BAYER Young Investigator Research Grant (L.A.J.). We thank Zaverio Ruggeri, Yilong Wang, Liping Liu, Jing-fei Dong and Yi Qian for helpful discussion. Y.C. is a MERU (Medolago-Ruggeri) Foundation post-doctoral awardee. L.A.J. is an Australian Research Council DECRA fellow (DE190100609) and a National Heart Foundation Future Leader fellow (102532).
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent for publication: Not required.
Provenance and peer review: Commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
References
- 1. Jackson SP. Arterial thrombosis--insidious, unpredictable and deadly. Nat Med 2011;17:1423–36. 10.1038/nm.2515 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, et al. Heart disease and stroke Statistics-2018 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation 2018;137:e67–492. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000558 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Angiolillo DJ, Bernardo E, Sabaté M, et al. Impact of platelet reactivity on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;50:1541–7. 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.05.049 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. McFadyen JD, Schaff M, Peter K. Current and future antiplatelet therapies: emphasis on preserving haemostasis. Nat Rev Cardiol 2018;15:181–91. 10.1038/nrcardio.2017.206 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Nesbitt WS, Westein E, Tovar-Lopez FJ, et al. A shear gradient–dependent platelet aggregation mechanism drives thrombus formation. Nat Med 2009;15:665–73. 10.1038/nm.1955 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Chen Y, Ju L, Rushdi M, et al. Receptor-Mediated cell mechanosensing. Mol Biol Cell 2017;28:3134–55. 10.1091/mbc.e17-04-0228 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Hansen CE, Qiu Y, McCarty OJT, et al. Platelet mechanotransduction. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 2018;20:253–75. 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-062117-121215 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Mazzucato M, Pradella P, Cozzi MR, et al. Sequential cytoplasmic calcium signals in a 2-stage platelet activation process induced by the glycoprotein Ibalpha mechanoreceptor. Blood 2002;100:2793–800. 10.1182/blood-2002-02-0514 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Nesbitt WS, Kulkarni S, Giuliano S, et al. Distinct Glycoprotein Ib/V/IX and Integrin α IIb β 3 -dependent Calcium Signals Cooperatively Regulate Platelet Adhesion under Flow. J Biol Chem 2002;277:2965–72. 10.1074/jbc.M110070200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Kasirer-Friede A, Cozzi MR, Mazzucato M, et al. Signaling through GP Ib-IX-V activates αIIbβ3 independently of other receptors. Blood 2004;103:3403–11. 10.1182/blood-2003-10-3664 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Qiu Y, Brown AC, Myers DR, et al. Platelet mechanosensing of substrate stiffness during clot formation mediates adhesion, spreading, and activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014;111:14430–5. 10.1073/pnas.1322917111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Chen Y, Ju LA, Zhou F, et al. An integrin αIIbβ3 intermediate affinity state mediates biomechanical platelet aggregation. Nat Mater 2019;18:760–9. 10.1038/s41563-019-0323-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Savage B, Almus-Jacobs F, Ruggeri ZM. Specific synergy of multiple Substrate–Receptor interactions in platelet thrombus formation under flow. Cell 1998;94:657–66. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81607-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Furlan M. Von Willebrand factor: molecular size and functional activity. Ann Hematol 1996;72:341–8. 10.1007/s002770050184 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Ikeda Y, Handa M, Kawano K, et al. The role of von Willebrand factor and fibrinogen in platelet aggregation under varying shear stress. J Clin Invest 1991;87:1234–40. 10.1172/JCI115124 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Springer TA. Biology and physics of von Willebrand factor concatamers. J Thromb Haemost 2011;9:130–43. 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04320.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Farrell DH, Thiagarajan P, Chung DW, et al. Role of fibrinogen alpha and gamma chain sites in platelet aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1992;89:10729–32. 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10729 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Peter K, Schwarz M, Ylänne J, et al. Induction of fibrinogen binding and platelet aggregation as a potential intrinsic property of various glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (alphaIIbbeta3) inhibitors. Blood 1998;92:3240–9. 10.1182/blood.V92.9.3240.421k21_3240_3249 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Rooney MM, Farrell DH, van Hemel BM, et al. The contribution of the three hypothesized integrin-binding sites in fibrinogen to platelet-mediated clot retraction. Blood 1998;92:2374–81. 10.1182/blood.V92.7.2374 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Ni H, Yuen PST, Papalia JM, et al. Plasma fibronectin promotes thrombus growth and stability in injured arterioles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003;100:2415–9. 