Abstract
Several enzymes are known to have evolved from non-catalytic proteins such as solute-binding proteins (SBPs). Although attention has been focused on how a binding site can evolve to become catalytic, an equally important question is: how do the structural dynamics of a binding protein change as it becomes an efficient enzyme? Here we performed a variety of experiments, including propargyl-DO3A-Gd(III) tagging and double electron–electron resonance (DEER) to study the rigid body protein dynamics of reconstructed evolutionary intermediates to determine how the conformational sampling of a protein changes along an evolutionary trajectory linking an arginine SBP to a cyclohexadienyl dehydratase (CDT). We observed that primitive dehydratases predominantly populate catalytically unproductive conformations that are vestiges of their ancestral SBP function. Non-productive conformational states, including a wide-open state, are frozen out of the conformational landscape via remote mutations, eventually leading to extant CDT that exclusively samples catalytically relevant compact states. These results show that remote mutations can reshape the global conformational landscape of an enzyme as a mechanism for increasing catalytic activity.
Subject terms: Enzymes, X-ray crystallography, Molecular evolution, Molecular modelling
Cyclohexadienyl dehydratase (CDT) evolved from a cationic amino acid binding protein ancestor without enzymatic activity (AncCDT-1) via a series of intermediates. Here, the authors combine EPR, X-ray crystallography and MD simulations to study the structural dynamics of these evolutionary intermediates and observe that they predominantly populate catalytically unproductive conformations, while CDT exclusively samples catalytically relevant compact states, and which reveals how the conformational landscape changes along the evolutionary trajectory.
Introduction
Solute-binding proteins (SBPs) comprise a large superfamily of extra-cytoplasmic receptors that are predominantly involved in sensing and the uptake of nutrients, including amino acids, carbohydrates, vitamins, metals and osmolytes1–4. The SBP fold consists of two α/β domains linked by a flexible hinge region that mediates a conformational change in solution, with hinge-bending and hinge-twisting motions moving the two domains together (closed state) and apart (open state; Fig. 1a). Ligands bind at the cleft between the two domains and stabilise the closed state by forming bridging interactions between the two domains and the hinge region1. The ligand-induced open-to-closed conformational switch is important for the function of SBPs in ATP-binding cassette transporter systems1,5,6, tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic transporter systems7 and signalling cascades4.
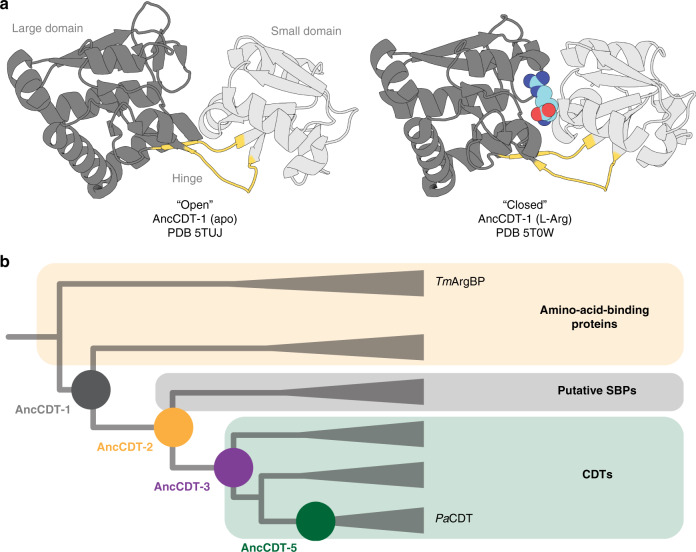
Fig. 1. The conformational change of SBPs and the evolution of PaCDT.
a X-ray crystal structures of SBPs that are specialised for binding solutes, such as AncCDT-1 (shown), typically capture open ligand-free (left, PDB 5TUJ) and closed liganded (right, PDB 5T0W) states. b Schematic drawing (not to scale) of the phylogenetic tree used for ancestral sequence reconstruction in Clifton et al.40, which highlights the evolutionary relationship between the polar amino acid-binding proteins (e.g., Thermotoga maritima L-arginine-binding protein, TmArgBP), AncCDT-1, AncCDT-3, AncCDT-5 and PaCDT. Clades are collapsed. Figure adapted from Clifton et al.40.
Although the open conformation is the ground state for most ligand-free SBPs1,5,8–19, numerous SBPs also sample semi-closed and closed states in the absence of ligands. For example, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), molecular dynamics (MD) simulation, double electron–electron resonance (DEER, a.k.a. PELDOR) and Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) studies on the maltose-binding protein (MBP)20–22, glucose–galactose-binding protein23,24, histidine-binding protein25, ferri-bacillibactin-binding protein26, glutamine-binding protein27,28 and choline/acetylcholine-binding protein29 demonstrate a sampling of both open and closed conformations in the absence of ligands. The intrinsic open/closed equilibrium is fundamental to determining the binding affinity21,23,30,31 and binding promiscuity5,32 of SBPs, and controlling the transport activity of SBP-associated systems5,28. Indeed, the extent of the open/closed motion differs between SBPs1, and the function of an SBP can be changed by mutations that alter conformational sampling, without changing the architecture of the SBP-ligand interface15,21,30.
While most SBPs are non-catalytic binding proteins, a small fraction of proteins within the periplasmic binding protein-fold superfamily have evolved enzymatic activity33–37. One example is cyclohexadienyl dehydratase (CDT), which is closely related to the polar and cationic amino acid-binding proteins, such as the arginine-binding protein (ArgBP)37,38. Like ArgBP, CDT adopts a periplasmic type-II SBP fold, but instead of binding amino acids, it catalyzes the Grob-like fragmentation of prephenate and L-arogenate to form phenylpyruvate and L-phenylalanine, respectively39. We previously used ancestral sequence reconstruction to show that the trimeric CDT from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PaCDT) plausibly evolved from a monomeric cationic amino acid-binding protein ancestor (AncCDT-1) via a series of intermediates (AncCDT-2 to AncCDT-5)40 (Fig. 1b). While AncCDT-1 and AncCDT-2 did not display any enzymatic activity and appeared to be binding proteins, low-level CDT activity became detectable in two alternative reconstructions of AncCDT-3(P188/L188) (kcat/KM ~101/102 s−1 M−1) and increased along the trajectory towards the efficient extant enzyme PaCDT (kcat/KM ~106 s−1 M−1). Despite the large difference in catalytic efficiency, AncCDT-3 and PaCDT share 14/15 inner-shell residues, including all catalytic residues, but only about 50% amino acid sequence identity over the rest of the protein (the outer shells). This suggests that these outer-shell substitutions must be substantially responsible for the ~105-fold increase in catalytic efficiency. For example, the remote P188L substitution in AncCDT-3 was shown to result in a 27-fold increase in kcat/KM40.
In this study, we investigated two plausible explanations for how remote mutations could have led to an increase in catalytic activity along this evolutionary trajectory: they may have (i) altered the sampling of rotamers of active site residues, such as the general acid Glu173, thereby changing the structure and character of the active site and controlling the configuration of active site residues, and/or (ii) altered the equilibrium between open and closed states of the protein to minimise sampling of the catalytically unproductive open state. To test these hypotheses, we used a combination of protein crystallography, MD simulations and DEER distance measurements on protein variants into which we incorporated the unnatural amino acid p-azidophenylalanine (AzF) to allow biorthogonal conjugation, making it specific even in the presence of native cysteine residues, to a propargyl-DO3A-Gd(III) tag, which encapsulates the Gd(III) ion in a hydrophilic complex of neutral charge, while providing a relatively rigid linker between the Gd(III) ion and protein backbone41. The Gd(III)–Gd(III) DEER measurements were carried out at W-band frequency (94.9 GHz), affording superior sensitivity and measurements free from orientation selection42,43 and multi-spin effects44–47. The results from these experiments showed that the ancestral proteins, which all displayed either no catalytic activity (AncCDT-1) or very high KM values that were outside the physiologically relevant substrate concentration (AncCDT-3, AncCDT-5), significantly or even predominantly sampled open states, including a wide-open state that is not observed in the extant and efficient enzyme PaCDT. Finally, the structural analysis revealed that multiple changes to intra- and intermolecular (via oligomerization) interaction networks have shifted the conformational equilibrium towards more compact states along the evolutionary trajectory.
Results
The evolution of prephenate dehydratase activity
We previously showed that while AncCDT-1 binds L-arginine with comparable affinity to extant L-arginine-binding proteins, the P188 AncCDT-3 reconstruction (hereafter AncCDT-3/P188), AncCDT-5 and PaCDT have all lost the ancestral ability to bind proteogenic amino acids40. Instead, along with the AncCDT-3/L188 AncCDT-3 reconstruction, they can rescue the growth of a phenylalanine auxotroph of E. coli (ΔpheA) grown in the absence of L-phenylalanine, indicating their capacity to deliver the dehydratase activity required to synthesise L-phenylalanine from L-arogenate, or the precursor phenylpyruvate from prephenate40. Furthermore, these variants exhibited prephenate dehydratase activity in vitro, which increased about 105-fold (kcat/KM) between AncCDT-3/P188 and PaCDT. In this work, we have additionally assessed the dehydratase activity of AncCDT-5, which proved to be an intermediate between the AncCDT-3 variants and the extant enzyme PaCDT (Table 1 and Supplementary Fig. 1). Although the kcat value of AncCDT-5 (4 s−1) exceeds the level observed in the AncCDT-3 variants (~10−2 s−1) almost as much as PaCDT (18 s−1), the KM of AncCDT-5 remains ~15-fold higher than that of PaCDT (277 μM vs. 19 μM). This value is well above the likely physiological concentration of the substrate (the intracellular concentrations of molecules in this biosynthetic pathway are ~14–18 μM in Gram-negative bacteria48).
Table 1.
