The T3SS is a key virulence factor required for C. trachomatis infection. The control of the T3SS has not been well studied in this obligate intracellular pathogen. Here, we show that Scc4 plays a major role for precise control of the pathogenic T3SS at the levels of gene expression and effector secretion through genetically separable protein networks, allowing a fast adaptive mode of C. trachomatis development during infection in human epithelial cells.
KEYWORDS: Chlamydia trachomatis, CopN, RNA polymerases, RpoB, Scc4, developmental cycle, gene expression, sigma 66, type III secretion system, transcription regulation
ABSTRACT
Chlamydia trachomatis Scc4 (formerly CT663) engages the transcription machinery and the pathogenic type III secretion system (T3SS). Both machines are required for Chlamydia infection. These requirements and the limited ability for genetic manipulation in Chlamydia have hampered dissection of Scc4’s contributions. Here, by developing bacterial systems that permit the controlled expression and stable maintenance of Scc4, we assess Scc4’s effects on chlamydial growth phenotype, secretion, and the patterns of T3SS gene expression. Expressing Scc4 in Escherichia coli lacking a T3SS injectisome causes a growth defect. This deficiency is rescued by overexpressing the β-subunit of RNA polymerase (RNAP) or by exploiting sigma 70 (σ70) (homologous to chlamydial σ66) mutants that strengthen the interaction between σ70 region 4 and the β-flap, confirming Scc4’s distinction as a module of RNAP holoenzyme capable of modulating transcription. Yersinia pestis expressing Scc4 sustains a functional T3SS, through which CopN secretion is boosted by cooption of Scc4 and Scc1. Finally, conditional expression of Scc4 in C. trachomatis results in fast expansion of the Chlamydia-containing vacuole and accelerated chlamydial development, coupled to selective up- or downregulation of gene expression from different T3SS genes. This work reveals, for the first time, the context-dependent action of Scc4 linking it to diverse protein networks in bacteria. It establishes that Scc4, when overexpressed, exerts incredible effects on chlamydial development by reinforcing control of the T3SS.
IMPORTANCE The T3SS is a key virulence factor required for C. trachomatis infection. The control of the T3SS has not been well studied in this obligate intracellular pathogen. Here, we show that Scc4 plays a major role for precise control of the pathogenic T3SS at the levels of gene expression and effector secretion through genetically separable protein networks, allowing a fast adaptive mode of C. trachomatis development during infection in human epithelial cells.
INTRODUCTION
Successful host cell infections require a fast and efficient adaptation of the virulence program by bacterial pathogens. Type III secretion systems (T3SSs) of the injectisome class are virulence determinants in numerous medically important bacteria, including Yersinia, Chlamydia, Escherichia, Shigella, and Salmonella spp. (1–3). T3SSs target bacterial effector proteins to the eukaryotic host’s cells for promoting pathogenesis. This infection mechanism holds particularly true for C. trachomatis. This obligate intracellular bacterium causes the most prevalent bacterial sexually transmitted diseases worldwide (4, 5). C. trachomatis relies on the T3SS to translocate more than 100 effectors into the host cell in order to invade, multiply within a membrane-bound vacuole called an “inclusion,” exit from the host cell, and reinitiate new infections (6–8). During the unique chlamydial developmental cycle, the organism transits between two functionally and morphologically distinct forms, the infectious elementary body (EB) and the dividing reticulate body (RB) (8, 9). The signal that triggers the interconversion between EBs and RBs remains unclear. However, studies show that chlamydial development requires transcription of early-stage (EB-to-RB transition), midstage (RB replication), and late-stage (RB-to-EB transition) genes (10–12). Predictably, C. trachomatis administrates its virulence gene expression program in a developmentally stage-specific manner.
Control of transcription, the first step of gene expression, is crucial for correct gene expression and orderly development. Bacterial transcription is determined by the RNA polymerase (RNAP) holoenzyme, which consists of a core enzyme (α2ββ′ω subunits) and a σ factor (13). Transcription can be regulated by proteins that bind to a specific subunit(s) of RNAP and modulate the activity of the enzyme. These regulatory proteins include CarD from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (14), Rsd from Escherichia coli (15), DakA1 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (16), and Scc4 from Chlamydia trachomatis (17). The puzzle of transcription has been increasingly understood in C. trachomatis with methodological advances. C. trachomatis encodes conserved RNAP subunits (except ω) and three σ factors (σ66, σ54, and σ28) to support its biphasic lifestyle (18, 19). Because the σ factors are not expressed in a typical cascade fashion, their levels alone cannot fully explain the temporal gene expression in C. trachomatis. The majority of chlamydial housekeeping genes, including all T3SS genes (20), are preceded by E. coli σ70-like promoter sequences. Their expression requires chlamydial σ66 or E. coli σ70 in vitro and in E. coli (20–24). The availability of σ66 is regulated by the Rsb phosphoregulatory networks in C. trachomatis (25). Whereas some late genes are transcribed by σ28 and/or σ66, the target genes of σ54 are unknown. Despite a central role in pathogenesis, the mechanisms coordinating chlamydial morphological differentiation and virulence gene expression remain largely unknown.
The premise of an intimate link between gene transcription and T3SS activation in Chlamydia has emerged through the discovery of the bifunctional Scc4 protein (17, 26). Scc4’s role as a transcriptional regulator was originally detected by its interaction with the flap domain of RNAP β-subunit (β-flap) and region 4 of σ66 (σ70) in a bacterial two-hybrid-based genetic screening (17). Later, in vitro transcription assays showed that Scc4-bound σ66 (σ70) RNAP holoenzyme had specific inhibitory effects on transcription from −35/−10 promoters but had few effects on extended −10 promoters lacking a −35 motif. Apart from its regulatory function, Scc4 forms a heterodimer with Scc1 to chaperone CopN (26–28), a T3SS-exported effector and a gatekeeper, which is homologous to Yersinia YopN. By binding to its cognate chaperones, SycN/YscB and TyeA, YopN negatively regulates the secretion of the Yersinia outer membrane proteins (Yops) by preventing premature secretion of Yops until Yersinia receive an inductive signal (e.g., low Ca2+) (29).
Despite these findings, the functional relevance of Scc4 in Chlamydia biology remains elusive. We hypothesize that Scc4’s dual functions are switchable and contribute to precise coordination of T3SS activity and transcription events, stimulating the chlamydial developmental cycle. This theory has not been experimentally tested yet. It is difficult to dissect Scc4’s exact contributions because both transcription and the T3SS are required for Chlamydia infection. Recently, several methods for genetic manipulation of Chlamydia have developed (30–33). To test the functional importance of the specific interplay between Scc4 and its associated proteins, here, we evaluate Scc4’s effects on (i) bacterial growth phenotype, (ii) secretion of CopN via the T3SS, and (iii) the dynamic expression of genes encoding the T3SS components in C. trachomatis. To achieve these goals, we utilized genetic tools in E. coli and Yersinia, as well as the recently developed genetic transformation of C. trachomatis. These findings reveal a context-dependent action of Scc4 involving interconnected protein networks and suggest novel mechanisms of Scc4’s function to support dedicated control of the T3SS during the C. trachomatis developmental cycle.
RESULTS
Scc4 overexpression causes a growth defect in E. coli by blocking the σ70 region 4/β-flap interplay.
We began our study by utilizing suitable vectors allowing for expression of stable Scc4 in E. coli strains lacking the T3SS injectisome. E. coli BL21(DE3) cells were transformed with pCDFScc4 expressing Scc4 tagged with His6 at its N terminus. A single colony of bacteria was cultured in LB medium, and isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) was added to induce protein expression. The growth curve (Fig. 1a) shows that E. coli expressing Scc4 displayed a growth defect in an IPTG dose-dependent manner, while the control (no IPTG addition) grew normally, indicating that the growth inhibition was Scc4 dependent. The IPTG-induced Scc4 expression was confirmed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and immunoblotting (Fig. 1b). Similar results were obtained in E. coli transformed with pXDCM expressing tag-free Scc4 (17). When a high concentration of IPTG was added (≥100 μM) into the early log-phase culture for 1 h, the amount of viable bacteria identified by plating assays sharply decreased (Fig. 1c). Consistent with this, E. coli exhibited a marked decrease in expression of σ66-specific ompA promoter, σ28-specific hctB promoter (34), and E. coli σ32-specific groE promoter (35), as identified by a β-galactosidase reporter assay (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). These results could be explained by transcription inhibition and bacterial death induced by Scc4 expression at a high level; thus, bacteria did not synthesize β-galactosidase.
FIG 1.