10.1073/pnas.2628067100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Wang Y, Reheman A, Spring CM, et al. Plasma fibronectin supports hemostasis and regulates thrombosis. J Clin Invest 2014;124:4281–93. 10.1172/JCI74630 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Cho J, Mosher DF. Impact of fibronectin assembly on platelet thrombus formation in response to type I collagen and von Willebrand factor. Blood 2006;108:2229–36. 10.1182/blood-2006-02-002063 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Savage B, Saldívar E, Ruggeri ZM. Initiation of platelet adhesion by arrest onto fibrinogen or translocation on von Willebrand factor. Cell 1996;84:289–97. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80983-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Ruggeri ZM. Platelet adhesion under flow. Microcirculation 2009;16:58–83. 10.1080/10739680802651477 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Goto S, Ikeda Y, Saldívar E, et al. Distinct mechanisms of platelet aggregation as a consequence of different shearing flow conditions. J Clin Invest 1998;101:479–86. 10.1172/JCI973 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Ruggeri ZM, Orje JN, Habermann R, et al. Activation-Independent platelet adhesion and aggregation under elevated shear stress. Blood 2006;108:1903–10. 10.1182/blood-2006-04-011551 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Sakurai Y, Fitch-Tewfik JL, Qiu Y, et al. Platelet geometry sensing spatially regulates α-granule secretion to enable matrix self-deposition. Blood 2015;126:531–8. 10.1182/blood-2014-11-607614 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. McCarty OJT, Calaminus SDJ, Berndt MC, et al. von Willebrand factor mediates platelet spreading through glycoprotein Ib and alpha(IIb)beta3 in the presence of botrocetin and ristocetin, respectively. J Thromb Haemost 2006;4:1367–78. 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.01966.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Merten M. & Thiagarajan, P. P-selectin expression on platelets determines size and stability of platelet aggregates. Circulation 2000;102:1931–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Zhang D, Gao Z-G, Zhang K, et al. Two disparate ligand-binding sites in the human P2Y1 receptor. Nature 2015;520:317–21. 10.1038/nature14287 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Hollopeter G, Jantzen H-M, Vincent D, et al. Identification of the platelet ADP receptor targeted by antithrombotic drugs. Nature 2001;409:202–7. 10.1038/35051599 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Offermanns S. Activation of platelet function through G Protein–Coupled receptors. Circ Res 2006;99:1293–304. 10.1161/01.RES.0000251742.71301.16 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Coughlin SR. How the protease thrombin talks to cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999;96:11023–7. 10.1073/pnas.96.20.11023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Kaplan ZS, Jackson SP. The role of platelets in atherothrombosis. Hematology 2011;2011:51–61. 10.1182/asheducation-2011.1.51 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Bennett JS, Vilaire G. Exposure of platelet fibrinogen receptors by ADP and epinephrine. J Clin Invest 1979;64:1393–401. 10.1172/JCI109597 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Damman P, Woudstra P, Kuijt WJ, et al. P2Y12 platelet inhibition in clinical practice. J Thromb Thrombolysis 2012;33:143–53. 10.1007/s11239-011-0667-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Smith JB, Araki H, Lefer AM. Thromboxane A2, prostacyclin and aspirin: effects on vascular tone and platelet aggregation. Circulation 1980;62:V19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Ageno W, Gallus AS, Wittkowsky A, et al. Oral anticoagulant therapy: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ED: American College of chest physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2012;141:e44S–88. 10.1378/chest.11-2292 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Chesebro JH, Badimon JJ, Hassinger NL, et al. Acute myocardial infarction and the role of aspirin, heparin, and warfarin. J Thromb Thrombolysis 1995;1:231–5. 10.1007/BF01060732 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Zhang XF, Cheng X. Platelet mechanosensing axis revealed. Nat Mater 2019;18:661–2. 10.1038/s41563-019-0393-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Springer TA, factor vonW. Jedi knight of the bloodstream. Blood 2014;124:1412–25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Ulrichts H, Udvardy M, Lenting PJ, et al. Shielding of the A1 domain by the D'D3 domains of von Willebrand factor modulates its interaction with platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX-V. J Biol Chem 2006;281:4699–707. 10.1074/jbc.M513314200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Aponte-Santamaría C, Huck V, Posch S, et al. Force-sensitive autoinhibition of the von Willebrand factor is mediated by interdomain interactions. Biophys J 2015;108:2312–21. 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.03.041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Martin C, Morales LD, Cruz MA. Purified A2 domain of von Willebrand factor binds to the active conformation of von Willebrand factor and blocks the interaction with platelet glycoprotein Ibalpha. J Thromb Haemost 2007;5:1363–70. 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02536.