Abstract
Accumulating evidence shows that cellular and acellular components in tumor microenvironment (TME) can reprogram tumor initiation, growth, invasion, metastasis, and response to therapies. Cancer research and treatment have switched from a cancer-centric model to a TME-centric one, considering the increasing significance of TME in cancer biology. Nonetheless, the clinical efficacy of therapeutic strategies targeting TME, especially the specific cells or pathways of TME, remains unsatisfactory. Classifying the chemopathological characteristics of TME and crosstalk among one another can greatly benefit further studies exploring effective treating methods. Herein, we present an updated image of TME with emphasis on hypoxic niche, immune microenvironment, metabolism microenvironment, acidic niche, innervated niche, and mechanical microenvironment. We then summarize conventional drugs including aspirin, celecoxib, β-adrenergic antagonist, metformin, and statin in new antitumor application. These drugs are considered as viable candidates for combination therapy due to their antitumor activity and extensive use in clinical practice. We also provide our outlook on directions and potential applications of TME theory. This review depicts a comprehensive and vivid landscape of TME from biology to treatment.
Subject terms: Cancer microenvironment, Cancer microenvironment, Translational research
Persistent updating concept of TME
The concept of tumor microenvironment (TME) dates back to 1863 when Virchow proposed the relationship between inflammation and cancer and 1889 upon the emergence of Pagets’s theory of “seed and soil”1–3. In 2011, Hanahan and Weinberg enhanced their understanding of cancer on the basis of the great progress made over the past decade and expanded their proposed hallmarks of cancer from six to ten. They also recognized the emerging participation of TME in cancer development.4
Cancer is a complicated disease that metastasizes through vessels, lymph nodes, or transcoelomic seeding, is innervated by nerves, and involves the participation of the whole organism. Thus, a concern exists on whether TME is sufficiently comprehensive to reflect true situations and serve as an effective target for cancer treatment.5 Laplane et al.5,6 introduced a term called tumor organismal environment (TOE), representing microenvironments that are distant from the lesions of cancer but can affect its development. Considering the lack of consensus in defining TME combined with the fact that the tumor environment (TE) of different locations may differ greatly, they also divided TE into six layers, including tumor cell to tumor-cell environment (TCTCE), niche, confined TE, proximal TE, peripheral TE, and TOE.6
The conventional concept of TME excludes peripheral TE with distally located lymphatic tissues and TOE, which is even more distant and comprises microbiota or some exosomes. TME comprises nonmalignant cells, vessels, lymphoid organs or lymph nodes, nerves, intercellular components, and metabolites located at the center, margin, or within the vicinity of the tumor lesion (Fig. 1). Classical theory suggests that the oncogenic mutations of malignant cells cause the initiation of cancer. Subsequently, the surrounding non-transformed cells are recruited and adapted, accompanied by the release of diverse intercellular communicators, including cytokines, chemokines, and vesicles. The consequences are TME formation and close interaction with cancer cells.7 Some studies have shown that chronic inflammation or wound-healing process in abnormal microenvironment activates oncogenic signaling and promotes tumorigenesis.8–11
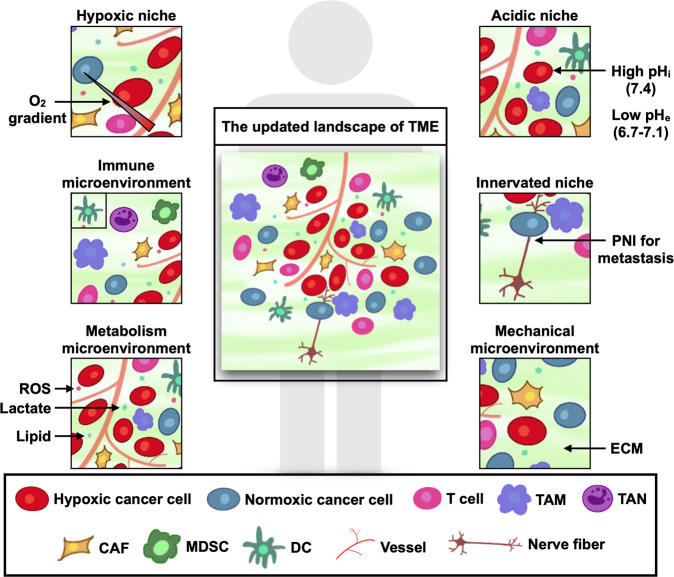
Fig. 1.
The updated landscape of tumor microenvironment (TME). TME comprises cancer cells, stromal cells, blood vessels, nerve fibers, extracellular matrix, and associated acellular components. TME is home for cancer cells and serves as a bridge connecting cancer with the whole organism. TME can be classified into six specialized microenvironments, namely, hypoxic niche, immune microenvironment, metabolism microenvironment, acidic niche, innervated niche, and mechanical microenvironment
TME is shaped and trained by cancer cells to assist the development of cancer hallmarks, respond to intrinsic or extrinsic stress, stimulation and treatment, and ultimately assist these cells’ survival and migration in an organism. Compared with a whole TME, a specialized microenvironment seems to be a better target for cancer treatment. Hypoxia and immunosuppression are two properties of cancer.4 Hypoxia was viewed as a hallmark of TME as early as 1955, whereas immune microenvironment was recognized in 1975 when tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) were identified.2 Hypoxic niche and immune microenvironment are regarded as two vital specialized microenvironments that can reprogram cancer biology in various aspects and serve as a potential target for cancer therapy, especially targeted therapy and immunotherapy.12–17 Many studies have confirmed that metabolism microenvironment,18–21 acidic niche,22–24 innervated niche in TME25–31 and mechanical niche32–37 remarkably affect cancer development. However, these specialized microenvironments are arranged in a crisscross pattern, suggesting the necessity to recognize the function of each microenvironment and the crosstalk among one another (Fig. 1). The latent capacity of combination therapy cannot be ignored as well.
Notably, TME is heterogeneous and can be considered as a double-edged sword.38–41 Specially, TME at an early stage tends to exert an antitumor effect.2,42 This review primarily focuses on how specialized TMEs assist the development of cancer hallmarks.
Hallmarks of TME
Hypoxic niche: a constant and heterogeneous TME
In 2019, Kaelin, Ratcliffe, and Semenza were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work in cellular sensation and adaptation to oxygen. In response to normoxia-hypoxia transition, cells rely largely on the elevation of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF) and HIF signaling to adapt to a low-oxygen condition.43,44 In cancer, intratumoral hypoxia is induced by the outgrowth of cancer cells and the unmatched angiogenesis and oxygen supply, accompanied by the altered metabolism level of cancer cells. Hypoxia is a common, constant, and complex condition for malignant and stromal cells. Intratumoral hypoxia is often correlated with poor prognosis and cancer progression.13 Hypoxia can exist in cancer cells and its microenvironment, subsequently reprogramming cancer biology in various aspects, including cancer progression, stemness, and dormancy, as well as redox adaptation, intercellular communication, and therapeutic resistance (reviewed by ref. 13). Hypoxia activates vascular endothelial cells, upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) transcription, and stimulates excessive angiogenesis, thereby affecting TME and therapeutic efficacy.45–47
Buffa et al.48 listed the 15 top-ranked hypoxia-associated genes, namely, VEGFA, SLC2A1, PGAM1, ENO1, LDHA, TP11, P4HA1, MRPS1, CDKN3, ADM, NDRG1, TUBB6, ALDOA, MIF, and ACOT7, which are collectively considered to be hypoxia signature (Buffa signature) to assess hypoxia status. Bhandari et al.49 studied 1188 cancers from 27 cancer types, including solid cancer and hematologic malignancies, to investigate hypoxia in cancer. They subjected 2658 cancers from 38 cancer types to whole-genome sequencing. The pan-cancer landscape reveals that hypoxia possesses intra- and inter-heterogeneity among different cancer types and different patients with the same type.49 For example, lung and cervical squamous cell carcinoma are regarded as the most hypoxic cancer types, whereas chronic lymphocytic leukemia and thyroid adenocarcinoma have the lowest hypoxia scores; biliary adenocarcinoma, lymphoid B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and lung adenocarcinoma indicate great variances within the same cancer types.49 These results are consistent with those observed from a study on about 10 000 cancer samples across 21 cancer types in The Cancer Genome Atlas.50 Both studies are based on 15 Buffa signatures instead of low-oxygen level as a direct indicator because it is not contained in the databases. Moreover, higher hypoxic signaling and hypoxia-associated genes tend to occur in tumors with higher diversity and are correlated with a poorer overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS).51 The intra- and inter-heterogeneity of hypoxic niche may explain the varied response to hypoxia-targeted therapy.
Hypoxic niche is also associated with increased mutational load of somatic variations and alterations of oncogenes and tumor suppressors, such as TP53, PTEN, and MYC.49,52
Immune microenvironment: distinct in healthy tissues, primary lesions, and metastases
Turning cold cancers into hot ones is the goal of cancer immunotherapy nowadays. The former refers to treatment-naive cancers involving the inhibition of cytotoxic T cells, whereas the latter requires the generation and activation of cancer-associated T cells.14,53,54 TME encompasses malignant cells and T cells, as well as B cells, natural killer (NK) cells, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), mast cells, granulocytes, dendritic cells (DCs), tumor-associated neutrophils, cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), adipocytes, vascular endothelial cells, and pericytes.7,55 The suppressive immune microenvironment helps cancer avoid immune destruction. The infiltration of immune cells in TME, located at the core or margin of cancer or the adjacent lymphoid organ or lymph nodes (also called tertiary lymphoid structures), is closely related to the prognosis in cancer7,55–61).
Cancer metastasis accounts for 90% cancer-related death for solid tumor.62 Undetectable micrometastases and unsatisfactory therapeutic responses are regarded as the two main problems causing high mortality through cancer metastasis. Pan et al.63 developed deep learning-enabled metastasis analysis in cleared tissue (DeepMACT) based on deep learning to detect micrometastatic foci and test the therapeutic targeting efficiency on mice with metastatic breast, lung, or pancreatic cancer. They demonstrated that antibody drugs are prone to be distributed to micrometastases within a close vicinity, suggesting probable participation of metastatic niche in determining targeting efficiency.63 TME plays a vital role in accomplishing metastatic cascade and is relatively distinct from normal tissues, primary tumors, and metastatic sites, especially when immune cells are involved.7,64–66 Malignant cells should escape immune surveillance, induce extracellular matrix (ECM) remolding, and achieve sufficient cell motility to migrate. CD4+CD25+ FOXP3+ regulatory T (Treg) cells, Ly6G+ neutrophils, MDSCs, and macrophages help build an immunosuppressive pre-metastatic niche, whereas TH1 CD4+ or CD8+ T cells, Ly6G- neutrophils, and NK cells have the opposite functions.67 NK cells are downregulated in primary lung adenocarcinomas and lung cancer metastases compared with those in normal lung tissues.68,69 Fischer et al.70 compared the molecular profile of 88 melanoma brain metastases (MBMs) and 42 matched extracranial metastases with RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) data. They found that compared with extracranial metastasis, MBMs have less diverse T cell repertoire, fewer monocytes and DCs, comparable PAX5+ B cells and NK cells, more neutrophils, and greater activation of nervous system pathways.70
Friebel et al.71 revealed the leukocyte landscape for brain tumors through high-dimensional single-cell profiling. TME is distinct between gliomas and brain metastases: glioma TME has predominant tissue residence and reactive microglia, whereas brain metastasis TME possesses tissue-invading leukocytes. These findings are consistent with those of Klemm et al. (2020) obtained through flow cytometry, RNA sequencing, protein arrays, culture assays, and spatial tissue characterization. We used single-cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) to analyze the immune landscape of brain metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma.72 Analysis indicates that TAMs in brain metastasis inhibit T cell activation and infiltration, high levels of immune-suppressive macrophages, a unique alternative M2 activation signature, and a lack of conventional T cell co-stimulatory factors.72 The disparity of immune microenvironments among primary lesions and metastasis foci has provided an explanation for treatment failure in advanced patients with metastasis, especially brain metastasis. Besides, clinical trials often exclude patients with brain metastasis (except some clinical trials focusing on brain metastasis), thereby hindering the exploration of effective therapies for patients with brain metastasis. Insights into distinct immune microenvironments partially compensate for the situation, but more related clinical trials are still required.
