Abstract
Background: We aimed to perform a systematic search and meta-analysis to evaluate the prognostic value of on-admission liver function tests and pre-existing liver diseases on the clinical course of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Methods: The study was registered on PROSPERO (CRD42020182902). We searched five databases between 01/01/2020 and 04/23/2020. Studies that reported on liver-related comorbidities and/or laboratory parameters in patients with COVID-19 were included. The main outcomes were COVID-19 severity, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and in-hospital mortality. Analysis of predictive models hierarchical summary receiver-operating characteristic (HSROC) was conducted with a 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results: Fifty studies were included in the meta-analysis. High specificity was reached by acute liver failure associated by COVID-19 (0.94, 95% CI: 0.71–0.99) and platelet count (0.94, 95% CI: 0.71–0.99) in the case of mortality; chronic liver disease (CLD) (0.98, 95% CI: 0.96–0.99) and platelet count (0.82, 95% CI: 0.72–0.89) in the case of ICU requirement; and CLD (0.97, 95% CI: 0.95–0.98), chronic hepatitis B infection (0.97, 95% CI: 0.95–0.98), platelet count (0.86, 95% CI: 0.77–0.91), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (0.80, 95% CI: 0.66–0.89) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (0.84, 95% CI: 0.77–0.88) activities considering severe COVID-19. High sensitivity was found in the case of C-reactive protein (CRP) for ICU requirement (0.92, 95% CI: 0.80–0.97) and severe COVID-19 (0.91, 95% CI: 0.82–0.96).
Conclusion: On-admission platelet count, ALT and AST activities, CRP concentration, and the presence of acute and CLDs predicted the severe course of COVID-19. To highlight, pre-existing liver diseases or acute liver injury associated by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection plays an important role in the prediction of mortality.
Keywords: SARS—CoV-2, COVID-19, prognosis, hepatology, pandemic (COVID-19)
Introduction
In December 2019, a local outbreak of pneumonia caused by a novel coronavirus, namely, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), was detected in Wuhan, China. In most cases, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an acute, self-limiting disease with a relatively brief period of symptoms and resolution within days. However, it can reach in-hospital mortality of 3–7% (1), which can result from massive alveolar damage, consequential acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), respiratory failure, septic shock, or multiple organ dysfunction (2, 3).
It is important to explore the prognostic factors, which have a significant impact on the disease course, given the rapid spread of COVID-19 and its high mortality rate. The detrimental effects of hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, kidney disease, and diabetes mellitus on the disease course are already proven (4–6). Due to the limited number of reports on COVID-19 with underlying chronic liver disease (CLD) to date, the impact of pre-existing liver pathologies on COVID-19 progression and outcomes is unknown.
Although coronaviruses cause the worst damage on the lungs, studies suggest that other organs, such as the liver, intestines, heart, and central nervous system, could also be affected (7–11). In COVID-19, almost half of the hospitalized patients have various degrees of liver test abnormalities, and liver impairment was also observed in 14–53% of the patients (12).
We aimed to appraise the currently available literature of confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infections critically and to investigate the prognostic value of on-admission liver function and liver conditions on the clinical course of COVID-19.
Materials and Methods
Our systematic review and meta-analysis was planned and reported according to the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) 2009 Statement (13) (Supplementary Table 1). This study was registered in advance on PROSPERO under registration number CRD42020182902 (see https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero).
Search and Selection
A systematic search was conducted by two independent reviewers (LS and NZ) to identify all the relevant records on the prognostic value of liver impairment in COVID-19 patients published from January 1, 2020 to April 23, 2020. The search was performed in MEDLINE via PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science with the terms (“covid 19”) OR (“Wuhan virus”) OR (“coronavirus”) OR (“2019 nCoV”) OR (“SARS-CoV-2”) without language or other restrictions. References were managed by the EndNote X9 software (Clarivate Analytics, Philadelphia, PA, USA). Following the removal of duplicates, title and abstract screening were performed by two independent reviewers (PJH and NV) to identify potentially eligible articles. Disagreements were reviewed by a third review author (KJ) and resolved by consensus. The reference lists of the relevant articles were hand-searched, and additional eligible records were included.
We included studies without any restriction that reported on (C) liver diseases (as defined by eligible studies) and/or on-admission liver function tests in (P) patients with confirmed COVID-19. Concerning the laboratory parameters, cut-off values predefined by the individual studies were used for abnormal parameters (O). The assessed outcomes were as follows: in-hospital mortality, severe SARS-CoV-2 infection defined by eligible studies, and intensive care unit (ICU) requirement defined by eligible studies. Severity of COVID-19 was classified according to the guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of COVID-19 issued by the National Health Commission of China (14). Details are presented in Supplementary Table 2. Studies with a sample size of fewer than 15 subjects were excluded because of the small effect size. When there were multiple publications using data with overlapping study populations, we included the one with a greater sample size.
Data Extraction and Outcomes
Relevant data were independently extracted from studies by review authors ZRD and FD. These included: first author, year of publication, country of origin, time interval and place of the study, study design, basic characteristics of the study population (age, percentage of females, and size of the study groups), the proportion of event (in-hospital mortality, severe SARS-CoV-2 infection, and need for ICU care) in patients with and without liver impairment, time of measurement for outcomes, and serum laboratory parameters [total bilirubin, albumin, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), platelet count, international normalized ratio (INR), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and C-reactive protein (CRP)], predefined cut-off values, and information for risk of bias assessment. Extracted data were validated by MF and SK.
Statistical Analysis
Calculations were performed by Stata 15 data analysis and statistical software (StataCorp LLC, College Station, TX, USA). The first preference was the analysis of hierarchical summary receiver-operating characteristic (HSROC) predictive models with 95% confidence interval (CI) when at least five articles were available for the given outcome. The area under the curve (AUC) values and their 95% CIs for each prognostic factor and outcome were collected, and a meta-analysis using the random effect model to gain pooled AUC estimates with 95% CI was performed. Second preference in case of dichotomous variables (mortality, severe vs non-severe, and ICU vs. non-ICU) was the calculation of odds ratios (OR) with a 95% CI. A p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Heterogeneity was tested with I2 and χ2 tests. As suggested by the Cochrane Handbook, I2 values were interpreted as moderate (30–60%), substantial (50–90%), and considerable (75–100%) heterogeneity (15). A p < 0.10 was considered significant. Forest plots and HSROC curves were used to present the results of the meta-analyses. Publication bias was checked by Egger's test (alpha = 0.1) when at least 10 studies were available (16). A p < 0.1 was chosen because of the low number of studies included in our analyses, since it can determine a significant heterogeneity with greater certainty (17).
