Abstract
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a type of endogenous non-coding RNAs that are connected at the 3′ and 5′ ends by exon or intron cyclization, which forms a covalently closed loop. They are stable, well conserved, exhibit specific expression in mammalian cells and can function as microRNA (miRNA or miR) sponges to regulate the target genes of miRNAs, which influences biological processes. Such as tumor proliferation, invasion, metastasis, apoptosis and tumor stage. circRNAs represent promising candidates for clinical diagnosis and treatment. In the present review, the biogenesis, classification and functions of circRNAs in tumors are briefly summarized and discussed. In addition, the participation of circRNAs in signal transduction pathways regulating gastrointestinal cancer cellular functions is highlighted.
Keywords: circular RNAs, miRNA sponges, gastrointestinal cancer, regulation, biomarkers
1. Introduction
Circular RNAs (circRNAs), arising from the non-canonical splicing of linear pre-mRNAs, are long non-coding RNAs that lack 5' and 3' ends and a poly(A) tail, and exhibit a circular form (1,2). They were initially identified in RNA viruses as viroids extracted from plants in 1976 (3) and were considered to present a low abundance and to represent errors in splicing (4). With the development of high-throughput RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis, >30,000 circRNAs have been discovered to date (5,6). The discovery that the RNA sponge function of circRNAs is involved in carcinogenesis and the malignant behavior of cancers has revealed a novel molecular mechanism involved in cancer and a number of other diseases, such as atherosclerosis and Alzheimer's disease (7).
Gastrointestinal cancer represents a class of cancers affecting the digestive system (8), such as colorectal cancer (CRC), gastric cancer (GC), esophageal cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and gallbladder cancer. These cancers constitute a serious threat to human health worldwide (9). Due to a lack of effective markers for early diagnosis, a number of patients are first diagnosed at an advanced stage of gastrointestinal cancer with the characteristics of regional or distant metastasis, which severely reduces the total 5-year survival rate (10). In recent years, circRNAs have been found to possess clinical potential for regulating the biological behavior and acting as critical biomarkers and treatment targets of gastrointestinal cancer. Therefore, in the present review, the potential significance and latent function of circRNAs in cancer diagnosis, prognosis and therapy in gastrointestinal cancer are briefly discussed, with an aim to provide a better understanding of the regulatory role of circRNAs in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal cancer and to assist in the identification of effective therapeutic targets.
2. Biogenesis, biology and function of circRNAs
Biogenesis and categories of circRNAs
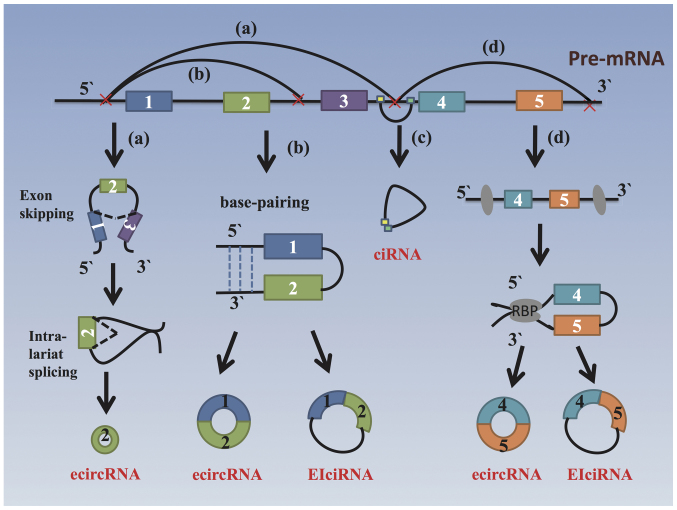
circRNAs are derived from the exons of coding regions or from 5′ - or 3′ -untranslated regions, introns, intergenic genomic regions as antisense RNAs (6). Among the identified circRNAs, >80% originate from a single exon or several exons and can be referred to as exonic circRNAs (ecircRNAs), which result from by back-splicing, a process that differs from canonical linear RNA splicing (11). The generation of circRNAs can be facilitated by reverse complementary sequences, specific protein factors or exon-skipping (12). Currently, there are 4 possible models of circRNA biogenesis, as illustrated in Fig. 1: i) Exon-skipping mechanism or lariat-driven circularization model: The pre-mRNA transcript brings the original non-adjacent exons close to each other, followed by a reverse covalent connection between the 3' donor of the downstream exon and the 5' splice acceptor, which forms a lariat structure containing exon 2 (13). ii) Intron-pairing-driven circularization or back-splicing model: This involves a circulation structure and a linear product can be formed based on the pairing of the complementary motifs in the transcripts (such as Alu elements) when introns are removed or retained (11,14), forming an ecircRNA (circulatory structure containing exons 1 and 2) or an exon-intron circRNA (eiciRNA, a circulatory structure containing exons 1 and 2 and introns). iii) Intron cyclization model: A circular intronic RNA (ciRNA) is produced from intron lariats that escape debranching, and the production of such ciRNAs is highly associated with consensus motifs near splice sites and branchpoint sites (15). iv) RNA-binding protein (RBP)-driven circularization model: In this case, RBPs such as muscleblind-specific motifs within the flanking introns of the pre-mRNA and non-sequential flanking introns can form a bridge between the introns (16).
Figure 1.
Models of circRNA biogenesis. Exons are indicated by rectangles and introns by thin lines, while dotted lines indicate base pairing. (a) Exon skipping or lariat-driven circularization. In this model, an exon-skipping event creates a lariat containing exon 2. This lariat is spliced internally, removing the intronic sequence and producing a circular RNA. (b) Direct back-splicing or intron-pairing-driven circularization. The flanking introns of exons 1 and 2 contain inverted repeats or complementary sequences, which form a circular structure through direct base pairing. The introns are removed or retained to form ecirRNA or eiciRNA. (c) Intron cyclization model. Some conserved motifs at both ends of the intron can promote the formation of a circular structure by an intron by preventing intron debranching through the debranching enzyme after splicing, which produces stable ciRNAs. (d) RBP-driven circularization. In this case, RBPs bind to introns upstream and downstream of exons 4 and 5. The RBPs are then attracted to each other and form a bridge between the introns. The 2'-hydroxyl group of the upstream intron then reacts with the 5'-phosphate of the downstream intron, which is followed by the 3'-hydroxyl of the 3'-exon reacting with the 5'-phosphate of the 5'-exon. The introns are removed or retained to form ecirRNA or eiciRNA. circRNA, circular RNA; ecirRNA, exonic circRNA; eiciRNA, exon-intron circRNA; RBP, RNA-binding protein.
Functions of circRNAs
Due to the closed loop structures of circRNAs without 5'-3' polarity or a polyadenylated tail, circRNAs are much more stable than linear RNAs and impervious to deregulation by an RNA exonuclease or RNase (6,17). circRNAs with orthologous exons are highly structurally conserved in the third codons compared with intergenic and ciRNAs (18). They are widely expressed in a tissue-specific manner in the body. Although the abundance of circRNAs accounts for approximately 2-4% of all mRNAs, some of them are highly abundant in specific cell types, such as fibroblasts (19). All the characteristics mentioned above suggest that circRNAs are capable of indirectly or directly targeting RNAs and proteins, thereby regulating gene expression at multiple levels. Therefore, the development and progression of non-cancerous and cancerous diseases are affected. The various funcions of circRNAs are discussed below as follows:
i) Indirect regulation of the expression of genes as miRNA sponges
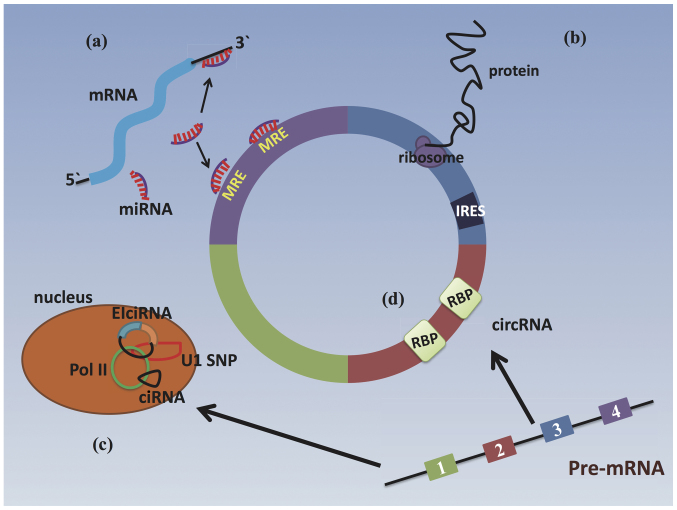
The most vital function of competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) is to function as inhibitors of microRNA (miRNA or miRs) by sponging a specific miRNA at multiple binding sites in the circular sequence. miRNAs are small, endogenous RNAs (22 nucleotides in length) that play critical regulatory roles in animals and plants by targeting 3'UTRs of mRNAs for the cleavage or translational repression of protein-coding genes (20). ceRNAs contain several different miRNA response elements (MREs) within their sequences. ceRNAs act as miRNA sponges to restrain miRNAs, suppressing the expression of their target genes (Fig. 2). It has previously been demonstrated that several abundant ceRNAs can act as miRNA sponges in the cytoplasm, e.g., ciRS-7/CDR1 (21). CiRS-7, as an antisense transcript of the human circRNA cerebellar degeneration-related protein 1 transcript (CDR1), contains over 70 conserved binding sites for miRNA-7. The relatively high expression of CiRS-7 in a number of human tissues increases the expression of miR-7 target genes by suppressing miR-7 activity. The sponging of miR-7 by ciRS-7 affects the proliferation, migration and invasion of cancer cells by regulating oncogenes in cancer-related signaling pathways (16,22,23).
Figure 2.
Regulatory mechanisms of circRNAs. (a) circRNAs function as miRNA sponges to protect their target mRNAs from miRNA attack, promoting the more efficient translation of target mRNAs. (b) circRNAs containing an IRES upstream of the start codon can be translated to produce proteins. (c) Model of circRNAs regulating the expression of a parental gene: ciRNAs can bind to RNA pol II and function in the promoter regions of genes. eiciRNA can interact with the U1 snRNP and then bind to RNA Pol II in the promoter to stimulate host gene expression. (d) circRNAs can function as RBP sponges that interact with RBPs. circRNA, circular RNA; IRES, internal ribosome entry site; ciRNA, circular intronic RNA; RNA Pol II, RNA polymerase II; snRNP, small nuclear ribonucleoprotein.
ii) Interacting with RNA-binding proteins
In addition to acting as miRNA sponges, circRNAs are also able to interact with, sequester and transport RBPs and subsequently influence target protein activities (24) (Fig. 2). Examples include circ-Foxo3, circ-MBL (muscleblind) and circCcnb1, etc (25). circ-Foxo3 is highly expressed in non-cancer cells and can bind cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)2 and CDK inhibitor 1 (p21). The circ-Foxo3-p21-CDK2 complex can suppress the formation of the cyclin E/CDK2 complex, which results in the arrest of the cell cycle from the G1 to the S phase (26). In p53 mutant cells, circ-Ccnb1 can form a complex by interacting with H2AX and Bclaf1, which induces the death of breast cancer cells, whereas circ-Ccnb1 can prevent the cancer-suppressing effects by binding H2AX and wild-type p53 (25).
iii) Regulation of parental gene transcription and splicing
Some subclasses of circRNAs are enriched in the nucleus. They can function as post-transcriptional regulators of genes with various mechanisms. ciRNAs and eiciRNAs can participate in parental gene transcription and splicing under different regulatory models. ci-ankrd52 and ci-sirt7 positively promote parental gene transcription in cis regulatory elements by interacting with the RNA polymerase II (Pol II) complexes at the transcription sites of their host genes (16). In HeLa and 293 cells, eiciRNAs, such as circEIF3J and circPAIP can promote the transcription of parental genes in a cis-acting manner by interacting with U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) and further combining with RNA polymerase II (Pol II) complexes (14) (Fig. 2).
iv) Translation and the modulation of translation
circRNAs have long been considered to be a type of endogenous non-coding RNA, which largely do not encode proteins (27). However, some researchers have demonstrated that a few circRNAs have the potential to be translated into proteins in vitro and in vivo when they possess internal ribosome entry sites (IRESs) upstream of start codons (28) (Fig. 2). Circular zinc-finger protein 609 (Circ-ZNF609) contains an open reading frame (ORF) and can be translated into a protein in murine myoblasts when driven by an IRES (29). The ORFs of circ-SHPRH and circ-FBXW7 are driven by IRESs and can be translated into functional proteins in a similar pattern to circ-ZNF609 (30,31). In addition, the most abundant base modification of RNAs, the N6-methy-ladenosine (m6A) residues found in circRNAs, have been suggested to accelerate the cap-independent translation of circRNAs (32). Furthermore, the translation of certain linear mRNAs can be modulated by their cognate circRNAs. In HeLa cells, circPABPN1 can bind HuR, an RNA-binding protein that promotes translation, and the complex that is formed inhibits HuR binding to PABPN1 mRNA. Finally, the translation of PABRN1 is reduced (33).
v) Biomarkers
Due to their conservation, specificity and stability, circRNAs can be used as potential biomarkers for various diseases, particularly cancers (34). Growing evidence has indicated that a single circRNA possesses moderate diagnostic value, whereas combined circRNAs improve the diagnostic efficacy (35). circLPAR1 exhibits a low expression level in muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) and predicts a poor prognosis. It may regulate the invasion and metastasis of MIBC by targeting miR-762 and has the potential to serve as a stable biomarker for the prognosis of MIBC (36). In HCC, circSMARCA5 can stimulate apoptosis and suppress proliferation, invasion and metastasis. It exhibits a high accuracy for the diagnosis of HCC and may function as a potential biomarker for monitoring HCC (37). circ_0068871 can promote bladder cancer progression by modulating the miR-181a-5p/FGFR3 axis and activating STAT3 (38). Therefore, it may function as a potential biomarker.
3. circRNAs and gastrointestinal cancer
circRNAs are involved in the regulation of tumor progression. The deregulation of circRNAs affects cell proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, apoptosis, angiogenesis and the cell cycle (39). Thus, circRNAs have the potential to serve as tumor-targeted sites in tumor metastasis therapy. In this section, the diagnostic and prognostic significance of circRNAs in the development of tumor metastasis in gastrointestinal cancer is emphasized.
circRNAs in CRC
Colorectal cancer is a common type of malignant tumor with the third highest occurrence rate; however, it represents the second leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Over 1.8 million new cases and 881,000 deaths were attributed to CRC in 2018 (40). The majority of patients have already developed metastasis at the initial diagnosis. The development of CRC is a multistep process involving various factors, such as the BRAF gene, the APC gene and the KRAS oncogene mutations, abnormal chromosome segregation, abnormal hypermethy lation of gene promoter region, loss of function of the p53 gene (41,42). The more in depth understanding of the underlying molecular mechanisms of the development and progression of CRC is of utmost importance in order to identify and develop novel therapeutic markers and strategies. During CRC progression, some circRNAs play a positive regulatory role in the disease, while others do not. circRNAs play critical roles in the biological behavior of tumors.
circ-1569, located on the plus strand of chromosome 16q13.1, is upregulated in CRC tissues and is associated with aggressive characteristics in CRC. It directly inhibits miR-145 transcription by acting as a sponge. The miR-145 functional targets (E2F5, BAG4 and FMNL2) are then upregulated, which carry out a tumor-promoting function in CRC cells (43). This finding reveals a novel mechanistic connection between miR-145 and circ-1569 in regulating the progression of CRC, which may provide new insight into CRC progression and may lead to the development of therapeutic strategies for CRC prevention and treatment.