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Sing CE, Alexander-Katz A. Elongational Flow Induces the Unfolding of von Willebrand Factor at Physiological Flow Rates. Biophys J 2010;98:L35–7. 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.01.032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Fu H, Jiang Y, Yang D, et al. Flow-Induced elongation of von Willebrand factor precedes tension-dependent activation. Nat Commun 2017;8:324 10.1038/s41467-017-00230-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Barg A, Ossig R, Goerge T, et al. Soluble plasma-derived von Willebrand factor assembles to a haemostatically active filamentous network. Thromb Haemost 2007;97:514–26. 10.1160/TH06-05-0274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Schneider SW, Nuschele S, Wixforth A, et al. Shear-Induced unfolding triggers adhesion of von Willebrand factor fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;104:7899–903. 10.1073/pnas.0608422104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Löf A, Müller JP, Brehm MA. A biophysical view on von Willebrand factor activation. J Cell Physiol 2018;233:799–810. 10.1002/jcp.25887 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Savage B, Sixma JJ, Ruggeri ZM. Functional self-association of von Willebrand factor during platelet adhesion under flow. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002;99:425–30. 10.1073/pnas.012459599 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Dayananda KM, Singh I, Mondal N, et al. Von Willebrand factor self-association on platelet GpIbα under hydrodynamic shear: effect on shear-induced platelet activation. Blood 2010;116:3990–8. 10.1182/blood-2010-02-269266 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Butera D, Passam F, Ju L, et al. Autoregulation of von Willebrand factor function by a disulfide bond switch. Sci Adv 2018;4:eaaq1477 10.1126/sciadv.aaq1477 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Murphy DA, Hockings LE, Andrews RK, et al. Extracorporeal membrane Oxygenation—Hemostatic complications. Transfus Med Rev 2015;29:90–101. 10.1016/j.tmrv.2014.12.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Doggett TA, Girdhar G, Lawshé A, et al. Selectin-Like kinetics and biomechanics promote rapid platelet adhesion in flow: the GPIbα-vWF tether bond. Biophys J 2002;83:194–205. 10.1016/S0006-3495(02)75161-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Yago T, Lou J, Wu T, et al. Platelet glycoprotein Ibalpha forms catch bonds with human WT vWF but not with type 2B von Willebrand disease vWF. J Clin Invest 2008;118:3195–207. 10.1172/JCI35754 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Doggett TA, Girdhar G, Lawshe A, et al. Alterations in the intrinsic properties of the GPIbα–VWF tether bond define the kinetics of the platelet-type von Willebrand disease mutation, Gly233Val. Blood 2003;102:152–60. 10.1182/blood-2003-01-0072 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Ju L, Dong J-fei, Cruz MA, et al. The N-terminal flanking region of the A1 domain regulates the force-dependent binding of von Willebrand factor to platelet glycoprotein Ibα. J Biol Chem 2013;288:32289–301. 10.1074/jbc.M113.504001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Ju L, Lou J, Chen Y, et al. Force-Induced unfolding of leucine-rich repeats of glycoprotein Ibα strengthens ligand interaction. Biophys J 2015;109:1781–4. 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.08.050 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Le Behot A, Gauberti M, Martinez De Lizarrondo S, et al. GpIbα-VWF blockade restores vessel patency by dissolving platelet aggregates formed under very high shear rate in mice. Blood 2014;123:3354–63. 10.1182/blood-2013-12-543074 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Ju L, Chen Y, Xue L, et al. Cooperative unfolding of distinctive mechanoreceptor domains transduces force into signals. eLife 2016;5:e15447 10.7554/eLife.15447 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Yap CL, Hughan SC, Cranmer SL, et al. Synergistic adhesive interactions and signaling mechanisms operating between platelet glycoprotein Ib/IX and integrin alpha IIbbeta 3. Studies in human platelets ANS transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem 2000;275:41377–88. 10.1074/jbc.M005590200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Nesbitt WS, Giuliano S, Kulkarni S, et al. Intercellular calcium communication regulates platelet aggregation and thrombus growth. J Cell Biol 2003;160:1151–61. 10.1083/jcb.200207119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Ju L, Chen Y, Li K, et al. Dual biomembrane force probe enables single-cell mechanical analysis of signal crosstalk between multiple molecular species. Sci Rep 2017;7:14185 10.1038/s41598-017-13793-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Gu M, Xi X, Englund GD, et al. Analysis of the Roles of 14-3-3 in the Platelet Glycoprotein Ib-IX–Mediated Activation of Integrin α IIb β 3 Using a Reconstituted Mammalian Cell Expression Model. J Cell Biol 1999;147:1085–96. 10.1083/jcb.147.5.1085 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Feng S, Reséndiz JC, Lu X, et al. Filamin a binding to the cytoplasmic tail of glycoprotein Ibα regulates von Willebrand factor–induced platelet activation. Blood 2003;102:2122–9. 