Abstract
Cancer is characterised by an accumulation of somatic mutations. These can generate cancer-specific neoepitopes that are recognised by autologous T cells in the tumour-bearing host. As neoepitopes are not subject to central immune tolerance and not expressed in healthy tissues, they are attractive targets for therapeutic cancer vaccines. However, the vast majority of cancer mutations are unique for the individual patient. Harnessing the full potential of this rich source of targets requires individualised treatment approaches. A large body of computational algorithms and machine learning tools were developed for identification of mutations in sequence data, prioritisation of those likely to be recognised by T cells and the design of a tailored vaccine for every patient that is composed of multiple cancer mutations. The main scope of this review is to fill gaps in the integrated understanding of basic mechanisms of T-cell recognition of neoantigens and computational approaches for somatic mutation discovery and neoantigen prediction for cancer immunotherapy. We present a new classification distinguishing between guarding, restrained, and ignored neoantigens that is motivated by the key question of how neoantigens confer competent anti-tumour immunity in a given clinical context. Such a context-based differentiation will contribute to a framework connecting neoantigen science to clinical settings and medical peculiarities of cancer disease and will enable future neoantigen-dependent therapies to provide greater clinical benefit.
1. Introduction
Mutated gene products can act as tumour neoantigens when their peptide breakdown products are presented as neoepitopes [G] on major histocompatibility complex (MHC) [G] molecules of the patient and recognised by CD4+ or CD8+ T cells1–4. T cells recognising neoepitopes with high avidity have been shown to drive efficacy of cancer immunotherapies such as immune checkpoint blockade (ICB)5–10 and adoptive T-cell transfer [G]11,12 The number of somatic mutations in a tumour correlates with T-cell infiltration and is predictive for overall response rate and survival prolongation by immunotherapies across various cancer types13.
Not every mutation gives rise to a neoantigen. It has been reported that spontaneously occurring neoepitope-specific T cells reflect only 1-2% of the mutations in an individual tumour14,15. Also, not all neoantigens are equal in their ability to mediate T-cell mediated tumour cell killing and an anti-tumour effect. This review is focussed on neoantigens of relevance. These are defined as somatic mutations in cancer cells that are recognised by T cells and do contribute to manifesting an anti-tumour effect.
As somatic cancer mutations are not expressed in healthy cells and as T cells that may recognise them are not subject to central immune tolerance, neoantigens are considered safe and potent targets for T-cell-based immunotherapies. Due to the random nature of occurrence, somatic cancer mutations are highly individual. Each cancer patient has a unique mutation profile and presents a unique composition of neoepitope/MHC complexes (called ‘neoantigenome’) on their cancer cells16. Therefore, the clinical use of cancer mutations calls for a truly individualised approach, which is associated with multi-faceted challenges.
While individualised cancer vaccines are the main scope of this review, predicting neoepitopes is also of interest for clinical applications in the cell therapy field, e.g. ex vivo stimulation of autologous T cells for enrichment of neoepitope specificities or cloning of neoantigen-specific TCRs (T-cell receptor) for T-cell reprogramming.
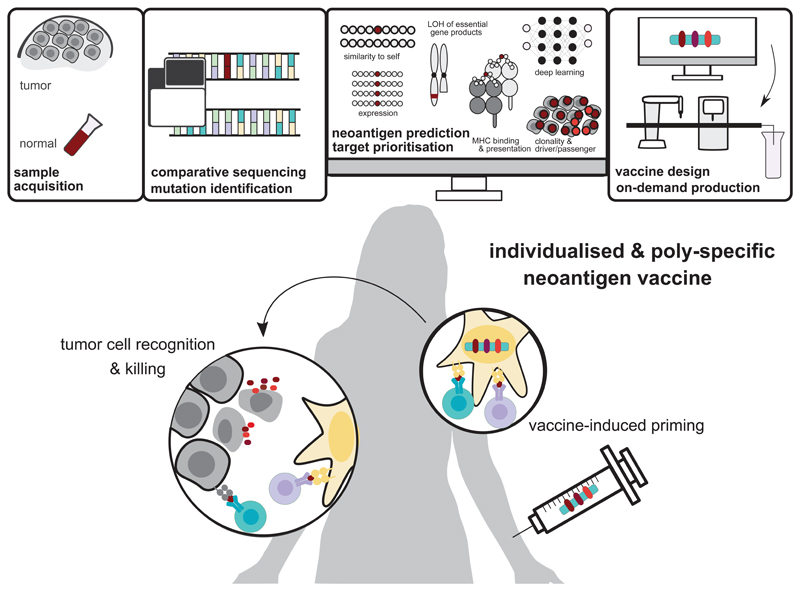
Engineering of an individualised cancer vaccine (Fig. 1) starts with the identification of tumour-specific non-synonymous [G] variants in protein-coding genes by comparing next-generation sequencing (NGS) data from the patient’s tumour and healthy tissue. Multi-component computational pipelines assess the mutant peptide regions for binding to the patient’s HLA (human leukocyte antigen) alleles and evaluate additional features of that mutated region (e.g. transcript expression level, clonality [G] and dissimilarity to self) that may contribute to the capability of a neoantigen candidate to induce potent and clinically meaningful anti-tumour T cells. Such data informs the selection of a tailored set of neoantigen candidates for on-demand production of a vaccine of unique composition for each patient17–20.
Figure 1. Engineering individualised neoantigen vaccines.
Next-generation sequencing of a patient’s healthy tissue (e.g., PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells) and tumour biopsies is performed. The sequencing data from tumour and normal DNA is compared to identify tumour-specific mutations. Mutations are prioritised as vaccine candidates based on their likelihood to elicit a T-cell response by computational methods such as MHC binding prediction, quantification of mutated transcript expression, clonality of the mutation and other features. Using the vaccine platform of choice (e.g. mRNA, long peptides) an individualised and poly-specific neoantigen vaccine is manufactured on-demand under GMP conditions. Neoantigen vaccination aims at restoring the cancer immunity cycle by inducing de novo T-cell responses that induce tumour killing and by supporting the shift from ignorance toward anti-tumour immunity. LOH: loss of heterozygosity, GMP: good manufacturing practice
Accurate identification of mutations and selection of relevant neoantigen candidates guided by biological knowledge are the rosetta stone for clinical success of individualised neoantigen vaccination. The need for algorithms to serve this purpose has created a new, fast-evolving and highly cross-disciplinary research field.
This review explains basic immunological mechanisms involved in the mode of action of neoantigen vaccines. It gives a comprehensive overview of currently used algorithms and computational pipelines to predict neoepitope candidates, the biological features they assess, and their implementation from the perspective of clinical translation. It proposes a novel concept for classification of neoantigens based on the clinical context for which they are of interest. Challenges met in clinical translation of neoepitope cancer vaccines when computational approaches become a part of the highly regulated drug development process are discussed, as are future directions for the field.
2. Basic principles of neoantigen presentation, T-cell recognition and immunity
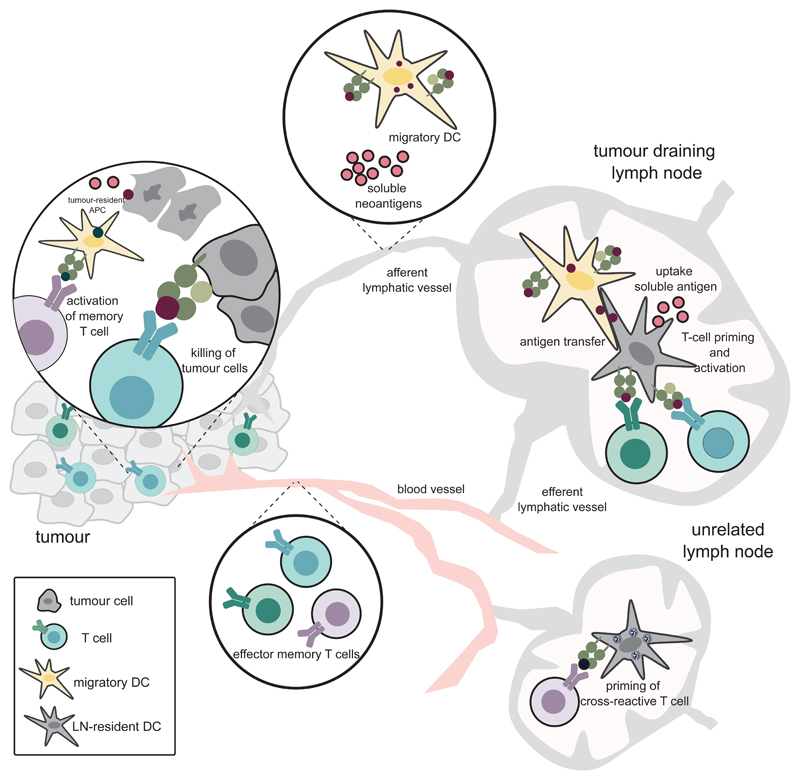
Neoantigen-specific T-cell immunity follows basic principles of T-cell priming, activation and effector function, which involve mechanisms occurring in two compartments, namely in the tumour and in lymphatic tissue (Fig 2).
Figure 2. Mechanisms of neo-antigen-mediated tumour control.
Dying tumour cells release neoantigens that reach the draining lymph node either in a soluble form within the extracellular fluid or are transported from the tumour site by migratory antigen presenting cells (APCs). In the lymph node, highly specialised dendritic cells present the neoantigen on MHC-I or MHC-II molecules to naïve T cells for priming and activation. Activated neoantigen-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells leave the lymph node, enter the tumour and exert anti-tumour activities. APCs in the tumour microenvironment can activate antigen specific memory CD4+ and CD8+
2.1. Presentation of neoantigens
Like any other endogenous cellular protein, neoantigens expressed in cancer cells undergo proteasomal degradation into smaller peptides. The peptides are processed in the endoplasmic reticulum and are loaded onto MHC-I molecules [G]. The resulting peptide/MHC-I complexes including those, which harbour neoepitopes, are presented on the cancer cell surface for recognition by CD8+ T cells. Tumour cells may express MHC-II molecules either constitutively (which is rarely the case) or upon induction by interferon (IFN)-γ21. MHC-II molecules preferentially present peptides originating from exogeneous proteins or peptides from endogenous proteins that accessed the secretory and endocytic compartments. Binding of a peptide to MHC-II has less stringent sequence and length requirements than binding to MHC-I. Therefore, the likelihood of mutant peptides to be presented on MHC-II and the diversity of neoepitope/MHC-II complexes is higher and the mutanome [G] is particularly poised for immune recognition by CD4+ T-cells 22,23,20. The same mutation can be presented by both MHC-I as well as MHC-II when the respective neoantigen accesses both processing pathways and when the patient has an MHC-I as well as an MHC-II allele that is capable of complexing the respective mutated peptide with sufficient affinity19,20
In addition to tumour cells, cancers harbour immune cell infiltrates, including dendritic cells (DCs), macrophages and B cells that can act as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Antigen uptake by these APCs occurs by mechanisms such as macropinocytosis of soluble antigens, receptor-mediated uptake of apoptotic vesicles by DCs, phagocytosis of tumour cells by tumour-associated macrophages, or Fc-receptor-mediated uptake of immune complexes. Tumour-infiltrating APCs activate antigen specific memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells that have previously undergone cognate priming.
However, neither cancer cells nor tumour-infiltrating APCs are capable of direct priming naïve T cells. Priming of naïve T cells occurs almost exclusively in lymph nodes (LN) through highly specialised LN resident DCs. These professional APCs either sample soluble neoantigens from the extracellular fluid drained by lymph vessels from the tumour tissue24,25 or by active transfer from migratory APCs that had taken up the respective neoantigens in the peripheral tumour tissue26–28. Endocytosed antigens are processed and presented on MHC-II complexes for scanning by CD4+ T cells. DCs are also capable of routing endocytosed antigens into cytosolic compartments for proteasomal degradation and presentation on MHC-I molecules. This process called ‘cross-presentation’ is critical for priming and stimulation of antigen-specific cytotoxic CD8+ T cells29,30.
2.2. Priming of neoantigen specific T cell responses
The priming, activation, expansion and subsequent fate of neoantigen-specific T cells is tightly controlled by fine-tuned mechanisms and affected by parameters, such as the density and stability of the peptide/MHC complexes on APCs, the precursor frequency and avidity of antigen-specific T cells, and the presence of costimulatory signals. The naïve T cell repertoire is shaped by central immune tolerance [G] established during thymic development, which involves the elimination of high-avidity autoreactive T cells that recognise MHC-I and MHC-II epitopes derived from germline-encoded self-antigens. As neoepitopes are non-self, they are not impacted by this mechanism. Naïve T cells recognising neoantigens remain susceptible to mechanisms of peripheral tolerance [G] which encompass clonal deletion31, conversion to regulatory T cells32 or induction of dysfunctional states such as anergy [G]33 and exhaustion34,35. Priming of naïve T cells requires a high level of peptide/MHC complexes along with co-stimulation36. Once they have been primed in the LN and transitioned to the memory state, cognate activation of T cells can be achieved with much lower levels of neoantigen presentation. The quantity of peptide/MHC complexes i.e. the level of epitope presentation is a function of gene expression, affinity of peptide/MHC binding and stability of the peptide/MHC complex37,38. Accordingly, neoantigens that are expressed at a robust level in the tumour and provide neoepitopes of sufficiently high affinity to MHC-I or II have a higher likelihood for effective cross-presentation of endocytosed antigens and priming of naïve T cells. Below these critical levels, neoantigens will induce neither T cell immunity nor tolerance.
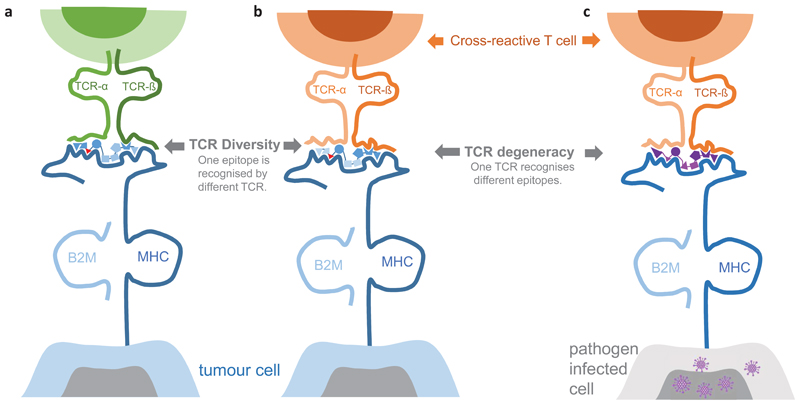
2.3. TCR diversity [G] and TCR degeneracy [G]
TCRs bind to peptide/MHC complexes by interacting with a few contact sites of the peptide’s side chains that project out of the MHC groove (reviewed in39,40). The same neoepitope/MHC complex can engage T cells with diverse TCRs that may be composed of molecularly different TCR alpha and beta chains20,41–44 (Fig 3a,b). TCR diversity is expected to be broader for neoepitopes that have a higher dissimilarity to MHC ligands derived from self-antigens45, e.g. mutations that convert a non-binding peptide to a binding neoepitope, or novel open reading frames created by INDELs and gene fusions which alter more than merely a single amino acid. Also, higher dissimilarity to self is associated with a higher likelihood that potential high affinity binders were not deleted by central immune tolerance mechanisms.
Figure 3. TCR diversity and degeneracy.
A neoepitope (blue, mutant amino acid red) can be recognised by different T cells with molecularly different TCR alpha and beta chains (left, middle). The TCR/neoepitope contact residues (dark blue) may differ for individual T cells that recognise the same neoepitope. This is in particular the case for neoantigens resulting from a mutation that converts a non-binding wild type peptide into a binding mutant peptide. Also, a single TCR can recognise unrelated MHC peptide epitopes (right). For example, a T cell primed against a pathogen-derived epitope (purple) may cross-recognise a neoepitope presented on a tumour cell. MHC: major histocompatibility complex; TCR: T-cell receptor, B2M: Beta-2-Microglobulin.
Given the low affinity of a functional TCR/peptide/MHC interaction, a single TCR is able to bind various different peptide/MHC complexes, including epitopes that do not necessarily share sequence homology with each other and differ structurally46–48. Due to this TCR degeneracy, a mutant peptide may be recognised by cross-reactive memory T cells that were primed against an unrelated antigen e.g. from commensal bacteria or microbial pathogens49,50. Activation of T cells which were primed by an unrelated antigen is known as heterologous immunity [G] (Fig 3b,c).
2.4. Neoantigen driven immune effector mechanisms
Upon encountering antigens under conditions of co-stimulation, naïve CD8+ and CD4+ T cells are activated, expand by repeated cycles of cell division, leave the LN, and differentiate into PD1+ effectors and memory T cells that are capable of infiltrating tumours. In the presence of a favourable tumour microenvironment (TME), activated neoantigen-specific T cells exhibit their effector functions by recognition of their antigens on intratumoural APCs and tumour cells and may indirectly or directly contribute to tumour control11,18,51–54.
CD4+ and CD8+ T cells collaborate in the eradication of tumours. While CD8+ T cells exert direct cancer cell killing, neoantigen-specific CD4+ T cells have a variety of effects that may promote profound inflammatory remodelling of the TME. CD4+ T cells may also exhibit direct cytotoxicity against tumour cells expressing MHC-II53,55–59 IFN-γ secretion by CD8+ and CD4+ T cells upon cognate antigen recognition induces an upregulation of MHC-I and II presentation on tumour cells and APCs which further sensitises recognition of neoantigens. Inflammation supports the cytotoxic activity of neoantigen-specific CD8+ T cells. The killing of tumour cells and release of tumour antigens results in antigen spreading51,60,61 and further re-stimulation and expansion of memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. The iteration of this sequence, called the cancer-immunity cycle51 is counteracted by numerous immune suppressive mechanisms that have evolved to safeguard from autoimmunity62,63.
