Abstract
Infectious diarrhea affects over four billion individuals annually and causes over a million deaths each year. Though not typically prescribed for treatment of uncomplicated diarrheal disease, antimicrobials serve as a critical part of the armamentarium used to treat severe or persistent cases. Due to widespread over- and misuse of antimicrobials, there has been an alarming increase in global resistance, for which a standardized methodology for geographic surveillance would be highly beneficial. To demonstrate that a standardized methodology could be used to provide molecular surveillance of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) genes, we initiated a pilot study to test 130 diarrheal pathogens (Campylobacter spp., Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Shigella spp.) from the USA, Peru, Egypt, Cambodia, and Kenya for the presence/absence of over 200 AMR determinants. We detected a total of 55 different determinants conferring resistance to ten different categories of antimicrobials: genes detected in ≥ 25 samples included blaTEM, tet(A), tet(B), mac(A), mac(B), aadA1/A2, strA, strB, sul1, sul2, qacEΔ1, cmr, and dfrA1. The number of determinants per strain ranged from none (several Campylobacter spp. strains) to sixteen, with isolates from Egypt harboring a wider variety and greater number of genes per isolate than other sites. Two samples harbored carbapenemase genes, blaOXA-48 or blaNDM. Genes conferring resistance to azithromycin (ere(A), mph(A)/mph(K), erm(B)), a first-line therapeutic for severe diarrhea, were detected in over 10% of all Enterobacteriaceae tested: these included >25% of the Enterobacteriaceae from Egypt and Kenya. Forty-six percent of the Egyptian Enterobacteriaceae harbored genes encoding CTX-M-1 or CTX-M-9 families of extended-spectrum β-lactamases. Overall, the data provide cross-comparable resistome information to establish regional trends in support of international surveillance activities and potentially guide geospatially informed medical care.
Keywords: diarrheal pathogen, antimicrobial resistance, Campylobacter, Shigella, Escherichia coli, Salmonella, microarray
1. Introduction
Diarrheal disease ranks among the top 10 leading causes of death for all ages and fifth for children under five years of age, affecting over four billion individuals globally each year in 2016 and 2017 [1,2,3]. Low-income countries are still disproportionately affected by infectious diarrhea [1,4], likely due to poor access to safe drinking water, sanitation, and healthcare [3,5,6].
Many cases of intestinal disease are self-limiting and can be effectively treated with oral rehydration solutions and antisecretory/antimotility drugs [7,8]. While antimicrobial use is not generally recommended as a standard treatment, it is, however, indicated for some clinically recognizable severe or persistent cases (e.g., cholera, dysenteric shigellosis), in immunocompromised individuals or those with underlying risk factors [7,8,9], and to reduce the severity and duration of travelers’ diarrhea [10]. In spite of recommendations for limited use, up to 40% of children under five with diarrhea and up to 80% of persons with acute diarrhea are treated with antimicrobials, regardless of presentation or cause [6,11,12].
Veterinary and aquaculture use is also responsible for a large proportion of global antimicrobial consumption [13,14,15,16,17,18]. For terrestrial animal farming, antimicrobials are used as both prophylactics and growth promoters, whereas they are used in aquaculture to both treat and avoid opportunistic infections of farmed species due to crowded, stressful, or suboptimal culture conditions [18]. To mitigate the potential for animal-to-human transmission of resistance to clinically relevant drugs, many developed countries have restricted antimicrobial use in veterinary and aquacultural practices; however, many low- and middle-income nations lack such national policies or the ability to enforce them [15,19]. Furthermore, though the aquaculture industry has made great strides in antimicrobial stewardship and limiting the number of compounds used, drug spillover from aquacultural use has the potential to affect multiple ecosystems [16,17,20] whereas spillover of drugs from terrestrial animal husbandry is more limited to soil ecosystems. Regardless of the original source of selective pressure for development of drug resistance—human, livestock, or aquaculture—there exists an interplay between multiple ecosystems to disseminate and exchange antimicrobial resistance determinants (ARDs) [16,21,22]. For this reason, a unified, multifaceted approach (e.g., One Health) is needed in order to address both the causes and sequelae of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) [16,23].
Pertinent to the current study, there has been an alarming increase in resistance to drugs commonly used to treat diarrheal illness throughout the world [6,10,24]. This AMR is associated with increased morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs and has resulted in significant reductions in gross domestic product in many nations [2,25,26].
Compounding the problem of global AMR are geographical differences in pathogen and resistance profiles. Therefore, selecting an appropriate and effective therapeutic strategy for infectious diarrhea—when needed—requires situational awareness of the prevalence and types of AMR pathogens and mechanisms for resistance within each geographic region. To demonstrate that a standardized methodology could be used to provide cross-comparable molecular surveillance of AMR genes, we initiated a pilot study to test four genera of diarrheal pathogens for > 200 ARDs. Human clinical isolates were obtained from five geographic locations spanning four continents (North and South America, Southeast Asia, and North and East Africa). Not surprisingly, testing in this manner elucidated some generalized trends in AMR in the three Enterobacteriaceae in various geographic regions.
2. Results and Discussion
The United States (US) Department of Defense has established its Global Emerging Infections Surveillance and Response System (GEIS) to provide geographically relevant disease surveillance outside the continental US. While the GEIS centralized laboratories have developed standardized protocols for molecular characterization of infectious diseases, many of the surveillance laboratories implement their own protocols for disease detection, identification, and analysis, making comparisons between partner laboratories challenging. For this reason, we sought to demonstrate a harmonized strategy for molecular AMR surveillance in isolates collected at the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and four GEIS laboratories with their own laboratory-specific and/or narrow spectrum protocols.
In this study, we tested a set of diarrheal isolates collected at clinical sites in the USA, Cambodia, Egypt, Peru, and Kenya. Isolates included Campylobacter spp., Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Shigella spp. These genera were chosen to reflect the top four global bacterial diarrheal pathogens and were responsible for over 430,000 deaths in 2016 [3]. Up to 32 strains from each of the four genera were selected on the basis of phenotypic tetracycline (TET) resistance. Effective against a wide variety of bacteria and protozoan parasites, TETs are first-line antimicrobials used worldwide as therapeutics, are among the most commonly used drugs in agriculture and aquaculture [13,18,27,28], and have been categorized as highly important antimicrobials—with tigecycline considered a critically important antimicrobial [29]. As a result of this widespread selective pressure, ARDs for TET are now the most common of those found within the healthy human fecal microbiome in both industrialized and non-industrialized nations [30]. As TET ARDs are often co-localized on mobilizable elements with other ARDs, we posited that phenotypic TET resistance would serve as an appropriate selection criterion for surveillance of both TET-specific ARDs and those directed against other categories of antimicrobials.
2.1. Overall Population Characteristics
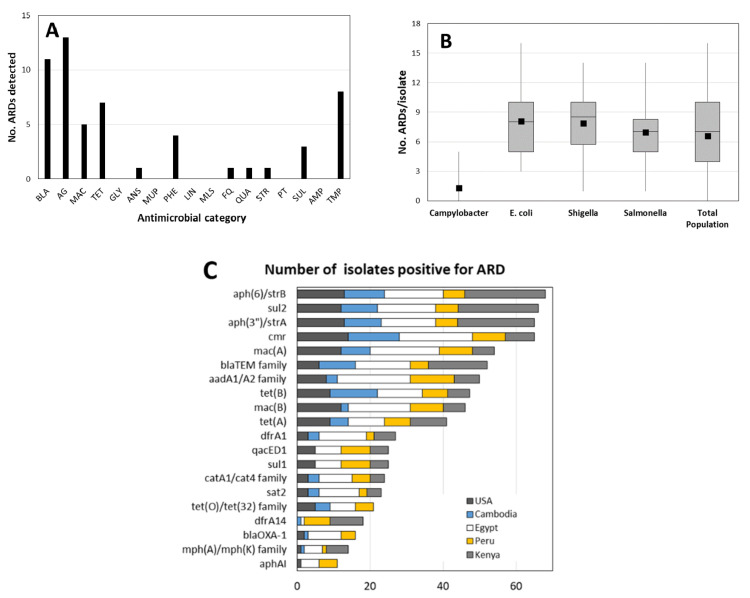
We detected a total of 55 different ARDs conferring resistance to eleven different categories of antimicrobials: β-lactams, aminoglycosides, macrolides, TETs, phenicols, streptothricins, sulfonamides, diaminopyrimidine (trimethoprim), ansamycins, and quaternary amines (Figure 1A). None of the thirteen glycopeptide, ten streptogramin, eight macrolide/lincosamide/streptogramin (MLS) resistance determinants, or ten multidrug efflux pumps were detected in the tested population. All isolates tested were negative for the following carbapenemase genes: blaGES (including extended-spectrum β-lactamase variants), blaIMI, blaIMP, blaKPC, blaOXA-23, blaOXA-24, blaOXA-51, blaOXA-58, blaSIM, blaSME, blaVIM. However, genes for OXA-48- and NDM-type carbapenemases were detected in one isolate each (described below). Given the TET-resistant selection criteria for inclusion in the study, we were somewhat surprised that fifteen isolates (two Campylobacter spp., three Shigella spp., four E. coli, and six Salmonella) were negative for all 38 TET-specific ARDs represented on the microarray. However, phenotypic TET resistance can arise from multiple intrinsic mechanisms not interrogated or detected by the microarray used here (reviewed by [31,32]): elimination or reduced expression of some outer membrane proteins, constitutive or over-expression of non-specific active efflux or araC family activators, and mutations of TET binding sites on rRNA or ribosomal proteins. Furthermore, at least 20 recently documented or predicted TET ARDs are not included in the content of the Antimicrobial Resistance Determinant Microarray (ARDM) v.2 used in this study [33,34,35,36].
Figure 1.
(A) Number of antimicrobial resistance determinants (ARDs) detected in tested population, by category; numbers in parentheses indicate total ARDs represented on microarray for that category. BLA = β-lactams (53); AG = aminoglycosides (44); MAC = macrolide (40); TET = tetracyclines (38); GLY = glycopeptides (13); ANS = ansamycins (1); MUP = mupirocin (1); PHE = phenicols (20); LIN = lincosamides (6); MLS = macrolides/lincosamides/streptogramins (13); FQ = fluoroquinolones (4); QUA = quaternary amines (2); STR = streptothricin; PT = platensimycin + platencin (1); SUL = sulfonamides (3); AMP = antimicrobial peptides (1); TMP = diaminopyrimidine. (B) Number of ARDs detected per isolate. (C) Prevalence of unique ARDs detected in >10 isolates.
The number of ARDs per strain ranged from none (several Campylobacter spp. strains) to sixteen, with median and mean values of seven and 6.58 genes per isolate, respectively (Figure 1B). Among the Enterobacteriaceae, 91% harbored genes which were predicted to cause resistance to at least three categories of antimicrobials (Table 1, top).