Kinetic parameters for prephenate dehydratase activity of CDT variants related to this studya.
| Protein | KM (μM) | kcat (s−1) | kcat/KM (M−1 s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AncCDT-140 | ND | ND | ND |
| AncCDT-3/P18840 | 1830 ± 190 | (1.04 ± 0.07) × 10−2 | 5.67 ± 0.70 |
| AncCDT-3/L18840 | 294 ± 27 | (4.58 ± 0.30) × 10−2 | 155 ± 18 |
| AncCDT-5 | 277 ± 4 | 4.1 ± 0.2 | (1.5 ± 0.1) × 104 |
| PaCDT40 | 18.7 ± 2.9 | 18.4 ± 0.7 | (9.8 ± 1.6) × 105 |
ND not detected.
aThe results are reported as mean ± standard error for KM and kcat. Errors for kcat/KM were obtained by propagation. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
Remote mutations affect active site configurations and catalysis
Sequence and structural analysis of AncCDT-3/L188 and PaCDT revealed that although their catalytic efficiency differs by ~105 M−1 s−1, they share 14 of 15 residues in the active/substrate-binding site (the only difference being a conservative Thr80Ser substitution)40. Comparison between the structures of AncCDT-3/L188 and PaCDT revealed that the catalytic general acid Glu173 adopts a rotameric state in AncCDT-3/L188 that differs from that observed in PaCDT (Fig. 2a)40. This conformational difference appears to be caused by the neighbouring Tyr177Gln mutation that occurs on the branch between AncCDT-3 and AncCDT-5; the presence of Tyr177 in AncCDT-3 prevents Glu173 from adopting the catalytically competent conformation observed in PaCDT40. Additionally, this mutation causes coupled conformational changes in the neighbouring residues Phe156 and Met167, which leads to further changes in the shape and electrostatic character of the active site. These findings are analogous to those from recent work on enzyme variants produced through directed evolution and computational design that show how second-shell mutations affect enzyme activity by constraining the conformational sampling of catalytic residues49,50.
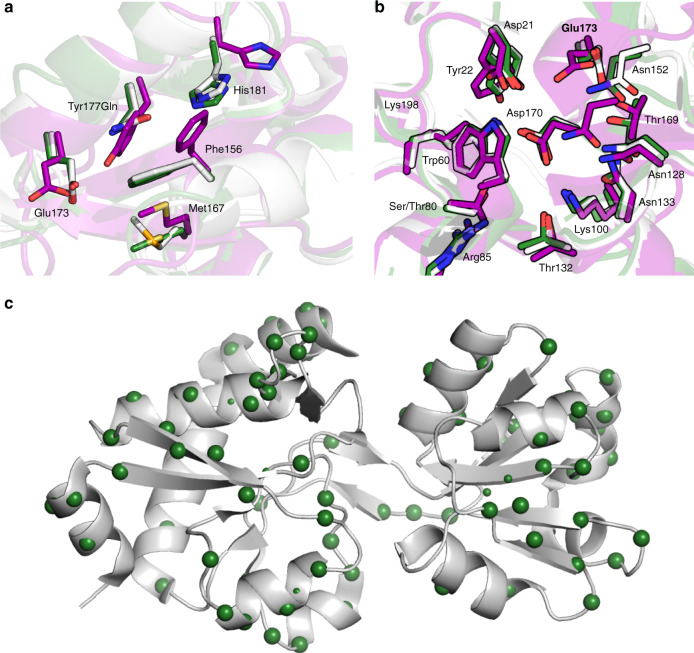
Fig. 2. Crystal structures of AncCDT-3/P188, AncCDT-5 and PaCDT.
a Structural overlay of the small domains of AncCDT-3/L188 (purple, PDB 5JOS), AncCDT-5 (green) and PaCDT (white, PDB 3KBR). The Tyr177Gln substitution that occurs between AncCDT-3 and AncCDT-5 contributes to the repositioning of Glu173. b Structural alignment of the active sites of AncCDT-3/L188 (purple, PDB 5JOS), AncCDT-5 (green) and PaCDT (PDB 3KBR, white). The small domain (residues 99–194) and large domain (residues 1–98 and 195–236) of AncCDT-3/L188 and AncCDT-5 were individually aligned with the corresponding domains of PaCDT. The sidechains of the 15 inner-shell residues identified by Clifton et al.40 are shown as sticks (Gly131 not shown), highlighting identical active site residues and side-chain conformations between AncCDT-5 and PaCDT. The HEPES molecules present in the crystal structures are omitted for clarity. c The locations of the substitutions (green spheres) between AncCDT-5 and PaCDT are shown projected onto the structure of PaCDT (PDB 3KBR).
To better understand how the mutations along this evolutionary trajectory affect activity, we also solved a 1.49 Å X-ray crystal structure of AncCDT-5 (Supplementary Table 1), which shares 15/15 residues in the active/substrate-binding site with PaCDT. In contrast to the comparison between AncCDT-3 and PaCDT, a structural alignment of AncCDT-5 and PaCDT (PDB 3KBR) reveals that these two proteins not only share identical binding sites in terms of amino acid composition but that these residues also adopt identical conformations (Fig. 2b). Since these active/binding sites are identical, the ~15-fold decrease in KM and ~5-fold increase in kcat of the dehydratase activity must be attributed to amino acid substitutions that are outside of the binding site. The sequences of AncCDT-5 and PaCDT differ at 98 positions. Excluding the nine amino acid C-terminal extension of PaCDT, the remaining 89 positions are evenly distributed around the SBP fold (Fig. 2c), making it difficult to rationalise how individual mutations contribute to changes in catalytic profiles. Instead, it is possible that some of the substitutions may be affecting catalysis by altering the open/closed dynamics of these proteins.
Solution dynamics of AncCDT-1, evolutionary intermediates and PaCDT
Next, we investigated whether the accumulation of substitutions between AncCDT-1 and PaCDT at positions remote from the active site could have affected catalytic activity by altering the open/closed dynamics of these proteins. To do so, we used DEER distance measurements and MD simulations to investigate whether the distribution of the open and closed solution states differed between the ancestral amino acid-binding protein (AncCDT-1), the intermediate low-activity CDTs (AncCDT-3, AncCDT-5) and the efficient extant enzyme, PaCDT.
AncCDT-1
First, we confirmed that AncCDT-1 was monomeric (>95%) in solution using size-exclusion chromatography multi-angle light scattering (SEC-MALS; Supplementary Fig. 2a). We then assessed the solution conformations of AncCDT-1 using DEER distance measurements with Gd(III)-tags introduced through unnatural amino acid (UAA) mutagenesis (Supplementary Fig. 3). Amber stop codons were used to incorporate the UAA AzF into the small (Lys138) and large (Gln68) domains of AncCDT-1. These sites were chosen because they (i) are known to be located in regions of the protein that undergo substantial changes in their relative distance upon ligand binding40, (ii) are located on rigid α-helices, (iii) are surrounded by residues that will minimise unwanted tag motions via packing and (iv) are solvent-exposed, which minimises the risk that mutagenesis and tagging at these positions will significantly affect the protein conformations. The mutant protein heterologously expressed in soluble form in E. coli, yielding ~15 mg of purified protein per litre of cell culture. To remove any co-purified ligands, on-column protein denaturation and refolding were performed to obtain ligand-free samples. This is referred to as refolded AncCDT-1. The AzF residues were modified with propargyl-DO3A-Gd(III) tags as previously described (Supplementary Fig. 3a)41,51, and mass spectrometry analysis indicated that the tag ligation yields were sufficient to deliver at least 75% doubly tagged samples, except for the AncCDT-1 mutant at sites 138 and 161, where at least 25% of the sample was doubly tagged (Supplementary Fig. 4).
DEER measurements of refolded AncCDT-1-propargyl-DO3A-Gd(III) revealed a distance distribution with two dominant peaks with maxima corresponding to Gd(III)–Gd(III) distances of 3.2 nm and 4.4 nm (Fig. 3a, Supplementary Table 2 and Supplementary Fig. 5a, b, i). When saturating concentrations of L-arginine were added to the refolded sample, the distance distribution revealed an almost complete shift to the shorter distance (Fig. 3a), as expected for a ligand-induced open-to-closed transition. Together, these data indicate that the Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance varies by ~1.2 nm between the closed state and any open conformations and that the DEER approach employed here can be used to differentiate between distinct conformational substates of an SBP. Experiments with natively purified protein rather than unfolded/refolded protein showed similar results (Supplementary Fig. 5a, b, i), except that a greater proportion of the protein adopted the closed state (3.2 nm Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance) in the absence of exogenous L-arginine than in the sample subjected to unfolding and renaturation. This was expected, as the protein is known to co-purify from E. coli with some ligand-bound, which stabilises the closed conformation40. A ligand-induced shift towards a more closed state was also observed when L-arginine was added to a sample of a lysine-arginine-ornithine binding protein from Salmonella enterica (SeLAOBP, Supplementary Fig. 6).
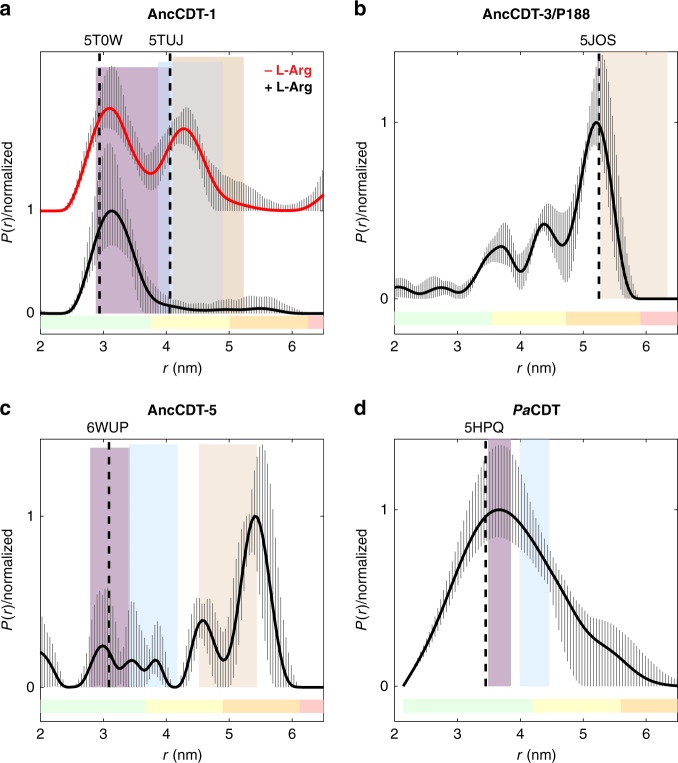
Fig. 3. Solution dynamics of AncCDT-1, AncCDT-3/P188, AncCDT-5 and PaCDT probed by DEER.
Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance distributions for samples of propargyl-DO3A-Gd(III)-tagged a refolded AncCDT-1 (-/+ L-Arg, tagged at positions 68 and 138), b natively purified AncCDT-3/P188 (tagged at positions 68 and 138), c natively purified AncCDT-5 (tagged at positions 68 and 138) and d natively purified PaCDT (tagged at positions 68 and 139 and diluted by a factor of 10 using unlabelled PaCDT). Distance distributions were obtained using DeerAnalysis77; the solid lines represent the distributions with the best r.m.s.d. from the experimental data, and the striped regions represent the variation of alternative distributions (± 2 times the standard deviation) obtained by varying the parameters of the background correction and noise. The coloured bars at the bottom of each panel reflect the reliability of each region of the distribution, corresponding to the DEER evolution time used, as defined in DeerAnalysis (pale green: the shape of the distance distribution is reliable; pale yellow: the mean distance and distribution width are reliable; pale orange: the mean distance is reliable; pale red: long-range distance contributions may be detectable, but cannot be quantified.). The original DEER data and DEER form factor traces are shown in Supplementary Figs. 5, 7 and 8. Vertical dashed lines represent the Gd(III)–Gd(III) distances estimated by modelling propargyl-DO3A-Gd(III) tags onto the crystal structures of each protein. The shaded areas represent the range of calculated Gd(III)–Gd(III) distances when propargyl-DO3A-Gd(III) tags are modelled onto a number of individual MD snapshots representing the closed (magenta), open (blue) and wide-open (orange) states.
We also performed experiments on AncCDT-1 that had been tagged at two sites on either the large domain (positions 68 and 219, Supplementary Fig. 5c) or small domain (positions 138 and 161; Supplementary Fig. 5d). These each showed a peak in the distance distribution that was in agreement with Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance predictions based on crystal structures of AnCDT-1 (Supplementary Fig. 5g, h). These results confirm that the two distances measured for refolded AncCDT-1 are due to rigid-body motions of the two domains, rather than any intra-domain flexibility or tag dynamics.
We next sought to correlate the distance changes observed through DEER to structural changes in the protein. We previously solved the crystal structure of AncCDT-1 bound to L-arginine (PDB 5T0W), which has a Cα–Cα distance between Gln68 and Lys138 of 2.6 nm (equivalent to a Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance of ~2.9 nm, Supplementary Fig. 5e). We also solved a structure of the protein in an open state (PDB 5TUJ), in which the Cα–Cα distance between Gln68 and Lys138 is 3.4 nm (Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance of ~4.1 nm, Supplementary Fig. 5f). This crystal structure presents a snapshot of an open conformation, but additional open states may be accessible to the protein in solution. To probe these, we also explored the solution dynamics of AncCDT-1 using MD simulations initiated from the closed X-ray crystal structure of AncCDT-1 (PDB 5T0W) with the ligand, L-arginine, removed. These were conducted solely to identify conformational substates that can be accessed on the ns–μs timescale (i.e., easily accessible, low-energy states), not to obtain quantitative predictions of the solution dynamics or the relative occupancy of each state. The simulations suggest that AncCDT-1 can easily access three dominant conformational substates (Fig. 4a and Supplementary Table 2): the closed state corresponding to PDB 5T0W (68–138 Cα–Cα distance range of 2.5–2.9 nm; equivalent to a Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance range of ~2.9–3.4 nm), an intermediate open state corresponding to PDB 5TUJ (68–138 Cα–Cα distance 3.2–3.7 nm; equivalent to a Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance range of ~3.9–4.9 nm) and an additional wide-open state (68–138 Cα–Cα distance 3.6–4.2 nm; equivalent to a Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance range of ~4.1–5.2 nm).
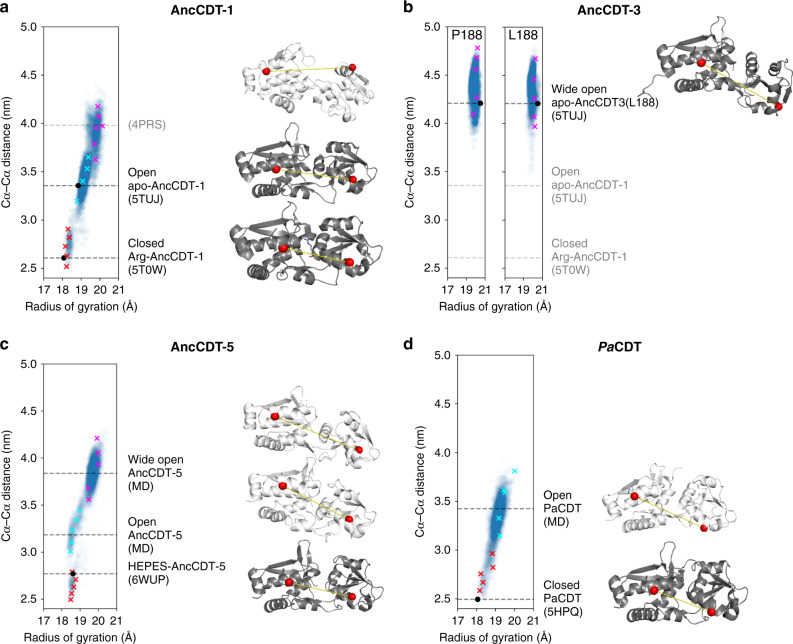
Fig. 4. Conformational substates captured by MD and crystallography.
Conformational substates of (a) AncCDT-1, (b) AncCDT-3, (c) AncCDT-5 and (d) PaCDT captured by MD and X-ray crystallography. The plot of Cα–Cα distances between tagged residues vs. radius of gyration obtained from MD simulation snapshots highlights populations (or lack thereof) of closed, open and wide-open conformational states. Each data point represents a single frame of the MD simulation (sampled every 0.1 ns). Crosses represent snapshots of closed (red), open (cyan) and wide-open (magenta) states that were used to model Gd(III)–Gd(III) distances. Representative structures of each of these states are shown on the right and highlight the extent of the open/closed transition, with distances between Cαs (red spheres) of tagged sites shown by yellow lines. Dark grey structures are crystal structures (corresponding to black dots on the plot), while white structures are MD snapshots. The time evolution of Cα–Cα distances are shown in Supplementary Fig. 10.
The results obtained by DEER suggest that the dominant states are indeed the closed state and an open conformation closely related to the open state observed through protein crystallography, but which might also include the wide-open state, as there is significant overlap between the modelled Gd(III)–Gd(III) distances in the snapshots obtained from MD. Although we do not have crystallographic evidence that AncCDT-1 samples the wide-open state, analogous wide-open states have been observed in crystal structures of extant L-arginine-binding proteins, such as that from Thermotoga maritima (TmArgBP, PDB 4PRS)38, which has a Cα–Cα distance of 4.0 nm between positions equivalent to 68–138 in AncCDT-1 (which is similar to the 3.6–4.2 nm range observed for the wide-open state in AncCDT-1 MD simulations). Indeed, it has been suggested that the specific open states of SBPs observed crystallographically can be dictated by crystal packing interactions16–19. The wide-open state thus is a part of the conformational landscape for L-arginine-binding proteins, although we could not unambiguously detect it in our DEER experiments on AncCDT-1 owing to overlap with the open state. Altogether, the data from DEER, protein crystallography and MD demonstrate that AncCDT-1 can sample both open and closed states in the absence of ligands, and that ligand binding shifts the conformational equilibrium towards the closed state.
AncCDT-3 and AncCDT-5
Considering the significant difference in dehydratase activity between AncCDT-3, AncCDT-5 and PaCDT, as well as our inability to fully rationalise these differences through protein crystallography, we next used DEER and MD to investigate the solution conformational distributions of these proteins. Like AncCDT-1, SEC-MALS indicated that AncCDT-3/P188 and AncCDT-5 were predominantly monomeric in solution (>95%), as reported previously40 (Supplementary Fig. 2b, c). We tagged the small and large domains of AncCDT-3/P188 and AncCDT-5 at sites 68 (large domain) and 138 (small domain) in the same way as AncCDT-1 and performed DEER experiments (Fig. 3b, c and Supplementary Fig. 7a, b). For natively purified AncCDT-3/P188, the DEER distance distributions showed a maximum that corresponded to a Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance of ~5.2 nm (Fig. 3b and Supplementary Fig. 7a). Likewise, AncCDT-5 displayed the most prominent distance-distribution peak at ~5.4 nm (Fig. 3c and Supplementary Fig. 7b). Similar results were obtained for the refolded proteins (Supplementary Fig. 7a, b), where the observed shifts are within experimental error. Although the confidence ranges identify clear peak maxima, we also calculated mean distance distributions (caption of Supplementary Fig. 7) to further assess the reliability of these peak positions due to the limited evolution time with respect to the long distance observed. This resulted in shifts of at most about 0.25 nm.
We previously solved a crystal structure of AncCDT-3/L188 and found a conformation analogous to the wide-open conformation observed in the MD simulation of AncCDT-1 (PDB 5JOS)40. In this structure, the Q68-R138 Cα–Cα distance is 4.2 nm (Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance: ~5.3 nm). In triplicate 500 ns MD simulations initiated from the open AncCDT-3/L188 and AncCDT-3/P188 structures (after modelling the L188P mutation), the protein did not sample the closed state at all across the combined 1.5 μs of simulation time and the wide-open state was the major conformation (Fig. 4b), exhibiting a Cα–Cα distance range of 4.0–4.8 nm (Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance range: 5.0–6.3 nm).
Unlike the wide-open crystal structure of AncCDT-3/L188, the 1.49 Å crystal structure of AncCDT-5 determined in this work adopts the closed conformation (a HEPES molecule is bound in the active site), with a Q68-R138 Cα–Cα distance of 2.8 nm (Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance: 3.1 nm). Beginning from this closed state, we again performed triplicate 500 ns MD simulations after removing the HEPES molecule. The simulations predict that the protein rapidly adopts a wide-open conformation, with a Q68-R138 Cα–Cα distance range of 3.6–4.2 nm (Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance range: 4.5–5.4 nm) that is analogous to the wide-open conformation seen in the MD simulations of AncCDT-1, the crystal structure of the L-arginine-binding protein from T. maritima, and the crystal structure of AncCDT-3 (Fig. 4c). An intermediate state, analogous to the open crystal structure of unliganded AncCDT-1 was also briefly sampled, which corresponded to a Q68-R138 Cα–Cα distance range of 3.0–3.4 nm (Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance range: 3.4–4.2 nm). The combination of the DEER, crystallographic and MD data for the experiments performed on AncCDT-3 and AncCDT-5 suggest that both proteins predominantly access a wide-open state in solution. Smaller peaks in the distance distribution could correspond to minor fractions of intermediate states but are too small to be unambiguous.