Assessment of Risk of Bias
Bias assessment was performed by two authors independently (PHa and TH) using the modified Quality In Prognosis Studies (QUIPS) assessment tool (18). Disagreements were resolved by a third investigator (GP). Details of the used QUIPS tool are shown in the footnote of Supplementary Table 5.
Protocol Deviation
We waived the need for data extraction and analysis regarding the continuous variables and Funnel plots after statistical consultation as it did not provide additional value.
Results
Overall, 19,609 records were identified through the comprehensive search, from which 1,647 full texts were reviewed, and 50 studies were included in the qualitative and quantitative syntheses. The selection process is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
PRISMA flowchart.
Basic characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 1 and Supplementary Table 3. Detailed eligibility criteria for each included study are presented in Supplementary Table 4.
Table 1.
Basic characteristics of the included studies.
| Study | Country | Cohort type | Total number of patients (female %) | Age (year)‡ | Outcome(s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Event number (event rate %) | |||||
| Cai et al. (19) | China | Retrospective | 298 (51) | 48 | Severe COVID-19 | 58 (19) |
| Cai et al. (20) | China | Retrospective | 318 (NR) | NR | Severe COVID-19 | 85 (27) |
| Cao et al. (21) | China | Prospective | 102 (48) | 54 | Mortality | 17 (17) |
| Chen et al. (22) | China | Retrospective | 21 (19) | 56 | Severe COVID-19 | 11 (52) |
| Chen et al. (4) | China | Retrospective | 1,590 (43) | NR | Mortality | 50 (3) |
| Chen et al. (23) | China | Retrospective | 274 (38) | 62 | Mortality | 113 (41) |
| Chen et al. (24) | China | Retrospective | 203 (38) | 74 | Mortality | 19 (9) |
| Chen et al. (25) | China | Retrospective | 48 (23) | 65 | ICU admission | 17 (35) |
| Colombi et al. (26) | Italy | Retrospective | 236 (25) | 68 | ICU admission | 108 (46) |
| Du et al. (27) | China | Retrospective | 109 (32) | 71 | ICU admission | 51 (47) |
| Fan et al. (28) | Singapore | Retrospective | 67 (45) | 42 | ICU admission | 9 (13) |
| Fan et al. (29) | China | Retrospective | 148 (NR) | NR | Mortality | 1 (1) |
| ICU admission | 10 (7) | |||||
| Feng et al. (30) | China | Retrospective | 476 (43) | 53 | ICU admission | 70 (15) |
| Goyal et al. (31) | USA | Retrospective | 393 (39) | 62 | ICU admission | 130 (33) |
| Grein et al. (32) | Multiple† | Retrospective | 53 (25) | 64 | ICU admission | 34 (64) |
| Guan et al. (5) | China | Retrospective | 1,099 (42) | 47 | Severe COVID-19 | 173 (16) |
| Guan et al. (33) | China | Retrospective | 1,590 (43) | 49 | ICU admission | 99 (6) |
| Severe COVID-19 | 254 (16) | |||||
| Huang et al. (34) | China | Prospective | 41 (27) | 49 | ICU admission | 13 (32) |
| Ji et al. (35) | China | Retrospective | 202 (44) | 45 | Severe COVID-19 | 39 (19) |
| Ji et al. (36) | China | Retrospective | 208 (44) | 44 | Severe COVID-19 | 40 (19) |
| Li et al. (37) | China | Retrospective | 548 (49) | 60 | Severe COVID-19 | 269 (49) |
| Liu et al. (38) | China | Retrospective | 383 (58) | 46 | Mortality | 49 (13) |
| Qi et al. (39) | China | Prospective | 70 (NR) | NR | Severe COVID-19 | 3 (4) |
| Qian et al. (40) | China | Retrospective | 324 (49) | 51 | Severe COVID-19 | 26 (8) |
| Qin et al. (41) | China | Retrospective | 452 (48) | 58 | Severe COVID-19 | 286 (63) |
| Richardson et al. (42) | USA | Retrospective | 2,634 (NR) | NR | Mortality | 553 (21) |
| Ruan et al. (43) | China | Retrospective | 150 (32) | NR | Mortality | 68 (45) |
| Shen et al. (44) | China | Retrospective | 119 (53) | 49 | Severe COVID-19 | 20 (17) |
| Shi et al. (45) | China | Retrospective | 487 (47) | 46 | Severe COVID-19 | 49 (10) |
| To et al. (46) | China | Retrospective | 23 (43) | 62 | Severe COVID-19 | 10 (43) |
| Tu et al. (47) | China | Retrospective | 174 (55) | NR | Mortality | 25 (14) |
| Wan et al. (48) | China | Retrospective | 135 (47) | 47 | Severe COVID-19 | 40 (30) |
| Wan et al. (49) | China | Retrospective | 123 (46) | NR | Severe COVID-19 | 21 (17) |
| Wang et al. (50) | China | Retrospective | 339 (51) | 69 | Mortality | 65 (19) |
| Wang et al. (51) | China | Retrospective | 55 (60) | 49 | Severe COVID-19 | 2 (4) |
| Wang et al. (52) | China | Retrospective | 69 (54) | 42 | ICU admission | 14 (20) |
| Wu et al. (53) | China | Retrospective | 280 (46) | 43 | ICU admission | 83 (30) |
| Yang et al. (54) | China | Retrospective | 93 (40) | 46 | Severe COVID-19 | 24 (26) |
| Yang et al. (55) | China | Retrospective | 1,476 (47) | 57 | Mortality | 238 (16) |
| Yang et al. (56) | China | Retrospective | 52 (33) | 60 | Mortality | 32 (62) |
| Zhang et al. (57) | China | Retrospective | 221 (51) | 55 | Severe COVID-19 | 55 (25) |
| Zhang et al. (58) | China | Retrospective | 663 (52) | 56 | Mortality | 25 (4) |
| Zhang et al. (59) | China | Retrospective | 140 (49) | 57 | Severe COVID-19 | 58 (41) |
| Zhang et al. (60) | China | Retrospective | 120 (64) | 45 | Severe COVID-19 | 30 (25) |
| Zhang et al. (61) | China | Retrospective | 115 (57) | 50 | Severe COVID-19 | 31 (27) |
| Zheng et al. (62) | China | Retrospective | 161 (50) | 45 | Severe COVID-19 | 30 (19) |
| Zheng et al. (63) | China | Retrospective | 96 (40) | 55 | Severe COVID-19 | 74 (77) |
| Zhou et al. (64) | China | Retrospective | 191 (38) | 56 | Mortality | 54 (28) |
| Zhou et al. (65) | China | Retrospective | 15 (33) | 62 | Mortality | 7 (47) |
| Zhou et al. (66) | China | Retrospective | 21 (38) | 66 | ICU admission | 13 (62) |
COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; ICU, intensive care unit admission; NR, not reported.
