Abstract
On average, the Peruvian population is among the shortest in the world1. Here we show that Native American ancestry is associated with reduced height in an ethnically diverse group of Peruvians, and identify a novel, population-specific, missense variant in FBN1 (E1297G) that is significantly associated with lower height. Each copy of the minor allele (frequency=4.7%) reduces height by 2.2 cm (4.4 cm in homozygous individuals). This is the largest effect size known for a common height-associated variant. FBN1 encodes the extracellular matrix protein fibrillin-1, a major structural component of microfibrils. We observed less densely packed fibrillin-1-rich microfibrils with irregular edges in the skin of individuals homozygous for G1297 compared to individuals homozygous for E1297. Moreover, we show that E1297G locus is under positive selection in non-African populations, and the E1297 variant shows subtle evidence of positive selection within the Peruvian population specifically. This variant is also significantly more frequent in coastal Peruvian populations than in populations from the Andes or the Amazon, suggesting that short stature might be the result of adaptation to factors associated with the coastal environment in Peru.
With average male and female heights of 165.3 cm and 152.9 cm respectively, Peruvians are among the shortest people in the world1. The genetic makeup of Peruvians is shaped by admixture between Native American residents of Peru and the incoming Europeans, Africans, and Asians who arrived in Peru since the 18th century2,3. A previous study of height in South and Latin Americans reported that Native American ancestry is correlated with lower height in these populations4, however, this association may have been the result of confounding socioeconomic or environmental factors that were not captured by socioeconomic covariates in that study (education and wealth). Even if the association between Native American ancestry and height was driven by genetic factors, the specific genes and adaptive processes remain unclear.
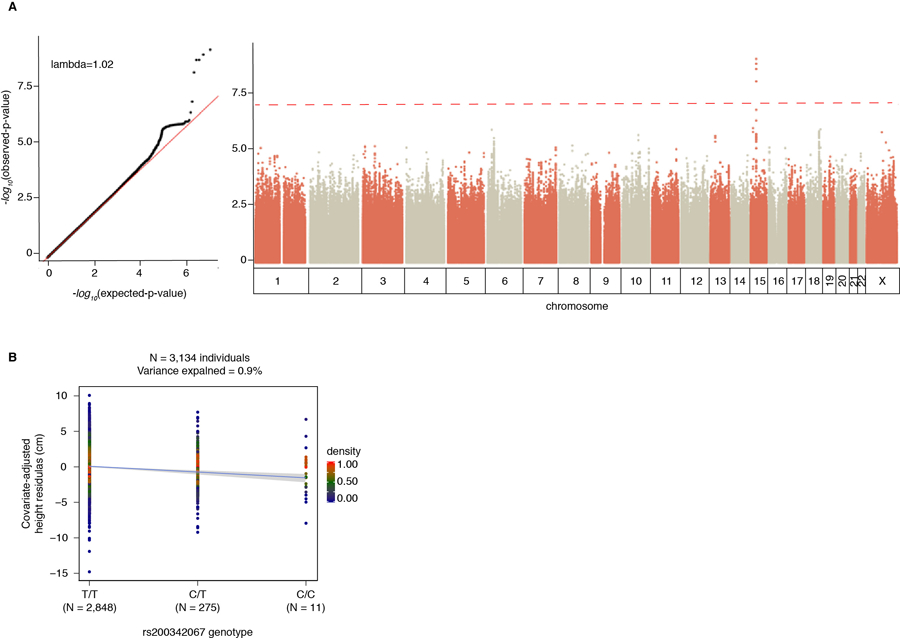
In order to define genetic factors contributing to height in Peruvians, we obtained height and genotyping data from 3,134 individuals in 1,947 households in Lima, Peru (Methods, Supplementary Information Section 1). We inferred the Native American ancestry proportion in each individual (Extended Data Figure 1) and observed a negative correlation between height and Native American ancestry proportion (Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r)=−0.28, 95% confidence interval (CI)=−0.31–−0.25, p-value=9.3×10−58, Figure 1A, Supplementary Information section 2). Native American ancestry remained significantly associated with lower height after adjusting for age, sex, African, and Asian ancestry proportions and a random household effect, as a proxy for unmeasured environmental factors (p-value=7.2×10−43, effect size=−14.75 cm for 100% Native American versus 100% European ancestry, standard error (se)=1.06, Figure 1B).
Figure 1: Genetic architecture of height in the Peruvian population.
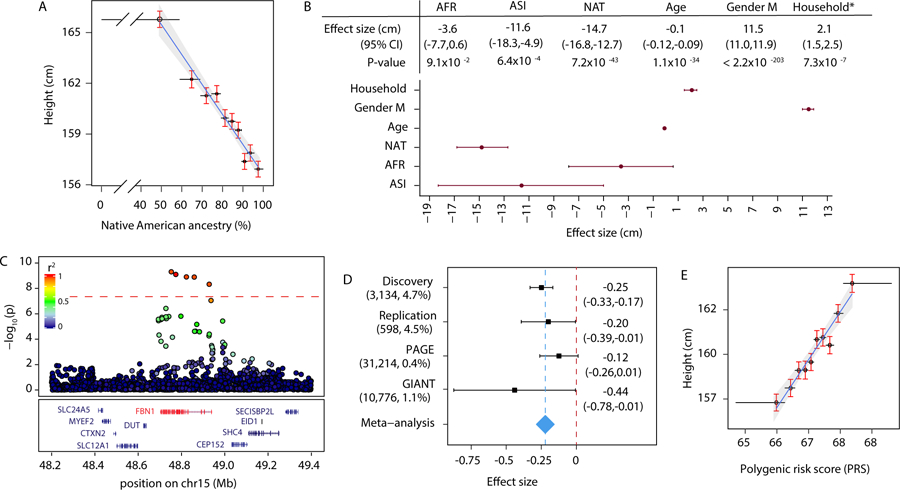
A) Height is negatively correlated with Native American ancestry proportion (N=3,134 individuals, Pearson’s r=−0.28, CI=−0.31 −0.25, t-value = −16.36, degrees of freedom (df) = 3132, one-sample t-test two-sided p-value=9.3×10−58). Point: median for a decile of Native American ancestry (x-axis) and the average height for that decile (y-axis). Error bars: range (x-axis) and standard error (se, y-axis). B) Increased Native American ancestry is associated with lower height after adjusting for age, sex, African and Asian ancestry proportions, household as a proxy for socioeconomic factors, and genetic relatedness (N=3,134 individuals). *Household effect size is calculated as the standard deviation (sd) in the model’s intercept. The effect sizes for African, Asian, and Native American ancestry are given relative to European ancestry. P-values are two-sided p-values from χ2 difference test. C) Locus-specific Manhattan plot of -log10 transformed GWAS p-values. One locus on chromosome 15 passed the genome-wide significance threshold (p-value<5×10−8, N=3,134 individuals). P-values are two-sided Wald test p-values. Dots: variants colored according to their LD with rs200342067 (total number of variants tested=7,756,401, number of variants shown=3,176). D) rs200342067 showed a similar MAF, direction of effect, and effect size in an independent cohort of Peruvians (N=598 individuals), and two independent cohorts of Latino/Hispanics (N=31,214 and 10,776 individuals respectively). Squares: rs200342067’s effect size on inverse normally transformed height, dashed blue line: meta-analysis effect size, diamond: meta-analysis se, error bars: 95% CI. Cohort’s size and rs200342067’s MAF is shown in parentheses and effect sizes (CIs) on the right. E) Height is positively correlated with polygenic risk scores (PRS) (N=3,134 individuals, Pearson’s r=0.22, CI=0.18–0.25, t-value = 12.36, df = 3132, one-sample t-test two-sided p-value=2.7×10−34). Points: median for a PRS decile (x-axis) and the average height for that decile (y-axis). Error bars: range (x-axis) and se (y-axis).
To identify variants deriving this effect, we performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS). We observed association at five highly linked SNPs within a single locus overlapping FBN1 (15q21.1, p-value<5×10−8, Extended Data Figure 2A). One SNP, rs200342067 (minor allele frequency (MAF)=4.72%, effect size=−2.22 cm, se=0.36, p-value=6.8×10−10), is a missense variant (E1297G) while the other four are intronic (Figure 1C, Extended Data Table 1). Accounting for additional covariates, such as population PCs or identity-by-descent5, did not impact the association results (Supplementary Information Section 3).
To replicate this association, we genotyped an independent cohort of Peruvians (N=598, Methods, Supplementary Information Section 1) and observed a similar allele frequency and effect size for rs200342067 in the replication cohort (MAF=4.52%, effect size=−1.70 cm, se=0.82, p-value=0.04, Table 1). Meta-analysis of the discovery and replication cohorts increased the association’s significance (effect size=−2.14 cm, se=0.33, p-value=9.2×10−11, Table 1). We also tested association of rs200342067 with inverse normally transformed height in GIANT6 and PAGE7, two publicly available datasets of Hispanic/Latino individuals. While allele frequencies were lower in these datasets (<1.15%), we observed similar effect sizes across cohorts (effect size (se) for discovery, replication, PAGE, and GIANT cohorts respectively: −0.25 (0.04), −0.20 (0.10), −0.12 (0.07), and −0.44 (0.22); Table 1). Meta-analysis of these cohorts further augmented association’s strength (effect size=−0.22 (se=0.03), p-value=9.8×10−12, Table 1, Figure 1D). These results confirm that the association between rs200342067 and height is not driven by statistical fluctuation or genotyping artifact specific to the discovery cohort. We did not find any additional association in gene-based analysis of rare (MAF<1%) or common variants (Supplementary Information Section 4).
Table 1: Replication of rs200342067 association.
We replicated the association between rs200342067 and height in an independently collected cohort (N=598 individuals). We also tested the association of rs200342067 with inverse normally transformed height in two publicly available datasets of Hispanic/Latino individuals (PAGE and GIANT, N=31,214 and 10,776 individuals respectively) and observed a similar direction of effect and effect size in these independent cohorts. P-values are two-sided Wald test p-values. Numbers are rounded to two decimal places.
| phenotype | cohort | N | rs | allele1 | allele2 | MAF (%) | effect size | se | z-score | Wald p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height in cm | Discovery | 3,134 | rs200342067 | C | T | 4.72 | −2.22 | 0.36 | −6.17 | 6.8×10−10 |
| Replication | 598 | rs200342067 | C | T | 4.52 | −1.70 | 0.82 | −2.07 | 0.04 | |
| Meta-analysis | −2.14 | 0.33 | −6.48 | 9.2×10−11 | ||||||
| inverse normally transformed height | Discovery | 3,134 | rs200342067 | C | T | 4.72 | −0.25 | 0.04 | −6.25 | 4.1×10−10 |
| Replication | 598 | rs200342067 | C | T | 4.52 | −0.20 | 0.10 | −2.00 | 0.05 | |
| PAGE | 31,214 | rs200342067 | C | T | 0.37 | −0.12 | 0.07 | −1.71 | 0.09 | |
| GIANT | 10,766 | rs200342067 | C | T | 1.15 | −0.44 | 0.22 | −2.00 | 0.05 | |
| Meta-analysis | −0.22 | 0.03 | −6.81 | 9.8×10−12 |
Previous large-scale height GWAS, done predominantly in Europeans, have identified 3,290 independent common height-associated variants8. To assess the predictive power of these European-biased variants in the Peruvian population we generated polygenic risk scores (PRS) using conditional effect sizes of 2,993 common height-associated variants that were present in our cohort (Methods, Supplementary Information Section 5). Greater PRS values were associated with increased height (Pearson’s r=0.22, CI=0.18–0.25, p-value=2.7×10−34, Figure 1E). The estimated genetic heritability (h2g) of height was similar for Peruvians (h2g=57.6%, se=9.7) and Europeans (h2g=62.5%)9; however, previously identified height-associated variants explained only 6.1% (CI=4.6–7.8, p-value=6.7×10−45,) of height phenotypic variance in our cohort compared to 24.6% (CI=22.0–27.2) in the original European cohort.