10.1182/blood-2002-12-3805 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Yin H, Liu J, Li Z, et al. Src family tyrosine kinase Lyn mediates VWF/GPIb-IX–induced platelet activation via the cGMP signaling pathway. Blood 2008;112:1139–46. 10.1182/blood-2008-02-140970 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Estevez B, Du X. New concepts and mechanisms of platelet activation signaling. Physiology 2017;32:162–77. 10.1152/physiol.00020.2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Clemetson J, Clemetson K. Platelet GPIb complex as a target for anti-thrombotic drug development. Thromb Haemost 2008;99:473–9. 10.1160/TH07-12-0718 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Chen J, Tan K, Zhou H, et al. Modifying murine von Willebrand factor A1 domain for in vivo assessment of human platelet therapies. Nat Biotechnol 2008;26:114–9. 10.1038/nbt1373 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Chen J, Zhou H, Diacovo A, et al. Exploiting the kinetic interplay between GPIbα–VWF binding interfaces to regulate hemostasis and thrombosis. Blood 2014;124:3799–807. 10.1182/blood-2014-04-569392 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Ulrichts H, Silence K, Schoolmeester A, et al. Antithrombotic drug candidate ALX-0081 shows superior preclinical efficacy and safety compared with currently marketed antiplatelet drugs. Blood 2011;118:757–65. 10.1182/blood-2010-11-317859 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Momi S, Tantucci M, Van Roy M, et al. Reperfusion of cerebral artery thrombosis by the GPIb–VWF blockade with the nanobody ALX-0081 reduces brain infarct size in guinea pigs. Blood 2013;121:5088–97. 10.1182/blood-2012-11-464545 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Kanaji S, Orje JN, Kanaji T, et al. Humanized GPIbα-von Willebrand factor interaction in the mouse. Blood Adv 2018;2:2522–32. 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018023507 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Wadanoli M, Sako D, Shaw G, et al. The von Willebrand factor antagonist (GPG-290) prevents coronary thrombosis without prolongation of bleeding time. Thromb Haemost 2007;98:397–405. 10.1160/TH06-10-0582 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Bae O-N. Targeting von Willebrand factor as a novel anti-platelet therapy; application of ARC1779, an anti-vWF aptamer, against thrombotic risk. Arch Pharm Res 2012;35:1693–9. 10.1007/s12272-012-1000-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Cauwenberghs N, Meiring M, Vauterin S, et al. Antithrombotic effect of platelet glycoprotein Ib-blocking monoclonal antibody Fab fragments in nonhuman primates. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2000;20:1347–53. 10.1161/01.ATV.20.5.1347 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Kleinschnitz C, et al. Targeting platelets in acute experimental stroke: impact of glycoprotein Ib, VI, and IIb/IIIa blockade on infarct size, functional outcome, and intracranial bleeding. Circulation 2007;115:2323–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Yeh C-H, Chang M-C, Peng H-C, et al. Pharmacological characterization and antithrombotic effect of agkistin, a platelet glycoprotein Ib antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 2001;132:843–50. 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703865 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Lei X, Reheman A, Hou Y, et al. Anfibatide, a novel GPIb complex antagonist, inhibits platelet adhesion and thrombus formation in vitro and in vivo in murine models of thrombosis. Thromb Haemost 2014;111:279–89. 10.1160/TH13-06-0490 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Stoll G, Kleinschnitz C, Nieswandt B. Molecular mechanisms of thrombus formation in ischemic stroke: novel insights and targets for treatment. Blood 2008;112:3555–62. 10.1182/blood-2008-04-144758 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Xu XR, Carrim N, Neves MAD, et al. Platelets and platelet adhesion molecules: novel mechanisms of thrombosis and anti-thrombotic therapies. Thromb J 2016;14:29 10.1186/s12959-016-0100-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Li T-T, Fan M-L, Hou S-X, et al. A novel snake venom-derived GPIb antagonist, anfibatide, protects mice from acute experimental ischaemic stroke and reperfusion injury. Br J Pharmacol 2015;172:3904–16. 10.1111/bph.13178 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Zheng L, Mao Y, Abdelgawwad MS, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of the platelet glycoprotein Ib antagonist anfibatide in murine models of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood Advances 2016;1:75–83. 10.1182/bloodadvances.2016000711 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Sinha G. Ablynx drops lead nanobody. Nat Biotechnol 2012;30:124 10.1038/nbt0212-124a 22318018 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Markus HS, McCollum C, Imray C, et al. The von Willebrand inhibitor ARC1779 reduces cerebral embolization after carotid endarterectomy. Stroke 2011;42:2149–53. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.616649 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Duggan S. Caplacizumab: first global approval. Drugs 2018;78:1639–42. 10.1007/s40265-018-0989-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Scully M, Cataland SR, Peyvandi F, et al. Caplacizumab treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med 2019;380:335–46. 