Multiple countries (USA, Japan, Italy, Austria, France, Germany, Netherlands, Spain, and Canada);
mean or median.
Diagnostic Metrics
For the prediction of mortality, a high specificity was reached by liver failure (specificity: 0.94, 95% CI: 0.71–0.99) and platelet count (specificity: 0.94, 95% CI: 0.71–0.99) and a moderate sensitivity by LDH (sensitivity: 0.81, 95% CI: 0.78–0.85).
For the prediction of possible ICU requirement, CLD (specificity: 0.98, 95% CI: 0.96–0.99) and platelet count (specificity: 0.82, 95% CI: 0.72–0.89) proved to be specific, whereas CRP was associated with high sensitivity (sensitivity: 0.92, 95% CI: 0.80–0.97).
For the prediction of severe disease course, CLD (specificity: 0.97, 95% CI: 0.95–0.98) and chronic hepatitis B infection (specificity: 0.97, 95% CI: 0.95–0.98) were highly specific, and platelet count (specificity: 0.86, 95% CI: 0.77–0.91), ALT (specificity: 0.80, 95% CI: 0.66–0.89), and AST (specificity: 0.84, 95% CI: 0.77–0.88) were moderately specific, whereas high sensitivity was reached by CRP (sensitivity: 0.91, 95% CI: 0.82–0.96).
CLD for mortality and total bilirubin in case of severe COVID-19 could not be analyzed because it was not feasible despite the number of included studies.
Detailed results about the AUC, sensitivity, specificity, likelihood ratios, and heterogeneity are shown in Table 2. The HSROC curves are summarized in Supplementary Figures 1–3.
Table 2.
Summary table of mortality, severe COVID-19, and intensive care unit requirement based on the HSROC analysis.
| Prognostic factor |
No. of studies (no. of cases) |
AUC (95% CI) |
Sensitivity (95% CI) |
I2 (%) | Chi2 |
Specificity (95% CI) |
I2 (%) | Chi2 |
PLR (95% CI) |
NLR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality | ||||||||||
| Liver failure | 5 (3,523) | 0.67 (0.63–0.71) | 0.31 (0.12–0.59) | 99 | 0.001 | 0.94 (0.71–0.99) | 99 | 0.001 | 5.5 (1.6–19.4) | 0.73 (0.55–0.97) |
| Platelet count | 5 (3,259) | 0.71 (0.67–0.75) | 0.40 (0.23–0.59) | 95 | 0.001 | 0.89 (0.75–0.96) | 99 | 0.001 | 3.7 (1.5–9) | 0.68 (0.5–0.91) |
| ALT | 5 (2,127) | 0.76 (0.72–0.79) | 0.41 (0.30–0.53) | 71 | 0.01 | 0.77 (0.75–0.80) | 0 | 0.63 | 1.8 (1.4–2.4) | 0.76 (0.64–0.92) |
| LDH | 5 (2,149) | 0.81 (0.78–0.85) | 0.87 (0.74–0.94) | 71 | 0.01 | 0.58 (0.41–0.73) | 95 | 0.001 | 2.1 (1.4–3.1) | 0.22 (0.1–0.48) |
| Intensive care unit requirement | ||||||||||
| Chronic liver disease | 5 (831) | 0.80 (0.77–0.84) | 0.03 (0.01–0.06) | 0 | 0.48 | 0.98 (0.96–0.99) | 59 | 0.04 | 1.3 (0.5–3.3) | 0.99 (0.97–1.02) |
| Platelet count | 5 (628) | 0.47 (0.43–0.52) | 0.18 (0.11–0.28) | 35 | 0.19 | 0.82 (0.72–0.89) | 63 | 0.03 | 1 (0.6–1.6) | 1 (0.9–1.12) |
| ALT | 5 (1,190) | 0.58 (0.54–0.62) | 0.32 (0.25–0.41) | 33 | 0.20 | 0.76 (0.70–0.81) | 52 | 0.08 | 1.3 (1.1–1.7) | 0.89 (0.81–0.98) |
| AST | 6 (1,229) | 0.65 (0.61–0.69) | 0.55 (0.47–0.62) | 37 | 0.16 | 0.69 (0.62–0.75) | 78 | 0.001 | 1.7 (1.5–2.1) | 0.66 (0.57–0.76) |
| CRP | 6 (1,412) | 0.75 (0.72–0.79) | 0.92 (0.80–0.97) | 88 | 0.001 | 0.31 (0.14–0.54) | 95 | 0.001 | 1.3 (1.1–1.7) | 0.27 (0.16–0.46) |
| Severe COVID-19 | ||||||||||
| Chronic liver disease | 10 (2,182) | 0.65 (0.60–0.69) | 0.03 (0.02–0.07) | 75 | 0.001 | 0.97 (0.95–0.98) | 76 | 0.001 | 1.2 (0.6–2.1) | 1 (0.97–1.02) |
| Chronic hepatitis B | 7 (3,911) | 0.71 (0.67–0.75) | 0.03 (0.01–0.08) | 84 | 0.001 | 0.97 (0.95–0.98) | 85 | 0.001 | 1.2 (0.6–2.4) | 1 (0.97–1.02) |
| Platelet count | 7 (1,868) | 0.66 (0.62–0.70) | 0.26 (0.15–0.42) | 88 | 0.001 | 0.86 (0.77–0.91) | 92 | 0.001 | 1.8 (1.2–2.7) | 0.86 (0.75–0.99) |
| ALT | 8 (1,625) | 0.60 (0.55–0.64) | 0.31 (0.19–0.48) | 94 | 0.001 | 0.80 (0.66–0.89) | 96 | 0.001 | 1.6 (1.1–2.2) | 0.86 (0.74–0.99) |
| AST | 9 (2,780) | 0.70 (0.65–0.74) | 0.40 (0.30–0.50) | 88 | 0.001 | 0.84 (0.77–0.88) | 90 | 0.001 | 2.4 (1.8–3.2) | 0.72 (0.63–0.83) |
| LDH | 9 (2,500) | 0.75 (0.71–0.79) | 0.67 (0.57–0.77) | 93 | 0.001 | 0.72 (0.62–0.80) | 95 | 0.001 | 2.4 (1.8–3.1) | 0.45 (0.35–0.58) |
| CRP | 6 (2,253) | 0.68 (0.64–0.72) | 0.91 (0.82–0.96) | 89 | 0.001 | 0.34 (0.23–0.47) | 94 | 0.001 | 1.4 (1.2–1.5) | 0.27 (0.18–0.42) |
COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; HSROC, hierarchical summary receiver-operating characteristic; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; AUC, area under the curve; CI, confidence interval; CRP, C-reactive protein; I2 and Chi2, heterogeneity; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; NLR, negative likelihood ratio; PLR, positive likelihood ratio.