CDR1as (ciRS-7) harbors ~70 conserved binding sites. It exhibits a higher expression in CRC tissues than in the adjacent normal mucosa. CDR1as may influence tumor biological behavior as an miRNA sponge. The tumor inhibitory effect of miR-7 can be reversed by the overexpression of ciR-7 in HCT116 and HT29 cells. The target gene EGFR is then activated, which results in the increased proliferation, invasion and migration of CRC cells. This finding reveals that aberrant CDR1as/miR-7/EGFR may serve as a promising molecular target for the development of novel therapies to control CRC progression (44).
Several studies have demonstrated that miR-21 and miR-31 act as oncogenic molecules in various types of cancer. miR-21 can increase the proliferation and migration of colon cancer cells, such as SW480 and HCT116 cells (45). miR-31 can promote the resistance of CRC cells to 5-fluorouracil (46). circ-0026344, which is downregulated >5-fold in CRC tissues compared to normal tissues (47), acts as an miRNA sponge for miRNA-21 and miRNA-31. The low expression of circ-0026344 increases the expression of miR-21 and miR-31, which promotes the growth and invasion, but suppresses the apoptosis of CRC cells. The circ_0026344/miR-21/miR-31 regulatory axis plays an important role in the progression of CRC, and circ-0026344 can be used as a reliable prognostic biomarker in patients with CRC (41).
circRNA_103809 expression in colorectal cancer cell lines is lower than that in normal colorectal epithelial cells and can promote the proliferation and migration of CRC cells. As circRNA-103809 has a binding site within miR-532-3p, the deregulation of miR-532-3p can increase the expression of circRNA-103809 and Foxo4 in SW620 cells. This indicates that circRNA-103809 competitively binds to miR-532-3p as a ceRNA, which in turn regulates FOXO4 expression and thereby restrains the proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells (48).
Overall, almost 30 circRNAs participate in the progression of the cell cycle, proliferation, invasion, metastasis and apoptosis by functioning as oncogenes or antioncogenes in CRC. Further information on this matter is presented in Table I.
Table I.
Summary of the expression of circRNAs and the circRNA/miRNA axis in signaling pathways related to colorectal cancer.
| circRNA | Expression | miRNA sponge | Intersection molecules and/or pathway | Function | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa_circ_001569 | ↑ | miR-145 | E2F5, BAG4, | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (43) |
| FMNL2↑ | |||||
| hsa_circ_0071589 | ↑ | miR-600 | EZH2↑ | Viability (+) | (49) |
| Proliferation (+) | |||||
| Invasion (+) Migration (+) | |||||
| ciRS-7 | ↑ | miR-7 | EGFR/RAF1/ | Invasion (+) Metastasis (+) | (50) |
| MPK pathway | |||||
| hsa_circ_0020397 | ↑ | miR-138 | TERT, PD-L1↓ | Viability (+) Apoptosis (−) | (42) |
| Circular RNA ZNF609 | ↓ | miR-150-5p | AKT3↑ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (51) |
| hsa_circ_0000284 | ↑ | miR-7 | FAK, IGF1R, | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (52) |
| EGFR, YY1↑ | Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | ||||
| hsa_circ_000984 | ↑ | miR-106b | CDK6↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (53) |
| Invasion (+) Cell Cycle (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0026344 | ↓ | miR-21 | PTEN↓ | Proliferation (−) | (40,54) |
| miR-31 | SATB2, FIH-1α↓ | Invasion (−) | |||
| miR-183 | Apoptosis (+) | ||||
| circRNA_100290 | ↑ | miR-516b | FEDZ4-Wnt/ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (55) |
| β-catenin signal | Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | ||||
| pathway↑ | |||||
| hsa_circRNA_103809 | ↓ | miR-532-3p | FOXO4↓ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (48) |
| circRNA-ACAP2 | ↓ | miR-21-5p | Tiam1↑ | Proliferation (+) | (56) |
| Clonogenicity (+) Migration (+) | |||||
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circITGA7 | ↓ | miR-370-3p | NF1↓-Ras signaling pathway↑ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (57) |
| cir-ITCH | ↓ | miR-7/20a | Wnt/β-catenin; ITCH, TCF, c-myc, cyclinD1 | - | (58) |
| circ-BANP | ↑ | - | PI3K/Akt pathway↑ | Proliferation (+) | (59) |
| hsa_circ_104700 | ↓ | miR-141/500a/509-5p | - | (24) | |
| miR-619-3p/578 | |||||
| hsa_circ_0007031 | ↑ | miR-885-3p | - | (60) | |
| hsa_circ_0007006 | ↑ - | AKT3 | - | (24) | |
| hsa_circ_0048234 | ↓ | miR-671-5p | EGFR↓ | Crr (−) | (60) |
| hsa_circ_105055 | ↑ | miR-7 | PRKCB, EPHA3, | Proliferation (+) Apoptosis (−) | (61) |
| BRCA1, ABCC1 | |||||
| hsa_circ_0000504 | ↑ | miR-485-5p | STAT3↓ | 5-FU resistance | (60) |
| circCCDC66 | ↑ | miRNA-33b | MYC↑ | Proliferation (+) | (62) |
| miR-93 | Migration (+) | ||||
| hsa_circ_0005075 | ↑ - | Wnt/β-catenin | Metastasis (+) Invasion (+) | (63,64) | |
| pathways↑ | Growth (+) | ||||
| circPIP5K1A | ↑ | miR-1273a | - | Migration (+) Invasion (+) | (65) |
| circ_0000218 | ↑ | miR-139-3p | RAB1A↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (66) |
| circ_0079993 | ↑ | miR-203a-3p.1 C | REB1↑ | Proliferation (+) | (67) |
| circ_0021977 | ↓ | miR-10b-5p | P21↓/P53↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) Invasion (−) | (68) |
| circ_0055625 | ↑ | miR-106b-5p (miR-106b) | ITGB8↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (69) |
| Circular RNA CBL.11 | ↑ | miR-6778-5p | YWHAE↑ | Proliferation (−) | (70) |
| circDDX17 | ↓ | miR-31-5p | KANK1↓ | Metastasis (−) Invasion (−) 5-Fu resistance (−) Apoptosis (+) | (71) |
| circDENND4C | ↑ | miR-760 | GLUT1↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) Glycolysis (+) | (72) |
| hsa_circ_0007534 | ↑ | miR-613 | SLC25A22↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) Invasion (+) Glycolysis (+) Colony formation (+) | (73) |
| circ_0056618 | ↑ | miR-206 | CXCR4, VEGF-A↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) Angiogenesis (+) | (74) |
| circ_0001313 | ↑ | miR-510-5p | AKT2↑ | Proliferation (+) Apoptosis (−) | (75) |
| circAPLP2 | ↑ | miR-101-3p | NOTCH↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (76) |
| miR-485-5p | FOXK1↑ | Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | |||
| circ_001971 | ↑ | miR-29c-3p | VEGFA↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) Angiogenesis (+) | (77) |
| circPRKDC | ↑ | miR-375 | FOXMI↑ | 5-Fu resistance (+) | (78) |
| circHUWE1 | ↑ | miR-486 | - | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) Invasion (+) | (79) |
| circSAMRCC1 | ↑ | miR-140-3p | MMPs↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) Invasion (+) Metastasis (+) | (80) |
| circCTNNA1 | ↑ | miR-149-5p | FOXM1↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) Invasion (+) | (81) |
| circRUNX1 | ↑ | miR-145-5P | IGF1↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (82) |
| Metastasis (+) Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circ_0001946 | ↑ | miR-135a-5p | EMT pathway↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (83) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0038646 | ↑ | miR-331-3p | GPIK3↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (84) |
| circIFT80 | ↑ | miR-1236-3p | HOXB7↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (85) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circFAT1 | ↑ | miR-520b | UHRF1↑ | Proliferation (+) Glycolysis (+) | (86) |
| miR-302c-3p | Apoptosis (−) | ||||
| hsa_circ_001680 | ↑ | miR-340 | BMI1↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (87) |
| hsa_circ_102209 | ↑ | miR-761 | RIN1↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (88) |
| Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circCBL.11 | ↓ | miR-6778-5p | YWHAE↓p53↓ | Proliferation (+) | (70) |
| circCCT3 | ↑ | miR-613 | WNT3↑VEGFA↑ | Metastasis (+) Invasion (+) | (89) |
| Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circFARSA | ↑ | miR-330-5p | LASP1↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (90) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0079993 | ↑ | miR-203a-3p C | REB1↑ | Proliferation (+) | (67) |
| hsa_circ_0005615 | ↑ | miR-149-5p | TNKS↑ | Proliferation (+) | (91) |
| circ_0000218 | ↑ | miR-139-3p | RAB1A↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (66) |
| hsa_circ_0001178 | ↑ | miR-382/587/616 | ZEB1↑ | Metastasis (+) Invasion (+) | (92) |
| circPACRGL | ↑ | miR-142-3p | TGF-β1↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (93) |
| miR-506-3p | Invasion (+) | ||||
| hsa_circ_0001806 | ↑ | miR-193-5p C | OL1A1↑ | Metastasis (+) Invasion (+) | (94) |
| hsa_circ_0008285 | ↓ | miR-382-5p | PTEN↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (95) |
| hsa_circ_0128846 | ↑ | miR-1184 | AJUBA↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (96) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0060745 | ↑ | miR-4736 | CSE1L↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (97) |
| hsa_circ_0005963 | ↑ | miR-122 | PKM2↑ | Chemoresistance (+) | (98) |
| hsa_circ_0053277 | ↑ | miR-2467-3p | MMP14↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (99) |
| EMT (+) | |||||
| circHIPK3 | ↑ | miR-1207-5p | FMNL2↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (100) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circPRMT5 | ↑ | miR-377 | E2F3↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (101) |
| circ_0004277 | ↑ | miR-512-5p | PTMA↑ | Proliferation (+) Apoptosis (−) | (102) |
| hsa_circ_0137008 | ↓ | miR-338-5p | - | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (103) |
| Invasion (−) | |||||
| circ_0007142 | ↑ | miR-122-5p CDC | 25A↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (104) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_100876 | ↑ | miR-5166 | - | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (105) |
| Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circAGFG1 | ↑ | miR-4262 | YY1↑CTNNB1↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (106) |
| miR-185-5p | Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | ||||
| circPIP5K1A | ↑ | miR-1273a | - | Migration (+) Invasion (+) | (65) |
| circVAPA | ↑ | miR-125a | CREB5↑ | Migration (+) Invasion (+) | (107) |
| Glycolysis (+) | |||||
| circNOL10 | ↓ | miR-135a/b-5p | KLF9↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (108) |
| Invasion (−) | |||||
| circCAMSAP1 | ↑ | miR-328-5p | E2f1↑ | Proliferation (+) | (109) |
circRNA, circular RNA; ↓, downregulation; ↑, upregulation; -, no finding; (+), promotion; (−), inhibition.
circRNAs in GC.GC is the most common type of tumor in the digestive system and was responsible for over 1,000,000 new cases in 2018, resulting in an estimated 783,000 deaths (110). These statistics render GC the fifth most frequently diagnosed type of cancer and the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality (40). Due to the high pateint mortality due to GC, the identification of appropriate molecular biomarkers for its early diagnosis and potential targets for GC therapy re urgently required.
circHIPK3 can sponge miR-124 and miR-29. The upregulation of circHIPK3 decreases the expression of miR-124 and miR-29b, which promotes GC cell proliferation. During this process, the mRNA transcriptional levels of 3 target genes (COL1A1, COL4A1 and CDK6) of the circHIPK3-miRNA-124/miRNA-29b axes are upregulated in GC cells. The survival status of GC can be predicted by detecting the expression levels of COL1A1 and COL4A1. These findings indicate that not only circHIPK3, but also COL1A1 and COL4A1 can serve as prognostic biomarkers of the survival of patients with GC, which expands our understanding of the transcriptional mechanisms in GC (111).
miR-206 has been reported to function as an inhibitory miRNA in GC, and its overexpression can inhibit the expression of CXCR4. circ_0056618, which is upregulated in GC, can sponge miR-206 in GC, and suppress cell proliferation and invasion by upregulating CXCR4. Therefore, circ_0056618/miR-206/CXCR4 is able to improve the survival rates of patients with GC by inhibiting GC cell proliferation and metastasis (112).
circRNAs also function as anti-oncogenes. circLARP4, derived from exons 9 and 10 of the LARP4 gene, is overex-pressed in GC. It can inhibit DNA synthesis, cell proliferation and invasion by sponging miR-424 and subsequently upregulates the expression of the LATS1 and YAP genes in GC. Thus, circLARP4 may function as a tumor-suppressive factor in GC by regulating the miR-424/LATS1/YAP signaling pathway. circLARP4 can also serve as an independent prognostic marker for the 5-year overall survival rate of patients with GC and patients undergoing chemotherapy (113).
Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is a tumor suppressor that is mutated in various types of cancers at a high frequency (114). It can be targeted and regulated by miR-130a and miR-107, thereby affecting the activity of cancer cells (115,116). circ-ZFR can regulate the expression of miR-130a and miR-107 by sponging these miRNAs, thereby regulating the expression of PTEN. This indicates that circ-ZFR can suppress GC cell propagation and the cell cycle, and can promote apoptosis by sponging miR-107/miR-130a and modulating PTEN, which provides comprehensive insight into the regulatory role of the circ-ZFR/miR-130a/miR-107/PTEN axis in GC and facilitates the discovery of novel therapeutic targets for the treatment of GC (117).
Although there are many circular RNAs that serve as biomarkers for GC, further clinical and basic research is required to improve the survival time of patients with GC. Over 15 circRNAs participate in the cell cycle, proliferation, invasion, metastasis and apoptosis by functioning as oncogenes or anti-oncogenes in GC. For further information on circRNAs in GC, please refer to Table II.
Table II.