The lower predictive power of PRS calculated based on a European GWAS in a non-European population might be the result of differences in factors related to population demography (such as LD, allele frequency, sex, and age composition)10–12, non-transmitted genetic factors (such as genetic makeup of the parent13 and peers14), non-genetic factors (such as environmental exposure15), or genetic interaction with non-genetic factors16. In line with previous reports11,12, we observed that the European-biased PRS explains a higher proportion of height phenotypic variance in individuals with high European ancestry proportion compared to the individuals with low European ancestry proportion suggesting that the reduced effect of PRS in Peruvians may be at least in part related to genetic differences (Supplementary Information Section 5).
Of previously identified common height-associated variants, 99% have effect sizes <0.5 cm/allele (Figure 2A). In contrast, rs200342067 reduces height by 2.2 cm/allele and explains 0.9% of height phenotypic variance in our cohort (Extended Data Figure 2B). This effect size is comparable to a few other extremely rare (MAF<0.5%) height-associated variants that are believed to be under purifying selection6,8. In the 1000 Genomes Project17, rs200342067 is specific to Mexican (MAF=0.78%) and Peruvian (MAF=4.12%) populations. However, the genomic region overlapping rs200342067 is under hard selective sweep in certain European, South Asian, East Asian, and South American populations18,19 (Supplementary Information Section 6). This observation led us to the hypothesis that rs200342067 might have risen in frequency in the Peruvian population as a result of positive selection.
Figure 2: rs200342067 is positively selected in the Peruvian population.
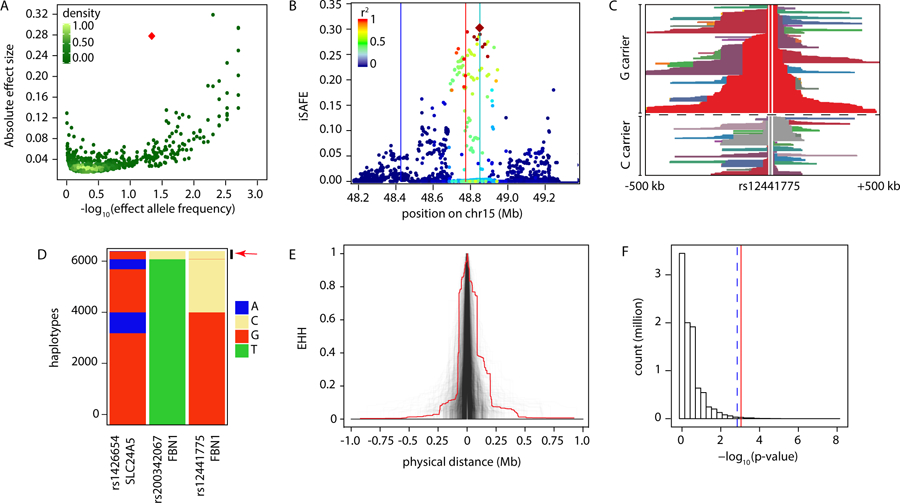
A) Conditional effect sizes and allele frequencies of 3,290 previously identified height-associated variants in the European population (N ~ 700,000 individuals, green dots) compared with the effect size and allele frequency of rs200342067 (red diamond) from this study (N=3,134 individuals, MAF=4.7%). Effect sizes are shown as the absolute effect size on invers normally transformed height. B) iSAFE plot for a 1.2Mb region around rs200342067 in our cohort (N=3,134 individuals). x-axis: physical position, y-axis: iSAFE score. Dots: variants colored according to their LD with rs12441775 (red diamond); Red, cyan, and blue vertical lines: physical position of rs200342067, rs12441775, and rs1426654 respectively. C) Haplotype decay around rs12441775 in our cohort (N=3,134 individuals). rs12441775’s position is marked above the haplotype, haplotypes above the dashed line carry rs12441775*G (derived/major, N=4,063 haplotypes) and haplotypes below the dashed carry rs12441775*C (ancestral/minor, N=2,205 haplotypes). D) Stacked barplot of haplotypes carrying rs200342067, rs12441775, and rs1426654 in our cohort (N=6,268 haplotypes). Only 3% of the haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C allele (red arrow) also carry rs12441775*G allele (AF=64.8%) and only 4% carry rs1426654*A (AF=17.9%). x-axis: SNPs, y-axis: haplotypes carrying derived or alternate allele of rs200342067, rs12441775, and rs1426654. E) Extended Haplotype Homozygosity (EHH) plots for haplotypes carrying the rs200342067*C (red line, N=297 haplotypes) compared to haplotypes carrying 2,380 variants that are overlapping the neutral regions of the genome and have similar DAF to rs200342067*C (4.7±1%, gray lines). Haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C are longer than 99.2% of the haplotypes in the neutral genomic regions. F) Histogram of Fisher’s exact test results comparing the extent of allele frequency differences between coastal (N=46 individuals) and non-coastal (N=104 individuals) regions in Peru. x-axis: -log10 p-value of two-sided Fisher’s exact test (N=9,381,550 variants), dashed blue line: 99th percentile, solid red line: rs200342067’s -log10 p-value (0.7th percentile, Fisher’s exact test two-sided p-value=0.0005); y-axis: variant count in millions.
To test this hypothesis, we used the integrated Selection of Allele Favored by Evolution (iSAFE)20 to search for variants under positive selection in a 1.2Mb region around rs200342067. The top positive selection signal was from rs12441775 (Figure 2B), an intronic variant in FBN1 with unknown function. The derived rs12441775*G allele has a much higher frequency in all non-African populations than African populations (58% (IQR=51–64) versus 4% (IQR=1–5)17, Extended Data Figure 3). This allele shows evidence of positive selection (integrated Haplotype Score (iHS)18,19<−2 and Extended Haplotype Homozygosity21 (EHH)) in European, South Asian, and South American populations including the Peruvian population (DAF=61%, iHS=−2.16, Figure 2C, Extended Data Figure 3, Supplementary Information Section 6) suggesting an out-of-Africa positive selection on rs12441775.
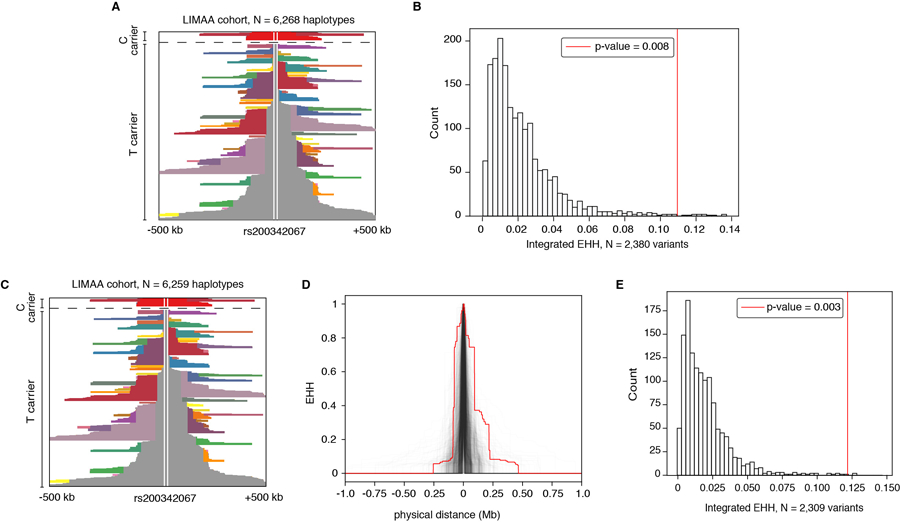
Since rs12441775 is located 77kb upstream of rs200342067, we considered that increased frequency of rs200342067 in Peruvians may be the result of positive selection at rs12441775. Interestingly, rs12441775*G (derived/major) and rs200342067*C (derived/minor) alleles are out of phase with each other and rarely co-occur on the same extended haplotypes. In our cohort, only 3% (9/297) of the haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C (AF=4.7%) also carry rs12441775*G (AF=64.8%, Figure 2D, Supplementary Information Section 6). Therefore, positive selection at rs12441775 cannot explain the increased frequency of rs200342067*C in Peruvians.
The presence of strong positive selection at haplotypes carrying rs200342067*T prevents the detection of potentially weaker selection signals at haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C using methods such as iHS18 or pairwise nucleotide diversity (π)22. However, if rs200342067*C is under independent positive selection, the length of haplotypes carrying this allele is expected to be longer than haplotypes carrying other derived alleles with similar allele frequencies in neutral regions of the genome23. Indeed, we observed that haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C are longer than 99.2% of haplotypes carrying similar alleles in the neutral genomic regions (N=2,380 variants, N=3,134 individuals, Figure 2E, Methods). Excluding the nine haplotypes that carry both rs200342067*C and rs12441775*G alleles does not change this result (Extended Data Figure 4). Similarly, haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C were longer than 100% of haplotypes simulated under a neutral demographic model that matches Peru’s population history (Methods, Extended Data Figure 5). Altogether, these results suggest that the rs200342067*C is under positive selection independent of rs12441775*G. Almost all other missense variants in FBN1 are under purifying selection, causing this gene to have a significantly lower burden of missense variants than expected (z-score=5.53, p-value=3.2×10−8, Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC), N=60,706)24.
The selection signal at rs200342067*C is weaker than rs12441775*G this difference may be due to the difference in alleles’s age (484 (CI=373–605) versus 2,382 (CI=2,286–2,479) generations old25 for rs200342067*C and rs12441775*G respectively). It is also not clear whether the same evolutionary pressures are driving selection at both alleles. We also note that the positive selection signal at rs200342067 is weaker than known examples of recent hard selective sweeps (such as SLC24A5 or LCT)19. While alleles under strong positive selection have |iHS| values>219, the iHS value for rs200342067 is −1.5. This value is more extreme than reported19 iHS values of 95.3% variants with similar DAF and local recombination rate in the Peruvian population (Extended Data Figure 6A). Similarly, EHH for rs200342067 is more extreme than EHH of 97.5% variants with similar DAF and recombination rates in our cohort (Extended Data Figure 6B–C).
FBN1 is 266kb downstream of SLC24A5 (Figure 1C), a well-known example of positive selection due to its role in skin pigmentation26,27. However positive selection at rs200342067 is unlikely to be the result of selection at extended haplotypes carrying positively selected alleles in SLC24A5 as there is no linkage between variants overlapping FBN1 and variants overlapping SLC24A5 (r2<0.05). We also investigated the structure of haplotypes carrying rs1426654*A, a SLC24A5 allele associated with light skin pigmentation26,28 that is known to be under positive selection29 specifically; we observed that rs200342067*C and rs1426654*A are out of phase with each other and almost never co-occur on the same extended haplotypes. Only 4% (12/297) of haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C (AF=4.7%) also carry rs12441775*G (AF=17.9%, Figure 2D, Supplementary Information Section 6). Moreover, FBN1 and SLC24A5 are in different topologically associating domains (TADs) suggesting that rs200342067 (or other FBN1 variants) are unlikely to have been selected due to long-range regulatory effects on SLC24A5.
Since adaptation to the local environment can drive dramatic allele frequency shifts, we compared the frequency of rs200342067 among 150 individuals collected separately from our cohort through the Peruvian Genome Project3 (PGP) from three different geographical regions in Peru: Coast (N=46), Amazon (N=28), and Andes (N=76). The rs200342067 variant is more frequent in the Coast compared to the Andes or Amazon (MAF=9.7%, 1.7%, and 0% respectively, coast vs. non-coast Fisher’s exact test p-value=0.0005, Figure 2F, Supplementary Information Section 7). Allele frequency differences as extreme as this is observed in <0.7% of all variants (N=9,381,550 variants, Figure 2F) and in <1.1% of variants matched on DAF and local recombination rate to rs200342067 (N=2,062 variants, Extended Data Figure 6D). We also used Bayenv230 to check the deviation of rs200342067 from a neutral population structure model after correction for population structure. The deviation of rs200342067 from the neutral population structure was more extreme than 91.7% of variants in the same DAF and recombination bin (Extended Data Figure 6E, Methods). Among coastal populations, the Moches population, native to the North coast of Peru, had an especially high frequency of rs200342067 (N=21, minor allele count=4, MAF=9.5%). Notably, the average height of Moches people is far below Peru’s average height (158 cm and 147 cm for Moches male and female31 versus 164 cm and 152 cm for Peruvian male and female in the same year1), suggesting rs200342067 may have been selected as a result of adaptation to factors associated with the coastal environment.