Analysis of the Strength of the Association
Liver failure (OR: 7.59; 95% CI: 1.84–31.30), platelet count (OR: 5.36; 95% CI: 1.28–22.37), albumin level (OR: 6.32; 95% CI: 1.40–28.60), and ALT (OR: 2.49; 95% CI: 1.75–3.56), AST (OR: 5.39; 95% CI: 3.67–7.91), and LDH (OR: 9.23; 95% CI: 2.56–33.31) activities were related to a high rate of mortality. CLD, hepatitis B infection, and CRP concentration did not show significant difference, considering mortality.
Albumin (OR: 3.79; 95% CI: 2.08–6.93), ALT (OR: 1.56; 95% CI: 1.61–2.11), AST (OR: 2.53; 95% CI: 1.92–3.35), and LDH (OR: 7.95; 95% CI: 4.54–13.92) levels and CRP (OR: 4.72; 95% CI: 2.59–8.58) concentration were accompanied with high rate of ICU admission. A significant difference could not be stated regarding the need for ICU considering CLD, liver dysfunction, and platelet count.
Fatty liver disease (OR: 3.86; 95% CI: 1.20–12.47), liver failure (OR: 3.27; 95% CI: 1.20–8.87), total bilirubin (OR: 1.89; 95% CI: 1.35–2.63), platelet count (OR: 2.34; 95% CI: 1.53–3.58), albumin level (OR: 3.11; 95% CI: 1.61–6.01), ALT (OR: 1.82; 95% CI: 1.18–2.81), AST (OR: 3.34; 95% CI: 2.37–4.71), LDH (OR: 5.02; 95% CI: 3.41–7.40), CRP (OR: 4.52; 95% CI: 3.16–6.49), and GGT (OR: 3.03; 95% CI: 1.60–5.7) were accompanied with a higher risk for more severe course. CLD, hepatitis B infection, and elevated level of ALP did not show significant difference concerning severity.
Results of the analysis of association and heterogeneity are presented in Table 3. Forest plots for each analysis are shown in Supplementary Figures 4–17.
Table 3.
Summary of findings.
| Prognostic factor | Mortality | Intensive care unit requirement | Severe COVID-19 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
No. of studies (no. of pts) |
Odds ratio (95% CI) |
I2 (%) | Chi2 |
No. of studies (no. of pts) |
Odds ratio (95% CI) |
I2 (%) | Chi2 |
No. of studies (no. of pts) |
Odds ratio (95% CI) |
I2 (%) | Chi2 | |
| Chronic liver disease | 4 (646)† | 1.5 (0.42–5.41) | 0 | 0.54 | 5 (831) | 1.42 (0.56–3.63) | 0 | 0.72 | 10 (2,182) | 1.45 (0.87–2.42) | 0 | 0.7 |
| Liver dysfunction | 2 (145) | 1.13 (0.36–3.58) | 0 | 0.33 | 2 (384) | 1.77 (0.62–5.06) | 0 | 0.98 | 2 (163) | 1.11 (0.36–3.47) | 0 | 0.56 |
| Chronic hepatitis B | 2 (1,864) | 1.18 (0.42–3.34) | 0 | 0.97 | 1 (1,590) | 0.55 (0.07–4.11) | NR | NR | 7 (3,911) | 1,55 (0.85–2.83) | 13 | 0.33 |
| Fatty liver disease | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 4 (964) | 3.86 (1.2–12.47)* | 79 | 0 |
| Liver failure | 5 (3,523) | 7.59 (1.84–31.30)* | 91 | 0 | 1 (43) | 1.88 (0.47–7.54) | NR | NR | 4 (1,185) | 3.27 (1.2–8.87)* | 70 | 0.02 |
| Total bilirubin | 1 (975) | 5 (2.48–10.07)* | NR | NR | 2 (395) | 1.66 (0.45–6.06) | 33 | 0.22 | 6 (2,059) | 1.89 (1.35–2.63)* | 0 | 0.57 |
| Platelet count | 5 (3,259) | 5.36 (1.28–22.37)* | 95 | 0 | 5 (628) | 0.95 (0.63–1.44) | 0 | 0.79 | 7 (1,868) | 2.34 (1.53–3.58)* | 46 | 0.09 |
| International normalized ratio | NR | NR | NR | NR | 1 (20) | 5 (0.18–139.17) | NR | NR | 1 (115) | 0.72 (0.31–1.66) | NR | NR |
| Albumin | 3 (944) | 6.32 (1.4–28.6)* | 63 | 0.07 | 3 (744) | 3.79 (2.08–6.93)* | 0 | 0.81 | 4 (1,205) | 3.11 (1.61–6.01)* | 69 | 0.02 |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 5 (2,127) | 2.49 (1.75–3.56)* | 10 | 0.35 | 5 (1,190) | 1.56 (1.16–2.11)* | 0 | 0.99 | 8 (1,625) | 1.82 (1.18–2.81)* | 70 | 0 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase | 4 (1,966) | 5.39 (3.67–7.91)* | 0 | 0.63 | 6 (1,229) | 2.53 (1.92–3.35)* | 0 | 0.48 | 9 (2,780) | 3.34 (2.37–4.71)* | 60 | 0.01 |
| Lactate dehydrogenase | 5 (2,149) | 9.23 (2.56–33.31)* | 85 | 0 | 4 (748) | 7.95 (4.54–13.92)* | 0 | 0.75 | 9 (2,500) | 5.02 (3.41–7.4)* | 66 | 0 |
| C-reactive protein | 4 (1,846) | 9.19 (0.84–100.63) | 77 | 0 | 6 (1,412) | 4.72 (2.59–8.58)* | 35 | 0.17 | 6 (2,253) | f4.52 (3.16–6.49)* | 31 | 0.21 |
| Alkaline phosphatase | NR | NR | NR | NR | 1 (19) | 0.11 (0–2.73) | NR | NR | 4 (623) | 1.71 (0.66–4.46) | 24 | 0.27 |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase | NR | NR | NR | NR | 1 (19) | 1.39 (0.22–8.92) | NR | NR | 3 (635) | 3.03 (1.6–5.72)* | 50 | 0.14 |
CI, confidence interval; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; I2 and Chi2, heterogeneity; NR, not reported.