PaCDT
We next aimed to probe the open/closed dynamics of PaCDT. SEC-MALS experiments confirmed that PaCDT is primarily homotrimeric in solution40, with a small population (<5%) of higher-order or aggregated species (Supplementary Fig. 2d), which complicates the measurement of intra-monomer distances by DEER experiments. To confirm the existence of the tagged trimer, we first measured samples with propargyl-DO3A-Gd(III) tags at single AzF residues of each PaCDT monomer, at either the large domain (position 68) or the small domain (position 139). The maxima of the DEER distance distributions measured were consistent with those expected for the trimeric structure observed by X-ray crystallography (3.5 nm vs. 3.3 nm for proteins tagged at position 68, 5.4 nm vs. 4.6 nm for samples tagged at position 139; Supplementary Fig. 8a, b). This indicated that the trimeric structure was preserved under the conditions of the DEER experiments, including sample preparation and freezing. When we attempted to measure the open/closed distribution via labelling at sites on both the large and small domain (68 and 139, respectively) the observed Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance distribution was very broad as was expected due to multiple inter-chain Gd(III)–Gd(III) distances in a trimer (Supplementary Fig. 8c). In order to extract the inter-domain distance from a single PaCDT monomer, a protein sample labelled at sites 68 and 139 was diluted tenfold with unlabelled protein and allowed to equilibrate at room temperature, with the aim of obtaining a mixture in which there would be a ~24%, 3% and 0.1% chance of encountering a trimer consisting of 1, 2 or 3 tagged monomers, respectively. DEER experiments on samples prepared in this way yielded a significantly narrower peak that indicated 3.5 nm was the predominant Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance (Fig. 3d and Supplementary Fig. 8d).
We again used protein crystallography and MD simulation to identify stable conformations of PaCDT. There are three crystal structures, one with HEPES bound at the active site (Structural Genomics Project, PDB 3KBR) and two with acetate bound at the active site40. The highest resolution acetate-bound structure (PDB 5HPQ) and the HEPES-bound structure (PDB 3KBR) display Q68-A139 Cα–Cα distances of 2.5 nm (Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance: ~3.5 nm). A MD simulation initiated from the trimeric X-ray crystal structure of acetate-PaCDT (PDB 5HPQ), with acetate removed, indicated that the monomers can sample both closed (Cα–Cα distance range of 2.5–3.0 nm; equivalent to a Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance range of ~3.5–3.9 nm) and open (Cα–Cα distance range of 3.2–3.8 nm; equivalent to a Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance range of ~4.0–4.5 nm) conformations, but there was no evidence of a wide-open conformation (Fig. 4d). The Gd(III)–Gd(III) distances predicted for the closed and open states notably fall either side of the broad peak centred at 3.9 nm. This could be consistent with a broad distribution of rapidly interconverting open and closed states that have been snap-frozen, in contrast with the AncCDT-1 DEER analysis, which displayed two distinct peaks corresponding to similar distances.
All three crystal structures of PaCDT display closed conformations, which leave limited access to the active site. To allow the exchange of substrate and product, the enzyme must also populate open conformations, which are likely related to those obtained in the MD simulations. Interestingly, however, the wide-open conformation, which appears in MD simulations of AncCDT-1, AncCDT-3 and AncCDT-5, was not significantly sampled. This is again consistent with the DEER measurements, where the prominent peaks at ~5.4 nm in AncCDT-3 and AncCDT-5 were absent for PaCDT. Altogether, the combined use of DEER, crystallography and MD simulations suggests that the wide-open conformation observed in the ancestral reconstructions of CDT (computationally observed in all variants and empirically observed in AncCDT-3, AncCDT-5 and orthologs of AncCDT-1) has been largely eliminated from the conformational landscape of the extant PaCDT. This provides a molecular explanation for the observed change in KM between AncCDT-5 and PaCDT; despite their identical substrate-binding sites when closed, the open ligand-binding state of PaCDT likely has a higher affinity for the substrate as it is much closer to the conformation of the Michaelis complex than the wide-open state that is predominantly populated in AncCDT-3 and AncCDT-5.
Structural basis for the increased dehydratase activity of PaCDT
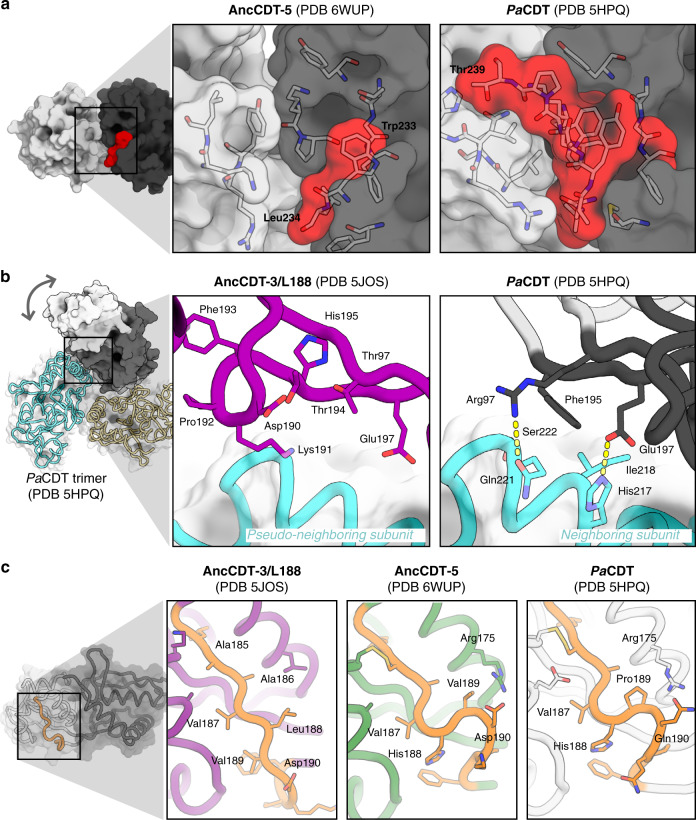
Having established that the conformational sampling of PaCDT is different from AncCDT-5, we compared the structures of AncCDT-5 and PaCDT to ascertain the molecular basis for this change. Structural comparison between the two proteins revealed three regions with substantial differences (unlike the substrate-binding site) that could collectively stabilise the closed state and/or destabilise the wide-open state. First, in comparison to AncCDT-5, which terminates at Lys235 (although it is not present in clear electron density), PaCDT has an additional nine amino acids at the C-terminus (RWPTAHGKL), of which the first four and six residues produce clear electron density in crystal structures of PaCDT (PDB 5HPQ and 6BQE, respectively). As shown in Fig. 5a, these amino acids interact extensively with both the small and large domains, substantially increasing the number of van der Waals and hydrogen bond interactions between the two domains in the closed and open, but not wide-open, conformations.
Fig. 5. Structural basis for the change in conformational sampling.
a Comparison of the crystal structures of AncCDT-5 (left) and PaCDT (5HPQ, right) highlight how the C-terminal extension (residues beyond 232 are highlighted in red) in PaCDT facilitates additional interactions between the small (white) and large (grey) domains. b PaCDT is a trimer in solution, and analysis of the crystal structures of PaCDT (e.g., 5HPQ, shown here) reveals several interactions between the hinge region of chain A with the large domain of chain B that are likely to prevent the wide-open conformation from being sampled. These include packing of Phe195 against the neighbouring subunit, and polar interactions between neighbouring residues. Overlay of the crystal structure of AncCDT-3/L188 (purple, PDB 5JOS) further highlights how the wide-open state is likely to be incompatible with the trimeric arrangement of PaCDT. c The flexibility of the hinge region is known to control the open/closed dynamics of SBPs. Sequence and structural comparison of these regions in AncCDT-3/L188 (purple, PDB 5JOS), AncCDT-5 (green, PDB 6WUP) and PaCDT (white, PDB 5HPQ) highlight that this is an intrinsically flexible region, which is likely affected by mutations.
Second, one of the most substantial structural differences between AncCDT-5 and PaCDT is the oligomerization of PaCDT, which forms a trimer (Fig. 5b). A number of key residues that contribute to the inter-subunit interfaces in the crystal structures of PaCDT are not found in AncCDT-5, explaining this difference in oligomeric states. For example, the substitutions T97R, M221Q and L217H introduce specific electrostatic interactions between chains in PaCDT, while H195F, H218I and P83L appear to improve packing between the subunits. However, oligomerization is a complex process and remote and unpredictable mutations can also have a substantial influence on oligomeric states52. Accordingly, we cannot exclude the possibility that additional mutations remote from the interface also play a role.
In the resulting trimeric form of PaCDT, the small domain remains free to move, allowing fluctuation between the closed and open states. However, there are inter-subunit contacts at the hinge region that appear to preclude some of the conformational changes expected in the wide-open state. Specifically, the crystal structure of the wide-open conformation of AncCDT-3 shows that the hinge region with His195 at the centre is fully solvent-exposed and extended. The equivalent region of PaCDT, however, is in a retracted conformation, with Phe195 (chain A; the equivalent position to His195 in AncCDT-3) being stabilised in a buried hydrophobic pocket formed by Ile218 (chain A) and the non-polar region of Ser222 (chain A), as well as the non-polar regions of two hydrogen-bonded pairs, Arg97 (chain A):Gln221 (chain B) and Glu197 (chain A):His217 (chain B). The positioning of these residues and interactions with the neighbouring subunit would likely stabilise PaCDT in the closed and open conformations, while limiting the sampling of wide-open states.
Finally, for the proteins to adopt the wide-open state, the region between Val187 and Pro191 must undergo a conformational change, from the tightly kinked conformation seen in the closed structures of AncCDT-5 and PaCDT (PDB 5HPQ, 6BQE; it is in an altered conformation due to crystal packing interactions in 3KBR), to an extended conformation seen in the crystal structure of the wide-open conformation of AncCDT-3 (Fig. 5c). In AncCDT-3/5, the region between Val187 and Pro191 is relatively flexible, consisting of polar and relatively small hydrophobic residues (Leu/Val/Glu in AncCDT-3; His/Val/Glu in AncCDT-5). In contrast, in PaCDT, the central residue in the kink is mutated to proline, and the neighbouring glutamine forms a hydrogen bond to Arg186, stabilising the kinked structure. Further support for the hypothesis that this region is important in conformational sampling and dehydratase activity can be found in the observation that (i) the P188L mutation in AncCDT-3 causes a large decrease in KM40, (ii) it was observed to be a mutational hotspot during the directed evolution of ancestral CDTs for increased dehydratase activity40 and (iii) this region has been recognised to be important for dynamics and affinity in other SBPs such as MBP21,30.