Table 1.
Percentage of isolates with potential resistance to multiple classes of antimicrobial compounds based on their microarray profiles.
| By Genus | ||||||||
| No. of Antimicrobial Classes | Campylobacter | E. coli | Salmonella | Shigella | ||||
| 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 1 | 74 | 0 | 3 | 4 | ||||
| 2 | 9 | 3 | 6 | 7 | ||||
| 3 | 4 | 17 | 13 | 11 | ||||
| 4 | 4 | 13 | 13 | 4 | ||||
| 5 | 0 | 10 | 25 | 20 | ||||
| 6 | 0 | 13 | 31 | 4 | ||||
| 7 | 0 | 27 | 9 | 31 | ||||
| 8 | 0 | 17 | 0 | 16 | ||||
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | ||||
| % potentially resistant to: | ||||||||
| ≥3 classes | 8 | 97 | 91 | 89 | ||||
| ≥6 classes | 0 | 57 | 40 | 53 | ||||
| No. of isolates tested | 23 | 30 | 32 | 45 | ||||
| By geographic location | ||||||||
| No. of Antimicrobial Classes | USA | Cambodia | Egypt | Peru | Kenya | |||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | |||
| 1 | 15 | 30 | 16 | 17 | 0 | |||
| 2 | 7 | 13 | 6 | 4 | 0 | |||
| 3 | 19 | 17 | 0 | 8 | 17 | |||
| 4 | 15 | 13 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 15 | 4 | 9 | 25 | 33 | |||
| 6 | 7 | 4 | 16 | 13 | 17 | |||
| 7 | 19 | 17 | 22 | 13 | 25 | |||
| 8 | 4 | 0 | 28 | 4 | 4 | |||
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | |||
| % potentially resistant to: | ||||||||
| ≥3 classes | 78 | 57 | 78 | 71 | 100 | |||
| ≥6 classes | 30 | 21 | 66 | 34 | 46 | |||
| No. of isolates tested | 27 | 23 | 32 | 24 | 24 | |||
The genes most commonly observed amongst all of the tested isolates were strA, strB, sul2, and cmr, which were all detected in at least 40% of all isolates and in over half of the Enterobacteriaceae isolates tested (Figure 1C). The relative proportion of isolates harboring each gene varied by both genus and geographic location (Table 1, bottom); geographic differences will be discussed in greater depth in Section 2.3.
2.2. AMR Genotypes Detected in Each Genus
2.2.1. Campylobacter spp.
Campylobacter spp. cause diarrheal disease in over 150 million persons each year globally, resulting in 75,000 deaths [3,37]. Though the true incidence of campylobacteriosis is poorly described, its global prevalence has risen in parallel with increasing resistance to commonly used antimicrobials [37,38]. Of the 23 Campylobacter spp. isolates tested, fourteen were C. jejuni, six were C. coli, and three belonged to other or undefined species.
Overall, Campylobacter spp. isolates had both a more limited variety of unique ARDs detected (six in total; Figure 2) and a more limited number of genes detected per isolate than the other three genera (p < 0.001) (Table 2, Figure 1B). Resistance in Campylobacter is commonly conferred by point mutations, active efflux mechanisms, and the intrinsic low permeability of their cell membranes. Therefore, the number of horizontally transferred ARDs described in Campylobacter is limited to a few genes; coverage for Campylobacter spp. and other ε-proteobacteria accounts for < 1% of total microarray content [39].
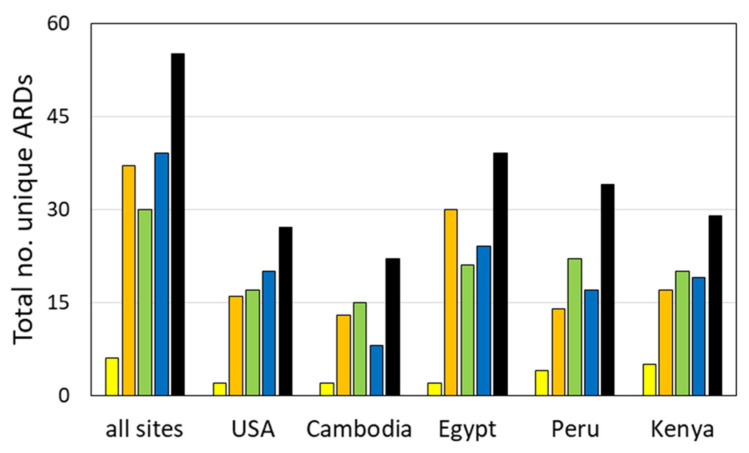
Figure 2.
Numbers of unique ARDs observed for Campylobacter spp. (yellow), E. coli (orange), Shigella spp. (green), Salmonella (blue), and all species (black) detected in isolates from each collection site.
Table 2.
ARDs detected in Campylobacter spp. by geographic location (percent of isolates positive).
| ARD | USA (n = 5) | Cambodia (n = 4) | Egypt (n = 6) | Peru (n = 7) | Kenya (n = 1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aadE | nd * | nd | nd | 14% | 100% |
| aphA3 | 20% | nd | nd | 14% | 100% |
| erm(B) | nd | nd | nd | nd | 100% |
| tet(M) | nd | nd | nd | nd | 100% |
| tet(O)/tet(32) | 100% | 100% | 100% | 71% | nd |
| sat4 | nd | nd | 17% | 14% | 100% |
* not detected.
All but three isolates harbored tet(O)/tet(32) (83%), the most common ARD for TET resistance in Campylobacter spp. Two samples were negative for all 38 TET resistance determinants on the microarray, and the third was positive for tet(M). It is likely that the two negative samples harbored tet(44) [40] (not included in microarray content) or that TET resistance arose from rRNA sequence mutations, constitutive expression of cmeABC, or over-expression of one or more efflux pumps [41]. Constitutive expression of cmeABC also contributes to fluoroquinolone resistance, which was also observed in 65% of the Camplyobacter spp. isolates where phenotypic data were reported. The tet(M)-positive sample was potentially a false-positive, as this gene has never been detected in Campylobacter spp.; however, this gene has the broadest host range of all TET ARDs [27,42]. The tet(M) reference sequence is 80% identical to tet(O)/tet(32) over the entire gene and some regions have significantly higher identity. Understanding that the microarray used here requires approx. 85–90% sequence identity for detection of similar genes (or families of genes) [43,44], it is unclear whether the redesign of probes for this gene will improve microarray specificity.
Four additional ARDs were detected amongst the Campylobacter spp. isolates. Two isolates co-harbored aadE, aphA3 family, and sat4, which are often found as part of resistance clusters in C. coli and C. jejuni plasmids and in the chromosome of some C. jejuni strains [45,46]. Erm(B) was also observed in one of these isolates; this gene confers high-level resistance to macrolides such as azithromycin (AZM), which is a first-line therapeutic for campylobacteriosis in locations where fluoroquinolone (FQ) resistance is prevalent [9,10]. Since erm(B)-aadE-aphA3-tet(O) clusters have been documented in a number of plasmids [47], co-carriage of these four genes suggests that this strain may harbor a plasmid. The prevalence of erm(B) amongst Campylobacter spp., while not historically high, has recently increased in East Asia and Southern Africa [47,48].
Other ARDs occasionally observed in Campylobacter spp. were either not detected (tet(S), aph(2)-Ic) or not included in the microarray content (tet(44), ant(6)-Ib, blaOXA-61; aacA/aphD, aac, aad6, aad9, aph(2)-3a).
2.2.2. E. coli
Diarrheagenic E. coli are responsible for over 100 million illnesses and 60,000 deaths each year [49]. Of the 30 E. coli samples provided, 12 were categorized into pathotypes based on their mechanism of virulence: enterotoxigenic—three from Kenya, two from Cambodia, two from Peru; enteroaggregative—one each from Kenya and Cambodia; enterohemorrhagic—one from Kenya; enteropathogenic—one each from Cambodia and Peru. Pathotypes for the remaining samples were not provided.
Thirty-seven unique ARDs were detected among the tested E. coli strains (Table 3, Figure 2). As expected, TET ARDs were harbored in > 80% of the E. coli strains: tet(A) (nine isolates, 30%), tet(B) (16 isolates, 53%), tet(C) (two isolates, 6%), and tet(D) (one isolate, 3%). Two Egyptian isolates harbored both tet(A) and tet(B) genes, and four isolates were negative for all 38 TET genes represented on the microarray. Other genes with high prevalence included blaTEM (64%), strA and strB (70% each), mac(A) and mac(B) (77% and 67%, respectively), cmr (83%), and sul2 (67%) (Figure 1C). Of potential clinical concern was the presence of mph(A)/mph(K) in eight isolates (27%); genes in this family confer resistance to AZM, an alternative therapeutic for severe travelers’ diarrhea and shigellosis in both children and adults [9,10,50,51,52]. While AZM is relatively ineffective for E. coli infections, interspecies transfer of AZM resistance plasmids has been documented between E. coli and Shigella spp. [53,54,55], further supporting the role of E. coli as a potential reservoir for ARDs causing clinically relevant drug resistance in Shigella spp.
Table 3.
ARDs detected in E. coli, by geographic location (percent of isolates positive).
| ARD | USA (n = 7) | Cambodia (n = 4) | Egypt (n = 8) | Peru (n = 3) | Kenya (n = 8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bla LEN | nd * | nd | 13% | nd | nd |
| blaOXA-1 family | nd | nd | 13% | nd | nd |
| blaOXA-9 family | nd | nd | 13% | nd | nd |
| blaSHV family | nd | nd | 25% | nd | nd |
| blaTEM family | 14% | 100% | 88% | 67% | 63% |
| blaCTX-M-1 family | nd | nd | 38% | nd | nd |
| blaCTX-M-9 family | nd | nd | 38% | nd | nd |
| bla NDM | nd | nd | 13% | nd | nd |
| aac(6)-Ib | nd | nd | 13% | nd | nd |
| aadA1/A2 | nd | nd | 63% | 67% | nd |
| aphA1 | nd | nd | 25% | nd | nd |
| aphA4 | 14% | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| strA | 57% | 75% | 75% | 33% | 88% |
| strB | 57% | 75% | 75% | 33% | 88% |
| aphA6 | nd | nd | 13% | nd | nd |
| mac(A) | 86% | 100% | 88% | 100% | 38% |
| mac(B) | 86% | 25% | 88% | 100% | 38% |
| mph(A)/mph(K) | 14% | 25% | 50% | nd | 25% |
| tet(A) | 29% | 25% | 50% | nd | 25% |
| tet(B) | 43% | 75% | 50% | 33% | 50% |
| tet(C) | 29% | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| tet(D) | nd | nd | 3% | nd | nd |
| catA1/cat4 | nd | 25% | 25% | 33% | 25% |
| cmr | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 38% |
| qnrS | nd | 25% | 13% | nd | nd |
| qacE Δ 1 | 14% | nd | 13% | 33% | 13% |
| sat2 | nd | nd | 38% | 33% | nd |
| sul1 | 14% | nd | 25% | 33% | 13% |
| sul2 | 57% | 75% | 63% | 33% | 88% |
| dfrA1 | nd | nd | 50% | nd | nd |
| dfrA5 | nd | nd | nd | nd | 13% |
| dfrA7 | 14% | nd | nd | nd | 13% |
| dfrA8 | nd | 50% | nd | 33% | 25% |
| dfrA12 | nd | nd | 13% | nd | nd |
| dfrA14 | nd | nd | nd | nd | 63% |
| dfrA17 | 14% | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| dfrA19 | nd | nd | 25% | nd | nd |
* not detected.