Metabolism microenvironment: focusing on lactate, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and lipid
Metabolic reprogramming (alteration in metabolism or nutrient supply) is one of the hallmarks of cancer. Cancer often shows increased metabolism of glucose, lipid, glutamine, and amino acids, lactate accumulation, and ROS addiction.73–76 Increased attention is being paid to the regulative effect of metabolism microenvironment on cancer cells. Organoid, Transwell, and tissue slice cultures have been applied to recapitulate cancer heterogeneity and metabolism.18
Lactate metabolism is involved in malignant and stromal cells
Normal cells tend to obtain energy through oxidative phosphorylation, and glycolysis is inhibited under normoxic condition. Cancer cells prefer enhanced glycolysis and elevated lactate metabolism even under normoxia, instead of oxidative phosphorylation.20 This phenomenon was first introduced by Warburg a century ago and named it the Warburg effect or aerobic glycolysis. Later on, Warburg stated that cancer cells prefer glycolysis over oxidative phosphorylation regardless of oxygen content.77 Since then, researchers have been interested in and focused on the following: (1) why cancer cells prefer aerobic glycolysis instead of oxidative phosphorylation, which can provide more energy; (2) how cancer cells utilize lactate metabolism; and (3) the potential ability of target lactate metabolism pathways to treat cancer. Although these issues remain unaddressed, we have achieved great progress over the past decades. Lactate is produced by malignant and immune cells in TME through the following: (1) conversion from glucose to pyruvate to lactate with the participation of lactate dehydrogenase; and (2) a series of processes starting from glutamine to glutamate to α-ketoglutarate, joining into the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and conversion of pyruvate with the participation of lactate dehydrogenase-A.20
Lactate has been regarded as a byproduct of metabolism, but emerging evidence shows that it may be a metabolite able to reprogram cancer cells and stromal cells in TME. It promotes macrophage polarization toward a pro-tumor and pro-inflammatory (M2-like) phenotype.22,78 The expression of Foxp3 suppresses Myc and glycolysis to promote the survival of Treg in a high lactate microenvironment, thereby providing a supportive immunosuppressive microenvironment for cancer cells.79 Lactate promotes angiogenesis and the survival of hypoxic cells and induces an acidic microenvironment.80 Glutamine and glucose are two vital substrates for lactate metabolism, with glutamine being dominant when glucose is in deficit.81 Glutamine produces energy, carbon, and nitrogen for cancer cells and stromal cells, such as lymphocytes. Cancer cells uptake proteins, which can be degraded to glutamine that fuels the cancer cells through RAS-activated macropinocytosis.82 Several investigations have provided explicit and detailed introductions of glutamine metabolism in cancer82–85 revealed that breast cancer cells consume pyruvate in TME to cause collagen hydroxylation (not collagen synthesis) independently, induce ECM remodeling, and reprogram the lung metastatic niche. The pyruvate-mediated hydroxylation of collagen is driven by the activation of prolyl-4-hydroxylases regulated by α-ketoglutarate. In particular, pyruvate reportedly plays a role in the growth of spheroid rather than monolayer of breast cancer cells.85 Investigation of the products involved in lactate metabolism, including glucose, pyruvate, and glutamine can lead to the discovery of more potential therapeutic targets, as is being currently conducted.
ROS metabolism in TME
The elevation of ROS levels has been observed in cancers and is closely related with tumorigenesis, tumor immunity, and TME reprogramming.86 Under hypoxia, mitochondrial ROS are required in HIF stabilization,87,88 which may further induce autophagy and enhance tumorigenicity.89 Tumor cells and stromal cells in TME can produce ROS, whereas elevated ROS in local TME can affect the growth of cancer cells in return.90 Interestingly, as cancer cells evolve, they become tolerant to ROS accumulation and strike a balance with ROS, a phenomenon called ROS addiction.73 ROS in microenvironment can also affect the regulation of MDSCs, TAMs, CAFs, and T cells.91–93 Increased oxidative status in Treg cells in ovarian cancer mice enhances its immunosuppressive function and resistance to programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)/programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) therapy.94 Ligtenberg et al.95 demonstrated that decreased oxidative state facilitates better maintenance of T cell and antitumor activity with co-expressing catalase having chimeric antigen receptor T cell. Normalizing ROS metabolism in TME may assist immunotherapy to increase the effectiveness of their antitumor activity.
Lipid metabolism and formation of pre-metastatic niche
Lipids, including cholesterol, fatty acids, and triglycerides are materials for the generation of cancer cell membranes, post-translational modification of proteins, and energy for cancer cells.75 Lipid metabolism in TME regulates cancer growth, recurrence, and link diet with tumor. High cholesterol level is seen in TME and positively correlated with CD8+ T cell exhaustion.51 In a murine melanoma model, cholesterol increases endoplasmic reticulum stress, activates X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1), and upregulates PD-1 expression on CD8+ T cells, indicating that the combination of immunotherapy and cholesterol-reducing therapy may have great benefits.96 Strikingly, lipid metabolism promotes the formation of pre-metastatic niche in ovarian cancer. Hematogenous, lymphatic metastasis, and transcoelomic seeding are the three main routes for ovarian cancer metastasis. More than 80% ovarian cancer cells or spheroids have a tendency to migrate to the omentum, which is rich in adipocytes.97 Fatty acids are released during the lipolysis of adipocytes and are uptaken by cancer cells to fuel their growth. Previous studies have reported the ability of fatty acid-binding protein 4 (FABP4) to assist the solubilization, transport, and metabolism of fatty acids. It is upregulated in adipocytes and omental metastasis but primary ovarian cancer in patients and contributes to poor prognosis.97,98 The inhibition of FABP4 further induces lipid accumulation and inhibits adipocyte-mediated invasion.97 Lipid metabolism in TME may be a potential target for the prevention of cancer metastasis.
Acidic niche: a result of hypoxia and lactate metabolism
Dysregulated or reversed pH has become a commonly recognized feature of cancer. Elevated intracellular pH (pHi) promotes cancer-cell survival, proliferation, migration, invasion, and glycolysis and inhibits apoptosis. Cancer cells tend to have a higher pHi (7.4 vs. ~7.2) but a lower extracellular pH (pHe)(6.7–7.1 vs. ~7.4) compared with nonmalignant cells.99 It raises the acidic niche, manifesting as the acidosis of tumor and its microenvironment. Acidic niche cannot be separated from hypoxic niche and metabolism microenvironment, particularly the lactate metabolism microenvironment, because it is produced during lactate metabolism or by CO2 hydration.24 Hypoxia causes increased lactate production, proton accumulation in hypoxic niche, and tumor-cell adaptation through TME acidification.100 Lactate is exported by monocarboxylate transporter (MCT) 4, and is imported into cancer cells by MCT1 and co-transport of H+.101 During this process, tumor acidosis promotes tumor invasion and metastasis, and acidic niche has a synergic effect on lactate metabolism in providing a supportive microenvironment for cancer development. For the first time, lactate-based metabolic symbiosis has been recognized.101 Acidic niche increases oxidative phosphorylation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and invasiveness of melanoma cells.102 Similar results have been found in breast cancer and neuroblastoma cells.103,104 Oncogene activation (e.g., Ras and Myc) and inactivation of tumor suppressors (e.g., p53) also drive acidic niche generation.100 Acidosis has regulative effects on immune cells. For instance, low pHe switch induces macrophage polarization toward M2 (alternatively activated) phenotype, activates neutrophil or DCs, and inhibits the cytotoxicity activity of TILs.100,105 Extracellular vesicle (EV) and exosome trafficking are also increased to transfer waste and excess acid under this situation.106,107 Acidic pHe induces p-glycoprotein activation followed by p38 MAPK activation and causes resistance to daunorubicin. Meanwhile, vacuolar-type H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) is involved in intracellular alkalization. The inhibition of p38 MAPK or V-ATPase prevents metastasis and multidrug resistance,100,108 thereby confirming that maintaining pH homeostasis can serve as an approach against acidic niche.
Innervated niche in TME
Awareness of the close relationship between neurology and cancer science has increased. Accordingly, Monje and other scientists have proposed a novel field called “cancer neuroscience” to better study how the nervous system communicates with cancer. Focus is given on electrochemical interactions, paracrine interactions, systemic neural-cancer interactions, and cancer-therapy effects on the nervous system.109 Moreover, increasing studies have confirmed that the nervous system participates in the development and metastasis of solid (e.g., prostate and brain) and hematological cancers.28,31,110–112
Innervated niche: an emerging specialized microenvironment focusing on the neural regulation of TME
The phenomenon of perineural invasion (PNI), representing cancer invasion in or around or penetrate nerve or route for cancer metastasis, is correlated with poor cancer prognosis.31,110 PNI has been reported in multiple cancers, such as those in the head and neck, pancreas, prostate, breast, colon, and ovaries.28,30,110,113 Amit et al.114 showed that oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma cancer cells with loss of TP53 can reprogram tumor-associated neurons to adrenergic phenotype depending on the signal transduction of EVs, which further promotes tumor progression. Injection of the nonselective adrenergic receptor blocker carvedilol to sensory fibers alleviates tumor proliferation and progression, indicating the significance of neural regulation in cancer.114 The communication mediated by EVs may partially explain the past failure of adrenergic nerve denervation in inhibiting tumor growth. We propose that the communications between nerve and cancer mediated by nerve-derived neurotransmitters or neuropeptides build a specialized localized microenvironment called “innervated niche”. Previous studies may refer to it as “perineural niche” or “neural regulation in TME”112,115 or “nerve microenvironment” in brain tumors.116 The innervated niche contains peripheral nerve (sympathetic, parasympathetic, or sensory), which has physical contact with cancer parenchyma or nerve located in the proximity of cancer that affects cancer cells. The innervation of cancer cells or stromal cells always relies on the release of neurotransmitters or neuropeptides, such as dopamine, catecholamine, and acetylcholine.27 The axonal microenvironment promotes the formation and development of schwannoma, a benign nerve sheath neoplasm.116,117 Gastric cancer secretes neurotrophins to promote nerve infiltration in TME.117 Active neurons promote the growth of high-grade gliomas via the neuroligin-3 (NLGN3)-activated PI3K-mTOR pathway.118 NLGN3 also upregulates synapse-related genes in glioma cells.118 In hematological cancers, the sympathetic nervous system innervates the egress of hematopoietic stem cells from the hematopoietic niche of bone marrow.29,119 Primary brain tumors including glioblastoma, schwannoma, astrocytomas, and brain metastasis are closely related with or even originated from neuron or nerve fibers; thus, their innervated niche is distinct from that for cancers of other organs.116,117,120–123 Accordingly, we suggest that the innervated niche be categorized as two main categories: intracranial and extracranial innervated niches.
Latest understanding of intracranial innervated niche
Venkataramani et al.121 and Venkatesh et al.122 verified that TME has a neural regulation of cancer and vice versa. Functional neurogliomal synapses generate AMPA receptor-mediated potassium currents,121 which can be amplified by gap junctions.122 This phenomenon occurs in about 5–10% of glioma cells, creates a direct electrochemical communication between glioblastoma cells and neuron, and promotes glioblastoma invasion and proliferation.121,122 Conversely, glioblastoma cells enhance neuronal excitability in TME, further altering currents dependent or independent on neurogliomal synapse formation. The depolarization of glioma cell membrane promotes cancer proliferation in xenografts.122 Tumor microtubes driven by growth-associated protein-43 also enhance astrocytoma progression and resistance.120 Approximately, 20% of cancer patients eventually develop brain metastasis, and the incidence of brain metastasis is even higher than that of a primary brain tumor.65,124 Zeng et al.123 have shown that brain metastasis also has a close crosstalk with its microenvironment. Gap junctions formed between breast/lung cancer and astrocytes assist cancer cells to transfer cGAMP to astrocytes, produce cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor and interferon-α, activate the STING pathway, and further stimulate NF-κB and STAT1 signaling in brain metastatic cells via paracrine; consequently, cancer growth and resistance to chemotherapy are promoted.125,126 In breast-to-brain metastasis, pseudo-tripartite synapses are generated between cancer cells and neurons. The activation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-mediated colonization is triggered such that the reprogramed metastatic innervated niche becomes more supportive for cancer survival. Tumor co-opting nerves for survival and migration increase difficulty of cancer treatment but also serve as an entry point for therapies targeting the innervated niche.
Mechanical microenvironment in TME
Mechanical microenvironment is another newly investigated specialized microenvironment.32,34,36 Its formation relies largely on intracellular components (vimentin, actin, and neurofilaments), extracellular components (collagen and fibrin), intercellular signaling (integrin), and stromal cells (fibroblasts).127 CAFs secrete matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) including MMP2, MMP3, and MMP9 or activate yes-associated protein to promote ECM degradation and remodeling, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and cancer-stem-cell stemness.128–132
Mechanical microenvironment influences oncogenes or tumor suppressors, cell morphology, cancer carcinogenesis, and therapeutic responses. Moreover, the mechanical stiffness of ECM is reported to accelerate glioblastoma cell progression.36 Cancer-produced ECM promotes the colonization of breast cancer lung metastasis through platelet recruitment via heat shock protein 47/type I collagen axis.133 Lu et al.134 and Leight et al.,33 provided informative discussions on the role of ECM in the modulation of cancer biology and treatment. HIF1 promotes lysyl oxidase production to enhance integrin signaling and increase the tumor-matrix stiffness.135 Park et al.35 confirmed that the mechanical microenvironment regulates glycolysis via tripartite motif-containing protein 21 and phosphofructo-1-kinase Isozyme C axis. They also demonstrated that the stiffness of cancer cells promotes their maintenance of fast metabolism, thereby further elucidating the heterogeneous specialized TME.32
Crosstalk and nexus among specialized microenvironments
Awareness of crosstalk among TMEs has increased because of the advancements made in cancer research.