To ensure that the association between rs200342067 and height in the Peruvian population is not driven by population structure and stratification between individuals from different geographical regions, we performed a PCA analysis in the PGP cohort3 (N=150) using a set of common variants (MAF≥5%) and used SNP loadings from the PCA analysis in the PGP cohort to infer populations PCs in our cohort (N=3,134, Supplementary Information Section 7, Methods). Correction for these PCs did not change the effect size or the strength of the observed association between rs200342067 and height (N=3,134, MAF=4.72%, effect size=−2.30 cm, se=0.36, p-value=3.0×10−10) confirming that the observed association between rs200342067 and height is not a result of confounding population structure.
The rs200342067 (E1297G) variant changes the conserved T (major/ancestral) allele to a C (minor/derived) allele in FBN1 exon 31 (g.48773926T>C, Extended Data Figures 7). This change substitutes a large, negatively charged glutamic acid for a glycine, the smallest amino acid in fibrillin-1, encoded by FBN1. Fibrillin-1 is an extracellular matrix (ECM) glycoprotein that serves as the structural backbone of force-bearing microfibrils in elastic and non-elastic tissues32 and is also involved in tissue development, homeostasis, and repair by interacting with transforming growth factor (TGFβ) and other growth factors32. While the clinical significance of fibrillin-1 E1297G is not known, other fibrillin-1 mutations cause nine dominantly inherited Mendelian diseases33. Most of these diseases include skeletal anomalies and changes in skin elasticity33. To investigate possible clinical consequences of fibrillin-1 E1297G we performed dermatological and rheumatological clinical exams on 11 individuals from our cohort: 2 homozygous (C/C) cases, 2 heterozygous (C/T) cases, and 7 matched controls with reference (T/T) genotype (Methods). While the musculoskeletal examination revealed no differences between individuals, one C/C genotype individual had notably thicker skin upon a total body skin examination and appeared older than the stated age. The other C/C genotype individual had no clinically abnormal cutaneous findings and none of the C/T or T/T individuals had an abnormal skin exam (Supplementary Information Section 8).
We also obtained skin biopsies from two individuals with rs200342067 C/C genotype (alternate homozygous) and two with rs200342067 T/T genotypes (reference homozygous, Methods). We matched each C/C genotype individual with T/T genotype individuals based on age, sex, and ancestry proportions. Immunohistochemical staining showed that the individuals with C/C genotype have shorter microfibrillar projections from the dermal-epidermal junction into the superficial (papillary) dermis as well as less fibrillin-1 deposition in the deeper dermis (Extended Data Figure 8, Methods). Scanning electron microscopy (EM) showed that individuals with C/C genotype have less densely packed microfibrils with irregular edges and with microfibrils embedded in less dense collagen bundles confirming the abnormal appearance of fibrillin-1 observed in immunohistochemical analysis of skin biopsies (Figure 3, Extended Data Figure 9). Together these experiments suggest that rs200342067 alter the amount and architecture of microfibrillar deposits in the skin.
Figure 3: Fibrillin-1 electron microscopy (EM) in the skin.
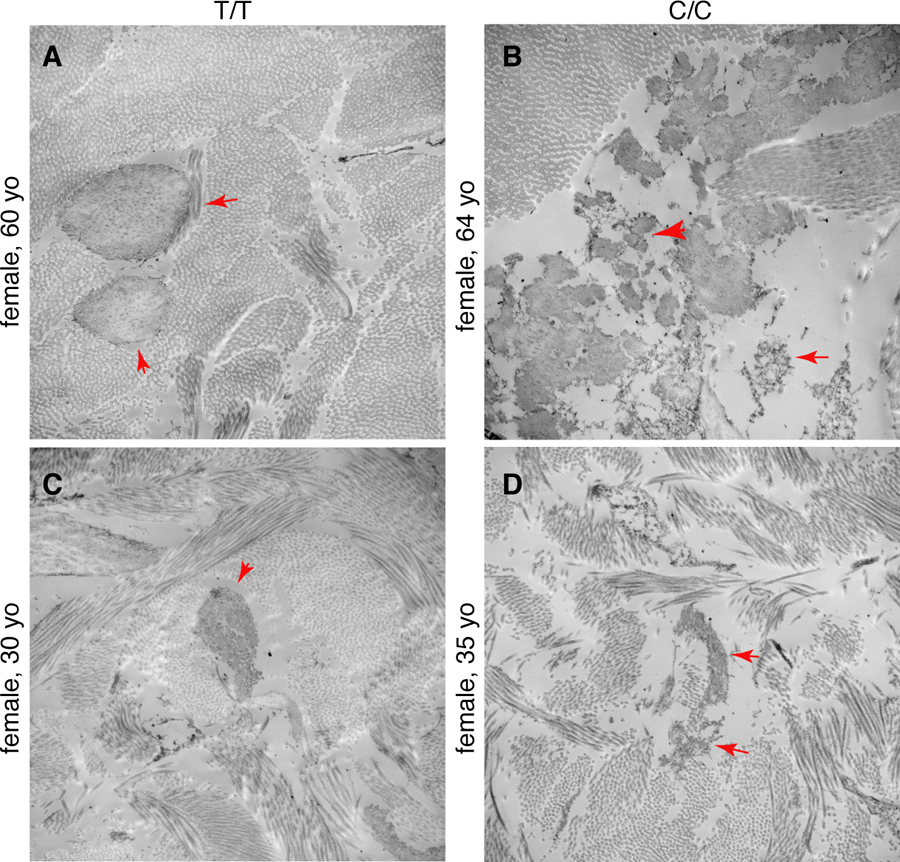
A–C) EM of the dermal-epidermal junction in two individuals with rs200342067 T/T genotype and B–D) two individuals with rs200342067 C/C genotype which are matched for age, sex, and ancestry proportions. Individuals with C/C genotype have short, fragmented, and less densely packed microfibrils with irregular edges (red arrows) and their microfibrils are embedded in less dense collagen bundles compared to the individuals with T/T genotype. Magnification: 11000x.
While all the reported fibrillin-1 mutations causing short stature phenotypes occur in the TGFβ-binding domains, mutations in the cbEGF-domains of fibrillin-1 predominantly lead to Marfan or Marfan-like syndromes34. Notably, missense mutations in cbEGF-domains 11 to 18 of fibrillin-1 (a.k.a. neonatal region, Extended Data Figure 7) have previously been associated with severe neonatal forms of Marfan syndrome, mortality within the first two years of postnatal life, and poor disease prognosis in adults33,35. To our knowledge, E1297G is the first report of a mutation in the fibrillin-1’s neonatal region that leads to short stature, in contrast to the tall stature common in Marfan syndrome.
E1297G is located in fibrillin-1 calcium binding epidermal growth factor domain 17 (cbEGF-domain 17), between a conserved cysteine (C1296) involved in forming a disulfide bond with C1284, and a conserved asparagine (N1298) involved in calcium binding36 (Extended Data Figures 7, Supplementary Information Section 8) and may play a role in calcium-binding37. Calcium binding at fibrillin-1 cbEGF domains stabilizes the protein by making the microfibrils more rigid and protecting them from degradation by proteases38. The short fragmented and less packed phenotype seen in the skin of rs200342067 C/C individuals compared to T/T individuals (Figure 3, Extended Data Figures 8 and 9) might reflect the higher susceptibility of mutated fibrillin-1 to proteolysis compared to the wild-type protein. The few previous studies that have reported amino acid changes at positions similar to E1297G in other fibrillin-1 cbEGF-like domains have associated this change with Marfan syndrome34 highlighting the importance of domain context for studying the molecular effect of fibrillin-1 mutations39,40. Understanding the cellular mechanisms that connect E1297G to microfibril structures and height requires further functional follow-up (Supplementary Information Section 8).
Common variants with large effect sizes on height might increase in frequency in population as a result of positive selection. A study of height in Sardinian islanders found an intronic variant in KCNQ1, which encodes a voltage-gated potassium channel, that reduces height by an average of 1.8 cm (rs150199504, MAF=7.7%, MAF in Central European population (CEU)=0.67%); they suggested that this variant is positively selected in Sardinians as a result of adaptation to the island environment41. A study of signatures of genetic adaptation in Greenland Inuits found an intronic variant in FADS3, a gene involved in fatty acid metabolism, that reduces height by 1.9 cm possibly due to the influence of fatty acid composition on the regulation of growth hormones (rs7115739, DAF=62.7%−81.9%, DAF in CEU=2.9%−3.6%); they suggested that this variant is positively selected in Greenland Inuits as a result of adaptation to their fat-rich diet42. Similarly, it is plausible that short stature in Peruvians is the result of adaptation to the factors associated with the coastal environment. It is also possible that other FBN1-related traits like changes in cardiovascular system performance have offered an evolutionary advantage in this population. Understanding the exact adaptive processes that could have caused the selection of rs200342067 in the Peruvian population is a challenging task and requires further investigation.
Besides its implications in medical and population genetics, this study highlights the importance of large-scale genetic studies in underrepresented and founder populations. Our findings show that genetic studies in novel populations can uncover novel trait-associated variants of large effects in functionally relevant genes. Similar studies in diverse populations are required to capture the extent of human genetic diversity and to expand the benefits of genetic research to all human populations.
Methods
Study participants
Discovery cohort:
The individuals in the discovery cohort (e.g. LIMAA cohort) are a subset of 4,002 individuals that were collected in Lima, Peru to study the genetics of tuberculosis in the Peruvian population43. The catchment area included 12 of the 43 districts of metropolitan Lima, Peru and 3.3 million inhabitants. This catchment area reflects a mix of urban and peri-urban areas and informal settlements44. Participants were collected in any of the 106 public health centers in this catchment area. Informed written consent was obtained from all the participants. The study protocol was approved by the Harvard School of Public Health’s Institutional Review Board (IRB) and the Research Ethics Committee of the National Institute of Health of Peru.
Replication cohort:
We collected 889 individuals from the same catchment area as the discovery cohort. Similar to the discovery cohort, we followed the guidelines of the Harvard School of Public Health’s IRB and the Research Ethics Committee of the National Institute of Health of Peru guidelines and obtained informed consent from all participants.
Phenotype
In both discovery and replication cohorts, height in centimeters was measured by trained healthcare staff upon recruitment of study participants. We excluded the individuals<19 years of age, individuals without height measurement, and individuals with a measured height ±3.5 SD away from the population average from the cohort. In addition to height, sex, age, and individuals’ TB status were also collected. We also collected household-level socioeconomic factors on housing quality, water supply and sanitation45 and summarized these factors using principal component analysis (PCA)45 to calculated household-level composite socioeconomic scores (SES scores). The continuous SES scores were then categorized into tertiles corresponding to low, middle, and upper socioeconomic groups45.
Genotyping and quality control
Discovery Cohort:
We collected genotyping data for 4,002 individuals from 2,272 households in Lima, Peru, using a customized Affymetrix Axiom array. The array details, as well as the genotyping quality control, phasing, and imputation have been described in detail in a prior publication43; in brief, we designed a ~720K marker array based on exome-sequencing data from 116 Peruvians in order to optimize for population-specific rare and coding variants. Out of 4002 recruited individuals, 22 individuals were excluded during quality control due to missing more than 5% of the genotype data, excess of heterozygous genotypes (±3.5 SD), duplicated with identity-by-state>0.9, or TB cases with age-at-diagnosis above 4043. We further excluded 846 individuals from the analysis: individuals below 19 years of age, individuals without height measurement, and individuals with a measured height ±3.5 SD away from the population average. The final cohort for the current study included 3,134 from 1,947 households. We used GRCh37 as the reference genome for all our genetic analyses.