Of additional concern, six of the E. coli strains (20%) harbored a gene encoding a CTX-M type of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL). Furthermore, some blaTEM and blaSHV alleles—detected in 63% of all E. coli strains—may also encode ESBLs. ESBL phenotype is conferred to TEM and SHV β-lactamases by a wide variety of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs; see https://externalwebapps.lahey.org/studies/webt.aspx for classification and nomenclature of blaTEM and blaSHV alleles). The microarray used here is unable to detect these SNPs and therefore cannot identify the blaTEM and blaSHV alleles. We anticipate that our estimate of approx. 20% ESBL carriage in E. coli (i.e., from blaCTX-M-positive isolates) may be an underestimate; analogous situations hold for Salmonella and Shigella spp. strains. These results illustrate that techniques offering greater sequence resolution, such as amplicon or genome sequencing, may provide additional information that is important for molecular surveillance.
The blaNDM carbapenemase gene was detected in a single Egyptian E. coli isolate. Coincidentally, many of the ARDs often found on plasmids with blaNDM (e.g., blaOXA-1 family, blaTEM family, blaCTX-M-1 family, aadA1/A2, qnrS, aac(6’)-Ib) were also observed in this isolate, suggesting that this gene might be plasmid-borne. However, we did not attempt to isolate or sequence plasmids from any of the isolates tested.
Four E. coli strains harbored both qacEΔ and sul1, which are components of the 3′-conserved region of many, but not all, class 1 integrons. Similarly, three E. coli isolates co-carried three genes commonly associated with class 2 integrons—dfrA1, aadA1/A2, and sat2—suggesting the presence of class 2 integrons within these isolates. Integrase-specific PCRs confirmed the presence of class 1 (intI1) and class 2 (intI2) integrons within all samples that co-carried these ARDs (13% and 7%, respectively). These numbers likely underestimate the carriage of class 1 and class 2 integrons within this population, as they did not account for integrons with alternative structures lacking one or more “marker” genes [39,56,57,58]. Furthermore, some samples deemed microarray-positive for these “marker” genes did not have sufficient volume for the confirmatory PCRs.
Other possible gene assemblages were detected. Positive results for strA, strB, and sul2 were highly correlated (p < 0.001) and co-carriage was observed in 64% of the E. coli strains. These genes are commonly observed as a cluster in plasmids of clinical Enterobacteriaceae isolates, as well as in integrative and conjugative elements in Vibrio spp. [59,60]. Similarly, mac(A) was highly correlated with mac(B) (p < 0.001)—not surprising, since these genes are typically found in a single operon [61]. Carriage of one of both of these genes was also correlated with the presence of cmr (p < 0.001); while also part of the E. coli chromosome, cmr is found up to 40 kb away from the macAB operon.
2.2.3. Shigella spp.
Shigella spp. have a low infectious dose (only 10–100 organisms) compared to other diarrheagenic organisms and were the second leading cause of global diarrheal mortality in 2016 [3,62]. In contrast to most illnesses arising from other gastrointestinal pathogens, antimicrobials are recommended to reduce the clinical course of shigellosis and to prevent transmission. The increasing prevalence and spread of Shigella spp. resistant to first-line therapeutics are therefore of tremendous concern, particularly in Asia and Africa [62].
The 45 shigellae tested here were roughly divided between S. flexneri (13 isolates), S. sonnei (13 isolates), and Shigella sp. (12 isolates), with the remaining strains split between S. boydii (four isolates) and S. dysenteriae (three isolates). Thirty unique ARDs were detected amongst the Shigella spp. isolates (Table 4)—somewhat more limited than in E. coli or Salmonella (Figure 2). The per-isolate carriage rate was higher in Shigella spp. (Figure 1B, p < 0.025).
Table 4.
ARDs detected in Shigella spp., by geographic location (percent of isolates positive).
| ARD | USA (n = 7) | Cambodia (n = 11) | Egypt (n = 12) | Peru (n = 6) | Kenya (n = 9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bla LEN | nd * | nd | 8% | nd | nd |
| blaOXA-1 family | 29% | 9% | 67% | 67% | nd |
| blaSHV family | nd | nd | 8% | nd | nd |
| blaTEM family | 14% | 18% | 25% | 17% | 56% |
| blaCTX-M-1 family | nd | nd | 8% | nd | nd |
| blaCTX-M-9 family | nd | nd | 17% | nd | nd |
| aac(6)-Ib | nd | nd | nd | 17% | nd |
| aadA1/A2 | 57% | 18% | 100% | 67% | 44% |
| aadA4 | nd | nd | nd | 17% | nd |
| strA | 57% | 27% | 50% | 50% | 100% |
| strB | 57% | 36% | 50% | 50% | 100% |
| mac(A) | 86% | 18% | 100% | 100% | 33% |
| mac(B) | 86% | 9% | 83% | 100% | 33% |
| mph(A)/mph(K) | nd | nd | nd | 17% | 33% |
| tet(A) | 57% | 18% | 33% | nd | 78% |
| tet(B) | 29% | 73% | 67% | 100% | 11% |
| arr | nd | nd | nd | 17% | nd |
| catA1/cat4 | 14% | 18% | 58% | 67% | nd |
| cmr | 100% | 73% | 100% | 100% | 44% |
| qnrS | nd | nd | 8% | nd | 11% |
| qacEΔ1 | 14% | nd | 8% | 17% | 11% |
| sat2 | 43% | 18% | 67% | 17% | 44% |
| sul1 | 14% | nd | nd | 14% | 11% |
| sul2 | 57% | 27% | 75% | 67% | 100% |
| dfrA1 | 43% | 18% | 75% | 17% | 44% |
| dfrA5 | nd | nd | nd | nd | 11% |
| dfrA7 | 14% | nd | nd | nd | 11% |
| dfrA8 | nd | nd | nd | 14% | 11% |
| dfrA14 | nd | 9% | 8% | 33% | 11% |
| dfrA17 | nd | nd | nd | 17% | nd |
* not detected.
As shigellae and E. coli are very closely related [63], we were not surprised to see many of the same ARDs detected in Shigella spp. with similar frequencies as in E. coli: strA (56%), strB (58%), mac(A) (64%), mac(B) (58%), cmr (82%), and sul2 (64%) (Figure 1C). TET ARDs detected amongst the shigellae were limited to tet(A) (39%) and tet(B) (59%); three strains were negative for all tested TET ARDs. Plasmid-borne FQ ARD, qnrS, was observed in two isolates, and the ansamycin resistance gene, arr, was detected in a Cambodian S. dysenteriae isolate. Notably, blaCTX-M-1 and blaCTX-M-9 family genes were detected at a much lower rate in the Shigella spp. strains than in E. coli—2% and 5%, respectively. Other notable differences between Shigella spp. and the closely related E. coli were the lower carriage of blaTEM (27% versus 63%) and mph(A)/mph(K) (9% versus 27%) and higher carriage of the blaOXA-1 family (34% versus 3%) in Shigella spp. isolates.
As with E. coli, the presence of some sets of genes was highly correlated: strA, strB, and sul2 (p < 0.001); mac(A), mac(B), and cmr (p < 0.001); qacEΔ and sul2 (p < 0.001), and aadA1/A2, sat2, and dfrA1 (p < 0.005). IntI1-specific PCR confirmed the presence of class 1 integrons in 7% of the Shigella spp. strains, similar to observations in E. coli. However, intI2-specific PCR detected class 2 integrons in a much larger proportion of shigellae (29%). As only those isolates with integron-associated markers were tested, these numbers are likely underestimates.
Twelve Shigella spp. strains (27%) carried the same four genes found in the Shigella resistance island (SRL; aadA1, blaOXA-1, tet(B), and catA1), a chromosomal pathogenicity island found in S. flexneri, S. sonnei, and S. dysenteriae with wide global distribution [64]. No samples from the other three genera carried this unique combination of genes.
2.2.4. Salmonella spp.
Salmonella gastroenteritis affects nearly 200 million persons, causing over 80,000 deaths in 2016 [62]. As typhoid fever can also cause diarrhea in young children and adults with HIV [65,66], four S. enterica subsp. enterica serotype Typhi isolates were included amongst the 32 samples tested here. Serotypes for 21 additional non-typhoidal Salmonella (NTS) isolates were also provided: five isolates of serotype B (four from Cambodia, one from USA) and one strain each of serotypes Newport, Anatum, Heidelberg, Dublin, and Agona (all USA isolates); one isolate each of serotype A and O (Kenya); one isolate of serogroup 3 (Egypt), and three isolates each from serogroups B and D, and two from serogroup C1 (Peru).
Thirty-eight ARDs were detected among the Salmonella strains (Figure 2, Table 5). Eighty-five percent of the Salmonella isolates harbored a TET ARD, comprising a wider variety of TET resistance genes than observed in E. coli or Shigella spp.: tet(A) (47%), tet(B) (22%), tet(C) (3%), tet(D) (6%), and tet(G) (6%). The following genes were also detected in a significant proportion of the Salmonella isolates: strB (63%), blaTEM (56%), strA (56%), qacEΔ, (53%), sul1 (53%), sul2 (50%), and aadA1/A2 (50%) (Figure 1C).
Table 5.