p < 0.05; one study could not be included in the analysis, because there were no events.
Risk of Bias Assessment
Results of the risk of bias assessment between studies are shown in Supplementary Table 5.
The assessment of publication bias could only be performed in the case of CLD on severe COVID-19. It did not suggest the presence of publication bias (p = 0.764).
Discussion
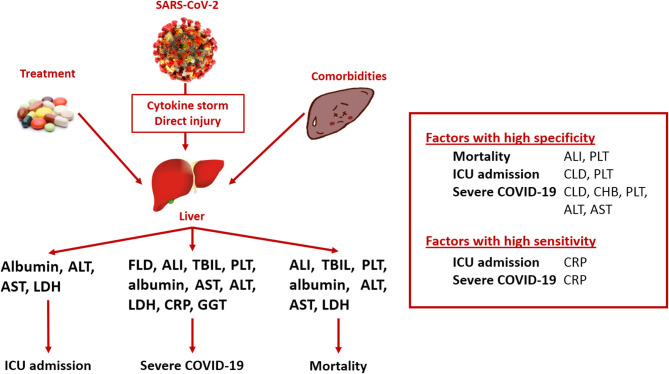
This meta-analysis aimed to investigate the association between pre-existing liver diseases and on-admission liver functions and outcomes in COVID-19 infection, focusing on mortality, ICU admission, and severe disease course (Figure 2). Considering the prediction of mortality, liver failure and platelet count are highly specific, whereas LDH is moderately sensitive. For the prediction of ICU requirement, CLD was associated with high specificity, platelet count with moderate specificity, and CRP with high sensitivity. Regarding severe disease course, CLD and chronic hepatitis B infection were proven to be highly specific, and platelet count and ALT and AST activities were moderately specific, whereas CRP was highly sensitive.
Figure 2.
Summary of findings. ALI, acute liver injury; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; CRP, C-reactive protein; FLD, fatty liver disease; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase; ICU, intensive care unit; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; TBIL, total bilirubin.
In relation to the investigated factors and poorer outcomes, acute liver failure; platelet count; albumin level; ALT, AST, and LDH activities; and CRP concentration were associated with higher mortality. Albumin, ALT, AST, LDH, and CRP influenced the admission to the ICU. Fatty liver disease, liver injury, total bilirubin, ALT, AST, LDH, CRP, GGT, platelet count, and albumin level were associated with more severe disease course.
The knowledge about the impact of liver-related comorbidities in the clinical outcome of COVID-19 is limited. In line with our results, an earlier meta-analysis concluded that CLD is not associated with severity or mortality (67). However, clinicians should be skeptical about it, because these patients are more prone to infection due to cirrhosis-associated immune dysfunction and are more likely to have poor outcomes from ARDS (68, 69). This may account for the relatively low baseline prevalence of CLD in the included patients, as one previous meta-analysis suggests (70), or it was not well-reported. Further on, in a recently published letter on the involvement of the liver in COVID-19, the authors found an increased odds of severe infection and mortality in patients with liver injury (71). Another study analyzed the frequency of abnormal liver function derangements in severe COVID-19 and concluded that hypoalbuminemia followed by derangements in GGT and aminotransferases were more frequent in severe disease (72). On the other hand, another study highlights that digestive symptoms and liver injury are not uncommon in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection (73).
Dysregulated hepatic immune responses caused by metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) may contribute to cytokine storm in younger patients (74), whereas chronic low grade inflammation known to be associated with MAFLD may worsen outcome. Post-mortem liver biopsy showed overactivation of T cells in the liver, and liver injury is likely mediated by immune response rather than direct cytopathic damage (35).
Compared with previous results (12, 75, 76), our study reasserts that in severe forms of COVID-19, alterations of on-admission level of the liver enzymes can be observed, probably due to the virally induced cytotoxic T cells and the innate immune response against the virus. Another reason behind the liver test abnormalities in COVID-19 patients could be the cholangiocyte dysfunction due to direct infection of bile duct cells via angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor (8). However, according to our results, ALP does not seem to be a significant predictive marker in COVID-19. Additionally, moderate microvesicular steatosis, mild lobular, and portal activity can be observed in the pathological samples of patients who died from COVID-19 (77).
Despite the lack of coagulation factors in liver diseases, a hypercoagulable state could also be present in COVID-19. A recent study concluded that COVID-19 disease has prominent manifestations from the hematopoietic system and is often associated with a major blood hypercoagulability (78). In histopathological findings, it was highlighted that extensive vascular portal and sinusoidal thrombosis could lead to abnormal high level of transaminases (79).
Considering the strengths of our meta-analysis, a rigorous methodology was followed. To our knowledge, this is the first study that addresses the prognostic value of on-admission liver parameters, underlying liver comorbidities, and COVID-19 induced hepatic failure on the level of sensitivity and specificity. On the other hand, our study has several limitations. We only included cohort studies that mostly originate from Asia, which might carry a high risk of bias. The definitions of the investigated outcomes were not uniform among the included reports; to estimate this problem, we applied a modified QUIPS. The cut-off values of laboratory parameters and the definition of liver diseases (Supplementary Tables 6, 7) were also slightly different among articles, causing probably significant heterogeneity in our analysis. However, the different laboratory methodologies among the centers might justify this difference. Furthermore, previous drug treatment before admission of COVID-19 was not investigated. Multivariate analysis was not applied; thus, the investigated prognostic factors should not be regarded as independent risk factors. This all could contribute to the significant heterogeneity in some of our results.