Replication cohort:
We collected genotyping data for 889 individuals from 273 households in the same population and catchment area as our discovery cohort. We collected blood using the Whatman® protein saver cards (Dried Blood Spot (DBS) cards) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: WHA10534320). We extracted genomic DNA from the collected blood and genotyped all the samples using the Illumina Multi-Ethnic Genotyping Array (MEGA). rs200342067 is included on the MEGA array and was directly genotyped in all individuals. We used Plink (version 1.90b3w) to estimate the level of genotyping missingness and the proportion of heterozygous variants per individual. Height data was not available for 127 individuals. Moreover, 164 individuals were excluded due to age<19 years old. The final cohort included 598 individuals from 242 households.
Genetic relatedness matrix (GRM) and Kinship estimation
To avoid spurious association results, it is important to account for both recent genetic relatedness, such as family structure (kinship), and more distant genetic relatedness, such as population structure. To this end, we used GEMMA46 (version 0.96), with default options, to generate a GRM after removing rare variants (MAF ≤ 1%), regions with known long-range linkage disequilibrium (LD)47, and variants in high LD (r2>0.2 in a window of 50kb and a sliding window of 5kb). We used PLINK (version 1.90b3w) for pruning the genotypes. We generated a separate GRM following the same steps for the Peruvian individuals that were included in the replication cohort.
Many kinship estimation methods perform under the assumption of sampling from a single population with no underlying ancestral diversity. Kinship estimates are inflated when this assumption is violated 48. In the presence of population structure and admixture, methods that replace population allele frequencies with ancestry-specific allele frequencies are preferred48. We used PC-Relate49 implemented in the GENESIS R package (version 2.6.1) to estimate the kinship coefficients between individuals. This method uses ancestry representative PCs to correct for population structure before calculating the kinship coefficients. For this analysis, we removed rare variants (MAF<1%), regions with known long-range linkage disequilibrium (LD)47, and variants in high LD (r2>0.2 in a window of 50kb and a sliding window of 5kb). Individuals were considered unrelated if their estimated kinship coefficients were ≤ 0.0625, corresponding to second-degree genetic relatedness or closer. 476 individuals had kinship coefficients>0.0625.
Next, we inferred pairwise IBD segments between the individuals in our cohort using Refined IBD5. Refined IBD uses a haplotype dictionary to find exact short matches between phased haplotypes from different individuals and then expand these matches to identify long, nearly identical IBD segments between these individuals50. Refine IBD then evaluates candidate IBD segments with a probabilistic approach to assess the strength of evidence for IBD and reports the segment above a threshold as IBD segments. To calculate IBD segments using Refined IBD, we first used PLINK (version 1.90b3w)51 on QCed genotypes (N=677,675 markers) to generate one VCF file per chromosome. We then used Refined IBD function5 implemented in Beagle (version 4.1) to phase these genotypes and to calculate IBD segments in our cohort (N=3,134). We used Refined IBD with nthreads=8, overlap=3000, default options for other parameters, and genetic maps from HapMap II (Build GRCh37/hg19) (provided on Beagles website). Finally, we calculate the proportion of IBD by dividing the length of IBD segments by the length of diploid GRCh37 autosomal chromosomes excluding GRCh37 gap regions such as centromere (e.g accessible genome, 5.7×109 bp). We used the Pearson correlation coefficient in R (version 3.4) to compare the GENESIS and Refined IBD results.
The Peruvian Genome Project (PGP)
In some analyses, we have used whole-genome sequencing data from the Peruvian Genome Project (PGP)3. This cohort is, previously described by Harris et al, PNAS, 20173, includes 150 Peruvian individuals that were collected separately from our cohort from three different geographical regions in Peru: Coast (N=46), Amazon (N=28), and Andes (N=76). Assigning individuals to different Native American groups from the three geographical regions is described in Harris et al, PNAS, 20173 as follows: “Native American population cohort participants were recruited from the Matzes, Uros, Afroperuvians, Chopccas, Moches, Q’eros, Nahuas, and Matsiguenka populations. We applied three criteria to optimize individuals to best represent the Native American populations: (i) the place of birth of the participant and that of his or her parents and grandparents, (ii) their last names (only those corresponding to the region), and (iii) age (eldest to mitigate effects of the last generation). Participants of the mestizo population cohorts were recruited from the cities Iquitos, Puno, Cusco, Trujillo, and Lima and were randomly selected. The Afroperuvians were sampled as a Native American population; however, for all analyses, we treated them as a mestizo group due to their expected admixture between multiple ancestries.”
rs200342067 allele frequency difference between the coast and non-coastal regions
We compared the extent of the allele frequency difference between individuals from the coastal regions in Peru (N=46) and individuals that were not from the coastal regions in Peru (N=104) using two-sided Fisher’s exact test (N=9,381,550 variants). Next, to ensure adequate control for population structure, we used Bayenv2.0 (version 2.0)30 to calculate a covariance matrix between the coast and non-coast populations using 63,758 SNPs with MAF>10% in the PGP cohort3 using the default options. We then used Bayenv2.0 (version 2.0)30 to calculate standardized allele frequencies and XTX statistics, a population differentiation statistic that is designed to detect variant level deviations from the neutral patterns of population structure while correcting for population structure30, for rs200342067 as well as all the 2,062 SNPs randomly selected SNPs that were matched in MAF and local recombination rate to rs200342067 using the default options.
Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
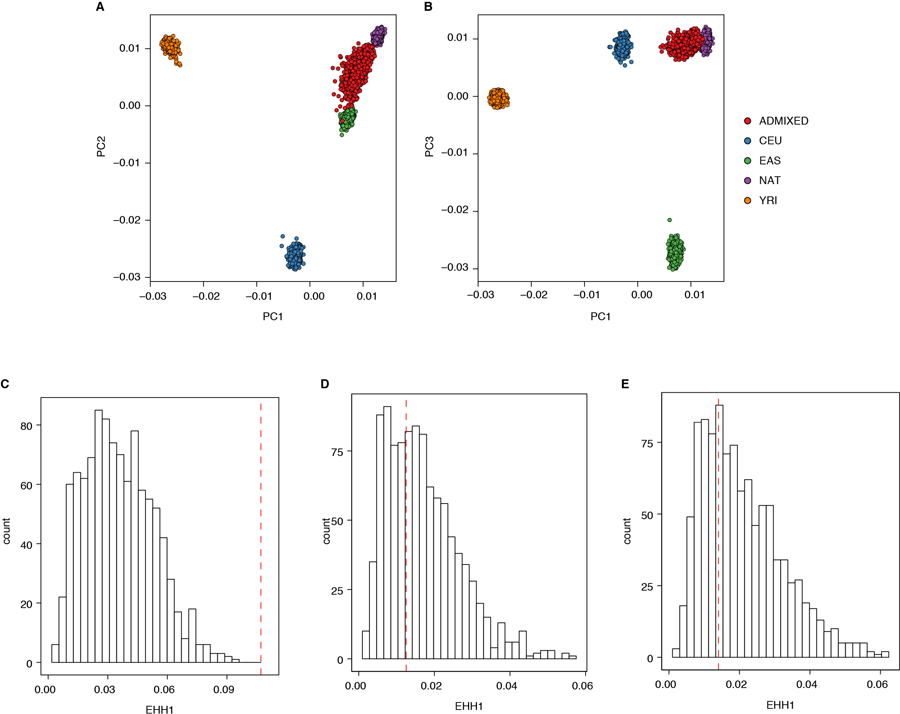
To obtain PCs within the LIMAA cohort, we merged our genotype data with data from the continental populations of phase 3 of the 1000 Genomes Project17 and genotype data from Siberian and Native American populations from the Reich et al. 2012 Nature study52 by matching on the chromosome, position, reference, and alternate alleles. After merging the datasets, variants with an overall MAF<1% were excluded. We used GCTA53 (version 1.26.0) to perform PCA. We used PLINK (version 1.90b3w)51 for LD pruning, merging, and quality control. The merged dataset included 34,936 variants.
To ensure adequate control for population structure and differences in ancestry that might exist within the different geographical regions of Peru, we also calculated PCs of the LIMAA cohort (N=3,134) projected into the PC space of PGP cohort3 (N=150). To do this we selected 247,940 common (MAF≥5%) variants that were shared between the PGP and LIMAA cohorts. We then calculated PCs in the PGP cohort using the EIGENSOFT (version 6.1.4)54 smartpca function. Finally, we used the SNP loadings from the smaptpca analysis to project the individuals from the LIMAA cohort to the PC space of PGP cohort using the SNPWEIGHTS (version 2.1) software55. We used ANOVA (R version 3.4) to test the association of the first ten PCs of PGP cohort with coast-non-coast status. We tested the association between PCs of LIMAA cohort with Native American ancestry proportion (NAT), height, or rs200342067 minor allele count using lme4qtl56 (R version 3.4), a linear mixed model framework, with age, and sex, and a genetic relatedness matrix to account for genetic relatedness (calculated using GEMMA46, version 0.96) as covariates.
Global ancestry inference
We used ADMIXTURE57 (version 1.3) at K=4 clusters, for global ancestry inference. The choice of four ancestral populations for ADMIXTURE analysis was based on Peru’s demographic history and previous studies of Peruvian population structure2–4. We used the merged dataset described above as input for the ADMIXTURE analysis. We used PLINK (version 1.90b3w)51 to exclude variants with genotyping missingness rate>5% and to perform LD pruning by removing the markers with r2>0.1 with any other marker within a sliding window of 50 markers per window and an offset of 10 markers.
Correlation between global ancestry proportions and height
We used the R package lme4qtl56, a linear mixed model framework, to measure the correlation between global ancestry proportions and height. We included the following covariates in the base model: age, sex, African and Asian ancestry proportions, as well as a GRM to account for population structure and genetic relatedness generated using PC-Relate49 which is implemented in the GENESIS R package (version 2.6.1). We repeated this analysis after adding a random effect to account for the individual’s household as a proxy for unmeasured environmental factors. Finally, to ensure adequate control for environmental factors, we randomly assigned height to individuals within each household 10,000 times and recalculated the Native American ancestry effect size using the base model to generate an empirical null distribution. We compared the null distribution with the observed Native American ancestry effect size from the original data to generate an empirical permutation p-value.
Common variant association analysis
In the discovery cohort, Imputed SNPs with an imputation quality score r2<0.4, HWE P-value<10−5, or a missing rate per SNP>5%. After filtering, 7,756,401 SNPs were left for further association analyses. We used GEMMA46 (version 0.96) to perform the single variant genome-wide association analysis, with age, sex, and a GRM generated using GEMMA46 (version 0.96) as covariates. We repeated the association for chromosome 15 by adding one or more of the following covariates: 10 PCs, 20 PCs, socioeconomic status, African global ancestry proportion, Asian global ancestry proportion, and European global ancestry proportion. To ensure adequate control for population structure, we also repeated the association test between height (cm) and rs200342067 with age, sex, 10PCs derived from projecting the LIMAA cohort into the PC space of PGP cohort3 (see PCA section above for details), and a GRM generated using GEMMA46 (version 0.96). To ensure that our choice of GRM does not affect the association between rs200342067 and height, we repeated the association analysis using two new GRMs. First, a GRM calculated using PC-Relate49, with age, sex, and 10 principal components as fixed covariates. Second, a GRM calculated using Refined IBD5 with age, sex, and 10 principal components as fixed covariates. All association p-values are reported as two sided Wald test p-values.
To ensure that local (e.g per chromosome) relatedness patterns such as autozygosity segments do not bias the relatedness, we generated 23 GRMs, leaving one chromosome out in each GRM using PC-Relate49 and repeated the association for all imputed variants on each chromosome using a GRM generated without that chromosome. Age, sex, and 10 PCs were included as additional covariates in this analysis. For the replication analysis in the Peruvian population, we used the minor allele count information of rs200342067, directly genotyped on the Illumina MEGA array, from 598 Peruvian individuals (see above for details about the replication cohort). Similar to the discovery cohort, we tested the association of rs200342067 with height (cm) using a linear mixed model framework implemented in GEMMA46 (version 0.96) with age, sex, and a GRM (calculated using GEMMA) as covariates.