ARDs detected in Salmonella spp., by geographic location (percent of isolates positive).
| ARD | USA (n = 8) | Cambodia (n = 4) | Egypt (n = 6) | Peru (n = 8) | Kenya (n = 6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bla CMY/LAT | 25% | nd * | nd | nd | nd |
| bla LEN | nd | nd | 33% | nd | nd |
| blaOXA-48 family | nd | nd | nd | nd | 17% |
| bla PSE/CARB | 13% | nd | 17% | nd | nd |
| blaSHV family | nd | nd | 50% | nd | nd |
| blaTEM family | 50% | 50% | 83% | 25% | 83% |
| blaCTX-M-1 family | nd | 25% | 17% | nd | nd |
| blaCTX-M-9 family | nd | nd | 33% | nd | nd |
| aac(3)-Id | nd | nd | 50% | nd | nd |
| aac(3)-III | nd | nd | nd | 13% | nd |
| aadA1/A2 | 50% | nd | 50% | 75% | 50% |
| aadA7 | nd | nd | 50% | nd | nd |
| aphA1 | 13% | nd | 50% | 63% | nd |
| strA | 63% | 75% | 50% | 25% | 83% |
| strB | 63% | 75% | 67% | 25% | 100% |
| aphA6 | 13% | nd | 33% | nd | nd |
| rmtD | 13% | nd | nd | nd | 17% |
| ere(A2) | nd | nd | 33% | nd | nd |
| mph(A)/mph(K) | nd | nd | 17% | nd | 17% |
| tet(A) | 38% | 50% | 33% | 88% | 17% |
| tet(B) | 50% | 50% | nd | nd | 17% |
| tet(C) | 13% | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| tet(D) | nd | nd | 17% | 13% | nd |
| tet(G) | 13% | nd | 17% | nd | nd |
| catA1/cat4 | 25% | nd | nd | nd | 33% |
| floR | 25% | nd | 17% | 13% | 17% |
| cmr | nd | nd | nd | nd | 17% |
| qnrS | nd | 25% | nd | nd | nd |
| qacEΔ1 | 38% | nd | 83% | 75% | 50% |
| sul1 | 38% | nd | 83% | 75% | 50% |
| sul2 | 50% | 75% | 33% | 13% | 100% |
| sul3 | nd | nd | nd | 13% | nd |
| dfrA1 | nd | nd | nd | 13% | 33% |
| dfrA7 | 25% | nd | nd | nd | 17% |
| dfrA8 | nd | nd | nd | nd | 17% |
| dfrA12 | nd | nd | 17% | 13% | nd |
| dfrA14 | nd | nd | nd | 63% | 50% |
| dfrA19 | nd | nd | 19% | nd | nd |
* not detected.
A variety of genes not detected amongst the other Enterobacteriaceae isolates was observed in a few Salmonella strains (< 10%): blaCMY/LAT, blaPSE/CARB, blaOXA-48-like, aac(3)-Id, aac(3)-III, aadA7, rmtD, tet(G), floR, and sul3.
Of clinical concern, genes encoding CTX-M-type ESBLs were detected in 12% of the Salmonella isolates, conferring resistance to first-line therapeutics for NTS diarrhea in areas with multidrug resistance (MDR) [9]. On the other hand, rmtD—detected in two isolates—is not clinically relevant for Salmonella-derived infections but confers resistance to all aminoglycosides and can be transferred horizontally to other species for which aminoglycosides serve as common therapeutics. Also alarming was detection of the carbapenemase gene, blaOXA-48, in a Kenyan Salmonella isolate. While its presence in Enterobacteriaceae in East Africa has recently been reported [67,68,69,70], to our knowledge, this is the first description of an OXA-48-like-containing diarrheal isolate in Kenya.
The qacEΔ and sul1 genes were co-harbored in over half of the Salmonella strains, and the presence of intI1 in these strains was confirmed by PCR. The prevalence of class 1 integrons in the Salmonella strains was therefore significantly higher (51%) than observed in E. coli (13%) or Shigella spp. strains (7%). However, no Salmonella isolates co-harbored the combination of aadA1/A2 + sat2 + dfrA1, supporting previous observations that class 2 integrons are infrequently harbored by Salmonella [71,72,73].
Several isolates harbored ARDs commonly associated with Salmonella genomic island 1 (SGI1; aadA1/A2, qacEΔ, sul1, floR, tet(G), blaPSE/CARB) [74] or its SGI1-K variant (aac(3)-id, aadA7, qacEΔ, sul1, tet(A), blaTEM) [75].
2.3. Geographic Trends
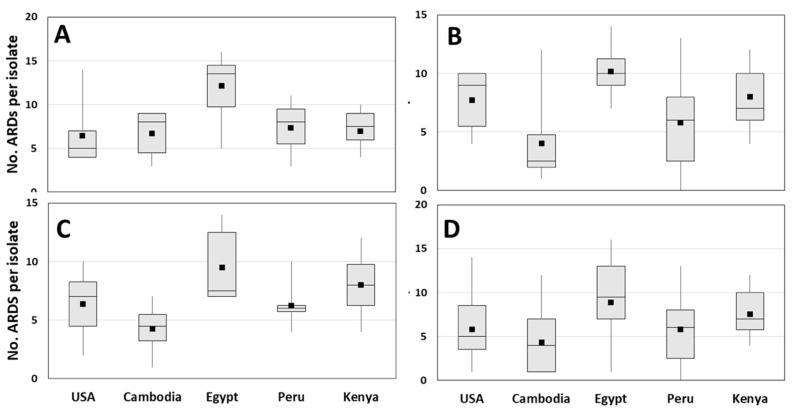
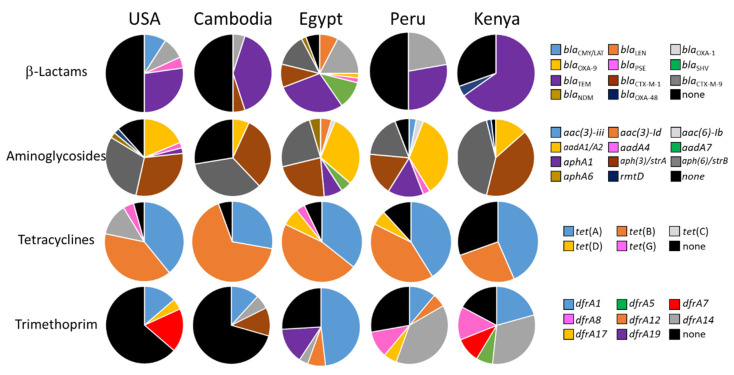
As a pilot-scale study, the numbers of isolates obtained per genus and per site hindered attempts to draw strong statistical conclusions from the data. However, a number of general trends were observed. Of the five collection sites surveyed, Egypt had the largest total number of ARDs detected in E. coli (30), in Salmonella (23), and overall (39) (Figure 2, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6). Not surprisingly, the number of unique ARDs on a per-isolate basis was also highest in Egyptian samples for the three Enterobacteriaceae, suggesting that Egyptian isolates were more likely to possess MDR (Table 1 and Table 6, Figure 3). The high ARD carriage rate in the Egyptian isolates was largely due to the high diversity and rates of carriage of genes encoding β-lactamases (90%) and aminoglycoside modifying enzymes (100%) (Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6, Figure 4). Over half harbored at least three aminoglycoside ARDs and nearly half of those with β-lactamases encoded a CTX-M-type ESBL. In comparison, 30% to 50% of Enterobacteriaceae isolates from the USA, Cambodia, Peru, or Kenya were negative for all β-lactamase genes, and fewer aminoglycoside ARDs were present in each. The high prevalence of blaCTX-M-1 and blaCTX-M-9 families in Egyptian isolates also supports previous observations of high ESBL carriage [76,77] and may be related to the preferential consumption of extended-spectrum cephalosporins over narrow-spectrum penicillins in Egypt [78,79]. Furthermore, high carbapenem consumption in Egypt [79] may also have provided selective pressure for the single blaNDM-positive sample, also observed within this population. Of additional note, a significant percentage (27%) of the Egyptian Enterobacteriaceae harbored genes conferring resistance to AZM (two isolates with ere(A), five with mph(A)/mph(K)); Kenya was the only other site where AZM ARDs were carried at a similar rate (30% in Enterobacteriaceae).
Table 6.
Percentage of E. coli, Shigella spp., and Salmonella isolates harboring at least one ARD to each of 11 classes of antimicrobial compounds.
| Antimicrobial Class | Geographic Location | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | Cambodia | Egypt | Peru | Kenya | |
| β-Lactams | 50.0 | 42.1 | 88.5 | 47.1 | 65.2 |
| Aminoglycosides | 77.3 | 52.6 | 100.0 | 88.2 | 95.7 |
| Macrolides | 54.5 | 31.6 | 80.8 | 52.9 | 47.8 |
| Tetracyclines | 95.4 | 94.7 | 92.3 | 88.3 | 70.0 |
| Ansamycins | nd ** | nd | nd | 5.9 | nd |
| Phenicols | 81.8 | 63.2 | 80.8 | 64.7 | 47.8 |
| Quinolones | nd | 10.5 | 7.7 | nd | 4.3 |
| Quaternary amines | 22.7 | nd | 26.9 | 47.1 | 21.7 |
| Streptothricins | 13.6 | 10.5 | 42.3 | 1.8 | 17.4 |
| Sulfonamides | 63.6 | 47.4 | 73.1 | 82.4 | 95.7 |
| Trimethoprim | 31.8 | 26.3 | 69.2 | 70.6 | 78.3 |
| Class 1 integron * | 18.2 | n/a *** | 19.2 | 47.1 | 17.4 |
| Class 2 integron * | 9.1 | n/a | 34.7 | 5.9 | 13.0 |
* confirmed by intI1- and intI2-specific PCRs; ** not detected; *** not available for PCR confirmation.
Figure 3.
Box and whisker charts showing number of unique ARDs per isolate for (A) E. coli; (B) Shigella spp.; (C) Salmonella; (D) each population as a whole (including Campylobacter spp.). Black squares in each chart indicate mean values.
Figure 4.
Pie charts showing carriage rates of ARDs conferring resistance to β-lactams, aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, and trimethoprim among E. coli, Shigella spp., and Salmonella. Black pie slices indicate the percentage of isolates that were negative for all tested ARDs in that category. Note that many strains carried multiple β-lactamase and aminoglycoside ARDs.
Cambodia had the lowest total number of unique ARDs detected for the population as a whole and for each of the four genera tested. The lowest number of ARDs per isolate for Shigella spp., Salmonella spp., and all genera combined were also observed in the Cambodian samples (Figure 3). Interestingly, neither the high levels of phenotypic resistance nor genotypic profiles observed in two previous studies of fecal isolates from Southeast Asia [80,81] were evident from the current study. This apparent contradiction suggests that the current study may have underestimated the true prevalence of AMR genes in the Cambodian samples. One explanation for this possible underestimation is that the Cambodian samples were isolated, extracted, prepared for microarray analysis, and subsequently tested on the ARDM v.2 microarray in Naval Medical Research Unit-2 (NAMRU-2) facilities. DNA from isolates collected at the other sites (USA, Egypt, Kenya, and Peru) was extracted at the site of collection and then the DNA was shipped to the US Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) in Washington, DC, USA; these extracted DNA preparations were then further prepared and analyzed on the microarrays within NRL facilities. Slight differences in instrumentation or handling between NAMRU-2 and NRL (e.g., ramp speed during fragmentation steps, cold blocks versus ice baths) may have affected the size and distribution of the tested nucleic acids, resulting in altered test sensitivity [82]. It should be noted, however, that a study of Cambodian wound isolates performed at the same time documented higher rates of carriage of specific ARDs in E. coli than observed here [83].