10.1056/NEJMoa1806311 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Donadelli R, Orje JN, Capoferri C, et al. Size regulation of von Willebrand factor–mediated platelet thrombi by ADAMTS13 in flowing blood. Blood 2006;107:1943–50. 10.1182/blood-2005-07-2972 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Shida Y, Swystun LL, Brown C, et al. Shear stress and platelet-induced tensile forces regulate ADAMTS13-localization within the platelet thrombus. Res Pract Thromb Haemost 2019;3:254–60. 10.1002/rth2.12196 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Chen X, Cheng X, Zhang S, et al. Adamts13: an emerging target in stroke therapy. Front Neurol 2019;10:772 10.3389/fneur.2019.00772 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Zhao B-Q, Chauhan AK, Canault M, et al. Von Willebrand factor–cleaving protease ADAMTS13 reduces ischemic brain injury in experimental stroke. Blood 2009;114:3329–34. 10.1182/blood-2009-03-213264 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Yin H, Stojanovic-Terpo A, Xu W, et al. Role for platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX and effects of its inhibition in endotoxemia-induced thrombosis, thrombocytopenia, and mortality. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2013;33:2529–37. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Dai K, Bodnar R, Berndt MC, et al. A critical role for 14-3-3ζ protein in regulating the vWF binding function of platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX and its therapeutic implications. Blood 2005;106:1975–81. 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0440 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Labrijn AF, Janmaat ML, Reichert JM, et al. Bispecific antibodies: a mechanistic review of the pipeline. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2019;18:585–608. 10.1038/s41573-019-0028-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Takagi J, Petre BM, Walz T, et al. Global conformational rearrangements in integrin extracellular domains in outside-in and inside-out signaling. Cell 2002;110:599–611. 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00935-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Ye F, Hu G, Taylor D, et al. Recreation of the terminal events in physiological integrin activation. J Cell Biol 2010;188:157–73. 10.1083/jcb.200908045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Ye F, Kim C, Ginsberg MH. Reconstruction of integrin activation. Blood 2012;119:26–33. 10.1182/blood-2011-04-292128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Xiao T, Takagi J, Coller BS, et al. Structural basis for allostery in integrins and binding to fibrinogen-mimetic therapeutics. Nature 2004;432:59–67. 10.1038/nature02976 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Peterson JA, Nelson TN, Kanack AJ, et al. Fine specificity of drug-dependent antibodies reactive with a restricted domain of platelet GPIIIa. Blood 2008;111:1234–9. 10.1182/blood-2007-09-112680 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Mitchell WB, Li J, Murcia M, et al. Mapping early conformational changes in alphaIIb and beta3 during biogenesis reveals a potential mechanism for alphaIIbbeta3 adopting its bent conformation. Blood 2007;109:3725–32. 10.1182/blood-2006-11-058420 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Litvinov RI, Barsegov V, Schissler AJ, et al. Dissociation of bimolecular αIIbβ3-fibrinogen complex under a constant tensile force. Biophys J 2011;100:165–73. 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.11.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Litvinov RI, Mekler A, Shuman H, et al. Resolving two-dimensional kinetics of the integrin αIIbβ3-fibrinogen interactions using binding-unbinding correlation spectroscopy. J Biol Chem 2012;287:35275–85. 10.1074/jbc.M112.404848 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Litvinov RI, Farrell DH, Weisel JW, et al. The platelet integrin αIIbβ3 differentially interacts with fibrin versus fibrinogen. J Biol Chem 2016;291:7858–67. 10.1074/jbc.M115.706861 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Shen B, Zhao X, O'Brien KA, et al. A directional switch of integrin signalling and a new anti-thrombotic strategy. Nature 2013;503:131–5. 10.1038/nature12613 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 2002;110:673–87. 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00971-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106. Yang J, Zhu L, Zhang H, et al. Conformational activation of talin by RIAM triggers integrin-mediated cell adhesion. Nat Commun 2014;5:5880 10.1038/ncomms6880 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Schürpf T, Springer TA. Regulation of integrin affinity on cell surfaces. Embo J 2011;30:4712–27. 10.1038/emboj.2011.333 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Luo B-H, Carman CV, Springer TA. Structural basis of integrin regulation and signaling. Annu Rev Immunol 2007;25:619–47. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141618 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109. Xie C, Zhu J, Chen X, et al. Structure of an integrin with an alphaI domain, complement receptor type 4. Embo J 2010;29:666–79. 10.1038/emboj.2009.367 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110. Nishida N, Xie C, Shimaoka M, et al. Activation of leukocyte beta2 integrins by conversion from bent to extended conformations. Immunity 2006;25:583–94. 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.07.