Additional replication cohorts
PAGE:
The PAGE study is a meta-analysis of multiple existing major population-based cohorts7. The cohorts included in PAGE height study include the BioMe biobank (BioMe), the Hispanic Community Health Study / Study of Latinos (HCHS/SOL), The Multiethnic Cohort (MEC), and the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI)7. Height in centimeters was measured by trained clinic staff in the SOL and WHI studies at the time of enrollment. In MEC and BioMe height was self-reported by questionnaire. Individuals with height measurements ±6 standard deviations (SD)) from the mean (based on sex and race), individuals<18 years of age and women who were pregnant were excluded from the height GWAS analysis in PAGE. To get comparable phenotypes between different cohorts, PAGE uses inverse normal transformation of sex-specific height residuals adjusted for age as dependent variable in a linear mixed model that includes self-identified ancestry, study, study center, and 10 principal components (measured from unrelated individuals) as fixed and a genetic relatedness matrix (using GENESIS58) as random effect7. See7 for detailed information about the phenotype and statistical analysis of the PAGE cohort. We used the summary statistics from 31,214 Hispanic and Latino individuals from the PAGE study in our replication analysis.
GIANT:
The Genetic Investigation of ANthropometric Traits (GIANT) consortium exome array study is a meta-analysis of 147 studies comprising 458,927 adult individuals6. Height in centimeters was corrected for age and the genomic principal components, as well as any additional study-specific covariates (e.g. recruiting center), in a linear regression separately by sex. For family-based studies, sex was included as a covariate in the model. Additionally, residuals for case/control studies were calculated separately. Similar to the PAGE cohort, GIANT uses the inverse normal transformation of calculated residuals as the dependent variable in an ancestry-specific linear mixed model that corrects for cryptic relatedness using a kinship matrix in each cohort separately followed by a meta-analysis of the results. See6 for detailed information about the phenotype and statistical analysis of the GIANT cohort. We used the summary statistics from 10,776 Hispanic individuals from the GIANT study in our replication analysis.
Meta-analysis
We used the meta R package59 (version 4.9–3) to perform inverse variance-based meta-analysis using summary statistics from the height GWAS in LIMAA discovery cohort and the Peruvian replication cohort in which the measured phenotype was the height in cm. To perform meta-analysis using the GIANT6 and PAGE7 cohorts we repeated our association analysis in both the discovery and the replication cohorts as described above with age, sex, and a GRM generated using GEMMA46 (version 0.96) as covariates and inverse normally transformed height as the dependent variable. We used summary statistics from these analyses as well as summary statistics form the GIANT6 and PAGE7 cohorts to perform Inverse variance-based meta-analysis using the meta R package59.
Heritability analysis
We used GREML analysis in GCTA60 (version 1.26.0) to calculate the amount of variance in height explained by all common variants (MAF>1%). We included 423,108 variants from 2,667 unrelated individuals in this analysis with age, sex, and the first 10 PCs as covariates in the analysis. To calculate height heritability in each sex, we repeated the heritability analysis in men and women separately.
Polygenic risk score (PRS) analysis
Out of 3,290 independent genome-wide significant variants reported by Yengo et al8, 2,993 were present in our cohort. We constructed polygenic risk scores (PRSs) for each individual using height-increasing effect sizes of these 2,993 previously published height-associated variants8 as follows:
Where βi is the reported conditional effect size for variant i in the European population, nij is the allele count of variant i in individual j in our Peruvian cohort, and m is the total number of variants used in the construction of the PRS. We calculated the amount of variance explained (r2) using lm function in R (version 3.4) with height residuals adjusted for age, sex, and a GRM generated using GEMMA46 (version 0.96) to account for relatedness and cryptic population structure as the dependent variable and PRS as the explanatory variable. Out of 3,290 independent genome-wide significant variants reported by Yengo et al8, 2,388 reached genome-wide significance in unconditional analysis. We repeated the PRS calculation using the unconditional effect sizes of 2, 195 of these variants that were also present in our cohort. We used the cocor package in R (version 1.1–3) to test the significance of the difference between the amount of variance explained using different PRS.
For the sex-specific analysis, we first calculated height residuals in each sex separately after adjustment for age and a GRM generated using GEMMA46. We then calculated the r2 using lm(), with height residuals as the dependent variable and PRS as the explanatory variable for each sex separately. For the analysis in individuals with high or low European ancestry proportions, we separated the cohort to individuals with high European ancestry proportions (top quartile) and low European ancestry proportions (1st, 2nd, and 3rd quartile) and calculated height residuals after adjustment for age, sex, and a GRM generated using PC-Relate49 to account for relatedness but not population structure. We then calculated the r2 using lm function, with height residuals as the dependent variable and PRS as the explanatory variable in each group separately.
Gene-based association analysis
We used SKAT61 (version 1.3.2.1) for gene-based association testing of rare (MAF<1%) variants. Null distributions were generated using SKAT_NULL_emmaX, which incorporates kinship structure in the calculation of SKAT parameters and residuals. Age and sex were included as covariates. The statistical significance threshold was set at p-value<2.5×10−6 which is the Bonferroni correction threshold for 20,000 protein-coding genes. For common variants (MAF≥1%) we used fastBAT analysis in GCTA62 to perform gene-based association testing using GWAS summary statistics.
Positive selection analyses
Integrated Selection of Allele Favored by Evolution (iSAFE)20:
We used SHAPEIT2 (version v2.r837) to phase the imputed genotypes for chromosome 15 for all the individuals in our cohort (N=3,134). We then used iSAFE (version v1.0.4) software, available at https://github.com/alek0991/iSAFE with the following options MaxRank=300, MaxFreq=0.85, and enabling IgnoreGaps flag to detect variants under positive selection in a 1.2Mb window around rs200342067.
Extended haplotype homozygosity (EHH)21:
We used selscan63 (version 1.2.0a) to calculate EHH in our cohort (N=3,134) or in the simulated data. The analysis was restricted to variants with MAF>1%. For all variants, including rs200342067, we calculate EHH in a 2Mb window around the variant. For EHH, we interpolated the genetic position based on the average recombination rate of the chromosome to get a comparable measure of haplotype length between positively selected regions, regions under neutral selection, and simulated data. To ensure that the EHH calculation at rs200342067*C is not biased due to selection at the nearby selected locus rs12441775*G, we repeated the EHH calculation for at rs200342067*C after removing the nine haplotypes that harbored both rs200342067*C and rs12441775*G (update MAF for rs200342067*C=4.6%). For integrated EHH values we calculated the area under the EHH curve. The global map of rs12441775*G was generated using the Geography of Genetic Variants (GGV) browser64 at: http://www.popgen.uchicago.edu/ggv
Comparing EHH of rs200342067 with similar variants under neutral selection:
We selected 2,380 variants that were overlapping the previously published putative neutral regions of the genome23 and had similar DAF to rs2003420678*C allele in our cohort (4.7±1 %). We calculated EHH for these variants using selscan63 (version 1.2.0a) and compared the EHH decay plots as well as the integrated EHH values for rs2003420678*C and these variants. In a second step we removed the nine haplotypes carrying rs12441775*G from our cohort and repeated the EHH analysis using 2,309 variants that were overlapping the previously published putative neutral regions of the genome23 and had similar DAF to the updated frequency of rs2003420678*C allele (AF=4.6±1 %).
Selecting variants in the same derived allele frequency (DAF) and recombination bin as rs200342067:
We restricted the analysis to biallelic variants, the ancestral allele was assigned using the “Ancestral allele” information provided in the 1000 Genomes Project17. We calculated the derived allele frequency of each common variant (MAF>1%) in the Peruvians from the 1000 Genomes Project17 (N=85). We also interpolated the genetic position of each common variant (MAF>1%) using the 1000 Genomes Project17 phase 3 genetic maps. The recombination rate was calculated as follows: genetic position (cM) / physical position (Mb). Variants on each chromosome were divided into 100 DAF bins, and 20 recombination bins. The DAF for rs200342067 in the Peruvians from the 1000 Genomes Project17 is 4.1% (DAF bin 4) and its recombination rate is 1.4 (recombination bin 5). For comparison with rs200342067, we selected 2,062 variants that were in the same DAF and recombination bin as rs200342067 and that was at least 1Mb apart (e.g independent).
Integrated Haplotype Score (iHS)18:
iHS values for the Peruvians and other populations from the 1000 Genomes Project17 were obtained from a previously published study by Johnson and Voight, 201819. Full dataset available at: http://coruscant.itmat.upenn.edu/data/JohnsonEA_iHSscores.tar.gz.
Testing the extent of rs200342067 MAF difference between the coastal and non-coastal regions
Fisher’s Exact test:
We used minor allele counts for rs200342067 as well as 2,062 independent variants matched in DAF and local recombination rates to rs200342067 (see above) in populations from the coastal regions (N=46) or non-coastal regions (e.g Andes and Amazon, N=104) of the Peruvian Genome Project cohort3, to perform Fisher’s exact test in R (version 3.4).
XTX analysis:
We used Bayenv2.030 to calculate a covariance matrix between the coast and non-coast populations using 63,758 SNPs with MAF>10% in the PGP cohort 3. We then used Bayenv2.030 to calculate standardized allele frequencies and XTX statistics for rs200342067 as well as all the 2,062 SNPs randomly selected SNPs that were matched in DAF and local recombination rate to rs200342067.
Simulation of haplotypes under a neutral demographic model
We used msprime (version 0.7.3)65, a coalescent model with recombination, to simulate 2000 Peruvian individuals with the recombination map from HapMap Project66 1000 times. We adapted and constructed the population structures from out of Africa model proposed by Gravel et al67 with parameters previously inferred from 1000 Genomes Project17. To mirror the Peruvian migration history, we created a three-way admixture event around 500 years (25 generations) ago. We used the 1000 Genomes Project 17 phase 3 genetic maps for chromosome 15 to interpolated the recombination rate of in our simulation. We set the admixture to have 80% Native American, 16% European, and 4% African ancestry, inferred from the LIMMA cohort. We compared the integrated EHH values for 1000 simulated variants that had similar DAF to rs200342067 (DAF=4.7±1 %) and were overlapping the same region on the simulated chromosome (physical position 48773926±20kb) with the integrated EHH value of rs200342067 in our cohort (N=6,628 haplotypes). We repeated the analysis for two putative neutral regions on the chromosome 15 in the simulated data (N=2,000 haplotypes) and compared the integrated EHH values with the integrated EHH values for two variants, rs17580697 (DAF=4.6%) and rs305008 (DAF=4.6%), which are overlapping these neutral regions of chromosome 1523 in our cohort (N=6,628 haplotypes).
Mutation age
We used the pre-calculated mutation age estimates based on the 1000 Genomes Project populations17 from the human genome dating server (https://human.genome.dating/, accessed December 2019)25.
FBN1 cbEGF-domain 17, 3D structure
The 3D structure was obtained based on homology with fibrillin-1 cbEGF-domains 12 and 13, 1LMJ, previously published by Smallridge et al, J Biol Chem 200336 in the Protein Data Bank (PDB).
Clinical examination
Clinical examination was approved by the local Institutional Review Board (IRB). Individuals with T/T genotype (controls) were matched with cases (individuals with C/C and C/T genotypes) for sex, age±5 years, Native American ancestry proportion±0.05, and European ancestry proportion±0.05. A board-certified rheumatologist performed a musculoskeletal exam and history, including a detailed musculoskeletal history with review of systems, past medical history, medication history, social history, and family history; vital signs; range of motion on knees, wrists, elbows, index fingers, middle fingers, and hips; joint exam of hands for bony changes, synovitis or other abnormalities; joint exam of knees, feet, and spine for instability, bony changes, inflammation or other abnormalities. A board-certified dermatologist performed a standardized total body skin exam. This includes an examination of the skin of the face, eyelids, ears, scalp, neck, chest, axillae, abdomen, back, buttocks, genitalia, upper extremities, lower extremities, hands, feet, digits, nails, lips, mouth, mucosae, and lymph nodes. We also obtained skin biopsies for two individuals with C/C genotype and two age, sex, and ancestry matched individuals with T/T genotype patients at 5cm lateral to the umbilicus (in clinically normal skin) to assess histologic differences associated with genotype.