Other interesting observations included the detection of ARDs associated with SGI1-K (Salmonella: aac(3)-id, aadA7, qacEΔ, sul1, tet(A), blaTEM; [75]) or plasmid pSLBT (E. coli: aadA1, strA, strB, blaTEM, catA1, dfrA1, sul1, sul2, qacEΔ; [84]) in African isolates only. Both assemblages, SGI1-K and pSLBT, were originally described in Nigeria and Kenya, respectively [75,84]. While we did not attempt to confirm the presence of either SGI1-K or pSLBT (or pSLBT-like plasmids) in any of these strains, the African origin of these strains suggests that mobilizable elements such as these may be circulating within East and North Africa.
Twenty-seven percent (27%) of the Shigella spp. isolates also harbored ARDs associated with SRL, but carriage rates were not consistent between collection sites: the rates of co-carriage were much higher amongst Egyptian and Peruvian strains (58% and 50%, respectively, versus 0–14% for the other sites). These different carriage rates may be related to the prevalence of the various global Shigella spp. lineages (and related absence/presence of SRL) within each site [85].
A correlation between national antimicrobial consumption and prevalence of ARDs at specific sites was sometimes, but not always, observed. For example, the high prevalence and wide variety of sul and dfrA genes in Kenyan Enterobacteriaceae (Table 2, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5, Figure 4) may potentially be due to selective pressure from the widespread prophylactic use of SXT for HIV-infected individuals [86]. The high prevalence of ESBLs and the observation of blaNDM amongst Egyptian samples, where these antimicrobials are widely consumed, serve as a second example. On the other hand, we detected blaOXA-48 in an isolate from Kenya, where carbapenems are expensive and presumably not widely used [79,87]. These observations support other studies reporting significant increases in carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in East Africa, in spite of this presumably low selective pressure [69,88]. While a large number of plasmids carrying blaOXA-48 and related carbapenemase genes have few or no additional ARDs, many of these plasmids have minimal associated fitness cost and can be stably maintained in the absence of selective pressure [89,90,91]. Others have documented the maintenance of plasmids harboring larger numbers of ARDs in the absence of selective pressure [92,93,94].
A key limitation of the current study is the low numbers and variability of isolates of each species obtained from the five sampling sites, constraining our ability to perform robust statistical comparisons. This limitation is further compounded when pathotypes (E. coli), species (Shigella, Campylobacter), serotypes (Salmonella), or sampled populations (e.g., hospital inpatients versus outpatients) vary between sites or were not fully characterized. Furthermore, Cambodian and Kenyan subject populations (mean subject ages 7.9 and 8.0 years, respectively) tended to be younger than those from the USA or Peru (mean subject ages 30.9 and 22.4 years, respectively; see Supplementary Materials). Another key concern was the difference in methods used to extract DNA, as partnering labs were asked to provide DNA extracted as per their standard operating procedures, which we erroneously assumed would be uniform between sites; future studies should standardize the extraction procedures as well as the analysis. Though rapid and easy, the boil method (Peru) may not provide DNA of the same quality as commercial kits. Furthermore, the kit used to prepare Kenyan samples is designed to enrich for plasmid and cosmid DNA and may have affected the recovery of chromosomal DNA; for example, some chromosomal ARDs (mac(A), mac(B), cmr) were detected at lower-than-expected rates in Kenyan samples. More importantly, with regard to study design, it is also unclear whether the sample set used here—selected for TET resistance—accurately reflects the overall prevalence of various ARDs within the larger populations, including both resistant and susceptible pathogens from these collection sites; TET ARDs are commonly found in assemblages with other ARDs. Future study designs will emphasize a single species or serotype, with a larger number of samples collected from each site. Integrating a whole genome sequencing approach into a follow-on study would improve both the analytical depth and breadth. Whole genome sequencing—while more computationally intense—would enable rapid discrimination of closely related alleles or variants conferring different phenotypes (e.g., aac(6’)-ib versus aac(6’)-ib-cr) and detect chromosomal mutations conferring resistance (e.g., FQ resistance from gyrA or parC mutations, TET resistance from rRNA gene mutations, etc.); the microarray used here does not provide this capability. Next generation sequencing can further provide high resolution epidemiological tracking and “One Health” linkages [95,96], provide context for genes, and even detect promoter modifications that significantly affect gene expression [97,98]. However, a key limitation of any molecular technology approach is that genotype may not always be predictive of phenotype if differential expression and/or functionality of expressed proteins is not known or fully characterized. Furthermore, cooperative interactions amongst members of an ecosystem consortium can significantly affect individual species’ phenotypic traits and survivability in native environments [22,99,100,101,102]. Therefore, while molecular techniques are useful for AMR surveillance, they should be complemented with approaches that address additional mechanisms for AMR and survival and (potentially uncharacterized) contributions of components of the ecosystem consortium.
The current study does address the presence of a large number of resistance markers covering multiple classes of antimicrobials across a diverse collection of organisms comprising four genera using a standardized and broad-spectrum detection platform. This approach allowed us to detect possible assemblages and make some surprising observations. With the exception of Campylobacter spp., a high rate of ARD carriage in all populations was observed (average = 6.58 genes/isolate; median = 7 genes/isolate among the Enterobacteriaceae). While the prevalence of ESBLs was alarming—especially in Egypt—we observed only two samples that harbored carbapenemase genes; other studies have reported much higher levels of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae within fecal samples [103,104].
Genes conferring resistance to AZM were observed in > 10% of the entire population, with Enterobacteriaceae strains from Egypt and Kenya having the highest rates of carriage (27% and 30%, respectively). The high prevalence of these ARDs is particularly concerning, as AZM has replaced FQs as a first-line therapeutic for moderate travelers’ diarrhea in Southeast Asia and for severe travelers’ diarrhea globally [105]. The low prevalence of the FQ resistance gene, qnrS, observed from all collection sites mirrored results from other studies [106,107,108]. This and other plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance (PMQR) genes reduce susceptibility to quinolones, albeit not always to the level of clinical resistance [98,109]. High-level resistance to first-line FQ therapeutics is generally conferred by point mutations in gyrA and parC in Enterobacteriaceae, which are not detectable by the microarray technology used here; the ability to interrogate samples for such point mutations would be an advantage of any sequencing-based approach.
While the selection criteria used here (TET resistance) may have artificially raised the overall prevalence of ARDs directed against other antimicrobials, we were somewhat surprised to see such a broad variety and high carriage rate of many ARDs in isolates collected from all sites. In particular, the large numbers of strains among the Egyptian samples positive for ARDs directed against WHO’s critically important antimicrobials (carbapenems, third generation cephalosporins, AZM) suggest an urgent need for improving awareness of AMR, more in-depth surveillance for resistant pathogens, and improved antimicrobial stewardship within this region.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Isolates
A total of 23 Campylobacter spp., 30 Escherichia coli, 32 Salmonella spp., and 45 Shigella spp. diarrheal isolates were selected from pre-existing collections at the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC, Atlanta, GA, USA; n = 27), US Army Medical Research Directorate, Africa/Kenya Microbiology Hub, Kericho (USAMRD-A/K, Kericho, Kenya; n = 24), US Naval Medical Research Unit No. 2 (NAMRU-2, Phnom Penh, Cambodia; n = 25), US Naval Medical Research Unit No. 3 (NAMRU-3, Cairo, Egypt; n = 32), and US Naval Medical Research Unit No. 6 (NAMRU-6, Lima and Cusco, Peru, n = 24, NAMRU6.2017.0012 protocol). Collection dates ranged from 2006 to 2013 (Supplementary Materials), and isolates were identified as previously described [110]; prior to use in this study, all isolates were stripped of all identifiers that could be used to trace them back to an individual. Isolates were selected based on tetracycline (TET) non-susceptibility, using breakpoints determined by Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) standards [111]. Limited phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility profiles and isolate metadata were available for some, but not all, isolates (Supplementary Materials). We therefore had an insufficient number of isolates to allow statistically robust genotype–phenotype correlations.
3.2. Processing and DNA Hybridization
Genomic DNA was extracted from archived stool isolates at each collection site using the following: the boil method (used in Peru [112]), Masterpure DNA and RNA Complete Purification Kit (Epicentre Biotechnologies, Madison, WI, USA; used in Egypt), R.E.A.L. Prep Kit (used in Kenya), DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (used in USA), or QIAamp DNA mini (used in Cambodia) (last three kits from QIAGEN, Germantown, MD, USA; USA), according to manufacturers’ instructions.
With the exception of Cambodia, all subsequent steps were performed in NRL facilities (amplification, labeling, hybridization, microarray interrogation) as previously described [113]; all steps for preparation and analysis of Cambodian samples were performed on-site in NAMRU-2 facilities (Phnom Penh, Cambodia). Each sample was amplified using 10 ng of template DNA and Illustra GenomiPhi v.2 DNA Amplification Kits (GE Healthcare, Pittsburgh, PA, USA), as per the manufacturer’s instructions. After quantification using Qubit 2.0 fluorometer (Thermofisher, Rockland, IL, USA), 2 µg of the whole genome amplicons were fragmented for 1 min at 37 °C with 2.7 units DNase I (total volume of 60 µL; enzyme and buffer from GeneChip Resequencing Assay Kit, AffyMetrix, Santa Clara, CA, USA), incubated for 10 min at 95 °C to inactivate the DNase I, then purified on DNA Clean & Concentrator-5 columns (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA). Fragmented, purified DNA was then biotinylated using ULS Platinum Bright Biotin Nucleic Acid Labeling Kits (Kreatech Diagnostics, Durham, NC, USA; 10 µL reaction volume), as per the manufacturer’s instructions. The resulting biotinylated fragments were then applied to pre-hybridized ARDM v.2 microarrays (Customarray, Bothell, WA, USA [39]), hybridized overnight at 60 °C, and labeled with 1000 × diluted multimeric streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase (65R-S104PHRP; Fitzgerald Industries, North Acton, MA, USA), washed, processed, and electrochemically interrogated using the ElectraSense reader (Customarray), as previously described [39]. The content of the ARDM v.2 microarray includes 25- to 35-mer probes directed against 238 gene sequences (between 8 and 10 probes per gene) predicted to confer resistance to 15 categories of antimicrobials: β-lactams (n = 46 genes), aminoglycosides (n = 42), macrolides (n = 27), lincosamides (n = 22), streptogramins (n = 18), quaternary amines (n = 2), ansamycins (n = 1), diaminopyrimidines (n = 28), antimicrobial peptides (n = 1), tetracyclines (n = 38), phenicols (n = 10), glycopeptides (n = 12), platensimycin/platensin (n = 1), fluoroquinolones (n = 4), sulfonamides (n = 3). Many of the macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin ARDs overlap in specificity. Samples with > 85–90% gene sequence identity to the reference sequence can successfully hybridize to the microarray, allowing a broader variety of ARDs—i.e., families of genes—to be detected. However, the microarray is unable to distinguish between these similar genes. A gene was deemed present if at least 50% of its representative probes had signals above the 95% probe threshold (mean signal from lowest 2128 probes + 3 SD) or if ≥ 70% of its probes had signals above either of two less stringent thresholds (mean signal from lowest 2016 probes + 3 SD or mean signal from lowest 2128 probes + 2 SD) [39,113]. Using these algorithms, the sensitivity and specificity of the microarray were calculated as 96.3–100% and 97.9–100%, respectively [39,44].