The ultimate objective of a cancer vaccine is to re-ignite the cancer immunity cycle by priming of novel neoantigen-specific T cells or by activation of pre-formed ones, thus fostering a sustained adaptive anti-tumour immune response until tumour cells are completely eliminated.
Early evidence suggests that intratumour presentation of MHC-II neoepitopes is capable of stimulating and clonally expanding neoantigen-specific CD4+ T cells with a FoxP3+ regulatory T-cell (Treg) phenotype64. The TCR repertoire of the intratumorally expanded oligoclonal Treg T-cell population overlaps with the repertoire of peripheral blood Tregs and differs markedly from the intratumoral TCR repertoire of the conventional FoxP3- CD4+ T-cell population64,65. This suggests that intratumoral Treg cells are either specific for neoantigens that differ from those recognised by conventional CD4+ helper T cells or that they are derived from a different T-cell pool. It is also not clear whether these neoantigen-specific Treg cells arise from suboptimal priming of naïve CD4+ T cells driven by exposure to neoantigens under noninflammatory tolerogenic conditions66 or are derived from already established cross-reactive Treg T-cell populations67. It is conceivable that neoantigen-specific Treg cells could attenuate anti-tumour immunity in an antigen-specific manner, regardless of their origin, and that a better understanding of their specificity could help to improve neoantigen prediction algorithms.
2.5. Immune surveillance [G], immune escape [G] and immune editing
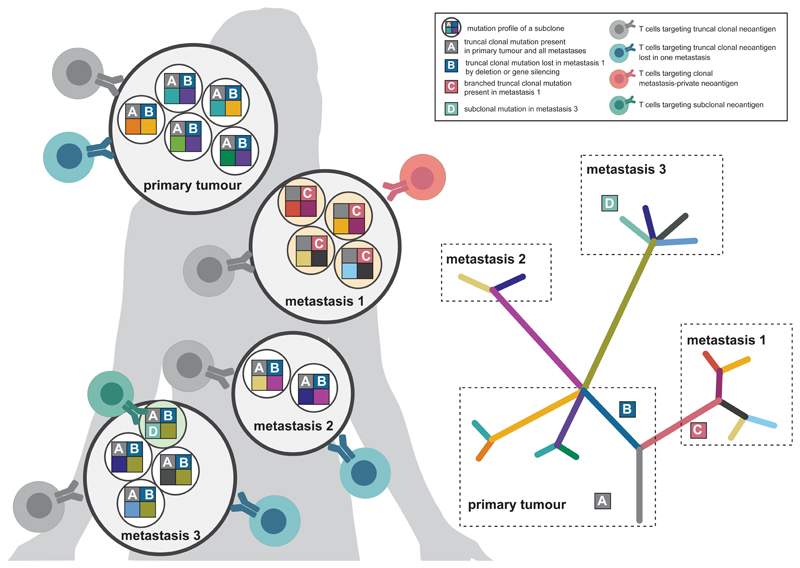
Heterogeneity is a hallmark of cancer. The genetic evolution of tumours is driven by selection of clones with fitness advantage. The dynamic interplay between immune surveillance and tumour progression50 results in primary and metastatic lesions of diverse clonal composition (Fig. 4).
Figure 4. Factors affecting neoantigen recognition and evolution.
Each lesion (primary or metastasis) of an individual tumour disease consists of different subclones, each of which may contribute sets of different neoantigens to the patient’s neoantigenome. Depending on whether the neoantigen is truncal clonal (neoantigen A), truncal clonal but lost in a metastasis by deletion or gene silencing (neoantigen B), clonal in a certain metastasis (neoantigen C) or specific for a certain subclone in a single metastasis (neoantigen D), neoepitope-specific T cells would target either all tumour cells (neoantigen A), all tumour cells of the lesions harbouring the neoantigen (neoantigen B), tumour cells of a distinct lesion (neoantigen C) or merely a single tumour subclone (neoantigen D).
Evasion from T-cell immunity does occur in the course of a tumour’s natural evolution as well as under treatment and there are various mechanisms for tumours to escape immune surveillance.
Tumours may create an immuno-suppressive TME by up-regulating molecules such as PD-L168, TGF-beta69 or by promoting expansion of regulatory T cells70 that protect them from neoantigen-specific T cell immunity.
Further, tumour clones that are recognised by functional neoantigen-specific T cells may become subject to immune editing50. Selection of neoantigen-loss variants appears to occur frequently in immune-infiltrated tumours of treatment-naïve patients71–73, yet rarely in tumours with insufficient immune cell infiltration70,74. Combining multiple neoantigens in a vaccine rather than relying on a single antigen mitigates the risk of escape by antigen loss.
Alternatively, cancer cell clones may be selected that have defects in the antigen-processing/-presentation machinery, such as loss of heterozygosity (LOH) [G] of MHC genes, downregulation and mutation of MHC molecules75, dysfunction of the transporter for antigen presentation (TAP)76 or mutations in the beta-2-microglobulin (B2M)77. These alterations disable cognate anti-tumour immunity at its roots and render tumours resistant to any treatment that is based on activity of neoantigen-specific T cells. This is where combination therapy comes in play with the objective of combining therapeutic vaccines with treatment modalities that have non-overlapping modes-of-action.
The risk for tumour immune escape is higher in metastatic disease. Each metastatic lesion can be viewed as independent island with its own immune microenvironment, immune escape strategies, evolution dynamics and neoantigenome78–80.
ICB can indirectly contribute to eliciting new neoantigen-specific T-cells as neoantigens released from dying tumour cells are taken up by APCs and T cells are primed and undergo efficient activation and expansion under the effect of ICB. This process is called antigen spreading and plays an important role in broadening and enriching the repertoire of anti-tumour T-cell responses60,61,81. Patients may develop resistance to ICB by outgrowth of subclones that do not express the restrained neoantigens and thus are not recognised by ICB-mobilised T cells (Fig. 4).
3. A context-based classification of neoantigens
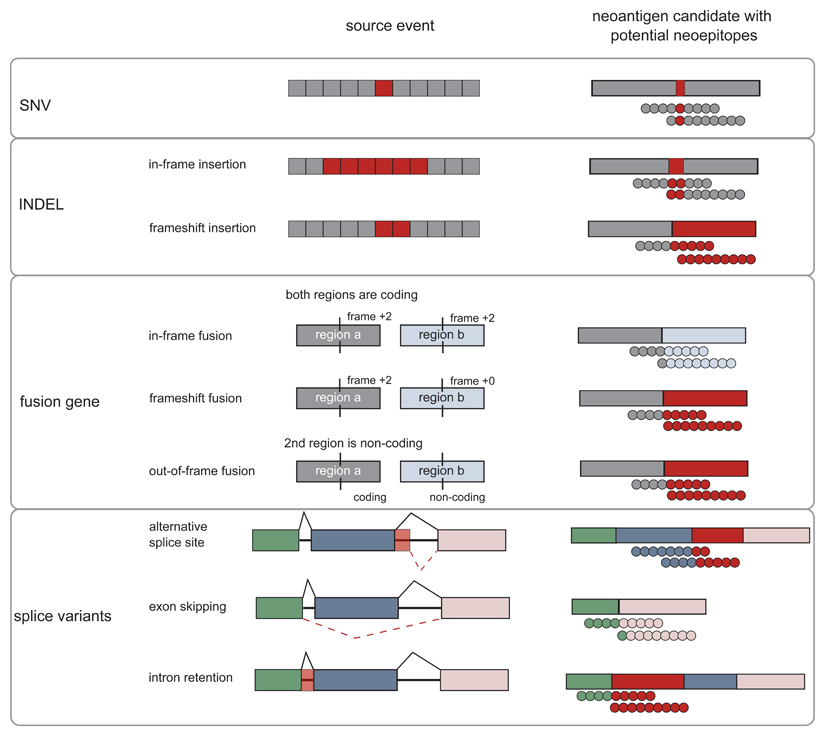
One way to categorise neoantigens is based on the type of somatic mutation that creates the altered epitope and defines its molecular characteristics (Box 1). Single nucleotide variations (SNVs) in coding regions are the mutation type that is best studied in clinical testing. An important future field is to develop discovery tools for neoantigens created by cancer-specific INDELs (insertions and deletions), fusion genes and splice variants that have a lower degree of similarity to self-antigens than SNV-derived neoantigens.
Box 1. Classification of neoantigens according to molecular characteristics.
Somatic mutations that are the basis for the foreignness of cancer cells may result in protein sequences that depending on the type of mutation are altered in different ways (FIG BOX1). An important future field of development is to tap the various categories described below and others (e.g. non-coding regions of the genome) to broaden the discovery space out of which neoepitopes can be predicted.
SNVs
Single nucleotide variants (SNVs) represent the exchange of single nucleotides within the genome and are the most abundant mutation type in the majority of cancers260. Most SNVs generate neoantigens with a single amino acid substitution. In very rare cases, e.g. if a native stop codon is destructed, SNVs may create longer neoantigen sequences.
SNVs were the focus of the first efforts of predicting neoepitopes and their application in clinical trials. SNV burden is predictive for the clinical efficacy of ICB8,261 and SNV-derived neoantigens were successfully targeted in individualised neoantigen vaccination trials, e.g. in melanoma and glioblastoma19,20,104,106
Whereas individualised treatment remains the mainstream approach for the broader patient population, efforts to discover shared SNVs that would enable standard clinical trial and development routes are being pursued. Several experimental studies report neoantigens that derive from shared mutations (Table 1). The common oncogenic mutations KRAS G12D in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and other tumour types, and IDH1 R132H in glioma can trigger antigen-specific immune responses associated with tumour regression42,52,108,146. However, overall, the vast majority of shared SNVs are rare and in general confined to small subsets of patients.
INDELs
Insertions or deletions of nucleotides (INDELs) can result in neoepitopes, however those generated by frameshift INDELs may be longer and unrelated to known sequences and thus have a higher likelihood to be immunogenic262.
However, INDEL mutations may introduce premature stop codons, which in turn can induce non-sense mediated decay (NMD) of the respective RNA. Of note, INDELs that are predicted to escape NMD, were shown to correlate better with clinical response to ICB as compared to INDELs in general or to SNVs263. Neoepitope candidates from INDELs show superior MHC binding capability as compared to SNVs. Tumour mutational burden analyses that include INDEL frameshift mutations correlate better with clinical response of melanoma patients to anti-PD1 or anti-CTLA4 than analysis based on SNV alone96.
The high incidence of INDEL mutations in tumour entities with low SNV burden96,264, may expand the application of neoepitope-based immune therapies to these tumour entities.
Fusion Genes
Intra- and inter-chromosomal rearrangements may join two unrelated genes to produce a fusion gene. A prominent example is the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene in chronic myelogenous leukaemia (CML), that is found in ~90% of CML patients265. Experimental evidence supports immunogenicity of this shared fusion (TABLE 1). The vast majority of fusion genes, however, appear to be individual266.
In a head and neck cancer patient responding to PD-1 blockade, despite low SNV burden, a T-cell response against the DEK–AFF2 fusion gene was observed, while no neoantigens from other mutation classes were identified99.
Overall, gene fusions are considered to be relatively rare events267 and the immunotherapeutic utility of fusion gene-derived neoantigens is not fully grasped yet.
Splice Variants
Alternative splicing generates diversity and lineage-specificity by expression of multiple RNA and protein isoforms from one gene, is dysregulated in cancer cells and may generate neoepitope sequences268–272. If a somatic mutation in the respective gene results directly in its altered splicing, tumour specificity of the splice variant (which is a key defining criterion for a neoantigen) can be assumed. This may not be true for aberrant splice variants generated by other mechanisms such as cancer-associated epigenetic alterations. Here, physiologically expressed splice variants in a distinct cell lineage may be ectopically activated in cells of unrelated lineage.
Figure Box 1. Mutation classes and neoantigen and neoepitopes derived thereof.
SNVs change a single amino acid. INDELs and fusion genes may be in-frame and preserve the original open reading frame or they may cause a frameshift, creating novel open reading frames downstream of the mutation site. Alternative splicing may occur by various mechanisms including the usage of alternative splice sites, skipping of exons or intron retention events. All of these classes may generate neoepitope sequences that are foreign to the immune system. Novel sequence regions derived from mutations are indicated in red.
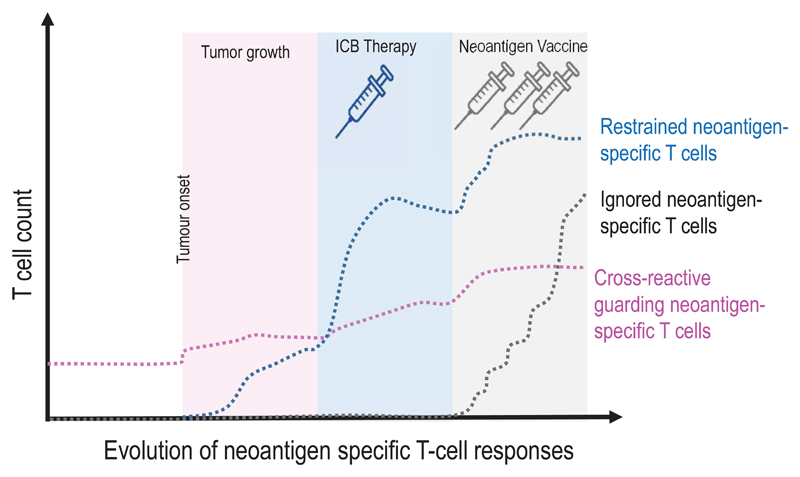
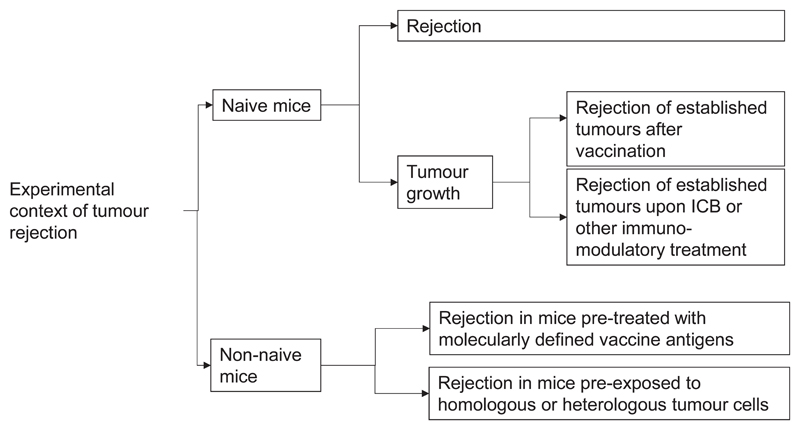
We propose an orthogonal classification of neoantigens (Fig. 5, Table 2) that is motivated by the key question how to identify relevant neoantigens that convey proficient anti-tumour immunity. We believe that the answer to this question may differ depending on the clinical context and needs to consider that mechanisms and cancer life cycle effects that may drive the formation of neoantigen-specific immune responses are diverse. It is yet not clear why some neoantigens induce functional T-cell responses spontaneously and others need intervention to do so. Another unknown is whether we can learn from neoantigens targeted by the most abundant, immunodominant, prognostically favourable T-cell specificities in treatment-naïve patients or from those which are associated with deriving clinical benefit from ICB therapy in order to improve computational pipelines for neoantigen vaccine design. Also, while the term ‘tumour rejection antigen’ has been coined for relevant antigens that induce proficient immunity and several such neoantigens have been reported in mouse models, the context, within which those tumour rejections occurred, differ as do the implications those individual studies may have for vaccine design (Fig.6).
Figure 5. A context based classification of neoantigens.