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111. Takagi J, Strokovich K, Springer TA, et al. Structure of integrin alpha5beta1 in complex with fibronectin. Embo J 2003;22:4607–15. 10.1093/emboj/cdg445 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112. Li J, Springer TA. Energy landscape differences among integrins establish the framework for understanding activation. J Cell Biol 2018;217:397–412. 10.1083/jcb.201701169 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113. Zhu J, Zhu J, Springer TA. Complete integrin headpiece opening in eight steps. J Cell Biol 2013;201:1053–68. 10.1083/jcb.201212037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114. Bledzka K, Smyth SS, Plow EF. Integrin αIIbβ3: from discovery to efficacious therapeutic target. Circ Res 2013;112:1189–200. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.300570 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115. Hodivala-Dilke KM, McHugh KP, Tsakiris DA, et al. Beta3-integrin-deficient mice are a model for Glanzmann thrombasthenia showing placental defects and reduced survival. J Clin Invest 1999;103:229–38. 10.1172/JCI5487 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116. Ni H, Denis CV, Subbarao S, et al. Persistence of platelet thrombus formation in arterioles of mice lacking both von Willebrand factor and fibrinogen. J Clin Invest 2000;106:385–92. 10.1172/JCI9896 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117. Ley K, Rivera-Nieves J, Sandborn WJ, et al. Integrin-Based therapeutics: biological basis, clinical use and new drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2016;15:173–83. 10.1038/nrd.2015.10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118. Li A, Guo Q, Kim C, et al. Integrin αII B tail distal of GFFKR participates in inside-out αII B β3 activation. J Thromb Haemost 2014;12:1145–55. 10.1111/jth.12610 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119. Feral CC, Nishiya N, Fenczik CA, et al. Cd98Hc (SLC3A2) mediates integrin signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005;102:355–60. 10.1073/pnas.0404852102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120. Sharda A, Furie B. Regulatory role of thiol isomerases in thrombus formation. Expert Rev Hematol 2018;11:437–48. 10.1080/17474086.2018.1452612 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121. Passam FH, Lin L, Gopal S, et al. Both platelet- and endothelial cell-derived ERp5 support thrombus formation in a laser-induced mouse model of thrombosis. Blood 2015;125:2276–85. 10.1182/blood-2013-12-547208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122. Jasuja R, Passam FH, Kennedy DR, et al. Protein disulfide isomerase inhibitors constitute a new class of antithrombotic agents. J Clin Invest 2012;122:2104–13. 10.1172/JCI61228 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123. Cho J, Furie BC, Coughlin SR, et al. A critical role for extracellular protein disulfide isomerase during thrombus formation in mice. J Clin Invest 2008;118:1123–31. 10.1172/JCI34134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124. Cho J, Kennedy DR, Lin L, et al. Protein disulfide isomerase capture during thrombus formation in vivo depends on the presence of β3 integrins. Blood 2012;120:647–55. 10.1182/blood-2011-08-372532 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125. Passam F, Chiu J, Ju L, et al. Mechano-redox control of integrin de-adhesion. Elife 2018;7 10.7554/eLife.34843. [Epub ahead of print: 22 06 2018]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126. Wang L, Wu Y, Zhou J, et al. Platelet-Derived ERp57 mediates platelet incorporation into a growing thrombus by regulation of the αIIbβ3 integrin. Blood 2013;122:3642–50. 10.1182/blood-2013-06-506691 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127. Holbrook L-M, Sasikumar P, Stanley RG, et al. The platelet-surface thiol isomerase enzyme ERp57 modulates platelet function. J Thromb Haemost 2012;10:278–88. 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04593.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128. Zhu G, Zhang Q, Reddy EC, et al. The integrin PSI domain has an endogenous thiol isomerase function and is a novel target for antiplatelet therapy. Blood 2017;129:1840–54. 10.1182/blood-2016-07-729400 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129. Jordan PA, Stevens JM, Hubbard GP, et al. A role for the thiol isomerase protein ERP5 in platelet function. Blood 2005;105:1500–7. 10.1182/blood-2004-02-0608 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130. Huang J, Li X, Shi X, et al. Platelet integrin αIIbβ3: signal transduction, regulation, and its therapeutic targeting. J Hematol Oncol 2019;12 10.1186/s13045-019-0709-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131. Kam PCA, Egan MK. Platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists: pharmacology and clinical developments. Anesthesiology 2002;96:1237–49. 10.1097/00000542-200205000-00029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132. Derex L, Paris C, Nighoghossian N. Combining intravenous thrombolysis and antithrombotic agents in stroke: an update. J Am Heart Assoc 2018;7 10.1161/JAHA.117.007454. [Epub ahead of print: 13 01 2018]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133. Kastrati A, Mehilli J, Neumann F-J, et al. Abciximab in patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention after clopidogrel pretreatment: the ISAR-REACT 2 randomized trial. JAMA 2006;295:1531–8. 