TME reprogramming within hypoxic niche
Hypoxic niche occupies almost the entire tumor and external microenvironment. It influences cancer cells, reprograms other specialized microenvironments, and initiates a hypoxia-induced cascade. Particularly, immune, lactate and ROS metabolism microenvironment, and acidic niche are well-known top-affected TMEs. Hypoxia-induced VEGF expression is a typical product of the reshaping of immune microenvironment96 Horikawa et al.136,137 Sonveaux et al.101 demonstrated a phenomenon called “glycolytic switch” and “metabolic symbiosis”, and stated that oxidative cancer cells prefer utilizing lactate rather than glucose, in which MCT1 mediates a lactate exchange in tumors.138 Hypoxic cells consume glucose and produce lactate, which can diffuse based on the concentration gradient, whereas oxidative cancer cells uptake lactate via MCT1. After MCT1 inhibition, oxidative cancer cells change to utilize glucose rather than lactate. As the glucose gradient follows the gradient of oxygen supply, oxidative cancer cells are more likely to uptake glucose than hypoxic cells, causing their starvation for glucose and necrosis.101 Zhang et al.139 demonstrated that the hypoxia-lactate axis directly regulates gene expression through histone post-translational modification, which is called histone lactylation, thereby further inducing macrophage polarization toward being M2-like.140 This finding indicates a novel link between oncometabolites and histone code in hypoxic niche and highlights a counterbalancing homeostatic function for the hypoxia-lactate axis in regulating tumor immunity.
Hypoxic niche also has bidirectional communication with mechanical microenvironment mediated by CAFs. On one hand, they are involved in ECM remolding and the formation of hypoxic microenvironment.141 On the other hand, HIF-1 triggers the activation of PLOD2, P4HA1, and P4HA2 in response to hypoxia. CAFs become elongated and spindle shaped, secrete an increased amount of type I collagen, promote matrix adhesion and mesenchymal morphology, and produce ECM with increased stiffness and collagen fiber alignment, all of which support the invasion and migration of breast cancer cells.142 Recapitulating hypoxic niche while exploring the mechanisms may help fundamental researches obtain results close to clinical outcomes.
Tumor-nerve-immunity cycle in TME
Recent studies have demonstrated a tumor-nerve-immunity cycle in TME, which mediates communication among cancer cells, immune microenvironment, and innervated niche, thereby disclosing the relationship among stress, immunity, and cancer.143,144 Nerve innervation in TME affects immune-cell recruitment and activation, cancer proliferation, metastasis, and response to immunotherapy.28 Released catecholamine may promote lymphocyte apoptosis and macrophage infiltration, inhibit NK cells and cytotoxic T cells, and thus facilitate tumor metastasis.27,145,146 High levels of norepinephrine suppress DC development and recruit MDSC to TME, causing tumor progression.147 The sympathetic nervous system guides the recruitment of macrophages or NK cells to tumor via β-adrenergic signaling.148 Elevated intratumoral IL-6 levels are seen in excised samples of stressed ovarian cancer patients compared with control patients.28,149
Conventional drugs with new use: candidate for TME-targeting combination therapy
Numerous comprehensive reviews summarize the therapeutic strategies targeting cancer cells and TME.18,28,72,150–156 However, to our knowledge, drugs targeting TME are unsatisfactory. For example, treatment of BLZ945 (colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor inhibitor) inhibits macrophages, induces tumors regression, and prolongs survival in glioblastoma-bearing mice, whereas over 50% glioblastomas recur.157,158 Quail et al.158 demonstrated that the high relapse rate is due to acquired resistance and thus proposed the requirement of combination therapy. As TME is made up of various specialized microenvironments that overlap and communicate frequently with one another, targeting one specialized microenvironment may induce a series of changes in other specialized microenvironments and related pathways. Combination therapy targeting several specialized microenvironments may greatly benefit cancer treatment, along with intensive studies on the crosstalk within TME. The introduction of conventional drugs into the new application of targeting TME and treating cancer may enable its use in clinical practice and guide treatment choices.
Drug repurposing in cancer
The appeal of drug repurposing in cancer is increasing for several reasons, such as the following: (1) it helps lower the cost (time, money, etc.) of developing a new drug; (2) it reduces the failure risk of clinical trials because those these drugs already have sufficient safety, toxicity, and pharmacological data; (3) drugs can be introduced to the market once sufficient antitumor effect is established.159,160 As reviewed in Pushpakom et al.,159 diverse approaches toward drug repurposing exist, including computational (signature matching, computational molecular docking, genome-wide association studies, pathway or network mapping, and retrospective clinical analysis) and experimental (binding assays to identify target interactions and phenotypic screening) approaches. To date, more than 200 noncancer drugs (cardiovascular, antibiotics, antiviral, antipsychotics, and antidepressants) have shown off-label antitumor effects. Among them, aspirin is the most frequently mentioned for drug repurposing in cancer considering its immunomodulatory effect on TME. Based on retrospective clinical data, aspirin was recommended to prevent colorectal cancer in 2015 (https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/Page/Document/RecommendationStatementFinal/aspirin-to-prevent-cardiovascular-disease-and-cancer).
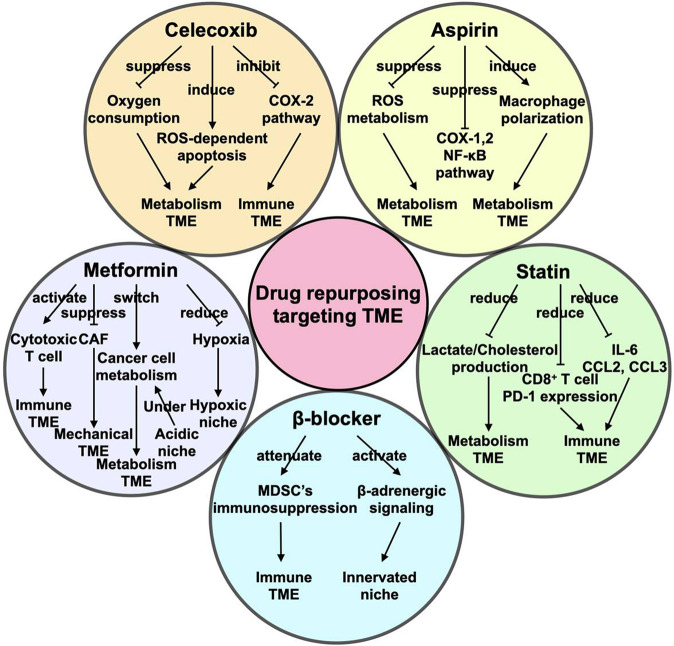
Herein, we focus primarily on five promising drug-repurposing candidates, namely, aspirin, celecoxib, β-adrenergic antagonist, metformin, and statin (Fig. 2). These drugs have the following features: (1) they are well-known and commonly used in cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and heart disease and have typical anti-inflammatory activity,161,162 and their retrospective electronic health records and pharmacological data are easily available; (2) they have been demonstrated to target TME and exert an antitumor effect in preclinical models; (3) they have been applied in abundant completed, recruiting, or registered clinical trials in cancer therapy alone or combined with standard treatment modalities (Table 1); and (4) they are required to treat the above-mentioned chronic comorbidities in cancer patients and may thus guide treatment selections in these patients.
Fig. 2.
New life of old drugs in targeting TME. TME is regarded as a target for cancer therapy. Aspirin, celecoxib, β-adrenergic antagonist, metformin, and statin are five conventional drugs with antitumor capability that show potential use in combination therapy by targeting TME
Table 1.
Clinical trials of conventional drugs in combination therapy against cancer
| Conventional Drug | Combination Therapy | Targeting Cancer | ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier | Recruitment Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspirin | Immunotherapy (atezolizumab, bevacizumab, pembrolizumab, avelumab, nivolumab, ipilimumab, lenalidomide) | Ovarian cancer, HNSCC, TNBC, solid adult tumor, multiple myeloma | NCT04188119 | Not yet recruiting |
| NCT02659384; NCT03245489; NCT03728179; NCT03428373 | Recruiting | |||
| Combination immunomodulatory cocktail (Vitamin D, aspirin, CTX and lansoprazole), pembrolizumab, radiation and curcumin | Cervical cancer, endometrial cancer, uterine cancer | NCT03192059 | Recruiting | |
| Targeted therapy (osimertinib) | NSCLC | NCT03532698; NCT03543683; NCT04184921 | Not yet recruiting | |
| Celecoxib | Immunotherapy (nivolumab) | Metastatic cancer | NCT03864575 | Not yet recruiting |
| Targeted therapy (erlotinib, toripalimab, cetuximab, gefitinib, carboplatin, exemestane, depsipeptide) | Squamous cell carcinoma of oral cavity, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, NSCLC, HNSCC, ovarian cancer, pulmonary and pleural malignancies | NCT02748707 | Active, not recruiting | |
| NCT03926338 | Recruiting | |||
| NCT00466505; NCT00068653; NCT00400374; NCT00072072; NCT00062101; NCT00499655; NCT01124435; NCT00201773; NCT00037817 | Completed | |||
| Chemotherapy (cisplatin, gemcitabine, docetaxel, paclitaxel and carboplatin, etoposide, irinotecan, capecitabine CTX, methotrexate, docetaxel, fluorouracil, vinblastine, 6-TG, temozolomide, CCNU, decitabine, DFMO, topotecan) | Pancreatic cancer, NSCLC, bladder cancer, TNBC, GBM, advanced cancer, colorectal cancer, cholangiocarcinoma, sarcoma, pulmonary and pleural malignancies, neuroblastoma, relapsed or progressive cancer | NCT02770378; NCT02030964 | Active, not recruiting | |
| NCT02885974; NCT04081389; NCT03498326 | Recruiting | |||
| NCT00176813; NCT00030407; NCT00030420; NCT00062179; NCT00551005; NCT00101686; NCT00084721; NCT00551889; NCT02280694; NCT00320918; NCT00073866; NCT00064181; NCT00230399; NCT00085163; NCT00061893; NCT00047281; NCT00504660; NCT00037817; NCT00165451 | Completed | |||
| Radiation therapy | NSCLC | NCT00046839 | Completed | |
| Targeted therapy and chemotherapy | Recurrent and/or refractory solid and CNS tumors | NCT02574728 | Recruiting | |
| Chemoradiotherapy | Rectal cancer, cervix neoplasms, GBM, NSCLC, operable esophageal cancer | NCT00931203; NCT00336960; NCT00152828; NCT00112502; NCT00188565; NCT00346801; NCT00137852 | Completed | |
| DC Vaccine, IFN alpha-2 and rintatolimod | Melanoma, peritoneal surface malignancies | NCT04093323 | Not yet recruiting | |
| NCT02151448 | Completed | |||
| DC vaccine and cisplatin | Ovarian cancer | NCT02432378 | Recruiting | |
| Gemcitabine and gene therapy (rAd-IFN) | Malignant pleural mesothelioma | NCT03710876 | Recruiting | |
| Chemotherapy (carboplatin, gemcitabine) and 5-LOX inhibitor zileuton | Advanced NSCLC | NCT00070486 | Completed | |
| Etoposide, CTX, thalidomide, fenofibrate | Relapsed or progressive cancer | NCT00357500 | Completed | |
| ARTA and itraconazole | Multiple myeloma | NCT02401295 | Completed | |
| β-blocker | Immunotherapy (pembrolizumab) | Cutaneous melanoma | NCT03384836 | Recruiting |
| Chemotherapy (doxorubicin, vinorelbine, paclitaxel, nab-paclitaxel, doxorubicin, CTX) | EOC, primary peritoneal carcinoma, fallopian tube cancer, breast cancer, gastric cancer, Malignant soft tissue sarcoma, pediatric cancer | NCT02897986 | Not yet recruiting | |
| NCT01847001 | Active, not recruiting | |||
| NCT04005365; NCT03108300 | Recruiting | |||
| NCT01308944 | Completed | |||
| NASIDs (etodolac) | Colorectal cancers; Pancreatic cancer | NCT03919461; NCT03838029 | Recruiting | |
| Prednisone | Hemangioma | NCT01072045 | Completed | |
| Relaxation/guided imagery audio intervention | Cervical cancer | NCT01902966 | Active, not recruiting | |
| Metformin | Immunotherapy (nivolumab, pembrolizumab, sintilimab) | NSCLC, SCLC, melanoma, solid tumors | Recruiting | |
| NCT02145559 | Completed | |||
| Targeted therapy (temsirolimus, vandetanib, sirolimus, lapatinib, erlotinib, irinotecan, gefitinib, sapanisertib, dabrafenib, trametinib, ritonavir, nelfinavir, toremifene, everolimus, letrozole, lanreotide) | Advanced cancers, kidney cancer, TNBC, colorectal cancer, NSCLC, advanced or metastatic relapsed or refractory cancers, lymphoma, melanoma, multiple myeloma or chronic lymphocytic leukemia, breast cancer, endometrial carcinoma, neuroendocrine tumors | NCT01529593; NCT02948283; NCT01797523 | Active, not recruiting | |
| NCT01930864; NCT03017833; NCT02143050; NCT03829020; NCT02506790; NCT02823691 | Recruiting | |||
| Completed | ||||
| Chemotherapy (docetaxel, carboplatin, paclitaxel, oxaliplatin, gemcitabine, vincristine, irinotecan, temozolomide, CTX, myocet, VPLD, R-CHOP, FDC) | Ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer, primary peritoneal cancer; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, prostate cancer, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, glioblastoma, pediatric tumor, childhood ALL, diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma | NCT03833466 | Not yet recruiting | |
| NCT02336087; NCT01528046; NCT03200015 | Active, not recruiting | |||
| NCT02437812; NCT02122185; NCT04170465; NCT01929811; NCT03243851; NCT02506777 | Recruiting | |||
| NCT01796028; NCT01210911; NCT02312661; NCT02005419; NCT01666730; NCT01971034; NCT01442870; NCT01885013; NCT01324180 | Completed | |||
| Chemoradiotherapy | Cervix cancer, lung cancer, HNSCC, rectal cancer | NCT02115464; NCT02325401; NCT01430351 | Active, not recruiting | |
| NCT02394652; NCT02949700 | Recruiting | |||
| NCT02437656 | Completed | |||
| Chemotherapy and targeted therapy | Endometrial cancer | NCT02755844 | Active, not recruiting | |
| Antiandrogen (enzalutamide, bicalutamide) | Prostate cancer | NCT02339168 | Active, not recruiting | |
| NCT02640534; NCT02614859 | Recruiting | |||
| Antibiotic (doxycycline) | Breast cancer, uterine cancer, HNSCC | NCT03076281 | Active, not recruiting | |
| NCT02874430 | Recruiting | |||
| Chloroquine | IDH1/2-mutated solid tumors | NCT02496741 | Completed | |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | Early stage breast cancer | NCT02278965 | Active, not recruiting | |
| Vitamin C | Hepatocellular cancer, pancreatic cancer, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer | NCT04033107 | Recruiting | |