3.3. Confirmatory PCR
Where sufficient sample was available, PCR amplifications confirming the presence of intI1 and intI2 [114] were performed on all isolates that were positive for qacEΔ1 + sul1 or aadA1/A2 + sat2 + dfrA1, respectively. Retrospective analysis of samples from Cambodia could not be performed.
3.4. Statistics
Statistical comparisons between populations were performed using two-tailed t-tests and analysis of variance (ANOVA) when normally distributed and using Mann Whitney rank sum test when not normally distributed. Chi-square tests were used to compare binomial proportions (presence/absence) in independent samples (2 × n contingency tables). P < 0.05 indicates significance.
4. Conclusions
This pilot study—using DNA preparations from 130 human diarrheal isolates—demonstrated that a standardized methodology could be used to provide molecular surveillance for over 200 AMR genes. We detected a wide variety of ARDs amongst the tested isolates and observed some generalized trends, although the small sample size limited our ability to make many conclusions with sufficient statistical power. Overall, we detected the greatest numbers and diversity of ARDs in isolates from Egypt and the lowest numbers and diversity in isolates from Cambodia. Though we could not make any conclusions regarding the phenotypes based on the ARDs detected, this preliminary study serves as a valuable starting point for more detailed follow-on investigations. The present study’s findings suggest that the implementation of molecular detection platforms with sufficient breadth—when used in conjunction with complementary techniques—have the ability to improve surveillance efforts that seek to monitor the migration and evolution of MDR organisms over time and space.
Acknowledgments
DNA from isolates originating in USA were a generous gift from Jean Whichard and Jason P. Folster at the Division of Foodborne, Waterborne, and Environmental Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and were collected and provided as part of the National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System. The authors also wish to thank Isabelle A. Nakla (NAMRU-3) for her assistance in the collection and characterization of the Egyptian isolates.
Abbreviations
| AG | Aminoglycoside |
| AMP | Antimicrobial peptide |
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| ANS | Ansamycins |
| ARD | Antimicrobial resistance determinant |
| ARDM | Antimicrobial Resistance Determinant Microarray |
| AZM | Azithromycin |
| BLA | β-Lactamase |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| ESBL | Extended-spectrum β-lactamase |
| FQ | Fluoroquinolone |
| GEIS | Global Emerging Infections Surveillance and Response System |
| GLY | Glycopeptides |
| LIN | Lincosamides |
| MAC | Macrolides |
| MLS | Macrolide/lincosamide/streptogramin |
| MUP | Mupirocin |
| NAMRU | Naval Medical Research Unit |
| NRL | Naval Research Laboratory |
| NTS | Non-typhoidal Salmonella |
| PHE | Phenicols |
| PMQR | Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance |
| PT | Platensimycin + platencin |
| QUA | Quaternary amines |
| SGI | Salmonella genomic island |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| SRL | Shigella resistance island |
| STR | Streptothricin |
| SUL | Sulfonamides |
| SXT | Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole |
| TET | Tetracycline |
| TMP | Diaminopyrimidine/trimethoprim |
| USAMRD | US Army Medical Research Directorate, Africa/Kenya Microbiology Hub, Kericho |
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be found at https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/16/5928/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.J.V.; methodology, C.R.T., T.A.L. and G.J.V.; validation, C.R.T., T.A.L. M.G.P., B.L.H., M.J.G., G.P., B.A.D. and G.J.V.; formal analysis, C.R.T. and G.J.V.; investigation, C.R.T., T.A.L., M.G.P., G.W.F., V.H., B.L.H., S.Y.L., J.A.C., A.M., H.E.M., M.W., D.H.T., M.J.G., M.R.K., J.R., P.R., C.E.H., E.A.O., A.N.O., E.K.C. and C.O.P.; resources, M.G.P., G.W.F., V.H., B.L.H., S.Y.L., J.A.C., A.M., H.E.M., M.W., D.H.T., M.J.G., M.R.K., J.R., P.R., G.P., B.A.D., C.E.H., E.A.O., A.N.O. E.K.C. and C.O.P.; data curation, C.R.T., T.A.L., M.G.P., G.L.H., G.P., B.A.D. and C.E.H.; writing—original draft preparation, C.R.T.; writing—review and editing, C.R.T., T.A.L., M.G.P., G.W.F., V.H., B.L.H., S.Y.L., J.A.C., A.M., H.E.M., M.W., D.H.T., M.J.G., M.R.K., J.R., P.R., G.P., B.A.D., C.E.H., E.A.O., A.N.O., E.K.C., C.O.P. and G.J.V.; visualization, C.R.T. and G.J.V.; supervision, G.J.V.; project administration, B.L.H., M.J.G., G.P., B.A.D., C.E.H. and G.J.V.; funding acquisition, G.J.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Office of Naval Research and the Naval Research Laboratory though internal core funds.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results. This manuscript is approved for public release: distribution is unlimited. The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Department of the Navy, Department of Defense, or the US Government. C.R.T., T.A.L., M.G.P., G.W.F., S.Y.L., D.H.T., M.J.G., M.R.K., J.R., P.R., G.P., and G.J.V. are employees of the US Government. This work was prepared as part of their official duties. Title 17, USC, §105 states that copyright protection under this title is not available for any work of the US Government. Title 17, USC, §101 defines a US Government work as a work prepared by a military service member or employee of the US Government as part of that person’s official duties.
References
- 1.Liu L., Johnson H.L., Cousens S., Perin J., Scott S., Lawn J.E., Rudan I., Campbell H., Cibulskis R., Li M., et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality: An updated systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000. Lancet. 2012;379:2151–2161. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60560-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.James S.L., Abate D., Abate K.H., Abay S.M., Abbafati C., Abbasi N., Abbastabar H., Abd-Allah F., Abdela J., Abdelalim A., et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Reiner R.C., Blacker B.F., Khalil I.A., Rao P.C., Cao S., Zimsen S.R., Albertson S.B., Stanaway J.D., Deshpande A., Abebe Z., et al. Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of diarrhoea in 195 countries: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018;18:1211–1228. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30362-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Prüss-Ustün A., Bartram J., Clasen T., Colford J.M., Jr., Cumming O., Curtis V., Bonjour S., Dangour A.D., De France J., Fewtrell L., et al. Burden of disease from inadequate water, sanitation and hygiene in low- and middle-income settings: A retrospective analysis of data from 145 countries. Trop. Med. Int. Health. 2014;19:894–905. doi: 10.1111/tmi.12329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cairncross S., Hunt C., Boisson S., Bostoen K., Curtis V., Fung I.C.H., Schmidt W.P. Water, sanitation and hygiene for the prevention of diarrhoea. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010;39:i193–i205. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyq035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Araya P., Hug J., Joy G., Oschmann F., Rubinstein S. The Impact of Water and Sanitation on Diarrhoeal Disease Burden and Over-Consumption of Antibiotics. London School of Economics and Political Science; London, UK: 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Casburn-Jones A.C., Farthing M.J. Management of infectious diarrhea. Gut. 2004;53:296–305. doi: 10.1136/gut.2003.022103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.World Health Organization . The Treatment for Diarrhoea: A Manual for Physicians and Other Senior Heath Workers. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gilbert D.N., Chambers H.F., Eliopoulos G.M., Saag M.S. The Sanford Guide to Antimicrobial Therapy 2014. 44th ed. Antimicrobial Therapy Inc; Sperryville, VA, USA: 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tribble D.R. Resistant pathogens as causes of traveller’s diarrhea globally and impact(s) on treatment failure and recommendations. J. Travel Med. 2017;24:S6–S12. doi: 10.1093/jtm/taw090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Keusch G.T., Walker C.F., Das J.K., Horton S., Habte D. Chapter 9. Diarrheal diseases. In: Black R.E., editor. Reproductive, Maternal, Newborn, and Child Health: Disease Control Priorities. 3rd ed. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank; Washington, DC, USA: 2016. pp. 163–185. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Holloway K.A., Rosella L., Henry D. The impact of WHO Essential Medicines policies on inappropriate use of antibiotics. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0152020. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Van Boeckel T.P., Brower C., Gilbert M., Grenfell B.T., Levin S.A., Robinson T.P., Teillant A., Laxminarayan R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2015;112:5649–5654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1503141112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Van Boeckel T.P., Glennon E.E., Chen D., Gilbert M., Robinson T.P., Grenfell B.T., Levin S.A., Bonhoeffer S., Laxminarayan R. Reducing antimicrobial use in food animals. Science. 2017;357:1350–1352. doi: 10.1126/science.aao1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Van Boeckel T.P., Pires J., Silvester R., Zhao C., Song J., Criscuolo N.G., Gilbert M., Bonhoeffer S., Laxminarayan R. Global trends in antimicrobial resistance in animals in low- and middle-income countries. Science. 2019;365:eaaw1944. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw1944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Palma E., Tilocca B., Roncada P. Antimicrobial resistance in veterinary medicine: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:1914. doi: 10.3390/ijms21061914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Henriksson P.J.G., Troell M., Rico A. Antimicrobial use in aquaculture: Some complementing facts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2015;112:E3317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1508952112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Santos L., Ramos F. Antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture: Current knowledge and alternatives to tackle the problem. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2018;52:135–143. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schar D., Sommanustweechai A., Laxminarayan R., Tangcharoensathien V. Surveillance of antimicrobial consumption in animal production sectors of low- and middle-income countries: Optimizing use and addressing antimicrobial resistance. PLoS Med. 2018;15:e1002521. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Huijbers P.M.C., Blaak H., De Jong M.C.M., Graat E.A.M., Vandenbroucke-Grauls C.M.J.E., Husman A.M.D.R., Venbroucke-Grauls C.M.J.E. Role of the environment in the transmission of antimicrobial resistance to humans: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015;49:11993–12004. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b02566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Richardson E.J., Bacigalupe R., Harrison E.M., Weinert L.A., Lycett S.J., Vrieling M., Robb K., Hoskisson P.A., Holden M.T.G., Feil E.J., et al. Gene exchange drives the ecological success of a multi-host bacterial pathogen. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018;2:1468–1478. doi: 10.1038/s41559-018-0617-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Banerji A., Jahne M., Herrmann M., Brinkman N., Keely S. Bringing community ecology to bear on the issue of antimicrobial resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2019;10:2626. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Collignon P.A., McEwen S. One Health—Its importance in helping to better control antimicrobial resistance. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019;4:22. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed4010022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Laxminarayan R., Duse A., Wattal C., Zaidi A.K.M., Wertheim H.F.L., Sumpradit N., Vlieghe E., Hara G.L., Gould I.M., Goossens H., et al. Antibiotic resistance—The need for global solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013;13:1057–1098. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70318-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.O’Neill J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. United Kingdom Government, Wellcome Trust; London, UK: 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 26.O’Neill J. The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. United Kingdom Government, Wellcome Trust; London, UK: 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chopra I., Roberts M.C. Tetracycline antibiotics: Mode of action, applications, molecular biology, and epidemiology of bacterial resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001;65:232–260. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.65.2.232-260.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.World Health Organization . WHO Report on Surveillance of Antibiotic Consumption: 2016–2018 Early Implementation. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 29.World Health Organization . Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine, 5th Revision 2016. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bryce A., Costelloe C., Hawcroft C., Wootton M., Hay A.D. Faecal carriage of antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli in asymptomatic children and associations with primary care antibiotic prescribing: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016;16:359. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1697-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Grossman T.H. Tetracycline antibiotics and resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016;6:a025387. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a025387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cox G., Wright G.D. Intrinsic antibiotic resistance: Mechanisms, origins, challenges and solutions. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013;303:287–292. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Forsberg K.J., Patel S., Wencewicz T.A., Dantas G. The tetracycline destructases: A novel family of tetracycline-inactivating enzymes. Chem. Biol. 2015;22:888–897. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.05.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Alcock B.P., Raphenya A.R., Lau T.T.Y., Tsang K.K., Bouchard M., Edalatmand A., Huynh W., Nguyen A.L.V., Cheng A.A., Liu S., et al. CARD 2020: Antibiotic resistome surveillance with the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:D517–D525. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mechanism of Resistance for Characterized Tet and Otr Genes. [(accessed on 3 August 2020)]; Available online: https://faculty.washington.edu/marilynr/tetweb1.pdf.