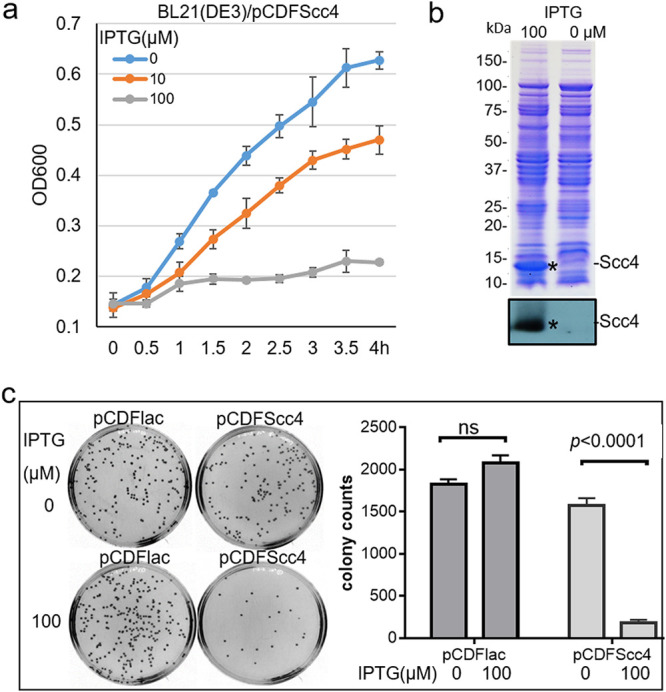
E. coli expressing Scc4 displayed an arrested growth phenotype. (a) Growth curves showing impaired E. coli growth in an IPTG-dependent manner. E. coli BL21(DE3) carrying pCDFScc4 was grown in LB medium in the presence of increasing concentrations of IPTG (0, 10, and 100 μM). Representative data for growth plotted every 30 min by measuring the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) are shown. Bacterial growth experiments were repeated three times. (b) IPTG-induced Scc4 expression. Stars indicate the bands corresponding to the inducible Scc4 protein detected using 10% (wt/vol) sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) stained with Coomassie blue (upper panel) or by immunoblotting with anti-Scc4 antibody (lower panel). (c) Plating assay analyzing bacterial viability. E. coli strains carrying pCDFScc4 or pCDFlac (vector control) were cultivated in LB medium for an initial 1-h incubation at 37°C, followed by adding IPTG at 100 μM. After culturing for an additional 1 h, bacteria were diluted and plated on LB agar plates. Colonies were counted after incubation for 16 h, and the data are presented as the means ± standard deviations (SD) from triplicate plates in a representative experiment. The P value was obtained using unpaired t test. ns, no significance.
Scc4 bound to the conserved σ70 RNAP in E. coli (17). To determine whether toxicity to E. coli is attributed to Scc4’s interaction with the σ70 RNAP, E. coli carrying pXDCM was transformed with pI545 encoding the full-length E. coli β-subunit of RNAP (RpoB) or pET15b (vector control). Protein expression was induced by IPTG. Overexpressing RpoB restored E. coli growth to the levels seen without Scc4 induction (Fig. 2a). A partial rescue from Scc4’s toxicity occurred in E. coli expressing a fusion protein of σ70 region 1 and σ66 regions 2 to 4 (σ66R24) (36). The purified σ66R24 protein showed transcription activity in vitro (36). However, the growth was unchanged when full-length σ66 was expressed in E. coli. The reason for the inability of σ66 to rescue is unclear, but we and others noted inefficient transcription using recombinant σ66 and E. coli RNAP core enzyme in vitro (22). The phenotypical rescue observed could be explained by (i) excessive RpoB or σ66R24 binding to Scc4 and (ii) changes in dedicated Scc4-σ70 RNAP interactions induced by RpoB or σ66R24, thus alleviating Scc4-meditaed growth inhibition. The possibility of poor expression or a low level of Scc4 was ruled out, as steady-state levels of Scc4 were detected by immunoblotting (Fig. 2b).
FIG 2.
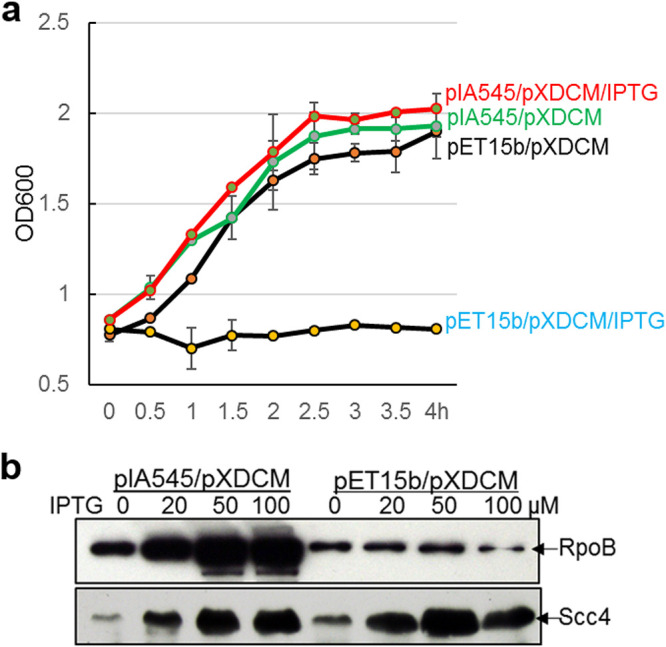
Overexpression of RpoB rescues the growth defect of E. coli expressing Scc4. (a) Growth curve. The indicated E. coli strains were grown in LB medium in the presence or absence of IPTG at a concentration of 100 μM, with OD600 measured at the indicated time points. Data are presented as mean ± SD from three replicates. (b) IPTG-induced expression of proteins in E. coli. The indicated E. coli strains were cultured in LB medium containing increasing concentrations of IPTG (0, 20, 50, and 100 μM) and harvested at 2.5 h for preparation of lysates. Samples were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-RpoB and anti-Scc4 antibodies, respectively, followed by visualization of protein by probing with alkaline phosphatase-conjugated secondary antibodies. Note that a small amount of Scc4 expression was observed without IPTG addition.
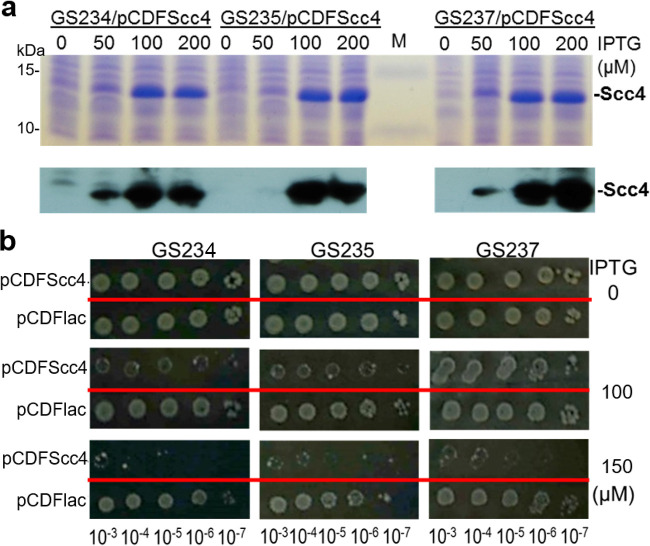
If Scc4 binds the interfaces of σ70 RNAP and interferes with transcription, the creation of mutations that enhance the strength of the σ70region 4/β-flap interaction should be sufficient to reduce toxicity. To test this possibility, we used the following group of E. coli K-12 MG1655 strains (kindly provided by A. Hochschild, Harvard Medical School): GS234 with wild-type chromosomal rpoD encoding σ70, and its isogenic strains, GS235 (rpoD A544I) and GS237 (rpoD A544I/D581G). These rpoD mutations have been shown to strengthen the interactions between σ70 region 4 and the β-flap (37). The strains were transformed with pCDFScc4 or pCDFlac (vector control). The levels of scc4 expression were fine-tuned by IPTG concentrations (Fig. 3a). All resultant strains exhibited comparable capacities for colony formation in the absence of IPTG, as analyzed by colony formation (Fig. 3b). In contrast, upon the induction of Scc4 at similar levels by adding IPTG at the concentration of 100 μM, the bacterial dose responses to Scc4 were notably different. Whereas E. coli GS234 expressing Scc4 grew poorly, GS237 was best suited to tolerate Scc4, and GS235 had an intermediate level of tolerance.
FIG 3.
Exploiting rpoD mutations strengthening σ70 region 4/β-flap interaction circumvents the impaired growth of E. coli expressing Scc4. (a) IPTG-induced Scc4 expression. Scc4 expression was induced by adding IPTG at increasing concentrations (0, 50, 100, and 200 μM). Cellular lysates were prepared from the indicated E. coli strains at 2.5 h and separated by 10% SDS polyacrylamide gels. The upper panel shows a Coomassie blue-stained gel along with the protein markers (M). Lower panels show the results of immunoblotting with anti-Scc4 antibody. (b) Colony formation assay. Equal volumes (5 μl) of the serial bacterial dilutions indicated at the bottom of the panel were spotted on a LB agar plate in the presence of IPTG (at 0, 50, or 100 μM) and incubated for 16 h at 37°C.
These data indicate that Scc4 acts as a module of σ70 (σ66) RNAP that is capable of dysregulating E. coli transcription, thereby causing growth arrest. The results of phenotypical rescue by overexpression of RpoB or σ66R24 and by exploiting σ70 mutants that strengthen the σ70 region 4/β-flap interplay suggest that the change in degree of Scc4’s interactions with the σ70 (σ66) RNAP holoenzyme represents a mechanism of transcriptional regulation.
C. trachomatis Scc4 joining with Scc1 promotes CopN secretion through the injectisome.
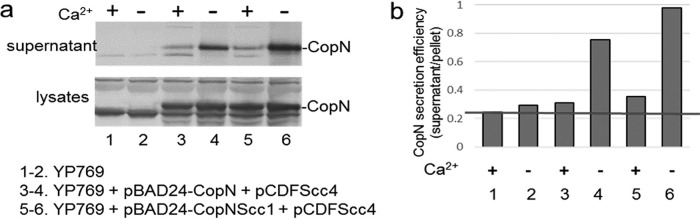
Previously, Silva-Herzog et al. reported that Chlamydia pneumoniae Scc4 and Scc1 assisted in C. pneumoniae CopN secretion in Y. pestis (28). However, the secretion chaperones are highly specific, and noted differences in biochemical properties exist between C. trachomatis CopN and C. pneumoniae CopN (38, 39). To determine the specific role of Scc4 in the secretion of C. trachomatis CopN, a secretion assay was initially performed using Y. pestis strain YP1283, which carries pCD1 encoding all the Y. pestis T3SS components and effector Yops except YopE. No apparent increase in CopN secretion was evident in Y. pestis YP1283 expressing CopN, Scc1, and/or Scc4 (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material). However, the secretion of CopN was induced under a low-Ca2+-level condition, indicating a functional T3SS. We suspected that the level of CopN secretion was limited due to competition from the other highly expressed endogenous effector Yops with their chaperones. Thus, the secretion assay was conducted with the Y. pestis strain YP769 that carried a mini-pCD1 with the minimal genetics required for type III secretion and lacking genes encoding all six effector Yops (40). YP769 cells were cotransformed with pCDFScc4 and pBAD24-CopN, which carried copN, or with pBAD24-CopN-Scc1, which carried both C. trachomatis copN and scc1. In these systems, the expression of scc4 was induced by adding IPTG, while the expression of scc1 and/or copN was induced by adding arabinose. Coexpressing Scc4 and Scc1 in YP769 clearly resulted in increased CopN secretion under secretion inducing conditions (37°C; without Ca2+) (Fig. 4, lane 6). This increase did not occur in strains that lacked Scc1, consistent with previous studies showing that Scc4 and Scc1 must form a heterodimer to chaperone CopN and that Scc4 acted to bridge the Scc1 and CopN interactions (26).