The combination of these three structural effects is likely sufficient to substantially change the relative conformational free energy of the closed, open and wide-open states, consistent with the DEER and MD results. Interestingly, none of the structural changes observed between AncCDT-3 and PaCDT preclude PaCDT from adopting the open conformation, but essentially prevent it from adopting the wide-open conformation. Given the large number of changes between AncCDT-5 and PaCDT, it is impossible to ascribe the difference in populations of open and wide-open conformations to a single mutation or structural rearrangement. Indeed, recent work has highlighted the gradual nature by which protein conformational sampling can change, and the overlapping and often redundant effects of mutations49.
Discussion
SBPs have become a model system for understanding the role of rigid-body motions in determining ligand and substrate-binding affinity, specificity and kinetics. Early crystallographic studies suggested that SBPs act as simple binary switches, adopting a closed conformation when in complex with ligands and an open conformation in the ligand-free state4. More recently, however, NMR, FRET and MD studies have probed the intrinsic dynamics of SBPs, showing that they can adopt closed and semi-closed states in the absence of ligands20–29, and have provided evidence that the extent of the open-closed dynamics evolves to support specific binding properties and function. Indeed, altering the open-closed dynamics of SBPs is now also being used as an additional parameter for engineering new binding functions into SBPs21 and the development of novel SBP-based biosensors53. Such efforts, however, are complicated by the fact that very subtle changes to protein motion can alter SBP function and the structural basis for changes in these open-closed dynamics are poorly understood. Here, we have expanded on this work, demonstrating that SBPs of this protein fold can access three relatively well-defined conformational substates, including a wide-open state for which the possible physiological role must still be determined. In view of the ease with which it is sampled in MD simulations and unambiguously observed by DEER experimentally in two of the native proteins we studied (AncCDT-3 and AncCDT-5), as well as the apo-state of the L-arginine-binding protein from T. maritima38, it is unlikely to be an artefact. The apparently facile sampling of both closed and wide-open states could explain why FRET experiments, which have been conducted with fluorescent tags attached to either domain, sometimes report smaller changes in signal upon ligand binding than would be expected if a single open conformation was fully populated in the apo-protein54,55.
We previously suggested that mutations accumulated during evolution most likely increased the dehydratase activity of PaCDT by shifting the conformational equilibrium away from the catalytically unproductive open state to the catalytically competent closed state40. Crystal structures and MD simulations provided some preliminary evidence that this is the case, but now we have strong quantitative evidence in solution. First, the crystal structure of AncCDT-5 revealed identical active/binding sites of AncCDT-5 and PaCDT, demonstrating that amino acid substitutions remote from the active site can have very large effects on activity via mechanisms other than controlling the structure of the active site. Second, the dramatic shift in the open/closed equilibrium of the proteins is the main change along the evolutionary trajectory. These results show that the wide-open state, which is the lowest-energy state in AncCDT-3 and AncCDT-5 and is unlikely to play any catalytic role owing to low affinity for substrate owing to the spatial separation between the binding site/catalytic residues, appears to be depopulated in the final evolutionary step between AncCDT-5 and PaCDT. Third, the extant and efficient PaCDT appears to exist in a broad distribution between a closed state optimised for catalysis of the chemical step in the reaction and a moderately open state that retains the shape of the binding pocket but opens a pathway for substrate/product diffusion. The structural analysis provides a molecular explanation for this shift in conformational sampling, with a number of structural changes stabilising the open/closed states at the expense of the wide-open state. Interestingly, this seems to have occurred at least in part through oligomerization, suggesting that evolution can favour oligomerization both for stability and activity52.
The role of the wide-open state along the evolutionary trajectory from AncCDT-1 to PaCDT is more difficult to interpret. We observe this state in crystal structures of extant relatives of AncCDT-1, it is stable for several hundred ns in MD simulations of AncCDT-1 and (because of the overlap of the DEER signals between the wide-open and open states) it is also consistent with the DEER data. However, it is clear that there was a shift towards the wide-open state after AncCDT-1 (as seen in AncCDT-3 and AncCDT-5). In our previous work40, we were unable to identify a natural ligand for the non-enzymatic binding protein AncCDT-2 (which predates AncCDT-3 and AncCDT-5); although it had lost its ancestral arginine-binding function, it (and its descendants such as Pu1068 from the aquatic bacterium Pelagibacter ubique) retain the genomic organisation and biophysical properties of solute-binding proteins. Thus, we speculate that the shift towards the wide-open state in the intermediate ancestors could have resulted from the selective pressure for the (still unknown) solute-binding function that preceded the evolution of CDT activity.
The findings from this work add to growing evidence that the modification of protein dynamics often plays an important role in the evolution of new protein function. While the current work provides a unique example for pronounced, historical conformational changes between a non-catalytic ancestral protein and an efficient enzyme, our findings mirror those of other work that highlight how catalytic activity can be enhanced along evolutionary trajectories through the accumulation of remote substitutions that alter conformational dynamics49,56–60. Modified protein dynamics are not mutually exclusive with the well-established concept of evolution of protein function via specific changes in the shape or electrostatic character of active/binding sites, but serve as a complementary mechanism that may often overlap with these other more easily observable changes.
In addition, this work expands the scope of the DEER approach15,61–65 for use in this context by using Gd(III) spin labels; it is the first time that the propargyl-DO3A-Gd(III)/DEER approach has been used to study rigid-body protein dynamics and it demonstrates the excellent performance of the propargyl-DO3A-Gd(III) tag. The tag is independent of cysteine residues as it can be ligated to AzF residues and the small size, lack of net charge and hydrophilic character of the DO3A-Gd(III) complex disfavours specific interactions with the protein surface, thus increasing the reliability of computational predictions of the Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance distributions obtained with this tag41. This study highlights its efficiency (the DEER measurements requiring only nanogram amounts of protein) in studying the protein dynamics of a series of states along an evolutionary trajectory and how it afforded distribution widths that were sufficiently narrow to observe the co-existence of open and closed protein conformations that differ by only about 1 nm, to show the presence of two conformations simultaneously sampled in solution and to detect ligand-induced conformational changes.
Considering that DEER data are recorded of frozen solutions, it cannot be ruled out that conformational equilibria established at room temperature change during the snap-freezing of the samples. In principle, the freezing point of 20% deuterated glycerol solutions is at most 10° below 0 °C66, but the actual temperature at which the dynamics stopped is difficult to determine. As all samples were frozen in the same way, however, the conformational differences observed between the samples refer to similar conditions. It is thus significant that the energy landscape of the extant enzyme PaCDT led to the freezing out of a continuous range of conformations, whereas that of the amino acid-binding protein AncCDT-1 funnelled the protein into two clearly distinct conformations. Importantly, the distances measured by DEER here are in good agreement with distances predicted from the crystal structures and states obtained from MD simulations.
In this work, we have studied the structural dynamics of a series of states along an evolutionary trajectory from an ancestral L-arginine solute-binding protein (AncCDT-1) to an extant dehydratase (PaCDT). The challenge of accurately defining the conformational landscape of a protein is substantial: virtually all approaches have serious limitations or are so demanding that they are not practical for studying more than a single protein. Here, by following an integrated structural biology approach involving the combined use of the three methods, the shortcomings of each approach (crystal packing forces in single crystals, imperfect force fields in MD simulations, potential overlap in the signals from different states for DEER measurements, etc.) could be compensated for. We compared crystal structures of AncCDT-3, a new structure of AncCDT-5, and PaCDT, which revealed that second-shell residues alter the active site configuration between AncCDT-3 and AncCDT-5, but that AncCDT-5 and PaCDT display large differences in catalytic activity despite identical active site configurations. Using a propargyl-DO3A-Gd(III) tag and W-band DEER distance measurements, we were able to experimentally assess the distribution of different conformational substates in frozen solutions along this evolutionary trajectory, with reference to structures obtained through protein crystallography and MD simulations. These data provide new insight into how proteins can evolve new functions: while the correct active site configuration must be established, this study shows that the ability of an enzyme to adopt a range of conformational states that are tailored to its catalytic role is equally important. This result contributes to the growing body of literature that suggests molecular evolution is a relatively smooth process, whereby conformational substates that are not productive are gradually depopulated while beneficial substates are enriched.
Methods
Protein numbering convention
Residues of all proteins are referred to using the equivalent position in the reconstructed ancestral sequences (i.e., not including N-terminal tags), as described in the previous work40 (see sequence alignment, Supplementary Fig. 9). As a consequence, residue numbers mentioned in this work differ from the residue numbers in the published PDB files of 3KBR (shift of −25), 5HPQ (−11), 6BQE (−11), 5T0W (−11), 5TUJ (−11), 5JOS (−11) and 6WUP (−11).
Materials
The genes encoding SeLAOBP (UniProt: P09551), AncCDT-1, AncCDT-3/P188, AncCDT-3/L188, AncCDT-5 and PaCDT (UniProt: Q01269, residues 26–268) in pDOTS7 vectors (a derivative of pQE-28L, Qiagen) were obtained from previous work32,40 (DNA sequences supplied in Source Data file). The ΔpheA strain of E. coli K-12 from the Keio collection (strain JW2580-1) was obtained from the Coli Genetic Stock Center (Yale University, CT).
Prephenate dehydratase assay
Protein expression and purification, prephenate preparation and spectrophotometric assays were performed as described previously40.
To prepare sodium prephenate, 40 mM barium chorismate (Sigma, 60–80% purity) was mixed with an equimolar amount of 1 M Na2SO4. An equal volume of 100 mM Na2HPO4 (pH 8.0) was added to the mixture, the BaSO4 precipitate was removed, and the resulting sodium chorismite solution was heated at 70 °C for 1 h to yield sodium prephenate. The concentration of prephenate was measured by quantitative conversion of prephenate to phenylpyruvate under acidic conditions (0.5 M HCl, 15 min, 25 °C) and spectrophotometric determination of phenylpyruvate concentration by measuring absorbance at 320 nm, as described previously61.