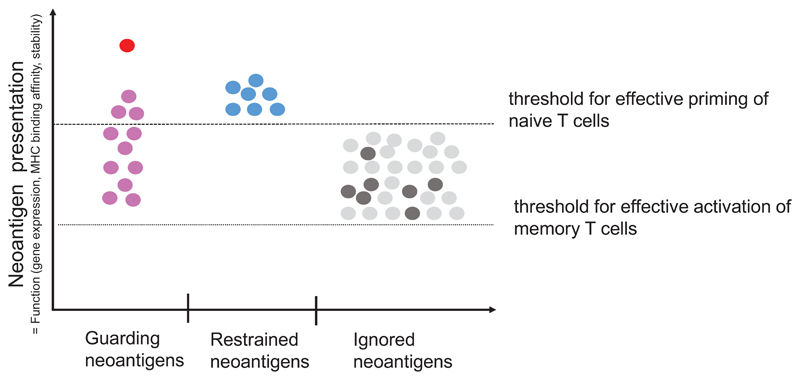
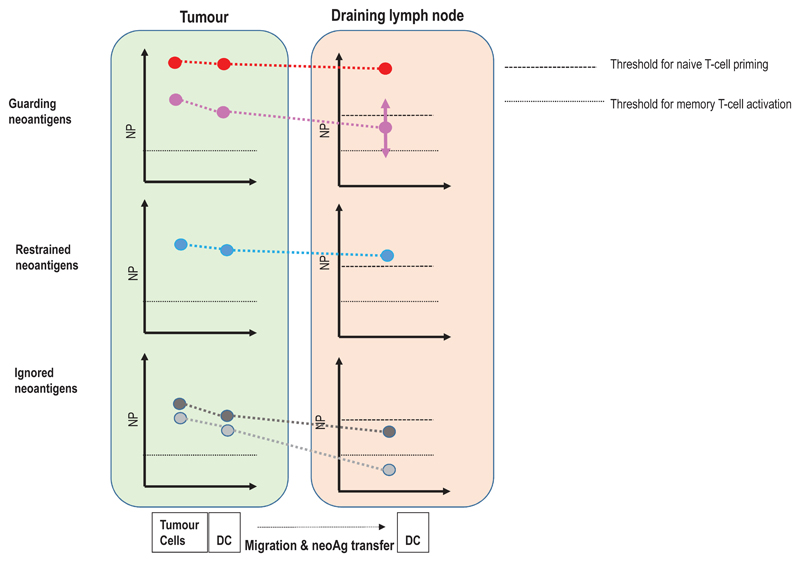
(a) The formation and evolution of neoantigen-specific T-cell responses depends on the clinical context. While ICB therapy boosts pre-existing T-cell responses, neoantigen cancer vaccines induce de novo responses or amplify preformed ones. (b) The robustness and level of a neoantigen presentation on LN-resident DCs defines the efficiency of cognate priming of T cells, while presentation on tumour-resident APCs and tumour cells activates primed cells at the tumour site. Neoantigen presentation is a function of expression level of the mutated protein, the binding ability of the mutated peptide to MHC and stability of the respective peptide/MHC complex. Memory T cell activation can be achieved with neoantigen presentation levels 50 fold lower than those required for priming of naive T cells. Dark red: supreme neoantigen; pink cross-reactive guarding neoantigen (c) Neoantigen-specific T cell responses are driven by the presentation of neoepitopes on tumour cells, on tumour-infiltrating APCs, and on DCs in the draining lymph node. Priming of naïve T cells in the lymph node requires substantially higher neoantigen presentation than is required for stimulation of memory T cells. Guarding neoantigens are either highly expressed with superior binding and stability of the respective neoepitope/MHC complex (red) or exploit cross-reactivity to heterologously primed memory T cells (purple). Restrained neoantigens exhibit robust expression and strong MHC binding affinity/stability and are able to prime and expand naive neoantigen-specific T cells in the lymph node. Ignored neoantigens require a vaccine to generate neoantigen presentation levels in the LN that allow priming. As long as neoantigen presentation is moderate (e.g., low expression/high affinity MHC binding (dark gray) or high expression/low MHC binding (light gray), T cells can be activated for effector functions in the tumour. NP: level of neoepitope presentation, LN: lymph node, APC: antigen-presenting cell, ICB: immune checkpoint blockade
Table 2. Classification of neoantigens by potential functional impact.
| Guarding neoantigens | Restrained neo antigens | Ignored neoantigens | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic features | Supreme neoantigens with a strong antigenicity driving early priming and rapid expansion of neoantigen specific cytotoxic T cells | neoantigens cross-recognised by pre-formed memory T cells induced by heterologous immunity | Neoantigens that are immunogenic in the immunotherapy-naïve host and induce PD1+ memory T cells which proliferate and expand under ICB | Neoantigens which do not induce a relevant immune response in the tumour-bearing host but are able to drive tumour immunity once memory effector T cells are induced by vaccination, |
| Frequency | Extremely rare | <2% of all mutations | <2% of all mutations | 15-25% of all mutations |
| Examples in mice | DDX585, SPTBN283 | SIY87 | LAMA46,53, ITGB153 | KIF18b23,102 |
| Examples in human | n.a. | MUC1650 | ATR5 | RETSAT19,20 |
| Clinical relevance | Prognostically relevant drivers of anti-tumour immunity in the immunotherapy-naïve host. | Inactive due to immunosuppression in immunotherapy-naïve host. Main drivers of clinical ICB activity. | No impact on tumour control in immunotherapy-naïve or ICB-treated host. Confer poly-specific anti-tumour T-cell control by broadening the repertoire of tumour-specific T cells upon neoantigen vaccination. | |
Figure 6. Discovery of tumour rejection antigens.
As the term “tumour rejection“ and the conditions under which to assess it are not standardised, experimental mouse model setups are used that differ conceptually and provide answers to different questions. These include tumour challenge of naive mice83,84 as well as of tumour- or vaccine-experienced mice258,259 and assessment of rejection spontaneously83,84 or upon various modalities of immunotherapy6,23,53,102.
The classification below differentiates neoantigens based on the clinical setting in which they gain relevance. It is meant to provide a framework that guides neoantigen discovery and characterisation studies, and helps to structure and analyse new and available datasets to address gaps in our understanding and develop a tailored approach to define neoantigen candidate features for vaccine design and beyond.
3.1. Guarding neoantigens [G]
Tumours are subject to T-cell surveillance. Consequently, spontaneously occurring neoantigen-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are found in patients with treatment-naïve cancers15,41,50,82 Such neoantigens may have a guarding function by mediating early tumour rejection before a tumour becomes clinically apparent. Or they may decelerate tumour growth, inhibit metastatic dissemination and prevent recurrences after surgical removal of the primary tumour. The characteristic feature of guarding neoantigens is that their expression in the tumour is sufficient to drive clinically relevant anti-tumour immunity in the absence of immunotherapy. Guarding neoantigens may come in two flavours. Firstly, strongly antigenic ‘ supreme’ neoantigens that are robustly expressed in tumour cells and form neoepitopes with extraordinarily high-affinity MHC binding83 and stability (Fig 5). These features promote early onset priming and rapid and strong expansion of neoantigen-specific cytotoxic T cells that infiltrate and suppress the growth and metastatic dissemination of the primary tumour early in its life cycle before full manifestation of an immunosuppressive TME83. Guarding neoantigens are difficult to identify in human. The strongest evidence for the existence of such tumour rejection antigens comes from engraftment studies of very high mutational load mouse tumours with thousands of somatic mutations induced by UV irradiation or carcinogens. In these models, wild-type tumour cells expressing the respective neoantigens are rejected by naïve mice, whereas immune-edited tumour cell clones that have lost the respective neoantigens but express all other mutations grow aggressively83–85. Immunodominant neoantigens are derived from extremely rare mutational events and contribute to an improved clinical prognosis probably only in very high-mutational load tumours such as microsatellite instable cancers86.
The second guarding neoantigen type is recognised by pre-established, cross-reactive memory T cells. Examples are neoantigens cross-recognised by T cells formed against gut microbiota, previously encountered pathogens or persistent viruses50,87. Neoantigen recognition by heterologous T cells has two important effects. Firstly, memory T cells have a 50-fold lower functional activation threshold and respond faster as compared to naïve T cells88. Thus, cancer mutations with low MHC binding affinity, low peptide/MHC/complex stability or with low expression level that are incapable of priming naïve T cells may engage and expand pre-established cross-reactive memory T cells. Second, by definition pre-formed heterologous immunity is existent prior occurrence of tumour disease. Neoantigen recognition by cross-reactive, memory T cells early in the life cycle of a tumour may significantly shape the tumour-specific TCR repertoire towards high-affinity TCR binders, promote T-cell infiltration and growth inhibition of tumours, including those with low mutational load41. Heterologous immunity may explain that more than a quarter of neoantigen-specific T-cell responses identified by an unbiased screening with tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) is directed against neoepitopes with low (>500 nM) predicted HLA binding affinity15. Accordingly, clinically relevant heterologous T-cell immunity against neoantigens is expected to be largely driven by memory T-cell repertoire and by the affinity of the TCR to the peptitde/MHC complex rather than by MHC binding affinity of the mutant peptide. Neopitopes that are able to stimulate a more diverse TCR repertoire, e.g. those with a higher dissimilarity to self-antigens45 may be more likely to qualify for this subclass of cross-reactive neoantigens.
By definition, guarding neoantigens control the natural course of the disease and are associated with favourable prognosis of immunotherapy-naïve patients irrespective of the treatment. Only a few studies investigated the correlation between molecular neoantigen features [G] and favourable disease outcomes in suitable populations. One study showed that tumours of long-term survivors with pancreatic cancer in contrast to those from short-term survivors harbour neoepitope candidates displaying a composite quality feature of (i) sequence homology with pathogen-derived peptides and (ii) stronger predicted HLA binding affinity of the neoepitope relative to its wild-type50 (differential agretopicity index [G]; DAI). Similarly, another study identified the mean DAI across all clonal mutations in a given tumour as predictor for increased survival in melanoma and lung cancer patients89.
ICB treatment or neoantigen vaccination may further augment pre-existent T-cell responses against guarding neoantigens qualitatively or quantitatively. A potential disadvantage of guarding neoantigens is that they are targeted early in the course of disease and thus are at risk for early immunoediting [G]41,72.
3.2. Restrained neoantigens [G]
Not all neoepitope-specific T cells that occur spontaneously in patients are fully functional. Neoantigen-specific T cells that are pre-existent but functionally impaired may require further invigoration to contribute to a favourable course of the tumour disease. This can be achieved by ICB therapy for which durable clinical responses have been shown to correlate with the expansion of neoepitope-specific T cells5–7.
We designated targets that are recognised by ICB reinvigorated T cells as restrained neoantigens. While restrained neoantigens are capable of priming T-cell responses, their antigenicity is weaker compared to supreme neoantigens and the primed T cells are not proficient or not sufficiently expanded to prevent disease progression. T cells primed by restrained neoantigens infiltrate tumours and recognise their targets on cancer cells and APCs but are outpaced by tumour growth and immunosuppressed by the established TME. Antigen-pulsed migratory DCs require several days to get from the tumour to LN-resident DCs36 and priming of naïve T cells in lymphoid tissues requires a high level of neoantigen presentation. Thus, mutated peptides need to be robustly expressed in the tumour, exert high-affinity MHC binding and build stable peptide/MHC complexes to give rise to restrained neoantigens (Fig 5b).
In contrast to guarding neoantigens that are identified based on their prognostic [G] impact, restrained neoantigens are defined by their predictiveness [G] for the clinical benefit conveyed by immunotherapies such as ICB (Table 2). Datasets for studying restrained neoantigens and their specific features may e.g. come from randomised trials that compare ICB treatment to some non-T-cell-activating standard of care.
One study showed that all identified T-cell responses in patients responding to ICB were directed against clonal neoantigens90. The clonality of mutations and the number of predicted neoepitope candidates per mutation91, the DAI89 and sequence similarity to known pathogen epitopes combined with the ratio-based DAI92 were found to be associated with clinical response to ICB. Oncogenic driver mutations [G] are typically clonal as they are critical for the survival of tumour clones and therefore less likely to be lost during immune editing. Neoantigen candidates derived from driver mutations were predicted more frequently in patients who responded to ICB93. In turn, patients with MHC alleles predicted to have poor presentation of driver mutations were shown to less likely respond to ICB94. SNVs5,7,95, as well as frameshift mutations and gene fusions have been reported to act as restrained neoantigens96–99.
Restrained neoantigens are discussed in this review in the context of ICB due to the clear association of their clinical effect with reactivation of impaired T cells. This principle can be extended to other immune-modulating therapies, e.g. T-cell homeostatic cytokines such as interleukin-2 (IL-2)100, once they have been shown to convey clinical benefit through pre-existent yet functionally impaired neoantigen-specific T cells.
3.3. Ignored neoantigens [G]
Only a very small fraction of mutations in a given human cancer appear to induce spontaneously occurring T-cell response14,15,101. Similarly in mice, a substantial fraction of mutations identified by NGS in syngeneic tumours were not spontaneously immunogenic23.
The lack of spontaneous immunogenicity does not mean that T cells against these ignored antigens would not be capable of contributing to tumour rejection. In fact, systematic immunogenicity studies in mice showed that 15-40% of the cancer mutations identified by NGS in murine tumours induce robust T-cell responses (with more CD4+ than CD8+ ones) when used as vaccine antigens23,102. A large portion of the induced immune responses were of high magnitude and resulted in shrinkage and rejection of established tumours, antigen spreading [G] and changes to the immunosuppressive environment23. Several clinical trials using individualised neoantigen vaccines in patients with high and low mutational load tumours such as melanoma, lung cancer, glioblastoma, ovarian cancer and pancreatic cancer19,20 103–108 (reviewed in109,110) showed up to 70% immunogenicity across all neoepitopes used in those vaccines. The vast majority of these immune responses were not detectable prior therapy and de novo induced by vaccination19,20. The relevance of vaccine-induced neoantigen immune responses was supported by detection of infiltrating vaccine-induced T cells in post-treatment biopsies, killing of autologous patient-derived tumour cell lines in vitro, and patients with shrinkage of tumour lesions, objective clinical responses or reduction of recurrences20.
We propose the term ignored neoantigens for these mutant gene products that, although presented on MHC molecules, are incapable of eliciting a T-cell response and require vaccination to induce a clinically relevant T-cell response. We hypothesise that ignored neoantigens are characterised by a moderate level of neoepitope presentation which is below the threshold for priming of naïve T cells but above the level for recognition by memory T cells (Fig. 5). The purpose of a vaccine is to load LN-resident DCs with sufficient amounts of neoantigen to achieve priming. A substantial proportion of mutations encode neoantigens with either low expression and high MHC binding affinity, high expression and low binding affinity, or moderate expression and binding affinity. Thus, ignored neoantigens are a rich and complementary source of targets for neoantigen vaccines or cell therapy with individualised TCR-engineered T cells. Ignored neoantigens may be particularly relevant to stimulate poly-specific T-cell responses in patients with low mutational load tumours. Even though lower in frequency, guarding and restrained neoantigen candidates may be also highly relevant targets, to include into personalised vaccines.
As vaccine-induced T cells up-regulate PD120,111 even patients who are resistant or refractory to ICB monotherapy may benefit form combining vaccines and ICB and vaccines may expand the repertoire of pre-existent T cells for ICB107 to include ignored neoantigens. Moreover, by counteracting immunosuppressive mechanisms, ICB may lower the neoantigen presentation threshold required for priming naïve T cells, thereby broadening T cell responses by antigen spreading60,61,81.
4. Prediction of neoantigen candidates
4.1. Immunobiology driven approaches
The most basic prerequisite for an immune response is that the aberrant gene product that results from the somatic mutation is transcribed, translated, processed and presented on MHC molecules. Therefore, verification of expression and prediction of binding affinity to the patient’s MHC alleles are the two key upfront elements of current neoantigen prediction computational pipelines [G] (Supplementary Table 1).
Beyond these, other potentially relevant biological features are implemented into algorithms to rank neoantigen candidates (Table 3).
Table 3. Hypothesis-driven neoantigen features and prediction algorithms. WT: wild-type.
| Name | Function | Input | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| MHC-I binding | MHC-I binding prediction | Neoantigen candidate sequence, MHC-I alleles | Several tools, e.g. netMHCpan118 |
| MHC-II binding | MHC-II binding prediction | Neoantigen candidate sequence, MHC-II alleles | Several tools e.g. netMHCIIpan234 |
| MixMHCpred score 120,235 | Prediction of cell surface presentation of MHC-I epitopes | Neoepitope candidate sequence, MHC-I alleles | Trained on eluted ligands |
| MixMHC2pred score 236 | Prediction of cell surface presentation of MHC-II epitopes | Neoepitope candidate sequence, MHC-II alleles | Trained on eluted ligands |
| Transcript expression 23,102 | Transcript expression in FPKM, RPKM or TPM | - | Sveral tools, e.g. kallisto114 |
| Clonality 90 | The fraction of tumour clones in which a neoantigen is present | Number of reads that cover WT and mutated allele | Several tools, e.g. pyclone138 |
| Differential Agretopicity Index (DAI)89,206. | Difference in MHC-I binding affinities between mutated and WT peptide | MHC-I binding affinity of neoepitope candidate and corresponding WT | - |
| Self-Similarity 132 | Sequence similarity between mutated and WT peptide | Neoepitope candidate and corresponding WT sequence | Relevant for neoepitopes with similar MHC binding as WT peptide |
| Pathogen similarity 50 | Similarity to known pathogen epitopes | Neoepitope candidate sequence | BLAST search against pathogen-derived epitopes IEDB database |
| IEDB immunogenicity 237 | Summed up position-weighted enrichment of residues in immunogenic peptide sequences | Neoepitope candidate sequence | - |
| Neoantigen dissimilarity 133 | Dissimilarity of epitope sequence to self-proteome | Neoepitope candidate sequence | BLAST against WT proteome |
| PHBR-I 128 | Mutation presentation by multiple patient MHC-I alleles | Best MHC binding score for each MHC-I allele | - |
| PHBR-II 129 | Mutation presentation by multiple patient MHC-II alleles | Best MHC binding score for each MHC-II allele | - |
| Generator rate 238 | Mutation presentation by multiple neoepitopes | MHC-I binding affinities | - |
| Recognition potential 50,92 | Combinatorial score considering pathogen-similarity and differential MHC binding of mutated and WT epitope | Neoepitope candidate sequence, MHC-I binding affinities | - |
| Vaxrank 239,240 | Combinatorial score considering the presentation of a mutation by multiple epitopes and mutated transcript expression | Transcript expression of mutation, MHC-I binding affinities of neoepitope candidates related to a mutation | - |
| Priority score 241 | Combinatorial score considering MHC binding and expression | MHC-I binding affinity of neoepitope candidate and WT, transcript expression, variant allele frequency | - |
| Tcell predictor 242 | Random Forest Model considering several epitope features such as expression, hydrophobicity | Gene name, substitution, neoepitope candidate sequence | - |
| neoag 243 | Gradient Boosting Model considering epitope sequence intrinsic features | Neoepitope candidate sequence, corresponding WT sequence, variant position, MHC-I binding | Trained on a immunogenicity data set from mouse tumour models |
These include features that may impact proficiency of a presented neoepitope candidate to activate T cells (dissimilarity to self-antigens tested by sequence homology queries) or its likelihood of immune escape by outgrowth of antigen-loss variants (such as clonality of the mutation computed by DNA sequencing data analysis or driver mutations determined by database queries).