Implication for Practice
The establishment of a prognostic score assessing the possible outcomes of patients suffering from any liver pathology is needed. This meta-analysis succeeded to identify some factors, with high specificity, which might be a footstone for such a prognostic tool that might be completed by additionally recognized risk factors, for example, elevated absolute white blood cell count, decreased lymphocyte count, and elevated interleukin-6 and serum ferritin concentrations (80). Patients who are affected by the underlying liver pathology might need advanced therapy earlier to avoid undesired clinical outcomes.
Implication for Research
Based on our results and previously published analyses, further basic research is crucial for a better understanding of the liver injury caused by COVID-19, hepatic comorbidities, and treatment itself.
Conclusion
In conclusion, on-admission platelet count, ALT and AST activities, CRP concentration, and the presence of acute and CLDs predicted the severe course of COVID-19. To highlight, investigating hepatic injury associated by SARS-CoV-2 infection may play an important role in the prediction of mortality and may be used for the establishment of prognostic tools to identify patients with possible poorer outcomes.
Data Availability Statement
All datasets generated for this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author Contributions
SV, PJH, NZ, LS, and NV conceived the study. SV, PHe, and GP wrote the protocol. LS and NZ did the literature search. PJH, NV, ZD, and FD screened the records and extracted the data. KJ, MF, and SK validated the extracted data. PHa and TH assessed the quality of included studies. DN did the statistical analysis. SV, ZS, ZR, and KO prepared the tables. NZ, LS, NV, SV, and PJH wrote the first draft of this manuscript. BE, ZS, GP, and PHe supervised the manuscript and approved the submitted draft. GP is the guarantor of this paper and, as a hepatologist, provided the team with an expert background. All authors provided critical conceptual input, interpreted the data analysis, and critically revised and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Funding.This study was supported by the Human Resources Development Operational Program Grant (EFOP-362-16-2017-00006), co-financed by the European Union (European Regional Development Fund) within the framework of the Széchenyi 2020 Program. The sponsor or the funders of the study had no role in the study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, or writing of the report. The corresponding author had full access to all the data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2020.572115/full#supplementary-material
References
- 1.Coronavirus Disease (COVID-2019): Situation Report 113 (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports/ (accessed May 12, 2020).
- 2.Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. (2020) 323:1239–42. 10.1001/jama.2020.2648 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Arentz M, Yim E, Klaff L, Lokhandwala S, Riedo FX, Chong M, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of 21 critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Washington State. JAMA. (2020) 323:1612–4. 10.1001/jama.2020.4326 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chen R, Liang W, Jiang M, Guan W, Zhan C, Wang T, et al. Risk factors of fatal outcome in hospitalized subjects with coronavirus disease 2019 from a nationwide analysis in China. Chest. (2020) 158:97–105. 10.1016/j.chest.2020.04.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Guan W-j, Ni Z-y, Hu Y, Liang W-h, Ou C-q, He J-x, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382:1708–20. 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zádori N, Váncsa S, Farkas N, Hegyi P, Erőss BJICM. The negative impact of comorbidities on the disease course of COVID-19. Intensive Care Med. (2020) 46:1784–6. 10.1007/s00134-020-06161-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wu Y, Xu X, Chen Z, Duan J, Hashimoto K, Yang L, et al. Nervous system involvement after infection with COVID-19 and other coronaviruses. Brain Behav Immun. (2020) 87:18–22. 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.03.031 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chai X, Hu L, Zhang Y, Han W, Lu Z, Ke A, et al. Specific ACE2 expression in cholangiocytes may cause liver damage after 2019-nCoV infection. BioRxiv [pre print]. (2020). 10.1101/2020.02.03.931766 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Li YC, Bai WZ, Hashikawa T. The neuroinvasive potential of SARS-CoV2 may play a role in the respiratory failure of COVID-19 patients. J Med Virol. (2020) 92:552–5. 10.1002/jmv.25728 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kang Y, Chen T, Mui D, Ferrari V, Jagasia D, Scherrer-Crosbie M, et al. Cardiovascular manifestations and treatment considerations in covid-19. Heart. (2020) 106–1132–41. 10.1136/heartjnl-2020-317056 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Organization WH Modes of transmission of virus causing COVID-19: implications for IPC precaution recommendations: scientific brief. World Health Organization; (2020). Available online at: WHO/2019-nCoV/Sci_Brief/Transmission_modes/2020.2 (accessed May 12, 2020). [Google Scholar]
- 12.Xu L, Liu J, Lu M, Yang D, Zheng X. Liver injury during highly pathogenic human coronavirus infections. Liver Int. (2020) 40:998–1004. 10.1111/liv.14435 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. (2009) 339:b2535 10.1136/bmj.b2535 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zu ZY, Jiang MD, Xu PP, Chen W, Ni QQ, Lu GM, et al. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a perspective from China. Radiology. (2020) 296:E15–E25. 10.1148/radiol.2020200490 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. (2003) 327:557–60. 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. (1997) 315:629–34. 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Deeks JJ, Higgins JP, Altman DG, interventions CSMGJChfsro. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. (2019) :241-84. 10.1002/9781119536604.ch10 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hayden JA, van der Windt DA, Cartwright JL, Côté P, Bombardier C. Assessing bias in studies of prognostic factors. Ann Intern Med. (2013) 158:280–6. 10.7326/0003-4819-158-4-201302190-00009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cai Q, Huang D, Ou P, Yu H, Zhu Z, Xia Z, et al. COVID-19 in a designated infectious diseases hospital outside Hubei Province, China. Allergy. (2020) 75:1742–52. 10.1101/2020.02.17.20024018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cai Q, Huang D, Yu H, Zhu Z, Xia Z, Su Y, et al. COVID-19: Abnormal liver function tests. J Hepatol. (2020) 73:566–74. 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cao J, Tu W-J, Cheng W, Yu L, Liu Y-K, Hu X, et al. Clinical Features and short-term outcomes of 102 patients with corona virus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis. (2020) 71:748–55. 10.1093/cid/ciaa243 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chen G, Wu D, Guo W, Cao Y, Huang D, Wang H, et al. Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:2620–9. 10.1172/JCI137244 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chen T, Wu D, Chen H, Yan W, Yang D, Chen G, et al. Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: retrospective study. BMJ. (2020) 368:m1091. 