Proteins were expressed in ΔpheA cells (from pDOTS7 plasmids) to exclude the possibility of contamination with endogenous prephenate dehydratase. Cells were grown in Terrific Broth (TB) media at 37 °C to OD600 0.8, induced with 0.5 mM IPTG and incubated for an additional 12 h at 30 °C. Cells were resuspended in equilibration buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, 500 mM NaCl, 20 mM imidazole, pH 7.4), lysed by sonication and fractionated by ultracentrifugation (24,200 × g for 1 h at 4 °C). The supernatant was filtered through a 0.45-µm filter and loaded onto a 5 mL HisTrap HP column (GE Healthcare, USA) equilibrated with equilibration buffer. The column was washed with 50 mL of equilibration buffer and 25 mL of wash buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, 500 mM NaCl, 44 mM imidazole, pH 7.4), and the target protein was eluted in 25 mL of elution buffer (50 mM Na2HPO4, 500 mM NaCl, 500 mM imidazole, pH 7.4). Proteins were concentrated using a centrifuge filter (Amicon Ultra-15 filter unit with 10 kDa cut-off) and purified by size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) on a HiLoad Superdex 75 16/600 column (GE Healthcare, USA), eluting in SEC buffer (20 mM Na2HPO4, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4). Protein purity was confirmed by SDS-PAGE, and protein concentrations were measured spectrophotometrically using predicted molar absorption coefficients62.
Prephenate dehydratase activity of each protein was determined by end-point spectrophotometric measurement of phenylpyruvate formation, as described previously61. Protein solutions were prepared in 20 mM Na2HPO4, 150 mM NaCl (pH 7.4), and prephenate solutions were prepared in 50 mM Na2HPO4 (pH 8.0). After equilibration at room temperature (20–25 °C) for 5 min, the reaction was initiated by mixing equal volumes of protein and substrate solutions. Aliquots (50 µL or 100 µL) were regularly removed from the reaction mixture and quenched by the addition of an equal volume of 2 M NaOH. Absorbance at 320 nm was measured using an Epoch Microplate Spectrophotometer (BioTek), and phenylpyruvate concentrations were determined assuming a molar extinction coefficient of 17,500 M−1 cm−1. Reaction times and enzyme concentrations were adjusted to ensure that <20% conversion of prephenate to phenylpyruvate. The rate of non-enzymatic turnover was subtracted from the observed rate of enzyme-catalysed turnover. GraphPad Prism (8.3.1) was used for fitting a Michaelis–Menten model to the data.
Measurement of oligomeric state
IMAC-purified, His6-tagged AncCDT-1, AncCDT-3/P188, AncCDT-5 and PaCDT (expressed in ΔpheA cells) were transferred into size-exclusion chromatography multi-angle light scattering (SEC-MALS) buffer (20 mM Na2HPO4, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4) and concentrated using an Amicon centrifuge filter (10 kDa molecular weight cut-off, MWCO). Samples (100 μL) of each protein were loaded at 10 mg mL−1 onto a pre-equilibrated Superdex 200 10/300 GL size-exclusion column (GE Healthcare) attached to multi-angle light scattering (DAWN HELEOS 8; Wyatt Technologies) and refractive index detection (Optilab rEX; Wyatt Technologies) units. A flow rate of 0.5 mL min−1 was used. The multi-angle detectors were normalised using monomeric bovine serum albumin (Sigma, A1900). A dn/dc value of 0.186 g−1 was used for each sample. The data were processed using ASTRA 5..3.4 (Wyatt Technologies). Data were collected from a single experiment (n = 1).
Protein sample preparation for DEER experiments
For DEER experiments, genes encoding each protein were cloned into pETMCSIII67 and expressed with an N-terminal His6-tag followed by a TEV cleavage site. In order to minimise tag side-chain dynamics, the crystal structures of the native proteins were inspected in PyMOL (The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.0 Schrödinger, LLC.) to select mutation sites where the sidechains of AzF residues were predicted to populate single χ1-angle conformations. Amber stop codons were introduced at these positions (Supplementary Table 3) by a modified QuikChange protocol using mutant T4 DNA polymerase68. Primer sequences are provided in Supplementary Table 4.
All proteins for DEER experiments were expressed in RF1-free E. coli strain B-95.ΔA cells69 co-transformed with a plasmid for the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase/tRNA pair70 for the incorporation of AzF (Chem-Impex, USA). To minimise the amount of AzF required (provided at 1 mM), 1 L of cell culture grown in LB medium was concentrated to 300 mL (by centrifugation and resuspension) before induction with 1 mM IPTG. Expression was conducted at 37 °C and limited to 3 h after IPTG induction to minimise the chemical reduction of AzF. Cells were harvested by centrifugation at 5000 × g for 15 min, and lysed by passing two times through a French Press (SLM Aminco, USA) at 830 bars. The lysate was centrifuged at 13,000 × g for 30 min, and the filtered supernatant was loaded onto a 5-mL Ni-NTA HisTrap HP column (GE Healthcare, USA) equilibrated with binding buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 5% w/v glycerol). The protein was eluted using elution buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 5% w/v glycerol, 300 mM imidazole) and fractions were analysed by 12% SDS-PAGE.
To liberate and remove ligand molecules that may have bound during protein expression, the preparation of the second set of protein samples included a denaturation and on-column refolding step. After cell lysis, guanidinium hydrochloride was added to the supernatant to a final concentration of 6 M. The filtered solution was then loaded onto a Ni-NTA column and washed with binding buffer containing 8 M urea to remove any bound ligand. Refolding was achieved using a gradient of binding buffer with decreasing amounts of urea overnight at a flow rate of 0.5 mL min−1. Refolded protein was eluted as described above.
His6-tags were removed by digestion with His6-tagged TEV protease71 in 1:100 molar ratio overnight at 4 °C in TEV cleavage buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 300 mM NaCl and 1 mM β-mercaptoethanol). Finally, the cleaved His6-tag and TEV protease were removed by passing through the Ni-NTA column (pre-equilibrated with binding buffer) prior to ligation with the propargyl-DO3A tag loaded with Gd(III).
Click reactions with the propargyl-DO3A-Gd(III) tag were performed overnight at room temperature as described previously (Supplementary Fig. 3a)51 and samples were exchanged into EPR buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 in D2O) using a Amicon Ultra-15 filter unit (10 kDa MWCO). The tagging yields were assessed by mass spectrometry, using an Elite Hybrid Ion Trap-Orbitrap mass spectrometer coupled with an UltiMate S4 3000 UHPLC (Thermo Scientific, USA).
DEER measurements were done on samples containing 100 μM protein and 20% w/v glycerol-d8 in D2O. A 1.5-fold molar excess of L-arginine was added to one sample of refolded AncCDT-1 and one sample of SeLAOBP prior to the DEER measurement. Samples were flash-frozen by quick insertion of the sample holder into the cold (10 K) magnet bore.
DEER measurements
DEER measurements were conducted at 10 K on a home-built pulse EPR spectrometer operating at W-band (94.9 GHz)72,73. For the doubly labelled AncCDT-1 samples, a variant of the standard four-pulse DEER sequence (π/2(νobs) – τ1– π(νobs) – (τ1 + t) – π(Δνpump) – (τ2 – t) – π(νobs) – τ2 – echo) was used74,75. The DEER echo was observed at 94.9 GHz with π/2 and π pulses of 15 ns and 30 ns, respectively, and the field was positioned at the peak of the Gd(III) spectrum. The pump pulse was replaced by two consecutive chirp pulses produced by an arbitrary waveform generator74–76 which were positioned on both sides of the centre of the Gd(III) spectrum with frequency ranges of 94.5–94.8 GHz and 95–95.3 GHz, respectively. The length of each chirp pulse was 96 ns. The cavity was tuned at 94.9 GHz with a maximal microwave amplitude, ω1/2π, of ~30 MHz. Other parameters used were τ1 = 350 ns, a repetition rate of 0.8 ms, and τ2 typically ranging between 4 and 7 μs for samples with shorter and longer distances, respectively. The delay t was varied during the experiments. For the rest of the samples, a reverse DEER (rDEER) sequence (π/2(νobs) – τ1 – π(νobs) – (τ1 − t) – π(νpump) – (τ2 + t) – π(νobs) – τ2 – echo) was used to reduce artefacts74. The chirp pump pulses and the positioning of the observed and the pump pulses were unchanged. In this implementation, both τ2 and τ1 typically ranged between 4 and 7 μs for shorter and longer distances, respectively.
The data were analysed using DeerAnalysis77, and distance distributions were obtained using Tikhonov regularisation. The regularisation parameter was chosen either by the L-curve criterion or by visual inspection in order to obtain reasonable fits. Estimation of uncertainties in distance distributions due to background correction and noise were obtained using the validation option in DeerAnalysis77.
Crystallisation of AncCDT-5 and structure determination
A solution of TEV-cleaved AncCDT-5 (expressed in BL21(DE3) cells and purified by IMAC as described above) was further purified by SEC using a HiLoad 16/600 Superdex 75 pg column (GE Healthcare, USA) in 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 20 mM NaCl, and was concentrated to 30 mg mL−1 using an Amicon Ultra-15 filter unit (10 kDa MWCO). The protein was crystallised using the vapour diffusion method at 18 °C. Crystallisation screens were set up using the PACT premier HT-96 C10 screen from Molecular Dimensions (Newmarket, USA) with drops containing 200 nL reservoir solution and 200 nL AncCDT-5 solution. AncCDT-5 crystals formed in 28 days in 20% w/v PEG 6000, 0.2 M MgCl2, 0.1 M HEPES, pH 7.0.
Crystals were cryoprotected (30% w/v PEG 6000, 0.2 M MgCl2, 0.1 M HEPES pH 7.0) and frozen in liquid nitrogen. Data were collected at 100 K on the MX2 beamline of the Australian Synchrotron. The data were indexed and integrated in XDS78 and scaled in AIMLESS79. The structure was solved by molecular replacement in Phaser80 using the two domains of PaCDT as search models (PDB 3KBR small domain = residues 122–223; large domain = residues 27–121 and 224–258). The structure was refined by real-space refinement in Coot81 and using REFMAC82 and phenix.refine83. Data collection and refinement statistics are given in Supplementary Table 1. Residues in the AncCDT-5 structure were numbered according to the equivalent positions in AncCDT-1 (PDB 5TUJ)40 and the coordinates deposited in the Worldwide Protein Data Bank (PDB 6WUP).