Whereas the features described below are based on sound rationales, how to weight each of them for prioritising neoantigen candidates for vaccine design is not established, in particular given that features have not been correlated with context-based neoantigen classes. Our own benchmarking studies of neoantigen features indicate that a critical mass of available datasets for accurate prediction of immunogenicity does not yet exist, and datasets are too diverse and not standardised. Most immunogenicity studies use datasets derived from testing of pre-existing T cell specificities. These T cells are most likely a mixed basket including T cells primed by the neoantigen itself or T cells that benefit from heterologous priming by unrelated antigens. The context-based classification provided in Chapter 3 may contribute to a framework that differentiates neoantigen candidates based on the clinical question asked and tailors data mining approaches accordingly.
4.1.1. Transcript Expression
The density of detected peptide/MHC complexes correlates with protein levels and transcript expression112. Tumour cell clones that express neoantigens derived from high abundance transcripts are efficiently cleared under ICB therapy113 and downregulation of neoantigen candidates is an immune escape strategy72. Further, transcript abundance has been shown to compensate for low MHC binding affinity of a mutation 37. In aggregate, these data support the notion that high transcript expression is associated with a higher likelihood of functional T-cell response. Therefore, various studies use gene expression to rank neoantigen candidates15,20,23.
To quantify the expression of a mutation and its wild-type counterpart, both transcripts are searched in bulk RNA-seq data generated by NGS of RNA extracted from a tumour biopsy. Usually, expression analysis is performed only for the tumour tissue and not for the corresponding healthy tissue sample and tumour specificity of the mutation is confirmed by exome sequencing. Quantification of altered transcripts can be fast and reliable with tools such as kallisto, which pseudoaligns [G] reads against a reference transcriptome to detect the most likely transcript for each read114.
4.1.2. MHC binding, stability and cell surface presentation
The capability of a mutation to bind to at least one of the MHC alleles of the patient in question is the most elementary requirement for T-cell recognition. Collaboration of antigen-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells is critical for efficient anti-tumour immunity115. Expression of a single MHC-I neoantigen alone is not sufficient and at least one additional MHC-II neoantigen is required for meaningful anti-tumour immunity in mouse tumour models 53. Accordingly, an individualised vaccine should combine neoepitopes predicted to bind to MHC-I as well as MHC-II alleles of the patient.
Published tools that predict MHC binding affinity are trained on wet lab binding affinity data and/or eluted ligands detected by mass spectrometry. Recent benchmarking studies used ROC (receiver operating characteristic)-curve [G] analysis as the performance metric to assess prediction tools for MHC-I binding and presentation in humans116 or for T-cell responses in mice117. NetMHCpan118 and MHCflurry119 achieved the best ‘area under the ROC curve’ (ROC-AUC) in these studies. Whereas these both tools are trained on binding affinity and eluted ligand data, MixMHCpred120,121 is trained on eluted ligands only. MixMHCpred predicts the likelihood of a given peptide sequence to be presented on the cell surface and achieves higher ROC-AUCs in comparison to the MHC binding tools in a benchmark study using ROC-curve analysis on a larger dataset of experimentally verified MHC-I-binding epitopes122. All tools perform sufficiently well for enriching peptides with decent MHC-binding properties. The lack of ligand data for rare MHC alleles is a limitation and is addressed by tools such as NetMHCpan that use MHC sequence homology with more frequent MHC alleles to infer potential ligand preferences123.
The stability of the neoeptiope/MHC complex has been proposed to be more important for immunogenicity prediction than the binding affinity, as higher stability may increase the probability of the complex being recognised by T cells124. Tools for stability prediction, e.g. NetMHCstabpan perform well to enrich for immunogenic mutations and will improve further with bigger training datasets becoming available 125,126
Patients with a complete germline heterozygosity at MHC-I loci have a better survival upon ICB therapy than patients exhibiting homozygosity for one or more MHC-I genes127, as a higher diversity of alleles increases the likelihood for a given neoantigen to find an allele to bind127–129.
NetChop130 or NetCTL131 predict proteasomal cleavage and transport into the endoplasmic reticulum by the TAP protein complex [G], which are prerequisites for an epitope to eventually be loaded onto an MHC-I molecule. However, as methods for predicting MHC presentation are trained on ligands eluted from MHC, which have gone through those earlier processing steps, the value of combining cleavage, transport and binding prediction tools is questionable.
4.1.3. Dissimilarity to self and similarity to pathogen-associated epitopes
Dissimilarity to the non-mutated wild-type sequence (in particular if it is presented by one of the
patient’s MHC alleles) and, more broadly, to the self-proteome, may lower the likelihood that the respective neoepitope is subject to immune tolerance and increases the likelihood for the presence high-affinity T cells in the T-cell repertoire132,133. One approach to leverage the dissimilarity hypothesis is to use alignment scores resulting from BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) [G] searches against the non-mutated proteome as substitute for TCR binding energies133. Another approach uses a kernel similarity measure for the mutated and the corresponding wild-type epitope132. These metrics were reported as predictive for identifying neoepitopes derived from SNVs and may be even more so for frameshift INDELs or fusion genes.
Sequence similarity of a neoepitope to pathogen sequences may be associated with a higher likelihood for cross-reactivity with preformed T cells directed against frequently encountered pathogens (reviewed in49). A study characterising neoantigens in pancreatic cancer patients identified the combination of DAI and sequence similarity to pathogen-associated epitopes as features for guarding neoantigens discriminating long-term and short-term survivors50.
4.1.4. TCR recognition
Methods that address the TCR’s interaction with the peptide/MHC complex are based on predicting the amino acid side chains of the TCR that will face the MHC-bound peptide134 or the stability of the peptide-MHC complex which is associated with higher likelihood of TCR binding135. Exploratory approaches are underway that subject the amino acid sequence of the TCR to an artificial neural network [G] to predict the binding of a given TCR to the peptide/MHC complex136, thus circumventing the use of structural modelling. Another approach claims to predict the most likely cognate peptide/MHC target of a TCR137 based on the TCR sequence. However, these methods are not mature yet, operate at the limit of current computational algorithms, as the diversity of the MHC/peptide/TCR combination space is huge and the available experimental training data is not sufficient to train algorithms.
4.1.5. Mutation clonality and indispensibility
The clonal architecture of a cancer sample can be assessed by analysing the variant allele frequency [G] identified in a patient with PyClone138 or SciClone139 The robustness of the prediction depends on sample quality. A sample with low tumour content, for example, is unlikely to deliver an accurate clonal architecture. For robustness, multiple samples from the same tumour may be required, which is difficult to implement in a routine clinical setting.
Clonal and truncal mutations [G] may be preferable over subclonal and branched mutations [G], as they allow to address tumour heterogeneity, and target tumour cells with potentially higher fitness and tumour-promoting function140. T-cell specificities that target a few high quality neoantigens may be sufficient to drive tumour control in treatment-naïve cancer patients and may be predictive for prolonged survival in ICB treated patients90,141. Neoantigens that exist prior to genome doubling will have higher variant allele frequencies than those generated after genome doubling. In NSCLC more than 70% of patients have whole genome doubling as an early clonal event142.
The majority of driver mutations appear typically early in tumour evolution and have a high likelihood of being clonal94,143. Driver mutations per definition promote cancer cell fitness and are considered to be stable. Databases like COSMIC144 or DriverDB145 list known and functionally validated driver genes. While experimentally validated immunogenic driver mutations are rare42,146, computational methods have been developed that allow screening for novel driver mutations147.
Passenger mutations may also occur early and be clonal148. The designation ‘passenger’ is misleading as it implies that the respective mutated gene is dispensable and that the mutation does not provide an advantage for tumour cell survival and is prone to be lost during tumour evolution. Validation of a mutation to be a driver requires extensive experimental characterisation and proof that it transforms normal cells into tumour cells. Such studies are not undertaken for rare or unique mutations. As lack of evidence is not evidence of absence, mutations dubbed as ‘passenger’ may well provide a biological advantage in the setting of the individual cancer disease.
Computational analyses indicate that driver mutations are less frequently presented on MHC-I and MHC-II128,129,149,150. For inducing anti-tumour immunity, the degree of foreignness of the vaccine antigens may be much more relevant than their functional role in the cancer cell.
4.1.6. Loss of heterozygosity of essential gene products
Genes are usually present in two copies within the genome. If an essential gene is subject to LOH and generates a neoantigen from the remaining allele, the tumour cannot escape by neoantigen loss, as the remaining allele is required for tumour cell survival. Therefore, mutations in essential genes undergoing LOH may be particularly excellent targets for neoantigen vaccination151. LOH in coding regions can be reliably predicted from deep sequencing152 and microarray data analysis153. Genetic knockouts and gene silencing studies have provided lists of about 1,600-2,500 genes that appear to be essential for cell survival154–156 and may facilitate prioritisation of neoantigen candidates.
4.2. Deep learning based approaches
Artificial neural networks are inspired by biological neural networks. To predict binding of epitopes to MHC molecules, artificial neural networks that were trained on data from MHC binding assays are explored119,136,157,158. Neural networks trained on high quality immunopeptidome data from monoallelic cell lines show excellent performance for prediction of MHC-I and MHC-II binding37,38,159. Also, physico-chemical properties (for example energies of attraction and repulsion, hydrogen bond energies and confirmation energies) derived from three-dimensional (3D) structure models of peptide/MHC interactions are being used to train neural networks with early promising results160. Experimentally generated 3D structural data (e.g. crystal structures from X-ray refraction experiments) is limited in availability. Structure-based neoantigen prediction strategies may benefit from availability of broader experimental data or as in silico modelled 3D structures improve in accuracy for predicting MHC/ligand interactions.
Deep learning [G] models (Box 2) have led to critical breakthroughs in image analysis and speech recognition161 and are now being explored for immunogenicity prediction. Deep networks use multil-ayer architecture to adapt to complex relationships within the training dataset. They have the potential to uncover patterns in peptide sequences that are missed by other machine learning algorithms or are not reflected in current biological hypotheses.
Box 2. Machine learning and deep learning.
Machine learning refers to the use of algorithms for learning patterns in data. Machine learning tasks may be divided into supervised (predicting a label) and unsupervised learning (pattern recognition). Deep learning describes a class of machine learning algorithms that employ deep neuronal networks mainly for supervised classification tasks. However, both regression as well as unsupervised learning can be performed with deep learning tools as well. Artificial neural networks are inspired by biological neuronal networks. In general, their architecture comprises an input layer, hidden layer(s) and an output layer. The input layer receives the data as numerical values. The association with weights and nonlinear transformation abstracts the input data during propagation across the hidden layers. Neural networks that support deep learning have more than one hidden layer, and the number of hidden layers defines the deepness of the network. The output layer provides the predicted class label. Training of a network involves comparison of the predicted label with the true label to calculate the loss function [G] that is optimised by updating the weights on the hidden layers. While deep learning is regularly applied in areas such as image processing, it is still in its infancy in fields in which the amount of high quality labelled data for the respective subject matter is insufficient; interpretation of neuronal networks is also not straightforward. Deep learning and its applications in biomedicine has been extensively reviewed elsewhere166,273.
Such networks were published for MHC-I and MHC-II binding and ligand prediction162. The deep learning approaches EDGE and MARIA model the presentation of MHC-I or MHC-II epitopes, and use transcript abundance and flanking sequence as additional features163,164. Application of MARIA164 to perform retrospective analysis of a dataset obtained from a melanoma neoantigen vaccine study showed that enrichment for neoepitopes that induced high-magnitude CD4+ T-cell responses. EDGE163 was used for neoepitope prediction in melanoma, gastrointestinal cancer and breast cancer and enriched for neoepitopes that expanded pre-existing CD8+ T-cell responses (Table 4). DeepHLA combines the prediction of a MHC binding score and an immunogenicity score in one model165. Another approach subjects the amino acid sequence of the TCR to a deep artificial neural network to predict the binding of a given TCR to the peptide/MHC complex136.
Table 4. Examples for neoantigen prediction algorithms that are based on neural network and deep learning based.
| Name | Short Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| HLAathena | Neural network for prediction of MHC-I epitope presentation | 159 |
| Neomhc2 | Convolutional neural network for the prediction of MHC-II epitope presentation | 38 |
| EDGE | Deep learning model for prediction of MHC-I epitope presentation | 163,163 |
| MARIA | Multimodal recurrent neural network for predicting the likelihood of antigen presentation (MHC-II) | 164 |
| DeepHLA | Deep learning model combining binding and immunogenicity model (MHC-I) | 165 |
| Structure | Neural network on structural features that influence T-cell receptor (TCR) and peptide binding energies | 160 |
While deep learning algorithms show promising results to a certain extent, further maturation is required prior broad use. One obstacle is the lack of sufficiently large and standardised datasets with high quality T-cell response data and discrimination between datasets reflecting immunogenicity [G] versus antigenicity [G]. Another obstacle is that datasets have to be well curated and balanced, with comparable numbers of positive and negative training samples for the network to learn correct patterns166. Precise deconvolution of the allele-specific peptide/MHC binding patterns is critical for the use of pan-allelic data from mass spectroscopy experiments. Moreover, deep learning approaches often lack interpretability, making it difficult for the user to deduce critical biological features.
5. Challenges in Translation
5.1. Technological challenges
5.1.1. Biosamples as analytes
As heterogeneity is a hallmark of cancer, multiple biopsies of the same tumour lesion result in different molecular profiles78,80 and neoantigen candidates identified in one metastatic lesion of a patient differ from those in a second metastatic lesion or the primary tumour79.
The primary tumour, even if it is a historical and archived sample, may inform on clonal and truncal mutations and on the seed clones of disseminated metastatic lesions140. Metastatic lesions that are biopsied at a point of time close to the planned vaccination reflect the most recent status of the neoantigenome167. There is evidence that guarding neoantigens expressed in the primary tumour are lost from metastatic lesions50. Ignored neoantigens are not subject to selective pressure and likely to be more homogenously expressed and preserved across different lesions even in advanced disease, higher metastatic load and increasing immune suppressive mechanisms.
Many protocols are based on a single biopsy that may neither fully capture the heterogeneity of the probed individual tumour lesion, nor be representative in case of oligo- or multi-metastatic disease168. Thus, the resultant composite neoantigen vaccines may represent a minor proportion of the targets in a patient’s lesion, generating mixed responses at best.
Multi-region or even multi-lesion sequencing would require additional invasive procedures and is difficult to implement into clinical practice routines142,169. This dilemma is not new: standard-of-care treatments such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors or checkpoint inhibitors, for which a companion diagnostic approach determines eligibility, rely on single biopsies. This dilemma could be overcome by computational algorithms that untangle the tumour heterogeneity and infer higher order organisation of tumours based on single biopsies.
Collection and storage conditions of biosamples may affect sequencing data. Fresh frozen samples deliver the best data quality but require complex logistics. Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples are broadly available, but the fixation process is associated with sequencing artefacts170. Biopsies are more convenient for patients than surgical resectates but may yield insufficient amounts of analyte or even no tumour cells 171. As trivial as these hurdles may sound, they are relevant in practise172. A less invasive method such as liquid biopsy, which analyses circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) from the patients’ blood, may provide a more comprehensive representation of multi-site disease and is easier to collect. While conceptually attractive the allele frequency of mutations in plasma DNA samples is often low and current technologies are limited to the detection of a predetermined set of mutations173. Further technological breakthroughs are required to enable a highly sensitive, unbiased identification of cancer mutations by liquid biopsies.
5.1.2. Mutation calling
The mutation calling process [G] begins with cleaning of sequencing reads, followed by sequence alignment [G] to a reference genome. The subsequent mutation calling has to distinguish accurately somatic variants from sequencing errors, sample preparation artefacts and germline mutations. Many software tools exists to address critical limitations of mutation calling. Commonly used tools (Table 5) vary in their ability to detect different mutation classes such as SNVs or INDELs, to handle tumour heterogeneity while maintaining acceptable levels of accuracy, and to deliver within an acceptable runtime. No single perfect solution exists and often the approach is to base the called mutations on the consensus of different tools174. Detection of SNVs is most advanced in terms of sensitivity and specificity, whereas these performance metrics are less favourable for e.g. INDELs175,176 or fusion genes177.