FIG 4.
Scc4 and Scc1 enhance the secretion of CopN in Yersinia. (a) Immunoblotting analysis of CopN secretion in YP769. Y. pestis was cultivated in HIB medium in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 2.5 mM Ca2+. After an initial 2 h of incubation at 26°C, IPTG (100 μM) was added. Bacterial cultures were then shifted to 37°C, and culturing was continued for 4 h prior to harvesting. Samples representing culture supernatant and bacterial lysates were resolved on 12% polyacrylamide gels and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-CopN antibody, followed by visualization of protein by probing with alkaline phosphatase-conjugated secondary antibodies. (b) Analysis of the ratio of secreted CopN levels (in supernatants) to the intracellular levels (lysates). Protein blots in panel a were measured using ImageJ. The red line represents the background.
Given the successful CopN secretion in Yersinia expressing Scc4, it is unlikely that Scc4 harshly compromised the synthesis and the assembly of the T3SS under our experimental conditions. Unlike the impaired growth of E. coli, Scc4 expression does not cause significant growth restriction of Y. pestis (data not shown), indicating that Scc4 does not appear to not strongly inhibit the Yersinia RNAP. In this context, the effects observed are likely due to a role of the chaperone in possibly stabilizing its substrate CopN.
It is possible that the Y. pestis chaperones are preventing Scc4 from interacting with RNAP because of a tight binding of Scc4 with its chaperone pattern (26). Similarities have been shown in the predicted structural properties between chlamydial Scc4 and Y. pestis YscB and SycN (26). To test whether Scc4 directly interacts with Y. pestis YscB/SycN, a bacterial two-hybrid assay was performed. This assay, using Y. pestis YscB or SycN fused to the N-terminal domain of RNAP α subunit (αNTD) and Scc4 fused to DNA binding domain λCI, revealed that Scc4 bound to YscB and SycN (Fig. 5). Because a heterodimeric chaperone is required for the secretion of YopN/CopN proteins (26–29), the significant secretion of CopN seen in the presence of Scc4 alone may be due to minimal functional Scc4/SycN or Scc4/YscB in Y. pestis (Fig. 4 lane 4). Potential Scc4 interaction with YscB/SycN in Y. pestis may also explain the disparity in Scc4-mediated growth inhibition between Y. pestis and avirulent E. coli strains. These T3SS proteins are not present in E. coli, and thus it is unsurprising that bacteria display a growth defect when Scc4 is overexpressed.
FIG 5.
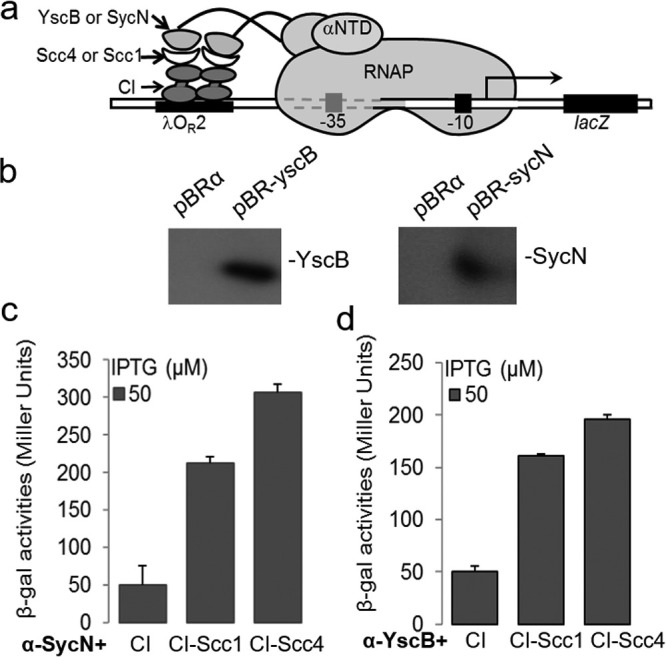
Scc4 or Scc1 directly interacted with SycN and YscB in a bacterial two-hybrid assay. (a) Schematic showing a transcription activation-based bacterial two-hybrid assay. In this system, protein-protein interactions between the indicated hybrid proteins in a reporter E. coli strain, FW102 OL2-62, are quantified by measuring β-galactosidase activities. (b) Immunoblot analysis of protein expression in strain FW102 OL2-62 carrying pBR-yscB, pBR-sycN, or pBRα (vector control). Rabbit anti-YscB or anti-SycN antibody was used to probe proteins as indicated. (c and d) Results of β-galactosidase activities illustrating the protein-protein interactions. Note that SycN-Scc4 interactions (c) were stronger than those of YscB-Scc4 (d). Protein expression in culture was induced by the addition of IPTG (50 μM). Result obtained from the negative control (CI) represents the background. Shown are the means ± SD from three biological replicates, each in technical triplicates.
These results indicate that C. trachomatis Scc4 functioning with Scc1 helps promote the secretion of CopN through the Yersinia injectisome in the presence of RNAP subunits and some other T3SS components from Yersinia. This specific chaperone-assisted system should prove useful to further probe the determinants on the Scc4/Scc1/CopN complex and their role in T3SS substrate recognition.
Inducible Scc4 protein is expressed from an E. coli-chlamydial shuttle plasmid in C. trachomatis.
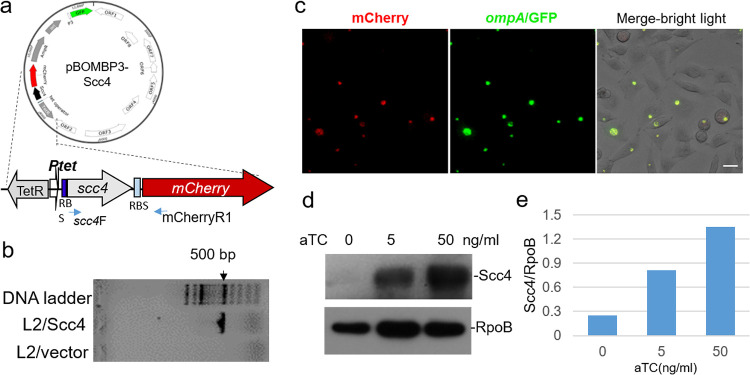
We predict that Scc4 exerts distinct regulatory effects on chlamydial biology. To determine the functional relevance of Scc4 in the unique chlamydial developmental cycle, we sought to utilize recently developed chlamydial genetic systems. Attempts to delete the chromosomal scc4 gene using the allelic exchange replacement with fluorescence protein mutagenesis (31) failed, perhaps because scc4 is an essential gene in Chlamydia. We conducted an E. coli-C. trachomatis shuttle plasmid transformation. Because Scc4 is highly toxic to E. coli, a tightly controlled strategy is desirable. We chose pBOMBP3 to make an Scc4 expression vector (36) because it contains (i) a tetracycline-inducible tetA promoter (PtetA) that drives expression of the gene of interest in the presence of anhydrotetracycline hydrochloride (aTC) (41), (ii) a β-lactamase gene conferring ampicillin resistance that permits selection for the transformants, and (iii) a robust PompA-gfp reporter that allows for the easy visualization of the growth behaviors of the transformants in live cells during the course of infection (42, 43). We found that the native scc4 ribosome binding site (RBS) weakly functioned to direct initiation of Scc4 synthesis in E. coli (see Fig. S3 in the supplemental material). The DNA fragment containing the coding region and the scc4 RBS from C. trachomatis L2/434/Bu was cloned into the pBOMBP3, allowing efficient scc4 expression under the control of PtetA in Chlamydia.
The resultant expression vector, pBOMBP3-Scc4 (Fig. 6a), was obtained and then transformed into the plasmid-free C. trachomatis strain, L2/25667R. A single transformant isolate, designated L2/Scc4, carrying the cloned scc4 gene was confirmed by PCR (Fig. 6b) combined with Sanger sequencing. Ptet was responsive to aTC, and inducible mCherry expression was visualized by immunofluorescence microscopy (Fig. 6c). In the presence of aTC at the concentrations of 5 and 50 ng/ml added immediately after infection (0 hours postinfection [hpi]), inducible Scc4 protein was detected in L2/Scc4-infected L929 cells or HeLa cells at 24 hpi using immunoblotting (Fig. 6d and e). No inducible Scc4 was detected in the cells infected with the pBOMBP3-carrying control strain, L2/vector. When the same multiplicity of infection (MOI) was used, consistent levels of infection with L2/Scc4 and L2/vector were obtained, suggesting no apparent adverse impact of Scc4 on infection efficiency. An aTC dose of 10 ng/ml was chosen for subsequent experiments.
FIG 6.