Histology
Following Harvard Medical School Institutional Review Board Approval, samples were obtained by skin punch biopsy performed as per routine by a Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) dermatologist and placed into specimen jars containing 10% neutral buffered formalin. The specimens were shipped via courier to MGH at ambient temperature, placed into tissue cassettes, processed routinely, and paraffin-embedded tissue blocks were prepared at the Histopathology Research Core of the Massachusetts General Hospital. One hematoxylin & eosin (H&E) stained glass slide was prepared for each block and additional unstained 5 micrometer thick sections cut from the tissue blocks were placed onto Fisher superfrost slides (protein-coated).
Immunohistochemical Analysis
Anti-fibrillin 1 antibody staining was performed using citrate buffer antigen retrieval technique. Appropriate negative control sections (primary antibody omitted to monitor for background staining) and positive control sections (human placental tissue known to express the antigen, as recommended by the manufacturer) were evaluated. Tissue sections were manually stained with rabbit polyclonal anti-fibrillin 1 antibody (FBN1, dilution 1:250, HPA021057, MilliporeSigma, St. Louis, MO) and counterstained with hematoxylin following deparaffinization of 5 micrometers cut sections. Antigen expression was assessed by a board-certified pathologist in dermal fibroblasts for each specimen in a blinded fashion.
Electron Microscopy on Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded Tissues
Areas of interest were identified on H&E stained slides and matched to the corresponding paraffin blocks. Under a dissecting microscope these areas were cut out using a sharp razor blade and placed into glass vials containing 100% xylene. The vials were left overnight at room temperature and the xylene changed the following morning. The vials were then left gently rotating for an additional three hours before rehydrating for one hour each in a series of ethanol (100%, 95%, 70%, 50%, and 25%) solutions. Tissues were then rinsed in sodium cacodylate buffer and fixed for 1.5 hours with our routine glutaraldehyde fixative (2.5% GTA, 2.0% PFA, 0.025% calcium chloride, in a 0.1M sodium Cacodylate buffer pH 7.4). Tissues were further processed in a Leica Lynx automatic tissue processor. Briefly, tissues were post fixed with osmium tetroxide, dehydrated in a series of ethanol solutions, en bloc stained during the 70% ethanol dehydration step for one hour, infiltrated with propylene oxide epoxy mixtures, embedded in pure epoxy, and polymerized overnight at 60°C. Thick sections were cut and stained with toluidine blue and examined with a light microscope. Thin sections were cut from representative areas, stained with lead citrate and examined with an FEI Morgagni transmission electron microscope. Images were captured with an AMT (Advanced Microscopy Techniques) 2K digital CCD camera.
FBN1 and SLC24A5 Hi-C data
To investigate whether rs200342067 or the other four variants in linkage with it our cohort can act as an enhancer for SLC24A5, we investigated ENCODE’s H3K27ac marks to search for active enhancer’s overlapping these variants (data accessed on 08.22.2019 from the ENCODE portal) as well as Hi-C data in published cell types68–70 for evidence of physical interaction between these variants and SLC24A5 (3D Genome Browser data accessed on 08.22.2019 from http://promoter.bx.psu.edu/hi-c/view.php).
Extended Data
Extended Data Figure 1:
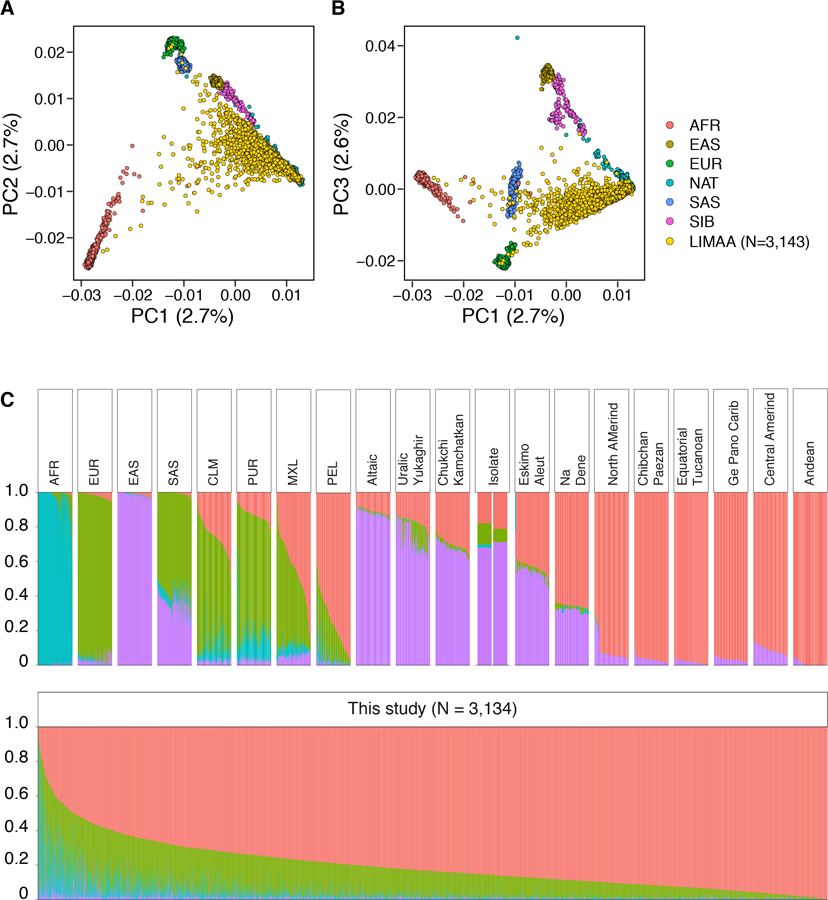
A and B) PCA analysis of genotyping data from Peruvians included in this study (N=3,134 individuals) merged with the data from continental populations from the 1000 Genomes Project phase 3 (N=3469 individuals) as well as the data from Siberian and Native American populations from Reich et al. 2012 Nature study (N=738 individuals) as reference panel (number of variants=34,936). Dots: individuals, color: populations (AFR: Africa, AMR: South America, EAS: East Asia, SAS: South Asia, EUR: Europe, SIB: Siberian, NAT: Native American). C) Global ancestry analysis using ADMIXTURE (K=4). We observed varying levels of European, African, and Asian admixture in our cohort (N=3,134 individuals) with a median proportion of Native American, European, African, and Asian ancestry per individual of 0.83 (Interquartile range (IQR)=0.72–.91), 0.14 (0.08–0.21), 0.01 (0.003–0.03), and 0.003 (10−5–0.01) respectively. Vertical lines: individuals, colors: genomic proportion of a given ancestry in an individual’s genome. ADMIXTURE analysis (K=4) is done using all populations in 1000 Genomes Project phase 3 as well as Siberian and Native American populations from the Reich et al. 2012 Nature study as reference. AFR: African ancestry includes: Yoruba in Ibadan, Nigeria, Luhya in Webuye, Kenya, Gambian in Western Divisions in the Gambia, Mende in Sierra Leone, Esan in Nigeria, Americans of African Ancestry in SW USA; EUR: European ancestry, includes: Central European, Utah Residents (CEPH) with Northern and Western European Ancestry, Toscani in Italy, Finnish in Finland, British in England and Scotland, Iberian Population in Spain; EAS: East Asian, includes: Han Chinese in Beijing, China, Japanese in Tokyo, Japan, Southern Han Chinese, Chinese Dai in Xishuangbanna, China, Kinh in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam; SAS: South Asian, includes: Gujarati Indian from Houston, Texas, Punjabi from Lahore, Pakistan, Bengali from Bangladesh, Sri Lankan Tamil from the UK, Indian Telugu from the UK; PUR: Puerto Ricans from Puerto Rico; CLM: Colombian from Medellin, Colombia; MXL: Mexicans from Los Angeles, California; PEL: Peruvians from Lima, Peru. Altic: Altaic language family, includes: Yakut, Buryat, Evenki, Tuvinians, Altaian, Mongolian, Dolgan. North Amerind: Northern Amerindian language family, includes: Maya, Mixe, Kaqchikel, Algonquin, Ojibwa, and Cree. Central Amerind: Central Amerindian language family, includes Pima, Chorotega, Tepehuano, Zapotec, Mixtec, and Yaqui. Andean: Andean language family, includes: Quechua, Aymara, Inga, Chilote, Diaguita, Chono, Hulliche, and Yaghan. For a full list of all populations in all language groups see the Reich et al. 2012 Nature study.
Extended Data Figure 2: Association of rs200342067 and height.
A) Single variant association analysis (N=3,134 individuals and 7,756,401 variants), dotted red line: genome-wide significance threshold of 5×10−8. Five SNPs overlapping the coding sequence of FBN1, passed the genome-wide significance threshold. We did not observe any inflation in test statistics (λ=1.02). Association p-values are two-sided Wald test p-values. B) rs200342067 in heterozygous individuals reduces height by 2.2 cm (4.4 cm in homozygous individuals, including 11 individuals with C/C genotype, 275 C/T genotype, and 2,848 T/T genotype) and could explain 0.9% of height phenotypic variance in our cohort (N=3,143 individuals). x-axis: rs200342067 genotype, y-axis: height residuals after adjustments for age, sex, and a GRM as random effect.
Extended Data Figure 3: rs12441775 derived allele frequency (DAF, rs12441775*G) and extended haplotype structure in the 1000 Genomes Project.
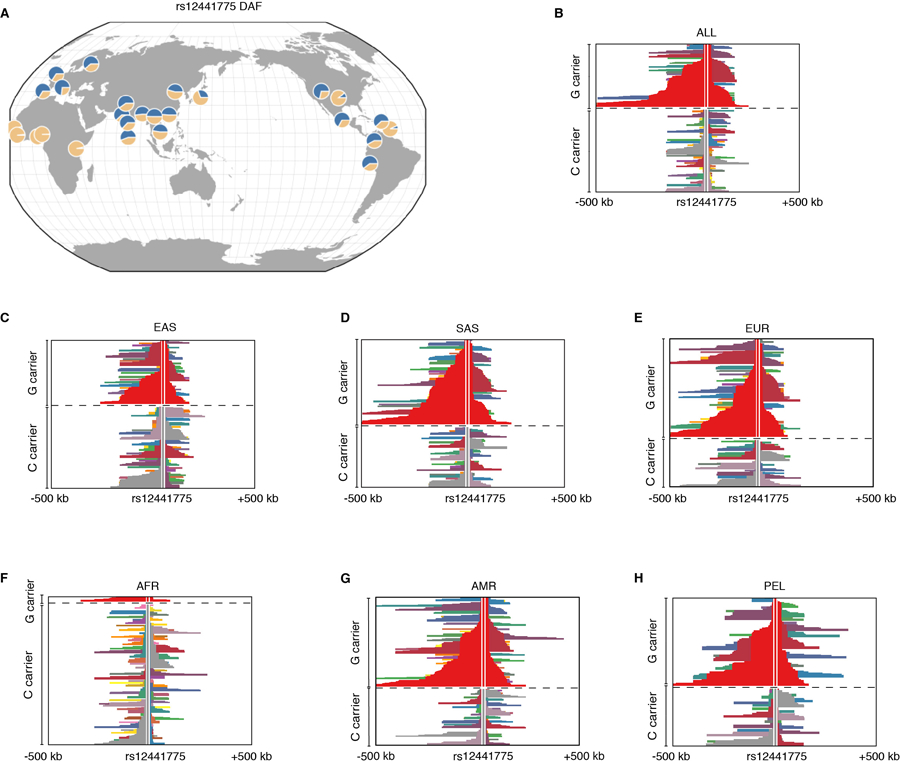
A) The derived allele, rs12441775*G, have a high frequency in all non-African populations in the 1000 Genomes Project (average DAF in non-Africans=58% IQR=51–64 and in Africans=4% (1–5)). The Map is generated using the Geography of Genetic Variants (GGV) browser, see Marcus and November, 2016, Bioinformatics study and http://www.popgen.uchicago.edu/ggv. B–H) Haplotypes carrying rs12441775*G (major/derived) are longer than haplotypes carrying rs12441775*C (minor/ancestral) in the non-African population. Horizontal lines: haplotypes, rs12441775’s position is marked above the haplotype. At any given position, adjacent haplotypes with the same color carry identical genotypes between the core SNP (rs12441775) and the that site, dashed line separates the haplotypes carrying the derived (above the line) and ancestral (below the line). SAS: South Asian, EUR: European, EAS: East Asian, AFR: African, AMR: American, PEL: Peruvians from Lima, Peru.