| Statin | Targeted therapy (sorafenib, erlotinib, anti-HER2 therapy, fulvestrant, aromatase Inhibitors) | hepatocellular carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, NSCLC, breast cancer | NCT03275376; NCT03324425; NCT02958852 | Recruiting |
| NCT00966472 | Completed | |||
| Chemotherapy (capecitabine, topotecan, CTX, zoledronate, bortezomib, bendamustin) | Rectal cancer, multiple myeloma, pediatric solid and CNS tumors, TNBC | NCT02569645; NCT02390843; NCT03358017 | Recruiting | |
| NCT02161822; NCT00399867 | Completed | |||
| Chemoradiotherapy | GBM | NCT02029573 | Completed | |
| Digoxin and enzalutamide | Prostate cancer | NCT04094519 | Recruiting | |
| Ezetimibe | Prostate cancer | NCT02534376 | Completed | |
| Combination | Combination statin and celecoxib | Optico-chiasmatic gliomas | NCT02115074 | Active, not recruiting |
| Combination celecoxib, β-blocker, CTX, etoposide and vinblastin | Neuroblastoma | NCT02641314 | Recruiting | |
| Combination aspirin, celecoxib and PD-1 antibody BAT1306 | Colorectal cancer | NCT03638297 | Recruiting | |
| Combination metformin and statin | Breast cancer | NCT01980823 | Recruiting | |
| Combination statin, aspirin and dutasteride | Prostate cancer | NCT01428869 | Completed |
NSCLC non-small cell lung cancer, SCLC small cell lung cancer, TNBC triple negative breast cancer, CTX cyclophosphamide, VPLD vincristine, dexamethasone, doxorubicin, and PEG-asparaginase, R-CHOP rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone, FDC fluoruracil, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, ALL acute lymphoblastic leukemia, HNSCC head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, IDH isocitrate dehydrogenase, EOC epithelial ovarian cancer, NASIDs non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, HER2 human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, CNS central nervous system, GBM glioblastoma, 6-TG 6-thioguanine, CCNU lomustine, DFMO α-difluoromethylornithine, DC dendritic cell, IFN interferon, 5-LOX 5-lipoxygenase, PD-1 programmed death-1
Aspirin
Aspirin, also called acetylsalicylic acid, is an extensively used anti-inflammatory agent, antiplatelet drug, and chemopreventive drug for inflammation-associated cancers. Regular use of aspirin is associated with lower risk of BRAF-wild-type colon cancer.163 It also exhibits antitumor activity in cancers including ovarian, gastric, and pancreatic through diverse mechanisms.164–166 Aspirin has an inhibitory effect on the cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and COX-2 pathway to inhibit cancer proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis. The non-COX antitumor mechanism of aspirin includes the inhibition of the NF-κB or STAT3 pathway.164 Aspirin induces apoptosis by upregulating tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and DR5 receptor or autophagy by inhibiting the mTOR pathway in cancer cells and xenografts.167,168 Numerous investigations have demonstrated that aspirin can target specialized TME.
Targeting the immune microenvironment
Previous studies have shown that platelet activation results in an immunosuppressive TME and spares cancer cells from immune surveillance, leading to their growth and migration.139,169 Considering that aspirin is one of the most commonly used antiplatelet drugs, Riesenberg et al.169 revealed its antitumor activity on the immune microenvironment and found its potential use in combination with PD-1 blockade. Similar results have been observed in breast cancer cells accompanied by decreased IL-8 secretion.170 Additionally, aspirin’s inhibition of the COX-1/thromboxane A2 pathway occurs through platelets, which involves the suppression of platelet aggregation on cancer cells, the recruitment of monocytes or macrophages, and the stepwise formation of premetastatic niche and tumor metastasis.171 Aspirin induces the polarization of macrophages toward M1 phenotype by increasing M1 marker expression while decreasing M2 marker expression and inhibiting cancer cell growth and migration in breast cancer cell lines.172 Aspirin also activates macrophage activity in eliminating therapy-generated tumor cell debris and inhibits macrophage-secreted proinflammatory cytokines.173 Aspirin further plays an immunomodulation role on other immune cells, including MDSCs and Treg cells.139 These results suggest that aspirin regulates the immune microenvironment and is an attractive agent for combination therapy.
A recruiting phase II clinical trial (PRIMMO) has shown that aspirin, together with vitamin D, cyclophosphamide, and lansoprazole, forms an immunomodulatory cocktail and can be combined with immunotherapy pembrolizumab and radiotherapy to treat cervical and uterine cancers (NCT03192059) (Table 1). This accomplishment may provide additional data for aspirin’s effect on antitumor immunity.
Targeting the metabolism microenvironment
In 2002, aspirin was reported to inhibit cyclooxygenase, suppress oxidative stress and ROS metabolism, and inhibit ROS-mediated DNA damage.174 It has also been proposed to inhibit energy metabolism through AMPK activation and mTORC1 inhibition.175 Recently, Liu et al.176 revealed that aspirin regulates glucose metabolism to inhibit hepatoma cell proliferation.
In a study on the role of aspirin in reducing cancer risk, various doses, frequencies, and duration have been selected, such as the following: ≥975 mg/w for more than 5 years,177 ≥150 mg/d for more than 1 year,178 ≥325 mg/d for more than 5 years,179 600 mg/d for a mean of 25 months,180 100 mg/d for at least 104 d/y.50 Similarly, when assessing aspirin’s role in combination with other treatment modalities, these indices should also be carefully selected. Gastrointestinal bleeding is always a concern when using aspirin. Fortunately, data from patients with chronic viral hepatitis in Sweden show that low-dose aspirin does not significantly increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding and lowers the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver-related mortality compared with non-users.181 However, the adverse effects and safety liabilities of aspirin should be carefully assessed under each condition.
Celecoxib
Celecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Different from aspirin, celecoxib selectively inhibits COX-2 and is thus viewed as a COX-2 inhibitor. COX-2 is overexpressed in gastric, breast, and lung cancers, among others.182
Targeting the immune microenvironment
COX-2 induces immune escape and promotes cancer growth, suggesting the possible benefits of the COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib combined with immunotherapy.183 Over the past several years, a number of clinical trials on neoadjuvant immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) have been carried out in MMR-deficient (dMMR) and MMR-proficient (pMMR) colon cancer (NCT03026140). Compared with adjuvant ICI, neoadjuvant ICI is believed to stimulate a highly diverse immune response with the activation of TILs, especially in dMMR patients considering their higher mutational burden and more neoantigens.184,185 As celecoxib attenuates TIL suppression by inhibiting prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), it is introduced to neoadjuvant ICI (ipilimumab and nivolumab) in pMMR colon cancer patients hoping to achieve an improved clinical response.186
Targeting the metabolism microenvironment
Celecoxib suppresses oxygen consumption and induces ROS-dependent apoptosis in the metabolism microenvironment of metastatic melanoma and breast cancer, suggesting its potential as an enhancer for chemotherapy or radiotherapy.187
A large number of clinical trials focusing on the combination of celecoxib with targeted therapy, immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy have been completed or is recruiting. In a study on NVALT-4, celecoxib combined with docetaxel and carboplatin promotes survival in COX-2-high advanced NSCLC patients.188 However, most results are not encouraging. Altorki et al.189 showed that celecoxib introduction decreases prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), but COX-2 is induced by chemotherapy in NSCLC. Csiki et al.190 revealed that adding celecoxib to docetaxel inhibits COX-2 but does not improve the outcome of recurrent NSCLC patients. In a REMAGUS02 trial, a phase II randomized controlled trial, celecoxib combined with sequential neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) (epirubicin + cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel) shows poorer event-free survival and distant relapse-free survival and OS than the NAC group, particularly the prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS2; also called COX-2)-low or estrogen receptor-negative group.191 The effects of celecoxib on breast cancer depend on the expression of PTGS2 and estrogen receptor status, as validated in PTGS2-low/high breast cancer cell lines. In vitro data show that adding celecoxib promotes cancer cell survival only in PTGS2-low cell lines.191 Another noteworthy phenomenon is that celecoxib may induce COX-2 expression in lung cancer cells. Expressed COX-2 protein could reportedly be transferred by exosomes to other cells such as monocytes and THP-1 cells, thereby increasing PGE2 and VEGF production.192 The reason behind the celecoxib-induced elevation of COX-2 expression remains unknown, but it confirms that celecoxib affects TME. Studies on the mechanism of the celecoxib and COX-2 pathway in cancer and TME can solve the complicated effect of celecoxib. Meanwhile, as more clinical trials reach completion, we may further understand of the positive and negative roles of celecoxib in cancer treatment.
β-Adrenergic antagonist
As proposed by Tang et al.,193 β-adrenergic signaling is involved in eight hallmarks of cancer development, including proliferation, inhibition of tumor suppressors, cell death resistance, unlimited replication, angiogenesis, cancer invasion and metastasis, cellular energetics deregulation, and insensitive immune destruction.
Targeting the innervated niche
β-Adrenergic signaling is regarded as a significant pathway in innervated niche. Catecholamine-mediated β-adrenergic receptor activation causes the activation of β-adrenergic signaling, which plays a crucial role in cancer proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis.148,193 Catecholamine-mediated immunesuppression activity is even higher after surgery and likely attributed to psychological distress and pain. The cytotoxicity of NK cells also decreases. The use of β-adrenergic antagonist (β-blocker) or celecoxib days before surgery can improve immune surveillance.194 β-Blockers are other commonly used drugs for hypertension and arrhythmia. They can be categorized into selective β1-blocker (β1), nonselective β-blocker (β1 and β2), and α/β-blocker. In ovarian cancer, nonselective β-blockers prolong patients’ OS.195 The selective β1 blocker landiolol reduces lung cancer recurrence after operation.196 Additionally, β-blockers positively affect cancer patients by reducing their intrusive thoughts.197 Overall, the effects of β-blockers on TME and the whole organism indicate their potential application in future cancer treatments.
Targeting the immune microenvironment
β-Blockers attenuate MDSCs’ immunosuppression, promote the infiltration of T-lymphocytes and their cytotoxicity, and enhance immunotherapy efficacy.143,198,199 Chronic stress leads to MDSC accumulation and an immunosuppressive microenvironment; thus, tumor progression occurs through the activation of β2 adrenergic signaling; β2 blockers assist in attenuating MDSCs’ immunosuppression and sensitizing immunotherapy.143,198 Interestingly, β2 adrenergic signaling activation suppresses the glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation of CD8+ T cells, suggesting that β2 blockers may be used to promote the cytotoxicity activity of CD8+ T cells.200
Apart from targeting TME and exerting an antitumor effect, β-blockers have been shown to prevent cancer therapy-induced complications such as cardiomyopathy and hypertension; thus, β-blockers are competitive in combinatorial therapy. Some studies have suggested that β-blockers prevent the ventricular dysfunction and cardiotoxicity induced by chemotherapy, and the reduction in the left ventricular ejection fraction mediated by β-blockers is <10%.201,202 To date, dexrazoxane is the only FDA-approved agent for anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity prevention.203 The potential mechanism behind anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity includes ROS production, iron-metabolism alteration, and Ca2+ channel change.204
Although VEGF inhibitor has been applied in various cancers due to its ability to reduce hypoxia-induced excessive angiogenesis,205,206 a great number of hypertension cases in cancer patients and increased arterial vascular events have been reported.207 Carvedilol may benefit the reversal of VEGF-induced hypertension due to its vasodilatory effect.207
However, the use of selective β1 (metoprolol) or β2 (bisoprolol) blockers may also promote VEGF-triggered microvessel sprouting, which does not apply to carvedilol (a nonselective β blocker).208 Some unsupportive data from several clinical trials have indicated that the use of β-blockers is correlated with higher overall mortality and recurrence rate, with the mechanism remaining undiscovered.209,210 The category of the β blocker is important to recognize and so pay attention could be paid to its side effects during the investigation.