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations
500 ns simulations were performed in Desmond84 (in Schrödinger 2019-11) using the OPLS3e force field85. These simulations were initiated from the PaCDT–acetate trimer (PDB 5HPQ, residues 13–250 in PDB, n = 1), unliganded AncCDT-1 (PDB 5T0W, chain A, residues 14–246, n = 3), AncCDT-3/L188 (PDB 5JOS, residues 12–247, n = 3), AncCDT-3/P188 (n = 3) and AncCDT-5 (PDB 6WUP, residues 13–245, n = 3) structures, with all small molecules removed. The AncCDT-3/P188 structure was obtained by making the L188P mutation and local minimisation in Maestro (Schrödinger Release 2019-1: Maestro, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2019). Desmond was used to add N-terminal acetyl caps and C-terminal amide caps to each structure and for energy minimisation of the protein structures. Each protein was solvated in an orthorhombic box (15 Å buffer periodic boundary) with SPC water molecules. The smallest number of counter ions (Na+ or Cl−) needed to neutralise the net charge of each system were added. Energy minimisation was achieved using a hybrid method of the steepest descent algorithm and the limited-memory Broyden–Fletcher–Goldfarb–Shanno algorithm (maximum of 2000 iterations and a convergence threshold of 1 kcal mol−1 Å−1). The system was relaxed using the default relaxation procedure in Desmond. For production MD simulations of the NPT ensemble, the temperature was maintained at 300 K using a Nosé–Hoover thermostat (relaxation time = 1.0 ps) and the pressure was maintained at 1.01 bar (relaxation time = 2.0 ps) using a Martyna–Tobias–Klein barostat. Otherwise, default Desmond options were used. Following relaxation of the system, each simulation was run for 500 ns. Distances between the α-carbons of the tagged residues and the radii of gyration were calculated using the ProDy package on snapshots sampled every 0.1 ns86. In addition, representative snapshots (with a range of Cα–Cα distances) corresponding to the closed, open and wide-open states (if sampled) were selected for modelling of Gd(III)–Gd(III) distances. Allocation of states (closed/open/wide-open) was done based on Cα–Cα measurements. For AncCDT-1, conformations with Cα–Cα distances between ~3.3 and 3.7 nm could be separated into the open and wide-open conformations by principal component analysis. Plots of Cα–Cα distances over the course of each simulation are provided in Supplementary Fig. 10.
Modelling Gd(III)–Gd(III) distances
To calculate predicted Gd(III)–Gd(III) distances of different conformations, propargyl-DO3A-Gd(III) tags were modelled onto the crystal structures of AncCDT-1 (PDB 5T0W, 5TUJ), AncCDT-3/L188 (PDB 5JOS), AncCDT-5 (PDB 6WUP), PaCDT (PDB 3KBR, 5HPQ) and selected MD snapshots. To do this, the mutation tool in PyMOL was used to identify the side-chain dihedral angles χ1 and χ2 of a phenylalanine residue that produced the least amount of steric clashes with the rest of the protein; these angles were used when modelling the tag. The angles χ9 and χ10 (Supplementary Fig. 3b) were fixed to −140° and 70°, respectively, to allow coordination of the metal ion by the nearest nitrogen of the triazole ring. The angle χ6 was set to 180°. As in previous work with a closely related cyclen tag51, setting χ6 to 180° (Supplementary Fig. 3c) yielded a better correlation between experimental and back-calculated Gd(III)–Gd(III) distances compared with setting χ6 to 0° (Supplementary Fig. 3d). Adding additional flexibility to the model by allowing rotation around χ9 (any angle) and χ10 (−60°, 60° or 180°) increased the width of modelled distance distributions but did not significantly change the positions of the peaks within these distributions, which still correlated well with experimental measurements (Supplementary Fig. 3e) and the distances predicted using the single conformation approach mentioned above.
Reporting summary
Further information on experimental design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this paper.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
J.A.K. acknowledges financial support from an Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship. B.E.C. acknowledges financial support from a Rod Rickards PhD Scholarship. Funding by the Australian Research Council, including a Laureate Fellowship to G.O., is gratefully acknowledged. D.G. acknowledges the support of the Minerva Foundation, and this research was made possible in part by the historic generosity of the Harold Perlman Family (D.G.). D.G. holds the Erich Klieger Professorial Chair in Chemical Physics. We thank Yasmin Ben-Ishay for her help with sample preparation and DEER measurements.
Source data
Author contributions
J.A.K. performed prephenate dehydratase assays (including protein purification), ran SEC-MALS experiments, processed crystallographic data, solved the structure of AncCDT-5 and performed molecular dynamics simulations. M.C.M. selected tagging sites, performed cloning of genes into pETMCSIII, expressed and purified protein for crystallography and DEER experiments, tagged these variants, modelled Gd(III)–Gd(III) distances and crystallised AncCDT-5. A.F. performed DEER measurements on the samples and analysed the DEER data. B.E.C. performed essential preliminary work and guided the direction of this project. L.A.A. prepared the propargyl-DO3A tags. J.A.K., M.C.M, A.F., D.G., G.O. and C.J.J. analysed the data and wrote the paper. J.A.K., M.C.M. & A.F. produced the figures. D.G., G.O. and C.J.J. supervised the project. All authors reviewed the paper.
Data availability
The atomic coordinates and structure factors for AncCDT-5 (PDB 6WUP) have been deposited in the Worldwide Protein Data Bank (http://wwpdb.org/). Any other relevant data are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request. Source data are provided with this paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Peer review information Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Joe A. Kaczmarski, Mithun C. Mahawaththa, Akiva Feintuch
These authors jointly supervised this work: Daniella Goldfarb, Gottfried Otting, Colin J. Jackson.
Contributor Information
Daniella Goldfarb, Email: daniella.goldfarb@weizmann.ac.il.
Gottfried Otting, Email: gottfried.otting@anu.edu.au.
Colin J. Jackson, Email: colin.jackson@anu.edu.au
Supplementary information
Supplementary information is available for this paper at 10.1038/s41467-020-19695-9.
References
- 1.Davidson AL, Dassa E, Orelle C, Chen J. Structure, function, and evolution of bacterial ATP-binding cassette systems. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2008;72:317–364. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00031-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Berntsson RPA, Smits SHJ, Schmitt L, Slotboom DJ, Poolman B. A structural classification of substrate-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 2010;584:2606–2617. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.04.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Scheepers GH, Lycklama a Nijeholt JA, Poolman B. An updated structural classification of substrate-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 2016;590:4393–4401. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tam R, Saier MH. Structural, functional, and evolutionary relationships among extracellular solute-binding receptors of bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 1993;57:320–346. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.57.2.320-346.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.De Boer M, et al. Conformational and dynamic plasticity in substrate-binding proteins underlies selective transport in ABC importers. Elife. 2019;8:1–28. doi: 10.7554/eLife.44652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Quiocho FA, Ledvina PS. Atomic structure and specificity of bacterial periplasmic receptors for active transport and chemotaxis: variation of common themes. Mol. Microbiol. 1996;20:17–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1996.tb02484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mulligan C, et al. The substrate-binding protein imposes directionality on an electrochemical sodium gradient-driven TRAP transporter. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:1778–1783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809979106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Loeffler HH, Kitao A. Collective dynamics of periplasmic glutamine binding protein upon domain closure. Biophys. J. 2009;97:2541–2549. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.08.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chu BCH, De Wolf T, Vogel HJ. Role of the two structural domains from the periplasmic Escherichia coli histidine-binding protein HisJ. J. Biol. Chem. 2013;288:31409–31422. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.490441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sooriyaarachchi S, Ubhayasekera W, Park C, Mowbray SL. Conformational changes and ligand recognition of Escherichia coli D-xylose binding protein revealed. J. Mol. Biol. 2010;402:657–668. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.07.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Skrynnikov NR, et al. Orienting domains in proteins using dipolar couplings measured by liquid-state NMR: differences in solution and crystal forms of maltodextrin binding protein loaded with β-cyclodextrin. J. Mol. Biol. 2000;295:1265–1273. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kang CH, et al. Crystal structure of the lysine-, arginine-, ornithine-binding protein (LAO) from Salmonella typhimurium at 2.7-Å resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:23893–23899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Oh BH, et al. Three-dimensional structures of the periplasmic lysine/arginine/ornithine- binding protein with and without a ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:11348–11355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Stockner T, Vogel HJ, Tieleman DP. A salt-bridge motif involved in ligand binding and large-scale domain motions of the maltose-binding protein. Biophys. J. 2005;89:3362–3371. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.069443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Glaenzer J, Peter MF, Thomas GH, Hagelueken G. PELDOR spectroscopy reveals two defined states of a sialic acid TRAP transporter SBP in solution. Biophys. J. 2017;112:109–120. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.12.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Magnusson U, Salopek-Sondi B, Luck LA, Mowbray SL. X-ray structures of the leucine-binding protein illustrate conformational changes and the basis of ligand specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:8747–8752. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M311890200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Magnusson U, et al. Hinge-bending motion of D-allose-binding protein from Escherichia coli. Three open conformations. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:14077–14084. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200514200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lau AY, Roux B. The free energy landscapes governing conformational changes in a glutamate receptor ligand-binding domain. Structure. 2007;15:1203–1214. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2007.07.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Björkman AJ, Mowbray SL. Multiple open forms of ribose-binding protein trace the path of its conformational change. J. Mol. Biol. 1998;279:651–664. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.1785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tang C, Schwieters CD, Clore GM. Open-to-closed transition in apo maltose-binding protein observed by paramagnetic NMR. Nature. 2007;449:1078–1082. doi: 10.1038/nature06232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Seo MH, Park J, Kim E, Hohng S, Kim HS. Protein conformational dynamics dictate the binding affinity for a ligand. Nat. Commun. 2014;5:3724. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Selmke B, et al. Open and closed form of maltose binding protein in its native and molten globule state as studied by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 2018;57:5507–5512. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ortega G, Castaño D, Diercks T, Millet O. Carbohydrate affinity for the glucose-galactose binding protein is regulated by allosteric domain motions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012;134:19869–19876. doi: 10.1021/ja3092938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Flocco MM, Mowbray SL. The 1.9 Å X-ray structure of a closed unliganded form of the periplasmic glucose/galactose receptor from Salmonella typhimurium. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:8931–8936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chu BCH, Chan DI, DeWolf T, Periole X, Vogel HJ. Molecular dynamics simulations reveal that apo-HisJ can sample a closed conformation. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinforma. 2014;82:386–398. doi: 10.1002/prot.24396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.de Boer M, Gouridis G, Muthahari YA, Cordes T. Single-molecule observation of ligand binding and conformational changes in FeuA. Biophys. J. 2019;117:1642–1654. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Feng Y, et al. Conformational dynamics of apo-GlnBP revealed by experimental and computational analysis. Angew. Chem. - Int. Ed. 2016;55:13990–13994. doi: 10.1002/anie.201606613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gouridis G, et al. Conformational dynamics in substrate-binding domains influences transport in the ABC importer GlnPQ. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015;22:57–64. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Oswald C, et al. Crystal structures of the choline/acetylcholine substrate-binding protein ChoX from Sinorhizobium meliloti in the liganded and unliganded-closed states. J. Biol. Chem. 2008;283:32848–32859. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806021200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Marvin JS, Hellinga HW. Manipulation of ligand binding affinity by exploitation of conformational coupling. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001;8:795–798. doi: 10.1038/nsb0901-795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Marvin JS, Hellinga HW. Conversion of a maltose receptor into a zinc biosensor by computational design. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2001;98:4955–4960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091083898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Clifton BE, Jackson CJ. Ancestral protein reconstruction yields insights into adaptive evolution of binding specificity in solute-binding protein. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016;23:236–245. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cho Y, Sharma V, Sacchettini JC. Crystal structure of ATP phosphoribosyltransferase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:8333–8339. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M212124200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kreinbring CA, et al. Structure of a eukaryotic thiaminase I. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:137–142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315882110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Brownlie PD, et al. The three-dimensional structures of mutants of porphobilinogen deaminase: toward an understanding of the structural basis of acute intermittent porphyria. Protein Sci. 1994;3:1644–1650. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560031004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Arai R, et al. Crystal structure of MqnD (TTHA1568), a menaquinone biosynthetic enzyme from Thermus thermophilus HB8. J. Struct. Biol. 2009;168:575–581. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2009.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tam R, Saier MH. A bacterial periplasmic receptor homologue with catalytic activity: cyclohexadienyl dehydratase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is homologous to receptors specific for polar amino acids. Res. Microbiol. 1993;144:165–169. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(93)90041-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ruggiero A, et al. A loose domain swapping organization confers a remarkable stability to the dimeric structure of the arginine binding protein from Thermotoga maritima. PLoS One. 2014;9:e96560. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhao G, Xia T, Fischer R, Jensen R. Cyclohexadienyl dehydratase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: molecular cloning of the gene and characterization of the gene product. J. Biol. Chem. 1992;267:2487–2493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Clifton BE, et al. Evolution of cyclohexadienyl dehydratase from an ancestral solute-binding protein. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018;14:542–547. doi: 10.1038/s41589-018-0043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mahawaththa MC, et al. Small neutral Gd(III) tags for distance measurements in proteins by double electron-electron resonance experiments. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018;20:23535–23545. doi: 10.1039/C8CP03532F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Denysenkov VP, Prisner TF, Stubbe J, Bennati M. High-field pulsed electron–electron double resonance spectroscopy to determine the orientation of the tyrosyl radicals in ribonucleotide reductase. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2006;103:13386–13390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605851103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Polyhach Y, Godt A, Bauer C, Jeschke G. Spin pair geometry revealed by high-field DEER in the presence of conformational distributions. J. Magn. Reson. 2007;185:118–129. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2006.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Jeschke G, Sajid M, Schulte M, Godt A. Three-spin correlations in double electron–electron resonance. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009;11:6580–6591. doi: 10.1039/b905724b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Junk MJN, Spiess HW, Hinderberger D. DEER in biological multispin-systems: a case study on the fatty acid binding to human serum albumin. J. Magn. Reson. 2011;210:210–217. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2011.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Goldfarb D. Gd3+ spin labeling for distance measurements by pulse EPR spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014;16:9685–9699. doi: 10.1039/c3cp53822b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Feintuch, A., Otting, G. & Goldfarb, D. Gd3+ Spin labeling for measuring distances in biomacromolecules: why and how? in Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Investigations of Biological Systems by Using Spin Labels, Spin Probes, and Intrinsic Metal Ions, Part A (eds Qin, P. Z. & Warncke, K. B. T.-M.) Vol. 563 415–457 (Academic Press, 2015).
- 48.Bennett BD, et al. Absolute metabolite concentrations and implied enzyme active site occupancy in Escherichia coli. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009;5:593–599. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Campbell E, et al. The role of protein dynamics in the evolution of new enzyme function. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016;12:944–950. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hong N-S, et al. The evolution of multiple active site configurations in a designed enzyme. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:3900. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06305-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Abdelkader EH, et al. Protein conformation by EPR spectroscopy using gadolinium tags clicked to genetically encoded p-azido-L-phenylalanine. Chem. Commun. 2015;51:15898–15901. doi: 10.1039/C5CC07121F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Fraser NJ, et al. Evolution of protein quaternary structure in response to selective pressure for increased thermostability. J. Mol. Biol. 2016;428:2359–2371. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Clifton, B. E. et al. Ancestral Protein Reconstruction and Circular Permutation for Improving the Stability and Dynamic Range of FRET Sensors. in Synthetic Protein Switches: Methods and Protocols (ed. Stein, V.) 71–87 (Springer New York, New York, 2017). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 54.Whitfield JH, et al. Construction of a robust and sensitive arginine biosensor through ancestral protein reconstruction. Protein Sci. 2015;24:1412–1422. doi: 10.1002/pro.2721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Mitchell JA, et al. Rangefinder: A semisynthetic FRET sensor design algorithm. ACS Sens. 2016;1:1286–1290. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.6b00576. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Tokuriki N, Tawfik DS. Protein dynamism and evolvability. Science. 2009;324:203–207. doi: 10.1126/science.1169375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Vu PJ, Yao XQ, Momin M, Hamelberg D. Unraveling allosteric mechanisms of enzymatic catalysis with an evolutionary analysis of residue-residue contact dynamical changes. ACS Catal. 2018;8:2375–2384. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b04263. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Curado-Carballada C, Feixas F, Iglesias-Fernández J, Osuna S. Hidden conformations in Aspergillus niger monoamine oxidase are key for catalytic efficiency. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019;58:3097–3101. doi: 10.1002/anie.201812532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Bhabha G, et al. Divergent evolution of protein conformational dynamics in dihydrofolate reductase. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013;20:1243–1249. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kaltenbach M, et al. Evolution of chalcone isomerase from a noncatalytic ancestor. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018;14:548–555. doi: 10.1038/s41589-018-0042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Marinelli F, Fiorin G. Structural characterization of biomolecules through atomistic simulations guided by DEER measurements. Structure. 2019;27:359–370. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2018.10.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Stelzl LS, Erlenbach N, Heinz M, Prisner TF, Hummer G. Resolving the conformational dynamics of DNA with Ångstrom resolution by pulsed electron–electron double resonance and molecular dynamics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017;139:11674–11677. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b05363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Puljung MC, DeBerg HA, Zagotta WN, Stoll S. Double electron–electron resonance reveals cAMP-induced conformational change in HCN channels. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:9816–9821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1405371111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Joseph B, Sikora A, Cafiso DS. Ligand induced conformational changes of a membrane transporter in E. coli cells observed with DEER/PELDOR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016;138:1844–1847. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b13382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Joseph B, et al. In situ observation of conformational dynamics and protein ligand–substrate interactions in outer-membrane proteins with DEER/PELDOR spectroscopy. Nat. Protoc. 2019;14:2344–2369. doi: 10.1038/s41596-019-0182-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Georgieva ER, et al. Effect of freezing conditions on distances and their distributions derived from double electron electron resonance (DEER): a study of doubly-spin-labeled T4 lysozyme. J. Magn. Reson. 2012;216:69–77. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2012.01.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Neylon C, et al. Interaction of the Escherichia coli replication terminator protein (Tus) with DNA: a model derived from DNA-binding studies of mutant proteins by surface plasmon resonance. Biochemistry. 2000;39:11989–11999. doi: 10.1021/bi001174w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Qi R, Otting G. Mutant T4 DNA polymerase for easy cloning and mutagenesis. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0211065. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Mukai T, et al. Highly reproductive Escherichia coli cells with no specific assignment to the UAG codon. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:9699. doi: 10.1038/srep09699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Young DD, et al. An evolved aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase with atypical polysubstrate specificity. Biochemistry. 2011;50:1894–1900. doi: 10.1021/bi101929e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Cabrita LD, et al. Enhancing the stability and solubility of TEV protease using in silico design. Protein Sci. 2007;16:2360–2367. doi: 10.1110/ps.072822507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Goldfarb D, et al. HYSCORE and DEER with an upgraded 95 GHz pulse EPR spectrometer. J. Magn. Reson. 2008;194:8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2008.05.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Mentink-Vigier F, et al. Increasing sensitivity of pulse EPR experiments using echo train detection schemes. J. Magn. Reson. 2013;236:117–125. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2013.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Doll A, et al. Gd(III)–Gd(III) distance measurements with chirp pump pulses. J. Magn. Reson. 2015;259:153–162. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2015.08.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Bahrenberg T, et al. Improved sensitivity for W-band Gd(III)-Gd(III) and nitroxide-nitroxide DEER measurements with shaped pulses. J. Magn. Reson. 2017;283:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2017.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bahrenberg T, Yang Y, Goldfarb D, Feintuch A. rDEER: a modified DEER sequence for distance measurements using shaped pulses. Magnetochemistry. 2019;5:20. doi: 10.3390/magnetochemistry5010020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Jeschke G, et al. DeerAnalysis2006—a comprehensive software package for analyzing pulsed ELDOR data. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2006;30:473–498. doi: 10.1007/BF03166213. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Kabsch W. XDS. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 2010;66:125–132. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909047337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Evans PR, Murshudov GN. How good are my data and what is the resolution? Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 2013;69:1204–1214. doi: 10.1107/S0907444913000061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.McCoy AJ, et al. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Cryst. 2007;40:658–674. doi: 10.1107/S0021889807021206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Emsley P, Lohkamp B, Scott WG, Cowtan K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 2010;66:486–501. doi: 10.1107/S0907444910007493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Murshudov GN, Vagin AA, Dodson EJ. Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 1997;53:240–255. doi: 10.1107/S0907444996012255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Afonine PV, et al. Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.refine. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 2012;68:352–367. doi: 10.1107/S0907444912001308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Bowers, K. J. et al. Scalable algorithms for molecular dynamics simulations on commodity clusters. In Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE SC Conference on Supercomputing (SC06) 43 (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Tampa, FL, 2007).
- 85.Roos K, et al. OPLS3e: extending force field coverage for drug-like small molecules. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019;15:1863–1874. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.8b01026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Bakan A, Meireles LM, Bahar I. ProDy: protein dynamics inferred from theory and experiments. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:1575–1577. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The atomic coordinates and structure factors for AncCDT-5 (PDB 6WUP) have been deposited in the Worldwide Protein Data Bank (http://wwpdb.org/). Any other relevant data are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request. Source data are provided with this paper.