Table 5. State-of-the-art tools for mutation calling.
| Software | Scope | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Mutect / Mutect 2 | Somatic SNVs + INDELs | 244/176 |
| Strelka / Strelka 2 | Somatic SNVs + INDELs | 245/175 |
| VarScan 2 | Somatic SNVs + INDELs. Germline variants. copy number variants | 152 |
| SomaticSniper | Somatic SNVs | 246 |
| RADIA | Somatic SNVs from DNA and matched RNA | 247 |
| FreeBayes | SNP calling | 248 |
| samtools / bcftools | Basic variant calling | 249 |
| Platypus | SNP calling | 250 |
| CaVEMan | Somatic SNVs | 251 |
| cgpPindel | Somatic INDELs | 252 |
| SvABA | Somatic INDELs | 253 |
| MuSE | Somatic SNVs | 254 |
| SMuFIN | Somatic SNVs + INDELs | 255 |
| GATK | All purpose toolkit. including germline genotyper | 256 |
| NeuSomatic | Deep Learning based somatic SNV detection | 257 |
Tumour samples display a high degree of heterogeneity, e.g. with regards to clonality, somatic copy numbers and sample contamination with healthy cells178–180. Data generated by sequencing represents the average across all sampled cells. Therefore, the signal-to-noise ratio for the actual computational variant detection process is compressed. Heterozygous somatic SNVs in genes with a duplicated WT allele in a sample with only 30% purity can be a typical use case. In this example, the expected number of reads with the mutant variant would been reduced more than ten-fold to less than 5%, making the sequence change difficult to distinguish from noise.
The challenges that are posed by the intra- and inter-tumour heterogeneity call for improved approaches of integrating multiple data sources and variant types, as well as a structured reproducible workflow for analysing multiple samples from a single patient.
5.1.3. Dataset availability and quality
Setting parameters for neoantigen prediction algorithms and training them relies on the availability of well-curated datasets. Data integration and comparability is compromised by the lack of harmonised protocols for sequencing, mutation detection, neoantigen candidate prioritisation and immunogenicity testing. Immunogenicity datasets are often unbalanced, as the most likely immunogenic candidates are preferred for testing and the rules guiding candidate selection differ between studies. For many such datasets clear and consistent biological definitions are either not provided or not acknowledged. For example, depending on the question to be answered, meta-analyses pooling datasets of patients treated with different ICBs (e.g. blocking PD-1, PD-L1, CTLA4 or PD-1/CTLA4 in combination) or of datasets derived from patients in the adjuvant versus metastatic advanced setting is not advisable.
Furthermore, various methods are used for assessing neoantigen-specific T-cell responses, including IFN-γ ELISpot assays with or without prior expansion of T cells in cell culture, intracellular cytokine staining and flow cytometry and peptide/MHC multimers (reviewed in181). The T-cell assays differ with regard to their sensitivity, accuracy and which T-cell phenotype they detect. Consequently, depending on the assay, pre-existing responses may be missed due to low sensitivity and guarding or restrained neoantigens may falsely be classified as ignored neoantigens. For instance, an immunogenicity dataset may represent CD8+ or CD4+ T-cell responses or both, may describe neoantigen-specific T cells that occur spontaneously, upon ICB therapy or vaccination, or may have been obtained with non-comparable assay methods. Efforts to compile sets of neoantigens identified in different studies are often compromised by missing essential technical and biological information that had not been documented182,183.
Long-term clinical outcome data differentiating efficacy endpoints such as objective response, progression-free survival, and overall survival from on-going clinical trials that study neoantigen vaccination, will be a valuable addition and could reflect anti-tumour efficacy of selected neoantigen candidates.
While there is some effort to achieve harmonised datasets, such as studies done by the TESLA (Tumour Neoantigen Selection Alliance) consortium126, the many variables involved and the polymorphic nature and inter- and intra-patient variability of key biological determiners (TCRs, MHCs) will likely require several thousands or more data points rather than the few hundreds that are available nowadays. Algorithms that allow the creation of accurate prediction models while trained on relatively few data points and application of advanced techniques such as active learning184 or transfer learning185 are required.
5.1.4. Vaccine design
Vaccine design has two components: (i) selection of the technology platform, and (ii) selection of the set of individual neoepitope candidates to be delivered by this platform.
The molecular nature of MHC-presented epitopes derived from mutations allows combination or concatenation of multiple short sequences representing neoepitope candidates. Published clinical studies used between 2 and 20 mutations per individual vaccine19,20,104. Many vaccine formats would allow administration of dozens of mutations per patient. Thus, a vaccine can be designed to feature different complementary categories of neoepitopes e.g. MHC-I and MHC-II, clonal and subclonal, ignored spiked with a few restrained and guarding neoantigens. This mitigates the risk of betting on a biological hypothesis which may later prove to be wrong.
Vaccine technologies are still at an experimental stage and various formats are being explored in clinical studies for individualised as well as off-the-shelf cancer vaccines (for review of cancer vaccine formats see186,187).
The most frequently used vaccine formats are mixtures of 15-30 aa long peptides corresponding to the mutated sequences with poly-ICLC as adjuvant19, and mRNA formulations with intrinsic adjuvant activity which encode a string of multiple predicted neoepitopes20.
Moreover, pre-clinical or clinical trials explore viral vectors188–191 or DNA192–194 in conjunction with various adjuvants. For each vaccine format, the need for adjuvant and the specific vaccination schedule (requirement and frequency of boosts after initial priming) need to be determined individually. It complicates learning exercises that the vaccine technology will affect substantially whether a neoepitope candidate is delivered in a way that its potential to induce an immune response is actualised.
The vaccine format impacts speed, scalability and costs of manufacturing that is probably the most critical element for the viable implementation of individualised vaccines into clinical practice. A vaccine technology that is synthetic and allows for fast production at low cost by an unsophisticated, robust, invariant, and GMP (good manufacturing practice)-compliant process is favourable.
Manufacturing individualised cancer vaccines requires a multitude of simultaneous, highly parallelised production campaigns, with each campaign representing a drug product for one individual. This is very different from the pure bulk-upscaling paradigm of manufacturing processes pursued in conventional pharmaceutical development. Suitable production technologies are required to be innovative, cost- and time-optimised and will benefit from. Emerging solutions for the mass production of customised products in the imminent future are potential enablers for individualised vaccine manufacturing. These may include full digitisation of production processes and autonomous cloud-controlled production plants that may arise based on advances in computational power, connectivity, human-machine interactions, robotics and innovative 3D technology enabling the building of parallelised miniaturised production lines at scale195,196.
5.2. Challenges for clinical application
This review focuses on the process of getting from a patient sample to an injectable vaccine composed of a unique set of neoepitope candidates. There are further critical challenges to get such a vaccine into clinical development and on a sustainable path suitable for potential registration and implementation into clinical practice (reviewed in16,197–199).
As for any drug, clinical efficacy and superiority over standard of care have to be shown in randomised trials. What is different, though, is that each patient in the investigational arm receives a drug of distinctive composition that is manufactured on-demand during the ongoing trial via a standardised process rather than being ready and released before the trial has started. This paradigm shift from a drug-centred to a patient-centred approach requires regulatory approval not of a single compound but rather the process from sample acquisition to vaccine design and production161,199,200 (Box 3).
Box 3. Principles of technical and analytical software validation.
The entire neoantigen prediction process relies heavily on software and computerised systems. For the application of such systems in clinical studies and later in a pharmaceutical product, the technical validation of the systems is a regulatory requirement. Validation is the continuous process of demonstrating that a computerised system is fit for the intended use and part of a quality assurance program. Good Automated Manufacturing Practice274 represents the industry standard for validation of automated systems, which includes any computer system, ranging from programmable calculators and embedded devices to super computers and any software running on those machines. GAMP reflects the requirements of the legislation called Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), as is codified e.g. in the United States 21 CFR 210/211 or the European Union GMP guidelines. The basic validation process follows traditional software engineering practices, including detailed documentation of the requirements at different abstraction levels (e.g. user, functional and configuration), followed by documented qualification and testing of system components and finally the whole system. A key difference to pure software engineering is the inclusion of detailed risk evaluations at every stage, focusing on potential safety issues for the patient. Novel software engineering and computational concepts like agile development or cloud computing have been introduced into the GAMP framework in the recent years.
For analytical validation of the performance, robustness and repeatability of the process, the NGS process poses a challenge. A typical exome-sequencing experiment involves analysis of about 50 million genomic nucleotides as data points and random erroneous mutation calls will occur to some extent. Quality controls include demonstration of reproducibility and whole exome coverage. Optimised lab protocol and robust mutation calling algorithms are required to account for data obtained from low quality clinical samples. Machine learning based neoantigen prediction methods rely on the amount and quality of training data, which continuously and swiftly is growing. Increasing the size and quality of training datasets may improve the performance of such software tools even if the underlying algorithms are not substantially changed. Quality improvements on the fly may translate into better and more efficacious vaccines. As long as iterative improvements of the neoantigen prediction and individual vaccine design are not associated with safety concerns it is desirable to enable quality improvements updates within an ongoing clinical trial, a clinical development program or even once a product is approved. To this aim, a regulatory path must be defined, which allows the necessary degree of flexibility for process improvements while maintaining the safety properties of the product itself.
One pertinent question is the most suitable clinical setting. Targeting patients with minimal residual disease has the advantage that immune-suppressive mechanisms are not firmly established and that turnaround time of a vaccine production is not a limiting factor. Efficient control of larger tumour loads, in contrast, may require combination immunotherapies. Neoepitope vaccines are safe and well tolerated. Thus, combining them with other drugs carries low risk of added toxicities while leveraging synergistic modes of action. The combination of neoepitope vaccines with checkpoint inhibition keeps the repertoire of vaccine-induced T-cell specificities functional.
The most likely escape mechanisms from a strong multi-antigen T-cell response involve loss of the target antigen or of components of the antigen-presentation machinery. This can be addressed by combining the vaccine with approaches that do not depend on HLA-presented antigens, e.g. chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered T cells, antibodies or bispecific T-cell engagers.
6. Outlook
Boosted by technologies such as NGS, increased computing power and advanced algorithms the field of neoantigen identification has evolved enormously in the past decade. In parallel to the continuous progress and efforts invested in improving neoantigen prediction tools, clinical trials explore neoantigens as single or combinatorial targets for immunotherapy and generate data that contribute to an ever-clearer knowledge of the underlying science. ClinicalTrials.gov currently lists 61 clinical studies associated with the search terms “neoantigen AND vaccine”201. Reports from individualised neoantigen vaccination studies indicate early clinical activity signals of vaccines alone and in combination with PD(L)-1 blockade19,20,104,106.
Further progress in NGS technologies202 and mass spectrometry-based MHC ligandome analysis121,203 will support the neoantigen field with higher resolution and lower noise. Technology advances will tap new neoantigen classes, for instance derived from non-coding and ‘dark matter’ regions of the genome and from non-canonical translation204,205.
While the understanding of anchor and TCR-facing residues within T-cell epitopes is evolving206,207, the potential of connecting neoantigen and TCR profiling datasets is not yet fully actualised. New prediction tools and studies incorporate TCR sequences and model the interaction of mutated peptide/MHC complexes with TCRs e.g. 136,137,208,209. Structural analyses of the interaction between TCRs and their cognate neoepitopes will provide deeper insights into the structure-dependent mechanisms of mutation-specific T-cell recognition that cannot be inferred from the sequence alone210. The underlying complexity needs to be tamed with new artificial intelligence-based applications and by substantially increasing computing power. Standardised datasets generated by using well-thought through experimental designs and accurate and sensitive computational workflows and featuring biological and clinical information will shape a robust foundation for closing existent knowledge gaps. Approaches towards true translational medicine such as the proposed context-based differentiation between guarding, restrained and ignored neoantigens will contribute to a framework that connects neoantigen science to clinical settings and medical features and peculiarities of cancer diseases enabling future neoantigen-dependent therapies to provide greater clinical benefit.
Finally, once the technology to pinpoint the relevant neoantigens for an individualised vaccine design at a given time point is optimised and paired with concepts to use sequencing data for early recognition of acquired resistance mechanisms of an individual tumour, adaptation of an individual’s vaccine boosters to the dynamics of their disease over time is conceivable.
Supplementary Material
Glossary.
- Adoptive T-cell therapy
Immunotherapy in which T cells are taken from the patient’s tumour tissue or blood, expanded in vitro and then transferred back to the patient to support the immune system’s natural fight against the cancer.
- Alignment of NGS reads
Mapping sequencing reads to a reference genome to determine the genomic loci of origin.
- Anchor residue
Position in a MHC epitope with specific amino acid preference.
- Anergy
A hyporesponsive state in which an antigen experienced T cell is functionally impaired and does not adequately respond to cognate antigen exposure.
- Antigen spreading
Expansion of an immune response to secondary epitopes, or other antigens that were not targeted by immunotherapy.
- Antigenicity
Immune responses induced by vaccination as in the case of ignored neoepitopes.
- Artificial neural network
Computing system which is inspired by biological neural networks and that applies tasks based on learned patterns.
- BLAST
A tool to find local regions of similarity between biological sequences. It enables to compare a sequence of interest to a database of sequences and identify the sequences with highest local similarities.
- Branched mutation
A mutation that occurs later during tumour evolution and is only present in a subset of tumour cells.
- Cancer mutanome
Set of all non-synonymous somatic mutations occurring in a tumour.
- Central tolerance
Thymic elimination of self-reactive T cells
- Clonality
The fraction of tumour subclones that harbour a given mutation
- Clonal mutation
A mutation that is present in all subclones of a tumour. In practise, the definition of clonal vs sublconal mutation is not standardised and depends on the experimental setting and bioinformatics tools as these provide a numeric estimation of clonality (e.g. PyClone138).
- Mutation calling process
Mutation calling strategy in which the overlap (consensus) from at least two different mutation callers is used to define the final set of mutational events.
- Co-stimulatory signal
Secondary signal required to activate immune responses in the presence of antigen-presenting cells.
- de novo immune response
Vaccine induced antigen-specific T cell response that was not detectable prior vaccination. Used as opposed to the augmentation of a pre-existing T cell response.
- Deep learning
Machine-learning methods using multi-layer models for feature extraction and pattern learning.
- Driver mutation
A mutation that improves fitness of a tumour cell.
- Differential agretopicity index (DAI)
Difference in MHC-I binding affinity between neoepitope and corresponding non-mutated peptide.
- Guarding neoantigen
A neoantigen that drives a prognostically relevant tumour immunity in the absence of an immunotherapy
- Heterologous immunity
Cross-reactive T cell immunity induced by an unrelated antigen, often pre-existent before tumour onset.
- Ignored neoantigen
A neoantigen lacks intrinsic antigenicity but could serve as target for immunotherapy
- Immune surveillance
A hypothesis that assumes that immune cells monitor, identify and eliminate pre-malignant or malignant cells in the body.
- Immune escape
Mechanisms of tumour evolution allowing tumour cells to escape from a host’s immune response.
- Immunoediting
A hypothesis that describes the close interaction between tumour and immune system and transition between immune protection against tumour development and tumour outgrowth in three phases: elimination, equilibrium, and escape.
- Immunogenicity
Induction of immune responses without vaccination as in the case of guarding and restrained neoepitopes.
- Loss function
A function that calculates how well or poorly an algorithm models the given data by comparing the predicted values to the actual values.
- Loss of heterozygosity
A locus with two different alleles loses one of these two copies.
- MHC/HLA
Cell surface proteins that present peptide fragments for recognition by T-cells. MHC is the general term; HLA is used in the human context only.
- MHC-I
The MHC-I molecule is a protein complex formed by beta-2 microglobulin and an alpha chained encoded in the HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C locus in human. MHC-I is expressed on the cell surface of all nucleated cells and presents intracellularly synthesised peptides to CD8+ T-cells. Antigen presentation has been reviewed in211,212.
- MHC-II
The MHC-II molecule is a protein complex formed by an alpha and a beta chain that are encoded in the HLA-DR, HLA-DP and HLA-DQ locus in human. MHC-II is mainly expressed on the cell of specialised antigen presenting cells and presents mainly extracellular peptides to CD4+ T-cells. Antigen presentation has been reviewed in211,212.
- Neoantigen feature
A feature or algorithm that can be used to rank neoantigen candidates.
- Neoantigen prediction pipeline
Computational tool for neoantigen prediction, starting with mutation calling or a set of called mutation and covering the translation into mutated peptide sequences and ranking of neoantigen candidates by a neoantigen feature.
- Neoepitope
A major histocompatibility complex (MHC) bound peptide that arises from a tumour-specific mutation.
- Non-synonymous mutation
A mutation that causes changes in the amino acid sequence of a protein.
- Peripheral tolerance
Elimination or suppression of autoreactive T-cells or B-cell clones that escaped to the periphery.
- Prognostic
Statement about the expected development of a disease based on its biology irrespective of a given treatment
- Predictive
Statement about the expected response to therapy
- Pseudoalignment
A pseudoalignment identifies the transcripts a RNA-seq read is most likely related to but does not specify how each nucleotide matches the reference like in a normal alignment.
- Restrained neoantigen
A neoantigen that drives tumour immunity upon immune checkpoint inhibition
- ROC curve
A graphical plot that reflects the quality of a classifier by showing the true positive versus false positive rate across varying thresholds.
- Spontaneous tumour immunity
T cell responses induced spontaneously in the course of tumour growth
- TCR degeneracy
The ability of a single TCR to recognise diverse peptide/MHC complexes.
- TCR diversity
The ability of a single peptide/MHC complex to engage antigen-specific T cells with diverse TCR alpha / beta chains
- TAP protein complex
Protein complex of TAP-1 (Transporter associated with antigen processing 1) and TAP-2 that imports peptides from the cytosol in to the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Truncal mutation
A mutation that occurs early during tumour evolution.
- Vaccine mediated immunity
T cell responses amplified or de novo induced by delivery and active exposure of the host to neoantigens.
- Variant allele frequency
The fraction of sequence reads observed covering a mutation divided by the overall number of reads at that locus.