Metformin
Metformin is a well-known traditional antidiabetic drug, but its involvement in cancer, tuberculosis infection, and myotonic dystrophy has been increasingly observed.211–213 Metformin reportedly exerts antitumor activity in multiple cancers, such as gastric and thyroid cancers.214,215 More than 100 clinical trials have focused on the combination of metformin with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy in multiple cancers, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), gynecological cancer, myeloma, acute lymphocytic leukemia, and acute myeloid leukemia (Table 1). The use of metformin reportedly prolongs OS for high-grade glioma patients216 and decreases the incidence of colorectal cancer in type 2 diabetes patients in a dose-dependent manner.217
Targeting the immune microenvironment
Metformin can enhance immunotherapy or targeted therapy mostly due to its effect on the immune microenvironment. For example, adding metformin extends the PFS of patients with advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors who are treated with everolimus and/or somatostatin analogs, lanreotide, or octreotide.218 Cha et al.219 demonstrated that metformin promotes the effect of anti-CTLA4 without toxicity in breast cancer cell lines, including triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) by activating the tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic T cells and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway. AMPK activation further induces endoplasmic reticulum accumulation, endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation, and decrease in PD-L1 level through PD-L1 phosphorylation and subsequent glycosylation.219 Tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic T cells are correlated with better prognosis in breast cancer.220 Meanwhile, increased TIL infiltration and PD-L1 level are also seen in patients with TNBC.221 In particular, some conventional drugs, including aspirin and atenolol can enhance the antitumor activity of metformin. In breast cancer, the AMPK pathway and complex I of the respiratory chain are two targets of metformin function. Adding aspirin activates the AMPK pathway and induces tumor cell apoptosis, whereas adding atenolol inhibits pericytes in breast cancer microenvironment; both increase the metformin-induced inhibition of complex I.222
Targeting the acidic niche
Metformin impairs the proliferation and colony formation of acidic melanoma cells and suppresses their metabolic adaptation in a dose-dependent manner (1–10 mM).102 As acidic niche is correlated with metabolic reprogramming, suppression of antitumor immunity, poor prognosis, and resistance to chemotherapy, metformin may help conquer chemotherapy-induced therapeutic resistance.102
Targeting the metabolism microenvironment
Preclinical models have revealed that metformin reprograms cancer cell metabolism.102,223 Metformin switches the metabolism of prostate cancer cells from being glucose dependent to being glutamine dependent223 and impairs metabolic adaptation and invasiveness of acidic melanoma cells.102 Metformin also influences lipid metabolism by suppressing adipocytes and inhibiting ovarian cancer growth and metastasis.224
Targeting the hypoxic niche microenvironment
Metformin inhibits the stabilization of HIF1α in mesothelial cells to impair ovarian cancer invasion.225 Metformin-mediated hypoxia reduction205 enhances the antitumor effect of PD-1 inhibitor in cancer cells.226 Hypoxia may predict who are irresponsive to metformin according to Sivalingam et al.227 They showed that metformin response decreases under hypoxic and hyperglycemia, and that cancer-cell metabolism is reprogrammed toward glycolysis under a hypoxic, high-glucose condition.
Targeting the mechanical niche microenvironment
Chen et al.228 showed that the effect of metformin on the survival of CAFs is relatively slight; in their study, the metformin concentration reaches 1 mM. They then co-cultured CAFs and cancer cells to explore metformin’s effect on CAFs and found that 0.2 mM metformin administered for 48 h significantly impairs the stimulatory effect of CAFs by upregulating the Calmodulin-like protein Calml3, thereby inhibiting the proliferation of gastric cancer cells.228 Metformin also downregulates the NF-kB signaling induced by CAFs to inhibit tumor progression.229
Metformin has been demonstrated to affect all proposed specialized microenvironments, suggesting this drug’s potential use in combination therapy. Interestingly, a recent study has shown that metformin displays its antitumor activity in mice only under hypoglycemia resulting from fasting dependent on the activation of PP2A-GSK3β-MCL-1 signaling.230 Together with Sivalingam et al.’s results (2020), metformin’s role in TME may be concluded to be significant under a normoxic, hypoglycemic condition. Thus, future studies should consider glucose and oxygen levels.
Statin
Statin is an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase and is used to downregulate the lipid level, thereby playing a role in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases.231 Statins can be classified as lipophilic (e.g., simvastatin and lovastatin) or hydrophilic (e.g., pravastatin and rosuvastatin). The intensive antitumor effects of lipophilic statins but not of hydrophilic ones in multiple cancers, such as lung, prostate, and breast cancers have been observed.232–234
Targeting the metabolism microenvironment
Statins affect the metabolism microenvironment. For instance, simvastatin induces metabolic reprogramming in HNSCC mice, reducing lactate production and promoting cancer sensitivity to MCT1 inhibitor. Simvastatin synergizes with MCT1 inhibitor AZD3965 to suppress cancer growth.235 Clendening et al.236 demonstrated that 7 of 16 multiple myeloma cell lines are sensitive to lovastatin-induced apoptosis. Lovastatin also influences DNA replication-associated genes, glycolysis, and cholesterol metabolism and exerts its antitumor effect in the ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma mevalonate pathway.237 However, Kutner et al.238 showed that statin use in end-stage patients (48.8% with cancer) with an estimated 7-month life expectancy is correlated with a shorter survival than those who stopped statin use (190 vs. 229 days) resulting from the reduced quality of life and low sense of well-being. No difference exists in the incidence of cardiovascular diseases (about 6%) between the two groups. These data indicate that statins may be stopped in terminal patients when considering the quality of life.238,239 Thus, the benefits and risks of statin use in cancer require great attention.
Targeting the immune microenvironment
Statins also reportedly target the immune microenvironment through cytokines or chemokines and immune checkpoints. In primary squamous lung cancer, statins break the communication between cancer cells and mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) by inhibiting CCL3 secreted by cancer cells and IL-6 and CCL2 produced by MSCs. This phenomenon suppresses the survival of lung cancer cells and indicates statin’s repurposing application in targeting the immune microenvironment.240 In a B16 melanoma lung metastatic model, statin lowers PD-1 expression in CD8+ T cells and effectively restores antitumor activity.96 These findings support the adjuvant role of statins combined with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and targeted therapy (Table 1).
The above-mentioned drugs are only the tip of the iceberg in reference to all drugs that exert off-label antitumor effects. However, all these drugs target multiple specialized microenvironments and exhibit great potential in combination therapy, such as immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. Our findings provide guidance for future drug repurposing, i.e., identifying TME-targeting drugs for combination therapy considering the great crosstalk among specialized microenvironments. Data from already completed clinical trials are not always supportive, which we believe is due to the poor understanding of the antitumor mechanisms behind each drug. Indeed, more preclinical experiments and clinical trials are needed to explore the right drug type, dose, frequency, duration, and suitable participator. Some issues requiring further clarification are as follows: (1) the advantages and disadvantages of using of β1, β2, and nonselective β blockers in cancer therapy; (2) the suitable dose of aspirin; and (3) the adverse effects of repurposed drugs and combination therapy considering the differences among diseases and patients. Challenges in drug repurposing for cancer treatment remain, including the lack of platforms for data analysis and high-throughput screening technologies.159,161 Dealing with these problems can promote and accelerate drug repurposing for cancer treatment.
Discussion and outlook
TME comprises various specialized microenvironments that overlap and crosstalk with one another. In the above sections, we propose six specialized microenvironments in TME, focusing on their interaction with malignant cells and the crosstalk among them. We then provide a sophisticated landscape of TME. The understanding of TME as a compartment and a whole can provide directions for investigating combination therapy.
Hypoxic niche is more likely to cover the entire TME, as hypoxia is a constant status for a tumor and the microenvironment around it. All responses may not be isolated from the adaptation to the low-oxygen situation. Dewhirst et al.241 classified hypoxia in tumors into two categories: chronic hypoxia caused by hypoperfusion and acute hypoxia induced by change in perfusion. How does hypoxia proceed in actual solid tumors? How does each type of cell respond to hypoxia or tolerate it? These questions remain unanswered. Immune microenvironment is another key target for cancer treatment. Devalaraja et al.242 showed that tumor immune microenvironment facilitates the production of retinoic acid (RA) by tumor cells in sarcoma mice. RA promotes TAM differentiation and interferes with tumor immunity, and blocking the RA pathway induces a synergistic effect with anti-PD-1 therapy. The metabolism microenvironment, acidic niche, innervated niche, and mechanical microenvironment as emerging compartments of TME are under vigorous investigation.
In the classification proposed by Laplane et al.,6 microbiota is considered as an element of TOE beyond the TME. However, emerging evidence shows that apart from gut microbiota, microbiome can also be found in conjunctiva, mouth, nose, skin, and vagina and eventually become a part of TME. Thus, microbiome can directly interact with cancer, for instance, cervicovaginal microbiome for cervical or endometrial cancer and gut microbiome for gastrointestinal cancer.243 Microbiome is an emerging acellular component in TME that can influence carcinogenesis, genomic instability, and therapies and may even be involved in the process of metastases.243,244 Colorectal cancer cells can transport Fusobacterium to metastatic sites.245 A. vaginae and Porphyromonas sp. in the gynecologic tract are correlated with the occurrence of endometrial cancer for unknown reasons.245 Microbiota (Bifidobacterium) accumulated in colon adenocarcinoma promotes immunotherapy by activating STING signaling.246 Nejman et al.247 demonstrated that bacteria are present in cancer or immune cells, further confirming the presence of microbiomes in TME, although its role remains unknown. This area is largely unknown, and the definition of microbiome microenvironment requires consensus. Other acellular components such as EV/exosomes, cytokines, and chemokines in TME also play significant roles in cancer growth, metastasis, and drug resistance, as has been reviewed by Kalluri, LeBleu1 and Dassler-Plenker et al.248
With the aid of advanced research techniques such as scRNA-seq and organoids, exploring the compositions and functions of immune cells, as well as TME and its application potential, can be performed. Nearly 30% of metastatic sites may be undetected by traditional detection methods, such as computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or bioluminescence imaging, whose results are read by an expert.63 DeepMACT has revolutionized the recognition and detection of micrometastasis. Meanwhile, the introduction of scRNA-seq, ATAC-seq, chromatin immunocleavage sequencing, or CUT&;RUN has expanded studies into single-cell scale over the past decade.249 Among them, scRNA-seq is viewed as one of the most helpful tools to analyze the cell subpopulation state. However, scRNA-seq alone cannot accurately reflect the interaction of the whole tumor with its microenvironment, especially in terms of spatial structure. Researchers have realized the limitation of scRNA-seq and attempted to solve this problem by integrating scRNA-seq with spatial transcriptomics (ST).250 ST was invented to obtain complete transcript data (spatial barcodes).249,251–253 The integration of scRNA-seq and multi-omics (transcriptomics, proteomics, metabonomics, and microbiome) may enhance our understanding of TME in a single-cell scale.
In this review, we propose that combination therapy may aid the new use of conventional drugs. As aforementioned, conventional drugs are highly available and have additional protective effects on other organs. Understanding their antitumor effect may guide the treatment of cancer patients with comorbidity. However, selecting the best treatment modality relies on the assessment of benefits and risks rather than focusing only on lowering risks and ignoring clinical efficacy. Combining conventional drugs with standard therapies is just one way for combination therapy or cancer therapy, but it may not always be the best one. Fortunately, we are moving forward. Corsello et al.254 have examined the antitumor activities of 4518 non-oncology drugs on 578 human cancer cell lines through the technique of profiling relative inhibition simultaneously in mixtures Their findings may be a revolutionary step in transitional cancer medicine and provide promising directions for repurposing drugs in cancer treatment.
We now understand that TME is a complicated ecosystem full of heterogeneity and can affect almost every aspect of cancer biology. It can be a target for cancer treatment, which still needs to be discussed and examined. However, the same as cancer, TME is an inevitable part of a patient. The close interactions of the TME with the whole organism and the effect of therapy on the whole body should be considered. As our understanding of TME is updated, we become more equipped to treat cancer.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (no. 2017FYA0205302) to Wei-Lin Jin and from the 12th Undergraduate Training Program for Innovation of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine (no. 1218201) to Ming-Zhu Jin.