Summary of the expression of circRNAs and the circRNA-miRNA axis in signaling pathways related to gastric cancer.
| circRNA | Expression | miRNA sponge | Intersection molecules and/or pathway | Function | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| circRNA-100269 | ↓ | miR-630 | - | Proliferation (+) | (118) |
| circLARP4 | ↓ | miR-424 | LATS1↓ | Proliferation (−) Invasion (−) | (113) |
| circPVT1 | ↑ | miR-125b | E2F2↑ | Proliferation (+) | (119) |
| hsa_circ_0005075 | ↓ | miR-23b-5p | Wnt/β-catenin | (120) | |
| signal pathway | |||||
| hsa_circ_000425 | - | miR-17/ | p21/BIM↑ | Cell growth (−) | (121) |
| miR-106b | |||||
| circRBMS3 | ↑ | miR-153 | SNAI1↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (122) |
| hsa_circ_0000673 | ↓ | miR-532-5p | RUNX3↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (123) |
| circ_0056618 | ↑ | miR-206 | CXCR4↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (112) |
| circHIPK3 | ↑ | miR-124/ | - | Proliferation (+) | (111) |
| miR-29b | |||||
| hsa_circ_0000993 | ↓ | miR-214-5p | - | Migration (+) Invasion (+) | (124) |
| Proliferation (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0000096 | ↓ | miR-224/200a | cyclinD1, CDK6, | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (125) |
| MMP2/9, Ki67, | Cell Cycle (−) | ||||
| VEGF↓ | |||||
| hsa_circ_0000026 | ↓ | miR-23a/23b/ | - | Regulates transcription, | (126) |
| 581/146a/450a | RNA metabolism, | ||||
| gene expression and | |||||
| gene silencing | |||||
| hsa_circ_104916 | ↓ - | E-cadherin↓; | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (127) | |
| N-cadherin↑ | |||||
| hsa_circ_0000520 | ↓ | miR-556-5p/ | - | TNM stage of gastric cancer (−) | (128) |
| 521/1204/ | |||||
| 512-5p/663b/ | |||||
| 1258/1233/ | |||||
| 1296/146b-3p | |||||
| circ-ZFR | ↓ | miR-130a/107 | PTEN, p53↓ | Proliferation (−) Apoptosis (+) | (117) |
| circ-ERBB2 | ↑ | miR-503/ | CACUL1↑/ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (129) |
| miR-637 | MMP-19↑ | ||||
| hsa_circ_0001368 | ↓ | miR-6506-5p | FOXO3↓ | Proliferation (−) Invasion (−) | (130) |
| hsa_circ_0001821 | ↓ | miR-197 | MTDH/PTEN/ | Proliferation (−) Metastasis (−) | (131) |
| AKT↓ | |||||
| circ-ZNF609 | ↑ | miR-145-5p | - | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (132) |
| circ-GRAMD1B | ↓ | miR-130a-3p | PTEN/P21↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (133) |
| Invasion (−) | |||||
| circ-NOTCH1 | ↑ | miR-637 | Apelin↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (134) |
| Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0000291 | ↑ | miR-183 | ITGB1↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (135) |
| circ_SPECC1 | ↓ | miR-526b | KDM4A/ | Proliferation (−) Invasion (−) | (136) |
| YAP1 pathway (+) | Apoptosis (+) | ||||
| hsa_circ_0092306 | ↑ | miR-197-3p | PRKCB↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (137) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_PRMT5 | ↑ | miR-145/1304 | MYC↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (138) |
| Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| hsa_circ_006100 | ↑ | miR-195 | GPRC5A↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (139) |
| Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circ_EIF4G3 | ↑ | miR-335 | - | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (140) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_LMTK2 | ↑ | miR-150-5p | c-Myc↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (141) |
| circ_DCAF6 | ↑ | miR-1231/1256 | - | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (142) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0067997 | ↑ | miR-515-5p | XIAP↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (143) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_NHSL1 | ↑ | miR-1306-3p | SIX1↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (144) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_0000267 | ↑ | miR-503-5p | HMGA2↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (145) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circRHOBTB3 | ↓ | miR-654-3p | p21↓ | Proliferation (−) | (146) |
| circREPS2 | ↓ | miR-558 | RUNX3↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (147) |
| β-catenin signaling | Invasion (−) | ||||
| pathway (+) | |||||
| circ_0006282 | ↑ | miR-155 | FBXO22↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (148) |
| circMTO1 | ↓ | miR-3200-5p | PEBP1↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (149) |
| Invasion (−) | |||||
| hsa-circ-0017639 | ↑ | miR-224-5p | USP3↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (150) |
| circ_0008035 | ↑ | miR-599 | EIF4A1↑ | Proliferation (+) Apoptosis (−) | (151) |
| hsa_circ_0001017 | ↓ | miR-197 | RHOB↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (152) |
| Invasion (−) | |||||
| circ_PRL15 | ↑ | miR-502-3p | OLFM4↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (153) |
| STAT3 pathway (+) | Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | ||||
| circNRIP1 | ↑ | miR-182 | ROCK1↑ | Migration (+) Invasion (+) | (154) |
| Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circCYFIP2 | ↑ | miR-1205 | E2F1↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (155) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_000684 | ↑ | miR-186 | ZEB1↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (156) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_OXCT1 | ↓ | miR-136 | SMAD4↓ | Metastasis (−) | (157) |
| circ_MAT2B | ↑ | miR-515-5p | HIF-1α↑ | Metastasis (+) | (158) |
| hsa_circ_0000670 | ↑ | miR-384 | SIX4↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (159) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_CEP85L | ↓ | miR-942-5p | NFKBIA↓ | Proliferation (−) Invasion (−) | (160) |
| circ_RanGAP1 | ↑ | miR-877-3p | VEGFA↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (161) |
| circCCDC9 | ↓ | miR-6792-3p C | AV1↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (162) |
| Invasion (−) | |||||
| circPIP5K1A | ↑ | miR-376c-3p | ZNF146↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (163,164) |
| miR-671-5p | KRT80↑ | Invasion (+) | |||
| hsa_circ_0000467 | ↑ | miR-326-3p | - | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (165) |
| circHIAT1 | ↓ | miR-21 | - | Proliferation (−) | (166) |
| circMAN2B2 | ↑ | miR-145 | JNK↑ PI3K/ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (167) |
| AKT pathway (−) | |||||
| circ_0000190 | ↓ | miR-1252 | PAK3↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (168) |
| hsa_circ_0003159 | ↓ | miR-223-3p | NDRG1↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (169) |
| Invasion (−) Apoptosis (+) | |||||
| circRBM33 | ↑ | miR-149 | IL-6↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (170) |
| Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circ_0001023 | ↑ | miR-409-3p | PHF10↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (171) |
| Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circ_104433 | ↑ | miR-497-5p CDC | 25A↑ | Proliferation (+) Apoptosis (−) | (172) |
| circ_0005075 | ↑ | miR-431 | p52/EMT↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (173) |
| hsa_circ_0001546 | ↓ | miR-421 | ATM↓ Chk2/ | Proliferation (−) | (174) |
| p52 pathway (−) | Chemoresistance (−) | ||||
| circSMC3 | ↑ | miR-4720-3p | TJP1↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (175) |
| circSHKBP1 | ↑ | miR-582-3p | HUR/VEGF↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (176) |
| Invasion (+) Angiogenesis (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0007766 | ↑ | miR-1233-3p | GDF15↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (177) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_100876 | ↑ | miR-136 | MIEN1↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (178) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_ATAD1 | ↑ | miR-140-3p | YY1↑/ | Proliferation (+) | (179) |
| PCIF1 signaling | |||||
| pathway (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0023642 | ↑ | miR-223 | - | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (180) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_DUSP16 | ↑ | miR-145-5p | - | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (181) |
| circATXN7 | ↑ | miR-4319 | ENTPD4↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (182) |
| Apoptosis (−) |
circRNA, circular RNA; ↓, downregulation; ↑, upregulation; -, no finding; (+), promotion; (−), inhibition.
circRNAs in esophageal cancer.Esophageal cancer is one of the most common gastrointestinal malignancies and was ranked 7th in terms of its incidence and 6th overall in 2018. Patients with esophageal cancer present various symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing, a hoarse voice and weight loss (40,183). However, the clinical diagnosis of esophageal cancer is mainly dependent on biopsy using an endoscope, and the most common treatments are surgery, chemotherapy and radiation, depending on the cancer stage and location (184). circRNAs mainly function as oncogenes in esophageal cancer. These circRNAs influence the expression of specific genes or their associated signaling pathways. In the present review, the findings of recent investigations into the role of circRNAs in the development and progression of esophageal cancer are discussed and summarized.
The most well-known circRNA, ciRS-7, has been reported to contain >70 binding sites for miR-7. It can suppress miR-7 activity by acting as an miR-7 sponge (185,186). In addition, it also harbors 19 miR-876-5p-binding sites and functions as a sponge of miR-876-5p, which directly targets the tumor antigen MAGE-A family and suppresses the migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells. The discovery of ciRS7 provides a novel potential therapeutic target for the treatment of ESCC (187).
cir-ITCH is expressed in low levels in esophageal carcinoma. As a potential tumor suppressor, it upregulates the expression of the miRNA target gene, ITCH, by sponging miRNAs, such as miR-7, miR-17 and miR-214, which results in the suppression of the canonical Wnt pathway by inhibiting phosphorylated Dvl2, preventing oncogenesis. This indicates that the low expression of cir-ITCH increases cell viability and promotes proliferation via the cir-ITCH/miR-7/miR-17/miR-214/ITCH/Dvl2/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in ESCC cells (188). For further information regarding the regulation of signaling by other circRNAs in esophageal cancer, please refer to Table III.
Table III.
Summary of the expression of circRNAs and the circRNA-miRNA axis in signaling pathways related to esophageal cancer.
| circRNA | Expression | miRNA sponge | Intersection molecules and/or pathway | Function | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cir_ITCH | ↓ | miR-7/17 | ITCH↑-Dvl2↑- | Viability (−) | (188) |
| miR-214 | Wnt/β-catenin | Proliferation (−) | |||
| signaling pathway (−) | |||||
| ciRS_7 | ↑ | miR-876-5p | MAGE-A↑ | Metastasis (+) | (187) |
| miR-7 | HOXB13-mediated | Proliferation (+) | (183) | ||
| NF-κB/p65 | Invasion (+) | ||||
| pathway(+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_001059 | ↑ | miR-30c-1*/ | - | Influence Radiotherapy | (189) |
| 30c-2*/122*/ | Resistance | ||||
| 139-3p/ | |||||
| 339-5p/1912 | |||||
| hsa_circRNA_100873 | ↑ | miR-663a | - | Metastasis (+) | (190) |
| hsa_circ_0006948 | ↑ | miR-490-3p | HMGA2↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (191) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_100367 | ↑ | miR-217 | Wnt3 pathway↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (192) |
| Radioresistance (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0004771 | ↑ | miR-339-5p CDC | 25A↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (193) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_0003340 | ↑ | miR-564 | TPX2↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (194) |
| Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circRAD23B | ↑ | miR-5095 | PARP2↑ AKT2↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (195) |
| circZNF292 | ↑ | miR-206 | AMPK/PI3K/AKT | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (196) |
| signaling pathway (−) | Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | ||||
| circPRKCI | ↑ | miR-186-5p | PARP9↑ | Proliferation (+) | (197) |
| Radiosensitivity (−) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0006168 | ↑ | miR-100 | mTOR↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (198) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circUBAP2 | ↑ | miR-422a | Rab10↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (199) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0000654 | ↑ | miR-149-5p | IL-6↑/STAT3 | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (200) |
| signaling pathway (+) | Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | ||||
| circLARP4 | ↓ | miR-1323 | PTEN↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (201) |
| Apoptosis (+) |
circRNA, circular RNA; ↓, downregulation; ↑, upregulation; -, no finding; (+), promotion; (−), inhibition.
circRNAs in HCC.HCC is the 4th most common cause of cancer-related mortality and the 6th most diagnosed type of cancer worldwide, accounting for approximately 841,000 new cases and 782,000 deaths annually (40). However, due to the high frequency of disease metastasis, recurrence and poor diagnoses, HCC remains one of the most lethal forms of cancer worldwide, and liver resection and transplantation are the main therapies applied (202). Therefore, it is necessary to identify potential biomarkers for the early detection of HCC and to explore new strategies for HCC treatment. A large amount of evidence related to cancer diagnostics and therapeutics indicates that circRNAs are involved in HCC progression, and may therefore serve as sensitive biomarkers and miRNA sponges for the detection of carcinogenesis, as well as for the monitoring of therapies for HCC (203,204). However, the expression profiles, functions and deregulation of circRNAs in HCC remain to be determined.
Hsa_circ_0005057 was first found to be expressed at significantly higher levels in HCC tissues than in adjacent liver tissues. Hsa_circ_0005057 inhibits the expression and function of miR-23b-5p, and miR-23b-5p is subsequently downregulated. In addition, a potential interaction between miR-23b-5p and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway has been identified. The ultimate effect of hsa_circ_0005057 is to promote the growth of tumors (120).
It has been demonstrated that Cdr1as expression is upregulated in HCC tissues compared with adjacent non-tumor tissues. The knockdown of Cdr1as inhibits HCC cell proliferation and invasion by targeting miR-7 and CCNE1 and PIK3CD, and Cdr1as functions as an oncogene partly by targeting miR-7 in HCC (202,205,206). Hsa_circ_0001649, which is significantly downregulated in HCC tissues, exhibits miRNA-binding sites for miR-1283, miR-4310 and miR-182-3p and is positively associated with the metastasis and invasion of HCC (207). circRNA mitochondrial translation optimization 1 homologue (circMTO1; hsa_circRNA_0007874/hsa_circRNA_104135) is downregulated in HCC tissues, and miR-9 is overexpressed in HCC, which results in the HCC cell proliferation and invasion. The finding that circMTO1 co-localizes with miR-9 in the cytoplasm and that this co-localization is decreased in tumors compared to adjacent non-tumor tissues, has indicated that circMTO1 can inhibit the progression of HCC by serving as a sponge of oncogenic miR-9 to promote p21 expression (208). For further information on circRNAs in HCC, please refer to Table IV.
Table IV.
Summary of the expression of circRNAs and the circRNA-miRNA axis in signaling pathways related to hepatocellular carcinoma.