Ectopic expression of Scc4 in C. trachomatis from a shuttle plasmid. (a) Map of pBOMBP3-Scc4. (b) Verification of the stable presence of a plasmid-encoded scc4 gene in C. trachomatis strain L2/Scc4 but not in L2/vector (control) using PCR with primers scc4F and mCherryR1 (see Table S2 in the supplemental material). (c) Microscopic analysis of anhydrotetracycline hydrochloride (aTC)-induced mCherry expression in C. trachomatis. Images were taken at 24 hpi. Bar, 20 μm. (d) Immunoblot analysis of aTC-induced Scc4 expression in C. trachomatis-infected HeLa cells. Cells were cultured in medium containing increasing amounts of aTC (0, 5, and 50 ng/ml) at 0 hpi, harvested at 24 hpi, and lysed in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.6) and 8 M urea buffer. Samples were isolated on SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with antibodies specific to Scc4 or RpoB (as a protein loading control). (e) Quantitative analysis of protein blot from panel d.
Ectopic expression of Scc4 induces changes in C. trachomatis development.
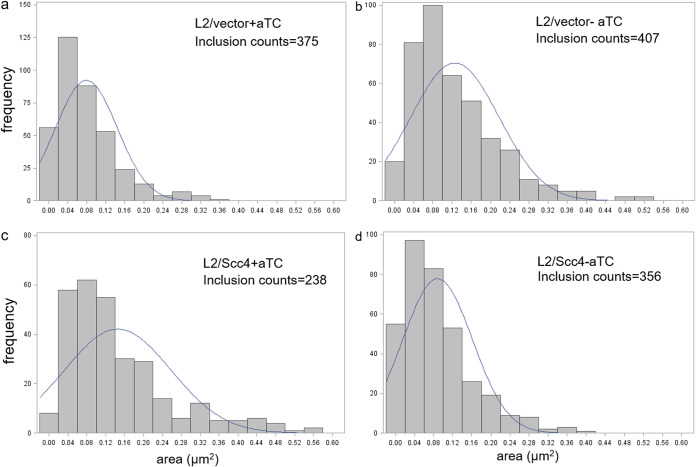
Productive C. trachomatis infection is signified by expansion of the chlamydial inclusions in parallel, the EB-to-RB differentiation at the early stage, RB replication at the midstage, and RB-to-EB differentiation at the late stage (8). To assess the effects that Scc4 had on Chlamydia development, we employed HeLa cells, rather than L929 cells, because of their cervical origin and their wide use in C. trachomatis research. HeLa cells were equally infected with L2/Scc4 or L2/vector and cultured in medium containing or lacking aTC added immediately after infection (0 hpi) for an early induction of Scc4 expression. The morphology of chlamydial inclusions was monitored using microscopy at 16 hpi and 24 hpi, respectively. Infection of HeLa cells with L2/Scc4 or L2/vector resulted in morphologically normal inclusions, but there were differences in the inclusion sizes in the absence or presence of aTC. Figure 7a shows that histograms of the areas of L2/vector inclusions measured at 16 hpi are biased toward the left in the presence of aTC, indicating a small number of large inclusions compared to the control without aTC addition (Fig. 7b). In contrast, in the presence of aTC, there were more large inclusions in L2/Scc4-infected cells (Fig. 7c) than in those without aTC (Fig. 7d). As the chlamydial inclusions grew with time, differences in inclusion sizes between L2/Scc4 and L2/vector were not obvious when analyzed at 24 hpi and later.
FIG 7.
Histogram of C. trachomatis inclusion areas in HeLa cells in the absence or presence of aTC. (a and b) L2/vector; (c and d) L2/Scc4. HeLa cells were infected with C. trachomatis with the same multiplicity of infection (MOI) (1:0.5), cultured in the aTC-free (−aTC) or aTC-containing (+aTC) medium (at a concentration of 10 ng/ml) starting from 0 hpi, and imaged at 16 hpi. The individual inclusions were analyzed using ImageJ software. The numbers of inclusions analyzed per condition are indicated. The histogram was made with R software. In each case, the frequency of an inclusion is equal to the number of observations falling in that category.
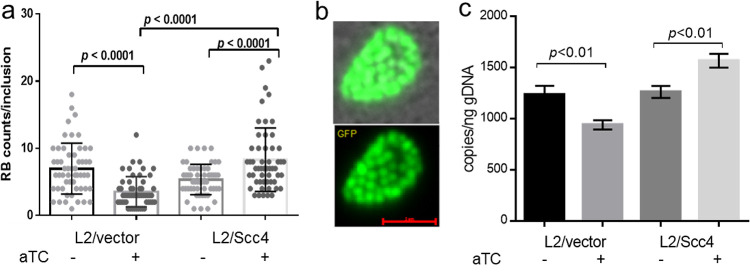
To address whether the expansion of the inclusions correlated with RB progeny production, we enumerated RBs at 16 hpi when few EBs were being produced. Fifty inclusions per condition were analyzed. Although normal RBs were produced with C. trachomatis L2/Scc4 or L2/vector, the number of RBs in L2/Scc4 was more numerous than that in L2/vector when Scc4 was induced (Fig. 8). We next assessed the chlamydial genome copies by performing quantitative PCR with primers specific to tufA encoding the translation elongation factor EF-Tu (21). Like other cells, C. trachomatis duplicates its genomes prior to dividing. Consistent with the results of RB counts, the genome copies were significantly higher in L2/Scc4 than L2/vector. These data suggest the positive impact of early Scc4 induction on RB replication.
FIG 8.
Effect of Scc4 on RB replication. (a) Numeration of RBs. Live cell images were taken at 16 hpi. The number of each single inclusion was counted manually and presented as the mean ± SD. In total, 50 different inclusions per condition were analyzed. The P value was obtained by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a Bonferroni posttest. (b) Representative live cell imaging of RBs within a chlamydial inclusion. Bar, 5 μm. (c) Quantification of chlamydial genome copies by real-time qPCR. The primers designed to amplify tufA were used for PCR with DNA prepared from C. trachomatis-infected HeLa cells harvested at 16 hpi. The serial dilution of genomic DNA from purified EBs was used to generate a standard curve, with which the corresponding genome copies of the testing samples were calculated and presented as means ± SD. gDNA, genome DNA. Data from two individual experiments are shown; each experiment was performed in triplicate.
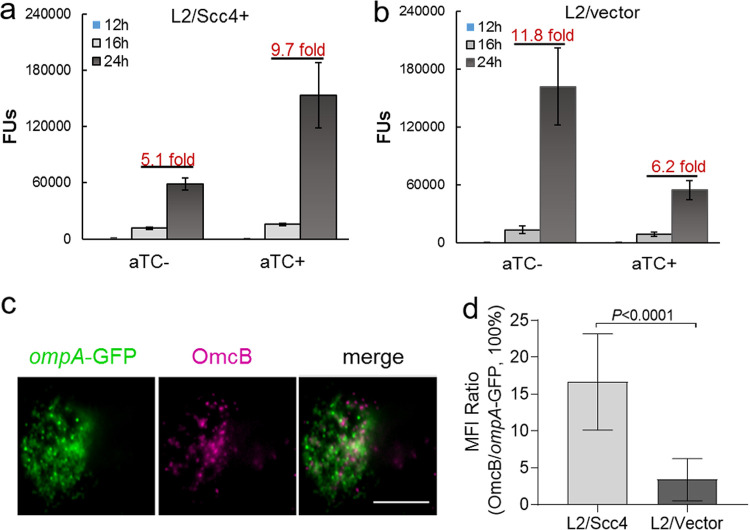
We next compared the production of EB progeny by monitoring the appearance of EBs in the presence or absence of aTC. Equally infected HeLa cells were harvested at different time points after infection to enumerate EB progeny using the inclusion-forming unit (IFU) assay. As expected, IFUs were extremely few at 12 hpi and significantly increased at 16 and 26 hpi in all samples (Fig. 9 and Fig. S3). In the presence of aTC, the yield of EBs increased by ∼9.7-fold in L2/Scc4 from 16 to 24 hpi. The increase is significantly compared to that (6.2-fold) in L2/vector (P < 0.05). In contrast, fewer EBs were produced in L2/Scc4 from 16 to 24 hpi (5.1-fold increase) than in L2/vector (11.8-fold increase) in the absence of aTC (P < 0.05). The difference was less appreciable between C. trachomatis L2/Scc4 and L2/vector when measured at 32 hpi, regardless the use of aTC (Fig. S3). To validate the IFU data, the levels of EB-specific OmcB expression were determined using an immunofluorescence assay (IFA). In the presence of aTC, OmcB-positive chlamydial organisms were readily detected in L2/Scc4 culture at 24 hpi, and fewer were seen in L2/vector culture (Fig. 9c).
FIG 9.
Effect of Scc4 on EB production. (a and b) Monitoring the appearance of EBs in the presence or absence of aTC. HeLa cells were infected with L2/Scc4 (a) or L2/vector (b). EB progeny were assessed by IFU assays with samples collected at different time points as indicated (for a one-step growth curve, see Fig. S4 in the supplemental material). The data are presented as means ± SD. Numbers above the bars give the fold increase from 16 to 24 hpi. (c and d) Analysis of EB-specific OmcB expression using IFA. C. trachomatis-infected cells were cultured in the medium containing aTC, fixed at 24 hpi, and subjected to IFA with anti-OmcB antibody, followed by staining with Alexa Fluor 405-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG. (c) Shown are chlamydial inclusions containing green fluorescent protein (GFP)-positive C. trachomatis (green) and OmcB-labeled EBs (purple pseudocolor). Bar, 10 μm. (d) Ratio of mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of OmcB-labeled EBs to GFP-positive organisms per inclusion. Error bars represent means ± SD obtained from 30 inclusions per condition. The P value was obtained using an unpaired t test.