10.1136/bmj.m1091 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Chen T, Dai Z, Mo P, Li X, Ma Z, Song S, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of older patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China (2019) : a single-centered, retrospective study. J Gerontol. (2020) 75:1788–95. 10.1093/gerona/glaa089 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chen X, Zhao B, Qu Y, Chen Y, Xiong J, Feng Y, et al. Detectable serum SARS-CoV-2 viral load (RNAaemia) is closely correlated with drastically elevated interleukin 6 (IL-6) level in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Clin Infect Dis. (2020). 10.1101/2020.02.29.20029520 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Colombi D, Bodini FC, Petrini M, Maffi G, Morelli N, Milanese G, et al. Well-aerated lung on admitting chest CT to predict adverse outcome in COVID-19 pneumonia. Radiology. (2020) 296:E86–E96. 10.1148/radiol.2020201433 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Du RH, Liu LM, Yin W, Wang W, Guan LL, Yuan ML, et al. Hospitalization and critical care of 109 decedents with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. Ann Am Thorac Soc. (2020) 17:839–46. 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-225OC [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fan BE, Chong VCL, Chan SSW, Lim GH, Lim KGE, Tan GB, et al. Hematologic parameters in patients with COVID-19 infection. Am J Hematol. (2020) 95:E131–E4. 10.1002/ajh.25774 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fan Z, Chen L, Li J, Cheng X, Yang J, Tian C, et al. Clinical features of COVID-19-related liver damage. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 18:1561–6. 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.04.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Feng Y, Ling Y, Bai T, Xie Y, Huang J, Li J, et al. COVID-19 with different severity: a multi-center study of clinical features. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2020) 201:1380–8. 10.1164/rccm.202002-0445OC [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Goyal P, Choi JJ, Pinheiro LC, Schenck EJ, Chen R, Jabri A, et al. Clinical characteristics of Covid-19 in New York City. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382:2372–4. 10.1056/NEJMc2010419 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Grein J, Ohmagari N, Shin D, Diaz G, Asperges E, Castagna A, et al. Compassionate Use of remdesivir for patients with severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382:2327–36. 10.1056/NEJMoa2007016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Guan W-j, Liang W-h, Zhao Y, Liang H-r, Chen Z-s, Li Y-m, et al. Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with Covid-19 in China: a nationwide analysis. Eur Respir J. (2020) 55:2000547. 10.1183/13993003.01227-2020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. (2020) 395:497–506. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ji D, Qin E, Xu J, Zhang D, Cheng G, Wang Y, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases in patients with COVID-19: retrospective study. J Hepatol. (2020) 73:451–3. 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.044 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ji D, Zhang D, Xu J, Chen Z, Yang T, Zhao P, et al. Prediction for progression risk in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: the CALL Score. Clin Infect Dis. (2020) 71:1363–9. 10.1093/cid/ciaa414 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Li X, Xu S, Yu M, Wang K, Tao Y, Zhou Y, et al. Risk factors for severity and mortality in adult COVID-19 inpatients in Wuhan. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2020) 146:110–18. 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Liu Y, Sun W, Guo Y, Chen L, Zhang L, Zhao S, et al. Association between platelet parameters and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019: Retrospective cohort study. Platelets. (2020) 31:490–6. 10.1080/09537104.2020.1754383 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Qi X, Liu C, Jiang Z, Gu Y, Zhang G, Shao C, et al. Multicenter analysis of clinical characteristics and outcome of COVID-19 patients with liver injury. J Hepatol. (2020) 73:455–8. 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Qian ZP, Mei X, Zhang YY, Zou Y, Zhang ZG, Zhu H, et al. [Analysis of baseline liver biochemical parameters in 324 cases with novel coronavirus pneumonia in Shanghai area]. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. (2020) 28:229–33. 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20200229-00076 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Qin C, Zhou L, Hu Z, Zhang S, Yang S, Tao Y, et al. Dysregulation of immune response in patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis. (2020) 71:762–8. 10.1093/cid/ciaa248 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, Crawford JM, McGinn T, Davidson KW, et al. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA. (2020) 323:2052–9. 10.1001/jama.2020.6775 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ruan Q, Yang K, Wang W, Jiang L, Song J. Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China. Intensive Care Med. (2020) 46:846–8. 10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Shen L, Li S, Zhu Y, Zhao J, Tang X, Li H, et al. Clinical and laboratory-derived parameters of 119 hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Xiangyang, Hubei Province, China. J Infect. (2020) 81:147–78. 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.038 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Shi Y, Yu X, Zhao H, Wang H, Zhao R, Sheng J. Host susceptibility to severe COVID-19 and establishment of a host risk score: findings of 487 cases outside Wuhan. Crit Care. (2020) 24:108. 10.1186/s13054-020-2833-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.To KK-W, Tsang OT-Y, Leung W-S, Tam AR, Wu T-C, Lung DC, et al. Temporal profiles of viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva samples and serum antibody responses during infection by SARS-CoV-2: an observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. (2020) 20:565–74. 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30196-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tu W-J, Cao J, Yu L, Hu X, Liu Q. Clinicolaboratory study of 25 fatal cases of COVID-19 in Wuhan. Intensive Care Med. (2020) 46:1117–20. 10.1007/s00134-020-06023-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wan S, Xiang Y, Fang W, Zheng Y, Li B, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features and treatment of COVID-19 patients in northeast Chongqing. J Med Virol. (2020) 92:797–806. 10.1002/jmv.25783 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wan S, Yi Q, Fan S, Lv J, Zhang X, Guo L, et al. Relationships among lymphocyte subsets, cytokines, and the pulmonary inflammation index in coronavirus (COVID-19) infected patients. Br J Haematol. (2020) 189:428–37. 10.1111/bjh.16659 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wang L, He W, Yu X, Hu D, Bao M, Liu H, et al. Coronavirus disease 2019 in elderly patients: characteristics and prognostic factors based on 4-week follow-up. J Infect. (2020) 80:639–45. 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wang Y, Liu Y, Liu L, Wang X, Luo N, Li L. Clinical outcomes in 55 patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 who were asymptomatic at hospital admission in Shenzhen, China. J Infect Dis. (2020) 221:1770–4. 10.1093/infdis/jiaa119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wang Z, Yang B, Li Q, Wen L, Zhang R. Clinical Features of 69 Cases With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis. (2020) 71:769-77. 