| circRNA | Expression | miRNA sponge | Intersection molecules and/or pathway | Function | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| circRNA_10720 | ↑ | miRNA | Vimentin↓ | EMT (+) | (209) |
| hsa_circ_103809 | ↓ | miR-620 | - | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (210) |
| Invasion (−) | |||||
| circRNA_CDYL | ↑ | miR-328-3p | HIF1N↑ | Proliferation (+) | (211) |
| miR-892a | NOTCH2↓ | Self-renewal (+) | |||
| SURVIVIN↓ | Chemoresistance (+) | ||||
| HDGF↑ | |||||
| NC↑ | |||||
| PI3K/Akt pathway | |||||
| hsa_circ_0005986 | ↓ | miR-129-5p | NOTCH1↓ | Cell cycle (−) Proliferation (−) | (212) |
| Hsa_circ_0004018 | ↓ | miR-30e-5p | MYC pathway | - | (213) |
| miR-626 | |||||
| hsa_circ_0001649 | ↓ | miR-127-5p | SHPRH↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (214) |
| miR-4688 | Invasion (−) | ||||
| miR-612 | |||||
| hsa_circ_101280 | ↑ | miR-375 | JAK2↑ | Proliferation (+) Apoptosis (−) | (215) |
| hsa_circ_0016788 | ↑ | miR-486 | CDK4 pathway | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (216) |
| Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circRNA-ZNF652 | ↑ | miR-203 | Snail↑ | Metastasis (+) Poor Prognosis | (217) |
| miR-502-5p | |||||
| hsa_circ_0000673 | ↑ | miR-767-3p | SET↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (218) |
| hsa_circ_0005075 | ↑ | miR-431 | - | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (219) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_001569 | ↑ | miR-411-5p | - | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (220) |
| miR-432-5p | Poor prognosis | ||||
| circ_0021093 | ↑ | miR-766-3p | MTA3 pathway | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (221) |
| Invasion (+) Poor prognosis | |||||
| Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circ_0000267 | ↑ | miR-646 | - | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (222) |
| Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circ_PRKC1 | ↑ | miR-545 | AKT3↓ | Invasion (+) Apoptosis (+) | (223) |
| hsa_circ_0091570 | ↓ | miR-1307 | ISM1↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (224) |
| Apoptosis (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0078710 | ↑ | miR-31 | HDAC2 | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | |
| CDK2↑ | Invasion (+) | ||||
| circ_SETD3 | ↓ | miR-421 | MAPK14↓ | Proliferation (−) | (225) |
| circ_0008450 | ↑ | miR-548p | - | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (226) |
| Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0079929 | ↓ | - | PI3K/Akt/ | Proliferation (−) Cycle (−) | (227) |
| mTOR pathway | |||||
| cdr1as | ↑ | miR-7 | CCNE1, PIK3CD↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (206) |
| circ_ADAMTS14 | ↓ | miR-572 | RCAN1↓ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (228) |
| Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circ_TRIM33-12 | ↓ | miR-191 | TET1↑ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (229) |
| 5hmC↓ | Invasion (−) Immune evasion (−) | ||||
| circ_MTO1 | ↓ | miR-9-p21 | - | Proliferation (−) Invasion (−) | (208) |
| hsa_circ_0000594 | ↑ | miR-217 | SIRT1↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (230) |
| Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circ_0067934 | ↑ | miR-1324 | FZD5↑-β-catenin↓ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (231,232) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circVAPA | ↑ | miR-377-3p | PSAP↑ | Proliferation (+) | (233) |
| circSETD3 | ↓ | miR-421 | MAPK14↓ | Proliferation (−) | (225) |
| circ_ZFR | ↑ | miR-3619-5p C | TNNB1↑ | Proliferation (+) | (234) |
| circ_SMAD2 | ↓ | miR-629 | - | Migration (−) Invasion (−) | (235) |
| circABCB10 | ↓ | miR-340-5p | NRP1/ABL2↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (236) |
| miR-452-5p | Invasion (−) | ||||
| hsa_circ_0056836 | ↑ | miR-766-3p | FOSL2↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (237) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0003141 | ↑ | miR-1827 | UBAP2↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (238) |
| Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0101145 | ↑ | miR-548c-3p | LAMC2↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (239) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circMYLK | ↑ | miR-362-3p | Rab23↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (240) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0008450 | ↑ | miR-214-3p | EZH2↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (241) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_0015756 | ↑ | miR-7 | FAK↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (242) |
| Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circ_5692 | ↓ | miR-328-5p D | AB2IP↓ | Proliferation (−) | (243) |
| hsa_circ_0070269 | ↓ | miR-182 | NPTX1↓ | Proliferation (−) Invasion (−) | (246) |
| hsa_circ_0000204 | ↓ | miR-191 | KLF6↓ | Proliferation (−) | (244) |
| circZFR | ↑ | miR-511 | AKT1↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (245) |
| Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circ_0005075 | ↑ | miR-335 | MAPK1↑ | Proliferation (+) | (246) |
| circ_0001955 | ↑ | miR-515a-5p | TRAF6/MAPK1↑ | Proliferation (+) | (247) |
| circPVT1 | ↑ | miR-203 | HOXD3↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (248) |
| hsa_circ_0101432 | ↑ | miR-1258 | MAPK1↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (249) |
| miR-622 | Apoptosis (−) | ||||
| hsa_circ_103809 | ↑ | miR-1270 | PLAG1↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (250) |
| miR-377-3p | FGFR1↑ | Invasion (+) ETM (+) | |||
| circ_PRMT5 | ↑ | miR-188-5p | HK2↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (251) |
| Glycolysis (+) | |||||
| circ_MAN2B2 | ↑ | miR-217 | MAPK1↑ | Proliferation (+) | (252) |
| circ_TCF4.85 | ↑ | miR-486-5p | ABCF2↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (253) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_0001178 | ↑ | miR-382 | VEGFA↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (254) |
| Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| circ_ZNF609 | ↑ | miR-15a/b-5p | GLI2↑ | Proliferation (+) Metastasis (+) | (255) |
| Hedgehog pathway (+) | Apoptosis (−) | ||||
| circMET | ↑ | miR-30-5p | Snail↑ | Invasion (+) Metastasis (+) | (256) |
| DPP4↑ | EMT (+) | ||||
| circ_PTN | ↑ | miR-326 | - | Proliferation (+) | (257) |
| circNFATC3 | ↓ | miR-5481 | NFATC3↓ | Proliferation (−) Migration (−) | (258) |
| Invasion (−) Apoptosis (+) | |||||
| circFBXO11 | ↑ | miR-605 | FOXO3/ABCB1↑ | Proliferation (+) | (259) |
| OXA Resistance (+) | |||||
| circZNF566 | ↑ | miR-4738-33p | TDO2↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (260) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circPVT1 | ↑ | miR-3666 | SIRT7↑ | Proliferation (+) Apoptosis (−) | (261) |
| circGprc5a | ↑ | miR-1283 | YAPI↑/TEADI | Proliferation (+) | (262) |
| signaling pathway (+) | Apoptosis (−) | ||||
| circ_0091579 | ↑ | miR-490-5p C | ASC3↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (263) |
| Invasion (+) Glycolysis (+) | |||||
| circ_DENND4C | ↑ | miR-195-5p | TCF4↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (264) |
| Apoptosis (−) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0000092 | ↑ | miR-338-3p | HN1↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (265) |
| Invasion (+) Angiogenesis (+) | |||||
| hsa_circ_0003998 | ↑ | miR-143-3p | FOSL2↑ | Invasion (+) | (266) |
| EMT (+) | |||||
| circ_CSPP1 | ↑ | miR-577 | CCNE2↑ | Proliferation (+) | (267) |
| circ_FOXP1 | ↑ | miR-875-3p | SOX9↑ | Proliferation (+) Invasion (+) | (268) |
| miR-421 | Apoptosis (−) | ||||
| hsa_circ_0091581 | ↑ | miR-5266 | c-MYC↑ | Proliferation (+) | (269) |
| circ_100084 | ↑ | miR-23a-5p | IGF2↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (270) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circMAST1 | ↑ | miR-1299 C | TNND1↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (271) |
| Invasion (+) | |||||
| circ_0000517 | ↑ | miR-1296-5p | TXNDC5↑ | Apoptosis (−) | (272) |
| hsa_circ_0026134 | ↑ | miR-127-5p | TRIM25/IGF2BP3↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (273) |
| circ_HOMER1 | ↑ | miR-1322 C | XCL6↑ | Proliferation (+) Migration (+) | (274) |
| Invasion (+) Apoptosis (−) |
circRNA, circular RNA; ↓, downregulation; ↑, upregulation; -, no finding; (+), promotion; (−), inhibition.
circRNAs in gallbladder cancer
Gallbladder cancer is the most common malignant neoplasm of the biliary tract, with a low 5-year overall survival rate of 5-10% (275,276). Gallbladder cancers are detected either incidentally or by clinical manifestation (277). However, patients with gallbladder cancer who present symptoms are usually at the advanced disease stage. Therefore, 90% of gallbladder cancers are diagnosed at regional or metastatic stages. It is widely acknowledged that surgical resection is the only curative method for gallbladder cancer, and other treatment modalities, such as chemoradiotherapy, are not effective in most cases without surgical resection (278). Due to the high recurrence, morbidity and mortality of gallbladder cancer, further research is warranted to discover potential biomarkers for the early detection and prognosis predication of this type of cancer.
Recent studies have demonstrated that circHIPK3 plays a critical role, not only in CRC, but also in gallbladder cancer. It is upregulated in human gallbladder cancer tissues and can modulate miR-124 downregulation and ROCK1-CDK6 upregulation as an miRNA sponge, thereby promoting gallbladder cancer cell growth (279). circFOXP1 (hsa_circ_0008234), derived from the exon region of the FOXP1 gene, is upregulated in GBC tissues and cells. It can promote PKLR expression by sponging miR-370 in GBC cells, resulting in the promotion of the Warburg effect in GBC progression. The effects include the promotion of cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and the inhibition of cell apoptosis in GBC (280). circERBB2, derived from the ERBB2 gene locus, differs from general circRNAs that are located in the cytoplasm and function as miRNA sponges. circERBB2 is enriched in nucleoli. It regulates the nucleolar localization of proliferation-associated protein 2G4 (PA2G4), thereby forming a circERBB2/PA2G4/TIFIA regulatory axis to upregulate Pol I activity and rDNA transcription. Finally, it promotes GBC proliferation and progression (281). Generally, only 3 circRNAs to date have been found to participate in GBC progression by functioning as oncogenes or anti-oncogenes.
4. Detection and therapeutic applications of circRNAs in gastrointestinal cancer
An ideal biomarker should be non-invasive, accurate, inexpensive, specific, sensitive and reliable, and reproducible body fluids are ideal material for use in the diagnosis of human cancer (282). circRNAs are usually stable both inside cells and in extracellular plasma, including blood and saliva (22). In addition, they are involved in the pathogenesis of a variety of diseases, such as diabetes, Alzheimer's disease and cancer. Therefore, the stability of circRNAs in bodily fluids and the specificity of circRNAs in diseases have made them promising non-invasive alternatives for use as diagnostic biomarkers for diseases, such as for the real-time monitoring of tumor progression and therapeutic responses, cancer screening, and susceptibility evaluation, particularly in gastrointestinal cancer (2). Currently, a few available clinical biomarkers, such as CEA and CA19-9, have been reported to exhibit low sensitivity and specificity for the early detection of CRC (283,284). circ_0014717 exists stably in human gastric juices and can potentially be used as a biomarker for the screening of high-risk GC (285). It has been discovered that the hsa_circ_0001017 and hsa_circ_0061276 levels are tightly associated with the main clinicopathological features of patients with GC, which indicates that they can serve as valuable blood-based biomarkers (282).
Some circRNAs function as oncogenes, and several therapeutic strategies have been proposed to target these. An exogenously delivered siRNA can accurately target unique back-splice junctions of circRNAs. The expression of circRNAs can then be suppressed (119,286,287). Another approach is the use of artificial miRNA sponges, such as TuD, with the aim of deceasing the level of oncomiRs (288).
The early diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancer is a main strategy to decrease the mortality rate associated with gastrointestinal cancer, and the regulation of circRNA expression will be the next therapeutic method tested for patients with gastrointestinal cancer. It is considered that more accurate disease detection will be achieved via the combined analysis of body fluid circRNAs and specific biological biomarkers.
5. Conclusion and future perspectives
In summary, circRNAs have been discovered as novel molecules in recent years and are no longer recognized as products of transcription errors. Some circRNAs present unique advantages, such as high abundance, stability and widespread expression. These unique characteristics of circRNAs indicate that they are potentially valuable biomarkers for assessing the prognosis and diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancers. Some circRNAs function as miRNA sponges and regulators of parental gene transcription and possess the ability to bind with RBPs. The functions and regulatory roles of circRNAs in tumors indicate that they are a potential target for the treatment of cancer. These findings provide new insight and potential therapeutic strategies for cancer prevention and treatment in the future.
However, the underlying molecular mechanisms of circRNAs are more complex than discussed in the present review. They may exhibit multiple interactions in cancers, that are not yet clearly understood. A number of studies have focused on the 'sponge' function of certain circRNAs. In fact, not all circRNAs possess a sponge function, as only a small number of circRNAs exhibit rich binding sites for certain target miRNAs (289). It is necessary to pay attention to other roles and uncover additional functions of circRNAs, such as the binding of RBPs and the mechanisms through which they affect gene translation. Furthermore, as the current methods for the detection and characterization of circRNAs are still limited and challenging, circRNAs are far from being implicated into clinical practice. These fundamental problems require further investigation.
Therefore, due to the numerous amounts of unanswered questions, circRNAs warrant further investigation. The regulatory networks of circRNAs/miRNAs/mRNAs and circRNAs/RBPs and other roles of circRNAs in gastrointestinal cancers need to be clarified in the future. The full elucidation of all the ceRNA and RNA/protein crosstalk that occurs under pathophysiological conditions in gastrointestinal cancers will certainly have exciting applications for the development of promising therapeutic approaches related to circRNAs.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The current study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 81760550 and 81460462), the Postgraduate Innovation Fund Project of Nanchang University (grant no. CX2019168).