10.1001/jama.295.13.joc60034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134. Bosch X, Marrugat J, Sanchis J. Platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa blockers during percutaneous coronary intervention and as the initial medical treatment of non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndromes. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2013:CD002130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American heart Association/American stroke association. Stroke 2019. 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 136. Wang Y, Gao H, Shi C, et al. Leukocyte integrin Mac-1 regulates thrombosis via interaction with platelet GPIbα. Nat Commun 2017;8:15559 10.1038/ncomms15559 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137. Xu XR, Wang Y, Adili R, et al. Apolipoprotein A-IV binds αIIbβ3 integrin and inhibits thrombosis. Nat Commun 2018;9:3608 10.1038/s41467-018-05806-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138. Jackson SP, Schoenwaelder SM, Goncalves I, et al. Pi 3-kinase p110beta: a new target for antithrombotic therapy. Nat Med 2005;11:507–14. 10.1038/nm1232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139. Ju L, McFadyen JD, Al-Daher S, et al. Compression force sensing regulates integrin αIIbβ3 adhesive function on diabetic platelets. Nat Commun 2018;9:1087 10.1038/s41467-018-03430-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140. Khodier C, et al. Identification of ML359 as a Small Molecule Inhibitor of Protein Disulfide Isomerase. Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 141. Zwicker JI, Schlechter BL, Stopa JD, et al. Targeting protein disulfide isomerase with the flavonoid isoquercetin to improve hypercoagulability in advanced cancer. JCI Insight 2019;4 10.1172/jci.insight.125851. [Epub ahead of print: 21 02 2019]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142. Chien C-Y, Hung Y-J, Shieh Y-S, et al. A novel potential biomarker for metabolic syndrome in Chinese adults: circulating protein disulfide isomerase family A, member 4. PLoS One 2017;12:e0179963 10.1371/journal.pone.0179963 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143. Raturi A, Miersch S, Hudson JW, et al. Platelet microparticle-associated protein disulfide isomerase promotes platelet aggregation and inactivates insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta 2008;1778:2790–6. 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.07.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144. Rosetti F, Chen Y, Sen M, et al. A Lupus-associated Mac-1 variant has defects in integrin allostery and interaction with ligands under force. Cell Rep 2015;10:1655–64. 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.02.037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145. Schwarz M, Meade G, Stoll P, et al. Conformation-Specific blockade of the integrin GPIIb/IIIa: a novel antiplatelet strategy that selectively targets activated platelets. Circ Res 2006;99:25–33. 10.1161/01.RES.0000232317.84122.0c [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146. Armstrong PC, Peter K. Gpiib/Iiia inhibitors: from bench to bedside and back to bench again. Thromb Haemost 2012;107:808–14. 10.1160/TH11-10-0727 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147. Hohmann JD, Wang X, Krajewski S, et al. Delayed targeting of CD39 to activated platelet GPIIb/IIIa via a single-chain antibody: breaking the link between antithrombotic potency and bleeding? Blood 2013;121:3067–75. 10.1182/blood-2012-08-449694 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148. Stoll P, Bassler N, Hagemeyer CE, et al. Targeting ligand-induced binding sites on GPIIb/IIIa via single-chain antibody allows effective anticoagulation without bleeding time prolongation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2007;27:1206–12. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.106.138875 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149. Wang X, Palasubramaniam J, Gkanatsas Y, et al. Towards effective and safe thrombolysis and thromboprophylaxis: preclinical testing of a novel antibody-targeted recombinant plasminogen activator directed against activated platelets. Circ Res 2014;114:1083–93. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302514 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150. Li J, Vootukuri S, Shang Y, et al. RUC-4: a novel αIIbβ3 antagonist for prehospital therapy of myocardial infarction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2014;34:2321–9. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303724 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151. Lecut C, Schoolmeester A, Kuijpers MJE, et al. Principal role of glycoprotein VI in alpha2beta1 and alphaIIbbeta3 activation during collagen-induced thrombus formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004;24:1727–33. 10.1161/01.ATV.0000137974.85068.93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152. Kee MF, Myers DR, Sakurai Y, et al. Platelet mechanosensing of collagen matrices. PLoS One 2015;10:e0126624 10.1371/journal.pone.0126624 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153. Mammadova-Bach E, Ollivier V, Loyau S, et al. Platelet glycoprotein VI binds to polymerized fibrin and promotes thrombin generation. Blood 2015;126:683–91. 