Table 1.
Shared neoantigens. Most frequent tumour type and mutation frequency in the respective tumour entity has been estimated using SNV data from TCGA. Index tumours are those, which are most frequently affected. MUT: mutation, RE: restriction element. MHC allele frequencies were derived from the NCBI dbMHC database213.
| Gene(s) | Mutation (MUT) | Reference | Restriction element (RE) c% of RE in European/North American population, Population with next highest % of RE and its % of RE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNVs | |||
| KRAS | G12V | 42 | HLA-A*11:01 (4.2%, Oceania: 20.7%) |
| KRAS | G12D | 42,108,146 | HLA-A*02:01 (22.3%, South America: 22.1%), HLA-C*08:02 (-), HLA-DRB1*08:01 (1.2%, North Africa: 1.4%) |
| IDH1 | R132H | 52 | HLA-DRB1*01:01 (4.3%, North-East Asia: 5.7%) |
| TP53 | R175H | 17,43 | HLA-A*02:01 (22.3%, South America: 22.1%), HLA-DRB1*13:01 (2.37%, South India: 13.8%) |
| H3.3 | K27M | 214,215 | HLA-A*02:01 (22.3%, South America: 22.1%), HLA-DR1 (-) |
| JAK2 | V617F | 216 | HLA-A2 (-) |
| PIK3A | H1047L | 217 | HLA-A*03:01 (8.6%, South India: 8.0%) |
| BRAF | V600E | 218 | HLA-DQB1*03 |
| CDK4 | R24C | 1 | HLA-A2.1 (22.3%, South America: 22.1%) |
| CDK12 | E928K | 11 | HLA-A*11:01 (4.2%, Oceania: 20.72%) |
| NRAS | Q61R | 219 | HLA-A*01:01 (10.0%, North Africa: 12.59%) |
| CTNNB1 | F37S | 220 | HLA-A24+ (-) |
| INDELs | |||
| GAS7 | H225Y | 11 | HLA-A*02:01 (22.3%. South America: 22.1%) |
| NPM | 4 bp hotspot insertion in exon 12 | 221 | HLA-A*02:01 (22.3%. South America: 22.1%) |
| CALR | INDELs in exon 9 | 98 | Mixed |
| TGFβRII | 1bp deletion in poly(A)10 tract (nucleotides 709-718) | 222,223 | HLA-A2+ (-), HLA-DPB1*03:01 (8.1%, Central America: 10.0%), HLA-DRB1*14:01 (23%, SouthEast Asia 13.4%) |
| Fusion Genes | |||
| BCR-ABL | fusion protein b3a2 | 224–227 | HLA-A3+ (-),HLA-DR+ (-) |
| dek-can | t(6;9) | 226 | HLA-DR53+ (-) |
| SYT-SSX | t(X; 18)(p11;q11) | 228,229 | HLA-A24+ (-) |
| pml/RAR alpha | - | 230 | HLA-DR11+ (-) |
| PAX-FKHR | t(2;13) | 231 | HLA-B7+ (-) |
| ETV6-AML1 | t(12;21) | 232,233 | Mixed (-) |
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by a European Research Council Advanced Grant to U.S. (ERC-AdG 789256). The authors thank K. Chu for proofreading of the manuscript and helpful comments. They further thank the ERC, the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) for supporting their research in this field.
Footnotes
Competing Interest
F.L. has nothing to disclose. B.S., M.L., Ö.T. and U.S. are inventors on patents related to some of the technologies described in this article. Ö.T. is shareholder and CMO at BioNTech SE. U.S. is co-founder, shareholder and CEO at BioNTech SE.
References
- 1.Wolfel T, et al. A p16INK4a-insensitive CDK4 mutant targeted by cytolytic T lymphocytes in a human melanoma. Science. 1995;269:1281. doi: 10.1126/science.7652577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chiari R, et al. Two antigens recognized by autologous cytolytic T lymphocytes on a melanoma result from a single point mutation in an essential housekeeping gene. Cancer Research. 1999;59:5785–5792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pieper R, et al. Biochemical identification of a mutated human melanoma antigen recognized by CD4(+) T cells. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 1999;189:757–766. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.5.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kubuschok B, et al. Naturally occurring T-cell response against mutated p21 ras oncoprotein in pancreatic cancer. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2006;12:1365–1372. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.van Rooij N, et al. Tumor exome analysis reveals neoantigen-specific T-cell reactivity in an ipilimumab-responsive melanoma. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2013;31:e439–42. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.47.7521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gubin MM, et al. Checkpoint blockade cancer immunotherapy targets tumour-specific mutant antigens. Nature. 2014;515:577. doi: 10.1038/nature13988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Snyder A, et al. Genetic Basis for Clinical Response to CTLA-4 Blockade in Melanoma. New England Journal of Medicine. 2014;371:2189–2199. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1406498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rizvi NA, et al. Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science. 2015;348:124. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hugo W, et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Features of Response to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Metastatic Melanoma. Cell. 2016;165:35–44. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Riaz N, et al. Tumor and Microenvironment Evolution during Immunotherapy with Nivolumab. Cell. 2017;171:934–949.:e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Robbins PF, et al. Mining exomic sequencing data to identify mutated antigens recognized by adoptively transferred tumor-reactive T cells. Nature Medicine. 2013;19:747–752. doi: 10.1038/nm.3161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Prickett TD, et al. Durable Complete Response from Metastatic Melanoma after Transfer of Autologous T Cells Recognizing 10 Mutated Tumor Antigens. Cancer Immunology Research. 2016;4:669–678. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Samstein RM, et al. Tumor mutational load predicts survival after immunotherapy across multiple cancer types. Nature Genetics. 2019;51:202–206. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0312-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tran E, et al. Immunogenicity of somatic mutations in human gastrointestinal cancers. Science. 2015;350:1387. doi: 10.1126/science.aad1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Parkhurst MR, et al. Unique neoantigens arise from somatic mutations in patients with gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Discovery. 2019:CD-18-1494. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Türeci Ö, et al. Targeting the Heterogeneity of Cancer with Individualized Neoepitope Vaccines. Clinical Cancer Research. 2016;22:1885. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lo W, et al. Immunologic Recognition of a Shared p53 Mutated Neoantigen in a Patient with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Immunology Research. 2019;7:534. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tran E, et al. Cancer Immunotherapy Based on Mutation-Specific CD4+ T Cells in a Patient with Epithelial Cancer. Science. 2014;344:641. doi: 10.1126/science.1251102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ott PA, et al. An immunogenic personal neoantigen vaccine for patients with melanoma. Nature. 2017;547:217. doi: 10.1038/nature22991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sahin U, et al. Personalized RNA mutanome vaccines mobilize poly-specific therapeutic immunity against cancer. Nature. 2017;547:222. doi: 10.1038/nature23003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Brady MS, Eckels DD, Ree SY, Schultheiss KE, Lee JS. MHC class II-mediated antigen presentation by melanoma cells. Journal of immunotherapy with emphasis on tumor immunology : official journal of the Society for Biological Therapy. 1996;19:387–397. doi: 10.1097/00002371-199611000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Arnold PY, et al. The majority of immunogenic epitopes generate CD4+ T cells that are dependent on MHC class Il-bound peptide-flanking residues. The Journal of Immunology. 2002;169:739. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.2.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kreiter S, et al. Mutant MHC class II epitopes drive therapeutic immune responses to cancer. Nature. 2015;520:692–696. doi: 10.1038/nature14426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sixt M, et al. The conduit system transports soluble antigens from the afferent lymph to resident dendritic cells in the T cell area of the lymph node. Immunity. 2005;22:19–29. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2004.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hirosue S, Dubrot J. Modes of Antigen Presentation by Lymph Node Stromal Cells and Their Immunological Implications. Frontiers in Immunology. 2015;6:446. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Saeki H, Moore AM, Brown MJ, Hwang ST. Cutting edge. Secondary lymphoid-tissue chemokine (SLC) and CC chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7) participate in the emigration pathway of mature dendritic cells from the skin to regional lymph nodes. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 1999;162:2472–2475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Flament H, et al. Modeling the specific CD4+ T cell response against a tumor neoantigen. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md: 1950) 2015;194:3501–3512. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Spiotto MT, et al. Increasing tumor antigen expression overcomes “ignorance” to solid tumors via crosspresentation by bone marrow-derived stromal cells. Immunity. 2002;17:737–747. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(02)00480-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Albert ML, Sauter B, Bhardwaj N. Dendritic cells acquire antigen from apoptotic cells and induce class I-restricted CTLs. Nature. 1998;392:86–89. doi: 10.1038/32183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bode K, et al. Dectin-1 Binding to Annexins on Apoptotic Cells Induces Peripheral Immune Tolerance via NADPH Oxidase-2. Cell Reports. 2019;29:4435–4446.:e9. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rocha B, von Boehmer H. Peripheral selection of the T cell repertoire. Science. 1991;251:1225. doi: 10.1126/science.1900951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chen W, et al. Conversion of peripheral CD4+CD25-naive T cells to CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells by TGF-beta induction of transcription factor Foxp3. JEM. 2003;198:1875–1886. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ramsdell F, Lantz T, Fowlkes BJ. A nondeletional mechanism of thymic self tolerance. Science. 1989;246:1038. doi: 10.1126/science.2511629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rocha B, Grandien A, Freitas AA. Anergy and exhaustion are independent mechanisms of peripheral T cell tolerance. JEM. 1995;181:993–1003. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.3.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Blank CU, et al. Defining ‘T cell exhaustion’. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19:665–674. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0221-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Obst R. The Timing of T Cell Priming and Cycling. Frontiers in Immunology. 2015;6:563. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Abelin JG, et al. Mass Spectrometry Profiling of HLA-Associated Peptidomes in Mono-allelic Cells Enables More Accurate Epitope Prediction. Immunity. 2017;46:315–326. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.02.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Abelin JG, et al. Defining HLA-II Ligand Processing and Binding Rules with Mass Spectrometry Enhances Cancer Epitope Prediction. Immunity. 2019;51:766–779.:e17. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hennecke J, Wiley DC. T cell receptor-MHC interactions up close. Cell. 2001;104:1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Szeto C, Lobos CA, Nguyen AT, Gras S. TCR Recognition of Peptide-MHC-I. Rule Makers and Breakers. International journal of molecular sciences. 2020;22 doi: 10.3390/ijms22010068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bobisse S, et al. Sensitive and frequent identification of high avidity neo-epitope specific CD8+T cells in immunotherapy-naive ovarian cancer. Nature Communications. 2018;9:1092. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03301-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Cafri G, et al. Memory T cells targeting oncogenic mutations detected in peripheral blood of epithelial cancer patients. Nature Communications. 2019;10:449. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08304-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Malekzadeh P, et al. Antigen Experienced T Cells from Peripheral Blood Recognize p53 Neoantigens. Clinical Cancer Research. 2020 doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hu Z, et al. Personal neoantigen vaccines induce persistent memory T cell responses and epitope spreading in patients with melanoma. Nat Med. 2021 doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-01206-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nelson RW, et al. T cell receptor cross-reactivity between similar foreign and self peptides influences naive cell population size and autoimmunity. Immunity. 2015;42:95–107. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.12.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wooldridge L, et al. A single autoimmune T cell receptor recognizes more than a million different peptides. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2012;287:1168–1177. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.289488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Birnbaum ME, et al. Deconstructing the peptide-MHC specificity of T cell recognition. Cell. 2014;157:1073–1087. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Cameron BJ, et al. Identification of a Titin-derived HLA-A1-presented peptide as a cross-reactive target for engineered MAGE A3-directed T cells. Science Translational Medicine. 2013;5:197ra103. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Leng Q, Tarbe M, Long Q, Wang F. Pre-existing heterologous T-cell immunity and neoantigen immunogenicity. Clinical & translational immunology. 2020;9:e01111. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Balachandran VP, et al. Identification of unique neoantigen qualities in long-term survivors of pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2017;551:512. doi: 10.1038/nature24462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Chen DS, Mellman I. Oncology Meets Immunology. The Cancer-Immunity Cycle. Immunity. 2013;39:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Schumacher T, et al. A vaccine targeting mutant IDH1 induces antitumour immunity. Nature. 2014;512:324–327. doi: 10.1038/nature13387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Alspach E, et al. MHC-II neoantigens shape tumour immunity and response to immunotherapy. Nature. 2019;574:696–701. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1671-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Greenman C, et al. Patterns of somatic mutation in human cancer genomes. Nature. 2007;446:153–158. doi: 10.1038/nature05610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Antony PA, et al. CD8+ T cell immunity against a tumor/self-antigen is augmented by CD4+ T helper cells and hindered by naturally occurring T regulatory cells. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 2005;174:2591–2601. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.5.2591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Xie Y, et al. Naive tumor-specific CD4(+) T cells differentiated in vivo eradicate established melanoma. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2010;207:651–667. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Quezada SA, et al. Tumor-reactive CD4(+) T cells develop cytotoxic activity and eradicate large established melanoma after transfer into lymphopenic hosts. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2010;207:637–650. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Oh DY, et al. Intratumoral CD4+ T Cells Mediate Anti-tumor Cytotoxicity in Human Bladder Cancer. Cell. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Robbins PF, et al. Multiple HLA Class II-Restricted Melanocyte Differentiation Antigens Are Recognized by Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes from a Patient with Melanoma. The Journal of Immunology. 2002;169:6036. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.10.6036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lehmann PV, Forsthuber T, Miller A, Sercarz EE. Spreading of T-cell autoimmunity to cryptic determinants of an autoantigen. Nature. 1992;358:155–157. doi: 10.1038/358155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Lo JA, et al. Epitope spreading toward wild-type melanocyte-lineage antigens rescues suboptimal immune checkpoint blockade responses. Science Translational Medicine. 2021;13:eabd8636. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abd8636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Sahin U, Türeci Ö. Personalized vaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Science. 2018;359:1355. doi: 10.1126/science.aar7112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Chen DS, Mellman I. Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer−immune set point. Nature. 2017;541:321–330. doi: 10.1038/nature21349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ahmadzadeh M, et al. Tumor-infiltrating human CD4+ regulatory T cells display a distinct TCR repertoire and exhibit tumor and neoantigen reactivity. Science Immunology. 2019;4 doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aao4310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Golding A, Darko S, Wylie WH, Douek DC, Shevach EM. Deep sequencing of the TCR-β repertoire of human forkhead box protein 3 (FoxP3)+ and FoxP3-T cells suggests that they are completely distinct and non-overlapping. Clinical and experimental immunology. 2017;188:12–21. doi: 10.1111/cei.12904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Sotomayor EM, et al. Cross-presentation of tumor antigens by bone marrow-derived antigen-presenting cells is the dominant mechanism in the induction of T-cell tolerance during B-cell lymphoma progression. blood. 2001;98:1070–1077. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.4.1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Pontes-de-Carvalho L, Mengel J, Figueiredo CA, Alcântara-Neves NM. Antigen Mimicry between Infectious Agents and Self or Environmental Antigens May Lead to Long-Term Regulation of Inflammation. Frontiers in Immunology. 2013;4:314. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Taube JM, et al. Colocalization of Inflammatory Response with B7-H1 Expression in Human Melanocytic Lesions Supports an Adaptive Resistance Mechanism of Immune Escape. Science Translational Medicine. 2012;4:127ra37. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Beck C, Schreiber H, Rowley DA. Role of TGF-β in immune-evasion of cancer. Microsc Res Tech. 2001;52:387–395. doi: 10.1002/1097-0029(20010215)52:4<387::AID-JEMT1023>3.0.CO;2-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Efremova M, et al. Targeting immune checkpoints potentiates immunoediting and changes the dynamics of tumor evolution. Nature Communications. 2018;9:32. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02424-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Rooney MS, Shukla SA, Wu CJ, Getz G, Hacohen N. Molecular and Genetic Properties of Tumors Associated with Local Immune Cytolytic Activity. Cell. 2015;160:48–61. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.12.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Rosenthal R, et al. Neoantigen-directed immune escape in lung cancer evolution. Nature. 2019;567:479–485. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1032-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Zapata L, et al. Negative selection in tumor genome evolution acts on essential cellular functions and the immunopeptidome. Genome biology. 2018;19:67. doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1434-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.van den Eynden J, Jiménez-Sánchez A, Miller ML, Larsson E. Lack of detectable neoantigen depletion signals in the untreated cancer genome. Nature Genetics. 2019;51:1741–1748. doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0532-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Campoli M, Ferrone S. HLA antigen changes in malignant cells. Epigenetic mechanisms and biologic significance. Oncogene. 2008;27:5869–5885. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Johnsen AK, Templeton DJ, Sy M-S, Harding CV. Deficiency of Transporter for Antigen Presentation (TAP) in Tumor Cells Allows Evasion of Immune Surveillance and Increases Tumorigenesis. The Journal of Immunology. 1999;163:4224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Sade-Feldman M, et al. Resistance to checkpoint blockade therapy through inactivation of antigen presentation. Nature Communications. 2017;8:1136. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01062-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Brastianos PK, et al. Genomic Characterization of Brain Metastases Reveals Branched Evolution and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Cancer Discovery. 2015;5:1164. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Jiménez-Sánchez A, et al. Heterogeneous Tumor-Immune Microenvironments among Differentially Growing Metastases in an Ovarian Cancer Patient. Cell. 2017;170:927–938.:e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Angelova M, et al. Evolution of Metastases in Space and Time under Immune Selection. Cell. 2018;175:751–765.:e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Kvistborg P, et al. Anti-CTLA-4 therapy broadens the melanoma-reactive CD8+ T cell response. Science Translational Medicine. 2014;6:254ra128. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3008918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Novellino L, et al. Identification of a Mutated Receptor-Like Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase K as a Novel, Class II HLA-Restricted Melanoma Antigen. The Journal of Immunology. 2003;170:6363. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.12.6363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Matsushita H, et al. Cancer exome analysis reveals a T-cell-dependent mechanism of cancer immunoediting. Nature. 2012;482:400–404. doi: 10.1038/nature10755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.De Plaen E, et al. Immunogenic (tum-) variants of mouse tumor P815. Cloning of the gene of tum-antigen P91A and identification of the tum-mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988;85:2274–2278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Dubey P, et al. The Immunodominant Antigen of an Ultraviolet-induced Regressor Tumor Is Generated by a Somatic Point Mutation in the DEAD Box Helicase p68. JEM. 1997;185:695–706. doi: 10.1084/jem.185.4.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Samowitz WS, et al. Microsatellite instability in sporadic colon cancer is associated with an improved prognosis at the population level. Cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention : a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive Oncology. 2001;10:917–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Bessell CA, et al. Commensal bacteria stimulate antitumor responses via T cell cross-reactivity. JCI Insight. 