The serial quantitative analyses of inclusion size, RB progeny, and EB progeny provide direct evidence that C. trachomatis adapts an accelerated mode of growth with early Scc4 induction. The appearance of small inclusion sizes and the small amounts of RBs and RBs in L2/vector-infected cells in the presence of aTC might be the reflection of a bacterial response to a low dose of aTC or fitness cost of the transformed plasmid expressing exogenous proteins, such as mCherry. Conversely, the better growth of L2/Scc4 in the presence of aTC could be explained by the induction of Scc4 that facilitates the chlamydial organisms to overcome the barriers of fitness cost. The enhancement of chlamydial growth observed at 16 to 24 hpi is relevant to the induced exogenous Scc4 because endogenous Scc4 content does not reach a high level until the late stage (17, 26). However, the interpretation of Scc4’s effect at the late stage might be more complex due to the increase in endogenous Scc4 and/or its associated proteins and the natural asynchrony of C. trachomatis growth.
Expression of T3SS genes is altered by induction of Scc4 expression in C. trachomatis.
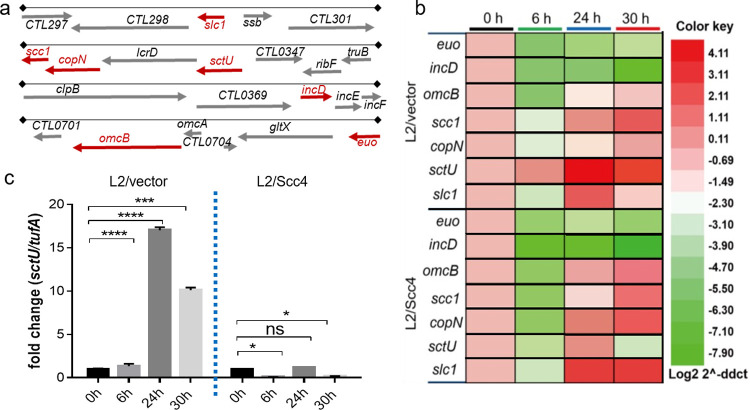
Our data thus far have suggested that Scc4 expression accelerates the developmental cycle of C. trachomatis. Most genes encoding the T3SS components are tightly regulated due to their role in pathogenesis (1–3). To test whether Scc4 affects virulence gene expression in the intracellular milieu, we assessed transcript levels of genes encoding chlamydial T3SS components during the course of infection using real-time reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). HeLa cells infected with C. trachomatis L2/Scc4 or L2/vector were cultured in medium containing aTC (at 10 ng/ml) and harvested at 0, 6, 24, and 30 hpi for RNA extraction. Unlike many other bacteria that possess T3SS gene clusters in a pathogenicity island on the chromosomes or plasmids, Chlamydia encodes T3SS genes scattered throughout the chromosome in different operons. Therefore, the representative T3SS genes encoding functionally diverse T3SS components, including the secretion chaperones (scc1 and slc1), effectors (incD and CopN), and T3SS inner membrane protein (sctU), were analyzed (Fig. 10a). Scc1 acts as a class 1a chaperone to interact with CopN together with Scc4. Slc1 serves as a class 1b chaperone, which, like EPEC CesT, binds multiple effectors, including Tarp (44) and TepP (45). Whereas incD codes for a Chlamydia-specific Inc protein crucial for recruitment of the lipid transfer protein CERT (46), sctU codes for a T3SS inner membrane protein that regulates the export apparatus (1, 2). The reference early gene, euo (47), and late gene, omcB (48), were also tested. The validated chlamydial housekeeping gene tufA was used as an internal control for quantitation of mRNA levels.
FIG 10.
Altered transcription patterns of select T3SS genes induced by Scc4. (a) Map of T3SS genes/operons analyzed. The expression of genes marked in red was assessed by RT-qPCR. (b) The heat map shows relative transcript abundance of genes in L2/vector or L2/Scc4 culture at 0, 6, 24, and 30 hpi as indicated by RT-qPCR. (c) Comparison of relative transcript abundance of sctU in L2/vector and L2/Scc4. Data were normalized to transcript of tufA and calibrated against the 0-hpi control (set to 1.0). Each value shows the mean ± SD of three technical replicates of a representative experiment. At least three independent experiments were performed. P values were obtained using one-way ANOVA. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.
There was almost full concordance in euo and incD transcript levels in the C. trachomatis strains L2/Scc4 and L2/vector (Fig. 10b), consistent with their nature of early expression (49). In contrast, we found striking differences in the transcription profiles of scc1, slc1, copN, and sctU between L2/Scc4 and L2/vector over the same time course. Such discrepancies were more apparent at 30 hpi. Whereas the transcript levels were significantly low for sctU and high for scc1, copN and slc1 in L2/Scc4 and L2/vector exhibited different patterns (Fig. 10c). The increased levels of scc1, copN, and slc1 in L2/Scc4 are comparable to that of omcB in the same culture, in good agreement with the findings showing accelerated EB accumulation in L2/Scc4 using both IFU assays and IFA (Fig. 9). However, the low sctU levels opposing the high levels of scc1 and copN in L2/Scc4 are not easily explained, as a previous study indicated that sctU is located in the same operon as copN and scc1 (20). The low sctU level is not due to gene mutation, as DNA sequencing data prove the integrity of this region in L2/Scc4. The observations showing that the extent and the pattern of transcript expression are unique to the Scc4-expressing strain, L2/Scc4, support the hypothesis that Scc4 induces a specific gene expression signature during infection.
DISCUSSION
Although the developmental cycle of C. trachomatis has been widely studied, there is scarce information regarding how C. trachomatis executes its virulence program during infection. In the studies presented, we obtained several lines of evidence in support of the notion that Scc4 plays a major role for precise control of pathogenic T3SS expression through genetically separable protein networks involving σ66RNAP holoenzyme and the T3SS in this pathogen. Importantly, our work supports a functional role for Scc4 in C. trachomatis virulence gene expression in its unique intracellular niche. These data indicate a complexity of T3SS control that would not be apparent without identifying the mode of action of Scc4 dynamically interacting with its numerous protein partners.
The current study uses several heterologous systems for the inducible expression of target proteins at a given time, enabling the rigorous investigation of Scc4’s context-dependent actions in bacteria. An interesting finding was that Scc4 expression had a dramatic inhibitory effect on the growth of E. coli. We characterized the mechanisms of growth suppression of Scc4 for E. coli and established that Scc4 acted as an active module of the σ70 (σ66) RNAP holoenzyme and modulated bacterial transcription (Fig. 1 and 3). The ability of C. trachomatis Scc4, by cooperation with Scc1, to promote the secretion of CopN via the T3SS injectisome was observed in an engineered Y. pestis strain (Fig. 4 and 5), consistent with results of previous work with C. pneumoniae CopN (28). The observations in the CopN secretion, growth phenotype, and bacterial two-hybrid assays suggest that interconnected protein networks influence Scc4’s action. These data suggest that well-designed heterologous systems are useful to study how Scc4 functions with the conserved RNAP or T3SS components through dedicated protein-protein interactions in bacteria.
In an important extension to chlamydial genetic manipulation using plasmid transformation, we showed that the early induction of Scc4 clearly accelerated C. trachomatis development (Fig. 6 and 9). Our RT-qPCR data demonstrated the ability of Scc4 to selectively up- or downregulate T3SS gene expression during C. trachomatis infection (Fig. 10). A previous in vitro study (17) only suggested Scc4’s inhibitory effect on transcription from chlamydial rRNA P1 (24) and tuf P1 (21), both of which have architectures similar to those of E. coli σ70-directed promoters. This highlights the need to investigate the widespread influence of Scc4 on C. trachomatis promoters that may be diverse in structure in their native state during Chlamydia infection. It is noteworthy that Scc4 shares an intrinsic feature with T4 AsiA (50, 51), with both being a module of the RNAP holoenzyme and modulating this enzyme’s activity without interacting with DNA. AsiA is not a typical anti-σ factor, because it acts to inhibit transcription from the σ70-recognized −35/−10 promoters and also serves as a coactivator for T4 middle promoters that hold the canonical σ70 −10 consensus sequence but retains a MotA-box site centered at −30 rather than the σ70 −35 sequence (52). There may be similarities with the function of Scc4, for example, as either a repressor or coactivator in the presence of certain activators and dependent on the intrinsic properties of promoters.
It is interesting that the transcript level of sctU is significantly lower than that of other genes in the sctU-lcrD-copN-scc1-malQ gene cluster in L2/Scc4. In principle, the low levels of sctU suggest decreased synthesis or increased mRNA decay. Given sctU’s position at the start of the gene cluster, these results raise two different possibilities. The first possibility is the existence of two divergent mRNAs derived from different promoters, one containing the coding regions for the copN-scc1-malQ gene cluster and the other containing only the region for sctU-lcrD. In supporting this idea, Albrecht et al. (53) identified separate transcription start sites at the 5′ ends of copN and sctU, respectively, using deep RNA sequencing. The second possibility is that Scc4 takes part in the regulation of sctU mRNA decay. Ferreira et al. (54) have stated that the interplay between transcript production and degradation is driven by complex transcriptional networks in Chlamydia. It remains to be determined whether Scc4 directly affects sctU transcription. Alternatively, downregulation of sctU expression results from an indirect mechanism, for example, an RNA binding protein or noncoding RNA (ncRNA) whose expression and functions are regulated by Scc4. Notably, all C. trachomatis ncRNAs identified were expressed from σ66 promoters (55), and an ncRNA, ctrR3, was proposed to regulate sctU and other genes (53).