Extended Data Figure 4: Haplotypes carrying rs200342067 are longer than what is expected under neutral selection.
A) Haplotype decay around rs200342067 in our cohort (N=6,268 haplotypes). The rs200342067’s position is marked above the haplotype, haplotypes above the dashed line are the haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C (derived/minor, N=297 haplotypes) and haplotypes under the dashed line are the haplotypes carrying rs200342067*T (ancestral/major, N=5,971 haplotypes). B) Integrated Extended Haplotype Homozygosity (integrated EHH) for haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C (N=297 haplotypes) compared to integrated EHH for haplotypes carrying 2,380 variants with similar DAF (4.7±1%) that are overlapping the neutral regions of the genome in our cohort (N=3,134 individuals). Haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C are longer than 99.2% of the haplotypes in neutral regions of the genome. Vertical red line: integrated EHH for haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C (integrated EHH=0.115). C) The same as A excluding the nine haplotypes that carry both rs200342067*C and rs12441775*G alleles. D) EHH decay curves for haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C excluding the nine haplotypes that carry both rs200342067*C and rs12441775*G (N=288 haplotypes) compared to haplotypes carrying 2,309 variants that have similar DAF to the updated frequency of rs200342067*C (4.6±1%) and are overlapping the neutral regions of the genome in our cohort (N=3,134 individuals). Haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C are longer than 99.7% of the haplotypes in the neutral genomic regions. E) Integrated EHH for haplotypes shown in D. Vertical red line: integrated EHH for haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C but not rs12441775*G (integrated EHH=0.124).
Extended Data Figure 5: Simulation of haplotypes under neutral demographic model.
A) PCA plot of simulated individuals (N=1000 simulated individuals and 2000 simulated haplotypes). Individuals were simulated using a demographic model matching Peru’s population history and under neutral selection. red dots: simulated individuals, other dots: reference populations from the 1000 Genomes project. B) We compared rs200342067*C’s integrated EHH with integrated EHH of 1000 variants that had similar DAF to rs200342067 (DAF=4.7±1%) and were overlapping the same genomic region as rs200342067 on simulated chromosome 15 (physical position 48773926±20kb). rs200342067’s integrated EHH is more extreme than integrated EHH observed for any of the variants in the simulated data. x-axis: integrated EHH, distribution: integrated EHH of variants in simulated haplotypes (N=2000 haplotypes), vertical red line: integrated EHH value of rs200342067 in our cohort (N=6,628 haplotypes, integrated EHH=0.115). C and D) Similar to A for two different neutral regions on chromosome 15. vertical red lines: integrated EHH of rs17580697 (C, integrated EHH=0.012, 76th percentile) and rs305008 (D, integrated EHH=0.010, 74th percentile) in our cohort (N=6,628 haplotypes).
Extended Data Figure 6: Comparison of different selection statistics for rs200342067 and other variants with similar DAF and recombination rate.
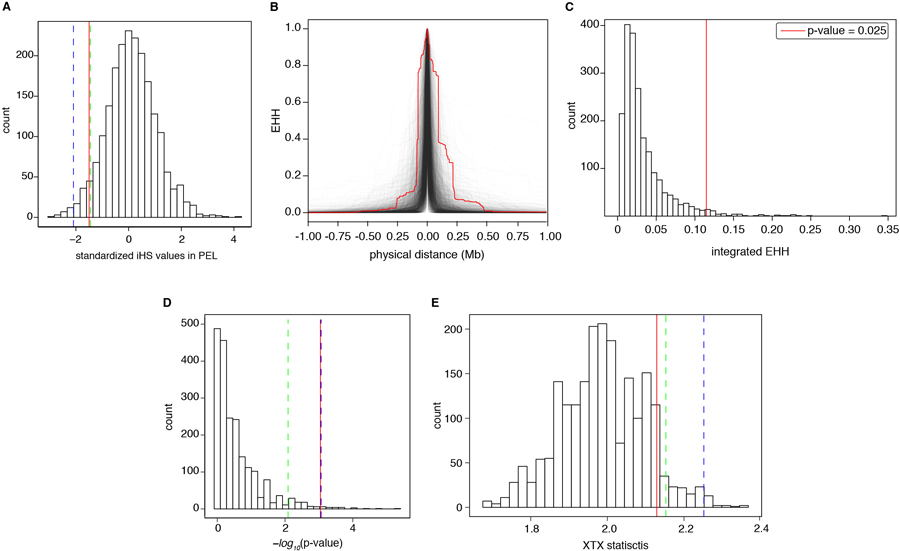
A) Distribution of iHS for 2,062 independent (at least 1Mb apart) variants matched in DAF and local recombination rate to rs200342067. iHS values are calculated for Peruvian individuals in the 1000 Genomes Project (N=85 individuals) and were obtained from Johnson and Voight, 2018, Nature Evolution and Ecology, study. red line: rs200342067’s iHS (iHS=−1.5, 4.7th percentile), green and blue lines: 5th and first percentile of iHS distribution. B) EHH decay curves for rs200342067 (red line) as well as haplotypes carrying 2,062 independent variants (at least 1Mb apart) matched in DAF and local recombination rate to rs200342067 in our cohort (N=6,268 haplotypes (gray lines). C) Distribution of integrated EHH for haplotypes shown in B, haplotypes carrying rs200342067*C are longer than 97.5% of haplotypes carrying similar variants. x-axis: integrated EHH, red line: integrated EHH for rs200342067*C allele (integrated EHH=0.115). D) Histogram of Fisher’s exact test results comparing the extent of allele frequency differences between coastal (N=46 individuals) and non-coastal (N=104 individuals) regions in Peru for 2,062 independent variants that were matched in DAF and local recombination rate to rs200342067. x-axis: -log10 of two-sided Fisher’s exact test p-value, dashed blue and green vertical lines: 99th and 95th percentiles respectively, solid red line: -log10 of two-sided Fisher’s exact test p-value for rs200342067 (1.1% percentile, two-sided Fisher’s exact test p-value=0.0005). E) Bayenv2.0 XTX statistics, a measure of deviation from neutral patterns of population structure, for 2,062 independent variants that were matched in DAF and local recombination rate to rs200342067. x-axis: XTX statistics, red line: XTX value for rs200342067 (XTX= 2.13, 8.3th percentile), green and blue lines: 5th and first percentile of XTX distribution respectively.
Extended Data Figure 7: Genomic context of rs200342067 (E1297G).
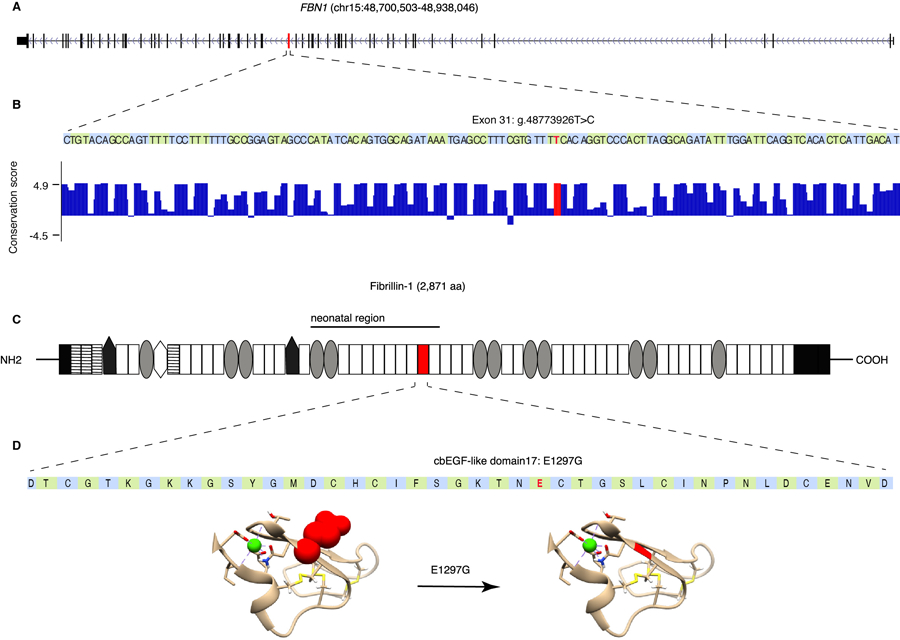
A) Schematic representation of FBN1, exons are shown as black bars. Exon 31 (ENSE00001753582) is shown in red. B) FBN1 exon 31 sequence and PhyloP per-nucleotide conservation score based on multiple sequence alignment of 100 vertebrate species (obtained from UCSC genome browser GRCh37 assembly conservation track). The T>C change due to rs200342067 occurs in a conserved nucleotide. C) Schematic representation of Fibrillin-1 (ENST00000316623.5). Fibrillin-1 consists of the following domains: N and C terminal (black rectangles), EGF-like domains (stripped rectangles), hybrid domains (black pentagons), TGFβ-binding domains (gray ovals), a proline-rich domain (white hexagon), and 43 calcium binding cbEGF-like domains (white rectangles). cbEGF-domain 17, the domain affected by rs200342067 (E1297G), is shown in red, E1297G is located between a conserved cysteine (p.Cys1296) involved in forming a disulfide bond with p.Cys1284 and a conserved asparagine (p.Asp1298) involved in calcium binding. D) Fibrillin-1 cbEGF-domain 17 sequence and 3D structure of cbEGF-domains 17 and 18 (the 3D structure was obtained based homology with fibrillin-1 cbEGF-domains 12 and 13 previously published by Smallridge et al, J Biol Chem 2003 (1LMJ in the Protein Data Bank). rs200342067 changes glutamic acid, a large amino acid with a negatively charged side chain, to glycine, the smallest amino acid with no side chain (shown in red). The side chains are shown for rs200342067 (red spheres), the calcium-interacting residues (beige sticks), and the cysteine residues involved in disulfide bonds (yellow sticks). Calcium ion is shown in green.
Extended Data Figure 8: Immunohistochemical staining of fibrillin-1.
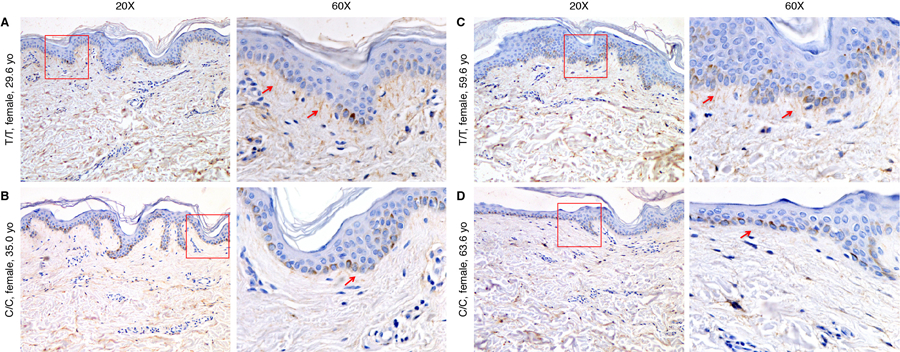
A–B) Fibrillin-1 staining in skin biopsies in two individuals with rs200342067 C/C genotype and C–D) two individuals with T/T genotype matched for age, sex, and ancestry proportions. Individuals with C/C genotype have less fibrillin-1 deposition in the dermal extracellular matrix (ECM) and shorter microfibrillar projections from the dermal-epidermal junction into the superficial (papillary) dermis (red arrows, 20x) as well as less fibrillin-1 deposition in the deeper dermis. Two magnification have been shown, the red rectangles in the first column (20x magnification) are magnified in the second column (60x).
Extended Data Figure 9: Electron microscopy (EM) of fibrillin-1 in skin.