2020;5 doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.135597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Pihlgren M, Dubois PM, Tomkowiak M, Sjögren T, Marvel J. Resting memory CD8+ T cells are hyperreactive to antigenic challenge in vitro. JEM. 1996;184:2141–2151. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.6.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ghorani E, et al. Differential binding affinity of mutated peptides for MHC class I is a predictor of survival in advanced lung cancer and melanoma. annonc. 2017;29:271–279. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.McGranahan N, et al. Clonal neoantigens elicit T cell immunoreactivity and sensitivity to immune checkpoint blockade. Science. 2016;351:1463. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Lu T, et al. Tumor neoantigenicity assessment with CSiN score incorporates clonality and immunogenicity to predict immunotherapy outcomes. Science Immunology. 2020;5:eaaz3199. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aaz3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Łuksza M, et al. A neoantigen fitness model predicts tumour response to checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Nature. 2017;551:517. doi: 10.1038/nature24473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Miao D, et al. Genomic correlates of response to immune checkpoint blockade in microsatellite-stable solid tumors. Nature Genetics. 2018;50:1271–1281. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0200-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Goodman AM, et al. MHC-I genotype and tumor mutational burden predict response to immunotherapy. Genome Medicine. 2020;12:45. doi: 10.1186/s13073-020-00743-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Subudhi SK, et al. Neoantigen responses, immune correlates, and favorable outcomes after ipilimumab treatment of patients with prostate cancer. Science Translational Medicine. 2020;12:eaaz3577. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaz3577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Turajlic S, et al. Insertion-and-deletion-derived tumour-specific neoantigens and the immunogenic phenotype. A pan-cancer analysis. The Lancet Oncology. 2017;18:1009–1021. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30516-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Le DT, et al. Mismatch repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumors to PD-1 blockade. Science. 2017;357:409. doi: 10.1126/science.aan6733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Cimen Bozkus C, et al. Immune Checkpoint Blockade Enhances Shared Neoantigen-Induced T-cell Immunity Directed against Mutated Calreticulin in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Cancer Discovery. 2019;9:1192. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Yang W, et al. Immunogenic neoantigens derived from gene fusions stimulate T cell responses. Nature Medicine. 2019;25:767–775. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0434-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Boyman O, Kovar M, Rubinstein MP, Surh CD, Sprent J. Selective Stimulation of T Cell Subsets with Antibody-Cytokine Immune Complexes. Science. 2006;311:1924. doi: 10.1126/science.1122927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Linnemann C, et al. High-throughput epitope discovery reveals frequent recognition of neoantigens by CD4+ T cells in human melanoma. Nat Med. 2015;21:81–85. doi: 10.1038/nm.3773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Castle JC, et al. Exploiting the Mutanome for Tumor Vaccination. Cancer Research. 2012;72:1081. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Carreno BM, et al. A dendritic cell vaccine increases the breadth and diversity of melanoma neoantigen-specific T cells. Science. 2015;348:803. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa3828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Hilf N, et al. Actively personalized vaccination trial for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Nature. 2019;565:240–245. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0810-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Fang Y, et al. A Pan-cancer Clinical Study of Personalized Neoantigen Vaccine Monotherapy in Treating Patients with Various Types of Advanced Solid Tumors. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2020;26:4511–4520. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Keskin DB, et al. Neoantigen vaccine generates intratumoral T cell responses in phase Ib glioblastoma trial. Nature. 2019;565:234–239. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0792-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Ott PA, et al. A Phase Ib Trial of Personalized Neoantigen Therapy Plus Anti-PD-1 in Patients with Advanced Melanoma, Non-small Cell Lung Cancer, or Bladder Cancer. Cell. 2020;183:347–362.:e24. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Chen F, et al. Neoantigen identification strategies enable personalized immunotherapy in refractory solid tumors. J Clin Invest. 2019;129:2056–2070. doi: 10.1172/JCI99538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Blass E, Ott PA. Advances in the development of personalized neoantigen-based therapeutic cancer vaccines. Nature reviews Clinical oncology. 2021;18:215–229. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-00460-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Supabphol S, Li L, Goedegebuure SP, Gillanders WE. Neoantigen vaccine platforms in clinical development. Understanding the future of personalized immunotherapy. Expert opinion on investigational drugs. 2021:1–13. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2021.1896702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Lee KL, et al. Efficient Tumor Clearance and Diversified Immunity through Neoepitope Vaccines and Combinatorial Immunotherapy. Cancer Immunology Research. 2019 doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Bassani-Sternberg M, Pletscher-Frankild S, Jensen LJ, Mann M. Mass Spectrometry of Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I Peptidomes Reveals Strong Effects of Protein Abundance and Turnover on Antigen Presentation. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 2015;14:658. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.042812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Anagnostou V, et al. Evolution of Neoantigen Landscape during Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Discovery. 2017;7:264. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Bray NL, Pimentel H, Melsted P, Pachter L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nature Biotechnology. 2016;34:525–527. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Schoenberger SP, Toes RE, van der Voort EI, Offringa R, Melief CJ. T-cell help for cytotoxic T lymphocytes is mediated by CD40-CD40L interactions. Nature. 1998;393:480–483. doi: 10.1038/31002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Zhao W, Sher X. Systematically benchmarking peptide-MHC binding predictors. From synthetic to naturally processed epitopes. PLOS Computational Biology. 2018;14:e1006457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Paul S, et al. Benchmarking predictions of MHC class I restricted T cell epitopes in a comprehensively studied model system. PLOS Computational Biology. 2020;16:e1007757. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Jurtz V, et al. NetMHCpan-4.0. Improved Peptide−MHC Class I Interaction Predictions Integrating Eluted Ligand and Peptide Binding Affinity Data. The Journal of Immunology. 2017;199:3360. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.O’Donnell TJ, et al. MHCflurry. Open-Source Class I MHC Binding Affinity Prediction. Cell Systems. 2018;7:129–132.:e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2018.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Bassani-Sternberg M, et al. Deciphering HLA-I motifs across HLA peptidomes improves neoantigen predictions and identifies allostery regulating HLA specificity. PLOS Computational Biology. 2017;13:e1005725. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Gfeller D, Bassani-Sternberg M. Predicting Antigen Presentation-What Could We Learn From a Million Peptides? Frontiers in Immunology. 2018;9:1716. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Mei S, et al. A comprehensive review and performance evaluation of bioinformatics tools for HLA class I peptide-binding prediction. Brief Bioinform. 2020;21:1119–1135. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Nielsen M, et al. NetMHCpan, a method for quantitative predictions of peptide binding to any HLA-A and -B locus protein of known sequence. PLOS ONE. 2007;2:e796. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Blaha DT, et al. High-Throughput Stability Screening of Neoantigen/HLA Complexes Improves Immunogenicity Predictions. Cancer Immunology Research. 2019;7:50–61. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Rasmussen M, et al. Pan-Specific Prediction of Peptide-MHC Class I Complex Stability, a Correlate of T Cell Immunogenicity. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md: 1950) 2016;197:1517–1524. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Wells DK, et al. Key Parameters of Tumor Epitope Immunogenicity Revealed Through a Consortium Approach Improve Neoantigen Prediction. Cell. 2020;183:818–834.:e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Chowell D, et al. Patient HLA class I genotype influences cancer response to checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Science. 2018;359:582. doi: 10.1126/science.aao4572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Marty R, et al. MHC-I Genotype Restricts the Oncogenic Mutational Landscape. Cell. 2017;171:1272–1283.:e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Marty Pyke R, et al. Evolutionary Pressure against MHC Class II Binding Cancer Mutations. Cell. 2018;175:416–428.:e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.08.048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Keçmir C, Nussbaum AK, Schild H, Detours V, Brunak S. Prediction of proteasome cleavage motifs by neural networks. Protein engineering. 2002;15:287–296. doi: 10.1093/protein/15.4.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Stranzl T, Larsen MV, Lundegaard C, Nielsen M. NetCTLpan. Pan-specific MHC class I pathway epitope predictions. Immunogenetics. 2010;62:357–368. doi: 10.1007/s00251-010-0441-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Bjerregaard A-M, et al. An Analysis of Natural T Cell Responses to Predicted Tumor Neoepitopes. Frontiers in Immunology. 2017;8:1566. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Richman LP, Vonderheide RH, Rech AJ. Neoantigen Dissimilarity to the Self-Proteome Predicts Immunogenicity and Response to Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Cell Systems. 2019;9:375–382.:e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2019.08.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Trolle T, Nielsen M. NetTepi. An integrated method for the prediction of T cell epitopes. Immunogenetics. 2014;66:449–456. doi: 10.1007/s00251-014-0779-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Jørgensen KW, Rasmussen M, Buus S, Nielsen M. NetMHCstab - predicting stability of peptide-MHC-I complexes; impacts for cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope discovery. Immunology. 2014;141:18–26. doi: 10.1111/imm.12160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Jurtz VI, et al. NetTCR. Sequence-based prediction of TCR binding to peptide-MHC complexes using convolutional neural networks. bioRxiv. 2018:433706. doi: 10.1101/433706. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Lanzarotti E, Marcatili P, Nielsen M. T-Cell Receptor Cognate Target Prediction Based on Paired α and β Chain Sequence and Structural CDR Loop Similarities. Frontiers in Immunology. 2019;10:2080. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Roth A, et al. PyClone. Statistical inference of clonal population structure in cancer. Nature Methods. 2014;11:396–398. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Miller CA, et al. SciClone. Inferring clonal architecture and tracking the spatial and temporal patterns of tumor evolution. PLOS Computational Biology. 2014;10:e1003665. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Levine AJ, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG. The Roles of Initiating Truncal Mutations in Human Cancers. The Order of Mutations and Tumor Cell Type Matters. Cancer Cell. 2019;35:10–15. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.11.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Gejman RS, et al. Rejection of immunogenic tumor clones is limited by clonal fraction. Elife. 2018;7:e41090. doi: 10.7554/eLife.41090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Jamal-Hanjani M, et al. Tracking the Evolution of Non−Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:2109–2121. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1616288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.McGranahan N, et al. Clonal status of actionable driver events and the timing of mutational processes in cancer evolution. Science Translational Medicine. 2015;7:283ra54. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Tate JG, et al. COSMIC. The Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:D941–D947. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Liu S-H, et al. DriverDBv3. A multi-omics database for cancer driver gene research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:D863–D870. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Tran E, et al. T-Cell Transfer Therapy Targeting Mutant KRAS in Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:2255–2262. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1609279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Chen H, et al. Comprehensive assessment of computational algorithms in predicting cancer driver mutations. Genome biology. 2020;21:43. doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-01954-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Bozic I, et al. Accumulation of driver and passenger mutations during tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:18545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010978107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Charoentong P, et al. Pan-cancer Immunogenomic Analyses Reveal Genotype-Immunophenotype Relationships and Predictors of Response to Checkpoint Blockade. Cell Reports. 2017;18:248–262. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Claeys A, Luijts T, Marchal K, van den Eynden J. Low immunogenicity of common cancer hot spot mutations resulting in false immunogenic selection signals. PLoS genetics. 2021;17:e1009368. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.McGranahan N, Swanton C. Neoantigen quality, not quantity. Science Translational Medicine. 2019;11:eaax7918. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aax7918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Koboldt DC, et al. VarScan 2. Somatic mutation and copy number alteration discovery in cancer by exome sequencing. Genome research. 2012;22:568–576. doi: 10.1101/gr.129684.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Mei R, et al. Genome-wide detection of allelic imbalance using human SNPs and high-density DNA arrays. Genome research. 2000;10:1126–1137. doi: 10.1101/gr.10.8.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Wang T, et al. Identification and characterization of essential genes in the human genome. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2015;350:1096–1101. doi: 10.1126/science.aac7041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Georgi B, Voight BF, Bućan M. From mouse to human. Evolutionary genomics analysis of human orthologs of essential genes. PLoS genetics. 2013;9:e1003484. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Blomen VA, et al. Gene essentiality and synthetic lethality in haploid human cells. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2015;350:1092–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.aac7557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Buus S, et al. Sensitive quantitative predictions of peptide-MHC binding by a ‘Query by Committee’ artificial neural network approach. Tissue Antigens. 2003;62:378–384. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2003.00112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Hoof I, et al. NetMHCpan, a method for MHC class I binding prediction beyond humans. Immunogenetics. 2008;61:1. doi: 10.1007/s00251-008-0341-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Sarkizova S, et al. A large peptidome dataset improves HLA class I epitope prediction across most of the human population. Nature Biotechnology. 2020;38:199–209. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0322-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Riley TP, et al. Structure Based Prediction of Neoantigen Immunogenicity. Frontiers in Immunology. 2019;10:2047. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015;521:436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Phloyphisut P, Pornputtapong N, Sriswasdi S, Chuangsuwanich E. MHCSeqNet. A deep neural network model for universal MHC binding prediction. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019;20:270. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2892-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Bulik-Sullivan B, et al. Deep learning using tumor HLA peptide mass spectrometry datasets improves neoantigen identification. Nature Biotechnology. 2018;37:55. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Chen B, et al. Predicting HLA class II antigen presentation through integrated deep learning. Nature Biotechnology. 2019;37:1332–1343. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0280-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Wu J, et al. DeepHLApan. A Deep Learning Approach for Neoantigen Prediction Considering Both HLA-Peptide Binding and Immunogenicity. Frontiers in Immunology. 2019;10:2559. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Zou J, et al. A primer on deep learning in genomics. Nature Genetics. 2019;51:12–18. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0295-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Wang Di, et al. Multiregion Sequencing Reveals the Genetic Heterogeneity and Evolutionary History of Osteosarcoma and Matched Pulmonary Metastases. Cancer Research. 2019;79:7–20. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Leong TL, et al. Deep multi-region whole-genome sequencing reveals heterogeneity and gene-by-environment interactions in treatment-naive, metastatic lung cancer. Oncogene. 2019;38:1661–1675. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0536-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Gerlinger M, et al. Genomic architecture and evolution of clear cell renal cell carcinomas defined by multiregion sequencing. Nature Genetics. 2014;46:225–233. doi: 10.1038/ng.2891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Haile S, et al. Sources of erroneous sequences and artifact chimeric reads in next generation sequencing of genomic DNA from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:e12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Robinson DR, et al. Integrative clinical genomics of metastatic cancer. Nature. 2017;548:297–303. doi: 10.1038/nature23306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Aguilar-Mahecha A, et al. The identification of challenges in tissue collection for biomarker studies. The Q-CROC-03 neoadjuvant breast cancer translational trial experience. Modern Pathology. 2017;30:1567–1576. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2017.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Chen M, Zhao H. Next-generation sequencing in liquid biopsy. Cancer screening and early detection. Human genomics. 2019;13:34. doi: 10.1186/s40246-019-0220-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.ICGC/TCGA Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes Consortium. Pan-cancer analysis of whole genomes. Nature. 2020;578:82–93. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1969-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Kim S, et al. Strelka2. Fast and accurate calling of germline and somatic variants. Nature Methods. 2018;15:591–594. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Benjamin D, et al. Calling Somatic SNVs and Indels with Mutect2. bioRxiv. 2019:861054. doi: 10.1101/861054. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Wang K, et al. MapSplice. Accurate mapping of RNA-seq reads for splice junction discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:e178. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Aran D, Sirota M, Butte AJ. Systematic pan-cancer analysis of tumour purity. Nature Communications. 2015;6:8971. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Dagogo-Jack I, Shaw AT. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nature reviews Clinical oncology. 2018;15:81–94. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Li Y, et al. Patterns of somatic structural variation in human cancer genomes. Nature. 2020;578:112–121. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1913-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Garcia-Garijo A, Fajardo CA, Gros A. Determinants for Neoantigen Identification. Frontiers in Immunology. 2019;10:1392. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Zhou W-J, et al. NeoPeptide. An immunoinformatic database of T-cell-defined neoantigens. Database : the journal of biological databases and curation. 2019;2019 doi: 10.1093/database/baz128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Tan X, et al. dbPepNeo. A manually curated database for human tumor neoantigen peptides. Database : the journal of biological databases and curation. 2020;2020 doi: 10.1093/database/baaa004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Reker D, Schneider P, Schneider G, Brown JB. Active learning for computational chemogenomics. Future medicinal chemistry. 2017;9:381–402. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2016-0197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Eraslan G, Avsec Z, Gagneur J, Theis FJ. Deep learning. New computational modelling techniques for genomics. Nature reviews Genetics. 2019;20:389–403. doi: 10.1038/s41576-019-0122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Hollingsworth RE, Jansen K. Turning the corner on therapeutic cancer vaccines. npj Vaccines. 2019;4:7. doi: 10.1038/s41541-019-0103-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Roy S, Sethi TK, Taylor D, Kim YJ, Johnson DB. Breakthrough concepts in immuneoncology. Cancer vaccines at the bedside. J Leukoc Biol. 2020;108:1455–1489. doi: 10.1002/JLB.5BT0420-585RR. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.D’Alise AM, et al. Adenoviral vaccine targeting multiple neoantigens as strategy to eradicate large tumors combined with checkpoint blockade. Nature Communications. 2019;10:2688. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10594-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Leoni G, et al. A Genetic Vaccine Encoding Shared Cancer Neoantigens to Treat Tumors with Microsatellite Instability. Cancer Research. 2020;80:3972. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.US National Library of Medicine. NCT03639714. 2020. Available at https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03639714.