It has been documented that the activity of the T3SS is carefully regulated at multiple steps (3), which include (i) expression of the T3SS genes, (ii) assembly of protein components into a structural apparatus, (iii) substrate recognition and selection, and (iv) spatiotemporal effector secretion. While transcription modulation by Scc4 per se certainly affects the T3SS synthesis, evidence for Scc4’s role in facilitating CopN secretion through the T3SS was also obtained here (Fig. 4), consistent with previous work with C. pneumoniae CopN (28). Thus, Scc4 may influence control of the T3SS at the levels of gene expression and effector secretion. Tight control of the T3SS leads to efficient T3SS function, allowing correct and suitable levels of effectors being translocated into the host cell. The inducible Scc4 system alone cannot easily determine Scc4’s influence on secretion activity in diverse chlamydial developmental forms due to the presence of endogenous Scc4, asynchronous Chlamydia development and the inherent difficulty in accurate measurement of the spatiotemporal secretion of T3SS effectors in C. trachomatis-infected cells. Nevertheless, the view for the common function of the YopN gatekeeper family is that upon completion of the apparatus assembly, the gatekeepers are secreted or alter their interaction with the T3S apparatus, thereby controlling the substrate specificity of the T3SS apparatus (29). These findings support the appealing model proposed (1, 26, 28) that association or dissociation of CopN with the Scc4-Scc1 complex might affect T3SS substrate recognition and, in turn, the effective secretion of effectors. Inputs of dynamic Chlamydia-host interactions are likely critical for the adaptable control of the activity of the T3SS.
All of the evidence presented supports a vital role for Scc4 and its associated proteins in controlling the T3SS in C. trachomatis. How does Scc4 exert its dual function to contribute to the chlamydial developmental cycle? Our prevailing model suggests that Scc4 undergoes a developmental stage-specific functional and structural switch, leading to cooperativity of key events of transcription and the T3SS during the chlamydial developmental cycle. Whereas an EB is fully equipped for the T3SS apparatus, its contact with the host cell induces secretion of CopN, followed by other effectors to promote EB entry and transition to RB. Scc4 is freed from the Scc4-Scc1 complex and/or is newly synthesized in RBs, where Scc4 performs its regulatory duties by binding and remodeling σ66RNAP. When RBs differentiate to EBs, there are the low levels of σ66RNAP due to modulation of σ66 by Rsb kinases/phosphatases and the high abundance of σ28 accumulation. Scc4 rather binds to the accumulated Scc1 to form a heterodimeric chaperone that stabilizes CopN as a gatekeeper in the T3SS, blocking premature effector secretion from EBs. Because the affinity of the T3SS chaperone complex is very high, the presence of Scc1 may provide negative feedback for Scc4’s interaction with RNAP in EBs. In support of this switch model, we have recently uncovered a unique allosteric mechanism of Scc4 toward RNAP over T3SS components using mutation, biochemical, and nuclear magnetic resonance approaches (our unpublished data). It is important to take into account the developmental stage-specific function of Scc4. These mechanisms may not necessarily be mutually exclusive during chlamydial infection, because diverse chlamydial forms coexist at the late developmental stage in particular. In this case, Scc4’s dual function, in combination, may mediate adaptation of the chlamydial organisms as heterogeneous multiple cell population.
In conclusions, our data indicate that Scc4 plays a multitude of roles in the chlamydial developmental cycle. Scc4 participates in quality control of gene expression by binding and modulating RNAP activity, allowing for the expression of the correct class of genes at the correct time and order. On the other hand, Scc4 brings an additional layer of plasticity to enable spatiotemporal control of ordered T3SS secretion and other related processes. Further work using RNA sequencing combining with other methods is warranted to understand the nature of Scc4’s effects on genome-wide chlamydial gene expression and how this leads to the developmental stage-dependent control of T3SS activity during infection. In addition, it is merited to use site-directed mutagenesis in the chlamydial Scc4 expression system to differentiate Scc4’s transcriptional effects from chaperone function in future. The practical aspects of the strategy described and the extended methodologies for vector and strain improvement to obtain the desired yield of target protein would be broadly applicable to address other mechanistic questions and accomplish molecular details useful for a therapeutic strategy against Chlamydia infection.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Molecular cloning.
Plasmids used in this study are listed in Table S1 in the supplemental material. The expression vectors pCDFScc4, pXDCM, pLN-σ66R24, and pIA545 were reported previously (17, 26, 36). These plasmids encode Scc4 with an N-terminal His6 tag, tag-free Scc4, tag-free σ70 (residues 1 to 327) fused to C. trachomatis σ66 regions 2 to 4 (residues 315 to 571), and E. coli RpoB with an N-terminal His6 tag, respectively. To construct expression plasmids pBAD24-CopN-Scc1 or pBAD24-Scc1, the target genes were generated as PCR products using C. trachomatis serovar D genomic DNA as a template as a restriction enzyme-digested fragment and then cloned in pBAD24 (56). Both copN and scc1 or scc1 alone are controlled by an arabinose-inducible Para promoter. pQF50k-groE carrying the lacZ gene driven by the E. coli σ32-dependent groE promoter (35) was kindly provide by Petier deHaseth (Case Western Reserve University). The plasmid pRVhctB containing the lacZ gene driven by the chlamydial σ28-dependent hctB promoter was reported previously (34). To construct the reporter plasmid pRVompA, the PCR fragment containing ompA P2 and P3 was inserted into the EcoRI and SalI sites of pRVhctB. To construct plasmids encoding the fusion proteins of the E. coli N-terminal domain of the RNAP α subunit (α-NTD; residues 1 to 236) and Yersinia YscB or SycN, the gene fragments were amplified by PCR, digested with NotI/SpeI, and cloned into the NotI/SpeI sites of pRBR (17). Plasmids pRAC, pACλcI-CT663 (here renamed pACScc4), and pACScc1 have been described previously (17, 26). They express DNA binding protein λCI, λCI fused to Scc4, and λCI fused to Scc1, respectively. The identities of the final cloned DNA inserts for all plasmids were confirmed by restriction mapping and Sanger sequencing.
E. coli DH5α and its derivative 5-α F′Iq cells (no. C2992; New England Biolabs [NEB]) were used as host cells for molecular cloning. A methylation-deficient E. coli strain (ER2925; NEB) was used to prepare the plasmids for C. trachomatis transformation. The E. coli cells were grown in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium or on agar plates. When appropriate, antibiotics were used at the following concentrations: kanamycin, 25 μg/ml; carbenicillin, 50 μg/ml; chloramphenicol, 30 μg/ml; and spectinomycin, 100 μg/ml.
Cell culture, C. trachomatis infection, and IFU assay.
Human cervix adenocarcinoma epithelial HeLa 229 cells (ATCC CCL-2.1) or mouse fibril blast cell L929 (ATCC CCL-1) were cultured in RPMI 1640 (Gibco) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Sigma) and l-glutamine (2 mM) (RPMI 1640-10) at 37°C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. For infection, C. trachomatis EBs were added to the cell monolayers (MOI = 0.5), followed by centrifugation at 255 × g for 45 min at 37°C. Infected cells were cultured in medium at 37°C for various times as indicated in Results. EB progeny were evaluated by endpoint IFU assays. Briefly, serial dilutions of cellular lysates from the harvested cultures were subcultured in HeLa 229 cells. The cells were processed at 42 hpi for indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA) as described below using antibody against the major outer membrane protein (MOMP). EB amounts were determined by enumeration of the inclusion numbers in triplicate wells using fluorescence microscopy. The total EB numbers are presented as the number of IFUs per ml.
Transformation of C. trachomatis.
C. trachomatis was transformed with the shuttle plasmids according to a method described previously (36, 57). Briefly, plasmid-free C. trachomatis L2/25667R EBs (1 × 107) were mixed with 7 μg of plasmid DNA in 100 μl of CaCl2 buffer (5 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.4] and 100 mM CaCl2) and incubated at room temperature for 30 min. Freshly trypsinized L929 cells (6 × 106) resuspended in 200 μl CaCl2 buffer were added to the plasmid/EB mixture and incubated at 37°C for an additional 20 min. Aliquots of this mixture were then added to a 6-well plate with 1.0 ml of prewarmed medium in each well. After culturing in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) containing 10% FBS without antibiotics at 37°C for 24 h, cells were incubated in the presence of ampicillin (5 μg/ml) and cycloheximide (2 μg/ml) for an additional 24 h. The infected cells were harvested and lysed by vortexing with glass beads and passed onto the fresh monolayer cells. The cloned, transformed C. trachomatis strains were used to infect HeLa 229 cells. EBs were isolated by density gradient purification as described previously (58) and resuspended in sucrose-phosphate-glutamic acid (SPG) buffer. The aliquots were stored at −80°C until use.
Antibodies.
The primary antibodies used in this study were (i) polyclonal mouse antibody against Scc4 (17), (ii) monoclonal antibody 8RB13 (recognized E. coli β and C. trachomatis β) purchased from NeoClone, (iii) polyclonal anti-CopN (kindly provided by Ken Fields, University of Kentucky), (iv) polyclonal anti-OmcB (kindly provided by Thomas P. Hatch, University of Tennessee), (v) mouse monoclonal antibody against LGV L2 MOMP (kindly provided by You-xun Zhang, Boston University), and (vi) rabbit anti-YscB and anti-SycN (29). The secondary antibodies, goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L)–Alexa Fluor 405, goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L)–Alexa Fluor 488, goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L)–Alexa Fluor 567, and goat anti-mouse or anti-rabbit IgG–alkaline phosphatase (Invitrogen), were purchased from Invitrogen.
Microscopic analysis and IFA assay.