Author contributions
W.L.J. and M.Z.J. conceived the paper. M.Z.J. wrote the paper and developed the figures and tables. W.L.J. edited the paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- 1.Paget S. The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. 1889. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1989;8:98–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kalluri R, LeBleu VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367:eaau6977. doi: 10.1126/science.aau6977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Maman S, Witz IP. A history of exploring cancer in context. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2018;18:359–376. doi: 10.1038/s41568-018-0006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Laplane L, et al. Beyond the tumour microenvironment. Int. J. Cancer. 2019;145:2611–2618. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Laplane L, et al. The multiple layers of the tumor environment. Trends Cancer. 2018;4:802–809. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2018.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Balkwill FR, Capasso M, Hagemann T. The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2012;125:5591–5596. doi: 10.1242/jcs.116392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Khosravi N, et al. IL22 Promotes Kras-Mutant lung cancer by induction of a protumor immune response and protection of stemness properties. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018;6:788–797. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-17-0655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008;454:436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature07205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Todoric J, Karin M. The fire within: cell-autonomous mechanisms in inflammation-driven cancer. Cancer Cell. 2019;35:714–720. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Deng S, et al. Understanding the complexity of the tumor microenvironment in K-ras mutant lung cancer: finding an alternative path to prevention and treatment. Front Oncol. 2019;9:1556. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Abou Khouzam, R. et al. Integrating tumor hypoxic stress in novel and more adaptable strategies for cancer immunotherapy. Semin. Cancer Biol.65, 140–154 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 13.Qiu GZ, et al. Reprogramming of the tumor in the hypoxic niche: the emerging concept and associated therapeutic strategies. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2017;38:669–686. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2017.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ros XR, Vermeulen L. Turning cold tumors hot by blocking TGF-beta. Trends Cancer. 2018;4:335–337. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2018.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Thorsson V, et al. The Immune Landscape of Cancer. Immunity. 2018;48:812–830.e814. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.03.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Toor, S. M., Sasidharan Nair, V., Decock, J. & Elkord, E. Immune checkpoints in the tumor microenvironment. Semin Cancer Biol.65, 1–12 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 17.Ackerman D, Simon MC. Hypoxia, lipids, and cancer: surviving the harsh tumor microenvironment. Trends Cell Biol. 2014;24:472–478. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lau AN, Vander Heiden MG. Metabolism in the tumor microenvironment. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2020;4:17–40. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nakazawa MS, Keith B, Simon MC. Oxygen availability and metabolic adaptations. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2016;16:663–673. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Romero-Garcia S, Moreno-Altamirano MM, Prado-Garcia H, Sanchez-Garcia FJ. Lactate contribution to the tumor microenvironment: mechanisms, effects on immune cells and therapeutic relevance. Front Immunol. 2016;7:52. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Garcia-Canaveras JC, Chen L, Rabinowitz JD. The tumor metabolic microenvironment: lessons from lactate. Cancer Res. 2019;79:3155–3162. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Paolini L, et al. Lactic acidosis together with GM-CSF and M-CSF induces human macrophages toward an inflammatory protumor phenotype. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020;8:383–395. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Boedtkjer E, Pedersen SF. The acidic tumor microenvironment as a driver of cancer. Annu Rev. Physiol. 2020;82:103–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021119-034627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Corbet C, Feron O. Tumour acidosis: from the passenger to the driver’s seat. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2017;17:577–593. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Magnon C, et al. Autonomic nerve development contributes to prostate cancer progression. Science. 2013;341:1236361. doi: 10.1126/science.1236361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Saloman JL, Albers KM, Rhim AD, Davis BM. Can stopping nerves, stop cancer? Trends Neurosci. 2016;39:880–889. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2016.10.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shurin MR, Shurin GV, Zlotnikov SB, Bunimovich YL. The neuroimmune axis in the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunol. 2020;204:280–285. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zahalka AH, Frenette PS. Nerves in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2020;20:143–157. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0237-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cole SW, et al. Sympathetic nervous system regulation of the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2015;15:563–572. doi: 10.1038/nrc3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Faulkner S, et al. Tumor neurobiology and the war of nerves in cancer. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:702–710. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jobling P, et al. Nerve-cancer cell cross-talk: a novel promoter of tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2015;75:1777–1781. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ayad NME, Weaver VM. Tension in tumour cells keeps metabolism high. Nature. 2020;578:517–518. doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-00314-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Leight JL, Drain AP, Weaver VM. Extracellular matrix remodeling and stiffening modulate tumor phenotype and treatment response. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2017;1:313–334. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liu YY, et al. Fibrin stiffness mediates dormancy of tumor-repopulating Cells via a Cdc42-driven Tet2 epigenetic program. Cancer Res. 2018;78:3926–3937. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-3719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Park JS, et al. Mechanical regulation of glycolysis via cytoskeleton architecture. Nature. 2020;578:621–626. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1998-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ulrich TA, de Juan Pardo EM, Kumar S. The mechanical rigidity of the extracellular matrix regulates the structure, motility, and proliferation of glioma cells. Cancer Res. 2009;69:4167–4174. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wisdom KM, et al. Matrix mechanical plasticity regulates cancer cell migration through confining microenvironments. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:4144. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06641-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Liao Z, Tan ZW, Zhu P, Tan NS. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment—accomplices in tumor malignancy. Cell Immunol. 2019;343:103729. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sun W, Luo JD, Jiang H, Duan DD. Tumor exosomes: a double-edged sword in cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2018;39:534–541. doi: 10.1038/aps.2018.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Greten FR, Grivennikov SI. Inflammation and cancer: triggers, mechanisms, and consequences. Immunity. 2019;51:27–41. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.06.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hui L, Chen Y. Tumor microenvironment: sanctuary of the devil. Cancer Lett. 2015;368:7–13. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.07.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Klein-Goldberg A, Maman S, Witz IP. The role played by the microenvironment in site-specific metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2014;352:54–58. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.08.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Schito L, Semenza GL. Hypoxia-inducible factors: master regulators of cancer progression. Trends Cancer. 2016;2:758–770. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2016.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Semenza GL, Wang GL. A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol. Cell Biol. 1992;12:5447–5454. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Palazon A, et al. An HIF-1alpha/VEGF-A axis in cytotoxic T cells regulates tumor progression. Cancer Cell. 2017;32:669–683 e665. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.10.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ribatti D. Tumor refractoriness to anti-VEGF therapy. Oncotarget. 2016;7:46668–46677. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fukumura D, et al. Hypoxia and acidosis independently up-regulate vascular endothelial growth factor transcription in brain tumors in vivo. Cancer Res. 2001;61:6020–6024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Buffa FM, Harris AL, West CM, Miller CJ. Large meta-analysis of multiple cancers reveals a common, compact and highly prognostic hypoxia metagene. Br. J. Cancer. 2010;102:428–435. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bhandari V, et al. Divergent mutational processes distinguish hypoxic and normoxic tumours. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:737. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14052-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ye S, et al. Association of Long-term use of low-dose aspirin as chemoprevention with risk of lung cancer. JAMA Netw. Open. 2019;2:e190185. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.0185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ma LC, et al. Tumor cell biodiversity drives microenvironmental reprogramming in liver cancer. Cancer Cell. 2019;36:418–430.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.08.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Bhandari V, et al. Molecular landmarks of tumor hypoxia across cancer types. Nat. Genet. 2019;51:308–318. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0318-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bonaventura P, et al. Cold tumors: a therapeutic challenge for immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2019;10:168. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Joyce JA, Fearon DT. T cell exclusion, immune privilege, and the tumor microenvironment. Science. 2015;348:74–80. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa6204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Fridman WH, Pages F, Sautes-Fridman C, Galon J. The immune contexture in human tumours: impact on clinical outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2012;12:298–306. doi: 10.1038/nrc3245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Nonomura N, et al. Decreased number of mast cells infiltrating into needle biopsy specimens leads to a better prognosis of prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer. 2007;97:952–956. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ribatti D, et al. Tumor vascularity and tryptase-positive mast cells correlate with a poor prognosis in melanoma. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2003;33:420–425. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.2003.01152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Iamaroon A, et al. Increase of mast cells and tumor angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2003;32:195–199. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0714.2003.00128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ribatti D, Crivellato E. The controversial role of mast cells in tumor growth. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009;275:89–131. doi: 10.1016/S1937-6448(09)75004-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Chang DZ, et al. Mast cells in tumor microenvironment promotes the in vivo growth of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011;17:7015–7023. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sahai E, et al. A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2020;20:174–186. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0238-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Gupta GP, Massague J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 2006;127:679–695. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Pan C, et al. Deep learning reveals cancer metastasis and therapeutic antibody targeting in the entire body. Cell. 2019;179:1661–1676.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Olkhanud PB, et al. Tumor-evoked regulatory B cells promote breast cancer metastasis by converting resting CD4(+) T cells to T-regulatory cells. Cancer Res. 2011;71:3505–3515. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Valiente M, et al. The evolving landscape of brain metastasis. Trends Cancer. 2018;4:176–196. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2018.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ceelen W, et al. Targeting the tumor microenvironment in colorectal peritoneal metastases. Trends Cancer. 2020;6:236–246. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Lopez-Soto A, Gonzalez S, Smyth MJ, Galluzzi L. Control of metastasis by NK cells. Cancer Cell. 2017;32:135–154. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Laughney AM, et al. Regenerative lineages and immune-mediated pruning in lung cancer metastasis. Nat. Med. 2020;26:259–269. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0750-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Lavin Y, et al. Innate immune landscape in early lung adenocarcinoma by paired single-cell analyses. Cell. 2017;169:750–765.e717. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.04.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Fischer GM, et al. Molecular profiling reveals unique immune and metabolic features of melanoma brain metastases. Cancer Disco. 2019;9:628–645. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Friebel E, et al. Single-cell mapping of human brain cancer reveals tumor-specific instruction of tissue-invading leukocytes. Cell. 2000;181:1626–1642.e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Wang, L. et al. Single-cell map of diverse immune phenotypes in the metastatic brain tumor microenvironment of non small cell lung cancer. bioRxiv. Preprint at 10.1101/2019.12.30.890517 (2019).