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors' contributions
XZ, YW, PY, QZ and XY collected the related literature and drafted the manuscript. QY and DG participated in the design of the review and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Wang Y, Mo Y, Gong Z, Yang X, Yang M, Zhang S, Xiong F, Xiang B, Zhou M, Liao Q, et al. Circular RNAs in human cancer. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:25. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0598-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhang Y, Liang W, Zhang P, Chen J, Qian H, Zhang X, Xu W. Circular RNAs: Emerging cancer biomarkers and targets. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36:152. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0624-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sanger HL, Klotz G, Riesner D, Gross HJ, Kleinschmidt AK. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1976;73:3852–3856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zheng Q, Bao C, Guo W, Li S, Chen J, Chen B, Luo Y, Lyu D, Li Y, Shi G, et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11215. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Harder JM, Braine CE, Williams PA, Zhu X, MacNicoll KH, Sousa GL, Buchanan RA, Smith RS, Libby RT, Howell GR, John SWM. Early immune responses are independent of RGC dysfunction in glaucoma with complement component C3 being protective. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:E3839–E3848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1608769114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Benitez-Herreros J, Lopez-Guajardo L, Camara-Gonzalez C, Vazquez-Blanco M, Castro-Rebollo M. Association between macular perfusion and photoreceptor layer status in diabetic macular edema. Retina. 2015;35:288–293. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000000299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhao ZJ, Shen J. Circular RNA participates in the carcinogenesis and the malignant behavior of cancer. RNA Biol. 2017;14:514–521. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1122162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ren X, Du Y, You L, Zhao Y. Potential functions and implications of circular RNA in gastrointestinal cancer. Oncol Lett. 2017;14:7016–7020. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ying X, Hanmin C, Wenqi Y, Zhichang L, Zhengming Z. Research progress on the role of circRNA in gastrointestinal tumor. China J Clin Oncol. 2017;44:778–781. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Li B, Huang C. Regulation of EMT by STAT3 in gastrointestinal cancer (Review) Int J Oncol. 2017;50:753–767. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.3846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhang XO, Wang HB, Zhang Y, Lu X, Chen LL, Yang L. Complementary sequence-mediated exon circularization. Cell. 2014;159:134–147. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhang Z, Yang T, Xiao J. Circular RNAs: Promising biomarkers for human diseases. EBioMedicine. 2018;34:267–274. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.07.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jeck WR, Sharpless NE. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32:453–461. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, Chen L, Lin M, Wang X, Zhong G, Yu B, Hu W, Dai L, et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015;22:256–264. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen LL, Yang L. Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2015;12:381–388. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1020271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhang Y, Zhang XO, Chen T, Xiang JF, Yin QF, Xing YH, Zhu S, Yang L, Chen LL. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 2013;51:792–806. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wang Q, Qu L, Chen X, Zhao YH, Luo Q. Progress in understanding the relationship between circular RNAs and neurological disorders. J Mol Neurosci. 2018;65:546–556. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1125-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chen LL. The biogenesis and emerging roles of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17:205–211. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2015.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK, Burd CE, Liu J, Marzluff WF, Sharpless NE. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA. 2013;19:141–157. doi: 10.1261/rna.035667.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wei CC, Luo Z, Song YF, Pan YX, Wu K, You WJ. Identification of autophagy related genes LC3 and ATG4 from yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco and their transcriptional responses to waterborne and dietborne zinc exposure. Chemosphere. 2017;175:228–238. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ebbesen KK, Kjems J, Hansen TB. Circular RNAs: Identification, biogenesis and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1859:163–168. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Li X, Yang L, Chen LL. The biogenesis, functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Mol Cell. 2018;71:428–442. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kulcheski FR, Christoff AP, Margis R. Circular RNAs are miRNA sponges and can be used as a new class of biomarker. J Biotechnol. 2016;238:42–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Qian L, Yu S, Chen Z, Meng Z, Huang S, Wang P. The emerging role of circRNAs and their clinical significance in human cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2018;1870:247–260. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fang L, Du WW, Lyu J, Dong J, Zhang C, Yang W, He A, Kwok YSS, Ma J, Wu N, et al. Enhanced breast cancer progression by mutant p53 is inhibited by the circular RNA circ-Ccnb1. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:2195–2208. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0115-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Du WW, Yang W, Liu E, Yang Z, Dhaliwal P, Yang BB. Foxo3 circular RNA retards cell cycle progression via forming ternary complexes with p21 and CDK2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:2846–2858. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wilusz JE. A 360° view of circular RNAs: From biogenesis to functions. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2018;9:e1478. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pamudurti NR, Bartok O, Jens M, Ashwal-Fluss R, Stottmeister C, Ruhe L, Hanan M, Wyler E, Perez-Hernandez D, Ramberger E, et al. Translation of CircRNAs. Mol Cell. 2017;66:9–21.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Legnini I, Di Timoteo G, Rossi F, Morlando M, Briganti F, Sthandier O, Fatica A, Santini T, Andronache A, Wade M, et al. Circ-ZNF609 Is a circular RNA that can be translated and functions in myogenesis. Mol Cell. 2017;66:22–37.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhang M, Huang N, Yang X, Luo J, Yan S, Xiao F, Chen W, Gao X, Zhao K, Zhou H, et al. A novel protein encoded by the circular form of the SHPRH gene suppresses glioma tumorigen-esis. Oncogene. 2018;37:1805–1814. doi: 10.1038/s41388-017-0019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yang Y, Gao X, Zhang M, Yan S, Sun C, Xiao F, Huang N, Yang X, Zhao K, Zhou H, et al. Novel role of FBXW7 circular RNA in repressing glioma tumorigenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2018;110:304–315. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djx166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yang Y, Fan X, Mao M, Song X, Wu P, Zhang Y, Jin Y, Yang Y, Chen LL, Wang Y, et al. Extensive translation of circular RNAs driven by N6-methyladenosine. Cell Res. 2017;27:626–641. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Abdelmohsen K, Panda AC, Munk R, Grammatikakis I, Dudekula DB, De S, Kim J, Noh JH, Kim KM, Martindale JL, Gorospe M. Identification of HuR target circular RNAs uncovers suppression of PABPN1 translation by CircPABPN1. RNA Biol. 2017;14:361–369. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1279788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Li HM, Ma XL, Li HG. Intriguing circles: Conflicts and controversies in circular RNA research. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019;10:e1538. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Li J, Li H, Lv X, Yang Z, Gao M, Bi Y, Zhang Z, Wang S, Cui Z, Zhou B, Yin Z. Diagnostic performance of circular RNAs in human cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019;7:e00749. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lin G, Sheng H, Xie H, Zheng Q, Shen Y, Shi G, Ye D. circLPAR1 is a novel biomarker of prognosis for muscle-invasive bladder cancer with invasion and metastasis by miR-762. Oncol Lett. 2019;17:3537–3547. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.9970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Li Z, Zhou Y, Yang G, He S, Qiu X, Zhang L, Deng Q, Zheng F. Using circular RNA SMARCA5 as a potential novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Chim Acta. 2019;492:37–44. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mao W, Huang X, Wang L, Zhang Z, Liu M, Li Y, Luo M, Yao X, Fan J, Geng J. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0068871 regulates FGFR3 expression and activates STAT3 by targeting miR-181a-5p to promote bladder cancer progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:169. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1136-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hou LD, Zhang J. Circular RNAs: An emerging type of RNA in cancer. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2017;30:1–6. doi: 10.1177/0394632016686985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yuan Y, Liu W, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Sun S. CircRNA circ_0026344 as a prognostic biomarker suppresses colorectal cancer progression via microRNA-21 and microRNA-31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503:870–875. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zhang XL, Xu LL, Wang F. Hsa_circ_0020397 regulates colorectal cancer cell viability, apoptosis and invasion by promoting the expression of the miR-138 targets TERT and PD-L1. Cell Biol Int. 2017;41:1056–1064. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Xie H, Ren X, Xin S, Lan X, Lu G, Lin Y, Yang S, Zeng Z, Liao W, Ding YQ, Liang L. Emerging roles of circRNA_001569 targeting miR-145 in the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:26680–26691. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Tang W, Ji M, He G, Yang L, Niu Z, Jian M, Wei Y, Ren L, Xu J. Silencing CDR1as inhibits colorectal cancer progression through regulating microRNA-7. Onco Targets Ther. 2017;10:2045–2056. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S131597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zhang Z, Fu C, Xu Q, Wei X. Long non-coding RNA CASC7 inhibits the proliferation and migration of colon cancer cells via inhibiting microRNA-21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;95:1644–1653. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.09.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wang CJ, Stratmann J, Zhou ZG, Sun XF. Suppression of microRNA-31 increases sensitivity to 5-FU at an early stage, and affects cell migration and invasion in HCT-116 colon cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:616. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chen S, Zhang L, Su Y, Zhang X. Screening potential biomarkers for colorectal cancer based on circular RNA chips. Oncol Rep. 2018;39:2499–2512. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bian L, Zhi X, Ma L, Zhang J, Chen P, Sun S, Li J, Sun Y, Qin J. Hsa_circRNA_103809 regulated the cell proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer via miR-532-3p/FOXO4 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;505:346–352. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yong W, Zhuoqi X, Baocheng W, Dongsheng Z, Chuan Z, Yueming S. Hsa_circ_0071589 promotes carcinogenesis via the miR-600/EZH2 axis in colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;102:1188–1194. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Weng W, Wei Q, Toden S, Yoshida K, Nagasaka T, Fujiwara T, Cai S, Qin H, Ma Y, Goel A. Circular RNA ciRS-7-A promising prognostic biomarker and a potential therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:3918–3928. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Peng L, Chen G, Zhu Z, Shen Z, Du C, Zang R, Su Y, Xie H, Li H, Xu X, et al. Circular RNA ZNF609 functions as a competitive endogenous RNA to regulate AKT3 expression by sponging miR-150-5p in Hirschsprung's disease. Oncotarget. 2017;8:808–818. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zeng K, Chen X, Xu M, Liu X, Hu X, Xu T, Sun H, Pan Y, He B, Wang S. CircHIPK3 promotes colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by sponging miR-7. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:417. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0454-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 53.Xu XW, Zheng BA, Hu ZM, Qian ZY, Huang CJ, Liu XQ, Wu WD. Circular RNA hsa_circ_000984 promotes colon cancer growth and metastasis by sponging miR-106b. Oncotarget. 2017;8:91674–91683. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Shen T, Cheng X, Liu X, Xia C, Zhang H, Pan D, Zhang X, Li Y. Circ_0026344 restrains metastasis of human colorectal cancer cells via miR-183. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47:4038–4045. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2019.1669620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Fang G, Ye BL, Hu BR, Ruan XJ, Shi YX. CircRNA_100290 promotes colorectal cancer progression th rough miR-516b-induced downregulation of FZD4 expression and Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;504:184–189. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.He JH, Li YG, Han ZP, Zhou JB, Chen WM, Lv YB, He ML, Zuo JD, Zheng L. The CircRNA-ACAP2/Hsa-miR-21-5p/Tiam1 regulatory feedback circuit affects the proliferation, migration, and invasion of colon cancer SW480 cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49:1539–1550. doi: 10.1159/000493457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Li X, Wang J, Zhang C, Lin C, Zhang J, Zhang W, Zhang W, Lu Y, Zheng L, Li X. Circular RNA circITGA7 inhibits colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by modulating the Ras pathway and upregulating transcription of its host gene ITGA7. J Pathol. 2018;246:166–179. doi: 10.1002/path.5125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Huang G, Zhu H, Shi Y, Wu W, Cai H, Chen X. cir-ITCH plays an inhibitory role in colorectal cancer by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0131225. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhu M, Xu Y, Chen Y, Yan F. Circular BANP, an upregu-lated circular RNA that modulates cell proliferation in colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;88:138–144. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Xiong W, Ai YQ, Li YF, Ye Q, Chen ZT, Qin JY, Liu QY, Wang H, Ju YH, Li WH, Li YF. Microarray analysis of circular RNA expression profile associated with 5-fluorouracil-based chemo-radiation resistance in colorectal cancer cells. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:8421614. doi: 10.1155/2017/8421614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zeng Y, Xu Y, Shu R, Sun L, Tian Y, Shi C, Zheng Z, Wang K, Luo H. Altered expression profiles of circular RNA in colorectal cancer tissues from patients with lung metastasis. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40:1818–1828. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Hsiao KY, Lin YC, Gupta SK, Chang N, Yen L, Sun HS, Tsai SJ. Noncoding effects of circular RNA CCDC66 promote colon cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2017;77:2339–2350. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Zhong D, Li P, Gong PY. Hsa_circ_0005075 promotes the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells. Int J Biol Markers. 2019;34:284–291. doi: 10.1177/1724600819872765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Jin YD, Ren YR, Gao YX, Zhang L, Ding Z. Hsa_ circ_0005075 predicts a poor prognosis and acts as an oncogene in colorectal cancer via activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:3311–3319. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201904_17693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Zhang Q, Zhang C, Ma JX, Ren H, Sun Y, Xu JZ. Circular RNA PIP5K1A promotes colon cancer development through inhibiting miR-1273a. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25:5300–5309. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i35.5300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Pei FL, Cao MZ, Li YF. Circ_0000218 plays a carcinogenic role in colorectal cancer progression by regulating miR-139-3p/RAB1A axis. J Biochem. 2020;167:55–65. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvz078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Lu X, Yu Y, Liao F, Tan S. Homo sapiens circular RNA 0079993 (hsa_circ_0079993) of the POLR2J4 gene acts as an oncogene in colorectal cancer through the microRNA-203a-3p1 and CREB1 axis. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:6872–6883. doi: 10.12659/MSM.916064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Lu C, Jiang W, Hui B, Rong D, Fu K, Dong C, Tang W, Cao H. The circ_0021977/miR-10b-5p/P21 and P53 regulatory axis suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion in colorectal cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235:2273–2285. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Zhang J, Liu H, Zhao P, Zhou H, Mao T. Has_circ_0055625 from circRNA profile increases colon cancer cell growth by sponging miR-106b-5p. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:3027–3037. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Li H, Jin X, Liu B, Zhang P, Chen W, Li Q. CircRNA CBL.11 suppresses cell proliferation by sponging miR-6778-5p in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 2019;19:826. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6017-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Ren TJ, Liu C, Hou JF, Shan FX. CircDDX17 reduces 5-fluorouracil resistance and hinders tumorigenesis in colorectal cancer by regulating miR-31-5p/KANK1 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24:1743–1754. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202002_20351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zhang ZJ, Zhang YH, Qin XJ, Wang YX, Fu J. Circular RNA circDENND4C facilitates proliferation, migration and glycolysis of colorectal cancer cells through miR-760/GLUT1 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24:2387–2400. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202003_20506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Ding DY, Wang D, Shu ZB. Hsa_circ_0007534 knockdown represses the development of colorectal cancer cells through regulating miR-613/SLC25A22 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24:3004–3022. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202003_20665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Zheng X, Ma YF, Zhang XR, Li Y, Zhao HH, Han SG. Circ_0056618 promoted cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis through sponging with miR-206 and upregulating CXCR4 and VEGF-A in colorectal cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24:4190–4202. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202004_20999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Tu FL, Guo XQ, Wu HX, He ZY, Wang F, Sun AJ, Dai XD. Circ-0001313/miRNA-510-5p/AKT2 axis promotes the development and progression of colon cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12:281–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Wu HB, Huang SS, Lu CG, Tian SD, Chen M. CircAPLP2 regulates the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting miR-101-3p to activate the Notch signalling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12:2554–2569. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Chen C, Huang Z, Mo X, Song Y, Li X, Li X, Zhang M. The circular RNA 001971/miR-29c-3p axis modulates colorectal cancer growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis through VEGFA. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39:91. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01594-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 78.Chen H, Pei L, Xie P, Guo G. Circ-PRKDC contributes to 5-fluorouracil resistance of colorectal cancer cells by regulating miR-375/FOXM1 axis and Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:5939–5953. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S253468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Chen HY, Li XN, Ye CX, Chen ZL, Wang ZJ. Circular RNA circHUWE1 is upregulated and promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in colorectal cancer by sponging miR-486. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:423–434. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S233338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Chen MS, Lin CH, Huang LY, Qiu XM. CircRNA SMARCC1 sponges MiR-1403p to regulate cell progression in colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:4899–4910. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S254185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Chen P, Yao Y, Yang N, Gong L, Kong Y, Wu A. Circular RNA circCTNNA1 promotes colorectal cancer progression by sponging miR-149-5p and regulating FOXM1 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:557. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02757-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Chen ZL, Li XN, Ye CX, Chen HY, Wang ZJ. Elevated levels of circRUNX1 in colorectal cancer promote cell growth and metastasis via miR-145-5p/IGF1 signalling. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:4035–4048. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S254133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Deng Z, Li X, Wang H, Geng Y, Cai Y, Tang Y, Wang Y, Yu X, Li L, Li R. Dysregulation of circRNA_0001946 contributes to the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells by targeting MicroRNA-135a-5p. Front Genet. 2020;11:357. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Du H, He Z, Feng F, Chen D, Zhang L, Bai J, Wu H, Han E, Zhang J. Hsa_circ_0038646 promotes cell proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer via miR-331-3p/GRIK3. Oncol Lett. 2020;20:266–274. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Feng W, Gong H, Wang Y, Zhu G, Xue T, Wang Y, Cui G. circIFT80 Functions as a ceRNA of miR-1236-3p to promote colorectal cancer progression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;18:375–387. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.08.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 86.Hu B, Xian Z, Zou Q, Zhang D, Su D, Yao J, Ren D. CircFAT1 suppresses colorectal cancer development through regulating miR-520b/UHRF1 axis or miR-302c-3p/UHRF1 axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020 May 5; doi: 10.1089/cbr.2019.3291. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Jian X, He H, Zhu J, Zhang Q, Zheng Z, Liang X, Chen L, Yang M, Peng K, Zhang Z, et al. Hsa_circ_001680 affects the proliferation and migration of CRC and mediates its chemore-sistance by regulating BMI1 through miR-340. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:20. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-1134-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Li C, Zhou H. Circular RNA hsa_circRNA_102209 promotes the growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer through miR-761-mediated Ras and Rab interactor 1 signaling. Cancer Med. 2020 Jul 24; doi: 10.1002/cam4.3332. Epub ahead of print). :101002/cam4.3332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Li W, Xu Y, Wang X, Cao G, Bu W, Wang X, Fang Z, Xu Y, Dong M, Tao Q. circCCT3 modulates vascular endothelial growth factor A and Wnt signaling to enhance colorectal cancer metastasis through sponging miR-613. DNA Cell Biol. 2020;39:118–125. doi: 10.1089/dna.2019.5139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Lu C, Fu L, Qian X, Dou L, Cang S. Knockdown of circular RNA circ-FARSA restricts colorectal cancer cell growth through regulation of miR-330-5p/LASP1 axis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020;689:108434. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Ma Z, Han C, Xia W, Wang S, Li X, Fang P, Yin R, Xu L, Yang L. circ5615 functions as a ceRNA to promote colorectal cancer progression by upregulating TNKS. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:356. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2514-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Ren C, Zhang Z, Wang S, Zhu W, Zheng P, Wang W. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001178 facilitates the invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer through upregulating ZEB1 via sponging multiple miRNAs. Biol Chem. 2020;401:487–496. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2019-0350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Shang A, Gu C, Wang W, Wang X, Sun J, Zeng B, Chen C, Chang W, Ping Y, Ji P, et al. Exosomal circPACRGL promotes progression of colorectal cancer via the miR-142-3p/miR-506-3p-TGF-β1 axis. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:117. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01235-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Sun J, Liu J, Zhu Q, Xu F, Kang L, Shi X. Hsa_circ_0001806 Acts as a ceRNA to facilitate the stemness of colorectal cancer cells by increasing COL1A1. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:6315–6327. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S255485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Wang J, Luo J, Liu G, Li X. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0008285 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and migration via the miR-382-5p/PTEN axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;527:503–510. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Wang X, Chen Y, Liu W, Liu T, Sun D. Hsa_circ_0128846 promotes tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer by sponging hsa-miR-1184 and releasing AJUBA and inactivating Hippo/YAP signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jul 18; doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15590. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Wang X, Ren Y, Ma S, Wang S. Circular RNA 0060745, a novel circRNA, promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and metastasis through miR-4736 sponging. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:1941–1951. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S240642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Wang X, Zhang H, Yang H, Bai M, Ning T, Deng T, Liu R, Fan Q, Zhu K, Li J, et al. Exosome-delivered circRNA promotes glycol-ysis to induce chemoresistance through the miR-122-PKM2 axis in colorectal cancer. Mol Oncol. 2020;14:539–555. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Xiao H, Liu M. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0053277 promotes the development of colorectal cancer by upregulating matrix metallopeptidase 14 via miR-2467-3p sequestration. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235:2881–2890. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Yan Y, Su M, Qin B. CircHIPK3 promotes colorectal cancer cells proliferation and metastasis via modulating of miR-1207-5p/FMNL2 signal. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;524:839–846. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Yang B, Du K, Yang C, Xiang L, Xu Y, Cao C, Zhang J, Liu W. CircPRMT5 circular RNA promotes proliferation of colorectal cancer through sponging miR-377 to induce E2F3 expression. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24:3431–3437. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Yang L, Sun H, Liu X, Chen J, Tian Z, Xu J, Xiang B, Qin B. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0004277 contributes to malignant phenotype of colorectal cancer by sponging miR-512-5p to upregulate the expression of PTMA. J Cell Physiol. 2020 Jan 21; doi: 10.1002/jcp.29484. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Yang Z, Zhang J, Lu D, Sun Y, Zhao X, Wang X, Zhou W, He Q, Jiang Z. Hsa_circ_0137008 suppresses the malignant phenotype in colorectal cancer by acting as a microRNA-338-5p sponge. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:67. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-1150-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Yin W, Xu J, Li C, Dai X, Wu T, Wen J. Circular RNA circ_0007142 facilitates colorectal cancer progression by modulating CDC25A expression via miR-122-5p. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:3689–3701. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S238338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Zhang J, Wang H, Wu K, Zhan F, Zeng H. Dysregulated circRNA_100876 contributes to proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting microRNA-516b (miR-516b) Cancer Biol Ther. 2020;21:733–740. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2020.1776075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Zhang L, Dong X, Yan B, Yu W, Shan L. CircAGFG1 drives metastasis and stemness in colorectal cancer by modulating YY1/CTNNB1. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:542. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2707-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Zhang X, Xu Y, Yamaguchi K, Hu J, Zhang L, Wang J, Tian J, Chen W. Circular RNA circVAPA knockdown suppresses colorectal cancer cell growth process by regulating miR-125a/CREB5 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:103. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01178-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Yi Y, Wang Y, Fu J. CircNOL10 acts as a sponge of miR-135a/b-5p in suppressing colorectal cancer progression via regulating KLF9. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:5165–5176. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S242001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Zhou C, Liu HS, Wang FW, Hu T, Liang ZX, Lan N, He XW, Zheng XB, Wu XJ, Xie D, et al. circCAMSAP1 promotes tumor growth in colorectal cancer via the miR-328-5p/E2F1 axis. Mol Ther. 2020;28:914–928. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.12.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Sun HD, Xu ZP, Sun ZQ, Zhu B, Wang Q, Zhou J, Jin H, Zhao A, Tang WW, Cao XF. Down-regulation of circPVRL3 promotes the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2018;8:10111. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27837-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Cheng J, Zhuo H, Xu M, Wang L, Xu H, Peng J, Hou J, Lin L, Cai J. Regulatory network of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA contributes to the histological classification and disease progression in gastric cancer. J Transl Med. 2018;16:216. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1582-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Li H, Yao G, Feng B, Lu X, Fan Y. Circ_0056618 and CXCR4 act as competing endogenous in gastric cancer by regulating miR-206. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119:9543–9551. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Zhang J, Liu H, Hou L, Wang G, Zhang R, Huang Y, Chen X, Zhu J. Circular RNA_LARP4 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by sponging miR-424-5p and regulating LATS1 expression. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:151. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0719-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Li J, Yen C, Liaw D, Podsypanina K, Bose S, Wang SI, Puc J, Miliaresis C, Rodgers L, McCombie R, et al. PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science. 1997;275:1943–1947. doi: 10.1126/science.275.5308.1943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Namløs HM, Meza-Zepeda LA, Barøy T, Østensen IH, Kresse SH, Kuijjer ML, Serra M, Bürger H, Cleton-Jansen AM, Myklebost O. Modulation of the osteosarcoma expression phenotype by microRNAs. PLoS One. 2012;7:e48086. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Lee KH, Lotterman C, Karikari C, Omura N, Feldmann G, Habbe N, Goggins MG, Mendell JT, Maitra A. Epigenetic silencing of MicroRNA miR-107 regulates cyclin-dependent kinase 6 expression in pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 2009;9:293–301. doi: 10.1159/000186051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Liu T, Liu S, Xu Y, Shu R, Wang F, Chen C, Zeng Y, Luo H. Circular RNA-ZFR inhibited cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis in gastric cancer by sponging miR-130a/miR-107 and modulating PTEN. Cancer Res Treat. 2018;50:1396–1417. doi: 10.4143/crt.2017.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 118.Liu R, Lu Z, Gu J, Liu J, Huang E, Liu X, Wang L, Yang J, Deng Y, Qian J, et al. MicroRNAs 15A and 161 activate signaling pathways that mediate chemotaxis of immune regulatory B cells to colorectal tumors. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:637–651.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.09.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Hu ZY, Chen B, Zhang JP, Ma YY. Up-regulation of autophagy-related gene 5 (ATG5) protects dopaminergic neurons in a zebrafish model of Parkinson's disease. J Biol Chem. 2017;292:18062–18074. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.764795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Shang X, Li G, Liu H, Li T, Liu J, Zhao Q, Wang C. Comprehensive circular RNA profiling reveals that hsa_ circ_0005075, a new circular RNA biomarker, is involved in hepatocellular crcinoma development. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e3811. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Liu Z, Huang S, Cao Y, Yao Y, Li J, Chen J, Jiang B, Yuan X, Xiang X, Xiong J, Deng J. YAP1 inhibits circRNA-000425 expression and thus promotes oncogenic activities of miR-17 and miR-106. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503:2370–2375. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Li G, Xue M, Yang F, Jin Y, Fan Y, Li W. CircRBMS3 promotes gastric cancer tumorigenesis by regulating miR-153-SNAI1 axis. J Cell Physiol. 2018;234:3020–3028. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Chang P, Wang F, Li Y. Hsa_circ_0000673 is down-regulated in gastric cancer and inhibits the proliferation and invasion of tumor cells by targetting miR-532-5p. Biosci Rep. 2018;38:BSR20180538. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 124.Zhong S, Wang J, Hou J, Zhang Q, Xu H, Hu J, Zhao J, Feng J. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000993 inhibits metastasis of gastric cancer cells. Epigenomics. 2018;10:1301–1313. doi: 10.2217/epi-2017-0173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Li P, Chen H, Chen S, Mo X, Li T, Xiao B, Yu R, Guo J. Circular RNA 0000096 affects cell growth and migration in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 2017;116:626–633. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Huang YS, Jie N, Zou KJ, Weng Y. Expression profile of circular RNAs in human gastric cancer tissues. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16:2469–2476. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Li J, Zhen L, Zhang Y, Zhao L, Liu H, Cai D, Chen H, Yu J, Qi X, Li G. Circ-104916 is downregulated in gastric cancer and suppresses migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2017;10:3521–3529. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S136347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Sun H, Tang W, Rong D, Jin H, Fu K, Zhang W, Liu Z, Cao H, Cao X. Hsa_circ_0000520, a potential new circular RNA biomarker, is involved in gastric carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2018;21:299–306. doi: 10.3233/CBM-170379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Li X, He M, Guo J, Cao T. Upregulation of circular RNA circ-ERBB2 predicts unfavorable prognosis and facilitates the progression of gastric cancer via miR-503/CACUL1 and miR-637/MMP-19 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;511:926–930. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Lu J, Zhang PY, Li P, Xie JW, Wang JB, Lin JX, Chen QY, Cao LL, Huang CM, Zheng CH. Circular RNA hsa_ circ_0001368 suppresses the progression of gastric cancer by regulating miR-6506-5p/FOXO3 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;512:29–33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.02.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Kong S, Yang Q, Tang C, Wang T, Shen X, Ju S. Identification of hsa_circ_0001821 as a novel diagnostic biomarker in gastric cancer via comprehensive circular RNA profiling. Front Genet. 2019;10:878. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Liu Z, Pan HM, Xin L, Zhang Y, Zhang WM, Cao P, Xu HW. Circ-ZNF609 promotes carcinogenesis of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting miRNA-145-5p expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:9411–9417. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201911_19433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Dai X, Guo X, Liu J, Cheng A, Peng X, Zha L, Wang Z. Circular RNA circGRAMD1B inhibits gastric cancer progression by sponging miR-130a-3p and regulating PTEN and p21 expression. Aging (Albany NY) 2019;11:9689–9708. doi: 10.18632/aging.102414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Guan E, Xu X, Xue F. circ-NOTCH1 acts as a sponge of miR-637 and affects the expression of its target gene Apelin to regulate gastric cancer cell growth. Biochem Cell Biol. 2020;98:164–170. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2019-0079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Cao C, Han S, Yuan Y, Wu Y, Lian W, Zhang X, Pan L, Li M. Downregulated circular RNA hsa_circ_0000291 suppresses migration and proliferation of gastric cancer via targeting the miR-183/ITGB1 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:9675–9683. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S213830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Chen LH, Wang LP, Ma XQ. Circ_SPECC1 enhances the inhibition of miR-526b on downstream KDM4A/YAP1 pathway to regulate the growth and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;517:253–259. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.07.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Chen Z, Ju H, Zhao T, Yu S, Li P, Jia J, Li N, Jing X, Tan B, Li Y. hsa_circ_0092306 targeting miR-197-3p promotes gastric cancer development by regulating PRKCB in MKN-45 cells. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;18:617–626. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.08.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Du W, Li D, Guo X, Li P, Li X, Tong S, Tong J, Kuang L, Liang D. Circ-PRMT5 promotes gastric cancer progression by sponging miR-145 and miR-1304 to upregulate MYC. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47:4120–4130. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2019.1671857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Liang M, Huang G, Liu Z, Wang Q, Yu Z, Liu Z, Lin H, Li M, Zhou X, Zheng Y. Elevated levels of hsa_circ_006100 in gastric cancer promote cell growth and metastasis via miR-195/GPRC5A signalling. Cell Prolif. 2019;52:e12661. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Wang Q, Wang T, Hu Y, Jiang W, Lu C, Zheng W, Zhang W, Chen Z, Cao H. Circ-EIF4G3 promotes the development of gastric cancer by sponging miR-335. Pathol Res Pract. 2019;215:152507. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Wang S, Tang D, Wang W, Yang Y, Wu X, Wang L, Wang D. circLMTK2 acts as a sponge of miR-150-5p and promotes proliferation and metastasis in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:162. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1081-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Wu L, Liu D, Yang Y. Enhanced expression of circular RNA circ-DCAF6 predicts adverse prognosis and promotes cell progression via sponging miR-1231 and miR-1256 in gastric cancer. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019;110:104273. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Zhang H, Wang X, Huang H, Wang Y, Zhang F, Wang S. Hsa_circ_0067997 promotes the progression of gastric cancer by inhibition of miR-515-5p and activation of X chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47:308–318. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2018.1553787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Zhu Z, Rong Z, Luo Z, Yu Z, Zhang J, Qiu Z, Huang C. Circular RNA circNHSL1 promotes gastric cancer progression through the miR-1306-3p/SIX1/vimentin axis. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:126. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1054-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Cai X, Nie J, Chen L, Yu F. Circ_0000267 promotes gastric cancer progression via sponging MiR-503-5p and regulating HMGA2 expression. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020;8:e1093. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Deng G, Mou T, He J, Chen D, Lv D, Liu H, Yu J, Wang S, Li G. Circular RNA circRHOBTB3 acts as a sponge for miR-654-3p inhibiting gastric cancer growth. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39:1. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1487-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Guo X, Dai X, Liu J, Cheng A, Qin C, Wang Z. Circular RNA circREPS2 acts as a sponge of miR-558 to suppress gastric cancer progression by regulating RUNX3/β-catenin signaling. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;21:577–591. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.06.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.He Y, Wang Y, Liu L, Liu S, Liang L, Chen Y, Zhu Z. Circular RNA circ_0006282 contributes to the progression of gastric cancer by sponging miR-155 to upregulate the expression of FBXO22. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:1001–1010. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S228216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Hu K, Qin X, Shao Y, Zhou Y, Ye G, Xu S. Circular RNA MTO1 suppresses tumorigenesis of gastric carcinoma by sponging miR-3200-5p and targeting PEBP1. Mol Cell Probes. 