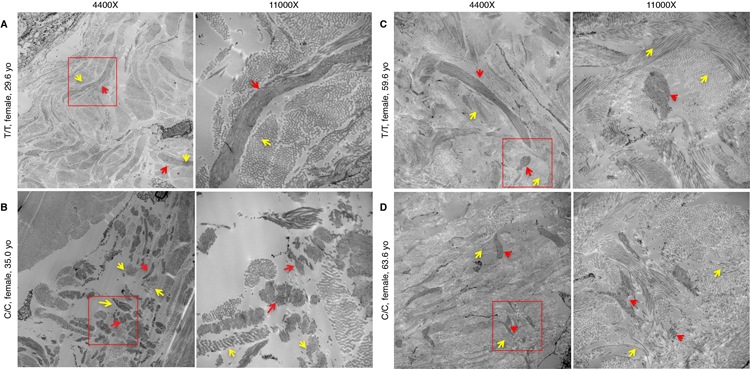
A–C) EM of the dermal-epidermal junction in two individuals with rs200342067 T/T genotype B–D) and two individuals with rs200342067 C/C genotype which are matched for age, sex, and ancestry proportions. Individuals with C/C genotype have short, fragmented, and less densely packed microfibrils with irregular edges (red arrows) and their microfibrils are embedded in less dense collagen bundles (yellow arrows) compared to the individuals with T/T genotype. Two magnification have been shown, the white rectangles in the first column (4400x magnification) are magnified in the second column (11000x).
Extended Data Table 1: SNPs overlapping 15q15–21.1 locus.
In our height GWAS (N=3,134 individuals) one locus reached the genome-wide significance threshold (p-value<5×10−8). This locus overlaps FBN1 on chromosome 15 and includes five tightly linked SNPs. One SNP, rs200342067, is a missense variant and the other four are intronic variants. Association p-values are two-sided Wald test p-values. Numbers are rounded to two decimal places. se: standard error.
| rs | position | allele1 | allele2 | MAF (%) | effect size (cm) | se | z-score | Wald p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs193211234 | 48752674 | A | T | 4.66 | −2.37 | 0.38 | −6.24 | 4.4×10−10 |
| rs200342067 | 48773926 | C | T | 4.72 | −2.22 | 0.36 | −6.17 | 6.8×10−10 |
| rs544786245 | 48822780 | T | G | 4.46 | −2.32 | 0.38 | −6.11 | 1 ×10−9 |
| rs143730951 | 48858921 | T | C | 4.72 | −2.27 | 0.37 | −6.14 | 8.2×10−10 |
| rs180913076 | 48928052 | C | A | 4.56 | −2.22 | 0.38 | −5.84 | 5.2×10−9 |
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments:
We thank David Branch Moody for helpful discussions, Thomas Horn for his feedback on optimizing skin immunohistochemistry, and Jeffrey Neil Katz for advising us on a structured clinical assessment of the musculoskeletal system. The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) TB Research Unit Network, Grants U19-AI111224–01, and U01-HG009088. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH. S. A. was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) postdoc mobility fellowships P2ELP3_172101 and P400PB_183823.
Footnotes
Competing interests: Authors declare no competing interests.
Data and materials availability: Genotyping data will be made available through dbGAP.
Code availability: No costume code was used to draw the central conclusions of this work. All the softwares and packages used in this work are presented in the Methods section of the manuscript.
References:
- 1.NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). A century of trends in adult human height. Elife 5, (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Homburger JR et al. Genomic Insights into the Ancestry and Demographic History of South America. PLoS Genet. 11, e1005602 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Harris DN et al. Evolutionary genomic dynamics of Peruvians before, during, and after the Inca Empire. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 115, E6526–E6535 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ruiz-Linares A et al. Admixture in Latin America: geographic structure, phenotypic diversity and self-perception of ancestry based on 7,342 individuals. PLoS Genet. 10, e1004572 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Browning BL & Browning SR Improving the accuracy and efficiency of identity-by-descent detection in population data. Genetics 194, 459–471 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Marouli E et al. Rare and low-frequency coding variants alter human adult height. Nature 542, 186–190 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wojcik GL et al. Genetic analyses of diverse populations improves discovery for complex traits. Nature 570, 514–518 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yengo L et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for height and body mass index in ∼700000 individuals of European ancestry. Hum. Mol. Genet (2018) 10.1093/hmg/ddy271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 9.Wood AR et al. Defining the role of common variation in the genomic and biological architecture of adult human height. Nat. Genet 46, 1173–1186 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Vilhjálmsson BJ et al. Modeling Linkage Disequilibrium Increases Accuracy of Polygenic Risk Scores. Am. J. Hum. Genet 97, 576–592 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Martin AR et al. Human Demographic History Impacts Genetic Risk Prediction across Diverse Populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet 100, 635–649 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Martin AR et al. Clinical use of current polygenic risk scores may exacerbate health disparities. Nat. Genet 51, 584–591 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kong A et al. The nature of nurture: Effects of parental genotypes. Science 359, 424–428 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Domingue BW et al. The social genome of friends and schoolmates in the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 115, 702–707 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rask-Andersen M, Karlsson T, Ek WE & Johansson Å Gene-environment interaction study for BMI reveals interactions between genetic factors and physical activity, alcohol consumption and socioeconomic status. PLoS Genet. 13, e1006977 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pelova N Considerations on the so-called myelolipoma of the adrenals. Nauchni Tr. Vissh. Med. Inst. Sofiia 48, 31–35 (1969). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Consortium, 1000 et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 526, 68–74 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Voight BF, Kudaravalli S, Wen X & Pritchard JK A map of recent positive selection in the human genome. PLoS Biol. 4, e72 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Johnson KE & Voight BF Patterns of shared signatures of recent positive selection across human populations. Nat Ecol Evol 2, 713–720 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Akbari A et al. Identifying the favored mutation in a positive selective sweep. (2018) 10.1038/nmeth.4606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 21.Sabeti PC et al. Detecting recent positive selection in the human genome from haplotype structure. Nature 419, 832–837 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nei M & Li WH Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 76, 5269–5273 (1979). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Arbiza L, Zhong E & Keinan A NRE: a tool for exploring neutral loci in the human genome. BMC Bioinformatics 13, 301 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lek M et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 536, 285–291 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Albers PK & McVean G Dating genomic variants and shared ancestry in population-scale sequencing data. PLoS Biol. 18, e3000586 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lamason RL et al. SLC24A5, a putative cation exchanger, affects pigmentation in zebrafish and humans. Science 310, 1782–1786 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fan S, Hansen MEB, Lo Y & Tishkoff SA Going global by adapting local: A review of recent human adaptation. Science 354, 54–59 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Adhikari K et al. A GWAS in Latin Americans highlights the convergent evolution of lighter skin pigmentation in Eurasia. Nat. Commun 10, 358 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sturm RA & Duffy DL Human pigmentation genes under environmental selection. Genome Biol. 13, 248 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Günther T & Coop G Robust identification of local adaptation from allele frequencies. Genetics 195, 205–220 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lasker GW Differences in anthropometric measurements within and between three communities in Peru. Hum. Biol 34, 63–70 (1962). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sengle G & Sakai LY The fibrillin microfibril scaffold: A niche for growth factors and mechanosensation? Matrix Biol. 47, 3–12 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schrenk S, Cenzi C, Bertalot T, Conconi MT & Di Liddo R Structural and functional failure of fibrillin- 1 in human diseases (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med 41, 1213–1223 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Collod-Béroud G et al. Update of the UMD-FBN1 mutation database and creation of an FBN1 polymorphism database. Hum. Mutat 22, 199–208 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tiecke F et al. Classic, atypically severe and neonatal Marfan syndrome: twelve mutations and genotype–phenotype correlations in FBN1 exons 24–40. Eur. J. Hum. Genet 9, 13 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Smallridge RS et al. Solution structure and dynamics of a calcium binding epidermal growth factor-like domain pair from the neonatal region of human fibrillin-1. J. Biol. Chem 278, 12199–12206 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Booms P, Tiecke F, Rosenberg T, Hagemeier C & Robinson PN Differential effect of FBN1 mutations on in vitro proteolysis of recombinant fibrillin-1 fragments. Hum. Genet 107, 216–224 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Jensen SA, Robertson IB & Handford PA Dissecting the fibrillin microfibril: structural insights into organization and function. Structure 20, 215–225 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jensen SA, Corbett AR, Knott V, Redfield C & Handford PA Ca2+-dependent interface formation in fibrillin-1. J. Biol. Chem 280, 14076–14084 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.McGettrick AJ, Knott V, Willis A & Handford PA Molecular effects of calcium binding mutations in Marfan syndrome depend on domain context. Hum. Mol. Genet 9, 1987–1994 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zoledziewska M et al. Height-reducing variants and selection for short stature in Sardinia. Nat. Genet 47, 1352–1356 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fumagalli M et al. Greenlandic Inuit show genetic signatures of diet and climate adaptation. Science 349, 1343–1347 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Methods References:
- 43.Luo Y et al. Early progression to active tuberculosis is a highly heritable trait driven by 3q23 in Peruvians. Nat. Commun 10, 3765 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zelner JL et al. Identifying Hotspots of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis Transmission Using Spatial and Molecular Genetic Data. J. Infect. Dis 213, 287–294 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Odone A et al. Acquired and Transmitted Multidrug Resistant Tuberculosis: The Role of Social Determinants. PLoS One 11, e0146642 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zhou X & Stephens M Efficient multivariate linear mixed model algorithms for genome-wide association studies. Nat. Methods 11, 407–409 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Price AL et al. Long-range LD can confound genome scans in admixed populations. American journal of human genetics vol. 83 132–5; author reply 135–9 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Manichaikul A et al. Robust relationship inference in genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics 26, 2867–2873 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Conomos MP, Reiner AP, Weir BS & Thornton TA Model-free Estimation of Recent Genetic Relatedness. Am. J. Hum. Genet 98, 127–148 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gusev A et al. Whole population, genome-wide mapping of hidden relatedness. Genome Res 19, 318–326 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Chang CC et al. Second-generation PLINK: rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience 4, 7 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Reich D et al. Reconstructing Native American population history. Nature 488, 370–374 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Yang J, Lee SH, Goddard ME & Visscher PM GCTA: a tool for genome-wide complex trait analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet 88, 76–82 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Price AL et al. Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet 38, 904–909 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Chen C-Y et al. Improved ancestry inference using weights from external reference panels. Bioinformatics 29, 1399–1406 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ziyatdinov A et al. lme4qtl: linear mixed models with flexible covariance structure for genetic studies of related individuals. BMC Bioinformatics 19, 68 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Alexander D, Novembre J & Lange K Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Biotechfor 19, 1655–1664 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Schick UM et al. Genome-wide Association Study of Platelet Count Identifies Ancestry-Specific Loci in Hispanic/Latino Americans. Am. J. Hum. Genet 98, 229–242 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Balduzzi S, Rücker G & Schwarzer G How to perform a meta-analysis with R: a practical tutorial. Evid. Based. Ment. Health 22, 153–160 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Yang J et al. Common SNPs explain a large proportion of the heritability for human height. 42, 565–569 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Wu MC et al. Rare-Variant Association Testing for Sequencing Data with the Sequence Kernel Association Test. Am. J. Hum. Genet 89, 82–93 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bakshi A et al. Fast set-based association analysis using summary data from GWAS identifies novel gene loci for human complex traits. Sci. Rep 6, 32894 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Szpiech ZA & Hernandez RD selscan: an efficient multithreaded program to perform EHH-based scans for positive selection. Mol. Biol. Evol 31, 2824–2827 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Marcus JH & Novembre J Visualizing the geography of genetic variants. Bioinformatics 33, 594–595 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kelleher J, Etheridge AM & McVean G Efficient Coalescent Simulation and Genealogical Analysis for Large Sample Sizes. PLoS Comput. Biol 12, e1004842 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.International HapMap Consortium. The International HapMap Project. Nature 426, 789–796 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Gravel S et al. Demographic history and rare allele sharing among human populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 108, 11983–11988 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Rao SSP et al. A 3D map of the human genome at kilobase resolution reveals principles of chromatin looping. Cell 159, 1665–1680 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Lin D et al. Digestion-ligation-only Hi-C is an efficient and cost-effective method for chromosome conformation capture. Nat. Genet 50, 754–763 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Dixon JR et al. Chromatin architecture reorganization during stem cell differentiation. Nature 518, 331–336 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