- 73.Mao XY, et al. Live or let die: neuroprotective and anti-cancer effects of nutraceutical antioxidants. Pharm. Ther. 2018;183:137–151. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Parks SK, Mueller-Klieser W, Pouyssegur J. Lactate and acidity in the cancer microenvironment. Annu Rev. Canc Biol. 2020;4:141–158. [Google Scholar]
- 75.Peck B, Schulze A. Lipid metabolism at the nexus of diet and tumor microenvironment. Trends Cancer. 2019;5:693–703. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Vaupel P, Kallinowski F, Okunieff P. Blood flow, oxygen and nutrient supply, and metabolic microenvironment of human tumors: a review. Cancer Res. 1989;49:6449–6465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Warburg O, Wind F, Negelein E. The metabolism of tumors in the body. J. Gen. Physiol. 1927;8:519–530. doi: 10.1085/jgp.8.6.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Colegio OR, et al. Functional polarization of tumour-associated macrophages by tumour-derived lactic acid. Nature. 2014;513:559–563. doi: 10.1038/nature13490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Angelin A, et al. Foxp3 Reprograms T Cell Metabolism to Function in Low-Glucose, High-Lactate Environments. Cell Metab. 2017;25:1282–1293.e1287. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.12.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Hunt TK, et al. Aerobically derived lactate stimulates revascularization and tissue repair via redox mechanisms. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007;9:1115–1124. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Hensley CT, Wasti AT, DeBerardinis RJ. Glutamine and cancer: cell biology, physiology, and clinical opportunities. J. Clin. Invest. 2013;123:3678–3684. doi: 10.1172/JCI69600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Altman BJ, Stine ZE, Dang CV. From Krebs to clinic: glutamine metabolism to cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2016;16:619–634. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Li T, Le A. Glutamine metabolism in cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018;1063:13–32. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-77736-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Yang L, Venneti S, Nagrath D. Glutaminolysis: a hallmark of cancer metabolism. Annu Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017;19:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071516-044546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Elia I, et al. Breast cancer cells rely on environmental pyruvate to shape the metastatic niche. Nature. 2019;568:117–121. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0977-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Weinberg, F., Ramnath, N. & Nagrath, D. Reactive oxygen species in the tumor microenvironment: an overview. Cancers (Basel)11, 1191 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 87.Chandel NS, et al. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species trigger hypoxia-induced transcription. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1998;95:11715–11720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.20.11715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Chandel NS, et al. Reactive oxygen species generated at mitochondrial complex III stabilize hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha during hypoxia: a mechanism of O2 sensing. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:25130–25138. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M001914200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Capparelli C, et al. CTGF drives autophagy, glycolysis and senescence in cancer-associated fibroblasts via HIF1 activation, metabolically promoting tumor growth. Cell Cycle. 2012;11:2272–2284. doi: 10.4161/cc.20717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Weinberg F, et al. Mitochondrial metabolism and ROS generation are essential for Kras-mediated tumorigenicity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:8788–8793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1003428107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Qu P, Boelte KC, Lin PC. Negative regulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer. Immunol. Invest. 2012;41:562–580. doi: 10.3109/08820139.2012.685538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Sena LA, et al. Mitochondria are required for antigen-specific T cell activation through reactive oxygen species signaling. Immunity. 2013;38:225–236. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.10.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Costa A, Scholer-Dahirel A, Mechta-Grigoriou F. The role of reactive oxygen species and metabolism on cancer cells and their microenvironment. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;25:23–32. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Maj T, et al. Oxidative stress controls regulatory T cell apoptosis and suppressor activity and PD-L1-blockade resistance in tumor. Nat. Immunol. 2017;18:1332–1341. doi: 10.1038/ni.3868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ligtenberg MA, et al. Coexpressed catalase protects chimeric antigen receptor-redirected T cells as well as bystander cells from oxidative stress-induced loss of antitumor activity. J. Immunol. 2016;196:759–766. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ma XZ, et al. Cholesterol induces CD8(+) T cell exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Metab. 2019;30:143–156.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Nieman KM, et al. Adipocytes promote ovarian cancer metastasis and provide energy for rapid tumor growth. Nat. Med. 2011;17:1498–U1207. doi: 10.1038/nm.2492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Gharpure KM, et al. FABP4 as a key determinant of metastatic potential of ovarian cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:2923. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04987-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Webb BA, Chimenti M, Jacobson MP, Barber DL. Dysregulated pH: a perfect storm for cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2011;11:671–677. doi: 10.1038/nrc3110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Chiche J, Brahimi-Horn MC, Pouyssegur J. Tumour hypoxia induces a metabolic shift causing acidosis: a common feature in cancer. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2010;14:771–794. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00994.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Sonveaux P, et al. Targeting lactate-fueled respiration selectively kills hypoxic tumor cells in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008;118:3930–3942. doi: 10.1172/JCI36843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Peppicelli S, et al. Metformin is also effective on lactic acidosis-exposed melanoma cells switched to oxidative phosphorylation. Cell Cycle. 2016;15:1908–1918. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1191706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Lamonte G, et al. Acidosis induces reprogramming of cellular metabolism to mitigate oxidative stress. Cancer Metab. 2013;1:23. doi: 10.1186/2049-3002-1-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Mazzio EA, Boukli N, Rivera N, Soliman KFA. Pericellular pH homeostasis is a primary function of the Warburg effect: Inversion of metabolic systems to control lactate steady state in tumor cells. Cancer Sci. 2012;103:422–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02206.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Gillies RJ, Pilot C, Marunaka Y, Fais S. Targeting acidity in cancer and diabetes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer. 2019;1871:273–280. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Parolini I, et al. Microenvironmental pH is a key factor for exosome traffic in tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009;284:34211–34222. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.041152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Yanez-Mo M, et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2015;4:27066. doi: 10.3402/jev.v4.27066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Sauvant C, et al. Acidosis induces multi-drug resistance in rat prostate cancer cells (AT1) in vitro and in vivo by increasing the activity of the p-glycoprotein via activation of p38. Int. J. Cancer. 2008;123:2532–2542. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Monje M, et al. Roadmap for the emerging field of cancer neuroscience. Cell. 2020;181:219–222. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Liebig C, et al. Perineural invasion in cancer: a review of the literature. Cancer. 2009;115:3379–3391. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.You H, et al. Sight and switch off: nerve density visualization for interventions targeting nerves in prostate cancer. Sci. Adv. 2020;6:eaax6040. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax6040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Hanoun M, Maryanovich M, Arnal-Estape A, Frenette PS. Neural regulation of hematopoiesis, inflammation, and cancer. Neuron. 2015;86:360–373. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.01.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Coarfa C, et al. Influence of the neural microenvironment on prostate cancer. Prostate. 2018;78:128–139. doi: 10.1002/pros.23454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Amit M, et al. Loss of p53 drives neuron reprogramming in head and neck cancer. Nature. 2020;578:449–454. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1996-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Amit M, Na’ara S, Gil Z. Mechanisms of cancer dissemination along nerves. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2016;16:399–408. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Schulz A, et al. The importance of nerve microenvironment for schwannoma development. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;132:289–307. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1583-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Gillespie S, Monje M. The neural regulation of cancer. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2020;4:371–390. [Google Scholar]
- 118.Venkatesh HS, et al. Neuronal activity promotes glioma growth through neuroligin-3 secretion. Cell. 2015;161:803–816. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.04.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Katayama Y, et al. Signals from the sympathetic nervous system regulate hematopoietic stem cell egress from bone marrow. Cell. 2006;124:407–421. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.10.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Osswald M, et al. Brain tumour cells interconnect to a functional and resistant network. Nature. 2015;528:93–98. doi: 10.1038/nature16071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Venkataramani V, et al. Glutamatergic synaptic input to glioma cells drives brain tumour progression. Nature. 2019;573:532–538. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1564-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Venkatesh HS, et al. Electrical and synaptic integration of glioma into neural circuits. Nature. 2019;573:539–545. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1563-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Zeng Q, et al. Synaptic proximity enables NMDAR signalling to promote brain metastasis. Nature. 2019;573:526–531. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1576-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Achrol AS, et al. Brain metastases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019;5:5. doi: 10.1038/s41572-018-0055-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Mao XY, et al. Gap junction as an intercellular glue: Emerging roles in cancer EMT and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2016;381:133–137. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.07.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Chen Q, et al. Carcinoma-astrocyte gap junctions promote brain metastasis by cGAMP transfer. Nature. 2016;533:493–498. doi: 10.1038/nature18268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Nagelkerke A, Bussink J, Rowan AE, Span PN. The mechanical microenvironment in cancer: How physics affects tumours. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015;35:62–70. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Panciera T, Azzolin L, Cordenonsi M, Piccolo S. Mechanobiology of YAP and TAZ in physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017;18:758–770. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Plaks V, Kong NW, Werb Z. The cancer stem cell niche: how essential is the niche in regulating stemness of tumor cells? Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16:225–238. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.02.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Vermeulen L, et al. Wnt activity defines colon cancer stem cells and is regulated by the microenvironment. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010;12:468–476. doi: 10.1038/ncb2048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Calvo F, et al. Mechanotransduction and YAP-dependent matrix remodelling is required for the generation and maintenance of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013;15:637–646. doi: 10.1038/ncb2756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Junttila MR, de Sauvage FJ. Influence of tumour micro-environment heterogeneity on therapeutic response. Nature. 2013;501:346–354. doi: 10.1038/nature12626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Xiong G, et al. Hsp47 promotes cancer metastasis by enhancing collagen-dependent cancer cell-platelet interaction. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2020;117:3748–3758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1911951117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Lu PF, Weaver VM, Werb Z. The extracellular matrix: a dynamic niche in cancer progression. J. Cell Biol. 2012;196:395–406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201102147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Cooper J, Giancotti FG. Integrin signaling in cancer: mechanotransduction, stemness, epithelial plasticity, and therapeutic resistance. Cancer Cell. 2019;35:347–367. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.01.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Horikawa N, et al. Anti-VEGF therapy resistance in ovarian cancer is caused by GM-CSF-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cell recruitment. Br. J. cancer. 2020;122:778–788. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0725-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Tamura R, et al. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the hypoxic and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment: perspectives for therapeutic implications. Med. Oncol. 2019;37:2. doi: 10.1007/s12032-019-1329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Semenza GL. Tumor metabolism: cancer cells give and take lactate. J. Clin. Investig. 2008;118:3835–3837. doi: 10.1172/JCI37373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Zhang X, et al. Beyond a chemopreventive reagent, aspirin is a master regulator of the hallmarks of cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019;145:1387–1403. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-02902-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Ivashkiv LB. The hypoxia-lactate axis tempers inflammation. Nature Rev. Immunol. 2020;20:85–86. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0259-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Deepak KGK, et al. Tumor microenvironment: Challenges and opportunities in targeting metastasis of triple negative breast cancer. Pharm. Res. 2020;153:104683. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Gilkes DM, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) promotes extracellular matrix remodeling under hypoxic conditions by inducing P4HA1, P4HA2, and PLOD2 expression in fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2013;288:10819–10829. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.442939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 143.Mohammadpour H, et al. beta2 adrenergic receptor-mediated signaling regulates the immunosuppressive potential of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J. Clin. Invest. 2019;129:5537–5552. doi: 10.1172/JCI129502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Inigo-Marco I, Alonso MM. Destress and do not suppress: targeting adrenergic signaling in tumor immunosuppression. J. Clin. Invest. 2019;129:5086–5088. doi: 10.1172/JCI133115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Sloan EK, et al. The sympathetic nervous system induces a metastatic switch in primary breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70:7042–7052. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Inbar S, et al. Do stress responses promote leukemia progression? An animal study suggesting a role for epinephrine and prostaglandin-E-2 through reduced NK activity. PLos ONE. 2011;6:e19246. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Mohammadpour H, et al. Blockade of host beta2-adrenergic receptor enhances graft-versus-tumor effect through modulating APCs. J. Immunol. 2018;200:2479–2488. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Cole SW, Sood AK. Molecular pathways: beta-adrenergic signaling in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012;18:1201–1206. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Cole SW, et al. Computational identification of gene-social environment interaction at the human IL6 locus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:5681–5686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911515107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Li Y, et al. Targeting the tumor microenvironment to overcome immune checkpoint blockade therapy resistance. Immunol. Lett. 2020;220:88–96. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2019.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.McCarty MF, Whitaker J. Manipulating tumor acidification as a cancer treatment strategy. Alter. Med. Rev. 2010;15:264–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Roma-Rodrigues C, Mendes R, Baptista PV, Fernandes AR. Targeting tumor microenvironment for cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:840. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Semenza GL. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2003;3:721–732. doi: 10.1038/nrc1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Semenza GL. Pharmacologic targeting of hypoxia-inducible factors. Annu. Rev. Pharm. 2019;59:379–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010818-021637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Binnewies M, et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat. Med. 2018;24:541–550. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0014-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Taube JM, et al. Implications of the tumor immune microenvironment for staging and therapeutics. Mod. Pathol. 2018;31:214–234. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2017.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Pyonteck SM, et al. CSF-1R inhibition alters macrophage polarization and blocks glioma progression. Nat. Med. 2013;19:1264–1272. doi: 10.1038/nm.3337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Quail DF, et al. The tumor microenvironment underlies acquired resistance to CSF-1R inhibition in gliomas. Science. 2016;352:aad3018. doi: 10.1126/science.aad3018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Pushpakom S, et al. Drug repurposing: progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Disco. 2019;18:41–58. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2018.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Verbaanderd C, Meheus L, Huys I, Pantziarka P. Repurposing drugs in oncology: next steps. trends. Trends Cancer. 2017;3:543–546. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2017.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Sleire L, et al. Drug repurposing in cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2017;124:74–91. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Sung H, et al. Global patterns in excess body weight and the associated cancer burden. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019;69:88–112. doi: 10.3322/caac.21499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Nishihara R, et al. Aspirin use and risk of colorectal cancer according to BRAF mutation status. JAMA. 2013;309:2563–2571. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.6599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Ma J, et al. The anti-tumor effect of aspirin: what we know and what we expect. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017;95:656–661. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Vaughan LE, et al. Aspirin use and the incidence of breast, colon, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers in elderly women in the Iowa Women’s Health Study. Cancer Causes Control. 2016;27:1395–1402. doi: 10.1007/s10552-016-0804-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Coyle C, et al. ADD-ASPIRIN: a phase III, double-blind, placebo controlled, randomised trial assessing the effects of aspirin on disease recurrence and survival after primary therapy in common non-metastatic solid tumours. Contemp. Clin. Trials. 2016;51:56–64. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2016.10.