2020;52:101562. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2020.101562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Li B, Jin M, Cao F, Li J, Wu J, Xu L, Liu X, Shi Y, Chen W. Hsa_circ_0017639 expression promotes gastric cancer proliferation and metastasis by sponging miR-224-5p and upregulating USP3. Gene. 2020;750:144753. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Li C, Tian Y, Liang Y, Li Q. Circ_0008035 contributes to cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis and ferroptosis in gastric cancer via miR-599/EIF4A1 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:84. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01168-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 152.Li H, Shan C, Wang J, Hu C. CircRNA hsa_circ_0001017 inhibited gastric cancer progression via acting as a sponge of miR-197. Dig Dis Sci. 2020 Aug 1; doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06516-8. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Li Y, Gong Y, Ma J, Gong X. Overexpressed circ-RPL15 predicts poor survival and promotes the progression of gastric cancer via regulating miR-502-3p/OLFM4/STAT3 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;127:110219. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Liang L, Li L. Down-regulation of circNRIP1 promotes the apoptosis and inhibits the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by miR-182/ROCK1 axis. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:6279–6288. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S221633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Lin J, Liao S, Li E, Liu Z, Zheng R, Wu X, Zeng W. circ-CYFIP2 acts as a sponge of miR-1205 and affects the expression of its target gene E2F1 to regulate gastric cancer metastasis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;21:121–132. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Lin S, Song S, Sun R, Zhang M, Du Y, Zhang D, Xu W, Wang H. Oncogenic circular RNA Hsa-circ-000684 interacts with microRNA-186 to upregulate ZEB1 in gastric cancer. FASEB J. 2020;34:8187–8203. doi: 10.1096/fj.201903246R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Liu J, Dai X, Guo X, Cheng A, Mac SM, Wang Z. Circ-OXCT1 suppresses gastric cancer EMT and metastasis by attenuating TGF-β pathway through the circ-OXCT1/miR-136/SMAD4 axis. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:3987–3998. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S239789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Liu J, Liu H, Zeng Q, Xu P, Liu M, Yang N. Circular RNA circ-MAT2B facilitates glycolysis and growth of gastric cancer through regulating the miR-515-5p/HIF-1α axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:171. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01256-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Liu P, Cai S, Li N. Circular RNA-hsa-circ-0000670 promotes gastric cancer progression through the microRNA-384/SIX4 axis. Exp Cell Res. 2020;394:112141. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Lu J, Wang YH, Huang XY, Xie JW, Wang JB, Lin JX, Chen QY, Cao LL, Huang CM, Zheng CH, Li P. circ-CEP85L suppresses the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by regulating NFKBIA expression via miR-942-5p. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235:6287–6299. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Lu J, Wang YH, Yoon C, Huang XY, Xu Y, Xie JW, Wang JB, Lin JX, Chen QY, Cao LL, et al. Circular RNA circ-RanGAP1 regulates VEGFA expression by targeting miR-877-3p to facilitate gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2020;471:38–48. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.11.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Luo Z, Rong Z, Zhang J, Zhu Z, Yu Z, Li T, Fu Z, Qiu Z, Huang C. Circular RNA circCCDC9 acts as a miR-6792-3p sponge to suppress the progression of gastric cancer through regulating CAV1 expression. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:86. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01203-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Ma Y, Cong X, Zhang Y, Yin X, Zhu Z, Xue Y. CircPIP5K1A facilitates gastric cancer progression via miR-376c-3p/ZNF146 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:81. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-1122-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Song H, Xu Y, Xu T, Fan R, Jiang T, Cao M, Shi L, Song J. CircPIP5K1A activates KRT80 and PI3K/AKT pathway to promote gastric cancer development through sponging miR-671-5p. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;126:109941. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Mo WL, Jiang JT, Zhang L, Lu QC, Li J, Gu WD, Cheng Y, Wang HT. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000467 promotes the development of gastric cancer by competitively binding to MicroRNA miR-326-3p. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:4030826. doi: 10.1155/2020/4030826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Quan J, Dong D, Lun Y, Sun B, Sun H, Wang Q, Yuan G. Circular RNA circHIAT1 inhibits proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer cell lines through downregulation of miR-21. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020;34:e22458. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Sun B, Sun H, Wang Q, Wang X, Quan J, Dong D, Lun Y. Circular RNA circMAN2B2 promotes growth and migration of gastric cancer cells by down-regulation of miR-145. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020;34:e23215. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Wang GJ, Yu TY, Li YR, Liu YJ, Deng BB. Circ_0000190 suppresses gastric cancer progression potentially via inhibiting miR-1252/PAK3 pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:351. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01422-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Wang J, Lv W, Lin Z, Wang X, Bu J, Su Y. Hsa_ circ_0003159 inhibits gastric cancer progression by regulating miR-223-3p/NDRG1 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:57. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-1119-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Wang N, Lu K, Qu H, Wang H, Chen Y, Shan T, Ge X, Wei Y, Zhou P, Xia J. CircRBM33 regulates IL-6 to promote gastric cancer progression through targeting miR-149. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;125:109876. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Wang Y, Zhang J, Chen X, Gao L. Circ_0001023 promotes proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer cells through miR-409-3p/PHF10 axis. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:4533–4544. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S244358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Wei W, Mo X, Yan L, Huang M, Yang Y, Jin Q, Zhong H, Cao W, Wu K, Wu L, et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals that circRNA_104433 regulates cell growth by targeting miR-497-5p in gastric cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:15–30. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S219307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 173.Wu J, Chen Z, Song Y, Zhu Y, Dou G, Shen X, Zhou Y, Jiang H, Li J, Peng Y. CircRNA_0005075 suppresses carcinogenesis via regulating miR-431/p53/epithelial-mesenchymal transition axis in gastric cancer. Cell Biochem Funct. 2020 Mar 4; doi: 10.1002/cbf.3519. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Wu Q, Wang H, Liu L, Zhu K, Yu W, Guo J. Hsa_circ_0001546 acts as a miRNA-421 sponge to inhibit the chemoresistance of gastric cancer cells via ATM/Chk2/p53-dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;521:303–309. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.10.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Xia T, Pan Z, Zhang J. CircSMC3 regulates gastric cancer tumorigenesis by targeting miR-4720-3p/TJP1 axis. Cancer Med. 2020;9:4299–4309. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Xie M, Yu T, Jing X, Ma L, Fan Y, Yang F, Ma P, Jiang H, Wu X, Shu Y, Xu T. Exosomal circSHKBP1 promotes gastric cancer progression via regulating the miR-582-3p/HUR/VEGF axis and suppressing HSP90 degradation. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:112. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01208-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Xu W, Zhou B, Wu J, Jiang P, Chen H, Yan F. Circular RNA hsa-circ-0007766 modulates the progression of gastric carcinoma via miR-1233-3p/GDF15 axis. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17:1569–1583. doi: 10.7150/ijms.46261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Yu X, Xiao W, Song H, Jin Y, Xu J, Liu X. CircRNA_100876 sponges miR-136 to promote proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer by upregulating MIEN1 expression. Gene. 2020;748:144678. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Zhang L, Chang X, Zhai T, Yu J, Wang W, Du A, Liu N. A novel circular RNA, circ-ATAD1, contributes to gastric cancer cell progression by targeting miR-140-3p/YY1/PCIF1 signaling axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;525:841–849. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Zhang Y, Xia L, Wu J, Xu X, Li G. Hsa_circ_0023642 promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration of gastric cancer by sponging microRNA-223. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Jun 19; doi: 10.1002/jcla.23428. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Zhang Z, Wang C, Zhang Y, Yu S, Zhao G, Xu J. CircDUSP16 promotes the tumorigenesis and invasion of gastric cancer by sponging miR-145-5p. Gastric Cancer. 2020;23:437–448. doi: 10.1007/s10120-019-01018-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Zhang Z, Wu H, Chen Z, Li G, Liu B. Circular RNA ATXN7 promotes the development of gastric cancer through sponging miR-4319 and regulating ENTPD4. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:25. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-1106-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Li RC, Ke S, Meng FK, Lu J, Zou XJ, He ZG, Wang WF, Fang MH. CiRS-7 promotes growth and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via regulation of miR-7/HOXB13. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:838. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0852-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Aliahmad P, Kaye J. Development of all CD4 T lineages requires nuclear factor TOX. J Exp Med. 2008;205:245–256. doi: 10.1084/jem.20071944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Piwecka M, Glažar P, Hernandez-Miranda LR, Memczak S, Wolf SA, Rybak-Wolf A, Filipchyk A, Klironomos F, Cerda Jara CA, Fenske P, et al. Loss of a mammalian circular RNA locus causes miRNA deregulation and affects brain function. Science. 2017;357:eaam8526. doi: 10.1126/science.aam8526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Geng HH, Li R, Su YM, Xiao J, Pan M, Cai XX, Ji XP. The circular RNA Cdr1as promotes myocardial infarction by mediating the regulation of miR-7a on its target genes expression. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0151753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Sang M, Meng L, Sang Y, Liu S, Ding P, Ju Y, Liu F, Gu L, Lian Y, Li J, et al. Circular RNA ciRS-7 accelerates ESCC progression through acting as a miR-876-5p sponge to enhance MAGE-A family expression. Cancer Lett. 2018;426:37–46. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.03.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Li F, Zhang L, Li W, Deng J, Zheng J, An M, Lu J, Zhou Y. Circular RNA ITCH has inhibitory effect on ESCC by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6:6001–6013. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Su H, Lin F, Deng X, Shen L, Fang Y, Fei Z, Zhao L, Zhang X, Pan H, Xie D, et al. Profiling and bioinformatics analyses reveal differential circular RNA expression in radioresistant esophageal cancer cells. J Transl Med. 2016;14:225. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0977-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Zheng B, Wu Z, Xue S, Chen H, Zhang S, Zeng T, Xu G, Wu W, Zheng W, Chen C. hsa_circRNA_100873 upregulation is associated with increased lymphatic metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2018;18:6836–6844. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.11003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Pan Z, Lin J, Wu D, He X, Wang W, Hu X, Zhang L, Wang M. Hsa_circ_0006948 enhances cancer progression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the miR-490-3p/HMGA2 axis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY) 2019;11:11937–11954. doi: 10.18632/aging.102519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Liu J, Xue N, Guo Y, Niu K, Gao L, Zhang S, Gu H, Wang X, Zhao D, Fan R. CircRNA_100367 regulated the radiation sensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinomas through miR-217/Wnt3 pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 2019;11:12412–12427. doi: 10.18632/aging.102580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Huang E, Fu J, Yu Q, Xie P, Yang Z, Ji H, Wang L, Luo G, Zhang Y, Li K. CircRNA hsa circ 0004771 promotes esophageal squamous cell cancer progression via miR-339-5p/CDC 25A axis. Epigenomics. 2020;12:587–603. doi: 10.2217/epi-2019-0404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Hou Y, Liu H, Pan W. Knockdown of circ_0003340 induces cell apoptosis, inhibits invasion and proliferation through miR-564/TPX2 in esophageal cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 2020;394:112142. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Lan X, Liu X, Sun J, Yuan Q, Li J. CircRAD23B facilitates proliferation and invasion of esophageal cancer cells by sponging miR-5095. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;516:357–364. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.06.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Liu Z, Hu G, Zhao Y, Xiao Z, Yan M, Ren M. Silence of cZNF292 suppresses the growth, migration, and invasion of human esophageal cancer Eca-109 cells via upregulating miR-206. J Cell Biochem. 2019;121:2354–2362. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Ma Y, Zhang D, Wu H, Li P, Zhao W, Yang X, Xing X, Li S, Li J. Circular RNA PRKCI silencing represses esophageal cancer progression and elevates cell radiosensitivity through regulating the miR-186-5p/PARP9 axis. Life Sci. 2020;259:118168. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118168. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Shi Y, Guo Z, Fang N, Jiang W, Fan Y, He Y, Ma Z, Chen Y. hsa_circ_0006168 sponges miR-100 and regulates mTOR to promote the proliferation, migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;117:109151. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Wu Y, Zhi L, Zhao Y, Yang L, Cai F. Knockdown of circular RNA UBAP2 inhibits the malignant behaviours of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by microRNA-422a/Rab10 axis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2020;47:1283–1290. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Xu Z, Tie X, Li N, Yi Z, Shen F, Zhang Y. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000654 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by regulating the miR-149-5p/IL-6/STAT3 pathway. IUBMB Life. 2020;72:426–439. doi: 10.1002/iub.2202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Chen Z, Yao N, Gu H, Song Y, Ye Z, Li L, Lu P, Shao Q. Circular RNA_LARP4 sponges miR-1323 and hampers progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through modulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Dig Dis Sci. 2020;65:2272–2283. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05973-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Xu L, Zhang M, Zheng X, Yi P, Lan C, Xu M. The circular RNA ciRS-7 (Cdr1as) acts as a risk factor of hepatic microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017;143:17–27. doi: 10.1007/s00432-016-2256-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Yu J, Xu QG, Wang ZG, Yang Y, Zhang L, Ma JZ, Sun SH, Yang F, Zhou WP. Circular RNA cSMARCA5 inhibits growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018;68:1214–1227. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Lin X, Chen Y. Identification of potentially functional circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in hepatocellular carcinoma by integrated microarray analysis. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2018;24:70–78. doi: 10.12659/MSMBR.909737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Zhang X, Hu S, Zhang X, Wang L, Zhang X, Yan B, Zhao J, Yang A, Zhang R. MicroRNA-7 arrests cell cycle in G1 phase by directly targeting CCNE1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;443:1078–1084. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Yu L, Gong X, Sun L, Zhou Q, Lu B, Zhu L. The circular RNA Cdr1as Act as an oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma through targeting miR-7 expression. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0158347. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 207.Qin M, Liu G, Huo X, Tao X, Sun X, Ge Z, Yang J, Fan J, Liu L, Qin W. Hsa_circ_0001649: A circular RNA and potential novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2016;16:161–169. doi: 10.3233/CBM-150552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Han D, Li J, Wang H, Su X, Hou J, Gu Y, Qian C, Lin Y, Liu X, Huang M, et al. Circular RNA circMTO1 acts as the sponge of microRNA-9 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Hepatology. 2017;66:1151–1164. doi: 10.1002/hep.29270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Meng J, Chen S, Han JX, Qian B, Wang XR, Zhong WL, Qin Y, Zhang H, Gao WF, Lei YY, et al. Twist1 regulates vimentin through Cul2 circular RNA to promote EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2018;78:4150–4162. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-3009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Li X, Shen M. Circular RNA hsa_circ_103809 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion by sponging miR-620. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:555–566. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201902_16868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Wei Y, Chen X, Liang C, Ling Y, Yang X, Ye X, Zhang H, Yang P, Cui X, Ren Y, et al. A noncoding regulatory RNAs network driven by Circ-CDYL acts specifically in the early stages hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2020;71:130–147. doi: 10.1002/hep.30795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Fu L, Chen Q, Yao T, Li T, Ying S, Hu Y, Guo J. Hsa_ circ_0005986 inhibits carcinogenesis by acting as a miR-129-5p sponge and is used as a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8:43878–43888. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Fu L, Yao T, Chen Q, Mo X, Hu Y, Guo J. Screening differential circular RNA expression profiles reveals hsa_circ_0004018 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8:58405–58416. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Su Y, Xu C, Liu Y, Hu Y, Wu H. Circular RNA hsa_ circ_0001649 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression via multiple miRNAs sponge. Aging (Albany NY) 2019;11:3362–3375. doi: 10.18632/aging.101988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Cao S, Wang G, Wang J, Li C, Zhang L. Hsa_circ_101280 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating miR-375/JAK2. Immunol Cell Biol. 2019;97:218–228. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Guan Z, Tan J, Gao W, Li X, Yang Y, Li X, Li Y, Wang Q. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0016788 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis through miR-486/CDK4 pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2018;234:500–508. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Guo J, Duan H, Li Y, Yang L, Yuan L. A novel circular RNA circ-ZNF652 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through inducing snail-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition by sponging miR-203/miR-502-5p. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;513:812–819. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.03.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Jiang W, Wen D, Gong L, Wang Y, Liu Z, Yin F. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000673 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma malignance by decreasing miR-767-3p targeting SET. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;500:211–216. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Li MF, Li YH, He YH, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Li XF, Meng XM, Huang C, Li J. Emerging roles of hsa_circ_0005075 targeting miR-431 in the progress of HCC. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;99:848–858. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Liu H, Xue L, Song C, Liu F, Jiang T, Yang X. Overexpression of circular RNA circ_001569 indicates poor prognosis in hepa-tocellular carcinoma and promotes cell growth and metastasis by sponging miR-411-5p and miR-432-5p. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503:2659–2665. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Liu L, Qi X, Gui Y, Huo H, Yang X, Yang L. Overexpression of circ_0021093 circular RNA forecasts an unfavorable prognosis and facilitates cell progression by targeting the miR-766-3p/MTA3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gene. 2019;714:143992. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.143992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Pan H, Tang L, Jiang H, Li X, Wang R, Gao J, Li Q. Enhanced expression of circ_0000267 in hepatocellular carcinoma indicates poor prognosis and facilitates cell progression by sponging miR-646. J Cell Biochem. 2019 Feb 5; doi: 10.1002/jcb.28411. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Qi SX, Sun H, Liu H, Yu J, Jiang ZY, Yan P. Role and mechanism of circ-PRKCI in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25:1964–1974. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Wang YG, Wang T, Ding M, Xiang SH, Shi M, Zhai B. hsa_circ_0091570 acts as a ceRNA to suppress hepatocellular cancer progression by sponging hsa-miR-1307. Cancer Lett. 2019;460:128–138. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Xu L, Feng X, Hao X, Wang P, Zhang Y, Zheng X, Li L, Ren S, Zhang M, Xu M. CircSETD3 (Hsa_circ_0000567) acts as a sponge for microRNA-421 inhibiting hepatocellular carcinoma growth. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:98. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1041-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Zhang J, Chang Y, Xu L, Qin L. Elevated expression of circular RNA circ_0008450 predicts dismal prognosis in hepa-tocellular carcinoma and regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion via sponging miR-548p. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:9487–9494. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Zheng H, Chen T, Li C, Xu C, Ding C, Chen J, Ju S, Zhang Z, Liang Z, Cui Z, Zhao J. A circular RNA hsa_circ_0079929 inhibits tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:443–454. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S189338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Song C, Li D, Liu H, Sun H, Liu Z, Zhang L, Hu Y. The competing endogenous circular RNA ADAMTS14 suppressed hepatocellular carcinoma progression through regulating microRNA-572/regulator of calcineurin 1. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:2460–2470. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Zhang PF, Wei CY, Huang XY, Peng R, Yang X, Lu JC, Zhang C, Gao C, Cai JB, Gao PT, et al. Circular RNA circTRIM33-12 acts as the sponge of MicroRNA-191 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:105. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1031-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Song H, Bian ZX, Li HY, Zhang Y, Ma J, Chen SH, Zhu JB, Zhang X, Wang J, Gu S, et al. Characterization of hsa_circ_0000594 as a new biomarker and therapeutic target for hepatoblastoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:8274–8286. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201910_19138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Ding Y, Fang A, Yan J, Duan J, Wang N, Yi Y, Shen C. Selective downregulation of distinct circRNAs in the tissues and plasma of patients with primary hepatic carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2019;18:5255–5268. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Zhu Q, Lu G, Luo Z, Gui F, Wu J, Zhang D, Ni Y. CircRNA circ_0067934 promotes tumor growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma through regulation of miR-1324/FZD5/Wnt/β-catenin axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;497:626–632. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Liu C, Zhong X, Li J, Xu F. Circular RNA circVAPA promotes cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Gene Ther Clin Dev. 2019;30:152–159. doi: 10.1089/humc.2019.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Tan A, Li Q, Chen L. CircZFR promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through regulating miR-3619-5p/CTNNB1 axis and activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2019;661:196–202. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2018.11.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Zhang X, Luo P, Jing W, Zhou H, Liang C, Tu J. circSMAD2 inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting miR-629 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:2853–2863. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S158008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Yang W, Ju HY, Tian XF. Circular RNA-ABCB10 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression through upregulating NRP1/ABL2 via sponging miR-340-5p/miR-452-5p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24:2347–2357. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202003_20501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Li Z, Liu Y, Yan J, Zeng Q, Hu Y, Wang H, Li H, Li J, Yu Z. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0056836 functions an oncogenic gene in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulating miR-766-3p/FOSL2 axis. Aging (Albany NY) 2020;12:2485–2497. doi: 10.18632/aging.102756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 238.Wang Y, Gao R, Li J, Tang S, Li S, Tong Q, Mao Y. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0003141 promotes tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma via a miR-1827/UBAP2 axis. Aging (Albany NY) 2020;12:9793–9806. doi: 10.18632/aging.103244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Jin J, Liu H, Jin M, Li W, Xu H, Wei F. Silencing of hsa_circ_0101145 reverses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma via regulation of the miR-548c-3p/LAMC2 axis. Aging (Albany NY) 2020;12:11623–11635. doi: 10.18632/aging.103324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Li Z, Hu Y, Zeng Q, Wang H, Yan J, Li H, Yu Z. Circular RNA MYLK promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by increasing Rab23 expression by sponging miR-362-3p. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:211. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0926-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 241.Lin T, Dai Y, Guo X, Chen W, Zhao J, Cao L, Wu Z. Silencing of hsa_circ_0008450 represses hepatocellular carcinoma progression through regulation of microRNA-214-3p/EZH2 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:9133–9143. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S222716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Liu L, Yang X, Li NF, Lin L, Luo H. Circ_0015756 promotes proliferation, invasion and migration by microRNA-7-dependent inhibition of FAK in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Cycle. 2019;18:2939–2953. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1664223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Liu Z, Yu Y, Huang Z, Kong Y, Hu X, Xiao W, Quan J, Fan X. CircRNA-5692 inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by sponging miR-328-5p to enhance DAB2IP expression. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:900. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2089-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Tian F, Yu C, Wu M, Wu X, Wan L, Zhu X. MicroRNA-191 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by has_ circ_0000204/miR-191/KLF6 axis. Cell Prolif. 2019;52:e12635. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Yang X, Liu L, Zou H, Zheng YW, Wang KP. circZFR promotes cell proliferation and migration by regulating miR-511/AKT1 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis. 2019;51:1446–1455. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2019.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Yang X, Song H, Zi Z, Kou J, Chen S, Dai Y, Wang J, Yuan L, Gao K. Circ_0005075 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by suppression of microRNA-335. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:21937–21946. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.Yao Z, Xu R, Yuan L, Xu M, Zhuang H, Li Y, Zhang Y, Lin N. Circ_0001955 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumorigenesis by sponging miR-516a-5p to release TRAF6 and MAPK11. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:945. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2176-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Zhu Y, Liu Y, Xiao B, Cai H, Liu M, Ma L, Yin H, Wang F. The circular RNA PVT1/miR-203/HOXD3 pathway promotes the progression of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biol Open. 2019;8:bio043687. doi: 10.1242/bio.043687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 249.Zou H, Xu X, Luo L, Zhang Y, Luo L, Yao Y, Xiang G, Huang X, Wang G. Hsa_circ_0101432 promotes the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by adsorbing miR-1258 and miR-622. Cell Cycle. 2019;18:2398–2413. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1618120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 250.Cao Y, Tao Q, Kao X, Zhu X. Hsa-circRNA-103809 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma development via MicroRNA-1270/PLAG1 like zinc finger 2 axis. Dig Dis Sci. 2020 Jul 18; doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06416-x. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Ding Z, Guo L, Deng Z, Li P. Circ-PRMT5 enhances the proliferation, migration and glycolysis of hepatoma cells by targeting miR-188-5p/HK2 axis. Ann Hepatol. 2020;19:269–279. doi: 10.1016/j.aohep.2020.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Fu X, Zhang J, He X, Yan X, Wei J, Huang M, Liu Y, Lin J, Hu H, Liu L. Circular RNA MAN2B2 promotes cell proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the miRNA-217/MAPK1 axis. J Cancer. 2020;11:3318–3326. doi: 10.7150/jca.36500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Gao J, Dai C, Yu X, Yin XB, Zhou F. Circ-TCF4.85 silencing inhibits cancer progression through microRNA-486-5p-targeted inhibition of ABCF2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Oncol. 2020;14:447–461. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 254.Gao S, Hu W, Huang X, Huang X, Chen W, Hao L, Chen Z, Wang J, Wei H. Circ_0001178 regulates miR-382/VEGFA axis to facilitate hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cell Signal. 2020;72:109621. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.He Y, Huang H, Jin L, Zhang F, Zeng M, Wei L, Tang S, Chen D, Wang W. CircZNF609 enhances hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, metastasis, and stemness by activating the Hedgehog pathway through the regulation of miR-15a-5p/15b-5p and GLI2 expressions. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:358. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2441-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 256.Huang XY, Zhang PF, Wei CY, Peng R, Lu JC, Gao C, Cai JB, Yang X, Fan J, Ke AW, et al. Circular RNA circMET drives immunosuppression and anti-PD1 therapy resistance in hepa-tocellular carcinoma via the miR-30-5p/snail/DPP4 axis. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:92. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01213-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 257.Jia B, Yin X, Wang Y, Qian J, He Y, Yang C, Yu G, Guo B, Meng X. CircRNA-PTN sponges miR-326 to promote proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:4893–4903. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S251300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Jia C, Yao Z, Lin Z, Zhao L, Cai X, Chen S, Deng M, Zhang Q. circNFATC3 sponges miR-548I acts as a ceRNA to protect NFATC3 itself and suppressed hepatocellular carcinoma progression. J Cell Physiol. 2020 Jul 15; doi: 10.1002/jcp.29931. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 259.Li J, Qin X, Wu R, Wan L, Zhang L, Liu R. Circular RNA circFBXO11 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma progress and oxaliplatin resistance through miR-605/FOXO3/ABCB1 axis. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24:5152–5161. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 260.Li S, Weng J, Song F, Li L, Xiao C, Yang W, Xu J. Circular RNA circZNF566 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by sponging miR-4738-3p and regulating TDO2 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:452. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2616-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 261.Li Y, Shi H, Yuan J, Qiao L, Dong L, Wang Y. Downregulation of circular RNA circPVT1 restricts cell growth of hepatocel-lular carcinoma through downregulation of Sirtuin 7 via microRNA-3666. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2020;47:1291–1300. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 262.Lin Y, Huang G, Jin H, Jian Z. Circular RNA Gprc5a promotes HCC progression by activating YAP1/TEAD1 signalling pathway by sponging miR-1283. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:4509–4521. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S240261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 263.Liu W, Yin C, Liu Y. Circular RNA circ_0091579 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through miR-490-5p/CASC3 axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020 Jul 14; doi: 10.1089/cbr.2019.3472. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 264.Liu X, Yang L, Jiang D, Lu W, Zhang Y. Circ-DENND4C up-regulates TCF4 expression to modulate hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and apoptosis via activating Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:295. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01346-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 265.Pu J, Wang J, Li W, Lu Y, Wu X, Long X, Luo C, Wei H. hsa_circ_0000092 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through up-regulating HN1 expression by binding to microRNA-338-3p. J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Feb 20; doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15010. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 266.Song LN, Qiao GL, Yu J, Yang CM, Chen Y, Deng ZF, Song LH, Ma LJ, Yan HL. Hsa_circ_0003998 promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by sponging miR-143-3p and PCBP1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39:114. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01576-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 267.Sun Q, Yu R, Wang C, Yao J, Zhang L. Circular RNA circ-CSPP1 regulates CCNE2 to facilitate hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth via sponging miR-577. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:202. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01287-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 268.Wang W, Li Y, Li X, Liu B, Han S, Li X, Zhang B, Li J, Sun S. Circular RNA circ-FOXP1 induced by SOX9 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via sponging miR-875-3p and miR-421. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;121:109517. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 269.Wei X, Zheng W, Tian P, He Y, Liu H, Peng M, Li X, Liu X. Oncogenic hsa_circ_0091581 promotes the malignancy of HCC cell through blocking miR-526b from degrading c-MYC mRNA. Cell Cycle. 2020;19:817–824. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1731945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 270.Yang J, Li Y, Yu Z, Zhou Y, Tu J, Lou J, Wang Y. Circular RNA Circ100084 functions as sponge of miR23a5p to regulate IGF2 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 2020;21:2395–2404. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 271.Yu X, Sheng P, Sun J, Zhao X, Zhang J, Li Y, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Wang J, Liu K, et al. The circular RNA circMAST1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration by sponging miR-1299 and regulating CTNND1 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:340. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2532-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 272.Zang H, Li Y, Zhang X, Huang G. Circ_0000517 contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma progression by upregulating TXNDC5 via sponging miR-1296-5p. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:3457–3468. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S244024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 273.Zhang W, Zhu L, Yang G, Zhou B, Wang J, Qu X, Yan Z, Qian S, Liu R. Hsa_circ_0026134 expression promoted TRIM25- and IGF2BP3-mediated hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion via sponging miR-127-5p. Biosci Rep. 2020;40:BSR20191418. doi: 10.1042/BSR20191418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 274.Zhao M, Dong G, Meng Q, Lin S, Li X. Circ-HOMER1 enhances the inhibition of miR-1322 on CXCL6 to regulate the growth and aggressiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 2020 Feb 9; doi: 10.1002/jcb.29672. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 275.Kim Y, Bang SS, Jee S, Park S, Shin SJ, Jang K. Prevalence and clinicopathological significance of MET overexpression and gene amplification in patients with gallbladder carcinoma. Cancer Res Treat. 2020;52:481–491. doi: 10.4143/crt.2019.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 276.McNamara MG, Metran-Nascente C, Knox JJ. State-of-the-art in the management of locally advanced and metastatic gallbladder cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2013;25:425–431. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0b013e3283620fd8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 277.Sung YN, Song M, Lee JH, Song KB, Hwang DW, Ahn CS, Hwang S, Hong SM. Validation of the 8th edition of the American joint committee on cancer staging system for gallbladder cancer and implications for the follow-up of patients without node dissection. Cancer Res Treat. 2020;52:455–468. doi: 10.4143/crt.2019.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 278.Kakaei F, Beheshtirouy S, Nejatollahi SM, Zarrintan S, Mafi MR. Surgical treatment of gallbladder carcinoma: A critical review. Updates Surg. 2015;67:339–351. doi: 10.1007/s13304-015-0328-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 279.Kai D, Yannian L, Yitian C, Dinghao G, Xin Z, Wu J. Circular RNA HIPK3 promotes gallbladder cancer cell growth by sponging microRNA-124. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503:863–869. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 280.Wang S, Zhang Y, Cai Q, Ma M, Jin LY, Weng M, Zhou D, Tang Z, Wang JD, Quan Z. Circular RNA FOXP1 promotes tumor progression and Warburg effect in gallbladder cancer by regulating PKLR expression. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:145. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1078-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 281.Huang X, He M, Huang S, Lin R, Zhan M, Yang D, Shen H, Xu S, Cheng W, Yu J, et al. Circular RNA circERBB2 promotes gallbladder cancer progression by regulating PA2G4-dependent rDNA transcription. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:166. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1098-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 282.Li T, Shao Y, Fu L, Xie Y, Zhu L, Sun W, Yu R, Xiao B, Guo J. Plasma circular RNA profiling of patients with gastric cancer and their droplet digital RT-PCR detection. J Mol Med (Berl) 2018;96:85–96. doi: 10.1007/s00109-017-1600-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 283.Su BB, Shi H, Wan J. Role of serum carcinoembryonic antigen in the detection of colorectal cancer before and after surgical resection. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:2121–2126. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i17.2121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 284.Lee WS, Baek JH, Kim KK, Park YH. The prognostic significant of percentage drop in serum CEA post curative resection for colon cancer. Surg Oncol. 2012;21:45–51. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2010.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 285.Shao Y, Li J, Lu R, Li T, Yang Y, Xiao B, Guo J. Global circular RNA expression profile of human gastric cancer and its clinical significance. Cancer Med. 2017;6:1173–1180. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 286.Wang T, Shigdar S, Shamaileh HA, Gantier MP, Yin W, Xiang D, Wang L, Zhou SF, Hou Y, Wang P, et al. Challenges and opportunities for siRNA-based cancer treatment. Cancer Lett. 2017;387:77–83. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.03.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 287.Zhang M, Xin Y. Circular RNAs: A new frontier for cancer diagnosis and therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11:21. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0569-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 288.Ebert MS, Sharp PA. MicroRNA sponges: Progress and possibilities. RNA. 2010;16:2043–2050. doi: 10.1261/rna.2414110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 289.Guo JU, Agarwal V, Guo H, Bartel DP. Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014;15:409. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0409-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.