10.1093/cid/ciaa272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wu J, Li W, Shi X, Chen Z, Jiang B, Liu J, et al. Early antiviral treatment contributes to alleviate the severity and improve the prognosis of patients with novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19). J Intern Med. (2020) 288:128–38. 10.1111/joim.13063 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Yang A-P, Liu J-P, Tao W-Q, Li H-M. The diagnostic and predictive role of NLR, d-NLR and PLR in COVID-19 patients. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 84:106504. 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106504 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Yang X, Yang Q, Wang Y, Wu Y, Xu J, Yu Y, et al. Thrombocytopenia and its association with mortality in patients with COVID-19. J Thromb Haemost. (2020) 18:1469–72. 10.1111/jth.14848 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, Shu H, Xia Ja, Liu H, et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Resp Med. (2020) 8:475–81. 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zhang G, Hu C, Luo L, Fang F, Chen Y, Li J, et al. Clinical features and short-term outcomes of 221 patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. J Clin Virol. (2020) 127:104364. 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104364 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zhang J, Wang X, Jia X, Li J, Hu K, Chen G, et al. Risk factors for disease severity, unimprovement, and mortality in COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, China. Clin Microbiol Infect. (2020) 26:767–72. 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.04.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhang J-j, Dong X, Cao Y-y, Yuan Y-d, Yang Y-b, Yan Y-q, et al. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy. (2020) 75:1730–41. 10.1111/all.14238 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zhang R, Ouyang H, Fu L, Wang S, Han J, Huang K, et al. CT features of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia according to clinical presentation: a retrospective analysis of 120 consecutive patients from Wuhan city. Eur Radiol. (2020) 30:4417–26. 10.1007/s00330-020-06854-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zhang Y, Zheng L, Liu L, Zhao M, Xiao J, Zhao Q. Liver impairment in COVID-19 patients: a retrospective analysis of 115 cases from a single center in Wuhan city, China. Liver Int. (2020) 40:2095–103. 10.1111/liv.14455 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Zheng F, Tang W, Li H, Huang YX, Xie YL, Zhou ZG. Clinical characteristics of 161 cases of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Changsha. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2020) 24:3404–10. 10.26355/eurrev_202003_20711 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Zheng S, Fan J, Yu F, Feng B, Lou B, Zou Q, et al. Viral load dynamics and disease severity in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Zhejiang province, China, January-March 2020: retrospective cohort study. BMJ. (2020) 369:m1443. 10.1136/bmj.m1443 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. (2020) 395:1054–62. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Zhou W, Liu Y, Tian D, Wang C, Wang S, Cheng J, et al. Potential benefits of precise corticosteroids therapy for severe 2019-nCoV pneumonia. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2020) 5:18. 10.1038/s41392-020-0127-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Zhou Y, Han T, Chen J, Hou C, Hua L, He S, et al. Clinical and autoimmune characteristics of severe and critical cases with COVID-19. Clin Transl Sci. (2020). 10.1111/cts.12805 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Lippi G, de Oliveira MHS, Henry BM. Chronic liver disease is not associated with severity or mortality in Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a pooled analysis. Eur J Gastroen Hepat. (2020). 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001742 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Gacouin A, Locufier M, Uhel F, Letheulle J, Bouju P, Fillatre P, et al. Liver cirrhosis is independently associated with 90-day mortality in ARDS patients. Shock. (2016) 45:16–21. 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000487 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Albillos A, Lario M, Álvarez-Mon M. Cirrhosis-associated immune dysfunction: distinctive features and clinical relevance. J Hepatol. (2014) 61:1385–96. 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.08.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Mantovani A, Beatrice G, Dalbeni A. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and prevalence of chronic liver disease: a meta-analysis. Liver Int. (2020) 65:235–6. 10.1007/s00038-020-01369-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Yadav DK, Singh A, Zhang Q, Bai X, Zhang W, Yadav RK, et al. Involvement of liver in COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut. (2020). 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322072 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kumar-M P, Mishra S, Jha DK, Shukla J, Choudhury A, Mohindra R, et al. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the liver: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatol Int. (2020) 14:711–22. 10.1007/s12072-020-10071-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Mao R, Qiu Y, He J-S, Tan J-Y, Li X-H, Liang J, et al. Manifestations and prognosis of gastrointestinal and liver involvement in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. (2020) 5:667–8. 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30126-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Zhou Y-J, Zheng KI, Wang X-B, Yan H-D, Sun Q-F, Pan K-H, et al. Younger patients with MAFLD are at increased risk of severe COVID-19 illness: a multicenter preliminary analysis. J Hepatol. (2020) 73:719–21. 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Parohan M, Yaghoubi S, Seraj A. Liver injury is associated with severe Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of retrospective studies. medRxiv [pre print]. (2020). 10.1101/2020.04.09.20056242 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Zippi M, Fiorino S, Occhigrossi G, Hong W. Hypertransaminasemia in the course of infection with SARS-CoV-2: incidence and pathogenetic hypothesis. World J Clin Cases. (2020) 8:1385–90. 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i8.1385 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Xu Z, Shi L, Wang Y, Zhang J, Huang L, Zhang C, et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Resp Med. (2020) 8:420–2. 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Terpos E, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos I, Elalamy I, Kastritis E, Sergentanis TN, Politou M, et al. Hematological findings and complications of COVID-19. Am J Hematol. (2020) 95:834–47. 10.1002/ajh.25829 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Sonzogni A, Previtali G, Seghezzi M, Grazia Alessio M, Gianatti A, Licini L, et al. Liver histopathology in severe COVID 19 respiratory failure is suggestive of vascular alterations. Liver Int. (2020) 40:2110–6. 10.1111/liv.14601 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Henry BM, De Oliveira MHS, Benoit S, Plebani M, Lippi G. Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis. Clin Chem Lab Med. (2020) 58:1021–8. 10.1515/cclm-2020-0369 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All datasets generated for this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material.