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Lu ML, et al. Aspirin sensitizes cancer cells to TRAIL-Induced apoptosis by reducing survivin levels. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008;14:3168–3176. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Yue W, Yang CS, DiPaola RS, Tan XL. Repurposing of metformin and aspirin by targeting AMPK-mTOR and inflammation for pancreatic cancer prevention and treatment. Cancer Prev. Res. (Philos.) 2014;7:388–397. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-13-0337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Riesenberg BP, et al. Cutting edge: targeting thrombocytes to rewire anticancer immunity in the tumor microenvironment and potentiate efficacy of PD-1 blockade. J. Immunol. 2019;203:1105–1110. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Johnson KE, et al. Aspirin inhibits platelets from reprogramming breast tumor cells and promoting metastasis. Blood Adv. 2019;3:198–211. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018026161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Lucotti S, et al. Aspirin blocks formation of metastatic intravascular niches by inhibiting platelet-derived COX-1/thromboxane A(2) J. Clin. Investig. 2019;129:1845–1862. doi: 10.1172/JCI121985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Hsieh, C. C. & Wang, C. H. Aspirin disrupts the crosstalk of angiogenic and inflammatory cytokines between 4T1 breast cancer cells and macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm.2018, 6380643 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 173.Gilligan MM, et al. Aspirin-triggered proresolving mediators stimulate resolution in cancer. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2019;116:6292–6297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1804000116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Hsu CS, Li Y. Aspirin potently inhibits oxidative DNA strand breaks: implications for cancer chemoprevention. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002;293:705–709. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00271-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Henry WS, et al. Aspirin suppresses growth in PI3K-mutant breast cancer by activating AMPK and Inhibiting mTORC1 signaling. Cancer Res. 2017;77:790–801. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Liu YX, et al. Aspirin inhibits the proliferation of hepatoma cells through controlling GLUT1-mediated glucose metabolism. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2019;40:122–132. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0014-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Harris RE, Beebe-Donk J, Alshafie GA. Reduced risk of human lung cancer by selective cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) blockade: results of a case control study. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2007;3:328–334. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.3.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Hernandez-Diaz S, Rodriguez LAG. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer. 2007;120:1565–1572. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Jacobs EJ, et al. A large cohort study of long-term daily use of adult-strength aspirin and cancer incidence. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:608–615. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djk132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Burn J, et al. Long-term effect of aspirin on cancer risk in carriers of hereditary colorectal cancer: an analysis from the CAPP2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2011;378:2081–2087. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61049-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Simon TG, Ludvigsson JF. Association between aspirin and hepatocellular carcinoma REPLY. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382:2481–2482. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2009497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Dannenberg AJ, Subbaramaiah K. Targeting cyclooxygenase-2 in human neoplasia: rationale and promise. Cancer Cell. 2003;4:431–436. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Zelenay S, et al. Cyclooxygenase-dependent tumor growth through evasion of immunity. Cell. 2015;162:1257–1270. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Le DT, et al. PD-1 blockade in tumors with mismatch-repair deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015;372:2509–2520. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1500596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Mandal R, et al. Genetic diversity of tumors with mismatch repair deficiency influences anti-PD-1 immunotherapy response. Science. 2019;364:485–491. doi: 10.1126/science.aau0447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Chalabi M, et al. Neoadjuvant immunotherapy leads to pathological responses in MMR-proficient and MMR-deficient early-stage colon cancers. Nat. Med. 2020;26:566–576. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0805-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Pritchard R, et al. Celecoxib inhibits mitochondrial O2 consumption, promoting ROS dependent death of murine and human metastatic cancer cells via the apoptotic signalling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018;154:318–334. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Groen HJ, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled phase III study of docetaxel plus carboplatin with celecoxib and cyclooxygenase-2 expression as a biomarker for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: the NVALT-4 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011;29:4320–4326. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.35.5214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Altorki NK, et al. Chemotherapy induces the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005;11:4191–4197. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Csiki I, et al. Targeting cyclooxygenase-2 in recurrent non-small cell lung cancer: a phase II trial of celecoxib and docetaxel. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005;11:6634–6640. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Hamy AS, et al. Celecoxib with neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer might worsen outcomes differentially by COX-2 expression and ER status: exploratory analysis of the REMAGUS02 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019;37:624–635. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Kim J, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is induced by celecoxib treatment in lung cancer cells and is transferred to neighbor cells via exosomes. Int. J. Oncol. 2018;52:613–620. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Tang J, et al. β-Adrenergic system, a backstage manipulator regulating tumour progression and drug target in cancer therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013;23:533–542. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Benish M, et al. Perioperative use of beta-blockers and COX-2 inhibitors may improve immune competence and reduce the risk of tumor metastasis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008;15:2042–2052. doi: 10.1245/s10434-008-9890-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Watkins JL, et al. Clinical impact of selective and nonselective beta-blockers on survival in patients with ovarian cancer. Cancer. 2015;121:3444–3451. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Yamamoto H, et al. Landiolol, an ultra-short acting beta-1 blocker, for preventing postoperative lung cancer recurrence: study protocol for a phase III, multicenter randomized trial with two parallel groups of patients. Trials. 2019;20:715. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3904-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Lindgren ME, et al. Beta-blockers may reduce intrusive thoughts in newly diagnosed cancer patients. Psycho-Oncol. 2013;22:1889–1894. doi: 10.1002/pon.3233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Qiao GX, et al. Adrenergic signaling: a targetable checkpoint limiting development of the antitumor immune response. Front. Immunol. 2018;9:164. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Jean Wrobel L, et al. Propranolol induces a favourable shift of anti-tumor immunity in a murine spontaneous model of melanoma. Oncotarget. 2016;7:77825–77837. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Qiao G, et al. beta-Adrenergic signaling blocks murine CD8(+) T-cell metabolic reprogramming during activation: a mechanism for immunosuppression by adrenergic stress. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019;68:11–22. doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-2243-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Avila MS, et al. Carvedilol for prevention of chemotherapy-related cardiotoxicity: The CECCY Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018;71:2281–2290. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.02.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Kalay N, et al. Protective effects of carvedilol against anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006;48:2258–2262. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.07.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Bansal N, et al. Strategies to prevent anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity in cancer survivors. Cardiooncology. 2019;5:18. doi: 10.1186/s40959-019-0054-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Cardinale D, Iacopo F, Cipolla CM. Cardiotoxicity of anthracyclines. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020;7:26. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.00026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Wang JC, et al. Suppression of hypoxia-induced excessive angiogenesis by metformin via elevating tumor blood perfusion. Oncotarget. 2017;8:73892–73904. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Chappell JC, Payne LB, Rathmell WK. Hypoxia, angiogenesis, and metabolism in the hereditary kidney cancers. J. Clin. Invest. 2019;129:442–451. doi: 10.1172/JCI120855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Touyz RM, Herrmann SMS, Herrmann J. Vascular toxicities with VEGF inhibitor therapies-focus on hypertension and arterial thrombotic events. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2018;12:409–425. doi: 10.1016/j.jash.2018.03.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Stati T, et al. beta-Blockers promote angiogenesis in the mouse aortic ring assay. J. Cardiovasc Pharm. 2014;64:21–27. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Sorensen GV, et al. Use of beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin ii receptor blockers, and risk of breast cancer recurrence: a Danish Nationwide Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013;31:2265–2272. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.43.9190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Jansen L, et al. Pre- and post-diagnostic beta-blocker use and prognosis after colorectal cancer: results from a population-based study. Int. J. Cancer. 2017;141:62–71. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Bassez G, et al. Improved mobility with metformin in patients with myotonic dystrophy type 1: a randomized controlled trial. Brain. 2018;141:2855–2865. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Tseng CH. Metformin decreases risk of tuberculosis infection in Type 2 diabetes patients. J. Clin. Med. 2018;7:264. doi: 10.3390/jcm7090264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Kurelac I, et al. The multifaceted effects of metformin on tumor microenvironment. Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 2020;98:90–97. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2019.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Cheung KS, et al. Metformin use and gastric cancer risk in diabetic patients after helicobacter pylori eradication. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 2019;111:484–489. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djy144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Cho YY, et al. Protective effect of metformin against thyroid cancer development: a population-based study in Korea. Thyroid. 2018;28:864–870. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Seliger C, et al. Use of metformin and survival of patients with high-grade glioma. Int. J. Cancer. 2019;144:273–280. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Chang YT, et al. Dose-dependent relationship between metformin and colorectal cancer occurrence among patients with type 2 diabetes-A nationwide cohort study. Transl. Oncol. 2018;11:535–541. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.02.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Pusceddu S, et al. Metformin use is associated with longer progression-free survival of patients with diabetes and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors receiving everolimus and/or somatostatin analogues. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:479–489.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Cha JH, et al. Metformin promotes antitumor immunity via endoplasmic-reticulum-associated degradation of PD-L1. Mol. Cell. 2018;71:606–620.e607. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.07.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Mahmoud SMA, et al. Tumor-infiltrating CD8(+) lymphocytes predict clinical outcome in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011;29:1949–1955. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.5037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Wimberly H, et al. PD-L1 Expression correlates with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015;3:326–332. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Talarico G, et al. Aspirin and atenolol enhance metformin activity against breast cancer by targeting both neoplastic and microenvironment cells. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:18673. doi: 10.1038/srep18673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Fendt SM, et al. Metformin decreases glucose oxidation and increases the dependency of prostate cancer cells on reductive glutamine metabolism. Cancer Res. 2013;73:4429–4438. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Tebbe C, et al. Metformin limits the adipocyte tumor-promoting effect on ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 2014;5:4746–4764. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Hart PC, et al. Mesothelial cell HIF1alpha expression is metabolically downregulated by metformin to prevent oncogenic tumor-stromal crosstalk. Cell Rep. 2019;29:4086–4098 e4086. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Scharping NE, et al. Efficacy of PD-1 blockade is potentiated by metformin-induced reduction of tumor hypoxia. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017;5:9–16. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Sivalingam VN, et al. Hypoxia and hyperglycaemia determine why some endometrial tumours fail to respond to metformin. Brit. J. Cancer. 2020;122:62–71. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0627-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Chen G, et al. Metformin suppresses gastric cancer progression through calmodulinlike protein 3 secreted from tumorassociated fibroblasts. Oncol. Rep. 2019;41:405–414. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Xu S, et al. Metformin suppresses tumor progression by inactivating stromal fibroblasts in ovarian cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018;17:1291–1302. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Elgendy M, et al. Combination of Hypoglycemia and Metformin Impairs Tumor Metabolic Plasticity and Growth by Modulating the PP2A-GSK3beta-MCL-1 Axis. Cancer Cell. 2019;35:798–815.e795. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990;343:425–430. doi: 10.1038/343425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Liu JC, et al. Statins dose-dependently exert a significant chemopreventive effect on colon cancer in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonarydisease: A population-based cohort study. Oncotarget. 2016;7:65270–65283. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Larsen SB, et al. Postdiagnosis statin use and mortality in danish patients with prostate cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017;35:3290–3297. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.71.8981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Beckwitt CH, Brufsky A, Oltvai ZN, Wells A. Statin drugs to reduce breast cancer recurrence and mortality. Breast Cancer Res. 2018;20:144. doi: 10.1186/s13058-018-1066-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Mehibel M, et al. Statin-induced metabolic reprogramming in head and neck cancer: a biomarker for targeting monocarboxylate transporters. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:16804. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35103-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Clendening JW, et al. Exploiting the mevalonate pathway to distinguish statin-sensitive multiple myeloma. Blood. 2010;115:4787–4797. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-230508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Kobayashi Y, et al. Mevalonate pathway antagonist suppresses formation of serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma and ovarian carcinoma in mouse models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015;21:4652–4662. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-3368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Kutner JS, et al. Safety and benefit of discontinuing statin therapy in the setting of advanced, life-limiting illness: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015;175:691–700. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.0289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Voelker R. Statin use may stop when illness is terminal, study says. JAMA. 2014;312:221. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.8845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Galland S, et al. Attenuation of the pro-inflammatory signature of lung cancer-derived mesenchymal stromal cells by statins. Cancer Lett. 2020;484:50–64. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Dewhirst MW, et al. Microvascular studies on the origins of perfusion-limited hypoxia. Br. J. Cancer Suppl. 1996;27:S247–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Devalaraja S, et al. Tumor-derived retinoic acid regulates intratumoral monocyte differentiation to promote immune suppression. Cell. 2020;180:1098–1114 e1016. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Kovacs T, et al. The microbiome as a component of the tumor microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020;1225:137–153. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-35727-6_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Xavier JB, et al. The cancer microbiome: distinguishing direct and indirect effects requires a systemic view. Trends Cancer. 2020;6:192–204. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.01.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Bullman S, et al. Analysis of Fusobacterium persistence and antibiotic response in colorectal cancer. Science. 2017;358:1443–1448. doi: 10.1126/science.aal5240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Shi YY, et al. Intratumoral accumulation of gut microbiota facilitates CD47-based immunotherapy via STING signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2020;217:e20192282. doi: 10.1084/jem.20192282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.Nejman D, et al. The human tumor microbiome is composed of tumor type-specific intracellular bacteria. Science. 2020;368:973–980. doi: 10.1126/science.aay9189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Dassler-Plenker J, Kuttner V, Egeblad M. Communication in tiny packages: exosomes as means of tumor-stroma communication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer. 2020;1873:188340. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 249.Smith EA, Hodges HC. The spatial and genomic hierarchy of tumor ecosystems revealed by single-cell technologies. Trends cancer. 2019;5:411–425. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.05.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Moncada R, et al. Integrating microarray-based spatial transcriptomics and single-cell RNA-seq reveals tissue architecture in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020;38:333–342. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0392-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Berglund E, et al. Spatial maps of prostate cancer transcriptomes reveal an unexplored landscape of heterogeneity. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:2419. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04724-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Stahl PL, et al. Visualization and analysis of gene expression in tissue sections by spatial transcriptomics. Science. 2016;353:78–82. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf2403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Thrane K, et al. Spatially Resolved Transcriptomics Enables Dissection of Genetic Heterogeneity in Stage III Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2018;78:5970–5979. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Corsello SM, et al. Discovering the anti-cancer potential of non-oncology drugs by systematic viability profiling. Nat. Cancer. 2020;1:235–248. doi: 10.1038/s43018-019-0018-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]