- 191.US National Library of Medicine. NCT03953235. 2020. Available at https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03953235.
- 192.Duperret EK, et al. A Synthetic DNA, Multi-Neoantigen Vaccine Drives Predominately MHC Class I CD8+ T-cell Responses, Impacting Tumor Challenge. Cancer Immunology Research. 2019;7:174. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Aurisicchio L, et al. Poly-specific neoantigen-targeted cancer vaccines delay patient derived tumor growth. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research. 2019;38:78. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1084-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.US National Library of Medicine. NCT04015700. 2020. Available at https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04015700.
- 195.Harrison RP, Ruck S, Rafiq QA, Medcalf N. Decentralised manufacturing of cell and gene therapy products. Learning from other healthcare sectors. Biotechnology advances. 2018;36:345–357. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.12.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Kagermann H. In: Management of Permanent Change. Albach H, Meffert H, Pinkwart A, Reichwald R, editors. Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden; Wiesbaden: 2015. Change Through Digitization-Value Creation in the Age of Industry 4.0; pp. 23–45. [Google Scholar]
- 197.Theobald Matthias. Current Immunotherapeutic Strategies in Cancer. Springer; Cham: 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 198.Vormehr M, Türeci Ö, Sahin U. Harnessing Tumor Mutations for Truly Individualized Cancer Vaccines. Annual Review of Medicine. 2019;70:395–407. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-042617-101816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Britten CM, et al. The regulatory landscape for actively personalized cancer immunotherapies. Nature Biotechnology. 2013;31:880–882. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Vormehr M, et al. Mutanome Engineered RNA Immunotherapy. Towards Patient-Centered Tumor Vaccination. Journal of Immunology Research. 2015;2015:595363. doi: 10.1155/2015/595363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.NIH. US National Library of Medicine, ClinicalTrials.gov. 2021. Available at https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=neoantigen+AND+vaccine&recrs=abdef&cond=Cancer.
- 202.Goodwin S, McPherson JD, McCombie WR. Coming of age. Ten years of next-generation sequencing technologies. Nature reviews Genetics. 2016;17:333–351. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2016.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Chen R, Fulton KM, Twine SM, Li J. Identification of MHC Peptides Using Mass Spectrometry for Neoantigen Discovery and Cancer Vaccine Development. Mass spectrometry reviews. 2019 doi: 10.1002/mas.21616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Laumont CM, et al. Noncoding regions are the main source of targetable tumor-specific antigens. Science Translational Medicine. 2018;10:eaau5516. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aau5516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Wang RF, Parkhurst MR, Kawakami Y, Robbins PF, Rosenberg SA. Utilization of an alternative open reading frame of a normal gene in generating a novel human cancer antigen. JEM. 1996;183:1131–1140. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.3.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Duan F, et al. Genomic and bioinformatic profiling of mutational neoepitopes reveals new rules to predict anticancer immunogenicity. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2014;211:2231. doi: 10.1084/jem.20141308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Fritsch EF, et al. HLA-Binding Properties of Tumor Neoepitopes in Humans. Cancer Immunology Research. 2014;2:522. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-13-0227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Bentzen AK, et al. T cell receptor fingerprinting enables in-depth characterization of the interactions governing recognition of peptide-MHC complexes. Nature Biotechnology. 2018;36:1191–1196. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Ogishi M, Yotsuyanagi H. Quantitative Prediction of the Landscape of T Cell Epitope Immunogenicity in Sequence Space. Frontiers in Immunology. 2019;10:827. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Devlin JR, et al. Structural dissimilarity from self drives neoepitope escape from immune tolerance. Nature Chemical Biology. 2020 doi: 10.1038/s41589-020-0610-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Neefjes J, Jongsma MLM, Paul P, Bakke O. Towards a systems understanding of MHC class I and MHC class II antigen presentation. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2011;11:823–836. doi: 10.1038/nri3084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Rock KL, Reits E, Neefjes J. Present Yourself! By MHC Class I and MHC Class II Molecules. Trends in immunology. 2016;37:724–737. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2016.08.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Gourraud P-A, et al. HLA diversity in the 1000 genomes dataset. PLOS ONE. 2014;9:e97282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Ochs K, et al. K27M-mutant histone-3 as a novel target for glioma immunotherapy. OncoImmunology. 2017;6:e1328340. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1328340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Chheda ZS, et al. Novel and shared neoantigen derived from histone 3 variant H3.3K27M mutation for glioma T cell therapy. JEM. 2017;215:141–157. doi: 10.1084/jem.20171046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Holmström MO, et al. The JAK2V617F mutation is a target for specific T cells in the JAK2V617F-positive myeloproliferative neoplasms. Leukemia. 2017;31:495–498. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Chandran S, et al. Abstract CN01-03. T cell receptor gene therapy for a public neoantigen derived from mutated PIK3CA, a dominant driver oncogene in breast and endometrial cancers. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 2019;18:CN01-03. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.TARG-19-CN01-03. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Veatch JR, et al. Tumor-infiltrating BRAFV600E-specific CD4+ T cells correlated with complete clinical response in melanoma. J Clin Invest. 2018;128:1563–1568. doi: 10.1172/JCI98689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Linard B, et al. A ras-Mutated Peptide Targeted by CTL Infiltrating a Human Melanoma Lesion. The Journal of Immunology. 2002;168:4802. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.9.4802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Robbins PF, et al. A mutated beta-catenin gene encodes a melanoma-specific antigen recognized by tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. JEM. 1996;183:1185–1192. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.3.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.van der Lee DI, et al. Mutated nucleophosmin 1 as immunotherapy target in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Invest. 2019;129:774–785. doi: 10.1172/JCI97482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Sæterdal I, et al. Frameshift-mutation-derived peptides as tumor-specific antigens in inherited and spontaneous colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:13255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.231326898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Inderberg EM, et al. T cell therapy targeting a public neoantigen in microsatellite instable colon cancer reduces in vivo tumor growth. OncoImmunology. 2017;6:e1302631. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1302631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Bosch GJ, Joosten AM, Kessler JH, Melief CJ, Leeksma OC. Recognition of BCR-ABL positive leukemic blasts by human CD4+ T cells elicited by primary in vitro immunization with a BCR-ABL breakpoint peptide. blood. 1996;88:3522–3527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Clark RE, et al. Direct evidence that leukemic cells present HLA-associated immunogenic peptides derived from the BCR-ABL b3a2 fusion protein. blood. 2001;98:2887–2893. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.10.2887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Makita M, et al. Leukemia-associated fusion proteins, dek-can and bcr-abl, represent immunogenic HLA-DR-restricted epitopes recognized by fusion peptide-specific CD4+ T lymphocytes. Leukemia. 2002;16:2400–2407. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Cai A, et al. Mutated BCR-ABL generates immunogenic T-cell epitopes in CML patients. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2012;18:5761–5772. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Worley BS, et al. Antigenicity of Fusion Proteins from Sarcoma-associated Chromosomal Translocations. Cancer Research. 2001;61:6868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Sato Y, et al. Detection and Induction of CTLs Specific for SYT-SSX-Derived Peptides in HLA-A24(+) patients with synovial sarcoma. The Journal of Immunology. 2002;169:1611. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.3.1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Gambacorti-Passerini C, et al. Human CD4 lymphocytes specifically recognize a peptide representing the fusion region of the hybrid protein pml/RAR alpha present in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Blood. 1993;81:1369–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.van den Broeke LT, Pendleton CD, Mackall C, Helman LJ, Berzofsky JA. Identification and epitope enhancement of a PAX-FKHR fusion protein breakpoint epitope in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma cells created by a tumorigenic chromosomal translocation inducing CTL capable of lysing human tumors. Cancer Research. 2006;66:1818–1823. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Yotnda P, et al. Cytotoxic T cell response against the chimeric ETV6-AML1 protein in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1998;102:455–462. doi: 10.1172/JCI3126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Zamora AE, et al. Pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia generate abundant and functional neoantigen-specific CD8+ T cell responses. Science Translational Medicine. 2019;11:eaat8549. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aat8549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Jensen KK, et al. Improved methods for predicting peptide binding affinity to MHC class II molecules. Immunology. 2018;154:394–406. doi: 10.1111/imm.12889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Gfeller D, et al. The Length Distribution and Multiple Specificity of Naturally Presented HLA-I Ligands. The Journal of Immunology. 2018:ji1800914. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Racle J, et al. Robust prediction of HLA class II epitopes by deep motif deconvolution of immunopeptidomes. Nature Biotechnology. 2019;37:1283–1286. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0289-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Calis JJA, et al. Properties of MHC Class I Presented Peptides That Enhance Immunogenicity. PLOS Computational Biology. 2013;9:e1003266. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Rech AJ, et al. Tumor Immunity and Survival as a Function of Alternative Neopeptides in Human Cancer. Cancer Immunology Research. 2018;6:276. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-17-0559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Rubinsteyn A, et al. Computational Pipeline for the PGV-001 Neoantigen Vaccine Trial. Frontiers in Immunology. 2018;8:1807. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Kodysh J, Rubinsteyn A. In: Bioinformatics for Cancer Immunotherapy: Methods and Protocols. Boegel S, editor. Springer US; New York, NY: 2020. OpenVax. An Open-Source Computational Pipeline for Cancer Neoantigen Prediction; pp. 147–160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Bjerregaard A-M, Nielsen M, Hadrup SR, Szallasi Z, Eklund AC. MuPeXI. Prediction of neo-epitopes from tumor sequencing data. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy. 2017;66:1123–1130. doi: 10.1007/s00262-017-2001-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Besser H, Yunger S, Merhavi-Shoham E, Cohen CJ, Louzoun Y. Level of neo-epitope predecessor and mutation type determine T cell activation of MHC binding peptides. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer. 2019;7:135. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0595-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Smith CC, et al. Machine-Learning Prediction of Tumor Antigen Immunogenicity in the Selection of Therapeutic Epitopes. Cancer Immunology Research. 2019 doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-19-0155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Cibulskis K, et al. Sensitive detection of somatic point mutations in impure and heterogeneous cancer samples. Nature Biotechnology. 2013;31:213–219. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Saunders CT, et al. Strelka. Accurate somatic small-variant calling from sequenced tumor-normal sample pairs. bioinformatics. 2012;28:1811–1817. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Larson DE, et al. SomaticSniper. Identification of somatic point mutations in whole genome sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:311–317. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.Radenbaugh AJ, et al. RADIA. RNA and DNA integrated analysis for somatic mutation detection. PLOS ONE. 2014;9:e111516. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Garrison E, Marth G. Haplotype-based variant detection from short-read sequencing. arXiv. 2012:1207.3907v2 [Google Scholar]
- 249.Li H, et al. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:2078–2079. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Rimmer A, et al. Integrating mapping-, assembly- and haplotype-based approaches for calling variants in clinical sequencing applications. Nature Genetics. 2014;46:912–918. doi: 10.1038/ng.3036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Jones D, et al. cgpCaVEManWrapper. Simple Execution of CaVEMan in Order to Detect Somatic Single Nucleotide Variants in NGS Data. Current protocols in bioinformatics. 2016;56:15.10.1–15.10.18. doi: 10.1002/cpbi.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Raine KM, et al. cgpPindel. Identifying Somatically Acquired Insertion and Deletion Events from Paired End Sequencing. Current protocols in bioinformatics. 2015;52:15.7.1–15.7.12. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi1507s52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Wala JA, et al. SvABA. Genome-wide detection of structural variants and indels by local assembly. Genome research. 2018;28:581–591. doi: 10.1101/gr.221028.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Fan Y, et al. MuSE. Accounting for tumor heterogeneity using a sample-specific error model improves sensitivity and specificity in mutation calling from sequencing data. Genome biology. 2016;17:178. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-1029-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Moncunill V, et al. Comprehensive characterization of complex structural variations in cancer by directly comparing genome sequence reads. Nature Biotechnology. 2014;32:1106–1112. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 256.DePristo MA, et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nature Genetics. 2011;43:491–498. doi: 10.1038/ng.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 257.Sahraeian SME, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks for accurate somatic mutation detection. Nature Communications. 2019;10:1041. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09027-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Geyer RJ, Tobet R, Berlin RD, Srivastava PK. Immune response to mutant neoantigens. Cancer’s lessons for aging. OncoImmunology. 2013;2:e26382. doi: 10.4161/onci.26382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 259.Prehn RT, Main JM. Immunity to methylcholanthrene-induced sarcomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1957;18:769–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 260.Smith CC, et al. Alternative tumour-specific antigens. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2019;19:465–478. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0162-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 261.van Allen EM, et al. Genomic correlates of response to CTLA-4 blockade in metastatic melanoma. Science. 2015;350:207. doi: 10.1126/science.aad0095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 262.Roudko V, et al. Shared Immunogenic Poly-Epitope Frameshift Mutations in Microsatellite Unstable Tumors. Cell. 2020;183:1634–1649.:e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 263.Litchfield K, et al. Escape from nonsense-mediated decay associates with anti-tumor immunogenicity. Nature Communications. 2020;11:3800. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17526-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 264.Alexandrov LB, et al. Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature. 2013;500:415–421. doi: 10.1038/nature12477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 265.Shtivelman E, Lifshitz B, Gale RP, Canaani E. Fused transcript of abl and bcr genes in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nature. 1985;315:550–554. doi: 10.1038/315550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 266.Gao Q, et al. Driver Fusions and Their Implications in the Development and Treatment of Human Cancers. Cell Reports. 2018;23:227–238.:e3. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 267.Dai X, Theobard R, Cheng H, Xing M, Zhang J. Fusion genes. A promising tool combating against cancer. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer. 2018;1869:149160. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 268.Smart AC, et al. Intron retention is a source of neoepitopes in cancer. Nature Biotechnology. 2018;36:1056–1058. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 269.Kahles A, et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Alternative Splicing Across Tumors from 8,705 Patients. Cancer Cell. 2018;34:211–224.:e6. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.07.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 270.Jayasinghe RG, et al. Systematic Analysis of Splice-Site-Creating Mutations in Cancer. Cell Reports. 2018;23:270–281.:e3. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 271.Ehx G, et al. Atypical acute myeloid leukemia-specific transcripts generate shared and immunogenic MHC class-I-associated epitopes. Immunity. 2021;54:737–752.:e10. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 272.Bigot J, et al. Splicing patterns in SF3B1 mutated uveal melanoma generate shared immunogenic tumor-specific neo-epitopes. Cancer Discovery. 2021 doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 273.Esteva A, et al. A guide to deep learning in healthcare. Nature Medicine. 2019;25:24–29. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0316-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 274.GAMP. GAMP 5 Guide: Compliant GxP Computerized Systems. Available at https://ispe.org/publications/guidance-documents/gamp-5.
Highlighted References
- 1).Alexandrov Ludmil B, Nik-Zainal Serena, Wedge David C, Aparicio Samuel AJR, Behjati Sam, Biankin Andrew V, et al. Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature. 2013;500(7463):415–421. doi: 10.1038/nature12477. [This article illustrates the prevalence of somatic point mutations across human cancers.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2).Alspach Elise, Lussier Danielle M, Miceli Alexander P, Kizhvatov Ilya, DuPage Michel, Luoma Adrienne M, et al. MHC-II neoantigens shape tumour immunity and response to immunotherapy. Nature. 2019;574(7780):696–701. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1671-8. [This article underlines the relevance of MHC class II neoantigens for an efficient anti-tumour response.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4).Balachandran Vinod P, Łuksza Marta, Zhao Julia N, Makarov Vladimir, Moral John Alec, Remark Romain, et al. Identification of unique neoantigen qualities in long-term survivors of pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2017;551:512. doi: 10.1038/nature24462. [This article highlights that neoantigen quality correlates with clinical outcome.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5).Rosenthal Rachel, Cadieux Elizabeth Larose, Salgado Roberto, Bakir Maise Al, Moore David A, Hiley Crispin T, et al. Neoantigen-directed immune escape in lung cancer evolution. Nature. 2019;567(7749):479–485. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1032-7. [ This article integrates genomic features of tumours with immune infiltrates and analyses neoantigen-dependent immune escape. ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6).Chen Daniel S, Mellman Ira. Oncology Meets Immunology. The Cancer-Immunity Cycle. Immunity. 2013;39(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.012. [ This article introduces the cancer-immunity cycle and proposes the associated biomarkers for tailoring individualised treatments. ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.