- 36.You Y., Hilpert M., Ward M.J. Identification of Tet45, a tetracycline efflux pump, from a poultry-litter-exposed soil isolate and persistence of tet(45) in the soil. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013;68:1962–1969. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.World Health Organization . The Global View of Campylobacteriosis: Report of an Expert Consultation. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2013. Utrecht, The Netherlands, 9–11 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kaakoush N.O., Castaño-Rodríguez N., Mitchell H.M., Man S.M. Global epidemiology of campylobacter infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015;28:687–720. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00006-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Taitt C.R., Leski T., Stockelman M.G., Craft D.W., Zurawski D.V., Kirkup J.B.C., Vora G.J. Antimicrobial resistance determinants in acinetobacter baumannii isolates taken from military treatment facilities. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013;58:767–781. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01897-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Abril C., Brodard I., Perreten V. Two novel antibiotic resistance genes, tet(44) and ant(6)-Ib, are located within a transferable pathogenicity island in Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010;54:3052–3055. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00304-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Charvalos E., Tselentis Y., Hamzehpour M.M., Kohler T., Pechere J.C. Evidence for an efflux pump in multidrug-resistant Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995;39:2019–2022. doi: 10.1128/AAC.39.9.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Roberts M.C., Schwarz S., Aarts H.J.M. Erratum: Acquired antibiotic resistance genes: An overview. Front. Microbiol. 2012;3:384. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Taitt C.R., Leski T., Chen A., Berk K.L., Dorsey R.W., Gregory M.J., Sozhamannan S., Frey K.G., Dutt D.L., Vora G.J. A survey of antimicrobial resistance determinants in category A Select Agents, exempt strains, and near-neighbor species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:1669. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Taitt C.R., Leski T.A., Colston S.M., Bernal M., Canal E., Regeimbal J., Rios P., Vora G.J. A comparison of methods for DNA preparation prior to microarray analysis. Anal. Biochem. 2019;585:113405. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2019.113405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nirdnoy W., Mason C.J., Guerry P. Mosaic structure of a multiple-drug-resistant, conjugative plasmid from Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005;49:2454–2459. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.6.2454-2459.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Qin S., Wang Y., Zhang Q., Chen X., Shen Z., Deng F., Wu C., Shen J. Identification of a novel genomic island conferring resistance to multiple aminoglycoside antibiotics in Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012;56:5332–5339. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00809-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang Y., Zhang M., Deng F., Shen Z., Wu C., Zhang J., Zhang Q., Shen J. Emergence of multidrug-resistant Campylobacter species isolates with a horizontally acquired rRNA methylase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014;58:5405–5412. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03039-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Igwaran A., Okoh A.I. Campylobacteriosis agents in meat carcasses collected from two distinct municipalities in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Foods. 2020;9:203. doi: 10.3390/foods9020203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.World Health Organization . WHO Estimates of the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases. 2018, World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Chesneau O., Tsvetkova K., Courvalin P. Resistance phenotypes conferred by macrolide phosphotransferases. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007;269:317–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Obiesie N., Flahart R., Hansen G., Sexton J., Pursell C., Sugg T.J., Thoroughman D.A., Humbaugh K.E., Zhu B.P., Hinkle C.J., et al. Outbreaks of multidrug-resistant Shigella sonnei gastroenteritis associated with day care centers—Kansas, Kentucky, and Missouri, 2005. Morb. Mortal. Weekly Rep. 2006;55:1068–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.World Health Organization . Guidelines for the Control of Shigellosis, Including Epidemics Due to Shigella Dysenteriae Type 1. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Tauxe R.V., Cavanagh T.R., Cohen M.L. Interspecies gene transfer in vivo producing an outbreak of multiply resistant shigellosis. J. Infect. Dis. 1989;160:1067–1070. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Nguyen M.C.P., Woerther P.L., Bouvet M., Andremont A., Leclercq R., Canu A. Escherichia coli as reservoir for macrolide resistance genes. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009;15:1648–1650. doi: 10.3201/eid1510.090696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Darton T.C., Tuyen H.T., The H.C., Newton P.N., Dance D.A., Phetsouvanh R., Davong V., Campbell J.I., Hoang N.V.M., Thwaites G.E., et al. Azithromycin resistance in Shigella spp. in Southeast Asia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018;62:e01748-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01748-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Taitt C.R., Leski T., Erwin D.P., Odundo E.A., Kipkemoi N.C., Ndonye J.N., Kirera R.K., Ombogo A.N., Walson J.L., Pavlinac P.B., et al. Antimicrobial resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae stool isolates circulating in Kenya. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0178880. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Amos G.C.A., Ploumakis S., Zhang L., Hawkey P.M., Gaze W.H., Wellington E.M.H. The widespread dissemination of integrons throughout bacterial communities in a riverine system. ISME J. 2018;12:681–691. doi: 10.1038/s41396-017-0030-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kiiru J., Butaye P., Goddeeris B., Kariuki S. Analysis for prevalence and physical linkages amongst integrons, ISEcp1, ISCR1, Tn21 and Tn7 encountered in Escherichia coli strains from hospitalized and non-hospitalized patients in Kenya during a 19-year period (1992–2011) BMC Microbiol. 2013;13:109. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Handford C., Stang C., Raivio T., Dennis J. The contribution of small cryptic plasmids to the antibiotic resistance of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli E2348/69. Can. J. Microbiol. 2009;55:1229–1239. doi: 10.1139/W09-079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Yau S., Liu X., Djordjevic S.P., Hall R. RSF1010-like plasmids in Australian Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium and origin of their sul2-strA-strB antibiotic resistance gene cluster. Microb. Drug Resist. 2010;16:249–252. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2010.0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kobayashi N., Nishino K., Yamaguchi A. Novel macrolide-specific ABC-type efflux transporter in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2001;183:5639–5644. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.19.5639-5644.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Khalil A.I., Troeger C., Blacker B.F., Rao P.C., Brown A.E., Atherly D., Brewer T.G., Engmann C.M., Houpt E.R., Kang G., et al. Morbidity and mortality due to Shigella and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea: The Global Burden of Disease Study 1990–2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018;18:1229–1240. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30475-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Chattaway M.A., Schaefer U., Tewolde R., Dallman T.J., Jenkins C. Identification of Escherichia coli and Shigella species from whole-genome sequences. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016;55:616–623. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01790-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Njamkepo E., Fawal N., Tran-Dien A., Hawkey J., Strockbine N., Jenkins C., Talukder K.A., Bercion R., Kuleshov K., Kolínská R., et al. Global phylogeography and evolutionary history of Shigella dysenteriae type 1. Nat. Microbiol. 2016;1:16027. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Roy S.K., Speelman P., Butler T., Nath S., Rahman H., Stoll B.J. Diarrhea associated with typhoid fever. J. Infect. Dis. 1985;151:1138–1143. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Parry C.M., Hien T.T., Dougan G., White N.J., Farrar J.J. Typhoid fever. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;347:1770–1782. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra020201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Mushi M.F., Mshana S.E., Imirzalioglu C., Bwanga F. Carbapenemase genes among multidrug resistant gram negative clinical isolates from a tertiary hospital in Mwanza, Tanzania. BioMed Res. Int. 2014;2014:1–6. doi: 10.1155/2014/303104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Okoche D., Asiimwe B.B., Katabazi F.A., Kato L., Najjuka C.F. Prevalence and characterization of carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae isolated from Mulago National Referral Hospital, Uganda. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0135745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Ssekatawa K., Byarugaba D.K., Wampande E., Francis E. A systematic review: The current status of carbapenem resistance in East Africa. BMC Res. Notes. 2018;11:629. doi: 10.1186/s13104-018-3738-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ampaire L.M., Katawera V., Nyehangane D., Boum Y., Bazira J. Epidemiology of carbapenem resistance among multi-drug resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Uganda. Br. Microbiol. Res. J. 2015;8:418–423. doi: 10.9734/BMRJ/2015/17055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Antunes P., Machado J., Peixe L. Characterization of antimicrobial resistance and class 1 and 2 integrons in Salmonella enterica isolates from different sources in Portugal. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006;58:297–304. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ploy M.C., Chainier D., Thi N.H.T., Poilane I., Cruaud P., Denis F., Collignon A., Lambert T. Integron-associated antibiotic resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi from Asia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003;47:1427–1429. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.4.1427-1429.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Van Essen-Zandbergen A., Smith H., Veldman K., Mevius D. Occurrence and characteristics of class 1, 2 and 3 integrons in Escherichia coli, Salmonella and Campylobacter spp. in The Netherlands. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007;59:746–750. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Boyd D., Peters G.A., Cloeckaert A., Sidi-Boumedine K., Chaslus-Dancla E., Imberechts H., Mulvey M.R. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 43-kilobase genomic island associated with the Multidrug Resistance Region of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium DT104 and its identification in phage type DT120 and serovar Agona. J. Bacteriol. 2001;183:5725–5732. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.19.5725-5732.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Le Hello S., Hendriksen R.S., Doublet B., Fisher I., Nielsen E.M., Whichard J.M., Bouchrif B., Fashae K., Granier S.A., Silva N.J.D., et al. International spread of an epidemic population of Salmonella enterica serotype Kentucky ST198 resistant to ciprofloxacin. J. Infect. Dis. 2011;204:675–684. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Abdulrahman E., El-Sherif R.H. High rates of intestinal colonization with extended-spectrum lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae among healthy individuals. J. Investig. Med. 2011;59:1284–1286. doi: 10.2310/JIM.0b013e318238748e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Abdallah H.M., Al Naiemi N., Reuland E.A., Wintermans B.B., Koek A., Abdelwahab A., Samy A., Abdelsalam K., Vandenbroucke-Grauls C.M.J.E. Fecal carriage of extended-spectrum β-lactamase- and carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in Egyptian patients with community-onset gastrointestinal complaints: A hospital -based cross-sectional study. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2017;6:62. doi: 10.1186/s13756-017-0219-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Borg M., Zarb P., Ferech M., Goossens H., on behalf of the ARMed Project Group Antibiotic consumption in southern and eastern Mediterranean hospitals: Results from the ARMed project. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008;62:830–836. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkn260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Center for Disease Dynamics . E.P. State of the World’s Antibiotics, 2015. CDDEP; Washington, DC, USA: 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Thompson C.N., Phan M.V.T., Hoang N.V.M., Van Minh P., Vinh N.T., Thuy C.T., Nga T.T.T., Rabaa M.A., Duy P.T., Dung T.T.N., et al. A prospective multi-center observational study of children hospitalized with diarrhea in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015;92:1045–1052. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.14-0655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Challacombe J.F., Altherr M.R., Xie G., Bhotika S.S., Brown N., Bruce D., Campbell C.S., Campbell M.L., Chen J., Chertkov O., et al. The complete genome sequence of Bacillus thuringiensis Al Hakam. J. Bacteriol. 2007;189:3680–3681. doi: 10.1128/JB.00241-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Liu Y.Q., Guo H., Wu J.H. Effects of target length on the hybridization efficiency and specificity of rRNA-based oligonucleotide microarrays. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006;73:73–82. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01468-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Taitt C.R., Lêski T., Heang V., Ford G.W., Prouty M.G., Newell S.W., Vora G.J. Antimicrobial resistance genotypes and phenotypes from multidrug-resistant bacterial wound infection isolates in Cambodia. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2015;3:198–204. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2015.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Kariuki S., Okoro C.K., Kiiru J., Njoroge S., Omuse G., Langridge G.C., Kingsley R.A., Dougan G., Revathi G. Ceftriaxone-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium sequence type 313 from Kenyan patients is associated with the blaCTX-M-15 gene on a novel IncHI2 plasmid. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015;59:3133–3139. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00078-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Connor T.R., Barker C., Baker K.S., Weill F.-X., Talukder K.A., Smith A.M., Baker S., Gouali M., Thanh D.P., Azmi I.J., et al. Species-wide whole genome sequencing reveals historical global spread and recent local persistence in Shigella flexneri. eLife. 2015;4 doi: 10.7554/eLife.07335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Global Antibiotic Resistance Partnership-Kenya Working Group . Situational Analysis and Recommendations—Antibiotic Use and Resistance in Kenya. Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics & Policy; Washington, DC, USA: 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 87.Henson S., Boinett C.J., Ellington M.J., Kagia N., Mwarumba S., Nyongesa S., Mturi N., Kariuki S., Scott J.A.G., Thomson N.R., et al. Molecular epidemiology of Klebsiella pneumoniae invasive infections over a decade at Kilifi County Hospital in Kenya. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017;307:422–429. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2017.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Manenzhe R.I., Zar H.J., Nicol M.P., Kaba M. The spread of carbapenemase-producing bacteria in Africa: A systematic review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014;70:23–40. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Hamprecht A., Sommer J., Willmann M., Brender C., Stelzer Y., Krause F.F., Tsvetkov T., Wild F., Riedel-Christ S., Kutschenreuter J., et al. Pathogenicity of clinical OXA-48 isolates and impact of the OXA-48 IncL plasmid on virulence and bacterial fitness. Front. Microbiol. 2019;10:2509. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Di Luca M.C., Johnsen P., Samuelsen Ø. Acquisition of Clinical Carbapenemase-Encoding Plasmids Confers Limited Fitness Cost but Results in Variable Plasmid Stability in Clinical Escherichia Coli Strains, in European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 2018. ECCMID; Madrid, Spain: 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 91.Mwansa B.J. The Effect of Sub-Lethal Concentration of Ciprofloxacin on the Transfer of Multidrug Resistance Plasmids, Fitness Costs on the Host and the Stability of the Newly Acquired Plasmids. University of Tromso; Tromso, Norway: 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 92.Wein T., Hülter N.F., Mizrahi I., Dagan T. Emergence of plasmid stability under non-selective conditions maintains antibiotic resistance. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:2595. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10600-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Carroll A.C., Wong A. Plasmid persistence: Costs, benefits, and the plasmid paradox. Can. J. Microbiol. 2018;64:293–304. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2017-0609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Porse A., Schønning K., Munck C., Sommer M.O. Survival and evolution of a large multidrug resistance plasmid in new clinical bacterial hosts. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016;33:2860–2873. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ludden C.M., Raven K.E., Jamrozy D., Gouliouris T., Blane B., Coll F., De Goffau M., Naydenova P., Horner C., Hernandez-Garcia J., et al. One health genomic surveillance of Escherichia coli demonstrates distinct lineages and mobile genetic elements in isolates from humans versus livestock. mBio. 2019;10:e02693-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02693-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Snitkin E.S., Zelazny A.M., Thomas P.J., Stock F., Henderson D.K., Palmore T.N., Segre J.A., NISC Comparative Sequencing Program Group Tracking a hospital outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with whole-genome sequencing. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012;4:148ra116. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Tyson G.H., McDermott P.F., Li C., Chen Y., Tadesse D.A., Mukherjee S., Bodeis-Jones S., Kabera C., Gaines S.A., Loneragan G.H., et al. WGS accurately predicts antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015;70:2763–2769. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkv186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Leski T.A., Stockelman M.G., Bangura U., Chae D., Ansumana R., Stenger D.A., Vora G.J., Taitt C.R. Prevalence of quinolone resistance in Enterobacteriaceae from Sierra Leone and the detection of qnrB pseudogenes and modified LexA binding sites. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016;60:6920–6923. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01576-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Adamowicz E.M., Flynn J., Hunter R.C., Harcombe W.R. Cross-feeding modulates antibiotic tolerance in bacterial communities. ISME J. 2018;12:2723–2735. doi: 10.1038/s41396-018-0212-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Adamowicz E.M., Muza M., Chacón J.M., Harcombe W.R. Cross-feeding modulates the rate and mechanism of antibiotic resistance evolution in a model microbial community of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica. PLoS Pathog. 2020;16:e1008700. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Olsen I. Biofilm-specific antibiotic tolerance and resistance. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015;34:877–886. doi: 10.1007/s10096-015-2323-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Islas-Espinoza M., Reid B.J., Wexler M., Bond P.L. Soil bacterial consortia and previous exposure enhance the biodegradation of sulfonamides from pig manure. Microb. Ecol. 2012;64:140–151. doi: 10.1007/s00248-012-0010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Sayed A.M., Behiry I.K., Elsherief R.H., Elsir S.A. Detection of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in rectal surveillance cultures in non-hospitalized patients. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2017;8:4. doi: 10.1186/s40543-017-0114-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Tran D.M., Larsson M., Olson L., Hoang N.T.B., Le N.K., Khu D.T.K., Nguyen H.D., Vu T.V., Trinh T.H., Le T.Q., et al. High prevalence of colonisation with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae among patients admitted to Vietnamese hospitals: Risk factors and burden of disease. J. Infect. 2019;79:115–122. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2019.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Riddle M.S., Putnam S.D., Tribble D.R., Sanders J.W. Incidence, etiology, and impact of diarrhea among long-term travelers (US military and similar populations): A systematic review. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006;74:891–900. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2006.74.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Lavilla S., González-López J.J., Sabaté M., Larrosa M.N., García-Fernández A., Bartolomé R.M., Carattoli A., Prats G. Prevalence of qnr genes among extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing enterobacterial isolates in Barcelona, Spain. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007;61:291–295. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkm448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Li B., Chen Y., Wu Z., Zhao Z., Wu J., Cao Y. Prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes among Escherichia coli in the gut of healthy people in Fuzhou, China. Ann. Lab. Med. 2018;38:384–386. doi: 10.3343/alm.2018.38.4.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Riveros M., Riccobono E., Durand D., Mosquito S., Ruiz J., Rossolini G.M., Ochoa T.J., Pallecchi L. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in enteroaggregative Escherichia coli from infants in Lima, Peru. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2012;39:540–542. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Hooper D.C., Jacoby G.A. Mechanisms of drug resistance: Quinolone resistance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015;1354:12–31. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Murray P.R., Baron E.J., Jorgensen J.H., Pfaller M.A., Yolken R.H. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 8th ed. American Society for Microbiology; Washington, DC, USA: 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 111.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute . Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Nineteenth Informational Supplement M100-S19. CLSI; Wayne, PA, USA: 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 112.Alexopoulou K., Foka A., Petinaki E., Jelastopulo E., Dimitracoupoulos G., Spiliopoulou I. Comparison of two commercial methods with PCR restriction fragment polymorphism of the tuf gene in the identification of coagulase-hegative staphylococci. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006;43:450–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2006.01964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Lêski T., Vora G.J., Barrows B.R., Pimentel G., House B.L., Nicklasson M., Wasfy M., Abdel-Maksoud M., Taitt C.R. Molecular characterization of multidrug resistant hospital isolates using the antimicrobial resistance determinant microarray. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e69507. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Koeleman J.G.M., Stoof J., Van Der Bijl M.W., Vandenbroucke-Grauls C.M.J.E., Savelkoul P.H. Identification of epidemic strains of Acinetobacter baumannii by integrase gene PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001;39:8–13. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.1.8-13.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.