10.1182/blood-2015-02-629717 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154. Alshehri OM, Hughes CE, Montague S, et al. Fibrin activates GPVI in human and mouse platelets. Blood 2015;126:1601–8. 10.1182/blood-2015-04-641654 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155. Gardiner EE. Proteolytic processing of platelet receptors. Res Pract Thromb Haemost 2018;2:240–50. 10.1002/rth2.12096 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156. Konishi H, Katoh Y, Takaya N, et al. Platelets activated by collagen through immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif play pivotal role in initiation and generation of neointimal hyperplasia after vascular injury. Circulation 2002;105:912–6. 10.1161/hc0802.105256 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157. Massberg S, Gawaz M, Grüner S, et al. A crucial role of glycoprotein VI for platelet recruitment to the injured arterial wall in vivo. J Exp Med 2003;197:41–9. 10.1084/jem.20020945 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158. Bigalke B, Stellos K, Geisler T, et al. Expression of platelet glycoprotein VI is associated with transient ischemic attack and stroke. Eur J Neurol 2010;17:111–7. 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2009.02754.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159. Induruwa I, Jung SM, Warburton EA. Beyond antiplatelets: the role of glycoprotein VI in ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke 2016;11:618–25. 10.1177/1747493016654532 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160. Al-Tamimi M, Gardiner EE, Thom JY, et al. Soluble glycoprotein VI is raised in the plasma of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2011;42:498–500. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.602532 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161. Thornton P, McColl BW, Greenhalgh A, et al. Platelet interleukin-1alpha drives cerebrovascular inflammation. Blood 2010;115:3632–9. 10.1182/blood-2009-11-252643 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162. Dütting S, Bender M, Nieswandt B. Platelet GPVI: a target for antithrombotic therapy?! Trends Pharmacol Sci 2012;33:583–90. 10.1016/j.tips.2012.07.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163. Ohlmann P, Hechler B, Ravanat C, et al. Ex vivo inhibition of thrombus formation by an anti-glycoprotein VI Fab fragment in non-human primates without modification of glycoprotein VI expression. J Thromb Haemost 2008;6:1003–11. 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.02976.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164. Muzard J, Bouabdelli M, Zahid M, et al. Design and humanization of a murine scFv that blocks human platelet glycoprotein VI in vitro. Febs J 2009;276:4207–22. 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07129.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165. Ungerer M, Rosport K, Bültmann A, et al. Novel antiplatelet drug revacept (dimeric glycoprotein VI-Fc) specifically and efficiently inhibited collagen-induced platelet aggregation without affecting general hemostasis in humans. Circulation 2011;123:1891–9. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.980623 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166. Pachel C, Mathes D, Arias-Loza A-P, et al. Inhibition of platelet GPVI protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2016;36:629–35. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305873 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167. Goebel S, Li Z, Vogelmann J, et al. The GPVI-Fc fusion protein Revacept improves cerebral infarct volume and functional outcome in stroke. PLoS One 2013;8:e66960 10.1371/journal.pone.0066960 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168. Jamasbi J, Megens RTA, Bianchini M, et al. Differential inhibition of human atherosclerotic Plaque-Induced platelet activation by dimeric GPVI-Fc and Anti-GPVI antibodies: functional and imaging studies. J Am Coll Cardiol 2015;65:2404–15. 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.03.573 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169. Jiang P, Loyau S, Tchitchinadze M, et al. Inhibition of glycoprotein VI clustering by collagen as a mechanism of inhibiting collagen-induced platelet responses: the example of losartan. PLoS One 2015;10:e0128744 10.1371/journal.pone.0128744 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170. Braunwald E. Aortic stenosis: then and now. Circulation 2018;137:2099–100. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.033408 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171. Cranmer SL, Ashworth KJ, Yao Y, et al. High shear-dependent loss of membrane integrity and defective platelet adhesion following disruption of the GPIbα-filamin interaction. Blood 2011;117:2718–27. 10.1182/blood-2010-07-296194 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172. Fan Z, McArdle S, Marki A, et al. Neutrophil recruitment limited by high-affinity bent β2 integrin binding ligand in cis. Nat Commun 2016;7:12658 10.1038/ncomms12658 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173. Schmaier AA, Stalker TJ, Runge JJ, et al. Occlusive thrombi arise in mammals but not birds in response to arterial injury: evolutionary insight into human cardiovascular disease. Blood 2011;118:3661–9. 10.1182/blood-2011-02-338244 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]