HeLa cell monolayers grown in a black 96-well culture plate were infected with C. trachomatis at an MOI of 0.5. The cultures were photographed directly with an inverted fluorescence microscope (Axio Observer D1; Zeiss). For IFA experiments, C. trachomatis-infected cells were fixed by 4% paraformaldehyde, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100, and immunostained with the antibody to OmcB overnight at 4°C. After washing extensively, the cells were incubated with Alexa Fluor 405-conjugated secondary antibody for 45 min at 37°C. Images were obtained with a fluorescence microscope (Zeiss) and processed using AxioVision software.
E. coli growth curve, plate assay, and colony formation assay.
A single bacterial colony was inoculated into LB medium containing the proper antibiotics and cultured at 37°C overnight. The overnight culture was diluted in fresh medium at a ratio of 1:100 and cultured in LB medium with or without IPTG and shaken at 37°C. Two complement methods were used to evaluate the growth of E. coli (Fig. 1). In the first, culture samples were taken to measure the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) every 30 min. The absorbance values were plotted against the growth time. In the second, growth was assessed by plating serially diluted cultures on LB agar in the absence of IPTG. CFU were enumerated after incubation at 37°C for 16 to 24 h. For the colony formation assay (Fig. 3), the overnight cultures were diluted in fresh medium at a ratio of 1:100 and cultured in LB medium without IPTG at 37°C for 2 h. The cultures (200 μl) were collected for the series of 1/10 dilutions. An equal volume (5 μl) of each dilution was spotted on a LB agar plate containing IPTG (at concentrations of 0, 50, or 100 μM) and incubated for 16 h at 37°C.
Yersinia growth and secretion assay.
Y. pestis strain YP1283 carries a pCD1 plasmid with a functional T3SS but the yopE gene is deleted (and a dhfr gene is inserted). YP769 carries a mini-pCD1 plasmid (pCD1-Δ1234) that is deleted for all six effector Yops and their chaperones (40). This strain also lacks the pPCP1 plasmid encoding Pla. Y. pestis cultures were routinely grown in heart infusion broth (HIB) or on tryptose blood agar base plates (BD Difco) at 27°C. For secretion assays, Y. pestis strains were grown in TMH medium in the presence or absence of 2.5 mM CaCl2 as described previously.
Determination of promoter activity in E. coli using β-galactosidase assay.
Promoter activity was determined by measurement of the β-galactosidase reporter genes in E. coli. Cells harboring the appropriate plasmid(s) were grown overnight in LB medium. Cultures were diluted 1:100 in fresh LB medium to an OD600 of 0.3, and the expression of protein was induced by adding IPTG to the culture. To quantify the β-galactosidase expressed in E. coli, 200-μl portions of cultured cells were collected at different times and subjected to a plate β-galactosidase assay as described previously (59).
Bacterial two-hybrid assay determination of protein-protein interaction.
The competent E. coli reporter strain FW102 OL2-62 was transformed with two compatible plasmids. One expressed the α fusion proteins (e.g., α-YscB or α-SycN). The other expressed the CI fusion proteins (e.g., CI-Scc1 or CI-Scc4). Each single colony of transformant was inoculated in LB medium containing ampicillin and chloramphenicol overnight. The overnight culture was then diluted at 1:50 in fresh LB medium and continued culturing in the presence of IPTG (50 μM) to induced protein expression. Cultures grown to log phase were harvested and subjected to a β-galactosidase plate assay as described above.
Real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) and reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR).
HeLa cells infected with C. trachomatis were harvested at the times postinfection as indicated in Results. DNA and RNA were isolated using the Quick DNA/RNA miniprep kit (Zymo). For qPCR, the tufA gene was amplified using the VeriQuest Fast SYBR green qPCR mastermix (USB) with primers tufF and tufR (see Table S2 in the supplemental material) in 10 μl of reaction mixture on a real-time PCR system (Bio-Rad). Each sample was run in triplicate in a 96-well plate. A negative control containing no C. trachomatis DNA was included in each reaction setup. The PCR cycle conditions were as follows: 50°C for 2 min, 95°C for 5 min, 95°C for 3 s, and 60°C for 30 s. A standard curve was taken from purified C. trachomatis genomic DNA with the serial dilutions.
For RT-qPCR, a total of 2 μg of RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA using the high-capacity cDNA reverse transcriptase kit (Thermo Fisher). Dilution of cDNA was used for amplification of the genes of interest in a total volume of 20 μl using the PowerUp SYBR green mastermix (Thermo Fisher) on a real-time PCR system (Bio-Rad). The primers used are listed in Table S2. Triplicate samples were run for each target transcript. The following conditions were used: 95 °C for 3 min, then 95 °C for 5 s and 63 °C for 30 s. The last two steps were repeated for 40 cycles with fluorescence levels detected at the end of each cycle. Specificity of the primers was ensured with gel electrophoresis and with melting curve analysis. The transcripts were normalized to quantification cycle (Cq) values for the tufA gene and the comparative threshold cycle CT method (2−ΔΔCT) (60) was used to obtain relative transcript levels.
Protein expression, sample preparation, and immunoblot analysis.
Strains containing the expression plasmids were grown in LB medium (for E. coli) or heart infusion broth (HIB) (for Y. pestis). When indicated, different concentrations of IPTG (Sigma) were added. The cultures were centrifuged (1 min, 12,000 × g), and the bacteria were lysed by boiling in 2× SDS loading buffer. C. trachomatis L2/Scc4-infected HeLa cells were cultured in RPMI 1640-10 medium containing aTC to induce Scc4 expression. Cells were harvested at 24 hpi and lysed in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.6) and 8 M urea buffer. To determine the protein levels, a bicinchoninic acid (BCA) kit (Thermo Fisher) was used. The proteins were separated on polyacrylamide gels, transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore), and subjected to immunoblot analysis using proper primary antibodies. Goat anti-mouse or anti-rabbit IgG–alkaline phosphatase (Invitrogen) was used as the secondary antibody. Blots were developed using a horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody and the SuperSignalP chemiluminescent detection kit (Pierce). Density of the signals on the immunoblot was determined using ImageJ.
Statistical analysis.
Data are presented as mean plus or minus standard deviation (SD). Statistical analyses were performed using Prism version 6.0 (GraphPad Software, Inc., San Diego, CA). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) or a t test was used for testing the differences between the groups; P values <0.05 were considered significant.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Research reported in this publication was supported by National Institutes of Allergy and Infectious Diseases grants AI055869, AI093565, and AI146454 (L.S.). L.G. thanks the Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, Department of Microbiology for providing support through research assistantships.
We thank Ann Hochschild for much advice and Ken Fields for helpful discussions and providing valuable reagents.
Footnotes
Supplemental material is available online only.
REFERENCES
- 1.Mueller KE, Plano GV, Fields KA. 2014. New frontiers in type III secretion biology: the Chlamydia perspective. Infect Immun 82:2–9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00917-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Deng W, Marshall NC, Rowland JL, McCoy JM, Worrall LJ, Santos AS, Strynadka NCJ, Finlay BB. 2017. Assembly, structure, function and regulation of type III secretion systems. Nat Rev Microbiol 15:323–337. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2017.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Galán JE, Lara-Tejero M, Marlovits TC, Wagner S. 2014. Bacterial type III secretion systems: specialized nanomachines for protein delivery into target cells. Annu Rev Microbiol 68:415–438. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092412-155725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.World Health Organization Department of Reproductive Health and Research. 2011. Prevalence and incidence of selected sexually transmitted infections. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brunham RC, Rey-Ladino J. 2005. Immunology of Chlamydia infection: implications for a Chlamydia trachomatis vaccine. Nat Rev Immunol 5:149–161. doi: 10.1038/nri1551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Weber MM, Bauler LD, Lam J, Hackstadt T. 2015. Expression and localization of predicted inclusion membrane proteins in Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun 83:4710–4718. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01075-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bugalhão JN, Mota LJ. 2019. The multiple functions of the numerous Chlamydia trachomatis secreted proteins: the tip of the iceberg. Microb Cell 6:414–449. doi: 10.15698/mic2019.09.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Elwell C, Mirrashidi K, Engel J. 2016. Chlamydia cell biology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:385–400. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Abdelrahman YM, Belland RJ. 2005. The chlamydial developmental cycle. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:949–959. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2005.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Belland RJ, Nelson DE, Virok D, Crane DD, Hogan D, Sturdevant D, Beatty WL, Caldwell HD. 2003. Transcriptome analysis of chlamydial growth during IFN-γ-mediated persistence and reactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:15971–15976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2535394100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nicholson TL, Olinger L, Chong K, Schoolnik G, Stephens RS. 2003. Global stage-specific gene regulation during the developmental cycle of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol 185:3179–3189. doi: 10.1128/jb.185.10.3179-3189.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shaw EI, Dooley CA, Fischer ER, Scidmore MA, Fields KA, Hackstadt T. 2000. Three temporal classes of gene expression during the Chlamydia trachomatis developmental cycle. Mol Microbiol 37:913–925. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Browning DF, Busby S. 2004. The regulation of bacterial transcription initiation. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:57–65. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhu DX, Garner AL, Galburt EA, Stallings CL. 2019. CarD contributes to diverse gene expression outcomes throughout the genome of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116:13573–13581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1900176116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jishage M, Ishihama A. 1998. A stationary phase protein in Escherichia coli with binding activity to the major sigma subunit of RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:4953–4958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.9.4953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Min KB, Yoon SS. 2020. Transcriptome analysis reveals that the RNA polymerase–binding protein DksA1 has pleiotropic functions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem 295:3851–3864. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rao X, Deighan P, Hua Z, Hu X, Wang J, Luo M, Wang J, Liang Y, Zhong G, Hochschild A, Shen L. 2009. A regulator from Chlamydia trachomatis modulates the activity of RNA polymerase through direct interaction with the β subunit and the primary σ subunit. Genes Dev 23:1818–1829. doi: 10.1101/gad.1784009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stephens RS, Kalman S, Lammel C, Fan J, Marathe R, Aravind L, Mitchell W, Olinger L, Tatusov RL, Zhao Q, Koonin EV, Davis RW. 1998. Genome sequence of an obligate intracellular pathogen of humans: Chlamydia trachomatis. Science 282:754–759. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5389.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Douglas AL, Hatch TP. 2000. Expression of the transcripts of the sigma factors and putative sigma factor regulators of Chlamydia trachomatis L2. Gene 247:209–214. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(00)00094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hefty PS, Stephens RS. 2007. Chlamydial type III secretion system is encoded on ten operons preceded by sigma 70-like promoter elements. J Bacteriol 189:198–206. doi: 10.1128/JB.01034-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shen L, Shi Y, Douglas AL, Hatch TP, O’Connell CM, Chen JM, Zhang YX. 2000. Identification and characterization of promoters regulating tuf expression in Chlamydia trachomatis serovar F. Arch Biochem Biophys 379:46–56. doi: 10.1006/abbi.2000.1854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Douglas AL, Saxena NK, Hatch TP. 1994. Enhancement of in vitro transcription by addition of cloned, overexpressed major sigma factor of Chlamydia psittaci 6BC. J Bacteriol 176:3033–3039. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.10.3033-3039.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Douglas AL, Hatch TP. 1995. Functional analysis of the major outer membrane protein gene promoters of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol 177:6286–6289. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.21.6286-6289.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tan M, Gaal T, Gourse RL, Engel JN. 1998. Mutational analysis of the Chlamydia trachomatis rRNA P1 promoter defines four regions important for transcription in vitro. J Bacteriol 180:2359–2366. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.9.2359-2366.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Thompson CC, Griffiths C, Nicod SS, Lowden NM, Wigneshweraraj S, Fisher DJ, McClure MO. 2015. The Rsb phosphoregulatory network controls availability of the primary sigma factor in Chlamydia trachomatis and influences the kinetics of growth and development. PLoS Pathog 11:e1005125. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shen LMM, Frohlich KM, Cong Y, Goodwin OY, Chou CW, LeCour L Jr, Krup KL, Luo M, Worthylake DK. 2015. Multipart chaperone-effector recognition in the type III secretion system of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Biol Chem 290:28141–28155. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.670232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ukwaththage TO, Goodwin OY, Songok AC, Tafaro AM, Shen L, Macnaughtan MA. 2019. Purification of tag-free Chlamydia trachomatis Scc4 for structural studies using sarkosyl-assisted on-column complex dissociation. Biochemistry 58:4284–4292. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Silva-Herzog E, Joseph SS, Avery AK, Coba JA, Wolf K, Fields KA, Plano GV. 2011. Scc1 (CP0432) and Scc4 (CP0033) function as a type III secretion chaperone for CopN of Chlamydia pneumoniae. J Bacteriol 193:3490–3496. doi: 10.1128/JB.00203-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Joseph SS, Plano GV. 2013. The SycN/YscB chaperone-binding domain of YopN is required for the calcium-dependent regulation of Yop secretion by Yersinia pestis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 3:1. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang Y, Kahane S, Cutcliffe LT, Skilton RJ, Lambden PR, Clarke IN. 2011. Development of a transformation system for Chlamydia trachomatis: restoration of glycogen biosynthesis by acquisition of a plasmid shuttle vector. PLoS Pathog 7:e1002258. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mueller KE, Wolf K, Fields KA. 2016. Gene deletion by fluorescence-reported allelic exchange mutagenesis in Chlamydia trachomatis. mBio 7:e01817-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01817-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bastidas RJ, Valdivia RH. 2016. Emancipating Chlamydia: advances in the genetic manipulation of a recalcitrant intracellular pathogen. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 80:411–427. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00071-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hooppaw AJ, Fisher DJ. 2015. A coming of age story: Chlamydia in the post-genetic era. Infect Immun 84:612–621. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01186-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hua Z, Rao X, Feng X, Luo X, Liang Y, Shen L. 2009. Mutagenesis of region 4 of sigma 28 from Chlamydia trachomatis defines determinants for protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions. J Bacteriol 191:651–660. doi: 10.1128/JB.01083-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wang Y, deHaseth PL. 2003. Sigma 32-dependent promoter activity in vivo: sequence determinants of the groE promoter. J Bacteriol 185:5800–5806. doi: 10.1128/jb.185.19.5800-5806.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cong Y, Gao L, Zhang Y, Xian Y, Hua Z, Elaasar H, Shen L. 2016. Quantifying promoter activity during the developmental cycle of Chlamydia trachomatis. Sci Rep 6:27244. doi: 10.1038/srep27244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nickels BE, Garrity SJ, Mekler V, Minakhin L, Severinov K, Ebright RH, Hochschild A. 2005. The interaction between σ70 and the β-flap of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase inhibits extension of nascent RNA during early elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:4488–4493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409850102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nawrotek A, Guimarães BG, Velours C, Subtil A, Knossow M, Gigant B. 2014. Biochemical and structural insights into microtubule perturbation by CopN from Chlamydia pneumoniae. J Biol Chem 289:25199–25210. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.568436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Huang J, Lesser CF, Lory S. 2008. The essential role of the CopN protein in Chlamydia pneumoniae intracellular growth. Nature 456:112–115. doi: 10.1038/nature07355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bartra SS, Jackson MW, Ross JA, Plano GV. 2006. Calcium-regulated type III secretion of Yop proteins by an Escherichia coli hha mutant carrying a Yersinia pestis pCD1 virulence plasmid. Infect Immun 74:1381–1386. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.2.1381-1386.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bauler LD, Hackstadt T. 2014. Expression and targeting of secreted proteins from Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol 196:1325–1334. doi: 10.1128/JB.01290-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gao L, Wang Y, Hua Z, Liu E, Shen L. 2018. Potency of solithromycin against fast- and slow-growing chlamydial organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 62:e00588-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00588-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhang Y, Xian Y, Gao L, Elaasar H, Wang Y, Tauhid L, Hua Z, Shen L. 2017. Novel detection strategy to rapidly evaluate the efficacy of antichlamydial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61:e02202-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02202-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Brinkworth AJ, Malcolm DS, Pedrosa AT, Roguska K, Shahbazian S, Graham JE, Hayward RD, Carabeo RA. 2011. Chlamydia trachomatis Slc1 is a type III secretion chaperone that enhances the translocation of its invasion effector substrate TARP. Mol Microbiol 82:131–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07802.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chen Y-S, Bastidas RJ, Saka HA, Carpenter VK, Richards KL, Plano GV, Valdivia RH. 2014. The Chlamydia trachomatis type III secretion chaperone Slc1 engages multiple early effectors, including TepP, a tyrosine-phosphorylated protein required for the recruitment of CrkI-II to nascent inclusions and innate immune signaling. PLoS Pathog 10:e1003954. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Derré I, Swiss R, Agaisse H. 2011. The lipid transfer protein CERT interacts with the Chlamydia inclusion protein IncD and participates to ER-Chlamydia inclusion membrane contact sites. PLoS Pathog 7:e1002092. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zhang L, Douglas AL, Hatch TP. 1998. Characterization of a Chlamydia psittaci DNA binding protein (EUO) synthesized during the early and middle phases of the developmental cycle. Infect Immun 66:1167–1173. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.3.1167-1173.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Allen JE, Stephens RS. 1989. Identification by sequence analysis of two-site posttranslational processing of the cysteine-rich outer membrane protein 2 of Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L2. J Bacteriol 171:285–291. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.285-291.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Belland RJ, Zhong G, Crane DD, Hogan D, Sturdevant D, Sharma J, Beatty WL, Caldwell HD. 2003. Genomic transcriptional profiling of the developmental cycle of Chlamydia trachomatis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:8478–8483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1331135100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Yuan AH, Nickels BE, Hochschild A. 2009. The bacteriophage T4 AsiA protein contacts the beta-flap domain of RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:6597–6602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812832106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hsieh M-L, James TD, Knipling L, Waddell MB, White S, Hinton DM. 2013. Architecture of the bacteriophage T4 activator MotA/promoter DNA interaction during sigma appropriation. J Biol Chem 288:27607–27618. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.475434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hinton DM. 2010. Transcriptional control in the prereplicative phase of T4 development. Virol J 7:289–289. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Albrecht M, Sharma CM, Reinhardt R, Vogel J, Rudel T. 2010. Deep sequencing-based discovery of the Chlamydia trachomatis transcriptome. Nucleic Acids Res 38:868–877. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ferreira R, Borges V, Borrego MJ, Gomes JP. 2017. Global survey of mRNA levels and decay rates of Chlamydia trachomatis trachoma and lymphogranuloma venereum biovars. Heliyon 3:e00364. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2017.e00364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.AbdelRahman YM, Rose LA, Belland RJ. 2011. Developmental expression of non-coding RNAs in Chlamydia trachomatis during normal and persistent growth. Nucleic Acids Res 39:1843–1854. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Guzman LM, Belin D, Carson MJ, Beckwith J. 1995. Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter. J Bacteriol 177:4121–4130. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.14.4121-4130.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gong S, Yang Z, Lei L, Shen L, Zhong G. 2013. Characterization of Chlamydia trachomatis plasmid-encoded open reading frames. J Bacteriol 195:3819–3826. doi: 10.1128/JB.00511-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Frohlich K, Hua Z, Wang J, Shen L. 2012. Isolation of Chlamydia trachomatis and membrane vesicles derived from host and bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 91:222–230. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2012.08.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Thibodeau SA, Fang R, Joung JK. 2004. High-throughput β-galactosidase assay for bacterial cell-based reporter systems. Biotechniques 36:410–415. doi: 10.2144/04363BM07. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ. 2008. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.